- 1Department of Clinical Pharmacology, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China
- 2Hunan Key Laboratory of Pharmacogenetics, Institute of Clinical Pharmacology, Central South University, Changsha, China
- 3National Clinical Research Center for Geriatric Disorders, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China
Junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs) are cell-cell adhesion molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily and are involved in the regulation of diverse atherosclerosis-related processes such as endothelial barrier maintenance, leucocytes transendothelial migration, and angiogenesis. To combine and further broaden related results, this review concluded the recent progress in the roles of JAMs and predicted future studies of JAMs in the development of atherosclerosis.
Introduction
A junctional adhesion molecule (JAM) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) (1–3), a large superfamily of cell surface and soluble proteins that are involved in the recognition, binding, or adhesion of cells. The membrane-located JAMs are immunoglobulin-like single-span transmembrane molecules expressed by leukocytes, platelets, epithelial and endothelial cells, localizing to cell-cell contacts and specifically enriched at tight junctions (2, 3).
Atherosclerosis (AS) plaques comprise lipids, fibers, and immune cells in the intima of large and medium-sized arteries, and immunological components are indispensable in both the initiation and the chronicity of the lesions (4). Several immune activities such as platelet aggregation and adhesion and the transendothelial migration (TEM) of monocytes and neutrophils (4, 5) are increasingly recognized as the leading cause of atherosclerosis. JAMs present more and more association with AS, as considerable molecules in vascular inflammation.
Thus, we briefly reviewed the classification, structure, primary ligands and receptors, and main physiological functions of JAMs, and summarized and speculated potential roles of JAMs in AS based on reported articles.
Junctional Adhesion Molecules Overview
Classification and Structure
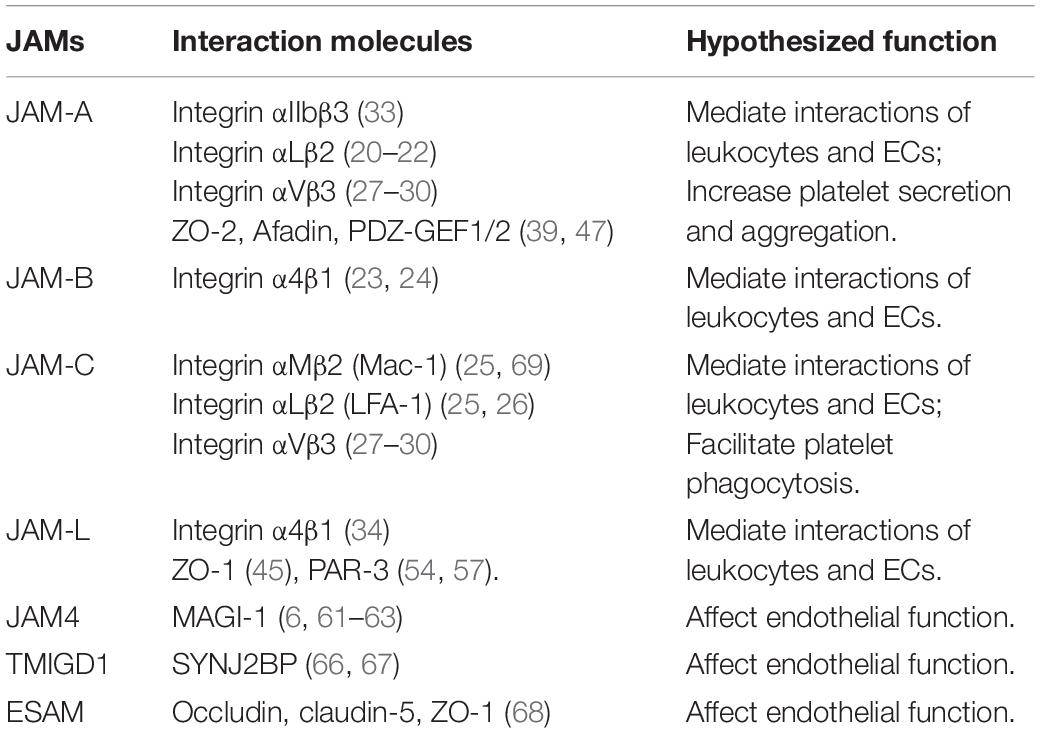
Current studies have focused on four major JAM molecules: JAM1, JAM2, JAM3, and JAM4 (6), also known as JAM-A, JAM-B, JAM-C, and JAM4 (7). Moreover, some other proteins are closely related to JAMs, including JAML (JAM-like) (8), CLMP [CAR (coxsackie and adenovirus receptor)-like membrane protein] (9), CAR (10), and ESAM (endothelial cell adhesion molecule) (11). Martìn-Padura et al. first reported JAMs as a new member of the immunoglobulin family concentrating endothelial and epithelial junctions and identified JAM1 (12). Further studies cloned JAM2 and JAM3 and identified them as counter-receptor (13–17). The shedding of JAM-A produces soluble JAM-A (sJAM-A). For instance, transmembrane-JAM-A was shed to generate proinflammatory sJAM-A and JAM-A-bearing microparticles when platelets were activated.
JAM proteins are around 30–50 kDa in size. Kostrewa et al. and Prota et al. respectively, described the crystal structure of the recombinant extracellular part of mouse JAM (rsJAM) and human JAMs (hJAM) (3, 18). There is a linker region Val127–Leu128–Val129 between the N- and C-terminal domains and the extensive hydrogen bond network between the main chain atoms of the linker tri-peptide and both domains. The side chain of Leu128 is tightly packed in a hydrophobic pocket formed by the side chains of Gln38, Pro40, Thr126, Pro159, and Tyr218. Several proline residues (Pro40, Pro130, Pro131, Pro159, and Pro160) stabilize the main chain conformation around the linker (3). Interactions involving the membrane-distal Ig-like domain stabilize the dimer of mJAM1, similar to that observed in hJAM1. A dimer formed by two hJAM1 molecules is stabilized by extensive ionic and hydrophobic contacts between the N-terminal domains (18). These U-shaped dimers and salt bridges are then formed by a R(V,I,L)E motif (3), which is important in dimer formation and common among different JAMs, including rsJAM, hJAM, JAM-1, JAM-2, and JAM-3 (18). Dimerization and homophilic binding may contribute to both adhesive function and the junctional organization of JAMs (19). Figure 1 is a brief structural diagram of JAMs.
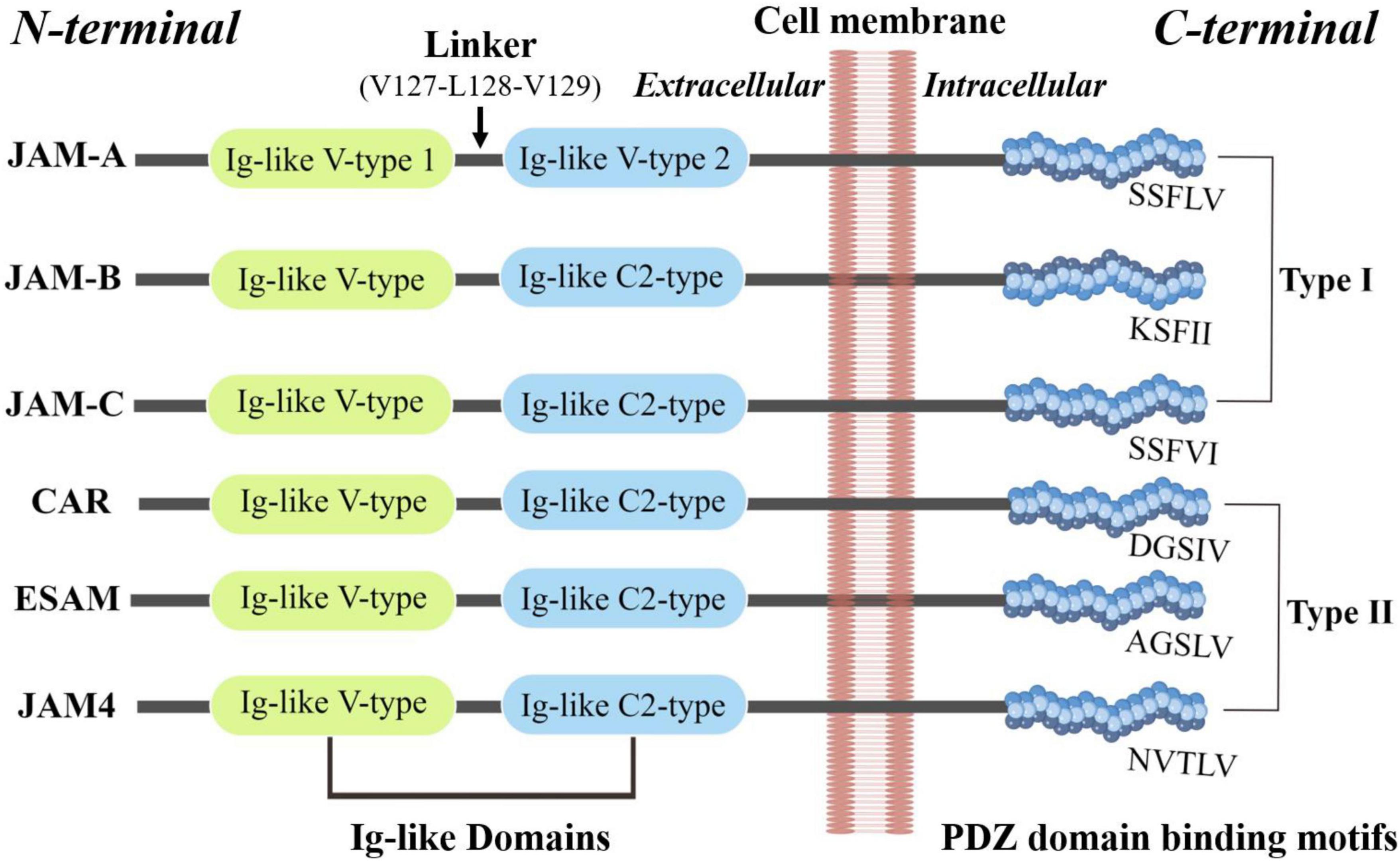
Figure 1. The basic structure of JAMs. JAM family proteins share common structural characteristics: a short N-terminal signal peptide, two extracellular Ig-like domains, a single transmembrane segment, and a short cytoplasmic tail with consensus phosphorylation sites and a C-terminal PDZ-binding motif (173).
Mendoza et al. explored the extracellular domain of the JAM family and found each member has a unique tertiary structure despite having similar secondary structures, whose heterotypic interactions can be greatly favored compared to homotypic interactions (7).
Interacting Proteins and Signaling Pathways
The physical and functional interactions with integrins contribute to the functions of JAMs to a great extent. The crosstalk between JAM-A and integrin αLβ2 (20–22), JAM-B and integrin α4β1 (23, 24), and JAM-C and integrin αLβ2 (LFA-1) (25, 26) mediates the transient interactions between leukocytes and endothelial cells. JAM-C expressed on platelets and integrin αMβ2 on leukocytes interact during inflammation (25). Meantime, JAM-integrin interactions in Cis also exert essential function, including JAM-A and JAM-C and integrin αVβ3 in endothelial cells (27–30), JAM-A and integrin αIIbβ3 in platelets (31–33), and JAM-L and integrin α4β1 in leukocytes (34). Accordingly, JAMs function substantially depending on physical and/or functional JAM-Integrin crosstalk (35).
