- 1Department of Hematology, Renji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
- 2Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 3Ganzhou Key Laboratory of Hematology, Department of Hematology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Gannan Medical University, Ganzhou, Jiangxi, China
Adverse events of atrial fibrillation (AF) have been commonly reported in lymphoma patients in treating Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitors (BTKi). The incidence rate of AF can vary depending on the specific types of BTKi and the patient population. Totally 45 published studies have revealed that the overall incidence rate of AF is 5% (95% CI 4%–7%). By performing a subtype single-rate analysis, the second-generation BTKi shows a lower AF incidence rate and lower cardiovascular toxicity. In the subtype single-rate analysis, we conclude the different AF incidence rates of Ibrutinib (10%, 95% CI 7%–13%), Acalabrutinib (4%, 95% CI 1%–6%), Orelabrutinib (0%, 95% CI 0%–1%), and Zanubrutinib (0%, 95% CI 0%–1%). The comprehensive analysis of AF inspires us to better predict and manage AF and other cardiovascular events in treating lymphoma. Meticulous evaluation, collaboration between cardiologists and hematologists, and discovery of new biomarkers are essential for its management.
Introduction
The applications of BTKi in the treatment of lymphoma
BTK inhibitors are a kind of small molecule targeting the critical component BTK on the signal pathway of B Cells, related to B cell proliferation and survival, making it a significant therapeutic target for B-cell lymphoma (1, 2). BTK inhibitors have gained considerable attention in recent years due to their demonstrated efficacy in treating B-cell lymphoma (3) (Table 1).
Indications and adverse events of BTK inhibitors
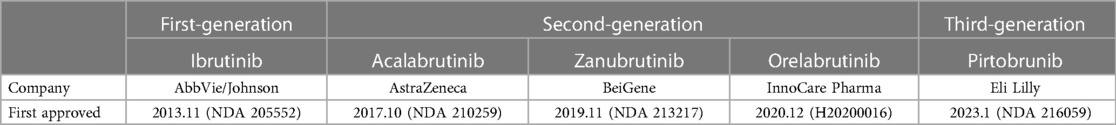
Since the emergence of the first-generation BTKi, Ibutinib, it has become a critical targeted drug for treating lymphoma, showing a good prognosis and relatively few side effects. The BTKi have been approved for marketing in many countries, and have been listed in chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL) (4), mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) (5), Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia (WM) (6) and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) (7), etc. Also, the different doses of BTKi are being tested, and indications' ranges are expanding to other B cell lymphoma or immune diseases. The different combinations of BTKi and other medications are being explored, like rituximab, Obinutuzumab, and venetoclax, for better outcomes and fewer side effects.
We may discover that the indications of BTKi are gradually expanding. Some of them have been proven while more indications are still in clinical trials. More than relatively common types of lymphoma, BTKi are in trials with central nervous system lymphoma (CNSL, NCT04438044) (8), large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL, NCT01855750) (9), and follicular lymphoma (FL, NCT02343120) (10). Furthermore, BTKi also plays a more curial role in autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis (MS, NCT02975349) (11), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE, NCT02975336) (3), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA, NCT03233230) (12).
In conclusion, we may find the importance and high risk of the incidence of AF in treating B-cell lymphoma. In contrast, the reports of AF and other cardiovascular events vary from each other. Thus, we may conclude different reports and have a more detailed description of AF in the different types of BTKi. Furthermore, we may find a better way to manage BTKi-related AF, improving the prognosis of lymphoma patients.
Methods
Due to the wide use of the BTKi in treating lymphoma and the noteworthy AEs of cardiotoxicity like AF in the clinical trial or normal therapeutic use, we collected related reports and paid special attention to AF events. Through extensive reading, different previous clinical trials and research suggest that diverse BTKi may act differently in the safety of AF. To further compare the safety of different generations of BTKi and have more reassuring guidance on clinical treatment, we systematically collected the clinical trials paper with NCT number (except Orelabrutinib) mentioned AF incidence rate. The data are collected from the most commonly used databases like Pubmed and Web of Science with keywords like BTKi and AF. All the clinical trials are collected from the published papers from 2013 to 2022, among a total of 657 papers from Web of Science and 225 papers from PubMed using the same strategy. After type filtering, eliminating duplicates, and screening contents, we finally reduced the scope to 45 papers Figure 1.
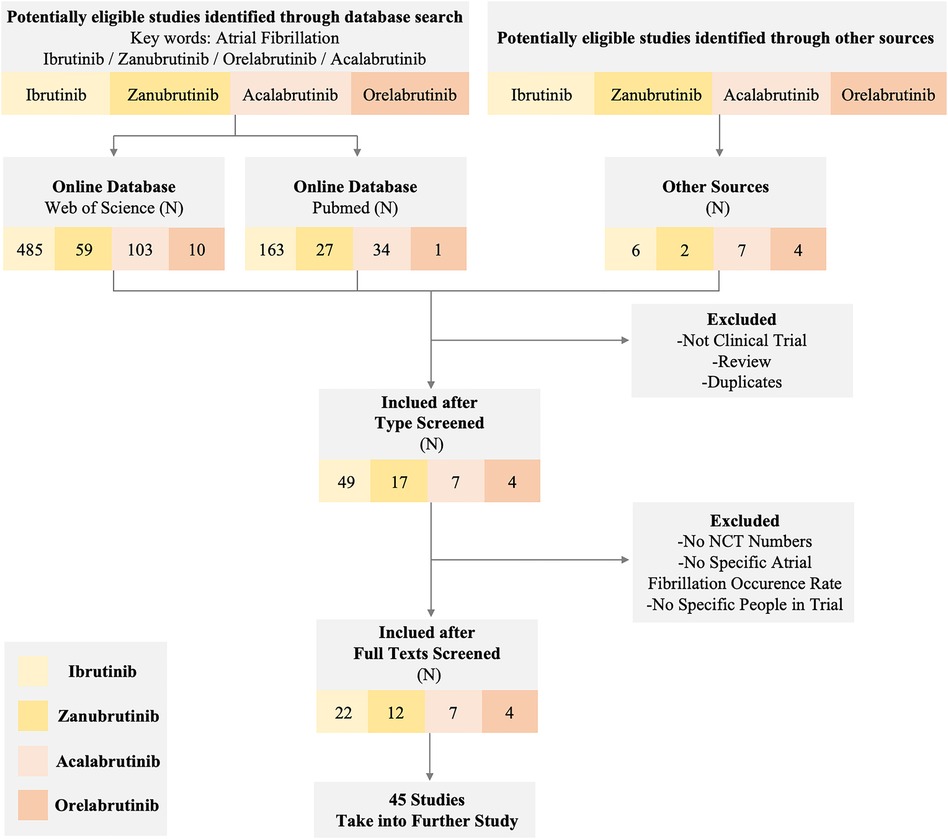
Figure 1 Flow diagram of the study. The diagram of the study shows the inclusion and exclusion criteria and a specific number of studies we obtained from different sources. We set atrial fibrillation and corresponding BTK inhibitors as keywords to exclude non-clinical trial studies and reviews. Eventually, 45 studies in different BTK inhibitors were taken into further research.
