- 1National Clinical Research Center for Chinese Medicine Cardiology, Xiyuan Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 2State Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine Syndrome, Xiyuan Hospital, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 3Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, Xiyuan Hospital of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, China
- 4Graduate School, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing, China
Objective: To investigate the causal relationship between 233 newly reported metabolites and coronary atherosclerosis through Mendelian randomization analysis.
Methods: Five different methods were used to perform Mendelian randomization analysis on the 233 metabolites and coronary atherosclerosis, with inverse variance weighting as the primary result, supplemented by other methods.
Results: The analysis identified that certain metabolites increase the susceptibility risk of coronary atherosclerosis, including: Total fatty acids (OR = 1.40, 95% CI: 1.28–1.53, P < 0.001), Saturated fatty acids (OR = 1.44, 95% CI: 1.30–1.60, P < 0.001), Serum total triglyceride levels (OR = 1.33, 95% CI: 1.22–1.46, P < 0.001), Conjugated linoleic acid (OR = 1.16, 95% CI: 1.04–1.30, P = 0.007). Conversely, certain metabolites were found to reduce the occurrence of coronary atherosclerosis, such as: Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in medium HDL (OR = 0.73, 95% CI: 0.67–0.78, P < 0.001), Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in large HDL (OR = 0.64, 95% CI: 0.58–0.71, P < 0.001), Total cholesterol to total lipids ratio in medium HDL (OR = 0.71, 95% CI: 0.65–0.77, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: There is a close relationship between metabolites and the occurrence of coronary atherosclerosis. This study conducted Mendelian randomization analysis on the causal relationship between 233 metabolites and coronary atherosclerosis, providing potential new insights for the treatment of this disease.
Introduction
Coronary atherosclerosis, the most common form of arteriosclerosis, is a major cause of coronary heart disease. It leads to the narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries, resulting in myocardial ischemia, hypoxia, and, in severe cases, infarction and other cardiovascular diseases (1). Emerging research has increasingly focused on metabolites, such as lipids, lipoproteins, and fatty acids, in the progression of atherosclerosis, as these metabolites influence coronary atherosclerosis through various pathways. For example, indole-3-propionic acid (IPA), a gut microbiota-derived metabolite, has been shown to mitigate atherosclerosis by promoting cholesterol efflux, while deficiency in indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) exacerbates atherosclerosis progression by disrupting kynurenine metabolism and inducing osteogenic changes in vascular smooth muscle cells (2, 3). These findings underscore the inextricable link between coronary atherosclerosis and metabolites.
Given the significant role of these metabolites, it is crucial to focus on the relationship between metabolites and coronary atherosclerosis. Fortunately, a study by Karjalainen et al. (4) identified 233 circulating metabolic biomarkers, including 213 lipids, lipoprotein parameters, and fatty acids, across over 135,000 participants, offering a comprehensive profile to enhance our understanding of atherosclerosis.
Mendelian randomization (MR) is a research method that uses genetic variation as instrumental variables to evaluate causal effects (5). In MR analysis, genetic variants, typically single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), serve as instrumental variables for particular risk factors. This method relies on Mendel's second law, where genetic alleles segregate independently during gamete formation, similar to the treatment assignment in randomized controlled trials (RCTs), thus reducing confounding (6). MR studies enable a deeper understanding of the causal relationship between metabolites and coronary atherosclerosis, offering new insights for disease prevention and potential therapeutic targets.
Materials and methods
Study design
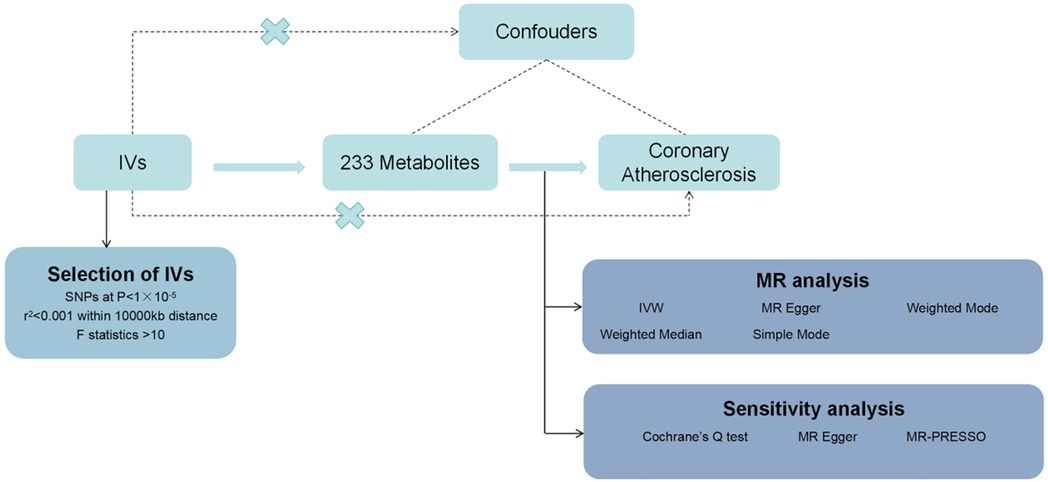
In this study, we used MR analysis to investigate the causal relationship between 233 metabolites and coronary atherosclerosis. Methods such as heterogeneity tests and gene pleiotropy tests were applied to verify the stability of these causal relationships. The flowchart of the study is shown in Figure 1. The analysis was conducted under the three fundamental assumptions of MR:
1. Instrumental variables are strongly associated with the metabolites.The primary criterion for selecting instrumental variables is a significant association with the metabolites under study. If the association is weak, MR analysis may lack sufficient statistical power, potentially leading to biased or imprecise results. Thus, we prioritize genetic variants that are strongly correlated with the metabolites to ensure the validity and accuracy of causal inference.