JAMs build bridges between different cells through their interaction with PDZ domain-containing proteins, mainly relying on their COOH-terminal PDZ domain-binding motifs and adjacent domains (36–40). Besides, JAMs also consist of two tandem NH2-terminal, ectoplasmic Ig domains as well as single transmembrane spans (41). JAMs interact with a variety of cytoplasmic scaffolding proteins (42). Interaction of JAM with the tight junction (TJ) components of the PDZ domain-containing proteins ZO-1, cingulin, occluding, and AF-6 is the earliest evidence (36, 43). ZO-1 directly binds to the COOH termini of claudins and JAM by its PDZ1 and PDZ3 domains, respectively (44). In JAM-L cells, L fibroblasts overexpressed exogenous JAM, ZO-1 is concentrated at cell-cell contact sites (45). JAM-A resides in the correct localization of proteins involved in TJ formation, such as PAR-3, ZO-1, and MUPP1 (46). JAM-A interacts with Afadin and PDZ-GEF2 to activate Rap1A, regulating the levels of integrin β1 subunit and enhancing cell migration (47). JAM-A regulates epithelial permeability via association with ZO-2, Afadin, and PDZ-GEF1 to activate Rap2c and controls the contraction of the apical cytoskeleton (39). JAM-A is necessary for the development of polarity in cultured hepatic cells via its possible phosphorylation and recruitment of relevant PDZ proteins, linking to the apical domain (41). The nectin-afadin unit plays a role in the localization of JAM-1 at TJs (48), associated with the PAR-3-aPKC-PAR-6 complex. PAR-3 first binds to nectin-1 or -3 and is then transferred to JAM-1 during the organization of the junctional complex in the epithelial cells equipped with TJs (49). Both JAM2 and JAM1 possess an SFII or SFLV sequence on their intracellular tails predicted to interact with PDZ domains and therefore highly like to display similar binding activities (15, 50). JAM-A/C possibly affects TJ formation by influencing AF-6/afadin localization and/or function, which correlates with multiple structural components including nectins, ZO-1, and ponsin/SH3P12 (46, 51–53). Further research found ZO-1 and PAR-3 associated with JAM-2/-3 in a PDZ domain-dependent manner (54). The PAR3-JAM interaction is proposed to be reversible, but junctions will eventually form even in the presence of inhibitory PAR6 (55). In normal breast cells, JAM-A signaling via AF-6 and PDZ-GEF2 leads to a low level of β1-integrin-mediated cell migration (56). Besides, the RA175 forms a ternary complex with JAM-C via interaction with PAR-3, facilitating specialized adhesion structures (57).
The PSD95/dlg/ZO-1 (PDZ) domain of calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine protein kinase (CASK) and the putative PDZ-binding motif Phe-Leu-Val (COOH) in the cytoplasmic tail of JAMs is essential for association of the CASK and JAMs (44). The interaction that occurs between Grasp55 and JAM-C attributes to PDZ-mediated interaction with the C-terminal PDZ-binding motifs of protein cargos, playing a central role in stemness maintenance of hematopoietic and spermatogenic cells (58, 59). CASK co-localizes with both PMCA4b and JAM-A on the proximal principal piece, and acts as a common interacting partner of both to maintain Ca2+ homeostasis in sperm (60).
Hirabayashi et al. group has conducted several studies about the functional role of JAM4 and observed that JAM4 binds the scaffold protein MAGUK with inverted domain structure-1 (MAGI-1) but not to ZO-1 (6, 61–63). Besides, JAM4 directly binds the second PDZ domain of LNX1 through its carboxyl terminus (64). The newly discovered Mouse V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 1 (VSIG1) interacts with Sertoli cells by heterophilic adhesion via its first Ig-like domain, critically depending on its binding to ZO-1 through the cytoplasmic domain (65). A PDZ domain-containing cytoplasmic protein, synaptojanin-2-binding protein (SYNJ2BP) expressed in human endothelial and epithelial cells was identified as a cytoplasmic binding partner of transmembrane and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 1 (TMIGD1), another member of the Ig-superfamily (IgSF) similar to the JAM subfamily, affecting endothelial function (66, 67). In brain and muscle blood capillaries, JAM-related endothelial cell-selective adhesion molecule (ESAM) clearly co-localized with the three TJ markers occludin, claudin-5, and ZO-1 (68). Some hypothesized AS-associated JAMs-interacting proteins are shown in Table 1.
Main Physiological Functions
Based on topic IgSF structures and related structure research above, some ligands and receptors for JAMS have been discovered and assist the role of AMs in regulating cell motility, polarity, and proliferation in multiple cell types, including cancer cells, epithelial, endothelial, fibroblasts, leukocyte, and germ cells.
Various partner molecules and receptors bring about JAMs to exert their intracellular and intercellular functions within the body. Tight junctions (TJs) are structurally defined by electron microscopy and these epithelial intercellular junctions are located at the most apical region of cell-cell contacts (3, 70). Major JAMs members such as JAM-1, JAM-2, and JAM-3 are all located in the TJs of both epithelial and endothelial cells to preserve the structure of the junctions. These three JAMs molecules adhere to other tight junction proteins like PAR-3 and ZO-1. JAM-3 is unable to adhere to leukocytes in the manner as other JAMs do (54, 71). They assist TJs in exerting adhesive properties and stabilize homophilic cell-cell binding as a dual role in controlling paracellular permeability and in maintaining cell polarity (3).
But instead, JAM4 formulates TJs with MAGI-1 and plays a role in enhancing kidney cell branching and scattering (6, 61–63). Ligand-of-Numb protein X1 facilitates endocytosis of JAM4 and participates in transforming growth factor beta-induced redistribution of JAM4 in mammary epithelial cells (64). JAML exhibits its notable function in regulating cell migration via interacting with the tight junction protein coxsackie-adenovirus receptor (CAR), encompassing neutrophil [polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN)] transepithelial migration (72, 73), monocyte transendothelial migration (74), germ cells migration across the blood-testis barrier (75). The CAR group of proteins, composed of CAR, CLMP, BT-IgSF, and ESAM, might modulate the assembly or function of TJs (76). Because of the similar structure to the CAR group, how JAM groups operate in TJs deserves further attention.
It is noteworthy that the role JAMs play in cell migration is high-profile, covering endothelial cells, epithelial cells, germ cells, keratinocytes, tumor cells, hematopoietic stem, progenitor cells, and leukocytes such as lymphocytes, platelets, neutrophils, monocytes, and dendritic cells. The participation of JAMs in TJs supports a variety of biological processes both during development and in the adult organism, including developmental and physiological processes such as epithelial cell differentiation, hematopoiesis, germ cell development, and development of the nervous system, epithelial barrier formation, inflammation, angiogenesis, and hemostasis (35, 42, 77). As these functions exhibit potential links with AS, we focused on their functions directly related to AS in this review.
Junctional Adhesion Molecules and Atherosclerosis
Platelet Activation and Thrombosis
The adherence of platelet to inflamed endothelium is one of the most important initiated stages of plaque formation in blood vessels. Platelet activation also plays a pivotal role in atherothrombosis and related physiological processes involving clotting, fibrinolysis activation, and binding to the sub-endothelial matrix (78). Naik et al. first illustrated JAM-1, the F11-receptor (F11R), as a novel platelet membrane surface glycoprotein and a stimulatory monoclonal antibody, mAb F11, recognized JAM-1 and induced aggregation, adhesion, and potentiation in human platelets (79, 80). Kornecki team validated that sF11R (an F11R recombinant protein) inhibited this induction by two functional domains: the N-terminus domain and the 1st Ig-fold domain (81, 82). JAM-1 was proved to be selectively expressed at intercellular junctions between endothelial cells and platelets (68, 83, 84). There are type 1 and type 2 mRNAs of JAM1. Type 1 mRNAs exist in endothelial cells, platelets, leucocytes, and several cancer cells, while type 2 mRNAs are especially present in ECs, indicating their different functions in different cell types (85). Several amino acid residues including serine, threonine, and tyrosine within the external domain of JAM-1 can be phosphorylated (81, 82), and phosphorylation of Ser284 might engage platelet activation (86). JAM-1 increases platelet secretion and aggregation via promoting the assembly of the actin filament, relying on phosphoinositide-3 kinase activation and dimerization, phosphorylation of the 32 and 35 kDa forms, and combination with GPIIIa and CD9 (33).
The role of JAMs in platelet-endothelial adhesion in AS has also been extensively studied. Babinska et al. from the State University of New York devoted to studying the nexus between JAM-A (F11R) and AS, and observed high expression of JAM-A mRNA and protein in AS plaques from patients and ApoE–/– mice (87). Plasma soluble JAM-A (sJAM-A) independently correlated with the severity of coronary arterial disease (CAD) defined by angiographic score and plasma levels of Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) (88). More interestingly, transmembrane-JAM-A and sJAM-A from platelet act as homophilic interaction partners to exacerbate thrombotic and thrombo-inflammatory interactions between platelet and monocyte (89). JAM-A expressed and adhered to cultured cytokine-inflamed ECs from human aortic and venous vessels (90), which was inhibited by treatment with actinomycin, parthenolide, or AG-480, similar to the result caused by Jam-A siRNAs, which related to NF-kappaB and JAK/STAT pathways (91). Crosslinking of platelet F11R/JAM-A with the FcγRII by monoclonal antibody F11 (M.Ab.F11) caused platelet aggregation, resulting from phosphoinositide-3 kinase-triggered actin filament assembly (33, 90). JAM-A mediates platelet adhesion and spread through filopodial extensions and lammelipodia development (33). Alternatively, supersensitivity of platelets to natural agonists thrombin and collagen with JAM-A stimulation is independent of the Fc gammaRII (33). Babinska et al. group developed F11R/JAM-A antagonistic [peptide 2HN-(dK)-SVT-(dR)-EDTGTYTC-CONH2, F11R peptide 4D] as a potential anti-atherosclerotic and/or anti-thrombotic therapeutic drug and confirmed that the F11R peptide 4D inhibited M.Ab.F11-induced platelet aggregation and cytokine-inflamed platelets adhesion to ECs, remarkably, reduced atherosclerotic plaque formation and inhibited platelet adhesion to the cytokine-inflamed arterial endothelium in ApoE–/– mice (92–94). Naik et al. reported thrombotic function of platelets was enhanced in Jam-A–/– mice in vivo and JAM-A suppressed integrin αIIbβ3 outside-in signaling to limit platelet accumulation and prevent premature platelet activation (31, 32). When stimulated by an agonist, the dephosphorylation of JAM-A on the tyrosine residue allowed the dissociation of JAM-A-recruited Csk from the integrin-c-Src complex and thus facilitated outside-in signaling (31, 32). Koenen group generated platelet-specific (tr) Jam-A-deficiency in ApoE–/– mice (trJam-A–/– ApoE–/–) and observed gain-of-function in platelets with more αIIbβ3 signaling-related proinflammatory effects, increased aortic plaque formation, and accelerated neointima formation in earlier stages after vascular injury (95, 96). JAM-A is associated with hypertension in humans, and JAM-A protein is upregulated in the brainstem microvasculature and brain endothelium in hypertensive rats models, possibly activated by AT (1) receptor-mediated signaling (97, 98). In rats injected with ADP-activated platelets, JAM-A and CD41 co-localized in the microvessels (98).