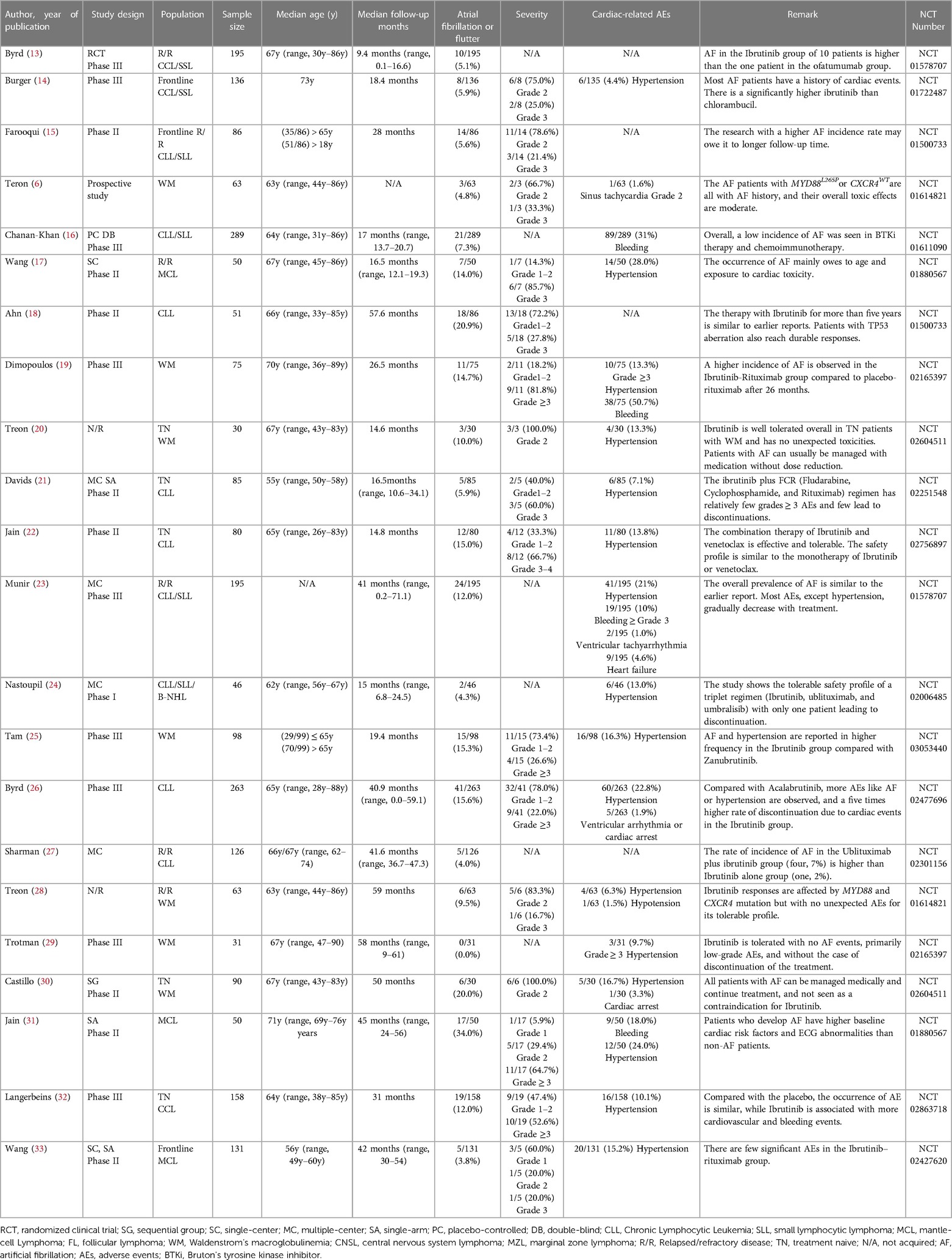
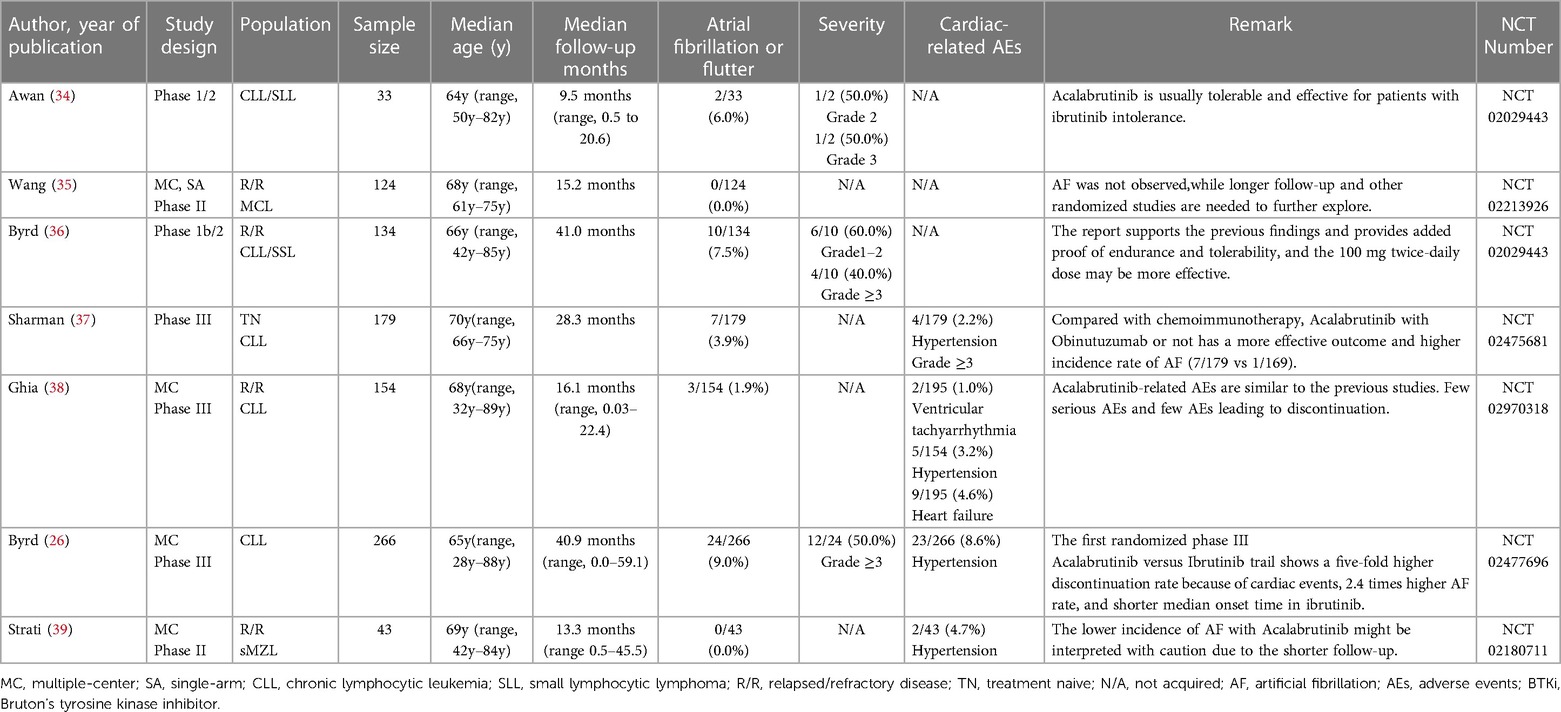
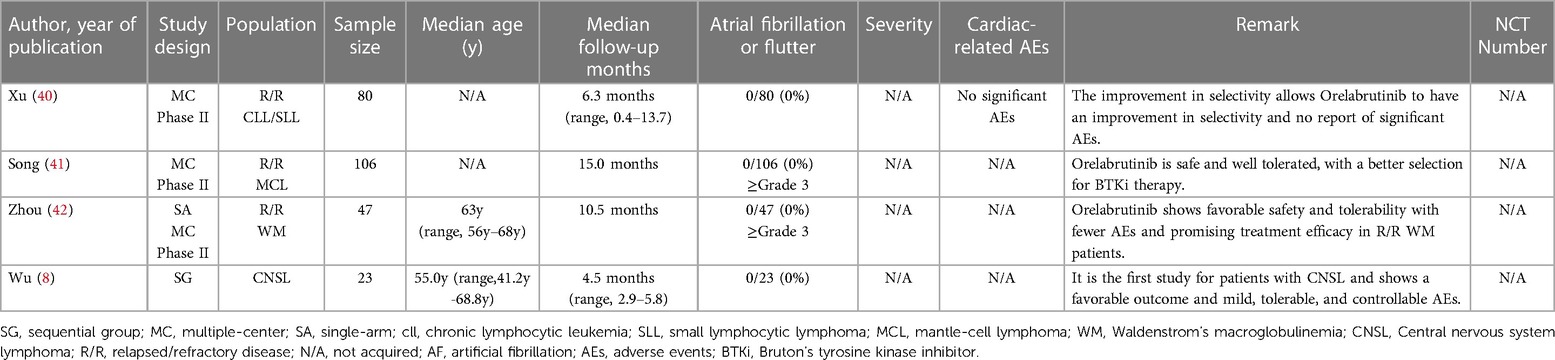
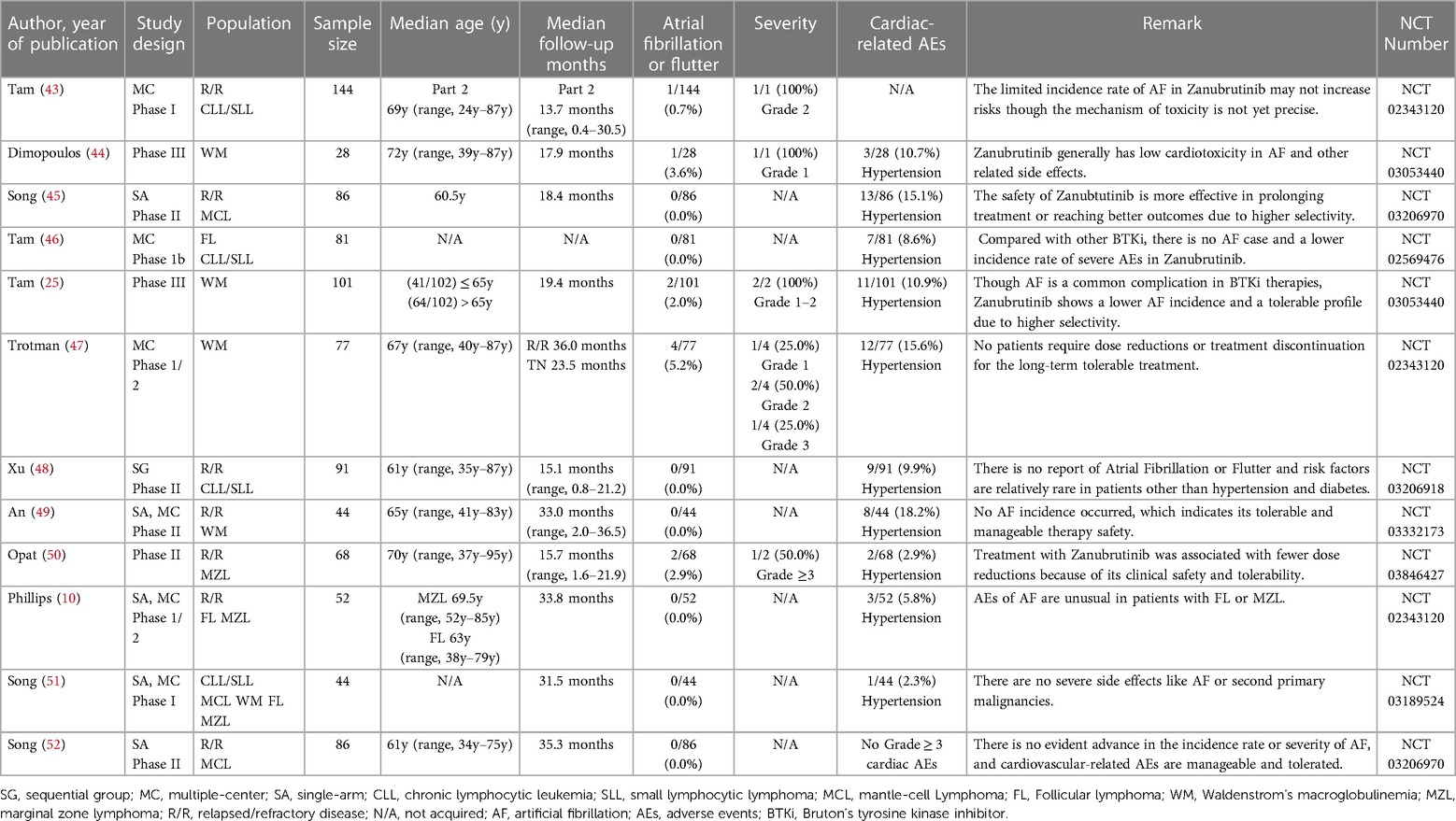
After overall criteria and careful reading, we finally collected papers on Ibrutinib (N = 22), Zanubrutinib (N = 12), Acalabrutinib (N = 7), and Orelabrutinib (N = 4). We mainly collect different AF incidence rates, related AE incidence rates, sample size, median age, severity, remark, etc.
Results
The AF incidence with BTK inhibitors
Through a comprehensive single-rate analysis encompassing data extracted from forty-two clinical trials conducted within the period spanning 2013–2022, we have concluded that the overall incidence rate of AF is relatively accurate at 5% (95% CI 4%–7% in the random effects model). It has been observed that second-generation BTKi exhibits fewer serious adverse events. Notably, the occurrence rate of AF displays significant variability, spanning from 0% to 35%. Having established an overall incidence rate of 5%, comparing the different BTKi therapies could provide valuable guidance for clinical treatment, particularly for patients with high cardiovascular risks. The heterogeneity observed between the four types of BTKi is evident (I2 = 85% > 50%, p < 0.01), indicating the need for subtype analysis to uncover differences and explore the underlying causes of heterogeneity. Through subtype analysis, we found the AF incidence rates for Ibrutinib (10%, 95% CI 7%–13% in random effects model) (Table 2), Acalabrutinib (4%, 95% CI 1%–6% in random effects model) (Table 3), Orelabrutinib (0%, 95% CI 0%–1% in common effects model) (Table 4), and Zanubrutinib (0%, 95% CI 0%–1% in common effects model) (Table 5).
Discussion
Based on comprehensive analysis results, the critical result of AF incidence is 6.0%. Nevertheless, our findings regarding the incidence rate of AF align with those of other systematic reviews and adhere to similar methodological approaches employed in meta-analyses of bleeding events (53). Meanwhile, through weighted mean, we can also approximately estimate incidence rates of the cardiac-related events: hypertension (14.8%) and heart failure (4.6%). The uncertainty of AEs will affect the prognosis of patients with lymphoma because of the discontinuation of treatment and the high risks for cardiovascular diseases like heart failure and stroke. Previous studies on Ibrutinib have reported common adverse events (AEs) including diarrhea (49%), upper respiratory tract infection (33%), fatigue (32%), cough (31%), and rash (27%) (4). Among these AEs, AF is a type of abnormal heart rhythm that affects the atria. When the atria are not beating coordinatedly, blood may form clots, travel to the brain vessels, and then lead to a stroke (54). Furthermore, it is imperative to underscore the strong correlation between AF and an elevated risk of heart failure, given that irregular atrial contractions can impede the heart's ability to efficiently pump blood. In summation, AF emerges as a salient and pivotal adverse event, particularly within the domain of BTKi treatment for lymphoma for its wide applications and potential risks.
