
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Built Environ., 11 March 2025
Sec. Sustainable Design and Construction
Volume 11 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fbuil.2025.1469398
This article is part of the Research TopicIntegrated Infrastructure Sustainability Assessment and ReportingView all 3 articles
With commercial refurbishment projects being identified as large contributors to landfill waste in the United Kingdom (United Kingdom), the aim of this paper is to identify effective Sustainable Waste Management strategies that could be implemented by Small and Medium-sized Enterprise (SME) construction businesses, specifically within the commercial refurbishment sector. The study adopted a mixed method approach engaging industry professionals working within SMEs through both questionnaires and interviews. Findings showed that although SME businesses aspire to make improvements, the construction industry is not making clients and consultants equally accountable. However, some of the most effective tactics that could be employed were low cost and easy to implement but it seems that some SME businesses are still averse to them for mostly economic reasons suggesting for better enlightenment of collaborative procurement routes, implementing sustainability regulations and comprehensive engagement of SMEs by industry authorities; substantial improvements can be made in the realm of sustainable waste management.
Commercial sector projects account for approximately one-third of the United Kingdom construction industry, with 50% of these being refurbishments or building improvements (Office for National Statistics, 2021; Great Britain. Efficiency and Reform Group, 2011). This suggests that roughly one-sixth of United Kingdom construction schemes are refurbishments in the commercial sector. Reasons for the high proportion of refurbishment projects range from the commercial benefits of refreshing over redeveloping, demolition restrictions of heritage listings, or alleviating the carbon footprint of demolition and rebuilding (Cohen et al., 2021; Ramos et al., 2019; Burton, 2001).
Commercial refurbishment is believed to generate immense waste due to increased short-term leases and diverse building uses, with large swathes of waste going to landfill, even though approximately 90% is recyclable (Hardie et al., 2006). There is a consensus amongst academics and industry professionals that refurbishment project waste is generated in greater quantities, on a given floor area, than it is on new build sites (Shah, 2012). Additionally, there is an argument that although better management standards and processes have been introduced, such as Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Methods (BREEAM) and Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) assessment frameworks, best practice in waste management and recycling tends to be executed by larger contractors, whilst Small Medium Enterprises (SMEs) are less financially and technically equipped to apply such measures (Sezer, 2017).
A small and medium-sized enterprise (SME) in the United Kingdom is an organization that has fewer than 250 employees and a turnover of less than £50 million or a balance sheet totalling less than £43 million (Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office, 2022). In 2018, the United Kingdom government outlined a strategy aimed at eliminating avoidable waste of all kinds by 2050, identifying construction as one of five key areas requiring improvement (DEFRA, 2018). Given that SMEs make up around 99% of construction businesses in the United Kingdom (Designing Buildings Ltd, 2021), it is safe to conclude that their proportion of waste contributions would be substantial, even if their processes were in line with more scrutinised Tier 1 companies. There is an argument that SMEs are often disregarded when it comes to environmental policy awareness, being even further less engaged regarding financing and implementing sustainable strategies (Revell and Blackburn, 2007). This is reinforced by the fact that research and guidance are often focused on larger organizations. Thus, there is a huge disparity between high level aims in construction waste reduction and their attempts to engage the largest part of the industry in attaining them.
As regards sustainable waste management strategies, and their implementation to achieve zero avoidable waste, there is limited guidance for SMEs in terms of practical application and commercial benefits; the latter being a documented barrier for SMEs that view improved environmental processes as too expensive to employ, with little-to-no financial gain (Revell and Blackburn, 2007). In addition, industry guidance tends to offer a broad approach to construction projects in general, without addressing the specific challenges refurbishment schemes face, such as restricted working space or previously undiscovered defects (Sezer, 2017).
Consequently, whilst smaller companies on renovation projects experience waste management inefficiency, there appears to be no targeted guidance to address these issues. This paper will attempt to piece together the silo topics of waste, refurbishment, and SME construction operations to recommend attainable measures that provoke more ambitious sustainability goals. Yuan and Shen (2011) and Sezer and Bosch-Sijtsema (2022), have highlighted that most waste management research and guidance is focused on the new build residential sector. To this end, there seems to be a demonstrable lack of information that relates to refurbishment projects in the commercial sector specifically built by SMEs.
Therefore, by critically examining the existing literature around waste management relating to refurbishment projects, the commercial sector, or SMEs, as well as engaging with construction managers specifically within this field, this paper will attempt to address this research gap and stimulate greater academic and industry focus on Sustainable Waste Management Practices. This paper aims to identify the most impactful actions SME construction refurbishment businesses can take to enhance the sustainability credentials of projects, through efficient waste management. The paper will evaluate opportunities for waste management improvement and identify key processes SMEs could implement, highlighting their benefits. Additionally, as industry adoption of digital construction methods rises, SME adoption of them remains low. The paper would explore the opportunities and potentials of digital construction tools in waste reduction both physically and administratively as documented in Vidalakis et al. (2020). The intention is not to provide a one-size-fits-all action plan that identifies all areas of betterment in this field, but to stimulate the conversation of how smaller constructors can employ greener waste management strategies to decrease the industry’s 5 million tonnes of site waste that goes to landfill annually, as reported in Adam and Thornback (2022).
Collective global scientific bodies and governments worldwide are increasingly raising awareness of a climate emergency, with the UN Secretary-General now stating that the earth is losing its battle to keep global warming below the 1.5°C target approved at the Paris Agreement (United Nations, 2023). With the global population rapidly on the rise, the generation of waste is increasing in conjunction to alarming levels; much of which is finding its way to landfill or being discarded openly (COP27 2022). Building activity is increasing in line with population growth creating an escalation of Construction, Renovation, and Demolition (CRD) wastes to unprecedented levels, whilst room for landfill disposal becomes increasingly scarce (Chen et al., 2022). Globally, waste contributes 20% of all methane generation, as well as black carbon and numerous other harmful pollutants that contaminate land and water sources (COP27 2022). UNEP (2015) advised that greenhouse emissions could be reduced by 10%–15% through improved waste management strategies such as recycling, reuse, mitigation and diversion. This figure could be pushed closer to 20% with waste prevention tactics.
Baldwin and Bordoli (2014) defined construction waste as a material generated due to damage, or non-use or as a by-product of the construction process that needs to be either discarded off-site or recycled and reused on-site. It represents a significant amount of industrial waste going to landfill (Newaz et al., 2022). Besides, construction waste has become a great challenge towards achieving sustainability as it results in environmental degradation (Gupta et al., 2022). When the United Kingdom government set out the intention to do away with avoidable waste of all kinds by 2050 (DEFRA, 2018), it highlighted construction as one of the key contributors. The Green Construction Board (2020) aimed to define a route map for how the United Kingdom industry might achieve this, but the report appears not to provide a definition of ‘avoidable waste’ in construction, recognising it to be highly subjective and open to challenge. Figure 1 shows that approximately 5 million tonnes of Construction and Demolition (C&D) waste ended in landfill, in the United Kingdom alone in 2018.
