- 1Department of Pharmacy, Institute of Health Science, Wallaga University, Nekemte, Ethiopia
- 2Department of Pharmacy, College of Health Science, Mattu University, Mattu, Ethiopia
- 3Department of Health Informatics, College of Health Science, Mattu University, Mattu, Ethiopia
- 4Department of Nursing, College of Health Science, Mattu University, Mattu, Ethiopia
Background: Heart failure is a significant worldwide health problem that leads to mortality. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate treatment outcomes and associated factors of heart failure patients who were admitted to hospitals in the southwest of Ethiopia.
Methods and participants: A multicenter prospective observational study was conducted from 1 February to 1 August 2021. Drug therapy problems were assessed as per the Cipolle, Strands, and Morley drug therapy problems classification method. The drug therapy was registered by using the drug-related problem registration format. The results of logistic regression analysis was interpreted as crude odds ratio and adjusted odds ratio (AOR) at 95% confidence interval (CI) to determine the association between dependent and independent variables.
Results: In our study settings, a total of 205 (85.1%) heart failure patients showed improvement and 36 (14.9%) died at hospital discharge. Being ≥65 years (AOR = 7.14, 95% CI: 2.04–.25.01, P = 0.002), a previous hospitalization (AOR = 6.20, 95% CI: 1.81–21.21, P = 0.004), and the presence of medication-related problems (AOR = 3.65, 95% CI: 1.13–11.73, P = 0.03) were the predictors of mortality.
Conclusion: The prevalence of in-hospital mortality among heart failure patients was found to be high. Previous hospitalization, older age, and the presence of drug therapy problems were the predictors of mortality among heart failure patients. Therefore, proper attention should be given to the management of elderly and re-admitted heart failure patients in addition to their regular care. In addition, hospitals should implement clinical pharmacy services to address any drug-related problems.
Background
Heart failure (HF) is a multifactorial clinical condition defined by the heart's diminished capacity to pump and/or fill with blood (1). The clinical presentations of the HF include dyspnea, exhaustion, low exercise tolerance, and fluid retention (2, 3).
There are 64.34 million cases of heart failure worldwide (4). Heart failure is a well-known public health issue that places a heavy burden on patients and healthcare systems (5), with a prevalence of 6.5 million in the United States (US) (6).
Africa is witnessing an increase in the prevalence of HF, especially in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) (7). There are various reports of the prevalence of heart failure across sub-Saharan Africa. It was 30% in Cameroon, it ranges from 9.4% to 42.5% in Nigeria, and it ranges from 25.6% to 28.6% in Togo (8). According to a study done in Ethiopia, 23.9% of people have HF, making it one of the most prevalent cardiovascular disorders (9), whereas in Burkina Faso it accounts for 17.62% (10).
Data from the eight SSA countries have shown that up to 75% of heart failure cases were non-ischemic in origin (7). Several studies have shown that the most common causes of heart failure in SSA are cardiomyopathies and hypertension (11). Patients with heart failure in sub-Saharan Africa were the youngest at onset, and most likely to be in New York Health Association functional class IV compared with those from Asia, the Middle East, and South America (7).
Even in affluent nations, HF is a primary cause of hospitalization, and treatment outcomes are still subpar (5, 12). Consequently, the goals of HF therapy are to increase functional ability, decrease hospitalization, and prolong life (13).
Hospitalizations and readmissions for heart failure are frequent, and residual mortality is still high even with the intensive use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs), angiotensin receptor blockers, beta-blockers, and aldosterone antagonists (14, 15). People with HF report a generally lower quality of life and considerable negative consequences on their ability to manage themselves at home (16).
Patients need medication treatment for both HF and related disorders since HF is the end-stage of several cardiovascular diseases and their inherent risk factors (17). Polypharmacy in the management of heart failure patients has been linked to worse treatment results, medication interactions, improper drug prescriptions, poor adherence, and an increased risk of drug-related problems (DRP) (18, 19). In lower middle income countries, HF patients' poor medication adherence significantly increases the chance of mortality and hospital readmissions (20). Heart failure–associated mortality increases among patients having medication-related problems (21).
For many years, heart failure syndrome has been acknowledged as a major factor in the burden of cardiovascular illness in sub-Saharan Africa (22). Hospital mortality in Angola was 23% (23). In Nigeria, the overall death rate was 4.3% (24). In Mozambique, the composite death rate was 21.1% (25). The death rate in Kenya was 7.6% (26). The total incidence of all-cause mortality in Uganda was 3.58 per 1,000 people (27).
Heart failure patients having lower left ventricular ejection fraction (EF) have poor treatment outcomes. In spite of this, there is a dearth of prospective and multicenter evidence regarding the outcomes and predictors of heart failure treatment. Thus, the study's objective was to evaluate the treatment outcome and associated factors of heart failure patients in southwest Ethiopia hospital.
