
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Built Environ., 17 February 2025
Sec. Geotechnical Engineering
Volume 11 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fbuil.2025.1523557
This article is part of the Research TopicRecent Advances in Numerical Modelling for Soil and Soil-Structure InteractionsView all 5 articles
In this paper, finite element (FE) modeling is conducted for a high-speed railway embankment on soft soils in Sebou, Morocco. Discrepancies arise between predicted and measured behaviors when using standard creep models. To address this, an advanced anisotropic creep constitutive model, known as Creep-SCLAY1S, is applied for comparison, focusing on the prefabricated vertical drain (PVD) treated soft soils. This advanced model incorporates fabric anisotropy, soil structure, and time-dependent behavior. The time-dependent soft soil creep model (SSCM) is also employed for further comparison. Numerical predictions are then compared with field instrumentation data. Results indicate that Creep-SCLAY1S offers improved predictions of in situ measurements, particularly post-construction, and provides a more accurate peak excess pore pressure during the embankment’s rapid surcharge phase.
Settlement problems for civil structures on soft soils are often tackled by means of 1D empirical methods based on simplified engineering parameters. Some go further into designing geotechnical engineering problems based on constitutive models, assuming that the subsoil is strictly isotropic (Huang and Griffiths, 2010). Using such simplified methods and constitutive models in practice leads to over-conservative designs and costly structures. In the majority of cases, the results disregard the long-term behavior in soft soils (Yildiz, 2009; Yildiz et al., 2009). Natural soil behavior is inherently anisotropic due to the sedimentary process and the likelihood of horizontally oriented deposition of the plate-shaped clay particles. Natural soft soils have a unique structure character (Guglielmi et al., 2024; Silva et al., 2024) that provides clay with additional undisturbed shear upon their remolded strength (Rezania et al., 2017). The clay soil particle structure at the micro-scale is geometrically arranged and called fabric. Additionally, the interparticle link “bond” reflects the clay composition, the stress state, and the deposition environment (Hosseinpour et al., 2017; Bagheri and Rezania, 2021).
Soft soils are known for their time-dependent character that affects their strength and long-term deformation (Rezania et al., 2017; Kelly et al., 2018; John, 2024). Employing a constitutive model that includes the clay inherent aspects is essential to precisely predict such complex soft soil responses (Taechakumthorn and Rowe, 2012; Hashemi et al., 2015; Nguyen and Indraratna, 2017; Rezania et al., 2017; Hosseinpour et al., 2017; Amavasai et al., 2018; Nguyen et al., 2018; Indraratna et al., 2018; Nguyen and Indraratna, 2020). Many researchers studied the issue of complex behavior of PVD-improved subsoil, including creep constitutive models (Rezania et al., 2017; Kelly et al., 2018; Nguyen et al., 2020; Cui et al., 2025) and discussed input parameters and modeling methods for the objective of better predicting soil deformations during the embankment construction in the short and long term. However, using advanced constitutive models in current practice for strategic projects with time constraints is still limited.
Due to the high computation effort of three-dimensional (3D) finite element (FE) modeling, the boundary value problems such as prefabricated vertical drain (PVD) improved ground are usually analyzed in the 2D plane-strain condition (Rezania et al., 2017; Kelly et al., 2018; Nguyen et al., 2022a; Nguyen et al., 2022b; Mridakh et al., 2022; Nguyen et al., 2023). In the field, water flows into PVDs in axisymmetric conditions; therefore, the conversion to a 2D representative analysis was based on a matching technique proposed by Chai et al. (2001) that is commonly used in this type of boundary problem.