JAM-C was expressed mostly on human platelets in mono- and dimeric forms and endothelial JAM-C was supposed to function in synergy with platelets JAM-C in the development of CAD (99). Direct interaction of human platelet JAM-C with myelomonocytic U937 cells, neutrophils, and dendritic cell β2-integrin Mac-1 (integrin αMβ2, CD11b/CD18) was corroborated to facilitate DC activation and platelet phagocytosis, aggravating the progression of atherosclerotic plaque (25, 69). sJAM-C markedly reduced the adhesion of DCs to platelets, purified JAM-3 blocked the platelet-neutrophil interaction and anti-JAM-C decreased platelet activation, platelet-neutrophil aggregation, and platelet macroaggregates, but greatly increased neutrophil degranulation (25, 69, 100). Antibodies against JAM-C thereby served as a prospective antibody to prevent atherothrombosis and AS.
In summary, the expression of JAM-A and JAM-C in platelets mediate the aggregation and adhesion of platelets and potentiate their role in atherothrombosis and AS. Soluble JAM-A correlates with the severity of CAD. Antibodies against JAM-A and JAM-C are promising for anti-atherosclerosis drug development.
Vascular Inflammation and Leukocyte Infiltration
Vascular inflammation is critically important in AS, one of the characteristics is the recruitment of leukocytes into the inflamed artery wall (101). Monocytes and the derived macrophages contribute to all stages of AS, including the recruitment into the intima, secretion of inflammatory cytokines, lipid accumulation, plaque progression, maturity, and break (102). JAMs play important roles in inflammation in various diseases. More serious steatohepatitis emerged in Jam-A–/– mice fed with a diet high in saturated fat, fructose, and cholesterol (HFCD) (103). Tyrosine phosphorylation of JAM-A (p-Y280) caused loss of epithelial barrier function during intestinal inflammation (104). JAM-A stably expressed on iPSC-cardiomyocytes (iPSC-CM) contributes to iPSC-CM inflammation (105). JAM-A is also necessary for peripheral mononuclear cells (PMN) infiltration into the heart upon ischemia-reperfusion injury (106). For vascular inflammation, Kiessling depicts JAM-A as the indicator of inflammatory arterial areas exposed to acutely alternated flow, as determined by molecular ultrasound imaging (107). TNF stimulates the disassembly of JAM-A from the TJs and subsequent redistribution as well as dispersal on the endothelial cell surface, which was reduced by fibronectin (108). Nonetheless, the loss and/or redistribution of JAM-A induced by the combined treatment of TNF-α and IFN-γ in ECs scarcely regulated leukocyte adhesion or transmigration (109). In some cases, endothelial JAM-A seems to not contribute to leukocyte adhesion or transcellular migration (110, 111). Shedding of soluble JAM-A (sJAM-A) on inflamed vascular endothelium mediated predominantly via ADAM17 and slightly by ADAM10 may signal vascular inflammation (112). ADAM17 surface expression and JAM-A cleavage are increased by flow cultivation (113), which results in impaired endothelial wall shear stress (WSS) mechanosensing (114). Jam-C–/– mice and mice treated with anti-JAM-C antibody present a significant reduction in intranodal homeostatic chemokine secretion, which in turn suppressed naive T cell exit from lymph nodes (115). Likewise, JAM-C antibodies substantially curtailed systemic and lung inflammatory cytokines and chemokine as well as pro-inflammatory aged neutrophils (116). Imaginably, the cyclic nitroxide 4-MethoxyTEMPO treatment minimized inflammatory cell recruitment into human aortic EC via JAM-C blockade (117).
As a biomarker of cell adhesion, JAM-A was independently associated with the endpoint of stable patients with chronic heart failure (CHF) (118). Also, sJAM-A secreted from cardiac progenitor cells attenuated neutrophil infiltration after myocardial infarction. Accumulating evidence has indicated that JAM-A accelerates the formation of AS lesions in mice. Oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) up-regulates Jam-A mRNA expression in human macrophages and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs), stimulates the redistribution of JAM-A in ECs, and subsequently increases the transmigration of monocytes, which could be counteracted by statins (119–122). Christian Weber’s group conducted long-term studies on the role of JAM-A in AS. In ApoE–/– mice fed with an atherogenic diet, endothelial JAM-A expression was upregulated, while JAM-A deficient mice displayed decreased neointima hyperplasia, reduced macrophage content, and attenuated monocyte arrest and transmigration in carotid arteries (123, 124). Atherosclerotic lesion formation in ApoE–/– mice was reduced by endothelial JAM-A deficiency with limited monocyte recruitment into the arterial wall but was aggregated by myeloid JAM-A deficiency with impaired monocyte de-adhesion (122). Compared to ApoE–/–Ldlr–/– mice, ApoEh/hLdlr–/– mice showed decreased endothelial JAM-A expression in the aortic arch (125). sJAM-A effectively blocked the recruitment of monocytes to atherosclerotic endothelium (123). Mechanically, the treatment of JAM-A siRNA in aortic endothelial cells inhibited the transmigration of monocytes (121). JAM-A was repressed by microRNA (miR)-145, which was upregulated under atheroprotective laminar flow (122). miR-145-rich exosomes inhibited the development of AS by downregulating JAM-A (126). JAM-A was suppressed by miR-156a in human aortic endothelial cells, which in turn depressed inflammatory monocyte adhesion induced by cytokines (127). Bilberry anthocyanin-rich extract is observed to attenuate AS development in ApoE–/– mice by downregulating the expression of Jam-A (128). Ginkgolide B almost abolished the upregulation of JAM-A expression in HUVECs induced by ox-LDL (119). In the Ldlr–/– mice fed with fish oil, the atherosclerotic lesions were diminished, which was accompanied by reduced circulating endothelial cell JAM-A expression (129).
An antibody against JAM-C reduced monocyte accumulation at vascular inflammation sites by increasing reverse transmigration instead of reducing transmigration (130). Exosomal miR-146a-5p bound to the 3’-untranslated region of JAM-C mRNA to curb monocyte transendothelial migration (131). In ApoE–/– mice, JAM-C expression was upregulated as spontaneous early lesions developed (132). Anti-JAM-C antibody caused increased reverse transendothelial migration (rTEM) of monocyte-derived cells as well as decreased neointima hyperplasia and neointima macrophage induced by wire injury of carotid arteries and atherogenic diet (133, 134). oxLDL upregulated JAM-C expression and induced disorganization of JAM-C localization on ECs (132). Blockage of JAM-C diminished monocyte arrest and adhesion to carotid artery smooth muscle cells (SMCs) under flow conditions (133). Unexpectedly, overexpression or gene silencing of JAM-C in human ECs under flow conditions showed similar higher rates of monocyte rTEM (134). JAML was induced during the differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells and promoted integrin-mediated adhesion of leukocytes to ECs (8, 34). JAML expression also correlated with the adhesion and TEM of monocytes (74). JAML was highly expressed in atherosclerotic plaques of ApoE–/– mice and AS patients as well as macrophages exposed to oxLDL (135). Silencing JAML expression attenuated the formation of atherosclerotic lesions and promoted plaque stability, possibly resulting from decreased expression of inflammatory cytokines (135, 136).
Overall, the expression of JAM-A, JAM-C, and JAML in ECs was increased in an atherosclerotic environment. These molecules play important roles in the recruitment and TEM of leucocytes into the intima. Related mediators and pathways remain to be investigated in deep. Soluble JAM-A and the antibody against JAM-C blocked the recruitment of monocytes to inflamed atherosclerotic endothelium. Silencing the expression of Jam-A and JamL attenuated AS.
Endothelial Barrier and Angiogenesis
Damage to the endothelial barrier and angiogenesis are essential events for plaque formation. The changes in the expression of related angiogenic factors, blood flow, nutrients, O2, and other events caused by neovascularization may take part in plaque progression, remodeling, destabilization, and thromboembolic events (137). JAM-A mediates human CD34+ progenitor cells differentiating into endothelial progenitor cells through interaction with LFA-1 (138). In the rat cortical cold injury model, JAM-A co-localized with occludin at TJs in the lesion vessels with blood-brain barrier (BBB) breakdown and expressed decreasingly at 12 h only (139). Although human brain EC (HBMEC) released sJAM-A into culture supernatants with non-inducibility, which favors protecting brain EC from inflammatory stimuli, sJAM-A was still speculated unsuitable as a biomarker of BBB breakdown (140). Mechanism study showed that JAM-A promoted CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-α (C/EBP-α) expression by suppressing β-catenin transcriptional activity and by activating exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (EPAC), thereby increasing transcription of downstream target Claudin-5 to decrease endothelial permeability and enhance vascular barrier function (141). Moreover, Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) was reported to upregulate JAM-A expression and further protect endothelial barrier function in human aortic endothelial cells (142). Similarly, Tongxinluo (a special formula of Chinese traditional medicines) reversed the endothelial barrier breakdown with enhanced expression of JAM-A (143, 144). JAM-A was proposed to disassemble the junctions caused by TNF (108). Strikingly, the levels of plasma sJAM-A and EC-expressed JAM-A protein were reduced by the tumor inducers Tβ4 and TGF-β1, and the F11R/JAM-A antagonistic peptide 4D (P4D) showed a prospective barrier-protecting effect (145). The junction structure reorganization for JAM-A changed under low laminar flow conditions (146). Of note, JAM-A rearranged from interendothelial TJs to the luminal surface of blood vessels under acute blood flow variations, which implied JAM-A as a marker of acute endothelial activation and dysfunction (147). Melatonin upregulated the expression of tight junction proteins to maintain the rat inner blood-retinal barrier (iBRB) integrity, such as ZO-1, Occludin, JAM-A, and Claudin-5 (148). In mouse retinal vascular, JAM-C deficiency increased the spreading of fibronectin and consequently enhanced endothelial cell sprouting and vessel normalization in vitro, dependent on β1-integrin and the small GTPase Rap1 activation (149). Consistently, VEGF or PDGF-C induced JAM-C translocating from cytoplasm to the cytomembrane to maintain the normal function of the human iBRB, while increased serum sJAM-C was identified as a potential marker of wet age-related macular degeneration (wAMD) (150). Besides, JAM-A, JAM-B, and especially JAM-C have readily been detected in liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs), as a part of special mixed-type intercellular junctions (151).
JAM-A is expressed prominently in embryonic vasculature and on the surface of hematopoietic precursors and has the potential to mark isolate long-term reconstituting HSC (LTR-HSC) (152, 153). JAM-A blocking mAb inhibited angiogenesis in vitro, in the embryo, and in vivo (154). FGF-2-induced microvessel sprouting failed in Jam-A–/– mice (155). JAM-A cleavage-mediated abnormal arterial remodeling in aging was also regulated by ADAM17 (114). Transfection with Jam-b siRNA promoted vessel sprouting, and intraperitoneal administration of anti-JAM-B antibody increased tumor blood vessel density, as unanimously observed in JAM-B-heterozygous mice (156). On the contrary, anti-JAM-C monoclonal antibody decreased vessel development from aortic rings in vitro and angiogenesis in the model of hypoxia-induced retinal neovascularization without pathological side effects in vivo (157). Unexpectedly, disrupting the interactions of JAM-B and JAM-C cytoplasmic tails and PAR3 with antibodies, siRNA, or dominant-negative mutants fully interferes with EC lumen formation and tubulogenesis (158).