2. The selected instrumental variables are independent of any potential confounding factors.This assumption ensures that the causal pathway remains singular, unaffected by confounding bias. Since genetic variants are determined at birth and are generally unrelated to environmental factors or other potential confounders in a randomly distributed population, MR is less prone to confounding issues compared to traditional observational studies.
3. Instrumental variables influence the risk of coronary atherosclerosis solely through the metabolites, without any other pathways.This assumption guarantees that the instrumental variables impact the outcome exclusively through their association with the metabolites, avoiding other direct or indirect effects. By selecting genetic variants specifically related to metabolites and conducting sensitivity analyses to exclude other potential pathways, we can substantiate the validity of this assumption.
Data sources
The data for the 233 metabolites were obtained from the GWAS database (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/), covering 33 cohorts. After variant filtering and quality control, up to 13,389,637 imputed autosomal SNPs were included in the analysis, involving up to 136,016 participants. Data on coronary atherosclerosis were sourced from the R10 version of summary data from the FinnGen database (https://www.finngen.fi/fi), including 51,589 cases and 343,079 controls.
Selection of instrumental variables
Using the “TwoSampleMR” package (version 0.5.7), we first selected instrumental variables (IVs) with P < 1 × 10−5, as referenced in relevant Mendelian randomization studies (7), to identify IVs significantly associated with the exposure factors. We set the clump parameter to TRUE to remove instrumental variables with linkage disequilibrium (LD), primarily measured using two parameters, r2 and kb, which were set to 0.001 and 10,000, respectively. This approach aimed to reduce collinearity and confounding bias, thereby enhancing the accuracy and reliability of causal inference analysis (8). Additionally, we calculated F values, defining F-statistics <10 as “weak IVs,” and excluded them.
Statistical analysis
This study employed five methods—MR Egger, Weighted Median, Inverse Variance Weighted (IVW), Simple Mode, and Weighted Mode—to verify the causal relationship between 233 metabolites and susceptibility to coronary atherosclerosis. The results are primarily based on the IVW method, with other methods serving as supplementary approaches. Cochrane's Q test and its corresponding p-value were used to assess the heterogeneity of the IVs; when P < 0.05, the random-effects IVW was applied instead of the fixed-effects IVW (9). To account for potential horizontal pleiotropy, the MR Egger method was used, where a significant intercept term would indicate pleiotropy (10). Additionally, to identify and address outliers, we applied the MR-PRESSO test; any identified outliers were removed, and the MR causal estimates were recalculated (11, 12). Statistical significance was determined at P < 0.05.
Results
Causal relationship between 233 metabolites and coronary atherosclerosis
To investigate the impact of 233 metabolites on coronary atherosclerosis, we employed two-sample MR analysis, with IVW as the primary analysis method. The results revealed that 118 metabolites had a causal relationship with the susceptibility to coronary atherosclerosis (see Figure 2 and Supplementary Table 1).
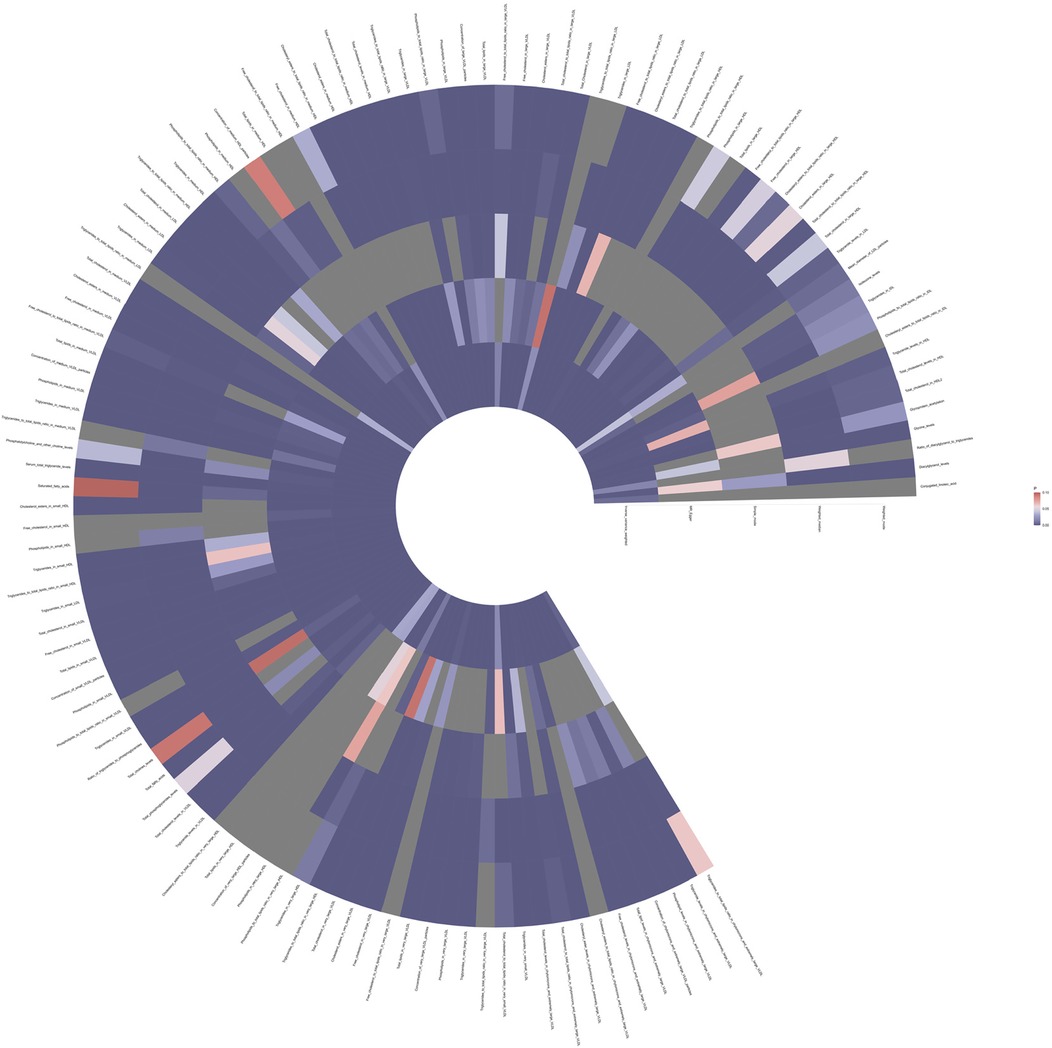
Figure 2. Full P-value results of five Mendelian randomized analyses of 118 metabolites associated with coronary atherosclerosis.
