- 1The Second School of Clinical Medicine, Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang, China
- 2Fujian Key Laboratory of Toxicant and Drug Toxicology, Medical College, Ningde Normal University, Ningde, Fujian, China
- 3Department of Human Anatomy, School of Basic Medicine, Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang, China
- 4Liaoning Province Key Laboratory for Phenomics of Human Ethnic Specificity and Critical Illness, Shenyang, China
- 5Shenyang Key Laboratory for Phenomics, Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang, China
Tumors, as a disease that seriously threatens human health, have always been a major challenge in the field of medicine. Currently, the main methods of tumor treatment include surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, etc., but these traditional treatment methods often have certain limitations. In addition, tumor recurrence and metastasis are also difficult problems faced in clinical treatment. In this context, the importance of metal-based nanomaterials in tumor therapy is increasingly highlighted. Metal-based nanomaterials possess unique physical, chemical, and biological properties, providing new ideas and methods for tumor treatment. Metal-based nanomaterials can achieve targeted therapy for tumors through various mechanisms, reducing damage to normal tissues; they can also serve as drug carriers, improving the stability and bioavailability of drugs; at the same time, some metal-based nanomaterials also have photothermal, photodynamic, and other characteristics, which can be used for phototherapy of tumors. This review examines the latest advances in the application of metal-based nanomaterials in tumor therapy within past 5 years, and presents prospective insights into the future applications.
1 Introduction
There are various essential metal ions in the human body that participate in many important life activities, such as signal pathway activation, enzyme catalysis, and protein composition (Lv et al., 2023). In normal cells, theprecise regulation of ion homeostasis is crucial for cell survival, metabolism, and immunity (Liu et al., 2024). The abnormal distribution or accumulation of certain metal ions can activate cell toxicity-related biochemical reactions and induce cell death. Based on this principle, a new treatment strategy has emerged, namely, metal ion-mediated tumor treatment, which inhibits tumor growth by directly or indirectly regulating the concentration of metal ions within cells (Feng et al., 2023; Sun et al., 2024). In addition, metal ions also play a key role in tumor immune regulation, and the concept of “cancer metal immunotherapy” has been proposed (Wang et al., 2023c). Therefore, an increasing number of compounds with the ability to regulate metal ions (such as curcumin, deferoxamine, disulfiram) have been developed for tumor treatment research (Wu et al., 2020). However, their clinical transformation is hindered by limited specific recognition ability and inadequate ion concentration changes. In recent years, nanomaterials have made significant progress and development in drug delivery, diagnosis and imaging, treatment, vaccines, and other fields (Wang G. et al., 2023). Various metal ion-regulated nanomaterials have also made great progress in tumor treatment research. They not only optimize the metal ion-based antitumor treatment system but also provide the possibility for the combination of metal ion treatment with other treatment strategies. These characteristics make metal-based nanomaterials show great potential for tumar treatment.
This article will comprehensively summarize the diverse types, intricate mechanisms, and the latest research advancements in the field of metal-based antitumor nanomaterials and offer insights into the anticipated directions of development.
2 Metal ions and tumors
2.1 The role of iron in antitumor therapy
2.1.1 Physicochemical properties, physiological functions of iron and ferroptosis
Iron (symbol: Fe) is the 26th metal element in the periodic table, with valences of Fe2+, Fe3+, and Fe6+, among which Fe2+ and Fe3+ are the most common and can convert into each other in the human body. Iron is an important essential trace element in the human body, mainly existing in two forms: heme iron and non-heme iron. Heme iron is an important component of hemoglobin in red blood cells and myoglobin in muscle, responsible for oxygen transport in the blood and oxygen storage in the muscle, respectively (Sawicki et al., 2023). Non-heme iron combines with iron-binding proteins, such as ferritin and hemosiderin. In addition to participating in hemoglobin synthesis and oxygen transport, iron also acts as a cofactor for various enzymes involved in many important cellular processes, such as DNA synthesis and repair, electron transfer, and respiration (Powell et al., 2023). The maintenance of iron homeostasis is crucial for the normal life activities of the body.
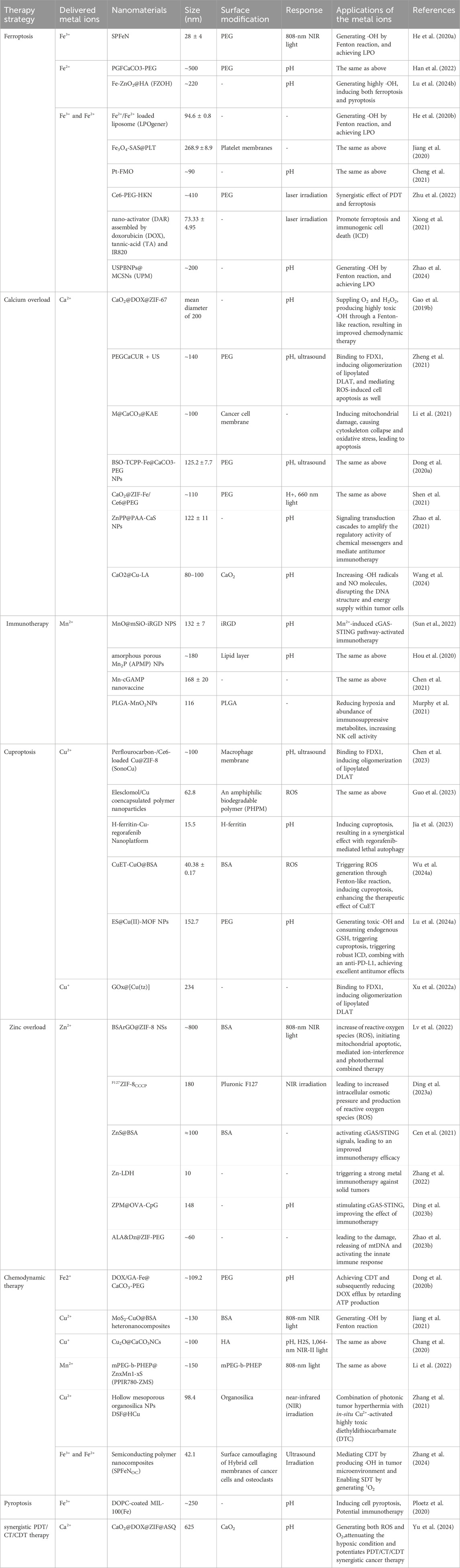
Inside cells, iron homeostasis is precisely regulated at the transcriptional and translational levels by iron regulatory proteins (IRPs) and iron response elements (IREs) to control iron uptake, storage, and efflux, as well as the management and distribution of iron within cells (Billesbolle et al., 2020). Fe2+ is the main active form of iron, participating as a structural or catalytic cofactor in redox reactions. When iron levels surge beyond normal, an abundance of Fe2+ can trigger oxidative stress and disrupt the equilibrium of the antioxidant defense system. Excess free radicals, generated through redox reactions, attack the polyunsaturated fatty acids within the cell membrane, thereby triggering a chain reaction of lipid peroxidation, which in turn leads to cell death, a phenomenon designated as ferroptosis. Ferroptosis is a programmed iron ion-dependent cell death mechanism that plays a role in various physiological and pathological processes (Mou et al., 2019; Nguyen et al., 2023). Ferroptosis is mainly caused by the excessive accumulation of intracellular iron ion-dependent reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the weakened elimination of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), which causes the homeostatic imbalance of ROS generation and degradation. When the cell’s own antioxidant capacity is insufficient to remove excessively accumulated lipid ROS, it causes ferroptosis. Iron accumulation and subsequent lipid peroxidation play an important role in mediating the occurrence of ferroptosis. Thus, the various molecules and signals involved in iron metabolism and lipid peroxidation are all critical for regulating iron death. The changes in cell metabolic pathways caused by ferroptosis mainly include inhibited GSH synthesis and LPO accumulates, iron metabolism and ROS metabolic pathway (as shown in Figure 1).
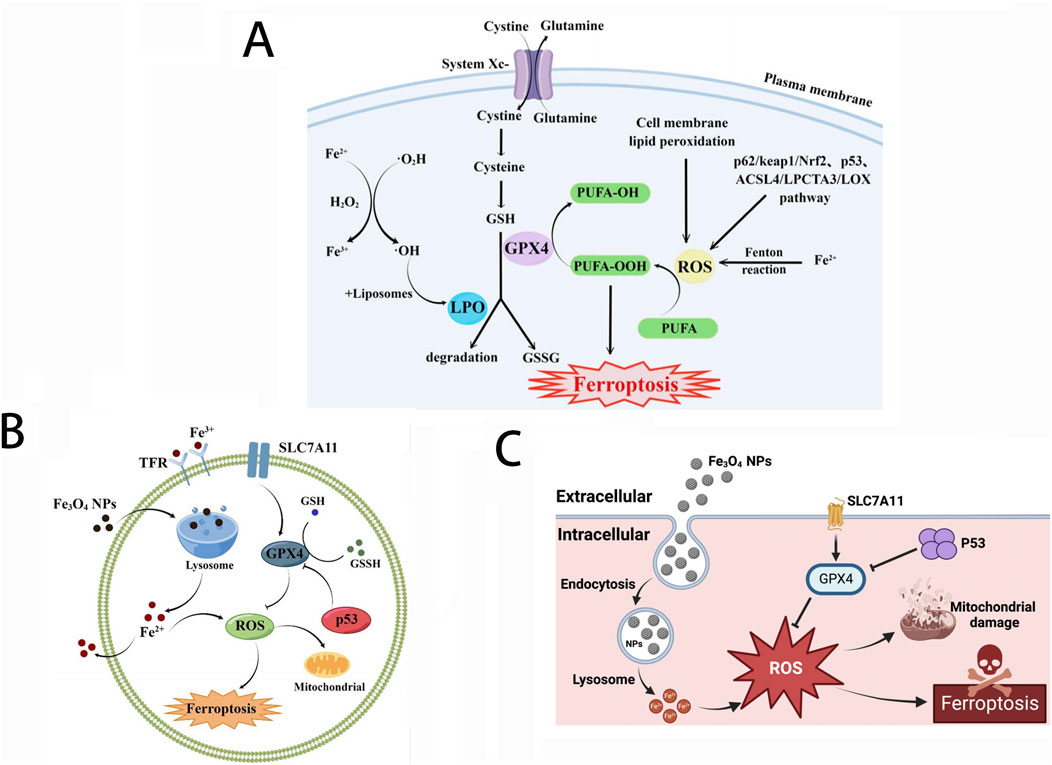
Figure 1. (A) Major metabolic pathways of ferroptosis; (B) Effect of Fe3O4-NPs on cell ferroptosis; (C) Mechanism of Fe3O4-NP-induced ferroptosis through upregulation of p53. Reproduced with permission from ref (Wang et al., 2023d); CC BY 4.0. Copyright © 2023 by the authors.
2.1.2 Antitumor mechanisms based on ferroptosis
Iron metabolism disorders are closely related to the occurrence and development of tumors. Since iron is an essential element for cell proliferation and metabolism, the rapid proliferation of tumor cells shows an abnormal demand for iron, so tumor cells promote the accumulation of iron in cells through iron metabolism reprogramming (Yang et al., 2023). Therefore, the iron content in tumor cells is higher than in normal cells. Due to the influence of the tumor microenvironment, tumor cells are more susceptible to ferroptosis inducers than normal cells, creating a fundamental prerequisite to undergo anti-tumor treatment utilizing ferroptosis (Lei et al., 2022). However, the vast majority of iron within tumor cells predominantly exists in the form of non-cytotoxic ferritin. Therefore, targeting ferritin to facilitate the liberation of iron ions or directly modulating the intracellular iron ion concentration are two feasible ferroptosis-based anti-tumor treatment strategies.
In addition, since the concentration of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in tumor cells is relatively higher than in normal cells, excessive iron ions will undergo the Fenton reaction with H2O2 (Huang L. et al., 2023). In the process of this reaction, the interaction between Fe2+ and H2O2 leads to the production of hydroxyl radicals (·OH), a highly biologically toxic ingredient capable of damaging lipids, proteins, DNA, and other vital cellular components, ultimately leading to the death of tumor cells. Therefore, increasing the concentration of free Fe2+ and H2O2 within tumor cells at the same time can mediate cell death through the Fenton reaction, which may become one effective anti-tumor strategy based on iron ion.