The focus of this paper is to assess the long-term performance of an embankment on soft clay deposits improved by prefabricated vertical drains (PVDs) and to analyze the practicability of using standard and advanced constitutive models. For this study, a Sebou high-speed railway embankment located in Northwestern Morocco, constructed on deep alluvial Holocene deposits (Mridakh et al., 2019), is numerically simulated by using an advanced Creep-SCLAY1S model (Sivasithamparam et al., 2015). The results from the advanced creep model are compared with results obtained from standard time-dependent soft soil creep (Neher et al., 2001) and time-independent soft soil (Vermeer and Neher, 1999) models. The prediction results were compared with measured in situ deformation from a well-monitored section during the embankment construction and the preloading phase.
The Creep-SCLAY1S model is an advanced model based on the critical state formulation. The model accounts for anisotropy, structuration degradation, and rate-dependency. Creep-SCLAY1S is an extension of the SCLAY1 model proposed by Wheeler et al. (2003), incorporating the rate-dependency response of clays. A step was added by including anisotropy and degradation of structure in the SCLAY1S formulation that was developed by Karstunen et al. (2005). Sivasithamparam et al. (2015) proposed a more developed version, including the anisotropy and rate-dependency effect for soft soil. In its latest formulation, the Creep-SCLAY1S model includes both anisotropy and degradation of structure in the formulation from SCLAY1S and the rate-dependent viscoplastic component used by the anisotropic creep model (ACM) (Leoni et al., 2008) into the formulation.
The constitutive model is shown in Figure 1A in triaxial stress space and in Figure 1B in general stress space from Sivasithamparam et al. (2015). The model is composed of three yield surfaces, as shown in Figure 1A. The first surface (NCS) is the outer surface Figure 1A, named as the normal consolidation surface

Figure 1. Illustration of the Creep-SCLAY1S model constitutive surfaces (Sivasithamparam et al., 2015). (A) triaxial stress space, (B) general stress space.
In addition to the soil parameters required for SCLAY1S (as presented in Karstunen et al., 2005), three additional parameters, named viscous parameters, are required: reference time
The soil in the Sebou site was extensively studied during the high-speed railway line investigation campaign (Mridakh et al., 2019). For the studied section, a total of 18 boreholes, 11 cone penetration tests (CPTs), and eight pressiometers were conducted on site. In addition, samples from boreholes were prepared and then tested in the laboratory. Mainly, Atterberg limits tests, oedometer tests, direct shear tests, and triaxial tests were conducted for most soil layers based on the up-to-date standards for each test (NF P94-051, 1993; XP-94-090-1, 1997; NF P94-071-1&2, 1993; NF P94-074, 1994), respectively. Based on Figure 2, the Sebou site is composed of fill material of the Sebou watershed alluvial recent plio-quaternary deposits. The initial layers to 5 m are characterized by stiff clays with an over-consolidated ratio (OCR)>1 that was mostly due to aging and water level variation. The silty clay sediments found between 5 m and 10 m represent a soft soil behavior with a normally consolidated state, with higher water content values than the liquid limit. The underplayed layers between 10 m–35 m and from 35 m to 47 m present a conservative soft soil character followed by a soft silty clay character due to the varying sand and silty content, thus presenting a varying compression index
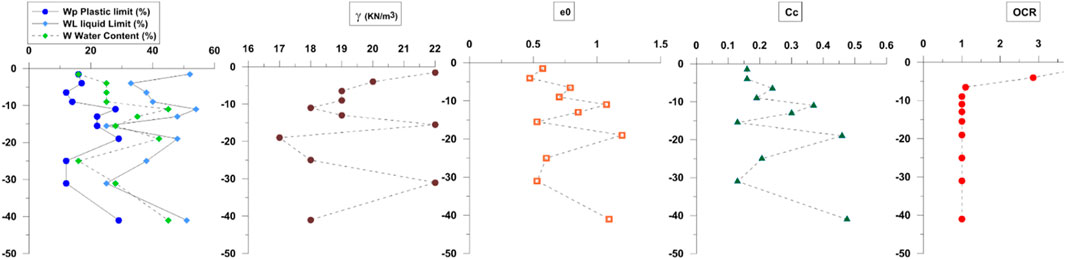
Figure 2. Soil parameters under the Sebou Embankment: W, water content; LL, liquid limit; PL, plastic limit;
For precise predictions, the Sebou Embankment subsoil is divided into 11 layers based on the parameter variation seen in Figure 2. Fifteen node triangular elements are used under plain strain conditions while using the very fine mesh option. The 2D plane-strain condition is used due to the soil layer symmetry in the N-S and E-W direction in the field, in addition to its light computation effort with quasi-similar results to the 3D model in this kind of boundary value geotechnical problems. The 2D model resulted in 1982 elements and 13,681 nodes (Figure 3).