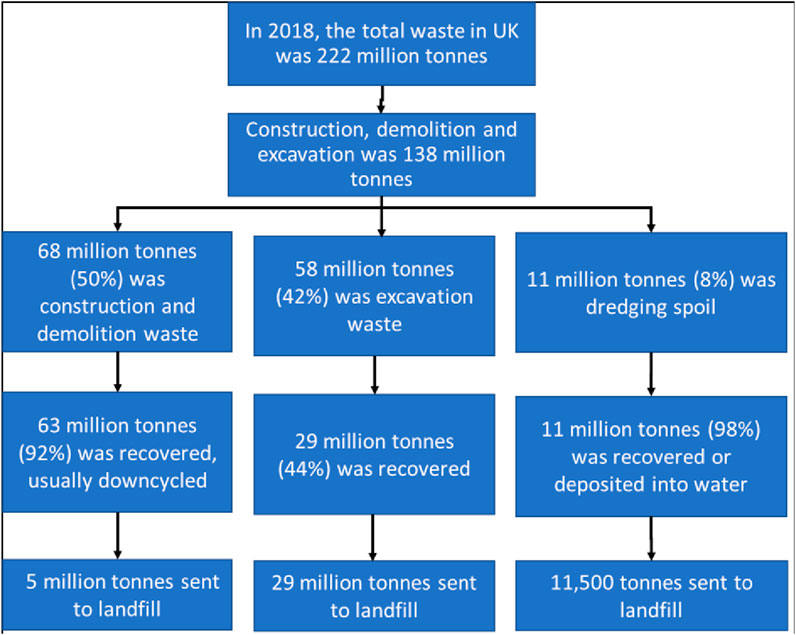
Figure 1. Breakdown of United Kingdom construction waste and its destination. source (Adam and Thornback, 2022, p. 3).
Besides this substantial figure, it is noteworthy that approximately 10% of this; circa 500,000 tonnes; was lost, damaged or over-ordered materials that arrived on site but were disposed of without use (Green Construction Board, 2020).
Although Weber (1997) noted that industry players were demonstrating a desire to improve and implement sustainable construction practices, there appears to be no significant change nearly three decades after, which raises questions about the large waste from C and D still ending up in landfill sites. Table 1 underlines this question, showing a yearly C and D waste increase of almost 1 million tonnes, with the recycling rate rising by less than 0.5% per year. With waste production growing faster than recycling rates it shows a consistent average of 5 m–6 m tonnes of construction waste still going to landfill every year, with no trend of improvement. The United Kingdom construction industry itself acknowledges that there is “very little information” on SME contribution to these waste statistics, whilst there is “no data” on waste generation and management related specifically to refurbishment projects; going further to underline the suggestion that there is insufficient guidance for SMEs on this subject (Green Construction Board, 2021). Therefore, it is important that whilst suggesting strategies for improvement to SME Commercial Refurbishment businesses; the United Kingdom government and industry bodies must go to greater lengths to better understand the sector to impact how it improves waste management.
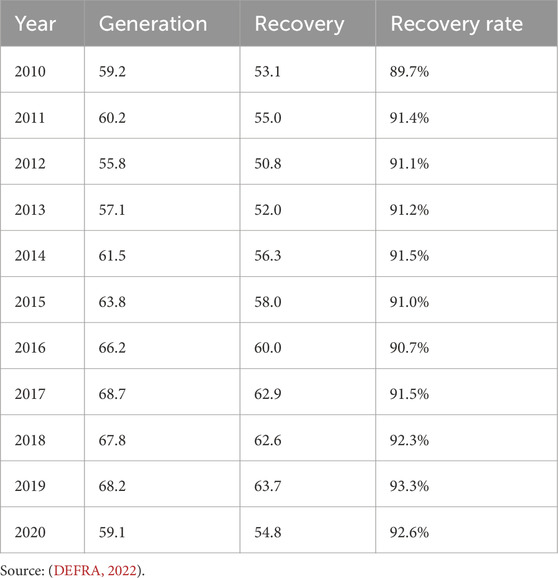
Table 1. United Kingdom construction and demolition waste generation and recycling/recovery quantities (million tonnes), with recycling rate as a percentage.
Holmes and Osmani (2014) noted that waste is attributed to poor design or neglect of a site waste management plan (SWMP) being implemented during preconstruction. Too often SWMPs are only considered to be relevant from the point of mobilisation on site when the best way to alleviate and deal with waste would be to heavily minimise the chances of its creation at the design stage (Ajayi, 2017). Price (2010) support this by proposing that designers have the greatest impact on increasing recyclability as they are the ones with the power to specify materials with a cyclical lifespan in the first place.
Sezer and Bosch-Sijtsema (2022) argued how the choice of procurement route can additionally have a major influence on waste generation during a project’s production phase. Traditional procurement routes lead to late contractor involvement and consultation, which negates the benefits that could be gained from leaning on their expertise from the outset, as would be possible in a Design and Build scenario. If SME refurbishment companies were to take an integrated holistic approach to sustainable design, as submitted by Edwards et al. (2019), they would have the opportunity to reduce waste from demolition, plan for recycling and reuse; as well as limit resource consumption through the exploration of off-site component manufacture. This can all be a cost benefit to a contractor as putting such consideration in at the front end, will reduce the costs of planning and enacting waste management logistics reactively on site (Ajayi, 2017).
Regardless of the size and profile of a construction business, and perceived access to guidance on best practices, there is a ‘duty of care’ to remove, transport and dispose of construction waste safely and responsibly (CITB, 2019). Improving the waste management policies could result in an opportunity to ensure that all team members are working to the same standard and expectations, which positively impacts teamwork with proven evidence to reduce waste creation (Baldwin and Bordoli, 2014).
Furthermore, writing and implementation of waste management strategies should not solely be the responsibility of the principal contractor or developer, it should be a collaborative approach that draws the participation of designers, subcontractors, and manufacturers in tandem to offer the best solutions for alleviating and managing waste.
In 2004, the United Kingdom government initiated SWMPs as a voluntary code of practice, aiming to stop waste to landfill and promote recycling and reuse, becoming mandatory for projects over £300,000 in 2008 (Baldwin and Bordoli, 2014). However, not only was this not broadly relatable to SMEs given many of their projects fall below this value, rendering them not compulsory (Lou et al., 2012), but DEFRA (2013) repealed the SWMP requirement as part of a government exercise to cut red tape legislation and allow businesses to operate more freely.
However, the CITB (2019) noted that more than 60% of businesses use SWMPs, valuing their assistance in executing their environmental policies, whilst acting as an instrument to find opportunities for cost-savings and material innovation. The SWMP becomes a project-wide strategy for identifying types and quantities of waste to be removed, disposed of, recycled, or reused. Baldwin and Bordoli (2014) recommended the plan be consistently updated for every stage of the project and impressed upon the site team through toolbox talks, specifically for refurbishment schemes where the nature of waste created will evolve with the project.
