- 1Bristol Heart Institute, Bristol, United Kingdom
- 2Departments of Physiology, Pharmacology, and Neuroscience, University of Bristol, Bristol, United Kingdom
Background: Efforts to maintain sinus rhythm in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation (PsAF) remain challenging, with suboptimal long-term outcomes.
Methods: All patients undergoing convergent PsAF ablation at our centre were retrospectively analysed. The Atricure Epi-Sense® system was used to perform surgical radiofrequency ablation of the LA posterior wall followed by endocardial ablation.
Results: A total of 24 patients underwent convergent PsAF ablation, and 21 (84%) of them were male with a median age of 63. Twelve (50%) patients were obese. In total, 71% of patients had a severely dilated left atrium, and the majority (63%) had preserved left ventricular function. All were longstanding persistent. Eighteen (75%) patients had an AF duration of >2 years. There were no endocardial procedure complications. At 36 months, all patients were alive with no new stroke/transient ischaemic attack (TIA). Freedom from documented AF at 3, 6, 12, 18, 24, and 36 months was 83%, 78%, 74%, 74%, 74%, and 61%, respectively. There were no major surgical complications, with five minor complications recorded comprising minor wound infection, pericarditic pain, and hernia.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that convergent AF ablation is effective with excellent immediate and long-term safety outcomes in a real-world cohort of patients with a significant duration of AF and evidence of established atrial remodelling. Convergent AF ablation appears to offer a safe and effective option for those who are unlikely to benefit from existing therapeutic strategies for maintaining sinus rhythm, and further evaluation of this exciting technique is warranted. Our cohort is unique within the published literature both in terms of length of follow-up and very low rate of adverse events.
What’s new?
• Successful maintenance of sinus rhythm in patients with longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation (AF) remains a significant challenge, with endocardial catheter ablation often suboptimal.
• Convergent AF ablation combines surgical epicardial ablation of the left atrial posterior wall followed by endocardial pulmonary vein isolation.
• Our single-centre real-world data show favourable rates of maintenance of sinus rhythm at 36 months, which is a longer follow-up period when compared with existing studies.
• Importantly, we describe excellent safety outcomes without major complications or mortality in our cohort.
• Convergent AF ablation could be a safe and effective option for those likely to have limited success with conventional endocardial ablation strategies.
Background
Catheter ablation (CA) of atrial fibrillation (AF) has been demonstrated to improve quality of life and symptoms in those with symptomatic AF (1–5). However, ablation of persistent AF (PsAF, defined as AF of continuous duration greater than 7 days) fares significantly worse in terms of medium- and long-term maintenance of sinus rhythm (6–8), likely related to progressive adverse remodelling of the atrial substrate (9).
Convergent (also known as “hybrid”) AF ablation involves a combination of surgical epicardial and endocardial catheter ablation to deliver durable pulmonary vein isolation (PVI). A minimally invasive thoracoscopic approach allows epicardial delivery of transmural left atrial (LA) posterior wall ablation. Subsequent endocardial studies are then used to confirm posterior wall isolation and further radiofrequency endocardial lesions delivered to complete PVI. Though relatively new with few published studies, it seems to offer significant promise in treating PsAF (10–13), although a significant increase in periprocedural complications is reported compared with endocardial CA alone (10, 12–14).
We undertook a single-centre retrospective observational study to investigate the safety, efficacy, and associated patient experience of the convergent ablation procedure to treat PsAF.
Methods
The patients included in the study included all those undergoing the procedure from its inception locally and for a period of 18 months at our institution, a tertiary referral centre with electrophysiology and cardiac surgical expertise. Demographic, clinical, echocardiographic, and procedural data were collected. All patients undergoing convergent ablation over the time period were included. Left atrial (LA) and left ventricular (LV) echocardiographic data were recorded. LA dilatation was quantified by volume as non-dilated (≤ 58 ml), mildly dilated (59–68 ml), moderately dilated (69–78 ml), or severely dilated (≥ 79 ml). LV systolic function was assessed by Simpson's biplane ejection fraction (EF) using transthoracic echocardiography within 1 year preceding ablation.