Metabolites increasing the risk of coronary atherosclerosis
Notably, among the 81 human metabolites identified as risk factors for the development of coronary atherosclerosis, the following were included:
Total fatty acids (TFA): The odds ratio (OR) for TFA was 1.40 (95% CI: 1.28–1.53, P < 0.001), indicating that a 1-unit increase in TFA levels is associated with a 40% higher risk of developing coronary atherosclerosis.
Saturated fatty acids (SFA): The OR for SFA was 1.44 (95% CI: 1.30–1.60, P < 0.001), indicating a 44% increase in the risk of coronary atherosclerosis per unit increase in SFA levels.
Serum total triglyceride levels: The OR for serum total triglycerides was 1.33 (95% CI: 1.22–1.46, P < 0.001), showing a 33% higher risk of coronary atherosclerosis with increased triglyceride levels.
Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA): The OR for CLA was 1.16 (95% CI: 1.04–1.30, P = 0.007), suggesting a 16% increase in the risk of coronary atherosclerosis per unit increase in CLA levels.
These metabolites are associated with an increased risk of developing coronary atherosclerosis (Figure 3 and Supplementary Table 1).
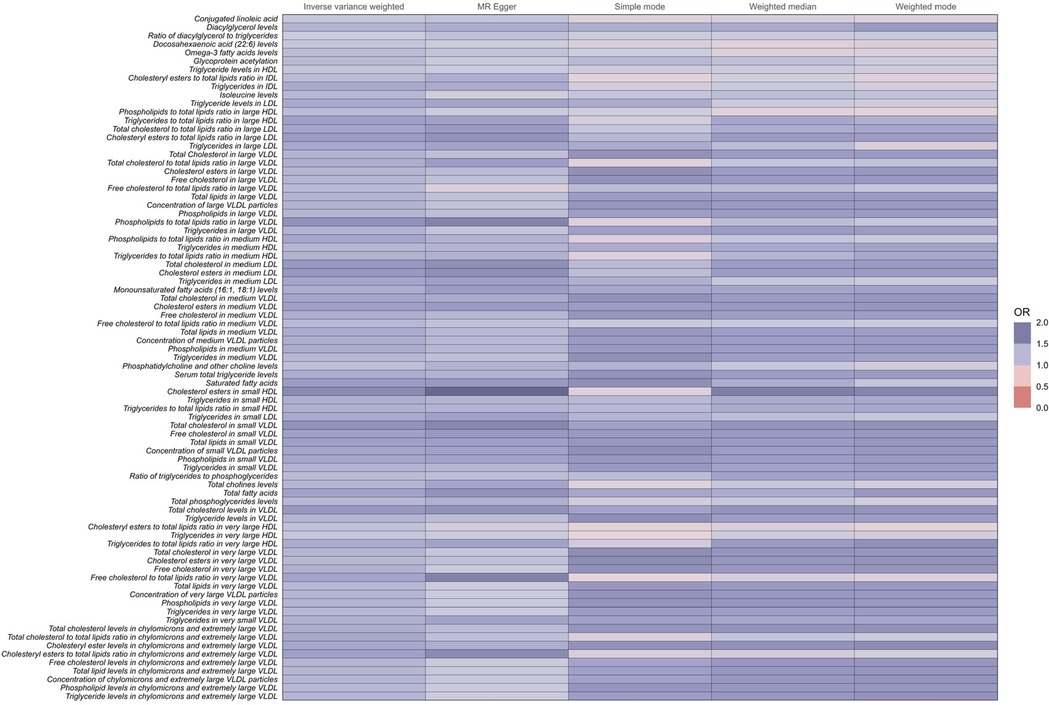
Figure 3. Full results of five Mendelian randomized OR values for 81metabolites associated with an increased risk of coronary atherosclerosis.
Metabolites reducing the risk of coronary atherosclerosis
Conversely, among the 37 human metabolites were found to reduce the risk of coronary atherosclerosis, the following were included:
Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in medium HDL: The OR for this ratio was 0.73 (95% CI: 0.67–0.78, P < 0.001), indicating that a 1-unit increase in this ratio reduces the risk of coronary atherosclerosis by 27%.
Cholesteryl esters to total lipids ratio in large HDL: The OR was 0.64 (95% CI: 0.58–0.71, P < 0.001), suggesting a 36% reduction in the risk of coronary atherosclerosis per unit increase in this ratio.
Total cholesterol to total lipids ratio in medium HDL: The OR was 0.71 (95% CI: 0.65–0.77, P < 0.001), demonstrating a 29% lower risk of coronary atherosclerosis with increased levels of this ratio.
Free cholesterol to total lipids ratio in large LDL: The OR was 0.70 (95% CI: 0.64–0.77, P < 0.001), reflecting a 30% reduced risk of coronary atherosclerosis per unit increase in this ratio.
Total cholesterol to total lipids ratio in large HDL: The OR was 0.70 (95% CI: 0.64–0.78, P < 0.001), suggesting a 30% reduction in the risk of coronary atherosclerosis.
