- 1Department of Civil Engineering, National University of Skills (NUS), Tehran, Iran
- 2Scientific and Technological Complex for Digital Engineering in Civil Engineering, Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, St. Petersburg, Russia
- 3Department of Construction Technology and Structural Materials, RUDN University, Moscow, Russia
- 4Department of Reinforced Concrete and Stone Structures, Moscow State University of Civil Engineering, Moscow, Russia
This article aims to investigate the mechanical properties and substrate adhesion of the pull-off method in polymer mortars modified with styrene-butadiene resin polymer (SBR) containing glass powder and composite fiber-reinforced slag. Different mix designs were investigated with and without SBR, taking into account different amounts of glass powder and slag separately and in combination, along with the effect of glass, polypropylene, and steel fibers alone and in combination. The flexural performance and energy absorption of beams retrieved with these layers were also assessed. The results revealed significant differences and increases in the substrate adhesion of the restored modified polymer layers containing SBR compared to the polymer-free repair overlays. Furthermore, an improvement was observed in the adhesion performance of the repair overlay using a combination of slag and glass powder and the glass and polypropylene fiber composite. The highest adhesion was related to the modified polymer mortar design containing composite fibers of glass, polypropylene, and steel with 25% replacement of SBR polymer for 10% glass powder, 10% slag, and 5% slag with 5% glass powder. The adhesion was increased by about 3.74, 3.72, and 3.78 times compared to the repair overlay of the control design. Modified polymer mortars had a higher
1 Introduction
Polymer-reinforced concrete has been present since the 1950s. These concretes include Portland cement containing a polymer modifier such as styrene-butadiene (SBR), acrylic, polyvinyl acetate, and ethylene-vinyl acetate. SBR is widely used to make modified polymer mortars for the repair and coating of floors and bridges (Barluenga and Herna’ndez, 2004; Diab et al., 2014). The advantages of SBR-modified polymer mortar are good concrete adhesion strength, high flexural strength, and low permeability (Manson, 1976; Beushausen and Gillmer, 2014; Beushausen et al., 2014). Since modified acrylic polymer concrete has a constant color, it is an attractive material in architecture. A construction technology similar to that of conventional cement mortars and concretes is the desirable feature of the modified polymer mortars and concretes. Normally, the amount of polymer used in this mix is almost 10%–20% of the cement. The use of fibers in modified polymer concrete was evaluated and it was found that some cracks were created in their structure due to the use of fibers. (Fowler, 1999).
It has been reported that the addition of polymer can result in reduced uniaxial compressive strength (UCS), although it significantly increases the tensile and flexural strengths (Mahdi et al., 2013; Lewis and Lewis, n.d.). Using SBR in modified polymer concretes containing crushed waste concrete materials reported a significant reduction in permeability and increased flexural strength along with a slight reduction in UCS (Hwang and Ko, 2008). It has been demonstrated that the modified polymer concretes have much better durability performance against acid attacks and corrosive environments than conventional concretes (Shaker et al., 1997; Rossignolo and Agnesini, 2002; n.d.) studied the effect of SBR on the durability of polymer aggregate lightweight concretes against sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, and acetic acid, which represented a reduction in the rate of concrete weight loss in corrosive environments.
Using the substrate concrete as a repair overlay in the modified polymer mortars yielded better bonding strength than conventional cement mortars (Thamboo et al., 2013). The test used to determine the bonding strength significantly affects the bonding of two layers. This bonding is based on factors such as surface adhesion profile, friction angle, aggregate engagement, and variable profile over time. The bonding based on adhesive factors, material compaction, surface cleanliness, repair overlay moisture, sample age, and surface roughness was studied (Julio et al., 2004; Espeche and León, 2011; Thamboo et al., 2013; Courard et al., 2014). Momayez et al. (Momayez et al., 2005) compared SBR-modified polymer concretes, and K100 polymer adhesive bonding strength with conventional concretes and concretes containing silica fume. The studies showed that the modified polymer concretes had much higher bonding strength values. The bonding strength of polymer concretes modified with SBR and acrylic polymers containing microsilica to the substrate concrete was evaluated (Sadrmomtazi and Kohani Khoshkbijari, n.d.). Increasing the replacement of water with soluble polymers by 50% increased the bonding strength in SBR polymer-modified concrete by about 30%. It also increased by about 28% in the polymer concrete modified with a polymer comprising acrylic compared to the control design. Moreover, Sadr Mumtazi and Kohani (Sadrmomtazi and Kohani Khoshkbijari, 2017) revealed that the repair overlays of modified polymer concrete containing SBR have much higher durability against the freeze-thaw cycles than the normal cement layers.