Safety outcomes including perioperative complications, death, and stroke/transient ischaemic attack (TIA), as well as efficacy outcomes including freedom from documented or symptomatic AF, were collected at 3, 6, 12, 18, 24, and 36 months.
Obesity was defined as a body mass index (BMI) of ≥ 30. A positive smoking history was recorded as ≥20 smoking pack-years. The symptom burden was quantified using the AF symptom score established by the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA).
Surgical epicardial ablation
Surgical ablation was performed under general anaesthesia and by one of two designated experienced cardiac surgeons with training in the procedure. Abdominal incisions and insufflation allowed access to the pericardium via the central tendon of the diaphragm. A pericardial window was created to allow access via a port to the posterior pericardium, and a 5 mm endoscope was introduced to visualise the posterior wall of the LA from left to right pulmonary veins. The Epi-Sense® Coagulation (Atricure® Inc, USA) ablation device was used to deliver lesions to the posterior left atrial wall under direct endoscopic vision. The transmurality of lesions was judged using preset energy delivery and impedance drop targets (> 10% from baseline). The sensing port of the Epi-Sense® device was used to confirm local electrical isolation and informed procedure completion. Continuous pericardial irrigation and oesophageal temperature monitoring were undertaken throughout lesion delivery. All patients received direct-current cardioversion at the end of the procedure.
Endocardial catheter ablation
Catheter ablation was undertaken by experienced operators via femoral venous access, 6–12 weeks following surgical ablation. Either local or general anaesthesia was used according to individual patient factors and patient preference. Anticoagulation was uninterrupted. Trans-septal puncture was fluoroscopically guided, using trans-oesophageal (TOE) guidance where necessary. Electro-anatomical mapping of the LA was generated using the CARTO® software package (Biosense Webster, USA). Ablation consisted of PVI via a wide area circumferential ablation (WACA) strategy to isolate the pulmonary veins. Where required, further ablation including roof and/or floor lines, and more extensive ablation (complex fractionated atrial electrograms, mitral/tricuspid isthmus or coronary sinus ablation) was undertaken to achieve PV isolation. Where posterior LA wall isolation was incomplete as demonstrated by voltage mapping, these gaps were addressed with additional ablation and posterior wall isolation confirmed. PV isolation was confirmed by pacing to confirm the entrance and exit block. SmartTouch® (Biosense Webster, USA) contact-force sensing ablation catheters were used, and the force–time integral guided the lesion delivery.
Follow-up
Patients were seen in an outpatient setting at 3, 6, and 12 months following their final endocardial ablation procedure, during which an office electrocardiogram (ECG) was performed. Further follow-up at 18, 24, and 36 months occurred either locally, in primary care, or at the referring local hospital. Further AF monitoring comprised symptom-led Holter recording at any point during follow-up. A team of specialised arrhythmia nurses facilitated enhanced patient education and provided a responsive and accessible point of contact for patients throughout the process.
Longstanding PsAF was defined as those suffering with AF episodes lasting for >1 year. AF freedom was defined as the absence of documented AF by office 12-lead ECG testing at follow-up. ECG AF documentation in primary care records or direct patient communication was included.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad PRISM (GraphPad Software, USA). Data are presented as median ± interquartile range.
The study was approved by the institutional clinical audit and research department and received NHS Health Research Authority (HRA) approval.
Results
Baseline characteristics
Over an 18-month period, 24 patients underwent the convergent ablation procedure for longstanding PsAF. Patient baseline characteristics and arrhythmia data are displayed in Table 1. In total, 84% (n = 21) of patients were male, with a median age of 63 and median BMI of 30. A total of 36% (n = 11) of patients suffered from hypertension, 17% (n = 4) patients suffered from obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA), and 8% (n = 2) of patients suffered from diabetes. A total of 38% (n = 9) of patients exhibited a significant smoking history, and the median alcohol units consumed per week was 14. The median CHA2DS2VASc score was 1, with 71% (n = 17) of patients falling in the 0–1 bracket.
