
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. , 20 March 2025
Sec. Biomechanics
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2025.1551993
 Yong-Jiang Li1,2
Yong-Jiang Li1,2 Hui-Min Hou3
Hui-Min Hou3 Zheng Liu3
Zheng Liu3 Chun-Dong Xue1,2
Chun-Dong Xue1,2 Jing-Tong Na1
Jing-Tong Na1 Qing-Mei Meng1
Qing-Mei Meng1 Zhe-Yuan Li1
Zhe-Yuan Li1 Hai-Yang Sun1
Hai-Yang Sun1 Yu-Lin Wu1
Yu-Lin Wu1 Shu-Xin Liu1,2*
Shu-Xin Liu1,2* Kai-Rong Qin1,2*
Kai-Rong Qin1,2*Introduction: The dramatic hemodynamic disturbances induced by arteriovenous fistula (AVF) creation are universally acknowledged as the triggering factors for AVF dysfunction. The postoperative blood redistribution is greatly relevant with the flow disturbances of the AVF, such as disturbed flow, low wall shear stress (WSS), and oscillating WSS. However, the relationship between blood redistribution and hemodynamic disturbances of AVF remains unexamined. The role of clinically observed retrograde blood flow at the distal radial artery is rarely understood.
Methods: In this study, an idealized AVF model was developed with clinical data collected from end-stage renal disease patients. By considering the postoperative blood redistribution, the influence of the blood flow rate ratio on hemodynamic disturbances is numerically studied.
Results and discussion: The results demonstrate that the creation of the AVF can result in flow disturbances such as vortex, reciprocating flow, and low and reciprocating WSS, whose occurrence regions are consistent with clinical observations. The flow rate ratio and flow direction of the distal radial artery play important roles in regulating the low-WSS area within the AVF anastomosis, especially for the flow rate of the proximal radial artery (PRA). Moreover, the clinically observed retrograde blood flow in the distal radial artery contributes to the reduction in the low-WSS area, revealing a compensatory mechanism. This study can provide valuable insights for understanding the effect of blood redistribution on flow disturbances in the AVF, as well as the compensatory role of the retrograde distal radial artery flow, which helps optimize blood redistribution for a well-functioning AVF.
Hemodialysis is the most common treatment method for patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). To achieve efficient hemodialysis, a well-functioning vascular access (VA) is required (Bello et al., 2022; Shahinian et al., 2020). Typically, the radial–cephalic arteriovenous fistula (AVF) is the most preferred VA and strongly recommended by clinical guidelines worldwide due to its advantages of longevity, low complications, and low morbidity (Lok et al., 2020; Arhuidese et al., 2022). Despite being the optimal VA, significant primary failure rates and unsuccessful maturation rates have been reported (Shiu et al., 2019; Jia et al., 2015; Shiu et al., 2019; Huber et al., 2021; Venkat Ramanan et al., 2022).
It is universally acknowledged that the dramatic changes in hemodynamic effects after AVF creation are mainly relevant to AVF maturation failure. The resulting flow disturbances referring to the disturbed flow, low wall shear stress (WSS), and oscillating WSS are considered critical hemodynamic factors leading to neointimal hyperplasia (NIH) and further AVF maturation failure (Tordoir et al., 2018; Jia et al., 2015; Shiu et al., 2019; Colley et al., 2020; Hyde-Linaker et al., 2022; Ene-Iordache et al., 2015; Browne et al., 2015; Sadaghianloo et al., 2019). AVF bypasses the resistance vessels of the distal extremity and forms a short circuit between the arterial and the venous systems. As a result, the rate of volume flow through AVF increases dramatically (Colley et al., 2020; Dixon, 2006). The dramatic hemodynamic changes are greatly relevant to AVF anastomosis techniques, including anastomosis types, size, and angle and AVF configuration Ene-Iordache et al. (2015); Ene-Iordache and Remuzzi (2017); Rosado-Toro et al. (2022); Pike et al. (2017); Van Canneyt et al. (2010); Iori et al. (2015); Carroll et al. (2019); Alam et al. (2022); Suqin et al. (2020). In some cases, owing to the overall resistance balance after AVF creation, there will be retrograde flow of blood from the distal artery to feed the low-resistance vein (Ene-Iordache and Remuzzi, 2012; Colley et al., 2020; Dixon, 2006; Ramuzat et al., 2003; Hyde-Linaker et al., 2022; Sivanesan et al., 1998). Hence, understanding the role of postoperative blood redistribution in the flow disturbances of AVF is essential for probing the hemodynamic mechanisms of AVF maturation failure.