In addition, other studies show that the addition of fibers and different types of structures can improve the mechanical properties of concrete. For example, basalt fibers have a great influence on the bending, tensile and compressive strength of concrete, respectively. In this regard (Vatin et al., 2024) studied the effect of adding basalt fibers to different types of concrete and found that reinforced concrete with a certain amount of basalt fibers can improve the mechanical properties of concrete. The particular volume of basalt fiber improves the mechanical properties. Some studies prove that if different materials are added to concrete, then mechanical properties are improving. In another example (Chiadighikaobi et al., 2024b), add Trichoderma Reesei Fungus to concrete to heal the cracks. O concrete to heal cracks. They found that the addition of Trichoderma Reesei Fungus to concrete can not only heal concrete cracks but also improve the compressive strength of concrete. Another similar example (Hematibahar et al., 2023a), added the gelatin powder to concrete. They found that adding adding gelatin powder can improve compressive strength of concrete more than 22% rather than conventional concrete. Some studies attempt to add 3D reinforced structure to concrete due to find the effect of mechanical properties of concrete beam. For example (Chiadighikaobi et al., 2024a), reinforced High-Performance Concrete (HPC) with different types of 3D printing trusses. They Found that HPC reinforced with a Warren truss performed better than other types of reinforced concrete. Another example (Hematibahar et al., 2023b), evaluated reinforced Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) with 3D printed hyperboloid shell structure. The reinforced hyperboloid shell structures can improve the energy absorbent of concrete while the mechanical properties of concrete decrease. Finally (Hematibahar et al., 2024), compared the mechanical properties of concrete reinforced with 3D printed trusses and hyperboloid shell structures. They found that the 3D printing geometry is an important factor in changing the mechanical properties and energy absorption of concrete. In general, there are different types of reinforced concrete and different materials for adding materials to concrete. In this way, the mechanical properties of concrete can be improved.
(Azadmanesh et al., 2021) investigated the mechanical properties of concrete modified with SBR and ethylene-vinyl acetate containing polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fibers. The presence of polymer in combination with fibers highly enhanced the performance of fibers in the composite structure. Besides, the tensile strain and deformability of the sample were also increased, as were the compressive and flexural strengths. SBR also performed better than other polymers.
Furthermore (Shi et al., 2020), indicated that in modified polymer mortars for repairs, the use of 8% SBR polymer increased the flexural strength and the toughness of the mortar by 62% and 62%, respectively. Idrees et al. (Idrees et al., 2021) reported using pozzolans such as nano-silica and nano-titanium could enhance the performance and mechanical properties of SBR-modified polymer mortars. In the present study, SBR-modified polymer mortars containing glass powder and slag reinforced with composite fibers are investigated. Different mix designs containing SBR were studied by considering different amounts of glass powder and slag separately and in the composite. Also, the effect of the separate and combined presence of glass, polypropylene, and steel fibers was considered. Different mix designs containing SBR and various amounts of glass powder and slag alone and in combination were considered. Furthermore, the effect of the presence of glass, polypropylene, and steel fibers alone and in combination was also regarded. In all designs, mechanical properties, energy absorption, and adhesion to substrate concrete were investigated.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
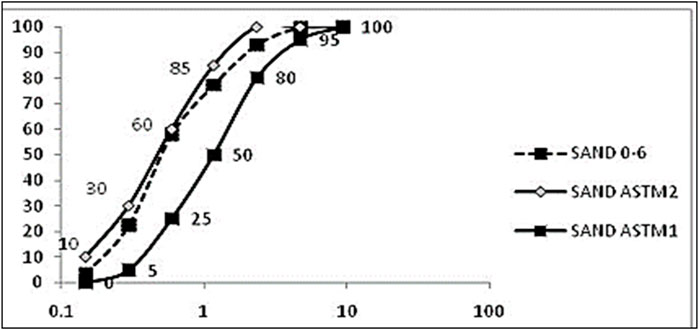
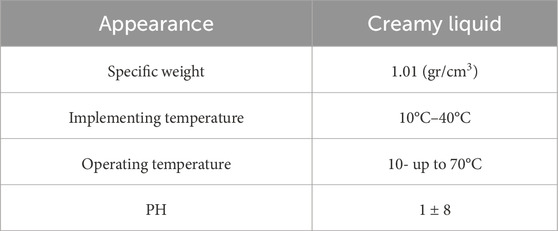
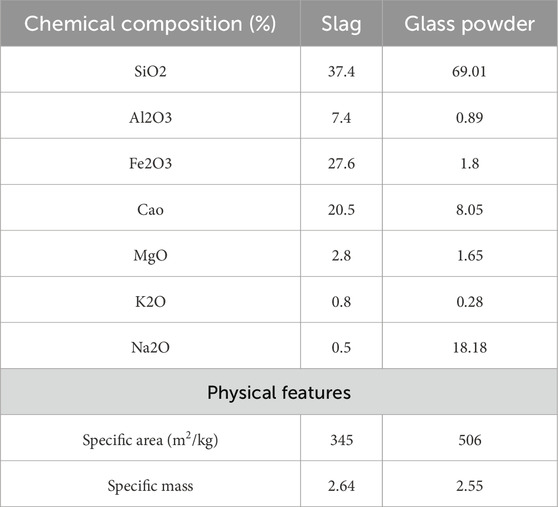
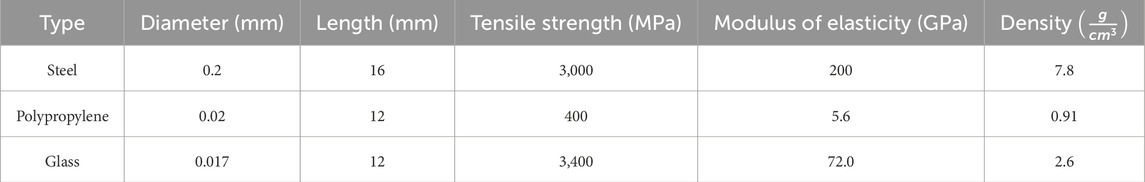
In this study, ordinary Portland cement (OPC), tap water, sand, Styrene-Butadiene Resin polymer (SBR), glass fiber, Polypropylene fibers (PP), and steel fiber were used. The OPC was Portland type 425-1 (Hegmatan cement factory), with the initial and final setting times at 90 and 240 min, respectively. Also, the blaine surface area of cement was 340 m2/kg. The materials used in this study were round river sands. The apparent specific gravity of sand is 2.6 g/cm3 with a water absorption of 2.5%. Soil grain distribution was performed based on ASTM C33 (ASTM C33/C33M-16: Standard Specification for ASTM C33/C33M-16, 2016) (Figure 1). The polymer used PAYA-L-310 resin. This type of polymer is a single-component SBR, which the Payajik company produces. Table 1 shows the PAYA-L-310 resin component and features. Table 2 illustrates the chemical properties of slag and glass powder, and Table 3 presents the properties of steel, PP, and glass fibers.