The elevated risks and unique off-target toxicities associated with AF have garnered significant attention, leading to the emergence of a sub-discipline known as Cardio-oncology. This discipline emphasizes the collaboration between hematologists and cardiologists, aiming to enhance the management and prevention of adverse events associated with BTKi. The BTKi-related AF has not been fully discovered. According to certain studies, BTKi-related AF may related to relatively broad selectivity and targets, including BTK, TEC (55), EGFR, and CSK (56). In comparing Ibrutinib and other second-generation BTKi, differences in the target of CSK may lead to the difference in the incidence of AF.
The first generation BTKi: Ibrutinib
As the original and first-generation BTKi used in the treatment of lymphoma, Ibrutinib has emerged as a successful paradigm and a catalyst for related research. With extensive experimental support and clinical trial data, the reliability of its efficacy in terms of progression-free survival (PFS) and incidence rates of serious adverse events (AEs) has increased. However, notable heterogeneity remains within the Ibrutinib-treated group due to lymphoma types, study designs, and baseline data variations. To conduct further analysis in detail, we categorized the data into more specific subtypes. Nevertheless, the currently available clinical trials have limitations in providing a more nuanced analysis of these subtypes. The reported incidence rate of AF at 10% in Ibrutinib-treated patients can be considered relatively accurate and a reliable clinical reference. Notably, a meta-analysis focusing on AF incidence rate in CLL patients treated with Ibrutinib reported an AF incidence rate of 5% (57). This discrepancy could be attributed to the extensive application of Ibrutinib in lymphoma cases, as CLL was among the earliest approved indications for Ibrutinib, with a relatively low incidence rate of AF. Furthermore, more recent clinical trials have reported rates higher than 10% (25–27). The 10% incidence rate is understandable given the inherent heterogeneity associated with a single-rate analysis.
The second generation BTKi: zanubrutinib, orelabrutinib, and acalabrutinib
The progress in BTKi therapy has notably lessened treatment complications and bolstered treatment endurance. Zanubrutinib was brought into sharp focus due to its PFS efficiency results or relatively fewer side effects. Safety has become a key factor in the recommendation of lymphoma treatment. Also, based on the NCCN guideline (Version 1.2023) of CLL/SLL, Zanubrutinib is taken as the highest level of clinical recommendation. In contrast, Ibrutinib is taken as another recommendation for its potential cardiovascular risks. According to the result, we may observe that the AF incidence rate is approximately 0% due to the high risks of bias in certain studies. In the head-to-head trials, the AF incidence rate is 2.5% (58). The difference may originate from the limitations of different independent research reports and the methodology of single-group rate analysis. Larger studies, more compact study designs, and real-world data are necessary for further evidence to support the encouraging results of Zanubrutinib.
Orelabrutinib is still at the stage of various clinical trials. Only a few studies disclosed the results, while it is still considered a promising drug as BTKi for more effective and fewer AEs treatment. Although the current results from the single-rate analysis suggest an incidence rate of 0% for AF and no reported cases of AF, it is vital to acknowledge such analyses' limitations and potential biases.
Based on the subtype meta-analysis, the incidence rate of AF with Acalabrutinib in the random effect model is about 4%. Though the induced studies are limited, there is no significant difference between trials or other previous reports. The incidence of AF in the first randomized phase III trial of Ibrutinib (41/263, 15.6%) vs. Acalabrutinib (24/266, 9.0%) may offer us newly updated supportive data.
New generation BTKi: pirtobrunib
The approval of Pirtobrutinib in January 2023 as a non-covalent BTK inhibitor for MCL patients resistant to covalent ones marks a significant advancement in the third-generation BTKi (59). Also, we may expect the emergence of more third-generation BTKi, including pirtobrutinib (60) and Fenebrutinib (61). These developments highlight the ongoing evolution of BTK inhibitor therapy and the potential for better outcomes in diverse disease contexts. The field of BTKi has evolved from the first generation of exploratory and innovative compounds. Subsequently, the focus shifted towards the second generation of inhibitors, aiming to improve efficacy while minimizing side effects. Presently, the introduction of third-generation non-covalent binding inhibitors represents a significant advancement, expanding the therapeutic indications, and narrowing adverse events.
Comparative analysis between ibrutinib and zanubrutinib
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) warn against the utilization of Ibrutinib for its cardiovascular risks. In the age of targeted therapy, survival time of CLL/SLL patients has been largely prolonged. Thus, monitoring and prevention of cardiovascular events is vital for clinical treatment choices based on comprehensive physical conditions and drug toxicity. Recently, based on a head-to-head experiment (Zanubrutinib vs. Ibrutinib), the incidence rate of AF significantly decreased (2.5% vs. 10.19%, P = 0.001). In the study of ALPINE, 6 cases of 652 patients died of cardiac events with Ibrutinib. Also, the PFS in the Zanubrutinib group was better than that in the Ibrutinib group (94.9% vs. 84.0%) (58).
Through the comparison of Ibrutinib and Zanubrutinib, we may observe a significant difference in that Zanubrutinib performs better in the cardiac safety profiles in Figure 2. Theoretically, we may agree with the higher inhibition effects of Ibrutinib in HER2, HER4, TEC (mainly related to AF) (62) and fewer off-target effects of Zanubrutinib with lower IC50 against BTK (mainly related to the treatment of lymphoma) and higher IC50 for other kinases like EGFR(21nM), TEC(44nM), ITK(50nM) (63). More Head-to-head clinical trials or more detailed disclosure of procedures and results may help us identify their PFS and cardiotoxicity. The different baselines of cardiac risk factors, the ignorant monitoring of AEs, and the median follow-up time may contribute to the difference between the BTKi.
