- 1Department of Pharmaceutics and Industrial Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Cairo university, Jeddah, Egypt
- 2Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
- 3Center of Excellence for Drug Research and Pharmaceutical Industries, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia
Introduction: Osteoarthritis (OA) is regarded as one of the most prevealent irreversible joint degenerative disorder worldwide. Recently, considerable interest in utilizing intra-articular (IA) injections for managing OA has been raised.
Methods: In this study, IA injectable surface modified iron oxide microparticles (SMIOMPs) loaded with Diacerein (DCN) were developed. The effects of formulation parameters on particle size, entrapment efficiency, and zeta potential were explored using factorial design. The optimized formulation was characterized regarding morphology and in vitro release. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) were done to assess interactions. Further, sterilization and in vivo performance in rats with induced arthritis has been performed for the optimized formulation.
Results and Discussion: The selected optimized system included 2M FeCL3 and 1% chitosan as a surface modifier achieved high drug entrapment of 85.25% with a PS of 1.54 µm and sustained DCN release. Morphological examination of the optimized formulation revealed spherical particles with chitosan coat. DSC and FTIR results indicated the absence of undesired interactions between DCN and the used components. No significant change in the measured parameters was observed following sterilization using gamma radiation. In vivo assessment revealed superior performance for the optimized formulation in reducing cartilage inflammation and degradation. Plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor α and Interleukin-1 beta, as well as knee diameter, were significantly reduced in the treated groups compared to the untreated ones.
Conclusion: Overall, the results suggest that the proposed DCN-loaded SMIOMPs represent a promising advancement in the arena of cartilage regeneration.
1 Introduction
Osteoarthritis (OA) is regarded as one of the most dominant, possibly an irreversible joint degenerative disorder globally. The worldwide incidence of knee OA was 16% in population aged ≥ 15 years and 22.9% in those aged ≥ 40 years. Moreover, in 2020 about 654.1 million aged ≥40 years individuals over the world had knee OA (Neogi, 2013; Cui et al., 2020a).
Tissue engineering, an innovative approach merging engineering and life sciences, aims to create biological substitutes for repairing and regenerating damaged tissues (Howard et al., 2008). Magnetic hydrogels, formulated via iron oxide particles combined with diverse biopolymers, are gaining prominence in biomedical tissue engineering due to their biocompatibility, well-defined structures, and responsiveness to magnetic fields (Liu et al., 2020). Other smart biomaterials, including scaffolds and biofilms, which are activated by external stimuli, offer great potential in the biomedical field; however, they have pitfalls including delayed response and less defined architectures compared to biomaterials responding to magnetic stimuli (Cui et al., 2020b; Yang et al., 2020b).
Biomaterials are allocated based on different parameters including origin, composition, and biodegradability. Based on chemical composition, biomaterials can be categorized into ceramics, polymers, and composites (Veeman et al., 2021). In tissue engineering, biopolymers like chitosan and collagen are extensively used, particularly for cartilage regeneration. Chitosan, derived from deacetylated chitin, is a highly versatile natural polymer known for its biocompatibility, biodegradability, cationic character, stability, non-toxicity, and ability to be sterilized. Chitosan has different applications in drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing. Its mucoadhesive characteristics allow it to serve as a scaffold anchorage to existing tissue (Comblain et al., 2017). Chitosan or modified chitosan enriched cartilage matrix compounds showed reduced inflammation and catabolic mediator’s levels by the chondrocytes in the in-vitro studies (Oprenyeszk et al., 2015).
Evolution of novel drug-delivery systems with high efficacy, low cytotoxicity and controlled drug release has recently gained much attention. Use of magnetic field and/or magnetic nanoparticles become one of the potential approaches to achieve such aims. Static magnetic field (SMF) is a is a persistent field that outlines the magnetic effect of electrical currents and magnetized materials on living matter. Widely applied in medicine, SMF is known to enhance wound healing and bone regeneration, particularly in physiotherapy for bone disorders such as osteoarthritis (Marycz et al., 2018). Magnetic discs, capable of generating SMF both in vitro and in vivo, provide practical applications in this field. The utilization of magnetic fields in clinical applications has attracted attention, particularly in magnetically guided delivery of biomolecules for tissue engineering, magnetic resonance imaging, and cancer therapy. However, ongoing debates surround the biological responses and potential adverse effects of SMF exposure (Marycz et al., 2018). Previous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of local SMF stimulation in treating pain, promoting nerve regeneration, and improving blood flow (Gmitrov et al., 2002; Veliks et al., 2004; Kanai et al., 2012) Furthermore, SMF has shown promise in the field of drug delivery. Its ability to concentrate magnetic particles and facilitate the targeted delivery of drug molecules underscores its potential significance in advancing medical treatments (Nguyen et al., 2021).
Magnetic systems have been recently regarded as a promising approach for the treatment of osteoarthritis, leveraging their ability to provide targeted therapy with minimal invasiveness. Magnetic particles are often employed because of their capacity to be directed by external magnetic fields, allowing precise localization to the damaged cartilage. Once localized, the particles can deliver therapeutic agents or induce hyperthermia, thereby promoting tissue repair and reducing pain and inflammation through cellular and molecular signaling pathways. Studies have shown that magnetic particles can effectively promote drug delivery and improve the bioavailability and retention of treatments in the affected joints, offering a novel pathway for osteoarthritis management (Wang et al., 2019; Kianfar, 2021; Materón et al., 2021). Research also suggests that MNP-based systems could be combined with tissue engineering strategies, such as scaffolds, to further improve cartilage repair in osteoarthritic joints (Fan et al., 2020; Dasari et al., 2022). The minimally invasive nature of magnetic systems, combined with their ability to limit off-target effects and reduce systemic toxicity, makes them a highly attractive therapeutic option for osteoarthritis safer alternative to conventional therapies (Liu et al., 2021; Materón et al., 2021).