2.2 Methods
The mixture designs were in two categories, with and without polymer. In this way, 0, 5%, and 10% of slag and glass powder were used as cement substitutes. ACI548.3R-09 instruction (ACI committee 548, 2009) was used to make the modified polymer mortars. The requirements of ASTM C192 (ASTM, 2002) were also followed due to using different types of pozzolans such as slag and. In SBR-containing designs, the amount of polymer was equal to 25% of water substitute (Sadrmomtazi and Kohani Khoshkbijari, n.d.). The ratio of total water of the mixture to the cementitious materials was constant at 0.35. Glass and PP fibers with 0.1 and 0.2 vol% were considered alone and in combination. The amount of steel fibers used was also fixed at 0.25 vol%. Table 4 shows the mixture design. According to Table 4, 18 mix designs and all samples were examined for flexural and compressive strengths.
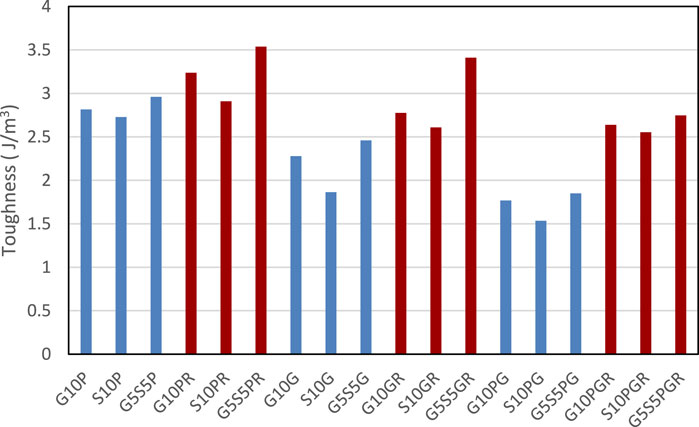
The control sample was placed in water for 28 days, while modified polymer concrete samples were kept in the water for 5 days and cured for 23 days in the laboratory (ACI committee 548. 3R-09: Report on Polymer-Modified Concrete, 2009). Half-cores with a depth of 3 cm were created on the samples such that 0.5 cm of the substrate was placed in the half-core. For all designs, compressive strength tests were performed following ASTM C109 (ASTM C109/C109M-05, 2005) on 5-cm cube samples for mortar cured for 7 and 28 days, water absorption according to ASTM C642 (ASTM C642-13, 2013), and tensile strength through the Brazilian method (cylinder halving) based on ASTM C496 standard (ASTM C496/C496M-17, n.d.). Pull-off strength determination test was performed on half-cores using a metal cap with a diameter and height of 5 and 2.5 cm, respectively, according to ASTM D7234 (ASTM D7234 - 12, 2012). In this test, a metal cylinder is first glued to the surface of the repair overlay. Then, the device pulls the cylinder until the connection breaks. This test can determine the bond strength of the two layers by occurring failure at the boundary between the repair overlay and the substrate. It is worth noting that the test results for failure outside the border were eliminated. Figure 2 presents the pull-off device and preparation and testing of the samples. In this study, substrate concretes with a compressive strength higher than 50 MPa were used to prevent errors caused by substrate concrete rupture during the pull-off bond strength test. After constructing the substrate concretes and curing them for 28 days, the samples were cut into three similar parts with dimensions of 15 × 15 × 15 cm3 by a stone cutting machine. The samples’ surfaces were perfectly smoothed to minimize the error caused by the roughness in the bond strength test. Then, the substrate samples were placed in a normal medium for about 6 months to complete their shrinkage while not affecting the bonding strength results. The energy absorption test was conducted based on the ASTM-C1609 standard (ASTM C1609, 2019) on the beams with dimensions of 50 × 10 × 10 cm3 restored (Figure 3). During the loading, the displacement of the middle of the beam was measured and calculated by the load-displacement diagram of the toughness index of each sample. The toughness index represents the energy absorption capacity of fiber-reinforced composites. This capacity is defined as the total area under the load-displacement curve in the middle of the beam to a displacement of 150/L. The toughness index is represented by
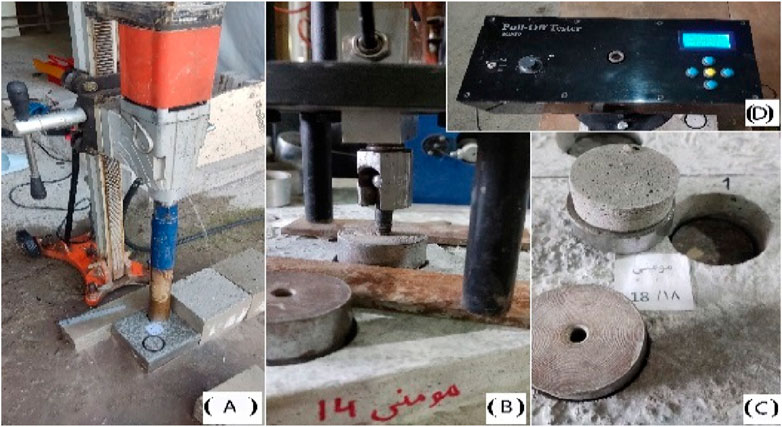
Figure 2. (A) The preparation of half core in the repair overlay; (B) The placement and Pull-Off test; (C) the sample removed from the repair overlay after testing; (D) Pull-Off device.