Methodology
Study area, design, and period
A multicenter prospective observational study was conducted at five hospitals in the Iluababor and Buno Bedele zone, southwestern Ethiopia, namely, Mettu Karl Comprehensive Specialized Hospital (MKSCH), Bedele Hospital (BH), Darimu Hospital (DH), Chora Hospital (CH), and Didesa Hospital (DIH) from 1 February to 1 August 2021.
Study participants and eligibility criteria
Patients who were over the age of 18, diagnosed with HF, hospitalized for more than 48 h, and receiving HF treatment during the study period were included in the study. Patients who declined to participate, who were transferred to another hospital, whose doctors did not confirm their diagnosis of congestive heart failure (CHF), and who chose to discharge themselves were excluded. CHF was diagnosed based on different investigations like chest X-ray, electrocardiogram, ejection fraction, and echocardiogram.
Study variables and outcome endpoints
The primary treatment outcome included mortality, improvement in signs and symptoms, ejection fraction, HF stage, and New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class. The patients HF stage and class were based on NYHA functional classification and American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA) stages (28).
On a daily basis, patients were observed to evaluate if the symptoms and indicators of HF had disappeared. Physicians conducted a thorough echocardiographic evaluation of regional wall anomalies, ventricular function, and valvular structure and function.
Drug therapy problems (DTPs) were assessed as per the Cipolle, Strands, and Morley drug therapy problems classification method (29). Mortality was evaluated at discharge from hospital from 1 February to 1 August 2021.
Sample size and sampling technique
Single population proportion formula was used to calculate the required sample size by considering the following assumptions: n is the required sample size, p is the hospital mortality and found to be 17.2% (0.172) (21), Z is the standardized normal distribution value at 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.96, and d is the margin of error of 5% (0.05).
A 10% loss to follow-up yielded a final sample size of 241. The study subjects were selected by proportional allocation based on the number of HF patients that the respective hospitals contained in their medical ward: 82 patients from MKSCH, 51 from BH, 43 from DH, 30 from CH, and 35 from DIH were included. The subjects were chosen by using the consecutive sampling technique from 1 February to 1 August 2021.
Data collection process and management
A questionnaire that was created after studying several works of literature was used to collect the data. Through patient interviews, information was gathered about the patients' socio-demographic traits, medication compliance, smoking status, alcohol intake, and chewing gum behavior. For the purpose of gathering data, five nurses and five pharmacists were enlisted. The task of overseeing the data collection procedure was given to five physicians and five pharmacists. The lead investigator and supervisor constantly monitored the procedure of gathering data on the spot. Following data collection, the lead investigator assessed the suitability of medical therapy using a variety of sources, including guidelines and references from Medscape, Up-to-date, Lexicom, and Micromedex. DTP was registered using the DRP registration format.
Data processing and analysis
The data were analyzed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 23. By utilizing odds ratio (OR) (95% CI), multivariable and binary logistic regression were utilized to identify the factors. The categorical variables were compared using the chi-square test. If the P-value is <0.05, we finally announce the relationships between the treatment outcome and the independent variables.
Operational definitions
Treatment outcome: The accomplishment of a predetermined goal, such as improvement or death (21).
Poor outcome: HF-related hospital mortality (21).
Good outcome: When patients are discharged having improved (21).
Drug therapy problem/drug-related problems: Drug interactions, unsuitable indications and dosages, non-adherence, adverse drug reactions (ADRs), and poor pharmacological therapy are all included in this study (30).
Preserved EF: A clinical diagnosis of HF and an LVEF of >40% (31).
Reduced EF: A clinical diagnosis of HF and an LVEF of ≤40% (31).
Results
Socio-demographic and life style characteristics of the study participants
From the 241 HF patients admitted to the medical wards of southwestern Ethiopian hospitals, 138 (57.3%) were males. Half of the patients [125 (51.9%)] were in the age range of 45–64 years, while the mean and standard deviation (SD) of the patients age was 52.09 ± 16.75. Regarding their area of residence, 131 (54.4%) were from rural areas. A total of 172 (71.4%) were married and 120 (49.8%) of them were farmers. Regarding their lifestyle, 53 (21.99%) of them drunk alcohol, 23 (9.54%) used tobacco, 82 (34.02%) chewed khat, 139 (57.68%) were physically active, and 145 (60.17%) consumed a salt (Table 1).