The water level is fixed at 2 m depth under the embankment base (while the updated mesh option is activated). Only half of the embankment is considered for symmetrical reasons. The model dimensions used are 60 m in the horizontal direction from the centerline of the full embankment and 47 m in the vertical direction. Lateral boundaries were restrained, and the drainage boundaries are considered to be at the piezometric level and at the bottom of the mesh.
The embankment is constructed from two filling materials: granular for the drainage layer in the embankment base and sandy material for the fill and the surcharge layers (see Figure 3). The Mohr–Coulomb model is selected for both materials, and the material parameters used are shown in Table 1.
The lateral earth coefficient is calculated based on the equation
For Creep-SCLAY1S, the initial anisotropy (
The parameter
Koskinen et al. (2002) suggested a procedure for determining the initial value of
where
Krenn (2008) suggested both parameters
The values from the intrinsic compression index
where e is the void ratio. Table 5 summarizes the parameter values for each soil layer.
PVD installation influences soil stiffness and hydraulic conductivity of the surrounding soils. This impact and soil disturbance is difficult to assess, as different equipment is used by each soil improvement company (different mandrel types and dimensions). Hence, explicitly modeling drains and their smear zone area with highly estimated parameters can lead to discrepancies, in addition to high computational efforts and cost. Numerous methods can be adopted to calculate the equivalent permeability for the PVD-improved subsoil. In this paper, the matching approach described by Chai et al. (2001) is used in the matching process. This method uses the parameter of equivalent hydraulic conductivity (
l = drainage length,
where n =
Sebou Embankment is 4 m high and 14 m wide at the crest, with a footing of 38 m and 1:2 slope gradients. At first, a 0.3 m drainage layer was constructed from gravel, followed by a sandy filling material for the upper layers, including a 1.5 m thick preloading. As presented in Figure 4 the embankment construction timeline extended to over 3 years during the three main phases, fill construction, surcharge, and consolidation periods. All materials were compacted during the construction, attaining a density of 20
Settlement cells were installed under embankment crests, slope toes, and the embankment centerline. The settlement measurements were taken based on a hydraulic comparison between the fixed settlement cell (reference settlement cell) and the settlement cells under the embankment. The measurements were taken with regular time intervals of approximately 3 days during the embankment construction, and the interval increased to one measurement each week during consolidation. Similarly, the pore pressure was measured in parallel with settlement measurements for the four interstitial pressure sensors. The measurement is done using a pressure gauge placed on the surface and connected to the probe by a tube filled with incompressible liquid. In addition, the water level was checked continuously.
The calculated settlement based on standard constitutive models under the embankment at three locations, SC3, SC4, and SC5 (at the center, under the crest, and under the toe of the embankment, respectively) versus time is compared with the measured settlement and presented in Figure 6. As seen in Figure 6, there are some pronounced differences between the predicted settlement based on the soft soil model (SSM) versus the measured settlement. This is due to cumulative creep behavior that was captured when the soft soil creep model (SSCM) was included. As shown in Figure 6, during the embankment construction (between the 400-day mark and the end of settlement measurement), the SSM highly underestimated settlement versus when using SSCM (Figures 6A–C). Based on the comparison, the SSCM underestimated the settlement by an acceptable 12% under the embankment centerline and crest (Figures 6A, B) while underestimating the settlement by about 11% under the embankment toe. In contrast, the SSM underestimated the settlement with a significant 30% value compared to the measured settlement in all positions.