Even though JAMs were proved to be functional in endothelial barrier and angiogenesis, there is still insufficient evidence supporting their key roles in atherosclerotic vascular endothelial barrier and angiogenesis in AS. The potential is worthy of further exploration.
Shear Stress and Cell Motility
Of equal concern for the development of AS and complications is wall shear stress (WSS). Chronically low oscillating WSS is most susceptible to causing local AS. However, stenosis-induced high WSS pushes plaque rupture (159, 160). As several of above mentioned AS-related events such as vascular inflammation, disruption of endothelial barrier, and angiogenesis are closed related to flow-induced shear stress, we made a separate summary in this section.
Without shear stress, Jam-A knock-out accelerated cell motility by enhanced directional persistence. Under shear stress, Jam-A knock-out escalated protrusion extension at the flow direction and elevated downstream cellular displacement (161). JAM-A shedding could be increased with ADAM17 maturation. Responded to flow exposure, the shedding of JAM-A increased but the Jam-A mRNA expression was retained (113). Noteworthy, ADAM17-activation and JAM-A/F11R cleavage impaired endothelial WSS mechanosensing (162).
Under high shear stress, JAM-A was expressed on human CD34+ progenitor cells and significantly decreased adhesion over immobilized platelets or inflammatory endothelium (138). The Mian Long group found that JAM-A and JAM-C were the ligands of Mac-1 when mediating PMN adhesion. Under high shear stress, LFA-1/Mac-1-JAM-C bonds hastened PMN crawling (163). Under shear flow at the physiological level, the high bond strength between LFA-1 and JAM-A raised a strong Ca2+ response in adherent PMNs especially (164). Rolling and sticking interactions of immobilized JAM-B protein with human T lymphocytes were barely observed at a high shear stress (1.0 dyn/cm2) but readily observed at a lower shear stress (0.3 dyn/cm2) (24).
Taken together, it is necessary to consider the flow-induced shear stress when discussing the roles of JAMs in AS, especially related to endothelial inflammation and leucocytes motility. More precise conditions of shear stress deserved to be explored.
Vascular Intercellular Interactions
Essentially, AS is caused by a series of cellular interactions. Multiple scRNA-seq data of plaques from mice and humans demonstrated the development of atherosclerosis resulting from the combined action of various types of cells (165, 166). As described above, monocytes TEM plays a vital role in the development of AS. At the same time, some additional research revealed the importance of other interactions. T cells are the second key leukocyte population in atherosclerotic lesions (167). JAM-A functioned in the interactions between CD4+ T cells and DC, possibly concerning vascular inflammation (168). sJAM-A can diminish the chemotaxis of activated T cells triggered by stromal cell-derived factor (SDF)-1α-transendothelial (123). Moreover, JAM-A expressed by human CD34+ cells regulated the interactions between platelets and endothelial cells to mediate the adhesion of platelet to inflammatory endothelium (138). Neutrophils play a role in vascular inflammation and plaque formation as well (169). JAM-A was also supposed to be an endothelial receptor of neutrophil transmigration (170). The JAM-C mediated neutrophil transmigration is dependent on Mac-1 (171). As a subsequent event in plaque formation, the proliferation and migration of inflamed smooth muscle cells seem to be inseparable from JAM-A (172).
Conclusion and Prospective
Taken together, a large body of evidence supports the crucial role of JAMs in AS. JAM-A and JAM-C were typically highly expressed in cellular components of atherosclerotic plaques from patients and ApoE–/– mice, including platelets, leucocytes, endothelial cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells (25, 69, 87). Representative receptors, pathways, and regulators were delineated in Figure 2. There are many issues needed to be studied. JAMs are expressed in different types of cells in AS plaque, but the similarities and differences between these JAMs are ambiguous. What are the downstream effects of different JAMs in different cells? Do JAMs mediate the interactions between these cells? If they do, how do they achieve that? How do environmental factors change those functions? The above questions still need to be answered in future studies.
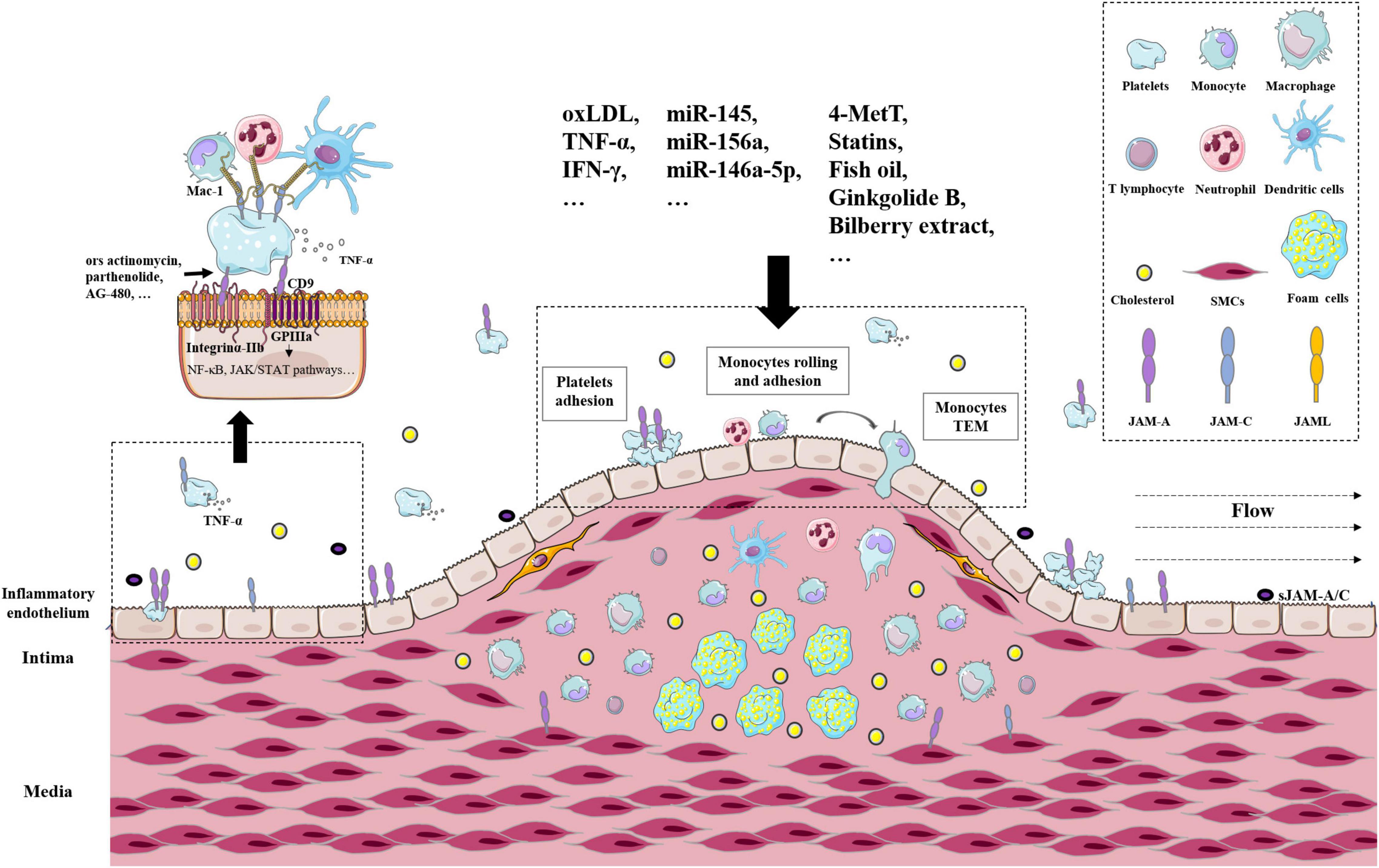
Figure 2. The roles of JAMs in atherosclerosis arteries. Representative receptors, pathways, and regulators of JAMs in atherosclerotic plaques. Related cell types include platelets, leucocytes, endothelial cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells.
Various models of animals and reagents have been developed in the functional study of JAMs. Jam-A–/– mice, Jam-C–/– mice, Jam-B-heterozygous mice (156), platelet-specific (tr) Jam-A-deficiency mice (trJam-A–/–) (95, 96), and their hybrid mice crossed with ApoE–/– mice have been used to illustrate the related mechanisms. sJAM-A and sJAM-C have been purified to demonstrate their physiological functions. Antibodies against JAM-A, JAM-B, and JAM-C have been also prepared and validated.
The value of JAMs in AS is reflected as potential anti-atherosclerotic and/or anti-thrombotic therapeutic targets. F11R/JAM-A antagonistic (F11Rpeptide 4D) developed by the Babinska et al. group (92–94) and antibodies against JAM-C demonstrated the potential to prevent the development of atherothrombosis and AS. The plasma level of JAM-A correlates with the severity of CAD, which indicates a potential biomarker for the disease (88). More data are awaited to show their value in clinical application.
Author Contributions
JW conceptualized and wrote the manuscript. XPC checked and revised the manuscript. Both authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
A part of Figure 1 was prepared by Figdraw.
References
1. Greene C, Campbell M, Janigro D. Chapter 1 - Fundamentals of brain–barrier anatomy and global functions. In: Lonser RR, Sarntinoranont M, Bankiewicz K editors. Nervous System Drug Delivery. Cambridge, MA: Academic Press (2019). p. 3–20.
