
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. , 07 January 2025
Sec. Industrial Biotechnology
Volume 12 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2024.1545045
This article is a correction to:
Enhancing Enzyme-Mediated Cellulose Hydrolysis by Incorporating Acid Groups Onto the Lignin During Biomass Pretreatment
 Jie Wu1
Jie Wu1 Richard P. Chandra1*
Richard P. Chandra1* Masatsugu Takada1,2
Masatsugu Takada1,2 Li-Yang Liu3
Li-Yang Liu3 Scott Renneckar3
Scott Renneckar3 Kwang Ho Kim4
Kwang Ho Kim4 Chang Soo Kim4
Chang Soo Kim4 Jack N. Saddler1*
Jack N. Saddler1*A Corrigendum on
Enhancing enzyme-mediated cellulose hydrolysis by incorporating acid groups onto the lignin during biomass pretreatment
by Wu J, Chandra RP, Takada M, Liu L-Y, Renneckar S, Kim KH, Kim CS and Saddler JN (2020). Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8:608835. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.608835
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 3 as published. During the initial submission process, an incorrect image of Figure 3 (showing the hydrolysis results using a less advanced cellulase mixture) was accidentally used during the final stage. This cellulase mixture lacks accessory enzymes, resulting in lower hydrolysis yields at elevated pH. In contrast, the more advanced enzyme cocktail CTec3, used in this study, contains accessory enzymes that reduce non-productive lignin-enzyme binding at elevated pH, as described in the main content of the article. The corrected Figure 3 and its caption appear below.
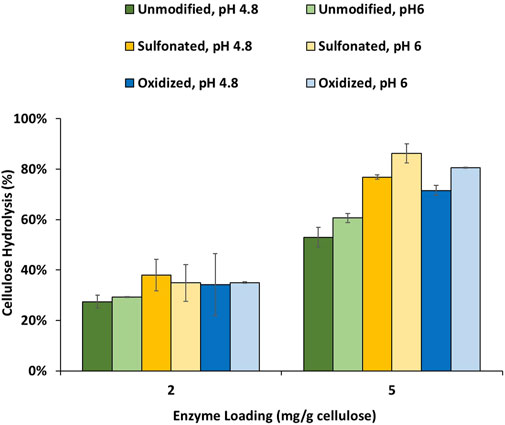
Figure 3. Enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulose-rich delignified Kraft pulp with added PTLs isolated from unmodified, sulfonated and oxidized mechanical pulps (MP) at 2% solids and enzyme loading of 2 and 5 mg/g cellulose. Enzymatic hydrolysis was performed for 48 h in a 50°C rotating incubator.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: lignin, oxidation, sulfonation, cellulase enzymes, non-productive binding, pH
Citation: Wu J, Chandra RP, Takada M, Liu L-Y, Renneckar S, Kim KH, Kim CS and Saddler JN (2025) Corrigendum: Enhancing enzyme-mediated cellulose hydrolysis by incorporating acid groups onto the lignin during biomass pretreatment. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 12:1545045. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1545045
Received: 13 December 2024; Accepted: 27 December 2024;
Published: 07 January 2025.
Edited and reviewed by:
Chunbao (Charles) Xu, Western University, CanadaCopyright © 2025 Wu, Chandra, Takada, Liu, Renneckar, Kim, Kim and Saddler. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Richard P. Chandra, cmljaGFyZGNoYW5kcmE3N0BnbWFpbC5jb20=; Jack N. Saddler, amFjay5zYWRkbGVyQHViYy5jYQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.