3 Results
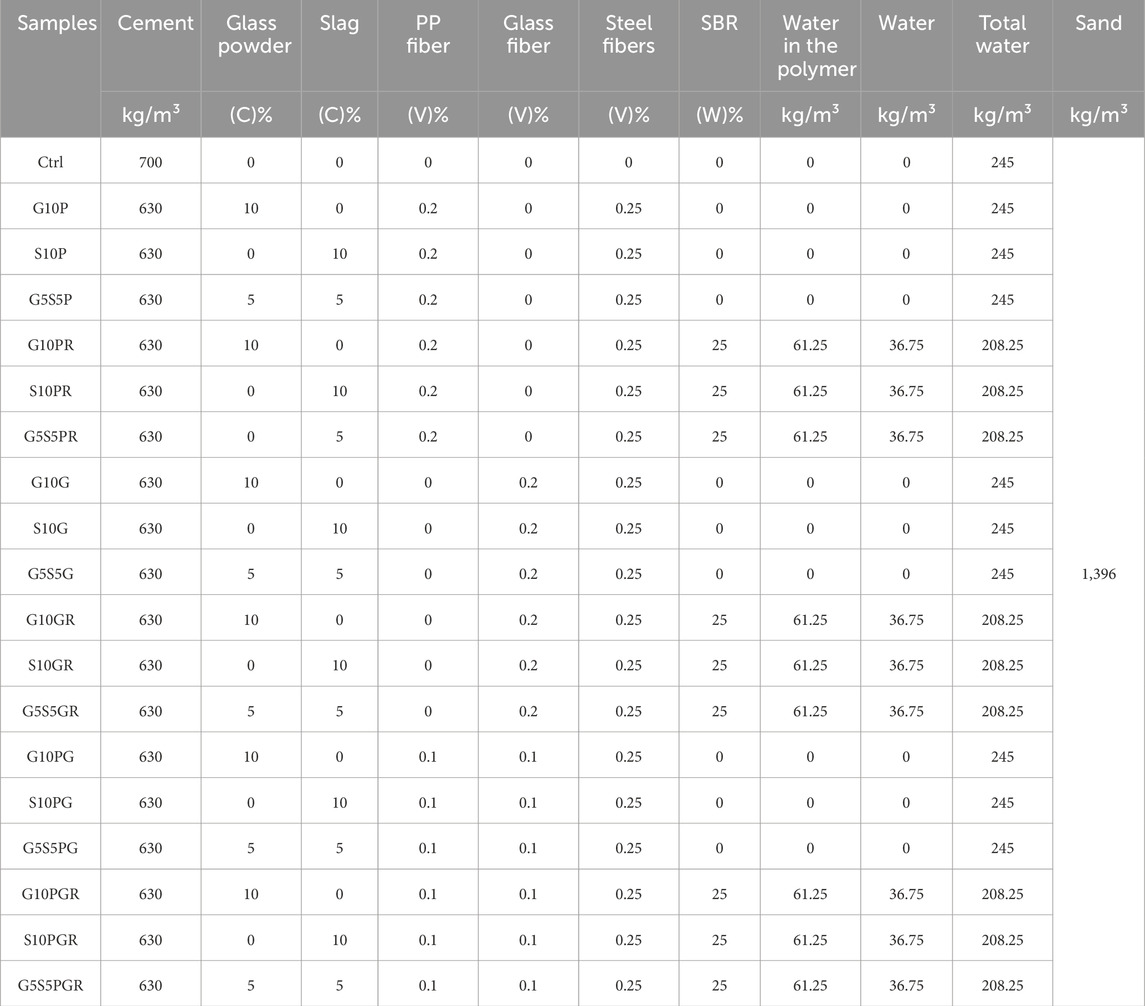
3.1 Compressive strength
The compressive strength results of the prepared specimens cured for 7, 28, and 90 days are presented in Figure 4. As can be seen, by adding slag, glass powder, pozzolans, and a polymer to the mix design, the 7-day compressive strength of all designs was decreased compared to the control design. The highest decrease was found in designs containing 10% glass powder and SBR. In this respect, the compressive strength reduction was 34.5%, 41.4%, and 43.3% for the designs containing polypropylene, glass, and composite fibers, respectively. The decrease in compressive strength was generally more severe in SBR-containing designs. It occurs possibly due to the lower compressive strength of hardened parts of the polymer inside the mortar structure compared to other hydration products in the microstructure. At the age of 28 days, the compressive strength of designs containing single polypropylene and glass fibers without SBR was close to the strength of the control design. The designs also showed higher strength after being cured for 90 days. It is noteworthy that a part of this decrease in strength at younger ages is also due to using pozzolans. In specimen G5S5P, consisting of 5% glass powder and 5% slag with polypropylene and steel fibers, the compressive strength was 47.01 MPa, which increased by 5.9% compared to the control specimen. In the G5S5G, which contained 5% glass powder and 5% slag along with glass and steel fibers, UCS was 48.06 MPa, which increased by 8.3% compared to the control specimen cured for 90 days. In the G5S5PR and G5S5GR, which were similar to the mentioned specimens but contained 25% SBR polymer, the compressive strength values were 36.37 and 36.06 MPa, respectively.