Naturally available iron oxides, such as magnetite, maghemite, and hematite exhibit unique properties. Magnetite, the most widely used form, displays inter-valence charge transfer between Fe2+ and Fe3+, resulting in absorption in the ultraviolet-visible and infrared spectral regions and a black appearance. Magnetic iron oxide particles, notably Fe3O4 and γ-Fe2O3, are valuable in scientific and technological applications due to their minimal toxicity, superparamagnetic properties, and simple separation techniques. Their significance is particularly evident in biomedical applications, including drug delivery, diagnostic imaging with magnetic resonance, and thermal therapy (Ali et al., 2016).
The preparation of iron oxide particles involves methods such as thermal decomposition and co-precipitation. Co-precipitation is gaining attention due to its large yield. Chemical coprecipitation is dependent on several factors including ionic strength, iron salt type, and pH. It could be achieved either by addition of a base to an aqueous solution containing Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions or partial oxidation of ferrous hydroxide utilizing different oxidizing factors (Wu et al., 2011). Prepared iron oxide particles often lack stability and require stabilization using low molecular weight agents like surfactants or functionalized polymers. Surface modification for preserving the particles stability involves either physical or chemical approaches. Chemical approach includes surface-controlled polymerization or grafting methods, while physical encapsulation modifies particles through self-assembly, surfactant adsorption, or layer-by-layer electrostatic adsorption (Jamshaid et al., 2016).
Magnetic hydrogels consist of a hydrogel matrix combined with a magnetically surface-modified biopolymer component. Recently, there has been a prevalent trend of surface modifying iron oxide-based magnetic particles with polymer matrices, to create a magnetically responsive hydrogels for tissue engineering, like γ-Fe2O3, Fe3O4, and cobalt ferrite nanoparticles (Zhang and Song, 2016; Rose et al., 2017). Several studies have successfully reported the development of chitosan and collagen coated magnetic iron oxide particles dispersed into hydrogel for various biomedical applications (Zhang et al., 2014; Tóth et al., 2015; Jauch et al., 2020).
In this work, we aimed to prepare iron oxide magnetic microparticles followed by surface modification with hydrogel forming biopolymers like chitosan oligosaccharide lactate (CS) or hydrolyzed collagen (CO) owing to their beneficial effect in the OA management regarding their lubricant and tissue regeneration ability. The developed surface modified iron oxide magnetic microparticles (SMIOMPs) were loaded with DCN to be delivered via IA injection. The prepared SMIOMPs characteristics were optimized for minimized particle size, maximized entrapment efficiency and absolute zeta potential. The optimal DCN-loaded SMIOMPs morphology was visualized using transmission electron microscopy. Further, in vivo performance of the optimized DCN-loaded system was assessed in rat model with induced arthritis. Reduction in cartilage inflammation and degradation was evaluated. In addition, inflammatory condition was evaluated via measuring plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor α and Interleukin-1 beta, as well as knee diameter.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Materials
Diacerein (DCN) was kindly gifted from EVA Pharmaceutical Industries (Cairo, Egypt). Ferric chloride (FeCl3), and Ferrous sulphate (FeSO4) was procured from Chemajet chemical company, Alexandria, Egypt. Cellulose dialysis membrane (molecular weight cut-off = 14,000 Da), Hydrolyzed collagen (CO), Chitosan oligosaccharide lactate (CS), Freund’s adjuvant, Ovalbumin, Hematoxylin and Eosin were obtained from Sigma Aldrich Co., St. Louis, MO, United States. Cal-Ex II Decalcifier, was obtained from Fisher Scientific, Leicestershire, United Kingdom ELISA kit was obtained from Glory Science Co, Ltd., Del Rio, TX, United States. All other chemicals and reagents were of analytical grade.
2.2 Preparation of DCN-loaded surface modified iron oxide magnetic microparticles (SMIOMPs)
Iron oxide particles were prepared via the co-precipitation technique (Lagrow et al., 2019), using ferric sulphate (FeSO4) and ferric chloride (FeCL3) solutions at the molar ratio of 1:1 or 1:2. Equal volumes of each solution were mixed on a magnetic stirrer (500 rpm) for 20 min at 55°C. The pH of mixture was increased via the addition of 4 mL basic solution (33% w/v ammonia solution) to allow the chemical precipitation of iron oxide particles. The prepared iron oxide particles were then collected by the aid of neodymium magnet. Washing of the collected particles was performed four times with deionized water to remove excess base, leaving a black precipitate of iron oxide microparticles; IOMPs (Sulistyaningsih et al., 2017). The prepared IOMPs were then mixed with 10 mL of either chitosan (CS) or hydrolyzed collagen (CO) solution at the specified concentration for surface modification. The dispersion was further stirred constantly for a further 12 h at 500 rpm to ensure surface modification. Finally, DCN (20 mg) was added into 10 mL of the resulted dispersion and stirring was continued for further 15 min to form DCN-loaded SMIOMPs.
2.3 In vitro characterization of the prepared DCN-Loaded IOMPs and SMIOMPs
2.3.1 DCN entrapment efficiency determination
Efficiency of DCN entrapment (EE%) was done indirectly via measuring the unentrapped (free) DCN. Magnetic separation of 1 mL sample of the magnetic particles using a neodymium magnet was done for free DCN from the SMIOMPs. The resulted supernatant was withdrawn and the concentration of free DCN was measured by UV spectrophotometry at λmax 258 nm after appropriate dilution (Eladawy et al., 2021). Drug EE% was determined according to the following equation:
Each measurement was repeated thrice, and the results were presented as mean ± SD.