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is a common methodology that allows for reconstruction and visualization of the AVF hemodynamic microenvironment (Ene-Iordache and Remuzzi, 2012; Hyde-Linaker et al., 2022; Ene-Iordache et al., 2015; Ene-Iordache and Remuzzi, 2017; Rosado-Toro et al., 2022; Pike et al., 2017; Van Canneyt et al., 2010; Iori et al., 2015; Carroll et al., 2019; Alam et al., 2022; Suqin et al., 2020; Carroll et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2020). CFD with idealized geometry has the advantages of low computational cost and facilitation of parametric analysis. Various CFD studies were conducted with ideal AVF models to analyze different AVF surgical techniques and optimize flow pathways (Ene-Iordache and Remuzzi, 2012). An ideal end-to-side AVF model was proposed to study the influence of anastomosis size and angle on hemodynamic factors (Van Canneyt et al., 2010; Yang et al., 2020). The pressure decreased with a larger anastomosis cross-sectional area and an angle wider than 43°. An anastomosis angle exceeding 58° would lead to a retrograde flow of blood from the distal artery. The effects of the arterial curvature on blood flow and oxygen transport patterns within the AVF were also investigated (Iori et al., 2015). The results revealed that a placing a vein graft onto the outer curvature of a curved artery would avoid unsteady flow and placing a vein graft onto a straight artery or the inner curvature of a curved artery would prevent low WSS and low lumen-to-wall oxygen flux that leads to the development of NIH. Some numerical studies (Ene-Iordache and Remuzzi, 2012; 2017; Remuzzi and Ene-Iordache, 2013) have been conducted to characterize the patterns of disturbed flow and WSS associated with stenosis and vascular remodeling, including the low and oscillating WSS as well as the multidirectional and reciprocating near-wall flow. The CFD simulations with an end-to-side configuration showed good agreement with experimental studies (Colley et al., 2020; Remuzzi and Ene-Iordache, 2013; Gunasekera et al., 2020). These abovementioned CFD studies elucidate complex hemodynamic factors related to AVF outcomes (NIH, stenosis, and thrombosis), which helps understand the etiology of AVF maturation failure. However, how post-operative blood redistribution affects flow disturbances in AVF remains unexamined. The role of clinically observed retrograde blood flow at the distal radial artery is not well understood.
In the present study, a CFD study is conducted to analyze the effect of blood redistribution on the flow disturbance of the AVF. An ideal AVF model is developed using realistic clinical data collected from ESRD patients. By considering the blood redistribution induced by AVF creation in terms of varying flow rate ratios, the hydrodynamic disturbances in the AVF are numerically studied, including flow patterns and abnormal areas with low and reciprocating WSS. Moreover, the role of retrograde blood flow at the distal radial artery is identified.
A female patient undergoing maintenance hemodialysis for 13 weeks was included in the trial and data collected. An end-to-side anastomosis was surgically created to construct a radiocephalic AVF for hemodialysis access (Figure 1). The waveforms of blood flow velocities at the proximal radial artery (PRA) and distal radial artery (DRA) of the AVF in the left forearm were measured using the Doppler ultrasonic detector (ARIETTA 60, Hitachi, Japan). The direction of blood flow (antegrade or retrograde) in the DRA is determined by the color (red or blue) of the ultrasound image for identification. Simultaneously, the diameters of the PRA, DRA, and distal cephalic vein (DCV) were measured 4 cm away from the anastomosis (Supplementary Table S1). The blood pressure at the distal cephalic vein is evaluated using the invasive pressure sensor (TRAM 451, GE Healthcare, United States). The absolute pressure at the cephalic vein is
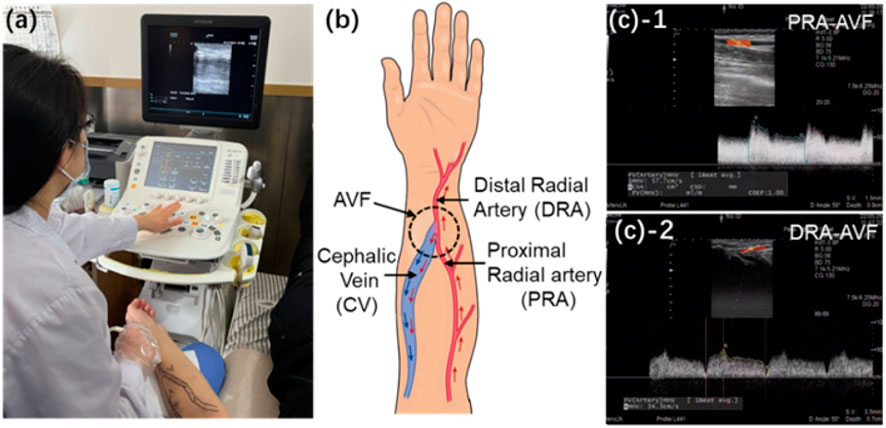
Figure 1. (a) Real image during ultrasonic acquisition of blood flow velocity. (b) Schematic of radial–cephalic AVF. (c) Clinical measurements of blood flow velocities at the PRA and DRA of AVF and RA and CV of the normal forearm.
