
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 17 February 2025
Sec. Biomaterials
Volume 13 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2025.1539566
 Zhuoming Xu1,2†
Zhuoming Xu1,2† Jintao Liu1,2†
Jintao Liu1,2† Hanyin Hu1,2
Hanyin Hu1,2 Jun Ma1,2
Jun Ma1,2 Haiyang Yang1,2
Haiyang Yang1,2 Jiayi Chen2
Jiayi Chen2 Hongwei Xu2
Hongwei Xu2 Haodong Hu1,2
Haodong Hu1,2 Huanhuan Luo2*
Huanhuan Luo2* Gang Chen2*
Gang Chen2*Osteoarthritis is one of the most common degenerative joint diseases, which seriously affects the life of middle-aged and elderly people. Traditional treatments such as surgical treatment and systemic medication, often do not achieve the expected or optimal results, which leads to severe trauma and a variety of side effects. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop novel therapeutic options to overcome these problems. Hydrogels are widely used in biomedical tissue repairing as a platform for loading drugs, proteins and stem cells. In recent years, smart-responsive hydrogels have achieved excellent results as novel drug delivery systems in the treatment of osteoarthritis. This review focuses on the recent advances of endogenous stimuli (including enzymes, pH, reactive oxygen species and temperature, etc.) responsive hydrogels and exogenous stimuli (including light, shear, ultrasound and magnetism, etc.) responsive hydrogels in osteoarthritis treatment. Finally, the current limitations of application and future prospects of smart responsive hydrogels are summarized.
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common degenerative joint disease that harms the health of many elderly people (Barnett, 2018; Hu et al., 2021; Yin et al., 2023). It is characterized by cartilage degeneration and local aseptic inflammation (Chen et al., 2024; Li Z. et al., 2024; Sun et al., 2024). The occurrence of osteoarthritis may be related to age, obesity, genetic, endocrine and metabolic diseases, inflammation, trauma and other factors (Palazzo et al., 2016; Berenbaum et al., 2018). Clinically, osteoarthritis patients have many symptoms such as joint pain, local deformity and mobility dysfunction, which seriously affect the life of patients (Abramoff and Caldera, 2020; Hall et al., 2022). According to the degree of lesion of OA, the pathophysiology usually divides it into three stages: early stages, middle stages and advanced stages (Martel-Pelletier et al., 2016; Jiang, 2022; Kalairaj et al., 2024). In the early stages of OA, the pathological changes inside the joint are mainly concentrated in the synovial region, manifested as synovial hyperplasia and fibrosis. At the same time, pro-inflammatory cytokines (also known as inflammatory mediators, such as IL-1β, IL-6, 15, 17, 18, 21, 22, and TNF-α) are increased in joint cells (including chondrocytes, osteoblasts, and synovial fibroblasts), and activate related inflammatory signaling pathways, for example, the pathogenic mechanism of IL-1β is mainly related to its binding to IL-1 receptor I (IL-1RI). When a large amount of IL-1β binds to the receptor, it will activate the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway and the signaling pathway mediated by nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB), and induce the expression of proteases related to chondrodecomposition such as MMP (Matrix metalloproteinase) and ADAMTS (A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs), which causes a lot of inflammation in the synovial area (Li et al., 2021a; van den Bosch, 2021; Liew et al., 2023), and gradually begin to stimulate cartilage breakdown (Ng et al., 2023). However, due to the mild early symptoms of OA, it is difficult for patients to detect and pay attention to it, and thus fail to carry out treatment in time, which will cause OA to progress to the next stage (Mahmoudian et al., 2021). In the middle stages of OA, inflammation inside the joints and synovium become more severer, and the lesion gradually spread to the cartilage, showing degeneration of the chondrocyte extracellular matrix, fibrosis in the calcified area, and cell hypertrophy (Wang et al., 2022). Due to the increase of a large number of inflammatory factors and the activation of inflammatory pathways such as NF-κB, MAPK and Wnt, a large number of proteases related to chondrolysis, such as MMP and ADAMTS, are continuously released from the diseased chondrocytes, aggravating cartilage injury and degeneration (Malemud, 2019; Li T. et al., 2022). At this stage, patients will feel obvious pain and discomfort in the joint. If OA progresses to an advanced stage, the lesion area extends to all joints, presenting with abnormal bone remodeling and hardening. Among them, transforming growth faction-β (TGF-β) in the cartilage microenvironment can be activated to accelerate the invasion of blood vessels inside cartilage, and accelerate angiogenesis by stimulating mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), resulting in a large number of blood vessels of subchondral bone passing through calcified cartilage and invading cartilage, promoting chondrocyte hypertrophy and abnormal proliferation of bone tissue (Rim et al., 2020; Yao et al., 2023). Finally, the patient has a large number of osteophytes in the joint, producing severe pain and severe limitation of movement (Yan et al., 2022).
However, the traditional treatment of OA aims to relieve the clinical symptoms of pain and improve joint function (Mandl, 2019). The methods mainly include non-drug treatment, such as the improvement of lifestyle habits, massage physiotherapy and functional exercise, which are generally suitable for patients in the early stage of OA (Bannuru et al., 2019; Bennell and Hunter, 2020; Ni et al., 2024). Medications commonly used include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), opioid analgesics, steroid hormones, and hyaluronic acid (HA) (Richard et al., 2023), which are employed through oral administration, intravenous administration, articular injection and transdermal administration (Jones et al., 2019). However, drugs can only slow down the process of degeneration, which can not effectively promote the repair and regeneration of articular cartilage (Ma L. et al., 2022). In addition, the drug is in poor bioavailable by oral or intravenous systemic administration, and long-term use may increase the risk of gastrointestinal, kidney, and even cardiovascular diseases (Maniar et al., 2018; Mao et al., 2021). In contrast, intra-articular injection can effectively improve the concentration of drugs in the joint, but there is also a phenomenon of excessive local microenvironment metabolism, resulting in short drug retention time and it is thus difficult to achieve the expected therapeutic effect (Li G. et al., 2023; Kawaguchi, 2024). Surgical treatment, commonly used clinical surgical protocols include arthroscopic debridement, osteotomy and joint replacement, etc., is generally suitable for advanced bone and joint patients (Marx, 2008; Price et al., 2018; Pacheco-Brousseau et al., 2024). However, the surgical treatment is expensive and difficult to deal as a series of postoperative complications often happened (Canizares et al., 2021; Li H. et al., 2024).
In view of the challenges in the current clinical treatment of OA and the limitations of therapeutic means, many researchers have turned their attention to the development of biomedical remediation materials (Li et al., 2023b; Kumar et al., 2024). As a three-dimensional cross-linked polymer network biomaterial, hydrogels have been widely used in many fields such as tissue engineering (Lai et al., 2024), regenerative medicine, drug delivery and disease diagnosis due to their hydrophilic properties, controllable mechanical properties, excellent biodegradability and biocompatibility (Cao et al., 2021; Gutierrez et al., 2022; Zhao et al., 2023; Yuan et al., 2025). By using hydrogels as carriers of therapeutic drugs, researchers have achieved significant benefits in cartilage regeneration, inflammation alleviation and immune regulation of OA (Enayati et al., 2024; Ma et al., 2024; Zhang S. et al., 2024). Therefore, hydrogels are a potential biomedical material in the treatment of OA (Xue et al., 2022).
In the past, hydrogels were usually divided into natural hydrogels and synthetic hydrogels according to the different sources (Catoira et al., 2019). Natural sources of hydrogels include polysaccharide hydrogels (such as hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate, chitosan, alginate, xanthan gum, heparin and fibroin, etc.) and polypeptide hydrogels (such as collagen, elastin, fibrin, gelatin and silk protein, etc. (Xu et al., 2024; Yadav et al., 2024). Synthetic hydrogels include poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA), polylactic acid (PLA), polycaprolactone (PCL), polyethylene glycol (PEG), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), etc., (Ahmed, 2015; Ho et al., 2022; Bramhe et al., 2024). At present, with the development and application of various new hydrogels, they have evolved from simple natural or synthetic hydrogels to hybrid intelligent responsive hydrogels with multiple characteristics to achieve accurate release (Tian and Liu, 2023; Liu L. et al., 2024). Smart responsive hydrogel is selected as a controlled drug release system for the treatment of osteoarthritis, which can respond to exogenous stimuli (light, ultrasound, pressure and magnetic field, etc.) or endogenous stimuli (temperature, enzyme, pH, ROS, etc.) to achieve controlled drug release, which has achieved remarkable results in the treatment of osteoarthritis (Jiang and Zhang, 2023).
This review focuses on the latest applications of stimulus-responsive smart hydrogels in osteoarthritis (Scheme 1) and it will be introduced from the two aspects of endogenous (Figure 1) and exogenous (Figure 2) responsive hydrogels.
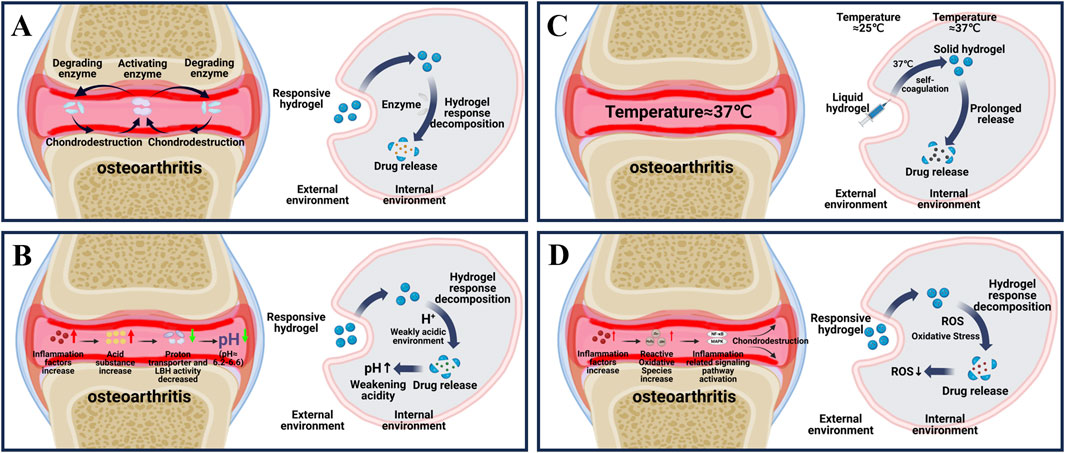
Figure 1. Principle of endogenous responsive hydrogels. (A) Changes in internal enzymes during osteoarthritis and the process by which enzyme responsive hydrogels release drugs in response to internal reactions. (B) Changes in internal PH during osteoarthritis and the internal response of PH-responsive hydrogels to release drugs. (C) Internal temperature during osteoarthritis and the process by which temperature-responsive hydrogels respond to self-coagulation and release drugs internally. (D) Changes in internal ROS during osteoarthritis and the process of drug release in response to ROS response hydrogels.
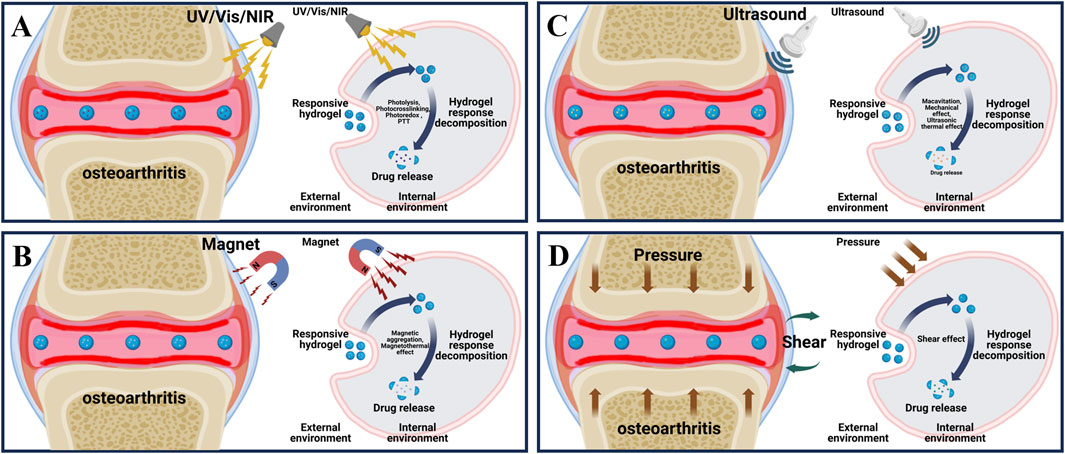
Figure 2. Principle of exogenous responsive hydrogels. (A) External light stimulation of the lesion area of osteoarthritis and the process of releasing drugs in response to external light stimulation of light responsive hydrogel. (B) External magnetic stimulation of the lesion area of osteoarthritis and the process of releasing drugs in response to external magnetic stimulation of magnetically responsive hydrogels. (C) External ultrasonic stimulation of the lesion area of osteoarthritis and the process of releasing drugs in response to external ultrasonic stimulation of the ultrasound-responsive hydrogel. (D) External shear stimulation in the lesion area of osteoarthritis and the process of drug release in response to external shear stimulation of shear-responsive hydrogel.
In recent years, the study of enzymes and their catalytic reactions has become a new hotspot (Buller et al., 2023). Due to the high selectivity, substrate specificity and good catalytic performance of enzyme-catalyzed reaction, enzyme-responsive hydrogels have more irreplaceable advantages compared with other biomaterials (Arcus and Mulholland, 2020; Sobczak, 2022; Reisenbauer et al., 2024). However, enzyme responsive hydrogels must also meet the following conditions: 1. The hydrogel network must be bound to a substrate with a high affinity to the enzyme, 2. The enzymatic reaction interacting with the enzyme must cause a significant change in the properties of the hydrogel, resulting in biodegradation or a change in structure that releases the loaded drug (Sobczak, 2022; Xiao and Huang, 2024).