2. Ebnet K, Suzuki A, Ohno S, Vestweber D. Junctional adhesion molecules (JAMs): more molecules with dual functions? J Cell Sci. (2004) 117(Pt 1):19–29. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00930
3. Kostrewa D, Brockhaus M, D’Arcy A, Dale GE, Nelboeck P, Schmid G, et al. X-ray structure of junctional adhesion molecule: structural basis for homophilic adhesion via a novel dimerization motif. Embo J. (2001) 20:4391–8. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.16.4391
4. Wang L, Luqmani R, Udalova IA. The role of neutrophils in rheumatic disease-associated vascular inflammation. Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2022) 18:158–70. doi: 10.1038/s41584-021-00738-4
5. Engelen SE, Robinson AJB, Zurke YX, Monaco C. Therapeutic strategies targeting inflammation and immunity in atherosclerosis: how to proceed? Nat Rev Cardiol. (2022):1–21. [Online ahead of print], doi: 10.1038/s41569-021-00668-4
6. Hirabayashi S, Tajima M, Yao I, Nishimura W, Mori H, Hata Y. JAM4, a junctional cell adhesion molecule interacting with a tight junction protein, MAGI-1. Mol Cell Biol. (2003) 23:4267–82. doi: 10.1128/mcb.23.12.4267-4282.2003
7. Mendoza C, Nagidi SH, Mizrachi D. Molecular characterization of the extracellular domain of human junctional adhesion proteins. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:3482. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073482
8. Moog-Lutz C, Cavé-Riant F, Guibal FC, Breau MA, Di Gioia Y, Couraud PO, et al. JAML, a novel protein with characteristics of a junctional adhesion molecule, is induced during differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells. Blood. (2003) 102:3371–8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-11-3462
9. Raschperger E, Engstrom U, Pettersson RF, Fuxe J. CLMP, a novel member of the CTX family and a new component of epithelial tight junctions. J Biol Chem. (2004) 279:796–804. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308249200
10. Bergelson JM, Cunningham JA, Droguett G, Kurt-Jones EA, Krithivas A, Hong JS, et al. Isolation of a common receptor for Coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5. Science. (1997) 275:1320–3. doi: 10.1126/science.275.5304.1320
11. Hirata K, Ishida T, Penta K, Rezaee M, Yang E, Wohlgemuth J, et al. Cloning of an immunoglobulin family adhesion molecule selectively expressed by endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. (2001) 276:16223–31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100630200
12. Martìn-Padura I, Lostaglio S, Schneemann M, Williams L, Romano M, Fruscella P, et al. Junctional adhesion molecule, a novel member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that distributes at intercellular junctions and modulates monocyte transmigration. J Cell Biol. (1998) 142:117–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.142.1.117
13. Arrate MP, Rodriguez JM, Tran TM, Brock TA, Cunningham SA. Cloning of human junctional adhesion molecule 3 (JAM3) and its identification as the JAM2 counter-receptor. J Biol Chem. (2001) 276:45826–32. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M105972200
14. Aurrand-Lions MA, Duncan L, Du Pasquier L, Imhof BA. Cloning of JAM-2 and JAM-3: an emerging junctional adhesion molecular family? Curr Topics Microbiol Immunol. (2000) 251:91–8. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-57276-0_12
15. Cunningham SA, Arrate MP, Rodriguez JM, Bjercke RJ, Vanderslice P, Morris AP, et al. A novel protein with homology to the junctional adhesion molecule. Characterization of leukocyte interactions. J Biol Chem. (2000) 275:34750–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002718200
16. Aurrand-Lions M, Duncan L, Ballestrem C, Imhof BA. JAM-2, a novel immunoglobulin superfamily molecule, expressed by endothelial and lymphatic cells. J Biol Chem. (2001) 276:2733–41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M005458200
17. Palmeri D, van Zante A, Huang CC, Hemmerich S, Rosen SD. Vascular endothelial junction-associated molecule, a novel member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, is localized to intercellular boundaries of endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. (2000) 275:19139–45. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003189200
18. Prota AE, Campbell JA, Schelling P, Forrest JC, Watson MJ, Peters TR, et al. Crystal structure of human junctional adhesion molecule 1: implications for reovirus binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2003) 100:5366. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0937718100
19. Bazzoni G, Martinez-Estrada OM, Mueller F, Nelboeck P, Schmid G, Bartfai T, et al. Homophilic interaction of junctional adhesion molecule. J Biol Chem. (2000) 275:30970–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M003946200
20. Ostermann G, Weber KS, Zernecke A, Schröder A, Weber C. JAM-1 is a ligand of the beta(2) integrin LFA-1 involved in transendothelial migration of leukocytes. Nat Immunol. (2002) 3:151–8. doi: 10.1038/ni755
21. Sladojevic N, Stamatovic SM, Keep RF, Grailer JJ, Sarma JV, Ward PA, et al. Inhibition of junctional adhesion molecule-A/LFA interaction attenuates leukocyte trafficking and inflammation in brain ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neurobiol Dis. (2014) 67:57–70. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.03.010
22. Fraemohs L, Koenen RR, Ostermann G, Heinemann B, Weber C. The functional interaction of the beta 2 integrin lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 with junctional adhesion molecule-A is mediated by the I domain. J Immunol. (2004) 173:6259–64. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.10.6259
23. Cunningham SA, Rodriguez JM, Arrate MP, Tran TM, Brock TA. JAM2 interacts with alpha4beta1. Facilitation by JAM3. J Biol Chem. (2002) 277:27589–92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C200331200
24. Ludwig RJ, Hardt K, Hatting M, Bistrian R, Diehl S, Radeke HH, et al. Junctional adhesion molecule (JAM)-B supports lymphocyte rolling and adhesion through interaction with alpha4beta1 integrin. Immunology. (2009) 128:196–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2009.03100.x
25. Santoso S, Sachs UJ, Kroll H, Linder M, Ruf A, Preissner KT, et al. The junctional adhesion molecule 3 (JAM-3) on human platelets is a counterreceptor for the leukocyte integrin Mac-1. J Exp Med. (2002) 196:679–91. doi: 10.1084/jem.20020267
26. Lamagna C, Meda P, Mandicourt G, Brown J, Gilbert RJ, Jones EY, et al. Dual interaction of JAM-C with JAM-B and alpha(M)beta2 integrin: function in junctional complexes and leukocyte adhesion. Mol Biol Cell. (2005) 16:4992–5003. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-04-0310
27. Naik MU, Mousa SA, Parkos CA, Naik UP. Signaling through JAM-1 and alphavbeta3 is required for the angiogenic action of bFGF: dissociation of the JAM-1 and alphavbeta3 complex. Blood. (2003) 102:2108–14. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-04-1114
28. Peddibhotla SS, Brinkmann BF, Kummer D, Tuncay H, Nakayama M, Adams RH, et al. Tetraspanin CD9 links junctional adhesion molecule-A to αvβ3 integrin to mediate basic fibroblast growth factor-specific angiogenic signaling. Mol Biol Cell. (2013) 24:933–44. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-06-0481
29. Naik MU, Naik UP. Junctional adhesion molecule-A-induced endothelial cell migration on vitronectin is integrin alpha v beta 3 specific. J Cell Sci. (2006) 119(Pt 3):490–9. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02771
30. Li X, Stankovic M, Lee BP, Aurrand-Lions M, Hahn CN, Lu Y, et al. JAM-C induces endothelial cell permeability through its association and regulation of {beta}3 integrins. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2009) 29:1200–6. doi: 10.1161/atvbaha.109.189217
31. Naik MU, Caplan JL, Naik UP. Junctional adhesion molecule-A suppresses platelet integrin αIIbβ3 signaling by recruiting Csk to the integrin-c-Src complex. Blood. (2014) 123:1393–402. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-04-496232
32. Naik MU, Stalker TJ, Brass LF, Naik UP. JAM-A protects from thrombosis by suppressing integrin αIIbβ3-dependent outside-in signaling in platelets. Blood. (2012) 119:3352–60. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-397398
33. Sobocka MB, Sobocki T, Babinska A, Hartwig JH, Li M, Ehrlich YH, et al. Signaling pathways of the F11 receptor (F11R; a.k.a. JAM-1, JAM-A) in human platelets: F11R dimerization, phosphorylation and complex formation with the integrin GPIIIa. J Receptor Signal Transduct Res. (2004) 24:85–105. doi: 10.1081/rrs-120034252
34. Luissint AC, Lutz PG, Calderwood DA, Couraud PO, Bourdoulous S. JAM-L-mediated leukocyte adhesion to endothelial cells is regulated in cis by alpha4beta1 integrin activation. J Cell Biol. (2008) 183:1159–73. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200805061
35. Kummer D, Ebnet K. Junctional Adhesion Molecules (JAMs): the JAM-Integrin Connection. Cells. (2018) 7:25. doi: 10.3390/cells7040025
36. Ebnet K, Schulz CU, Meyer Zu Brickwedde MK, Pendl GG, Vestweber D. Junctional adhesion molecule interacts with the PDZ domain-containing proteins AF-6 and ZO-1. J Biol Chem. (2000) 275:27979–88. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002363200
37. Utepbergenov DI, Fanning AS, Anderson JM. Dimerization of the scaffolding protein ZO-1 through the second PDZ domain. J Biol Chem. (2006) 281:24671–7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M512820200
38. Lee H-J, Zheng JJ. PDZ domains and their binding partners: structure, specificity, and modification. Cell Commun Signal. (2010) 8:8. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-8-8
39. Monteiro AC, Sumagin R, Rankin CR, Leoni G, Mina MJ, Reiter DM, et al. JAM-A associates with ZO-2, afadin, and PDZ-GEF1 to activate Rap2c and regulate epithelial barrier function. Mol Biol Cell. (2013) 24:2849–60. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E13-06-0298
40. Nomme J, Fanning AS, Caffrey M, Lye MF, Anderson JM, Lavie A. The Src homology 3 domain is required for junctional adhesion molecule binding to the third PDZ domain of the scaffolding protein ZO-1. J Biol Chem. (2011) 286:43352–60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.304089
41. Braiterman LT, Heffernan S, Nyasae L, Johns D, See AP, Yutzy R, et al. JAM-A is both essential and inhibitory to development of hepatic polarity in WIF-B cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. (2008) 294:G576–88. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00159.2007
42. Ebnet K. Junctional Adhesion Molecules (JAMs): cell adhesion receptors with pleiotropic functions in cell physiology and development. Physiol Rev. (2017) 97:1529–54. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00004.2017
43. Bazzoni G, Martinez-Estrada OM, Orsenigo F, Cordenonsi M, Citi S, Dejana E. Interaction of junctional adhesion molecule with the tight junction components ZO-1, cingulin, and occludin. J Biol Chem. (2000) 275:20520–6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M905251199
44. Itoh M, Sasaki H, Furuse M, Ozaki H, Kita T, Tsukita S. Junctional adhesion molecule (JAM) binds to PAR-3: a possible mechanism for the recruitment of PAR-3 to tight junctions. J Cell Biol. (2001) 154:491–7. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200103047
45. Nishimura M, Kakizaki M, Ono Y, Morimoto K, Takeuchi M, Inoue Y, et al. JEAP, a novel component of tight junctions in exocrine cells. J Biol Chem. (2002) 277:5583–7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110154200
