
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 26 February 2025
Sec. Biomaterials
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2025.1548675
This article is part of the Research TopicTranslational development of tailored implants based on new processing approaches and surface modifications for tissue regenerationView all 3 articles
Porous titanium implants are becoming an important tool in orthopedic clinical applications. This review provides a comprehensive survey of recent advances in porous titanium implants for orthopedic use. First, the review briefly describes the characteristics of bone and the design requirements of orthopedic implants. Subsequently, the pore size and structural design of porous titanium alloy materials are presented, then we introduce the application of porous titanium alloy implants in orthopedic clinical practice, including spine surgery, joint surgery, and the treatment of bone tumors. Following that, we describe the surface modifications applied to porous titanium implants to obtain better biological functions. Finally, we discuss incorporating environmental responsive mechanisms into porous titanium alloy materials to achieve additional functionalities.
In the 21st century, human beings are entering the aging society at an accelerated pace (Rudnicka et al., 2020), therefore the demand and requirements for biomedical materials based implant devices are increasing. Bone is the main support structure of the human body, but it is also susceptible to injury and disease, such as infection, trauma, and tumors (Wang et al., 2024a). Traditional orthopedic treatments, such as internal fracture fixation, have certain limitations, for instance, traditional steel plates cannot meet the needs of repairing bone defects or promoting bone tissue regeneration (Islam et al., 2025). Autologous bone has long been considered as the best alternative material for tackling bone defects, but factors such as the limited amount of bone available from the autologous body, the new trauma that can be caused by the bone extraction process, and the poor quality of pathologic bone limit the extensive use of autologous bone grafting (Li et al., 2018).
Thus, the need for effective, sustainable and personalized methods of bone tissue repair has driven the development of biomaterials science and technology. To meet the urgent clinical needs, bone tissue engineering has emerged. A variety of bone replacement materials with good mechanical properties and bionic structure have been developed, achieving satisfactory clinical therapeutic outcomes (Mochi et al., 2022). Titanium and its alloys are widely used in clinical trials and research due to their mechanical performance, corrosion resistance and non-magnetic properties (Pobloth et al., 2018). However, the elastic modulus of titanium alloy implants currently used in clinical applications reaches 90–115 GPa, which is much higher than that of human cortical bone and cancellous bone or cartilage (Pan et al., 2021a), the huge gap of elastic modulus causes an imbalance in the distribution of stress between the implant and the surrounding bone tissues, leading to stress shielding, which induces the loosening of the implant with respect to the bone tissues (Raffa et al., 2021).
It has been found that some porous materials have an elastic modulus that matches human bone tissue, which is an effective means to solve the elastic mismatch between implants and human bone (Maksoud et al., 2022), at the same time, the large number of pores that exist within the porous material is more conducive to the growth of tissues such as osteoblasts and blood vessels, which significantly promotes osteogenesis (Bose et al., 2018). Thus, porous materials are regarded as ideal materials for orthopedic implants (Losic, 2021), which have drawn extensive attention from both the academic and industrial field.
In this review, we discuss the development and current status of orthopedic porous titanium alloy implant technology, and focus on the development of porous titanium alloys through additive manufacturing technology, porous structure design, surface modification technology, microenvironment responsive and modulation, and current clinical applications to further address the major difficulties in orthopedic implant design, including stress caused by mismatch of elastic modulus between the implant and human bone tissue shieldingissues, bone regeneration obstacles caused by biologically inert surfaces, and biofilm-related periprosthetic infections. Meanwhile, the future development trend of orthopedic porous titanium implants is also prospected in the end of this review.
The composition of human bone varies with age, anatomical location and nutritional status. In general, bone mineral makes up about 50%–70% weight of adult human bone, organic matrix takes another 20%–40%, leaving about 5%–10% for water, and about 1%–5% for lipids (Gelse et al., 2003). About 90% of the organic matrix of bone consists of type I collagen, a triple helix molecule composed of two identical α-1 chains and a single α-2 chain (Avioli, 1991). Bone minerals make up about 75% of bone tissue and most of the bone minerals are in the form of hydroxyapatite, which consists of microcrystals with other components including carbonates and magnesium, providing the rigidity and strength for the bones to bear weight (Zhang et al., 2017a).
Bone can be divided into two categories based on structure and density: trabecular bone (cancellous bone) and cortical bone (dense bone). Cancellous bone is located in the interior of the bone and is spongy, consisting of interwoven trabeculae arranged in a 50%–90% porosity, which grow in the direction of extended stress to bear greater weight (Rho et al., 1993), while cortical bone is dense and distributed on the peripheral surface of the bone and consists of tightly arranged bone plates with a porosity of 3%–5% (Kenny and Raisz, 2002).
Bone is a metabolically active organ that undergoes constant remodeling throughout its life, and the remodeling cycle involves interactions between osteoblast and osteoclast and is regulated by human hormone levels and local factors (Hadjidakis and Androulakis, 2006). Bone remodeling consists of three successive phases: resorption, reversal and formation, where osteoclasts remove mineralized bone, followed by osteoblasts forming the bone matrix. Bone remodeling helps to adjust the bone structure to meet changing mechanical demands and responsible for repairing defects and preventing the accumulation of old bone (He and Li, 2018).
Ideal orthopedic implants should be similar to natural bone in the aspect of structure and performance, providing both physical function and bioactivity that promotes the regeneration of bone tissue under injury. Ideal orthopedic implants should have several properties: (i) biocompatibility; (ii) biodegradability; (iii) osteoconductivity and osteoinduction; (iv) plasticity and strength; (v) microenvironment on the surface of the material (Niinomi, 2003). Titanium and its alloys meet the key criteria required for the design of orthopedic implants and have become the most widely used metallic materials in the manufacture of existing implants. However, titanium is biologically inert and requires geometry optimization and surface modification to achieve desired clinical performance (Liang et al., 2019). In addition, since bone has microstructures that exhibit spatial anisotropy, ideal implants should have similar hierarchical structures in multiple dimensions to fulfill the mechanisms required for bone growth and to facilitate osseointegration induction (Velásquez-García and Kornbluth, 2021).
With advances in medical technology, patients are no longer satisfied with implants merely for pain relief and restoration of basic motion, but also for long-lasting and maximum restoration of their original function. This requires a new generation of implants with a better anatomical and kinematic match to individuals. Clinical existing limb fixation plates, artificial joints, spinal titanium cages and fusion devices, etc., are all of uniform design, assembly-line production, whose design and manufacturing mode is conducive to the formation of standardized treatment plans, which adapted to the majority of patients, but there are still a lot of patients encountered with mismatch of implant size or geometric configuration (Perera et al., 2021), which increases the risk of surgery and affects the surgical results.
Personalized medicine is promising and received much attention in the 21st century (Potyondy et al., 2021). Additive Manufacturing is an important branch of Rapid Prototyping Technology, which integrates Computer-Aided Design, Computer Numerical Control laser-assisted modeling technology and material technology (Van Bael et al., 2012), and is able to accurately design the physical parameters such as pore size, porosity, pore shape and surface morphology of the implant material, which pocessesbetter characters than traditional orthopaedic implants, can not only produce personalized implants that are more desirable in terms of biocompatibility and mechanical properties, but also make it possible for personalized and customizable implants.
Traditional implants are usually manufactured through molds or material reduction processes, and the production cost of single pieces or small quantities of complex products is often expansible. Meanwhile, traditional manufacturing methods can only mimic the biological appearance and process a fully dense or fully porous structure.
In contemporary manufacturing, a diverse array of techniques are employed to fabricate materials with specific pore structures. For instance, fibre or mesh sintering can produce materials with high porosity and large specific surface areas, which are widely utilized in filtration and burner energy applications (Li and Zhou, 2022). Space Holder Sintering is capable of manufacturing porous materials with intricate pore distributions (Adamek et al., 2022), while dynamic freeze casting enables the production of materials with directional pore structures (Christiansen et al., 2020). In contrast, additive manufacturing technology stands out as it can create highly complex and customized structures, particularly geometries that are challenging to achieve using conventional methods. This versatility extends to a broader range of materials and application scenarios.
Metal additive manufacturing technology has been developed for more than 20 years (Cai, 2015), benefiting from the development of 3D printing technologies and equipment such as electron beam melting and selective laser melting, according to the mechanical, chemical, and biological properties, with high precision and efficiency. It is possible to complete the manufacturing of small parts according to the mechanical, chemical and biological properties, what is more, the microporous structure can be controlled to realize the perfect reproduction of the real bone tissue (Papaefstathiou et al., 2022).
The process of additive manufacturing of porous titanium implants can be divided into four steps: (i) acquiring patient imaging data such as CT and MRI, (ii) creating a digital model of the implant based on the patient’s condition through CAD software, converting it into a series of 2D layer slices and saving it as STL data, (iii) computer-controlled, layer-by-layer melting of the metal material to print and shape it, (iv) further imparting biological functions through grinding, coating and surface modification techniques to further critical biological functions (Zhen et al., 2019) Figures 1, 2.
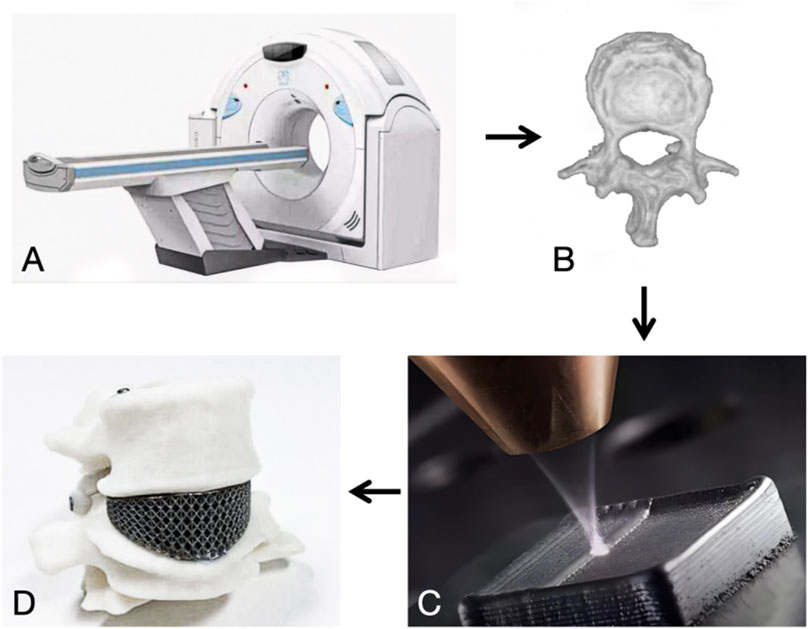
Figure 2. (A) CT scan. (B) Three-dimensional reconstruction. (C) Additive manufacturing. (D) 3D objects.
Traditional machining processes such as casting or subtractive manufacturing require customized molds or cutting of raw materials, and the production cost is usually high for single or small quantities. In contrast, additive manufacturing technology can be completed from design to manufacturing a product within 24 h, which greatly shortens the delivery time (Li et al., 2021a). At the same time, additive manufacturing technology can be personalized according to the morphological characteristics of the patient’s native bone, without being restricted by the differences in the patient’s anatomical structure, to create an implant that perfectly matches the patient, thus reducing the damages and improve the prognosis (Thomsen et al., 2005).
The layer of titanium powder melted by 3D technology is about 150 μm of thickness, which is close to the size of bone trabeculae of 100–140 μm (Kou and Tan, 2010). The bone trabeculae grow in the direction of delayed stress, which is not a homogeneous pore structure, so the non-uniform void structure can better mimic the biological structure of bone, and historically, the majority of non-uniform pore structures came from the method of reverse engineering the patient’s CT after three-dimensional reconstruction (Zhang et al., 2017b). With the proposal of VoronoiTessellation mathematical modeling method in recent years, it is able to construct an approximate model of biomimetic heterogeneous porous materials (MacBarb et al., 2017), and the controllable pore and surface morphology design is more conducive to the adhesion and proliferation of osteoclasts to achieve a strong biofixation between the implant and the bone tissues and to promote bone healing (El-Hajje et al., 2014). At the same time, by mimicking the natural structure of cancellous and cortical bone, the pore size and porosity of the material can be adjusted to obtain the appropriate modulus of elasticity and strength, so that the shape and mechanical properties of the implant can achieve a dual fit with the natural bone (Weber, 2019).
The selection of materials for additively manufactured orthopaedic implants is crucial, as they must possess good biocompatibility, mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
Stainless steel was one of the earliest metal materials used in orthopaedic implants, known for its corrosion resistance and strength (Marcomini et al., 2014). It is cost-effective to produce and can be shaped into various forms, with high strength and toughness, making it suitable for fracture fixation devices and artificial joints (Uhthoff et al., 2006). However, stainless steel corrodes in physiological environments, releasing metal ions that may be toxic to the human body, particularly nickel ions. The release of nickel ions can cause allergic reactions, tissue inflammation and osteolysis. Moreover, corrosion diminishes the mechanical properties of implants, increasing the risk of fracture (Agarwal et al., 2025). Cobalt alloys are primarily used in arthroplasty devices, exhibiting high mechanical strength, good wear resistance and corrosion resistance in body fluid environments (Sun et al., 2024). Although cobalt alloys are biocompatible, they are less biologically active. Their surface is typically biologically inert, resulting in weak bonding with bone tissue and potential implant loosening and failure. Additionally, the surface properties of cobalt alloys may impair cell adhesion and growth, thereby hindering the bone healing process (Safari-Gezaz et al., 2025). Titanium alloys are now of great interest due to their excellent biocompatibility and mechanical properties. The new β-type titanium alloys, enriched with elements such as Nb, Zr and Mo, have a significantly reduced modulus of elasticity, closely resembling human bone tissue while maintaining high strength and biocompatibility, thus being widely used in orthopaedic implants. The surface of titanium alloys usually forms a stable and firmly bonded oxide film, which is the primary reason for their corrosion resistance (Feng et al., 2024). Furthermore, surface modification enhances the corrosion resistance of titanium alloys by preventing chloride ions and proteins in body fluids from corroding the oxide film, which could otherwise lead to dissolution and stripping.
Polymer materials are also extensively used in orthopaedic implants, particularly polyether ether ketone (PEEK) and polylactic acid (PLA). PEEK overcomes the drawbacks of metallic materials, such as stress masking and radiation artefacts, and enables the rapid manufacturing of customised PEEK bone implants via additive manufacturing techniques (Li et al., 2015). PLA, a biodegradable polymer widely used in bone tissue engineering, can gradually degrade in vivo to promote natural bone tissue regeneration (Tajbakhsh and Hajiali, 2017). However, its relatively weak mechanical properties limit its use in load-bearing sites.
Composites integrate the advantages of metals and polymers to achieve better biocompatibility and mechanical properties. Metal-polymer composites enhance these properties by combining metal particles or fibres with a polymer matrix. For instance, titanium-PEEK composites have demonstrated excellent performance in orthopaedic implants for complex clinical needs (Tsai et al., 2021). Ceramic-polymer composites combine the high hardness of ceramics with the flexibility of polymers to provide good biocompatibility and mechanical properties. Hydroxyapatite-PLA composites, for example, have shown excellent osteoinductive ability and biocompatibility in bone tissue engineering (Fan et al., 2022a).
The structural features of additively manufactured porous titanium alloy materials include pore size and void ratio, pore shape and surface morphology (Van Bael et al., 2012), in addition to the direct impact on mechanical properties, the porous structure provides important biological properties of the implant. A suitable pore structure facilitates osteoblast growth and migration and proliferation of osteogenic sites, allows nutrient and oxygen transfer through the structure, and supports vascular infiltration and growth into the structure, all of which can promote bone growth within the implant (Hollister, 2005).
Gradient pore size materials are a class of porous materials with gradual changes in pore size, porosity and solid composition phase. Bone trabeculae grow in the direction of extended stress and are not homogeneous pore structures, so non-uniform pore structures can better mimic the biological structure of bone and improve biocompatibility. By adjusting the size and relative density of pores, it not only endows open-pore structure high strength while possessing high porosity, but also optimizes the growth of bone tissue and adapt to changing stresses in specific regions (Faverani et al., 2014).
Most of the existing implants in orthopedic clinics are ordinary titanium alloy products, and the modulus of elasticity of solid titanium alloy implants is much higher than that of human cortical bone, cancellous bone or cartilage (Niinomi and Nakai, 2011). Since the modulus of elasticity of titanium alloy is far beyond that of the surrounding bone tissue, the force received cannot be normally transmitted to the surrounding, resulting in stress shielding phenomenon (Wang et al., 2023a), which causes atrophy or even necrosis of the bone tissue nearby, resulting in loosening or dislodging of the implant, and ultimately leading to shortening of implant life. Porous design can effectively reduce its elastic modulus and better match the surrounding bone tissue. The gradient pore size design can further optimize the stress distribution in a uniform way.
Over small of the pore size in implant materials will hinder bone tissue growth in, which should be adjusted into around 600 μm has a good ability to induce new bone formation, while with the increase of pore size, when the pore size reaches 600 μm, the mechanical properties of the material, including the compressive strength, will be significantly reduced (Liu et al., 2017). Therefore, not only the elastic modulus is reduced by porous material to reduce the stress shielding phenomenon, but also to make the stress distribution more uniform, the porous implant is designed through a gradient to transmit a greater force by a structure with a small pore size and high stiffness to match the cortical bone, and a structure with a large pore size and low stiffness to match the cancellous bone, respectively, to induce the bone tissues to grow in to promote the osseointegration Figure 3.
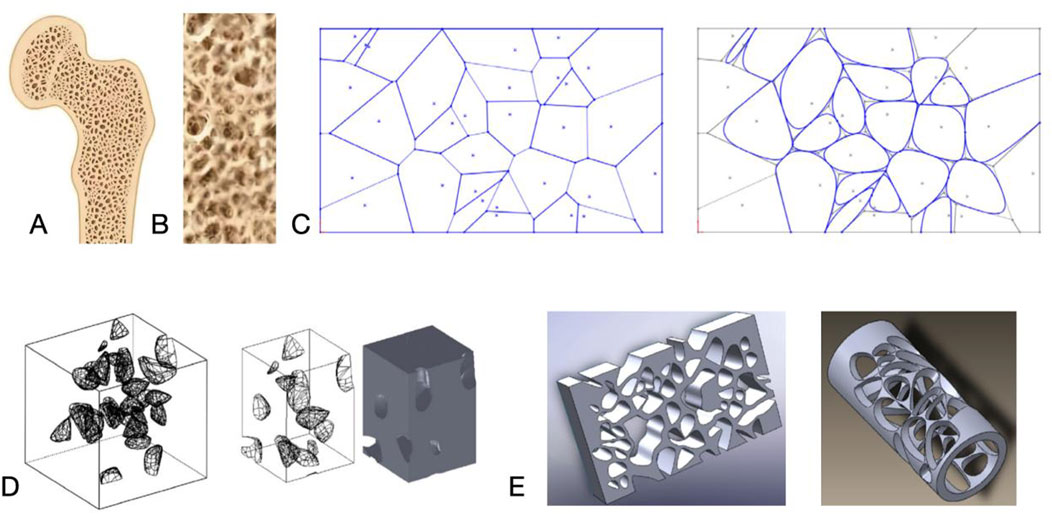
Figure 3. (A) Cross-section of bone. (B) Trabecular bone morphology. (C) Nature inspired geometric representation for irregular porous structure modeling. (D, E) 3D porous structures. Reproduced with permission (Kou and Tan, 2010).
Orthopedic implants have high requirements for fatigue resistance to ensure the safety, stability, and long-term performance of the implants. Studies have shown that fatigue strength is highly correlated with porosity, and the fatigue strength decreases with the increase of porosity Zhao et al. (2018). Itälä et al. (2001) found that, under equal strain conditions, mechanical properties of materials depend on their structure and gradient, and fatigue cracks in the cyclic deformation process of the components in the sequential sprouting, resulting in the continuous redistribution of the stress in its various layers, which significantly inhibits fatigue cracks in the porous material expansion, and effectively improves the fatigue resistance of the implant.