2.3.2 Size and zeta potential assessment
Estimation of the average particle size (PS), polydispersity index (PDI), and zeta potential (ZP) of the prepared SMIOMPs was done using dynamic light scattering technique by Zetasizer (Maguire et al., 2018). Each system was examined after being diluted with distilled water to an appropriate dilution that could provide an appropriate scattering intensity allowing for proper size assessment. To observe the electrophoretic mobility of the particles within the electric field, ZP measurements were conducted using the same apparatus. Each sample was examined in triplicate, and the average value was displayed in the findings.
2.4 Formulation and optimization of DCN-loaded SMIOMPs using full factorial design
Various systems of DCN-loaded SMIOMPs were prepared according to 23 full factorial design. Each variable was used at two levels as follows: molar concentration of FeCl3 (0.1 and 0.2 M), type of surface modifier (CO and CS), and concentration of surface modifier (0.5, 1%). Eight formulations were developed as per the experimental design employed. The composition of various systems formulated is represented in Table 1. The effects of the studied variables on the EE%, PS, PDI, and absolute ZP of the prepared formulations were investigated. Iron oxide microparticles were prepared without surface modification using 0.1 and 0.2 M FeCl3 were prepared for comparison. Design expert® 13.0 was applied to analyze the responses and outline the optimal formulation with least PS and highest EE and absolute zeta potential.
2.5 Characterization of the optimal DCN-loaded SMIOMPs
2.5.1 In vitro release
The release of DCN from the selected DCN-loaded SMIOMPs compared to the corresponding formulation without surface modification (DCN-loaded IOMPs) and DCN aqueous dispersion was studied using dialysis bag diffusion technique (Elsherif et al., 2021). The dialysis membrane was soaked in phosphate buffer saline (PBS, pH = 7.4) overnight before the experiment. One mL of each of the tested formulation and the drug dispersion (each equivalent to 2 mg DCN) was put in a dialysis bag. Immersing the dialysis bag in a bottle with 20 mL of PBS (pH = 7.4) was done in a shaking water bath operated at 50 strokes per minute. The water bath was thermostatically controlled at 37°C ± 0.5 °C. At predetermined intervals of 2, 4, 6, 8, 24, and 48 h, samples of the release media were taken out and replaced with an equivalent amount of release medium. The samples were subjected to spectrophotometric analysis at λmax 258 nm and the amount released was then computed with reference to the constructed calibration curve. The study was done in triplicate and the results were displayed as mean ± SD.
2.5.2 Shape and morphology assessment
The morphology of the selected DCN-loaded SMIOMPs and the corresponding DCN-loaded IOMPs without surface modification was investigated using transmission electron microscopy (TEM). One drop of each undiluted sample was mounted onto a carbon-coated copper grid. A drop of 1% (w/v) phosphotungstic acid was then applied to stain the samples, which were then allowed to dry in the air at ambient temperature before being examined at an 80 kV accelerating voltage (El Zaafarany et al., 2010).
2.5.3 Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy
FTIR spectra, ranging from 4,000 to 400 cm−1, of DCN, FeCl3, FeSO4, CS, and the optimal freeze-dried DCN-loaded and blank SMIOMPs were recorded using the KBr disc technique (Nafee et al., 2018). The recorded spectra were examined for the presence of any chemical interaction.
2.5.4 Thermal behavior analysis
The thermal analysis of DCN, FeCl3, FeSO4, CS, and the optimal freeze dried DCN-loaded and the corresponding blank SMIOMPs was performed via differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Each sample was placed in a flat-bottom aluminum pan and heated steadily in nitrogen atmosphere (Rostamnezhad et al., 2023).
2.5.5 pH evaluation
pH values for the prepared system were assessed utilizing a pH meter (Jenway 3505, Bibby Scientific) as previously reported (Abdelhakeem et al., 2021).
2.6 Sterilization of DCN-loaded SMIOMPs
Gamma irradiation (60Co irradiator) at a low dosage of 10 kGy (1.19 kGy/h for 8 h) was used to sterilize the optimized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs (Da Costa Martins et al., 2009). The gamma-sterilized formulation was re-evaluated for PS, ZP, and EE%.
2.7 In-vivo study
Experimental procedures followed the guide of the National Institute of Health for care and use of Laboratory animals (NIH Publications No.8023, revised 1978), and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Faculty of Pharmacy Cairo University (PI 2847).
For this investigation, 42 male Albino rats weighing between 250 and 300 g were housed in an air-conditioned room at 25°C ± 0.5°C, with free access to water and a standard pellet diet. The animals were accommodated in cages with 12-h day and night cycles. 0.5 mL of ovalbumin (5 mg/mL) in complete Freund’s adjuvant was injected into rats knee joints two times for 2 weeks (at days 1 and 7) to induce OA (Kamel et al., 2016).
Rats were randomized into five groups; with each group comprising six rats.
• Group 1 (negative control) is a group of rats with healthy knee joints with no induction of OA.
• Group 2 (positive control) is a group of rats without any treatment.
• Group 3 is a group of rats that received 0.5 mL of blank SMIOMPs via intra-articular injection.
• Group 4 is a group of rats that received 0.5 mL of DCN aqueous dispersion (2 mg/mL) via intra-articular injection.
• Group 5 is a group of rats IA that received 0.5 mL of the optimized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs (F6) via intra-articular injection.