2.1.3 Iron ion-based anti-tumor nanomedicines
With the in-depth study of ferroptosis and the development of nanotechnology, nanomaterials have been proven to induce ferroptosis more effectively than biological drugs. First, it can break the iron homeostasis both through ex vivo delivery mechanisms and endogenous iron utilization pathways, enhancing the elevation of intracellular free iron levels. Currently, various nanodrugs containing Fe2+/Fe3+ or capable of delivering Fe2+/Fe3+ have been developed for anti-tumor treatment, such as polydopamine (PDA) and amorphous CaCO3 nanoparticles, etc (Han et al., 2022). Iron-bearing nanoparticles can not only release Fe2+ in acidic lysosomes but also deliver antitumor medications, such as a chemotherapeutic drug cisplatin, achieving a synergistic antitumor effect (Cheng et al., 2021). Biocompatible iron nanoparticles, Fe3O4-NPs, not only promote the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) but also participate in iron metabolism, leading disruption of intracellular iron balance and induction of ferroptosis. In addition, Fe3O4-NPs combined with other technologies, such as photodynamic therapy (PDT), thermal stress, and sonodynamic therapy (SDT), can further induce cellular ferroptosis, thereby enhancing the antitumor effects (Wang et al., 2023d; Yao et al., 2021).
Another method to increase the level of free Fe2+ within cells is to target iron-related proteins, among which ferritin degradation is considered an effective approach. A ferritin-hijacking nanoparticle (Ce6-PEG-HKN15) is fabricated, by conjugating the ferritin-homing peptide HKN15 with the photosensitizer chlorin e6 (Ce6) for endogenous ferroptosis without introducing Fenton-reactive metals (Zhu et al., 2022). Since the HKN15 peptide can target ferritin, the photosensitizer chlorin e6 (Ce6) can specifically aggregate around ferritin. Under laser irradiation, the activated Ce6 in these nanoparticles synergizes with the generated ROS to effectively destroy ferritin and release Fe2+. In turn, the released iron partially interacts with intracellular excess H2O2 to produce O2, thereby enhancing photodynamic therapy and further amplifying oxidative stress. Xiong et al. prepared a nano-activator (DAR) which was assembled by doxorubicin (DOX), tannic-acid (TA) and IR820 as a photosensitizer to make full use of endogenous iron stored in endo-lysosome, realizing ferroptosis and its related oxidative stress through artificially intracellular positive feedback loop, providing an innovative solution for the development of antitumor treatment based on ferroptosis-immunotherapy (Xiong et al., 2021).
2.2 The role of calcium in antitumor therapy
2.2.1 Physicochemical properties and physiological functions of calcium
Calcium (symbol: Ca) is a chemical element with an atomic number of 20, and its ionic form is Ca2+. Calcium is the most abundant metal element in the human body and is crucial for the formation of bones and teeth. In the body, calcium exists in three main forms: free calcium, complex calcium, and protein-bound calcium, which can convert into each other. Among them, free calcium is the only physiologically active form. As an indispensable second messenger in cells, calcium ions (Ca2+) participate in the regulation of almost all physiological processes by activating specific target proteins. Due to the importance of Ca2+, its concentration is strictly controlled (Berridge et al., 2000; Carafoli, 2002; Liu et al., 2020; Marchi et al., 2020; Monteith et al., 2017). The concentration of free calcium within cells is only 100 nM, much lower than the extracellular calcium concentration (Bagur and Hajnoczky, 2017). Fluctuations in Ca2+ concentration will affect normal calcium signal transmission and thus affect cellular physiological functions. The homeostasis of intracellular Ca2+ mainly relies on the orderly cooperation of various Ca2+ channels in the cell membrane and organelles (such as the endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, and lysosomes) (Berridge, 2016; Clapham, 2007; Huang et al., 2022). When this homeostatic mechanism is disrupted, excessive intracellular calcium ion concentration may lead to calcium overload, resulting in cell death (Hof et al., 2019).
2.2.2 Antitumor mechanism based on calcium overload
Ca2+ is the most abundant metal element and the second messenger in the human body, regulating specific biological functions that involve all aspects of cell life, and closely participate in the formation, proliferation, and migration of tumor cells (Bagur and Hajnoczky, 2017; Wu Y. et al., 2024). The expression of Ca2+ signal pathway-related proteins in tumor cells is different from that in normal cells, and the Ca2+ signal pathways are related to the pathogenesis of specific tumors such as breast cancer, colon cancer, lung cancer, liver cancer, etc (Jing et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2015). Compared to normal cells, tumor cells such as breast cancer, prostate cancer, and melanoma exhibit reduced Ca2+ influx mediated by stromal interaction molecules to avoid cell death caused by intracellular Ca2+ overload. This mechanism promotes the proliferation of tumor cells (Dubois et al., 2014; Faouzi et al., 2013; Sun et al., 2014). Therefore, tumor cell death caused by calcium overload can be achieved by correcting the abnormal Ca2+ signaling pathway or introducing exogenous Ca2+ into the cytoplasm via calcium ion carriers (Cao et al., 2024). When a large amount of Ca2+ enters the mitochondria, it can inhibit the synthesis and biological activity of drug-resistant proteins, promote the uptake and retention of cells for anticancer drugs. In addition, mitochondrial Ca2+ overload can also increase the level of intracellular ROS, causing the release of cytochrome C (Cyt C), thereby activating cysteine protease 3 (caspase-3) and GSDME protein, jointly promoting the occurrence of cell pyroptosis (as shown in Figure 2) (Bao et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2024; Yu et al., 2021). In summary, nanodrugs that can directly introduce Ca2+ into cells or organelles can provide new ideas for tumor treatment.
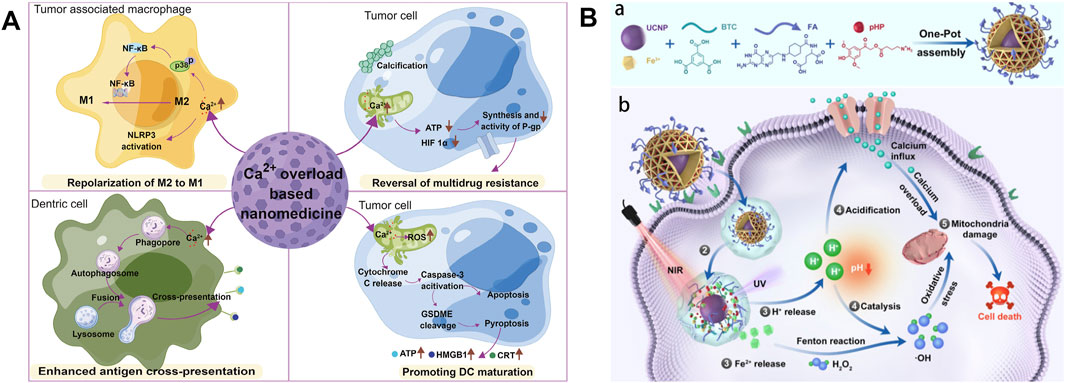
Figure 2. (A) Schematic diagram of antitumor mechanisms of Ca2+ overload-based nanomedicines. Reproduced with permission from ref (Xu et al., 2024). (B) Schematic Illustration of the construction of FMUP nanoagent and the underlying anticancer mechanism. (a) Core-shell type FMUP nanoagents with UCNP as the core and photoacid (pHP) encapsulated in the cavity of FA-doped MOFs shell were constructed by one-pot self-assembly. The FMUP nanoagent was synthesized by coordination of carboxyl groups on BTC and FA with Fe3+. The UCNP as the core was located in the shell and simultaneously the pHP was loaded in the pore of the nanoagent. (b) Corresponding anticancer mechanism of FMUP nanoagent. ① Active internalization of FMUP in tumor cells helped by FA functionalization. ② Lysosome escape of FMUP induced by the increase of osmotic pressure after NIR light irradiation. ③ Fe2+ and H+ release from FMUP upon NIR light irradiation. ④ Photoacidification of intracellular microenvironment induced calcium influx and therefore calcium overload in the mitochondria and simultaneously generated a key acidic environment for efficient Fenton reactions. The release of Fe2+ and photoacidification synergistically reinforced Fenton reactions and therefore produced a large number of ·OH within the close proximity of mitochondria. ⑤ As a result, the calcium overloaded and plentiful ·OH enabled dual damage to mitochondria and further induced cell death. Reproduced with permission from ref (Bao et al., 2021); CC BY 4.0. Copyright © 2023 by the authors.
2.2.3 Calcium-based antitumor nanodrugs
With the continuous development of nanotechnology, the functions of nanomaterials are constantly being engineered. The emergence of calcium-based nanocomposites has well solved the problem of low efficiency in directly delivering Ca2+ to tumor tissues, greatly expanding the application of Ca2+ in the field of tumor treatment (Bai et al., 2022). Calcium-based nanocomposites used in tumor treatment include calcium phosphate (CaP), calcium carbonate (CaCO3), calcium peroxide (CaO2), etc. (Li et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2018; Zhao et al., 2021; Zheng et al., 2021), which have excellent pH response capabilities and are often used in the design of pH-dependent nanodrug delivery platforms (An et al., 2020). In addition, calcium-based nanocomposites can also target tumor tissues or cells. After internalization, they can degraded under the action of acidic organelles (such as lysosomes), and release a large amount of free Ca2+. This process, when combined with Ca2+ influx promoters or Ca2+ efflux inhibitors, can further elevate the intracellular Ca2+ concentration that consequently induce cell apoptosis due to Ca2+ overload (Gao S. et al., 2019). Therefore, calcium-based nanodrugsits are very promising material for antitumor treatment.
2.3 The role of manganese in antitumor therapy
2.3.1 Physicochemical properties and physiological functions of manganese
Manganese (element symbol: Mn) is a transition element with an atomic number of 25, having various valence states, including Mn2+, Mn3+, Mn4+, Mn6+, and Mn7+. The most common form of manganese found in living tissues is Mn2+ and Mn3+. Manganese plays an important role in various physiological processes, including development, energy metabolism, antioxidant defense, and immune function. Manganese acts as a cofactor for various enzymes in the body, such as arginase, manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), and cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase (cGAS), etc. (Liu et al., 2022; Zhu et al., 2019). Among them, the cGAS protein is an important DNA sensor that activates the host immune response, and the cGAS-STING signaling pathway plays a crucial role in innate immune responses (Wang et al., 2018). Therefore, manganese is an important immune activator and the level of manganese in cells also needs precise regulation. Manganese efflux pumps and metal transporters ZIP8, ZIP14, and ZnT10 play a key role in this process (Xin et al., 2017). Due to the chemical properties of strong redox capabilities that similarity to iron, manganese can also produce ·OH through a Fenton-like reaction, increasing oxidative stress and producing cytotoxic effects (Ju et al., 2022).
2.3.2 Antitumor mechanism of manganese
Numerous epidemiological investigations have found a significant positive correlation between low manganese and tumor occurrence (Kim, 2010; Tu et al., 2010). The purpose of antitumor manganese nanodrugs is to increase the concentration of intracellular free Mn2+. After nanoparticles are internalized by cells, the release of Mn2+ depletes intracellular glutathione (GSH), enabe the sufficient generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and effectively kill tumor cells. In addition, Mn2+ can also catalyze conversion of cellular H2O2 to ·OH through a Fenton-like reaction. It also promotes the decomposition of H2O2 to O2 and continuously catalyzes the conversion of O2 to cytotoxic ·O2- via oxidase-like activity that enhance the therapeutic effects of radiotherapy and starvation therapy (Zhu et al., 2021).
Manganese possesses strong immune activation capabilities. The cGAS-STING signaling pathway plays a crucial role in innate immune responses, where cGAS, as a DNA sensor, can detect double-stranded DNA released into the cytoplasm or extracellularly from damaged tumor cells, triggering an immune response (Wang et al., 2018). As a cofactor for cGAS, Mn2+ is a strong activator of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway, which can promote the production of type I interferon (IFN), enhance antigen presentation efficiency, and enhance the differentiation and activation of CD8+ T cells (as shown in Figures 3, 4) (Lv et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2018). After radiotherapy or chemotherapy, the accumulation of Mn2+ and the leakage of nuclear DNA can effectively promote the activation of the cGAS-STING signaling pathway, thereby enhancing the antitumor immunity induced by radiotherapy or chemotherapy (Zhang et al., 2023). Mn2+ combined with anti-TGF-β/PD-L1 bispecific antibodies reduces drug resistance by enhancing both innate and adaptive immune pathways. Manganese ion-based “Metalloimmunotherapy” plays a very important role in antitumor treatment.
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of the antitumor immune responses of Mn2+. Reproduced with permission from ref (Lv et al., 2020); CC BY 4.0. Copyright © 2020 by the authors.