The settlement underestimation in the Sebou area, as presented by Mridakh et al. (2019), is due to the pronounced creep behavior in the alluvial deposits. For that, including a creep (time-dependent) component into the constitutive model is mandatory to tackle underestimated deformation, especially in the long term.
Figure 7 shows the predicted and the measured excess pore pressure (EPP) at a depth of 8 m. The predicted pore pressure based on SSM was larger than the measured one during the embankment construction phase (the first 400 days), which explains the main reason for good fit settlement immediately after the construction of the embankment, which is due to overestimation of the pore pressure build-up and dissipation rate when using SSM. The time-dependent model (SSCM) matched the measured EPP during the embankment construction. However, both SSM and SSCM underpredicted EPP during the consolidation process after the end of the embankment construction.
Based on the previous analysis, it is believed that Sebou alluvial deposits have an inherent time-dependent behavior that contributes to the EPP rate dissipation, especially in the long term. This inherent character can present some further deformation at a specific mean effective stress after the embankment construction. In addition, other mechanisms can be the cause for underestimating settlement and excess pore pressure.
Based on our interpretation, SSCM loses its advantage when used in over-consolidated soft soils by underpredicting the time-dependent behavior and underestimating the shear deformation for the first 3 m (L1), as presented in Figure 2 OCR. After a systematic evaluation of discrepancies in the predicted settlement and EPP, some points were raised and are summarized below:
• The permeability varies significantly between layers L3 and L4
• SSCM mostly predicts incorrect shear strains for a shear mobilization larger than
Based on these possible reasons for discrepancies, we pushed the numerical modeling analysis to explore a more advanced constitutive model, Creep-SCLAY1S.
Figure 8 shows settlement prediction versus time at SC3, SC4, and SC5; it is observed that settlement prediction by the Creep-SCLAY1S model matches well with the measured settlement. Although some higher rates of consolidation, as seen during the embankment construction period (first 400 days), can be due to the effect of stress concentration when using the critical state constitutive model, the model demonstrates a better capability of providing a precise simulation for higher number of layers with PVD treatment.
Due to the effect of stress concentration discussed previously, some slight variation in the predictions is seen in the long term (after the 400-day mark). Under the embankment centerline Figure 8A, a slight overestimation is observed of no more than 3% under the embankment crest (Figure 8B). In addition, the matching was nearly exact under the embankment toe (Figure 7C), and an underestimation of no more than 4% is measured.
Considering the plot of EPP prediction versus time in Figure 9, the predicted EPP when using the Creep-SCLAY1S model presented a rather high peak during the embankment construction (the first 400 days) while having an exact matching during the dissipation phase. After the construction phase, the Creep-SCLAY1S model presented a good match with the higher EPP measured in the field.
The Creep-SCLAY1S model showed a high-quality resemblance to the field behavior when including creep, destructuration, and fabric. Based on the results, both creep and destructuration mechanisms influenced the behavior of the Sebou deposits, especially in the long term. Those effects can only be captured simultaneously while including a constitutive model with a yield surface shape with a rotational component that can go higher than the
This paper details the prediction procedure and data selection for prefabricated vertical drain (PVD) improved soft alluvial soils. A case study of the high-speed railway embankment in Sebou, Morocco, was analyzed numerically using two standard constitutive models, the soft soil model (SSM) and the soft soil creep model (SSCM), alongside an advanced model, Creep-SCLAY1S, to address the challenge of underestimating soil deformation in the naturally compressible soft alluvial deposits in the Sebou area. Based on the results, several conclusions were drawn:
✓ Incorporating creep and destructuration effects into the prediction process is crucial for accurate long-term behavior predictions in the Sebou area.