Pore design has a significant impact on the biomechanical properties of plant entry as well as the osteointegration capacity. Existing studies have shown that porous materials with pore sizes less than 50 μm limit osteoblast growth (Yue et al., 2014), and various pore shapes (e.g., cuboidal or rhombic) were successful in inducing inward growth of bone tissues in the range of 100–600 μm Taniguchi et al. (2016). Ran et al. (2018) found that a pore size of 632 μm had stronger osseointegration fixation than a pore size of 309 vs. 956 μm in a study that observed the implantation of a titanium plate in the tibia of rabbits, while a pore size of 632 μm had the strongest bone growth at weeks 2 and 4, respectively. The results of in vitro and in vivo evaluations of different pore sizes and fabrication methods confirmed that smaller pore sizes (<100 μm) impeded the entry of cells, nutrients, and transport of oxygen inward, leading to poor vascularization and bone regeneration (Biemond et al., 2011). Larger pores (>900 μm) decrease the inward bone growth ratio, which may be associated with a reduction in the rate of local bone regeneration and effective contact between bone tissue and the implant (Biemond et al., 2013).
In addition to the pore size and porosity of the material, the pore geometry and surface morphology are also important for osteoinduction. Van Bael et al. (2012) concluded from in vitro cellular experiments that right-angle pore shapes are more favorable for cell growth, and that obtuse angles are more likely to result in cellular buildup and clogging than acute angles.
Meanwhile, pore size and porosity directly affect the mechanical properties of implants. With the increase of pore size and porosity, the elastic modulus and yield strength of porous titanium alloy materials gradually decrease (Fujii et al., 2022). Li et al. (2023a) prepared a serial of porous titanium alloys with different pore sizes and porosities, and analyzed the effect of the porosity on the compression properties through tests and simulations. Liu et al. (2022a) designed a multistage gradient porous titanium implant, and the structural performance of which was found to be the best through finite-element simulation analysis, it was found that the implant with a porosity of 59.86% had the best structural performance.
Yang et al. (2017) performed finite element analysis on three types of structures: square holes, circular holes, and honeycomb holes. They found that, with the same pore diameter, the elastic modulus of honeycomb holes was the highest, followed by circular holes, and square holes had the lowest modulus. When porosity ranged from 78.4% to 89.6%, the modulus of elasticity was 21.25–13.04 GPa, which is comparable to the mechanical properties of the human femur. Molinari et al. (2018) investigated different types of porous titanium alloys produced by selective laser melting (SLM) with different geometries and porosities ranging from 47.8% to 82.6%. The results indicated that the porous structure’s strength was typically low when no struts were aligned with the load direction. The compressive strength of all specimens ranged from 10 to 250 MPa, and the modulus of elasticity ranged from 1 to 20 GPa, closely resembling the elasticity model of human cortical bone (Figure 4).
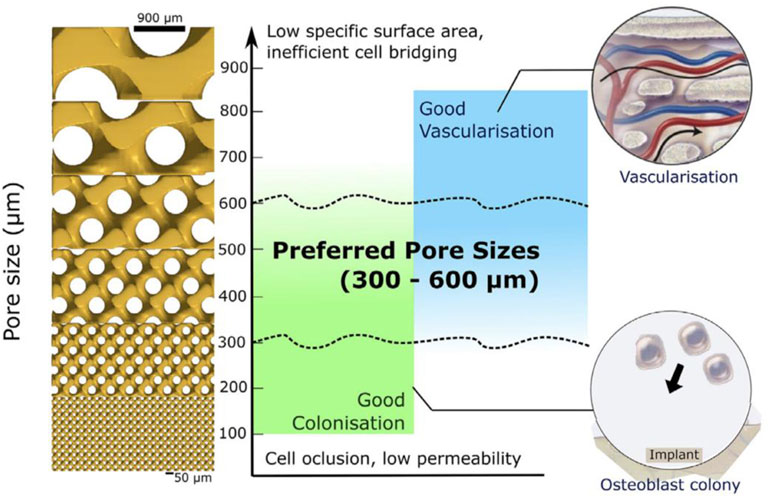
Figure 4. Approximate preferred regions for bone colonization and bone vascularization. Reproduced with permission (Barba et al., 2019).
Porous titanium alloy material, with its good biocompatibility, promotes the adhesion, proliferation and differentiation of bone cells (Figure 5). Its three-dimensional connected pore structure provides favourable conditions for cell growth and nutrient transport (Nune et al., 2015). By modulating the pore parameters, the modulus of elasticity of porous titanium can be adjusted to be close to that of human bone, thereby reducing the stress shielding effect (Liu et al., 2018). The porous structure facilitates inward bone tissue growth and stable bone bonding. Surface modification techniques, such as micro-arc oxidation, further enhance the osteoinductivity of porous titanium (Nune et al., 2018). Meanwhile, additive manufacturing technology allows porous titanium implants to be personalised according to the patient’s anatomical morphology, improving the match between the implant and the defect area (Kumar et al., 2021).
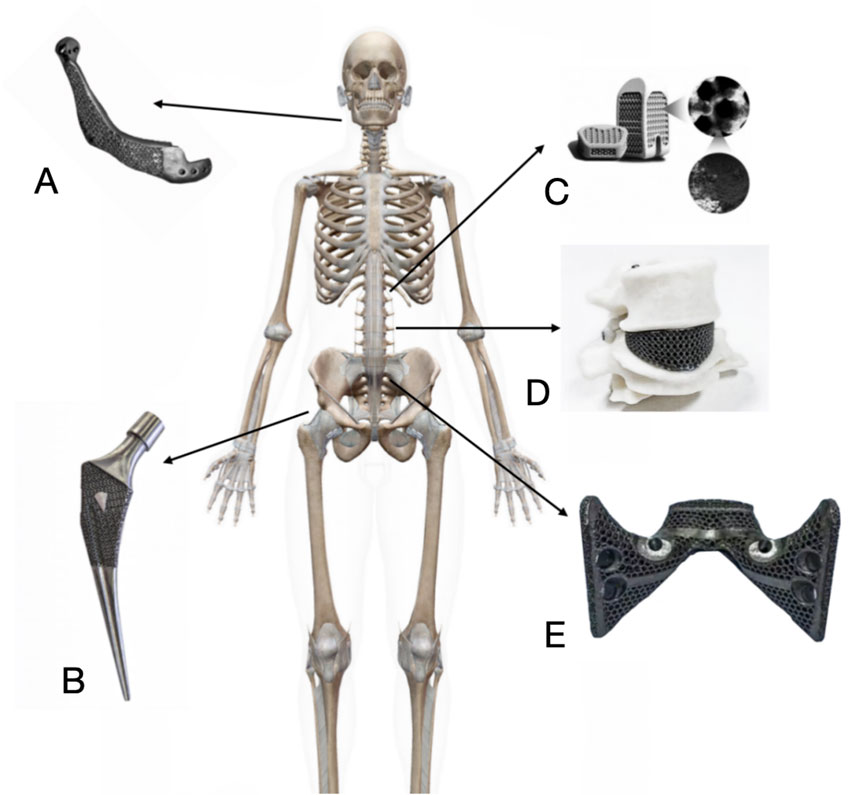
Figure 5. Clinical application of porous titanium alloy implants in orthopedics. (A) 3D print porous titanium alloy artificial mandible for mandible reconstruction after tumor resection. (B) Additively manufactured porous titanium alloy artificial femoral stem for hip arthroplasty. (C) Additively manufactured porous titanium alloy interbody fusion cage for spinal fusion surgery. (D) Additively manufactured porous titanium alloy artificial vertebral body for spinal reconstruction after Total En Bloc Spondylectomy or subtotal vertebrectomy. (E) Additively manufactured porous titanium alloy artificial sacrum for pelvic reconstruction after pelvic tumor surgery.
However, additively manufactured porous titanium orthopaedic implants also have drawbacks. Their mechanical strength is limited, with higher porosity resulting in lower compressive strength, which may not meet the demands of highly loaded sites (Chen et al., 2017). The porous structure increases the implant’s contact area with body fluids, potentially leading to localised corrosion. Corrosion products may trigger inflammatory reactions and affect the implant’s long-term stability (Liu et al., 2012). Moreover, to improve biocompatibility and osseointegration, porous titanium implants require complex surface treatments. These processes increase manufacturing costs and time, resulting in high costs and limiting their widespread application (Wu and Guo, 2020) (Table 1).
The spine, as the central axis skeleton of the human body, plays a key role in supporting body-weight and organs, protecting the spinal cord and nerves, and maintaining normal body movement. With the accelerated aging of the global population (Partridge et al., 2018) and the rapid development of transportation and manufacturing industries, spinal degeneration and trauma have become common clinical issues in spinal surgery (Otani et al., 2013). For those with cervical and lumbar spine disorders who have undergone standardized conservative treatment for 3 months or longer with unsatisfactory results, or those with obvious symptoms of limb pain who require immediate symptom relief, decompressive spinal surgery should be performed (Inose et al., 2021; Shen et al., 2018).
The interbody fusion devices used in spinal decompression have gone through several developmental milestones: autologous bone graft, where the amount of autologous bone extraction is limited while the patient needs to undergo additional iliac bone extraction surgery, which increases the surgical trauma and relevant risk (Schaaf et al., 2010); allogeneic bone graft, where the implanted allogeneic bone may trigger immune response in the patient, and there is a risk of immune rejection (Shi et al., 2014); and metal interbody fusion devices, which can provide immediate stability (Kandziora et al., 2002), but the large difference in the modulus of elasticity between metallic materials and bone leads to poor matching, insufficient strength of the bonding interface, susceptibility to complications such as stress masking, implant displacement, and vertebral body collapse (Kettler et al., 2001); non-metallic fusion devices, with the emergence of synthetic materials such as Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK), and carbon fibers, non-metallic fusion devices have been introduced to address the drawbacks of metallic fusion devices, but the excessive dispersion of stress and high demands on the nearby vertebral endplates handling can affect the non-metallic fusion devices. However, excessive stress dispersion and high demands on the handling of the contacting vertebral endplates can affect the efficacy of nonmetallic fusion devices for spinal fusion (Kim et al., 2015).
Precision and invasiveness medicine is the emerging trends in spine surgery. In this regard, ideal surgical fusion should be achieved by placing the fusion device through a small-sized bony structure gap, with the fusion device placed in place in close contact with the vertebral bone to minimize the surgical window, reduce surgical difficulty, and improve surgical efficiency and fusion rate. Today, additively manufactured porous materials make personalized and customized interbody fusion devices possible.
The elastic modulus of traditional fusion material is higher than that of vertebral bone, and the contact between the fusion and the vertebral body will form a stress mask, and the vertebral plates nearby will undergo osteoporosis due to the lack of sufficient mechanical stimulation, which in turn will cause fusion settlement (Pan et al., 2021b). Zhang et al. (2018) compared the traditional solid metal, PEEK, and additively fabricated porous titanium based on the finite element model of lumbar interbody fusion, under different biomechanical properties under different motion modes and found that the additively manufactured porous titanium fusion significantly reduced the contact interface stresses compared to traditional solid metal or PEEK. The height of the fusion device in fusion surgery is critical to the procedure, which cannot effectively restore the intervertebral space height and Cobb angle when the height is insufficient, leading to displacement and fusion failure at the same time (Landham et al., 2017). Otherwise, it will lead to excessive intervertebral pressure between the upper and lower vertebral bodies when over-heightened, which will accelerate the fusion device sinking. Additive manufacturing allows customizing the fusion device to perfectly match the anatomical height of the intervertebral space by modeling the patient’s vertebral body with CT and MRI (Qi, 2022), while increasing the contact area and further reducing the compression by fitting the curvature and slope of the vertebral plates nearby through the fusion device’s 3D design (Adl Amini et al., 2022).
Traditional fusion devices have smooth surfaces, few hydrophilic groups, high biological inertness, and cannot provide an environment for osteoblast adhesion, resulting in low fusion efficacy (Mao et al., 2021), and clinical practice often promotes intervertebral fusion by backfilling with autogenous bone in the fusion device, while most of the bone tissues obtained intraoperatively come from the articular eminence and the vertebral plate, and the cortical bone has poor osteoblast performance and is not easy to be completely cleaned up, which may hinder affects the osteogenesis. The oxidized layer on the surface of titanium alloy can promote the binding of extracellular matrix proteins such as fibronectin and human osteosialoglycoprotein (Rapuano et al., 2012). Meanwhile, the inter-connected pore structure of porous structure, reasonably designed porosity, and rough surface can provide spatial conditions for bone tissue adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation, which is more conducive to rapid intervertebral fusion (Fogel et al., 2022) (Table 2).
Table 2. Research on the application of additive manufacturing porous titanium alloy technology in spinal surgery.
Artificial hip replacement surgery is widely employed for a wide range of severe hip diseases and is considered to be one of the most successful surgical techniques in clinical application (Gwam et al., 2017). Nevertheless, modern artificial hip replacements still face many problems including infection, wear and tear, and loosening, among which, aseptic loosening of the postoperative prosthesis is particularly prominent. Aseptic loosening is a complex process, and wear of the prosthetic material and failure of bone growth into the prosthesis are considered to be the main causes of aseptic loosening (Howard et al., 2011). Wear particles from friction of joint prostheses during use, especially ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene particles, can cause severe biological reactions, leading to periprosthetic osteolysis such as Osteoclasts abnormally activated, etc (Zaveri et al., 2017). In addition, the smooth surface of the prosthesis is not conducive to bone growth, while the difference in the modulus of elasticity between the prosthesis and the bone causes stress masking, making it difficult for remodulation of bone tissue. The prosthesis gradually develops micromotion during the process of use, which in turn triggers osteolysis and eventually leads to loosening of the prosthesis (Kröger et al., 1998).
Friction in the artificial hip joint comes mainly from the femoral head and the acetabular liner. The artificial femoral heads widely used in clinical practice are usually made of ceramic and cobalt-chromium metal alloys. Ceramic have good biocompatibility due to their material inertness, but fracture and rattling of ceramic prostheses are not uncommon (Owen et al., 2014). Cobalt-chromium alloys have excellent mechanical properties such as high strength, hardness, and elasticity, but the frictional corrosion process increases the level of metal ions in locally and systemically, sometimes leading to significant necrotic and inflammatory changes in the surrounded tissues, which in turn increases the rate of bone resorption around the prosthesis (Lohmann et al., 2013).
Titanium and its alloys are by far one of the most widely used metals within the field of medical implants. Levine (2008) have shown that porous titanium alloys are relatively close to the microstructure and properties of cancellous bone trabeculae, exhibiting good biocompatibility and mechanical properties. The long-term stability of acetabular prosthesis depends on good prosthesis-osteointegration, which determines the effectiveness of bone healing and is the key to obtaining long term stable fixation of the prosthesis, and the capacity of the prosthesis surface for bone growth and osteoinductivity is an important factor in the prevention of complications. Additively fabricated porous titanium acetabular cups allow computer design of trabecular-like structures with ideal porosity and pore size, while drugs promoting bone regeneration, such as simvastatin as a blood ester modifier (Tan et al., 2015), can be encapsulated in the porous scaffolds, further improving the osseointegration effect at the bone-prosthesis interface and enhancing the long-term stability of the hip prosthesis.
The application of additively manufactured porous titanium alloy material in hip arthroplasty is not limited to the above, however, statistics showed that there are about 35,000 patients who need to perform hip revision in the United States each year (Kurtz et al., 2007), about half of whom are accompanied by varying degrees of loss of bone mass on the acetabular side (Ulrich et al., 2008), which leads to irregular acetabular morphology and inter-individual variations. In hip revision surgery there are often large acetabular defects, and conventional metal implants and reinforcements with a single morphology are often not good enough to increase the stability of the prosthesis and affect the results of revision (Hu et al., 2013). The main principles of acetabular bone defect reconstruction are to restore the normal center of rotation of the hip joint, to preserve the original bone volume, and to obtain better initial and long-term prosthesis stability (Gao et al., 2019), and additive manufacturing can create prostheses of arbitrary shapes to accurately match with the osteotomy surfaces, and pre-position the nail channel in either direction on the prosthesis to facilitate the fixation, to restore the mechanical conduction, and to enhance the strength and stability of the bonding (Ji et al., 2013), at the same time, greatly reduce the difficulty of the surgery (Table 3).
Table 3. Research on the application of additive manufacturing porous titanium alloy technology in hip surgery.
The knee joint is a vital weight-bearing joint in the human body, and its integrity is essential for the daily activities and overall quality of life of individuals. In the management of bone tumors, the reconstruction of the knee joint has long been a significant clinical challenge (Fuchs et al., 2008). Traditional therapeutic approaches, such as amputation or arthrodesis, may achieve a degree of tumor control but often result in the loss of knee joint function (Pala et al., 2015). In recent years, with the advancement of material science and manufacturing technology, the application of knee joint implants in the treatment of bone tumors has made substantial progress. The development of computer-assisted technology has led to the emergence of additively manufactured titanium porous scaffolds as a novel structural option for orthopedic implants. Additive manufacturing technology offers controllable and precise fabrication processes, enabling the production of individualized implants tailored to the specific needs of patients. These porous implants can be designed to match the structure of human bones by adjusting porosity, thereby mitigating the stress shielding effect often associated with implants. Moreover, the porous surface of the implants provides ample space to promote bone tissue growth and enhance the stability of the bone-prosthesis interface.
Liu et al. (2020) conducted a follow-up study on 12 patients with malignant bone tumors in the metaphyseal region around the knee joint from September 2016 to October 2018. These patients underwent joint-sparing mesenchymal tissue resection surgery. Utilizing preoperative CT and MRI data, computer-assisted design technology was employed to create three-dimensional models and design individualized osteotomy guides and prostheses. Accurate osteotomy was performed using 3D-printed osteotomy guides, followed by the implantation of 3D-printed prostheses that were precisely matched to the residual bone. The fixation methods for the prostheses were selected based on the patients’ age and bone maturity. The average follow-up duration postoperatively was 22.5 months. Tumor tissues were accurately resected in all patients, with a good match between the residual bone and the prosthesis, with discrepancies within 2 mm. The average postoperative Musculoskeletal Tumor Society (MSTS) score was 28 (range 26–30), and 10 patients achieved satisfactory knee joint range of motion (average flexion 108°, range 90°–125°). All patients were able to ambulate without assistance. Two patients experienced superficial infections; however, there were no deep infections or prosthesis-related complications. One patient had local soft tissue recurrence, but the recurrent tumor was distant from the metaphyseal resection plane; another patient developed lung metastasis 15 months after surgery. The use of individualized osteotomy guides and prostheses effectively facilitated accurate tumor resection and functional reconstruction while preserving the joint. The surgical outcomes were favorable, with satisfactory postoperative functional recovery and a low complication rate.
Shoulder arthroplasty is primarily employed to address severe shoulder pathologies, including complex proximal humerus fractures, severe osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and shoulder joint bone tumours in elderly patients (Reuther et al., 2010). Common postoperative complications encompass joint instability, infections, prosthesis loosening, periprosthetic fractures, and sports injuries, which are frequently implicated as a cause of shoulder arthroplasty failure (Fialka et al., 2008). The intricate anatomical structure of the shoulder joint presents challenges in matching bone defects during shoulder arthroplasty or humeral tumour resection with conventional shoulder prostheses (Weng et al., 2016). Moreover, the absence of tendon stops and soft tissue laxity in the rotator cuff can lead to postoperative shoulder instability or even dislocation. However, the advent of additive manufacturing technology has provided novel opportunities to address these challenges.
Zou et al. (2018) reported a case of shoulder arthroplasty revision utilizing a custom 3D-printed porous titanium shoulder implant. The patient had undergone proximal humeral resection and shoulder arthroplasty for chondrosarcoma of the shoulder. However, due to severe bone defects resulting from implant loosening, conventional implants were deemed inadequate for revision surgery. By leveraging additive manufacturing technology and computer-aided design, a customised porous titanium implant was successfully fabricated. This implant effectively reconstructed the anatomical structures and demonstrated satisfactory functional recovery and bone healing during postoperative follow-up. The study highlighted that customised porous titanium implants offer significant advantages in managing complex bone defects, providing superior anatomical fit and functional outcomes.
The ankle joint, characterized by its complex structure and significant load-bearing capacity, plays a crucial role in human locomotion. The primary therapeutic objective for treating ankle joint diseases and injuries is to restore the joint’s anatomical integrity and functionality while minimizing complications. Reconstruction following complex skeletal defects and resection of malignant tumors in the ankle remains a formidable challenge in the field of orthopedics (Nauth et al., 2018). Traditional treatment modalities, such as autologous and allogeneic bone grafting, are often associated with drawbacks, including donor site morbidity, infection risk, and the potential for non-union (Blair et al., 2015).