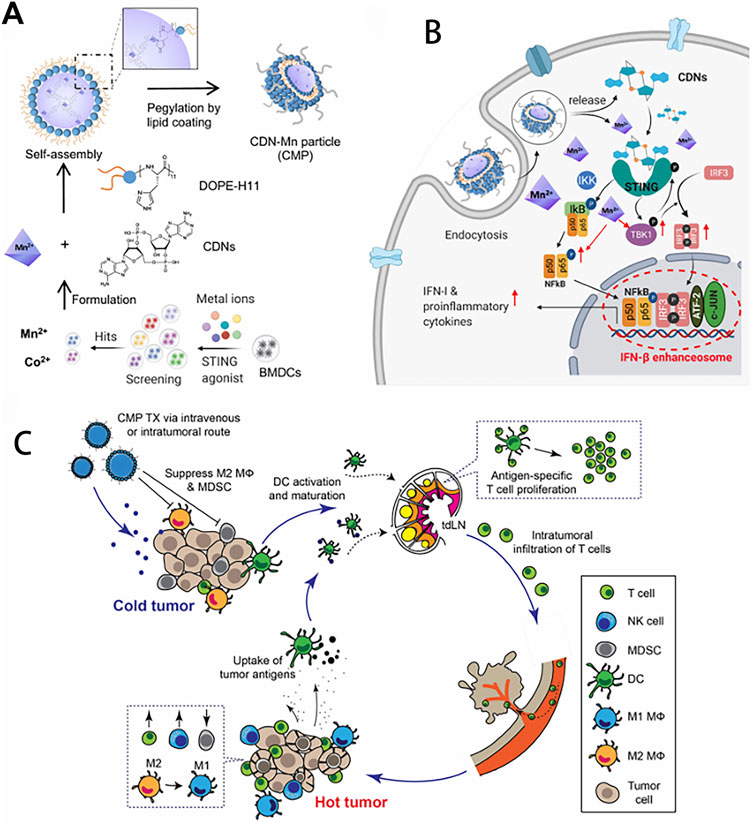
Figure 4. Amplifying STING activation with CDN-Manganese particles (CMP) for cancer metalloimmunotherapy. (A) CMP is composed of cyclic di-nucleotides (CDNs), Mn2+, DOPE-H11, and a PEG-lipid layer. Mn2+ potentiates type-I IFN activities of STING agonists. Mn2+ and CDNs self-assemble into coordination polymer. CDN-Mn2+ coordination polymer was coated with DOPE-H11 via Mn-histidine coordination to form CDN-Mn@DOPE, followed by PEGylation with PEG-lipid layer, resulting in the formation of CMP. (B) CMP boosts STING activation: 1) CMP promotes cellular uptake of CDNs and Mn2+; 2) Mn2+ augments CDN induced STING activation via STING-independent TBK1 and p65 phosphorylation, STING dependent IRF3 phosphorylation, and assembly of the IFN-β transcriptional enhanceosome. (C) CMP exerts potent anti-tumor efficacy after intratumoral (I.T.) or intravenous (I.V.) administration. CMP reverses immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment while activating T-cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and dendritic cells (DCs). Reproduced with permission from ref (Sun et al., 2021); PDM 1.0. Copyright © 2021 by the authors.
2.3.3 Manganese ion-based antitumor nanodrugs
As a simple and effective immune stimulant, manganese and its derived nanomaterials have shown significant effects in tumor treatment. Various manganese-based nanomaterials have been widely used as nanocarriers to deliver immunotherapeutic agents, or as immunomodulators to reshape the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, or as immune activators to activate the body’s immune system directly or indirectly for clinical tumor immunotherapy. Compared with commonly used tumor immunotherapies such as tumor vaccines, immune checkpoint blockade therapy, adoptive cell therapy, manganese-based tumor immunotherapy has significant advantages in terms of stability, applicability, convenience, price, etc. In 2020, a research from Peking University showed that manganese ions could effectively synergistically enhance the effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors in various tumor models and significantly reduce the dosage of PD-1 antibodies (Lv et al., 2020). Translating NK cell therapies to treat solid tumors has proven challenging due to the tumor microenvironment (TME). Hypoxia in the TME induces immunosuppression that inhibits the cytotoxic function of NK cells. Thus, reversing hypoxia-induced immunosuppression is critical for effective adoptive NK cell immunotherapy. The particles (PLGA-MnO2 NPs) were developed by encapsulating MnO2 NPs into poly (lactic-co-glycolicacid) (PLGA), which can catalyze the degradation of endogenous H2O2 to produce oxygen to alleviate tumor hypoxia, resulting in significantly enhanced cytotoxicity of NK cells. This manganese ion-based NPs are promising new tools to improve adoptive NK cell therapy (Murphy et al., 2021). Manganese-based nanomaterials combined with immune activators can synergistically activate the cGAS-STING pathway to enhance antitumor immune effects while reducing the side effects caused by excessive manganese. Chen et al. reported a thio-cGAMP-Mn2+ nanovaccine, which enhanced the antitumor immune response through direct cytosolic co-delivery of cGAMP and Mn2+. The fixation of cGAMP with Mn2+ ions not only improve its stability, but also potentiate the activation of STING pathway. The nanovaccine increased the production of cytokines, and activated CD8+ T cell immunity, and in turn suppressed the primary and distal tumors growth through long-term immune memory and led to long-term survival of poorly immunogenic B16F10 melanoma mice (Chen et al., 2021).
2.4 The role of copper in antitumor therapy
2.4.1 Physicochemical properties, physiological functions of copper and cuproptosis
Copper (chemical symbol: Cu) is a transition metal element with redox activity, with an atomic number of 29, and its main valences are Cu+ and Cu2+. Copper is a very important trace element in the human body, serving as a structural and catalytic cofactor for various enzymes, and is involved in regulating important life processes such as energy metabolism, antioxidation, neurotransmitter synthesis, and iron metabolism (Reznik et al., 2022; Schwarz et al., 2023). When Cu+ accumulates excessively in cells, it is oxidized by H2O2 to produce ·OH, which damages proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids within the cells, and interferes with the synthesis of iron-sulfur cluster proteins. Since iron-sulfur cluster proteins are essential for the activity of many important cellular enzymes, so excessive accumulation of copper in cells can be toxic. Therefore, maintaining copper homeostasis within cells is importantThe body’s homeostasis of copper must be precisely regulated by membrane transport systems (Campos et al., 2021). The concentration of copper within cells is strictly controlled by copper transport proteins and copper chaperones. Since only monovalent copper ions Cu+ are transportable, extracellular Cu2+ is often reduced to Cu+ before entering the cell. Copper transport proteins are responsible for the influx of Cu+ across the cell membrane, and copper transport enzymes α (ATP7A) and β (ATP7B) are necessary for expelling excess copper from the cell (Ash et al., 2021).
Cuproptosis is a unique type of cell death published in Science recently. The mechanism of cuproptosis is different from other known forms of programmed cell death such as apoptosis, pyroptosis, necrosis, and ferroptosis. By binding to the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, intracellular copper accumulation triggers the aggregation of mitochondrial lipoylated proteins and the destabilization of Fe-S cluster proteins, which in turn causes a protein toxicity reaction leading to cell death (Tsvetkov et al., 2022) (as shown in Figure 5). Studies have shown that necessary factors for cuproptosis include the presence of glutathione, mitochondrial metabolism of galactose and pyruvate, and glutamine metabolism. Endogenous intracellular glutathione, as a thiol-containing copper chelator, can inhibit cuproptosis (Saporito-Magriñá et al., 2018).
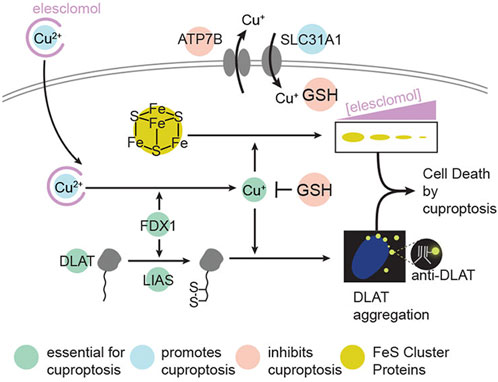
Figure 5. Schematic of mechanisms promoting cuproptosis. Reproduced with permission from ref (Tsvetkov et al., 2022), PDM 1.0. Copyright © 2022 by the authors.
2.4.2 Antitumor mechanisms based on copper homeostasis imbalance
Studies have found that the content of copper in the serum and tissues of patients with various types of tumors is significantly higher than that in normal populations, and is related to tumor staging or progression (Ge et al., 2022). Appropriate high concentrations of copper ions promote tumor cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Both excessively high and excessively low concentrations of copper ions can promote cell death. Therefore, regulating the concentration of intracellular copper ions (copper deficiency and copper overload) has become an attractive new target for tumor treatment. Copper ions participate in the regulation of the structure and activity of copper-related proteins or enzymes, which are crucial for the survival and development of tumors. Copper deficiency can lead to impaired function of copper-binding enzymes and a lack of copper-related proteins, and all processes that lead to cellular copper depletion result in cellular dysfunction (Nyvltova et al., 2022). In addition, copper depletion can lead to energy and nutrient deficiency in cells, as well as increased oxidative stress and mitochondrial membrane rupture, all of which lead to tumor cell apoptosis. Given this, reducing the level of intracellular copper is a promising strategy for tumor treatment.
Furthermore, copper overload is another effective method for killing tumor cells. Copper overload can induce a Fenton-like reaction, mediating cell death. The Cu+-mediated Fenton-like reaction can proceed at a higher reaction rate over a wider pH range, with a reaction rate about 160 times faster than that of Fe2+ (Qiao et al., 2024). Copper overload can also mediate tumor cell death through the cuproptosis pathway. Cells dependent on glycolytic respiration are more sensitive to cuproptosis. With the consumption of glucose and glutathione, Cu+ binds to the dihydrolipoamide S-acetyltransferase (DLAT) protein more effectively, causing the formation of DLAT oligomers. The aggregation of DLAT oligomers can downregulate Fe-S cluster proteins, thereby leading to cuproptosis of tumor cells (Tsvetkov et al., 2022). Studies have shown that exogenous copper can disrupt redox homeostasis through changes in copper-dependent glutathione, enhancing ferroptosis (Du et al., 2022). In addition, copper ions can also regulate antitumor immune responses. The increase in Cu2+ not only promotes dendritic cell maturation but also enhances the antitumor effect mediated by cytotoxic CD8+ T cells (Zhao F. et al., 2023). This new mode of cell death, cuproptosis, also suggests that using copper ion metal carriers to inhibit mitochondrial respiration and kill tumor cells may become a new treatment method.
2.4.3 Copper ion-based antitumor nanodrugs
Copper-based compounds and nanomaterials possess excellent biocompatibility, can selectively target malignant tissues, and have strong permeability and high local retention rates. During the preparation process, their structure, composition, morphology, and size can easier to be controled and adjusted. These advantages make them widely used in tumor imaging and combined tumor therapy (Zhong et al., 2022). Zhang et al. utilized hollow mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles to integrate ultrasmall photothermal CuS particles onto the surface of the organosilica and the molecular drug Disulfiram (DSF) inside the mesopores and hollow interiors. The ultrasmall CuS acted as both photothermal agent under near-infrared (NIR) irradiation for photonic tumor hyperthermia and Cu2+ self-supplier in an acidic tumor microenvironment to activate the nontoxic DSF drug into a highly toxic diethyldithiocarbamate (DTC)-copper complex for enhanced DSF chemotherapy (as shown in Figure 6), which effectively achieved a remarkable synergistic in-situ anticancer outcome with minimal side effects (Zhang et al., 2021).