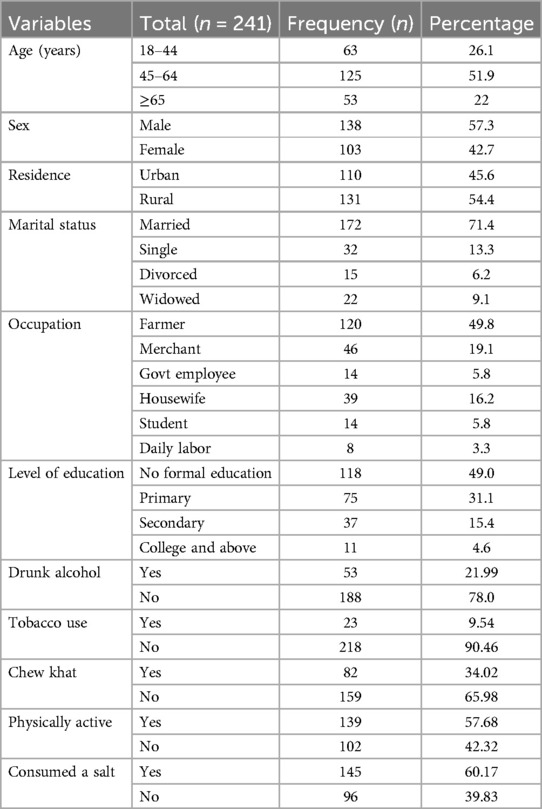
Table 1. Socio-demographic and life style factors of CHF patients admitted to the medical wards of southwestern Ethiopian hospitals from 1 February to 1 August 2021.
The clinical characteristics of the study respondents
Over the study period, about two-third [162 (67.2%)] of the HF patients were categorized under stage C and 147 (61.0%) of them were under NYHA class IV. A total of 131 (54.4%) patients had a previous history of admission for HF. About half 126 (52.3%) of the HF patients presented with two or more than two comorbid diseases, and most of them had hypertension [48 (19.92%)] (Table 2). The average length of hospital stay (LOS) was 11.13 ± 8.07 days. In relation to chronic kidney disease (CKD), the mean ± SD of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was 51 + 12.53 ml/min/1.73 m2.
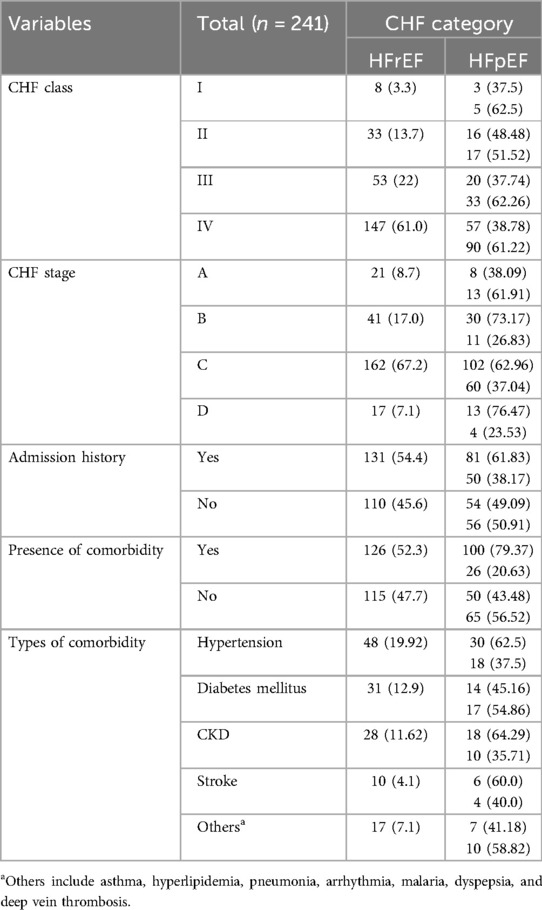
Table 2. Clinical characteristics of CHF patients admitted to the medical wards of southwestern Ethiopian hospitals from 1 February to 1 August 2021.
The most commonly prescribed drugs
The most commonly prescribed medications were furosemide [210 (87.14%)], spironolactone [96 (39.83%)], and enalapril [83 (34.44%)], whereas statins [4 (1.66%)] were the least likely prescribed medications for CHF patients (Table 3).
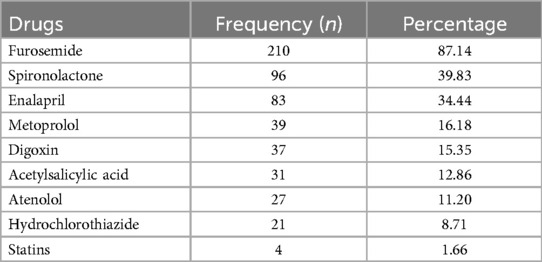
Table 3. The commonly prescribed heart failure medication at the medical wards of southwestern Ethiopian hospitals from 1 February to 1 August 2021.
The etiology of heart failure
In our study, the most common causes of heart failure was dilated cardiomyopathy [56 (23.24%)], coronary artery disease [48 (19.92%)], and hypertensive heart disease [35 (14.52%)], whereas congenital heart disease [12 (4.98%)] was the least likely cause (Table 4).