Among all groups the left knee joint was used as control and kept free of treatment, the right knee in groups 6 and 7 only were wrapped with a neodymium magnet (Allen et al., 2010). Blood samples were withdrawn from the retro-orbital plexus of the rats at the 28th day and kept in tube with a separator of gel barrier serum. Centrifugation of the samples was done at room temperature for 15 min at a speed of 5,000 rpm for obtaining serum. Finally, the serum samples were kept at 0 °C till further analysis. For rats’ knees diameter determination, the antero-posterior diameters were measured at 7-day interval time points from day 1 to day 28 to evaluate the swelling of knee joints (Hartmann et al., 2018). The knee diameter baseline value was recorded just prior to adjuvant injection in each rat. Tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1b) serum levels were determined using ELISA kit as per the manufacturer’s guidelines (Yin et al., 2018).
2.8 Histopathologic studies
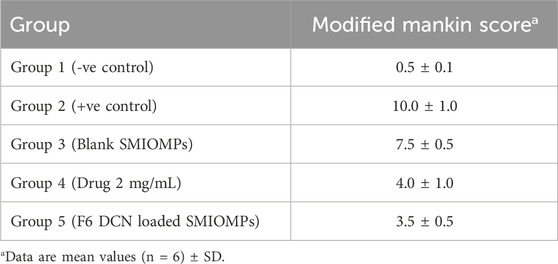
Sedation and euthanizing of the rats were achieved via sodium pentobarbital (50–80 mg/kg) intravenous delivery on the 28th day, then both knees were isolated. The knee joints samples were immersed in 10% neutral buffered formalin for 48h, then decalcification of the samples was done using Cal-Ex II Decalcifier for 18 days. Samples were processed by serial dilutions of ethanol, followed by clearing in xylene before being submerged in paraplast tissue embedding medium. Using a rotatory microtome, tissue sections of approximately 5 µm were cut. After being cut at mid joint level, serial sagittal tissue sections were mounted onto glass slides for staining with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) to be inspected for histological alterations. Ultimately, a full HD microscopic imaging system was used for samples imaging. The morphological assessment of tibiofemoral articular cartilage was performed using the Modified Mankin scoring system (Pauli et al., 2012; El-Gogary et al., 2020), with 0 corresponds to normal cartilage and 14 corresponds to the highest score of OA.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 In vitro characterization of DCN-loaded IOMPs and SMIOMPs
EE%, PS, PDI, and ZP of different DCN-loaded IOMPs and SMIOMPs systems are compiled in Table 1. Non-surface modified IOMPs containing 2 M FeCL3 (S2) could achieve better EE%, lower PS and higher absolute ZP than IOMPs with 1M FeCL3 (S1). This might be attributed to the initial Fe2+/Fe3+ molar ratio of 0.5 required for the formation of Fe3O4 (Mizutani et al., 2008). Increasing this ratio altered the particles properties, where absolute ZP become lower indicating particles instability, thus particles tend to agglomerate resulting in higher PS (Pochapski et al., 2021). All formulations showed suitable pH values for IA injection (pH 6.2–7.2) (Goldie and Nachemson, 1970; Petit et al., 2015; Küçüktürkmen et al., 2017).
Results revealed that surface modification of IOMPs resulted in a rise in the ZP of particles which indicates enhanced stability and lower particles aggregation tendency. DCN-loaded SMIOMPs containing CS had positive ZP values, while those containing CO had negative ZP values. This could be attributed to the positive charge of CS and the negative charge of CO, which serve as coating material (Cheung et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2020a).
SMIOMPs systems containing CS showed reasonable EE% (from 80% to 85%), while those containing CO showed lower EE% (from 22% to 73%). This might be credited to the acidic nature of DCN. The drug possesses an ionizable carboxylic group, which could possibly ionize and gain a negative charge in the neutral and alkaline pH. Since CO is also negatively charged, this could lead to their repulsion and decreased EE% (Aziz et al., 2018). This could be confirmed by the increased absolute ZP values and negative charge intensity upon increasing CO concentration. Additionally, the prepared systems showed PS ranging from 1.54 to 5.15 µm with appropriate size distribution (PDI from 0.03 to 0.79) and ZP from −51 to +41 mv.
3.2 Experimental design analysis
3.2.1 Impact of variables on EE%
ANOVA analysis of the EE% results showed that all the investigated variables (molar concentration of FeCL3, concentration of surface modifier and type of surface modifier) had significant effect at p ≤ 0.05. The main effects and the interactions between the tested parameters of DCN-loaded SMIOMPs on EE% are illustrated Supplementary Figure S1.
Increasing the molar concentration of FeCL3 increases the EE % of DCN in the prepared SMIOMPs (p < 0.0001). It is worthy to note that the ratio of Fe2+: Fe3+ ratio (1:2) was found to be the optimum ratio at which the co-precipitation reaction occurs for preparation of iron oxide particles (Alibeigi and Vaezi, 2008). A previous study by Gupta and Gupta (2005) reported that to avoid the formation of oxide mixtures, the theoretical molar ratio of Fe2+ and Fe3+ salts should be 1:2 for complete synthesis of Fe3O4. Hence, more stable particles allow higher EE% of DCN.
Regarding the surface modifier type, it was observed that CS modified SMIOMPs had higher DCN EE % than CO surface modified ones (p < 0.0001). This might be attributed to higher mechanical strength and higher viscosity of CS solution than CO solution (León-López et al., 2019; Prasanna Mallick et al., 2021), which lead to higher DCN EE % as it prevents drug leakage from the particles. Also, CS provides different functional groups including reactive hydroxyl and amino groups which may bind to the drug molecules leading to improved drug entrapment (Taherian et al., 2021).
