- 1Department of Cardiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, China
- 2Department of Cardiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Science and Technology, Liuzhou, Guangxi, China
Background: Acute myocardial infarction (AMI), particularly ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), significantly impacts global health, exacerbated by risk factors such as diabetes mellitus (DM). While the Gensini score effectively quantifies coronary artery lesions, its correlation with fasting blood glucose (FBG) levels, particularly in a non-linear fashion, has not been thoroughly explored in STEMI patients.
Methods: This study analyzed data from 464 STEMI patients treated with percutaneous coronary intervention at the First People's Hospital of Taizhou City, Zhejiang Province, China, from January 2010 to October 2014. We stratified patients into three FBG tertiles and utilized multiple statistical analyses, including least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression and curve fitting, to examine the potential U-shaped relationship between FBG levels and Gensini scores.
Results: Our analysis revealed significant differences in Gensini scores across FBG tertiles, with both hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic extremes showing higher scores compared to the normoglycemic range. The curve fitting analysis confirmed a U-shaped relationship, suggesting a significant, non-linear association between FBG levels and coronary artery lesion severity, regardless of diabetes status.
Conclusions: Our findings underscore the complexity of glycemic control in STEMI management and suggest that both hypo- and hyperglycemia are significant risk factors for severe coronary lesions as quantified by the Gensini score. This study highlights the importance of comprehensive FBG monitoring and management to improve outcomes for STEMI patients.
Introduction
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI), caused by occlusion or severe narrowing of coronary arteries due to clot formation in atherosclerotic plaque (1), affects over 7 million people globally each year (2) and carries a high mortality rate (3). ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is a particularly prevalent type of AMI and a leading cause of death and illness among major coronary events (4). Diabetes mellitus (DM) increases cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, especially in individuals with acute coronary syndrome (ACS), myocardial infarction (MI), or unstable angina pectoris (5). Poor glycemic control is typically associated with a worsening of coronary heart disease risk. Fasting hyperglycemia detected after a heart attack is linked to poorer outcomes (6). It can also help predict both future heart disease risk and the development of diabetes (7). The Gensini score reflects the severity of coronary artery lesions, and higher fasting blood sugar (FBG) levels are correlated with a higher Gensini score (8, 9). Over the years, studies have shown a significant positive correlation between fasting glucose and Gensini scores, even in people without diabetes (10–13). Previous research has suggested a linear relationship between blood sugar and Gensini score. However, these studies only considered the influence of blood sugar, not other factors like uric acid, creatinine, and age. Additionally, previous analyses used a single cutoff to define high-risk hyperglycemia (14). Both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia are well-established risk factors for AMI. Therefore, our study used three FBG cutoff values and adjusted for other variables to evaluate their association with Gensini scores. We aimed to investigate the potential U-shaped relationship between FBG concentration and Gensini score analysis in STEMI patients. By understanding this relationship, we hope to improve our understanding of STEMI pathophysiology and identify potential therapeutic targets to optimize patient management and improve outcomes.
Methodology and materials overview
Participant demographics and characteristics
All data for this study are publicly available on the Dryad Digital Repository (https://datadryad.org/stash/dataset/doi:10.5061/dryad.pf56m) without restrictions. The data emanated from a study titled “Predictive value of Apelin-12 in patients with STEMI with different renal function: a prospective observational study”. Between January 2010 and October 2014, 464 patients with symptoms of STEMI undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) were enrolled at the First People's Hospital of Taizhou City, Zhejiang Province, China. These patients presented with sustained chest pain (>30 min), prolonged electrocardiographic changes (including ischemic ST-segment elevation in two or more contiguous leads), along significantly elevated serum cardiac enzyme and troponin concentrations. This study involved secondary analysis of previously collected data, making participant consent or approval from an ethics committee unnecessary. Patients were excluded if they had non-STEMI acute coronary syndrome, prior balloon angioplasty without stenting, severe vascular heart disease, cardiogenic shock, secondary hypertension, history of stroke within the past year or ongoing stroke with significant neurological impairment, prior rescue PCI procedure, documented ventricular fibrillation, planned conservative treatment without PCI, chronic hepatitis or cirrhosis, untreated severe heart block, life expectancy less than 12 months, endocrine disorders like thyroid or adrenal dysfunction, severe kidney failure requiring dialysis, recent major infection, connective tissue disease, malignant tumor, known allergies to medications used in the study (statins, heparin, aspirin, clopidogrel, contrast dye, or GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors), active bleeding in the digestive or urinary tract, major surgery or trauma within the past 6 weeks with incomplete medical records, or ongoing severe bleeding.
Assessment methods
Coronary artery assessment was performed using coronary angiography on all participants. This procedure evaluated the degree of stenosis in the left main coronary artery, left anterior descending artery, left circumflex artery, and right coronary artery, along with imaging findings. A normal coronary artery had no narrowing or less than 50% stenosis. A single stenosis was identified if any of the arteries had 50% or more narrowing. In contrast, a multi-branch lesion was confirmed if two or three arteries had ≥50% stenosis. The American Heart Association's Gensini score was used to grade stenosis severity: 1 for ≤25%, 2 for 26%–50%, 4 for 51%–75%, 8 for 76%–90%, 16 for 91%–99%, and 32 for complete occlusion (15). Diabetes was defined as a pre-existing condition requiring medication or non-pharmacological interventions or new-onset diabetes diagnosed according to the American Diabetes Association criteria, which include a medical history of typical symptoms accompanied by elevated blood glucose levels [fasting plasma glucose ≥126 mg/dl during hospitalization or hemoglobin A1c≥6.5% (48 mmol/mol), or a random or 2-h postprandial blood glucose ≥200 mg/dl] (16). Hypertension was defined as repeated blood pressure readings ≥140/90 mmHg on at least two separate occasions and was presumed to be present in individuals taking antihypertensive medication. The Killip classification is a systematic method for assessing the severity and prognosis of acute AMI patients based on clinical signs at admission, including heart murmurs, lung congestion sounds (rales), edema, and low blood pressure. It has four levels: Killip I: No signs of heart failure; Killip II: Lung congestion sounds or murmurs without heart failure; Killip III: Lung congestion sounds and signs of heart failure; Killip IV: Cardiogenic shock (severe heart failure) (17).