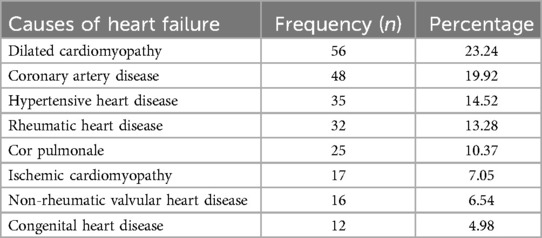
Table 4. The common etiologies of heart failure patients admitted to the medical wards of southwestern Ethiopian hospitals from 1 February to 1 August 2021.
Prevalence and types of drug therapy problems
Over the study period, total of 165 (68.5%) drug therapy problems were identified, whereas 76 (31.5%) patients were appropriately treated. The most commonly occurred drug therapy problems were the need for additional drug therapy [41 (17.02%)], too low dose [31 (12.86%)], and ineffective drug therapy [28 (11.62%)], whereas adverse drug reaction [8 (3.32%)] was the least likely occurred drug therapy problems (Table 5).
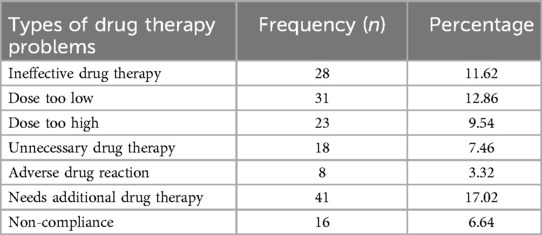
Table 5. Types of drug therapy problems of the heart failure patients admitted to the medical wards of southwestern Ethiopian hospitals from 1 February to 1 August 1.
Magnitudes and determinants of mortality among HF patients
Over the study period, a total of 205 (85.1%) HF patients showed improved and 36 (14.9%) died. The mortality rates in MKSCH, BH, DH, DIH, and CH were 12 (33.33%), 9 (25%), 6 (16.67), 5 (13.89%), and 4 (11.11%), respectively. Patients aged ≥65 years were seven times more likely to die than younger patients [adjusted odds ratio (AOR) = 7.14, 95% CI: 2.04–25.01, P = 0.002]. Heart failure patients who had a previous admission were six times more likely to die than naïve patients (AOR = 6.20, 95% CI: 1.81–21.21, P = 0.004). Finally, patients who had medication-related problems were 3.65 times more likely to die than patients who did not have any drug therapy problems (AOR = 3.65, 95% CI: 1.13–11.73, P = 0.03) (Table 6).
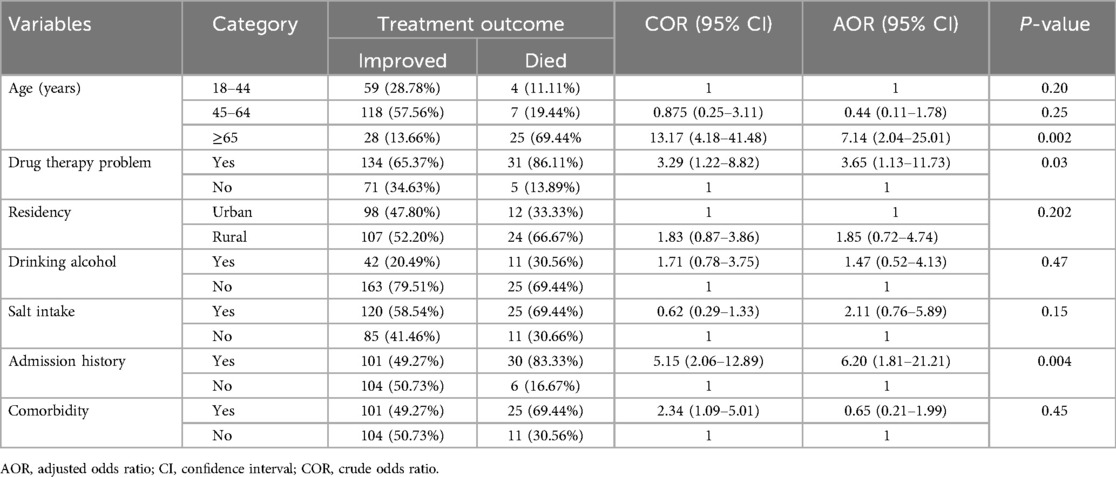
Table 6. Bivariable and multivariable logistic regression analysis of factors associated with the treatment outcomes of CHF patients admitted to the medical wards of southwestern Ethiopian hospitals from 1 February to 1 August 2021.
Discussion
In our study, the magnitude of mortality in congestive heart failure was 36 (14.9%). This was higher than the study conducted in the US (3.8%) (32) and Brazil (11.2%) (33), and lower than Spain (33.2%) (34), Saudi Arabia (19.09%) (35), and Tikur Anbessa Specialized Hospital (TASH) (17.2%) (21). As compared with other sub-Saharan African nations, the mortality rate was higher than Kenya (7.6%) (26), Nigeria (4.3%) (24), and Uganda (3.58 per 1,000 person-days) (27), and lower than the studies done in Tanzania (25.4%) (36), Burkina Faso (31%) (10), and Angola (23%) (23). The variety of outcomes reported might be due to the difference in the quality of HF management, methodology, and multicenter coverage of the study participants.