✓ The Creep-SCLAY1S model reasonably matches the measured behavior in Sebou.
✓ The time-independent soft soil model (SSM) is inadequate for predicting the delayed soil response in Sebou alluvial deposits.
✓ The soft soil creep model (SSCM) is suitable only for normally consolidated layers for settlement predictions in Sebou but does not accurately capture the delayed peak in excess pore pressure (EPP) after embankment construction.
✓ Although parameter selection for the Creep-SCLAY1S model is time-consuming, reliable methods and sensitivity analysis can lead to a better understanding of complex behaviors, which is beneficial for research and practical engineering applications
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
AM: conceptualization, methodology, validation, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing. BN: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, validation, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing. HE: investigation, validation, and writing–review and editing. HL: investigation, validation, and writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The work presented was supported by the LPEE (Laboratoire Public d’Essais et d’Etudes). The first author would like to thank all personnel in the LPEE for providing all data necessary for the completion of this work.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Amavasai, A., Sivasithamparam, N., Dijkstra, J., and Karstunen, M. (2018). Consistent class A and C predictions of the Ballina test embankment. Comput. Geotech. 93, 75–86. doi:10.1016/j.compgeo.2017.05.025
Bagheri, M., and Rezania, M. (2021). Geological and geotechnical characteristics of London clay from the Isle of Sheppey. Geotechnical Geol. Eng. 39, 1701–1713. doi:10.1007/s10706-020-01572-3
Chai, J. C., Shen, S. L., Miura, N., and Bergado, D. T. (2001). Simple method of modeling PVD-improved subsoil. J. Geotech. Geoenviron Eng. 127 (11), 965–972. doi:10.1061/(asce)1090-0241(2001)127:11(965)
Cui, P., Fang, H., Wang, F., Cao, W., Zhang, X., Peng, B., et al. (2025). Nonlinear creep consolidation of vertical drain-improved soft ground with time-dependent permeable boundary under linearly construction load. Geotext. Geomembranes 53, 121–139. doi:10.1016/j.geotexmem.2024.09.001
Guglielmi, S., Cotechia, F., Cafaro, F., and Gens, A. (2024). Analysis of the micro to macro response of clays to compression. Geotechnique 74 (2), 134–154. doi:10.1680/jgeot.21.00233
Hashemi, H., Naeimifar, I., Uromeihy, A., and Yasrobi, S. (2015). Evaluation of rock nail wall performance in jointed rock using numerical method. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 33 (3), 593–607. doi:10.1007/s10706-015-9842-3
Hosseinpour, I., Almeida, M. S. S., Riccio, M., and Baroni, M. (2017). Strength and compressibility characteristics of a soft clay subjected to ground treatment. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 35 (3), 1051–1066. doi:10.1007/s10706-017-0161-8
Huang, J., and Griffiths, D. (2010). One-dimensional consolidation theories for layered soil and coupled and uncoupled solutions by the finite-element method. Géotechnique 60 (9), 709–713. doi:10.1680/geot.08.p.038
Indraratna, B., Baral, P., Rujikiatkamjorn, C., and Perera, D. (2018). Class A and C predictions for Ballina trial embankment with vertical drains using standard test data from industry and large diameter test specimens. Comput. Geotech. 93, 232–246. doi:10.1016/j.compgeo.2017.06.013
John, P. C. (2024). Constitutive modelling in computational geomechanics – 61st Rankine lecture, British Geotechnical Association, 2023. Géotechnique 74 (13), 1511–1535. doi:10.1680/jgeot.23.RL.001
Karstunen, M., Krenn, H., Wheeler, S. J., Koskinen, M., and Zentar, R. (2005). Effect of anisotropy and destructuration on the behavior of murro test embankment. Int. J. Geomech. 5 (2), 87–97. doi:10.1061/(asce)1532-3641(2005)5:2(87)
Kelly, R., Sloan, S., Pineda, J. A., Kouretzis, G., and Huang, J. (2018). Outcomes of the Newcastle symposium for the pre-diction of embankment behaviour on soft soil. Comput. Geotech. 93, 9–41. doi:10.1016/j.compgeo.2017.08.005
Koskinen, M., Karstunen, M., and Wheeler, S. J. (2002). “Modeling destructuration and anisotropy of a natural soft clay,” in Proc.of the 5th European conf. Numerical methods in geotechnical engineering.