Statistical analysis
The study participants were stratified into three groups based on their blood glucose levels: tertile 1 (2.69–6.15 mmol/L), tertile 2 (6.19–8.61 mmol/L), and tertile 3 (8.64–14.81 mmol/L). Subsequently, the differences in Gensini scores among these groups were assessed. To assess data normality, the Shapiro-Wilk test was used. Normally distributed continuous data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and analyzed using ANOVA with LSD post hoc test for intergroup comparisons. Non-normally distributed data were presented as median (minimum-maximum), and analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test for group differences. Categorical variables were presented as counts and percentages (%). In univariate analysis, we investigated the relationship between various factors (independent variables) and the Gensini score (dependent variable). To further explore the association between blood glucose and Gensini score, we employed least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression analysis for covariate selection. We then performed multivariate regression analysis with the Gensini score as the dependent variable, glucose as the independent variable, and selected variables as covariates, aiming to adjust for confounding factors and assess the true association between glucose and the Gensini score. Recognizing that a linear relationship may not exist between blood glucose and the Gensini score, curve fitting was employed to observe the trend in blood glucose and the Gensini score. Statistical analysis was performed using R version 3.6.1 (https://www.r-project.org/), with a significance level set at p < 0.05 (two-sided) to denote statistical significance.
Results
Baseline patient characteristics in the study cohort
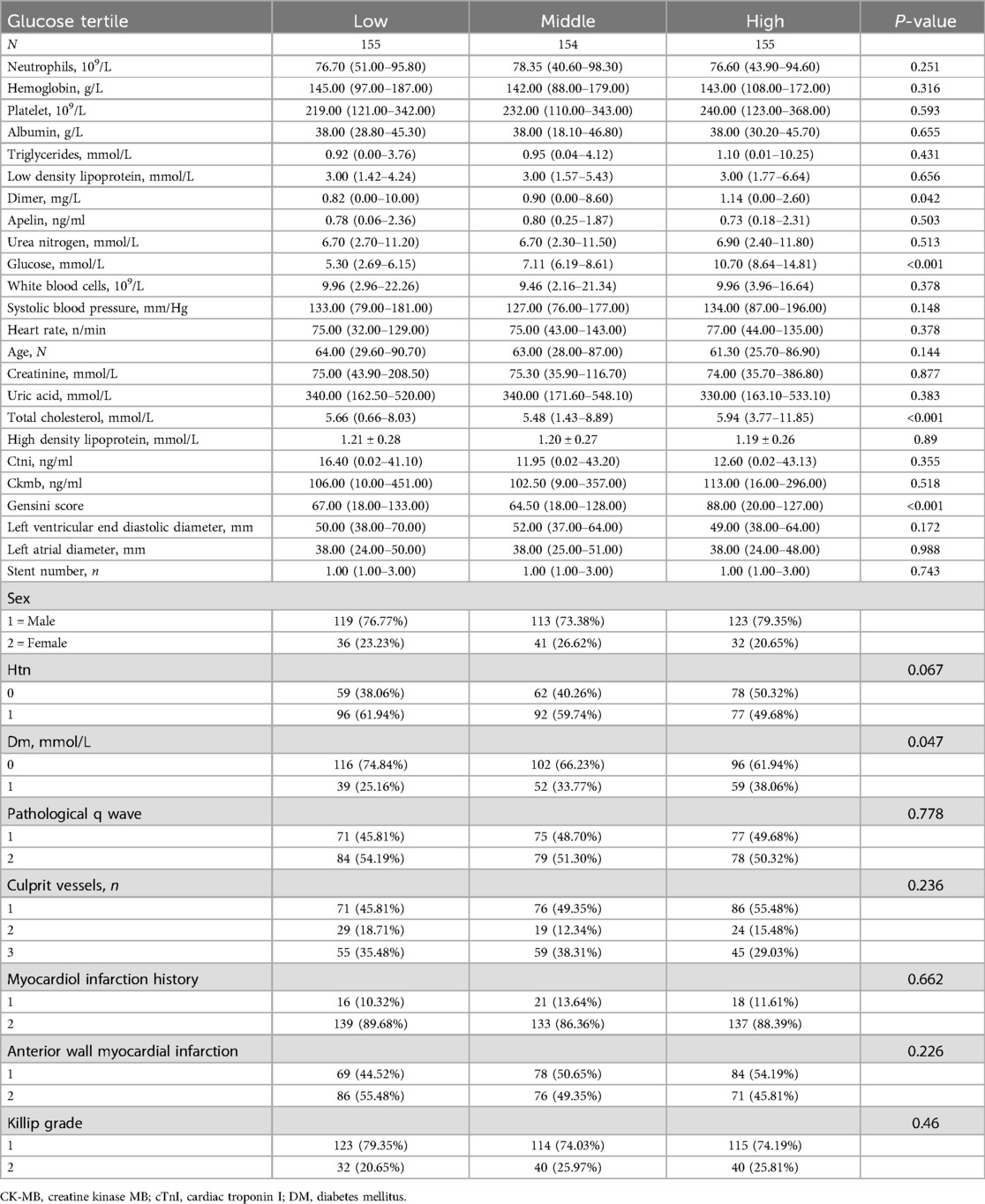
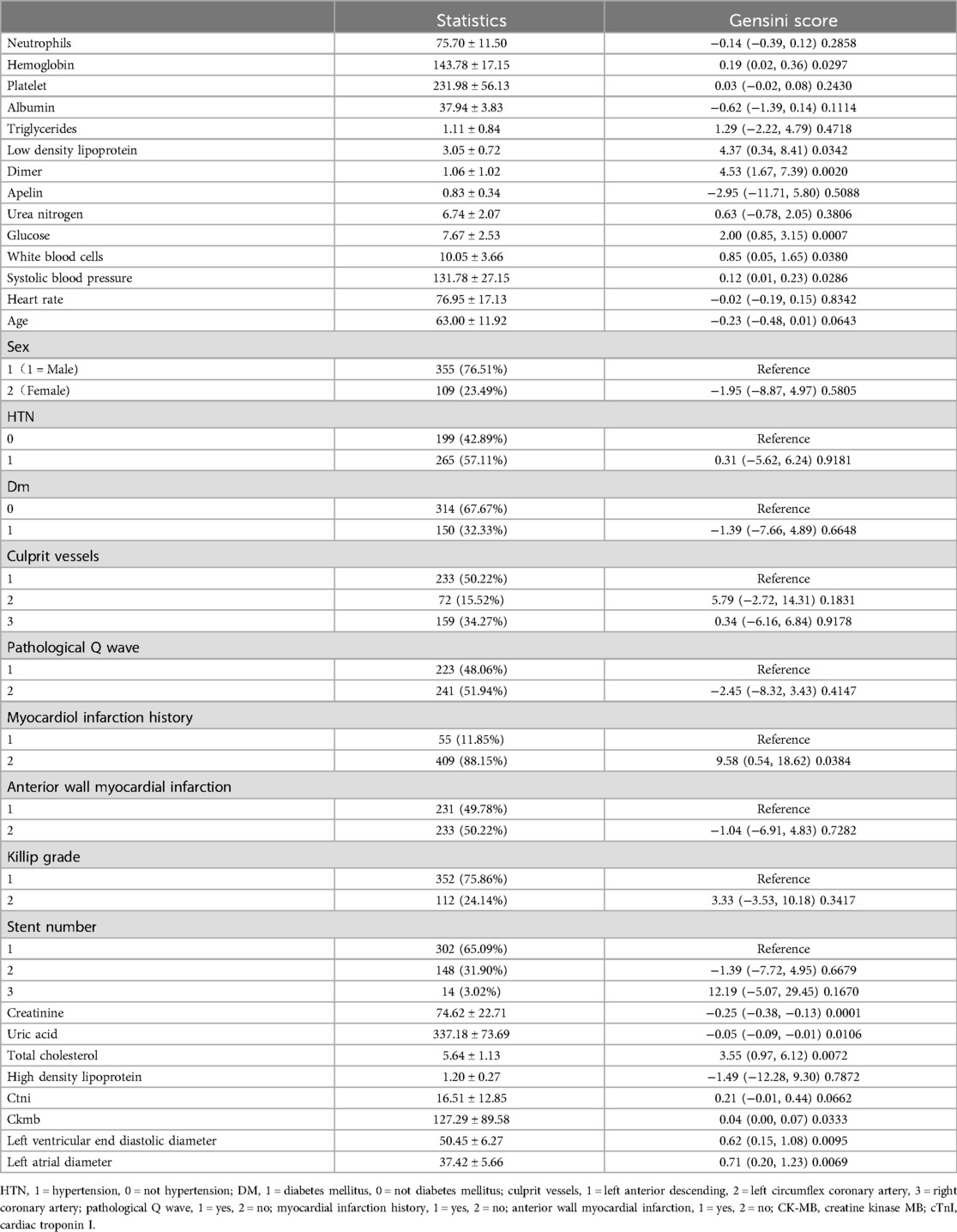
Table 1 presents a cohort of 464 subjects stratified into three groups based on fasting blood glucose levels. Tertile 1 had a mean level of 5.30 mmol/L (range: 2.69–6.15 mmol/L), tertile 2 had a mean of 7.11 mmol/L (range: 6.19–8.61 mmol/L), and tertile 3 had a mean of 10.70 mmol/L (range: 8.64–14.81 mmol/L). Baseline characteristics, including anatomical, hematological, and demographic parameters, were compared across these groups. Significant differences were observed in total cholesterol and Gensini score (p < 0.001). Detailed baseline characteristics are provided in Table 2. The overall cohort had a mean age of 63 years (63.00 ± 11.92) and a mean fasting blood glucose level of 7.67 mmol/L (7.67 ± 2.53). There were 355 males and 109 females, with 314 subjects without diabetes and 150 diagnosed with diabetes. Patients presented with KILLIP grades of 1–2, and the main culprit vessels in coronary artery disease leading to myocardial infarction were predominantly one or three vessels. Univariate analysis revealed significant correlations (p < 0.05) between Gensini scores and various parameters, including hemoglobin, low-density lipoprotein, D-dimer, blood glucose, leukocyte count, systolic blood pressure, myocardial infarction history, creatinine, uric acid, total cholesterol, CTN, CKM, left ventricular end-diastolic diameter, and left atrial diameter. Notably, fasting blood glucose exhibited a positive correlation with the Gensini score (r = 2.0, p < 0.0007).