46. Rehder D, Iden S, Nasdala I, Wegener J, Brickwedde MK, Vestweber D, et al. Junctional adhesion molecule-a participates in the formation of apico-basal polarity through different domains. Exp Cell Res. (2006) 312:3389–403. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2006.07.004
47. Severson EA, Lee WY, Capaldo CT, Nusrat A, Parkos CA. Junctional adhesion molecule A interacts with Afadin and PDZ-GEF2 to activate Rap1A, regulate beta1 integrin levels, and enhance cell migration. Mol Biol Cell. (2009) 20:1916–25. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e08-10-1014
48. Fukuhara A, Irie K, Nakanishi H, Takekuni K, Kawakatsu T, Ikeda W, et al. Involvement of nectin in the localization of junctional adhesion molecule at tight junctions. Oncogene. (2002) 21:7642–55. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205875
49. Takekuni K, Ikeda W, Fujito T, Morimoto K, Takeuchi M, Monden M, et al. Direct binding of cell polarity protein PAR-3 to cell-cell adhesion molecule nectin at neuroepithelial cells of developing mouse. J Biol Chem. (2003) 278:5497–500. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C200707200
50. Fanning AS, Anderson JM. PDZ domains: fundamental building blocks in the organization of protein complexes at the plasma membrane. J Clin Invest. (1999) 103:767–72. doi: 10.1172/jci6509
51. Takai Y, Nakanishi H. Nectin and afadin: novel organizers of intercellular junctions. J Cell Sci. (2003) 116(Pt 1):17–27. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00167
52. Yamamoto T, Harada N, Kano K, Taya S, Canaani E, Matsuura Y, et al. The Ras target AF-6 interacts with ZO-1 and serves as a peripheral component of tight junctions in epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. (1997) 139:785–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.139.3.785
53. Mandai K, Nakanishi H, Satoh A, Takahashi K, Satoh K, Nishioka H, et al. Ponsin/SH3P12: an l-afadin- and vinculin-binding protein localized at cell-cell and cell-matrix adherens junctions. J Cell Biol. (1999) 144:1001–17. doi: 10.1083/jcb.144.5.1001
54. Ebnet K, Aurrand-Lions M, Kuhn A, Kiefer F, Butz S, Zander K, et al. The junctional adhesion molecule (JAM) family members JAM-2 and JAM-3 associate with the cell polarity protein PAR-3: a possible role for JAMs in endothelial cell polarity. J Cell Sci. (2003) 116(Pt 19):3879–91. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00704
55. Gao L, Joberty G, Macara IG. Assembly of epithelial tight junctions is negatively regulated by Par6. Curr Biol. (2002) 12:221–5. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(01)00663-7
56. McSherry EA, Brennan K, Hudson L, Hill AD, Hopkins AM. Breast cancer cell migration is regulated through junctional adhesion molecule-A-mediated activation of Rap1 GTPase. Breast Cancer Res BCR. (2011) 13:R31. doi: 10.1186/bcr2853
57. Fujita E, Tanabe Y, Hirose T, Aurrand-Lions M, Kasahara T, Imhof BA, et al. Loss of partitioning-defective-3/isotype-specific interacting protein (par-3/ASIP) in the elongating spermatid of RA175 (IGSF4A/SynCAM)-deficient mice. Am J Pathol. (2007) 171:1800–10. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.070261
58. Cartier-Michaud A, Bailly AL, Betzi S, Shi X, Lissitzky JC, Zarubica A, et al. Genetic, structural, and chemical insights into the dual function of GRASP55 in germ cell Golgi remodeling and JAM-C polarized localization during spermatogenesis. PLoS Genet. (2017) 13:e1006803. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006803
59. Bailly AL, Grenier JMP, Cartier-Michaud A, Bardin F, Balzano M, Goubard A, et al. GRASP55 is dispensable for normal hematopoiesis but necessary for Myc-dependent leukemic growth. J Immunol. (2020) 204:2685–96. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901124
60. Aravindan RG, Fomin VP, Naik UP, Modelski MJ, Naik MU, Galileo DS, et al. CASK interacts with PMCA4b and JAM-A on the mouse sperm flagellum to regulate Ca2+ homeostasis and motility. J Cell Physiol. (2012) 227:3138–50. doi: 10.1002/jcp.24000
61. Tajima M, Hirabayashi S, Yao I, Shirasawa M, Osuga J, Ishibashi S, et al. Roles of immunoglobulin-like loops of junctional cell adhesion molecule 4; involvement in the subcellular localization and the cell adhesion. Genes Cells Devoted Mol Cell Mech. (2003) 8:759–68. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2443.2003.00673.x
62. Mori H, Hirabayashi S, Shirasawa M, Sugimura H, Hata Y. JAM4 enhances hepatocyte growth factor-mediated branching and scattering of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Genes Cells Devoted Mol Cell Mech. (2004) 9:811–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2004.00765.x
63. Hirabayashi S, Mori H, Kansaku A, Kurihara H, Sakai T, Shimizu F, et al. MAGI-1 is a component of the glomerular slit diaphragm that is tightly associated with nephrin. Lab Invest. (2005) 85:1528–43. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.3700347
64. Kansaku A, Hirabayashi S, Mori H, Fujiwara N, Kawata A, Ikeda M, et al. Ligand-of-Numb protein × is an endocytic scaffold for junctional adhesion molecule 4. Oncogene. (2006) 25:5071–84. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209468
65. Kim E, Lee Y, Kim JS, Song BS, Kim SU, Huh JW, et al. Extracellular domain of V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 1 (VSIG1) interacts with sertoli cell membrane protein, while its PDZ-binding motif forms a complex with ZO-1. Mol Cells. (2010) 30:443–8. doi: 10.1007/s10059-010-0138-4
66. Arafa E, Bondzie PA, Rezazadeh K, Meyer RD, Hartsough E, Henderson JM, et al. TMIGD1 is a novel adhesion molecule that protects epithelial cells from oxidative cell injury. Am J Pathol. (2015) 185:2757–67. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.06.006
67. Hartmann C, Schwietzer YA, Kummer D, Kirschnick N, Hoppe E, Thüring EM, et al. The mitochondrial outer membrane protein SYNJ2BP interacts with the cell adhesion molecule TMIGD1 and can recruit it to mitochondria. BMC Mol Cell Biol. (2020) 21:30. doi: 10.1186/s12860-020-00274-1
68. Nasdala I, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Wolburg H, Kuhn A, Ebnet K, Brachtendorf G, et al. A transmembrane tight junction protein selectively expressed on endothelial cells and platelets. J Biol Chem. (2002) 277:16294–303. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111999200
69. Langer HF, Daub K, Braun G, Schönberger T, May AE, Schaller M, et al. Platelets recruit human dendritic cells via Mac-1/JAM-C interaction and modulate dendritic cell function in vitro. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2007) 27:1463–70. doi: 10.1161/atvbaha.107.141515
70. Otani T, Furuse M. Tight junction structure and function revisited. Trends Cell Biol. (2020) 30:805–17. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2020.08.004
71. Naik UP, Eckfeld K. Junctional adhesion molecule 1 (JAM-1). J Biol Regulat Homeostatic Agents. (2003) 17:341–7.
72. Zen K, Liu Y, McCall IC, Wu T, Lee W, Babbin BA, et al. Neutrophil migration across tight junctions is mediated by adhesive interactions between epithelial coxsackie and adenovirus receptor and a junctional adhesion molecule-like protein on neutrophils. Mol Biol Cell. (2005) 16:2694–703. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e05-01-0036
73. Weber DA, Sumagin R, McCall IC, Leoni G, Neumann PA, Andargachew R, et al. Neutrophil-derived JAML inhibits repair of intestinal epithelial injury during acute inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. (2014) 7:1221–32. doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.12
74. Guo YL, Bai R, Chen CX, Liu DQ, Liu Y, Zhang CY, et al. Role of junctional adhesion molecule-like protein in mediating monocyte transendothelial migration. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2009) 29:75–83. doi: 10.1161/atvbaha.108.177717
75. Mirza M, Petersen C, Nordqvist K, Sollerbrant K. Coxsackievirus and adenovirus receptor is up-regulated in migratory germ cells during passage of the blood-testis barrier. Endocrinology. (2007) 148:5459–69. doi: 10.1210/en.2007-0359
76. Rathjen FG. The CAR group of Ig cell adhesion proteins-Regulators of gap junctions? Bioessays News Rev Mol Cellular Dev Biol. (2020) 42:e2000031. doi: 10.1002/bies.202000031
77. Díaz-Coránguez M, Liu X, Antonetti DA. Tight junctions in cell proliferation. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:5972. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235972
78. Violi F, Pastori D, Pignatelli P, Carnevale R. Nutrition, thrombosis, and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. (2020) 126:1415–42. doi: 10.1161/circresaha.120.315892
79. Naik UP, Ehrlich YH, Kornecki E. Mechanisms of platelet activation by a stimulatory antibody: cross-linking of a novel platelet receptor for monoclonal antibody F11 with the Fc gamma RII receptor. Biochem J. (1995) 310(Pt 1):155–62. doi: 10.1042/bj3100155
80. Naik UP, Naik MU, Eckfeld K, Martin-DeLeon P, Spychala J. Characterization and chromosomal localization of JAM-1, a platelet receptor for a stimulatory monoclonal antibody. J Cell Sci. (2001) 114(Pt 3):539–47. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.3.539
81. Babinska A, Kedees MH, Athar H, Sobocki T, Sobocka MB, Ahmed T, et al. Two regions of the human platelet F11-receptor (F11R) are critical for platelet aggregation, potentiation and adhesion. Thromb Haemost. (2002) 87:712–21.
82. Kedees MH, Babinska A, Swiatkowska M, Deitch J, Hussain MM, Ehrlich YH, et al. Expression of a recombinant protein of the platelet F11 receptor (F11R) (JAM-1/JAM-A) in insect cells: F11R is naturally phosphorylated in the extracellular domain. Platelets. (2005) 16:99–109. doi: 10.1080/09537100400010329
83. Williams LA, Martin-Padura I, Dejana E, Hogg N, Simmons DL. Identification and characterisation of human Junctional Adhesion Molecule (JAM). Mol Immunol. (1999) 36:1175–88. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(99)00122-4
84. Elrod JW, Park JH, Oshima T, Sharp CD, Minagar A, Alexander JS. Expression of junctional proteins in human platelets. Platelets. (2003) 14:247–51. doi: 10.1080/0953710031000118894
85. Sobocki T, Sobocka MB, Babinska A, Ehrlich YH, Banerjee P, Kornecki E. Genomic structure, organization and promoter analysis of the human F11R/F11 receptor/junctional adhesion molecule-1/JAM-A. Gene. (2006) 366:128–44. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2005.08.025
86. Ozaki H, Ishii K, Arai H, Horiuchi H, Kawamoto T, Suzuki H, et al. Junctional adhesion molecule (JAM) is phosphorylated by protein kinase C upon platelet activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2000) 276:873–8. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2000.3574
87. Babinska A, Azari BM, Salifu MO, Liu R, Jiang XC, Sobocka MB, et al. The F11 receptor (F11R/JAM-A) in atherothrombosis: overexpression of F11R in atherosclerotic plaques. Thromb Haemost. (2007) 97:272–81.
88. Cavusoglu E, Kornecki E, Sobocka MB, Babinska A, Ehrlich YH, Chopra V, et al. Association of plasma levels of F11 receptor/junctional adhesion molecule-A (F11R/JAM-A) with human atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2007) 50:1768–76. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.05.051
89. Rath D, Rapp V, Schwartz J, Winter S, Emschermann F, Arnold D, et al. Homophilic interaction between Transmembrane-JAM-A and Soluble JAM-A regulates thrombo-inflammation: implications for coronary artery disease. JACC Basic Transl Sci. (2022) 7:445–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2022.03.003
90. Babinska A, Kedees MH, Athar H, Ahmed T, Batuman O, Ehrlich YH, et al. F11-receptor (F11R/JAM) mediates platelet adhesion to endothelial cells: role in inflammatory thrombosis. Thromb Haemost. (2002) 88:843–50.