Edwards et al. (2019) discussed the suitability of employing an Environmental Assessment Method (EAM), such as BREEAM or LEED, where construction companies can work towards a points-based accreditation for the achievement of pre-determined sustainability goals on their project. According to BRE (2011), this approach is a useful way of getting client buy-in to support sustainability goals and thus sharing the risk on cost. However, Edwards et al. (2019) argued that these accreditations are not infallible, and the results or calculations of accreditation can be ambiguous, either down to mismeasuring parameters or variation of interpretation by the assessors. On the other hand, Ajayi (2017) suggested that some companies complete the paperwork (e.g., a SWMP) to get the assessment points but do not actually put them into practice. However, Edwards et al. (2019) posited that it is better to be setting some form of targets to improve waste management strategies than to set none.
The Green Construction Board (GCB) in a report recognised the crucial role of new technologies to deliver a more resourceful and less wasteful industry (Green Construction Board, 2020). Suggesting missing as-built drawings and material specification as a key barrier to better waste management planning in preconstruction, Okakpu et al. (2022) and Edwards et al. (2019) explore the feasibility of Building Information Modeling (BIM) and how digitally modelling an existing building, whilst applying the fabric data to it, would allow better planning of strip-out, recycling and reuse. Cheng and Ma (2013) promoted Quantitative Waste Prediction (QWP) as a concept, which requires a lot of work at the front end to physically survey the building fabric to effectively inform the BIM model data of the exact as-built information. Sawney et al. (2020) acknowledged that labour-intensive manual identification of existing building materials impacts time and cost, suggesting this can be sold to the client as a benefit for them. The smaller nature of SME project sizes would make this a less costly and laborious process so far they have the BIM capability in the first place. However, Edwards et al. (2019) raised a concern that BIM is still predominantly focussed on time-cost quality with more room to expand on its sustainable design possibilities.
Given the aim of this paper in identifying effective strategies SME commercial refurbishment businesses can employ, to set and achieve higher sustainable waste management goals, the pragmatism philosophical stance which allowed an exploration of the subject within its own context was adopted (Scott, 2016). The study employed the abductive approach (Roehrich and Lewis, 2014; Bukoye et al., 2022) analysing findings inductively and deductively. This was followed by a mixed-method strategy as further elaborated by Creswell and Plano Clark (2011). Using questionnaires (Denscombe, 2007), and interviews (Strauss and Corbin, 1998), data collection was directed toward organizations that match the criteria for SMEs.
Through purposive sampling, the potential list of participants for the questionnaire was drawn up firstly by identifying businesses that fit the criteria–namely, commercial refurbishment businesses. 65 construction businesses that fit the criteria (who were SME contractors with commercial refurbishment project in their portfolio) were approached to act as a voice for their respective businesses. 25 acceptable responses were received (giving a response rate of 38%). Each of the respondents worked within a management role. The characteristics of the respondents is presented in Figures 2–4.
As observed in Figure 2, there was an even spread of respondents from different size SMEs. Figure 3 shows a heavy weighting of construction workers more than 15 years’ experience, which is likely due both to the fact that experienced Managers were mostly sought to respond; as well as potentially reinforcing general industry fears of an ageing workforce, as discussed in the literature review. Additionally, the greater proportion of respondents worked either within Construction Management or Commercial roles, with just two in technical roles, offering a likely more holistic view toward sustainable waste management across preconstruction, commercial, operational, and post-completion activities.
On the other hand, the criteria for the interviewees were more specific to sufficiently provide qualitative support for the quantitative data from the questionnaire. The study sought built environment professionals who meet any of these three criteria:
(i) A construction sustainability expert with over 15 years of experience who could offer a perspective of SWMS from the client and design team view viewpoint. This length of experience was deemed to be sufficient for prospective participants to be able to share perceptions from practice from when major agenda for sustainability such as the SDGs were not in place to when they are now in operation. Several construction-related studies have adopted the same criteria of 15–20 years of work experience for interviewees. These include Agyekum-Mensah and Knight (2017); Tezel et al. (2021); and Too et al. (2023). In fact, some studies engaged a selected number of participants for interviews based on the high level of expertise required. For instance, Too et al. (2022) engaged 7 building professionals with high proficiency in construction project most especially in delivering carbon neutral and net zero developments.
(ii) Medium size business construction manager focusing on companies that demonstrated economic growth in recent years and thus were more likely to have improved their process in relation to SWMS.
(iii) Tier 1 Business Construction Manager to offer a comparison of SWMS within businesses at the forefront of the industry, in contrast to SMEs, and to offer opinions on practices they undertake that could be practically transferrable.
In all, three prospective interviewees who met the criteria were identified from the respondents of the questionnaire survey to represent their respective construction businesses. In terms of profile, interviewee 1 is the sustainability lead for AJ Top 100 SME Architectural Practice with 15 years of industry experience; interviewee 2 is a Chartered Construction Manager with 19 years of industry experience, working for a SME Refurbishment contractor with 10–50 employees; and interviewee 3 is a Chartered Senior Project Manager with 30+ years’ industry experience, working for London Construction division of Nationwide Tier 1 Contractor.
The surveys were conducted online by circulating an internet link to prospective participants. It was presumed that the ease of accessing and completing the survey in this manner would likely gain greater traction than sending out a hard copy for completion. One of the interviews was conducted face-to-face as demonstrated in Roehrich and Lewis (2014), whilst the other two interviews were conducted over MS Teams due to time constraints. The average duration of the interviews is about 1 h.
To this end, the unit of analysis (Judd and Kenny, 2024) for the study is the sustainability aspect of a waste management strategy in small and medium-sized enterprise involved in commercial refurbishment in the United Kingdom. The analysis was underpinned by sustainability criteria applied to data from both the questionnaires and the interviews (following a critical review of literature) which act as the unit of observation. This facilitated the identification of relatively appropriate strategies that could enhance waste management practice in the context of the study.
Additionally, by using a process of ‘triangulation’, a combined analysis of the Literature Review, Qualitative research and Quantitative data in tandem, deeper insights and points for discussion were drawn and developed upon; shown in Figure 5.