The increase in these ratios contributes to a decreased incidence of coronary atherosclerosis (Figure 4 and Supplementary Table 1).
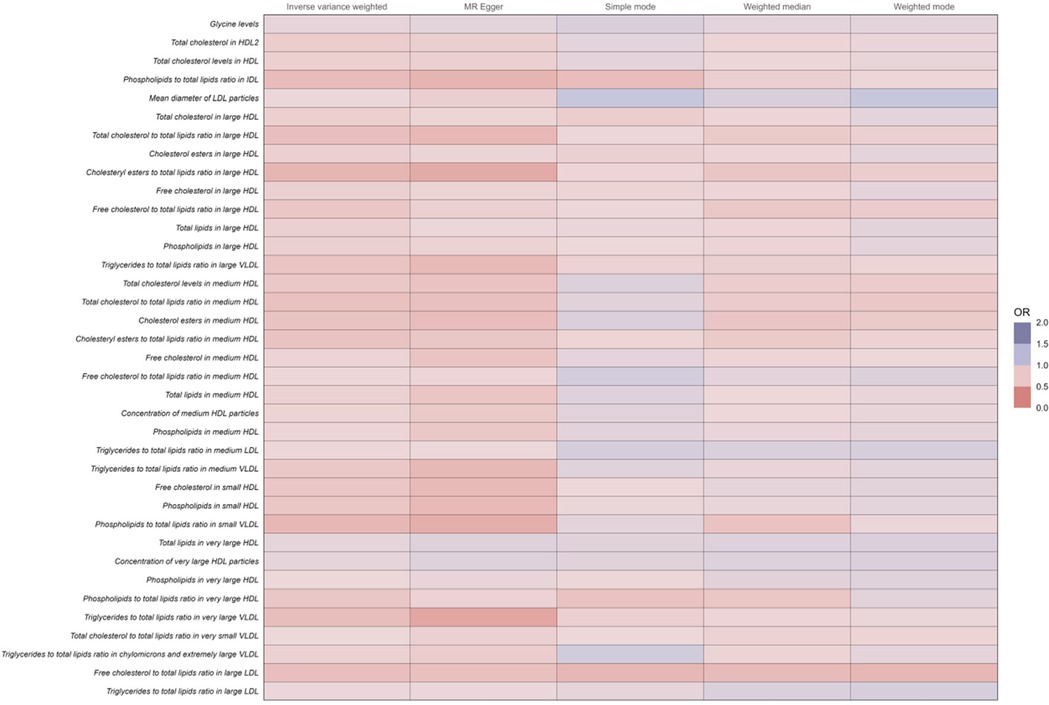
Figure 4. Full results of five Mendelian randomized analyses of OR values for 37 metabolites that reduce the risk of coronary atherosclerosis.
Sensitivity analysis
When using MR Egger, Weighted median, Simple mode, and Weighted mode for analysis, most results were consistent with those obtained using the IVW method (see Supplementary Table 1). In the MR-Egger analysis, there was no evidence of horizontal pleiotropy (see Supplementary Table 1, Figures 5, 6). Cochran's Q statistic indicated the presence of heterogeneity, so random effects IVW was used instead of fixed-effects IVW in these cases (see Supplementary Table 1, Figures 5, 6).
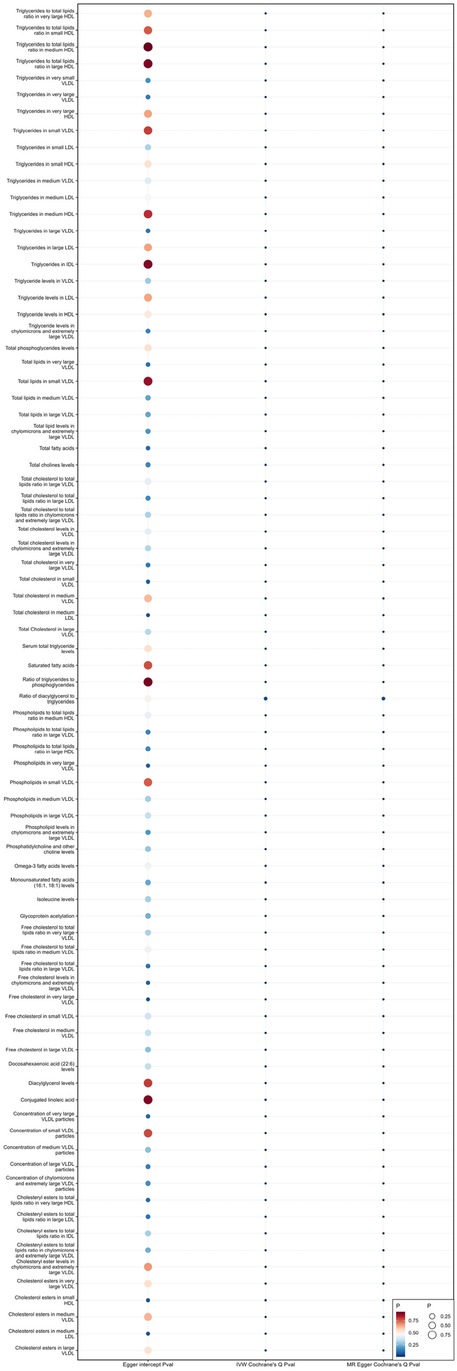
Figure 5. Heterogeneity and pleiotropy of 81 metabolites associated with increased risk of coronary atherosclerosis.