91. Azari BM, Marmur JD, Salifu MO, Ehrlich YH, Kornecki E, Babinska A. Transcription and translation of human F11R gene are required for an initial step of atherogenesis induced by inflammatory cytokines. J Transl Med. (2011) 9:98. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-9-98
92. Babinska A, Clement CC, Swiatkowska M, Szymanski J, Shon A, Ehrlich YH, et al. Development of new antiatherosclerotic and antithrombotic drugs utilizing F11 receptor (F11R/JAM-A) peptides. Biopolymers. (2014) 102:322–34. doi: 10.1002/bip.22503
93. Babinska A, Clement CC, Przygodzki T, Talar M, Li Y, Braun M, et al. A peptide antagonist of F11R/JAM-A reduces plaque formation and prolongs survival in an animal model of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. (2019) 284:92–101. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.02.014
94. Babinska A, Clement CC, Li Y, Wzorek J, Przygodzki T, Talar M, et al. In vivo data: treatment with the F11R/JAM-A peptide 4D decreases mortality and reduces the generation of atherosclerotic plaques in ApoE-deficient mice. Data Brief. (2020) 30:105516. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2020.105516
95. Karshovska E, Zhao Z, Blanchet X, Schmitt MM, Bidzhekov K, Soehnlein O, et al. Hyperreactivity of junctional adhesion molecule A-deficient platelets accelerates atherosclerosis in hyperlipidemic mice. Circ Res. (2015) 116:587–99. doi: 10.1161/circresaha.116.304035
96. Zhao Z, Vajen T, Karshovska E, Dickhout A, Schmitt MM, Megens RTA, et al. Deletion of junctional adhesion molecule A from platelets increases early-stage neointima formation after wire injury in hyperlipidemic mice. J Cell Mol Med. (2017) 21:1523–31. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13083
97. Xu H, Oliveira-Sales EB, McBride F, Liu B, Hewinson J, Toward M, et al. Upregulation of junctional adhesion molecule-A is a putative prognostic marker of hypertension. Cardiovasc Res. (2012) 96:552–60. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvs273
98. Bhat SA, Goel R, Shukla R, Hanif K. Platelet CD40L induces activation of astrocytes and microglia in hypertension. Brain Behav Immun. (2017) 59:173–89. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2016.09.021
99. Erpenbeck L, Rubant S, Hardt K, Santoso S, Boehncke WH, Schön MP, et al. Constitutive and functionally relevant expression of JAM-C on platelets. Thromb Haemost. (2010) 103:857–9. doi: 10.1160/th09-08-0572
100. Asberg AE, Videm V. Inhibition of platelet receptors involved in neutrophil-platelet interaction in model cardiopulmonary bypass. Artificial Organs. (2007) 31:617–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1594.2007.00432.x
101. Weber C, Fraemohs L, Dejana E. The role of junctional adhesion molecules in vascular inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. (2007) 7:467–77. doi: 10.1038/nri2096
102. Geovanini GR, Libby P. Atherosclerosis and inflammation: overview and updates. Clin Sci (Lond). (2018) 132:1243–52. doi: 10.1042/cs20180306
103. Rahman K, Desai C, Iyer SS, Thorn NE, Kumar P, Liu Y, et al. Loss of junctional adhesion molecule A promotes severe steatohepatitis in mice on a diet high in saturated fat, fructose, and cholesterol. Gastroenterology. (2016) 151:733–46.e12. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.06.022
104. Fan S, Weight CM, Luissint AC, Hilgarth RS, Brazil JC, Ettel M, et al. Role of JAM-A tyrosine phosphorylation in epithelial barrier dysfunction during intestinal inflammation. Mol Biol Cell. (2019) 30:566–78. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-08-0531
105. Sattler K, El-Battrawy I, Zhao Z, Schrottenberg C, Yücel G, Lan H, et al. Serum of patients with acute myocardial infarction prevents inflammation in iPSC-cardiomyocytes. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:5651. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42079-z
106. Corada M, Chimenti S, Cera MR, Vinci M, Salio M, Fiordaliso F, et al. Junctional adhesion molecule-A-deficient polymorphonuclear cells show reduced diapedesis in peritonitis and heart ischemia-reperfusion injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. (2005) 102:10634–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0500147102
107. Kiessling F. Molecular ultrasound imaging of JAM-A depicts early arterial inflammation. Aging. (2018) 10:2222–3. doi: 10.18632/aging.101555
108. Martinez-Estrada OM, Manzi L, Tonetti P, Dejana E, Bazzoni G. Opposite effects of tumor necrosis factor and soluble fibronectin on junctional adhesion molecule-A in endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2005) 288:L1081–8. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00289.2004
109. Shaw SK, Perkins BN, Lim YC, Liu Y, Nusrat A, Schnell FJ, et al. Reduced expression of junctional adhesion molecule and platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31) at human vascular endothelial junctions by cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha plus interferon-gamma Does not reduce leukocyte transmigration under flow. Am J Pathol. (2001) 159:2281–91. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63078-7
110. Shaw SK, Ma S, Kim MB, Rao RM, Hartman CU, Froio RM, et al. Coordinated redistribution of leukocyte LFA-1 and endothelial cell ICAM-1 accompany neutrophil transmigration. J Exp Med. (2004) 200:1571–80. doi: 10.1084/jem.20040965
111. Mamdouh Z, Mikhailov A, Muller WA. Transcellular migration of leukocytes is mediated by the endothelial lateral border recycling compartment. J Exp Med. (2009) 206:2795–808. doi: 10.1084/jem.20082745
112. Koenen RR, Pruessmeyer J, Soehnlein O, Fraemohs L, Zernecke A, Schwarz N, et al. Regulated release and functional modulation of junctional adhesion molecule A by disintegrin metalloproteinases. Blood. (2009) 113:4799–809. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-04-152330
113. Babendreyer A, Rojas-González DM, Giese AA, Fellendorf S, Düsterhöft S, Mela P, et al. Differential induction of the ADAM17 regulators iRhom1 and 2 in endothelial cells. Front Cardiovasc Med. (2020) 7:610344. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.610344
114. Tian Y, Fopiano KA, Buncha V, Lang L, Rudic RD, Filosa JA, et al. Aging-induced impaired endothelial wall shear stress mechanosensing causes arterial remodeling via JAM-A/F11R shedding by ADAM17. GeroScience. (2021) 44:349–69. doi: 10.1007/s11357-021-00476-1
115. Frontera V, Arcangeli ML, Zimmerli C, Bardin F, Obrados E, Audebert S, et al. Cutting edge: JAM-C controls homeostatic chemokine secretion in lymph node fibroblastic reticular cells expressing thrombomodulin. J Immunol. (2011) 187:603–7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1003441
116. Hirano Y, Ode Y, Ochani M, Wang P, Aziz M. Targeting junctional adhesion molecule-C ameliorates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by decreasing CXCR4(+) aged neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol. (2018) 104:1159–71. doi: 10.1002/jlb.3a0218-050r
117. Martin NJ, Chami B, Vallejo A, Mojadadi AA, Witting PK, Ahmad G. Efficacy of the piperidine Nitroxide 4-MethoxyTEMPO in ameliorating serum amyloid A-Mediated vascular inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:4549. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094549
118. Bouwens E, van den Berg VJ, Akkerhuis KM, Baart SJ, Caliskan K, Brugts JJ, et al. Circulating biomarkers of cell adhesion predict clinical outcome in patients with chronic heart failure. J Clin Med. (2020) 9:195. doi: 10.3390/jcm9010195
119. Liu X, Sun W, Zhao Y, Chen B, Wu W, Bao L, et al. Ginkgolide B inhibits JAM-A, Cx43, and VE-Cadherin expression and reduces monocyte transmigration in oxidized LDL-Stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2015) 2015:907926. doi: 10.1155/2015/907926
120. Gupta SK, Pillarisetti K, Ohlstein EH. Platelet agonist F11 receptor is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and identical with junctional adhesion molecule (JAM): regulation of expression in human endothelial cells and macrophages. IUBMB Life. (2000) 50:51–6. doi: 10.1080/15216540050176593
121. Schmitt MM, Fraemohs L, Hackeng TM, Weber C, Koenen RR. Atherogenic mononuclear cell recruitment is facilitated by oxidized lipoprotein-induced endothelial junctional adhesion molecule-A redistribution. Atherosclerosis. (2014) 234:254–64. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2014.03.014
122. Schmitt MM, Megens RT, Zernecke A, Bidzhekov K, van den Akker NM, Rademakers T, et al. Endothelial junctional adhesion molecule-a guides monocytes into flow-dependent predilection sites of atherosclerosis. Circulation. (2014) 129:66–76. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.113.004149
123. Ostermann G, Fraemohs L, Baltus T, Schober A, Lietz M, Zernecke A, et al. Involvement of JAM-A in mononuclear cell recruitment on inflamed or atherosclerotic endothelium: inhibition by soluble JAM-A. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2005) 25:729–35. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000157154.14474.3b
124. Zernecke A, Liehn EA, Fraemohs L, von Hundelshausen P, Koenen RR, Corada M, et al. Importance of junctional adhesion molecule-A for neointimal lesion formation and infiltration in atherosclerosis-prone mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2006) 26:e10–3. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000197852.24529.4f
125. Gaudreault N, Kumar N, Posada JM, Stephens KB, Reyes de Mochel NS, Eberlé D, et al. ApoE suppresses atherosclerosis by reducing lipid accumulation in circulating monocytes and the expression of inflammatory molecules on monocytes and vascular endothelium. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2012) 32:264–72. doi: 10.1161/atvbaha.111.238964
126. Yang W, Yin R, Zhu X, Yang S, Wang J, Zhou Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem-cell-derived exosomal miR-145 inhibits atherosclerosis by targeting JAM-A. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. (2021) 23:119–31. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.10.037
127. Hou D, He F, Ma L, Cao M, Zhou Z, Wei Z, et al. The potential atheroprotective role of plant MIR156a as a repressor of monocyte recruitment on inflamed human endothelial cells. J Nutr Biochem. (2018) 57:197–205. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.03.026
128. Mauray A, Felgines C, Morand C, Mazur A, Scalbert A, Milenkovic D. Bilberry anthocyanin-rich extract alters expression of genes related to atherosclerosis development in aorta of apo E-deficient mice. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis NMCD. (2012) 22:72–80. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2010.04.011
129. Speck N, Brandsch C, Schmidt N, Yazdekhasti N, Hirche F, Lucius R, et al. The antiatherogenic effect of fish oil in male mice is associated with a diminished release of endothelial ADAM17 and ADAM10 substrates. J Nutr. (2015) 145:1218–26. doi: 10.3945/jn.115.211375
130. Bradfield PF, Scheiermann C, Nourshargh S, Ody C, Luscinskas FW, Rainger GE, et al. JAM-C regulates unidirectional monocyte transendothelial migration in inflammation. Blood. (2007) 110:2545–55. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-03-078733
131. Hu W, Xu B, Zhang J, Kou C, Liu J, Wang Q, et al. Exosomal miR-146a-5p from Treponema pallidum-stimulated macrophages reduces endothelial cells permeability and monocyte transendothelial migration by targeting JAM-C. Exp Cell Res. (2020) 388:111823. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111823
132. Keiper T, Al-Fakhri N, Chavakis E, Athanasopoulos AN, Isermann B, Herzog S, et al. The role of junctional adhesion molecule-C (JAM-C) in oxidized LDL-mediated leukocyte recruitment. Faseb J. (2005) 19:2078–80. doi: 10.1096/fj.05-4196fje