Regarding the prediction of mortality among HF patients, patients aged ≥65 years were seven times more likely to die than younger patients (AOR = 7.14, 95% CI: 2.04–.25.01, P = 0.002). This was consistent with the study conducted at the US (32), Canada (37), Spain (34), Brazil (33), Korea (38), Uganda (27), and Saudi Arabia (26). However, the study conducted in Angola showed that mortality was high among young and middle-aged groups (23). This is due to the fact that as the age increased, the organ functions reduced, impairing the pharmacokinetics of the drugs, and elder patients presented with a variety of comorbidities that might impose the burden of worsening outcomes in HF patients.
The HF patients who had a previous admission were six times more prone to die than naïve patients (AOR = 6.20, 95% CI: 1.81–21.21, P = 0.004). This was in line with the finding from the International Congestive Heart Failure (INTER-CHF) study (39) and studies from Brazil (33) and Korea (38). Similarly, in North Middlesex University Hospital and the Acute Heart Failure Global Registry of Standard Treatment (ALARM-HF) global survey, long-term mortality was significantly lower in single admitters vs. re-admitters (p < 0.0001) (40, 41). The study conducted in Burkina Faso also revealed that the mortality was lower among newly admitted heart failure patients (10).
In our study the management of the decompensated heart failure was more complex and lifesaving positive inotropic medications were unavailable that results in the risk of mortality than HF naïve patients.
Over the study period, total of 165 (68.5%) drug therapy problems were identified, whereas 76 (31.5%) patients were appropriately treated. This was consistent with the study conducted at Jimma Medical Center and medical wards of Mettu Karl Hospital, Bedele General Hospital (BGH), and Darimu General Hospital (42, 43). The most commonly occurred drug therapy problems were the need for additional drug therapy [41 (17.02%)], too low dose [31 (12.86%)], and ineffective drug therapy [28 (11.62%)]. Patients who had medication-related problems were 3.65 times more prone to die than patients who did not have any drug therapy problems (AOR = 3.65, 95% CI: 1.13–11.73, P = 0.03). This is similar with the finding from TASH (21) and a systematic review and meta-analysis study done by Bekele et al. (44). Drug-related problem registration format was used to identify and record different types of drug-related problems.
There was no association between the stages and class of HF in our study area with the treatment outcomes of HF patients. Despite this, the advanced stages and HF classes were predictors of mortality according to the INTER-CHF study (39) and studies conducted in South India (45) and Saudi Arabia (35). In Uganda, NYHA class IV was the predictor of mortality (27). Therefore, the patients on advanced stage HF should not be ignored.
To improve heart failure outcomes in resource-limited settings, management of heart failure should be individualized based on each patient's clinical characteristics, preferences, and comorbidities. In addition, to improve the medication compliance, educating and counseling patients to increase their knowledge about HF therapy is paramount (46). Finally, self-care is viewed as the cornerstone of HF therapy and entails essential practices that have been shown to improve HF clinical outcomes. These include adjusting one's lifestyle by taking prescribed medications as directed, sodium diet restriction, exercising, reducing liquid intake, and routinely weighing oneself (47).
The three most common causes of heart failure in our study were hypertensive heart disease, coronary artery disease, and dilated cardiomyopathy. In Tanzania, the most often found cause of heart failure was uncontrolled hypertension (11). In Burkina Faso, the two most common causes of HF were idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy (19.80%) and hypertensive heart disease (50.34%) (10).
In contrast, sepsis, congenital heart disease, severe anemia, and respiratory tract infections were the leading causes of heart failure in Nigeria (48). In Kenya, the common causes were infection, anemia, rheumatic heart disease, and congenital heart disease (27). The variety of heart failure causes might be due to the different study participants and the race of the included patients.
As a strength, the study was a prospective and multicenter study that extensively followed the patients. In addition, the frequency of medication-related issues and their effect on congestive heart failure treatment results were evaluated.
The limitation of the study
The study only assessed the hospital mortality and some investigations like computed tomography scan was not available. The absence of this equipment might hinder the diagnosis and identification of the different causes of heart failure. The government should donate this machine to assist in rapid diagnosis of heart failure.
In addition, the data were collected during the COVID-19 pandemic that could impose a fear on data collectors. As the result, data collectors might not have addressed heart failure patients who had COVID-19. Therefore, personnel protective equipment should be available for all data collectors.
Conclusion
The prevalence of mortality in HF patients was found to be high and more than two-third of the patients presented with one or more drug-related problems. The most commonly prescribed medications were furosemide, spironolactone, and enalapril. Over the study period, about two-third of the HF patients were categorized under HF stage C and NYHA class IV.
