- 1Department of Mechanical Engineering, Malawi University of Business and Applied Sciences, Blantyre, Malawi
- 2School of Built Environment, Malawi University of Business and Applied Sciences, Blantyre, Malawi
- 3Department of Civil Engineering, Malawi University of Business and Applied Sciences, Blantyre, Malawi
Building information modelling is making waves in the global built environment, improving the architecture engineering and construction industry in many aspects. However, in Malawi, it is neither widely adopted nor well-researched. Therefore, this study aimed to identify and analyse the challenges of BIM implementation in Malawi. A quantitative methodology was used, collecting 189 questionnaires. Descriptive analysis (mean item score), one-sample t-test, and factor analysis were used to analyse the data. The descriptive analysis revealed differences in ranking the 20 BIM challenge factors among various groups, yet no statistically significant variances were found among them; all the challenges were deemed critical. However, the results of the one-sample t-test indicated statistically significant differences in 13 of the 20 challenges, including issues with expertise, experience, integrating multiple software, understanding BIM potential, implementation methods, change adaptation, legislative guidelines, high implementation costs, awareness, integration to traditional techniques, procurement procedures, and strategic vision for implementation. Thus, through factor analysis, the study divided the 20 BIM implementation challenges into three categories: BIM integration, collaborative workflow, and technical adaptability challenges. These findings would increase BIM awareness, best practices and solutions, collaboration and communication, training and education, and industry BIM adoption. The study further contributes to the body of knowledge by providing structured challenges for BIM implementation, filling the knowledge gap about BIM challenges in the Malawian construction industry.
1 Introduction
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is transforming construction practices globally by improving efficiency and reducing risks. However, its adoption in developing countries like Malawi remains limited, creating significant challenges to the industry’s growth and sustainability. Malawi has implemented policies to improve its financial landscape through infrastructure delivery. These policies include the Malawi Vision 2063, the Transport Masterplan, and the Malawi Vision 2063 First 10-Year Implementation Plan (MIP-1). Also, these policies align with the United Nations (UN) sustainable development goals (SDGs) (Yeboua et al., 2023). Nevertheless, the situation is not improving. Scholars have found that developing countries struggle a lot when it comes to adopting modern, innovative technologies in the construction industry and leveraging them for economic development and benefits (Hanna, 2010; Apulu, 2012; Kotabe and Kothari, 2016). Malawi is facing similar challenges in its quest to overcome declining economic difficulties (Bhalla et al., 2000; Mariotti et al., 2018).
BIM has been shown to bring advantages to the construction industry if well implemented and adopted (Sacks et al., 2018). It allows for more sustainable building projects and performance with fewer resources and lower risk than old methods. BIM aids design throughout the project life cycle, beginning with the concept and maintenance. As a result, it enhances all technical disciplines, including civil engineering, construction, machinery, electrical, and other construction-related fields. If well-received, BIM encourages an integrated design-build environment, allowing for higher-quality building projects at lower costs and less time (Eastman et al., 2011; Sacks et al., 2018). Given BIM capabilities, it could be assumed that BIM would be the top priority of many construction organisations in both developing and developed countries. However, according to Criminale and Langar (2017), this is not the case due to the many challenges associated with BIM implementation. BIM challenges include but are not limited to lack of customer interest, expertise, training, standardised tools and procedures, and concerns related to data ownership (Enegbuma et al., 2014; Hore et al., 2017).
Enegbuma et al. (2014) categorise BIM implementation challenges, mentioning that these challenges concern people, technology, and processes. However, Olanrewaju et al. (2020) stress that individual BIM readiness is a more significant threat than the process, technology, and management during implementation. Eastman et al. (2011) adds two types of challenges to adopting BIM: process barriers to the organisation, such as organisational and legal difficulties, and technical constraints relating to readiness and execution. Succar et al. (2013) affirm that three primary categories of challenges exist when implementing BIM: procedural, technological, and human factors. While BIM offers several benefits, Barlish and Sullivan (2012) concede that a notable risk lies in professional teams’ incomplete understanding of the technology. Succar (2009) asserts that the lack of familiarity with this technology might be attributed to the description of its capabilities, and the extent of BIM-related research is frequently either excessively broad or unclear.
The Malawian construction industry faces many challenges that BIM can help mitigate. These challenges include, but are not limited to, poor project communication, lack of stakeholder participation, low productivity, and high error and rework rates (Chilipunde and Shakantu, 2010). Phiri and Smallwood (2010) add pilfering, corruption, skills shortages, and poor project planning. The challenges result in project delays, poor quality, and cost overrun, affecting the industry’s growth (Kadangwe and Emuze, 2017). As a result, client satisfaction and investments are declining (Kulemeka et al., 2015). In addition, BIM is not well-researched in Malawi; few or no studies address BIM adoption (Ndwandwe et al., 2024). A lack of studies addressing the challenges of BIM adoption and/or implementation makes this study necessary for Malawi (Antwi-Afari et al., 2018). Unfortunately, there is also low BIM awareness among organisations in Malawi (Ndwandwe et al., 2024). However, this study aims to address the lack of BIM challenges gap by identifying and analysing the challenges related to BIM implementation, which would, in turn, indirectly address the low BIM awareness challenge. To achieve this aim, a questionnaire survey was prepared, collecting one hundred and eighty-nine questionnaires and descriptive analysis (mean item score), one sample t-test and factor analysis were used to analyse the data. The findings of the study could provide an all-inclusive understanding of the factors influencing BIM adoption in Malawi and offer practical recommendations for overcoming these challenges. Furthermore, the study would raise awareness and ultimately increase the implementation of BIM in the Malawian construction industry.
The findings of the study could provide an all-inclusive understanding of the factors influencing BIM adoption in Malawi and offer practical recommendations for overcoming these challenges. Furthermore, the study would raise awareness and ultimately increase the implementation of BIM in the Malawian construction industry. This study uniquely contributes to the body of knowledge by focusing on BIM implementation challenges in Malawi, an under-researched region. Unlike existing research that predominantly explores BIM implementation in more developed markets, this study categorizes BIM challenges specific to developing countries, particularly in areas such as integration, collaboration, and technological adaptability.
2 Literature review
2.1 Building information modeling
BIM is an “integration process based on coordinated trustworthy information about projects from design through construction” (Crotty, 2013). BIM stands for building information modeling (process) and a building information model (digital artefact) (Lévy, 2011). BIM is a modelling technology and a set of methods for developing, discussing, communicating, and evaluating architectural models (Eastman et al., 2011). BIM (nouns) is an example of a building data model containing numerous data specific to a building that characterises it. Successful implementation of BIM has relied on identifying potential challenges and then devising tailored strategies to overcome/mitigate them (Antwi-Afari et al., 2018; Sinoh et al., 2020). BIM is taking the world by storm, spreading throughout developed and developing countries through formulating policies and initiatives by private and public bodies (Aizat et al., 2019). In countries such as the United Kingdom (UK), Singapore, the United States of America (USA), Scandinavia, etc., BIM is endorsed by the governments, and there are mandates for compulsory use in public projects with varying conditions (Zhou et al., 2019; Jiang et al., 2022).
Malawi can adopt this (government endorsement) for successful implementation in public projects. However, there are no frameworks or standards for BIM implementation. Making a lack of training one of the most critical barriers that must be overcome to establish a satisfactory BIM implementation level and develop local frameworks. Many organisations believe implementing BIM or adopting new innovations would decrease efficiency due to staff inexperience. This leads to reluctance to invest in BIM technology, which often stems from the complexity of mastering BIM authoring software and its disruption to established processes, such as traditional methods. Therefore, the successful adoption of new technology relies heavily on education and training (Oke and Fernandes, 2020). Integrating BIM across higher education curricula and conducting trials of BIM-based tools are viable approaches to expand its application.
BIM has become integral to the global architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry, but its uptake varies significantly between countries and organizations. BIM adoption refers to an organization’s initial decision and commitment to incorporate BIM into its workflow, often marking a strategic choice influenced by management, policy, or external pressures (Succar, 2009; Crotty, 2013). It signifies the organization’s willingness to invest in BIM but does not necessarily mean BIM is used on actual projects. BIM implementation, on the other hand, occurs in the subsequent phase, where BIM tools, processes, and workflows are actively integrated into project management and execution (Eastman et al., 2011). This stage involves the practical use of BIM on specific projects, requiring staff training, process re-engineering, and investment in technology. The challenges associated with BIM implementation are more operational, focusing on the technical and procedural hurdles that arise once the decision to adopt BIM has been made (Enegbuma et al., 2014).
Recent studies have demonstrated that the distinction between BIM adoption and BIM implementation is especially appropriate in developing countries, where policy mandates or competitive pressures may drive the adoption phase, but implementation lags due to a lack of resources or expertise (Olanrewaju et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2019). For example, in the South African construction industry, Oke and Fernandes (2020) found that while many organizations had adopted BIM in principle, only a small percentage had moved forward with comprehensive BIM implementation on actual projects due to barriers such as training gaps, high costs, and resistance to workflow changes. Similar trends have been observed in other developing countries, such as Malaysia (Aizat et al., 2019) and Nigeria (Olanrewaju et al., 2020), where government and private sector organizations are pushing for BIM adoption, yet the real-world application of BIM remains limited due to operational challenges. These studies indicate that while adoption may signify progress, the implementation phase reveals the practical difficulties and opportunities associated with BIM. Furthermore, in developing countries, the terms “BIM adoption” and “BIM implementation” are often used interchangeably (Aizat et al., 2019; Olanrewaju et al., 2020), despite representing different phases. Therefore, in this study, the authors also use the terms interchangeably to match how they are commonly used in the field, even though this might make it harder to see the differences between each phase.