Principal findings
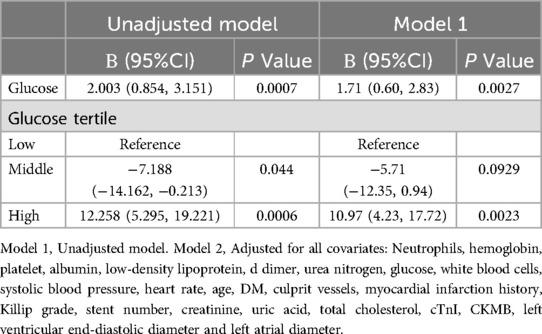
Figure 1 categorizes fasting blood glucose into three groups: hypoglycemic (5.30 mmol/L, range: 2.69–6.15 mmol/L), moderate glycemic (7.11 mmol/L, range: 6.19–8.61 mmol/L), and hyperglycemic (10.70 mmol/L, range: 8.64–14.81 mmol/L), with statistically significant differences across these subgroups (p < 0.05). Table 3 shows the Gensini scores without adjusting for other variables. Scores in the moderate glycemic and hyperglycemic groups exhibited significant clinical significance (moderate glycemic group: 95% CI −140,162–0.213, p = 0.044; hyperglycemic group: 95% CI 5.295–19.221, p = 0.0006). To identify relevant variables for further analysis (Model 2), the LASSO regression was employed. The screening criterion used was lambda = lambdam.min:0.8132 (−0.2068). This identified the following variables for inclusion: neutrophils, hemoglobin, platelets, albumin, low-density lipoprotein, D-dimer, urea nitrogen, glucose, white blood cells, systolic blood pressure, heart rate, age, DM diagnosis, culprit vessels, myocardial infarction history, Killip grade, number of stents, creatinine, uric acid, total cholesterol, cTnI, CKMB, left ventricular end-diastolic diameter, and left atrial diameter. Following adjustment for these confounding factors, only the hyperglycemic group remained significantly associated with the Gensini score (95% CI: −16.95 to −2.71, p = 0.015). Finally, curve fitting analysis (Figure 2) revealed a U-shaped, non-linear relationship between fasting glucose and the Gensini score in patients, regardless of their diabetes diagnosis (Figure 2).
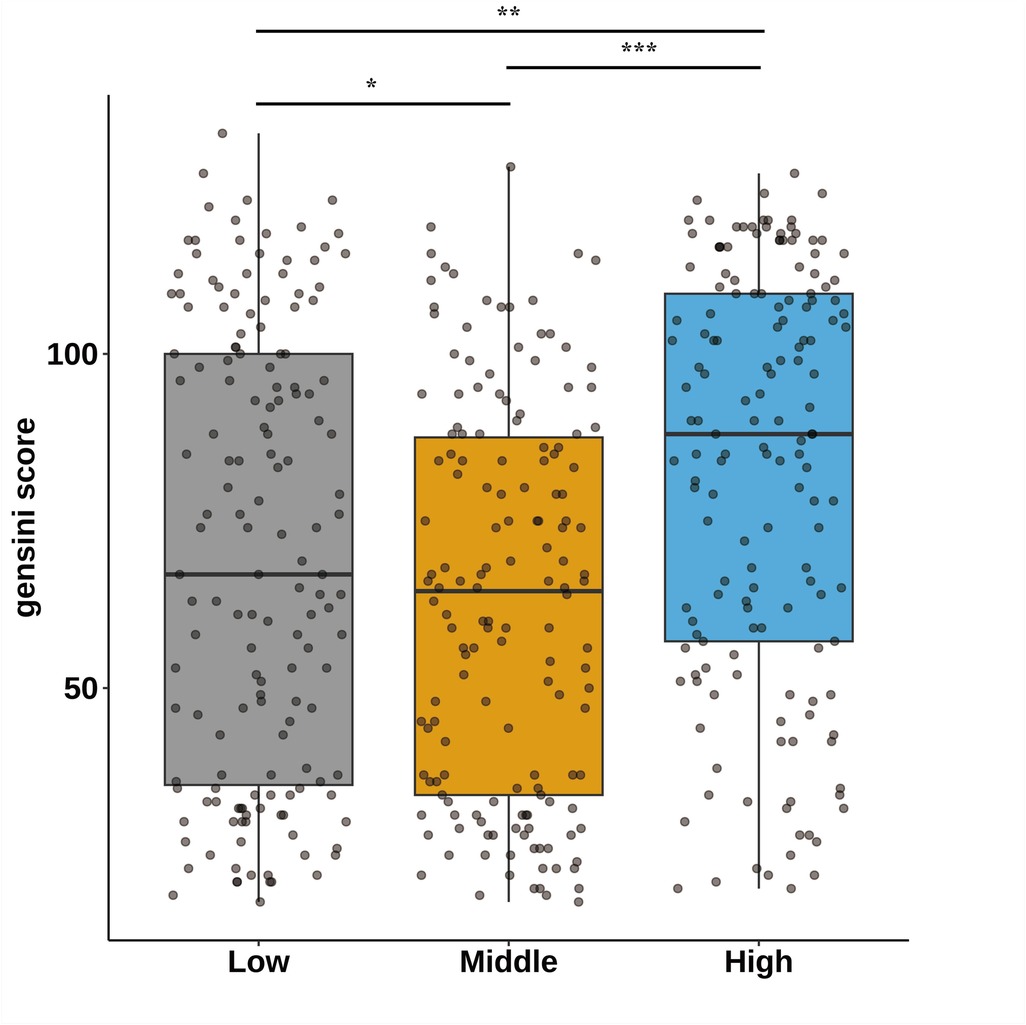
Figure 1. Characteristics of the study participants stratified by fasting blood glucose tertiles; *p < 0.05,*p < 0.01,*p < 0.001. Fasting blood glucose was divided into hypoglycemic group 5.30 mmol/L (2.69–6.15), moderate glycemic group 7.11 mmol/L (6.19–8.61), and hyperglycemic group 10.70 mmol/L (8.64–14.81).