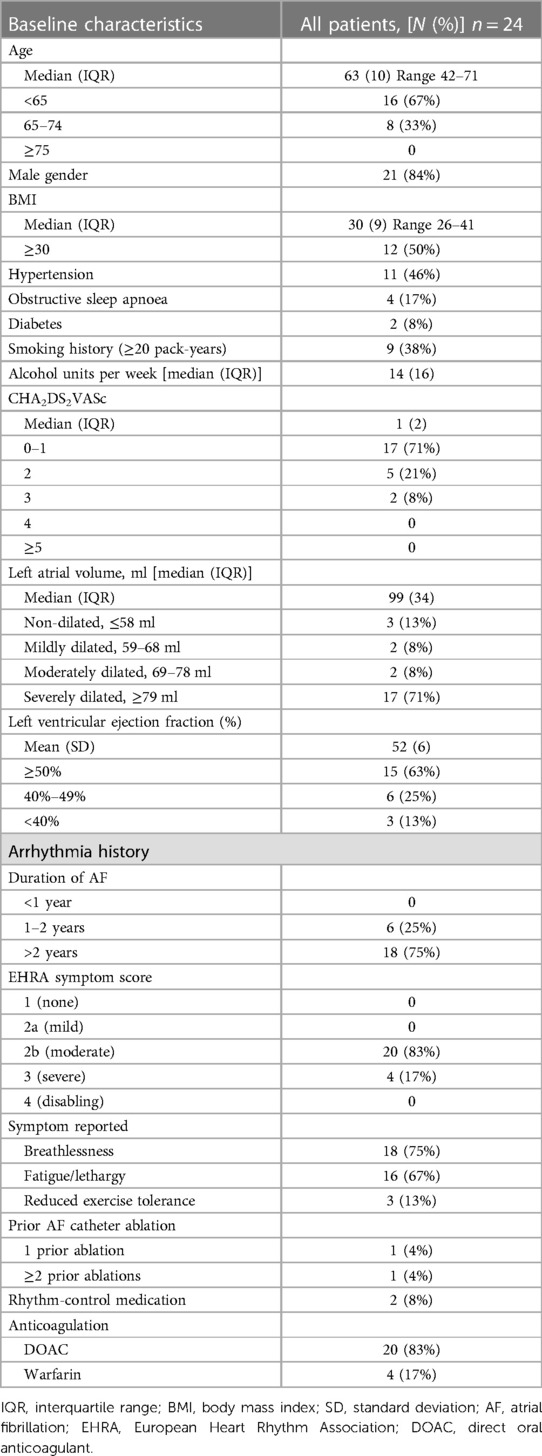
Table 1. Baseline characteristics and arrhythmia data of patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing convergent ablation procedure.
The majority of patients (71%; n = 17) had a severely dilated LA. The majority (63%; n = 15) of patients had preserved LV function (≥ 50%), 25% (n = 6) had mild impaired function (LVEF 40%–49%), and 13% (n = 3) suffering from significantly impaired function (LVEF < 40%), consistent with the 2016 ESC heart failure classification (15).
Arrhythmia data
All patients had longstanding PsAF, with AF duration exceeding 1 year, with 75% (n = 18) greater than 2 years, and 25% between 1 and 2 years. A total of 83% (n = 20) of patients had a “moderately disabling” EHRA symptom score, with 17% (n = 4) of patients having a “severely disabling” score. A total of 75% (n = 18) of patients reported breathlessness as a symptom, 67% (n = 16) reported fatigue or lethargy, and 13% (n = 3) reported reduced exercise tolerance. The observed overlap reflects the frequent multiple symptom burden in patients. Two patients had previously undergone AF catheter ablation, one of whom had undergone a single ablation and the other patient underwent three previous ablations. In total, 8% (n = 2) of patients were on rhythm-controlling medications at the time of work-up (flecainide, amiodarone). All patients were anticoagulated, with 83% (n = 20) of them on a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) and the remaining patients taking warfarin.
Procedural and outcome data
Full data are shown in Table 2. The median number of surgical lesions delivered was 25 (interquartile range of 12) with a minimum number of 13 lesions and a maximum of 41 lesions. The average number of lesions delivered seemed to increase over the study period: the first 12 patients had a mean of 21.6 lesions while the latter 12 patients had a mean of 26 lesions. However, this did not seem to correlate with any clear change in efficacy. The patients stayed in the hospital for a median of 2 days.