The distinction between BIM adoption and implementation in Malawi is particularly important as the construction industry is still in the early stages of integrating BIM. Adoption has been slow due to limited government mandates and low awareness, but there are signs of growing interest in the technology (Ndwandwe et al., 2024). Despite this interest, the actual implementation of BIM on projects remains minimal, as organizations face significant barriers such as a lack of expertise, inadequate technological infrastructure, and resistance to change (Chagunda et al., 2022). This suggests that while BIM adoption is gaining traction, the implementation challenges are where the focus of research and intervention must now shift. Studies from other developing countries indicate that addressing the operational challenges of BIM implementation, such as training, process integration, and technical support, is crucial to moving beyond the initial adoption phase. In this context, the present study aims to fill a significant gap by exploring the factors influencing BIM adoption and focusing on the practical challenges of BIM implementation in Malawi.
To enhance BIM implementation in Malawi, it is vital to acknowledge that the success of BIM is not solely dependent on technological advancements but also on fostering a collaborative culture within the construction industry (Brown and Dant, 2009). This cultural shift entails developing relationships among stakeholders and promoting a shared understanding of BIM processes and benefits. Collaborative efforts can facilitate knowledge exchange, thereby mitigating the reluctance to invest in BIM technologies. Moreover, Chagunda et al. (2022) emphasize the necessity of developing localized training programs tailored to the specific needs of Malawian construction professionals, which can address the skills gap and enhance confidence in using BIM tools. By prioritizing collaboration and education, Malawi can create a conducive environment for BIM, ensuring that the transition from adoption to implementation is not only smoother but also more effective, ultimately leading to improved project outcomes and greater efficiency in the construction sector.
2.2 BIM implementation challenges
While theoretically, one of the most substantial merits of BIM is its smooth integration (Rekola et al., 2010), this scenario is rarely witnessed in practice due to the array of software packages currently accessible in the market and the challenges in harmonising or merging diverse engineering domains along with architectural and quantity surveying functions (Manderson et al., 2017). Furthermore, the costs related to adopting BIM might be substantial in the early stages and may affect the financial viability of projects (Olatunji, 2011). Calitz and Wium (2022) explored the construction sector’s challenges when implementing BIM. These challenges directly or indirectly impact construction companies’ ability to plan for or embrace BIM. The challenges encompass insufficient expertise within the industry and education sector, a lack of BIM understanding and research, inadequate leadership and industry guidance, high costs of implementation and uncertain financial benefits, absence of a legal framework, cultural obstacles, inadequate government endorsement, limited enthusiasm and backing from all stakeholders involved in projects and industry organisations, instances of corruption, and inefficiencies in traditional procurement methods.
Moreover, due to a lack of awareness and additional learning procedures necessary for effective implementation and usage of the new innovations, slow uptake or acceptance of BIM is a constant issue in Malawi. The absence of public-sector backing is also a considerable factor associated with poor uptake in developing countries, including Malawi (Wong et al., 2011). Drucker (2007) clarified that there are always challenges to change. The United States, the United Kingdom, Canada, Ghana, China, India, South Africa, and Australia explored challenges to BIM adoption (Elmualim and Gilder, 2014). According to their findings, the key challenges are the lack of capital, the advantages of BIM that do not outweigh the implementation costs, the difficulty of starting processes, and the fact that BIM is too dangerous or unclear regarding accountability. These findings, in one way or the other, apply to the Malawian construction industry.
Olugboyega and Windapo (2019) added that a lack of BIM expertise and training is the main barrier to BIM adoption in developing countries like Malawi. Moodley et al. (2016) affirmed that most AEC sector specialists could not adopt BIM maturely and efficiently in developing countries because employees must be sent to costly and time-consuming BIM training sessions. After all, BIM is not taught as a stand-alone module in educational institutions (Puolitaival and Forsythe, 2016). According to Wong et al. (2011), a contributing factor to the absence of BIM education within academic institutions is the limited familiarity of instructors with the subject matter (BIM). Thus, since BIM is still relatively new in Malawi, it is unreasonable to anticipate instructors possessing hands-on BIM experience. Also, it might have to do with the inability to implement BIM instructions into an already hectic curriculum, adding to student workload (Moodley et al., 2016). This makes it very hard for organisations to adopt BIM or find experts to facilitate it, which explains why there is low BIM awareness in developing countries, including Malawi.
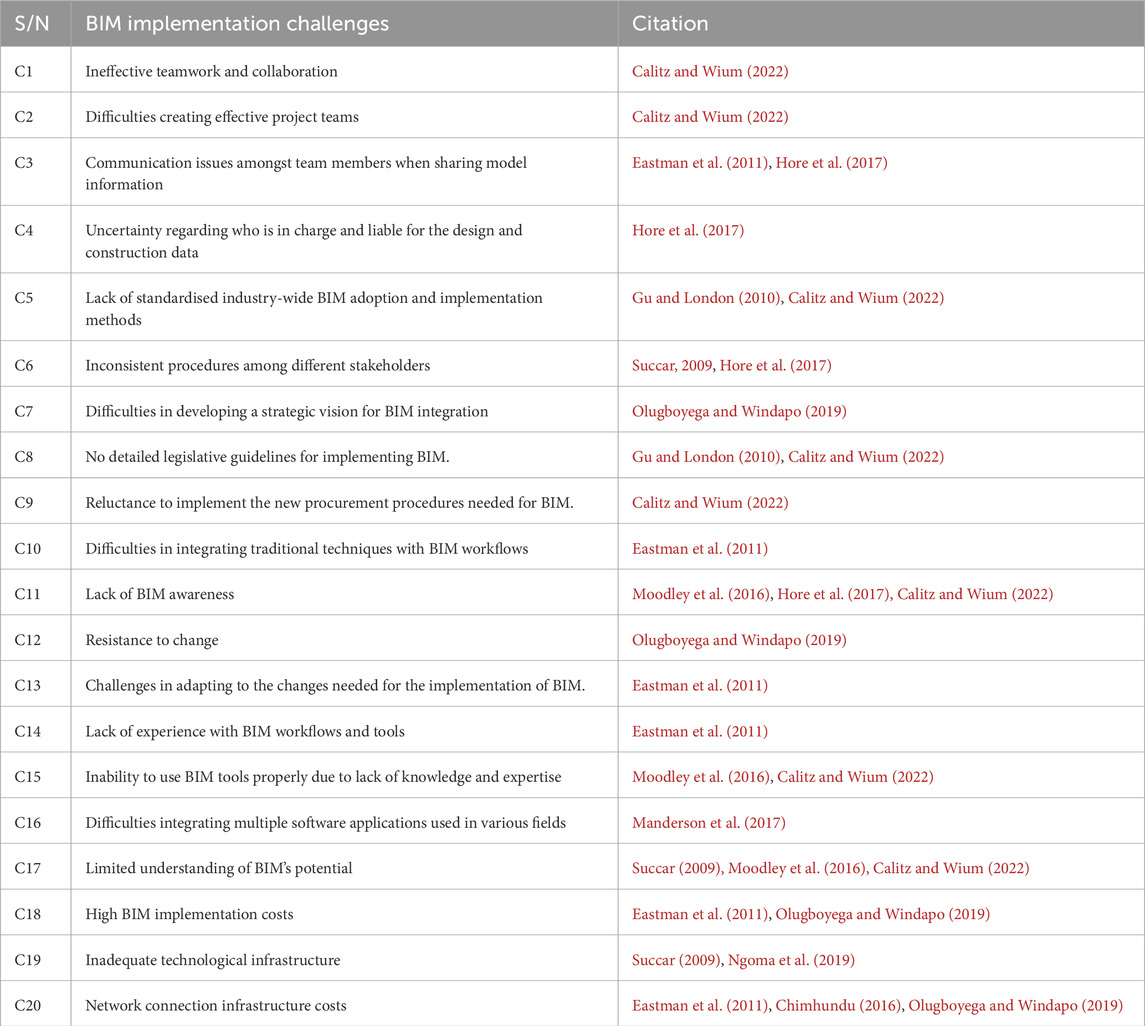
Very few organisations and institutions are driving BIM development in Malawi (Ndwandwe et al., 2024). This is due to the government and industry bodies offering nothing to stimulate or direct the adoption of BIM. Since these organisations are for profit, their objectives differ from the industry’s overall effectiveness and development. This gives rise to the need for the National Construction Industry Council (NCIC), the Ministry of Transport and Public Works, and all the industry bodies to provide Malawi construction industry guidelines and rules regarding digitalisation and aid in developing BIM implementation frameworks (Gu and London, 2010). Government backing is necessary for Malawi to adopt BIM. Firstly, they are pivotal as the principal clients within the construction industry. Secondly, the influence of government rules and regulations is paramount for the extensive adoption of BIM (Dim et al., 2015; Zhou et al., 2019). The absence of governmental regulations and support slows the successful implementation of BIM within Malawi’s construction industry. Table 1 below summarises the challenges associated with BIM implementation.
2.3 Research gap
The literature extensively covers BIM’s challenges, benefits, and implementation (Enegbuma et al., 2014; Hore et al., 2017). However, research on these parameters in Malawi, including readiness and other BIM-related research, is very scarce. This research is crucial for the Malawian construction industry’s growth and sustainability. Many studies have highlighted that for BIM to be successfully implemented, the local industry must investigate possible challenges, devise tailored strategies to mitigate those challenges and increase BIM uptake while using international experience for inspiration (Antwi-Afari et al., 2018; Sinoh et al., 2020). Thus, this study is needed in Malawi. Consequently, this study aims to identify and analyse BIM challenges and recommend possible strategies to combat them. BIM is essential for improving transparency, project planning, reducing project costs, enhancing communication and collaboration, and attracting investors, etc., in the construction industry.