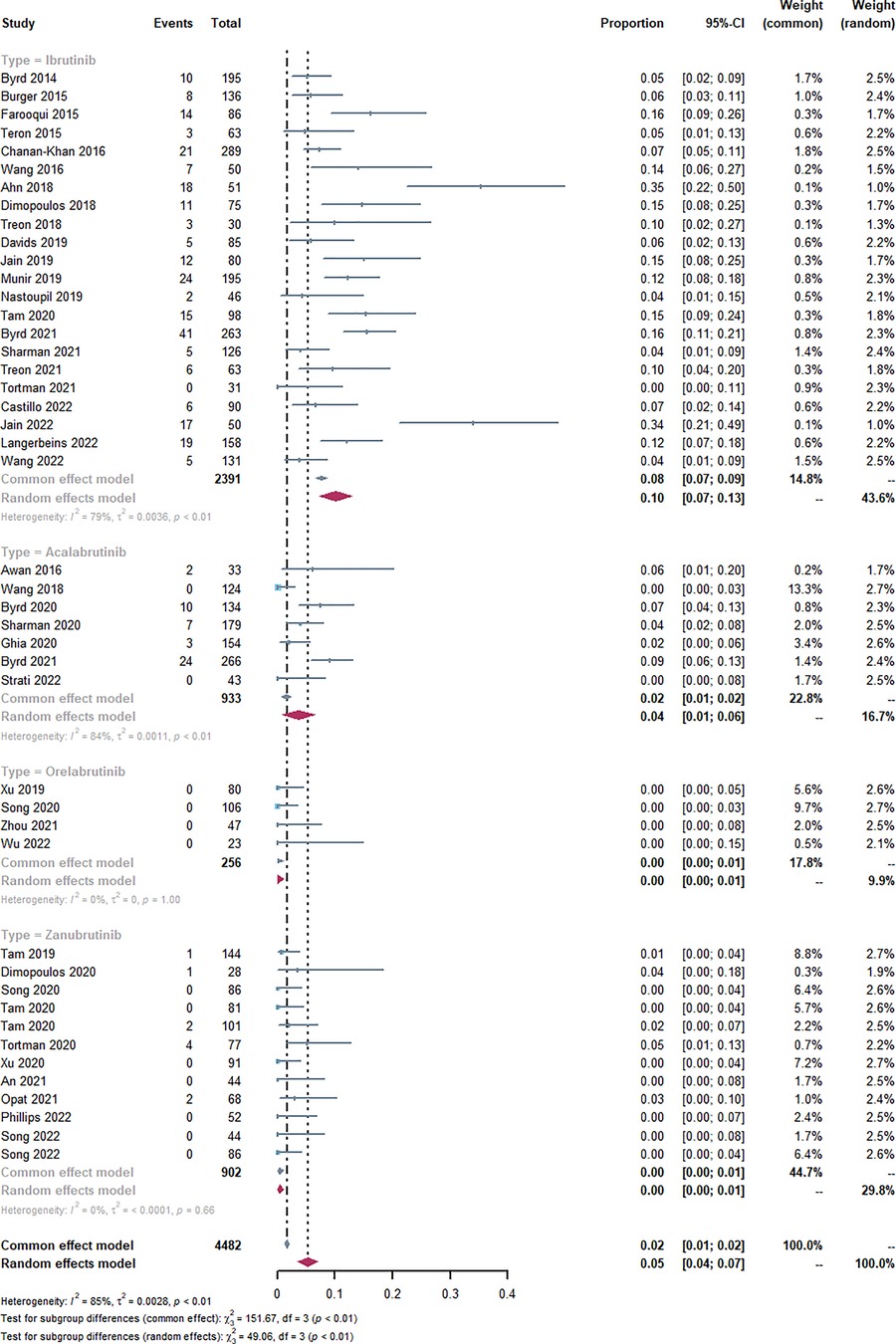
Figure 2 Forest plots of the included studies of atrial fibrillation or flutter occurrence rate and sub-type analysis. Through the single-rate analysis of AF incidence, we determined the AF incidence rates for Ibrutinib (10%, 95% CI 7%–13% in random effects model), Acalabrutinib (4%, 95% CI 1%–6% in random effects model), Orelabrutinib (0%, 95% CI 0%–1% in common effects model), Zanubrutinib (0%, 95% CI 0%–1% in common effects model), and overall AF incidence rate (5%, 95% CI 4%–7% in random effects model).
Generally, the incidence rate of AF would increase with longer follow-up time due to its stable long-term risks. However, some studies suggest that AF primarily occurs during a specific period and does not increase over time (62, 64). Comparing the median age and median follow-up time between the two groups, the mean age of both groups is approximately 65.2 months. However, the mean follow-up times differ, with 31.5 months in the Ibrutinib group and 23.38 months in the Zanubrutinib group. Furthermore, future clinical designs and systematic reviews should pay attention to baseline differences and the AF occurrence time.
Guidance for the management of AF in the treatment of BTKi
The advancements in BTKi have primarily focused on three key areas: developing new generations of BTKi, exploring different dosage regimens, and expanding medication options.
However, managing AF as a confirmed AE requires careful consideration before treatment initiation. A thorough assessment of high-risk factors, such as AF history, hypertension, bleeding history, age ≥ 65y, male sex, and underlying diseases, is necessary. Based on a recent study, reported Ibrutinib, age ≥ 65y, blood culture positive, hypertension, diabetes, and sex as risk factors for developed AF in CLL patients (65). Specifically, some studies may focus on AF-risk scores used in patients with CLL, if patients with a score ≥5 should be carefully monitored or changed to second-generation BTKi (66–68). Commonly used clinical tools like the CHA2DS2-VASc and the HAS-BLED aid in evaluating the risk-benefit balance of AF patients in the area of BTKi treatment. For instance, if the CHA2DS2-VASc score exceeds 2, oral anticoagulants such as aspirin are recommended (69). Also, newly developed AF prediction models like HARMS2-AF risk scores can be tested in future trials (70). The personalized treatment plans should be formulated based on patient-specific factors such as scores, electrocardiogram (ECG) results, and blood pressure, including tailored doses and durations of BTKi, anticoagulants, and other supportive treatments (71) (Figure 3).
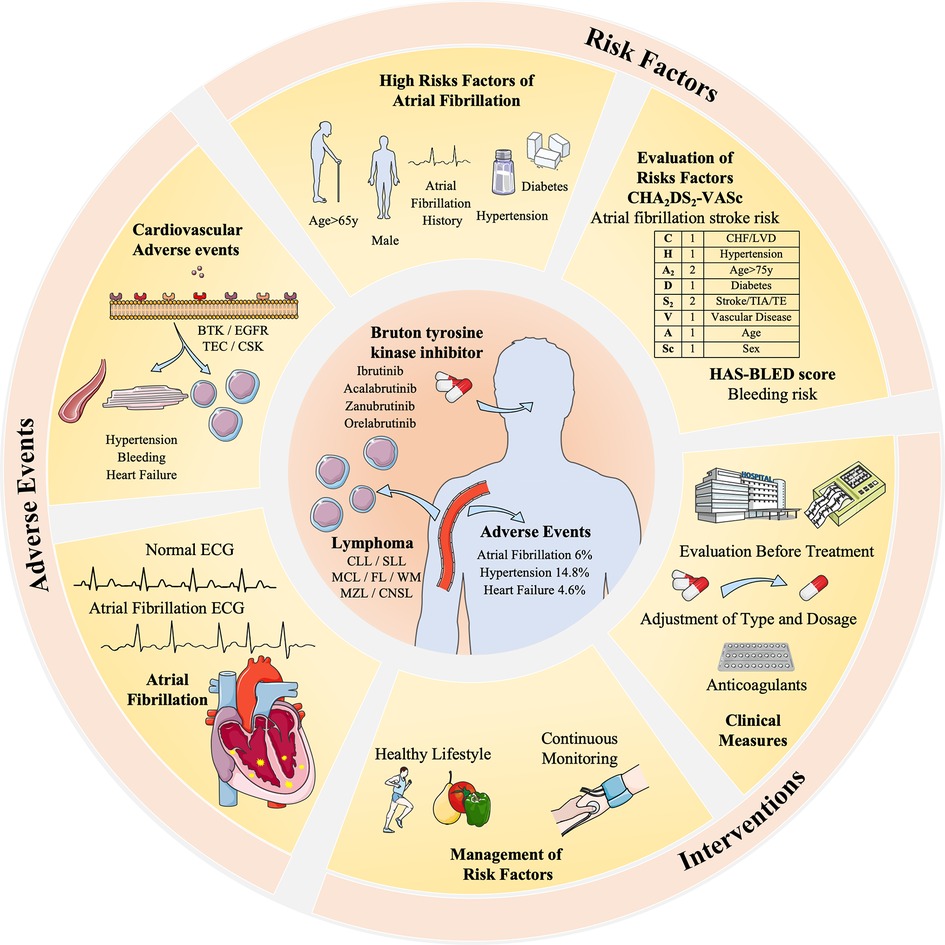
Figure 3 The risk factors, adverse events, and interventions of BTKi-related atrial fibrillation in the treatment of lymphoma. BTK inhibitors are related to different cardiovascular adverse events including AF (5%), hypertension (14.8%), and heart failure (4.6%). It is related to different receptors like BTK, EGFR, and TEC expressed by myocardial cells and vascular endothelial cells. Risk factors and evaluation methods like CHA2DS2-VASc and HAS-BLED are taken to evaluate its interventions. Dosage adjustment or anticoagulants are common clinical measures, and a healthy lifestyle and continuous monitoring are advised to manage risk factors, hypertension, and diabetes. Patients with an AF history are highly risky for BTKi-related AF and require special monitoring and decisions.