As shown in Figure 1A, osteoarthritis is accompanied by an overproduction of a series of enzymes that cause material degradation as the disease progresses (Coryell et al., 2021). The key enzymes are protein-degrading enzyme and activator enzyme. Degrading enzymes break down the extracellular matrix (ECM), leading to a reduction in the hyaline cartilage matrix, which in turn roughens the articular cartilage and creates mechanical friction when it moves (Arra and Abu-Amer, 2023). The activation of enzyme can further enhance the activity of degrading enzyme in articular cartilage through positive feedback, and aggravate the destruction of cartilage (Arra and Abu-Amer, 2023). Therefore, targeting the overproduction of protein-degrading enzymes is the key to treating OA. Among various degrading enzymes, MMP and ADAMTS, as typical degrading enzymes in osteoarthritis, have been fully studied and targeted to develop enzyme-responsive hydrogels for the treatment of osteoarthritis (Table 1) (Cho et al., 2021; Mukherjee and Das, 2024; Wang et al., 2024a).
Yi et al. developed an MMP-responsive composite hyaluronic acid hydrogel (Col-OHA) for the treatment of osteoarthritis by cross-linking oxidized hyaluronic acid (OHA) with type I collagen and successfully loading the anti-inflammatory drug DSP based on the specific biodegradation of collagen by MMP (Yi et al., 2022). Col-OHA has good mechanical properties and injectable properties, and can self-decompose and slowly release DSP in response to MMP-1 in vivo and in vitro studies, downregulate the expression of inflammatory factors IL-6 and TNF-α, effectively control the progression of OA, and obtain good therapeutic effects. In contrast, Tong et al. prepared injectable MMP-13-responsive hyaluronic acid hydrogel microspheres by loading MMP-13 sensitive peptide and using microfluidic technology (HAM-SA@HCQ). In response to the microenvironment with high expression of MMP-13 in OA, the anti-inflammatory drugs HCQ and sulfonated azocaliarene (SACA) were specifically degraded and released. Excess ROS was removed from RAW264.7 macrophages stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and IFN-γ, and the expression of HIF-1 was significantly reduced, and a good chondroprotective effect was achieved in vivo (Zhou et al., 2023). Similarly, Zhao et al., also based on MMP13 sensitive peptide, designed an MMP-13 responsive hydrogel (MREK) for early inflammation recognition and diagnosis of OA and coordination of cartilage repair (Figure 3A) (Tianyuan et al., 2023). MREK can respond to identify environments with high expression of MMP13, achieve early diagnosis and control of OA inflammation. As shown in (Figure 3B), MREK can effectively downregulate the expression of inflammatory factors (IL-6, TNF-α, IL-4 and IL-10) in the paracrine mediators of SMSCs, inhibit the inflammation of chondrocytes, and at the same time regulate the expression of genes (iNOS, CD86, Arg-1 and CD206) in macrophages, which plays a role in immune regulation. In addition, KGN, a supported chondro-inducing regenerative drug, is released through the response breakdown of MMP, achieving Col-II, ACAN and SOX9 were highly expressed.
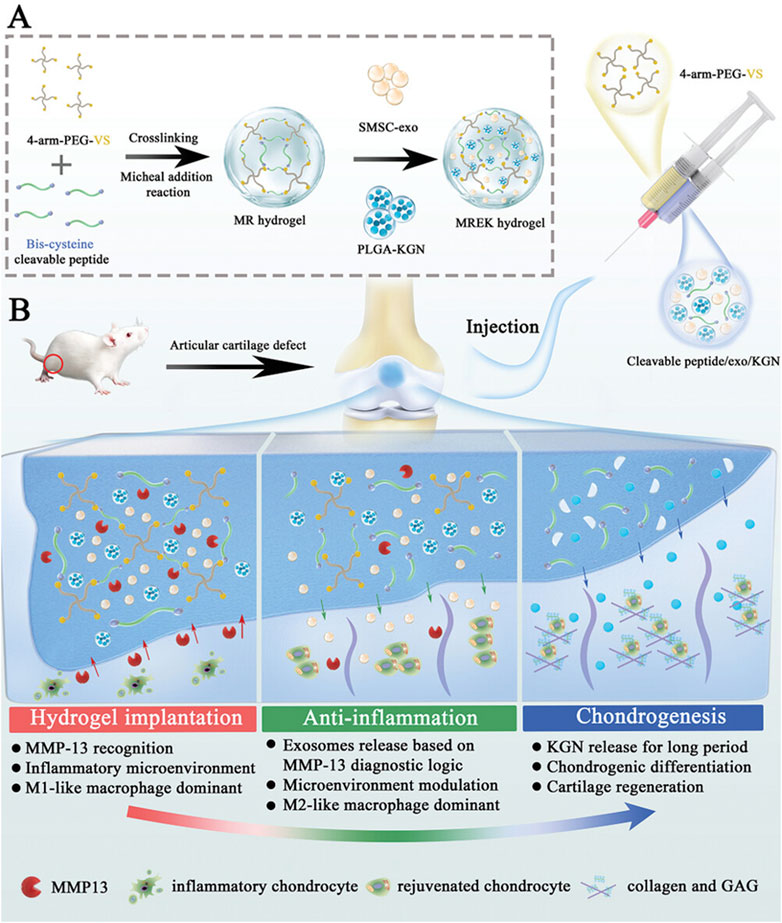
Figure 3. Preparation and working principle of MERK hydrogel. (A) Schematic diagram of the manufacture of MERK hydrogel. (B) Mechanism of action of MERK hydrogel after intraarticular injection. Reprinted with permission from (Tianyuan et al., 2023).
Miao et al., prepared an injectable microenvironmentally responsive bilayer hydrogel microsphere (ChsMA + CLX@Lipo@GelMA) for OA joint lubrication, inflammation alleviation, and cartilage repair (Miao et al., 2024). As shown in (Figure 4), ChsMA + CLX@Lipo@GelMA is prepared from GelMA containing CLX liposomes as the shell and ChsMA microspheres as the core. The working principle is simply that GelMA, as a shell, can release CLX and liposomes in response to decomposition with MMP, which lubricate joints and remove excessive inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IL-6 and MMP-13. The subsequent consumption of a large amount of CLX and liposomes exposed the ChsMA of the kernel, which was broken down into low-molecular weight chondroitin sulfate and chondroitin oligosaccharides, and increased the expression of chondrocyte protective factors Agg and Col2a1, thus achieving the effect of cartilage repair. In vivo and in vitro studies, ChsMA + CLX@Lipo@GelMA effectively controlled the progression of OA, achieving a combination of multi-layered response, precisely controlled drug release, multiple cartilage repair, inflammation clearance, and joint lubrication.
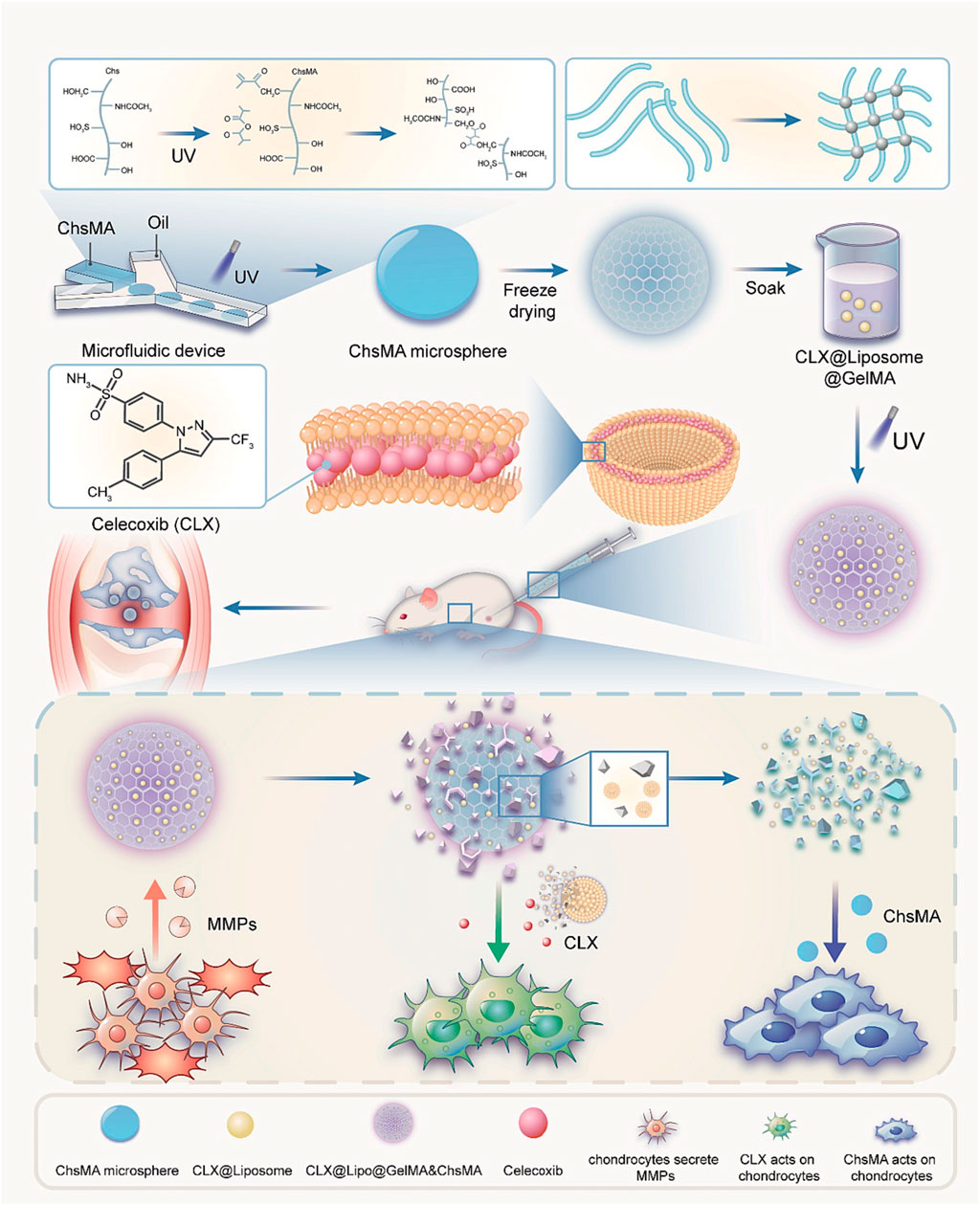
Figure 4. Preparation of ChsMA + CLX@Lipo@GelMA hydrogel and its working principle after injection into joint cavity. Reprinted with permission from (Miao et al., 2024).
At present, enzymatic responsive hydrogels show good drug administration and therapeutic effect in the treatment of osteoarthritis, but there are still many limitations in their further application. At this stage, the changes in the types and quantities of pathogenic enzymes in the progression of osteoarthritis diseases are still in the preliminary research stage, and the changes in the activity of pathogenic enzymes after treatment have not been reported in detail. Therefore, the types of pathogenic enzymes that can be designed for enzyme-responsive hydrogels are relatively limited at present, and future research directions may focus on these aspects.
Generally, in healthy joints, the pH of the microenvironment can be maintained in a stable state of 7.4–7.8 (Jiang and Zhang, 2023). As shown in Figure 1B, in the course of osteoarthritis, due to the increase of inflammatory factors, the increase of cell activity leads to the increase of cell oxygen consumption and the excessive production of acidic substances (McGarry et al., 2018). At the same time, the transport rate of proton transporters and lactate dehydrogenase a (LDHA), which maintain the pH of the microenvironment, is reduced, and excessive acidic substances cannot be excreted, resulting in a gradual transformation of the pH in the joint to a relatively weak acid (pH of about 6.2–6.6) (Zheng et al., 2021; Tan et al., 2022; Arra and Abu-Amer, 2023). In view of the pathological characteristics of osteoarthritis, researchers introduce acid reaction bonds (such as amino groups, carboxyl groups, etc.) or protonable chemical groups (such as o-esters, Schiff bases and vinyl ethers, etc.) into the pot-carrying gel to achieve the purpose of on-demand decomposition in the weak acid environment of osteoarthritis and precise release of drug therapy (Ding et al., 2022). At present, a variety of pH-responsive smart hydrogels have been used in the treatment of OA (Table 1).
As in Chen et al., inspired by the weakly acidic microenvironment of osteoarthritis, a pH-responsive injectable hydrogel microsphere for delivering siRNA of HIF-2 gene (associated with cartilage degradation) was prepared by protonation (HAMA/G1-NC5. HCl@siRNA) (Chen L. et al., 2023). When hydrogel microspheres were injected into the diseased joints, the protated phosphate-containing dendritic macromolecular derivatives would accurately anchor the injured cartilage in response to the weakly acidic microenvironment. It was found that Cy5.5 labeled siRNA could penetrate into the deep matrix of cartilage through fluorescence microscopy. In addition, radiological evaluation and histological analysis showed that siRNA delivery in diseased joints downregulated HIF-2 gene and inhibited MMP-13 protein expression, effectively slowed joint aging, promoted cartilage regeneration, reduced osteophytic formation, and improved OA joint stenosis. Based on ZIF-8 MOFs has a large specific surface area, high drug loading efficiency and pH sensitivity, Jiang et al., proposed a NBIF@ZIF-8/PHG hydrogel for the delivery of the anti-inflammatory drug NBIF for the treatment of OA (Jiang et al., 2023). NBIF@ZIF-8/PHG released a large amount of NBIF in vitro in a simulated OA microenvironment (pH 6.0), and co-incubated with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells BMSCs and macrophages RAW264.7, respectively, to successfully test the role of NBIF in inducing the expression of Col-II and Sox-9 to promote cartilage regeneration and inflammatory immune regulation. In vivo studies, the high expression of Col-II and Agg in tissue staining analysis once again demonstrated its excellent cartilage repair effect. And the injectable hydrogel containing selenium nanoparticles proposed by Hu et al. (OHA/HA-ADH@SeNPs) achieves pH responsiveness of the joint environment through Schiff base bonds (Hu et al., 2023). SeNPs encapsulated in the hydrogel networks are released by Schiff base rupture in a weakly acidic inflammatory microenvironment to treat osteoarthritis by clearing excess ROS, inhibiting apoptosis and promoting cartilage repair. As shown in (Figure 5A), Zhao et al., developed an injectable hydrogel drug delivery system (Met@V2C@DMH) based on metformin and a novel nanosheet MXenzymes with multiple enzyme simulated activities such as oxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) (Zhang Z. et al., 2024). The hydrogel utilizes the amide bond generated between metformin and MXenzyme to achieve pH response release. In vivo and in vitro studies have shown that Met@V2C@DMH can not only reduce the COF value of joint lubrication (Figure 5B), but also activate Nrf2-ARE antioxidation-related pathway (Figures 5D–H), downregulate the expression of inflammatory factors (TNF-α, COX2, iNOS and IL-6) (Figure 5C), MMP-13 and ADAMTS-5 proteins (Figures 5I, J). The chondrocyte damage was significantly reduced. In addition, Met@V2C@DMH downregulated the expression of Nlrp3 and Gsdmd proteins (Figures 5K, L), which proved that it had a certain anti-pyroptosis effect.