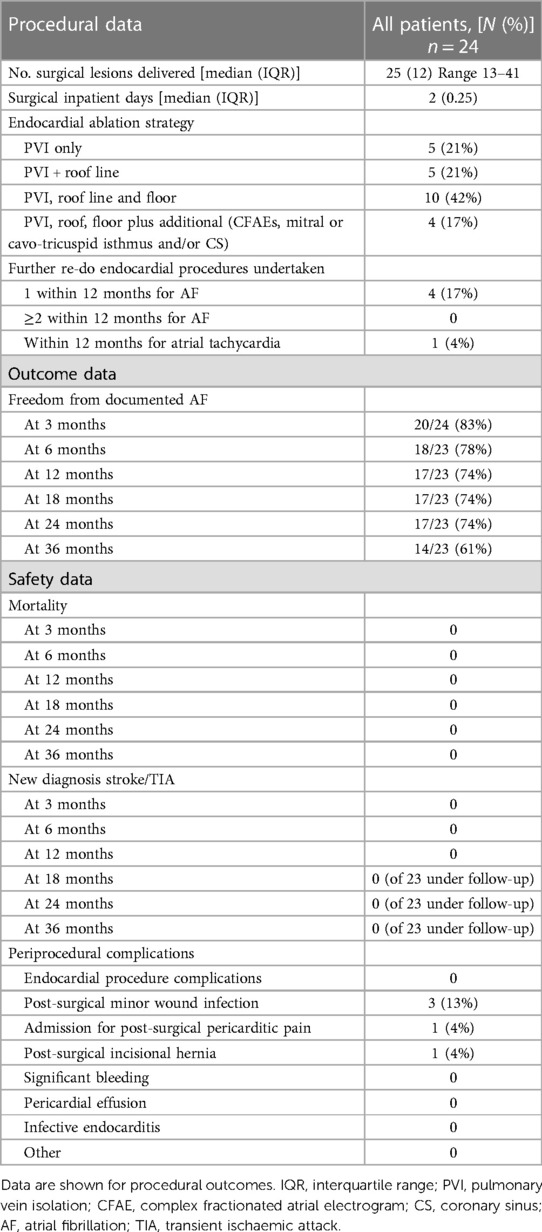
Table 2. Procedural and outcome data of patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing convergent ablation procedure.
The endocardial ablation strategies used included PVI only (21%; n = 5), PVI plus roof line (21%, n = 5), PVI, roof line, and floor (42%, n = 10), and more extensive ablation (complex fractionated atrial electrograms, mitral/tricuspid isthmus or coronary sinus ablation) in 17% (n = 4) of patients. Figure 1 demonstrates a representative 3D anatomical left atrial voltage map showing the extensive scar on the posterior wall, as well as the subsequent endocardial ablation undertaken to complete the PVI.
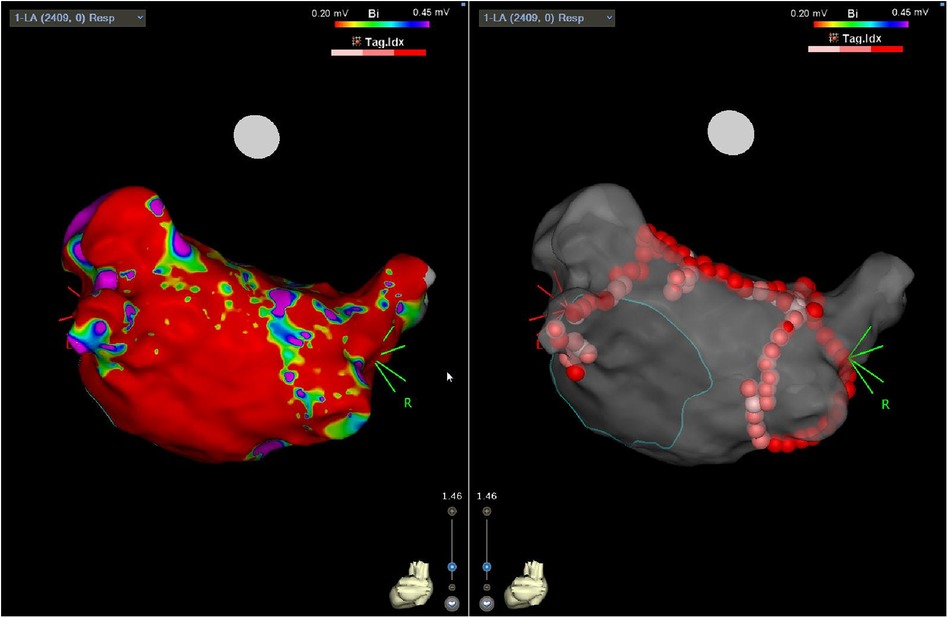
Figure 1. Three-dimensional electro-anatomical map showing posterior LA with diffuse regions of low voltage (left panel) following surgical epicardial ablation and subsequent endocardial PVI (right panel).