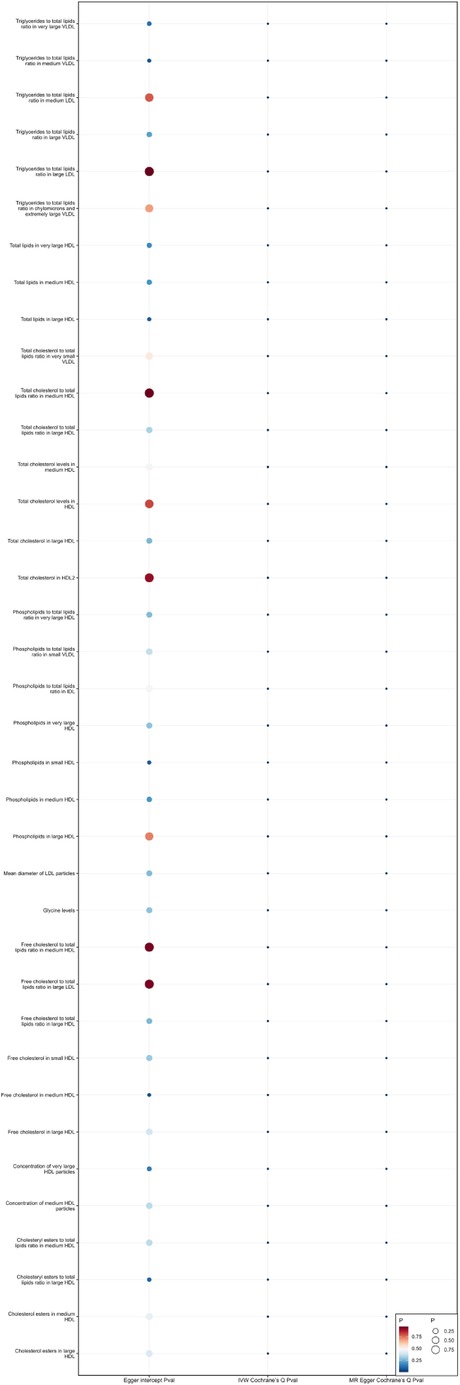
Figure 6. Heterogeneity and pleiotropy of 37 metabolites that reduce the risk of coronary atherosclerosis.
Discussion
This study identified 118 metabolites with a causal relationship to the development of coronary atherosclerosis through Mendelian randomization. Among these, 81 metabolites were found to increase the risk of coronary atherosclerosis. The dysregulated metabolic pathways through which these metabolites contribute to atherosclerosis include lipid metabolism, oxidative stress, and inflammatory responses.
TFA are composed primarily of saturated fatty acids, trans fatty acids, polyunsaturated fatty acids, and other types of fatty acids. Among them, saturated and trans fatty acids are known to elevate low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels. A study conducted on a Nigerian population found that TFA is positively correlated with LDL-C (13). Elevated LDL-C is a major risk factor for the initiation and progression of atherosclerosis (14). LDL penetrates the vascular wall through the endothelium and becomes retained in the subendothelial layer, where it undergoes modification into oxidized LDL (ox-LDL). Macrophages engulf ox-LDL, forming foam cells, which proliferate and fuse, eventually forming the lipid core of atherosclerotic plaques (15). This aligns with the “response-to-retention” hypothesis (16), which highlights the retention and modification of LDL in the subendothelial space as critical to atherogenesis. Additionally, high levels of fatty acids, particularly unsaturated fatty acids, generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) during oxidation. On one hand, ROS impair vascular endothelial function by reducing nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability (17); on the other hand, they damage vascular endothelial cells and trigger inflammatory responses, accelerating vascular stiffening (18). For example, arachidonic acid and its downstream metabolite leukotriene B4(LTB4) are known mediators in atherosclerosis (19). Studies have shown that LTB4-induced neutrophil recruitment exacerbates plaque destabilization in endotoxemic contexts, suggesting that LTB4 could be a potential therapeutic target in the treatment of atherosclerosis (20). These findings highlighting the importance of TFA in coronary atherosclerosis.
The role of triglycerides (TG) in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease (CVD) has gained attention since Austin MA et al.'s meta-analysis in 1998 highlighted its association with CVD (21). Elevated TG levels lead to dyslipidemia, generating small dense LDL particles (sdLDL). These sdLDL particles, due to their smaller size, can more easily penetrate endothelial gaps and bind to proteoglycans within the arterial wall, where they accumulate. This prolonged retention makes sdLDL more prone to oxidative and other atherogenic modifications, further amplifying its pro-atherogenic properties (22). In addition, changes in oxLDL levels are correlated with changes in the number of sdLDL particles (23). Elevated oxLDL not only induces the expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in endothelial cells—exacerbating inflammation and promoting atherosclerosis (24)—but also triggers endothelial apoptosis, accelerating endothelial dysfunction and the progression of atherosclerosis (25). Clinical studies support these findings, showing that elevated TG levels are associated with lipid-rich plaques, thin-cap fibroatheromas (TCFAs), and a higher prevalence of macrophages in atherosclerotic plaques (26–29). Hypertriglyceridemia has also been suggested by some researchers as a significant contributor to recurrent atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) events (30). Moreover, Arterial retention of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins (TRLs) and their remnants is linked to maladaptive responses central to plaque initiation and progression (31). Notably, research indicates that TRLs and their remnants are approximately four times more atherogenic than LDL (32). This mechanistic understanding of TG's role emphasizes its impact on the progression of coronary atherosclerosis.
SFA play a significant role in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) through multiple mechanisms, particularly by promoting inflammation and metabolic dysregulation. SFA activate inflammatory pathways via nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), inducing inflammatory cytokines and contributing to vascular endothelial injury (33). Diets rich in SFAs can also cause metabolic imbalance and alterations in cellular signaling causing insulin resistance (34). Insulin resistance also disrupts systemic lipid metabolism, leading to dyslipidemia and the development of the well-known lipid triad: (1) elevated plasma triglyceride levels, (2) reduced high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels, and (3) the presence of small dense low-density lipoprotein (sdLDL) particles. This lipid triad, along with endothelial dysfunction induced by aberrant insulin signaling, contributes to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques (35). Moreover, SFAs increase serum LDL levels, further promoting cardiovascular disease (36). Zong G et al. indicated that a high dietary intake of SFA correlates with increased coronary heart disease risk (37). Cross-sectional studies also link habitual SFA and trans fat intake with heightened subclinical atherosclerosis (38). These findings establish a close relationship between SFA intake and coronary atherosclerosis.