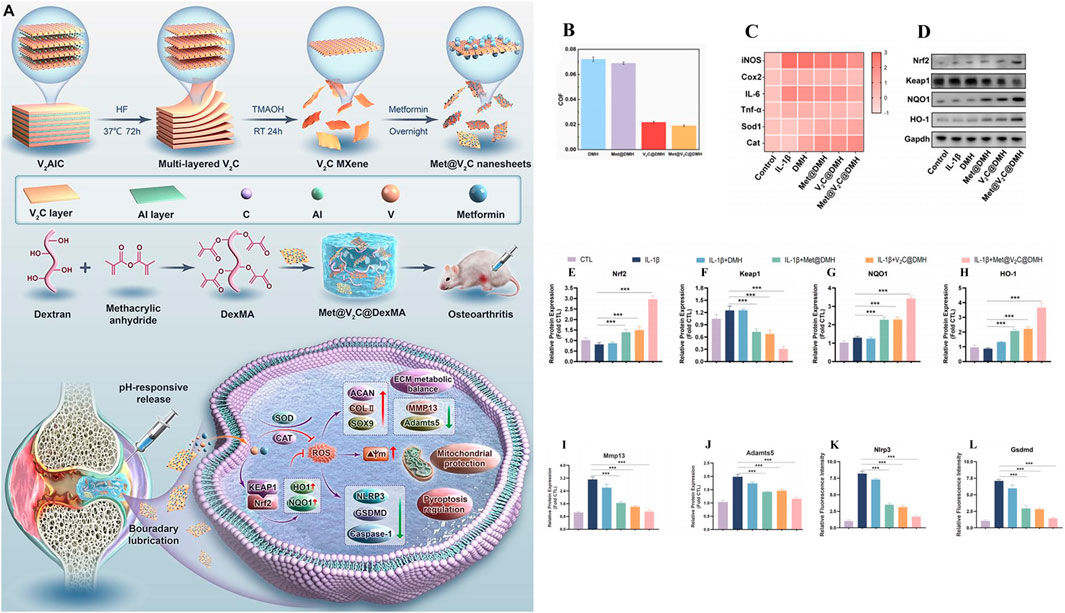
Figure 5. Preparation of hydrogel drug delivery system (Met@V2C@DMH) and in vitro study of therapeutic effect. (A) Preparation and working principle of Met@V2C@DMH. (B) Met@V2C@DMH lubrication effect. (C) Heat map of the relative mRNA expression levels of iNOS, Cox2, TNF-α, IL-6, Cat and Sod1 in chondrocytes of each group. (D–H) The expression of proteins in Nrf2-ARE antioxidant-related pathways in each group. (I, J) The protein expression of MMP13 and ADAMTS5 in chondrocytes of each group, (K, L) the expression of Nlrp3 and Gsdmd proteins associated with pyrodeath in chondrocytes in each group. (n = 3) (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001). Reprinted with permission from (Zhang Z. et al., 2024).
At present, pH-responsive hydrogels have achieved relatively considerable results in the treatment of osteoarthritis, but the changes of pH in the joint microenvironment after treatment lack long-term monitoring, and some chemical group changes in the joint have unknown effects. Therefore, the safety of future materials is also an aspect that cannot be ignored.
The temperature-responsive hydrogels have two aspects, which are different depending on the extra stimuli or not. In this section, the thermal-responsive hydrogels here are classified as endogenous reactions because the material itself is a fluid state at room temperature and can undergo morphological changes in response to internal temperature to self-aggregate into a gel state, where it is not affected by external stimuli. As for the other type of temperature-responsive hydrogel with external stimuli (such as magnetic force, ultrasound or light) mentioned below to influence temperature and cause conformation changes of hydrogels were classified as exogenous-responsive hydrogels. In this section, we pay attention to the endogenous responsive materials without extra stimulus.
The temperature of normal joints is usually slightly below 37°C (Xu et al., 2023). Based on the difference of internal and external environment of human joints, a thermo-responsive intelligent hydrogel for OA treatment was proposed (Li Y. et al., 2024). The core part is the successful loading of temperature-sensitive materials such as poly (n-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM), poly (ninylisobutyramide) (PAMAM), CS, poloxam, pluronic F127, etc., into the hydrogel. As shown in Figure 1C, in the external room temperature environment (25°C), the thermosensitive smart hydrogel is a fluid state, and when injected into the internal environment of human joint tissue (37°C), the thermosensitive smart hydrogel can be sensitive to recognition, produce obvious physical and chemical property changes, and self-condense into a stable gel state (Singla et al., 2022; Rahmani et al., 2023). At the same time, the load drug is slowly released to achieve long-term OA treatment (Table 1) (Lv et al., 2023).
As Yi et al., a temperature-sensitive poly PLGA-PEG-PLGA hydrogel (IL-36Ra@Gel) was successfully prepared (Yi et al., 2023). IL-36Ra, a receptor antagonist with IL-36, is used for OA control of inflammation and cartilage repair (Neurath, 2020). IL-36Ra@Gel is based on the fact that the temperature in the human joint is higher than room temperature. After injection into the joint, the hydrogen bond between PEG fragment and H2O molecule in the hydrogel in solution state becomes weak, and the hydrophobicity between PLGA fragment becomes stronger, resulting in the responsive cross-linking of the hydrogel from solution state to solid gel state, and the long-term release of IL-36Ra can be realized. By down-regulating MMP-13 and ADAMTS-5 and up-regulating the expression of Col-X and Agg, inflammation was inhibited and cartilage was protected in the treatment of OA. F-127 is a temperature-sensitive material based on hydrophobic polyethylene oxide (PEO) and hydrophobic polypropylene oxide (PPO) (PEO-PO-PEO) (Khaliq et al., 2023). Valentino et al. proposed a heat-response gel of chitosan nanoparticles based on F-127, HA and hydroxytyrosol Hyt (Hyt@tgel), which achieved intra-joint gelation through temperature changes after injection into joints, prolonged the release of polyphenol Hyt, and played a role in long-term inflammation alleviation (Valentino et al., 2022). Chen et al., prepared a heat-sensitive hydrogel (O3 NPs@MHPCH) using hydroxypropyl chitin (HPCH) for OA resistance to inflammation and cartilage protection (Wu H. et al., 2024). This composite hydrogel can self-gelatinize at 37°C, slowly release ozone (O3) and D-mannose, downregulate the expression of inflammatory factors IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α and iNOS, and promote the migration of chondrocytes, upregulate the expression of Col-II, and realize the self-repair of cartilage. Zhang et al., developed a temperature-sensitive hydrogel (Exo-Gel) that responds to the release of PRP-Exo for subtalar osteoarthritis (STOA) (Zhang Y. et al., 2022). Exo-Gel is temperature-controlled gelation via Pluronic-407 and 188, prolonging the release of Exo-Gel, which has anti-inflammatory effects and regulates cartilage regeneration. In vitro studies, Exo-Gel can maintain continuous drug release at 37°C for 1 month, and its promotion of proliferation and migration of mBMSCs was verified by CCK-8 and transwell scratch experiments. In addition, Exo-Gel can effectively inhibit the NF-κB inflammatory signaling pathway, decrease COLX and MMP13, and increase the expression of Col-II. In vivo studies, the animal model of STOA established by cutting ATFL/CFL was treated with Exo-Gel in the joint cavity for 8 weeks, and relatively complete and smooth cartilage was observed through histological staining analysis, which verified its excellent cartilage protection. Chen et al. also used the thermosensitive material Pluronic 407 and crosslinked with the HA and mTORC1 inhibitor rapamycin to prepare an injectable hydrogel (P-HA hydrogel) for the immune regulation of OA (Figure 6A) (Chen B. et al., 2023). In the incubation environment at 37°C, P-HA hydrogel can slowly release rapamycin in response to gelation (Figure 6B), downregulate the expression of pro-inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6, and upregulate the expression of anti-inflammatory factor IL-10 in macrophages induced by inflammation (Figures 6C–F). In addition, immunofluorescence staining suggested that P-HA hydrogel played a role in regulating the immune microenvironment by inducing macrophages to differentiate into M2 (Figures 6G–J). In vivo studies, P-HA hydrogel effectively inhibited synovial inflammation and mitigated cartilage destruction. It provides a new idea for the treatment of OA.
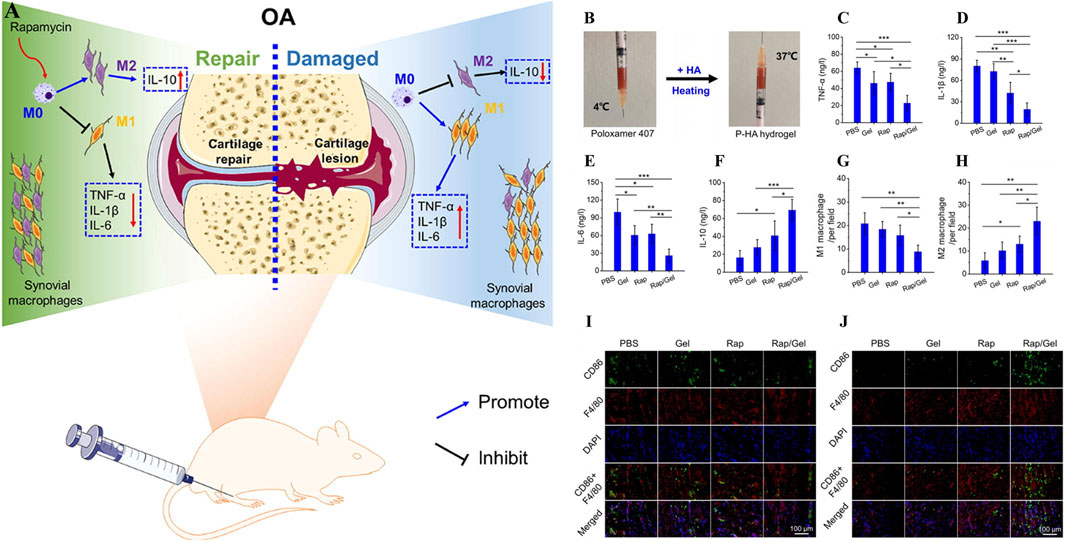
Figure 6. (A) Working principle of P-HA hydrogel. (B) Self-gelation of P-HA hydrogel. (C–F) Effects of P-HA hydrogel on synovial-related factors TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-10. (G–H) Quantitative analysis of M1 and M2 macrophages labeled by fluorescent staining in each group. (I, J) Immunofluorescence staining with CD86 or CD163 was added to F4/80 to label M1 or M2 macrophages in each group. (n = 3) (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001). Reprinted with permission from (Chen B. et al., 2023).
Thermo-responsive hydrogels greatly prolong the release of drugs through morphological changes, but inevitably affect the degradation rate of materials. In addition, the temperature of local joints often cannot maintain a constant physiological temperature for a long time due to the influence of external temperature, resulting in greatly reduced therapeutic effect. There is still a long way to go before thermo-responsive hydrogels can be widely used in the future.
In normal human joints, ROS, as a second messenger (Fang et al., 2024; Huang et al., 2024; Zhong et al., 2024), usually participates in the gene expression, signal transduction and cell cycle of chondrocytes, and plays an important role in maintaining the stability of the joint environment (Madreiter-Sokolowski et al., 2020; Hernansanz-Agustín and Enríquez, 2022). As shown in Figure 1D, in the pathogenesis of OA, high levels of ROS lead to the generation of intracellular oxidative stress, which then leads to the activation of signaling pathways related to inflammation and immune response (such as NF-κB and MAPK), damage the mitochondrial DNA and modified proteins of chondrocytes, and cause cell senescence and apoptosis (Bolduc et al., 2019; Ansari et al., 2020; Riegger et al., 2023). Therefore, the development of biological materials targeting oxidative stress is of great significance for OA treatment (Nakkala et al., 2021). At present, a variety of reactive oxygen species intelligent hydrogels designed in the study can deliver different drugs while removing ROS, and have achieved remarkable results in the treatment of OA (Table 1) (Zhang et al., 2023).
NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4) is an enzyme protein used to produce ROS and is closely associated with iron death (Szanto, 2022). Based on the ROS responsiveness of polyethylene glycol ketone mercaptan (mPEG-TK), Jin et al., developed a ROS responsive hydrogel microsphere (mPEG-TK-GLX@PVA-MMA), which is composed of methyl methacrylate (MMA) modified PVA as the shell of the microsphere (Zhen et al., 2024). A novel selective NOX4 inhibitor, GLX, was prepared with mPEG-TK. mPEG-TK-GLX@PVA-MMA can release GLX in response to inflammation induced macrophages, and inhibit iron death by down-regulating the expression of Fe2+, C11, and JC-1 while clearing ROS. Zhao et al., developed an injectable microgel (MPTK-C@MP) for the delivery of MP for the treatment of OA in response to the properties of azo groups that can change reductase structure in anoxic environment (Wang et al., 2024b). MPTK-C@MP is prepared from the MACA, MPC and PEG-4PTK with MP supported base acrylate. In vitro studies, MPTK-C@MP successfully verified the ROS responsiveness by loading fluorescent chromogenic agent Rh123 in the incubation with chemical reducing agent SDT. In an environment of strong oxidative stress, it rapidly decomposing and releasing MP, regulating the immune microenvironment, down-regulating the expression of IL-6 and TNF-α in macrophages induced by inflammation, and eliminating excess ROS. At the same time, due to the presence of MPC, microgels can effectively reduce COF and provide joint lubrication. Finally, in vivo studies, MPTK-C@MP downregulates HIF-1α levels and enhances Col-II expression through potent anti-inflammatory and lubricating effects, demonstrating excellent cartilage repair effects. Lie et al. designed a bifocal injectable hydrogel (oHA-PBA-PVA), which was crosslinked by 3-aminophenylboric acid modified hyaluronic acid and hydroxy-containing polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) (Lei et al., 2024). It utilized the phenylborate ester bond formed by phenylboric acid and hydroxyl group to achieve ROS response while removing excess ROS. In addition, HPP gel has good rheological and mechanical properties, which can effectively downregulate COF to lubricate joints and protect cartilage. As shown in (Figure 7), Liu et al., aiming at excessive senescent cells in the pathogenesis of OA, prepared a ROS response hydrogel carrier through the dynamic bond formed between APBA modified SF and PVA, and intelligently released IFN-γ microbubbles (iMVs) (Liu S. et al., 2023). The expression of Ki67, P16, P21 and P53 in chondrocytes induced by inflammation was downregulated by stem cell therapy to delay cell senescence. At the same time, Hydrogel@MVs/iMVs also enhanced the expression of ATP and respiratory chain complex II, III and V, and provided a new treatment strategy for OA by improving mitochondrial function and enhancing cellular antioxidant capacity.
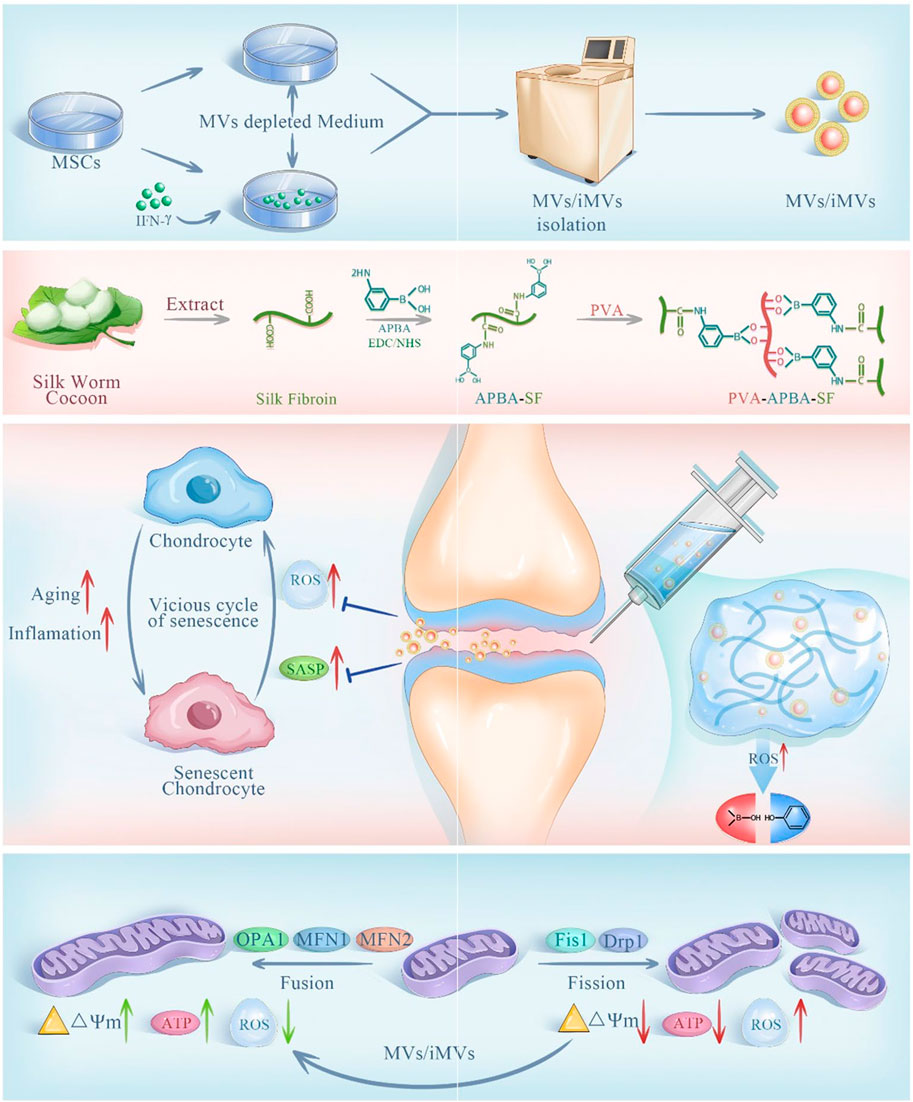
Figure 7. Preparation and principle of ROS responsive hydrogel @MVs/iMVs. Reprinted with permission from (Liu S. et al., 2023).
The balance of the redox system plays a crucial role in the stability of the biological environment. ROS responsive hydrogels will remove a large number of ROS during treatment, but it is doubtful whether the residual ROS can maintain the normal physiological activities of cells for a long time. In the future, how to balance the levels of physiological and pathological ROS may be the focus of optimization of such materials.
Light is considered as a promising new energy source because of its good adjustability, high accuracy in space and time, and portability (Rapp and DeForest, 2020). Currently, researchers have developed a variety of light responsive hydrogels for OA treatment, among which common light sources include ultraviolet (UV) (200–400 nm), visible light (Vis) (400–700 nm), and near-infrared light (NIR) (700–1,300 nm) (Shen et al., 2021; Xing et al., 2022). As shown in (Figure 2A), by adjusting the direction, intensity, polarization, wavelength and frequency of light, the researchers accurately penetrate the tissue to produce different light stimuli, so that the photosensitive groups in the light responsive hydrogel are isomerized, resulting in a variety of effects such as photolysis, photocrosslinking, photoredox and photothermal triggering (photothermal therapy (PTT)), so as to achieve accurate and controlled release of loaded drugs (Table 2) (Li et al., 2019).
For example, the gene therapy of OA is to deliver the target gene to the specific binding site in the joint, and achieve controllable long-term treatment by regulating gene expression (Grol, 2024). IL-1 is a gene associated with the inflammatory progression of OA (Lee et al., 2021). As shown in Figure 8A, Chen et al. successfully prepared a NIR responsive hydrogel (HA-SNAs) for delivering IL-1 interfering oligonucleotides. It is prepared by hybridization of spherical nucleic acids (SNAs) made from Au NRs modified with antisense DNA sequence of IL-1 mRNA and Ha-grafted SNAs complementary DNA sequence (Chen et al., 2021). In vitro studies, Au NRs in HA-SNAs can respond to near-infrared light and convert it into heat energy, promote DNA unhelix decomposition and release interfering IL-1 mRNA molecules, downregulate the expression of MMP-1 and MMP-13 in H2O2-induced chondrocytes, and upregulate the expression of Col-II and Agg (Figures 8B–F). It has significant anti-inflammatory and cartilage protective effects. In vivo studies, HA-SNAs can effectively reduce cartilage surface erosion and deformation, and upregulate Col2α protein expression (Figures 8G, H), once again verify its good role in protecting cartilage and controlling the progression of OA. In addition, Lim et al. developed a bifocal tyramine methylacrylyl gelatin (GelMA-Tyr) based on the visible light response (Lim et al., 2020). It uses Ru/SPS as photoinitiators, which can respond to light crosslinking and adhere to cartilage with low biotoxicity, improve the expression of Col-II and effectively promote cartilage repair.
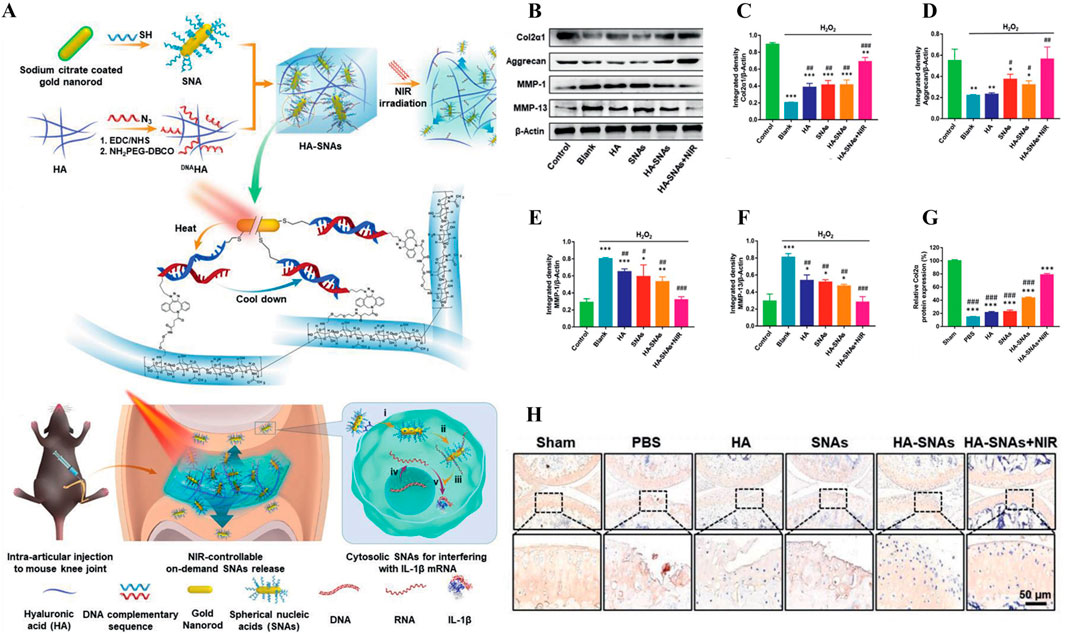
Figure 8. (A) Preparation and working principle of near-infrared photoresponsive hydrogel HA-SNAs, (B–F) Expression of Col2α1, Agg, MMP-1 and MMP-13 in cells treated with H2O2. (G–H) Immunohistochemical staining and quantification of joint Col2α1 in each group after treatment in vivo. n = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Reprinted with permission from (Chen et al., 2021).
Although light has good controllability, it is inevitable that different types of light sources will cause damage to biological normal cells (such as thermal burn, carcinogenic transformation and apoptosis, etc.), in addition, different types of light sources have different penetrability to tissues and carry different energy (Jägerbrand and Spoelstra, 2023). For example, long-wavelength light or near-infrared light has strong tissue penetration, up to 10 cm deep in the tissue, but carries less energy. The tissue penetration of short-wavelength light or ultraviolet light is weak, sometimes only 10 mm below the tissue, but it carries more energy and the risk is relatively large. Visible light is somewhere in between. Therefore, screening suitable types of light sources and designing efficient photo-responsive hydrogels, balancing safety and therapeutic effect in deep tissue may be a greater challenge for future research.
Magnetic force is widely used in many medical fields such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), drug delivery and monitoring, enzyme quantitative measurement and magnetic hyperthermia therapy due to its strong tissue penetration ability and relatively free of harmful ionization effects (Li et al., 2020; Ramos-Sebastian et al., 2022). The magnetically responsive hydrogels are mostly composed of drug-carrying magnetic nanoparticle core (such as iron oxide, cobalt oxide and nickel oxide, etc.) and hydrogel shell, as shown in (Figure 2B), under the stimulation of the external constant magnetic field or alternating magnetic field (AMF), the magnetic nanoparticles will undergo structural changes, thereby controlling drug release and achieving precision treatment (Hao and Mao, 2023).
Based on the advantages of magnetic force, many magnetically responsive hydrogels for OA treatment have been developed for drug delivery (Table 2) (Li et al., 2021b). For example, Ibrahiem1 et al. envisioned a magnetic thermosensitive hydrogel (LSB) for intramuscular (IM) administration based on magnetic targeting and magnetothermal effects (Ibrahiem et al., 2023). In order to improve the bioavailability of the drug, they prepared LSB by loading the anti-inflammatory drug Lornoxicam (LOR) and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) in a lipid bilayer gel and crosslinking it with a thermosensitive hydrogel containing Synperonic™PE/F127 (PE/F127). It was found that after LSB was injected into the thigh muscle, magnetic targeted aggregation of LSB was achieved by applying an external magnetic field to the knee joint. In addition, due to the thermal effect of magnetic aggregation, LSB is responsive to gelation, resulting in a slow and long-term release of LOR, successfully inhibiting the MAPK/ERK1 signaling pathway related to OA inflammation and regulating the expression of RANKL/OPG, effectively easing the progression of OA. To develop a new dynamic 3D model of OA in vitro. As show in Figure 9, Liu et al. designed a novel chip cartilage that uses a magnetic field to achieve dynamic cyclic stress regulation for simulating OA microenvironment changes (Liu H. et al., 2024). Researchers prepared a magnetic hydrogel (NdFeB-GelMA-HAMA) by combining the strong magnetic material NdFeB with GelMA-HAMA hydrogel, and cultured chondrocytes on this hydrogel. Through magnetic stimulation, the NdFeB-GelMA-HAMA responsive deformation is realized to simulate the change of stress during joint motion. Studies have found that chondrocytes will produce abnormalities under excessive mechanical stress, resulting in the reduction of type II collagen and the secretion of a large number of inflammatory factors such as MMP-13 and ADMTS-5 (Li et al., 2021b). Therefore, magnetic mechanical conversion chip cartilage prepared by magnetic effect has a good prospect as an ideal OA model for disease research and drug development. Liu et al. developed a pulsed electromagnetic field as a novel magnetically responsive smart hydrogel for controlling the specific chondrogenic differentiation of MSCs (Liu et al., 2019). Magnetic hydrogels were synthesized by chemical crosslinking of gelatin with β-cyclodextrin and magnetic embedding of Fe3O4. The adhesion, growth and proliferation of MSCs grown on magnetic hydrogels under pulsed electromagnetic field increased rapidly, and cartilage formation increased. In vitro experiments, it showed upregulation of Col-II, Agg and SOX9 genes. It provides a new direction for OA cartilage repair. Li et al. formed a novel magnetohydrogel by photocrosslinking Ac-β-CDs and gelatin and supplementing with dopamine-functionalized alginate (Alg-DA) (Li Y. et al., 2023). Similarly, Alg-DA/Ac-β-CD/gelatin hydrogel can promote cartilage repair and regeneration under pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF).