Moreover, based on clinical needs, early detection methods and specific biomarkers are essential for the management of lymphoma treatment. There are already biomarkers, including Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP), ST2, Galectin-3 (72), FGF-23 (73), and microRNAs (74). While we may expect further exploration of the specific biomarker for BTKi-related AF, working as a convenient and inexpensive method. In cases where medically managing BTK inhibitor-related AF proves challenging, discontinuation of BTK inhibitor treatment may be considered. However, this decision must be weighed against its potential impact on treatment efficacy. Thus, striking a balance between side effects and the continuity of treatment is imperative.
Conclusion
Through a relatively comprehensive collection, we conclude different types of AEs, mainly focusing on the incidence of AF. The incidence rate of AF varies from 0% to 35%, and through a single rate analysis, the overall AF incidence rate is considered as 5% (95% CI 4%-7%). The profiles of BTKi are tolerable and controllable, showing a great advancement in the second-generation BTK with less serious AEs. Also, the cardiac-related AEs indicate us to manage patients regularly and prevent the occurrence of AF during the treatment of lymphoma. In the future, we may further explore the mechanism of BTKi-related AF and find more measures to monitor cardiac-related AEs.
Author contributions
JD: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Z-YC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. X-RG: Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. TW: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. Z-FH: Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
BTKi, Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor; XLA, x-linked agammaglobulinemia; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; WM, Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia; MZL, marginal zone lymphoma; DLBCL, large B cell lymphoma; MS, multiple sclerosis; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; PI3 K, phosphoinositol 3-kinase; FGF, fibroblast factor; SG, sequential group; MC, multiple-center; PC, placebo-controlled; R/R, relapsed/refractory disease; N/A, not acquired; AF, atrial fibrillation; BCR, B-cell receptor; SLL, small lymphocytic lymphoma; MCL, mantle-cell lymphoma; CNSL, central nervous system leukemia; FL, follicular lymphoma; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; AE, adverse events; BNP, brain natriuretic peptide; RCT, randomized clinical trial; SC, single-center; SA, single-arm; DB, double-blind; TN, treatment naive.
References
1. Poyyamoli S, Mehta P, Cherian M, Anand R, Patil S, Kalva S, et al. Role of bruton’s tyrosine kinase in B cells and malignancies. Mol Cancer. (2018) 17(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0779-z
2. Cardenas-Morales M, Hernandez-Trujillo VP. Agammaglobulinemia: from X-linked to autosomal forms of disease. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2022) 63(1):22–35. doi: 10.1007/s12016-021-08870-5
3. Burger JA. Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors: present and future. Cancer J. (2019) 25(6):386–93. doi: 10.1097/PPO.0000000000000412
4. Byrd JC, Furman RR, Coutre SE, Flinn IW, Burger JA, Blum KA, et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. (2013) 369(1):32–42. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1215637
5. Wang ML, Rule S, Martin P, Goy A, Auer R, Kahl BS, et al. Targeting BTK with ibrutinib in relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. (2013) 369(6):507–16. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1306220
6. Treon SP, Tripsas CK, Meid K, Warren D, Varma G, Green R, et al. Ibrutinib in previously treated Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. (2015) 372(15):1430–40. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1501548
7. Noy A, de Vos S, Thieblemont C, Martin P, Flowers CR, Morschhauser F, et al. Targeting Bruton tyrosine kinase with ibrutinib in relapsed/refractory marginal zone lymphoma. Blood. (2017) 129(16):2224–32. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-10-747345
8. Wu JJ, Wang WH, Dong M, Ma SS, Zhang XD, Zhu LN, et al. Orelabrutinib-bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor-based regimens in the treatment of central nervous system lymphoma: a retrospective study. Invest New Drugs. (2022) 40(3):650–9. doi: 10.1007/s10637-022-01219-5
9. Wilson WH, Wright GW, Huang DW, Hodkinson B, Balasubramanian S, Fan Y, et al. Effect of ibrutinib with R-CHOP chemotherapy in genetic subtypes of DLBCL. Cancer Cell. (2021) 39(12):1643–1653.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.10.006
10. Phillips T, Chan H, Tam CS, Tedeschi A, Johnston P, Oh SY, et al. Zanubrutinib monotherapy in relapsed/refractory indolent non-hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv. (2022) 6(11):3472–9. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006083
11. Montalban X, Arnold DL, Weber MS, Staikov I, Piasecka-Stryczynska K, Willmer J, et al. Placebo-controlled trial of an oral BTK inhibitor in multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380(25):2406–17. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1901981
12. Montalban X, Wallace D, Genovese MC, Tomic D, Parsons-Rich D, Le Bolay C, et al. Characterisation of the safety profile of evobrutinib in over 1000 patients from phase II clinical trials in multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus: an integrated safety analysis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2023) 94(1):1–9. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2022-328799
13. Byrd JC, Brown JR, O'Brien S, Barrientos JC, Kay NE, Reddy NM, et al. Ibrutinib versus ofatumumab in previously treated chronic lymphoid leukemia. N Engl J Med. (2014) 371(3):213–23. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1400376
14. Burger JA, Tedeschi A, Barr PM, Robak T, Owen C, Ghia P, et al. Ibrutinib as initial therapy for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373(25):2425–37. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1509388
15. Farooqui M, Valdez J, Soto S, Bray A, Tian X, Wiestner A. Atrial fibrillation in CLL/SLL patients on ibrutinib. Blood. (2015) 126(23):2933–2933. doi: 10.1182/blood.V126.23.2933.2933
16. Chanan-Khan A, Cramer P, Demirkan F, Fraser G, Silva RS, Grosicki S, et al. Ibrutinib combined with bendamustine and rituximab compared with placebo, bendamustine, and rituximab for previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma (HELIOS): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. (2016) 17(2):200–11. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00465-9
17. Wang ML, Lee H, Chuang H, Wagner-Bartak N, Hagemeister F, Westin J, et al. Ibrutinib in combination with rituximab in relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma: a single-centre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2016) 17(1):48–56. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00438-6
18. Ahn IE, Farooqui MZH, Tian X, Valdez J, Sun C, Soto S, et al. Depth and durability of response to ibrutinib in CLL: 5-year follow-up of a phase 2 study. Blood. (2018) 131(21):2357–66. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-12-820910
19. Dimopoulos MA, Tedeschi A, Trotman J, García-Sanz R, Macdonald D, Leblond V, et al. Phase 3 trial of ibrutinib plus rituximab in Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. (2018) 378(25):2399–410. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1802917
20. Treon SP, Gustine J, Meid K, Yang G, Xu L, Liu X, et al. Ibrutinib monotherapy in symptomatic, treatment-naïve patients with waldenström macroglobulinemia. J Clin Oncol. (2018) 36(27):2755–61. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.78.6426