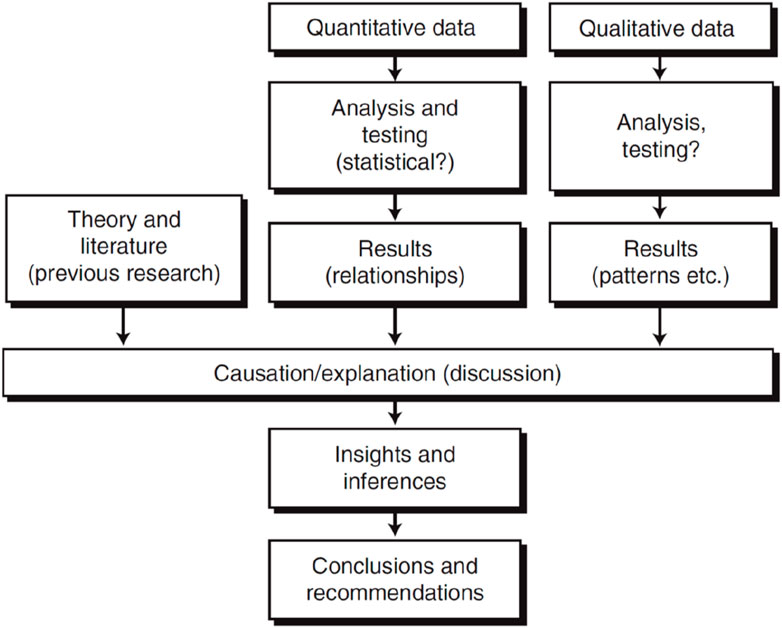
Figure 5. Triangulation of quantitative and qualitative data Source (Fellows and Liu, 2015, p. 10).
Lastly, ethics approval was sought prior to the data collection phase of the study from the Faculty of Engineering and Science Research Ethics Committee (FREC) at the University of Greenwich, which received approval with reference number: FES-FREC-22–04.04.05.
40% of respondents noted that their companies either “rarely” or “never” considered waste reduction as a priority during preconstruction, whilst another 40% answered positively that their companies “usually” or “always” consider it. Notably, 68% of respondents agreed that procurement routes offering early contractor involvement would be “fairly” or “very” important in reducing waste whilst the project is still in design, with only 16% still regarding it as “slightly Important” at the very least. Holistic waste management strategy design across all parties was deemed at the very least as “important” to all respondents, highlighting a desire that the client, design team and whole supply chain be held accountable–rather than just the main contractor, as is the current norm.
Reviewing responses to other further questions as presented in Figures 6, 7 below, an argument can be made that not enough businesses employ a SWMP as standard, whilst over a third of respondents stated that their companies do not review amounts of waste generated during project de-briefs. This shows that planning for and improving waste management is not being considered by a substantial proportion of SMEs both at project inception and completion.
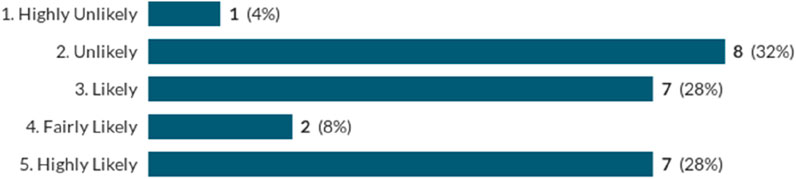
Figure 7. Likelihood that the volume of waste generated on a project, and its destination, considered as part of respondents’ company’s post-project de-brief.
The interview respondents were unanimous that clients should be setting sustainability goals and be truly investing in them. Interviewee 3 underlined that waste management should have a higher profile on a project’s sustainability charter, with it currently too often overlooked against the attractive elements of sustainable construction, such as photovoltaics and heat pumps. Interviewee 1 suggested mandating pre-demolition audits to identify what is readily available for reuse or recycling.
Interviewees 1 and 3 both agreed that sustainable waste management would be most effective when picked up at RIBA Stage 3 or earlier. Addressing this any later limits the impact of the contractor because any changes would not have been allowed for in the tender price. For instance, interviewee 3 noted that:
“The real key to integrating sustainable practices into a project, especially identifying areas of recycling and reuse is to pick them up at Stage 3 Design. This allows the opportunity to factor in pre-manufactured components to come to site ready-made and ideally negate any waste creation that would arise if they had to be made/joined on site”
Interviewee 1 went ahead to note that picking SWM up at this stage not only ensures that the client and contractor are aligned, but it allows the opportunity to factor in pre-manufactured components to come to the site ready-made and ideally negate any waste creation from manufacturing or joining components on site. Interviewee 1 submitted that:
“We rarely go beyond mandating waste reduction targets at design stage and insist on them being inserted within the project ‘charter’. Primarily right now we look more at what existing assets are available on site that could either be reused in their constituent form or recycled into a new product for use on site”
Interviewee 1 added that collaborative contracts provided an opportunity for contractors to engage earlier with the design team and provide insight that may achieve greater efficiency. This would also have the benefit of reducing the adversarial blame game that comes with traditional contracting.
Moreover, Interviewee 3 made the case that larger contractors and projects have an advantage in that they often undergo a 2-stage tender, allowing the opportunity to tackle the client’s sustainability requirements before or at RIBA Stage 3. However, they did recognize that 2-stage tenders are very rare for SMEs on smaller projects; with the likelihood they work for lump sums. This makes it difficult for contractors to allow for unexpected types or quantities of waste. This would be further compounded if not deemed necessary within the Employers Requirements.
Just over half of the participants have worked on projects that employed a sustainability certification, the vast majority having used BREEAM, which was mentioned 13 times, with other certifications being named no more than thrice. However, in response to the impact of digital tools on sustainable waste management, the response was muted with the majority of those that have used them suggesting their impact was positive to “some extent”, and only 8% judging it to be any higher. The result shows that the uptake of digital construction tools within SME contractors was very low, with only 28% of companies surveyed having used them. There was a great disparity between the different types of tools used, with none mentioned more than once. This suggests that not only its uptake is still very low with SMEs, but that there is currently no universally appreciated digital method for quantifying or managing waste on refurbishment projects.
Discussing the various waste management certifications, interviewees indicated that such schemes are client-led. As such the extent of success of waste management is generally determined before the contractor is even engaged. Interviewee 3 noted that the ability to amend the weighting of certification credits leaves them open to manipulation They can allow contractors to focus on sustainable practices they are most confident in adopting, whilst leaving accreditation for those they are less familiar or competent in leading to the schemes becoming a box-ticking exercise. Interviewee 3 submitted that:
“These are sadly a tick-box exercise, as the weighting of credits can be manipulated to allow contractors to aim toward the easily achievable targets. That said it is better to be working to some standard rather than none”.
As regards compliance to assessment frameworks, interviewee 1 went further to suggest that the schemes are more focused towards carbon output of completed projects. The participant noted that:
“These schemes have always focused on operational energy associated with new build projects. But embodied carbon in construction can form up to 50% of a building lifetime carbon emission, so there is a huge need for these rating systems to shift their focus to better reflect the impact available in construction phase”.
Nevertheless, both interviewees 1 and 3 agreed that without these systems, the industry would be far less advanced, and that it is better to be working toward some sustainability standard, rather than none. Interviewee 2 stated that their business had not had a client that would take up one of these schemes, due to cost, so could not pass any comment on their effectiveness.