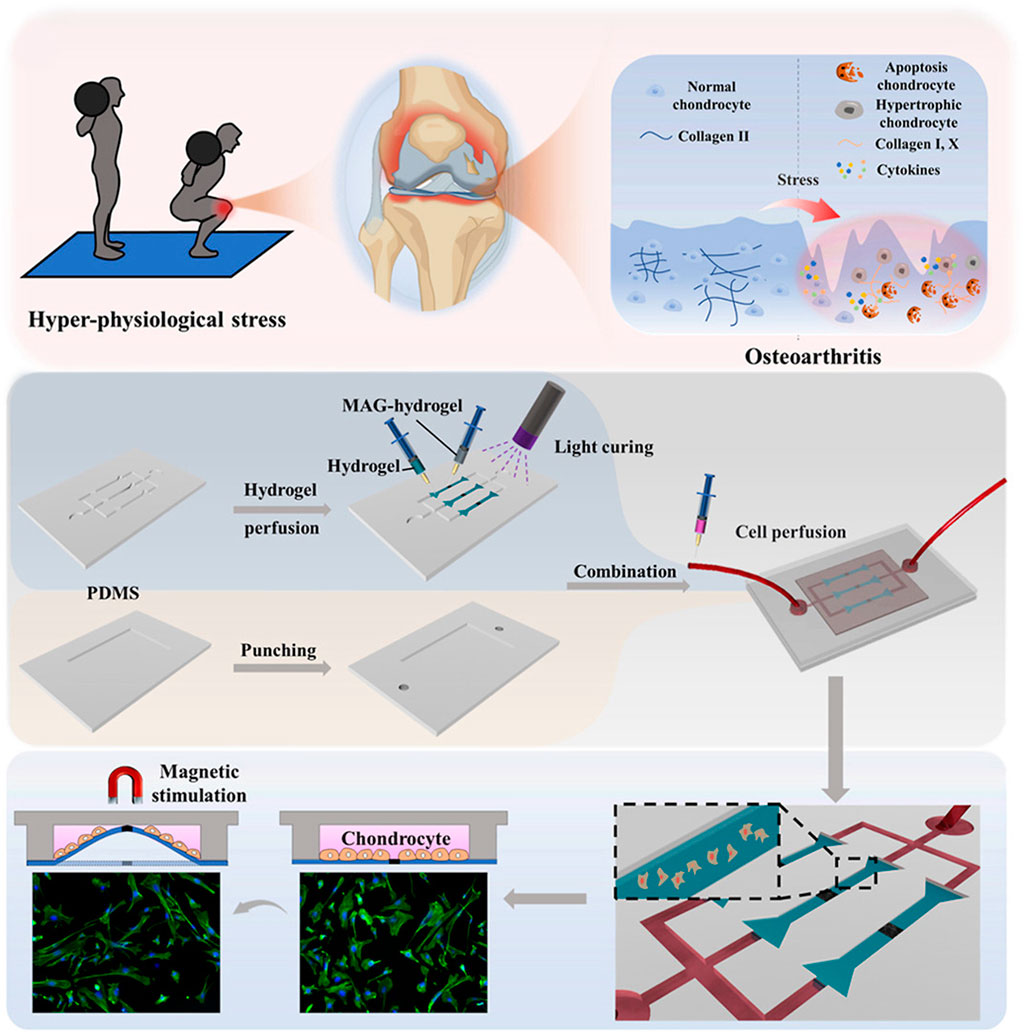
Figure 9. Preparation of magnetic hydrogels (NdFeB-GelMA-HAMA) and the working principle of simulating OA microenvironment change. Reprinted with permission from (Liu H. et al., 2024).
Because it is still difficult to establish a specific magnetic field outside the organism at this stage, and the impact of magnetic field on biosecurity is still unknown, the application of magnetic response hydrogels in osteoarthritis is still in the preliminary exploration stage, but with the progress of science and technology, it is believed that more new magnetic response materials will be developed and applied in the future.
Ultrasound has a promising future in drug delivery, disease diagnosis and treatment due to its relatively simple operation, effective focused energy and deep penetration (Chu et al., 2023; Liang et al., 2024). Ultrasound at 3–20 kHz frequencies has been widely used in clinical orthopedic (Song et al., 2023). As shown in (Figure 2C), since ultrasound can produce a variety of stimuli through the effects of cavitation, changing pressure, promoting acoustic fluid flow and ultrasonic local heat accumulation, various ultrasonic responsive hydrogels are designed to respond to various stimuli respectively, decompose and release loaded drugs for OA repair treatment (Table 2) (Zhou et al., 2022).
Jahanbekam et al. designed an ultrasonic thermal responsive hydrogel (MMH) made of Pluronic F-127, hyaluronic acid and gelatin based on the ultrasonic heat concentration effect, which successfully loaded hydrocortisone, a glucocorticoid drug, for the treatment of OA (Jahanbekam et al., 2023). In vivo and in vitro studies have found that liquid MMH can rapidly respond to temperature rise and gelate under ultrasonic waves at frequencies of 160 W and 35 kHz, achieving long-term controlled release of hydrocortisone, inhibiting OA synovial inflammation and easing cartilage degradation. SDF-1α is a factor closely related to the activation, mobilization, homing and migration of BMSCs (Li et al., 2023c). In order to achieve long-term effective release of SDF-1α, Liu et al. also prepared an ultrasound enhanced injectable chemotactic hydrogel (PFP@NDS-PEG-SDF-1α) based on the ultrasonic thermal effect for OA cartilage repair therapy (Figure 10A) (Liu et al., 2021). In vitro studies, PFP@NDS-PEG-SDF-1α hydrogel responded to ultrasonic gelation and promoted the migration of BMSCs based on the SDF-1-CXCR4 axis. In addition, in vivo studies, PFP@NDS-PEG-SDF-1α hydrogel can improve cell permeability and the expression of CD44, CD29 and Col-II under ultrasound (Figures 10B, C), promote the homing of BMSCs and repair cartilage defects at the same time, providing a new scheme for the treatment of OA. Yuan et al., combined KGN loaded PLGA hydrogel microspheres (MPs@KGN) with methyl chitosan oxidized chondroitin sulfate (CMC-OCS) hydrogel to prepare an ultrasonically responsive hydrogel for cartilage regeneration (CMC-OCS@MPs@KGN) (Yuan et al., 2021). The composite hydrogel can break under ultrasonic stimulation and quickly release high concentration of KGN, improve the expression of Col-II, and contribute to the repair of cartilage.
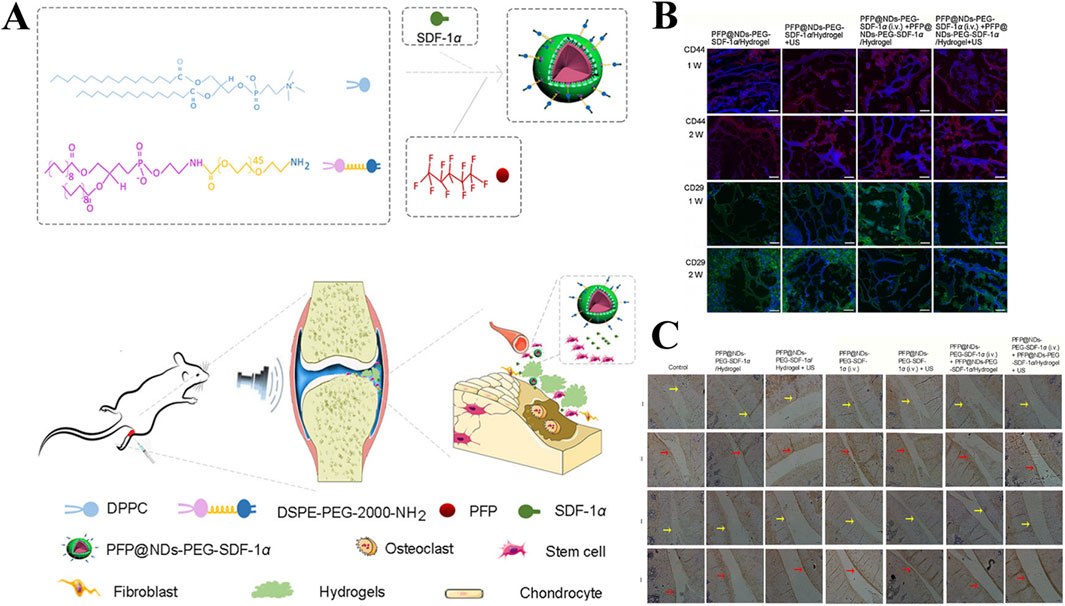
Figure 10. (A) Preparation and in vivo operation of ultrasonic responsive hydrogel (PFP@NDs-PEG-SDF-1α). (B) Expression of CD44 and CD26 in each group of rats after 1 and 2 weeks of treatment in PFP@NDs-PEG-SDF-1α. (C) type I and type II collagen expression after 6 and 12 weeks of treatment in PFP@NDs-PEG-SDF-1α in each group. Reprinted with permission from (Liu et al., 2021).
Although ultrasound can effectively penetrate many soft tissue structures in the body, in the joint, due to the obstruction of bone tissue, ultrasound is more or less weakened, affecting the therapeutic effect of ultrasonic responsive hydrogel. Therefore, improving the penetration of ultrasound in bone will be the next key breakthrough.
The bilateral cartilage of the normal joints of the human body has a smooth surface, and has very low shear friction under various physiological pressures, which can effectively maintain daily movement (Ristaniemi et al., 2024). Under the stimulation of the increase of external joint friction and shear, the articular cartilage wear will be caused, and the expression of cartilage degrading enzyme will increase the cartilage destruction, and then increase the joint friction again, and finally form a positive feedback leading to the generation of OA (Szabo et al., 2023). Hydrogels are widely used in bio-lubrication as three dimensional network structure hydrating materials, however, due to its relatively weak mechanical properties, it is easy to fail and can not achieve long-term lubrication effect (Baig et al., 2024). In response to this problem, as shown in (Figure 2D), researchers have developed a variety of shear-responsive hydrogels, which use the frictional shear of the joint to stimulate the hydrogels to deform and release drugs (Table 2). At the same time, the modification allows the hydrogels to be reassembled to form a long-term and effective lubricating hydration layer and effectively treat OA (Ma P. et al., 2022).
As show in Figure 11A, Lei et al., constructed a shear-responsive drug-loaded hyaluronic acid hydrogel (CLX@Lipo@HA-gel) for OA boundary lubrication and inflammation alleviation based on the application of phospholipids in boundary lubrication (Lei et al., 2022a). CLX@Lipo@HA-gel uses dynamic Schiff base bonds between HA-CHO and HA-ADH to implement shear response. Under the action of shear force, CLX@Lipo@HA-gel dynamically decompositions and releases hydrogenated soybean phosphatidylcholine (HSPC) liposomes containing celercoxib (CLX). On the one hand, HSPC can rearrange with HA structure to form boundary layer to achieve stable and long-term lubrication. On the other hand, the release of CLX can effectively resist inflammatory factors and reduce the destruction of cartilage. In vivo and vitro studies, CLX@Lipo@HA-gel effectively decreased the expression of COF (Figure 11B) and regulated the expression of Col-II and MMP-13 (Figures 11C–I), which played a good role in cartilage protection. Liu et al. designed a self-lubricating and shear-response hydrogel (HKDG) for meniscus, considering that meniscus wear is closely related to cartilage destruction and OA formation (Liu L. et al., 2023). Under the stimulation of shear friction, the outer gel responds to rupture, releasing HSPC liposomes containing KGN and DS, providing a lubricated hydration layer while reducing inflammation in the joint microenvironment and promoting cartilage regeneration, effectively reducing the damage of meniscus and cartilage, and preventing the occurrence of OA. In addition, Lei et al. prepared an improved hydrogel microsphere (RAPA@Lipo@HMs) with a self-renewing boundary lubrication layer with better injectivity and lubricity (Lei et al., 2022b). The composite hydrogel microspheres encapsulated HAMA in the outer layer of cationic HSPC liposomes containing RAPA using microfluidic devices and photopolymerization techniques. Under shear friction, the hydrogel shell ruptures to release positively charged HSPC liposomes that target negatively charged cartilage and provide long-term boundary lubrication. In addition, during the formation of hydration layer, HSPC continuously released RAPA to achieve excessive ROS clearance and inhibit apoptosis of chondrocytes to maintain cell homeostasis. In vivo studies, the injection of RAPA@Lipo@HM into diseased joints effectively reduced cartilage wear and osteophytic formation, and played a good role in OA treatment. Overall, shear-responsive hydrogels provide good cartilage protection through long-term lubrication, providing a new way to treat osteoarthritis.
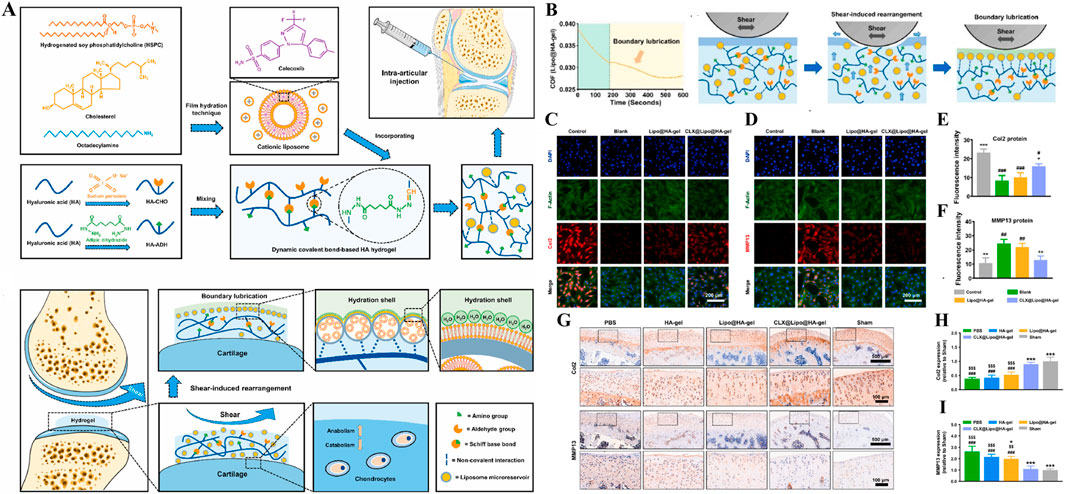
Figure 11. (A) Diagram of preparation and cartilage repair process of shear-responsive hydrogels (CLX@Lipo@HA-gels). (B) CLX@Lipo@HA-gels lubrication. (C–F) Immunofluorescence and quantitative characterization of Col2 and MMP13 after co-culture of chondrocytes in vitro with materials from each group. (G–I) Immunohistochemical staining and quantitative characterization of Col-II and MMP-13 in each group of tissue samples in vivo. n = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Reprinted with permission from (Lei et al., 2022a).