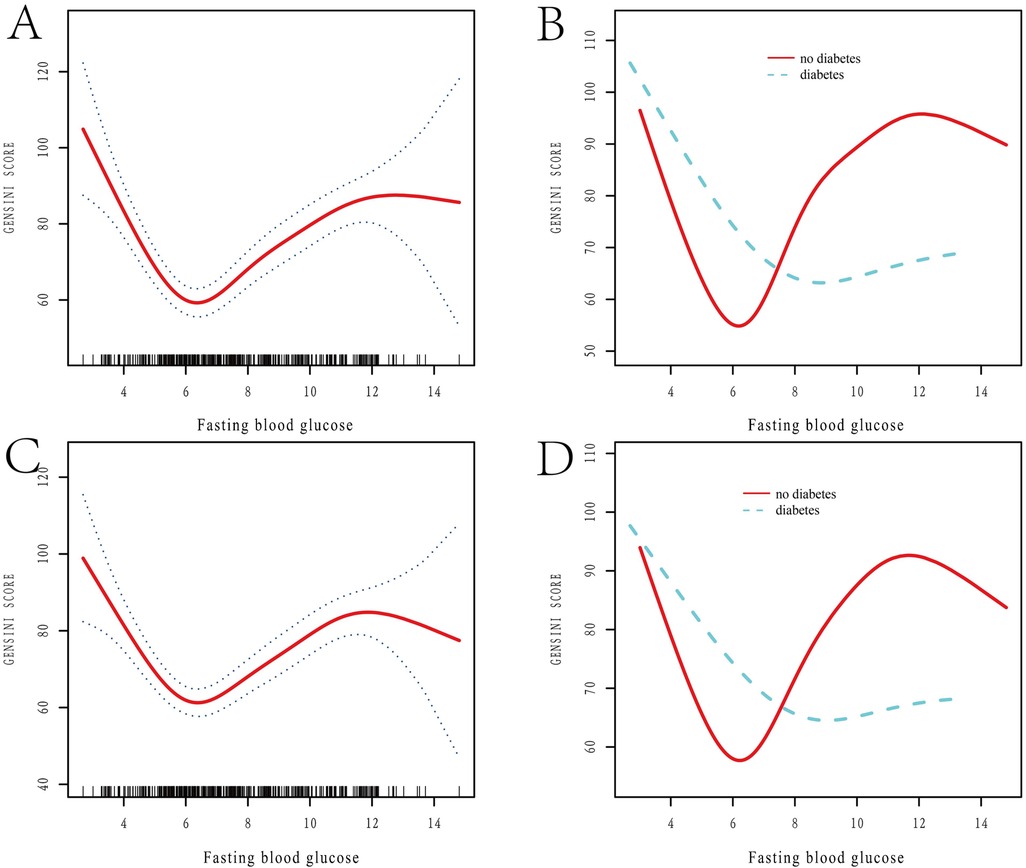
Figure 2. Restricted spline curve analysis of the relationship between FBG levels and Gensini score. (A,B) Unadjusted Variable Curves Fitted to Model-Constrained Spline Curves; (A) the relationship between FBG levels and Gensini score; (B) the relationship between FBG levels and Gensini score in diabetic and non-diabetic patients; FBG: fasting blood glucose. (C,D) Curve Fitting After Adjustment for Variables; Adjusted variables include neutrophils, hemoglobin, platelets, albumin, low-density lipoprotein, D-dimer, urea nitrogen, glucose, white blood cells, systolic blood pressure, heart rate, age, DM, culprit vessels, myocardial infarction history, Killip grade, stent number, creatinine, uric acid, total cholesterol, CTNI, CKMB, left ventricular end-diastolic diameter, and left atrial diameter. (C) The relationship between adjusted FBG levels and Gensini score, after controlling for variables; (D) the relationship between adjusted FBG levels and Gensini score in diabetic and non-diabetic patients, after controlling for variables. FBG, fasting blood glucose.
Discussion
MI is a common cause of death among diabetic patients (18). Studies have documented a U-shaped or J-shaped relationship between various blood glucose measures (fasting, admission, mean hospitalized) and in-hospital mortality in AMI patients (14, 19–21). However, some studies have reported contrasting findings. Park et al. found a J-shaped association between FBG and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (22). Several studies have explored the correlation between fasting blood glucose and the Gensini score, a measure of coronary artery disease severity. Yuhan Qin et al. observed a positive correlation (r = 0.171, p < 0.001) in 958 AMI patients (10). In a study by Tong Zhao et al., which included 64 patients with chest discomfort undergoing coronary angiography, FBG was positively correlated with Gensini score in both diabetic (r = 0.312, p < 0.012) and non-diabetic patients (r = 0.387, p < 0.010) (11). Besides, Jingjing Jiang et al. analyzed data from 1,852 patients who underwent coronary angiography. Their findings revealed a positive correlation between FBG and Gensini score (r = 0.09, p < 0.01). Regression analysis further demonstrated an independent correlation between FBG and Gensini score (12). In another study involving 85 patients with acute coronary syndrome who underwent emergency coronary angiography and received stent implantation when necessary, FBG was found to be positively correlated with the Gensini score (r = 0.568, p < 0.000) (8). Finally, a significant positive correlation was observed between FBG and Gensini score in 906 patients who underwent coronary angiography and had no history of diabetes (r = 0.172; p = 0.011) (13). Previous studies utilized a single truncation method to identify high-risk hyperglycemia (14). However, this approach overlooks the potential detrimental effects of hypoglycemia on coronary artery disease severity. To address this limitation, our study categorized participants into three fasting blood glucose groups: hypoglycemic (5.30 mmol/L, range: 2.69–6.15 mmol/L), moderate glycemic (7.11 mmol/L, range: 6.19–8.61 mmol/L), and hyperglycemic (10.70 mmol/L, range: 8.64–14.81 mmol/L). We further adjusted for a comprehensive set of covariates, including demographic factors (age), medical history (diabetes mellitus, myocardial infarction), laboratory values (neutrophils, hemoglobin, platelets, albumin, etc.), and measures of coronary artery disease severity (culprit vessels, Killip grade, stent number, etc.) to evaluate their association with Gensini scores. This approach revealed a U-shaped, rather than linear, relationship between fasting blood glucose and Gensini score in our population-based study.
