- 1The Center of Gerontology and Geriatrics, National Clinical Research Center for Geriatrics, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 2Division of Vascular Surgery, Department of General Surgery, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Objective: To evaluate the effect of malnutrition assessed by the Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index (GNRI) on major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE) in the elderly patients after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair (EVAR).
Materials and methods: This was a retrospective cohort study of elderly patients who underwent EVAR in a tertiary hospital. Malnutrition status was assessed by the GNRI. The primary outcome was MACCE. The predictive ability of the GNRI was compared with both the Revised Cardiac Risk Index (RCRI) and the modified Frailty Index (mFI) using Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
Result: A total of 453 patients underwent EVAR November 2015 and January 2020 was retrospectively analyzed, equally divided into three (low/medium/high) groups according to GNRI values which ranked from low to high. Five (1.10%) patients were lost in follow-up after surgery, and the median length of follow-up was 28.00 (15.00–47.00) months. The high GNRI values reduced length of hospital stay following EVAR in comparison to patients in low GNRI values group (β 9.67, 95% CI 4.01–23.32, p = 0.0113; adjusted β −1.96, 95% CI −3.88, −0.05, p = 0.0454). GNRI status was associated with a significantly increased risk of long-term mortality after EVAR (Medium GNRI, unadjusted HR 0.40, 95%CI 0.23–0.70, p = 0.0014; adjusted HR 0.47, 95%CI 0.26–0.84, p = 0.0107; high GNRI, 0.27 95%CI 0.14–0.55; p = 0.0003; adjusted HR 0.32 95%CI 0.15–0.68, p = 0.0029). Both medium and high GNRI values were linked to significantly reduced risks of MACCE compared to low GNRI score patients (Medium GNRI, unadjusted HR 0.34, 95%CI 0.13–0.88, p = 0.00265; adjusted HR 0.37, 95%CI 0.14–0.96, p = 0.0408; High GNRI, 0.26 95%CI 0.09–0.78; p = 0.0168; adjusted HR 0.21 95%CI 0.06–0.73, p = 0.0029). Compared with the RCRI and mFI, the GNRI had better discrimination in predicting long-term MACCE. An area under the curve (AUC) for GNRI mFI, and RCRI is 0.707, 0.614 and 0.588, respectively. (Z statistic, GNRI vs. mFI, p = 0.0475; GNRI vs. RCRI, p = 0.0017).
Conclusion: Malnutrition assessed by the GNRI may serve as a useful predictor of long-term MACCE in elderly patients after EVAR, with preferable discrimination abilities compared with both RCRI and mFI.
Introduction
Endovascular aortic aneurysm repair (EVAR) is the preferred intervention for abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), particularly in elderly patients with multiple comorbidities. Despite its minimally invasive procedures, EVAR patients remain susceptible to various adverse outcomes, including cardiac and cerebrovascular events (1, 2) with complication rates ranging from 0.94% to 4.5% (3, 4) during follow-up. Given the potentially profound impact of cardiovascular events on patient quality of life and survival, there is a critical need for robust predictive models to aid preoperative assessment and postoperative monitoring. While tools like the Modified Frailty Index (mFI) (5) and the Revised Cardiac Risk Index (RCRI) (6) have emerged in recent years, we previously found adverse event incidence, exhibiting significant variability across different risk calculators (7). Moreover, existing risk values primarily address short-term cardiovascular complications, with a dearth of predictors for long-term major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE).
Above tools primarily evaluate the physiological condition based on comorbidities to forecast surgical risks and prognosis, with limited consideration for the nutritional status of patients. The Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index (GNRI) (8) serves as a tailored nutritional assessment tool for elderly patients, specifically aimed at gauging the deleterious effects of nutritional elements on clinical endpoints. Nutritional risk among hospitalized elderly patients may lead to prolonged hospitalization, heightened healthcare expenditures, increased perioperative complications, and elevated mortality rates. GNRI has demonstrated significant associations with postoperative complications and prognostic outcomes across a spectrum of diseases (9–11). Our prior meta-analysis revealed that the validation of most frailty assessment instruments predominantly focuses on short-term survival outcomes post-vascular surgery, highlighting a notable deficiency in tools of high quality addressing both short-term and long-term cardiovascular endpoints (7).
Therefore, our study sought to ascertain the predictive efficacy of the GNRI concerning short-term and long-term outcome as well as adverse cardiovascular events in patients undergoing EVAR.
Materials and methods
Ethics
This retrospective cohort study was conducted at West China Hospital, a tertiary academic center in Chengdu, Sichuan, China. It adhered to the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) guidelines for cohort studies. The study protocol received approval from the institutional review board of West China Hospital, with a waiver of informed consent.
Selection and description of participants
Consecutive individuals aged over 60 years who underwent EVAR at West China Hospital between November 2015 and January 2020 were screened for eligibility. Exclusion criteria comprised patients lacking functional status records, readmitted individuals receiving reinterventions for prior EVAR, those with incorrect contact information, and individuals unable to communicate. Data for patients admitted were retrospectively gathered from our EVAR database, followed by prospective data collection thereafter. Patients underwent outpatient follow-up with Duplex ultrasound at 1, 6, and 12 months post-intervention, and subsequently annually. Telephone follow-up was utilized if patients failed to attend appointments. Any observed adverse events, such as endoleaks or limb thrombosis, during Duplex ultrasound examinations prompted further evaluation via computed tomography angiogram.
GNRI identification
This study compiled preoperative patient data that was available in the electronic medical record system, encompassing demographic variables such as gender and age, as well as medical histories pertaining to smoking, hypertension, diabetes, lung disease, heart disease, and other comorbidities, alongside perioperative mortality and complication rates. Additionally, measurements including height, body weight, body mass index (BMI), and serum protein levels were documented. The nutritional status of all patients was assessed using the Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index (GNRI) formula (8). GNRI = (14.89 × serum albumin level g/dl) + (41.7 × current body weight ÷ ideal body weight); Ideal body weight = height(m) × height(m) × 22. According to the calculated GNRI values, 453 patients included in this study were divided equally into three groups. Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) (12), RCRI (6) and mFI values (4, 5, 13) were also calculated for each patient according to previous report. Another baseline demographic and clinical parameters were gathered, including emergent case classification, severely angulated neck, concurrent common iliac artery aneurysm (CIAA) with a maximum diameter ≥25 mm, and maximum diameter of abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) (expressed in mm).