Abar et al. (2022) conducted a retrospective study on patients who received custom additive-manufactured titanium ankle implants between 1 June 2014, and 30 September 2019. The study revealed that 74% of patients did not require subsequent surgical intervention following the implantation of custom 3D-printed titanium implants. Moreover, the need for secondary surgery was significantly correlated with the presence of neuropathy. This investigation represents the most extensive study to date validating the efficacy of custom titanium ankle implants. Wang et al. (2025) reported a case in which additive manufacturing technology was utilized to fabricate an ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene-porous titanium calcaneal prosthesis for the treatment of ankle Ewing’s sarcoma. At the 12-month follow-up, the patient exhibited satisfactory wound healing and substantial pain relief. The range of motion of the ankle joint was measured at 10° for dorsiflexion, 35° for plantarflexion, 15° for inversion, and 10° for eversion. Radiographic evaluation demonstrated optimal prosthesis positioning, and T-SMART technology confirmed robust bone-prosthesis integration. Notably, no implant-related complications were observed within the 12-month postoperative period. Collectively, these findings underscore the promising outcomes of additive manufacturing porous titanium ankle implants in terms of postoperative functional recovery and bone integration.
Since the development of additively manufactured porous titanium alloys, a number of personalized implants and related anatomical models have been designed and fabricated for prosthetic reconstruction after resection of bone tumors. The principle of tumor treatment is complete and extensive resection, and bone tumors are highly challenging due to their complex anatomy and lack of reconstructive scaffolds. When faced with extensive and irregular bone defects after tumor resection, autologous bone grafts or allografts often fail to meet the clinical needs, and additively fabricated porous titanium scaffolds can be a good solution to this problem.
It has been reported that additively fabricated porous titanium alloy materials have shown promising efficacy in the surgical treatment of multiple sites and types of tumor invasion. Specifically, the material has been successfully applied in surgery for different types of tumors and invasion sites, such as atlantoaxial vertebrae infiltrated by Ewing’s sarcoma (Xu N. et al., 2016), vertebrae infiltrated by chordoma (Yang, 2016), iliac bone infiltrated by chondrosarcoma (Ye et al., 2015), and heel bone infiltrated by mesenchymal fibroma (Park et al., 2018). These studies have demonstrated that porous titanium alloy materials not only provide the necessary structural support, but also promote osseointegration and functional recovery, improving patients’ postoperative quality of life.
Patients with bone related tumors (sarcoma or bone metastasis) often need to receive systemic chemotherapy after the completion of bone defect repair and reconstruction in order to avoid tumor residue and recurrence as much as possible. The systemic use of chemotherapeutic drugs not only produces huge toxic side effects, but also the concentration of anti-tumor drugs at the site of tumorigenesis often fails to reach the standard due to the impaired blood supply. Porous titanium alloy implant has a unique porous structure. By modifying the surface of the implant or loading its internal space with anti-tumor drugs for controlled release, it can sustainably inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells and induce apoptosis of tumor cells to achieve the effect of local chemotherapy.
Studies have shown that hyaluronic acid-based nanoparticles can be used for the reversal of immune suppression and immunochemotherapy in osteosarcoma treatment. These nanoparticles can target the delivery of doxorubicin, cisplatin, and resiquimod, and release the drugs in the acidic tumor microenvironment, inducing tumor cell apoptosis, and triggering immunogenic cell death. They could also promote the presentation of tumor-associated antigens and the induction of anti-tumor immunity, which would significantly inhibiting tumor growth and lung metastasis (Zhang et al., 2021b), and the inhibitory effect on the proliferation of cancer cells is much greater than that to normal cells (Han et al., 2014). Zhang et al. (2019) prepared porous titanium alloy scaffolds by laser sintering, and then prepared n-HA coating on the surface of the porous titanium alloy scaffolds by slurry foaming method, and then implanted them into a rabbit femur tumor resection post-defect model. The results showed that the n-HA-loaded porous titanium alloy scaffolds could effectively prevent tumor metastasis, and the n-HA coating promoted the regeneration of new bone within the pores of the porous titanium alloy scaffolds while inhibiting the growth of tumors.
Magnesium and its alloys are biodegradable materials that not only promote bone regeneration at defects, but their degradation products also show good anti-tumor properties in vitro and in vivo. Meanwhile, the degradation cycle of magnesium in vivo can be adjusted to vary from half a year to several years, which can fight against bone tumor cells in vivo for a long period of time (Zhang et al., 2019). Wei et al. (2021) prepared porous titanium alloy scaffolds by using additive manufacturing technology, and magnesium coatings on the surface of the scaffolds were prepared by using multi-arc ion plating technology. The results showed that the implant released magnesium ions during magnesium degradation, and the appropriate concentration of magnesium ions could effectively inhibit the proliferation of bone tumor cells and increase the apoptosis of tumor cells.
In recent years, researchers have paid attention to the possibility of embedding antitumor drugs in porous titanium alloy implants. Jing et al. (2021) utilized porous titanium alloys as substrate scaffolds and injected hydrogels containing the antitumor drug cisplatin into these porous structures. It was found that this porous titanium alloy implant incorporated with cisplatin hydrogel showed significant anti-tumor effects both in vitro and in vivo. In particular, in a murine tumor model, local release of cisplatin through the implant not only reduced adverse effects but also enhanced anti-tumor effects compared to systemic cisplatin treatment. In addition, the integrative effect of this composite scaffold with the surrounding bone tissue was validated by assessing the index of inward bone growth (Table 4).
Table 4. Research on the application of additive manufacturing porous titanium alloy technology in bone tumor surgery.
Bone defect repair has always been one of the challenging topics in orthopedic clinics, and with the development of additive manufacturing technology and material science, accumulating advanced bone tissue engineering scaffolds with matched mechanical strength and biomimetic structures have been developed to meet the increasing demand for bone repair (Maresca et al., 2023).
Titanium and its alloys are well suited as bone tissue substitutes due to their excellent biocompatibility, outstanding corrosion resistance and low tissue responsiveness (Xu et al., 2022). However, poor adhesion between the implant-bone interface and stress shielding due to high stiffness remain major drawbacks of titanium implants (Kapat et al., 2017).
In recent years, the development of implant surface modification technology has provided new ideas to solve the above problems. By changing the surface morphology or modificating implant surface, in order to achieve anti-infection capacity, promote osteogenesis, optimize wear resistance, corrosion resistance and oxidation resistance. It has been demonstrated that physical and chemical-based surface modifications can influence cellular behavior (Sheng et al., 2022; Li et al., 2021c), while immobilization of biomolecules on the implant surface and local delivery of biotyping molecules at appropriate concentrations and rates can directly influence biochemical processes and effectively induce bone formation (Lutz et al., 2010; Le Nihouannen et al., 2008).
In addition, by applying surface coatings made of biomolecules with well-defined bioactivities, it is possible to tailor the biochemical properties of the implant surface to more effectively modulate the interactions between the biomaterials and the implanting microenvironment (Sobolev et al., 2019), to directionally regulate the adhesion behavior of specific cells, to influence their differentiation process, to shorten the healing cycle, and to enhance the long term stability of the implant (Villegas et al., 2022).
After the implant is placed into the body, its surface will have a direct contact effect with the tissue cells in the implanted environment, so the physicochemical properties of the implant surface are the key factors affecting the implantation success, stability, and longevity of the implant (Mendonça et al., 2008). In order to enhance the biocompatibility of titanium alloy implants, improve their stability in vivo, and further shorten the healing time, surface modification of the implant is required prior to implantation. Studies have shown that surfaces with micro- and nanocomposite structures can promote the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts (Hori et al., 2010), while the combination of nanoscale and microscale surface features that mimic the graded structure of bone can further improve the bone growth-promoting properties of implants and shorten the healing time (Gittens et al., 2011).
The surface of titanium alloys is susceptible to corrosion by chemicals and strong acids, and this corrosive effect changes the surface texture and roughness of the material. And the Topological structure of surface is a key determinant of biological processes such as adsorption, movement and differentiation of, proteins, bacteria and cells, respectively (Surmeneva et al., 2022). Civantos et al. (2019) investigated the effect of hydrofluoric acid etching time on the in vitro cellular behavior of powder sintered porous titanium scaffolds. By etching the scaffolds, the average surface roughness of the material gradually increased with etching time. In vitro experiments revealed that the surface characteristics not only affected osteoblast adhesion, but also promoted osteoblast differentiation by increasing the production of bone matrix proteins, including ALP, collagen, osteoblastin, and osteocalcin. However, etching improves the surface structure of the material while causing a decrease in the strength of the material (Wang et al., 2020a), while the surface morphology is difficult to control and may cause damage to the material, limiting its application.
Physical, chemical impregnation and deposition is a method of forming coatings on the surface of porous metallic materials by impregnation, deposition or chemical reaction after mixing uniformly in the liquid phase with bioactive inorganic salts such as hydroxyapatite or organic compounds such as polydopamine, peptides, amino acids, and so on as the precursors. Yuan et al. (2022) used deposition to coat hydroxyapatite particles on the surface of porous titanium scaffolds, and in vitro cellular assays showed that it induced no statistically significant increase in hFOB1.19 apoptosis, and the hydroxyapatite-coated group presented higher CCK-8 values compared to the control group. Wang et al. (2010) immersed porous titanium alloy scaffolds into sodium hydroxide solution for heating treatment and then immersed them in simulated body fluids for 1 week to make the calcium phosphate elements uniformly deposited on the surface of the scaffolds. Cell culture experiments demonstrated that the synthetic material significantly enhanced the osteointegration effect and enhanced the phenotypic osteogenic profile of mesenchymal cells and osteoblast synthesis activity. Wu (2019) immersed porous titanium alloy in alkaline polydopamine solution to form a coating of a certain thickness on the surface of the material through polydopamine self-polymerization reaction. Bio-mineralization experiments showed that the phenolic hydroxyl groups in polydopamine interact with calcium ions, which can provide more nucleation sites and improve the surface bio-mineralization properties. In addition to polydopamine, proteins such as extracellular matrix proteins, growth factors, polysaccharides and nucleotides have also been used for bioactive organic modifications (Che et al., 2022), however, some organic coatings are highly targeted in antimicrobial and osteogenic promotion. However, inorganic coatings such as hyaluronic acid do not bind well to the material and tend to break off under cyclic loading, affecting their therapeutic effect.
Electrochemical method is to utilize metal materials as electrodes in the electrolyte, through redox reaction on the surface of the material to form porous oxides or coatings containing specific components. According to the type of reaction and the principle of action is mainly divided into anodic oxidation, micro-arc oxidation, electrochemical deposition process.
Anodizing is a method of building oxide film, corrosion resistant pits and titanium nanotubes on the surface of the scaffold by the action of external current using titanium or its alloys as an anode and placed in an electrolyte of hydrofluoric acid system. Shokuhfar et al. (2014) anodized the surface of the material using tetrahydrofuran solution as an electrolyte and explored its biological properties. Osteoblast culture experiments showed that the presence of nanotubes increased the total cell density with the same matrix material.
Microarc oxidation is to increase the voltage or current on the basis of anodic oxidation, using the strong voltage to generate microarc discharge and local high temperature, so that the electrolyte ions in the discharge channel are vaporized at high temperature, forming plasma and oxidizing with porous implants, thus generating porous oxide coatings with titanium oxide as the main constituent (Li et al., 2023b). Luo et al. (2021) used a calcium acetate electrolyte solution for porous titanium alloy implants were subjected to micro-arc oxidation. A micro and nanostructure-containing layer with a thickness of 6–7 μm was formed on the material surface. It was found that Calcium in the coating and the porous structure significantly enhanced cell viability and increased the formation of new bone in vivo. Compared with anodic oxidation, the coatings prepared by microarc oxidation had high hardness, high bond strength and good wear resistance.
Electrochemical deposition, also known as electrodeposition, electrophoretic deposition, or electroplating, is a method of depositing materials (metals, polymers, ceramics, glass, and their composites) onto a substrate material using an electric current through a redox reaction (Weng et al., 2017). Vidal et al. (2021) performed pulsed electrodeposition of porous titanium alloy scaffolds prepared by ink-direct technology to achieve a uniform coverage of the Ca-P coating. The results of antimicrobial tests showed that the biofunctionalized scaffolds displayed antimicrobial activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative strains, effectively improving the biointegration properties of orthopaedic implants while reducing peri-implant infections. In addition, researchers plated Cu, Zn, Ag, Mg, and Ta onto the material surface to enhance wear and corrosion resistance and biocompatibility (Fan et al., 2022b). Electrochemical deposition produces coating materials with better uniformity, a wider range of thicknesses, and higher bond strengths than traditional chemical deposition (Figure 6).

Figure 6. (A) Preparation of the Scaffolds and the Chemical Etching Process. (B) SEM images of the surface layer formed on the scaffold. Reproduced with permission (Surmeneva et al., 2022).
Metal oxide coatings, as a crucial surface modification technique, markedly enhance the wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature oxidation resistance of metal materials. Current preparation methods primarily include vapour phase deposition, micro-arc oxidation, and plasma electrolytic oxidation.
Vapour phase deposition involves the gasification of components to be added, which then contact porous titanium to form a thin film on the surface. This process can be categorized into physical vapour phase deposition (PVD) and chemical vapour phase deposition (CVD) based on the gasification principle. PVD is a technique where the target material migrates and accumulates on the substrate surface in atomic, molecular, or ionic form through evaporation or sputtering in a vacuum environment, forming a thin film. Its main types include vacuum evaporation, sputtering coating, and ion plating (Wang et al., 2017b). Diez-Escudero et al. (2022) applied PVD to deposit silver coatings on porous Ti6Al4V alloys, with a thickness of (4.5 ± 1.5) μm. Compared to the blank group, these coatings reduced the adhesion of Staphylococcus aureus and inhibited biofilm formation on the material surface within 72 h. CVD involves depositing metallic or inorganic coatings on a substrate by vaporizing compounds containing the elements of the thin film and chemically reacting them with the substrate surface (Cui et al., 2022). Lascano et al. (2020) used CVD to transfer a monolayer of graphene onto porous titanium alloy surfaces, enhancing cellular adhesion and proliferation. Additionally, the graphene layer acts as a barrier, reducing cell contact with residual metallic heavy elements in the alloy.
Micro-arc oxidation (MAO) is a surface modification technique derived from anodizing. It involves immersing metal in an alkaline electrolyte and inducing micro-discharge on the metal surface via high voltage. The local high temperature generated by the discharge promotes oxidation of the base metal, forming a complex oxide ceramic coating dominated by substrate element oxides, with electrolyte components participating in doping modification (Rakoch et al., 2006). The coating formation mechanism, involving breakdown-channeling-melting effects, has been extensively studied. MAO coatings exhibit superior wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and fatigue resistance (Zhang et al., 2023). Additionally, MAO treatment enhances the cytocompatibility of titanium and its alloys, promoting cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation (Wen et al., 2023). However, the potential risk of bacterial infections in medical applications can be mitigated by incorporating bio-antimicrobial agents and metallic elements such as Cu, Ag, Zn, and Mg into the MAO coatings (Huang et al., 2021) (Figure 7).
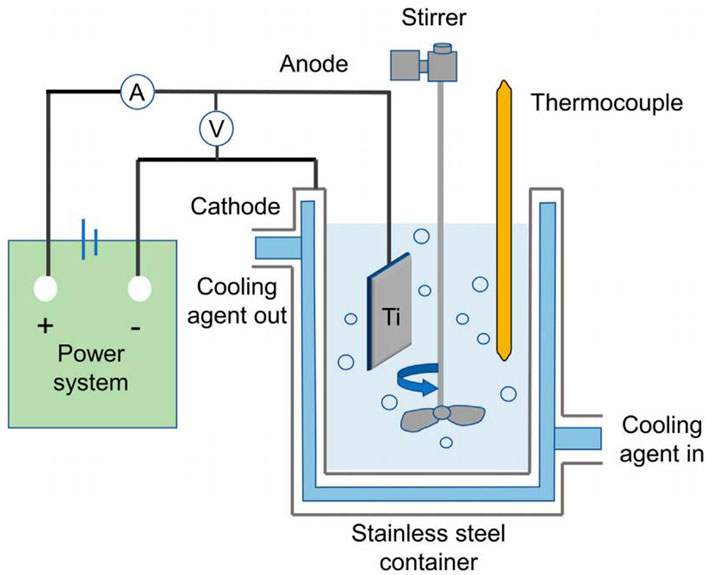
Figure 7. Schematic representation of the MAO coating system. Reproduced with permission (Wen et al., 2023).
Plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) is a surface treatment method that integrates electrochemical oxidation with plasma physics. By applying high-voltage pulses in an electrolyte solution, PEO induces plasma discharge on the metal surface to form a ceramic oxide coating (Hussein et al., 2013). In recent years, PEO has garnered significant attention due to its simple process, low cost, and superior coating properties. This method can create coatings on substrates with diverse geometries, enhancing bond strength. On titanium-based alloys, PEO can be performed with various electrolytes to produce calcium phosphate-based composite layers with distinct morphology, structure, thickness, and crystallinity (Rafieerad et al., 2015). These coatings typically exhibit hardness values above 1000 HV, significantly exceeding that of the base metal. Moreover, the wear resistance of PEO coatings can be further optimized through process parameter adjustments (Lederer et al., 2021).
The development of titanium alloy laser melting surface modification technology has progressed from laser surface quenching to laser surface remelting, laser surface synthesis, and ultimately to laser cladding (Zhao et al., 2023). Laser cladding entails spraying premixed powder onto the substrate surface via a nozzle, and forming a molten pool by adjusting laser power, spot size, and scanning speed. By varying the powder composition and continuously spraying into the pool, a functionally gradient coating is achieved (Song and Li, 2010).
Laser melting and cladding technology integrates the benefits of arc and electron beam melting, characterized by high energy density and environmental adaptability (Ouyang et al., 2022). It enables the deposition of thin layers on complex structural surfaces using powders or filaments. Combined with small laser spot diameters, the cladding layer thickness, surface roughness, and layer interfaces can be optimized through parameter adjustments (Wang et al., 2021c). These features facilitate the formation of metallurgically bonded cladding layers with superior mechanical properties, thereby enhancing coating quality (Arif et al., 2021). While laser cladding for thin film preparation is rapid, adaptable, and highly controlled, it is also associated with high equipment costs and process complexity (Figure 8).
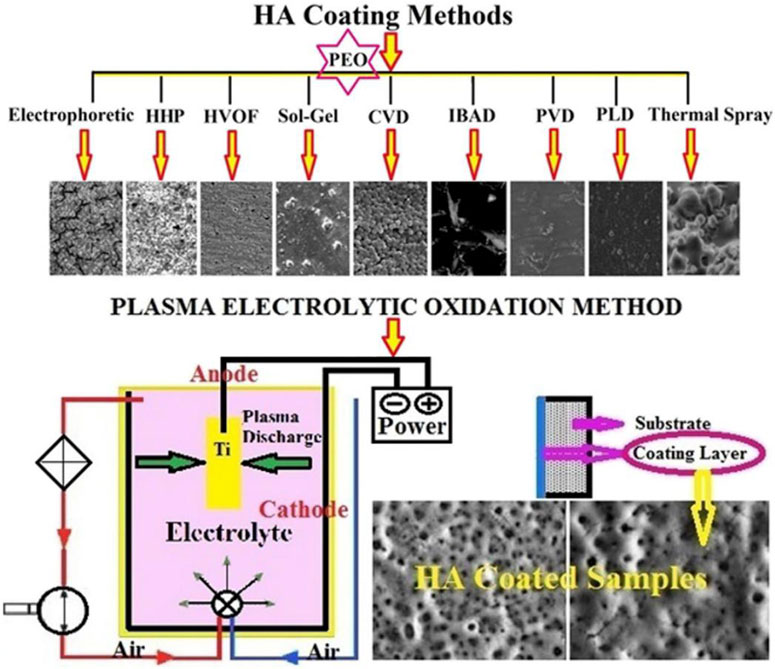
Figure 8. Morphology of the HA layer via different coating methods and schematic view of PEO method. Reproduced with permission (Rafieerad et al., 2015).