Both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia can exacerbate the severity of coronary artery lesions. To gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms underlying this relationship, we have proposed several hypotheses, attempting to explain the potential mechanisms from a pathophysiological perspective. It is now understood that hyperglycemia damages the microvascular endothelial barrier and promotes atherosclerosis (23). A key mechanism involves endothelial dysfunction through the protein kinase C (PKC) pathway. This dysfunction is caused by increased non-enzymatic glycosylation, oxidative stress, and decreased endothelial insulin action (24). High glucose concentrations further injure blood vessels by activating nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and inducing overexpression of genes in endothelial cells, macrophages, and smooth muscle cells (25). Prolonged exposure to high glucose leads to the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which generate reactive oxygen species (ROS). Glucose oxidation by ROS damages tissues in the artery walls, contributing to diabetic macrovascular complications (26). Diabetic patients exhibit increased ROS production in cardiovascular cells, and activation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) accelerates atherosclerosis progression (27, 28). Hyperglycemia also potentiates thrombosis, increasing the risk of coronary events (29, 30), mediated by augmenting platelet activation and aggregation, impairing fibrinolysis, and enhancing thrombin generation, ultimately leading to intravascular thrombus formation. Hyperglycemia disrupts the coagulation cascade, leading to increased fibrin deposition and stabilization within coronary arteries. This worsens luminal obstruction and can precipitate myocardial infarction (31). It also exacerbates myocardial oxygen demand and impairs coronary microvascular function, further promoting ischemic injury. The increased oxygen demand results from hyperglycemia-induced insulin resistance and impaired myocardial glucose utilization (32, 33). Impaired microvascular function by hyperglycemia compromises myocardial perfusion and worsens ischemic injury. Collectively, these mechanisms mediated by hyperglycemia contribute to elevated Gensini scores, reflecting the increased severity of coronary artery disease. These mechanisms play a critical role in the formation and progression of coronary artery blockages, constituting a crucial point on one end of the U-shaped relationship curve.
Both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia are linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Severe hypoglycemia can directly impact outcomes and mortality (34), with studies showing a higher incidence of stent thrombosis and artery occlusions following STEMI (35, 36). Hypoglycemia contributes to cardiovascular disease through various mechanisms, including vasoconstriction, activation of white blood cells, imbalances in the autonomic nervous system, and the release of inflammatory chemicals called cytokines (37). Research has shown that hypoglycemia increases levels of hormones like glucagon, cortisol, and growth hormone (38), which can elevate heart contractility and oxygen demand, potentially leading to adverse cardiovascular effects (35). Systematic reviews and meta-analyses encompassing over 325,000 hospitalized patients indicate that individuals experiencing hypoglycemia face an elevated risk of subsequent adverse cardiovascular events (39). These analyses consistently demonstrate a significant correlation between hypoglycemia and cardiovascular events across various patient populations, including critically ill and non-critically ill patients, diabetics and non-diabetics, and those with mild to severe hypoglycemia. The association remained consistent in both short-term and long-term follow-up studies (40). Hypoglycemia affects the severity of coronary artery lesions through these mechanisms, accounting for the other end of the U-shaped curve observed in our study.
FBG stands out as a superior prognostic indicator for mortality and fatal heart failure compared to admission blood glucose. Studies have shown that FBG is superior to admission blood glucose (ABG) in predicting 30-day mortality in patients with AMI without diabetes (41). Additionally, FBG is a better predictor of long-term mortality. Non-diabetic AMI patients with elevated ABG (>110 mg/dl or 6.11 mmol/L) have a nearly fourfold higher mortality risk compared to those with normal blood sugar levels (42). Interestingly, elevated ABG does not increase mortality risk if FBG is normal. Conversely, elevated FBG upon admission triples mortality rates, even if ABG is normal (43). These findings suggest that both high and low blood glucose levels have detrimental effects on the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of events. Our study investigated patients with STEMI and observed a U-shaped correlation between FBG and Gensini score. This relationship held true for both diabetic and non-diabetic patients, highlighting the negative impacts of both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia on the cardiovascular system. These findings suggest an optimal range for blood glucose control that may minimize the severity of coronary artery disease. In patients with low FBG levels, associated pathophysiological changes may lead to vascular instability, while high FBG levels could accelerate the progression of atherosclerosis. Therefore, maintaining FBG within an ideal range could be crucial for reducing the risk of severe coronary lesions and improving clinical outcomes. In future research, stem cell therapy could be explored as a potential approach to mitigate coronary artery lesions caused by glycemic abnormalities in STEMI patients. Stem cells not only have the potential to differentiate into cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells, but they also secrete anti-inflammatory and growth factors that may enhance microcirculation and facilitate myocardial repair. The observed U-shaped relationship between hyperglycemia and coronary lesion severity suggests that glycemic fluctuations play a crucial role in STEMI pathogenesis. Stem cell therapy may help reduce lesion risk by improving local microcirculation and alleviating inflammation and oxidative stress induced by hyperglycemia. Moreover, the combined application of stem cell therapy and glycemic management strategies represents a promising research avenue, offering new insights and therapeutic options for the treatment of STEMI patients. Despite its contributions, our study has limitations. First, we focused only on STEMI patients, leaving uncertainties about the generalizability of the FBG-Gensini score relationship to other types of myocardial infarction. Second, our analysis was limited to a specific blood glucose range (2.69–14.81 mmol/L). The relationship between Gensini score and blood glucose levels outside this range remains unexplored. Finally, our study's relatively small sample size may affect the strength of our findings. Further validation in larger cohorts is warranted.