Furthermore, in the designs containing composite fibers of glass, polypropylene, and steel, the compressive strength was reduced compared to the control design. This reduction is due to the higher density of fibers and the formation of unavoidable voids in the mortar structure. Since fibers are mainly used to increase the energy absorption profile and reduce shrinkage (Azadmanesh et al., 2021), this reduction in compressive strength should be considered related to the other specifications of the test.
3.2 Tensile strength
The results of the 28-day tensile strength by cylindrical fission method in fabricated specimens are presented in Figure 5. As can be seen, TS increased in all fibers-containing designs. The results also show a significant positive effect of polymer use. Sadrmomtazie also reported this increase in tensile strength via polymers and Kohani (Sadrmomtazi and Kohani Khoshkbijari, 2017) in polymer concretes modified with SBR and acrylic polymers. In addition, it was found that using composite fibers of polypropylene and glass along with steel fibers yielded higher results than using each of these fibers alone in the tensile strength of the designs. The simultaneous use of slag and glass powder enhanced the tensile strength of single pozzolans, which was similar to compressive strength. The tensile strength was 4.8 MPa in the G5S5PGR design, comprising 5% glass powder and 5% slag with glass, polypropylene, and steel fibers, along with 25% SBR polymer. This result indicates a 76.46% increase compared to the control design. Meanwhile, this increase was 73.5% and 74.26%, respectively, for G5S5GR (containing glass and steel fibers) and G5S5PR (containing polypropylene and steel fibers) designs, compared to the control design.
3.3 Bonding strength to substrate concrete
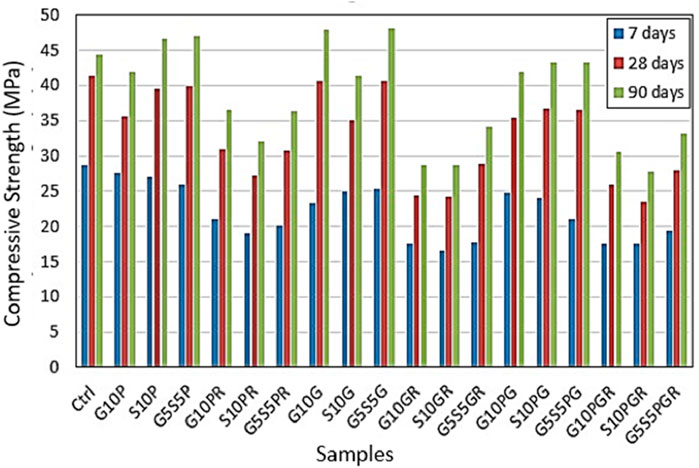
Figure 6 represents the bonding strength results of repair overlays made to substrate concrete by the pull-off method. The results of this experiment play a critical role in the performance and selection of a repair overlay. According to Figure 6, there is a very significant difference in the bonding of the modified polymer repair overlays containing SBR with the polymer-free repair overlays. This increment is significant regardless of the type of fibers and pozzolans used, which was also reported in previous studies (Fowler, 1999; Sadrmomtazi and Kohani Khoshkbijari, 2017). In addition, control sample bonding strength is 1.24 MPa, when 10% of glass powder and 10% of slag added to control sample bonding strength changed to 1.5 and 1.4 MPa respectively. According to results, when 25% SBR with 10% of glass powder, 10% slag and 10% of glass powder, 10% slag added to control the bonding strength improved to more than 4.5, 4.34 and 4.53 MPa respectively. According to Figure 6, when SBR was added to the control sample at a percentage of more than 25%, the bonding strength increased significantly.