Krenn, H. (2008). Numerical modelling of embankments on soft soils. Scotland: University of Strathclyde. Ph.D. thesis.
Leoni, M., Karstunen, M., and Vermeer, P. A. (2008). Anisotropic creep model for soft soils. Geotechnique 58 (3), 215–226. doi:10.1680/geot.2008.58.3.215
Mesri, G., and Godlewski, P. M. (1977). Time- and Stress Compressibility Interrelationship. J. Geotech. Engrg., ASCE 103 (5), 417–430.
Mridakh, A. H., Ejjaaouani, H., Nguyen, B. P., Lahlou, F., and Labied, H. (2022). Soft soil behavior under high-speed railway embankment loading using numerical modelling. Geotech. Geol. Engrg. 40 (5), 2751–2767. doi:10.1007/s10706-022-02059-z
Mridakh, A. H., Lahlou, F., Ejjaaouani, H., Mridekh, A., and Labied, H. (2019). Soil improvement of alluvial deposits under high-speed railway embankment: field case study. Geotech. Geol. Engrg. 37 (5), 3589–3603. doi:10.1007/s10706-019-00855-8
Neher, H. P., Wehnert, M., and Bonnier, P. G. (2001). “An evaluation of soft soil models based on trial embankment,” in Proceedings of 10th international conference on computer methods and advances in geomechanics (Tucson), 373–378.
NF P94-051 (1993). Sols: reconnaissance et essais- Détermination des limites d-atterberg – Limite de liquidité à la coupelle – Limite de plasticité au rouleau-Normes nationales et documents normatifs nationaux, 1–15.
NF P94-071-1&2 (1993). Sols: reconnaissance et essais – Essai de cisaillement rectiligne à la boite – Partie 1: cisaillement direct – Normes nationales et documents normatifs nationaux, 1–16.
NF P94-074 (1994). sols: reconnaissance et essais – Essai de cisaillement rectiligne à la boite – Partie 1/cisaillement direct – Normes nationales et documents normatifs nationaux, 1–36.
Nguyen, B. P., Do, T. H., and Kim, Y. T. (2020). Large strain analysis of vertical drain-improved soft deposit consolidation considering smear zone, well resistance, and creep effects. Comput. qnd Geotech. 13c, 103602. doi:10.1016/j.compgeo.2020.103602
Nguyen, B. P., Nguyen, T. T., and Mridakh, A. H. (2022a). Consolidation and load transfer characteristics of soft ground improved by combined PVD-SC column method considering finite discharge capacity of PVD’s. Indian geotech. J53, 127–138. doi:10.1007/s40098-022-00668-2
Nguyen, B. P., Nguyen, T. T., Nguyen, T., and Guo, W. (2023). Analytical model for consolidation and bearing capacity of soft soil stabilized by combined PVD-deep cement mixing columns. Bull. Eng. Geo. Environ. J82, 286. doi:10.1007/s10064-023-03287-0
Nguyen, B. P., Nguyen, T.-T., Nguyen, T. H. Y., and Tran, T.-D. (2022b). Performance of composite PVD–SC column foundation under embankment through plane-strain numerical analysis. Int. J. Geomechanics 22 (9), 04022155. doi:10.1061/(asce)gm.1943-5622.0002494
Nguyen, T. T., and Indraratna, B. (2017). Experimental and numerical investigations into hydraulic behaviour of coir fibre drain. Can. Geotechnical J. 54 (1), 75–87. doi:10.1139/cgj-2016-0182
Nguyen, T. T., and Indraratna, B. (2020). A coupled CFD–DEM approach to examine the hydraulic critical state of soil under increasing hydraulic gradient. ASCE-International J. Geomechanics 20 (9), 04020138. doi:10.1061/(asce)gm.1943-5622.0001782