Conclusion
Our study in STEMI patients reveals a U-shaped correlation between FBG concentration and Gensini score, underlining the negative effects of both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia on coronary artery disease severity. Understanding this relationship can inform the development of targeted therapies to improve patient outcomes.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://datadryad.org/stash/dataset/doi:10.5061/dryad.pf56m.
Ethics statement
The study constituted a secondary analysis derived from preceding research endeavors, thereby obviating the necessity to procure informed consent and ethical approval from a committee.
Author contributions
HL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. GZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. ZJ: Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 82060068 and 82160066).
Acknowledgments
Thanks to the Cardiac Medicine Collaborative Group for their support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Mitsis A, Gragnano F. Myocardial infarction with and without ST-segment elevation: a contemporary reappraisal of similarities and differences. Curr Cardiol Rev. (2021) 17(4):e230421189013. doi: 10.2174/1573403X16999201210195702
2. Bhatt DL, Lopes RD, Harrington RA. Diagnosis and treatment of acute coronary syndromes: a review. JAMA. (2022) 327(7):662–75. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.0358
3. Chang J, Liu X, Sun Y. Mortality due to acute myocardial infarction in China from 1987 to 2014: secular trends and age-period-cohort effects. Int J Cardiol. (2017) 227:229–38. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.11.130
4. Kilic S, Ottervanger JP, Dambrink JH, Hoorntje JC, Koopmans PC, Gosselink AT. The effect of thrombus aspiration during primary percutaneous coronary intervention on clinical outcome in daily clinical practice. Thromb Haemost. (2014) 111(1):165–71. doi: 10.1160/TH13-05-0433
5. Konstantinou DM, Chatzizisis YS, Louridas GE, Parcharidis GE, Giannoglou GD. Non-diabetic hyperglycaemia correlates with angiographic coronary artery disease prevalence and severity. Diabetes Metab. (2010) 36(5):402–8. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2010.04.005
6. O’Sullivan JJ, Conroy RM, Robinson K, Hickey N, Mulcahy R. In-hospital prognosis of patients with fasting hyperglycemia after first myocardial infarction. Diabetes Care. (1991) 14(8):758–60. doi: 10.2337/diacare.14.8.758
7. Ravid M, Berkowicz M, Sohar E. Hyperglycemia during acute myocardial infarction. A six-year follow-up study. JAMA. (1975) 233(7):807–9. doi: 10.1001/jama.1975.03260070065026
8. Zhang X, Dong L, Wang Q, Xie X. The relationship between fasting plasma glucose and MPO in patients with acute coronary syndrome. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2015) 15:93. doi: 10.1186/s12872-015-0088-z
9. Ford ES, Zhao G, Li C. Pre-diabetes and the risk for cardiovascular disease: a systematic review of the evidence. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2010) 55(13):1310–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.10.060
10. Qin Y, Yan G, Qiao Y, Ma C, Liu J, Tang C. Relationship between random blood glucose, fasting blood glucose, and Gensini score in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Biomed Res Int. (2019) 2019:9707513. doi: 10.1155/2019/9707513
11. Zhao T, Gong HP, Dong ZQ, Du YM, Lu QH, Chen HQ. Predictive value of fasting blood glucose for serious coronary atherosclerosis in non-diabetic patients. J Int Med Res. (2019) 47(1):152–8. doi: 10.1177/0300060518798252
12. Jiang J, Zhao L, Lin L, Gui M, Aleteng Q, Wu B. Postprandial blood glucose outweighs fasting blood glucose and HbA1c in screening coronary heart disease. Sci Rep. (2017) 7(1):14212. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14152-y
13. Gui MH, Li X, Lu ZQ, Gao X. Fasting plasma glucose correlates with angiographic coronary artery disease prevalence and severity in Chinese patients without known diabetes. Acta Diabetol. (2013) 50(3):333–40. doi: 10.1007/s00592-012-0405-2
14. Koraćević G, Mićić S, Stojanović M, Tomašević M, Kostić T, Koraćević M. Single prognostic cut-off value for admission glycemia in acute myocardial infarction has been used although high-risk stems from hyperglycemia as well as from hypoglycemia (a narrative review). Prim Care Diabetes. (2020) 14(6):594–604. doi: 10.1016/j.pcd.2020.09.004
15. He Q, Zhang P, Li Y, Cai C, Wang C. The application of gensini score and IL-1ra in assessing the condition and prognosis of patients with coronary artery disease. Am J Transl Res. (2021) 13(9):10421–7.34650711
16. Lee CH, Choi SW, Jun SW, Hwang J, Kim IC, Cho YK. Clinical impact of diabetes mellitus on 2-year clinical outcomes following PCI with second-generation drug-eluting stents; landmark analysis findings from patient registry: pooled analysis of the Korean multicenter drug-eluting stent registry. PLoS One. (2020) 15(6):e0234362. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234362
17. Mercado-Martínez J, Rivera-Fernández R, Aguilar-Alonso E, García-Alcántara A, Estivill-Torrull A, Aranda-León A, et al. APACHE-II score and Killip class for patients with acute myocardial infarction. Intensive Care Med. (2010) 36(9):1579–86. doi: 10.1007/s00134-010-1832-6
18. Fisher M. Diabetes and myocardial infarction. Baillieres Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. (1999) 13(2):331–43. doi: 10.1053/beem.1999.0024
19. Goyal A, Mehta SR, Díaz R, Gerstein HC, Afzal R, Xavier D. Differential clinical outcomes associated with hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation. (2009) 120(24):2429–37. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.837765
20. Ishihara M. Acute hyperglycemia in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circ J. (2012) 76(3):563–71. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-11-1376
21. Zhao S, Murugiah K, Li N, Li X, Xu ZH, Li J, Admission glucose and in-hospital mortality after acute myocardial infarction in patients with or without diabetes: a cross-sectional study. Chin Med J (Engl). (2017) 130(7):767–75. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.202733