In this study, the primary outcomes evaluated encompassed short-term and long-term major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE).MACCE was defined as a composition of death, myocardial infarction, stroke, chronic cardiac failure and repeat revascularization (14) Secondary outcomes included length of stay in hospital, 30-day mortality, overall survival, and adverse aortic events (AAE). AAE was defined as a composition of type I or III endoleaks, limb occlusion, and aortic-related reintervention.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were depicted as means ± standard deviations or as medians with interquartile ranges in cases of non-normal distribution. Categorical variables were articulated as numbers and percentages. Comparative analyses among the three groups involved ANOVA or Kruskal–Wallis H tests for continuous variables and χ2 or Fisher's exact tests for categorical variables. Long-term outcomes were delineated using absolute frequencies (patient count) and relative frequencies (percentages), with proportions presented alongside 95% confidence intervals (CI). Time-to-event data rates were computed using the Kaplan–Meier method. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated to evaluate the sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve (AUC) of mFI, RCRI and GNRI in predicting the outcome of interest. The optimal cutoff value was determined based on the maximum value of the Youden index. Statistical differences in the area under the ROCs were compared using the Delong's method (15).
Univariate analysis employing the log-rank test evaluated the correlation between GNRI and the outcomes of interest. Cox proportional hazard regression analysis was utilized to determine adjusted hazard ratios (HR) and corresponding 95% CI for long-term outcomes. Multivariate logistic regression was employed to compute adjusted odds ratios (OR) and 95% CI for short-term outcomes. Covariates integrated into the multivariate analyses were selected based on their impact on outcome measures during univariate analysis, wherein their inclusion altered the HR or OR by at least 10%. Baseline age, gender, CCI and emergent case were also included in the adjustment. Considering GNRI as a composite measure of nutrition risk, incorporating functional status and health conditions within its causal pathway, we refrained from adjusting for these factors in our analysis. All statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics Version 29.0.2.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY), MedCalc® Statistical Software version 22.017 (MedCalc Software Ltd, Ostend, Belgium; https://www.medcalc.org; 2024), and R studio Version.
1.2.1335 (http://www.R-project.org/).
Results
Baseline characteristics
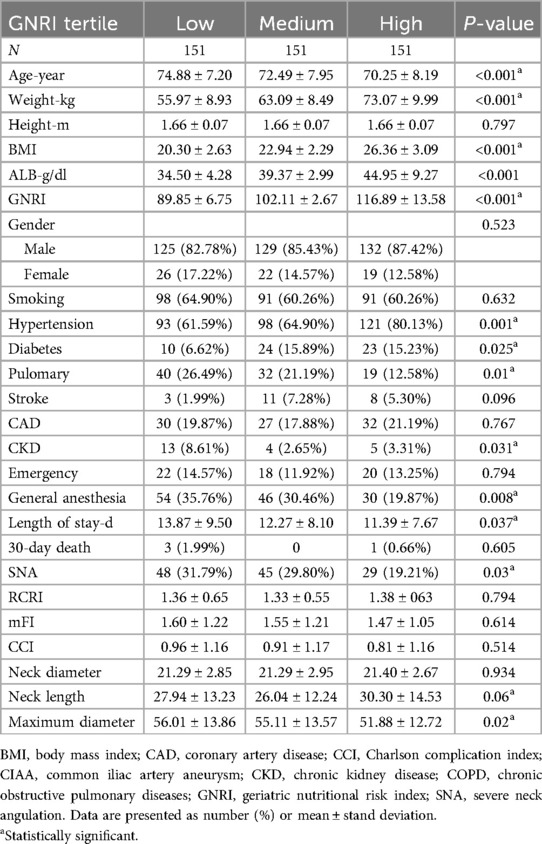
453 patients who underwent EVAR from November 2015 to January 2020 in West China Hospital were finally retrospective analyzed in our study, with detailed flow diagram shown in Figure 1. The median age of this cohort was 73 (67–78) years, and 85.21% of patients were male. Based on the calculated GNRI values ranking from low to high, these patients were divided equally into three groups, with 151 patients in each group. The median value was 102.03 (95.34–109.83). The CCI score was also calculated for each patient, with 48.34% of 0 point, 30.68% of 1 point, 10.38% of 2 points, 6.84% of 3 points 1.99% of 4 points, 1.33% of 5 points and 0.44% of 6 points. Five (1.10%) patients were lost in follow-up after surgery, and the median length of follow-up was 28.00 (15.00–47.00) months. The detailed baseline characteristics of low, medium and high GNRI values of patients were shown in Table 1.
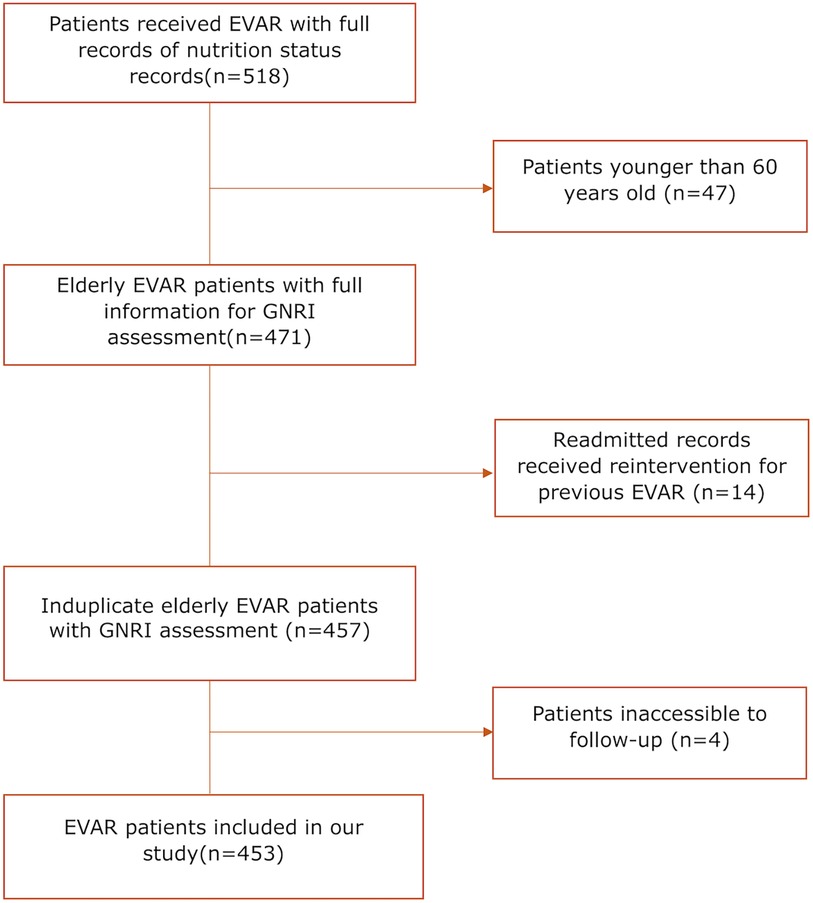
Figure 1. Flow diagram of patient inclusion and exclusion; EVAR, endovascular aortic repair; GNRI, geriatric nutritional risk Index.
