- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ryhov County Hospital, Region Jönköping County, Jönköping, Sweden
- 2Department of Health, Medicine and Caring Sciences, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden
- 3Department of Clinical Physiology in Linköping and Department of Health, Medicine and Caring Sciences, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden
- 4Center for Medical Imaging Science and Visualization, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden
- 5Department of Cardiology in Linköping and Department of Health Medicine and Caring Sciences, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden
- 6Department of Radiology in Linköping and Department of Health Medicine and Caring Sciences, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden
A corrigendum on
A head-to-head comparison of myocardial strain by fast-strain encoding and feature tracking imaging in acute myocardial infarction
by El-Saadi, W., Engvall J, E., Alfredsson, J., Karlsson, J.-E., Martins, M., Sederholm, S., Faisal Zaman, S., Ebbers, T., and Kihlberg, J. (2022). Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 9:949440. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.949440
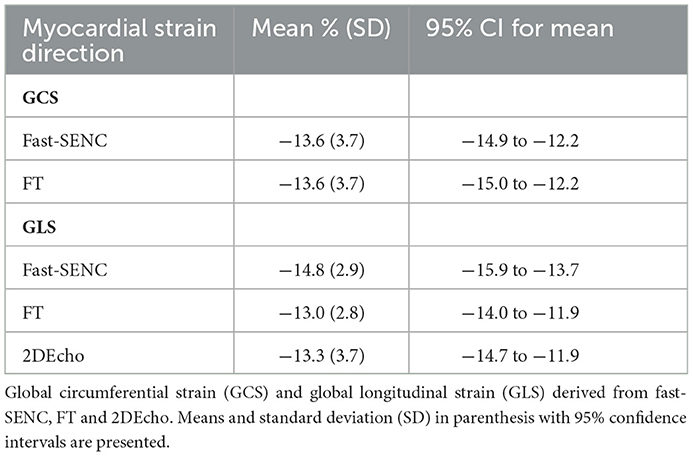
In the published article, measurements in Table 2 were displaced. A formatting error resulted in strain percentage with confidence interval for the first and third lines were displayed upwards. The published Table 2 is printed below, followed by the corrected Table 2 and its caption.
Faulty Table 2:
In the published article, three figures that displayed SD in the first paragraph under “Results” were printed as hyperlinks to the list of references.
The authors wish that a correction is made to “Results, scar and ejection fraction” in terms of removing the hyperlinks displayed below. These sentences previously stated:
“Scar and ejection fraction
The subjects were enrolled and treated with the pPCI after identification of the culprit artery in each case. The cohort displayed a median door-to-balloon time of 67 min. The average scar size was 15 (9) % of LVM with a median Troponin-T of 1,640 ng/l, equivalent to 164 × upper level of normal. LGE revealed scars in 240 out of 510 segments (47%) with 122 segments having scar transmurality <25%, 78 segments between 25 and 49%, and only 40 segments had a transmurality ≥50%. In 13 patients the LVEFCMR was little affected, LVEFCMR ≥ 50%. Patients with maintained LVEFCMR had smaller scar size 10 (5)% than those with depressed LVEFCMR <50% whose scar size was 19 (10)%, (p < 0.01). Patient demographics and CMR imaging characteristics are presented in Table 1.”
The corrected sentences appears below:
“The subjects were enrolled and treated with pPCI after identification of the culprit artery in each case. The cohort displayed a median door-to-balloon time of 67 min. Average scar size was 15 (9) % of LVM with a median Troponin-T of 1,640 ng/l, equivalent to 164 x upper level of normal. LGE revealed scar in 240 out of 510 segments (47%) with 122 segments having scar transmurality < 25%, 78 segments between 25 and 49% and only 40 segments had a transmurality ≥ 50%. In 13 patients the LVEFCMR was little affected, LVEFCMR ≥ 50%. Patients with maintained LVEFCMR had smaller scar size 10 (5) % than those with depressed LVEFCMR < 50% whose scar size was 19 (10) %, (p < 0.01). Patient demographics and CMR imaging characteristics are presented in Table 1.”
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Faulty Table 2:
Corrected Table 2:
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: cine magnetic resonance imaging, myocardial ischemia, ST elevation myocardial infarction, myocardial stunning, left ventricular dysfunction, left ventricular remodeling
Citation: El-Saadi W, Engvall JE, Alfredsson J, Karlsson J-E, Martins M, Sederholm S, Faisal Zaman S, Ebbers T and Kihlberg J (2023) Corrigendum: A head-to-head comparison of myocardial strain by fast-strain encoding and feature tracking imaging in acute myocardial infarction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 10:1140214. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1140214
Received: 08 January 2023; Accepted: 09 January 2023;
Published: 02 February 2023.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2023 El-Saadi, Engvall, Alfredsson, Karlsson, Martins, Sederholm, Faisal Zaman, Ebbers and Kihlberg. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Walid El-Saadi,  d2FsaWQuZWwtc2FhZGlAbGl1LnNl
d2FsaWQuZWwtc2FhZGlAbGl1LnNl
 Walid El-Saadi
Walid El-Saadi Jan Edvin Engvall
Jan Edvin Engvall Joakim Alfredsson5
Joakim Alfredsson5 Jan-Erik Karlsson
Jan-Erik Karlsson Marcelo Martins
Marcelo Martins Shaikh Faisal Zaman
Shaikh Faisal Zaman Tino Ebbers
Tino Ebbers Johan Kihlberg
Johan Kihlberg