To ensure that all challenges relevant to BIM implementation, particularly in developing contexts like Malawi, were captured, a mini scoping review was undertaken. This approach, based on Grant and Booth (2009), serves as an efficient method for a preliminary survey of the available literature’s scope and key themes, without necessitating formal quality assessments. A pilot search using Google Scholar and the keywords “Building Information Modelling,” “BIM”, “Challenges,” “Developing countries” and “Barriers” was conducted to gain an initial overview of related challenges. Using Google Scholar for this preliminary search was particularly effective as it provides a broad coverage of both peer-reviewed and grey literature, which is valuable for identifying emergent issues and themes that might otherwise be overlooked in traditional databases (Haddaway et al., 2015). Through this approach and further refinement to emphasize challenges unique to developing countries, the review helped identify 20 primary challenges. These were subsequently evaluated by a small group of construction professionals to ensure relevance and contextual alignment, with the feedback informing the final selection of challenges. This process underscored the need to further explore these challenges’ underlying structure, which led to the adoption of a factor analysis. This method facilitated a comprehensive grouping of the challenges, addressing a significant literature gap in BIM research focused on Malawi.
3 Methodology
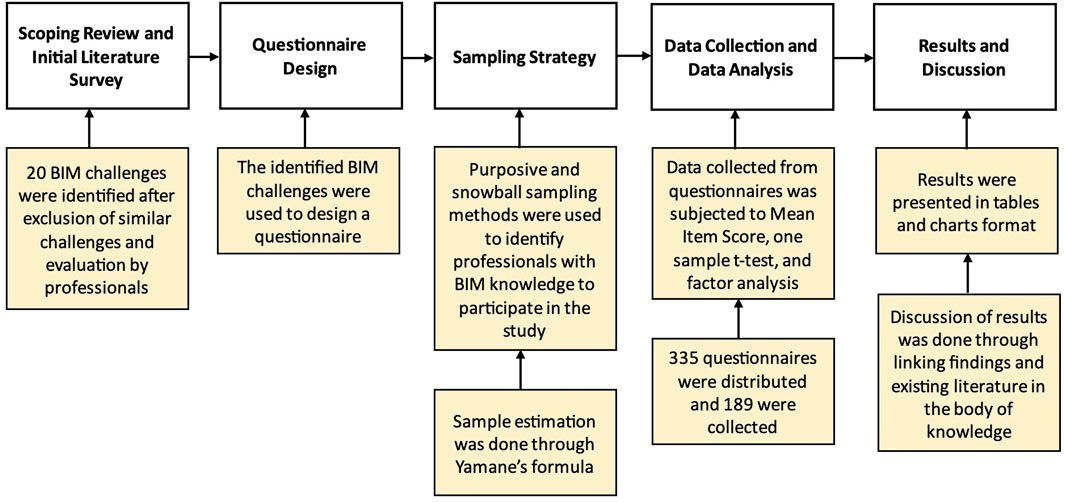
Research is a systematic search that involves gathering, analysing, and interpreting data to uncover novel knowledge using various tools and procedures (Leedy and Ormrod, 2015). This study is positivist in philosophical leaning, exploratory quantitative, and deductive in approach. Gray et al. (2012) clarifies that explanatory studies contribute to evaluating existing knowledge and offer insights into specific areas of interest, such as BIM, in this context. BIM is in its novel stage in Malawi, making this study a huge contributor to knowledge by identifying the issues that are hindering the adoption of BIM and offering industry-tailored solutions for how the issues could be dealt with. Figure 1 below illustrates the research methodology used in this study. The process involved reviewing relevant literature on BIM, developing a survey instrument, sampling participants, and using statistical tools such as descriptive analysis, t-tests, and factor analysis to interpret the results.
A quantitative methodology was adopted in this study, with a questionnaire survey chosen as a data collecting tool: chosen for its effectiveness in gathering objective and measurable data (Saunders et al., 2012). Due to low awareness and adoption of BIM in Malawi, purposive and snowball sampling methods were used to identify professionals with BIM knowledge to participate in the study. Purposive sampling was used to identify the initial BIM well-informed participants, and snowball sampling was used to expand the sample size through referrals, ensuring a broader and more comprehensive understanding of the study area (Etikan and Bala, 2017). Using the population of active construction companies in Malawi (2046) in 2023 (National Construction Industry Council, 2024) and a confidence level of 95%, the sample size was estimated using formula Yamane (1973) as follows:
where n = sample size; N = population size; e = margin of error.
The questionnaire was developed based on a comprehensive review of BIM literature and expert consultations. Twenty challenge variables were identified from prior studies. The questionnaire was designed to assess these variables in the context of the Malawian construction industry, with a focus on relevance to local practices. The questionnaire was then pilot tested with a small group of construction professionals to ensure its clarity and relevance. The questions focused on key BIM challenges identified from the literature and were refined based on feedback.
The ideal calculated sample size for this study was 335 completed questionnaires, aimed at adequately representing the population of active construction companies in Malawi. However, logistical constraints limited the final response to 189 questionnaires. Additional respondents from government and academic institutions were also included, effectively expanding the diversity of perspectives and strengthening the study’s insights, which would typically increase the sample size. Despite falling short of the initial target, recent literature supports that a sample size of 189 can still yield statistically significant results in survey research, particularly with response rates between 40% and 75% (Sataloff and Vontela, 2021). In this study, the response rate was 56.4%. This sample size aligns with findings from Bagozzi and Yi (2012) and Xiong et al. (2015), who suggest that while larger samples enhance precision, samples between 100 and 200 remain sufficiently reliable for drawing meaningful conclusions. Additionally, research by Kotrlik and Higgins (2001) indicates that studies employing factor analysis require a minimum of 100 observations, further validating the robustness of this sample. The diverse representation of construction professionals, government officials, and educators contributes to a comprehensive understanding of BIM challenges, reinforcing the validity and relevance of the findings.
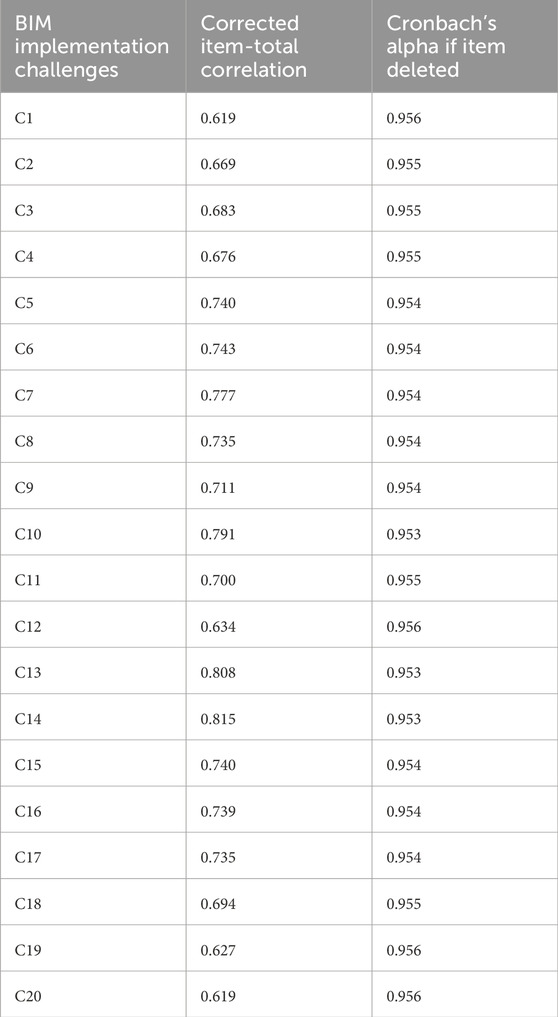
The collected data was then analysed using IBM SPSS (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences) version 29.0. Before the analysis, the data was cleaned and coded using Microsoft Excel. Descriptive analysis (mean item score), one-sample t-test, and factor analysis were performed. Descriptive analysis was used to present the participants’ demographics and rank the variables (BIM challenges). The reliability of the survey instrument was tested using Cronbach’s Alpha (Saunders et al., 2012). The analysis yielded a coefficient of 0.957, indicating high internal consistency among the 20 identified challenges (Tavakol and Dennick, 2011). Table 2 presents the corrected item-total correlation of the variables, which further validates the scale’s consistency (Saunders et al., 2012; Tavakol and Dennick, 2011). A one-sample t-test was conducted to further explore the relationship between the variables and assess their relevance to the Malawian construction industry. This test evaluated whether the mean ratings of the identified BIM implementation challenges in Malawi’s construction industry differed significantly from a hypothesized population mean (i.e., 3.5).
In assessing BIM implementation challenges, a Mean Item Score (MIS) threshold of 3.5 was applied to classify critical factors, consistent with established practices in construction industry research. This threshold has been widely adopted in studies involving construction management and technology integration to prioritise significant issues. Specifically, when an MIS score surpasses the 3.5 mark, it indicates a need for focused attention, as respondents perceive these factors to be of high importance or urgency. For instance, studies on construction information management have used the 3.5 threshold to highlight essential outcomes that warrant strategic action due to their impact on project success (Adekunle et al., 2022). Similarly, research involving Construction 4.0 practices applies this threshold in quality management frameworks, where it helps to identify critical areas for improvement and underscores their importance for industry advancement (Lekan et al., 2022). Such precedents validate the use of the 3.5 threshold in this study to isolate BIM challenges that are particularly critical for successful implementation in the Malawian construction industry. Since BIM is a relatively new concept in Malawi and there is limited literature on BIM challenges, the t-test provides a way to determine whether the challenges identified in this study are not only general but specifically applicable to the Malawian context. By statistically testing the significance of each challenge against the benchmark value, the study confirms that these challenges are critical to local industry practices, highlighting the need for targeted strategies to address them.