Length of stay in hospital and 30-day mortality
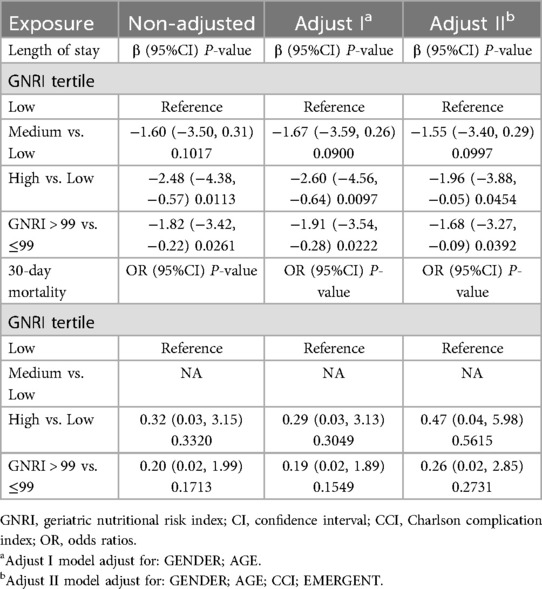
Two of these patients (2/453, 0.44%) died in hospital postoperatively, from heart failure and pulmonary infection. The cohort exhibited an overall 30-day mortality rate of 0.88% (4/453), for low/medium/high GNRI values groups were 1.99%, 0.00% and 0.66%, respectively. The median length of stay in hospital was 8 (11–14) days. The mean length of hospital stay was significantly different in three groups. Both univariate and multivariate analyses indicated a notable association between high GNRI values and reduced length of hospital stay following EVAR in comparison to patients with low GNRI values (β 9.67, 95% CI 4.01–23.32, p = 0.0113; adjusted β −1.96, 95% CI −3.88, −0.05, p = 0.0454),but not with 30-day mortality listed in Table 2.
Overall survival
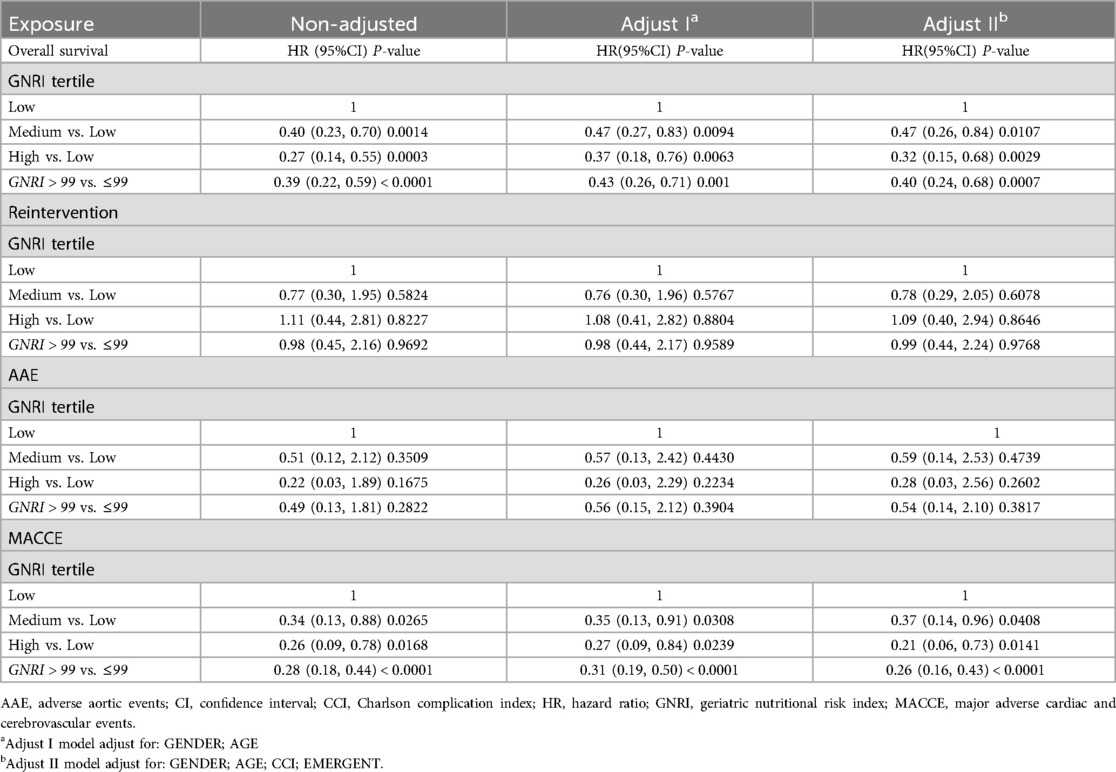
The rate of overall survival in 1-,3-,5-years during following up were 99.1%, 97.7%, and 95.6%, respectively, GNRI status significantly impacted on long-term all-cause death which was outlined in Figure 2; Table 3. Both univariate and multivariate regression analyses indicated a significantly heightened risk of long-term mortality associated with low GNRI values. (Medium GNRI, unadjusted HR 0.40, 95%CI 0.23–0.70, p = 0.0014; adjusted HR 0.47, 95%CI 0.26–0.84, p = 0.0107; High GNRI, 0.27 95%CI 0.14–0.55; p = 0.0003; adjusted HR 0.32 95%CI 0.15–0.68, p = 0.0029). Up to five years, survival for low, medium and high GNRI score patients were 79.2%, 92.7%, 96.5%, respectively.