Following the surgical ablation procedure, there were three (13%) minor wound infections, all treated successfully with oral antibiotics in the outpatient setting. There was a single occurrence of re-admission for postoperative pericarditic pain, and a single occurrence of a post-surgical incisional hernia. There were no major complications, significant pericardial effusion, bleeding, or infective endocarditis. There were no immediate endocardial catheter ablation complications. There was no post-procedural mortality.
There was no mortality recorded within the study population at 3, 6, 12, 18, 24, or 36-month follow-up. Similarly, there were no new diagnoses of stroke/TIA at 3, 6, 12, 18, 24, or 36-month follow-up.
Further re-do catheter ablation for AF was undertaken in four patients (17%), all undergoing a single further procedure within 12 months. Separately, one patient (4%) underwent a further catheter ablation procedure within 12 months for symptomatic atrial tachycardia.
The freedom from documented AF was 83% (n = 20/24) at 3 months, 78% (n = 18/23) at 6 months, 74% (n = 17/23) at 12 months, 74% (n = 17/23) at 18 months, 74% (n = 17/23) at 24 months, and 61% (n = 14/23) at 36 months. The survival plot is illustrated in Figure 2.
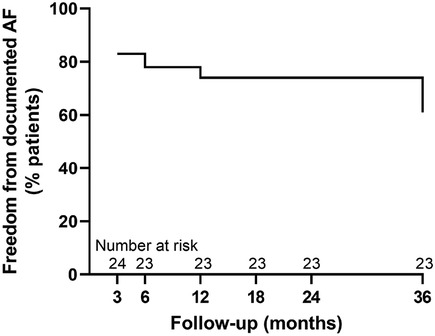
Figure 2. Survival plot showing single-procedure freedom from documented AF at 3-, 6-, 12-, 18-, 24- and 36-month follow-up.
One patient was lost to follow-up before 18 months due to disruption related to the COVID-19 pandemic, although the mortality data were confirmed for all 24 patients.
Discussion
Procedural outcomes and safety
A convergent approach to AF ablation has been described in several small studies (11, 13, 14, 16–19) as well as a recent meta-analysis (10) and randomised controlled trial (RCT) (12). They report very favourable rates of maintenance of sinus rhythm in the medium and long term. However, they also report a significant burden of periprocedural complications with associated morbidity and mortality. Our small study shows that the convergent ablation approach can be undertaken safely. Our cohort found a low number of minor procedural complications, which consisted of wound infections, pericarditic pain, and a postoperative incisional hernia. All wound infections were successfully treated with oral antibiotics in the outpatient setting. The number of surgical lesions delivered seemed to increase throughout the study period, although without observable effect on efficacy.
Importantly, and in contrast to other reported studies, there were no major periprocedural complications and no stroke, TIA, or mortality observed periprocedurally or during follow-up. Thus, despite the findings of the recent RCT (12) and other published reports with larger patient cohorts, our data are novel both in terms of the very low rate of serious periprocedural complications and the follow-up data—longer than any other published cohort, at 3 years.
Arrhythmia-free survival and quality of life
The rates of maintenance of sinus rhythm are favourable and in keeping with other published studies (1, 20) with 78% of patients maintaining sinus rhythm at 6 months, 74% at 12, 18, and 24 months, and 61% at 3 years, in a cohort of patients with longstanding PsAF and evidence of established remodelling.