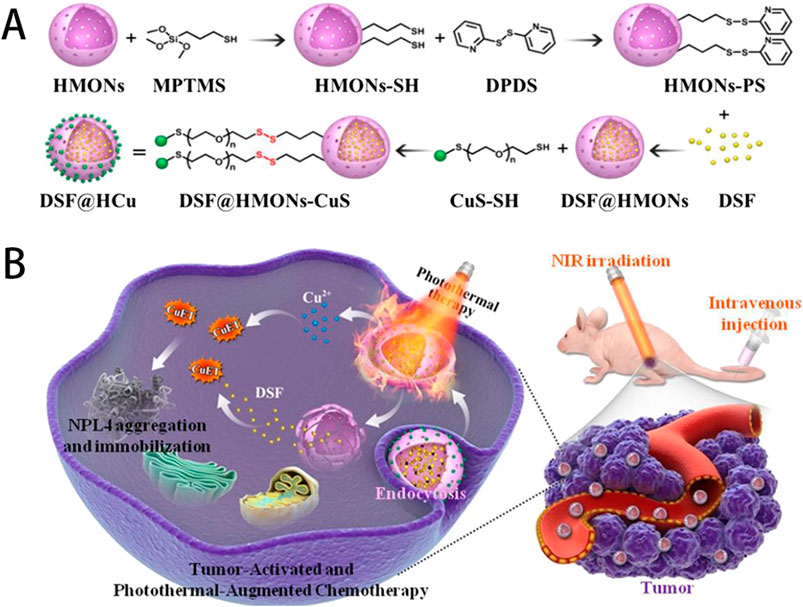
Figure 6. (A) Schematic illustration of the stepwise construction of DSF@HCu nanomedicine, and (B) NIR photothermal-augmented and in-situCu2+ release-activated DSF chemotherapy for the efficient killing of cancer cells and suppression of tumor growth with minimized side effects. Reproduced with permission from ref (Zhang et al., 2021), CC BY 4.0 Copyright © 2021 by the authors.
Chen et al. constructed CuS-pgh NMs by encapsulating copper sulfide nanoparticles using polylysine/glucose oxidase/hyaluronic acid shells (Chen et al., 2020), Liu et al. constructed a hybrid nanosystem composed of DNAzyme and Cu2+ (Liu et al., 2021), in which copper can mediate Fenton-like reactions to generate highly toxic hydroxyl radicals, enhancing thestarvation and chemodynamic tumor suppression effects. Cui et al. developed a safe, mitochondria-targeted copper-depleting nanoparticles. These nanoparticles can reduce the oxygen consumption and oxidative phosphorylation of triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), promote glycolysis metabolism, reduce ATP production, cause mitochondrial membrane potential damage and increased oxidative stress, thereby induce the apoptosis of TNBC (Cui et al., 2021). A kind of nanochelator, Imi-OSi, were reported that can inhibit tumor angiogenesis through copper consumption, and form secondary particles through the phosphate/Cu2+ reaction polymerization to block blood vessels (Yang et al., 2019). For starvation-augmented cuproptosis and photodynamic synergistic therapy, a glucose oxidase (GOx)-engineered nonporous copper coordination nanomaterial GOx@[Cu(tz)] was developed. It inhibited 92.4% of tumor growth in athymic mice with bladder tumors, and the systemic toxicity produced was extremely low (Xu WJ. et al., 2022). Chang et al. designed a Ce6@AT-PEG-MSN-Pt (CAPMP) nanomotor, consisting of a janus platinum-mesoporous silica core, with acyl thiourea groups (copper chelators) conjugated with polyethylene glycol on the surface, and chlorin e6 (photosensitizer) in the pores, which can spontaneously move in tumor tissues, while performing the enhanced manipulation of the copper level, oxygen level, local temperature, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) level in the tumor microenvironment, to achieve effective tumor treatment (Chang et al., 2022). Nevertheless, copper-based nanomaterials also have their own limitations, and their instability and characteristics of easily oxidized under physiological conditions need to be solved, and the biosafetyneed to be improved (Tsymbal et al., 2022).
2.5 The role of zinc in antitumor therapy
2.5.1 Physicochemical properties and physiological functions of zinc
Zinc (element symbol: Zn) is considered the second most abundant transition metal element in the body, after iron, with an atomic number of 30. Under physiological conditions, zinc exists in the form of divalent cations (Zn2+). Zinc is one of the essential trace elements required by the human body and is a core component of many proteins, playing the role of a “life gear” in the process of transporting substances and exchanging energy (Kambe et al., 2015). In mammalian cells, there are two forms of zinc: protein-bound zinc and free zinc. The former is used to maintain the catalytic activity and structural stability of metalloenzymes and transcription factors, while the latter acts as a signaling ion to regulate signal transduction (Maret, 2013). Therefore, zinc plays a significant role in many biological processes, including cell division, metabolic regulation, and immune responses. To maintain normal physiological functions, cellular zinc homeostasis is subtly coordinated by a set of zinc homeostasis regulatory proteins, including the Zrt-, Irt-like protein (ZIP) family for zinc influx, the zinc transporter (ZnT) family for zinc efflux, metallothioneins (MTs) for zinc intracellular storage, and metal-response-element-binding transcription factor (MTF)-1 for zinc cytosolic sensing (Colvin et al., 2010).
2.5.2 Antitumor mechanism of zinc ion
It has been confirmed that the imbalance of zinc homeostasis is related to the development, invasion, and metastasis of various tumors (Bendellaa et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2020). Increasing evidence suggests that the elevation of intracellular zinc levels is mainly due to the overexpression of zinc transporters (ZIPs), which may promote the progression of certain specific cancers such as breast and pancreatic cancer. For example, ZIP6, ZIP7, and ZIP10 are highly expressed in breast cancer. Additionally, although zinc itself does not have redox activity, it can indirectly participate in the regulation of redox metabolism by acting as a catalytic or structural cofactor for proteins such as metallothioneins (MTs), copper/zinc superoxide dismutase (Cu/Zn-SOD), and the tumor suppressor protein p53. The balance of zinc homeostasis successfully activates antioxidant defenses, while zinc deficiency can disrupt protein structures and impair protein function, ultimately leading to oxidative stress and causing cell death. Accordingly, zinc chelation therapy mediated by zinc chelators can be used to treat certain types of cancer. Similar to zinc deficiency, zinc overload also has pro-oxidant properties. Excessive intracellular zinc can enter the mitochondria through the mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter (MCU) (Medvedeva and Weiss, 2014), then irreversibly inhibit components of the electron transport chain (ETC.), which may stimulate the production of mitochondrial superoxide anions (·O2−) and damage mitochondrial function, leading to cell death. Furthermore, zinc overload can promote lysosomal dysfunction caused by increased lysosomal membrane permeability (LMP), which triggers cell death (Yu et al., 2009). Therefore, increasing intracellular zinc concentration is a viable therapeutic strategy to combat cancer.
2.5.3 Zinc ion-based antitumor nanodrugs
Zinc ion-based nanodrugs for cancer treatment can deliver exogenous Zn2+ to tumor cells and induce cell death (Yao et al., 2023). PH-responsive zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8), composed of 2-methylimidazole and Zn2+, can serve as a source of exogenous Zn2+ due to its excellent degradation ability (Gao L. et al., 2019). However, the hydrophobicity and relatively large size of ZIF-8 limit its antitumor application. Therefore, Lv et al. designed a multifunctional zinc-based nanoplatform, BSArGO@ZIF-8 NS, which can synergize ion interference and photothermal cancer treatment (Lv et al., 2022). BSArGO@ZIF-8 NSs can induce tumor cell apoptosis through intracellular Zn2+ overload, and at the same time, induce photothermal effects on cancer cells under (NIR) irradiation, showing higher lethality. In addition, Ding et al. synthesized F127ZIF-8CCCP nanoparticles for efficient cancer immunotherapy (Ding B. et al., 2023). F127ZIF-8CCCP nanoparticles achieve pH-sensitive Zn2+ release in tumor cells, leading to increased intracellular osmotic pressure and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which synergize with CCCP to strongly trigger caspase-1/GSDMD-dependent pyroptosis, thereby activating antitumor immunity and inhibiting tumor growth.
In addition to introducing Zn2+ exogenously into tumor cells, zinc overload caused by disrupting endogenous zinc homeostasis is another antitumor treatment strategy. Su et al. synthesized a series of platinum (IV) -terthiophene complexes for cancer chemotherapeutic immunotherapy (Su et al., 2023). Among these complexes, the cyclometalated platinum (IV) -terthiophene complex (Pt3) showed the best antiproliferative effect on triple-negative breast cancer (MDA-MB-231) cells. Mechanistically, Pt3 can induce DNA damage, disrupt intracellular zinc homeostasis, and disrupt intracellular redox homeostasis, ultimately activating tumor cell pyroptosis through the caspase-1/GSDMD pathway, and can activate antitumor immunity in mice (Riley and Tait, 2020).
In addition to inducing tumor cell death, zinc ions can also activate the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS)-stimulator of interferon genes (STING) signaling pathway to enhance the effect of cancer immunotherapy. Therefore, various zinc-containing nanomaterials have been developed for zinc-based tumor immunotherapy. For example, Cen et al. prepared a pH-responsive nanocluster (ZnS@BSA) to enhance the immunotherapeutic effect against hepatocellular carcinoma (Cen et al., 2021). Zhang et al. reported a Zn2+-doped layered double metal hydroxide (Zn-LDH) to trigger a strong metal immunotherapy against solid tumors (Zhang et al., 2022). Ding et al. constructed a zinc-based metal-organic framework vaccine (ZPM@OVA-CpG) that controllably releases Zn2+, providing a promising strategy to improve the effect of immunotherapy (Ding B. et al., 2023). Zhao et al. prepared a pH-responsive and photoactive nanoparticle (ALA&Dz@ZIF-PEG) to enhance the effect of photodynamic immunotherapy (Zhao X. et al., 2023).
3 Metal-based antitumor nanoplatforms and multiionic combined interference therapy
Metal ion therapy, as an emerging tumor treatment method, has shown the potential to overcome the resistance of traditional chemotherapy drugs (Urbano-Gamez et al., 2024), In recent years, research on metal-ion-based nanomaterials and platforms has been emerging continuously (Table 1).
Metal nanomaterials are forming a drug-free nanoplatform, in which metal ions are gradually replacing traditional drugs as part of the construction of nanomaterials (Chuang et al., 2023; Lei et al., 2023; Li et al., 2024; Naletova et al., 2023). These nanoparticles can specifically deliver metal ions to tumor cells, thereby reducing damage to normal tissues, improving treatment effects, and reducing side effects. In addition, nanoparticles can also enhance the solubility, stability, and biocompatibility of metal ions through their surface modification and functionalization, further optimizing the application of metal ion therapy. Additionally, the nanoplatform is capable of delivering multiple components simultaneously, achieving synergistic effects of different therapeutic mechanisms. Metal ions in combination with other treatment strategies can be used to design new synergistic anti-tumor regimens, improving tumor treatment outcomes, and reducing the potential toxicity of drugs to normal tissues. Additionally, strategies that modulate the homeostasis of multiple metals have shown promising anti-tumor effects. Recently, there has been considerable research on regulating the homeostasis of various metals for cancer treatment. For instance, Shen et al. reported a pH-responsive nanoplatform (CaO2@ZIF-Fe/Ce6@PEG) that simultaneously causes overload of iron and calcium within tumor cells, providing a robust self-supplied ROS pathway to further enhance the efficacy of CDT/PDT (Shen et al., 2021). Xu et al. constructed a novel copper/iron mixed hollow nanoplatform (DOX@Fe/CuTHHaMOF) to disrupt intracellular copper/iron metabolism and amplify intracellular oxidative stress, which effectively suppresses tumor growth through synergistic copper apoptosis/iron apoptosis/apoptosis (Xu Y. et al., 2022). Zheng et al. developed a Ca2+/Mn2+ ion reservoir (PEGCaMnUA) to increase intracellular oxidative stress, enhancing the effect of ion interference therapy (IIT) (Zheng et al., 2023). Deng et al. prepared a Ca&Mn dual-ion mixed nanostimulator (CMS) to simultaneously activate iron apoptosis and innate immunity, providing a new strategy for effective immunotherapy against triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) (Deng et al., 2024). Huang et al. constructed a Mn/Zn dual-metal nanoplatform (PMZH) to activate the cGAS-STING signaling pathway and ROS-mediated tumor cell death, achieving enhanced tumor immunotherapy (Huang Y. et al., 2023). Wang et al. prepared a carrier-free nanodrug (Mn-ZnO2 nanoparticles) for delivering zinc-manganese dual ions for the treatment of p53-mutated tumors (Wang J. et al., 2023). In summary, these strategies based on disrupting the homeostasis of multiple metals within cells will provide innovation for cancer treatment. These strategies are expected to address the issue of multiple drug resistance in tumors. In conclusion, combining the advantages of nanotechnology, metal ions have emerged as a new strategy for anticancer therapy.