Hydrogels are soft polymers with a three-dimensional mesh structure formed by cross-linking of monomers or polymer chains through covalent or non-covalent bonding interactions (e.g., hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interactions, host-guest complexation, and their combinations) (Ali et al., 2019). Hydrogels can be prepared from natural (e.g., filipin proteins, chitosan, and gelatin) or synthetic polymers [e.g., poly (vinyl alcohol), poly (ethylene glycol), and poly (betaine)] (Lee et al., 2013). Hydrogels composed of polysaccharides and proteins possess physical and chemical properties similar to those of most human tissue (Chen et al., 2019a). Due to the softness and wettability that hydrogels possess, they are very similar to the extracellular matrix (ECM) of biological tissues and can provide ideal ecological conditions for cell survival (Tibbitt and Anseth, 2009).
With the aging of the population in society, osteoporosis has become a common disease endangering the life and health of middle-aged and elderly people, usually seen in postmenopausal people aged over 65 years, which is characterized by a decrease in bone mineral density due to bone loss accompanied by an increase in bone fragility and sensitivity (Cruz et al., 2018). The treatment of osteoporotic bone defects is a complex clinical problem, and due to the bioinertness of titanium and its alloys and the fact that in the setting of osteoporotic pathology, although porous scaffolds facilitate bone growth into the scaffolds, bone regeneration is severely limited and implants may struggle to achieve good osseointegration. Therefore, it is necessary to stimulate bone regeneration to achieve better bone restore.
Silk proteins are natural protein with excellent biocompatibility and good mechanical properties make them ideal candidates for bone regeneration promotion (Tan et al., 2005). Silk proteins have been processed into various forms such as fibers, hydrogels, scaffolds, films, sponges, and microspheres through different techniques (e.g., electrostatic spinning, 3D printing, and freeze-drying) (Grigoryan et al., 2019). Among them, hydrogels are one of the important forms of silk protein-based materials. Silk protein hydrogels can be prepared by a variety of methods, and the prepared hydrogels have numerous tunable properties, and have been widely used in the field of medicine due to the advantages of mild preparation conditions, controllable reaction time, and reduced by-products (Pal et al., 2014).
Studies have shown that filipin protein itself can improve the interaction between osteoblasts and fibroblast biomaterials (Xu et al., 2020). In order to improve the integration of titanium implants with the surrounding bone tissue, Saha et al. (2019) coated the surface of titanium implants with filipin protein, and it was found that filipin protein enhanced osteoconductivity and osteoblastogenic properties. Lee et al. (2017) prepared a physically crosslinked filipin protein and poly (vinyl alcohol) by a high-strength filipin protein hydrogel, which had mechanical properties similar to those of human ear cartilage, and the hydrogel maintained its original shape throughout the culture process. Histological analysis showed that the prepared hydrogel had excellent biocompatibility and provided a good environment for chondrocyte adhesion and proliferation.
Scaffolds for clinical applications in bone tissue engineering not only need to have the ability to promote the generation of new bone, but they must also contain interconnected vascular networks to facilitate nutrient transport, oxygen exchange, metabolic waste elimination, and regulation of cells and signaling molecules (Wan et al., 2020). Therefore, when designing bone graft replacement materials, both osteogenesis and angiogenesis must be induced (Barati et al., 2016). During bone restoring, vascular endothelial growth factor (VGEF) secreted by osteoblasts promotes the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells, while VEGF also increases the level of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) in endothelial cells. Endothelial cells in turn secrete osteogenic factors, such as BMP-2 and BMP-4, to enhance osteoblast differentiation. Thus, it is clear that angiogenesis and osteogenesis are closely linked (Zhang et al., 2022a). Numerous studies have demonstrated the synergistic effect of angiogenic factors with osteogenesis-related factors (Bosetti et al., 2007; Liu et al., 2007; Izquierdo-Barba et al., 2019), which have also been used in combination with implants. For example, Schorn et al. (2017) developed an implant that consisted of a collagen scaffold containing BMP-2 and VEGF. Patel et al. (Orth et al., 2022) devised a method of mixing VEGF and BMP-2 into gelatin particles and implanting these particles into porous polypropylene fumarate scaffolds for use in a rat cranial defect model. Despite the effectiveness of these methods for bone regeneration, these scaffolds were unable to maximize osteogenesis because they were unable to control the release of VEGF and BMP-2. For this reason, Lv et al. (2015) combined porous titanium implants with fibrin glue containing growth factors to form a composite porous titanium scaffold. Fibrin was used as a carrier to control the release of BMP-2 and VEGF. Preliminary histologic evaluation showed that the incorporation of growth factors significantly promoted the formation of new bone tissue in the vasculature and stent pores.
By using additive manufacturing techniques, porous titanium scaffolds and their biomodification can be established, and the integration of which into bone can be significantly enhanced. On the surface of these titanium scaffolds, a hydrogel containing growth factors that promote osteogenesis and angiogenesis is coated. This composite system synergistically promotes the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) in vitro and accelerates the migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) as well as the formation of blood vessels in vitro, compared to a single growth factor. This composite system is capable of sustained releasing VEGF and BMP-9 in a sustained and coordinated manner to act on the localized bone defect area, thereby enhancing the integration of the bone-scaffold interface and improving the initial and long-term stability of the implant in the bone defect area (Che, 2023). This approach provides a new therapeutic avenue for bone defect management (Figure 9).
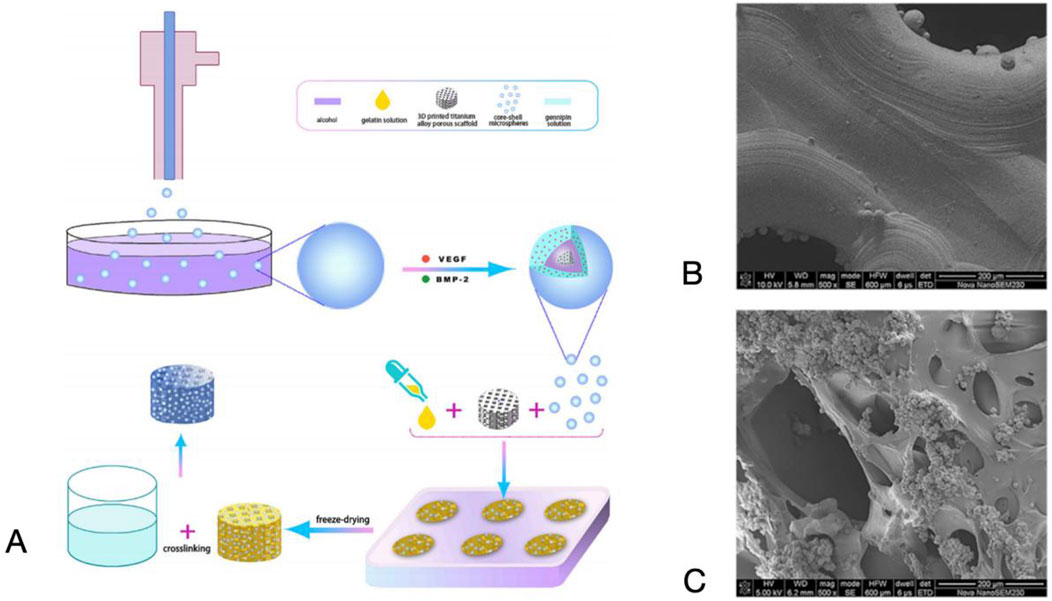
Figure 9. (A) Schematic diagram of the preparation process of the composite scaffold system. (B) SEM images of titanium alloy porous scaffolds. (C) Dual-factor loaded core-shell microspheres-gelatin coating-3D printing titanium alloy porous scaffold. Reproduced with permission (Liu et al., 2022c).
Traditional titanium implants lack antimicrobial properties, which may lead to post-implantation infections and patient discomfort (Alvand et al., 2017). Current clinical practice often involves 6–8 weeks of intravenous antibiotic therapy. However, this approach has several drawbacks, including difficulty in accurately managing antibiotic duration, low drug concentration at the target site, and the inability to achieve effective drug concentrations on the implant surface or within biofilms. Consequently, some patients require revision surgery, increasing their economic burden and that of society.
The antimicrobial mechanism of porous titanium implants involves both physical and chemical aspects. Physically, surface roughness and hydrophilicity can influence bacterial adhesion (Wu et al., 2011). Gasik et al. (2012) demonstrated that porous titanium with appropriate roughness and hydrophilicity significantly reduces bacterial adhesion compared to unmodified titanium surfaces. This also promotes cell proliferation and differentiation to some extent. Chemically, incorporating antibacterial metals such as copper or silver into titanium alloys can effectively inhibit bacterial growth and propagation (Xu et al., 2023).
Antibiotics remain the cornerstone for preventing and treating periprosthetic infections, despite extensive research into alternative antimicrobial methods such as metal ions and antimicrobial peptides (Kapadia et al., 2016). Antibiotic-loaded materials, like bone cements, are widely accepted for their effective antibacterial activity, with local delivery reducing systemic toxicity compared to intravenous administration (Spriano et al., 2018). Recent studies have explored topical antibiotic delivery through surface coatings, but additively manufactured porous materials offer superior drug-delivery potential (Orapiriyakul et al., 2018; Bakhshandeh et al., 2017).
Additive manufacturing enables the creation of titanium implants with specialized designs that enhance functionality. For instance, cavities within these implants can be filled with secondary therapeutic agents such as calcium phosphate or hydroxyapatite cement, forming lattice structures or external storage layers (Bezuidenhout et al., 2018). Parent et al. (2016) demonstrated enhanced efficacy against drug-resistant S. aureus by loading vancomycin onto porous hydroxyapatite surfaces. Additionally, broad-spectrum antimicrobial coatings have shown promise in combating diverse bacterial infections. Jianxin et al. (2019) combined levofloxacin, tinidazole, and methylprednisolone with a porous organic polymer to achieve broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, including anti-inflammatory effects. Other antibiotics, such as etimicin (van Oosten et al., 2013), ceftriaxone (Kundu et al., 2011), and amoxicillin (Kazek-Kęsik et al., 2019), have also been incorporated into antimicrobial coatings.
While traditional materials have specific surface characteristics and structural morphology, biomaterials are evolving from traditional static to dynamic design (Tibbitt et al., 2015). Traditional orthopedic implants provide mechanical support and osseointegration functions, which can already be properly accomplished with the development of porous titanium alloy technology. At the same time, advances in material design, dynamic chemistry and nanotechnology allow us to introduce dynamic response properties into the surface modification of titanium alloys, utilizing acoustic, optical, electromagnetic as well as pH and enzyme (Zarubova et al., 2022), in conjunction with specific coatings to externally stimulate function (Bril et al., 2022). After much research and effort, a series of environmentally responsive surfaces have been successfully constructed on titanium alloy substrates. These surfaces have the ability to regulate cellular signaling, reduce the risk of infection by precisely controlling the release of drugs, and are important for revealing the subsequential biological processes inside cells (Figure 10).
Ultrasound, as a mechanical wave, is capable of directly modulating cell-material interactions and controlling drug release in a non-invasive manner. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for improving bone tissue reconstruction in fresh fracture healing and delayed fracture healing (Liang et al., 2022). Studies have shown that low-intensity pulsed ultrasound combined with micro-arc oxidation technology, where low-intensity ultrasound vibration affects the permeability of cell membranes and intracellular material movement, enhances the binding of MG63 cells to the surface, accelerates proliferation, and improves the expression of osteogenic differentiation (Chen et al., 2019b).
Ultrasound can modulate the rate of drug release, for instance, Aw and Losic (2013) reported micelles containing an insoluble drug (indomethacin) in response to ultrasound stimulation. Ultrasound interacts with an aqueous buffer and rigid titanium nanotube structures to generate cavitation and heat, which induces the release of the drug from the super-hydrophobic titanium nanotube arrays, and is even able to achieve 100% release in the desired time.
Ultrasound therapy can also be combined with thermotherapy, where ultrasound waves penetrate deeply into tissues and are spatially focused to a single discrete point. Red phosphorus-coated titanium surfaces (Ti-RP) exhibited a significant increase in acoustic-thermal activity under ultrasound excitation, related to the ultrasound-activated conversion of mechanical energy into phonons by electronic motion. The Ti-RP surfaces were functionalized with nanoporous silica nanoparticles containing thermoresponsive NO precursor particles coating for functionalization, the antimicrobial efficiency against multidrug-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) under ultrasonic excitation was more than 93.40%, which was effective against MRSA bone infection without side effects (Wang et al., 2020b).
Light as a non-invasive physical stimulus has demonstrated its potential for precise control at the microscopic level (Tian et al., 2022). Light is able to activate titanium oxide, which in turn modulates cellular behavior in both the temporal and spatial dimensions. Through this mechanism, we were able to utilize light to control drug release, enhance antimicrobial efficacy, and promote cell and tissue repair.
Titanium oxide possesses potential as a drug carrier but suffers from uncontrolled release. To address this challenge, researchers have adopted a series of innovative strategies. Song et al. (2009) achieved precise control of drug release by immobilizing APTES vitamin C monolayer linkers on TiO2 nanotubes and using ODPA to close the ends of the nanotubes. When these structures were exposed to UV light, the photocatalytic properties of TiO2 were able to break down the ODPA and the linkers, thereby controlling the release of the enzyme molecules. Given the limited penetration of UV light, the researchers further added noble metals capable of generating surface plasmon resonance to the TiO2 nanotubes, enabling the drug release process to take place under visible or infrared light. This technology not only regulates drug release, but can also be used directly to rapidly remove biofilms without causing tissue damage.
Despite the great potential for clinical applications, the single mode of photodynamic action has the disadvantages of short lifetime as well as limited diffusion distance (Deng et al., 2021), for this reason, researchers have combined photodynamic and photothermal properties to enhance the photoconversion efficiency and enhance the antimicrobial ability. Xu J. et al. (2016) prepared a red phosphorus-IR780-RGDC coating on the surface of a titanium alloy, with red phosphorus acting as a photothermite and IR780 as a photosensitizer, which can eliminate bacteria more efficiently when exposed to near infrared light irradiation, which can generate both heat and singlet oxygen, resulting in improved drug release efficiency as well as enhanced antimicrobial capacity.
Electrical stimulation is a method of modulating cellular or tissue responses through external electrical signaling and involves a variety of behaviors and mechanisms, such as angiogenesis, mitosis, migration, and healing (Casella et al., 2021). It was shown that the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts were enhanced by biphasic electrical stimulation on the surface of titanium nanotubes (Ercan and Webster, 2010). A constant electric field was found to improve osteogenic differentiation of cloned rat MSCs even in the absence of bone-enhancing agents (Park et al., 2016). Although the behavior of cells stimulated by the application of electrical signals has been widely observed, the molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood (Ercan and Webster, 2010).
Mazare et al. (2019) prepared Arh2-reduced black TiO2 nanotube arrays, which significantly reduced the resistivity, and the enhanced conductivity of the TiO2 nanotube surface could trigger higher Ca2+ influx with minimal electric field stimulation, and increased of Ca2+ ions further regulated downstream signaling and improved cell proliferation.
Magnetic fields originate from static magnets or the flow of charge through source-based wires or electrical devices, which show high tissue penetration and minimal detrimental effects at low intensity magnetic fields (Jayasree et al., 2021). Magnetic fields can be utilized to trigger drug release using magnetic nanoparticles and stimulate cellular and tissue behaviors. Aw et al. (2012) prepared magnetically responsive delivery platforms on titanium nanotube arrays loaded with dopamine-modified iron oxide nanoparticles (MNPs) at the bottom and indomethacin-encapsulated polymer micelles at the top, achieving drug release controlled by an external magnetic field generated by the movement of electric magnetic fields. Fassina et al. (2008) constructed titanium alloy fiber mesh scaffolds and observed higher proliferation and matrix deposition of SAOS-2 cells under electromagnetic pulses, osteoblasts would be oriented along the magnetic field lines, and proliferation and expression of osteogenesis-related genes were upregulated.
X-rays, a form of ionizing radiation, are widely used in clinical diagnosis and therapy due to their high tissue penetration capacity and low autofluorescence background (Ying et al., 2022). X-rays are able to modulate osteoblast activity, trigger drug release, and assist in imaging of implant infections. Low-dose X-ray irradiation is beneficial for somatic osteoblast differentiation and mineralization, and also contributes to mineralization of fracture healing tissue in vivo (Karim and Judex, 2014). It has been shown that low-dose X-ray irradiation enhances bone growth towards the prosthetic surface, contributes to the stability of the prosthesis in the presence of wear particles, and inhibits the early development of aseptic loosening (She et al., 2016). Based on the response capability of TiO2, X-rays can be used to trigger drug release. Schmidt-Stein et al. (2009) used X-rays to induce the generation of electron-hole pairs from compact TiO2 layers and nanotube arrays to degrade organic compounds. Demonstrating the feasibility of X-ray activation for modulating potential drug release patterns.
X-ray excitation luminescence chemical imaging (XELCI) is a non-invasive technique used to detect and monitor bacterial infections on implant surfaces (Behbahani et al., 2022). The technique combines an X-ray scintillator layer and a pH-sensing layer to produce high-resolution images and optically detect the extent of infection through X-ray excitation. The ability of XELCI technology to image both acidic and basic pH regions around implants has shown potential applications for detecting local pH changes under acidotic conditions, including tumors, inflammation, and ischemia (Uzair et al., 2019), providing new strategy for implant infection treatment.
The ph response is achieved by pH-triggered protonation and deprotonation of chemical groups in the polymer cap of titanium surfaces (Lv et al., 2020). Chitosan, which is rich in amino groups, is one of the commonly used molecules for surface modification of titanium (Ning et al., 2019), and can be prepared to produce pH-sensitive coatings, which are capable of inhibiting bacterial growth by releasing more drugs, such as tobramycin, in acidic conditions (e.g., infected areas). This smart coating not only reduces bacterial adhesion, but also maintains the antimicrobial effect for a long time without harming normal cells (Zhou et al., 2018).
In addition to chitosan, polymethylmethacrylic acid (PMAA) has also been used to prepare pH-sensitive materials. Such material swells at neutral pH and shrinks under acidic conditions, thereby controlling drug release. Chen et al. (2020b) used PMAA to encapsulate antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) to prolong drug release under physiological conditions and rapidly release AMPs to kill bacteria under infected conditions. In addition, some pH-sensitive chemical bonds such as metal-ligand bonds and Schiff bases have also been used in the preparation of coatings (Wang et al., 2017c; Tao et al., 2019), which can be fractured in acidic environments to release the drug and effectively eliminate bacteria.
The pH-responsive mode can also be combined with other therapeutic approaches, such as catalytic therapy and gas therapy, for the treatment of infected joints. This strategy works by depositing special nanoparticles on titanium surfaces that trigger a chemical reaction in a bacterial-induced acidic environment, generating reactive oxygen species (ROS) and oxygen capable of killing bacteria while alleviating the hypoxic environment of the infected area (Zhang et al., 2022b).
Enzyme-responsive modes typically utilize enzymes to hydrolyze coatings as a way to trigger drug release or activate specific cellular behaviors. Hyaluronidase, for example, is commonly used to cleave coatings containing hyaluronic acid in order to modulate drug release kinetics. Yuan et al. (2018) loaded vancomycin (Van) into TiO2 nanotubes, and then sealed the titanium nanotubes using alternating layers of 3,4-dihydroxycinnamic acid-modified chitosan (Chi-c) and dopamine-modified hyaluronic acid (HA-c). In the presence of hyaluronidase or S. aureus, the degradation of the multilayered membrane controlled the titanium nanotubes to release more than 50% of Van within 24 h with an antimicrobial rate higher than 80%. At the same time, this hybridized surface significantly improved the initial adhesion of rat cranial osteoblasts and significantly cleared the surrounding medulla of infection. In some cases, hyaluronic acid can be further combined with antimicrobial agents. Yu et al. (2020) used sodium hyaluronate-laurate coupling or hyaluronic acid-gentamic acid coupling to cap BMP-2 or desferrioxamine-loaded titanium nanotubes, respectively. The designed and modified surfaces exhibited not only antifouling and antimicrobial properties, but also improved osteogenic differentiation.