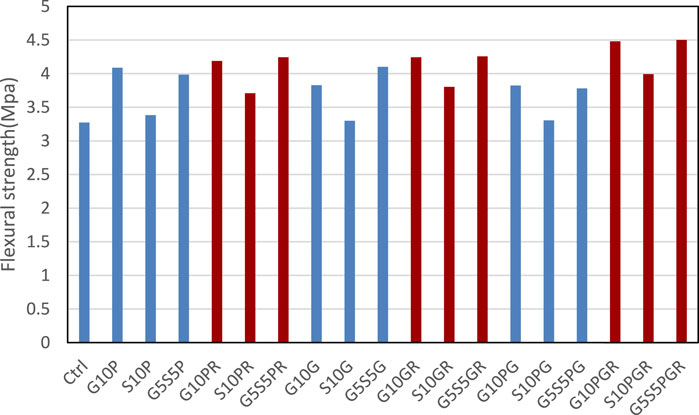
3.4 Flexural performance and energy absorption of the repair overlay
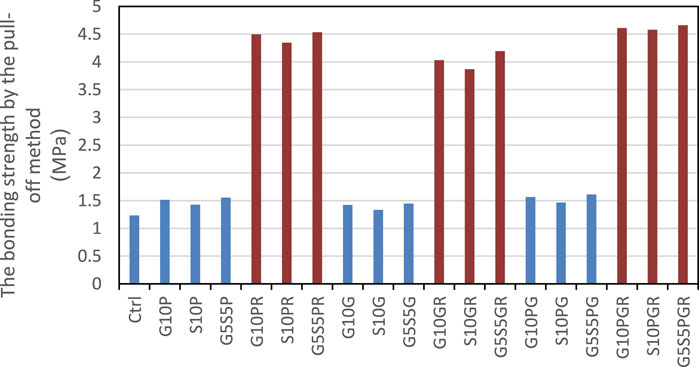
The results of the energy absorption test on the restored beams are presented in Figures 7-9. The flexural strength results of beams restored with mortars are presented in Figure 7. As can be seen, due to the 33% partial repair of the cross-section, the beam’s final flexural strength was not further increased by the restoration. However, an increase was found in the final flexural strength in all restored beams, which can be justified by the presence of fibers in all restoration projects. This increase was dominant in samples restored with modified polymer mortars, probably due to the higher TS in these designs (Sadrmomtazi and Kohani Khoshkbijari, 2017; Idrees et al., 2021). According to Figure 7, the control sample flexural sample is more than 3.27 MPa, adding 0.2% PP fiber, 0.2% glass fiber and 0.1% glass and 0.1% PP fiber tighter increase the flexural strength more than 25%, 17% and 16% recpectivly. The maximum effect of fibers and other types of material are adding 25% of SBR and 0.1% of PP and 0.1% of glass fibers and 10% of glass powder with more than 4.48 MPa flexural strength, 0.1% of PP and 0.1% of glass fibers and 10% of slag with flexural strength more than 4 MPa and 0.1% of PP and 0.1% of glass fibers and 5% glass powder and 5% of slag with flexural strength more than 4.5 MPa.
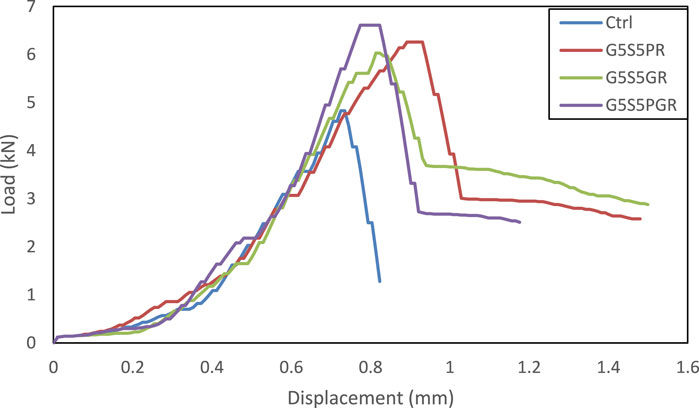
Figure 8. The comparison of load-displacement curves in control beams and restored beams containing pozzolans and composite fibers.
Figure 8 compares the load-displacement diagrams in non-restored samples and three restored samples G5S5PR, G5S5GR, and G5S5PGR, representing the highest final flexural strengths using any fibers. Such load-displacement diagrams were obtained for all designs. As mentioned earlier, the area in the charts represents the amount of energy absorbed in each sample. The toughness index is an indicator to determine this parameter. The toughness parameter
4 Conclusion
This article investigates polymer mortars modified with styrene-butadiene resin (SBR) containing glass powder and composite fiber-reinforced slag. Different mix designs with and without SBR were considered using different amounts of glass powder and slag alone and in combination. Moreover, the effect of glass, polypropylene, and steel fibers alone and in combination was considered. The mechanical properties and adhesion to the substrate concrete were assessed in all designs. Furthermore, the flexural performance and energy absorption of the beams restored with these repair overlays were investigated. Beefily, the following results were obtained in the present work.
• Generally, the UCS was reduced in SBR-containing designs. At the curing age of 28 days, the UCS of designs containing single polypropylene and glass fibers without SBR was close to the strength of the control design, which was also higher after 90 days.