4 Advantages of metal-based nanomaterials
Metal-based nanomaterials have been proven to have tremendous potential as targeted drug delivery systems, imaging agents, and therapeutics. Due to their unique advantages, metal nanomaterials have broad application prospects and significant research value in numerous fields. Compared to other types of nanomaterials, metal-based antitumor nanomaterials have the following advantages. First and foremost, metal-based nanomaterials can release a large amount of specific metal ions in the tumor microenvironment, thereby disrupting the metal ion balance required for cellular function. Therefore, metal-based nanomaterials hold great promise for enhancing the imbalance of metal homeostasis in cancer cells. Currently, metal-based nanomaterials under study either through metal chelation or metal overload lead to the disruption of metal homeostasis in cancer cells, ultimately resulting in cell death through various means such as apoptosis, pyroptosis, ferroptosis, cuproptosis, et al. Secondly, due to their small size and high surface area-to-volume ratio, metal nanomaterials exhibit unique physical, chemical, and optical properties, such as strong near-infrared absorption, magnetothermal effects, and the ability to easily accumulate, separate, or undergo targeted movement and localization. These properties enable metal nanomaterials to play a unique role in tumor diagnosis and treatment. For example, gold nanomaterials can rapidly heat up under laser irradiation through the photothermal conversion effect, thereby killing tumor cells and achieving photothermal therapy (Khoobchandani et al., 2020). Magnetic nanomaterials, on the other hand, can indirectly kill tumor cells through the magnetothermal effect, showing good antitumor effects. Furthermore, metal nanomaterials have a high surface area and abundant active sites, which can serve as carriers for anticancer drugs, enhancing the uptake of drugs by cancer cells and improving the efficacy of cancer treatment while reducing the dosage of antitumor drugs. Surface modification of metal nanomaterials can also further enhance their biocompatibility and safety, reducing their potential systemic side effects. Additionally, metal nanomaterials have shown great potential in tumor immunotherapy. For instance, by preparing ultra-small metal-organic nanomaterials, it is possible to achieve sufficient accumulation at the tumor site and rapid renal clearance, enhancing treatment efficacy and greatly reducing long-term toxicity caused by body retention. At the same time, by concentrating multiple functional drug molecules on a single metal nanoplatform, the preparation of multifunctional integrated nanohybrid materials is expected to achieve multimodal synergistic tumor treatment, improving cancer treatment efficiency and imaging resolution. In summary, metal-based antitumor nanomaterials, due to their unique physicochemical properties, high surface area-to-volume ratio, and abundant active sites, as well as their multifunctionality, tunability, and ability to interact with cellular processes, make them attractive candidates for targeted cancer therapy. They have a unique role in tumor diagnosis and treatment and show a broad application prospect.
5 Clinical trials of metal nanomaterials for tumor treatment
Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles are the earliest metal nanoscale agents applied clinically. They were initially used to treat clinical iron deficiency anemia, with a clinical history dating back to 1930, accumulating valuable data on safety and side effects. In the early 21st century, there was evidence that systemic exposure to iron oxide nanoparticles could induce anti-cancer immune effects. By directly injecting biocompatible iron oxide nanoparticles into tumors and then stimulating them with alternating magnetic fields to generate heat, i.e., using magnetic nanoparticles (Nano-Cancer® therapy) for intratumoral hyperthermia, tumor growth could be suppressed. Given this mechanism, this method was used clinically in the treatment of glioblastoma and prostate cancer about 20 years ago (Johannsen et al., 2007a; Johannsen et al., 2007b; Maier-Hauff et al., 2007). Subsequently, researches on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in tumor treatment has become more in-depth, with new formulations continuously emerging and complex mechanisms of action being revealed (Savitsky and Yu, 2019; Soetaert et al., 2020). For example, Nanotherm™ (EU) is used for the clinical treatment of recurrent neuroblastoma (Maier-Hauff et al., 2011). Zanganeh et al. revealed the hidden intrinsic therapeutic effects of iron oxide nanoparticle compounds ferumoxytol (an FDA-approved drug) on tumors (Zanganeh et al., 2016). After mixing ferumoxytol with tumor cells and co-injecting them into mice, compared to tumor cells not injected with ferumoxytol, the growth rate of the tumor was significantly slowed down. Furthermore, they demonstrated that systemic exposure to ferumoxytol in T cell-deficient mice, followed by intravenous injection of small cell lung cancer (SCLC) cells, could prevent liver metastasis. They concluded that the intrinsic therapeutic effect of ferumoxytol on cancer growth comes from the polarization of macrophages to a pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype. In other words, they showed that the innate immune cells in the experimental model tumor microenvironment respond to iron oxide nanoparticles, responsible for the anti-tumor immune effect, rather than T cells. In summary, iron oxide nanoparticles are truly effective agents for hyperthermia and immunotherapy for cancer.
Additionally, there are reports of clinical trials using gold nanoparticles as precious metals for breast cancer patients. The Nano Swarna Bhasma (NSB) Nano-Ayurvedic medicine-gold nanoparticles-based drug was developed using proprietary combinations of gold nanoparticles and phytochemicals through innovative green nanotechnology for human metastatic breast cancer patients. Patients treated with the NSB drug capsules along with the “standard of care treatment” (group B) exhibited 100% clinical benefits when compared to patients in the treatment group A, thus indicating the tremendous clinical benefits of NSB drug in adjuvant therapy (Khoobchandani et al., 2020). The results also indicate that Nano Swarna Bhasma can be safely used as a valuable adjuvant therapeutic agent to reduce the adverse effects of routine chemotherapeutic agents while providing measurable therapeutic efficacy in treating breast and other forms of human cancers.
6 Limitations and challenges in clinical translation of metal nanomaterials for tumor treatment
Although metal nanomaterials show great potential for tumor treatment at present, they still have many limitations. Firstly, although many anti-tumor mechanisms of metal ion based nanodrugs have been reported, but most of them have only been validated in cell lines. Therefore, further research on these mechanisms in more organoid and animal models is necessary to deeply elucidate the anti-tumor mechanisms and effects of metal ion-based nanodrugs. However, the lack of animal models that can accurately simulate human tumor conditions is one of the recognized deficiencies in the field, leading to a weak correlation between preclinical studies and clinical trial results. For this reason, researchers are trying to establish organoids from patients, which are innovative screening devices as close as possible to the in vivo environment. The established platform takes into account tumor angiogenesis and the 3D microenvironment, so as to select the best anti-tumor therapy for patients through the screening device, and collect lymphocytes from the patient’s blood to test the effectiveness of immunotherapy. Secondly, there are a series of biological barriers in the body, and if nanocarriers cannot efficiently pass through them, they will also limit the therapeutic effect; interactions between nanomaterials and biological entities in the blood can alter the physicochemical characteristics and stability of nanodrugs, hindering the specific binding of targeting molecules to receptors; most nanoparticles are taken up and cleared by macrophages in the liver or spleen after entering the body, preventing their further delivery to tumor tissues. Therefore, this also poses higher requirements for the design and development of clinical drugs. Lastly, the biological safety of nanomedicines in vivo remains the greatest challenge for their clinical application. Currently, most excellent studies have only examined the short-term toxicity of nanomedicines and the corresponding structural damage to major organs, lacking experiments on the long-term toxicity of metal nanomedicines. Therefore, it is necessary to conduct comprehensive studies on their absorption, biodistribution, metabolism, excretion, clearance, long-term tissue accumulation, chronic toxicity, and dose-dependent toxicity before clinical translation. In fact, metal nanomaterials for multimodal combination therapy have shown advantages of synergistic enhanced therapeutic effects and low cytotoxicity. By selecting metal ions with high biocompatibility (e.g., Ca2+, Fe2+/3+, Zn2+, etc.) and endogenous bioactive molecules as ligands, toxicity can be effectively prevented (Lai et al., 2021; Simon-Yarza et al., 2018). The additional cargo that may be loaded also needs to be considered, as they may pose a threat to the organism. In addition, there is an increasing need for extensive and in-depth research into the degradation mechanisms and pathways of metal nanomaterials in vivo.
Additionally, the synergistic and antagonistic effects among carriers used in cancer treatment, the metal nanoparticles embedded within them, and the complexes containing these metal ions remain unknown. Knowledge of the chemical interactions between metal nanoparticles and these metal ion complexes is still limited. There is currently no answer to the question of whether it is possible to precisely control the release of metal ions from the nanoparticle surface while increasing the biocompatibility of the materials and maximizing their anticancer activity. The properties of organic-inorganic systems, ligand substitution on the surface of metal nanoparticles, and the behavior of maintaining complex stability in the presence of biofluids also remain unexplored.
The clinical translation of metal ion-based nanodrugs for tumor treatment still faces some challenges. Although the valuable experience of intravenous injection of iron oxide nanoparticles for the treatment of anemia is a guide, clinical product iterations have also been carried out in subsequent studies to gain relevant knowledge and sufficient experience. However, nearly a century and the rich clinical experience gained from “three generations” of successful iron oxide nanoparticle formulations have not led to substantial progress in the field of metal nanoparticle anti-tumor drugs as expected. Even with such a long clinical history, new discoveries of complex biological interactions with iron oxide nanoparticles still indicate that our understanding of the complexity of cancer is insufficient. The interactions between nanoparticles and biological systems remain unknown, and incorporating these interactions into the design and function of cancer nanomedicine has greater potential than focusing solely on their engineering design. Cancer is a family of complex diseases, with considerable heterogeneity between subsets, within subsets of the same disease, and within individual patients (Tomasetti and Vogelstein, 2015). The tumor microenvironment is heterogeneous, dynamic, and complex, so each nanoparticle formulation must be evaluated in the context of a wide range of biological scenarios. In addition, preclinical data is not a universally reliable indicator of clinical benefit. Data suggest that more caution is needed when selecting preclinical animal models and that preclinical results need to be carefully assessed.
The historical reality of cancer treatment research and development is that most product concepts fail to translate into clinical applications. The development of small molecule cancer therapeutics has not yet overcome the challenges posed by tumor metastasis, which increases the need for rigorous clinical validation of preclinical data. Metal nanoparticles have great potential for anti-tumor effects, but they must also be modified and designed under the premise of a clear understanding of the specific disease context and interaction with host immune biology, and require the adoption of different research perspectives and multidisciplinary collaboration to achieve efficient therapeutic outcomes.
7 Conclusion and perspectives
In this review, we summarize the mechanisms of metal ions (Fe2+/3+, Ca2+, Mn2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+) in anti-tumor therapy, and the nanodrugs developed based on these ions over the past 5 years. We analyze the challenges faced by the clinical translation of current metal-based anti-tumor nanomaterials and their future application prospects, and propose suggestions to address related defects. With the proposal and elucidation of concepts such as ferroptosis and cuproptosis, research on metal ion-based anti-tumor nanomaterials has emerged, becoming a new research hotspot. Metal-based anti-tumor drugs can not only cause cell death individually by inducing intracellular ion imbalances but can also enhance the effects of other anti-tumor therapies such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, photothermal therapy, and photodynamic therapy. They play a role in comprehensive tumor treatment and achieve synergistic effects of different treatment mechanisms, and demonstrate significant potential. However, many obstacles need to be addressed in various aspects such as the selection of model drugs, the development of preclinical research models, drug safety in vivo, and patient screening in clinical research et al. The continuous development of new nanomaterial manufacturing processes and standardized procedures, as well as new experimental technologies such as organoid culture systems, will further promote the development of metal nanodrugs in the field of anti-tumor therapy.
With in-depth research on the mechanisms of cancer pathogenesis and the action of metal-based drugs, the design of metal nanodrugs will become more precise and efficient. The application of new strategies and technologies will further promote the development of metal nanodrugs in the field of anti-tumor therapy, and the application of metal nanodrugs in the field of anti-tumor therapy will become more extensive and profound.