Due to the difficulty of controlling the shear force around the joint, the development of shear-responsive hydrogels is limited. At present, there are only a few research applications of shear-responsive hydrogels. Therefore, it is hoped that more scholars will pay attention to this aspect in the future and explore shear-related therapeutic discoveries.
Smart responsive hydrogels can deliver a variety of drugs to the specified space at the appropriate dose and within a specific time, reducing the adverse factors of drugs to normal tissues and greatly improving the bioavailability of drugs (El-Husseiny et al., 2022b). The intelligent responsive hydrogel is applied to the treatment of OA, which can adjust the release of drugs in response to various changes in the internal and external microenvironment of OA, realizing the purpose of precision treatment and achieving remarkable therapeutic effects (Zhang M. et al., 2022). In addition, the ingenious design of the researchers and the excellent natural chemical and physical properties of the hydrogels have led to the development of more hydrogels with multiple reaction effects and multiple drug loads, and intelligent responsive hydrogels are full of prospects on the road of future OA treatment (Gan et al., 2024).
There is no denying that smart reactive hydrogels have excellent therapeutic effects, but there is still a long way to go to expand their application for clinical use. First, although many intelligent-responsive hydrogels have been shown to have no significant biotoxic effects at both in vivo and in vitro study levels, most research methods are primarily based on lower-level animal models such as rats, mice, and rabbits (Kumi et al., 2024). Because there are still many differences between the structure of the human joint microenvironment with these animals (such as the thickness of the articular cartilage layer, the composition of the synovial fluid, etc.), it is doubtful whether the therapeutic effects and toxicity obtained in these animal models can be replicated in humans. Secondly, some external stimuli in response to exogenous hydrogels will inevitably cause damage to normal tissues (for example, ultrasound may damage DNA when it penetrates tissues, near-infrared light irradiation and magnetic concentration will cause thermal burns to surrounding local tissues, etc.) (El-Husseiny et al., 2022a). In addition, the human joint microenvironment is relatively complex, there are many uncertain interference factors, exogenous stimulation is difficult to achieve the ideal conditions for designing and preparing intelligent response hydrogels (Li M. et al., 2022). These results in misalignment or off-target control of drug release, would greatly reduce the effectiveness of treatment. Furthermore, many smart hydrogel drug delivery platforms are still in the initial stage of development. In order to achieve multiple therapeutic effects of osteoarthritis, it needs to spend a lot of energy and expense to build and decorate, and it is difficult to achieve the goal of commercialization in the short term (Rezakhani et al., 2024; Zöller et al., 2025). Moreover, different individual physiological states differ greatly, in order to achieve the desired therapeutic effect, individualized treatment is needed, which will undoubtedly increase the production cost again (Thang et al., 2023; Wu J. et al., 2024). Therefore, how to balance efficacy and cost may become a new problem affecting the development of intelligent response hydrogel research in the future. Finally, there is no perfect responsive hydrogel material. In the treatment of clinical diseases, it is necessary to comprehensively consider various factors such as disease characteristics, drug efficacy, physical and chemical properties, dosage and method of administration, and material cost, and keep pace with the times to continuously develop new responsive hydrogel systems, so that responsive hydrogel materials can truly move from the laboratory to clinical application.
At present, a variety of intelligent stimulus-responsive hydrogels have been successfully prepared and achieved excellent results in the treatment of OA. This review focuses on recent developments in stimulus-responsive hydrogels for the treatment of OA in the last 3 years since this article was written. The therapeutic effect of hydrogels with multiple responsive factors on drug delivery in the treatment of OA diseases and some existing problems were reviewed and discussed. Thus, this review contributes to an understanding of the most advanced research findings and corresponding challenges related to spirogenic stimulus-responsive hydrogels in OA therapy.
ZX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. JL: Data curation, Writing–original draft. HH: Data curation, Writing–original draft. JM: Data curation, Writing–original draft. HY: Data curation, Writing–original draft. JC: Data curation, Writing–original draft. HX: Data curation, Writing–original draft. HH: Data curation, Writing–original draft. HL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Visualization, Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. GC: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Visualization, Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32201076), Jiaxing Public Welfare Research Program (2024AY30013), Jiaxing Key Research and Development Program (2024BZ20005), Joint Funds of the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LBY22H180011 and LBZ22H180001).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abramoff, B., and Caldera, F. E. (2020). Osteoarthritis: pathology, diagnosis, and treatment options. Med. Clin. North. Am. 104 (2), 293–311. doi:10.1016/j.mcna.2019.10.007
Ahmed, E. M. (2015). Hydrogel: preparation, characterization, and applications: a review. J. Adv. Res. 6 (2), 105–121. doi:10.1016/j.jare.2013.07.006
Ansari, M. Y., Ahmad, N., and Haqqi, T. M. (2020). Oxidative stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: role of polyphenols. Biomed. Pharmacother. 129, 110452. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110452
Arcus, V. L., and Mulholland, A. J. (2020). Temperature, dynamics, and enzyme-catalyzed reaction rates. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 49, 163–180. doi:10.1146/annurev-biophys-121219-081520
Arra, M., and Abu-Amer, Y. (2023). Cross-talk of inflammation and chondrocyte intracellular metabolism in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 31 (8), 1012–1021. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2023.04.003
Baig, M., Wong, L. K., Zia, A. W., and Wu, H. (2024). Development of biomedical hydrogels for rheumatoid arthritis treatment. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 19 (1), 100887. doi:10.1016/j.ajps.2024.100887
Bannuru, R. R., Osani, M. C., Vaysbrot, E. E., Arden, N. K., Bennell, K., Bierma-Zeinstra, S. M. A., et al. (2019). OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical management of knee, hip, and polyarticular osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 27 (11), 1578–1589. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2019.06.011
Bennell, K. L., and Hunter, D. J. (2020). Physical therapy before the needle for osteoarthritis of the knee. N. Engl. J. Med. 382 (15), 1470–1471. doi:10.1056/NEJMe2000718
Berenbaum, F., Wallace, I. J., Lieberman, D. E., and Felson, D. T. (2018). Modern-day environmental factors in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 14 (11), 674–681. doi:10.1038/s41584-018-0073-x
Bolduc, J. A., Collins, J. A., and Loeser, R. F. (2019). Reactive oxygen species, aging and articular cartilage homeostasis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 132, 73–82. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.08.038
Bramhe, P., Rarokar, N., Kumbhalkar, R., Saoji, S., and Khedekar, P. (2024). Natural and synthetic polymeric hydrogel: a bioink for 3D bioprinting of tissue models. J. Drug Deliv. Sci.Technol. 101, 106204. doi:10.1016/j.jddst.2024.106204
Buller, R., Lutz, S., Kazlauskas, R. J., Snajdrova, R., Moore, J. C., and Bornscheuer, U. T. (2023). From nature to industry: harnessing enzymes for biocatalysis. Science 382 (6673), eadh8615. doi:10.1126/science.adh8615
Canizares, M., Power, J., Perruccio, A. V., and Rampersaud, Y. (2021). High resource use prior to elective surgery for osteoarthritis associated with worse outcomes and high post-operative healthcare use and costs: a population-based study in Ontario, Canada. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 29, S389–S390. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2021.02.505
Cao, H., Duan, L., Zhang, Y., Cao, J., and Zhang, K. (2021). Current hydrogel advances in physicochemical and biological response-driven biomedical application diversity. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 6 (1), 426. doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00830-x
Catoira, M. C., Fusaro, L., Di Francesco, D., Ramella, M., and Boccafoschi, F. (2019). Overview of natural hydrogels for regenerative medicine applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 30 (10), 115. doi:10.1007/s10856-019-6318-7
Chen, B., Wang, J., Jin, X., Wang, X., Fan, Z., Zhang, Y., et al. (2023a). Rapamycin incorporating hydrogel improves the progression of osteoarthritis by inducing synovial macrophages polarization and reducing intra-articular inflammation. Mater. and Des. 225, 111542. doi:10.1016/j.matdes.2022.111542
Chen, L., Zhang, J., Wang, J., Lin, J., Luo, X., and Cui, W. (2023b). Inflammation-regulated auto aggregated hydrogel microspheres via anchoring cartilage deep matrix for genes delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33 (51). doi:10.1002/adfm.202305635
Chen, W., Xiao, J., Zhou, Y., Liu, W., Jian, J., Yang, J., et al. (2024). Curcumenol regulates histone H3K27me3 demethylases KDM6B affecting succinic acid metabolism to alleviate cartilage degeneration in knee osteoarthritis. Phytomed 133, 155922. doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155922
Chen, Z., Zhang, F., Zhang, H., Cheng, L., Chen, K., Shen, J., et al. (2021). DNA-grafted hyaluronic acid system with enhanced injectability and biostability for photo-controlled osteoarthritis gene therapy. Adv. Sci. 8 (9), 2004793. doi:10.1002/advs.202004793
Cho, Y., Jeong, S., Kim, H., Kang, D., Lee, J., Kang, S. B., et al. (2021). Disease-modifying therapeutic strategies in osteoarthritis: current status and future directions. Exp. Mol. Med. 53 (11), 1689–1696. doi:10.1038/s12276-021-00710-y
Chu, B., Chen, Z., Shi, H., Wu, X., Wang, H., Dong, F., et al. (2023). Fluorescence, ultrasonic and photoacoustic imaging for analysis and diagnosis of diseases. Chem. Commun. 59 (17), 2399–2412. doi:10.1039/d2cc06654h
Coryell, P. R., Diekman, B. O., and Loeser, R. F. (2021). Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of cellular senescence in osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 17 (1), 47–57. doi:10.1038/s41584-020-00533-7
Ding, H., Tan, P., Fu, S., Tian, X., Zhang, H., Ma, X., et al. (2022). Preparation and application of pH-responsive drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 348, 206–238. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.05.056
El-Husseiny, H. M., Mady, E. A., Hamabe, L., Abugomaa, A., Shimada, K., Yoshida, T., et al. (2022a). Smart/stimuli-responsive hydrogels: cutting-edge platforms for tissue engineering and other biomedical applications. Mater. Today Bio 13, 100186. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2021.100186
El-Husseiny, H. M., Mady, E. A., Hamabe, L., Abugomaa, A., Shimada, K., Yoshida, T., et al. (2022b). Smart/stimuli-responsive hydrogels: cutting-edge platforms for tissue engineering and other biomedical applications. Mater. Today Bio 13, 100186. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2021.100186
Enayati, M., Liu, W., Madry, H., Neisiany, R. E., and Cucchiarini, M. (2024). Functionalized hydrogels as smart gene delivery systems to treat musculoskeletal disorders. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 331, 103232. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2024.103232
Fang, Y., Nie, T., Li, G., Wang, L., Du, J., and Wu, J. (2024). Multifunctional antibiotic hydrogel doped with antioxidative lycopene-based liposome for accelerative diabetic wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 480, 147930. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2023.147930
Gan, X., Wang, X., Huang, Y., Li, G., and Kang, H. (2024). Applications of hydrogels in osteoarthritis treatment. Biomedicines 12 (4), 923. doi:10.3390/biomedicines12040923
Grol, M. W. (2024). The evolving landscape of gene therapy strategies for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 32 (4), 372–384. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2023.12.009
Gutierrez, A. M., Frazar, E. M., Mv, X. K., Paul, P., and Hilt, J. Z. (2022). Hydrogels and hydrogel nanocomposites: enhancing healthcare through human and environmental treatment. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 11 (7), e2101820. doi:10.1002/adhm.202101820
Hall, M., van der Esch, M., Hinman, R. S., Peat, G., de Zwart, A., Quicke, J. G., et al. (2022). How does hip osteoarthritis differ from knee osteoarthritis? Osteoarthr. Cartil. 30 (1), 32–41. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2021.09.010
Hao, L., and Mao, H. (2023). Magnetically anisotropic hydrogels for tissue engineering. Biomater. Sci. 11 (19), 6384–6402. doi:10.1039/d3bm00744h
Hernansanz-Agustín, P., and Enríquez, J. A. (2022). Sodium in mitochondrial redox signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal 37 (4-6), 290–300. doi:10.1089/ars.2021.0262
Ho, T. C., Chang, C. C., Chan, H. P., Chung, T. W., Shu, C. W., Chuang, K. P., et al. (2022). Hydrogels: properties and applications in biomedicine. Molecules 27 (9), 2902. doi:10.3390/molecules27092902
Hu, W., Chen, Y., Dou, C., and Dong, S. (2021). Microenvironment in subchondral bone: predominant regulator for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 80 (4), 413–422. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218089
Hu, W., Yao, X., Li, Y., Li, J., Zhang, J., Zou, Z., et al. (2023). Injectable hydrogel with selenium nanoparticles delivery for sustained glutathione peroxidase activation and enhanced osteoarthritis therapeutics. Mater. Today Bio 23, 100864. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100864