133. Shagdarsuren E, Djalali-Talab Y, Aurrand-Lions M, Bidzhekov K, Liehn EA, Imhof BA, et al. Importance of junctional adhesion molecule-C for neointimal hyperplasia and monocyte recruitment in atherosclerosis-prone mice-brief report. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2009) 29:1161–3. doi: 10.1161/atvbaha.109.187898
134. Bradfield PF, Menon A, Miljkovic-Licina M, Lee BP, Fischer N, Fish RJ, et al. Divergent JAM-C expression accelerates monocyte-derived cell exit from atherosclerotic plaques. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0159679. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159679
135. Sun Y, Guan J, Hou Y, Xue F, Huang W, Zhang W, et al. Silencing of junctional adhesion molecule-like protein attenuates atherogenesis and enhances plaque stability in ApoE(-/-) mice. Clin Sci (Lond). (2019) 133:1215–28. doi: 10.1042/cs20180561
136. Sokeechand BSH, Trigatti BL. Un-JAMming atherosclerotic arteries: JAM-L as a target to attenuate plaque development. Clin Sci (Lond). (2019) 133:1581–5. doi: 10.1042/cs20190541
137. Camaré C, Pucelle M, Nègre-Salvayre A, Salvayre R. Angiogenesis in the atherosclerotic plaque. Redox Biol. (2017) 12:18–34. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.01.007
138. Stellos K, Langer H, Gnerlich S, Panagiota V, Paul A, Schönberger T, et al. Junctional adhesion molecule A expressed on human CD34+ cells promotes adhesion on vascular wall and differentiation into endothelial progenitor cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2010) 30:1127–36. doi: 10.1161/atvbaha.110.204370
139. Yeung D, Manias JL, Stewart DJ, Nag S. Decreased junctional adhesion molecule-A expression during blood-brain barrier breakdown. Acta Neuropathol. (2008) 115:635–42. doi: 10.1007/s00401-008-0364-4
140. Haarmann A, Deiss A, Prochaska J, Foerch C, Weksler B, Romero I, et al. Evaluation of soluble junctional adhesion molecule-A as a biomarker of human brain endothelial barrier breakdown. PLoS One. (2010) 5:e13568. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013568
141. Kakogiannos N, Ferrari L, Giampietro C, Scalise AA, Maderna C, Ravà M, et al. JAM-A Acts via C/EBP-α to Promote Claudin-5 Expression and Enhance Endothelial Barrier Function. Circ Res. (2020) 127:1056–73. doi: 10.1161/circresaha.120.316742
142. Higashi Y, Sukhanov S, Shai SY, Danchuk S, Snarski P, Li Z, et al. Endothelial deficiency of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor reduces endothelial barrier function and promotes atherosclerosis in Apoe-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2020) 319:H730–43. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00064.2020
143. Qi K, Li X, Geng Y, Cui H, Jin C, Wang P, et al. Tongxinluo attenuates reperfusion injury in diabetic hearts by angiopoietin-like 4-mediated protection of endothelial barrier integrity via PPAR-α pathway. PLoS One. (2018) 13:e0198403. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198403
144. Qi K, Yang Y, Geng Y, Cui H, Li X, Jin C, et al. Tongxinluo attenuates oxygen-glucose-serum deprivation/restoration-induced endothelial barrier breakdown via peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-α/angiopoietin-like 4 pathway in high glucose-incubated human cardiac microvascular endothelial cells. Medicine. (2020) 99:e21821. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000021821
145. Bednarek R, Selmi A, Wojkowska D, Karolczak K, Popielarski M, Stasiak M, et al. Functional inhibition of F11 receptor (F11R/junctional adhesion molecule-A/JAM-A) activity by a F11R-derived peptide in breast cancer and its microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2020) 179:325–35. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05471-x
146. Ranadewa D, Wu J, Subramanianbalachandar VA, Steward RL Jr. Variable fluid flow regimes alter human brain microvascular endothelial cell-cell junctions and cytoskeletal structure. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken, NJ). (2021) 78:323–34. doi: 10.1002/cm.21687
147. Curaj A, Wu Z, Rix A, Gresch O, Sternkopf M, Alampour-Rajabi S, et al. Molecular ultrasound imaging of junctional adhesion molecule A depicts acute alterations in blood flow and early endothelial dysregulation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2018) 38:40–8. doi: 10.1161/atvbaha.117.309503
148. Tang L, Zhang C, Yang Q, Xie H, Liu D, Tian H, et al. Melatonin maintains inner blood-retinal barrier via inhibition of p38/TXNIP/NF-κB pathway in diabetic retinopathy. J Cell Physiol. (2021) 236:5848–64. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30269
149. Economopoulou M, Avramovic N, Klotzsche-von Ameln A, Korovina I, Sprott D, Samus M, et al. Endothelial-specific deficiency of Junctional Adhesion Molecule-C promotes vessel normalisation in proliferative retinopathy. Thromb Haemost. (2015) 114:1241–9. doi: 10.1160/th15-01-0051
150. Hou X, Du HJ, Zhou J, Hu D, Wang YS, Li X. Role of junctional adhesion Molecule-C in the regulation of inner endothelial blood-retinal barrier function. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 9:695657. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.695657
151. Géraud C, Evdokimov K, Straub BK, Peitsch WK, Demory A, Dörflinger Y, et al. Unique cell type-specific junctional complexes in vascular endothelium of human and rat liver sinusoids. PLoS One. (2012) 7:e34206. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034206
152. Parris JJ, Cooke VG, Skarnes WC, Duncan MK, Naik UP. JAM-A expression during embryonic development. Dev Dyn Off Publ Am Assoc Anatomists. (2005) 233:1517–24. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20481
153. Sugano Y, Takeuchi M, Hirata A, Matsushita H, Kitamura T, Tanaka M, et al. Junctional adhesion molecule-A, JAM-A, is a novel cell-surface marker for long-term repopulating hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. (2008) 111:1167–72. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-03-081554
154. Solimando AG, Da Vià MC, Leone P, Borrelli P, Croci GA, Tabares P, et al. Halting the vicious cycle within the multiple myeloma ecosystem: blocking JAM-A on bone marrow endothelial cells restores angiogenic homeostasis and suppresses tumor progression. Haematologica. (2021) 106:1943–56. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.239913
155. Cooke VG, Naik MU, Naik UP. Fibroblast growth factor-2 failed to induce angiogenesis in junctional adhesion molecule-A-deficient mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2006) 26:2005–11. doi: 10.1161/01.Atv.0000234923.79173.99
156. Reynolds LE, Watson AR, Baker M, Jones TA, D’Amico G, Robinson SD, et al. Tumour angiogenesis is reduced in the Tc1 mouse model of Down’s syndrome. Nature. (2010) 465:813–7. doi: 10.1038/nature09106
157. Lamagna C, Hodivala-Dilke KM, Imhof BA, Aurrand-Lions M. Antibody against junctional adhesion molecule-C inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cancer Res. (2005) 65:5703–10. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-04-4012
158. Sacharidou A, Koh W, Stratman AN, Mayo AM, Fisher KE, Davis GE. Endothelial lumen signaling complexes control 3D matrix-specific tubulogenesis through interdependent Cdc42- and MT1-MMP-mediated events. Blood. (2010) 115:5259–69. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-252692
159. Kojima K, Hiro T, Koyama Y, Ohgaku A, Fujito H, Ebuchi Y, et al. High wall shear stress is related to atherosclerotic plaque rupture in the aortic arch of patients with cardiovascular disease: a study with computational fluid dynamics model and non-obstructive general angioscopy. J Atheroscler Thromb. (2021) 28:742–53. doi: 10.5551/jat.56598
160. Malik J, Novakova L, Valerianova A, Chytilova E, Lejsek V, Buryskova Salajova K, et al. Wall shear stress alteration: a local risk factor of atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep. (2022) 24:143–51. doi: 10.1007/s11883-022-00993-0
161. Huang H, Cruz F, Bazzoni G. Junctional adhesion molecule-A regulates cell migration and resistance to shear stress. J Cell Physiol. (2006) 209:122–30. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20712
162. Tian Y, Fopiano KA, Buncha V, Lang L, Rudic RD, Filosa JA, et al. Aging-induced impaired endothelial wall shear stress mechanosensing causes arterial remodeling via JAM-A/F11R shedding by ADAM17. GeroScience. (2022) 44:349–69.
163. Li N, Yang H, Wang M, Lü S, Zhang Y, Long M. Ligand-specific binding forces of LFA-1 and Mac-1 in neutrophil adhesion and crawling. Mol Biol Cell. (2018) 29:408–18. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-12-0827
164. Shu X, Li N, Huang D, Zhang Y, Lü S, Long M. Mechanical strength determines Ca(2+) transients triggered by the engagement of β(2) integrins to their ligands. Exp Cell Res. (2020) 387:111807. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2019.111807
165. Hill CA, Fernandez DM, Giannarelli C. Single cell analyses to understand the immune continuum in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. (2021) 330:85–94. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2021.04.003
166. Vallejo J, Cochain C, Zernecke A, Ley K. Heterogeneity of immune cells in human atherosclerosis revealed by scRNA-Seq. Cardiovasc Res. (2021) 117:2537–43. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab260
167. Li J, Ley K. Lymphocyte migration into atherosclerotic plaque. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2015) 35:40–9. doi: 10.1161/atvbaha.114.303227
168. Bonilha CS, Benson RA, Scales HE, Brewer JM, Garside P. Junctional adhesion molecule-A on dendritic cells regulates Th1 differentiation. Immunol Lett. (2021) 235:32–40. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2021.05.001
169. Klopf J, Brostjan C, Eilenberg W, Neumayer C. Neutrophil extracellular traps and their implications in cardiovascular and inflammatory disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:559. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020559
170. Khandoga A, Kessler JS, Meissner H, Hanschen M, Corada M, Motoike T, et al. Junctional adhesion molecule-A deficiency increases hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury despite reduction of neutrophil transendothelial migration. Blood. (2005) 106:725–33. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-11-4416
171. Chavakis T, Keiper T, Matz-Westphal R, Hersemeyer K, Sachs UJ, Nawroth PP, et al. The junctional adhesion molecule-C promotes neutrophil transendothelial migration in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. (2004) 279:55602–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404676200
172. Azari BM, Marmur JD, Salifu MO, Cavusoglu E, Ehrlich YH, Kornecki E, et al. Silencing of the F11R gene reveals a role for F11R/JAM-A in the migration of inflamed vascular smooth muscle cells and in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. (2010) 212:197–205. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.05.014
Keywords: junctional adhesion molecules, atherosclerosis, inflammation, thrombosis, transendothelial migration
Citation: Wang J and Chen XP (2022) Junctional Adhesion Molecules: Potential Proteins in Atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 9:888818. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.888818
Received: 03 March 2022; Accepted: 21 June 2022;
Published: 07 July 2022.
Edited by:
Masuko Ushio-Fukai, Augusta University, United StatesReviewed by:
Bhupesh Singla, University of Tennessee Health Science Center (UTHSC), United StatesSudhahar Varadarajan, Augusta University, United States
Copyright © 2022 Wang and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoping Chen, Y2hlbnhpYW9waW5nQGNzdS5lZHUuY24=
 Junqi Wang
Junqi Wang Xiaoping Chen
Xiaoping Chen