Author contributions
YX: Data curation, Investigation, Writing–original draft. AR: Writing–original draft. WF: Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
An, J., Zhang, K., Wang, B., Wu, S., Wang, Y., Zhang, H., et al. (2020). Nanoenabled disruption of multiple barriers in antigen cross-presentation of dendritic cells via calcium interference for enhanced chemo-immunotherapy. ACS Nano 14, 7639–7650. doi:10.1021/acsnano.0c03881
Ash, D., Sudhahar, V., Youn, S. W., Okur, M. N., Das, A., O'Bryan, J. P., et al. (2021). The P-type ATPase transporter ATP7A promotes angiogenesis by limiting autophagic degradation of VEGFR2. Nat. Commun. 12, 3091. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-23408-1
Bagur, R., and Hajnoczky, G. (2017). Intracellular Ca(2+) sensing: its role in calcium homeostasis and signaling. Mol. Cell 66, 780–788. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2017.05.028
Bai, S., Lan, Y., Fu, S., Cheng, H., Lu, Z., and Liu, G. (2022). Connecting calcium-based nanomaterials and cancer: from diagnosis to therapy. Nanomicro Lett. 14, 145. doi:10.1007/s40820-022-00894-6
Bao, W., Liu, M., Meng, J., Liu, S., Wang, S., Jia, R., et al. (2021). MOFs-based nanoagent enables dual mitochondrial damage in synergistic antitumor therapy via oxidative stress and calcium overload. Nat. Commun. 12, 6399. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-26655-4
Bendellaa, M., Lelievre, P., Coll, J. L., Sancey, L., Deniaud, A., and Busser, B. (2024). Roles of zinc in cancers: from altered metabolism to therapeutic applications. Int. J. Cancer 154, 7–20. doi:10.1002/ijc.34679
Berridge, M. J. (2016). The inositol trisphosphate/calcium signaling pathway in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 96, 1261–1296. doi:10.1152/physrev.00006.2016
Berridge, M. J., Lipp, P., and Bootman, M. D. (2000). The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1, 11–21. doi:10.1038/35036035
Billesbolle, C. B., Azumaya, C. M., Kretsch, R. C., Powers, A. S., Gonen, S., Schneider, S., et al. (2020). Structure of hepcidin-bound ferroportin reveals iron homeostatic mechanisms. Nature 586, 807–811. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2668-z
Campos, O. A., Attar, N., Cheng, C., Vogelauer, M., Mallipeddi, N. V., Schmollinger, S., et al. (2021). A pathogenic role for histone H3 copper reductase activity in a yeast model of Friedreich's ataxia. Sci. Adv. 7, eabj9889. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abj9889
Cao, Z., Yang, X., Yang, W., Chen, F., Jiang, W., Zhan, S., et al. (2024). Modulation of dendritic cell function via nanoparticle-induced cytosolic calcium changes. ACS Nano 18, 7618–7632. doi:10.1021/acsnano.4c00550
Carafoli, E. (2002). Calcium signaling: a tale for all seasons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99, 1115–1122. doi:10.1073/pnas.032427999
Cen, D., Ge, Q., Xie, C., Zheng, Q., Guo, J., Zhang, Y., et al. (2021). ZnS@BSA nanoclusters potentiate efficacy of cancer immunotherapy. Adv. Mater 33, e2104037. doi:10.1002/adma.202104037
Chang, M., Hou, Z., Jin, D., Zhou, J., Wang, M., Wang, M., et al. (2020). Colorectal tumor microenvironment-activated bio-decomposable and metabolizable Cu(2) O@CaCO(3) nanocomposites for synergistic oncotherapy. Adv. Mater 32, e2004647. doi:10.1002/adma.202004647
Chang, X., Zhu, M., Tang, X., Yu, X., Liu, F., Chen, L., et al. (2022). Enhanced manipulation of tumor microenvironments by nanomotor for synergistic therapy of malignant tumor. Biomaterials 290, 121853. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121853
Chen, C., Tong, Y., Zheng, Y., Shi, Y., Chen, Z., Li, J., et al. (2021). Cytosolic delivery of thiolated Mn-cGAMP nanovaccine to enhance the antitumor immune responses. Small 17, e2006970. doi:10.1002/smll.202006970
Chen, K., Zhou, A., Zhou, X., Liu, Y., Xu, Y., and Ning, X. (2023). An intelligent cell-derived nanorobot bridges synergistic crosstalk between sonodynamic therapy and cuproptosis to promote cancer treatment. Nano Lett. 23, 3038–3047. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c00434
Chen, Q., Zheng, Z., He, X., Rong, S., Qin, Y., Peng, X., et al. (2020). A tumor-targeted theranostic nanomedicine with strong absorption in the NIR-II biowindow for image-guided multi-gradient therapy. J. Mater Chem. B 8, 9492–9501. doi:10.1039/d0tb01915a
Cheng, J., Zhu, Y., Xing, X., Xiao, J., Chen, H., Zhang, H., et al. (2021). Manganese-deposited iron oxide promotes tumor-responsive ferroptosis that synergizes the apoptosis of cisplatin. Theranostics 11, 5418–5429. doi:10.7150/thno.53346
Chuang, Y. C., Wu, P. H., Shen, Y. A., Kuo, C. C., Wang, W. J., Chen, Y. C., et al. (2023). Recent advances in metal-based NanoEnhancers for particle therapy. Nanomater. (Basel) 13, 1011. doi:10.3390/nano13061011
Colvin, R. A., Holmes, W. R., Fontaine, C. P., and Maret, W. (2010). Cytosolic zinc buffering and muffling: their role in intracellular zinc homeostasis. Metallomics 2, 306–317. doi:10.1039/b926662c
Cui, L., Gouw, A. M., LaGory, E. L., Guo, S., Attarwala, N., Tang, Y., et al. (2021). Mitochondrial copper depletion suppresses triple-negative breast cancer in mice. Nat. Biotechnol. 39, 357–367. doi:10.1038/s41587-020-0707-9
Deng, X., Liu, T., Zhu, Y., Chen, J., Song, Z., Shi, Z., et al. (2024). Ca and Mn dual-ion hybrid nanostimulator boosting anti-tumor immunity via ferroptosis and innate immunity awakening. Bioact. Mater 33, 483–496. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.11.017
Ding, B., Chen, H., Tan, J., Meng, Q., Zheng, P., Ma, P., et al. (2023a). ZIF-8 nanoparticles evoke pyroptosis for high-efficiency cancer immunotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 62, e202215307. doi:10.1002/anie.202215307
Ding, L., Liang, M., Li, Y., Zeng, M., Liu, M., Ma, W., et al. (2023b). Zinc-organometallic framework vaccine controlled-release Zn(2+) regulates tumor extracellular matrix degradation potentiate efficacy of immunotherapy. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 10, e2302967. doi:10.1002/advs.202302967
Dong, Z., Feng, L., Hao, Y., Li, Q., Chen, M., Yang, Z., et al. (2020a). Synthesis of CaCO3-based nanomedicine for enhanced sonodynamic therapy via amplification of tumor oxidative stress. Nano Res. 6, 1391–1407. doi:10.1007/s12274-020-2972-9
Dong, Z., Hao, Y., Li, Q., Yang, Z., Zhu, Y., Liu, Z., et al. (2020b). Metal-polyphenol-network coated CaCO3 as pH-responsive nanocarriers to enable effective intratumoral penetration and reversal of multidrug resistance for augmented cancer treatments. Nano Res. 13, 3057–3067. doi:10.1007/s12274-020-2972-9
Du, Y., Zhang, R., Yang, J., Liu, S., Zhou, J., Zhao, R., et al. (2022). A “Closed-Loop” therapeutic strategy based on mutually reinforced ferroptosis and immunotherapy. Adv. Funct. Mater 32, 2111784. doi:10.1002/adfm.202111784
Dubois, C., Vanden Abeele, F., Lehen'kyi, V., Gkika, D., Guarmit, B., Lepage, G., et al. (2014). Remodeling of channel-forming ORAI proteins determines an oncogenic switch in prostate cancer. Cancer Cell 26, 19–32. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2014.04.025
Faouzi, M., Kischel, P., Hague, F., Ahidouch, A., Benzerdjeb, N., Sevestre, H., et al. (2013). ORAI3 silencing alters cell proliferation and cell cycle progression via c-myc pathway in breast cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1833, 752–760. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.12.009
Feng, Z., Chen, G., Zhong, M., Lin, L., Mai, Z., Tang, Y., et al. (2023). An acid-responsive MOF nanomedicine for augmented anti-tumor immunotherapy via a metal ion interference-mediated pyroptotic pathway. Biomaterials 302, 122333. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122333
Gao, L., Chen, Q., Gong, T., Liu, J., and Li, C. (2019a). Recent advancement of imidazolate framework (ZIF-8) based nanoformulations for synergistic tumor therapy. Nanoscale 11, 21030–21045. doi:10.1039/c9nr06558j
Gao, S., Jin, Y., Ge, K., Li, Z., Liu, H., Dai, X., et al. (2019b). Self-supply of O(2) and H(2)O(2) by a nanocatalytic medicine to enhance combined chemo/chemodynamic therapy. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 6, 1902137. doi:10.1002/advs.201902137
Ge, E. J., Bush, A. I., Casini, A., Cobine, P. A., Cross, J. R., DeNicola, G. M., et al. (2022). Connecting copper and cancer: from transition metal signalling to metalloplasia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 22, 102–113. doi:10.1038/s41568-021-00417-2
Guo, B., Yang, F., Zhang, L., Zhao, Q., Wang, W., Yin, L., et al. (2023). Cuproptosis induced by ROS responsive nanoparticles with elesclomol and copper combined with αpd-L1 for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Adv. Mater 35, e2212267. doi:10.1002/adma.202212267
Han, Y., Dong, Z., Wang, C., Li, Q., Hao, Y., Yang, Z., et al. (2022). Ferrous ions doped calcium carbonate nanoparticles potentiate chemotherapy by inducing ferroptosis. J. Control Release 348, 346–356. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.06.002
He, S., Jiang, Y., Li, J., and Pu, K. (2020a). Semiconducting polycomplex nanoparticles for photothermal ferrotherapy of cancer. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 59, 10633–10638. doi:10.1002/anie.202003004
He, Y. J., Liu, X. Y., Xing, L., Wan, X., Chang, X., and Jiang, H. L. (2020b). Fenton reaction-independent ferroptosis therapy via glutathione and iron redox couple sequentially triggered lipid peroxide generator. Biomaterials 241, 119911. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.119911
Hof, T., Chaigne, S., Recalde, A., Salle, L., Brette, F., and Guinamard, R. (2019). Transient receptor potential channels in cardiac health and disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 16, 344–360. doi:10.1038/s41569-018-0145-2
Hou, L., Tian, C., Yan, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, H., and Zhang, Z. (2020). Manganese-based nanoactivator optimizes cancer immunotherapy via enhancing innate immunity. ACS Nano 14, 3927–3940. doi:10.1021/acsnano.9b06111
Huang, L., Zhu, J., Xiong, W., Feng, J., Yang, J., Lu, X., et al. (2023a). Tumor-generated reactive oxygen species storm for high-performance ferroptosis therapy. ACS Nano 17, 11492–11506. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c01369
Huang, T., Zhou, J., and Wang, J. (2022). Calcium and calcium-related proteins in endometrial cancer: opportunities for pharmacological intervention. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 18, 1065–1078. doi:10.7150/ijbs.68591
Huang, Y., Qin, G., Cui, T. T., Zhao, C. Q., Ren, J. S., and Xg, Q. (2023b). A bimetallic nanoplatform for STING activation and CRISPR/Cas mediated depletion of the methionine transporter in cancer cells restores anti-tumor immune responses. Nat. Commun. 14, 4647. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-40345-3
Jia, W., Tian, H., Jiang, J., Zhou, L., Li, L., Luo, M., et al. (2023). Brain-targeted HFn-Cu-rego nanoplatform for site-specific delivery and manipulation of autophagy and cuproptosis in glioblastoma. Small 19, e2205354. doi:10.1002/smll.202205354
Jiang, F., Ding, B., Liang, S., Zhao, Y., Cheng, Z., Xing, B., et al. (2021). Intelligent MoS(2)-CuO heterostructures with multiplexed imaging and remarkably enhanced antitumor efficacy via synergetic photothermal therapy/chemodynamic therapy/immunotherapy. Biomaterials 268, 120545. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120545
Jiang, Q., Wang, K., Zhang, X., Ouyang, B., Liu, H., Pang, Z., et al. (2020). Platelet membrane-camouflaged magnetic nanoparticles for ferroptosis-enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Small 16, e2001704. doi:10.1002/smll.202001704
Jing, Z., Sui, X., Yao, J., Xie, J., Jiang, L., Zhou, Y., et al. (2016). SKF-96365 activates cytoprotective autophagy to delay apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells through inhibition of the calcium/CaMKIIγ/AKT-mediated pathway. Cancer Lett. 372, 226–238. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2016.01.006