An idealized end-to-side AVF geometry (Figure 2) is reconstructed based on the measured data of the patient (Table 1). Two lumens with diameters of 3.0 mm and 1.2 mm are idealized accordingly as PRA and DRA by aligning their outer edges. A lumen with a diameter of 5.0 mm is modeled as the cephalic vein. The anastomotic segment is merged smoothly using a basis spline curve with an anastomosis angle of 45
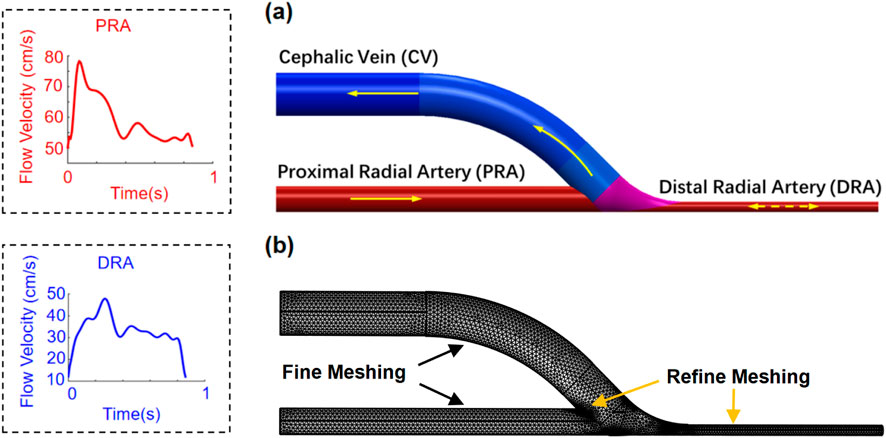
Figure 2. Geometry (a) and meshing (b) of the patient-specific idealized AVF model. Flow velocities at the PRA and DRA are presented in one cardiac cycle.
The idealized AVF model was reconstructed using SOLIDWORKS 2021 and further imported into the simulation software COMSOL Multiphysics® for analysis. To conduct the simulation, the boundary conditions were defined according to the clinical acquisition data. A uniform velocity condition (Figure 2) extracted from the ultrasonic image (Figure 1) was applied at the PRA inlet of the AVF model. At the DRA, a uniform velocity condition (Figure 2), referring to the same velocity across the entire cross-section, extracted from the ultrasonic image (Figure 1), was set, where the flow direction depends on the anterograde or retrograde flow of blood. A uniform pressure condition, referring to the same pressure across the entire cross-section, was adopted at the CV outlet. Infinite conditions were added to extend the PRA, DRA, and CV segments to allow sufficient length for flow to fully develop prior to entering the AVF anastomosis. Slip-free boundary conditions (the no-slip hypothesis that the fluid velocity at the wall is 0) were adopted at the walls of blood vessels. A mesh comprising
The creation of the AVF results in blood redistribution along the blood circulation circuits of the upper limb. The blood flow from the left ventricle to the PRA bifurcates into two main circuits: the first circuit goes to the upper extremity, then drains into the vein of the upper limb, and finally back to the right atrium, and the other circuit passes through the AVF anastomosis, then flows into the CV, and returns to the right atrium. As a result, the total flow rate of the PRA (defined as
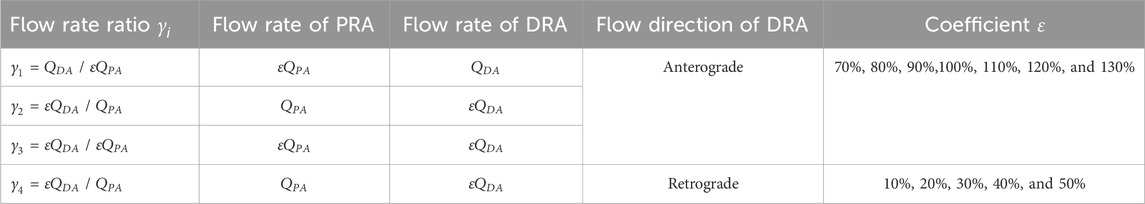
Table 2. Simulation conditions of AVF blood redistribution characterized by the flow rate ratio
After CFD simulations, the distributions of flow velocity, streamline, and WSS were exported. A coordinate system (Figure 3) is defined with the origin at the center of anastomosis. The y-axis is parallel to the direction of the proximal vein. The x-axis is in the positive direction to the outer edge of the anastomosis. To characterize the flow disturbance, the streamlines are displayed at the cross-section S1 near the anastomosis, with their normal vectors parallel to the y-axis. The evolutions of flow velocity at five evenly spaced points (red dots) are observed at the vortex region (Figure 3). To characterize the WSS, the distribution of the WSS magnitude is calculated across the whole computational domain, and the distribution of WSS is observed at the cross-section S1 around the vortex region. The evolutions of WSS at six evenly spaced points (black dots) are observed (Figure 3). At different flow rate ratios
The flow patterns and disturbances in the AVF are numerically characterized. The distributions of blood flow velocity are shown according to the intervals of maximum, average, and minimum velocities (Figure 4). In all cases, the regions of high flow velocity emerge, in which flow from the PRA normally to the outer edge of the anastomosis is observed (Figure 4A). The high-velocity stream separates two areas with low flow velocity and vortex flow. As indicated in Figure 4B, the distribution of streamlines clearly reflects two vortex areas located on both sides of the high-velocity stream. One emerges above the high-velocity stream and appears at the inner edge of the anastomosis to the CV end, while another emerges below the high-velocity stream and appears at the anastomosis opening to the PRA end. The findings are consistent with clinical observations and previous results (Colley et al., 2020; Iori et al., 2015; Remuzzi and Ene-Iordache, 2013).