By ranking five major barriers to SME SWMS Implementation, and adding the points for each element, there is no clear leading high barrier among those surveyed. The result shows that lack of resources as well as knowledge and innovation are the highest perceived barriers whilst organizational buy-in was the lowest perceived barrier as presented in Figure 8.
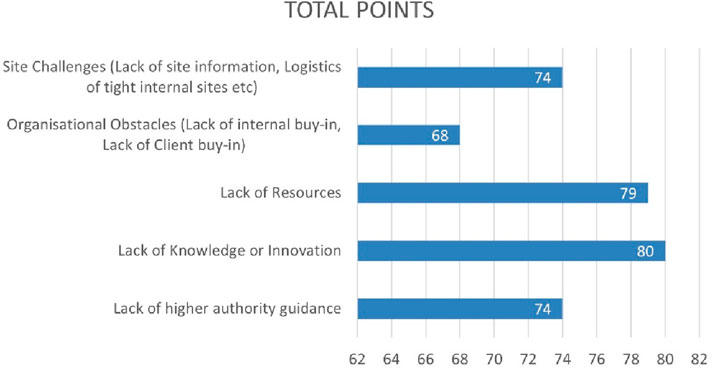
Figure 8. Total Ranking of barriers to sustainable waste management implementation on refurbishment projects? (1 point for low up to five for high).
In contrast with the survey findings, all three interviewees noted client attitudes or drivers as one of their biggest perceived barriers, which is at odds with the low ranking of organisational obstacles from the survey. Interviewee 2 raised site challenges as a barrier. Notably, their argument was focused on local authority obstacles involved in small refurbishment projects; raising the restriction of bay suspensions and skip permits as well as charging huge amounts of money to bring welfare onto pavements to enable more space for waste management and separation.
Almost two-thirds of those surveyed said that the target of zero avoidable waste by 2050 is not practically achievable, with lack of investment mentioned most as the driving factor. This was closely followed by the practicality of implementation and a poor industry attitude towards improvement. Amongst the 36% who thought it was achievable, most suggested improvements in company culture and attitude, as well as a proactive stance from the government and industry organizations as the way forward to attain the goal.
Interviewees 1 and 2 stated that they have not heard of any initiatives to engage SMEs, whilst interviewee 3 said that:
“The problem is even when there is guidance or engagement, it’s always top-level information without engaging those at grass roots level. Where we all fall down is that there’s all this documentation, but we don’t have the time and inclination to manage it on site. Bodies and even those in the office within our companies need to be proactive and engaging with those on site rather than issuing overcomplicated documents … keep it simple”
When asked to suggest two types of support that would be most effective for SMEs to improve their SWMS, new legislation, and waste reduction contract clauses were selected thirteen and twelve times respectively, with the next closest being finance selected nine times as shown in Figure 9.
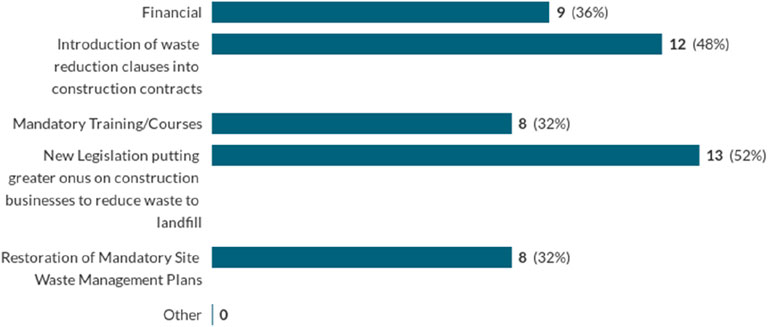
Figure 9. Options of higher authority support that would be most beneficial to SMEs to implement better sustainable waste management strategies (Each respondent had to pick two).
Interviewee 3 elaborated on this by suggesting that it should become mandatory for sites and companies to report their waste such as the type, how much and the destination. It was suggested that the client should, as an obligation outline their sustainability goals and requirements as a separate environmental specification within the tender pack. Interviewee 2 echoed the thought of client’s responsibility by noting that:
“Make the clients liable. But more so, there needs to be a massive improvement in interaction with builders and clients at all levels so that we’re actually educated in what’s expected and what is possible to achieve – especially the wins that don’t cost much that we’re just not aware of”
Interviewee 1 underlined that the effort needs to extend beyond construction companies and into the broader discussion with all stakeholders in the built environment, stating there are wasteful practices evident everywhere resulting in physical waste generation”.
Almost 75% of those surveyed either disagreed or were indifferent to the logistical challenges of small refurbishment sites being a major barrier to sustainable waste management, with nearly one-quarter strongly disagreeing. This contrasts with much of the available literature. The results suggest that the nature of the site should not impede waste separation and recycling, whilst, in fact, it is more likely that better logistical design and planning should alleviate or at least lessen the site’s impact.
A noteworthy finding is that a vast majority of the respondents support restoring mandatory site waste management plans, albeit with templates relevant to specific types of projects. This is particularly remarkable given that over half of the respondents were working in the industry when SWMP was abolished in 2013, due to a “red-tape reduction exercise”. Nonetheless, the respondents have a belief that they would have a positive impact on waste reduction and avoidance.
Interviewee 1 agreed that restoring SWMPs would be a positive step to take. Corroborating this, Interviewee 2 noted that:
“This would have a big impact; it would make clients and local authorities to more proactive and accommodating in this field”
Interviewee 3 asserted that the industry needs to go further than that by stating that:
“There needs to be legislation that makes clients more responsible for ensuring they are fully briefed on sustainable principles – make it their responsibility in the same way CDM regulations when it comes to Health and Safety”.
All respondents felt their employers held SWM to some degree of importance. Of note, there is a near-perfect four-way split between the levels of importance it is held at as presented in Figure 10.
What makes these results even more intriguing is that when cross-tabulated against the size of the organization respondents worked for, there is an evident trend that the degree of importance of sustainable waste management increases with the size of the company as shown in Figure 11 below:
When delving into how much the resources of SMEs affect their employment of SWM practices the respondents were split, with just over half believing it was the key underlying factor.
Figure 12 shows participants’ interpretations of their clients’ perspectives on sustainability. Surprisingly, whilst a significant majority stated their clients held environmental concerns to differing levels of importance, as high as 20% thought that is what was “not at all important” to their clients.

Figure 12. How important has setting and achieving sustainability goals been to clients you have worked with on commercial refurbishment projects?
This theme of clients’ attitudes towards sustainability in general was underlined by Interviewee 3, who stated that even local authority clients who have a high level of social responsibility, do not give any stipulations or incentivization for promoting sustainable criteria or setting goals for the reduction of waste to landfill.