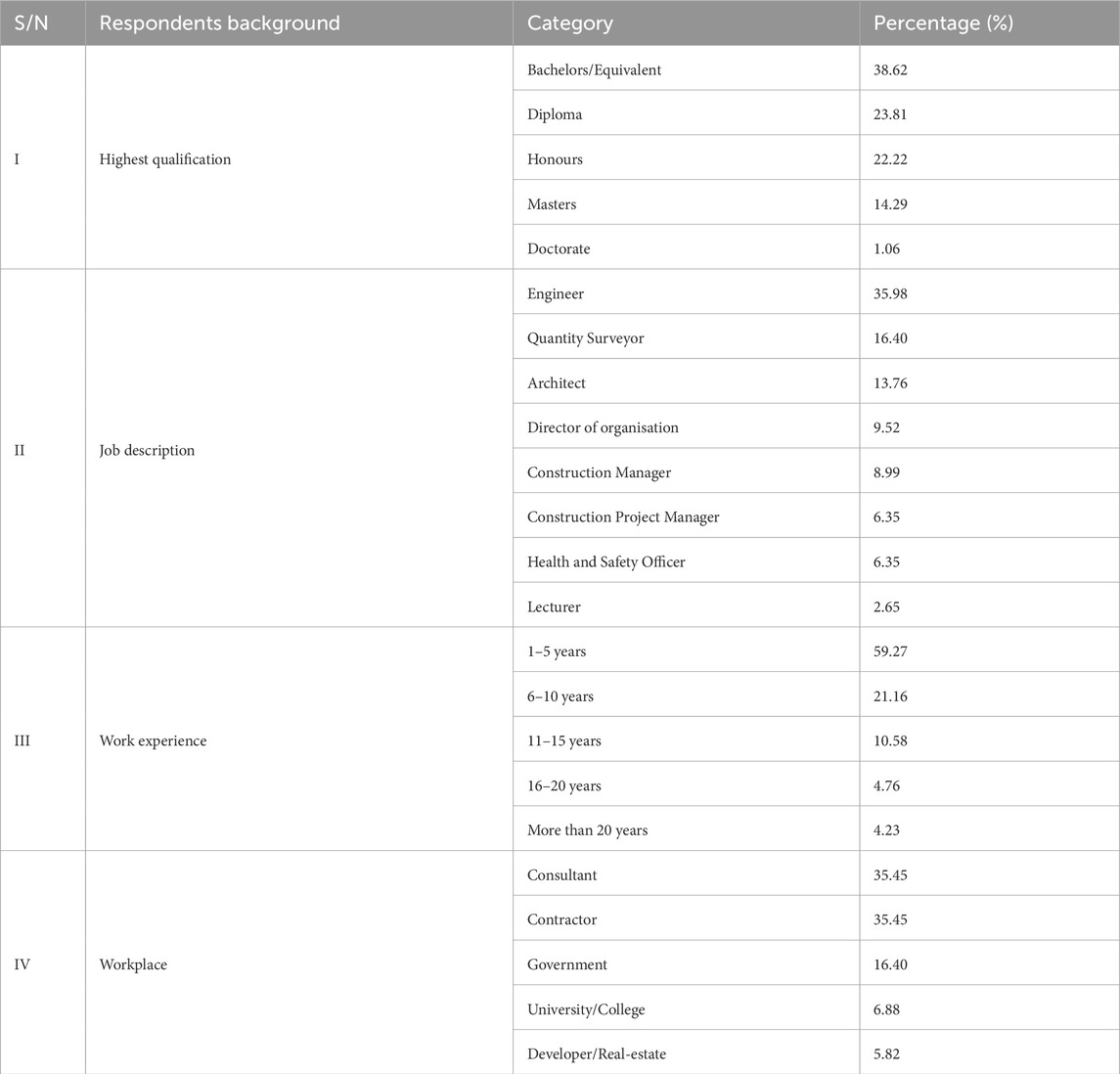
Furthermore, twenty variables were identified from the literature. Therefore, it was deemed necessary to reduce/group the challenges so it can be easy to devise solutions for all (Eastman et al., 2011). Hence, dimension reduction (factor analysis) analysis was done (Williams et al., 2010). The factor analysis was chosen to reduce the 20 observed variables (BIM challenges) into smaller set components that represent the main factors influencing BIM adoption in the Malawian context. This technique was appropriate given the exploratory nature of the study. Table 3 below presents the demographic information of the participants, and they included professionals associated with government and private agencies, contractors, and consultants.
In total, 189 respondents answered the questionnaire. With regard to their highest qualification, 23.81% had a Diploma, 38.62% had a Bachelor’s, 22.22% had Honours, 14.29% had a Master’s, and only 1.06% had a Doctorate degree. The majority of the respondents were engineers (35.98%), followed by quantity surveyors (16.40%), architects (13.76%), directors (9.52%), construction managers (8.99%), health and safety officers (6.35%), project managers (6.35%), and the least were lecturers (2.65%). When looking at the organisation they were working for, 35.45% were working for consulting organisations, 35.45% were working for contractors, 16.40% for government, 6.88% for academic institutions, and only 5.82% for property developers. In terms of work experience, the majority of the respondents had experience between 1 and 5 years (59.27%), followed by 6–10 years (21.16%), 11 and 15 years (10.58%), 16 and 20 years (4.76%), and the least were with the experience over 20 years (4.23%).
4 Results and discussions
4.1 Ranking of challenges associated with BIM implementation
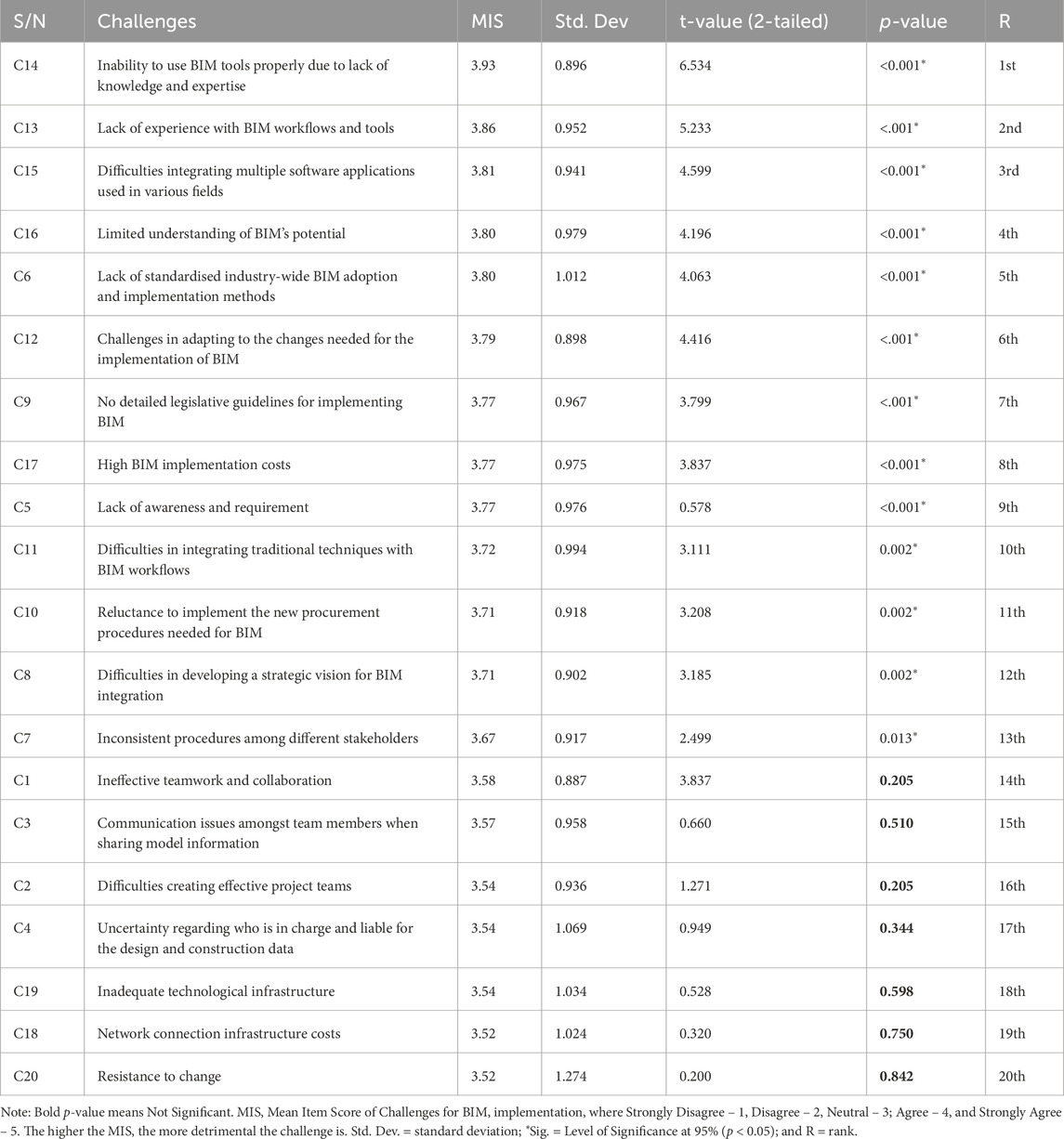
Using the twenty challenges that were summarised from the literature review, the descriptive statistics (standard deviation (Std. Dev.), mean item score (MIS), t-value (2-tailed), probabilities (p-value), and ranks) were determined and presented in Table 4.