Nguyen, T. T., Indraratna, B., and Rujikiatkamjorn, C. (2018). A numerical approach to modelling biodegradable vertical drains. Environ. Geotech., 1–9. doi:10.1680/jenge.18.00015
Rezania, M., Bagheri, M., Nezhad, M. M., and Sivasithamparam, N. (2017). Creep analysis of an earth embankment on soft soil deposit with and without PVD improvement. Geotext. Geomemb 45, 537–547. doi:10.1016/j.geotexmem.2017.07.004
Silva, I. N., Indraratna, B., Nguyen, T. T., and Rujikiatkamjorn, C. (2024). The influence of soil fabric on the monotonic and cyclic shear behaviour of consolidated and compacted specimens. Can. Geotech. J. 61, 1159–1176. doi:10.1139/cgj-2023-0141
Sivasithamparam, N., Karstunen, M., and Bonnier, P. (2015). Modelling creep behaviour of anisotropic soft soils. Comput. Geotech. 69, 46–57. doi:10.1016/j.compgeo.2015.04.015
Taechakumthorn, C., and Rowe, R. K. (2012). Performance of a reinforced embankment on a sensitive Champlain clay deposit. Can. Geotech. J. 49, 917–927. doi:10.1139/t2012-053
Vermeer, P. A., and Neher, H. P. (1999). “A soft soil model that accounts for creep,” in Beyound 2000 in computational geotechnics. Ten years of plaxis international balkema (Amsterdam), 249–261.
Wheeler, S. J., Naatanen, A., Karstunen, M., and Lojander, M. (2003). An anisotropic elastoplastic model for soft clays. Can. Geotech. J. 40, 403–418. doi:10.1139/t02-119
XP-94-090-1 (1997). sols: reconnaissance et essais – Essai oedométrique – Partie 1: essai de compressibilité sur matériaux fins quasi saturés avec chargement par paliers – Normes nationales et documents normatifs nationaux, 1–23.
Yildiz, A. (2009). Numerical analyses of embankments on PVD improved soft clays. Adv. Eng. Softw. 40 (10), 1047–1055. doi:10.1016/j.advengsoft.2009.03.011
Yildiz, A., Karstunen, M., and Krenn, H. (2009). Effect of anisotropy and destructuration on behavior of Haarajoki test embankment. Int. J. Geomechanics 9 (4), 153–168. doi:10.1061/(asce)1532-3641(2009)9:4(153)
M stress ratio at critical state
e void ratio
k* modified slope of swelling/recompression line from the e _ lnp0 diagram
NCS normal consolidation surface
k permeability
D equivalent diameter of unit cell
R equivalent radius of the unit cell
S drain spacing
Keywords: embankment, soft soil, deformation, vertical drains, creep, numerical analysis
Citation: Mridakh AH, Nguyen BP, Ejjaaouani H and Labied H (2025) Numerical analysis of time-dependent behavior of an embankment on PVD-installed Sebou soft soils. Front. Built Environ. 11:1523557. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2025.1523557
Received: 06 November 2024; Accepted: 17 January 2025;
Published: 17 February 2025.
Edited by:
Hoang Bao Khoi Nguyen, University of South Australia, AustraliaReviewed by:
Thanh Nguyen, University of Technology Sydney, AustraliaCopyright © 2025 Mridakh, Nguyen, Ejjaaouani and Labied. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: A. H. Mridakh, bXJpZGFraEBlbmltLmFjLm1h; B. P. Nguyen, bmd1eWVuYmFwaHVAaXVoLmVkdS52bg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.