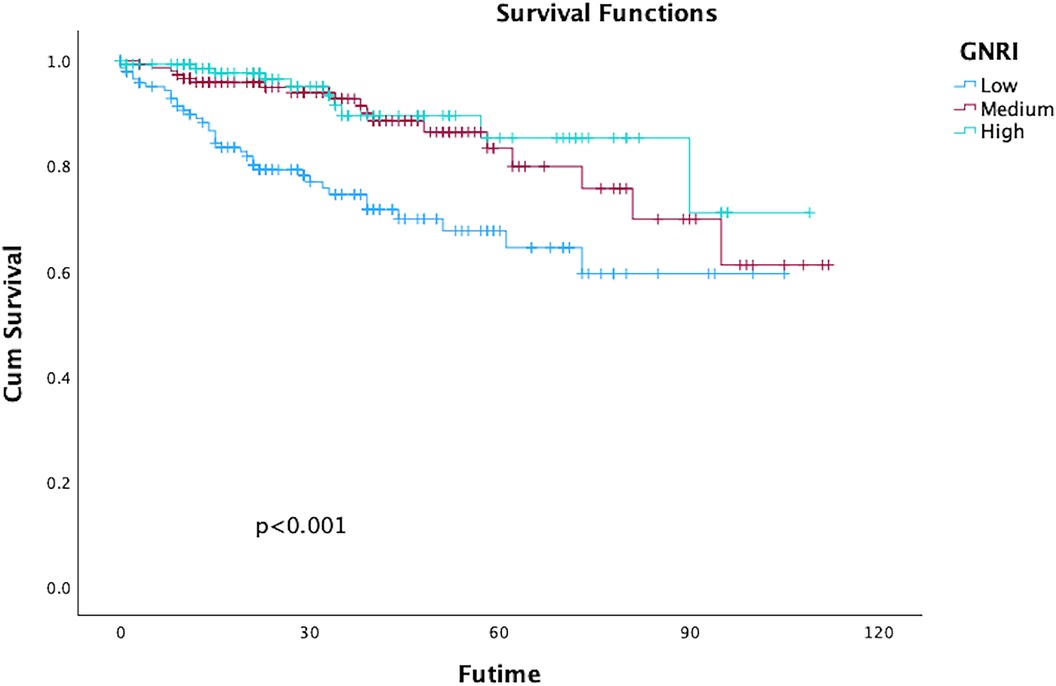
Figure 2. Kaplan–Meier curves of survival in patients with the different geriatric nutritional risk Index (GNRI) values after endovascular aortic repair (EVAR). (Log-rank test, P < 0.001).
Long-term major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events
In total, 80 patients (17.66%) experienced MACCE during the follow-up period, comprising 63 deaths, 12 adverse cardiac events, and 8 strokes. The five-year freedom from MACCE rates were 78.7.2% for low GNRI score patients, 93.9% for medium score patients, and 96.7% for high GNRI patients. The findings from both univariate and multivariate analysis indicated that both medium and high GNRI values were linked to significantly decreased risks of Major Adverse Cardiac and Cerebrovascular Events (MACCE) compared to low GNRI score patients (Medium GNRI, unadjusted HR 0.34, 95%CI 0.13–0.88, p = 0.00265; adjusted HR 0.37, 95%CI 0.14–0.96, p = 0.0408; High GNRI, 0.26 95%CI 0.09–0.78; p = 0.0168; adjusted HR 0.21 95%CI 0.06–0.73, p = 0.0029, Table 3). The freedom from MACCE was listed in Figure 3. During follow-up, 27 (5.96%) of patients had reinterventions, due to 8 (1.76%) type IA endoleaks, 7 (1.54%) type IB endoleaks, 3 (0.66%) type II endoleaks and 5 (1.10%) limb occlusions. The rate of freedom from reinterventions at three years in low, medium and high GNRI values patients were 97.8%, 97.2%, 98.9%, respectively (Figure 4). Various GNRI status did not demonstrate significant associations with aortic-related mortality or reintervention (Table 3).
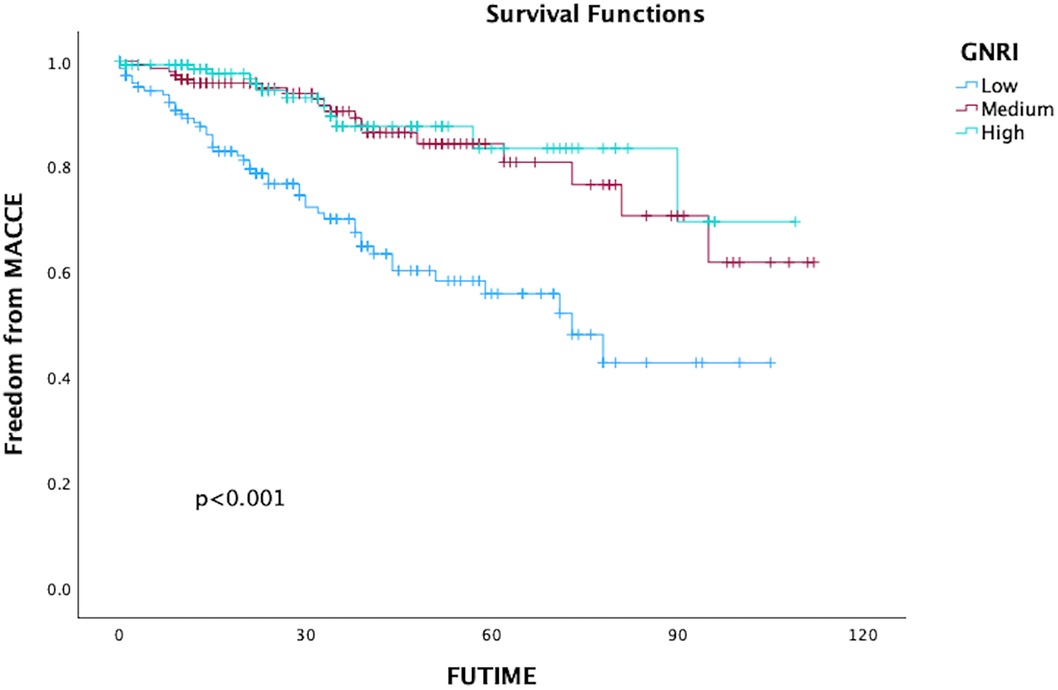
Figure 3. Kaplan–Meier curves of freedom of MACCE in patients with different geriatric nutritional risk Index (GNRI) status after endovascular aortic repair (EVAR).