Table 4 shows that the majority (13/20 = 65%) of the hypothesised challenges were statistically significant (p < 0.05) by the respondents using the one-sample t-test value of 3.5. The mean item score of the challenges ranges from 3.52 to 3.93. To get the most significant BIM implementation challenges in the Malawian construction industry based on the mean score, a threshold of 3.50 was set. Olanrewaju et al. (2020) used this same threshold to assess the significant variables. As a result, all the challenges had a mean item score greater than 3.5. Since this study focused on the challenges associated with BIM implementation, it was imperative to establish the essential variables that must be considered to allow for the seamless formulation of strategies to help mitigate these challenges.
From Table 4, it can be deduced that the MIS of all the challenges associated with BIM implementation were more significant than 3.5, which indicates the greater importance of all the variables (Tholibon et al., 2021). The challenges range from “inability to use BIM tools properly due to lack of knowledge and expertise” (MIS = 3.93 and p-value = 0.001), which is the most important, to “resistance to change” (MIS = 3.52 and p-value = 0.842) which is the least important but still vital to BIM implementation. Resistance to change was not significant based on the t-test but was found vital based on MIS. These challenges are widely covered in the literature; the lack of knowledge and expertise in BIM tools is a significant challenge when implementing BIM (Puolitaival and Forsythe, 2016). Furthermore, Olanrewaju et al. (2020) found the reluctance of other stakeholders to implement BIM as one of the significant challenges.
The challenges that were found significant using the level of significance (p-value) were thirteen, which included, inability to use BIM tools properly due to lack of knowledge and expertise (p < 0.001), lack of experience with BIM workflows and tools (p < 0.001), difficulties integrating multiple software applications used in various fields (p < 0.001), limited understanding of BIM’s potential (p < 0.001), lack of standardised industry-wide BIM adoption and implementation methods (p < 0.001), challenges in adapting to the changes needed for the implementation of BIM (p < 0.001), no detailed legislative guidelines for implementing BIM (p < 0.001), high BIM implementation costs (p < 0.001), lack of awareness and requirement (p < 0.001), difficulties in integrating traditional techniques with BIM workflows (p = 0.002), reluctance to implement the new procurement procedures needed for BIM (p = 0.002), difficulties in developing a strategic vision for BIM integration (p = 0.002), and inconsistent procedures among different stakeholders (p = 0.013). Using both approaches, the remaining challenges were found to be significant, with an MIS ranging from 3.52 to 3.58. They included ineffective teamwork and collaboration (MIS = 3.58 and p-value = 0.205), communication issues among team members when sharing model information (MIS = 3.57 and p-value = 0.510), difficulties in creating effective project teams (MIS = 3.54 and p-value = 0.205), uncertainty regarding who is in charge and liable for the design and construction data (MIS = 3.54 and p-value = 0.344), inadequate technological infrastructure (MIS = 3.54 and p-value = 0.598), network connection infrastructure costs (MIS = 3.52 and p-value = 0.750), and resistance to change (MIS = 3.52 and p-value = 0.842).
While some challenges yielded p-values greater than 0.05 in the t-test analysis, these challenges were still deemed important based on industry perceptions and MIS values. Despite not being statistically significant, these challenges, such as “Resistance to Change,” are recognized as having practical implications for BIM adoption, as seen in similar studies (Puolitaival and Forsythe, 2016). Industry-wide adoption of new technologies often faces resistance, and even non-significant results can reflect real-world barriers to change. All the identified challenges from the literature were found significant, meaning they seriously affect BIM implementation in the Malawian construction industry. A study by Bouhmoud and Loudyi (2020) revealed the following challenges as very prominent in Africa: inadequate Infrastructure, the lack of steady power supply, lack of Internet access or connectivity, resistance to change, lack of common standards and guidelines, high initial cost for implementation, and lack or absence of clear contractual terms adapter to BIM utilisation. Several scholars stress the importance of interoperability and advocate for standardised data exchange formats to overcome integration issues when implementing BIM (Succar and Kassem, 2015; Mzyece et al., 2019). Furthermore, organisations face challenges in adopting BIM open standards, prohibiting seamless communication among software tools (Azhar, 2011). Tezel and Aziz (2017) highlight the challenge of establishing a standardised framework, while Sacks et al. (2018) point out the challenge of implementing standardised processes to promote consistency and efficiency across the construction industry. Additionally, Howard et al. (2017) indicated that there is a challenge to a limited understanding of BIM’s potential, highlighting the need to create awareness regarding the potential benefits of BIM.
However, as much as these challenges prohibit the Malawian construction industry to implement and adopt BIM, they are many and need to be reduced/grouped to enable a direct focus on how to deal with them and enhance BIM implementation in the industry. The following section focuses on dimension reduction (factor analysis), reducing the twenty challenges into three categories that the small Malawian construction industry could be able to deal with: BIM integration, collaborative workflow, and technological adaptability.
4.2 Challenges reduction (factor analysis)
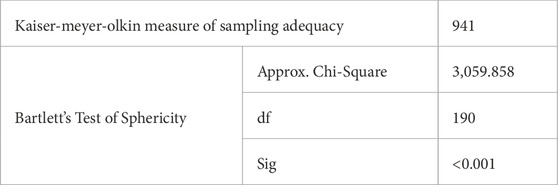
Factor analysis is a statistical technique used to reduce a large number of variables (in this case, 20) into smaller factors or components (Williams et al., 2010). Before the analysis, Bartlett’s test of sphericity and Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin (KMO) measure of sampling adequacy is done to test if the variables have a meaningful correlation different from zero or an identity matrix. Bartlett’s test is considered significant if it’s below the threshold of 0.05, while the KMO test is considered significant if it is over 0.5 (Williams et al., 2010). Table 5 below presents the results of these tests.
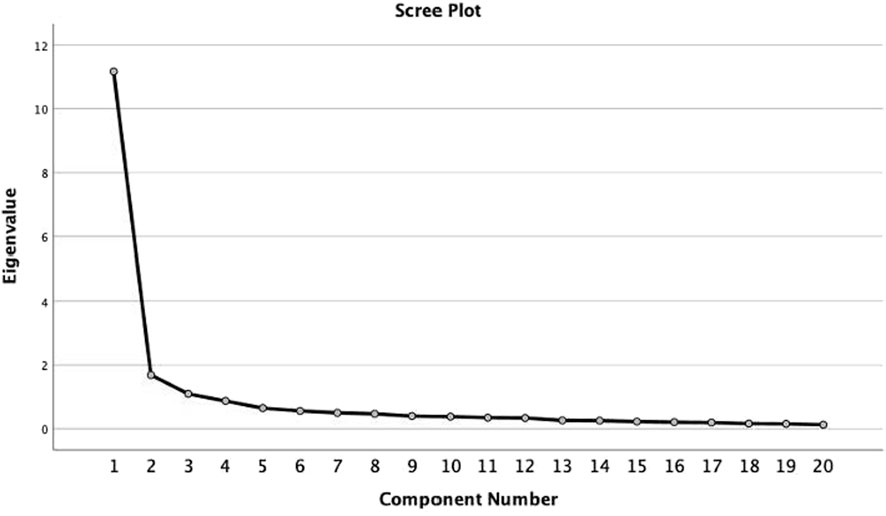
The KMO sample for this study was 0.941, indicating a high confidence level. This suggests that the variables in this study have a strong and significant correlation. Hence, the samples used for factor analysis are considered adequate. Moreover, the significance value is less than 0.05 (<0.001 to be exact), which assures that the variables have a strong correlation. The study then used Raymond Cattell’s scree plot as a method for factor extraction, as shown in Figure 2 (Hubbard and Allen, 1987). Table 6 presents an overview of the Rotated Factor Matrix, which demonstrates the 20 challenges that impact the adoption of BIM in the Malawian construction industry.