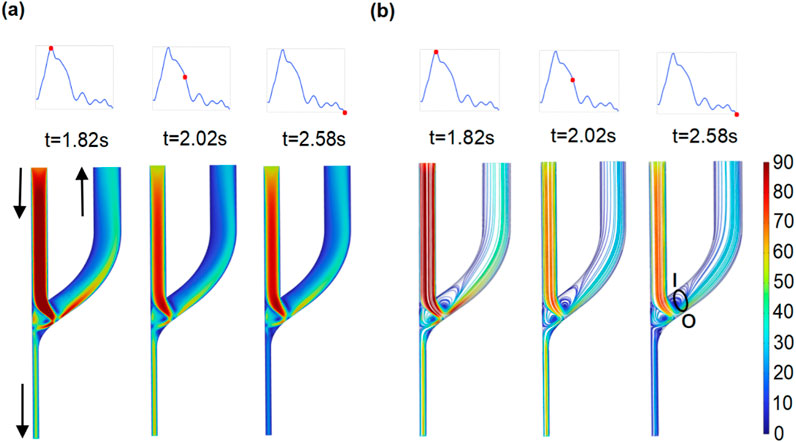
Figure 4. Distribution of flow velocity and streamline at the whole domain of the AVF model. (a) Flow velocity (cm/s). (b) Distribution of streamlines.
Within the vortex region, the topology of streamlines at the plane of S1 (Figure 5) is displayed. At selected time intervals, the area of the negative velocity opposite to the y-axis appears at the inner edge of plane S1 and varies with the flow velocity (Figure 5). Simultaneously, the circular current of streamlines reveals the existence of the vortex, which varies in size depending on the pulsatile blood flow velocity. At this specific section of the vortex, the evolutions of flow velocities are observed at five evenly spaced points of plane S1 (left subfigure in Figure 5). The alternatively positive and negative variations from the outer to inner edge of plane S1 probe once again the existence of the vortex, which is associated with the development of NIH (Remuzzi and Ene-Iordache, 2013; Cunnane et al., 2019).
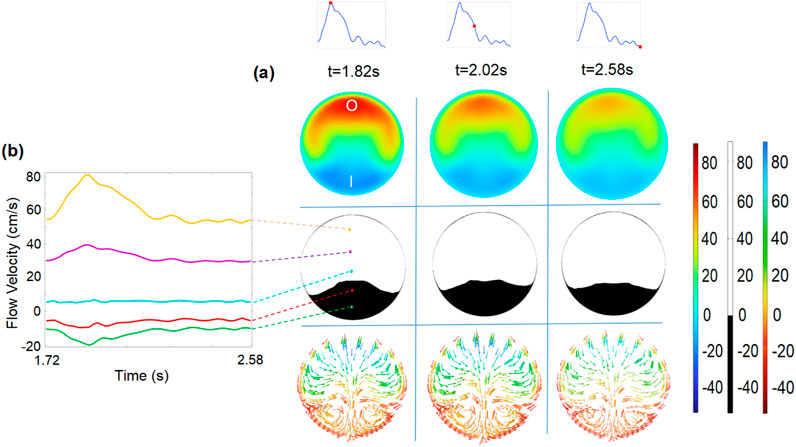
Figure 5. (a) Flow velocity (
The WSS is the critical hemodynamic factor associated with maintaining the function of the developed AVF. Therefore, the WSS values at the vessel walls of the AVF (Figure 6A) are analyzed. The high WSS (
The relatively low WSS (
Blood redistribution resulting from AVF creation varies with each individual and surgical method, ultimately leading to the change in the blood flow rate and the DRA ratio. Herein, we characterize the effect of the flow rate ratio
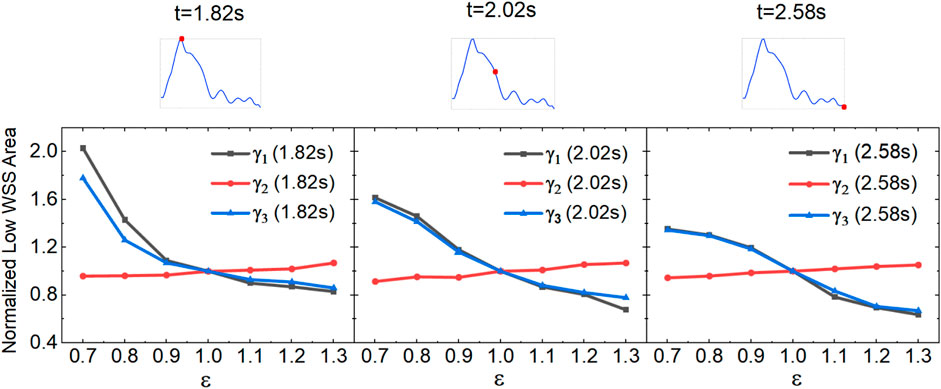
Figure 8. Variation of low-WSS areas at different flow rate ratios for the anterograde DRA blood flow.