• In all fibers-containing designs, the TS was increased due to the presence of SBR. The use of composite fibers of polypropylene and glass and steel fibers yielded higher results than the separate state of each of these fibers in the TS of designs. In addition, using slag and glass powder simultaneously, the TS of single pozzolans was improved like UCS.
• There was a significant difference and increase in the bonding strength of the modified polymer repair overlays containing SBR compared to the polymer-free repair overlays. This increase was significant regardless of the type of fibers and pozzolans used. An improvement was also identified in bonding to the repair overlay by using a combination of slag and glass powder and a combination of glass and polypropylene fibers.
• The highest bonding results were related to the modified polymer mortar designs containing composite fibers of glass, polypropylene, and steel with 25% replacement of SBR polymer for 10% glass powder, 10% slag, and 5% slag with 5% glass powder compared to the control layer with an increase of about 3.74, 3.72 and 3.78 times.
• The modified polymer mortars had higher
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
KM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Software, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. NV: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. MH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Resources, Software, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. TG: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The research is partially funded by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation as part of the World-class Research Center program Advanced Digital Technologies (contract No. 075-15-2022-311 dated 04/20/2022).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any 429 commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aminul Haque, M., Chen, B., Riaz Ahmad, M., and Ali shah, S. F. (2020). Mechanical strength and flexural parameters analysis of micro-steel, polyvinyl and basalt fibre reinforced magnesium phosphate cement mortars. Constr. Build. Mater. 235, 117447. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117447
ASTM (2002). C 192/C 192m-02: standard practice for making and curing concrete test specimens in the laboratory. West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM International.
ASTM C109/C109M-05 (2005). Standard test method for compressive strength of hydraulic cement mortars. West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM International.
ASTM C1609 (2019). C1609M – 19a: standard test method for flexural performance of fiber-reinforced concrete (using beam with third-point loading). West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM International.
ASTM C33/C33M-16 (2016). Standard specification for concrete aggregates. West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM International.
ASTM C496/C496M-17 (n.d.). Standard test method for splitting tensile strength of cylindrical concrete specimens. West Conshohocken: ASTM International.
ASTM D7234 - 12 (2012). Standard test method for pull-off adhesion strength of coatings on concrete using portable pull-off adhesion testers. West Conshohocken, PA: ASTM International.
Azadmanesh, H., Hashemi, S. A. H., and Ghasemi, S. H. (2021). The effect of styrene-butadiene rubber and ethylene vinyl acetate polymers on the mechanical properties of Engineered Cementitious Composites. Compos. Commun. 24, 100656. doi:10.1016/j.coco.2021.100656
Barluenga, G., and Herna´ndez, F. (2004). SBR latex modified mortar rheology and mechanical behaviour. Cem. Concr. Res. 34, 527–535. doi:10.1016/j.cemconres.2003.09.006
Bertelsen, I. M. G., Ottosen, L. M., and Fischer, G. (2020). Influence of fibre characteristics on plastic shrinkage cracking in cement-based materials: a review. Constr. Build. Mater. 230, 116769. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.116769
Beushausen, H., and Gillmer, M. (2014). The use of superabsorbent polymers to reduce cracking of bonded mortar overlays. Cem. and Concr. Compos. 52, 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2014.03.009
Beushausen, H., Gillmer, M., and Alexander, M. (2014). The influence of superabsorbent polymers on strength and durability properties of blended cement mortars. Cem. and Concr. Compos. 52, 73–80. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2014.03.008
Chiadighikaobi, P. C., Hasanzadeh, A., Hematibahar, M., Kharun, M., Mousavi, M. S., A. Stashevskaya, N., et al. (2024a). Evaluation of the mechanical behavior of high-performance concrete (HPC) reinforced with 3D-Printed trusses. Results Eng. 22, 102058. doi:10.1016/j.rineng.2024.102058
Chiadighikaobi, P. C., Hematibahar, M., Kharun, M., A. Stashevskaya, N., and Camara, K. (2024b). Predicting mechanical properties of self-healing concrete with Trichoderma Reesei Fungus using machine learning. Cogent Eng. 11, 2307193. doi:10.1080/23311916.2024.2307193
Courard, L., Piotrowski, T., and Garbacz, A. (2014). Near-to-surface properties affecting bond strength in concrete repair. Cem. and Concr. Compos. 46, 73–80. doi:10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2013.11.005
Diab, A. M., Elyamany, H. E., and Ali, A. H. (2014). The participation ratios of cement matrix and latex network in latex cement co-matrix strength. Alexandria Eng. J. 53, 309–317. doi:10.1016/j.aej.2014.01.008