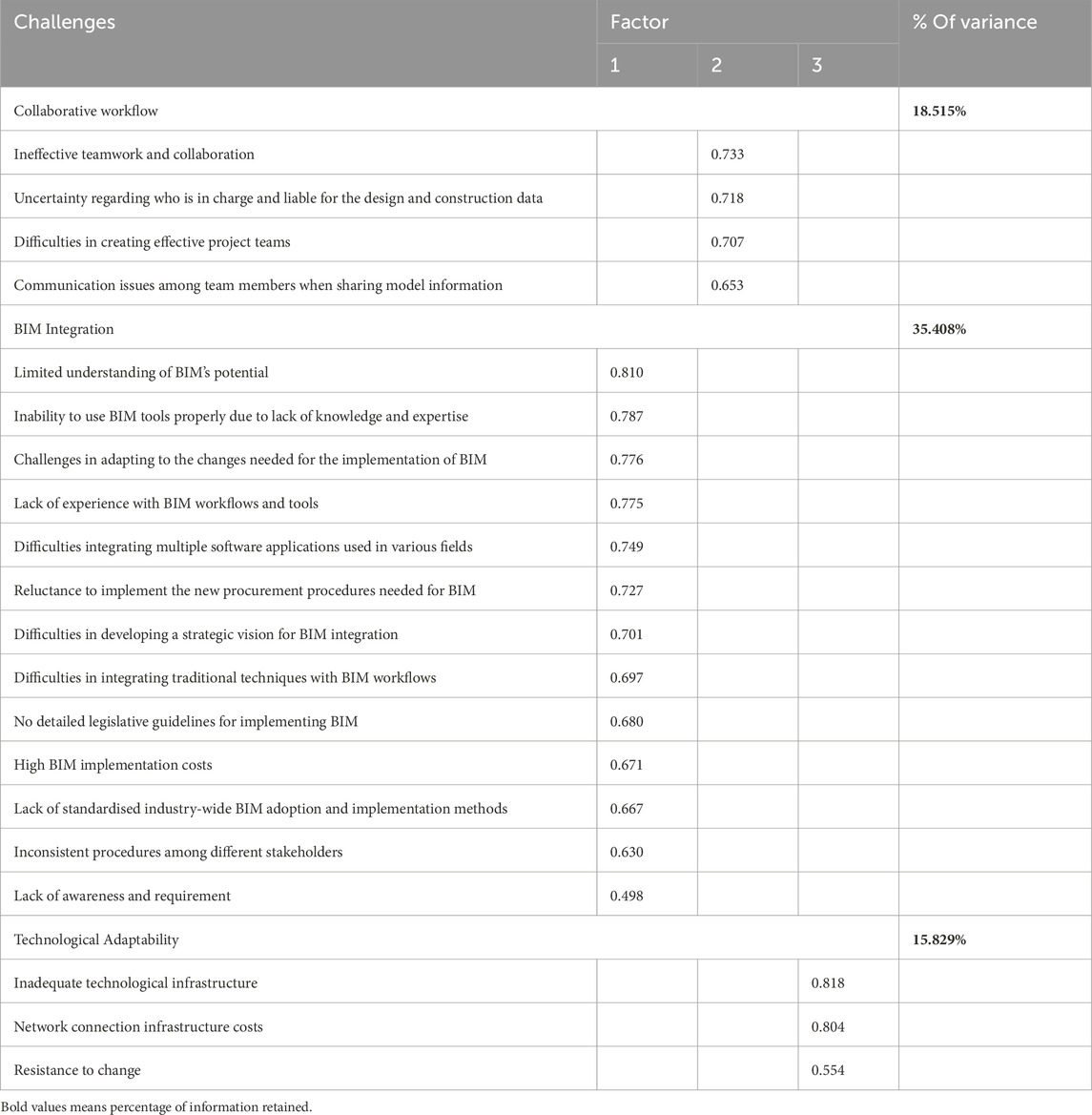
The factor analysis was performed using the Principal Component (PC) method with Varimax Rotation and Kaiser Normalisation, and the process of rotation reached convergence after 15 rounds (Hubbard and Allen, 1987). Out of the 20 variables, a total of three components were recovered, which jointly account for 69.753% of the overall variation while only losing 30.247% of the information. The focus of the discussion revolved around the Varimax rotated factor matrix, giving importance to factor loadings of above 0.300 (Williams et al., 2010).
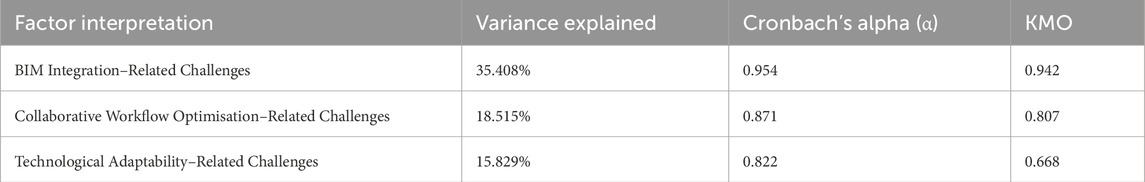
Component one consists of thirteen interconnected variables accounting for 35.408% of the total variance in this study following rotation. The thirteen separate variables collectively relate to BIM integration–related challenges. The second component, which accounted for 18.515% of the total variation, consisted of four different but interconnected independent variables jointly identified as collaborative workflow–related challenges. Lastly, component three, which had three independent variables loading onto it, accounted for 15.829% of the total variation in this study. The independent factors within this component were collectively referred to as technological adaptability–related challenges. The challenges within these components were ranked based on factor loading. A factor loading closer to −1 or 1 indicates that the variable strongly influences the component (Tavakol and Wetzel, 2020).
In order to confirm the accuracy of the factors, the unifactorial determination method was used (Table 7), which has been previously adopted in research by Ghosh and Jintanapakanont (2004). In this method, each factor is isolated and considered as an independent entity for future factor analysis. Unifactoriality is established when the average variance explained value exceeds the threshold of 0.5 (Rajabi et al., 2022). Furthermore, in this process, the KMO test was performed for each extracted factor to assess the sufficiency of the sample. The results show accuracy and reliability and that the samples were sufficient.
The factor analysis categorized the 20 challenges into three primary components: BIM integration, collaborative workflow, and technological adaptability. While each component focuses on distinct aspects of BIM implementation, some challenges inherently overlap between categories. For instance, “Inconsistent procedures among stakeholders” is primarily associated with BIM integration but also impacts collaborative workflow, as it affects how effectively different parties can coordinate. Similarly, “Lack of experience with BIM tools” influences both technological adaptability and integration, as technological proficiency is required to ensure seamless implementation across various disciplines. These overlaps suggest that certain challenges are multifaceted, influencing multiple BIM adoption and implementation areas. This interconnectivity reflects the complexity of BIM implementation, where addressing one challenge (e.g., improving technological infrastructure) could simultaneously mitigate related issues in other areas (e.g., enhancing collaboration). Therefore, while challenges have been grouped for clarity, solutions should be holistic, recognizing their broader impact across the BIM ecosystem, which this study has achieved.
4.3 Component 1: BIM integration–related challenges
The most critical challenge was the limited understanding of BIM’s potential (0.810) under this component. This challenge is followed by the inability to use BIM tools properly due to a lack of knowledge and expertise (0.787), ranked number two. The challenges follow in this sequence until challenge 13. The challenges include challenges in adapting to the changes needed for the implementation of BIM (0.776), the lack of experience with BIM workflows and tools, difficulties in integrating multiple software applications used in various fields (0.749), reluctance to implement the new procurement procedures needed for BIM (0.727), difficulties in developing a strategic vision for BIM integration (0.701), difficulties in integrating traditional techniques with BIM workflows (0.697), no detailed legislative guidelines for implementing BIM (0.680), high BIM implementation costs (0.671), lack of standardised industry-wide BIM adoption and implementation methods (0.667), inconsistent procedures among different stakeholders (0.630), and lack of awareness and requirement (0.498).
These challenges collectively show that they prohibit BIM integration. This is also seen in the work of Puolitaival and Forsythe (2016), who mention that a shortage of knowledge and proficiency in BIM technologies is a substantial problem for BIM integration. According to Succar (2009), education and training are critical in enhancing BIM competency. Challenges in BIM integration are well-researched in the literature. Several scholars stress the importance of interoperability and advocate for standardised data exchange formats to overcome integration issues (Succar and Kassem, 2015; Mzyece et al., 2019). Furthermore, Azhar (2011) suggest that organisations adopt BIM open standards to facilitate seamless communication among different software tools. Tezel and Aziz (2017) emphasise the need for a standardised framework, while Sacks et al. (2018) suggest that standardised processes can promote consistency and efficiency across the construction industry. Hence, it can be concluded that addressing the abovementioned challenges could help achieve seamless BIM integration in the Malawian construction industry processes and enforce widespread adoption.
4.4 Component 2: collaborative workflow–related challenges
It can be observed that the four variables under component two combine to present issues with BIM collaborative workflow. These challenges include “ineffective teamwork and collaboration (0.733),” “uncertainty regarding who is in charge and liable for the design and construction data (0.718),” “difficulties creating effective project teams (0.707),” and “communication issues amongst team members when sharing model information (0.653).” The challenges surrounding workflow, collaboration, data ownership, and liability are complex and widely researched in the context of BIM adoption. Barlish and Sullivan (2012) argue that legal frameworks must evolve to accommodate BIM’s collaborative nature, defining roles and responsibilities to mitigate uncertainties. This goes back to Succar and Kassem (2015), who mention that clear contractual agreements and industry-wide standards can contribute to resolving this challenge. Team dynamics play a pivotal role in the success of BIM implementation. Hence, Alreshidi et al. (2017) emphasised that creating an effective project team is critical. Furthermore, Bryde et al. (2013) highlight strategies such as team-building exercises, effective leadership, and fostering a collaborative culture that can enhance project team effectiveness. It can be deduced that all these challenges under this component are barriers to efficient collaborative workflow and mitigating them would allow for better BIM adoption.
4.5 Component 3: technological adaptability–related challenges
This component focused on technological infrastructure and change management. Hence, the challenges under this component include inadequate technological infrastructure (0.818), network connection infrastructure costs (0.804), and resistance to change (0.554). This component aligns with the findings of Olatunji and Sher (2015), who stress the importance of robust IT infrastructure for BIM implementation. According to Lu et al. (2017), organisations must invest in the latest technologies and ensure compatibility to harness the full potential of BIM. Herr and Fischer (2019) discussed network connection infrastructure cost issues, suggesting exploring cost-effective networking solutions, such as collaborating with technology providers and leveraging cloud-based platforms to alleviate financial burdens. Furthermore, Love et al. (2014) highlight stakeholders’ reluctance to embrace new processes and technologies in a study about the BIM framework for asset owners as a critical challenge. Anderson and Anderson (2010) suggest that change management strategies, including communication, education, and involving key shareholders early in the change process, are crucial for overcoming resistance.
5 Conclusion
This study utilised a questionnaire survey to investigate the challenges facing the adoption of BIM within the Malawian construction industry. The challenges range from the inability to use BIM tools properly due to lack of knowledge and expertise, ranked first, to resistance to change, ranked last. The findings indicated that all the challenges were critical, having an MIS above 3.5; although some challenges were found not significant for the Malawian construction industry through the one-sample t-test, they still have effects on the overall BIM adoption within the industry. Hence, they were considered for further analysis using factor analysis. The results of factor analysis identified three primary components—BIM Integration-related challenges, Collaborative Workflow-related challenges, and Technological Adaptability-related challenges—that significantly impact BIM implementation in the industry.