Regarding the treatment outcomes of HF, previous hospitalization, older age, and the presence of drug therapy problems were the predictors of mortality among HF patients. Inappropriate use of anti-heart failure medication was reported. Therefore, the patient should comply with the recommended guideline. In addition to usual care of the HF patients, due attention should be given in the management of elderly and re-admitted HF patients. Conversely, the clinical pharmacy services should be established in hospitals to tackle any drug-related problems in our study area. Clinical pharmacists should be assigned into medical wards and involved in daily patient rounds with physicians. The pharmaceutical care assessment checklist should be filled and evaluated by senior clinical pharmacy specialists for the presence of any medication-related problems.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Research Ethics Review Committee (RERC) of the Mattu University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
FB: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TS: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. TT: Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft. SP: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MS: Methodology, Writing – original draft. LT: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. WG: Validation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We thank Mattu University for providing the chance to conduct this study. We also thank the hospital administrators, data collectors, and study participants for extending their help toward our study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
ACC, American College of Cardiology; ACEI, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors; ADR, adverse drug reaction; AHA, American Heart Association; ALARM-HF, Acute Heart Failure Global Registry of Standard Treatment; AOR, adjusted odds ratio; BGH, Bedele General Hospital; CH, Chora Hospital; CHF, congestive heart failure; CI, confidence interval; COR, crude odds ratio; DH, Darimu Hospital; DIH, Didesa Hospital; DTP, drug therapy problem; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; INTER-CHF, International Congestive Heart Failure; MKSCH, Mettu Karl Specialized Comprehensive Hospital; NYHA, New York Heart Association; SD, standard deviation; SPSS, Statistical Package for Social Sciences; TASH, Tikur Anbessa Specialized Hospital; UK, United Kingdom; US, United States.
References
1. Savarese G, Lund LH. Global public health burden of heart failure. Card Fail Rev. (2017) 3(1):7. doi: 10.15420/cfr.2016:25:228785469
2. Fonarow GC. Refining classification of heart failure based on ejection fraction. JACC Heart Fail. (2017) 5(11):808–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jchf.2017.08.01129096789
3. Ziaeian B, Fonarow GC. Epidemiology and aetiology of heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol. (2016) 13(6):368–78. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2016.2526935038
4. Lippi G, Sanchis-Gomar F. Global epidemiology and future trends of heart failure. AME Med J. (2020) 5:1–6. doi: 10.21037/amj.2020.03.03
5. Callender T, Woodward M, Roth G, Farzadfar F, Lemarie J-C, Gicquel S, et al. Heart failure care in low-and middle-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. (2014) 11(8):e1001699. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.100169925117081
6. Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A, Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2019) 139(10):e56–528. doi: 10.1161/CIR.000000000000065930700139
7. Gallagher J, McDonald K, Ledwidge M, Watson CJ. Heart failure in sub-Saharan Africa. Card Fail Rev. (2018) 4(1):1. doi: 10.15420/cfr.2018:4:1
8. Nyaga UF, Bigna JJ, Agbor VN, Essouma M, Ntusi NA, Noubiap JJ. Data on the epidemiology of heart failure in sub-Saharan Africa. Data Brief. (2018) 17:1218–39. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2018.01.10029876481
9. Tefera YG, Abegaz TM, Abebe TB, Mekuria AB. The changing trend of cardiovascular disease and its clinical characteristics in Ethiopia: hospital-based observational study. Vasc Health Risk Manag. (2017) 13:143. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S13125928461753
10. Mandi DG, Bamouni J, Yaméogo RA, Naïbé DT, Kaboré E, Kambiré Y, et al. Spectrum of heart failure in sub-Saharan Africa: data from a tertiary hospital-based registry in the eastern center of Burkina Faso. Pan Afr Med J. (2020) 36(1):1–17. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2020.36.30.1932132550964