In addition, micrococcal nuclease and serine protease-like protease (SplB) secreted by S. aureus have been used to trigger the surface reaction. Ghimire et al. (2019) combined vancomycin with a polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate hydrogel coating on a titanium alloy surface with an oligonucleotide junction that was susceptible to S. aureus micrococcal nuclease (MN). The MN-triggered release of the Vancaused prompt eradication of S. aureus around the implant surface and effectively tethered vancomycin doses prevented S. aureus infections in mouse femoral tubes more than 200-fold lower than the amount of prophylactic antibiotics used in bone cement.
In addition to bacterial-associated enzymes, osteoblast-associated enzymes are also used to modify surface reactions. A coating consisting of acetylglucosan (acBSP) and alendronate (ALN) was constructed on the surface of a titanium alloy, and in vitro assays showed that acBSP activated macrophages to express osteoclastogenic cytokines containing oncostatin M, which is a member in the pro-inflammatory cytokines of interleukin-6 family of, and suppresses pro-inflammatory macrophages and directly induces osteogenesis. In vivo results in an osteoporotic rat model showed that this bioresponsive coating significantly improved bone-implant contact rates, which provides new ideas for immunomodulatory surface modifications (Wang et al., 2024b).
Porous titanium alloy implants play an important role in modern orthopedic medicine, especially in surgeries such as fracture fixation, spinal fusion, joint replacement, and bone tumor defect repair. However, despite their clinical success, these implants still face some challenges and have set new requirements for future development.
With the increasing demand for personalized medical care, traditional implant manufacturing methods cannot meet the needs of patients with specific anatomical and skeletal characteristics. Although additive manufacturing technology offers the possibility of manufacturing personalized implants, most orthopedic surgeons are unfamiliar with the operation methods of related software and equipment, which limits the popularization and development of this technology. At the same time, due to the diversity and rapid development of 3D printing technology, there are currently various types of 3D printing equipment, methods and materials, thus there are seldom unified clinical application specifications and standards, which limits the further development of the technology.
In the future, the combination of 4D printing and Artificial intelligence technology will make it possible to design more personalized and intelligent orthopedic implants that can self-adjust and optimize according to the specific conditions of the patient. The development of new bioactive coatings and drug release systems to promote osseointegration, angiogenesis, and infection control will be the focus of future research. As the technology develops, an international standard evaluation system needs to be established to ensure the quality and safety of customized implants while also addressing related ethical issues.
At present, most of the additive manufacturing porous titanium alloy technology is still limited to animal experiments and is still some way from clinical application and translation. There is still considerable gap for research in the field of orthopedics in the future. The future of additive manufacturing porous titanium alloy implants in orthopedics will focus more on personalized, intelligent and precision medicine, while interdisciplinary cooperation is needed to integrate material science, bioengineering, information technology and clinical needs to achieve safer and more effective treatment options, stimuli-and environment-responsive device, and jointly promote the progress and development of orthopedic medicine.
CG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. TD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. YC: Data curation, Software, Writing–review and editing, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision. JZ: Data curation, Software, Writing–review and editing. XF: Data curation, Software, Writing–review and editing. ZF: Data curation, Software, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abar, B., Kwon, N., Allen, N. B., Lau, T., Johnson, L. G., Gall, K., et al. (2022). Outcomes of surgical reconstruction using custom 3D printed porous titanium implants for critical-sized bone defects of the foot and ankle. Foot and Ankle Int. 43 (6), 750–761. doi:10.1177/10711007221077113
Adamek, G., Kozlowski, M., Junka, A., Siwak, P., and Jakubowicz, J. (2022). Preparation and properties of bulk and porous Ti-Ta-Ag biomedical alloys. Mater. Basel, Switz. 15 (12), 4332. doi:10.3390/ma15124332
Adl Amini, D., Moser, M., Oezel, L., Zhu, J., Okano, I., Shue, J., et al. (2022). Early outcomes of three-dimensional-printed porous titanium versus polyetheretherketone cage implantation for stand-alone lateral lumbar interbody fusion in the treatment of symptomatic adjacent segment degeneration. World Neurosurg. 162, e14–e20. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2021.11.122
Agarwal, A., Dewangan, S., Kulkarni, A. R., and Legutko, S. (2025). Microstructural analysis into stainless steel samples undergone into HCl solution treatment. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. D. doi:10.1007/s40033-025-00861-6
Ali, M., Pr, A. K., Yoo, J. J., Zahran, F., Atala, A., and Lee, S. J. (2019). A photo-crosslinkable kidney ECM-derived bioink accelerates renal tissue formation. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 8 (7), e1800992. doi:10.1002/adhm.201800992
Alvand, A., Rezapoor, M., and Parvizi, J. (2017). The role of biomarkers for the diagnosis of implant-related infections in orthopaedics and trauma. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 971, 69–79. doi:10.1007/5584_2017_11
Arif, Z. U., Khalid, M. Y., Rehman, E. u., Ullah, S., Atif, M., and Tariq, A. (2021). A review on laser cladding of high-entropy alloys, their recent trends and potential applications. J. Manuf. Process. 68 (B), 225–273. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.06.041
Arts, M., Torensma, B., and Wolfs, J. (2020). Porous titanium cervical interbody fusion device in the treatment of degenerative cervical radiculopathy; 1-year results of a prospective controlled trial. spine J. official J. North Am. Spine Soc. 20 (7), 1065–1072. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2020.03.008
Aw, M. S., Addai-Mensah, J., and Losic, D. (2012). Magnetic-responsive delivery of drug-carriers using titania nanotube arrays. J. Mater. Chem. 22 (14), 6561–6563. doi:10.1039/c2jm16819g
Aw, M. S., and Losic, D. (2013). Ultrasound enhanced release of therapeutics from drug-releasing implants based on titania nanotube arrays. Int. J. Pharm. 443 (1-2), 154–162. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.01.004
Axenhus, M., Salemyr, M., Mukka, S., Magnéli, M., and Sköldenberg, O. (2024). Long-term follow-up of bone density changes in total hip arthroplasty: comparative analysis from a randomized controlled trial of a porous titanium construct shell vs. a porous coated shell. Int. Orthop. 48 (11), 2835–2842. doi:10.1007/s00264-024-06289-z
Bakhshandeh, S., Gorgin Karaji, Z., Lietaert, K., Fluit, A. C., Boel, C. H. E., Vogely, H. C., et al. (2017). Simultaneous delivery of multiple antibacterial agents from additively manufactured porous biomaterials to fully eradicate planktonic and adherent Staphylococcus aureus. ACS Appl. Mater. and interfaces 9 (31), 25691–25699. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b04950
Barati, D., Shariati, S. R. P., Moeinzadeh, S., Melero-Martin, J. M., Khademhosseini, A., and Jabbari, E. (2016). Spatiotemporal release of BMP-2 and VEGF enhances osteogenic and vasculogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial colony-forming cells co-encapsulated in a patterned hydrogel. J. Control. release official J. Control. Release Soc. 223, 126–136. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.12.031
Barba, D., Alabort, E., and Reed, R. C. (2019). Synthetic bone: design by additive manufacturing. Acta Biomater. 97, 637–656. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2019.07.049
Behbahani, S. B., Kiridena, S. D., Wijayaratna, U. N., Taylor, C., Anker, J. N., and Tzeng, T. J. (2022). pH variation in medical implant biofilms: causes, measurements, and its implications for antibiotic resistance. Front. Microbiol. 13, 1028560. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.1028560
Bezuidenhout, M. B., Booysen, E., van Staden, A. D., Uheida, E. H., Hugo, P. A., Oosthuizen, G. A., et al. (2018). Selective laser melting of integrated Ti6Al4V ELI permeable walls for controlled drug delivery of vancomycin. ACS biomaterials Sci. and Eng. 4 (12), 4412–4424. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00676
Biemond, J. E., Aquarius, R., Verdonschot, N., and Buma, P. (2011). Frictional and bone ingrowth properties of engineered surface topographies produced by electron beam technology. Archives Orthop. trauma Surg. 131 (5), 711–718. doi:10.1007/s00402-010-1218-9
Biemond, J. E., Hannink, G., Verdonschot, N., and Buma, P. (2013). Bone ingrowth potential of electron beam and selective laser melting produced trabecular-like implant surfaces with and without a biomimetic coating. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 24 (3), 745–753. doi:10.1007/s10856-012-4836-7
Blair, C., Simela, A. T., and Cross, B. J. (2015). A challenging case of limb salvage requiring a combination of composite fixation and masquelet technique to address significant segmental bone loss. Case Rep. Orthop. 2015, 1–5. doi:10.1155/2015/369469
Bose, S., Banerjee, D., Shivaram, A., Tarafder, S., and Bandyopadhyay, A. (2018). Calcium phosphate coated 3D printed porous titanium with nanoscale surface modification for orthopedic and dental applications. Mater. and Des. 151, 102–112. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2018.04.049
Bosetti, M., Boccafoschi, F., Leigheb, M., and Cannas, M. F. (2007). Effect of different growth factors on human osteoblasts activities: a possible application in bone regeneration for tissue engineering. Biomol. Eng. 24 (6), 613–618. doi:10.1016/j.bioeng.2007.08.019
Bril, M., Fredrich, S., and Kurniawan, N. A. (2022). Stimuli-responsive materials: a smart way to study dynamic cell responses. Smart Mater. Med. 3, 257–273. doi:10.1016/j.smaim.2022.01.010
Cai, H. (2015). Application of 3D printing in orthopedics: status quo and opportunities in China. Ann. Transl. Med. 3 (Suppl. 1), S12. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.01.38
Casella, A., Panitch, A., and Leach, J. K. (2021). Endogenous electric signaling as a blueprint for conductive materials in tissue engineering. Bioelectricity 3 (1), 27–41. doi:10.1089/bioe.2020.0027
Che, Z., Zhu, Z., Zhu, L., Li, Y., Zhu, C., Huang, L., et al. (2022). The influence of biochemical surface modification of titanium implants on osseointegration. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 26 (16), 2576–2583.
Che, Z. J. (2023). Dual-functional hydrogels promote vascular regeneration and osseointegration at the interface of 3D-printed porous titanium alloy scaffolds. Dissertation, Jilin University. doi:10.27162/d.cnki.gjlin.2023.002226
Chen, G., Muheremu, A., Yang, L., Wu, X., He, P., Fan, H., et al. (2020a). Three-dimensional printed implant for reconstruction of pelvic bone after removal of giant chondrosarcoma: a case report. J. Int. Med. Res. 48 (4), 300060520917275. doi:10.1177/0300060520917275
Chen, G., Tang, W., Wang, X., Zhao, X., Chen, C., and Zhu, Z. (2019a). Applications of hydrogels with special physical properties in biomedicine. Polymers 11 (9), 1420. doi:10.3390/polym11091420
Chen, G., Wang, C. Y., Ma, Z., Yi, H. L., Bi, N. M., Zhu, W. J., et al. (2024). A prospective and consecutive study assessing short-term clinical and radiographic outcomes of Chinese domestically manufactured 3D printing trabecular titanium acetabular cup for primary total hip arthroplasty: evaluation of 236 cases. Front. Surg. 11, 1279194. doi:10.3389/fsurg.2024.1279194
Chen, G., Zhang, P., Wang, Y. C., Ma, Z., Bi, M. N., Zhang, S. S., et al. (2023). Short-term clinical and radiological evaluation of domestically produced 3D-printed titanium alloy trabecular acetabular cups in hip revision surgery. J. North Sichuan Med. Coll. 09, 1191–1196.
Chen, J., Li, J., Hu, F., Zou, Q., Mei, Q., Li, S., et al. (2019b). Effect of microarc oxidation-treated Ti6Al4V scaffold following low-intensity pulsed ultrasound stimulation on osteogenic cells in vitro. ACS biomaterials Sci. and Eng. 5 (2), 572–581. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b01000
Chen, J., Shi, X., Zhu, Y., Chen, Y., Gao, M., Gao, H., et al. (2020b). On-demand storage and release of antimicrobial peptides using Pandora's box-like nanotubes gated with a bacterial infection-responsive polymer. Theranostics 10 (1), 109–122. doi:10.7150/thno.38388
Chen, Y., Frith, J. E., Dehghan-Manshadi, A., Attar, H., Kent, D., Soro, N. D. M., et al. (2017). Mechanical properties and biocompatibility of porous titanium scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 75, 169–174. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2017.07.015
Christiansen, C. D., Nielsen, K. K., and Bjørk, R. (2020). Novel freeze-casting device with high precision thermoelectric temperature control for dynamic freezing conditions. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 91 (3), 033904. doi:10.1063/1.5134737
Civantos, A., Domínguez, C., Pino, R. J., Setti, G., Pavon, J. J., Martínez-Campos, E., et al. (2019). Designing bioactive porous titanium interfaces to balance mechanical properties and in vitro cells behavior towards increased osseointegration. Surf. and Coatings Technol. 368, 162–174. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2019.03.001
Colen, S., Harake, R., De Haan, J., and Mulier, M. (2013). A modified custom-made triflanged acetabular reconstruction ring (MCTARR) for revision hip arthroplasty with severe acetabular defects. Acta Orthop. Belg. 79 (1), 71–75.
Cruz, A. S., Lins, H. C., Medeiros, R. V. A., Filho, J. M. F., and da Silva, S. G. (2018). Artificial intelligence on the identification of risk groups for osteoporosis, a general review. Biomed. Eng. online 17 (1), 12. doi:10.1186/s12938-018-0436-1
Cui, Z., Zhu, J., Jiang, H., Wu, S., and Zhu, S. (2022). Research progress on surface modification of Ti and titanium alloys in the field of biomedical applications. Acta Metall. Sin. 58 (7), 837–856.
Deng, X., Shao, Z., and Zhao, Y. (2021). Solutions to the drawbacks of photothermal and photodynamic cancer therapy. Adv. Sci. Weinheim, Baden-Wurttemberg, Ger. 8 (3), 2002504. doi:10.1002/advs.202002504
Diez-Escudero, A., Andersson, B., Carlsson, E., Recker, B., Link, H., Järhult, J. D., et al. (2022). 3D-printed porous Ti6Al4V alloys with silver coating combine osteocompatibility and antimicrobial properties. Biomater. Adv. 133, 112629. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2021.112629
El-Hajje, A., Kolos, E. C., Wang, J. K., Maleksaeedi, S., He, Z., Wiria, F. E., et al. (2014). Physical and mechanical characterisation of 3D-printed porous titanium for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 25 (11), 2471–2480. doi:10.1007/s10856-014-5277-2
Ercan, B., and Webster, T. J. (2010). The effect of biphasic electrical stimulation on osteoblast function at anodized nanotubular titanium surfaces. Biomaterials 31 (13), 3684–3693. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.078
Fan, G., Yang, L., Liu, D., Wang, Y., Ji, W., Tukebai, , et al. (2022a). Repair of cranial defects in rabbits with 3D-printed hydroxyapatite/polylactic acid composites. bioMed Res. Int. 2022, 7562291. doi:10.1155/2022/7562291
Fan, H., Fu, J., Li, X., Pei, Y., Li, X., Pei, G., et al. (2015). Implantation of customized 3-D printed titanium prosthesis in limb salvage surgery: a case series and review of the literature. World J. Surg. Oncol. 13, 308. doi:10.1186/s12957-015-0723-2
Fan, J. Y., Ma, X., Li, W., Liu, P., Wang, J. J., Wang, H. B., et al. (2022b). Research progress on surface modification techniques of medical titanium alloys. J. Funct. Mater. 53 (7), 7027–7039.
Fang, T., Zhang, M., Yan, J., Zhao, J., Pan, W., Wang, X., et al. (2021). Comparative analysis of 3D-printed artificial vertebral body versus titanium mesh cage in repairing bone defects following single-level anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 27, e928022. doi:10.12659/MSM.928022
Fassina, L., Saino, E., Visai, L., Silvani, G., Cusella De Angelis, M. G., Mazzini, G., et al. (2008). Electromagnetic enhancement of a culture of human SAOS-2 osteoblasts seeded onto titanium fiber-mesh scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 87 (3), 750–759. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.31827
Faverani, L. P., Barão, V. A., Ramalho-Ferreira, G., Delben, J. A., Ferreira, M. B., Garcia Júnior, I. R., et al. (2014). The influence of bone quality on the biomechanical behavior of full-arch implant-supported fixed prostheses. C, Mater. Biol. Appl. 37, 164–170. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2014.01.013
Feng, D., He, J., Zhang, C., Wang, L., Gu, X., and Guo, Y. (2019). 3D-Printed prosthesis replacement for limb salvage after radical resection of an ameloblastoma in the tibia with 1 Year of follow up: a case report. Yonsei Med. J. 60 (9), 882–886. doi:10.3349/ymj.2019.60.9.882
Feng, Z., Duan, Y., Ma, L., Zheng, S., Li, M., Peng, M., et al. (2024). Microstructure and oxidation behavior of B Al layers on Ti-6Al-4V alloy by REO-boriding and aluminizing at 700 °C, 800 °C, and 900 °C. Surf. Coatings Technol. 487, 131044. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2024.131044
Fialka, C., Stampfl, P., Arbes, S., Reuter, P., Oberleitner, G., and Vécsei, V. (2008). Primary hemiarthroplasty in four-part fractures of the proximal humerus: randomized trial of two different implant systems. J. shoulder Elb. Surg. 17 (2), 210–215. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2007.07.002
Fogel, G., Martin, N., Lynch, K., Pelletier, M. H., Wills, D., Wang, T., et al. (2022). Subsidence and fusion performance of a 3D-printed porous interbody cage with stress-optimized body lattice and microporous endplates - a comprehensive mechanical and biological analysis. spine J. official J. North Am. Spine Soc. 22 (6), 1028–1037. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2022.01.003
Fuchs, B., Ossendorf, C., Leerapun, T., and Sim, F. H. (2008). Intercalary segmental reconstruction after bone tumor resection. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Surg. Oncol. Br. Assoc. Surg. Oncol. 34 (12), 1271–1276. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2007.11.010
Fujii, T., Murakami, R., Kobayashi, N., Tohgo, K., and Shimamura, Y. (2022). Uniform porous and functionally graded porous titanium fabricated via space holder technique with spark plasma sintering for biomedical applications. Adv. Powder Technol. 33, 103598. doi:10.1016/j.apt.2022.103598
Gao, Z., Long, N., Zhang, S., and Xiao, C. (2019). Research progress on the application of 3D printed implants in hip revision surgery. Chin. J. Jt. Surg. Electron. Ed. 13 (6), 731–735.
Gasik, M., Van Mellaert, L., Pierron, D., Braem, A., Hofmans, D., De Waelheyns, E., et al. (2012). Reduction of biofilm infection risks and promotion of osteointegration for optimized surfaces of titanium implants. Adv. Healthc. Mater 1 (1), 117–127. doi:10.1002/adhm.201100006
Gelse, K., Pöschl, E., and Aigner, T. (2003). Collagens-structure, function, and biosynthesis. Adv. drug Deliv. Rev. 55 (12), 1531–1546. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2003.08.002
Ghimire, A., Skelly, J. D., and Song, J. (2019). Micrococcal-nuclease-triggered on-demand release of vancomycin from intramedullary implant coating eradicates Staphylococcus aureus infection in mouse femoral canals. ACS central Sci. 5 (12), 1929–1936. doi:10.1021/acscentsci.9b00870
Girolami, M., Griffoni, C., Asunis, E., Falzetti, L., Bandiera, S., Barbanti Brodano, G., et al. (2022). Custom-made 3D-printed implants for anterior Column reconstruction in the upper cervical spine after intralesional extracapsular excision-report of 2 cases and literature review. J. Clin. Med. 11 (20), 6058. doi:10.3390/jcm11206058
Gittens, R. A., McLachlan, T., Olivares-Navarrete, R., Cai, Y., Berner, S., Tannenbaum, R., et al. (2011). The effects of combined micron-/submicron-scale surface roughness and nanoscale features on cell proliferation and differentiation. Biomaterials 32 (13), 3395–3403. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.01.029
Grigoryan, B., Paulsen, S. J., Corbett, D. C., Sazer, D. W., Fortin, C. L., Zaita, A. J., et al. (2019). Multivascular networks and functional intravascular topologies within biocompatible hydrogels. Sci. (New York, N.Y.) 364 (6439), 458–464. doi:10.1126/science.aav9750
Gwam, C. U., Mistry, J. B., Mohamed, N. S., Thomas, M., Bigart, K. C., Mont, M. A., et al. (2017). Current epidemiology of revision total hip arthroplasty in the United States: national inpatient sample 2009 to 2013. J. arthroplasty 32 (7), 2088–2092. doi:10.1016/j.arth.2017.02.046
Hadjidakis, D. J., and Androulakis, I. I. (2006). Bone remodeling. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1092, 385–396. doi:10.1196/annals.1365.035
Han, Q., Zhang, K., Zhang, Y., Wang, C., Yang, K., Zou, Y., et al. (2019). Individual resection and reconstruction of pelvic tumor with three-dimensional printed customized hemi-pelvic prosthesis: a case report. Medicine 98 (36), e16658. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000016658
Han, Y., Li, S., Cao, X., Yuan, L., Wang, Y., Yin, Y., et al. (2014). Different inhibitory effect and mechanism of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on normal cells and cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 4, 7134. doi:10.1038/srep07134
He, J., and Li, Z. (2018). Research progress on the osteoinductive properties of bone substitute materials. Oral Dis. Prev. Treat. 26 (2), 124–127.