These components represent the key challenges to BIM adoption within the Malawian construction industry. When looking at the ranking of the variables (BIM challenges), it can be noted that the most critical group of challenges is the BIM integration, followed by collaborative workflow, and lastly, technological adaptability-related challenges. This means that for successful BIM implementation in the Malawian construction industry, the main focus must be to address everything related to BIM integration as a foundation for everything that follows. While trying to deal with this group, it is highly possible that some of the challenges of the two other groups could be mitigated. This is because the challenges to BIM implementation are interconnected, making it possible to deal with a few and solve many.
Understanding these findings would help raise BIM awareness, trigger insights into best practices and solutions, enhance collaboration and communication, improve training and education, etc., resulting in widespread BIM adoption in the Malawian construction industry. The study further contributes by providing a collection of structured challenges for BIM implementation, filling the knowledge gap about BIM challenges in the Malawian construction industry (Brown and Dant, 2009), and extending the scope of BIM research in Sub-Saharan Africa, where adoption is still in its early stages (Chagunda et al., 2022), especially among Southern African Development Community (SADC) countries.
The study faced several limitations that may impact the generalisability and depth of its findings. One limitation is the interchangeable use of BIM implementation and adoption, which, although reflective of local terminology practices, may obscure critical distinctions between strategic decision-making and operational challenges associated with BIM. Additionally, sample size constraints due to limited access to BIM-aware professionals restricted the breadth of data, while logistical challenges in data collection, stemming from infrastructure limitations, further impacted participant recruitment. Lastly, the restricted availability of BIM resources within the Malawian construction industry limited the scope of analysis on technology deployment and practical implementation, underscoring the need for increased local BIM resources and infrastructure development to support further research and industry advancement.
6 Recommendations
During the study, many problems and ideas were discovered and realised. Thus, it was considered imperative to provide some recommendations. For BIM benefits to be realised in the Malawian construction industry, the study recommends that the government and industry bodies, together with all relevant stakeholders, embrace BIM and encourage its adoption through collaboration, education, training, and awareness of its fundamentals and methodologies. Through state-owned enterprises (SOEs) and Public Private Partnerships (PPPs), the government should also invest in research and innovations, policy development, implementation frameworks, and BIM project piloting to ease ways in which the Malawian construction industry can reduce implementation challenges and increase implementation benefits.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent from the [patients/participants OR patients/participants legal guardian/next of kin] was not required to participate in this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
MN: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. WK: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. TM: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the European Union (EU) through the Africa Sustainable Infrastructure Mobility (ASIM) scholarship.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adekunle, P., Aigbavboa, C., Akinradewo, O., Oke, A., and Aghimien, D. (2022). Construction information management: benefits to the construction industry. Sustainability 14, 11366. doi:10.3390/su141811366
Aizat, K., Jamal, A., Fadhil Mohammad, M., Hashim, N., Mohamed, M. R., and Ramli, M. A. (2019). Challenges of building information modelling (BIM) from the Malaysian architect’s perspective. MATEC Web Conf. 266, 05003. doi:10.1051/MATECCONF/201926605003
Alreshidi, E., Mourshed, M., and Rezgui, Y. (2017). Factors for effective BIM governance. J. Build. Eng. 10, 89–101. doi:10.1016/J.JOBE.2017.02.006
Anderson, D., and Anderson, L. A. (2010). Beyond change management: how to achieve breakthrough results through conscious change leadership. John Wiley and Sons.
Antwi-Afari, M. F., Li, H., Pärn, E. A., and Edwards, D. J. (2018). Critical success factors for implementing building information modelling (BIM): a longitudinal review. Autom. Constr. 91, 100–110. doi:10.1016/J.AUTCON.2018.03.010
Apulu, I. (2012). Developing a framework for successful adoption and effective utilisation of ICT by SMEs in developing countries: a case study of Nigeria. Available at: https://wlv.openrepository.com/handle/2436/249899 (Accessed March 28, 2024).
Azhar, S. (2011). Building information modeling (BIM): trends, benefits, risks, and challenges for the AEC industry. Leadersh. Manag. Eng. 11, 241–252. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)LM.1943-5630.0000127
Bagozzi, R. P., and Yi, Y. (2012). Specification, evaluation, and interpretation of structural equation models. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 40, 8–34. doi:10.1007/s11747-011-0278-x
Barlish, K., and Sullivan, K. (2012). How to measure the benefits of BIM — a case study approach. Autom. Constr. 24, 149–159. doi:10.1016/J.AUTCON.2012.02.008
Bhalla, A. S., Chipeta, C., Taye, H., and Mkandawire, M. L. C. (2000). Globalization and sustainable human development: progress and challenges for Malawi. Blantyre, Malawi: UNCTAD/UNDP.
Bouhmoud, H., and Loudyi, D. (2020). Building information modeling (BIM) barriers in Africa versus global challenges. Colloquium Inf. Sci. Technol. CIST 2020-June, 495–501. doi:10.1109/CIST49399.2021.9357248
Brown, J. R., and Dant, R. P. (2009). The theoretical domains of retailing research: a retrospective. J. Retail. 85, 113–128. doi:10.1016/J.JRETAI.2009.04.003
Bryde, D., Broquetas, M., and Volm, J. M. (2013). The project benefits of building information modelling (BIM). Int. J. Proj. Manag. 31, 971–980. doi:10.1016/J.IJPROMAN.2012.12.001
Calitz, S., and Wium, J. (2022). A proposal to facilitate BIM implementation across the South African construction industry. J. South Afr. Institution Civ. Eng. 64, 1–9. doi:10.17159/2309-8775/2022/V64N4A3
Chagunda, J. G., Kuotcha, W., and Kafodya, I. (2022). “Factors influencing Building Information (BIM) implementation in developing countries,” in Building smart, resilient and sustainable infrastructure in developing countries, 273–280. doi:10.1201/9781003325321-29
Chilipunde, R. L., and Shakantu, W. (2010). Constraints and challenges faced by small, medium and micro enterprise contractors in Malawi. Port Elizabeth. Nelson Mandela Metropolitan University. Available at: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/145052616.pdf (Accessed November 22, 2023).
Chimhundu, S. (2016). A study on the BIM adoption readiness and possible mandatory initiatives for successful implementation in South Africa. Available at: http://hdl.handle.net/10539/22184.
Criminale, A., and Langar, S. (2017). “Challenges with BIM implementation: a review of literature,” in 53rd ASC annual international conference proceedings, 329–335.
Crotty, R. (2013). The impact of building information modelling: transforming construction. London, United Kingdom: SPON Press and Routledge. doi:10.4324/9780203836019
Dim, N. U., Ezeabasili, A. C. C., and Okoro, B. U. (2015). Managing the change process associated with Building information modeling (BIM) implementation by the public and private investors in the Nigerian building industry. Donnish J. Eng. Manuf. Technol. 2, 1–6.
Drucker, P. (2007). Management challenges for the 21st century. 1st Edn. London, United Kingdom: Routledge. doi:10.4324/9780080942384
Eastman, C. M., Teicholz, P., Sacks, R., and Liston, K. (2011). BIM handbook: a guide to building information modeling for owners, managers, designers, engineers and contractors. 2nd Edn. John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Elmualim, A., and Gilder, J. (2014). BIM: innovation in design management, influence and challenges of implementation. Archit. Eng. Des. Manag. 10, 183–199. doi:10.1080/17452007.2013.821399
Enegbuma, W. I., Aliagha, U. G., and Ali, K. N. (2014). Preliminary building information modelling adoption model in Malaysia A strategic information technology perspective. Constr. Innov. 14, 408–432. doi:10.1108/ci-01-2014-0012
Etikan, I., and Bala, K. (2017). Sampling and sampling methods. Biom Biostat. Int. J. 5, 215–217. doi:10.15406/bbij.2017.05.00149
Ghosh, S., and Jintanapakanont, J. (2004). Identifying and assessing the critical risk factors in an underground rail project in Thailand: a factor analysis approach. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 22, 633–643. doi:10.1016/J.IJPROMAN.2004.05.004
Grant, M. J., and Booth, A. (2009). A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies. Health Info Libr. J. 26, 91–108. doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x
Gray, J., Chambers, L., and Bounegru, L. (2012). The data journalism handbook: how journalists can use data to improve the news. Sebastopol, CA: O’Reilly Media, Inc. Available at: http://shop.oreilly.com/product/0636920025603.do.
Gu, N., and London, K. (2010). Understanding and facilitating BIM adoption in the AEC industry. Autom. Constr. 19, 988–999. doi:10.1016/J.AUTCON.2010.09.002
Haddaway, N. R., Collins, A. M., Coughlin, D., and Kirk, S. (2015). The role of Google Scholar in evidence reviews and its applicability to grey literature searching. PLoS One 10, e0138237. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0138237
Hanna, N. K. (2010). Transforming government and building the information society: challenges and opportunities for the developing world.