CLA primarily found in the milk and meat of ruminant animals (39), includes over 28 isomers. In natural products, the predominant isomer (≥80% of total CLA) is cis-9, trans-11, while commercial preparations vary in isomer composition (40). Animal studies have produced conflicting findings, with some suggesting CLA's protective effects against atherosclerosis (41–44), while others indicate no benefit, or even a pro-atherosclerotic effect of trans10, cis12-CLA (45). In human studies, a randomized double-blind study involving healthy young men showed that a CLA diet increased levels of the lipid peroxidation marker 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α (8-iso-PGF2α), showing an 83% elevation compared to the control group (46), indicating heightened oxidative stress (47). The increased oxidative stress induced by CLA, as evidenced by elevated 8-iso-PGF2α, reduces NO bioavailability, contributing to endothelial dysfunction and vascular aging (17). Another study with postmenopausal women demonstrated that oil containing trans10, cis12-CLA increased lipid peroxidation, thereby promoting atherosclerosis development (48). Increased lipid peroxidation disrupts normal lipid metabolism, leading to the accumulation of oxLDL within the arterial intima and further advancing atherosclerosis (25). Future research should focus on isomer-specific effects of CLA and its role in cardiovascular health to inform dietary recommendations and therapeutic interventions.
In summary, our findings emphasize the role of lipid metabolism, oxidative stress, and inflammation as key dysregulated metabolic pathways through which these metabolites contribute to the pathogenesis of coronary atherosclerosis. The intricate interplay of these pathways suggests that targeting these metabolic disturbances may be effective in mitigating coronary atherosclerosis risk.
This study has several limitations. First, Although we have made every effort to minimize confounding factors and reduce the influence of pleiotropy at the genetic level, unmeasured confounding factors may still exist. For example, environmental factors and lifestyle variables, which are not fully considered in genetic analyses, may lead to potential bias. Additionally, pleiotropy remains a challenge, as genetic variants may influence the outcome through multiple biological pathways unrelated to the metabolites studied, potentially impacting the reliability of the causal estimates. Second, this study focuses primarily on the FinnGen database, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other populations. Future studies incorporating diverse populations and addressing these confounders more rigorously will be necessary to validate our findings.
In conclusion, this study conducted a two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis to explore the causal relationships between 233 metabolites and coronary atherosclerosis based on the summary statistics of a GWAS of 233 metabolites and the FinnGen R10 release data. These findings may help elucidate the impact of metabolites on coronary atherosclerosis and inspire the development of precision medicine in this field.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: 233 metabolites (GCST90301941-GCST90302173) available at https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/. Coronary atherosclerosis: summary statistics can be accessed at https://storage.googleapis.com/finngen-public-data-r10/summary_stats/finngen_R10_I9_CORATHER.gz
Author contributions
HZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. XZ: Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZY: Formal Analysis, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. LG: Formal Analysis, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Formal Analysis, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. DZ: Formal Analysis, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation. XM: Formal Analysis, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Funding acquisition.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFC1707401).
Acknowledgments
Thanks to all authors for their contributions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcvm.2024.1439699/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Fuchs A, Kühl JT, Sigvardsen PE, Afzal S, Knudsen AD, Møller MB, et al. Subclinical coronary atherosclerosis and risk for myocardial infarction in a danish cohort: a prospective observational cohort study. Ann Intern Med. (2023) 176(4):433–42. doi: 10.7326/m22-3027
2. Xue H, Chen X, Yu C, Deng Y, Zhang Y, Chen S, et al. Gut microbially produced indole-3-propionic acid inhibits atherosclerosis by promoting reverse cholesterol transport and its deficiency is causally related to atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. (2022) 131(5):404–20. doi: 10.1161/circresaha.122.321253
3. Ouyang L, Yu C, Xie Z, Su X, Xu Z, Song P, et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 deletion-mediated kynurenine insufficiency in vascular smooth muscle cells exacerbates arterial calcification. Circulation. (2022) 145(24):1784–98. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.121.057868
4. Karjalainen MK, Karthikeyan S, Oliver-Williams C, Sliz E, Allara E, Fung WT, et al. Genome-Wide characterization of circulating metabolic biomarkers. Nature. (2024) 628(8006):130–8. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07148-y
5. Burgess S, Thompson SG. Avoiding bias from weak instruments in Mendelian randomization studies. Int J Epidemiol. (2011) 40(3):755–64. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyr036
6. Larsson SC, Butterworth AS, Burgess S. Mendelian Randomization for cardiovascular diseases: principles and applications. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44(47):4913–24. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad73 6.37935836