Hollister, S. J. (2005). Porous scaffold design for tissue engineering. Nat. Mater. 4 (7), 518–524. doi:10.1038/nmat1421
Hori, N., Iwasa, F., Ueno, T., Takeuchi, K., Tsukimura, N., Yamada, M., et al. (2010). Selective cell affinity of biomimetic micro-nano-hybrid structured TiO2 overcomes the biological dilemma of osteoblasts. Dent. Mater. official Publ. Acad. Dent. Mater. 26 (4), 275–287. doi:10.1016/j.dental.2009.11.077
Howard, J. L., Kremers, H. M., Loechler, Y. A., Schleck, C. D., Harmsen, W. S., Berry, D. J., et al. (2011). Comparative survival of uncemented acetabular components following primary total hip arthroplasty. J. bone Jt. Surg. Am. volume 93 (17), 1597–1604. doi:10.2106/JBJS.J.00195
Hu, Q. S., Yang, J., Shen, B., Zhou, Z. K., Kang, P. D., Pei, F. X., et al. (2013). Application of cementless long stem prostheses in hip revision surgery. Chin. J. Jt. Surg. Electron. Ed. 7 (5), 615–621.
Hu, X., Kenan, S., Cheng, M., Cai, W., Huang, W., and Yan, W. (2022). 3D-Printed patient-customized artificial vertebral body for spinal reconstruction after total en bloc spondylectomy of complex multi-level spinal tumors. Int. J. bioprinting 8 (3), 576. doi:10.18063/ijb.v8i3.576
Huang, L., Cai, B., Huang, Y., Wang, J., Zhu, C., Shi, K., et al. (2021). Comparative study on 3D printed Ti6Al4V scaffolds with surface modifications using hydrothermal treatment and microarc oxidation to enhance osteogenic activity. ACS omega 6 (2), 1465–1476. doi:10.1021/acsomega.0c05191
Hussein, R. O., Northwood, D. O., and Nie, X. (2013). The effect of processing parameters and substrate composition on the corrosion resistance of plasma electrolytic oxidation (PEO) coated magnesium alloys. Surf. Coatings Technol. 237, 357–368. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2013.09.021
Inose, H., Hirai, T., Yoshii, T., Kimura, A., Takeshita, K., Inoue, H., et al. (2021). Predictors associated with neurological recovery after anterior decompression with fusion for degenerative cervical myelopathy. BMC Surg. 21 (1), 144. doi:10.1186/s12893-021-01147-w
Islam, M. T., Bulut, D., and Sharabidze, Z. (2025). Regenerative medicine in orthopaedic surgery: pioneering advances and their applications. EMJ Innov. doi:10.33590/emjinnov/FGDS3814
Itälä, A. I., Ylänen, H. O., Ekholm, C., Karlsson, K. H., and Aro, H. T. (2001). Pore diameter of more than 100 μm is not requisite for bone ingrowth in rabbits. J. Biomed. Mater Res. 58 (6), 679–683. doi:10.1002/jbm.1069
Izquierdo-Barba, I., Santos-Ruiz, L., Becerra, J., Feito, M. J., Fernández-Villa, D., Serrano, M. C., et al. (2019). Synergistic effect of Si-hydroxyapatite coating and VEGF adsorption on Ti6Al4V-ELI scaffolds for bone regeneration in an osteoporotic bone environment. Acta biomater. 83, 456–466. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2018.11.017
Jayasree, A., Ivanovski, S., and Gulati, K. (2021). ON or OFF: triggered therapies from anodized nano-engineered titanium implants. J. Control. release official J. Control. Release Soc. 333, 521–535. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.03.020
Ji, L. S., Wang, Y. P., Lu, T. S., Jia, Y. J., and Luo, C. S. (2022). 3D printed porous titanium alloy fusion cage and autologous iliac bone in the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 26 (18), 2817–2822.
Ji, T., Guo, W., Yang, R. L., Tang, X. D., and Wang, Y. F. (2013). Modular hemipelvic endoprosthesis reconstruction-experience in 100 patients with mid-term follow-up results. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Surg. Oncol. Br. Assoc. Surg. Oncol. 39 (1), 53–60. doi:10.1016/j.ejso.2012.10.002
Jianxin, W., Dan, L., Kun, L., Ning, X., Xiaojian, Y., and Orthopedics, D. O. (2019). Preparation and property analysis of drug-loaded sustained-release scaffold with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory roles. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res.
Jing, Z., Ni, R., Wang, J., Lin, X., Fan, D., Wei, Q., et al. (2021). Practical strategy to construct anti-osteosarcoma bone substitutes by loading cisplatin into 3D-printed titanium alloy implants using a thermosensitive hydrogel. Bioact. Mater. 6 (12), 4542–4557. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.05.007
Kandziora, F., Schollmeier, G., Scholz, M., Schaefer, J., Scholz, A., Schmidmaier, G., et al. (2002). Influence of cage design on interbody fusion in a sheep cervical spine model. J. Neurosurg. 96 (3 Suppl. l), 321–332. doi:10.3171/spi.2002.96.3.0321
Kapadia, B. H., Berg, R. A., Daley, J. A., Fritz, J., Bhave, A., and Mont, M. A. (2016). Periprosthetic joint infection. Lancet 387 (10016), 386–394. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61798-0
Kapat, K., Srivas, P. K., Rameshbabu, A. P., Maity, P. P., Jana, S., Dutta, J., et al. (2017). Influence of porosity and pore-size distribution in Ti6Al4 V foam on physicomechanical properties, osteogenesis, and quantitative validation of bone ingrowth by micro-computed tomography. ACS Appl. Mater. and interfaces 9 (45), 39235–39248. doi:10.1021/acsami.7b13960
Karim, L., and Judex, S. (2014). Low level irradiation in mice can lead to enhanced trabecular bone morphology. J. bone mineral metabolism 32 (5), 476–483. doi:10.1007/s00774-013-0518-x
Kazek-Kęsik, A., Nosol, A., Płonka, J., Śmiga-Matuszowicz, M., Gołda-Cępa, M., Krok-Borkowicz, M., et al. (2019). PLGA-amoxicillin-loaded layer formed on anodized Ti alloy as a hybrid material for dental implant applications. C, Mater. Biol. Appl. 94, 998–1008. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2018.10.049
Kenny, A. M., and Raisz, L. G. (2002). Mechanisms of bone remodeling: implications for clinical practice. J. reproductive Med. 47 (1 Suppl. l), 63–70.
Kettler, A., Wilke, H. J., and Claes, L. (2001). Effects of neck movements on stability and subsidence in cervical interbody fusion: an in vitro study. J. Neurosurg. 94 (1 Suppl. l), 97–107. doi:10.3171/spi.2001.94.1.0097
Kim, C. H., Chung, C. K., Jahng, T. A., Park, S. B., Sohn, S., and Lee, S. (2015). Segmental kyphosis after cervical interbody fusion with stand-alone polyetheretherketone (PEEK) cages: a comparative study on 2 different PEEK cages. J. spinal Disord. and Tech. 28 (1), E17–E24. doi:10.1097/BSD.0000000000000137
Kim, D., Lim, J. Y., Shim, K. W., Han, J. W., Yi, S., Yoon, D. H., et al. (2017). Sacral reconstruction with a 3D-printed implant after hemisacrectomy in a patient with sacral osteosarcoma: 1-year follow-up result. Yonsei Med. J. 58 (2), 453–457. doi:10.3349/ymj.2017.58.2.453
Kou, X. Y., and Tan, S. T. (2010). A simple and effective geometric representation for irregular porous structure modeling. Computer-Aided Des. 42 (10), 930–941. doi:10.1016/j.cad.2010.06.006
Kröger, H., Venesmaa, P., Jurvelin, J., Miettinen, H., Suomalainen, O., and Alhava, E. (1998). Bone density at the proximal femur after total hip arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 352 (352), 66–74. doi:10.1097/00003086-199807000-00009
Kumar, R., Kumar, M., and Chohan, J. S. (2021). The role of additive manufacturing for biomedical applications: a critical review. J. Manuf. Process. 64, 828–850. doi:10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.02.022
Kundu, B., Nandi, S. K., Dasgupta, S., Datta, S., Mukherjee, P., Roy, S., et al. (2011). Macro-to-micro porous special bioactive glass and ceftriaxone-sulbactam composite drug delivery system for treatment of chronic osteomyelitis: an investigation through in vitro and in vivo animal trial. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 22 (3), 705–720. doi:10.1007/s10856-010-4221-3
Kurtz, S., Ong, K., Lau, E., Mowat, F., and Halpern, M. (2007). Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J. bone Jt. Surg. Am. volume 89 (4), 780–785. doi:10.2106/JBJS.F.00222
Landham, P. R., Don, A. S., and Robertson, P. A. (2017). Do position and size matter? An analysis of cage and placement variables for optimum lordosis in PLIF reconstruction. Eur. spine J. official Publ. Eur. Spine Soc. Eur. Spinal Deformity Soc. Eur. Sect. Cerv. Spine Res. Soc. 26 (11), 2843–2850. doi:10.1007/s00586-017-5170-z
Lascano, S., Chávez-Vásconez, R., Muñoz-Rojas, D., Aristizabal, J., Arce, B., Parra, C., et al. (2020). Graphene-coated Ti-Nb-Ta-Mn foams: a promising approach towards a suitable biomaterial for bone replacement. Surf. and Coatings Technol. 401, 126250. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126250
Lederer, S., Arat, S., and Fuerbeth, W. (2021). Influence of process parameters on the tribological behavior of PEO coatings on CP-titanium 4+ alloys for biomedical applications. Mater. Basel, Switz. 14 (18), 5364. doi:10.3390/ma14185364
Lee, J. M., Sultan, M. T., Kim, S. H., Kumar, V., Yeon, Y. K., Lee, O. J., et al. (2017). Artificial auricular cartilage using silk fibroin and polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 18 (8), 1707. doi:10.3390/ijms18081707
Lee, S. C., Kwon, I. K., and Park, K. (2013). Hydrogels for delivery of bioactive agents: a historical perspective. Adv. drug Deliv. Rev. 65 (1), 17–20. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2012.07.015
Le Nihouannen, D., Komarova, S. V., Gbureck, U., and Barralet, J. E. (2008). Bioactivity of bone resorptive factor loaded on osteoconductive matrices: stability post-dehydration. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. official J. Arbeitsgemeinschaft fur Pharmazeutische Verfahrenstechnik e.V 70 (3), 813–818. doi:10.1016/j.ejpb.2008.07.018
Levine, B. (2008). A new era in porous metals: applications in orthopaedics. Adv. Eng. Mater. 10 (9), 788–792. doi:10.1002/adem.200800215
Li, C., and Zhou, Z. (2022). Preparation and characterization of permeability and mechanical properties of three-dimensional porous stainless steel. RSC Adv. 12 (43), 28079–28087. doi:10.1039/d2ra03893e
Li, C. S., Vannabouathong, C., Sprague, S., and Bhandari, M. (2015). The use of carbon-fiber-reinforced (CFR) PEEK material in orthopedic implants: a systematic review. Clin. Med. Insights Arthritis Musculoskelet. Disord. 8, CMAMD.S20354–45. doi:10.4137/CMAMD.S20354
Li, G., Ma, F., Liu, P., Qi, S., Li, W., Zhang, K., et al. (2023b). Review of micro-arc oxidation of titanium alloys: mechanism, properties, and applications. J. Alloys Compd. 948, 169773. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.169773
Li, H., Qu, X., Mao, Y., Dai, K., and Zhu, Z. (2016). Custom acetabular cages offer stable fixation and improved hip scores for revision THA with severe bone defects. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 474 (3), 731–740. doi:10.1007/s11999-015-4587-0
Li, H., Yao, B. B., Li, Z. H., Peng, Y., and Fan, H. (2023a). Compressive properties and deformation mechanism of selective laser melting of Ti6Al4V porous femoral implants based on topological optimization. Compos. Struct. 321, 117326. doi:10.1016/j.compstruct.2023.117326
Li, M., Liu, H., Zhang, Y. F., Di, Z. L., Zhang, J. H., He, Z. Y., et al. (2018). Preliminary follow-up results of autologous osteochondral transplantation combined with platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of knee cartilage defects. Chin. J. Bone Jt. Inj. 33(2): 138–140.
Li, S., Huan, Y., Zhu, B., Chen, H., Tang, M., Yan, Y., et al. (2021a). Research progress on the biological modifications of implant materials in 3D printed intervertebral fusion cages. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 33 (1), 2. doi:10.1007/s10856-021-06609-4
Li, X., Wang, Y., Zhao, Y., Liu, J., Xiao, S., and Mao, K. (2017). Multilevel 3D printing implant for reconstructing cervical spine with metastatic papillary thyroid carcinoma. Spine 42 (22), E1326–E1330. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000002229
Li, Y., Liu, Y., Bai, H., Li, R., Shang, J., Zhu, Z., et al. (2021c). Sustained release of VEGF to promote angiogenesis and osteointegration of three-dimensional printed biomimetic titanium alloy implants. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 9, 757767. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2021.757767
Li, Y., Zheng, G., Liu, T., Liang, Y., Huang, J., Liu, X., et al. (2020). Surgical resection of solitary bone plasmacytoma of atlas and reconstruction with 3-dimensional-printed titanium patient-specific implant. World Neurosurg. 139, 322–329. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2020.04.041
Li, Y. W., Wang, H. J., Cui, W., Li, C., Zhou, P., Xiao, W., et al. (2021b). Comparative efficacy of anterior cervical discectomy with 3D-printed microporous titanium alloy intervertebral fusion cages versus polyetheretherketone (PEEK) intervertebral fusion cages for the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Chin. J. Spine Spinal Cord 01, 16–24.
Liang, C., Liu, X., Yan, Y., Sun, R., Li, J., and Geng, W. (2022). Effectiveness and mechanisms of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on osseointegration of dental implants and biological functions of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem cells Int. 2022, 1–16. doi:10.1155/2022/7397335
Liang, H., Ji, T., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y., and Guo, W. (2017). Reconstruction with 3D-printed pelvic endoprostheses after resection of a pelvic tumour. bone and Jt. J. 99-B (2), 267–275. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.99B2.BJJ-2016-0654.R1
Liang, H., Yang, Y., Xie, D., Li, L., Mao, N., Wang, C., et al. (2019). Trabecular-like Ti-6Al-4V scaffolds for orthopedic: fabrication by selective laser melting and in vitro biocompatibility. J. Mater. Sci. and Technol. 35 (7), 1284–1297. doi:10.1016/j.jmst.2019.01.012
Liu, B., Xu, W., Chen, M., Chen, D., Sun, G., Zhang, C., et al. (2022a). Structural design and finite element simulation analysis of grade 3 graded porous titanium implant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (17), 10090. doi:10.3390/ijms231710090
Liu, B. D., Guo, Z., Hao, Y. L., Li, S. J., Wang, C. R., Yuan, C. F., et al. (2012). Effect of pore sizes of porous titanium alloys as bone materials on bone formation. Prog. Mod. Biomed. 12 (9), 1601–1604.
Liu, C., Zhang, K., and Yang, B. (2022b). Mid-term efficacy of standardized 3D-printed porous titanium alloy acetabular cups in total hip arthroplasty. J. Army Med. Univ. 15, 1538–1541. doi:10.16016/j.2097-0927.202203044
Liu, F., Zhang, D. Z., Zhang, P., Zhao, M., and Jafar, S. (2018). Mechanical properties of optimized diamond lattice structure for bone scaffolds fabricated via selective laser melting. Mater. Basel, Switz. 11 (3), 374. doi:10.3390/ma11030374
Liu, W., Shao, Z., Rai, S., Hu, B., Wu, Q., Hu, H., et al. (2020). Three-dimensional-printed intercalary prosthesis for the reconstruction of large bone defect after joint-preserving tumor resection. J. Surg. Oncol. 121 (3), 570–577. doi:10.1002/jso.25826
Liu, Y., Enggist, L., Kuffer, A. F., Buser, D., and Hunziker, E. B. (2007). The influence of BMP-2 and its mode of delivery on the osteoconductivity of implant surfaces during the early phase of osseointegration. Biomaterials 28 (16), 2677–2686. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.02.003
Liu, Y. J., Wang, H. L., Li, S. J., Wang, S. G., Wang, W. J., Hou, W. T., et al. (2017). Compressive and fatigue behavior of beta-type titanium porous structures fabricated by electron beam melting. Acta Mater. 126, 58–66. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2016.12.052
Liu, Z., Xu, Z., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Wu, Y., Jiang, D., et al. (2022c). Construction and osteogenic effects of 3D-printed porous titanium alloy loaded with VEGF/BMP-2 shell-core microspheres in a sustained-release system. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 1028278. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.1028278
Liu, Z. P., Wang, Y. H., Zhang, Y. L., Ming, Y., Sun, Z. J., and Sun, H. (2021). Half-year follow-up of cervical curvature and intervertebral height recovery after treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy with 3D-printed intervertebral fusion cages. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 06, 849–853.