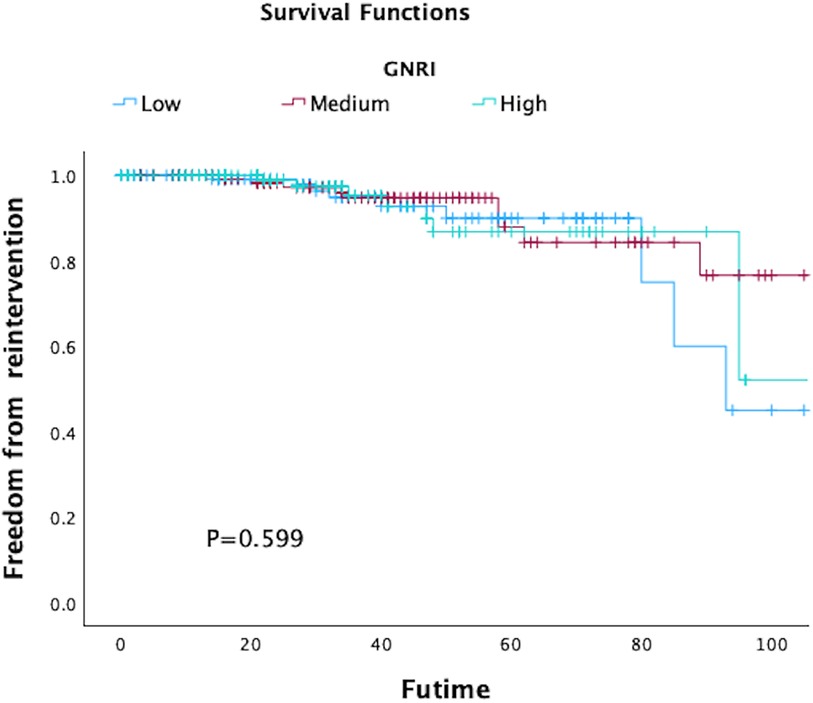
Figure 4. Kaplan–Meier curves of freedom of reintervention in patients with different geriatric nutritional risk Index (GNRI) status after endovascular aortic repair (EVAR).
Comparison of performance measures of both mFI and RCRI with GNRI
As shown in the ROC curve (Figure 5A), late MACCE was set as state variable. c-statistic (area under curve) was 0.707, 95% CI 0.662–0.749. The Area Under the Curve (AUC) analysis indicated superior discriminatory ability of the GNRI for MACCE compared to other assess tool including mFI and RCRI Figure 5A. When considering death as a competing risk, both GNRI (AUC 0.683, 95% CI 0.638–0.749) and mFI (AUC 0.622, 95% CI 0.575–0.667) showed similar better discriminatory ability for long-term survival compared to RCRI (AUC 0.535, 95% CI 0.488–0.582) (Figure 5B).
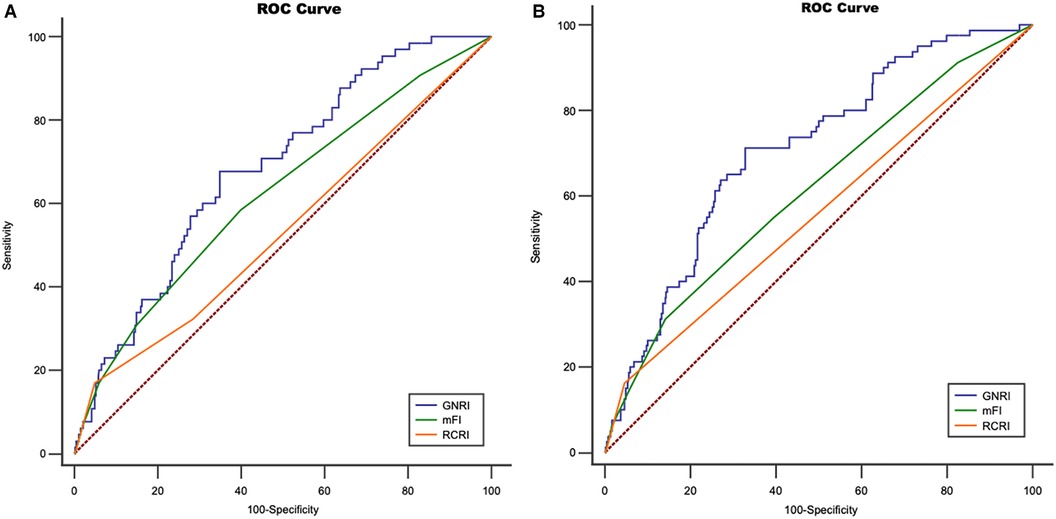
Figure 5. Receiver operating characteristic curve for (ROC) (A) geriatric nutritional risk index (GNRI), modified frailty index index(mFI) and revised cardiac risk Index (RCRI) regarding major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE), An area under the curve (AUC) for GNRI mFI, and RCRI is 0.707, 0.614 and, 0.588, respectively. (Z statistic, GNRI vs. mFI, p = 0.0475; GNRI vs. RCRI, p = 0.0017; mFI vs. RCRI, p = 0.0423); (B) ROC for GNRI, mFI and RCRI regarding long-term survival, AUC for GNRI, mFI, and RCRI is 0.683, 0.622, and 0.535, respectively. (Z statistic, GNRI vs. mFI, p = 0.2377; GNRI vs. RCRI, p = 0.0056; mFI vs. RCRI, p = 0.039).