21. Davids MS, Brander DM, Kim HT, Tyekucheva S, Bsat J, Savell A, et al. Ibrutinib plus fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab as initial treatment for younger patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. (2019) 6(8):e419–28. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(19)30104-8
22. Jain N, Keating M, Thompson P, Ferrajoli A, Burger J, Borthakur G, et al. Ibrutinib and venetoclax for first-line treatment of CLL. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380(22):2095–103. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1900574
23. Munir T, Brown JR, O'Brien S, Barrientos JC, Barr PM, Reddy NM, et al. Final analysis from RESONATE: up to six years of follow-up on ibrutinib in patients with previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma. Am J Hematol. (2019) 94(12):1353–63. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25638
24. Nastoupil LJ, Lunning MA, Vose JM, Schreeder MT, Siddiqi T, Flowers CR, et al. Tolerability and activity of ublituximab, umbralisib, and ibrutinib in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and non-hodgkin lymphoma: a phase 1 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet Haematol. (2019) 6(2):e100–9. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(18)30216-3
25. Tam CS, Opat S, D'Sa S, Jurczak W, Lee HP, Cull G, et al. A randomized phase 3 trial of zanubrutinib vs ibrutinib in symptomatic Waldenström macroglobulinemia: the ASPEN study. Blood. (2020) 136(18):2038–50. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020006844
26. Byrd JC, Hillmen P, Ghia P, Kater AP, Chanan-Khan A, Furman RR, et al. Acalabrutinib versus ibrutinib in previously treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia: results of the first randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39(31):3441–52. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01210
27. Sharman JP, Brander DM, Mato AR, Ghosh N, Schuster SJ, Kambhampati S, et al. Ublituximab plus ibrutinib versus ibrutinib alone for patients with relapsed or refractory high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (GENUINE): a phase 3, multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Haematol. (2021) 8(4):e254–66. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30433-6
28. Treon SP, Meid K, Gustine J, Yang G, Xu L, Liu X, et al. Long-term follow-up of ibrutinib monotherapy in symptomatic, previously treated patients with waldenström macroglobulinemia. J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39(6):565–75. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.00555
29. Trotman J, Buske C, Tedeschi A, Matous JV, MacDonald D, Tam CS, et al. Single-agent ibrutinib for rituximab-refractory waldenström macroglobulinemia: final analysis of the substudy of the phase III innovate(TM) trial. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27(21):5793–800. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-1497
30. Castillo JJ, Meid K, Gustine JN, Leventoff C, White T, Flynn CA, et al. Long-term follow-up of ibrutinib monotherapy in treatment-naive patients with waldenstrom macroglobulinemia. Leukemia. (2022) 36(2):532–9. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01417-9
31. Jain P, Zhao S, Lee HJ, Hill HA, Ok CY, Kanagal-Shamanna R, et al. Ibrutinib with rituximab in first-line treatment of older patients with mantle cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. (2022) 40(2):202–12. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01797
32. Langerbeins P, Zhang C, Robrecht S, Cramer P, Fürstenau M, Al-Sawaf O, et al. The CLL12 trial: ibrutinib vs placebo in treatment-naïve, early-stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood. (2022) 139(2):177–87. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021010845
33. Wang ML, Jain P, Zhao S, Lee HJ, Nastoupil L, Fayad L, et al. Ibrutinib–rituximab followed by R-HCVAD as frontline treatment for young patients (≤65 years) with mantle cell lymphoma (WINDOW-1): a single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2022) 23(3):406–15. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00638-0
34. Awan FT, Schuh A, Brown JR, Furman RR, Pagel JM, Hillmen P, et al. Acalabrutinib monotherapy in patients with ibrutinib intolerance: results from the phase 1/2 ACE-CL-001 clinical study. Blood. (2016) 128(22):638. doi: 10.1182/blood.V128.22.638.638
35. Wang M, Rule S, Zinzani PL, Goy A, Casasnovas O, Smith SD, et al. Acalabrutinib in relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (ACE-LY-004): a single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet. (2018) 391(10121):659–67. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33108-2
36. Byrd JC, Wierda WG, Schuh A, Devereux S, Chaves JM, Brown JR, et al. Acalabrutinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia: updated phase 2 results. Blood. (2020) 135(15):1204–13. doi: 10.1182/blood.2018884940
37. Sharman JP, Egyed M, Jurczak W, Skarbnik A, Pagel JM, Flinn IW, et al. Acalabrutinib with or without obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil and obinutuzumab for treatment-naive chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (ELEVATE-TN): a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. (2020) 395(10232):1278–91. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30262-2
38. Ghia P, Pluta A, Wach M, Lysak D, Kozak T, Simkovic M, et al. ASCEND: phase III, randomized trial of acalabrutinib versus idelalisib plus rituximab or bendamustine plus rituximab in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol. (2020) 38(25):2849–61. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.03355
39. Strati P, Coleman M, Champion R, Ma S, Patti C, Levy MY, et al. A phase 2, multicentre, open-label trial (ACE-LY-003) of acalabrutinib in patients with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma. Br J Haematol. (2022) 199(1):76–85. doi: 10.1111/bjh.18368
40. Xu W, Song Y, Li Z, Yang S, Liu L, Hu Y, et al. Safety, tolerability and efficacy of orelabrutinib, once a day, to treat Chinese patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small cell leukemia. Blood. (2019) 134:4319. doi: 10.1182/blood-2019-123331
41. Song Y, Song Y, Liu L, Zhang M, Li Z, Ji C, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of orelabrutinib monotherapy in Chinese patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma: a multicenter, open-label, phase II study. Blood. (2020) 136:1. doi: 10.1182/blood-2020-141781
42. Zhou D, Jin J, Fu ZZ, Yi S, Zhao WL, Sun Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of orelabrutinib in relapsed/refractory waldenstrom’s macroglobulinemia patients. Blood. (2021) 138:46. doi: 10.1182/blood-2021-149350
43. Tam CS, Trotman J, Opat S, Burger JA, Cull G, Gottlieb D, et al. Phase 1 study of the selective BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib in B-cell malignancies and safety and efficacy evaluation in CLL. Blood. (2019) 134(11):851–9. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019001160
44. Dimopoulos M, Sanz RG, Lee HP, Trneny M, Varettoni M, Opat S, et al. Zanubrutinib for the treatment of MYD88 wild-type waldenström macroglobulinemia: a substudy of the phase 3 ASPEN trial. Blood Adv. (2020) 4(23):6009–18. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003010
45. Song Y, Zhou K, Zou D, Zhou J, Hu J, Yang H, et al. Treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory mantle-cell lymphoma with zanubrutinib, a selective inhibitor of bruton’s tyrosine kinase. Clin Cancer Res. (2020) 26(16):4216–24. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-3703
46. Tam CS, Quach H, Nicol A, Badoux X, Rose H, Prince HM, et al. Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) plus obinutuzumab in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia and follicular lymphoma. Blood Advances. (2020) 4(19):4802–11. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020002183