There were a small number of re-do endocardial procedures within the study period (four re-do procedures for AF, one for focal atrial tachycardia). The use of repeat ablation procedures is common in real-world practise to promote sinus rhythm (21), allowing assessment of the PVI and further ablation to be delivered if required to address gaps, promoting durable block.
Our 36-month duration of long-term follow-up is unique within the literature and provides a useful insight into the long-term disease course of these patients.
Convergent AF ablation and arrhythmia mechanisms
Our study captures a cohort of patients undergoing ablation for longstanding PsAF which reflects real-life practise, with a high burden of reported symptoms and a significant duration of AF. Our cohort also reflects a group of patients with typical upstream AF disease drivers with significant rates of obesity, hypertension, and diabetes. These are individuals who are likely to experience a poor long-term outcome from conventional endocardial PsAF catheter ablation (6–8), and in whom satisfactory rhythm control for AF remains an ongoing unmet need. Indeed, 75% of patients in our cohort had an AF duration of greater than 2 years, and 71% of patients had a severely dilated LA. These individuals are likely to demonstrate established atrial remodelling and fibrosis. The mechanisms of failure of AF ablation in these types of individuals remain unclear, with increased difficulty in obtaining durable isolation of both PV (22, 23) and non-PV AF triggers (3, 24) likely playing a role. Indeed, repeated endocardial ablation procedures may indeed generate new non-PV triggers (23, 25), thus exacerbating the situation. However, extensive ablation in pursuit of such foci has failed to show any compelling benefit beyond PVI alone (7).
Convergent ablation offers the potential for durable posterior LA wall ablation. This is then confirmed at the time of endocardial ablation, and completed if required. PVI is then undertaken, at which point further ablation is performed if felt beneficial. This more extensive ablation lesion set may potentially recruit more PV as well as non-PV triggers, as there has been a suggestion that the posterior LA wall, and in particular localised atrial fat, may play an important role in persistent AF (26, 27). In addition, there may be some endocardial–epicardial dissociation contributing to arrhythmogenesis in those with persistent AF (28, 29), which is more effectively targeted by a convergent approach. The advent of novel ablation technologies such as pulsed field ablation (PFA) presents further opportunities for convergent AF ablation and merits further study.
Limitations
Our data are primarily limited by a lack of quantitative rhythm monitoring. The use of continuous rhythm monitoring such as with an implantable loop recorder (ILR) would have enhanced two aspects of the study: first, it would have enabled an accurate assessment of AF recurrence. Second, it would have allowed a quantitative assessment of AF burden before and after ablation. Indeed, the assessment of arrhythmia (as well as symptom) burden may be more important than binary absolute recurrence. A further limitation of the data was lack of consistently available procedural data as well as LA dwell time.
The low number of patients taking rhythm-control anti-arrhythmic medication may not be representative of the universal experience of patients with longstanding PsAF. However, it may be that medication intolerance or lack of efficacy was an influencing factor in the decision to pursue convergent ablation.
Conclusions
Convergent ablation offers favourable short- and long-term efficacy. Our study is the first to show that it can be undertaken safely without significant complications or mortality and with durable efficacy as far out as 36 months. As the technique continues to develop and experience with the procedure grows, we may see continued improvements in efficacy and safety.