Espeche, A. D., and León, J. (2011). Estimation of bond strength envelopes for old-to-new concrete interfaces based on a cylinder splitting test. Constr. Build. Mater. 25, 1222–1235. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2010.09.032
Fowler, D. W. (1999). Polymers in concrete: a vision for the 21st century. Cem. and Concr. Compos. 21, 449–452. doi:10.1016/s0958-9465(99)00032-3
Hematibahar, M., Esparham, A., Ivanovich Vatin, N., Kharun, M., and Gebre, T. (2023a). Effect of gelatin powder, almond shell, and recycled aggregates on chemical and mechanical properties of conventional concrete. Struct. Mech. Eng. Constr. Build. 19, 233–250. doi:10.22363/1815-5235-2023-19-2-233-250
Hematibahar, M., Hasanzadeh, A., Ivanovich Vatin, N., Kharun, M., and Shooshpasha, I. (2023b). Influence of 3D-printed reinforcement on the mechanical and fracture characteristics of Ultra high performance concrete. Results Eng., 19, 101365. doi:10.1016/j.rineng.2023.101365
Hematibahar, M., Hasanzadeh, A., Kharun, M., Beskopylny, A. N., Stel’makh, S. A., and Shcherban’, E. M. (2024). The influence of three-dimensionally printed polymer materials as trusses and shell structures on the mechanical properties and load-bearing capacity of reinforced concrete. Materials 17, 3413. doi:10.3390/ma17143413
Hwang, E. H., and Ko, Y. S. (2008). Comparison of mechanical and physical properties of SBR-polymer modified mortars using recycled waste materials. J. Industrial Eng. Chem. 14, 644–650. doi:10.1016/j.jiec.2008.02.009
Idrees, M., Saeed, F., Amin, A., and Hussain, T. (2021). Improvement in compressive strength of Styrene-Butadiene-Rubber (SBR) modified mortars by using powder form and nanoparticles. J. Build. Eng. 44, 102651. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102651
Julio, E. N. B. S., Branco, F. A. B., and Silva, V. D. (2004). Concrete-to-concrete bond strength. Influence of the roughness of the substrate surface. Constr. Build. Mater. 18, 675–681. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2004.04.023
Lewis, W. J., and Lewis, G. (n.d.). The influence of polymer latex modifiers on the properties of Concrete. COMPOSITES 21, 487–494. doi:10.1016/0010-4361(90)90421-R
Mahdi, F., Abbas, H., and Khan, A. A. (2013). Flexural, shear and bond strength of polymer concrete utilizing recycled resin obtained from post consumer PET bottles. Constr. Build. Mater. 44, 798–811. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.03.081
Manson, J. A. (1976). Modifications of concretes with polymers. Mater. Sci. Eng. 25, 41–52. doi:10.1016/0025-5416(76)90050-1
Momayez, A., Ehsani, M. R., Ramezanianpour, A. A., and Rajaie, H. (2005). Comparison of methods for evaluating bond strength between concrete substrate and repair materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 35, 748–757. doi:10.1016/j.cemconres.2004.05.027
Rossignolo, J. A., and Agnesini, M. V. C. (n.d.). Durability of polymer-modified lightweight aggregate concrete. Cem. and Concr. Compos. 26, 375–380. doi:10.1016/S0958-9465(03)00022-2
Rossignolo, J. A., and Agnesini, M. V. C. (2002). Mechanical properties of polymer-modified lightweight aggregate concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 32, 329–334. doi:10.1016/S0008-8846(01)00678-0
Sadrmomtazi, A., and Kohani Khoshkbijari, R. (n.d.). Determination and prediction of bonding strength of polymer modified concrete (PMC) as the repair overlay on the conventional concrete substrate. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 23, 1141–1149. doi:10.1007/s12205-019-0113-3
Sadrmomtazi, A., and Kohani Khoshkbijari, R. (2017). Bonding durability of Polymer Modified Concrete repair overlays under freeze–thaw conditions. Mag. Concr. Res. 69, 1268–1275. doi:10.1680/jmacr.17.00014
Shaker, F. A., El-Dieb, A. S., and Reda, M. M. (1997). Durability of styrene-butadiene latex modified concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 27, 711–720. doi:10.1016/S0008-8846(97)00055-0
Shi, C., Wang, P., Ma, C., Zou, X., and Yang, L. (2020). Effects of SAE and SBR on properties of rapid hardening repair mortar. J. Build. Eng. 35, 102000. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2020.102000
Thamboo, J. A., Dhanasekar, M., and Yan, C. (2013). Flexural and shear bond characteristics of thin layer polymer cement mortared concrete masonry. Constr. Build. Mater. 46, 104–113. doi:10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.04.002
Keywords: modified polymer mortar, SBR, energy absorption, bonding strength, fibers
Citation: Momeni K, Vatin NI, Hematibahar M and Gebre TH (2024) Repair overlays of modified polymer mortar containing glass powder and composite fibers-reinforced slag: mechanical properties, energy absorption, and adhesion to substrate concrete. Front. Built Environ. 10:1479849. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2024.1479849
Received: 12 August 2024; Accepted: 23 September 2024;
Published: 07 October 2024.
Edited by:
Gang Chen, Wuhan University of Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Ionut Ovidiu Toma, Gheorghe Adachi Technical University of Iași, RomaniaNahla Hilal, University of Fallujah, Iraq
Copyright © 2024 Momeni, Vatin, Hematibahar and Gebre. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nikolai Ivanovich Vatin, dmF0aW5AbWFpbC5ydQ==
 Komeil Momeni1
Komeil Momeni1 Nikolai Ivanovich Vatin
Nikolai Ivanovich Vatin Tesfaldet Hadgembes Gebre
Tesfaldet Hadgembes Gebre