7. Xiao G, He Q, Liu L, Zhang T, Zhou M, Li X, et al. Causality of genetically determined metabolites on anxiety disorders: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. J Transl Med. (2022) 20(1):475. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03691-2
8. Zhou Y, Zhang H, Yan H, Huang C, Liu Y. Mendelian Randomization based on immune cells in diabetic nephropathy. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). (2024) 15:1460652. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1460652
9. Burgess S, Small DS, Thompson SG. A review of instrumental Variable estimators for Mendelian randomization. Stat Methods Med Res. (2017) 26(5):2333–55. doi: 10.1177/0962280215597579
10. Burgess S, Thompson SG. Interpreting findings from Mendelian randomization using the mr-egger method. Eur J Epidemiol. (2017) 32(5):377–89. doi: 10.1007/s10654-017-0255-x
11. Verbanck M, Chen CY, Neale B, Do R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between Complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet. (2018) 50(5):693–8. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0099-7
12. Li J, Liu L, Luo Q, Zhou W, Zhu Y, Jiang W. Exploring the causal relationship between immune cell and all-cause heart failure: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2024) 11:1363200. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1363200
13. Yeh LL, Kuller LH, Bunker CH, Ukoli FA, Huston SL, Terrell DF. The role of socioeconomic Status and Serum fatty acids in the relationship between intake of animal foods and cardiovascular risk factors. Ann Epidemiol. (1996) 6(4):290–8. doi: 10.1016/s1047-2797(96)00023-3
14. Takaoka M, Zhao X, Lim HY, Magnussen CG, Ang O, Suffee N, et al. Early intermittent hyperlipidaemia alters tissue macrophages to fuel atherosclerosis. Nature. (2024) 634(8033):457–65. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07993-x
15. Joint committee issued Chinese guideline for the management of dyslipidemia in adults. 2016 Chinese guideline for the management of dyslipidemia in adults. Chin J Cardiol. (2016) 44(10):833–53. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3758.2016.10.005
16. Williams KJ, Tabas I. The response-to-retention hypothesis of early atherogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (1995) 15(5):551–61. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.15.5.551
17. Puca AA, Carrizzo A, Ferrario A, Villa F, Vecchione C. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase, vascular integrity and human exceptional longevity. Immun Ageing. (2012) 9(1):26. doi: 10.1186/1742-4933-9-26
18. Alhayaza R, Haque E, Karbasiafshar C, Sellke FW, Abid MR. The relationship between reactive oxygen Species and endothelial cell metabolism. Front Chem. (2020) 8:592688. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.592688
19. Ma S, He S, Liu J, Zhuang W, Li H, Lin C, et al. Metabolomics unveils the exacerbating role of arachidonic acid metabolism in atherosclerosis. Front Mol Biosci. (2024) 11:1297437. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1297437
20. Mawhin MA, Tilly P, Zirka G, Charles AL, Slimani F, Vonesch JL, et al. Neutrophils recruited by leukotriene B4 induce features of plaque destabilization during endotoxaemia. Cardiovasc Res. (2018) 114(12):1656–66. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy130
21. Austin MA, Hokanson JE, Edwards KL. Hypertriglyceridemia as a cardiovascular risk factor. Am J Cardiol. (1998) 81(4a):7b–12b. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(98)00031-9
22. Keremu M, Adi D, Wei X, Aizezi A, Ma Y. Research progress on the association between small dense low density lipoprotein and cardiovascular disease. Chin J Cardiol. (2023) 23(06):583–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5410.2023.06.016
23. Wang L, Tao L, Hao L, Stanley TH, Huang KH, Lambert JD, et al. A moderate-fat diet with one avocado per day increases plasma antioxidants and decreases the oxidation of small, dense ldl in adults with overweight and obesity: a randomized controlled trial. J Nutr. (2020) 150(2):276–84. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxz231
24. Vekic J, Stromsnes K, Mazzalai S, Zeljkovic A, Rizzo M, Gambini J. Oxidative stress, atherogenic dyslipidemia, and cardiovascular risk. Biomedicines. (2023) 11(11):2897. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11112897
25. Ahsan A, Han G, Pan J, Liu S, Padhiar AA, Chu P, et al. Phosphocreatine protects endothelial cells from oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis by modulating the Pi3k/akt/enos pathway. Apoptosis. (2015) 20(12):1563–76. doi: 10.1007/s10495-015-1175-4
26. Polonskaya YV, Shramko VS, Morozov SV, Chernyak EI, Chernyavsky AM, Ragino YI. Balance of fatty acids and their correlations with parameters of lipid metabolism and markers of inflammation in men with coronary atherosclerosis. Bull Exp Biol Med. (2017) 164(1):33–5. doi: 10.1007/s10517-017-3920-x
27. Yamashita M, Iwata A, Kato Y, Futami M, Imaizumi S, Kuwano T, et al. Impact of the triglyceride level on coronary plaque components in female patients with coronary artery disease treated with statins. Heart Vessels. (2018) 33(10):1175–84. doi: 10.1007/s00380-018-1173-x
28. Asakura K, Minami Y, Kinoshita D, Katamine M, Kato A, Katsura A, et al. Impact of triglyceride levels on plaque characteristics in patients with coronary artery disease. Int J Cardiol. (2022) 348:134–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2021.12.008
29. Asakura K, Minami Y, Nagata T, Katamine M, Muramatsu Y, Kinoshita D, et al. Higher triglyceride levels are associated with the higher prevalence of layered plaques in non-culprit coronary plaques. J Thromb Thrombolysis. (2024) 57(1):58–66. doi: 10.1007/s11239-023-02888-6
30. Sandesara PB, Virani SS, Fazio S, Shapiro MD. The Forgotten lipids: triglycerides, remnant cholesterol, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk. Endocr Rev. (2019) 40(2):537–57. doi: 10.1210/er.2018-00184