Convergent ablation for persistent AF offers an attractive option for a patient group suffering with an atrial substate that has already undergone advanced remodelling. They are not well served by existing conventional endocardial ablation and this continues to represent an unmet need in a cohort with a high symptom burden. This new technique offers an exciting new approach to improve quality of life and would be well served by further comprehensive evaluation.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, where appropriate without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the clinical audit and research department at University Hospitals Bristol and received approval from the NHS Health Research Authority (HRA). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
AC: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LP: Writing – original draft. SR: Writing – review & editing. KM: Writing – original draft. CR: Writing – review & editing. FC: Writing – review & editing. ED: Writing – review & editing. GT: Writing – review & editing. PB: Writing – review & editing. RB: Writing – review & editing. AN: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
AC received an MRC Clinical Research Training Fellowship (MR/S021299/1). LP receives a BHF Clinical Research Training Fellowship (BHF/FS/CRTF/21/24122) for unrelated work. AMN has received consulting fees from Atricure. The funder had no involvement with any aspects of the study, including but not limited to study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript. No other funding was received by any authors for the study. All authors declare no other conflicts of interest or funding sources.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Blomström-Lundqvist C, Gizurarson S, Schwieler J, Jensen SM, Bergfeldt L, Kennebäck G, et al. Effect of catheter ablation vs. antiarrhythmic medication on quality of life in patients with atrial fibrillation. JAMA. (2019) 321:1059. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.0335
2. Mark DB, Anstrom KJ, Sheng S, Piccini JP, Baloch KN, Monahan KH, et al. Effect of catheter ablation vs. medical therapy on quality of life among patients with atrial fibrillation. JAMA. (2019) 321:1275. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.0692
3. Gökoğlan Y, Mohanty S, Güneş MF, Trivedi C, Santangeli P, Gianni C, et al. Pulmonary vein antrum isolation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. (2016) 9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.115.003660
4. Knight BP, Novak PG, Sangrigoli R, Champagne J, Dubuc M, Adler SW, et al. Long-term outcomes after ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation using the second-generation cryoballoon. JACC Clin Electrophysiol JACC. (2019) 5:306–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jacep.2018.11.006
5. Kuck K-H, Brugada J, Fürnkranz A, Metzner A, Ouyang F, Chun KRJ, et al. Cryoballoon or radiofrequency ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. (2016) 374:2235–45. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1602014
6. Mont L, Bisbal F, Hernández-Madrid A, Pérez-Castellano N, Viñolas X, Arenal A, et al. Catheter ablation vs. antiarrhythmic drug treatment of persistent atrial fibrillation: a multicentre, randomized, controlled trial (SARA study). Eur Heart J. (2014) 35:501–7. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht457
7. Verma A, Jiang C, Betts TR, Chen J, Deisenhofer I, Mantovan R, et al. Approaches to catheter ablation for persistent atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. (2015) 372:1812–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1408288
8. Wynn GJ, El-Kadri M, Haq I, Das M, Modi S, Snowdon R, et al. Long-term outcomes after ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation: an observational study over 6 years. Open Hear Archives of Disease in Childhood. (2016) 3:e000394.
9. Nattel S, Harada M. Atrial remodeling and atrial fibrillation: recent advances and translational perspectives. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2014) 63:2335–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.02.555
10. Luo X, Li B, Zhang D, Zhu J, Qi L, Tang Y. Efficacy and safety of the convergent atrial fibrillation procedure: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. (2019) 28:169–76. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivy203
11. Geršak B, Jan M. Long-term success for the convergent atrial fibrillation procedure: 4-year outcomes. Ann Thorac Surg. (2016) 102:1550–7. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.04.018
12. Delurgio DB, Crossen KJ, Gill J, Blauth C, Oza SR, Magnano AR, et al. Hybrid convergent procedure for the treatment of persistent and long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation: results of CONVERGE clinical trial. Circ Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. (2020) 13:9288. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.120.009288
13. Pong T, Shah RL, Carlton C, Truong A, Fann B, Cyr K, et al. Hybrid ablation for atrial fibrillation: safety & efficacy of unilateral epicardial access. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2022) 0.
14. Jan M, Žižek D, Geršak ŽM, Geršak B. Comparison of treatment outcomes between convergent procedure and catheter ablation for paroxysmal atrial fibrillation evaluated with implantable loop recorder monitoring. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. (2018) 29:1073–80. doi: 10.1111/jce.13625
15. Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS, et al. 2016 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. (2016) 37:2129–200. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw128
16. Kiser AC, Landers M, Horton R, Hume A, Natale A, Gersak B. The convergent procedure: a multidisciplinary atrial fibrillation treatment. Heart Surg Forum. (2010) 13:E317–21. doi: 10.1532/HSF98.20091112
17. Civello K, Smith C, Boedefeld W. Combined endocardial and epicardial ablation for symptomatic atrial fibrillation: single center experience in 100+consecutive patients. J Innov Card Rhythm Manag. (2013):1–7.