Increasing the surface modifier concentration from 0.5% to 1% increased the DCN EE% (p < 0.0001). This might be attributed to increase in the viscosity of the media upon increasing the surface modifier concentration, which prevents the migration of DCN to the outer phase (Dhakar et al., 2012). Similar observations were reported by Huang et al. (2018) in their study on preparation of vancomycin-loaded silica xerogel/polymer composite nanoparticles. They observed that the possibility of particle breakage was reduced with increased polymer solution viscosity, explaining the increased drug encapsulations at higher polymer concentrations.
A significant interaction between the molar concentration of FeCL3 and the surface modifier type on EE% was revealed, where increasing FeCL3 molar concentration (from 1 to 2 M) resulted in higher increase in the % EE in presence of CS as a surface modifier than that in the presence of CO. This might be explained on the basis of the higher stability of particles at high FeCL3 concentration in presence of CS which was confirmed by the high ZP as well. In addition, the ability of CS to form a very strong gel (Sacco et al., 2018), which could enhance the EE% by preventing DCN leakage from the particles.
Regarding interaction between the concentrations of FeCl3 and surface modifier, it was found that increasing FeCL3 concentration (from 1 to 2M) at high surface modifier concentration (1%) resulted in higher increase in the EE% compared to that observed at low surface modifier concentration (0.5%). This might be attributed to that the higher concentration of both surface modifier and FeCL3 resulted in synergistic stabilization of particles, thus prevent the DCN from leakage (Franconetti et al., 2019), while at low surface modifier concentration particles were less stable and the tendency of DCN leakage was higher. In addition, it was observed that lower surface modifier concentration resulted in lower % EE in presence of CO than that in the presence of CS as a surface modifier, Figure 1F.
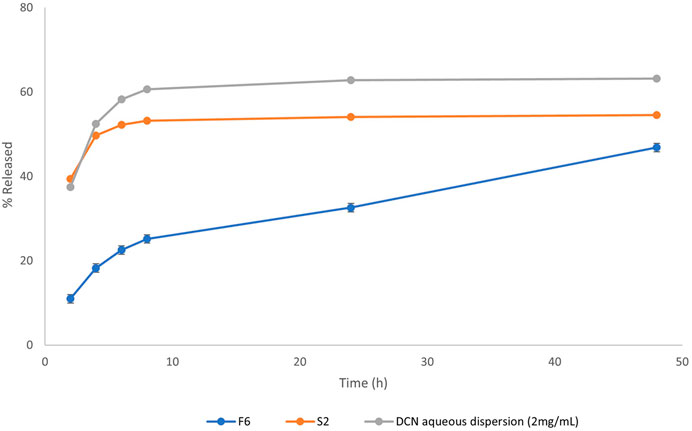
Figure 1. Release profiles of DCN from the optimized DCN-loaded magnetic particles formulation (F6) and DCN aqueous dispersion (2 mg/mL).
3.2.2 Impact of variables on PS
As per ANOVA analysis, PS of the prepared DCN-loaded SMIOMPs was significantly affected by all the tested variables at 95% level of significance; the effects are illustrated as Supplementary Figure S2. However, no significant interaction was observed between variables. It was found that increasing molar concentration of FeCL3 from (1–2 M) decreases the molar ratio of Fe2+ to Fe3+ ions from 1 to 0.5 and thus decreases the PS (p = 0.0066). This may be attributed to the fact that when Fe2+ to Fe3+ ions molar ratio was greater than 0.5, the crystallites of Fe3O4 nanoparticles grew up slowly using excess Fe (OH)2 as per Schikorr reaction resulting in particles aggregation with consequent increase in PS (Shipko and Douglas, 1956; Mizutani et al., 2008; Jiang et al., 2011).
In addition, using CS as surface modifier resulted in smaller PS compared to that when using CO as surface modifier (p < 0.0001). This may be attributed to the denser coat formed by CS. Similar results were obtained by Frank et al. (2020) who observed that using CS as surface modifier for nanoparticles have high coating efficiency and thus lead to dense electrically stable coated particles with small particle and tends to avoid aggregation.
Regarding the surface modifier concentration, inverse relationship was observed with PS (p < 0.0001). This may be attributed to increasing the charge intensity by increasing the surface modifier concentration which lead to repulsion and deaggregation of particles leading to smaller PS (Frank et al., 2020). Similarly, Üstündaǧ-Okur et al. (2014) concluded that particles with high ZP, are electrically stable and tends to avoid aggregation, thus having small PS.
3.2.3 Impact of variables on PDI
ANOVA analysis revealed a significant effect for only the surface modifier type on the PDI (P< 0.05). In addition, the surface modifier type exhibited a significant interaction with the concentration of either FeCL3 or surface modifier at the same significance level. Such significant effects and interactions are presented as Supplementary Figure S3. It was evident that CS surface-modified magnetic particles showed significantly lower PDI than CO surface-modified ones (p = 0.0019). This finding is in agreement with previous studies, where CS-coated nanoparticles achieved relatively lower PDI (≈0.34) then CO-based nanoparticles (≈0.77) (Cardoso et al., 2014; Wahyuni et al., 2021).