Johannsen, M., Gneveckow, U., Taymoorian, K., Thiesen, B., Waldofner, N., Scholz, R., et al. (2007a). Morbidity and quality of life during thermotherapy using magnetic nanoparticles in locally recurrent prostate cancer: results of a prospective phase I trial. Int. J. Hyperth. 23, 315–323. doi:10.1080/02656730601175479
Johannsen, M., Gneveckow, U., Thiesen, B., Taymoorian, K., Cho, C. H., Waldofner, N., et al. (2007b). Thermotherapy of prostate cancer using magnetic nanoparticles: feasibility, imaging, and three-dimensional temperature distribution. Eur. Urol. 52, 1653–1662. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2006.11.023
Ju, C., Zhang, Z., Deng, J., Miao, C., Wang, Z., Wallrad, L., et al. (2022). Ca(2+)-dependent successive phosphorylation of vacuolar transporter MTP8 by CBL2/3-CIPK3/9/26 and CPK5 is critical for manganese homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 15, 419–437. doi:10.1016/j.molp.2021.11.012
Kambe, T., Tsuji, T., Hashimoto, A., and Itsumura, N. (2015). The physiological, biochemical, and molecular roles of zinc transporters in zinc homeostasis and metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 95, 749–784. doi:10.1152/physrev.00035.2014
Khoobchandani, M., Katti, K. K., Karikachery, A. R., Thipe, V. C., Srisrimal, D., Dhurvas Mohandoss, D. K., et al. (2020). New approaches in breast cancer therapy through green nanotechnology and nano-ayurvedic medicine - pre-clinical and pilot human clinical investigations. Int. J. Nanomedicine 15, 181–197. doi:10.2147/IJN.S219042
Kim, A. (2010). Modulation of MnSOD in cancer: epidemiological and experimental evidences. Toxicol. Res. 26, 83–93. doi:10.5487/TR.2010.26.2.083
Lai, X., Jiang, H., and Wang, X. (2021). Biodegradable metal organic frameworks for multimodal imaging and targeting theranostics. Biosens. (Basel) 11, 299. doi:10.3390/bios11090299
Lei, G., Zhuang, L., and Gan, B. (2022). Targeting ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 22, 381–396. doi:10.1038/s41568-022-00459-0
Lei, H., Pei, Z., Jiang, C., and Cheng, L. (2023). Recent progress of metal-based nanomaterials with anti-tumor biological effects for enhanced cancer therapy. Explor. (Beijing) 3, 20220001. doi:10.1002/EXP.20220001
Li, Y., Wang, Y., Zhao, L., Stenzel, M. H., and Jiang, Y. (2024). Metal ion interference therapy: metal-based nanomaterial-mediated mechanisms and strategies to boost intracellular “ion overload” for cancer treatment. Mater Horiz. 11, 4275–4310. doi:10.1039/d4mh00470a
Li, Y., Zhou, S., Song, H., Yu, T., Zheng, X., and Chu, Q. (2021). CaCO(3) nanoparticles incorporated with KAE to enable amplified calcium overload cancer therapy. Biomaterials 277, 121080. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2021.121080
Li, Z., Chu, Z., Yang, J., Qian, H., Xu, J., Chen, B., et al. (2022). Immunogenic cell death augmented by manganese zinc sulfide nanoparticles for metastatic melanoma immunotherapy. ACS Nano 16, 15471–15483. doi:10.1021/acsnano.2c08013
Liu, C., Chen, Y., Zhao, J., Wang, Y., Shao, Y., Gu, Z., et al. (2021). Self-assembly of copper-DNAzyme nanohybrids for dual-catalytic tumor therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 60, 14324–14328. doi:10.1002/anie.202101744
Liu, H., Yi, P., Zhao, W., Wu, Y., Acher, F., Pin, J. P., et al. (2020). Illuminating the allosteric modulation of the calcium-sensing receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 117, 21711–21722. doi:10.1073/pnas.1922231117
Liu, M., Sun, X., Chen, B., Dai, R., Xi, Z., and Xu, H. (2022). Insights into manganese superoxide dismutase and human diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 15893. doi:10.3390/ijms232415893
Liu, Z. Y., Liu, Z. Y., Lin, L. C., Song, K., Tu, B., Zhang, Y., et al. (2024). Redox homeostasis in cardiac fibrosis: focus on metal ion metabolism. Redox Biol. 71, 103109. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2024.103109
Lu, X., Deng, W., Wang, S., Zhao, S., Zhu, B., Bai, B., et al. (2024a). PEGylated Elesclomol@Cu(Ⅱ)-based Metal‒organic framework with effective nanozyme performance and cuproptosis induction efficacy for enhanced PD-L1-based immunotherapy. Mater Today Bio 29, 101317. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101317
Lu, Y., Chen, Y., Hou, G., Lei, H., Liu, L., Huang, X., et al. (2024b). Zinc-iron bimetallic peroxides modulate the tumor stromal microenvironment and enhance cell immunogenicity for enhanced breast cancer immunotherapy therapy. ACS Nano 18, 10542–10556. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c12615
Lv, C., Kang, W., Liu, S., Yang, P., Nishina, Y., Ge, S., et al. (2022). Growth of ZIF-8 nanoparticles in situ on graphene oxide nanosheets: a multifunctional nanoplatform for combined ion-interference and photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 16, 11428–11443. doi:10.1021/acsnano.2c05532
Lv, M., Chen, M., Zhang, R., Zhang, W., Wang, C., Zhang, Y., et al. (2020). Manganese is critical for antitumor immune responses via cGAS-STING and improves the efficacy of clinical immunotherapy. Cell Res. 30, 966–979. doi:10.1038/s41422-020-00395-4
Lv, X., Huang, J., Min, J., Wang, H., Xu, Y., Zhang, Z., et al. (2023). Multi-signaling pathway activation by pH responsive manganese particles for enhanced vaccination. J. Control Release 357, 109–119. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.01.078
Maier-Hauff, K., Rothe, R., Scholz, R., Gneveckow, U., Wust, P., Thiesen, B., et al. (2007). Intracranial thermotherapy using magnetic nanoparticles combined with external beam radiotherapy: results of a feasibility study on patients with glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neurooncol 81, 53–60. doi:10.1007/s11060-006-9195-0
Maier-Hauff, K., Ulrich, F., Nestler, D., Niehoff, H., Wust, P., Thiesen, B., et al. (2011). Efficacy and safety of intratumoral thermotherapy using magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles combined with external beam radiotherapy on patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neurooncol 103, 317–324. doi:10.1007/s11060-010-0389-0
Marchi, S., Giorgi, C., Galluzzi, L., and Pinton, P. (2020). Ca(2+) fluxes and cancer. Mol. Cell 78, 1055–1069. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.04.017
Maret, W. (2013). Zinc biochemistry: from a single zinc enzyme to a key element of life. Adv. Nutr. 4, 82–91. doi:10.3945/an.112.003038
Medvedeva, Y. V., and Weiss, J. H. (2014). Intramitochondrial Zn2+ accumulation via the Ca2+ uniporter contributes to acute ischemic neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 68, 137–144. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2014.04.011
Monteith, G. R., Prevarskaya, N., and Roberts-Thomson, S. J. (2017). The calcium-cancer signalling nexus. Nat. Rev. Cancer 17, 373–380. doi:10.1038/nrc.2017.18
Mou, Y., Wang, J., Wu, J., He, D., Zhang, C., Duan, C., et al. (2019). Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: opportunities and challenges in cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 12, 34. doi:10.1186/s13045-019-0720-y
Murphy, D. A., Cheng, H., Yang, T., Yan, X., and Adjei, I. M. (2021). Reversing hypoxia with PLGA-encapsulated manganese dioxide nanoparticles improves natural killer cell response to tumor spheroids. Mol. Pharm. 18, 2935–2946. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.1c00085
Naletova, I., Tomasello, B., Attanasio, F., and Pleshkan, V. V. (2023). Prospects for the use of metal-based nanoparticles as adjuvants for local cancer immunotherapy. Pharmaceutics 15, 1346. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15051346
Nguyen, N. T., Kim, J., Le, X. T., Lee, W. T., Lee, E. S., Oh, K. T., et al. (2023). Amplified fenton-based oxidative stress utilizing ultraviolet upconversion luminescence-fueled nanoreactors for apoptosis-strengthened ferroptosis anticancer therapy. ACS Nano 17, 382–401. doi:10.1021/acsnano.2c08706
Nyvltova, E., Dietz, J. V., Seravalli, J., Khalimonchuk, O., and Barrientos, A. (2022). Coordination of metal center biogenesis in human cytochrome c oxidase. Nat. Commun. 13, 3615. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-31413-1
Ploetz, E., Zimpel, A., Cauda, V., Bauer, D., Lamb, D. C., Haisch, C., et al. (2020). Metal-organic framework nanoparticles induce pyroptosis in cells controlled by the extracellular pH. Adv. Mater 32, e1907267. doi:10.1002/adma.201907267
Powell, M. M., Rao, G., Britt, R. D., and Rittle, J. (2023). Enzymatic hydroxylation of aliphatic C-H bonds by a Mn/Fe cofactor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 145, 16526–16537. doi:10.1021/jacs.3c03419
Qiao, L., Zhu, G., Jiang, T., Qian, Y., Sun, Q., Zhao, G., et al. (2024). Self-destructive copper carriers induce pyroptosis and cuproptosis for efficient tumor immunotherapy against dormant and recurrent tumors. Adv. Mater 36, e2308241. doi:10.1002/adma.202308241
Reznik, N., Gallo, A. D., Rush, K. W., Javitt, G., Fridmann-Sirkis, Y., Ilani, T., et al. (2022). Intestinal mucin is a chaperone of multivalent copper. Cell 185, 4206–4215.e11. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.09.021
Riley, J. S., and Tait, S. W. (2020). Mitochondrial DNA in inflammation and immunity. EMBO Rep. 21, e49799. doi:10.15252/embr.201949799
Saporito-Magriñá, C., Musacco-Sebio, R., Andrieux, G., Kook, L., Orrego, M., Tuttolomondo, M., et al. (2018). Copper-induced cell death and the protective role of glutathione: the implication of impaired protein folding rather than oxidative stress. Metallomics Integr. biometal Sci. 10, 1743–1754. doi:10.1039/c8mt00182k
Savitsky, K., and Yu, X. (2019). Combined strategies for tumor immunotherapy with nanoparticles. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 21, 1441–1449. doi:10.1007/s12094-019-02081-3
Sawicki, K. T., De Jesus, A., and Ardehali, H. (2023). Iron metabolism in cardiovascular disease: physiology, mechanisms, and therapeutic targets. Circ. Res. 132, 379–396. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.122.321667
Schwarz, M., Meyer, C. E., Loser, A., Lossow, K., Hackler, J., Ott, C., et al. (2023). Excessive copper impairs intrahepatocyte trafficking and secretion of selenoprotein P. Nat. Commun. 14, 3479. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-39245-3
Shen, J., Yu, H., Shu, Y., Ma, M., and Chen, H. (2021). A robust ROS generation strategy for enhanced chemodynamic/photodynamic therapy via H2O2/O2 self-supply and Ca2+ overloading. Adv. Funct. Mater 31. doi:10.1002/adfm.202106106
Simon-Yarza, T., Mielcarek, A., Couvreur, P., and Serre, C. (2018). Nanoparticles of metal-organic frameworks: on the road to in vivo efficacy in biomedicine. Adv. Mater 30, e1707365. doi:10.1002/adma.201707365
Soetaert, F., Korangath, P., Serantes, D., Fiering, S., and Ivkov, R. (2020). Cancer therapy with iron oxide nanoparticles: agents of thermal and immune therapies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 163-164, 65–83. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2020.06.025
Su, X., Liu, B., Wang, W. J., Peng, K., Liang, B. B., Zheng, Y., et al. (2023). Disruption of zinc homeostasis by a novel platinum(IV)-Terthiophene complex for antitumor immunity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 62, e202216917. doi:10.1002/anie.202216917
Sun, J., Lu, F., He, H., Shen, J., Messina, J., Mathew, R., et al. (2014). STIM1-and Orai1-mediated Ca(2+) oscillation orchestrates invadopodium formation and melanoma invasion. J. Cell Biol. 207, 535–548. doi:10.1083/jcb.201407082
Sun, L., Gao, H., Wang, H., Zhou, J., Ji, X., Jiao, Y., et al. (2024). Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks-mediated degradation of mutant p53 proteins and activation of cGAS-STING pathway for enhanced cancer immunotherapy. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 11, e2307278. doi:10.1002/advs.202307278
Sun, X., Zhang, Y., Li, J., Park, K. S., Han, K., Zhou, X., et al. (2021). Amplifying STING activation by cyclic dinucleotide-manganese particles for local and systemic cancer metalloimmunotherapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 1260–1270. doi:10.1038/s41565-021-00962-9