Nevertheless, the GNRI showed a discernible impact on outcomes in long-term MACCE after EVAR. Hence, it is imperative to determine a cutoff value for GNRI to enhance its utility in guiding clinical practice, the GNRI value = 99 was selected as cutoff value with maximum discriminative power (sensitivity 71.3%, specificity 66.9%). 278 patients (61.3%) had GNRI ≥ 99, 175 patients had GNRI < 99. Significant differences were observed in all-cause mortality and long-term MACCE between the two groups, showed in Figure 6; Tables 2, 3.
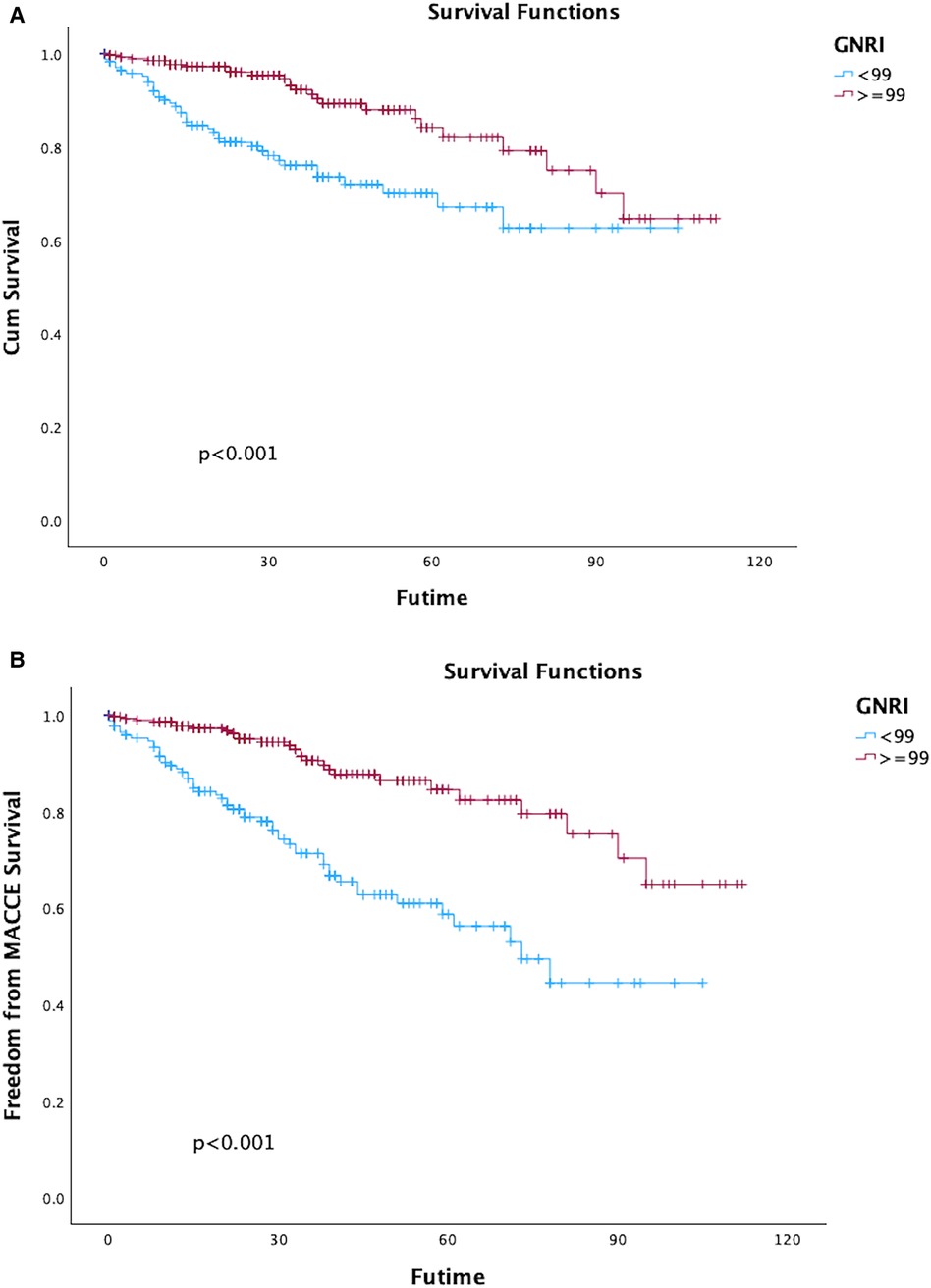
Figure 6. Kaplan–Meier curves of survival (A) and freedom of major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE) (B) in patients with geriatric nutritional risk index (GNRI) ≥ 99 vs. <99 after endovascular aortic repair (EVAR).
Discussion
This cohort study represented the first investigation into the impact of malnutrition status assessed by GNRI on long-term MACCE in patients following EVAR, while also assessing the predictive capacity of the GNGI tentatively compared to both RCRI and mFI. Our study indicated a significant association between low GNRI and extended perioperative hospitalization, elevated long-term all-cause mortality, and long-term MACCE in patients following EVAR. Moreover, our result suggested that may offer superior predictive capability for long-term MACCE and survival in patients undergoing EVAR compared to RCRI score.
The growing utilization of minimally invasive endovascular therapies for AAA highlighted the imperative need to identify patients considered ineligible for surgery (16). While cardiovascular, pulmonary, and renal diseases are common risk factors associated with heightened surgical risk, emerging studies indicate that diminished physiologic reserves, influenced by frailty, malnutrition, sarcopenia, cognitive impairment, and other factors, may diminish the ability to recuperate from surgical stresses (16–18). As cardiac complications can lead to over 40% of perioperative deaths after non-cardiac surgery (19), the contemporary AAA guidelines respectively developed by the European and American Society for Vascular Surgery pointed out the significance of perioperative cardiac risk assessment (20, 21). Apart from postoperative cardiac factors, long-term MACCE could significantly affect the prognosis of patients after EVAR during following-up, especially in the elderly with multiple comorbidities. Furthermore, current predictive models after vascular surgery have been found to underestimate short-term cardiovascular risk (3). There are no recognized predictive tools that are effective in predicting long-term MACCE, and there is a need to develop appropriate predictive tools for predicting short/long-term prognosis in patients undergoing EVAR (7).