A significant interaction between the surface modifier type and either FeCL3 concentration or surface modifier concentration on the PDI was observed (p = 0.0002 and 0.0013), respectively. Raising the FeCL3 concentration (from 1 to 2M) in the prepared DCN-loaded IOMPs surface modified with CS resulted in increasing the PDI, whereas it resulted in decreasing the PDI in those surfaces modified with CO. This may be attributed to the higher ZP of CS surface modified particles which resulted in higher repulsive forces between particles with high FeCL3 concentration leading to high PS variation, while CO coated ones have lower ZP and less PS variation. Further, Changing the type of surface modifier from CS to CO at high surface modifier concentration (1%) resulted in increasing the PDI whereas it resulted in slight decreasing in the PDI at low concentration of surface modifier (0.5%). This may be due to the better coating efficiency of CS compared to that of CO at high concentration which led to smaller PS variation (Frank et al., 2020). On the other hand, at low concentration, the repulsive force between CS surface modified particles due to CS positive charge leads to greater PS variation than in the CO surface modified ones.
3.2.4 Impact of variables on ZP
ANOVA results revealed that the absolute ZP of the DCN-loaded SMIOMPs is significantly affected by the three tested variables (p < 0.05). In addition, all the binary interactions between the tested variables were also significant at the same level of significance. The main effects and interactions between variables on absolute ZP are presented as Supplementary Figure S4. It was evident that higher FeCL3 molar concentration led to increased absolute ZP of the prepared DCN-loaded SMIOMPs (p < 0.0001). This could be credited to the fact that Fe2+: Fe3+ ion ratio of 0.5 tends to form more stable Fe2O3 than the higher ratio. Similarly, in their study on iron oxide nanoparticles, Alangari et al. (2022) reported higher positive charge on the surfaces of the developed Fe2O3 particles; they explained the high positive ZP due to using ammonia solution in the particles preparation and formation of positively charged Fe-OH2+ during Fe2O3 preparation.
The CS surface modified magnetic particles showed higher absolute ZP than those, whose surfaces are modified with CO (p < 0.0001) owing to higher charge density of CS compared to that of CO. Regarding the surface modifier concentration, a positive effect was observed on absolute ZP (p < 0.0001). This might be due to increasing the charge density with increasing the surface modifier concentration resulting in increasing the absolute ZP value of the prepared particles (Alangari et al., 2022).
A significant interaction between the molar concentration of FeCL3 and the surface modifier type on the absolute ZP values of the prepared DCN-loaded SMIOMPs was observed (p < 0.0001). Increasing FeCL3 molar concentration (from 1 to 2 M) resulted in higher absolute ZP in presence of CO than that in the presence of CS as a surface modifier. A significant synergistic interaction between the FeCL3 concentration (from 1 to 2M) and the surface modifier concentration on ZP was also observed (p < 0.0001). This might be attributed to the fact that charge density increases as the concentration of both FeCL3, and surface modifier increases. Further, a significant interaction between surface modifier concentration and type on the absolute ZP values of the prepared DCN-loaded SMIOMPs was detected (p < 0.0001). Low concentration of surface modifier (0.5%) resulted in higher absolute ZP values when using CS as a surface modifier compared to CO, while at high concentration of surface modifier (1%), there was no marked difference between CS and CO modified particles. This could be credited to the fact that CO is negatively charged (Alangari et al., 2022), thus may bind the positively charged iron oxide particles and decrease the overall charge intensity. On the other hand, CS is positively charged, thus may increase the overall charge intensity of the positively charged iron oxide particles.
3.3 Statistical optimization
The optimized magnetic particles that could yield the highest EE%, lowest PS, and highest absolute ZP was chosen using Design expert®7. DCN-loaded SMIOMPs formulation (F6) that was prepared using 2 M FeCl3 and coated with 1% CS was the optimized system with the greatest desirability (0.951) according to the set optimization goals. The predicted (88% for EE%, 1.84 µm for PS, and 42 mV for ZP) and actual responses of the prepared optimized SMIOMPs (F6), presented in Table 1, were closely related to each other. The relatively low difference between estimated and predicted results confirmed the reliability of the design in estimating the optimal formulation.
3.4 In-vitro characterization of the optimized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs
3.4.1 In vitro release
Release profile of the optimized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs (F6) compared to IOMPs (S2), and DCN aqueous dispersion is graphically presented in Figure 1. The optimized system (F6) was able to prolong DCN release compared to that from DCN-loaded IOMPs without surface modification (S2) and from DCN aqueous dispersion as well. Less than 50% of the drug was released throughout 48 h from the optimized DCN-SMIOMPs (F6), while about 50% of the drug was released during the first 4 h by the aqueous DCN dispersion and DCN-loaded IOMPs (S2). This demonstrates how crucial surface modification is for managing DCN release from the prepared SMIOMPs. Ebadi et al. (2021) achieved similar results in their study on the preparation of 5-fluorouracil loaded magnetic particles coated with polyvinyl alcohol. Their results revealed that the drug is located in the core and consequently, has to travel through a complex pathway, resulting in slow drug release.
3.4.2 Shape and morphology
The optimized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs and DCN-loaded IOMPs (without surface modification with CS) TEM micrographs revealed non-aggregating particles with spherical shape, particle appeared to have smooth surface and sharp boundaries as shown in Figure 2A. Furthermore, TEM micrographs showed that the observed diameter was in agreement with the recorded size. Figure 2B revealed the surface modification with CS in the outer surface of the prepared optimized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs. Similar results were obtained by by Taherian et al. (2021) who described chitosan coated magnetic nanoparticles for breast cancer management.