22. Park C, Guallar E, Linton JA, Lee DC, Jang Y, Son DK. Fasting glucose level and the risk of incident atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases. Diabetes Care. (2013) 36(7):1988–93. doi: 10.2337/dc12-1577
23. Yuan SY, Breslin JW, Perrin R, Gaudreault N, Guo M, Kargozaran H. Microvascular permeability in diabetes and insulin resistance. Microcirculation. (2007) 14(4–5):363–73. doi: 10.1080/10739680701283091
24. Feener EP, King GL. Endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus: role in cardiovascular disease. Heart Fail Monit. (2001) 1(3):74–82.12634871
25. Mazzone T, Chait A, Plutzky J. Cardiovascular disease risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus: insights from mechanistic studies. Lancet. (2008) 371(9626):1800–9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60768-0
26. Pennathur S, Heinecke JW. Mechanisms for oxidative stress in diabetic cardiovascular disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. (2007) 9(7):955–69. doi: 10.1089/ars.2007.1595
27. Shah MS, Brownlee M. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of cardiovascular disorders in diabetes. Circ Res. (2016) 118(11):1808–29. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.306923
28. Piga R, Naito Y, Kokura S, Handa O, Yoshikawa T. Short-term high glucose exposure induces monocyte-endothelial cells adhesion and transmigration by increasing VCAM-1 and MCP-1 expression in human aortic endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. (2007) 193(2):328–34. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.09.016
29. Newman JD, Echagarruga CT, Ogando YM, Montenont E, Chen Y, Fisher EA, et al. Hyperglycemia enhances arsenic-induced platelet and megakaryocyte activation. J Transl Med. (2017) 15(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1148-1
30. Yamagishi SI, Edelstein D, Du XL, Brownlee M. Hyperglycemia potentiates collagen-induced platelet activation through mitochondrial superoxide overproduction. Diabetes. (2001) 50(6):1491–4. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.50.6.1491
31. Undas A, Wiek I, Stêpien E, Zmudka K, Tracz W. Hyperglycemia is associated with enhanced thrombin formation, platelet activation, and fibrin clot resistance to lysis in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Diabetes Care. (2008) 31(8):1590–5. doi: 10.2337/dc08-0282
32. Madamanchi NR, Runge MS. Mitochondrial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circ Res. (2007) 100(4):460–73. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000258450.44413.96
33. Semenkovich CF. Insulin resistance and atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. (2006) 116(7):1813–22. doi: 10.1172/JCI29024
34. Yun JS, Park YM, Han K, Cha SA, Ahn YB, Ko SH. Severe hypoglycemia and the risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality in type 2 diabetes: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2019) 18(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0909-y
35. Batnyam U, Ko Ko N, Javaid A. Hypoglycemia-associated in-stent thrombosis: are we doing too much? Cureus. (2017) 9(9):e1712. doi: 10.7759/cureus.1712
36. Pinto DS, Kirtane AJ, Pride YB, Murphy SA, Sabatine MS, Cannon CP. Association of blood glucose with angiographic and clinical outcomes among patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (from the CLARITY-TIMI-28 study). Am J Cardiol. (2008) 101(3):303–7. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.08.034
37. Finfer S, Liu B, Chittock DR, Norton R, Myburgh JA, McArthur C. Hypoglycemia and risk of death in critically ill patients. N Engl J Med. (2012) 367(12):1108–18. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1204942
38. Pistrosch F, Hanefeld M. Hypoglycemia and cardiovascular disease: lessons from outcome studies. Curr Diab Rep. (2015) 15(12):117. doi: 10.1007/s11892-015-0678-2
39. Nusca A, Tuccinardi D, Proscia C, Melfi R, Manfrini S, Nicolucci A. Incremental role of glycaemic variability over HbA1c in identifying type 2 diabetic patients with high platelet reactivity undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2019) 18(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0952-8
40. Yeh JS, Sung SH, Huang HM, Yang HL, You LK, Chuang SY. Hypoglycemia and risk of vascular events and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Diabetol. (2016) 53(3):377–92. doi: 10.1007/s00592-015-0803-3
41. Suleiman M, Hammerman H, Boulos M, Kapeliovich MR, Suleiman A, Agmon Y. Fasting glucose is an important independent risk factor for 30-day mortality in patients with acute myocardial infarction: a prospective study. Circulation. (2005) 111(6):754–60. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000155235.48601.2A
42. Capes SE, Hunt D, Malmberg K, Gerstein HC. Stress hyperglycaemia and increased risk of death after myocardial infarction in patients with and without diabetes: a systematic overview. Lancet. (2000) 355(9206):773–8. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(99)08415-9
Keywords: acute myocardial infarction, Gensini score, fasting blood glucose, ST-elevation myocardial infarction, diabetes mellitus
Citation: Li H, Lin Q, Jiang Z and Zhong G (2024) Analyzing the non-linear relationship between fasting blood glucose levels and Gensini score in patients with STEMI. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 11:1427567. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1427567
Received: 4 May 2024; Accepted: 29 November 2024;
Published: 19 December 2024.
Edited by:
Danilo Menichelli, Sapienza University of Rome, ItalyReviewed by:
Arianna Pannunzio, Sapienza University of Rome, ItalyIlaria Maria Palumbo, Sapienza University of Rome, Italy
Copyright: © 2024 Li, Lin, Jiang and Zhong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhiyuan Jiang, bXJfanp5QDE2My5jb20=; Guoqiang Zhong, Z3FfemhvbmdAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Han Li
Han Li Quanzhi Lin2
Quanzhi Lin2 Zhiyuan Jiang
Zhiyuan Jiang Guoqiang Zhong
Guoqiang Zhong