Elderly individuals are prone to malnutrition (22). The GNRI, which is an assessment tool for nutritional status, has been utilized as a prognostic factor for complications and mortality in elderly patients (8). Several studies have identified poorer postoperative outcomes in abdominal surgery among patients with a low GNRI (8, 23). Limited data existed regarding the association between the GNRI and the postoperative prognosis of EVAR. NISHIBE (24) reported that the GNRI may serve as the more precise nutritional indicator for identifying a potentially high-risk group for mortality following Endovascular Aneurysm Repair EVAR, compared to both ALB and BMI. Another study illustrated that assessing both sarcopenia and nutritional status could forecast late mortality in patients undergoing EVAR (25). These studies solely concentrated on the adverse impact of the GNRI on overall mortality, without examining its predictive ability for MACCE. Similarly, our study found that the patients in the high GNRI group had a shorter hospital stay compared to patients in the low GNRI group, with an average reduction of 1.96 days. (95% CI, −3.88, −0.05, p = 0.0454) and the GNRI could predict long term survival up to 5 years. These results enhance the credibility of GNRI as a predictor for long-term outcomes following EVAR. In contrast to MACCE and overall survival, our findings indicate that the GNRI may exhibit limited predictive value for aortic-related mortality, or reintervention following EVAR. This could be attributed to the current nutrition assessment methods predominantly reflecting systemic conditions rather than anatomical features. In the original study, patients were stratified into four groups based on their GNRI values (8). In our investigation, patients were categorized into three groups based on their GNRI levels (low, medium, and high). Our findings also indicated that GNRI served as a robust predictor of overall long-term survival and risk of MACCE. Previous report suggested that the GNRI could serve as a prognostic predictor following both abdominal surgery and EVAR at 98 cutoff value (23, 25). We employed an approximate cutoff value of 99 to identify patients meeting the criteria for malnutrition.
The RCRI, a traditional cardiac risk score in vascular surgery, demonstrated an independent predictive effect on long-term major adverse cardiac events following carotid endarterectomy (26). Prior studies suggested that frailty evaluated by the mFI could effectively predict both short-term and long-term MACCE in elderly patients following EVAR, with enhanced discrimination and reclassification capabilities compared to the RCRI (4). In this investigation, we initially assessed the predictive capabilities of GNRI, mFI, and RCRI for long-term overall survival and MACCE using the area under the ROC curve. GNRI exhibited slightly higher AUC values compared to mFI, and demonstrated superior discrimination abilities in comparison to RCRI. Following treatment guidelines, EVAR has emerged as the primary therapeutic approach for elderly patients with high surgical risk abdominal aortic aneurysms at our institution. Previous study reported that EVAR did not alter the long-term overall survival of patients with frailty (27). It may be feasible to contemplate strategies such as expanding the aneurysm diameter as a surgical criterion or opting for non-surgical observation for patients exhibiting both frailty and malnutrition, which are closely associated with adverse outcomes post-intervention. Our upcoming investigation will concentrate on quantitatively evaluating the balance between aneurysm rupture risk and postoperative adverse events, integrating assessments of frailty index and nutritional status.
Our study has several limitations. First, this was a single-center retrospective study, characterized by selection bias towards EVAR. EVAR-treated patients were older and presented with more comorbidities, making them more prone to meeting the criteria for malnutrition. It cannot establish a causal relationship between malnutrition and MACCE or mortality. Second, a single preoperative measurement of GNRI may not entirely reflect a patient's nutritional status; changes in a patient's condition could have occurred between the nutrition assessment, operation, or follow-up, potentially remaining undetected. Third, the median follow-up time of 33 months in our study was relatively short, and longer field follow-up studies are needed in the future to further validate the predictive value of the GNRI. Finally, we did not perform external validation for comparison of these predictive models.
Conclusion
This cohort study suggested that malnutrition assessed by the GNRI may have significant effects on both long-term mortality and MACCE in elderly patients after EVAR. Further, the GNRI may serve as a better predictive tool for MACCE compared to the RCRI. This assessment tool could be useful for risk stratification of long-term MACCE in the elderly patients after EVAR. Enhanced cardiovascular risk management and stricter surveillance plan should be considered for malnutrition patients after EVAR.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the institutional review board of West China Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
YZ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization. JW: Data curation, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing, Resources. JZ: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Resources, Project administration. YM: Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Resources, Investigation. BH: Visualization, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Resources. DY: Writing – review & editing, Resources, Methodology. YL: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Software, Methodology, Formal Analysis. MH: Software, Writing – review & editing, Resources, Methodology, Investigation. HG: Writing – review & editing, Visualization, Supervision, Project administration, Conceptualization. YY: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Validation, Methodology, Formal Analysis, Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Resources, Project administration, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was granted by the Sichuan Foundation of Science and Technology [grant number: 2023YFS0248].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Bertges DJ, Goodney PP, Zhao Y, Schanzer A, Nolan BW, Likosky DS, et al. The vascular study group of new England cardiac risk index (VSG-CRI) predicts cardiac complications more accurately than the revised cardiac risk Index in vascular surgery patients. J Vasc Surg. (2010) 52(3):674–83. 83.e1–83.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2010.03.031
2. Bertges DJ, Neal D, Schanzer A, Scali ST, Goodney PP, Eldrup-Jorgensen J, et al. The vascular quality initiative cardiac risk index for prediction of myocardial infarction after vascular surgery. J Vasc Surg. (2016) 64(5):1411–21.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2016.04.045
3. Moses DA, Johnston LE, Tracci MC, Robinson WP 3rd, Cherry KJ, Kern JA, et al. Estimating risk of adverse cardiac event after vascular surgery using currently available online calculators. J Vasc Surg. (2018) 67(1):272–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.06.105
4. Wang J, Zhao J, Ma Y, Huang B, Yuan D, Han M, et al. Frailty as a predictor of major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. (2021) 74(2):442–50.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2021.01.025