To characterize the role of clinically observed retrograde DRA flow, the flow rate of the PRA is kept constant; the distributions of the blood flow velocity and the corresponding streamlines are shown in Figure 9. The blood flow distributions and the vortex locations are similar to those observed in the anterograde blood flow case. Interestingly, the area of the two vortex regions at the peri-anastomosis slightly decreases due to the increase in the total flow rates in the venous segment.

Figure 9. Distribution of flow velocity (a) and streamline (b) within AVF for the retrograde DRA blood flow (
To quantify the varying retrograde DRA flow on the low-WSS area, we measured the low-WSS area at different flow rate ratios
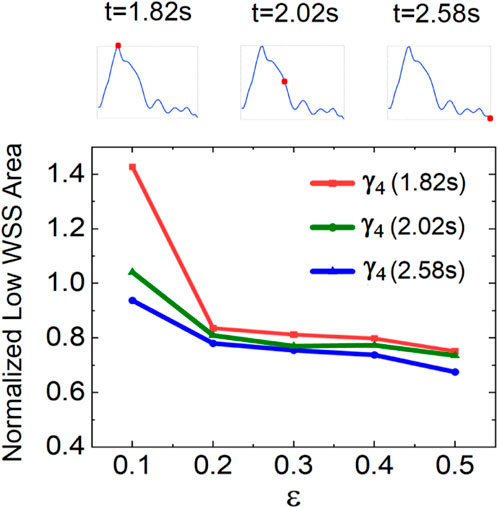
Figure 10. Variation in low-WSS areas at different flow rate ratios in the retrograde DRA blood flow.
The radiocephalic AVF is the optimal VA for hemodialysis. However, it suffers from high rates of early-maturation failure and peri-anastomotic restenosis owing to the dramatic hemodynamic disturbances after AVF creation (Colley et al., 2020; Dixon, 2006). In this study, an idealized end-to-side AVF model was constructed to analyze the effects of blood redistribution on AVF hemodynamic disturbances. The simulation results demonstrated the existence of the vortex, reciprocating flow, and low and reciprocating WSS around the AVF anastomosis (Figures 4–7); their occurrence regions are in agreement with clinical observations and previous results (Jia et al., 2015; Ene-Iordache and Remuzzi, 2012; Hyde-Linaker et al., 2022; Van Canneyt et al., 2010). The complex hemodynamic disturbances in the anastomotic region are proven to be highly prone to the AVF complications such as NIH and vascular stenosis (Colley et al., 2020). Therefore, understanding the hemodynamic disturbance after AVF creation and its related factors is essential for avoiding further AVF complications.
In the simulations, we have quantitatively characterized the low-WSS region, which is a critical hemodynamic factor for maintaining the AVF function. The dependence of the low-WSS area on the flow rate ratio of the PRA to DRA and the DRA flow direction was analyzed. The significant roles of the PRA flow rate and retrograde DRA flow in reducing the area of the low-WSS regions were revealed (Figures 8–10). For this reason, the optimization of blood redistribution within AVF can be beneficial to reduce the low-WSS area, especially for high PRA flow rate and retrograde DRA flow. Therefore, in surgical operations (Farber et al., 2016) or hemodialysis, the resistance and compliance of both extremities and distal CV should be considered (Sadaghianloo et al., 2019; Remuzzi and Ene-Iordache, 2013) to regulate the postoperative blood redistribution by enlarging the anastomotic opening and optimizing the artery-to-vein configuration (Gunasekera et al., 2021; Farrington et al., 2020; Shahverdyan et al., 2021). From another perspective, sports exercise and external counterpulsation are well-recognized non-invasive mechanical methods for improving the blood redistribution (Chen et al., 2023). Accordingly, appropriate exercise or counterpulsation intervention can regulate the blood redistribution after AVF creation, which may be an alternative non-invasive approach to reduce hemodynamic disturbance for a long-term AVF function (Wang et al., 2018; Andrade et al., 2021).