11. Hertz JT, Sakita FM, Limkakeng AT, Mmbaga BT, Appiah LT, Bartlett JA, et al. The burden of acute coronary syndrome, heart failure, and stroke among emergency department admissions in Tanzania: a retrospective observational study. Afr J Emerg Med. (2019) 9(4):180–4. doi: 10.1016/j.afjem.2019.07.00131890481
12. Taylor CJ, Ordóñez-Mena JM, Roalfe AK, Lay-Flurrie S, Jones NR, Marshall T, et al. Trends in survival after a diagnosis of heart failure in the United Kingdom 2000–2017: population based cohort study. Br Med J. (2019) 364:1–10. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l223
13. Yilmaz M, Mebazaa A. Definition and characteristics of the vulnerable phase in heart failure. Medicographia. (2015) 37(2):1–5. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000794
14. Benatar D, Bondmass M, Ghitelman J, Avitall B. Outcomes of chronic heart failure. Arch Intern Med. (2003) 163(3):347–52. doi: 10.1001/archinte.163.3.34712578516
15. Davidson BT, Allison TL. Improving heart failure patient outcomes utilizing guideline-directed therapy. Nurse Pract. (2017) 42:3–14. doi: 10.1097/01.NPR.0000520610.88962.0329176336
16. Johansson M, Athilingam P. A dual-pronged approach to improving heart failure outcomes: a quality improvement project. JMIR Aging. (2020) 3(1):e13513. doi: 10.2196/1351332039813
17. Flesch M, Erdmann E. The problem of polypharmacy in heart failure. Curr Cardiol Rep. (2006) 8(3):217–25. doi: 10.1007/s11886-006-0037-717543249
18. Rushton CA, Kadam UT. Polypharmacy in heart failure: a growing challenge. Br J Card Nurs. (2011) 6(5):214–20. doi: 10.12968/bjca.2011.6.5.214
19. Mastromarino V, Casenghi M, Testa M, Gabriele E, Coluccia R, Rubattu S, et al. Polypharmacy in heart failure patients. Curr Heart Fail Rep. (2014) 11(2):212–9. doi: 10.1007/s11897-014-0186-824493574
20. Pallangyo P, Millinga J, Bhalia S, Mkojera Z, Misidai N, Swai HJ, et al. Medication adherence and survival among hospitalized heart failure patients in a tertiary hospital in Tanzania: a prospective cohort study. BMC Res Notes. (2020) 13:1–8. doi: 10.1186/s13104-020-04959-w31898526
21. Tirfe M, Nedi T, Mekonnen D, Berha AB. Treatment outcome and its predictors among patients of acute heart failure at a tertiary care hospital in Ethiopia: a prospective observational study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2020) 20(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12872-019-01318-x31959121
22. Bloomfield GS, Barasa FA, Doll JA, Velazquez EJ. Heart failure in sub-Saharan Africa. Curr Cardiol Rev. (2013) 9(2):157–73. doi: 10.2174/1573403X1130902000823597299
23. Morais H, Alfredo A, Lopes I, Gonçalves MA. Etiology, clinical features, comorbidities and mortality in patients with acute heart failure. Experience of a tertiary public hospital in Angola. Cardiospace. (2023) 2:1–11. doi: 10.55976/cds.2202311211-11
24. Onwuchekwa AC, Asekomeh GE. Pattern of heart failure in a Nigerian teaching hospital. Vasc Health Risk Manag. (2009) 5:745–50. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S680419774215
25. Karaye KM, Dokainish H, ElSayed A, Mondo C, Damasceno A, Sliwa K, et al. Clinical profiles and outcomes of heart failure in five African countries: results from INTER-CHF study. Glob Heart. (2021) 16(1):50. doi: 10.5334/gh.94034381672
26. Ogeng'o JA, Gatonga PM, Olabu BO, Nyamweya DK, Ong'era D. Pattern of congestive heart failure in a Kenyan paediatric population: cardiovascular topics. Cardiovasc J Afr. (2013) 24(4):117–20. doi: 10.5830/CVJA-2013-015
27. Abeya FC, Lumori BA, Akello SJ, Annex BH, Buda AJ, Okello S. Incidence and predictors of 6 months mortality after an acute heart failure event in rural Uganda: the Mbarara Heart Failure Registry (MAHFER). Int J Cardiol. (2018) 264:113–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2018.03.11029655949
28. Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, Allen LA, Byun JJ, Colvin MM, et al. Guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2022) 79(17):e263–421. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.12.01235379503
29. Cipolle RJ, Strand LM, Morley PC. “Drug therapy problems”. In: Pharmaceutical Care Practice: The Patient-Centered Approach to Medication Management Services, 3rd ed. New York, NY: The McGraw-Hill Companies (2012). p. 1–4.