Interviewee 2 has a similar opinion that whilst they undergo multi-million-pound projects for well-funded clients, they do not even bring sustainable practices to the table from the very outset at Invitation to Tender and thus it is never a consideration when the project is priced. Additionally, Interviewee 1 noted that:
“Usually clients and colleagues have the best intentions when defining the sustainability strategy until the conversation comes to cost, then all of a sudden it becomes one of the lowest priorities. Designers I work with are just as guilty as they’ll often promote aesthetics over performance and substance, which is concerning given the environmental emergency, which is impossible to ignore”
The results show that 52% agreed that laser scanning and modelling existing sites would improve the quantification and management of refurbishment waste. However, the impact on time taken to do this coupled with the small size of the projects make it far less likely for SMEs to implement.
Interviewee 1 stated that:
“Proficiency is the largest barrier, particularly amongst smaller companies. This is not only a barrier of knowledge, but also of cost. Many mainstream digital tools with the compatibility necessary often cost a prohibitive amount and this can limit adoption amongst smaller SMEs”.
Interviewee 2 noted that:
“It’s a perfect storm, there are so many barriers. Where do you even start for looking for IT tools and how to learn and put them into practice? It takes so much time and usually we’re all already wearing more than one hat, so unless you employ someone specifically and ca afford the time for the business to slow down whilst they learn, it’s just no practical. Everyone has different IT capacity personally and it can be hard to learn and remember to keep using new processes, especially those that are longer in the tooth!”
The vast majority of responses alluded to aspects of improving company culture or attitudes, with suggestions such as “outline the waste management strategies as pre-start meetings and at tool-box talks throughout the project”, “Having sustainability champions that can focus on these strategies with full management support”, and; “put time and effort into the Site Waste Management Strategy and make it project specific, don’t just treat it as a box-checking exercise.”
Based on the results, there is a clear argument that employing collaborative procurement routes would improve sustainable waste management. This agrees with points made regarding “designing out waste” in the literature review, and the consensus of survey participants who rated early contractor involvement in the design process as “slightly important” or higher. Additionally, all three interviewees agreed that waste management needs to be addressed in preconstruction to have any chance of being successful at all, ideally captured at RIBA Stage 3 at the very latest. This again of course requires a form of procurement that allows early contractor involvement, which is not achievable through the traditional route as contractors do not become actively involved until awarded the tender at the end of Stage 4.
The unanimous findings from the participants on this matter, coupled with the previously noted academic findings, raise the question: are SMEs witnessing a lack of aligned thinking between clients, consultants and contractors when it comes to waste management? This would certainly correspond with Wu et al. (2016) that “most architects have little willingness to integrate waste reduction strategies into their design” as well as Holmes and Osmani (2014) and Ajayi (2017) who agreed that late design and introduction of a Site Waste Management Plan at the construction stage, if at all, is the greatest root cause of waste on a project. Thus, if design teams are empowered to design with waste reduction in mind; in collaboration with a preferred contractor and their supply chain; then surely this will benefit all concerned when it comes to programming and pricing the project accurately, providing clarity to all.
Interview discussions also raised strong opinions about the identification of both existing building fabric materials that could be reused, as well as opportunities to introduce premanufactured components at the earliest possible opportunity. Coupling this with the consensus that more collaborative procurement would be preferred amongst construction professionals, there is further alignment with the literature that designers, contractors, and specialist manufacturers work together from the earliest point to exploit all opportunities for waste avoidance before the project gets to the site (Edwards et al., 2019). However, within the qualitative data, there appears to be a general disgruntlement amongst those in industry that it is the SME contractors that are taking the blame for waste generated and its destination.
What has become clear through this study is that SWM should be a top priority for clients that need to be considered much earlier in the construction process, which requires a more collaborative form of procurement. This is because typically, contractors only become involved at the point of tender, which means that the procurement route has likely already been chosen. Furthermore, whilst there is a requirement for improvement of contractor engagement by Industry and Statutory Authorities, there also needs to be greater interaction with industry clients themselves to ensure they are effectively advised and briefed on how to set project aims, whether sustainability-related or other, as well as what the most efficient procurement routes are to attain them.
Continuing to address the subject of client briefing on procurement routes, there seems to be a need for greater consideration of client accountability when it comes to waste management. The client is the party responsible for setting the sustainability charter and should be held accountable for ensuring that contractors apply their goals to their programme and pricing.
A recurring theme throughout the data captured was that clients’ reluctance to release funds meant responsibility for executing the waste management strategy was left purely to the contractor post-tender, leaving them having to deal with any associated costs from their profit margin. This is exemplified by the comments of one interviewee who stated that on one scheme the client outlined a desire to “use this project as a flagship for sustainable practices” after they had won the tender; meaning that there was nothing allocated within the contractors’ price to work towards any form of sustainability charter or accreditation.
It appears that most commercial clients that SME contractors are engaging with are not aware of their responsibility to factor in the cost of sustainable waste management in their budget, and timeline formulation, before going out to tender. Sezer and Bosch-Sijtsema (2022) highlighted that contractors feel the client to be too far removed from the WMS, leaving it in the hands of the contractor. This is reinforced by 20% of those surveyed, and Interviewee 2, who all found working towards sustainability goals to be “not at all important” to their clients. The lack of shared beliefs causes friction and adversity, as stated by Interviewee 1. Thus, it makes more sense for the client to set the environmental charter ensuring that any party joining the project is invested in achieving these goals before being awarded a contract.
Furthermore, when given the opportunity to offer thoughts on one improvement that could be made to benefit SME contractor execution of SWMS, the suggestion of incentivizing the contractor for correctly separating, reusing, and recycling waste was raised by several participants. Essentially, the client can fulfil their responsibility by setting the targets for sustainable waste management pre-tender. By making allowances for them in their budget they will empower the bidding contractors to factor this into their submission. With reward mechanisms in the contract for achieving sustainability targets, the contractor will be more likely to attain them; whilst making a positive influence on the client’s competitive advantage and reputation by demonstrating their high regard for social responsibility (Lou et al., 2012).
Although there are a few Green Building Rating Systems (GBRS) that clients can choose to employ on their projects. Existing literature and the data from the research suggest that their true effect specifically on Sustainable Waste Management is not particularly impactful. GBRS are a voluntary accreditation that is implemented by the client. The cost of implementation will always be a leading driver; which is less likely for SME businesses that are more likely to engage with SME contractors.
Furthermore, considering there are so many varying sustainability standards to choose from, as noted in the survey, there is no consistency in how targets are set and attained. Wu et al. (2016), argued the very same point when assessing the impact of several GBRS and the data captured in this project supports this, showing that respondents have worked to varying accreditations and with a less than significant impact on SWM.
However, given that the likes of LEED and BREEAM offer credits for on-site sorting for reuse and avoiding waste in design, there was a consensus amongst those interviewed that it is better to be working toward some environmental standards rather than none. Additionally, certifications such as these require contractors to define a waste sorting plan as part of an obligatory Site Waste Management Plan; which has almost certainly increased the fluency of construction companies in preparing waste management strategies and managing waste on site.