Huang, C., Zhang, Z., Fang, Y., Huang, K., Zhao, Y., Huang, H., et al. (2024). Cost-effective and natural-inspired lotus root/GelMA scaffolds enhanced wound healing via ROS scavenging, angiogenesis and reepithelialization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 278, 134496. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.134496
Ibrahiem, B., Shamma, R., Salama, A., and Refai, H. (2023). Magnetic targeting of lornoxicam/SPION bilosomes loaded in a thermosensitive in situ hydrogel system for the management of osteoarthritis: optimization, in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo studies in rat model via modulation of RANKL/OPG. Drug Deliv. Trans. Res. 14 (7), 1982–2002. doi:10.1007/s13346-023-01503-8
Jägerbrand, A. K., and Spoelstra, K. (2023). Effects of anthropogenic light on species and ecosystems. Science 380 (6650), 1125–1130. doi:10.1126/science.adg3173
Jahanbekam, S., Mozafari, N., Bagheri-Alamooti, A., Mohammadi-Samani, S., Daneshamouz, S., Heidari, R., et al. (2023). Ultrasound-responsive hyaluronic acid hydrogel of hydrocortisone to treat osteoarthritis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 240, 124449. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.124449
Jiang, Q., and Zhang, S. (2023). Stimulus-responsive drug delivery nanoplatforms for osteoarthritis therapy. Small 19 (23), e2206929. doi:10.1002/smll.202206929
Jiang, Y. (2022). Osteoarthritis year in review 2021: biology. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 30 (2), 207–215. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2021.11.009
Jiang, Y., Liao, H., Yan, L., Jiang, S., Zheng, Y., Zhang, X., et al. (2023). A metal-organic framework-incorporated hydrogel for delivery of immunomodulatory neobavaisoflavone to promote cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 15 (40), 46598–46612. doi:10.1021/acsami.3c06706
Jones, I. A., Togashi, R., Wilson, M. L., Heckmann, N., and Vangsness, C. T. (2019). Intra-articular treatment options for knee osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 15 (2), 77–90. doi:10.1038/s41584-018-0123-4
Kalairaj, M. S., Pradhan, R., Saleem, W., Smith, M. M., and Gaharwar, A. K. (2024). Intra-articular injectable biomaterials for cartilage repair and regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13 (17), 2303794. doi:10.1002/adhm.202303794
Kawaguchi, H. (2024). Current status of treatments administered by intra-articular injection for knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 32 (11), 1353–1355. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2024.07.012
Khaliq, N. U., Lee, J., Kim, S., Sung, D., and Kim, H. (2023). Pluronic F-68 and F-127 based nanomedicines for advancing combination cancer therapy. Pharmaceutics 15 (8), 2102. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics15082102
Kumar, B., Jha, L. A., Pandey, P., Iqbal, S. F., Thaleshwari, S., Banerjee, K., et al. (2024). Unlocking the future of osteoarthritis: material engineering and drug delivery confluence for advanced therapeutic approaches. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 101, 106264. doi:10.1016/j.jddst.2024.106264
Kumi, M., Ejeromedoghene, O., Sudane, W. D., and Zhang, Z. (2024). Unlocking the biological response of smart Stimuli-Responsive hydrogels and their application in biological systems. Eur. Polym. J. 209, 112906. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2024.112906
Lai, Y., Wu, X., Jiang, Z., Fang, Y., Liu, X., Hong, D., et al. (2024). Topical treatment of tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitor through borneol-embedded hydrogel: evaluation for preventive, therapeutic, and Recurrent management of psoriasis. Bioact. Mater. 41, 83–95. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.07.013
Lee, W., Nims, R. J., Savadipour, A., Zhang, Q., Leddy, H. A., Liu, F., et al. (2021). Inflammatory signaling sensitizes Piezo1 mechanotransduction in articular chondrocytes as a pathogenic feed-forward mechanism in osteoarthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 118 (13), e2001611118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2001611118
Lei, L., Cong, R., Ni, Y., Cui, X., Wang, X., Ren, H., et al. (2024). Dual-functional injectable hydrogel for osteoarthritis treatments. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13 (5), e2302551. doi:10.1002/adhm.202302551
Lei, Y., Wang, X., Liao, J., Shen, J., Li, Y., Cai, Z., et al. (2022a). Shear-responsive boundary-lubricated hydrogels attenuate osteoarthritis. Bioact. Mater. 16, 472–484. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.02.016
Lei, Y., Wang, Y., Shen, J., Cai, Z., Zhao, C., Chen, H., et al. (2022b). Injectable hydrogel microspheres with self-renewable hydration layers alleviate osteoarthritis. Sci. Adv. 8 (5), eabl6449. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abl6449
Li, G., Liu, S., Chen, Y., Zhao, J., Xu, H., Weng, J., et al. (2023a). An injectable liposome-anchored teriparatide incorporated gallic acid-grafted gelatin hydrogel for osteoarthritis treatment. Nat. Commun. 14 (1), 3159. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-38597-0
Li, H., Li, Y., Wang, D., Huang, Q., and Liu, D. (2024a). Evaluation of risk factors for surgical site infections in osteoarthritis patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Int. Wound J. 21 (3), e14521. doi:10.1111/iwj.14521
Li, J., Zhang, H., Han, Y., Hu, Y., Geng, Z., and Su, J. (2023b). Targeted and responsive biomaterials in osteoarthritis. Theranostics 13 (3), 931–954. doi:10.7150/thno.78639
Li, J., Zhao, C., Xu, Y., Song, L., Chen, Y., Xu, Y., et al. (2023c). Remodeling of the osteoimmune microenvironment after biomaterials implantation in murine tibia: single-cell transcriptome analysis. Bioact. Mater. 22, 404–422. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.10.009
Li, L., Scheiger, J. M., and Levkin, P. A. (2019). Design and applications of photoresponsive hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 31 (26), e1807333. doi:10.1002/adma.201807333
Li, M., Yin, H., Yan, Z., Li, H., Wu, J., Wang, Y., et al. (2022a). The immune microenvironment in cartilage injury and repair. Acta Biomater. 140, 23–42. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2021.12.006
Li, T., Peng, J., Li, Q., Shu, Y., Zhu, P., and Hao, L. (2022b). The mechanism and role of ADAMTS protein family in osteoarthritis. Biomolecules 12 (7), 959. doi:10.3390/biom12070959
Li, Y., Ding, X., Hu, H., and Xu, F.-J. (2024b). Stimulus-responsive polysaccharide-based hydrogels: from design to biomedical applications. Precis. Med. Eng. 1 (1), 100001. doi:10.1016/j.preme.2024.100001
Li, Y., Li, L., Li, Y., Feng, L., Wang, B., Wang, M., et al. (2023d). Enhancing cartilage repair with optimized supramolecular hydrogel-based scaffold and pulsed electromagnetic field. Bioact. Mater. 22, 312–324. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.10.010
Li, Y., Wang, N., Huang, X., Li, F., Davis, T. P., Qiao, R., et al. (2020). Polymer-assisted magnetic nanoparticle assemblies for biomedical applications. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 3 (1), 121–142. doi:10.1021/acsabm.9b00896
Li, Z., Cheng, Q., Lin, L., Fu, X., and Wang, Y. (2024c). Plasma membrane-derived biomimetic apoptotic nanovesicles targeting inflammation and cartilage degeneration for osteoarthritis. Small Methods 9, 2400660. doi:10.1002/smtd.202400660
Li, Z., Huang, Z., and Bai, L. (2021a). Cell interplay in osteoarthritis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9, 720477. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.720477
Li, Z., Li, Y., Chen, C., and Cheng, Y. (2021b). Magnetic-responsive hydrogels: from strategic design to biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 335, 541–556. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.06.003
Liang, J., Qiao, X., Qiu, L., Xu, H., Xiang, H., Ding, H., et al. (2024). Engineering versatile nanomedicines for ultrasonic tumor immunotherapy. Adv. Sci. 11 (3), e2305392. doi:10.1002/advs.202305392
Liew, J. W., King, L. K., Mahmoudian, A., Wang, Q., Atkinson, H. F., Flynn, D. B., et al. (2023). A scoping review of how early-stage knee osteoarthritis has been defined. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 31 (9), 1234–1241. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2023.04.015
Lim, K. S., Abinzano, F., Bernal, P. N., Albillos Sanchez, A., Atienza-Roca, P., Otto, I. A., et al. (2020). One-step photoactivation of a dual-functionalized bioink as cell carrier and cartilage-binding glue for chondral regeneration. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 9 (15), e1901792. doi:10.1002/adhm.201901792
Liu, H., Wu, X., Liu, R., Wang, W., Zhang, D., and Jiang, Q. (2024a). Cartilage-on-a-chip with magneto-mechanical transformation for osteoarthritis recruitment. Bioact. Mater. 33, 61–68. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2023.10.030
Liu, H., Xiang, X., Huang, J., Zhu, B., Wang, L., Tang, Y., et al. (2021). Ultrasound augmenting injectable chemotaxis hydrogel for articular cartilage repair in osteoarthritis. Chin. Chem. Lett. 32 (5), 1759–1764. doi:10.1016/j.cclet.2020.12.004
Liu, K., Han, L., Tang, P., Yang, K., Gan, D., Wang, X., et al. (2019). An anisotropic hydrogel based on mussel-inspired conductive ferrofluid composed of electromagnetic nanohybrids. Nano Lett. 19 (12), 8343–8356. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b00363
Liu, L., Liu, H., Wang, R., Zhou, J., Zhao, L., Li, Q., et al. (2024b). Preparation and application of environmentally-responsive hydrogels in tissue engineering. Mater. Today Commun. 40, 109493. doi:10.1016/j.mtcomm.2024.109493
Liu, L., Xian, Y., Wang, W., Huang, L., Fan, J., Ma, W., et al. (2023a). Meniscus-inspired self-lubricating and friction-responsive hydrogels for protecting articular cartilage and improving exercise. ACS Nano 17 (23), 24308–24319. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c10139
Liu, S., Cheng, S., Chen, B., Xiao, P., Zhan, J., Liu, J., et al. (2023b). Microvesicles-hydrogel breaks the cycle of cellular senescence by improving mitochondrial function to treat osteoarthritis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 21 (1), 429. doi:10.1186/s12951-023-02211-8
Lv, Z., Hu, T., Bian, Y., Wang, G., Wu, Z., Li, H., et al. (2023). A MgFe-LDH nanosheet-incorporated smart thermo-responsive hydrogel with controllable growth factor releasing capability for bone regeneration. Adv. Mater. 35 (5), e2206545. doi:10.1002/adma.202206545
Ma, L., Zheng, X., Lin, R., Sun, A. R., Song, J., Ye, Z., et al. (2022a). Knee osteoarthritis therapy: recent advances in intra-articular drug delivery systems. Drug Des. devel. Ther. 16, 1311–1347. doi:10.2147/dddt.S357386
Ma, P., Lai, X., Luo, Z., Chen, Y., Loh, X. J., Ye, E., et al. (2022b). Recent advances in mechanical force-responsive drug delivery systems. Nanoscale Adv. 4 (17), 3462–3478. doi:10.1039/d2na00420h
Ma, Q., Lin, D., Liu, Y., Liu, X., Zhao, H., Zhou, G., et al. (2024). Recent research progress of hydrogel on cartilage. Eur. Polym. J. 213, 113115. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2024.113115
Madreiter-Sokolowski, C. T., Thomas, C., and Ristow, M. (2020). Interrelation between ROS and Ca(2+) in aging and age-related diseases. Redox. Biol. 36, 101678. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2020.101678
Mahmoudian, A., Lohmander, L. S., Mobasheri, A., Englund, M., and Luyten, F. P. (2021). Early-stage symptomatic osteoarthritis of the knee - time for action. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 17 (10), 621–632. doi:10.1038/s41584-021-00673-4
Malemud, C. J. (2019). Inhibition of MMPs and ADAM/ADAMTS. Biochem. Pharmacol. 165, 33–40. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2019.02.033
Mandl, L. A. (2019). Osteoarthritis year in review 2018: clinical. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 27 (3), 359–364. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2018.11.001
Maniar, K. H., Jones, I. A., Gopalakrishna, R., and Vangsness, C. T. (2018). Lowering side effects of NSAID usage in osteoarthritis: recent attempts at minimizing dosage. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 19 (2), 93–102. doi:10.1080/14656566.2017.1414802
Mao, L., Wu, W., Wang, M., Guo, J., Li, H., Zhang, S., et al. (2021). Targeted treatment for osteoarthritis: drugs and delivery system. Drug Deliv. 28 (1), 1861–1876. doi:10.1080/10717544.2021.1971798
Martel-Pelletier, J., Barr, A. J., Cicuttini, F. M., Conaghan, P. G., Cooper, C., Goldring, M. B., et al. (2016). Osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2, 16072. doi:10.1038/nrdp.2016.72
Marx, R. G. (2008). Arthroscopic surgery for osteoarthritis of the knee? N. Engl. J. Med. 359 (11), 1169–1170. doi:10.1056/NEJMe0804450
McGarry, T., Biniecka, M., Veale, D. J., and Fearon, U. (2018). Hypoxia, oxidative stress and inflammation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 125, 15–24. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.03.042
Miao, K., Zhou, Y., He, X., Xu, Y., Zhang, X., Zhao, H., et al. (2024). Microenvironment-responsive bilayer hydrogel microspheres with gelatin-shell for osteoarthritis treatment. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 261 (Pt 2), 129862. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.129862
Mukherjee, A., and Das, B. (2024). The role of inflammatory mediators and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in the progression of osteoarthritis. Biomater. Biosyst. 13, 100090. doi:10.1016/j.bbiosy.2024.100090
Nakkala, J. R., Li, Z., Ahmad, W., Wang, K., and Gao, C. (2021). Immunomodulatory biomaterials and their application in therapies for chronic inflammation-related diseases. Acta Biomater. 123, 1–30. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2021.01.025
Neurath, M. F. (2020). IL-36 in chronic inflammation and cancer. Cytokine and Growth Factor Rev 55, 70–79. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.06.006
Ng, J. Q., Jafarov, T. H., Little, C. B., Wang, T., Ali, A. M., Ma, Y., et al. (2023). Loss of Grem1-lineage chondrogenic progenitor cells causes osteoarthritis. Nat. Commun. 14 (1), 6909. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-42199-1
Ni, X., Hu, L., Zhang, X., Wang, Z., Yan, C., Peyrodie, L., et al. (2024). Physical therapy options for knee osteoarthritis: a review. Med. Baltim. 103 (30), e38415. doi:10.1097/md.0000000000038415