5. Ehlert BA, Najafian A, Orion KC, Malas MB, Black JH 3rd, Abularrage CJ. Validation of a modified frailty index to predict mortality in vascular surgery patients. J Vasc Surg. (2016) 63(6):1595–601.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2015.12.023
6. Gupta PK, Gupta H, Sundaram A, Kaushik M, Fang X, Miller WJ, et al. Development and validation of a risk calculator for prediction of cardiac risk after surgery. Circulation. (2011) 124(4):381–7. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.015701
7. Wang J, Zou Y, Zhao J, Schneider DB, Yang Y, Ma Y, et al. The impact of frailty on outcomes of elderly patients after major vascular surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. (2018) 56(4):591–602. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.07.012
8. Bouillanne O, Morineau G, Dupont C, Coulombel I, Vincent JP, Nicolis I, et al. Geriatric nutritional risk index: a new index for evaluating at-risk elderly medical patients. Am J Clin Nutr. (2005) 82(4):777–83. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/82.4.777
9. Morisaki K, Furuyama T, Yoshiya K, Kurose S, Yoshino S, Nakayama K, et al. Frailty in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm predicts prognosis after elective endovascular aneurysm repair. J Vasc Surg. (2020) 72(1):138–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2019.09.052
10. Unosawa S, Taoka M, Osaka S, Yuji D, Kitazumi Y, Suzuki K, et al. Is malnutrition associated with postoperative complications after cardiac surgery? J Card Surg. (2019) 34(10):908–12. doi: 10.1111/jocs.14155
11. Kotera A. Geriatric nutritional risk index and controlling nutritional status score can predict postoperative 180-day mortality in hip fracture surgeries. JA Clin Rep. (2019) 5(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s40981-019-0282-6
12. Lee TH, Marcantonio ER, Mangione CM, Thomas EJ, Polanczyk CA, Cook EF, et al. Derivation and prospective validation of a simple index for prediction of cardiac risk of major noncardiac surgery. Circulation. (1999) 100(10):1043–9. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.100.10.1043
13. Wahl TS, Graham LA, Hawn MT, Richman J, Hollis RH, Jones CE, et al. Association of the modified frailty index with 30-day surgical readmission. JAMA Surg. (2017) 152(8):749–57. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.1025
14. Kang SH, Ahn JM, Lee CH, Lee PH, Kang SJ, Lee SW, et al. Differential event rates and independent predictors of long-term Major cardiovascular events and death in 5795 patients with unprotected left main coronary artery disease treated with stents, bypass surgery, or medication: insights from a large international multicenter registry. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. (2017) 10(7):e004988. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.116.004988.
15. DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. (1988) 44(3):837–45. doi: 10.2307/2531595
16. Kolh P, De Hert S, De Rango P. The concept of risk assessment and being unfit for surgery. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. (2016) 51(6):857–66. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2016.02.004
17. Shen Y, Qi Y, Zhao J, Huang B, Yuan D, Wang T, et al. Predictive factors for major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events in octogenarians after elective endovascular aneurysm repair. Ann Vasc Surg. (2023) 88:363–72. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2022.07.029
18. Dakis K, Nana P, Brodis A, Kouvelos G, Behrendt CA, Giannoukas A, et al. Sarcopenia is a prognostic biomarker for long-term survival after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Vasc Surg. (2022) 83:358–68. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2022.02.025
19. Group PS, Devereaux PJ, Yang H, Yusuf S, Guyatt G, Leslie K, et al. Effects of extended-release metoprolol succinate in patients undergoing non-cardiac surgery (POISE trial): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. (2008) 371(9627):1839–47. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60601-7
20. Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, Jackson BM, Lee WA, Mansour MA, et al. The society for vascular surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. (2018) 67(1):2–77.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2017.10.044
21. Wanhainen A, Verzini F, Van Herzeele I, Allaire E, Bown M, Cohnert T, et al. Editor’s choice—European society for vascular surgery (ESVS) 2019 clinical practice guidelines on the management of abdominal aorto-iliac artery aneurysms. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. (2019) 57(1):8–93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.09.020
22. Doumit JH, Nasser RN, Hanna DR. Nutritional and health status among nursing home residents in Lebanon: comparison across gender in a national cross sectional study. BMC Public Health. (2014) 14:629. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-629
23. Hanada M, Yamauchi K, Miyazaki S, Hirasawa J, Oyama Y, Yanagita Y, et al. Geriatric nutritional risk index, a predictive assessment tool, for postoperative complications after abdominal surgery: a prospective multicenter cohort study. Geriatr Gerontol Int. (2019) 19(9):924–9. doi: 10.1111/ggi.13750
24. Nishibe T, Kano M, Matsumoto R, Ogino H, Koizumi J, Dardik A. Prognostic value of nutritional markers for long-term mortality in patients undergoing endovascular aortic repair. Ann Vasc Dis. (2023) 16(2):124–30. doi: 10.3400/avd.oa.22-00118
25. Ikeda S, Kodama A, Kawai Y, Tsuruoka T, Sugimoto M, Niimi K, et al. Preoperative sarcopenia and malnutrition are correlated with poor long-term survival after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Surg Today. (2022) 52(1):98–105. doi: 10.1007/s00595-021-02362-x
26. Vilarino-Rico J, Pita-Fernandez S, Segura-Iglesias RJ. Clinical predictors of major adverse cardiovascular events during long-term follow-up after carotid endarterectomy. Ann Vasc Surg. (2015) 29(3):419–25. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2014.08.018
27. Sweeting MJ, Patel R, Powell JT, Greenhalgh RM, Investigators ET. Endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm in patients physically ineligible for open repair: very long-term follow-up in the EVAR-2 randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg. (2017) 266(5):713–9. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002392
Keywords: malnutrition, aged, abdominal aortic aneurysms, endovascular procedures, prognosis
Citation: Zou Y, Wang J, Zhao J, Ma Y, Huang B, Yuan D, Liu Y, Han M, Gan H and Yang Y (2024) Predictive value of geriatric nutritional risk index in cardiac and cerebrovascular events after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 11:1399908. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1399908
Received: 12 March 2024; Accepted: 24 September 2024;
Published: 3 October 2024.
Edited by:
Pasqualino Sirignano, Sapienza University of Rome, ItalyReviewed by:
Francesco Andreoli, University Hospital of Modena, ItalyWassim Mansour, Sapienza University of Rome, Italy
Copyright: © 2024 Zou, Wang, Zhao, Ma, Huang, Yuan, Liu, Han, Gan and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yi Yang, eWFuZ3lAd2Noc2N1LmNu
 YuPei Zou1
YuPei Zou1 Jichun Zhao
Jichun Zhao Bin Huang
Bin Huang Ding Yuan
Ding Yuan Yang Liu
Yang Liu Yi Yang
Yi Yang