47. Trotman J, Opat S, Gottlieb D, Simpson D, Marlton P, Cull G, et al. Zanubrutinib for the treatment of patients with waldenström macroglobulinemia: 3 years of follow-up. Blood. (2020) 136(18):2027–37. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020006449
48. Xu W, Yang S, Zhou K, Pan L, Li Z, Zhou J, et al. Treatment of relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma with the BTK inhibitor zanubrutinib: phase 2, single-arm, multicenter study. J Hematol Oncol. (2020) 13(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00884-4
49. An G, Zhou D, Cheng S, Zhou K, Li J, Zhou J, et al. A phase II trial of the Bruton tyrosine-kinase inhibitor zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) in patients with relapsed/refractory Waldenström macroglobulinemia. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27(20):5492–501. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0539
50. Opat S, Tedeschi A, Linton K, McKay P, Hu B, Chan H, et al. The MAGNOLIA trial: zanubrutinib, a next-generation bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor, demonstrates safety and efficacy in relapsed/refractory marginal zone lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2021) 27(23):6323–32. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-1704
51. Song Y, Sun M, Qi J, Xu W, Zhou J, Li D, et al. A two-part, single-arm, multicentre, phase I study of zanubrutinib, a selective Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in Chinese patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies. Br J Haematol. (2022) 198(1):62–72. doi: 10.1111/bjh.18162
52. Song Y, Zhou K, Zou D, Zhou J, Hu J, Yang H, et al. Zanubrutinib in relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma: long-term efficacy and safety results from a phase 2 study. Blood. (2022) 139(21):3148–58. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021014162
53. Sestier M, Hillis C, Fraser G, Leong D. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitors and cardiotoxicity: more than just atrial fibrillation. Curr Oncol Rep. (2021) 23(10):113. doi: 10.1007/s11912-021-01102-1
54. Zimetbaum P. Atrial fibrillation. Ann Intern Med. (2017) 166(5):Itc33–itc48. doi: 10.7326/AITC201703070
55. McMullen JR, Boey EJ, Ooi JY, Seymour JF, Keating MJ, Tam CS. Ibrutinib increases the risk of atrial fibrillation, potentially through inhibition of cardiac PI3K-Akt signaling. Blood. (2014) 124(25):3829–30. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-10-604272
56. Christensen BW, Zaha VG, Awan FT. Cardiotoxicity of BTK inhibitors: ibrutinib and beyond. Expert Rev Hematol. (2022) 15(4):321–31. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2022.2067526
57. Caldeira D, Alves D, Costa J, Ferreira JJ, Pinto FJ. Ibrutinib increases the risk of hypertension and atrial fibrillation: systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. (2019) 14(2):e0211228. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211228
58. Brown JR, Eichhorst B, Hillmen P, Jurczak W, Kazmierczak M, Lamanna N, et al. Zanubrutinib or ibrutinib in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. (2023) 388(4):319–32. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2211582
59. Keam SJ. Pirtobrutinib: first approval. Drugs. (2023) 83(6):547–53. doi: 10.1007/s40265-023-01860-1
60. Aslan B, Kismali G, Iles LR, Manyam GC, Ayres ML, Chen LS, et al. Pirtobrutinib inhibits wild-type and mutant Bruton’s tyrosine kinase-mediated signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood Cancer J. (2022) 12(5):80. doi: 10.1038/s41408-022-00675-9
61. Elamin G, Aljoundi A, Alahmdi MI, Abo-Dya NE, Soliman MES. Battling BTK mutants with noncovalent inhibitors that overcome Cys481 and Thr474 mutations in Waldenström macroglobulinemia therapy: structural mechanistic insights on the role of fenebrutinib. J Mol Model. (2022) 28(11):355. doi: 10.1007/s00894-022-05345-y
62. Estupiñán HY, Berglöf A, Zain R, Smith CIE. Comparative analysis of BTK inhibitors and mechanisms underlying adverse effects. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:630942. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.630942
63. Kaptein A, de Bruin G, Emmelot-van Hoek M, van de Kar B, de Jong A, Gulrajani M, et al. Potency and selectivity of BTK inhibitors in clinical development for B-cell malignancies. Blood. (2018) 132(Suppl 1):1871–1871. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-99-109973
64. Furman RR, Byrd JC, Owen RG, O'Brien SM, Brown JR, Hillmen P, et al. Pooled analysis of safety data from clinical trials evaluating acalabrutinib monotherapy in mature B-cell malignancies. Leukemia. (2021) 35(11):3201–11. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01252-y
65. Parviz M, Agius R, Rotbain EC, Vainer N, Aarup K, Niemann CU. Identifying CLL patients at high risk of atrial fibrillation on treatment using machine learning. Leuk Lymphoma. (2024) 65(4):449–59. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2023.2299737
66. Archibald WJ, Rabe KG, Kabat BF, Herrmann J, Ding W, Kay NE, et al. Atrial fibrillation in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) treated with ibrutinib: risk prediction, management, and clinical outcomes. Ann Hematol. (2021) 100(1):143–55. doi: 10.1007/s00277-020-04094-3
67. Shanafelt TD, Parikh SA, Noseworthy PA, Goede V, Chaffee KG, Bahlo J, et al. Atrial fibrillation in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Leuk Lymphoma. (2017) 58(7):1630–9. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2016.1257795
68. Visentin A, Deodato M, Mauro FR, Autore F, Reda G, Vitale C, et al. A scoring system to predict the risk of atrial fibrillation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematol Oncol. (2019) 37(4):508–12. doi: 10.1002/hon.2655
69. Vrontikis A, Carey J, Gilreath JA, Halwani A, Stephens DM, Sweetenham JW. Proposed algorithm for managing ibrutinib-related atrial fibrillation. Oncology (Williston Park). (2016) 30(11):970–4. 980-1, c3. PMID: 27848243
70. Segan L, Canovas R, Nanayakkara S, Chieng D, Prabhu S, Voskoboinik A, et al. New-onset atrial fibrillation prediction: the HARMS2-AF risk score. Eur Heart J. (2023) 44(36):3443–52. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad375
71. Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, Ahlsson A, Atar D, Casadei B, et al. 2016 ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J. (2016) 37(38):2893–962. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw210
72. Oikonomou E, Zografos T, Papamikroulis GA, Siasos G, Vogiatzi G, Theofilis P, et al. Biomarkers in atrial fibrillation and heart failure. Curr Med Chem. (2019) 26(5):873–87. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170830100424
73. Chua W, Purmah Y, Cardoso VR, Gkoutos GV, Tull SP, Neculau G, et al. Data-driven discovery and validation of circulating blood-based biomarkers associated with prevalent atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. (2019) 40(16):1268–76. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy815
Keywords: atrial fibrillation, Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors, cardiovascular toxicity, lymphoma, Ibrutinib
Citation: Du J, Chen Z-Y, Gu X-R, Wang T and Huang Z-F (2024) Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor-related atrial fibrillation and its implications in the treatment of B-cell lymphoma. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 11: 1408983. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1408983
Received: 29 March 2024; Accepted: 12 July 2024;
Published: 26 July 2024.
Edited by:
Luigi Tarantini, IRCCS Local Health Authority of Reggio Emilia, Italy© 2024 Du, Chen, Gu, Wang and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ting Wang, dGluZ3dhbmcyMDAwQDEyNi5jb20=; Zou-Fang Huang, bmZ5eWpzampAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jun Du1,†
Jun Du1,† Ze-Yu Chen
Ze-Yu Chen Ting Wang
Ting Wang Zou-Fang Huang
Zou-Fang Huang