Pacheco-Brousseau, L., Stacey, D., Desmeules, F., Ben Amor, S., Dervin, G., Beaulé, P. E., et al. (2024). Determining appropriateness of total joint arthroplasty for hip and knee osteoarthritis: a patient-centred conceptual model. Musculoskelet. Care 22 (3), e1927. doi:10.1002/msc.1927
Palazzo, C., Nguyen, C., Lefevre-Colau, M. M., Rannou, F., and Poiraudeau, S. (2016). Risk factors and burden of osteoarthritis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 59 (3), 134–138. doi:10.1016/j.rehab.2016.01.006
Price, A. J., Alvand, A., Troelsen, A., Katz, J. N., Hooper, G., Gray, A., et al. (2018). Knee replacement. Lancet 392 (10158), 1672–1682. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(18)32344-4
Rahmani, F., Atabaki, R., Behrouzi, S., Mohamadpour, F., and Kamali, H. (2023). The recent advancement in the PLGA-based thermo-sensitive hydrogel for smart drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 631, 122484. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2022.122484
Ramos-Sebastian, A., Gwak, S. J., and Kim, S. H. (2022). Multimodal locomotion and active targeted thermal control of magnetic agents for biomedical applications. Adv. Sci. 9 (7), e2103863. doi:10.1002/advs.202103863
Rapp, T. L., and DeForest, C. A. (2020). Visible Light-responsive dynamic biomaterials: going deeper and triggering more. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 9 (7), e1901553. doi:10.1002/adhm.201901553
Reisenbauer, J. C., Sicinski, K. M., and Arnold, F. H. (2024). Catalyzing the future: recent advances in chemical synthesis using enzymes. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 83, 102536. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2024.102536
Rezakhani, L., Gharibshahian, M., Salehi, M., Zamani, S., Abpeikar, Z., Ghaderzadeh, O., et al. (2024). Recent advances in hydrogels applications for tissue engineering and clinical trials. Regen. Ther. 26, 635–645. doi:10.1016/j.reth.2024.08.015
Richard, M. J., Driban, J. B., and McAlindon, T. E. (2023). Pharmaceutical treatment of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 31 (4), 458–466. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2022.11.005
Riegger, J., Schoppa, A., Ruths, L., Haffner-Luntzer, M., and Ignatius, A. (2023). Oxidative stress as a key modulator of cell fate decision in osteoarthritis and osteoporosis: a narrative review. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 28 (1), 76. doi:10.1186/s11658-023-00489-y
Rim, Y. A., Nam, Y., and Ju, J. H. (2020). The role of chondrocyte hypertrophy and senescence in osteoarthritis initiation and progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (7), 2358. doi:10.3390/ijms21072358
Ristaniemi, A., Tuppurainen, J., Jäntti, J., Nippolainen, E., Afara, I. O., Mononen, M. E., et al. (2024). Comparison of site-specific tensile, compressive, and friction properties of human tibiofemoral joint cartilage and their relationship to degeneration. J. Biomech. 177, 112386. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2024.112386
Shen, K. H., Lu, C. H., Kuo, C. Y., Li, B. Y., and Yeh, Y. C. (2021). Smart near infrared-responsive nanocomposite hydrogels for therapeutics and diagnostics. J. Mater. Chem. B 9 (35), 7100–7116. doi:10.1039/d1tb00980j
Singla, P., Garg, S., McClements, J., Jamieson, O., Peeters, M., and Mahajan, R. K. (2022). Advances in the therapeutic delivery and applications of functionalized Pluronics: a critical review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 299, 102563. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2021.102563
Sobczak, M. (2022). Enzyme-responsive hydrogels as potential drug delivery systems-state of knowledge and future prospects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (8), 4421. doi:10.3390/ijms23084421
Song, X., Zhang, Q., Chang, M., Ding, L., Huang, H., Feng, W., et al. (2023). Nanomedicine-enabled sonomechanical, sonopiezoelectric, sonodynamic, and sonothermal therapy. Adv. Mater. 35 (31), e2212259. doi:10.1002/adma.202212259
Sun, W., Yue, J., Cui, Y., Feng, J., He, Q., Liang, J., et al. (2024). Wedelolactone alleviates inflammation and cartilage degeneration by suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway in osteoarthritis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 143 (Pt 1), 113359. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113359
Szabo, N., Brouillette, M. J., Johnson, J. E., and Goetz, J. E. (2023). Variations in articular surface collagen fibril orientations produce similar shear stresses and strain calculations throughout the depth of cartilage. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 31, S143–S144. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2023.01.102
Szanto, I. (2022). NADPH Oxidase 4 (NOX4) in cancer: linking redox signals to oncogenic metabolic adaptation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (5), 2702. doi:10.3390/ijms23052702
Tan, C., Li, L., Han, J., Xu, K., and Liu, X. (2022). A new strategy for osteoarthritis therapy: inhibition of glycolysis. Front. Pharmacol. 13, 1057229. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.1057229
Thang, N. H., Chien, T. B., and Cuong, D. X. (2023). Polymer-based hydrogels applied in drug delivery: an overview. Gels 9 (7), 523. doi:10.3390/gels9070523
Tian, B., and Liu, J. (2023). Smart stimuli-responsive chitosan hydrogel for drug delivery: a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 235, 123902. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.123902
Tianyuan, Z., Haoyuan, D., Jianwei, L., Songlin, H., Xu, L., Hao, L., et al. (2023). A smart MMP13-responsive injectable hydrogel with inflammatory diagnostic logic and multiphase therapeutic ability to orchestrate cartilage regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33 (16). doi:10.1002/adfm.202213019
Valentino, A., Conte, R., De Luca, I., Di Cristo, F., Peluso, G., Bosetti, M., et al. (2022). Thermo-responsive gel containing hydroxytyrosol-chitosan nanoparticles (Hyt@tgel) counteracts the increase of osteoarthritis biomarkers in human chondrocytes. Antioxidants 11 (6), 1210. doi:10.3390/antiox11061210
van den Bosch, M. H. J. (2021). Osteoarthritis year in review 2020: biology. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 29 (2), 143–150. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2020.10.006
Wang, Y., Liu, L., Le, Z., and Tay, A. (2022). Analysis of nanomedicine efficacy for osteoarthritis. Adv. NanoBiomed. Res. 2 (12). doi:10.1002/anbr.202200085
Wang, Z., Shi, W., Wu, L., Xiao, Y., Wang, M., Zhang, S., et al. (2024a). TMF inhibits extracellular matrix degradation by regulating the C/EBPβ/ADAMTS5 signaling pathway in osteoarthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 174, 116501. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116501
Wang, Z., Yao, S.-Y., Zhang, Y., Li, S., Zhou, T., Wang, S., et al. (2024b). Hypoxia-responsive microgels act as an intra-articular lubricant and inflammatory inhibitor for osteoarthritis therapy. Nano Today 57, 102373. doi:10.1016/j.nantod.2024.102373
Wu, H., Wang, J., Lin, Y., He, W., Hou, J., Deng, M., et al. (2024a). Injectable ozone-rich nanocomposite hydrogel loaded with d-mannose for anti-inflammatory and cartilage protection in osteoarthritis treatment. Small 20 (25), e2309597. doi:10.1002/smll.202309597
Wu, J., Xue, W., Yun, Z., Liu, Q., and Sun, X. (2024b). Biomedical applications of stimuli-responsive “smart” interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels. Mater. Today Bio 25, 100998. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.100998
Xiao, X., and Huang, J. (2024). Enzyme-responsive supramolecular self-assembly in small amphiphiles. Langmuir 40 (30), 15407–15420. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c01762
Xing, Y., Zeng, B., and Yang, W. (2022). Light responsive hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 10, 1075670. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2022.1075670
Xu, H., Che, Y., Zhou, R., Wang, L., Huang, J., Kong, W., et al. (2024). Research progress of natural polysaccharide-based and natural protein-based hydrogels for bacteria-infected wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 496, 153803. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2024.153803
Xu, R., Wu, J., Zheng, L., and Zhao, M. (2023). Undenatured type II collagen and its role in improving osteoarthritis. Ageing Res. Rev. 91, 102080. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2023.102080
Xue, X., Hu, Y., Wang, S., Chen, X., Jiang, Y., and Su, J. (2022). Fabrication of physical and chemical crosslinked hydrogels for bone tissue engineering. Bioact. Mater. 12, 327–339. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.10.029
Yadav, P., Singh, S., Jaiswal, S., and Kumar, R. (2024). Synthetic and natural polymer hydrogels: a review of 3D spheroids and drug delivery. Intern. J. Biol. Macromol. 280, 136126. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.136126
Yan, H., Guo, J., Zhou, W., Dong, C., and Liu, J. (2022). Health-related quality of life in osteoarthritis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychol. Health. Med. 27 (8), 1859–1874. doi:10.1080/13548506.2021.1971725
Yao, Q., Wu, X., Tao, C., Gong, W., Chen, M., Qu, M., et al. (2023). Osteoarthritis: pathogenic signaling pathways and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 8 (1), 56. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01330-w
Yi, X., Xu, Z., Liu, Q., Zhou, H., Yuan, L., Li, D., et al. (2022). Matrix metalloproteinase-responsive collagen-oxidized hyaluronic acid injectable hydrogels for osteoarthritic therapy. Biomater. Adv. 137, 212804. doi:10.1016/j.bioadv.2022.212804
Yi, Y. H., Chen, G., Gong, S., Han, L. Z., Gong, T. L., Wang, Y. X., et al. (2023). Injectable temperature-sensitive hydrogel loaded with IL-36Ra for the relief of osteoarthritis. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 9 (3), 1672–1681. doi:10.1021/acsbiomaterials.2c01144
Yin, P., Jiang, Y., Fang, X., Wang, D., Li, Y., Chen, M., et al. (2023). Cell-based therapies for degenerative musculoskeletal diseases. Adv. Sci. 10 (21), e2207050. doi:10.1002/advs.202207050
Yuan, F. Z., Wang, H. F., Guan, J., Fu, J. N., Yang, M., Zhang, J. Y., et al. (2021). Fabrication of injectable chitosan-chondroitin sulfate hydrogel embedding kartogenin-loaded microspheres as an ultrasound-triggered drug delivery system for cartilage tissue engineering. Pharmaceutics 13 (9), 1487. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics13091487
Yuan, Y., Zhang, Q., Lin, S., and Li, J. (2025). Water: the soul of hydrogels. Prog. Mater. Sci. 148, 101378. doi:10.1016/j.pmatsci.2024.101378
Zhang, M., Hu, W., Cai, C., Wu, Y., Li, J., and Dong, S. (2022a). Advanced application of stimuli-responsive drug delivery system for inflammatory arthritis treatment. Mater. Today Bio 14, 100223. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100223
Zhang, S., Li, X., Li, C., Cong, H., and Yu, B. (2024a). Research progress of injectable hydrogels in the treatment of bone tissue diseases. Chem. Eng. J. 498, 155139. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2024.155139
Zhang, S., Wang, L., Kang, Y., Wu, J., and Zhang, Z. (2023). Nanomaterial-based reactive oxygen species scavengers for osteoarthritis therapy. Acta Biomater. 162, 1–19. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2023.03.030
Zhang, Y., Wang, X., Chen, J., Qian, D., Gao, P., Qin, T., et al. (2022b). Exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma administration in site mediate cartilage protection in subtalar osteoarthritis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 20 (1), 56. doi:10.1186/s12951-022-01245-8
Zhang, Z., Cheng, D., Pan, J., Liu, D., Fu, J., and Fan, H. (2024b). Lubricating MXenzyme-based hybrid hydrogel reverses oxidative damage to alleviate osteoarthritis. Chem. Eng. J. 482, 148815. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2024.148815
Zhao, J., Qiu, P., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhou, J., Zhang, B., et al. (2023). Chitosan-based hydrogel wound dressing: from mechanism to applications, a review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 244, 125250. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125250
Zhen, J., Wan, T., Sun, G., Chen, X., and Zhang, S. (2024). A ROS-responsive microsphere capsule encapsulated with NADPH oxidase 4 inhibitor ameliorates macrophage inflammation and ferroptosis. Heliyon 10 (1), e23589. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23589
Zheng, L., Zhang, Z., Sheng, P., and Mobasheri, A. (2021). The role of metabolism in chondrocyte dysfunction and the progression of osteoarthritis. Ageing Res. Rev. 66, 101249. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2020.101249
Zhong, H., Fang, Y., Luo, M., Wang, L., Huang, J., Dai, G., et al. (2024). Deferoxamine-loaded injectable chitosan-grafted chlorogenic acid/oxidized hyaluronic acid hybrid hydrogel with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and angiogenesis-promoting properties for diabetic wound repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 16 (22), 28209–28221. doi:10.1021/acsami.4c04677
Zhou, T., Xiong, H., Yao, S. Y., Wang, S., Li, S., Chang, J., et al. (2023). Hypoxia and matrix metalloproteinase 13-responsive hydrogel microspheres alleviate osteoarthritis progression in vivo. Small 20 (19), e2308599. doi:10.1002/smll.202308599
Zhou, Y., Liu, G., and Guo, S. (2022). Advances in ultrasound-responsive hydrogels for biomedical applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 10 (21), 3947–3958. doi:10.1039/d2tb00541g
Keywords: osteoarthritis, articular cartilage, responsive hydrogel, drug delivery, biomaterial application
Citation: Xu Z, Liu J, Hu H, Ma J, Yang H, Chen J, Xu H, Hu H, Luo H and Chen G (2025) Recent applications of stimulus-responsive smart hydrogels for osteoarthritis therapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 13:1539566. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1539566
Received: 05 December 2024; Accepted: 20 January 2025;
Published: 17 February 2025.
Edited by:
Xinru You, Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, United StatesReviewed by:
Anirudh Sharma, Chandigarh University, IndiaCopyright © 2025 Xu, Liu, Hu, Ma, Yang, Chen, Xu, Hu, Luo and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Gang Chen, YWRjeXlAYWxpeXVuLmNvbQ==; Huanhuan Luo, bHVvaGhAemp4dS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.