Sun, Z., Wang, Z., Wang, T., Wang, J., Zhang, H., Li, Z., et al. (2022). Biodegradable MnO-based nanoparticles with engineering surface for tumor therapy: simultaneous fenton-like ion delivery and immune activation. ACS Nano 16, 11862–11875. doi:10.1021/acsnano.2c00969
Tomasetti, C., and Vogelstein, B. (2015). Variation in cancer risk among tissues can be explained by the number of stem cell divisions. Science 347, 78–81. doi:10.1126/science.1260825
Tsvetkov, P., Coy, S., Petrova, B., Dreishpoon, M., Verma, A., Abdusamad, M., et al. (2022). Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science 375, 1254–1261. doi:10.1126/science.abf0529
Tsymbal, S., Li, G., Agadzhanian, N., Sun, Y., Zhang, J., Dukhinova, M., et al. (2022). Recent advances in copper-based organic complexes and nanoparticles for tumor theranostics. Molecules 27, 7066. doi:10.3390/molecules27207066
Tu, H. K., Pan, K. F., Zhang, Y., Li, W. Q., Zhang, L., Ma, J. L., et al. (2010). Manganese superoxide dismutase polymorphism and risk of gastric lesions, and its effects on chemoprevention in a Chinese population. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 19, 1089–1097. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-09-1174
Urbano-Gamez, J. D., Guzzi, C., Bernal, M., Solivera, J., Martinez-Zubiaurre, I., Caro, C., et al. (2024). Tumor versus tumor cell targeting in metal-based nanoparticles for cancer theranostics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 5213. doi:10.3390/ijms25105213
Wang, C., Guan, Y., Lv, M., Zhang, R., Guo, Z., Wei, X., et al. (2018). Manganese increases the sensitivity of the cGAS-STING pathway for double-stranded DNA and is required for the host defense against DNA viruses. Immunity 48, 675–687.e7. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2018.03.017
Wang, G., Jiang, Y., Xu, J., Shen, J., Lin, T., Chen, J., et al. (2023a). Unraveling the plasma protein corona by ultrasonic cavitation augments active-transporting of liposome in solid tumor. Adv. Mater 35, e2207271. doi:10.1002/adma.202207271
Wang, J., Qu, C., Shao, X., Song, G., Sun, J., Shi, D., et al. (2023b). Carrier-free nanoprodrug for p53-mutated tumor therapy via concurrent delivery of zinc-manganese dual ions and ROS. Bioact. Mater 20, 404–417. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.06.005
Wang, J., Zhao, H., Xu, Z., and Cheng, X. (2020). Zinc dysregulation in cancers and its potential as a therapeutic target. Cancer Biol. Med. 17, 612–625. doi:10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2020.0106
Wang, L., Ge, K., Duan, J., Du, X., Zhou, G., Ma, L., et al. (2024). A double-gain theranostic nanoplatform based on self-supplying H(2)O(2) nanocomposites for synergistic chemodynamic/gas therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 654, 774–784. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2023.10.092
Wang, W., Yu, S., Huang, S., Deng, R., Ding, Y., Wu, Y., et al. (2019). A complex role for calcium signaling in colorectal cancer development and progression. Mol. Cancer Res. 17, 2145–2153. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-19-0429
Wang, Y., Gong, F., Han, Z., Lei, H., Zhou, Y., Cheng, S., et al. (2023c). Oxygen-deficient molybdenum oxide nanosensitizers for ultrasound-enhanced cancer metalloimmunotherapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 62, e202215467. doi:10.1002/anie.202215467
Wang, Y., Wu, X., Bao, X., and Mou, X. (2023d). Progress in the mechanism of the effect of Fe(3)O(4) nanomaterials on ferroptosis in tumor cells. Molecules 28, 4562. doi:10.3390/molecules28114562
Wu, W., Yu, L., Pu, Y., Yao, H., Chen, Y., and Shi, J. (2020). Copper-enriched prussian blue nanomedicine for in situ disulfiram toxification and photothermal antitumor amplification. Adv. Mater 32, e2000542. doi:10.1002/adma.202000542
Wu, X., Wu, Q., Hou, M., Jiang, Y., Li, M., Jia, G., et al. (2024a). Regenerating chemotherapeutics through copper-based nanomedicine: disrupting protein homeostasis for enhanced tumor therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater 13, e2401954. doi:10.1002/adhm.202401954
Wu, Y., Sun, B., Tang, Y., Shen, A., Lin, Y., Zhao, X., et al. (2024b). Bone targeted nano-drug and nano-delivery. Bone Res. 12, 51. doi:10.1038/s41413-024-00356-2
Xin, Y., Gao, H., Wang, J., Qiang, Y., Imam, M. U., Li, Y., et al. (2017). Manganese transporter Slc39a14 deficiency revealed its key role in maintaining manganese homeostasis in mice. Cell Discov. 3, 17025. doi:10.1038/celldisc.2017.25
Xiong, H., Wang, C., Wang, Z., Lu, H., and Yao, J. (2021). Self-assembled nano-activator constructed ferroptosis-immunotherapy through hijacking endogenous iron to intracellular positive feedback loop. J. Control Release 332, 539–552. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.03.007
Xu, L., Peng, M., Gao, T., Wang, D., Lian, X., Sun, H., et al. (2024). Nanoenabled intracellular metal ion homeostasis regulation for tumor therapy. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 11, e2306203. doi:10.1002/advs.202306203
Xu, L., Tong, G., Song, Q., Zhu, C., Zhang, H., Shi, J., et al. (2018). Enhanced intracellular Ca(2+) nanogenerator for tumor-specific synergistic therapy via disruption of mitochondrial Ca(2+) homeostasis and photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 12, 6806–6818. doi:10.1021/acsnano.8b02034
Xu, W. J., Qian, J. M., Hou, G. H., Wang, T. B., Wang, J. L., Wang, Y. P., et al. (2022a). A hollow amorphous bimetal organic framework for synergistic cuproptosis/ferroptosis/apoptosis anticancer therapy via disrupting intracellular redox homeostasis and copper/iron metabolisms. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 20222205013. doi:10.1002/adfm.202205013
Xu, Y., Liu, S. Y., Zeng, L., Ma, H., Zhang, Y., Yang, H., et al. (2022b). An enzyme-engineered nonporous copper(I) coordination polymer nanoplatform for cuproptosis-based synergistic cancer therapy. Adv. Mater 34, e2204733. doi:10.1002/adma.202204733
Yang, H., Yao, X., Liu, Y., Shen, X., Li, M., and Luo, Z. (2023). Ferroptosis nanomedicine: clinical challenges and opportunities for modulating tumor metabolic and immunological landscape. ACS Nano 17, 15328–15353. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c04632
Yang, Y., Tang, J., Zhang, M., Gu, Z., Song, H., Yang, Y., et al. (2019). Responsively aggregatable sub-6 nm nanochelators induce simultaneous antiangiogenesis and vascular obstruction for enhanced tumor vasculature targeted therapy. Nano Lett. 19, 7750–7759. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b02691
Yao, J., Zhang, A., Qiu, Y., Li, Z., Wu, X., Li, Z., et al. (2023). Navigating zinc-involved nanomedicine in oncotherapy. Nanoscale 15, 4261–4276. doi:10.1039/d2nr06857e
Yao, X., Xie, R., Cao, Y., Tang, J., Men, Y., Peng, H., et al. (2021). Simvastatin induced ferroptosis for triple-negative breast cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnology 19, 311. doi:10.1186/s12951-021-01058-1
Yu, B., Liu, M., Jiang, L., Xu, C., Hu, H., Huang, T., et al. (2024). Aggregation-induced emission photosensitizer-engineered anticancer nanomedicine for synergistic chemo/chemodynamic/photodynamic therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater 13, e2303643. doi:10.1002/adhm.202303643
Yu, H., Zhou, Y., Lind, S. E., and Ding, W. Q. (2009). Clioquinol targets zinc to lysosomes in human cancer cells. Biochem. J. 417, 133–139. doi:10.1042/BJ20081421
Yu, P., Zhang, X., Liu, N., Tang, L., Peng, C., and Chen, X. (2021). Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 6, 128. doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00507-5
Zanganeh, S., Hutter, G., Spitler, R., Lenkov, O., Mahmoudi, M., Shaw, A., et al. (2016). Iron oxide nanoparticles inhibit tumour growth by inducing pro-inflammatory macrophage polarization in tumour tissues. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11, 986–994. doi:10.1038/nnano.2016.168
Zhang, H., Song, F., Dong, C., Yu, L., Chang, C., and Chen, Y. (2021). Co-delivery of nanoparticle and molecular drug by hollow mesoporous organosilica for tumor-activated and photothermal-augmented chemotherapy of breast cancer. J. Nanobiotechnology 19, 290. doi:10.1186/s12951-021-01025-w
Zhang, K., Qi, C., and Cai, K. (2023). Manganese-based tumor immunotherapy. Adv. Mater 35, e2205409. doi:10.1002/adma.202205409
Zhang, L., Zhao, J., Hu, X., Wang, C., Jia, Y., Zhu, C., et al. (2022). A peritumorally injected immunomodulating adjuvant elicits robust and safe metalloimmunotherapy against solid tumors. Adv. Mater 34, e2206915. doi:10.1002/adma.202206915
Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhu, A., Yu, N., Xia, J., and Li, J. (2024). Dual-targeting biomimetic semiconducting polymer nanocomposites for amplified theranostics of bone metastasis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 63, e202310252. doi:10.1002/anie.202310252
Zhang, Z., Liu, X., Feng, B., Liu, N., Wu, Q., Han, Y., et al. (2015). STIM1, a direct target of microRNA-185, promotes tumor metastasis and is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 34, 4808–4820. doi:10.1038/onc.2014.404
Zhao, F., Liang, L., Wang, H., Wang, C., Su, D., Ying, Y., et al. (2023a). H2S-activated ion-interference therapy: a novel tumor targeted therapy based on copper-overload-mediated cuproptosis and pyroptosis. Adv. Funct. Mater 33, 2300941. doi:10.1002/adfm.202300941
Zhao, H., Wang, L., Zeng, K., Li, J., Chen, W., and Liu, Y. N. (2021). Nanomessenger-mediated signaling cascade for antitumor immunotherapy. ACS Nano 15, 13188–13199. doi:10.1021/acsnano.1c02765
Zhao, X., Cheng, H., Wang, Q., Nie, W., Yang, Y., Yang, X., et al. (2023b). Regulating photosensitizer metabolism with DNAzyme-loaded nanoparticles for amplified mitochondria-targeting photodynamic immunotherapy. ACS Nano 17, 13746–13759. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c03308
Zhao, X., Leng, D., Wang, H., Jin, H., Wu, Y., Qin, Z., et al. (2024). An acid-responsive iron-based nanocomposite for OSCC treatment. J. Dent. Res. 103, 612–621. doi:10.1177/00220345241238154
Zheng, P., Ding, B., Jiang, Z., Xu, W., Li, G., Ding, J., et al. (2021). Ultrasound-augmented mitochondrial calcium ion overload by calcium nanomodulator to induce immunogenic cell death. Nano Lett. 21, 2088–2093. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c04778
Zheng, P., Ding, B., Zhu, G., Lin, J., and Li, C. (2023). Usnea acid-incorporated Ca(2+)/Mn(2+) ions reservoirs for elevated ion-interference therapy through synergetic biocatalysis and osmolarity imbalance. Small 19, e2300370. doi:10.1002/smll.202300370
Zhong, X., Dai, X., Wang, Y., Wang, H., Qian, H., and Wang, X. (2022). Copper-based nanomaterials for cancer theranostics. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed Nanobiotechnol 14, e1797. doi:10.1002/wnan.1797
Zhu, L., You, Y., Zhu, M., Song, Y., Zhang, J., Hu, J., et al. (2022). Ferritin-hijacking nanoparticles spatiotemporally directing endogenous ferroptosis for synergistic anticancer therapy. Adv. Mater 34, e2207174. doi:10.1002/adma.202207174
Zhu, Y., Wang, W., Cheng, J., Qu, Y., Dai, Y., Liu, M., et al. (2021). Stimuli-responsive manganese single-atom nanozyme for tumor therapy via integrated cascade reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 60, 9480–9488. doi:10.1002/anie.202017152
Keywords: metal-based nanomaterials, tumor therapy, ferroptosis, calcium overload, cuproptosis, immunotherapy
Citation: Xu Y, Reheman A and Feng W (2025) Recent research progress on metal ions and metal-based nanomaterials in tumor therapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1550089. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1550089
Received: 22 December 2024; Accepted: 20 January 2025;
Published: 07 February 2025.
Edited by:
Liqun Yang, Shengjing Hospital of China Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Dan Li, Jinzhou Medical University, ChinaGuanqing Yang, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), China
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Reheman and Feng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenhua Feng, d2hmZW5nQHN5bWMuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Yongcheng Xu1†
Yongcheng Xu1† Wenhua Feng
Wenhua Feng