In clinical practice, the retrograde blood flow of the DRA is frequently observed and has been reported in previous studies (Ene-Iordache and Remuzzi, 2012; Colley et al., 2020; Dixon, 2006; Ramuzat et al., 2003; Hyde-Linaker et al., 2022; Sivanesan et al., 1998). However, the role of the retrograde DRA blood flow is rarely considered. Some studies (Ene-Iordache and Remuzzi, 2012; Colley et al., 2020; Sivanesan et al., 1998) demonstrated that the retrograde blood flow of the DRA is a result of the overall resistance balance in the newly created vascular access. Our findings suggest that the retrograde DRA flow can contribute to the reduction in the low-WSS region in the AVF anastomosis, which is the well-known risk factor for NIH formation and stenotic lesions. The retrograde DRA flow is beneficial to the vascular microenvironment. This finding reveals that the occurrence of retrograde blood flow at the DRA may be a compensatory mechanism for optimizing blood redistribution and improving the hydrodynamic microenvironment. Several studies have demonstrated that optimizing the AVF hemodynamic microenvironment can promote AVF maturation by regulating surgical techniques, anastomosis size and angle, and AVF graft design (Van Canneyt et al., 2010; Iori et al., 2015). Owing to individual differences in blood circulation among patients, it is still challenging to adjust the blood redistribution in the real AVF. Based on our findings, enhancing retrograde blood flow of the DRA would contribute to AVF hemodynamic micro-environment AVF maturation. Therefore, upper limb and handgrip exercises can be a good strategy to enhance the retrograde flow of the DRA for post-operative AVF maturation (Chen et al., 2023; Nantakool et al., 2022).
It should be noted that the proposed idealized AVF model is developed under the rigid wall assumption. The rigid model would fail to recognize the effect of circumferential stress induced by pulsating blood pressure (Rangel et al., 2023). As vascular remodeling during AVF maturation is affected simultaneously by WSS and blood pressure, the elasticity of blood vessels should be further considered in future research.
In this study, an idealized end-to-side AVF model is reconstructed using clinically measured data. The effect of blood redistribution on the flow disturbance of the AVF has been investigated by CFD analysis. The results indicated that flow vortex, reciprocating flow, and low and reciprocating WSS result from the creation of the AVF, and their occurrence regions are consistent with clinical observations. The hydrodynamic disturbances significantly depend on the flow rate ratio of the PRA to DRA and the DRA flow direction. The flow rate of the PRA plays an important role in affecting the low-WSS area. The retrograde DRA flow can contribute to the reduction of low-WSS region in the AVF anastomosis, revealing a compensatory mechanism. The findings provide essential information for understanding the hydrodynamic changes after AVF creation and the compensatory role of retrograde distal radial artery flow, which helps optimize blood redistribution to reduce the flow disturbance of the AVF.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
The patient was provided with detailed information and informed consent was written to participate in this study. The procedure was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Central Hospital of Dalian University of Technology.
Y-JL: Conceptualization, Writing–review and editing. H-MH: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing–original draft. ZL: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing–original draft. C-DX: Software, Visualization, Writing–original draft. J-TN: Software, Visualization, Writing–original draft. Q-MM: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–original draft. Z-YL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–original draft. H-YS: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–original draft. Y-LW: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–original draft. S-XL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing–review and editing. K-RQ: Conceptualization, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Applied Basic Research Project of Liaoning Province (Grant No. 2023144).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2025.1551993/full#supplementary-material
Alam, N., Walsh, M., and Newport, D. (2022). Experimental evaluation of a patient specific brachio-cephalic arterio venous fistula (avf): velocity flow conditions under steady and pulsatile waveforms. Med. Eng. and Phys. 106, 103834. doi:10.1016/j.medengphy.2022.103834
Andrade, F. P., Nolasco, T., Knorst, M. M., and Eidt Rovedder, P. M. (2021). Aerobic exercise increases vascular diameter of arteriovenous fistula in hemodialysis patients. Blood Purif. 51, 732–738. doi:10.1159/000519880
Arhuidese, I. J., Cooper, M. A., Rizwan, M., Nejim, B., and Malas, M. B. (2022). Vascular access for hemodialysis in the elderly. J. Vasc. Surg. 69, 517–525.e1. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2018.05.219
Bello, A. K., Okpechi, I. G., Osman, M. A., Cho, Y., Htay, H., Jha, V., et al. (2022). Epidemiology of haemodialysis outcomes. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 18, 378–395. doi:10.1038/s41581-022-00542-7