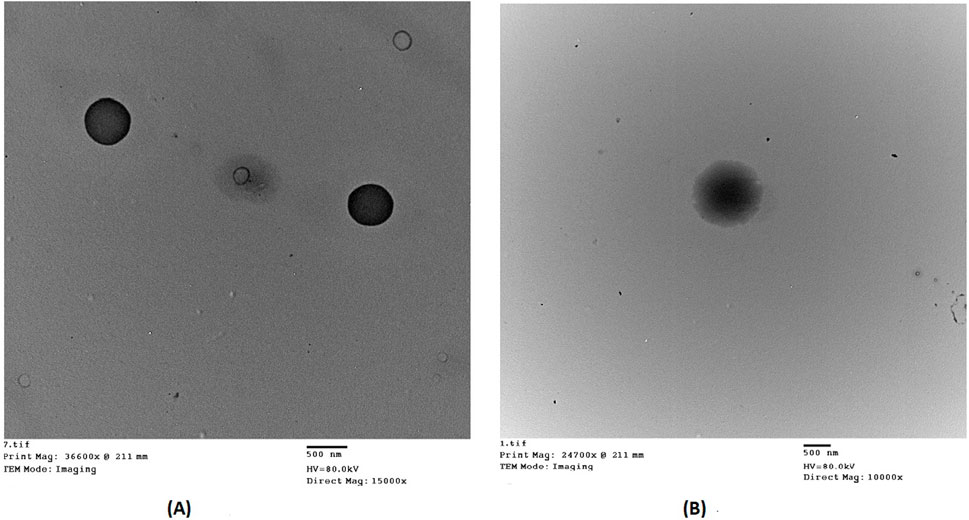
Figure 2. Transmission electron micrographs of: (A) DCN-loaded IOMPs (without CS); (B) optimized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs (with CS surface modification).
3.5 Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)
FTIR spectra were obtained for the individual components (DCN, FeCl3, FeSO4, and CS) as well as the blank SMIOMPs and the optimized lyophilized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs (F6), Figure 3. The IR chart of FeCl3, Figure 3A, showed bands near to 1,633 and 1739 cm−1, assigned to water molecules deformation, referring to the associated physiosorbed water on the surface of FeCl3. The band at 3249 cm−1 corresponding to the strong stretching vibrations of OH (Inam et al., 2018). The IR chart of FeSO4, Figure 3B, revealed sharp bands at 1,100 and 610 cm-1 which indicating the existence of SO42- ions. The adsorbed water molecules’ bending vibrations match the characteristic band at 1,640 cm-1. The broad absorption band between 3200 and 3500 cm-1 corresponds to the OH group presence (Ursescu et al., 2009). DCN IR spectrum, Figure 3C (Eladawy et al., 2021), exhibits distinctive bands at 3329 cm−1 assigned to the–OH stretching, 3070 cm−1 assigned to the aromatic C–H stretching, 2,939 cm−1 assigned to the aliphatic C–H stretching, 1770 cm−1 and 1,678 cm−1 assigned to the ester and carboxylic carbonyl groups, respectively, 1,593.20 cm−1 assigned to the aromatic C=C stretching, 705.96 cm−1 and 744.52 cm−1 assigned to the benzene and m-substituted benzene, respectively. The IR chart of CS, Figure 3D, revealed distinctive bands of polysaccharides in the fingerprint region from 1,156 to 890 cm−1 as that assigned to C–H on rings, C–O of alcohols, and C–O–C asymmetric band of glycoside bonds, also bands about 3300 cm−1, assigned to the hydrogen bonds of hydroxyl groups, and peaks at 1,633 and 1,523 cm-1 assigned to C=O and N–H bonds, respectively (Ataide et al., 2019). The IR chart of blank SMIOMPs, Figure 3E, showed the characteristic peaks for Fe2O3 particles and CS. The large broad band at 3398 cm-1 is assigned to the O-H stretching vibration in hydroxyl groups. The absorption bands around 1,635 cm-1, 1,508 cm-1 are due to the C=O asymmetric and symmetric bending vibration. The strong band below 700 cm-1 corresponds to Fe-O stretching mode. The band assigned to Fe-O stretching of Fe2O3 is seen at 567 cm-1 (Farahmandjou and Soflaee, 2015). The FTIR spectrum for the optimized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs system (F6), Figure 3F, shows the disappearance of the band 1770 cm−1 (corresponding to the stretching of C=O group of DCN carobxylic) as it could bind the amino group of CS (Taherian et al., 2021). There is not any undesired shift in the bands of both DCN and the single formulation components in the IR chart. Thus, based on FTIR spectra it can be concluded that the absence of any undesired chemical interaction between DCN and the components of the formulation.