However, unless working for a GBRS, contractors do not have to employ a SWMP following the abolition of their mandatory status in 2013. Over half the survey participants thought that restoring them and tailoring them to project specifics, such as commercial refurbishments, would have a high impact on improving sustainable waste management practices. One interviewee expressed a feeling that GBRS needs to go further than its current limits, and another argued that now is the time for mandating new Sustainability Regulations. These should be a separate set of regulations that are aligned with the government’s ZAW 2050 policy with all projects being compliant in the same way as they adhere to Building Regulations. In support of this, there were calls from some of the SME contractors for clients to be legally required to employ their waste management resources to guide and enforce the process on-site, similar in effect to the role of principal designer within the CDM regulations.
This paper aims to identify the most impactful improvements SME construction refurbishment businesses could make to deliver sustainable waste management practices on their projects. Considering the United Kingdom government’s Zero Avoidable Waste 2050 target, and construction being identified as an industry requiring vast improvement in reducing waste to landfill, there is much progress required in terms of waste avoidance on projects. Given the fact that SME construction businesses make up a vast proportion of the industry, coupled with the increasing requirement for refurbishment over new builds, it is surprising to see that there has been not much statistical analysis specifically of landfill waste quantities produced by projects of this nature. Even so, industry authorities are aware that SMEs and refurbishment projects require substantial engagement and attention to ensure they are better advised and supported in implementing sustainable waste management strategies.
However, although the initial focus of the study was purely on the onus of SME contractors to improve Sustainable Waste Management practices, a combination of existing literature and engaging SME operatives led to the inference that the government and industry authorities need to do more to offer the support that their documentation alludes to. Nevertheless, whilst SMEs may bemoan barriers such as a lack of higher authority guidance; as well as scarcity of resources to implement technological innovations that Tier 1 peers may employ; there are numerous strategies they can adopt that have little cost impact. These include factoring waste avoidance into pre-construction activities and developing Site Waste Management Plans that evolve through analyzing previous schemes.
Academics and industry professionals seem to align in the theory that the best sustainable waste management practice is defined and achieved at the end of the last project and the start of the next. By analysing the waste data from previous projects, SME construction businesses can set benchmarks for future jobs and identify opportunities to improve waste avoidance. This is not a costly strategy, these are simple methods to exercise; such as separating waste, identifying elements for recycling or reuse, recording quantities and retrieving all paperwork for the final destination of waste produced. However, if SME construction businesses fail to adopt these simple processes, then higher authority intervention will inevitably be required through tactics such as the establishment of sustainability regulations, restoring mandatory Site Waste Management Plans or applying penalties for excessive quantities of waste to landfill.
Commercial clients should also be held more accountable for the destination of waste on their projects. Through proper education and briefing, they should be made aware of GBRS and collaborative procurement routes that could be utilized on their projects. This would empower clients to identify their sustainability charter and ensure that productive relationships are established with contractors when tackling environmental project concerns. However, to address the issue at a site level, there is a drastic amount of industry and government authority activity required to educate and inspire best practices in the art of sustainable waste management.
This study has provided a better understanding of SWM from the perspective of SME in Commercial projects. This is an area that has not well been addressed in literature. It raises a theorical question on how best to develop an efficient relationship between the client and the contractor in the drive towards sustainability in SMEs. Several practical implications can be deduced from this study. Institutional stakeholders and regulatory authorities now has an empirical evidence that there is need for more to be done in advocating for waste management in construction from the start to finish of a project. Most importantly in providing support for SMEs. Additionally, assessment frameworks such as BREEAM need to have more mandatory criteria under the waste category for all levels of certifications. This is to prevent developers who may want to avoid some criteria under this category. Also, this study has further highlighted the need for more awareness and development of bespoke digital construction tool for waste management.
Further studies can begin to explore varying digital construction tools available for waste management, analysing their effectiveness and cost to employ thereby enhancing the awareness. A qualitative investigation into the effectiveness of compulsory Site Waste Management Plans before 2013 and the perceived benefits of reinstating them in the eyes of construction professionals could also be an area to investigate.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The studies involving humans were approved by University of Greenwich Faculty of Engineering and Science Research Ethics Committee. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
SG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AA: Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. EO: Writing–review and editing. VO: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AD: Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Adam, K., and Thornback, J. (2022). How much waste is produced by the construction sector? London. Constr. Prod. Assoc.
Agyekum-Mensah, G., and Knight, A. D. (2017). The professionals’ perspective on the causes of project delay in the construction industry. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 24 (5), 828–841. doi:10.1108/ecam-03-2016-0085
Ajayi, S. (2017). Design, procurement and construction strategies for minimizing waste in construction projects. Bristol: University of West of England.
Baldwin, A., and Bordoli, D. (2014). Handbook for construction planning and scheduling. Oxford: Wiley and Sons.
Bukoye, O. T., Ejohwomu, O. A., Roehrich, J., and Too, J. (2022). Using nudges to realize project performance management. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 40 (8), 886–905. doi:10.1016/j.ijproman.2022.10.003
Burton, S. (2001). “Energy efficient office refurbishment,”. London: James and James (Science Publishers) Ltd.
Chen, Z., Feng, Q., Yue, R., Chen, Z., Moselhi, O., Soliman, A., et al. (2022). Construction, renovation, and demolition waste in landfill: a review of waste characteristics, environmental impacts, and mitigation measures. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 46509–46526. doi:10.1007/s11356-022-20479-5
Cheng, J., and Ma, L. (2013). A BIM-based system for demolition and renovation waste estimation and planning. Waste Manag. 33, 1539–1551. doi:10.1016/j.wasman.2013.01.001
Cohen, R., Desai, K., Elias, J., and Twinn, R. (2021). Net zero carbon: energy performance targets for offices. Building services engineering, research and Technology, Global Waste Initiative 50 by 2050, Sharm-El-Sheikh: United Nations Climate Change, 42 (3). 349–369COP27.
Creswell, J., and Plano Clark, V. (2011). Designing and conducting mixed methods research. Thousands Oaks, CA: Sage.
DEFRA (2013). Proposed repeal of construction site wate management plan regulations (2009): summary of responses and government response. London: HM Government.
DEFRA (2022). UK statistics on waste. Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/uk-waste-data/uk-statistics-on-waste#recovery-rate-from-non-hazardous-construction-and-demolition-cd-waste (Accessed February 14, 2023).
Designing Buildings Ltd (2021). Small and medium-sized enterprises. SME. Available at: https://www.designingbuildings.co.uk/wiki/Small_and_medium-sized_enterprises_SME (Accessed November 12, 2022).
Edwards, R., Lou, E., Bataw, A., Kamaruzzaman, S., and Johnson, C. (2019). Sustainability-led design: feasibility of incorporating whole-life cycle energy assessment into BIM for refurbishment projects. J. Build. Eng. 24, 100697–7. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2019.01.027
Fellows, R., and Liu, A. (2015). Research construction methods. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons Ltd.