Browne, L. D., Bashar, K., Griffin, P., Kavanagh, E. G., Walsh, S. R., and Walsh, M. T. (2015). The role of shear stress in arteriovenous fistula maturation and failure: a systematic review. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 10, e0145795. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0145795
Carroll, J., Varcoe, R. L., Barber, T., and Simmons, A. (2019). Reduction in anastomotic flow disturbance within a modified end-to-side arteriovenous fistula configuration: results of a computational flow dynamic model. Nephrology 24, 245–251. doi:10.1111/nep.13219
Chen, J.-W., Fu, H.-Y., Hii, I.-H., Tseng, H.-W., Chang, P.-Y., Chang, C.-H., et al. (2023). A randomized trial of postoperative handgrip exercises for fistula maturation in patients with newly created wrist radiocephalic arteriovenous fistulas. Kidney Int. Rep. 8, 566–574. doi:10.1016/j.ekir.2022.12.019
Colley, E., Simmons, A., Varcoe, R., Thomas, S., and Barber, T. (2020). Arteriovenous fistula maturation and the influence of fluid dynamics. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H. 234, 1197–1208. doi:10.1177/0954411920926077
Cunnane, C. V., Cunnane, E. M., Moran, D. T., and Walsh, M. T. (2019). The presence of helical flow can suppress areas of disturbed shear in parameterised models of an arteriovenous fistula. Int. J. Numer. Method. Biomed. Eng. 35, e3259. doi:10.1002/cnm.3259
Dixon, B. S. (2006). Why don’t fistulas mature? Kidney Int. 70, 1413–1422. doi:10.1038/sj.ki.5001747
Ene-Iordache, B., and Remuzzi, A. (2012). Disturbed flow in radial-cephalic arteriovenous fistulae for haemodialysis: low and oscillating shear stress locates the sites of stenosis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 27, 358–368. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfr342
Ene-Iordache, B., and Remuzzi, A. (2017). Blood flow in idealized vascular access for hemodialysis: a review of computational studies. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 8, 295–312. doi:10.1007/s13239-017-0318-x
Ene-Iordache, B., Semperboni, C., Dubini, G., and Remuzzi, A. (2015). Disturbed flow in a patient-specific arteriovenous fistula for hemodialysis: multidirectional and reciprocating near-wall flow patterns. J. Biomech. 48, 2195–2200. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2015.04.013
Farber, A., Imrey, P. B., Huber, T. S., Kaufman, J. M., Kraiss, L. W., Larive, B., et al. (2016). Multiple preoperative and intraoperative factors predict early fistula thrombosis in the hemodialysis fistula maturation study. J. Vasc. Surg. 63, 163–170.e6. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2015.07.086
Farrington, C. A., Robbin, M. L., Lee, T., Barker-Finkel, J., and Allon, M. (2020). Early predictors of arteriovenous fistula maturation: a novel perspective on an enduring problem. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 31, 1617–1627. doi:10.1681/asn.2019080848
Gunasekera, S., Ng, O., Thomas, S., Varcoe, R., de Silva, C., and Barber, T. (2020). Tomographic piv analysis of physiological flow conditions in a patient-specific arteriovenous fistula. Exp. Fluids. 61, 253. doi:10.1007/s00348-020-03085-4
Gunasekera, S., Ng, O., Thomas, S., Varcoe, R., de Silva, C., and Barber, T. (2021). Impact of juxta-anastomotic stent implantation on the haemodynamics within a single representative patient avf. Int. J. Heat. Fluid Flow. 92, 108874. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2021.108874
Huber, T. S., Berceli, S. A., Scali, S. T., Neal, D., Anderson, E. M., Allon, M., et al. (2021). Arteriovenous fistula maturation, functional patency, and intervention rates. Jama. Surg. 156, 1111–1118. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2021.4527
Hyde-Linaker, G., Barrientos, P. H., Stoumpos, S., Kingsmore, D. B., and Kazakidi, A. (2022). Patient-specific computational haemodynamics associated with the surgical creation of an arteriovenous fistula. Med. Eng. Phys. 105, 103814. doi:10.1016/j.medengphy.2022.103814
Iori, F., Grechy, L., Corbett, R. W., Gedroyc, W., Duncan, N., Caro, C. G., et al. (2015). The effect of in-plane arterial curvature on blood flow and oxygen transport in arterio-venous fistulae. Phys. Fluids 27, 031903. doi:10.1063/1.4913754
Jia, L., Wang, L., Wei, F., Yu, H., Dong, H., Wang, B., et al. (2015). Effects of wall shear stress in venous neointimal hyperplasia of arteriovenous fistulae. Nephrology 20, 335–342. doi:10.1111/nep.12394
Jodko, D., Obidowski, D., Reorowicz, P., and Jóźwik, K. (2017). Blood flows in end-to-end arteriovenous fistulas: unsteady and steady state numerical investigations of three patient-specific cases. Biocybern. Biomed. Eng. 37, 528–539. doi:10.1016/j.bbe.2017.05.006
Lok, C. E., Huber, T. S., Lee, T., Shenoy, S., Yevzlin, A. S., Abreo, K., et al. (2020). Kdoqi clinical practice guideline for vascular access: 2019 update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 75, S1–S164. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.12.001
Nantakool, S., Reanpang, T., Prasannarong, M., Pongtam, S., and Rerkasem, K. (2022). Upper limb exercise for arteriovenous fistula maturation in people requiring permanent haemodialysis access. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 10, CD013327. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd013327.pub2