30. Vm JF, Horvat N, Tommy W. Pharmaceutical care network Europe foundation. Classification for drug related problems revised. Ann Pharmacother. (2018) 2(2):15–6. doi: 10.1345/aph.1D1
31. Kebe B, Getachew M, Molla Y, Bahiru B, Dessie B. Management, survival, and predictors of mortality among hospitalized heart failure patients at Debre Markos Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia: prospective cohort study. SAGE Open Med. (2021) 9:20503121211057336. doi: 10.1177/2050312121105733634925834
32. Abraham WT, Fonarow GC, Albert NM, Stough WG, Gheorghiade M, Greenberg BH, et al. Predictors of in-hospital mortality in patients hospitalized for heart failure: insights from the organized program to initiate lifesaving treatment in hospitalized patients with heart failure (OPTIMIZE-HF). J Am Coll Cardiol. (2008) 52(5):347–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2008.04.02818652942
33. Poffo MR, Assis AV, Fracasso M, Londero Filho OM, Alves SM, Bald AP, et al. Profile of patients hospitalized for heart failure in tertiary care hospital. Int J Cardiovasc Sci. (2017) 30(3):189–98. doi: 10.5935/2359-4802.20170044
34. Pons F, Lupón J, Urrutia A, González B, Crespo E, Díez C, et al. Mortality and cause of death in patients with heart failure: findings at a specialist multidisciplinary heart failure unit. Revista Española de Cardiología. (2010) 63(3):303–14. doi: 10.1016/S0300-8932(10)70089-0
35. Alem MM. Predictors of mortality in patients with chronic heart failure: is hyponatremia a useful clinical biomarker? Int J Gen Med. (2020) 13:407. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S26025632765046
36. Prattipati S, Sakita FM, Kweka GL, Tarimo TG, Peterson T, Mmbaga BT, et al. Heart failure care and outcomes in a Tanzanian emergency department: a prospective observational study. PLoS One. (2021) 16(7):e0254609. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.025460934255782
37. Lee DS, Austin PC, Rouleau JL, Liu PP, Naimark D, Tu JV. Predicting mortality among patients hospitalized for heart failure: derivation and validation of a clinical model. JAMA. (2003) 290(19):2581–7. doi: 10.1001/jama.290.19.258114625335
38. Buddeke J, Valstar G, van Dis I, Visseren F, Rutten F, den Ruijter H, et al. Mortality after hospital admission for heart failure: improvement over time, equally strong in women as in men. BMC Public Health. (2020) 20(1):1–10. doi: 10.1186/s12889-019-7934-331898494
39. Dokainish H, Teo K, Zhu J, Roy A, AlHabib KF, ElSayed A, et al. Global mortality variations in patients with heart failure: results from the International Congestive Heart Failure (INTER-CHF) prospective cohort study. Lancet Glob Health. (2017) 5(7):e665–72. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(17)30196-128476564
40. Parmar KR, Xiu PY, Chowdhury MR, Patel E, Cohen M. In-hospital treatment and outcomes of heart failure in specialist and non-specialist services: a retrospective cohort study in the elderly. Open Heart. (2015) 2(1):e000095. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2014-00009526019879
41. Follath F, Yilmaz MB, Delgado JF, Parissis JT, Porcher R, Gayat E, et al. Clinical presentation, management and outcomes in the Acute Heart Failure Global Survey of Standard Treatment (ALARM-HF). Intensive Care Med. (2011) 37(4):619–26. doi: 10.1007/s00134-010-2113-021210078
42. Sefera B, Getachew M, Babu Y, Bekele F, Fanta K. Drug-related problems and its predictors among hospitalized heart failure patients at Jimma Medical Center, south west Ethiopia: prospective interventional study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2022) 22(1):418. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02859-436123632
43. Bekele F, Tsegaye T, Negash E, Fekadu G. Magnitude and determinants of drug-related problems among patients admitted to medical wards of southwestern Ethiopian hospitals: a multicenter prospective observational study. PLoS One. (2021) 16(3):e0248575. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.024857533725022
44. Bekele F, Tafese L, Garbessa B, Tadasa S, Fekadu G. Burden and predictors of heart failure treatment outcomes in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol. PLoS One. (2023) 18(12):e0291686. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.029168638127971
45. John KJ, Turaka VP, Bharathy KM, Kumar CV, Jayaseelan L, Visalakshi J, et al. Predictors of mortality, strategies to reduce readmission, and economic impact of acute decompensated heart failure: results of the Vellore Heart Failure Registry. Indian Heart J. (2020) 72(1):20–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ihj.2020.03.00532423556
46. Jain P, Guha S, Kumar S, Sawhney JP, Sharma K, Sureshkumar KP, et al. Management of heart failure in a resource-limited setting: expert opinion from India. Cardiol Ther. (2024) 13:243–266. doi: 10.1007/s40119-024-00367-438687432
47. Bekele F, Tafese L, Demsash AW, Tesfaye H, Labata BG, Fekadu G. Adherence to self-care practices and associated factors among heart failure patients in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. (2023) 18(8):e0288824. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.028882437611019
Keywords: heart failure, mortality, associated factors, Ethiopia, prevalence
Citation: Bekele F, Sheleme T, Tsegaye T, Parameswari SA, Syed MA, Tafese L and Gezimu W (2024) Prevalence and risk factors of mortality among heart failure patients in low resource setting hospitals: a multicenter prospective observational study. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 11:1429513. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1429513
Received: 12 June 2024; Accepted: 4 November 2024;
Published: 21 November 2024.
Edited by:
Nicola Mumoli, ASST Ovest Milanese, ItalyReviewed by:
Francesco Monaco, Azienda Sanitaria Locale Salerno, ItalyMoon-Hyun Kim, Yonsei University, Republic of Korea
Serhat Günlü, Diyarbakır Gazi Yaşargil Training and Research Hospital, Türkiye
Copyright: © 2024 Bekele, Sheleme, Tsegaye, Parameswari, Syed, Tafese and Gezimu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Firomsa Bekele, Zmlyb21zYWJla2VsZTIxQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Firomsa Bekele
Firomsa Bekele Tadesse Sheleme2
Tadesse Sheleme2