Lohmann, C. H., Meyer, H., Nuechtern, J. V., Singh, G., Junk-Jantsch, S., Schmotzer, H., et al. (2013). Periprosthetic tissue metal content but not serum metal content predicts the type of tissue response in failed small-diameter metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasties. J. bone Jt. Surg. Am. volume 95 (17), 1561–1568. doi:10.2106/JBJS.L.01273
Losic, D. (2021). Advancing of titanium medical implants by surface engineering: recent progress and challenges. Expert Opin. drug Deliv. 18 (10), 1355–1378. doi:10.1080/17425247.2021.1928071
Lu, M., Li, Y., Luo, Y., Zhang, W., Zhou, Y., and Tu, C. (2018). Uncemented three-dimensional-printed prosthetic reconstruction for massive bone defects of the proximal tibia. World J. Surg. Oncol. 16 (1), 47. doi:10.1186/s12957-018-1333-6
Lu, M., Wang, J., Tang, F., Min, L., Zhou, Y., Zhang, W., et al. (2019). A three-dimensional printed porous implant combined with bone grafting following curettage of a subchondral giant cell tumour of the proximal tibia: a case report. BMC Surg. 19 (1), 29. doi:10.1186/s12893-019-0491-y
Luo, J., Wu, Z., Dai, Y., Wang, X., Ye, R., Huang, H., et al. (2021). Biofunctional micro/nanostructured “volcano-like” layer-coated 3D porous Ti-10Ta-2Nb-2Zr scaffolds improve osteogenesis and osseointegration for dental implants in vitro and in vivo. Surf. and Coatings Technol. 427, 127852. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2021.127852
Luo, W., Huang, L., Liu, H., Qu, W., Zhao, X., Wang, C., et al. (2017). Customized knee prosthesis in treatment of giant cell tumors of the proximal tibia: application of 3-dimensional printing technology in surgical design. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 23, 1691–1700. doi:10.12659/msm.901436
Lutz, R., Srour, S., Nonhoff, J., Weisel, T., Damien, C. J., and Schlegel, K. A. (2010). Biofunctionalization of titanium implants with a biomimetic active peptide (P-15) promotes early osseointegration. Clin. oral implants Res. 21 (7), 726–734. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0501.2009.01904.x
Lv, J., Xiu, P., Tan, J., Jia, Z., Cai, H., and Liu, Z. (2015). Enhanced angiogenesis and osteogenesis in critical bone defects by the controlled release of BMP-2 and VEGF: implantation of electron beam melting-fabricated porous Ti6Al4V scaffolds incorporating growth factor-doped fibrin glue. Biomed. Mater. Bristol, Engl. 10 (3), 035013. doi:10.1088/1748-6041/10/3/035013
Lv, X., Zhang, J., Yang, D., Shao, J., Wang, W., Zhang, Q., et al. (2020). Recent advances in pH-responsive nanomaterials for anti-infective therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 8 (47), 10700–10711. doi:10.1039/d0tb02177f
Macák, D., Džupa, V., and Krbec, M. (2021). Custom-made 3D printed titanium acetabular component: advantages and limits of use. Acta Chir. Orthop. traumatologiae Cechoslov. 88 (1), 69–74. doi:10.55095/achot2021/012
MacBarb, R. F., Lindsey, D. P., Bahney, C. S., Woods, S. A., Wolfe, M. L., and Yerby, S. A. (2017). Fortifying the bone-implant interface Part 1: an in vitro evaluation of 3D-printed and TPS porous surfaces. Int. J. spine Surg. 11 (3), 15. doi:10.14444/4015
Maksoud, F. J., Velázquez de la Paz, M. F., Hann, A. J., Thanarak, J., Reilly, G. C., Claeyssens, F., et al. (2022). Porous biomaterials for tissue engineering: a review. J. Mater. Chem. 10 (40), 8111–8165. doi:10.1039/d1tb02628c
Mao, Y. R., Sun, J. M., Zhou, X., Lian, X. K., Yang, W. Z., Deng, Y., et al. (2021). Medical special polymer polyether ether ketone implants and their surface interface engineering. Acta Polym. Sin. 34 (2), 144–160.
Mao, Y., Xu, C., Xu, J., Li, H., Liu, F., Yu, D., et al. (2015). The use of customized cages in revision total hip arthroplasty for Paprosky type III acetabular bone defects. Int. Orthop. 39 (10), 2023–2030. doi:10.1007/s00264-015-2965-6
Marcomini, J. B., Baptista, C. A., Pascon, J. P., Teixeira, R. L., and Reis, F. P. (2014). Investigation of a fatigue failure in a stainless steel femoral plate. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater 38, 52–58. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2014.06.011
Maresca, J. A., DeMel, D. C., Wagner, G. A., Haase, C., and Geibel, J. P. (2023). Three-dimensional bioprinting applications for bone tissue engineering. Cells 12 (9), 1230. doi:10.3390/cells12091230
Mazare, A., Park, J., Simons, S., Mohajernia, S., Hwang, I., Yoo, J. E., et al. (2019). Black TiO2 nanotubes: efficient electrodes for triggering electric field-induced stimulation of stem cell growth. Acta biomater. 97, 681–688. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2019.08.021
Mendonça, G., Mendonça, D. B., Aragão, F. J., and Cooper, L. F. (2008). Advancing dental implant surface technology-from micron-to nanotopography. Biomaterials 29 (28), 3822–3835. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2008.05.012
Mochi, F., Scatena, E., Rodriguez, D., Ginebra, M. P., and Del Gaudio, C. (2022). Scaffold-based bone tissue engineering in microgravity: potential, concerns and implications. NPJ microgravity 8 (1), 45. doi:10.1038/s41526-022-00236-1
Molinari, A., Klarin, J., Johansson, F., Benedetti, M., Fontanari, V., Magalini, E., et al. (2018). Mechanical properties of porous structures produced by selective laser melting of a Ti6Al4V alloy powder. J. Jpn. Soc. Powder Powder Metallurgy 65 (8), 481–485. doi:10.2497/jjspm.65.481
Nauth, A., Schemitsch, E., Norris, B., Nollin, Z., and Watson, J. T. (2018). Critical-size bone defects: is there a consensus for diagnosis and treatment? J. Orthop. Trauma 32, S7–S11. doi:10.1097/BOT.0000000000001115
Niinomi, M. (2003). Recent research and development in titanium alloys for biomedical applications and healthcare goods. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 4 (5), 445–454. doi:10.1016/j.stam.2003.09.002
Niinomi, M., and Nakai, M. (2011). Titanium-based biomaterials for preventing stress shielding between implant devices and bone. Int. J. biomaterials 2011, 1–10. doi:10.1155/2011/836587
Ning, C., Jiajia, J., Meng, L., Hongfei, Q., Xianglong, W., and Tingli, L. (2019). Electrophoretic deposition of GHK-Cu loaded MSN-chitosan coatings with pH-responsive release of copper and its bioactivity. C, Mater. Biol. Appl. 104, 109746. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2019.109746
Nune, K. C., Li, S., and Misra, R. D. K. (2018). Advancements in three-dimensional titanium alloy mesh scaffolds fabricated by electron beam melting for biomedical devices: mechanical and biological aspects. Sci. China Mater. 61, 455–474. doi:10.1007/s40843-017-9134-x
Nune, K. C., Misra, R. D., Gaytan, S. M., and Murr, L. E. (2015). Interplay between cellular activity and three-dimensional scaffold-cell constructs with different foam structure processed by electron beam melting. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. part A 103 (5), 1677–1692. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.35307
Orapiriyakul, W., Young, P. S., Damiati, L., and Tsimbouri, P. M. (2018). Antibacterial surface modification of titanium implants in orthopaedics. J. tissue Eng. 9, 2041731418789838. doi:10.1177/2041731418789838
Orth, M., Fritz, T., Stutz, J., Scheuer, C., Ganse, B., Bullinger, Y., et al. (2022). Local application of mineral-coated microparticles loaded with VEGF and BMP-2 induces the healing of murine atrophic non-unions. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 9, 809397. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2021.809397
Otani, K., Kikuchi, S., Yabuki, S., Igarashi, T., Nikaido, T., Watanabe, K., et al. (2013). Lumbar spinal stenosis has a negative impact on quality of life compared with other comorbidities: an epidemiological cross-sectional study of 1862 community-dwelling individuals. TheScientificWorldJournal 2013, 590652. doi:10.1155/2013/590652
Ouyang, W., Xu, Z., Chao, Y., Liu, Y., Luo, W., Jiao, J., et al. (2022). Effect of electrostatic field on microstructure and mechanical properties of the 316L stainless steel modified layer fabricated by laser cladding. Mater. Charact. 191, 112123. doi:10.1016/j.matchar.2022.112123
Owen, D. H., Russell, N. C., Smith, P. N., and Walter, W. L. (2014). An estimation of the incidence of squeaking and revision surgery for squeaking in ceramic-on-ceramic total hip replacement: a meta-analysis and report from the Australian Orthopaedic Association National Joint Registry. bone and Jt. J. 96-B (2), 181–187. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.96B2.32784
Pal, K., Banthia, A. K., and Majumdar, D. K. (2014). Hydrogels for biomedical applications: a short review. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 25 (9), 2215. doi:10.1007/s10856-007-3145-z
Pala, E., Trovarelli, G., Calabrò, T., Angelini, A., Abati, C. N., and Ruggieri, P. (2015). Survival of modern knee tumor megaprostheses: failures, functional results, and a comparative statistical analysis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 473 (3), 891–899. doi:10.1007/s11999-014-3699-2
Pan, C. T., Hsu, W. H., Cheng, Y. S., Wen, Z. H., and Chen, W. F. (2021a). A new design of porosity gradient Ti-6Al-4V encapsulated hydroxyapatite dual materials composite scaffold for bone defects. Micromachines 12 (11), 1294. doi:10.3390/mi12111294
Pan, C. T., Lin, C. H., Huang, Y. K., Jang, J. S. C., Lin, H. K., Kuo, C. N., et al. (2021b). Design of customize interbody fusion cages of Ti64ELI with gradient porosity by selective laser melting process. Micromachines 12 (3), 307. doi:10.3390/mi12030307
Papaefstathiou, S., Larochette, N., Liste, R. M. V., Potier, E., Petite, H., Vivace, B. J., et al. (2022). Three-dimensional printing of biomimetic titanium mimicking trabecular bone induces human mesenchymal stem cell proliferation: an in-vitro analysis. Spine 47 (14), 1027–1035. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000004317
Parent, M., Magnaudeix, A., Delebassée, S., Sarre, E., Champion, E., Viana Trecant, M., et al. (2016). Hydroxyapatite microporous bioceramics as vancomycin reservoir: antibacterial efficiency and biocompatibility investigation. J. biomaterials Appl. 31 (4), 488–498. doi:10.1177/0885328216653108
Park, J., Mazare, A., Schneider, H., von der Mark, K., Fischer, M. J., and Schmuki, P. (2016). Electric field-induced osteogenic differentiation on TiO2Nanotubular layer. Methods 22 (8), 809–821. doi:10.1089/ten.TEC.2016.0182
Park, J. W., Kang, H. G., Kim, J. H., and Kim, H. S. (2021). The application of 3D-printing technology in pelvic bone tumor surgery. J. Orthop. Sci. official J. Jpn. Orthop. Assoc. 26 (2), 276–283. doi:10.1016/j.jos.2020.03.004
Park, J. W., Kang, H. G., Lim, K. M., Kim, J. H., and Kim, H. S. (2018). Three-dimensionally printed personalized implant design and reconstructive surgery for a bone tumor of the calcaneus: a case report. JBJS case Connect. 8 (2), e25. doi:10.2106/JBJS.CC.17.00212
Partridge, L., Deelen, J., and Slagboom, P. E. (2018). Facing up to the global challenges of ageing. Nature 561 (7721), 45–56. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0457-8
Perera, K., Ivone, R., Natekin, E., Wilga, C. A., Shen, J., and Menon, J. U. (2021). 3D bioprinted implants for cartilage repair in intervertebral discs and knee menisci. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 9, 754113. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2021.754113
Pobloth, A. M., Checa, S., Razi, H., Petersen, A., Weaver, J. C., Schmidt-Bleek, K., et al. (2018). Mechanobiologically optimized 3D titanium-mesh scaffolds enhance bone regeneration in critical segmental defects in sheep. Sci. Transl. Med. 10 (423), eaam8828. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aam8828
Potyondy, T., Uquillas, J. A., Tebon, P. J., Byambaa, B., Hasan, A., Tavafoghi, M., et al. (2021). Recent advances in 3D bioprinting of musculoskeletal tissues. Biofabrication 13 (2), 022001. doi:10.1088/1758-5090/abc8de
Qi, J. (2022). Research on the design and key technologies of controllable 3D porous intervertebral fusion cages. Hangzhou: Hangzhou Dianzi University.
Raffa, M. L., Nguyen, V. H., Hernigou, P., Flouzat-Lachaniette, C. H., and Haiat, G. (2021). Stress shielding at the bone-implant interface: influence of surface roughness and of the bone-implant contact ratio. J. Orthop. Res. official Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 39 (6), 1174–1183. doi:10.1002/jor.24840
Rafieerad, A. R., Ashra, M. R., Mahmoodian, R., and Bushroa, A. R. (2015). Surface characterization and corrosion behavior of calcium phosphate-base composite layer on titanium and its alloys via plasma electrolytic oxidation: a review paper. C, Mater. Biol. Appl. 57, 397–413. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2015.07.058
Rakoch, A. G., Khokhlov, V. V., Bautin, V. A., Lebedeva, N. A., Magurova, Y. V., and Bardin, I. V. (2006). Model concepts on the mechanism of microarc oxidation of metal materials and the control over this process. Prot. Met. 42, 158–169. doi:10.1134/S003317320602010X
Ran, Q., Yang, W., Hu, Y., Shen, X., Yu, Y., Xiang, Y., et al. (2018). Osteogenesis of 3D printed porous Ti6Al4V implants with different pore sizes. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 84, 1–11. doi:10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.04.010
Rapuano, B. E., Lee, J. J., and MacDonald, D. E. (2012). Titanium alloy surface oxide modulates the conformation of adsorbed fibronectin to enhance its binding to α5β1 integrins in osteoblasts. Eur. J. oral Sci. 120 (3), 185–194. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0722.2012.954.x
Reuther, F., Mühlhäusler, B., Wahl, D., and Nijs, S. (2010). Functional outcome of shoulder hemiarthroplasty for fractures: a multicentre analysis. Injury 41 (6), 606–612. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2009.11.019
Rho, J. Y., Ashman, R. B., and Turner, C. H. (1993). Young's modulus of trabecular and cortical bone material: ultrasonic and microtensile measurements. J. biomechanics 26 (2), 111–119. doi:10.1016/0021-9290(93)90042-d
Rudnicka, E., Napierała, P., Podfigurna, A., Męczekalski, B., Smolarczyk, R., and Grymowicz, M. (2020). The World Health Organization (WHO) approach to healthy ageing. Maturitas 139, 6–11. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.05.018
Safari-Gezaz, M., Parhizkar, M., and Asghari, E. (2025). Effect of cobalt ions doping on morphology and electrochemical properties of hydroxyapatite coatings for biomedical applications. Sci. Rep. 15, 149. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-84055-2
Saha, S., Pramanik, K., and Biswas, A. (2019). Silk fibroin coated TiO2 nanotubes for improved osteogenic property of Ti6Al4V bone implants. C, Mater. Biol. Appl. 105, 109982. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2019.109982
Schaaf, H., Lendeckel, S., Howaldt, H. P., and Streckbein, P. (2010). Donor site morbidity after bone harvesting from the anterior iliac crest. Oral Surg. oral Med. oral pathology, oral radiology, Endod. 109 (1), 52–58. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2009.08.023
Schmidt-Stein, F., Hahn, R., Gnichwitz, J.-F., Song, Y. Y., Shrestha, N. K., Hirsch, A., et al. (2009). X-ray induced photocatalysis on TiO2 and TiO2 nanotubes: degradation of organics and drug release. Electrochem. Commun. 11 (11), 2077–2080. doi:10.1016/j.elecom.2009.08.036
Schorn, L., Sproll, C., Ommerborn, M., Naujoks, C., Kübler, N. R., and Depprich, R. (2017). Vertical bone regeneration using rhBMP-2 and VEGF. Head and face Med. 13 (1), 11. doi:10.1186/s13005-017-0146-0
She, C., Shi, G. L., Xu, W., Zhou, X. Z., Li, J., Tian, Y., et al. (2016). Effect of low-dose X-ray irradiation and Ti particles on the osseointegration of prosthetic. J. Orthop. Res. official Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 34 (10), 1688–1696. doi:10.1002/jor.23179
Shen, J., Xu, S., Xu, S., and Hao, J. (2018). Fusion or not for degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Pain physician 1, 1–8. doi:10.36076/ppj.2018.1.1
Sheng, X., Wang, A., Wang, Z., Liu, H., Wang, J., and Li, C. (2022). Advanced surface modification for 3D-printed titanium alloy implant interface functionalization. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 850110. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.850110
Shi, X. L., Liu, Q. G., Zhang, H., Tian, Y., Yang, Y. M., Yuan, W. D., et al. (2014). Reconstruction of injured vertebrae with different bone grafting materials for the repair of burst fractures of the thoracolumbar spine: verification of bone graft healing. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 18 (39), 6233–6239.
Shokuhfar, T., Hamlekhan, A., Chang, J. Y., Choi, C. K., Sukotjo, C., and Friedrich, C. (2014). Biophysical evaluation of cells on nanotubular surfaces: the effects of atomic ordering and chemistry. Int. J. nanomedicine 9, 3737–3748. doi:10.2147/IJN.S67344
Siu, T. L., Rogers, J. M., Lin, K., Thompson, R., and Owbridge, M. (2018). Custom-made titanium 3-dimensional printed interbody cages for treatment of osteoporotic fracture-related spinal deformity. World Neurosurg. 111, 1–5. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2017.11.160
Sobolev, A., Valkov, A., Kossenko, A., Wolicki, I., Zinigrad, M., and Borodianskiy, K. (2019). Bioactive coating on Ti alloy with high osseointegration and antibacterial Ag nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. and interfaces 11 (43), 39534–39544. doi:10.1021/acsami.9b13849
Song, J. L., and Li, Y. T. (2010). Research progress of laser cladding forming technology. J. Mech. Eng. 14, 000.