Herr, C. M., and Fischer, T. (2019). BIM adoption across the Chinese AEC industries: an extended BIM adoption model. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 6, 173–178. doi:10.1016/J.JCDE.2018.06.001
Hore, A., McAuley, B., and West, R. (2017). “BIM innovation capability programme of Ireland,” in LC3 2017: volume I – Proceedings of the joint Conference on Computing in construction (JC3), (heraklion, Greece: technological university dublin), 761–768. doi:10.24928/JC3-2017/0079
Howard, R., Restrepo, L., and Chang, C. Y. (2017). Addressing individual perceptions: an application of the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology to building information modelling. Int. J. Proj. Manag. 35, 107–120. doi:10.1016/J.IJPROMAN.2016.10.012
Hubbard, R., and Allen, S. J. (1987). An empirical comparison of alternative methods for principal component extraction. J. Bus. Res. 15, 173–190. doi:10.1016/0148-2963(84)90047-X
Jiang, R., Wu, C., Lei, X., Shemery, A., Hampson, K. D., and Wu, P. (2022). Government efforts and roadmaps for building information modeling implementation: lessons from Singapore, the UK and the US. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 29, 782–818. doi:10.1108/ecam-08-2019-0438
Kadangwe, S., and Emuze, F. (2017). Value creation and inherent constraints in the Malawian construction industry. Int. J. Constr. Supply Chain Manag. 7, 56–67. doi:10.14424/ijcscm702017-56-67
Kotabe, M., and Kothari, T. (2016). Emerging market multinational companies’ evolutionary paths to building a competitive advantage from emerging markets to developed countries. J. World Bus. 51, 729–743. doi:10.1016/J.JWB.2016.07.010
Kotrlik, J., and Higgins, C. (2001). Organizational research: determining appropriate sample size in survey research appropriate sample size in survey research. Inf. Technol. Learn. Perform. J. 19, 43.
Kulemeka, P. J., Kululanga, G., and Morton, D. (2015). Critical factors inhibiting performance of small-and medium-scale contractors in sub-Saharan region: a case for Malawi. J. Constr. Eng. 2015, 1–17. doi:10.1155/2015/927614
Leedy, P. D., and Ormrod, J. E. (2015). Practical research: planning and design. 11th Edn. Boston, MA: Pearson Education Limited.
Lekan, A., Clinton, A., Stella, E., Moses, E., and Biodun, O. (2022). Construction 4.0 application: industry 4.0, Internet of things and lean construction tools’ application in quality management system of residential building projects. Buildings 12, 1557. doi:10.3390/buildings12101557
Love, P. E. D., Matthews, J., Simpson, I., Hill, A., and Olatunji, O. A. (2014). A benefits realization management building information modeling framework for asset owners. Autom. Constr. 37, 1–10. doi:10.1016/J.AUTCON.2013.09.007
Lu, Y., Wu, Z., Chang, R., and Li, Y. (2017). Building Information Modeling (BIM) for green buildings: a critical review and future directions. Autom. Constr. 83, 134–148. doi:10.1016/J.AUTCON.2017.08.024
Manderson, A. D., Jefferies, M. C., and Brewer, G. J. (2017) “An analysis of the integration of Building Information Modelling (BIM) in standard construction contracts,” in Integrated building information modelling, 82–101.
Mariotti, C., Hamer, J., and Coffey, C. (2018). Closing the divide in Malawi: how to reduce inequality and increase prosperity for all. Nairobi, Kenya: Oxfam. doi:10.21201/2018.1794
Moodley, V., Mathye, K., and Radebe, S. (2016). Teaching BIM in schools of architecture of South African universities. Johannesburg: University of Witwatersrand. Available at: https://hdl.handle.net/10539/25411 (Accessed November 24, 2023).
Mzyece, D., Ndekugri, I. E., and Ankrah, N. A. (2019). Building information modelling (BIM) and the CDM regulations interoperability framework. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 26, 2682–2704. doi:10.1108/ecam-10-2018-0429
National Construction Industry Council (2024). Active registrations. Available at: https://www.ncic.mw/reg/active-registrations/ (Accessed June 2, 2024).
Ndwandwe, M., Kuotcha, W., and Mkandawire, T. (2024). Organizational readiness for building information modeling implementation in Malawi: awareness and competence. Buildings 14, 2279. doi:10.3390/buildings14082279
Ngoma, I., Kafodya, I., Kloukinas, P., Novelli, V., Macdonald, J., and Goda, K. (2019). Building classification and seismic vulnerability of current housing construction in Malawi. Malawi J. Sci. Technol. 11 (1), 57–72.
Oke, A., and Fernandes, F. A. P. (2020). Innovations in teaching and learning: exploring the perceptions of the education sector on the 4th industrial revolution (4IR). J. Open Innovation Technol. Mark. Complex. 6, 31. doi:10.3390/JOITMC6020031
Olanrewaju, O. I., Chileshe, N., Babarinde, S. A., and Sandanayake, M. (2020). Investigating the barriers to building information modeling (BIM) implementation within the Nigerian construction industry. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 27, 2931–2958. doi:10.1108/ecam-01-2020-0042
Olatunji, O. A. (2011). Modelling the costs of corporate implementation of building information modelling. J. Financial Manag. Prop. Constr. 16, 211–231. doi:10.1108/13664381111179206
Olatunji, O. A., and Sher, W. (2015). Estimating in geometric 3D CAD. J. Financial Manag. Prop. Constr. 20, 24–49. doi:10.1108/jfmpc-07-2014-0011
Olugboyega, O., and Windapo, A. (2019). A comprehensive BIM implementation model for developing countries: comprehensive BIM implementation model. J. Constr. Proj. Manag. Innovation 9, 83–104. doi:10.36615/jcpmi.v9i2.187
Phiri, M., and Smallwood, J. (2010). The impact of corruption on the Malawian construction industry. Acta Structilia J. Phys. Dev. Sci. 17, 107–125. Available at: https://hdl.handle.net/10520/EJC110051
Puolitaival, T., and Forsythe, P. (2016). Practical challenges of BIM education. Struct. Surv. 34, 351–366. doi:10.1108/ss-12-2015-0053
Rajabi, M. S., Rezaeiashtiani, M., Radzi, A. R., Famili, A., Rezaeiashtiani, A., and Rahman, R. A. (2022). Underlying factors and strategies for organizational BIM capabilities: the case of Iran. Appl. Syst. Innov. 5, 109–115. doi:10.3390/ASI5060109
Rekola, M., Kojima, J., and Mäkeläinen, T. (2010). Towards integrated design and delivery solutions: pinpointed challenges of process change. Archit. Eng. Des. Manag. 6, 264–278. doi:10.3763/AEDM.2010.IDDS4
Sacks, R., Eastman, C., Lee, G., and Teicholz, P. (2018). BIM handbook: a guide to building information modeling for owners, designers, engineers, contractors, and facility managers. John Wiley and Sons.
Sataloff, R. T., and Vontela, S. (2021). Response rates in survey research. J. Voice 35, 683–684. doi:10.1016/j.jvoice.2020.12.043
Saunders, M., Lewis, P., and Thornhill, A. (2012). Research methods for business students. Harlow, United Kingdom: Pearson education.
Sinoh, S. S., Othman, F., and Ibrahim, Z. (2020). Critical success factors for BIM implementation: a Malaysian case study. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 27, 2737–2765. doi:10.1108/ECAM-09-2019-0475
Succar, B. (2009). Building information modelling framework: a research and delivery foundation for industry stakeholders. Autom. Constr. 18, 357–375. doi:10.1016/J.AUTCON.2008.10.003
Succar, B., and Kassem, M. (2015). Macro-BIM adoption: conceptual structures. Autom. Constr. 57, 64–79. doi:10.1016/J.AUTCON.2015.04.018
Succar, B., Sher, W., and Williams, A. (2013). An integrated approach to BIM competency assessment, acquisition and application. Autom. Constr. 35, 174–189. doi:10.1016/J.AUTCON.2013.05.016
Tavakol, M., and Dennick, R. (2011). Making sense of Cronbach’s alpha. Int. J. Med. Educ. 2, 53–55. doi:10.5116/IJME.4DFB.8DFD
Tavakol, M., and Wetzel, A. (2020). Factor Analysis: a means for theory and instrument development in support of construct validity. Int. J. Med. Educ. 11, 245–247. doi:10.5116/IJME.5F96.0F4A
Tezel, A., and Aziz, Z. (2017). From conventional to IT based visual management:A conceptual discussion for lean construction.
Tholibon, D. A., Nujid, M. M., Mokhtar, H., Rahim, J. A., Aziz, N. F. A., and Tarmizi, A. A. A. (2021). Relative importance Index (RII) in ranking the factors of employer satisfaction towards industrial training students. Online Submiss. 2, 493–503. doi:10.46966/ijae.v2i4.187
Williams, B., Onsman, A., Brown, T., Andrys Onsman, P., and Ted Brown, P. (2010). Exploratory factor analysis: a five-step guide for novices. Australas. J. Paramedicine 8, 1–13. doi:10.33151/AJP.8.3.93
Wong, K. A., Wong, K. F., and Nadeem, A. (2011). Building information modelling for tertiary construction education in Hong Kong. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. (ITcon) 16, 467–476.
Xiong, B., Skitmore, M., and Xia, B. (2015). A critical review of structural equation modeling applications in construction research. Autom. Constr. 49, 59–70. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2014.09.006
Yeboua, K., le Roux, A., and Cilliers, J. (2023). Malawi: geographic futures. Available at: https://futures.issafrica.org/geographic/countries/malawi/ (Accessed April 3, 2024).
Keywords: BIM; BIM challenges, BIM implementation, building information modeling, construction industry, Malawi
Citation: Ndwandwe M, Kuotcha W and Mkandawire T (2024) Building information modeling: implementation challenges in the Malawian construction industry. Front. Built Environ. 10:1474032. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2024.1474032
Received: 31 July 2024; Accepted: 11 November 2024;
Published: 22 November 2024.
Edited by:
Changsu Shim, Chung-Ang University, Republic of KoreaReviewed by:
Quan Nguyen, National University of Civil Engineering, VietnamSeungjun Ahn, Hongik University, Republic of Korea
Copyright © 2024 Ndwandwe, Kuotcha and Mkandawire. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Melusi Ndwandwe, bWVsdXNpd2lzZUBnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Melusi Ndwandwe
Melusi Ndwandwe Witness Kuotcha2
Witness Kuotcha2