31. Ginsberg HN, Packard CJ, Chapman MJ, Borén J, Aguilar-Salinas CA, Averna M, et al. Triglyceride-Rich lipoproteins and their remnants: metabolic insights, role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, and emerging therapeutic strategies-a consensus statement from the European atherosclerosis society. Eur Heart J. (2021) 42(47):4791–806. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehab551
32. Björnson E, Adiels M, Gummesson A, Taskinen MR, Burgess S, Packard CJ, et al. Quantifying triglyceride-rich lipoprotein atherogenicity, associations with inflammation, and implications for risk assessment using non-hdl cholesterol. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2024) 84(14):1328–38. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2024.07.034
33. Kennedy A, Martinez K, Chuang CC, LaPoint K, McIntosh M. Saturated fatty acid-mediated inflammation and insulin resistance in adipose tissue: mechanisms of action and implications. J Nutr. (2009) 139(1):1–4. doi: 10.3945/jn.108.098269
34. Silva Figueiredo P, Carla Inada A, Marcelino G, Maiara Lopes Cardozo C, de Cássia Freitas K, de Cássia Avellaneda Guimarães R, et al. Fatty acids consumption: the role metabolic aspects involved in obesity and its associated disorders. Nutrients. (2017) 9(10):1158. doi: 10.3390/nu9101158
35. Ormazabal V, Nair S, Elfeky O, Aguayo C, Salomon C, Zuñiga FA. Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2018) 17(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0762-4
36. Sacks FM, Lichtenstein AH, Wu JHY, Appel LJ, Creager MA, Kris-Etherton PM, et al. Dietary fats and cardiovascular disease: a presidential advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2017) 136(3):e1–e23. doi: 10.1161/cir.0000000000000510
37. Zong G, Li Y, Wanders AJ, Alssema M, Zock PL, Willett WC, et al. Intake of individual saturated fatty acids and risk of coronary heart disease in US men and women: two prospective longitudinal cohort studies. Br Med J. (2016) 355:i5796. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i5796
38. Merchant AT, Kelemen LE, de Koning L, Lonn E, Vuksan V, Jacobs R, et al. Interrelation of saturated fat, trans fat, alcohol intake, and subclinical atherosclerosis. Am J Clin Nutr. (2008) 87(1):168–74. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/87.1.168
39. Schmid A, Collomb M, Sieber R, Bee G. Conjugated linoleic acid in meat and meat products: a review. Meat Sci. (2006) 73(1):29–41. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2005.10.010
40. Kramer JK, Parodi PW, Jensen RG, Mossoba MM, Yurawecz MP, Adlof RO. Rumenic acid: a proposed common name for the Major conjugated linoleic acid isomer found in natural products. Lipids. (1998) 33(8):835. doi: 10.1007/s11745-998-0279-6
41. Lee KN, Kritchevsky D, Pariza MW. Conjugated linoleic acid and atherosclerosis in rabbits. Atherosclerosis. (1994) 108(1):19–25. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(94)90034-5
42. Franczyk-Zarów M, Kostogrys RB, Szymczyk B, Jawień J, Gajda M, Cichocki T, et al. Functional effects of eggs, naturally enriched with conjugated linoleic acid, on the blood lipid profile, development of atherosclerosis and composition of atherosclerotic plaque in apolipoprotein E and low-density lipoprotein receptor double-knockout mice (apoe/ldlr-/-). Br J Nutr. (2008) 99(1):49–58. doi: 10.1017/s0007114507793893
43. Toomey S, Harhen B, Roche HM, Fitzgerald D, Belton O. Profound resolution of early atherosclerosis with conjugated linoleic acid. Atherosclerosis. (2006) 187(1):40–9. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2005.08.024
44. Kanter JE, Goodspeed L, Wang S, Kramer F, Wietecha T, Gomes-Kjerulf D, et al. 10,12 Conjugated linoleic acid-driven weight loss is protective against atherosclerosis in mice and is associated with alternative macrophage enrichment in perivascular adipose tissue. Nutrients. (2018) 10(10):1416. doi: 10.3390/nu10101416
45. Arbonés-Mainar JM, Navarro MA, Guzmán MA, Arnal C, Surra JC, Acín S, et al. Selective effect of conjugated linoleic acid isomers on atherosclerotic lesion development in apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Atherosclerosis. (2006) 189(2):318–27. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.01.015
46. Raff M, Tholstrup T, Basu S, Nonboe P, Sørensen MT, Straarup EM. A diet rich in conjugated linoleic acid and butter increases lipid peroxidation but does not affect atherosclerotic, inflammatory, or diabetic risk markers in healthy young men. J Nutr. (2008) 138(3):509–14. doi: 10.1093/jn/138.3.509
47. Basu S. F2-isoprostanes in human health and diseases: from molecular mechanisms to clinical implications. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2008) 10(8):1405–34. doi: 10.1089/ars.2007.1956
48. Tholstrup T, Raff M, Straarup EM, Lund P, Basu S, Bruun JM. An oil mixture with trans-10, cis-12 conjugated linoleic acid increases markers of inflammation and in vivo lipid peroxidation compared with cis-9, trans-11 conjugated linoleic acid in postmenopausal women. J Nutr. (2008) 138(8):1445–51. doi: 10.1093/jn/138.8.1445
Keywords: coronary atherosclerosis, metabolites, Mendelian randomization, causal relationship, two-sample
Citation: Zhang H, Zheng X, Yan Z, Guo L, Zheng Y, Zhang D and Ma X (2024) The causal relationship between 233 metabolites and coronary atherosclerosis: a Mendelian randomization study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 11:1439699. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1439699
Received: 28 May 2024; Accepted: 26 November 2024;
Published: 12 December 2024.
Edited by:
Isabella Russo, University of Turin, ItalyReviewed by:
Liu Ouyang, Georgia State University, United StatesRoland Wohlgemuth, Lodz University of Technology, Poland
Copyright: © 2024 Zhang, Zheng, Yan, Guo, Zheng, Zhang and Ma. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaochang Ma, bWF4aWFvY2hhbmdAeDI2My5uZXQ=; Dawu Zhang, ZGF3dTQ0MDNAc2luYS5jb20=
 Hongwei Zhang
Hongwei Zhang Xiaoyu Zheng
Xiaoyu Zheng Zian Yan1,2,4
Zian Yan1,2,4 Dawu Zhang
Dawu Zhang Xiaochang Ma
Xiaochang Ma