Song, Y. Y., Schmidt-Stein, F., Bauer, S., and Schmuki, P. (2009). Amphiphilic TiO2 nanotube arrays: an actively controllable drug delivery system. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131 (12), 4230–4232. doi:10.1021/ja810130h
Spetzger, U., Frasca, M., and König, S. A. (2016). Surgical planning, manufacturing and implantation of an individualized cervical fusion titanium cage using patient-specific data. Eur. spine J. official Publ. Eur. Spine Soc. Eur. Spinal Deformity Soc. Eur. Sect. Cerv. Spine Res. Soc. 25 (7), 2239–2246. doi:10.1007/s00586-016-4473-9
Spriano, S., Yamaguchi, S., Baino, F., and Ferraris, S. (2018). A critical review of multifunctional titanium surfaces: new frontiers for improving osseointegration and host response, avoiding bacteria contamination. Acta Biomater. 79, 1–22. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2018.08.013
Sun, C. W., Lau, L. C., Cheung, J. P., and Choi, S. W. (2024). The potential carcinogenicity of orthopaedic implants - a scoping review. BMC Cancer 24, 1519. doi:10.1186/s12885-024-13279-2
Sun, Z., Yin, M., Sun, Y., Cheng, M., Fang, M., Huang, W., et al. (2022). Customized multilevel 3D printing implant for reconstructing spine tumor: a retrospective case series study in a single center. Orthop. Surg. 14 (9), 2016–2022. doi:10.1111/os.13357
Surmeneva, M. A., Khrapov, D., Prosolov, K., Kozadaeva, M., Koptyug, A., Volkova, A., et al. (2022). The influence of chemical etching on porous structure and mechanical properties of the Ti6AL4V functionally graded porous scaffolds fabricated by EBM. Mater. Chem. Phys. 275, 125217. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2021.125217
Tajbakhsh, S., and Hajiali, F. (2017). A comprehensive study on the fabrication and properties of biocomposites of poly(lactic acid)/ceramics for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci. Eng. C Mater Biol. Appl. 70 (Pt 1), 897–912. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2016.09.008
Tan, J., Gemeinhart, R. A., Ma, M., and Saltzman, W. M. (2005). Improved cell adhesion and proliferation on synthetic phosphonic acid-containing hydrogels. Biomaterials 26 (17), 3663–3671. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.09.053
Tan, J., Yang, N., Fu, X., Cui, Y., Guo, Q., Ma, T., et al. (2015). Single-dose local simvastatin injection improves implant fixation via increased angiogenesis and bone formation in an ovariectomized rat model. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 21, 1428–1439. doi:10.12659/MSM.892247
Tang, X., Yang, Y., Zang, J., Du, Z., Yan, T., Yang, R., et al. (2021). Preliminary results of a 3D-printed modular vertebral prosthesis for anterior column reconstruction after multilevel thoracolumbar total en bloc spondylectomy. Orthop. Surg. 13 (3), 949–957. doi:10.1111/os.12975
Taniguchi, N., Fujibayashi, S., Takemoto, M., Sasaki, K., Otsuki, B., Nakamura, T., et al. (2016). Effect of pore size on bone ingrowth into porous titanium implants fabricated by additive manufacturing: an in vivo experiment. C, Mater. Biol. Appl. 59, 690–701. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2015.10.069
Tao, B., Deng, Y., Song, L., Ma, W., Qian, Y., Lin, C., et al. (2019). BMP2-loaded titania nanotubes coating with pH-responsive multilayers for bacterial infections inhibition and osteogenic activity improvement. Colloids surfaces. B, Biointerfaces 177, 242–252. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.02.014
Thayaparan, G. K., Owbridge, M. G., Thompson, R. G., and D'Urso, P. S. (2019). Designing patient-specific solutions using biomodelling and 3D-printing for revision lumbar spine surgery. Eur. spine J. official Publ. Eur. Spine Soc. Eur. Spinal Deformity Soc. Eur. Sect. Cerv. Spine Res. Soc. 28 (Suppl. 2), 18–24. doi:10.1007/s00586-018-5684-z
Thomsen, J. S., Laib, A., Koller, B., Prohaska, S., Mosekilde, L., and Gowin, W. (2005). Stereological measures of trabecular bone structure: comparison of 3D micro computed tomography with 2D histological sections in human proximal tibial bone biopsies. J. Microsc. 218 (Pt 2), 171–179. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2818.2005.01469.x
Tian, C., Zhang, J., Gu, J., Li, W., and Cao, Y. (2022). Light controlled biomaterials for regulating cell migration and differentiation. Smart Mater. Med. 3, 209–216. doi:10.1016/j.smaim.2022.01.005
Tibbitt, M. W., and Anseth, K. S. (2009). Hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics for 3D cell culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 103 (4), 655–663. doi:10.1002/bit.22361
Tibbitt, M. W., Rodell, C. B., Burdick, J. A., and Anseth, K. S. (2015). Progress in material design for biomedical applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112 (47), 14444–14451. doi:10.1073/pnas.1516247112
Tsai, P. I., Wu, M. H., Li, Y. Y., Lin, T. H., Tsai, J. S. C., Huang, H. I., et al. (2021). Additive-manufactured Ti-6Al-4 V/Polyetheretherketone composite porous cage for Interbody fusion: bone growth and biocompatibility evaluation in a porcine model. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 22 (1), 171. doi:10.1186/s12891-021-04022-0
Uhthoff, H. K., Poitras, P., and Backman, D. S. (2006). Internal plate fixation of fractures: short history and recent developments. J. Orthop. Sci. 11 (2), 118–126. doi:10.1007/s00776-005-0984-7
Ulrich, S. D., Seyler, T. M., Bennett, D., Delanois, R. E., Saleh, K. J., Thongtrangan, I., et al. (2008). Total hip arthroplasties: what are the reasons for revision? Int. Orthop. 32 (5), 597–604. doi:10.1007/s00264-007-0364-3
Uzair, U., Benza, D., Behrend, C. J., and Anker, J. N. (2019). Noninvasively imaging pH at the surface of implanted orthopedic devices with X-ray excited luminescence chemical imaging. ACS sensors 4 (9), 2367–2374. doi:10.1021/acssensors.9b00962
Van Bael, S., Chai, Y. C., Truscello, S., Moesen, M., Kerckhofs, G., Van Oosterwyck, H., et al. (2012). The effect of pore geometry on the in vitro biological behavior of human periosteum-derived cells seeded on selective laser-melted Ti6Al4V bone scaffolds. Acta biomater. 8 (7), 2824–2834. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2012.04.001
van Oosten, M., Schäfer, T., Gazendam, J. A., Ohlsen, K., Tsompanidou, E., de Goffau, M. C., et al. (2013). Real-time in vivo imaging of invasive- and biomaterial-associated bacterial infections using fluorescently labelled vancomycin. Nat. Commun. 4, 2584. doi:10.1038/ncomms3584
Velásquez-García, L. F., and Kornbluth, Y. (2021). Biomedical applications of metal 3D printing. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 23, 307–338. doi:10.1146/annurev-bioeng-082020-032402
Vidal, E., Guillem-Marti, J., Ginebra, M.-P., Combes, C., Ruperez, E., and Rodriguez, D. (2021). Multifunctional homogeneous calcium phosphate coatings: toward antibacterial and cell adhesive titanium scaffolds. Surf. and Coatings Technol. 405, 126557. doi:10.1016/j.surfcoat.2020.126557
Villegas, M., Zhang, Y., Badv, M., Alonso-Cantu, C., Wilson, D., Hosseinidoust, Z., et al. (2022). Enhancing osseointegration and mitigating bacterial biofilms on medical-grade titanium with chitosan-conjugated liquid-infused coatings. Sci. Rep. 12 (1), 5380. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-09378-4
Wan, Z., Zhang, P., Liu, Y., Lv, L., and Zhou, Y. (2020). Four-dimensional bioprinting: current developments and applications in bone tissue engineering. Acta biomater. 101, 26–42. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2019.10.038
Wang, C., Wu, J., Liu, L., Xu, D., Liu, Y., Li, S., et al. (2023a). Improving osteoinduction and osteogenesis of Ti6Al4V alloy porous scaffold by regulating the pore structure. Front. Chem. 11, 1190630. doi:10.3389/fchem.2023.1190630
Wang, D., He, G., Tian, Y., Ren, N., Liu, W., and Zhang, X. (2020a). Dual effects of acid etching on cell responses and mechanical properties of porous titanium with controllable open-porous structure. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B, Appl. biomaterials 108 (6), 2386–2395. doi:10.1002/jbm.b.34571
Wang, D., Zhu, Y., Qu, G., and Zhou, X. (2021c). Research on dilution of laser cladding assisted by pulsed current based on orthogonal experiment. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1965 (1), 012087. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/1965/1/012087
Wang, F., Zhang, C., Zhou, Y. Y., and Li, K. (2017b). Current status of surface coating technology research. Hot Work. Technol. 46 (10), 21–24+29.
Wang, J., An, J., Lu, M., Zhang, Y., Lin, J., Luo, Y., et al. (2021b). Is three-dimensional-printed custom-made ultra-short stem with a porous structure an acceptable reconstructive alternative in peri-knee metaphysis for the tumorous bone defect? World J. Surg. Oncol. 19 (1), 235. doi:10.1186/s12957-021-02355-7
Wang, J., Liu, M., Yang, C., Pan, Y., Ji, S., Han, N., et al. (2024a). Biomaterials for bone defect repair: types, mechanisms and effects. Int. J. Artif. organs 47 (2), 75–84. doi:10.1177/03913988231218884
Wang, S., Wang, L., Liu, Y., Ren, Y., Jiang, L., Li, Y., et al. (2017a). 3D printing technology used in severe hip deformity. Exp. Ther. Med. 14 (3), 2595–2599. doi:10.3892/etm.2017.4799
Wang, T., Liu, X., Zhu, Y., Cui, Z. D., Yang, X. J., Pan, H., et al. (2017c). Metal ion coordination polymer-capped pH-triggered drug release system on titania nanotubes for enhancing self-antibacterial capability of Ti implants. ACS biomaterials Sci. and Eng. 3 (5), 816–825. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.7b00103
Wang, W., An, J., Lu, M., He, X., Li, Z., Wang, Y., et al. (2025). 3D-Printed talus-calcaneus prosthesis in treating Ewing's sarcoma: a case report. Orthop. Surg. 17 (2), 288–294. doi:10.1111/os.14279
Wang, X., Li, Y., Hodgson, P. D., and Wen, C. (2010). Biomimetic modification of porous TiNbZr alloy scaffold for bone tissue engineering. Part A 16 (1), 309–316. doi:10.1089/ten.TEA.2009.0074
Wang, X., Zhong, X., Gong, F., Chao, Y., and Cheng, L. (2020b). Newly developed strategies for improving sonodynamic therapy. Mater. Horizons 7 (8), 2028–2046. doi:10.1039/d0mh00613k
Wang, Y., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y., Zhang, H., Sun, H., Hao, D., et al. (2021a). One-stage posterior en-bloc spondylectomy following reconstruction with individualized 3D printed artificial vertebrae for multi-segment thoracolumbar metastases: case report and literature review. Am. J. Transl. Res. 13 (1), 115–123.
Wang, Y. J., Zhou, Y. J., Wang, Y., Hao, Y. P., and Zhang, B. W. (2023b). Application of 3D printed porous titanium alloy intervertebral fusion cages in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion for the treatment of cervical spondylosis. Chin. J. Bone Jt. Inj. 01, 1–5.
Wang, Z., Niu, Y., Tian, X., Yu, N., Yin, X., Xing, Z., et al. (2024b). Switching on and off macrophages by a “Bridge-Burning” coating improves bone-implant integration under osteoporosis. Adv. Funct. Mater. doi:10.1002/adfm.202421243
Weber, F. E. (2019). Reconsidering osteoconduction in the era of additive manufacturing. Tissue Eng. Part B, Rev. 25 (5), 375–386. doi:10.1089/ten.TEB.2019.0047
Wei, F., Li, Z., Liu, Z., Liu, X., Jiang, L., Yu, M., et al. (2020). Upper cervical spine reconstruction using customized 3D-printed vertebral body in 9 patients with primary tumors involving C2. Ann. Transl. Med. 8 (6), 332. doi:10.21037/atm.2020.03.32
Wei, X., Tang, Z., Wu, H., Zuo, X., Dong, H., Tan, L., et al. (2021). Biofunctional magnesium-coated Ti6Al4V scaffolds promote autophagy-dependent apoptosis in osteosarcoma by activating the AMPK/mTOR/ULK1 signaling pathway. Mater. today 12, 100147. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2021.100147
Wen, X., Liu, Y., Xi, F., Zhang, X., and Kang, Y. (2023). Micro-arc oxidation (MAO) and its potential for improving the performance of titanium implants in biomedical applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11, 1282590. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2023.1282590
Weng, W. J., Zhuang, J. J., Lin, S. Y., Dong, L. Q., and Cheng, K. (2017). Research progress on electrochemical deposition of biofunctional coatings. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 45 (11), 1539–1547. doi:10.14062/j.issn.0454-5648.2017.11.01
Weng, X., Liao, Q., Li, X., and Wang, J. (2016). Zhong nan da xue xue bao. Yi xue ban = Journal of Central South University. Med. Sci. 41 (1), 83–87. doi:10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2016.01.013
Wu, H., and Guo, Z. (2020). 3D-printed porous titanium and tantalum orthopedic implants: a performance comparison and future prospects. 22(10), 916–920. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn115530-20200609-00382
Wu, J., Xie, K., Luo, D., Wang, L., Wu, W., Yan, M., et al. (2021). Three-dimensional printing-based personalized limb salvage and reconstruction treatment of pelvic tumors. J. Surg. Oncol. 124 (3), 420–430. doi:10.1002/jso.26516
Wu, J. C., Li, X. W., Fang, G. F., et al. (2020). Design and preliminary application of 3D-printed vertebral bodies in spinal tumor surgery. Chin. J. Orthop. Trauma 22 (10), 855–861.
Wu, X. (2019). Research on surface modification of 3D printed porous titanium-based implants. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics.
Wu, Y., Zitelli, J. P., TenHuisen, K. S., Yu, X., and Libera, M. R. (2011). Differential response of Staphylococci and osteoblasts to varying titanium surface roughness. Biomaterials 32 (4), 951–960. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.10.001
Xu, J., Lu, Y., Pan, X., Zhan, D., Wang, Q., and Zhang, N. (2023). Antibacterial performance of a porous Cu-bearing titanium alloy by laser additive manufacturing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11, 1226745. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2023.1226745
Xu, J., Zhou, X., Gao, Z., Song, Y. Y., and Schmuki, P. (2016). Visible-light-triggered drug release from TiO2 nanotube arrays: a controllable antibacterial platform. Angewandte Chemie Int. ed. Engl. 55 (2), 593–597. doi:10.1002/anie.201508710
Xu, N., Wei, F., Liu, X., Jiang, L., Cai, H., Li, Z., et al. (2016). Reconstruction of the upper cervical spine using a personalized 3D-printed vertebral body in an adolescent with ewing sarcoma. Spine 41 (1), E50–E54. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000001179
Xu, W., Yagoshi, K., Asakura, T., Sasaki, M., and Niidome, T. (2020). Silk fibroin as a coating polymer for sirolimus-eluting magnesium alloy stents. ACS Appl. bio Mater. 3 (1), 531–538. doi:10.1021/acsabm.9b00957
Xu, Z., Zhang, Y., Wu, Y., Zhang, Z., Jiang, D., Jia, R., et al. (2022). In vitro and in vivo analysis of the effects of 3D-printed porous titanium alloy scaffold structure on osteogenic activity. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 8494431. doi:10.1155/2022/8494431
Yang, D. (2016). The world's first 3D printed customized five-segment 19 cm long spine successfully treats malignant spinal tumor patient. Cap. Food Med. 15, 43–44.
Yang, L. J., Zhang, J., Wang, Z., and Yan, C. C. (2017). Finite element analysis of micro-porous structure design and mechanical properties of load-bearing bone scaffolds. Mech. Des. Manuf. 2017 (7), 157–160. doi:10.19356/j.cnki.1001-3997.2017.07.040
Yang, X., Wan, W., Gong, H., and Xiao, J. (2020b). Application of individualized 3D-printed artificial vertebral body for cervicothoracic reconstruction in a six-level recurrent chordoma. Turk. Neurosurg. 30 (1), 149–155. doi:10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.25296-18.2
Yang, X., Zhao, X., Qi, D., Wang, X., Jin, Y., Zhou, R., et al. (2020a). Changes in sagittal balance of the cervical spine after anterior cervical decompression and fusion using 3D-printed ACT titanium alloy intervertebral fusion cages. Chin. J. Tissue Eng. Res. 36, 5741–5748.
Ye, K., Wang, J. W., Hu, Z. G., Wang, C. T., Gan, Y. K., Wei, J. H., et al. (2015). Preliminary finite element analysis of biomechanics of 3D printed titanium alloy customized pelvic prostheses. Chin. J. Orthop. Trauma 17 (1), 5. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-7600.2015.01.006
Ying, X., Barlow, N. J., and Tatiparthi, A. (2022). Chapter 63 - micro-ct and volumetric imaging in developmental toxicology. Elsevier Inc.
Yu, Y., Ran, Q., Shen, X., Zheng, H., and Cai, K. (2020). Enzyme responsive titanium substrates with antibacterial property and osteo/angio-genic differentiation potentials. Colloids surfaces. B, Biointerfaces 185, 110592. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110592
Yuan, J., Ye, Z., Zeng, Y., Pan, Z., Feng, Z., Bao, Y., et al. (2022). Bifunctional scaffolds for tumor therapy and bone regeneration: synergistic effect and interplay between therapeutic agents and scaffold materials. Bio 15, 100318. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100318
Yuan, Z., Huang, S., Lan, S., Xiong, H., Tao, B., Ding, Y., et al. (2018). Surface engineering of titanium implants with enzyme-triggered antibacterial properties and enhanced osseointegration in vivo. J. Mater. Chem. 6 (48), 8090–8104. doi:10.1039/c8tb01918e
Yue, Y., Qi, Y., Yutao, J., Xinping, Z., and Ke, Z. (2014). Osteoconduction and influence of porosity and pore size of porous titanium on the early stage differentiation of mc3t3-e1 cells. Chinese Journal of Dental Materials and Devices.
Zarubova, J., Hasani-Sadrabadi, M. M., Ardehali, R., and Li, S. (2022). Immunoengineering strategies to enhance vascularization and tissue regeneration. Adv. drug Deliv. Rev. 184, 114233. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2022.114233
Zaveri, T. D., Dolgova, N. V., Lewis, J. S., Hamaker, K., Clare-Salzler, M. J., and Keselowsky, B. G. (2017). Macrophage integrins modulate response to ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene particles and direct particle-induced osteolysis. Biomaterials 115, 128–140. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.10.038
Zhang, J., Dai, W., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Yue, H., Li, Q., et al. (2023). Micro-arc oxidation of Al alloys: mechanism, microstructure, surface properties, and fatigue damage behavior. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 23, 4307–4333. doi:10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.02.028
Zhang, K., Zhou, Y., Xiao, C., Zhao, W., Wu, H., Tang, J., et al. (2019). Application of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in tumor-associated bone segmental defect. Sci. Adv. 5 (8), eaax6946. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aax6946
Zhang, R., Liu, Y., Qi, Y., Zhao, Y., Nie, G., Wang, X., et al. (2022a). Self-assembled peptide hydrogel scaffolds with VEGF and BMP-2 enhanced in vitro angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Oral Dis. 28 (3), 723–733. doi:10.1111/odi.13785
Zhang, S., Chai, Q., Man, Z., Tang, C., Li, Z., Zhang, J., et al. (2022b). Bioinspired nano-painting on orthopedic implants orchestrates periprosthetic anti-infection and osseointegration in a rat model of arthroplasty. Chem. Eng. J. 435, 134848. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2022.134848
Zhang, X., Tang, L., Liu, Z., Jiang, Z., Liu, Y., and Wu, Y. (2017b). Yield properties of closed-cell aluminum foam under triaxial loadings by a 3D Voronoi model. Mech. Mater. 104, 73–84. doi:10.1016/j.mechmat.2016.10.007
Zhang, X. Y., Fang, G., and Zhou, J. (2017a). Additively manufactured scaffolds for bone tissue engineering and the prediction of their mechanical behavior: a review. Mater. Basel, Switz. 10 (1), 50. doi:10.3390/ma10010050
Zhang, Y., Liu, Z. W., Fang, Z., Wu, W., and Li, F. (2021a). Clinical efficacy and changes in sagittal cervical parameters after treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy with 3D-printed titanium alloy intervertebral fusion cages. Orthopedics 02, 97–102.
Zhang, Y., Lu, M., Min, L., Wang, J., Wang, Y., Luo, Y., et al. (2021c). Three-dimensional-printed porous implant combined with autograft reconstruction for giant cell tumor in proximal tibia. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 16 (1), 286. doi:10.1186/s13018-021-02446-x
Zhang, Y., Yuan, T., Li, Z., Luo, C., Wu, Y., Zhang, J., et al. (2021b). Hyaluronate-based self-stabilized nanoparticles for immunosuppression reversion and immunochemotherapy in osteosarcoma treatment. ACS biomaterials Sci. and Eng. 7 (4), 1515–1525. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.1c00081
Zhang, Z., Li, H., Fogel, G. R., Xiang, D., Liao, Z., and Liu, W. (2018). Finite element model predicts the biomechanical performance of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion with various porous additive manufactured cages. Comput. Biol. Med. 95, 167–174. doi:10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.02.016
Zhao, D., Tang, F., Min, L., Lu, M., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., et al. (2020). Intercalary reconstruction of the “Ultra-Critical sized bone defect” by 3D-printed porous prosthesis after resection of tibial malignant tumor. Cancer Manag. Res. 12, 2503–2512. doi:10.2147/CMAR.S245949
Zhao, H., Zhao, C., Xie, W., Wu, D., Du, B., Zhang, X., et al. (2023). Research progress of laser cladding on the surface of titanium and its alloys. Mater. Basel, Switz. 16 (8), 3250. doi:10.3390/ma16083250
Zhao, S., Li, S. J., Wang, S. G., Hou, W. T., Li, Y., Zhang, L. C., et al. (2018). Compressive and fatigue behavior of functionally graded Ti-6Al-4V meshes fabricated by electron beam melting. Acta Mater. 150, 1–15. doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2018.02.060
Zhen, Z., Wang, J., Xi, T., and Liu, B. (2019). Current status of 3D printed titanium orthopedic implants. Chin. J. Biomed. Eng. 39 (2), 240–251.
Zhou, H., Liu, S., Li, Z., Liu, X., Dang, L., Li, Y., et al. (2022). 3D-printed vertebral body for anterior spinal reconstruction in patients with thoracolumbar spinal tumors. J. Neurosurg. Spine 37 (2), 274–282. doi:10.3171/2022.1.SPINE21900
Zhou, W., Jia, Z., Xiong, P., Yan, J., Li, M., Cheng, Y., et al. (2018). Novel pH-responsive tobramycin-embedded micelles in nanostructured multilayer-coatings of chitosan/heparin with efficient and sustained antibacterial properties. C, Mater. Biol. Appl. 90, 693–705. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2018.04.069
Keywords: additive manufacturing, 3D printing, orthopedic implants, surface modification, environment-responsive, bone tissue engineering
Citation: Guo C, Ding T, Cheng Y, Zheng J, Fang X and Feng Z (2025) The rational design, biofunctionalization and biological properties of orthopedic porous titanium implants: a review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1548675. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1548675
Received: 20 December 2024; Accepted: 06 February 2025;
Published: 26 February 2025.
Edited by:
Mike Barbeck, University Medical Center Rostock, GermanyReviewed by:
Raj Hazra, North Dakota State University, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Guo, Ding, Cheng, Zheng, Fang and Feng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chunliang Guo, aGx3Ym1nY2xAZ21haWwuY29t; Tao Ding, ZGluZ3Rhb0Buam11LmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.