Pike, D., Shiu, Y.-T., Somarathna, M., Guo, L., Isayeva, T., Totenhagen, J., et al. (2017). High resolution hemodynamic profiling of murine arteriovenous fistula using magnetic resonance imaging and computational fluid dynamics. Theor. Biol. Med. Modell. 14 (5), 5. doi:10.1186/s12976-017-0053-x
Ramuzat, A., How, T., and Bakran, A. (2003). Steal phenomenon in radiocephalic arteriovenous fistula.: in vitro haemodynamic and electrical resistance simulation studies. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 25, 246–253. doi:10.1053/ejvs.2002.1842
Rangel, J. F., Santos, W. B. d. A., Costa, T. H. d. C., de Bessa, K. L., and Melo, J. D. D. (2023). Pressure analysis in rigid and flexible real arteriovenous fistula with thickness variation in vitro. J. Funct. Biomater. 14, 310. doi:10.3390/jfb14060310
Remuzzi, A., and Ene-Iordache, B. (2013). Novel paradigms for dialysis vascular access: upstream hemodynamics and vascular remodeling in dialysis access stenosis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 8, 2186–2193. doi:10.2215/cjn.03450413
Rosado-Toro, J. A., Philip, R. C., Dunn, S. T., Celdran-Bonafonte, D., He, Y., Berceli, S. A., et al. (2022). Functional analysis of arteriovenous fistulae in non-contrast magnetic resonance images. Comput. Meth. Prog. Bio. 222, 106938. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.106938
Sadaghianloo, N., Contenti, J., Dardik, A., and Mazure, N. M. (2019). Role of hypoxia and metabolism in the development of neointimal hyperplasia in arteriovenous fistulas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 5387. doi:10.3390/ijms20215387
Shahinian, V. B., Zhang, X., Tilea, A. M., He, K., Schaubel, D. E., Wu, W., et al. (2020). Surgeon characteristics and dialysis vascular access outcomes in the United States: a retrospective cohort study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 75, 158–166. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.08.001
Shahverdyan, R., Beathard, G., Mushtaq, N., Litchfield, T. F., Vartanian, S., Konner, K., et al. (2021). Comparison of ellipsys percutaneous and proximal forearm gracz-type surgical arteriovenous fistulas. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 78, 520–529.e1. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.01.011
Shiu, Y.-T., Rotmans, J. I., Geelhoed, W. J., Pike, D. B., and Lee, T. (2019). Arteriovenous conduits for hemodialysis: how to better modulate the pathophysiological vascular response to optimize vascular access durability. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. 316, F794–F806. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00440.2018
Sivanesan, S., How, T., and Bakran, A. (1998). Characterizing flow distributions in av fistulae for haemodialysis access. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 13, 3108–3110. doi:10.1093/ndt/13.12.3108
Suqin, L., Mingli, Z., Shiteng, S., Honglan, M., Lan, Z., Qihong, N., et al. (2020). Assessment of the hemodynamics of autogenous arteriovenous fistulas with 4d phase contrast-based flow quantification mri in dialysis patients. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 51, 1272–1280. doi:10.1002/jmri.26936
Tordoir, J. H. M., Zonnebeld, N., van Loon, M. M., Gallieni, M., and Hollenbeck, M. (2018). Surgical and endovascular intervention for dialysis access maturation failure during and after arteriovenous fistula surgery: review of the evidence. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. 55, 240–248. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2017.12.001
Van Canneyt, K., Pourchez, T., Eloot, S., Guillame, C., Bonnet, A., Segers, P., et al. (2010). Hemodynamic impact of anastomosis size and angle in side-to-end arteriovenous fistulae: a computer analysis. J. Vasc. Access. 11, 52–58. doi:10.1177/112972981001100111
Venkat Ramanan, S., Prabhu, R. A., Rao, I. R., Chawla, A., Shenoy, S. V., Nagaraju, S. P., et al. (2022). Outcomes and predictors of failure of arteriovenous fistulae for hemodialysis. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 54, 185–192. doi:10.1007/s11255-021-02908-5
Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Li, S., Aziz, A. U. R., Liu, S., and Qin, K. (2018). The analysis of wall shear stress modulated by acute exercise in the human common carotid artery with an elastic tube model. Comput. Model. Eng. Sci. 116, 127–147. doi:10.31614/cmes.2018.03985
Keywords: arteriovenous fistula, blood redistribution, computational fluid dynamics, flow disturbance, hemodialysis
Citation: Li Y-J, Hou H-M, Liu Z, Xue C-D, Na J-T, Meng Q-M, Li Z-Y, Sun H-Y, Wu Y-L, Liu S-X and Qin K-R (2025) Adjusting blood redistribution to suppress flow disturbances of hemodialysis arteriovenous fistula: a computational fluid dynamics analysis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1551993. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1551993
Received: 27 December 2024; Accepted: 24 February 2025;
Published: 20 March 2025.
Edited by:
Philippe Sucosky, Kennesaw State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Yu Chen, Sichuan University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Li, Hou, Liu, Xue, Na, Meng, Li, Sun, Wu, Liu and Qin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kai-Rong Qin, a3JxaW5AZGx1dC5lZHUuY24=; Shu-Xin Liu, c2h1eGlubGl1QGRsdXQuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.