Foreign Commonwealth and Development Office (2022). Small to medium sized enterprise (SME) action plan. Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/fcdo-small-to-medium-sized-enterprise-sme-action-plan/small-to-medium-sized-enterprise-sme-action-plan#:∼:text=An%20SME%20is%20any%20organisation,is%20in%20the%20below%20table (Accessed April 4, 2023).
Great Britain. Efficiency and Reform Group (2011). Great Britain. Efficiency and Reform Group London: Cabinet Office: Government Construction Strategy.
Green Construction Board (2020). Zero Avoidable Waste in Construction: what do we mean by it and how best to interpret it. London: Construction Leadership Council.
Green Construction Board (2021). The routemap to zero avoidable waste in construction. London: Construction Leadership Council.
Gupta, S., Jha, K. N., and Vyas, G. (2022). Proposing building information modeling-based theoretical framework for construction and demolition waste management: strategies and tools. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 22 (12), 2345–2355. doi:10.1080/15623599.2020.1786908
Hardie, M., Khan, S., and Miller, G. (2006). Benchmarks for recycling practices in commercial office refurbishment: data collection challenges. Queensland: CRC for Construction Innovation: Second International Conference Clients Driving Innovation.
Holmes, S. J., and Osmani, M. (2014). “Planning for waste management,” in A handbook for construction scheduling and planning. Editors A. Baldwin, and D. Bordoli (Chichester: John Wiley and Sons), 216–228.
Judd, C. M., and Kenny, D. A. (2024). “Random factors and research generalization,” in Handbook of research methods in social and personality psychology. Editors H. T. Reis, C. M. Judd, and T. V. West 3rd ed. (New York: Cambridge University Press).
Lou, E., Lee, A., and Mathison, G. (2012). Corporate responsibility application–UK construction SME. Int. J. e-Education, e-Business, e-Management e-Learning 2 (5), 436–442. doi:10.7763/IJEEEE.2012.V2.160
Newaz, M. T., Davis, P., Sher, J., and Simon, L. (2022). Factors affecting construction waste management streams in Australia. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 22 (13), 2625–2633. doi:10.1080/15623599.2020.1815122
Office for National Statistics (2021). Construction statistics, great britain: 2020. London: Office for National Statistics (ONS) - London Datastore.
Okakpu, A., Ghaffarianhoseini, A., Tookey, J., Haar, J., Ghaffarianhoseini, A., and Ur Rehman, A. (2022). Risk factors that influence adoption of Building Information Modelling (BIM) for refurbishment of complex building projects: stakeholders perceptions. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 22 (13), 2446–2458. doi:10.1080/15623599.2020.1795985
Price, T. (2010). “Site waste management plans, the designer and the CDM principal contractor,” in Procs 26th Annual ARCOM Conference, Leeds, United Kingdom, September 6–8, 2010. Editors C. Egbu (Association of Researchers in Construction Management), 1381–1390.
Ramos, J., Servando, A., Mcarmen, P., Mcarmen, G., Rodriguez, L., and Rios, J. (2019). Design of the refurbishment of historic buildings with a cost-optimal methodology: a case study. Appl. Sci. 9 (15), 3104. doi:10.3390/app9153104
Revell, A., and Blackburn, R. (2007). The business case for sustainability? An examination of small firms in the UK's construction and restaurant sectors. Bus. Strategy Environ. 16, 404–420. doi:10.1002/bse.499
Roehrich, J. K., and Lewis, M. A. (2014). Procuring complex performance: implications for exchange governance complexity. Int. J. Operations and Prod. Manag. 32 (2), 221–241. doi:10.1108/ijopm-01-2011-0024
Scott, L. (2016). Theory and research in construction education: the case for pragmatism. Constr. Manag. Econ. 34 (7-8), 552–560. doi:10.1080/01446193.2016.1151539
Sezer, A., and Bosch-Sijtsema, P. (2022). Actor-to-actor tensions influencing waste management in building refurbishment projects: a service ecosystem perspective. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 22 (9), 1690–1699. doi:10.1080/15623599.2020.1741493
Sezer, A. A. (2017). Factors influencing building refurbishment site managers' waste management efforts. J. Facil. Manag. 15 (4), 318–334. doi:10.1108/jfm-10-2016-0041
Strauss, A., and Corbin, J. (1998). Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory. 2nd ed ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Tezel, A., Dobrucali, E., Demirkesen, S., and Kiral, I. A. (2021). Critical success factors for safety training in the construction industry. Buildings 11 (4), 139. doi:10.3390/buildings11040139
Too, J., Ejohwomu, O. A., Bukoye, T. O., Hui, F. K. P., and Oshodi, O. S. (2023). Standardising the route to project handover to improve the delivery of major building projects. Int. J. Bus. Perform. Manag. 24 (2), 175–199. doi:10.1504/ijbpm.2023.129847
Too, J., Ejohwomu, O. A., Hui, F. K., Duffield, C., Bukoye, O. T., and Edwards, D. J. (2022). Framework for standardising carbon neutrality in building projects. J. Clean. Prod. 373, 133858. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133858
UNEP (2015). Global waste management outlook. Nairobi: United Nations Environment Programme UNEP and International Solid Waste Association ISWA.
United Nations (2023). Secretary-General's remarks at the world economic forum. Available at: https://www.un.org/sg/en/content/sg/statement/2023-01-18/secretary-generals-remarks-the-world-economic-forum (Accessed January 24, 2023).
Vidalakis, C., Abanda, F., and Oti, A. (2020). BIM adoption and implementation: focusing on SMEs. Constr. Innov. 20 (1), 128–147. doi:10.1108/ci-09-2018-0076
Weber, L. (1997). Some reflections on barriers to the efficient use of energy. Energy Policy 25 (10), 833–835. doi:10.1016/s0301-4215(97)00084-0
Wu, Z., Shen, L., Yu, A., and Zhang, X. (2016). A comparative analysis of waste management requirements between five green building rating systems for new residential buildings. J. Clean. Prod. 112, 895–902. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.05.073
Keywords: construction, construction waste management, refurbishment, renovation, SME, sustainability, waste management
Citation: Garoghan S, Adewumi AS, Ofetotse EL, Onyango V and Dawodu A (2025) Enhancing sustainable waste management strategies for small and medium-sized enterprises: a focus on commercial refurbishment projects in the United Kingdom. Front. Built Environ. 11:1469398. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2025.1469398
Received: 23 July 2024; Accepted: 20 February 2025;
Published: 11 March 2025.
Edited by:
Md Motiar Rahman, University of Technology Brunei, BruneiReviewed by:
Hasim Altan, Prince Mohammad bin Fahd University, Saudi ArabiaCopyright © 2025 Garoghan, Adewumi, Ofetotse, Onyango and Dawodu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ayomikun Solomon Adewumi, YS5hZGV3dW1pQGdyZWVud2ljaC5hYy51aw==; Vincent Onyango, di5vbnlhbmdvQGR1bmRlZS5hYy51aw==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.