18. Gehi AK, Paul Mounsey J, Pursell I, Landers M, Boyce K, Chung EH, et al. Hybrid epicardial-endocardial ablation using a pericardioscopic technique for the treatment of atrial fibrillation. Hear Rhythm. (2013) 10:22–8. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2012.08.044
19. Gilligan DM, Joyner CA, Bundy GM. Multidisciplinary collaboration for the treatment of atrial fibrillation: convergent procedure outcomes from a single center. J Innov Card Rhythm Manag. (2013).
20. Packer DL, Mark DB, Robb RA, Monahan KH, Bahnson TD, Poole JE, et al. Effect of catheter ablation vs. antiarrhythmic drug therapy on mortality, stroke, bleeding, and cardiac arrest among patients with atrial fibrillation: the CABANA randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2019) 321:1261–74. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.0693
21. Kuck KH, Albenque JP, Chun KRJ, Fürnkranz A, Busch M, Elvan A, et al. Repeat ablation for atrial fibrillation recurrence post cryoballoon or radiofrequency ablation in the FIRE AND ICE trial. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. (2019) 12.
22. Santangeli P, Zado ES, Hutchinson MD, Riley MP, Lin D, Frankel DS, et al. Prevalence and distribution of focal triggers in persistent and long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation. Hear Rhythm. (2016) 13:374–82. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2015.10.023
23. Lo L-W, Lin Y-J, Chang S-L, Hu Y-F, Chao T-F, Chung F-P, et al. Predictors and characteristics of multiple (more than 2) catheter ablation procedures for atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. (2015) 26:1048–56. doi: 10.1111/jce.12748
24. Mohanty S, Trivedi C, Gianni C, Della Rocca DG, Morris EH, Burkhardt JD, et al. Procedural findings and ablation outcome in patients with atrial fibrillation referred after two or more failed catheter ablations. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. (2017) 28:1379–86. doi: 10.1111/jce.13329
25. Chang T-Y, Lo L-W, Te ALD, Lin Y-J, Chang S-L, Hu Y-F, et al. The importance of extrapulmonary vein triggers and atypical atrial flutter in atrial fibrillation recurrence after cryoablation: insights from repeat ablation procedures. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. (2019) 30:16–24. doi: 10.1111/jce.13741
26. Corradi D, Callegari S, Maestri R, Ferrara D, Mangieri D, Alinovi R, et al. Differential structural remodeling of the left-atrial posterior wall in patients affected by mitral regurgitation with or without persistent atrial fibrillation: a morphological and molecular study. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. (2012) 23:271–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2011.02187.x
27. van Rosendael AR, Dimitriu-Leen AC, van Rosendael PJ, Leung M, Smit JM, Saraste A, et al. Association between posterior left atrial adipose tissue mass and atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. (2017) 10. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.116.004614
28. Parameswaran R, Kalman JM, Royse A, Goldblatt J, Larobina M, Watts T, et al. Endocardial–epicardial phase mapping of prolonged persistent atrial fibrillation recordings: high prevalence of dissociated activation patterns. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. (2020) 13:e008512. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.120.008512
Keywords: hybrid, convergent, atrial fibrillation, ablation, AF
Citation: Carpenter A, Pannell LMK, Rizvi SIA, Maciver K, Rajakaruna C, Ciulli F, Duncan ER, Thomas G, Barman P, Bond R and Nisbet AM (2024) Convergent approach to persistent atrial fibrillation ablation: long-term single-centre safety and efficacy. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 10:1336801. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1336801
Received: 11 November 2023; Accepted: 29 December 2023;
Published: 8 February 2024.
Edited by:
Michael Brunner, St. Josefskrankenhaus, GermanyReviewed by:
Martin Manninger, Medical University of Graz, AustriaMasaya Watanabe, Hokkaido Hospital, Japan
© 2024 Carpenter, Pannell, Rizvi, Maciver, Rajakaruna, Ciulli, Duncan, Thomas, Barman, Bond and Nisbet. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Alexander Carpenter Y2FycGVudGVyLmFsZXhhbmRlckBnbWFpbC5jb20=
†ORCID Alexander Carpenter orcid.org/0000-0003-3650-1897
 Alexander Carpenter
Alexander Carpenter Laura M. K. Pannell1,2
Laura M. K. Pannell1,2 Richard Bond
Richard Bond