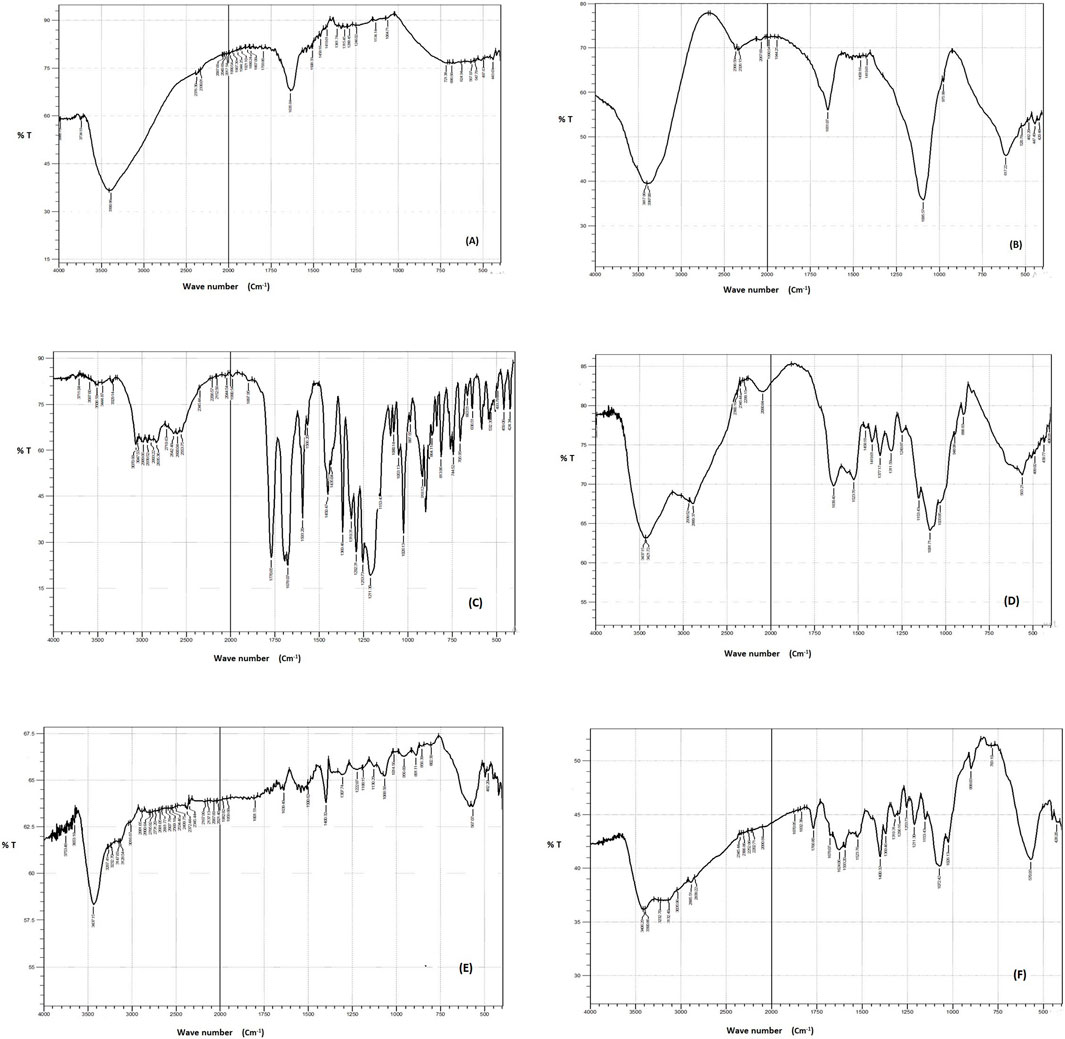
Figure 3. FTIR spectra of (A) FeCl3, (B) FeSO4, (C) DCN, (D) CS, (E) blank SMIOMPs, and (F) optimized SIOMPs F6. (C) is adopted from our previous work (Eladawy et al., 2021).
3.6 Results of differential scanning calorimetry (DSC)
DSC was used as a common tool to explore the melting and recrystallization behavior of the formulation and its individual components (Balestrieri et al., 1996). Figure 4 shows the DSC thermograms for DCN, FeCl3, FeSO4, CS, as well as the blank IOMPs and the optimized lyophilized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs (F6). The DCN DSC thermogram revealed a sharp endothermic peak around 255 °C representing its melting temperature (Eladawy et al., 2021; Garthe et al., 2013). The DSC thermogram of FeCl3 showed an FeCl3 had an obvious exothermic peak appeared at about 65°C (Liu et al., 2016). The DSC thermogram of FeSO4 heptahydrate revealed three endothermic peaks at 71.46, 88.95, 118.44°C. The first peak at 71.46 °C corresponds to the melting point of the compound. The second peak at 88.95 °C could be credited to the dehydration of two water molecules from FeSO4 •6H2O to FeSO4 •4H2O, while the third one at 118.44°C might be due to the removal of 3 molecules of water from FeSO4 •4H2O to FeSO4 •H2O (Trivedi and Jana, 2019). The DSC thermogram of the CS exhibited an endothermic peak at 227.4°C originating from the melting of CS with the collapse of its structure (Ignjatović et al., 2018).

Figure 4. DSC thermograms of DCN, FeSO4, FeCl3, CS, blank SMIOMPs, and optimized SIOMPs F6. DCN thermogram is adopted from our previous work (Eladawy et al., 2021).
The blank IOMPs thermogram did not show any new peaks indicating the absence of any physical interactions; however, reduction in peaks intensity was observed due to dilution. DCN peak total disappearance was observed in the thermogram of the optimized lyophilized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs (F6) indicating that presence of DCN in the amorphous state within the iron oxide microparticles or its molecular dispersion in the microparticles. Similar results were reported in previous studies (Eladawy et al., 2021).
3.7 Effect of sterilization on the stability of the optimized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs formulation
In order to evaluate the effect of the sterilization process on the optimized formulation, re-evaluation was done after sterilization. Results revealed that process of sterilization had no marked impact on the properties of the prepared DCN-loaded SMIOMPs, where there was no significant change in the drug EE%, PS, and ZP (p > 0.05), Table 2, proofing the stability of the SMIOMPs upon exposure to gamma sterilization under the specified conditions.
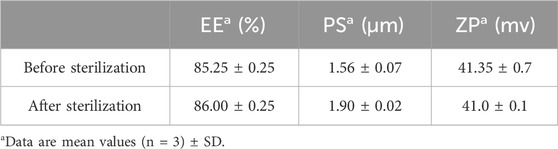
Table 2. Characterization of the optimized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs (F6) before and after gamma sterilization.
3.8 In-vivo study
The swelling of the knee of rats was estimated by determining their diameter, as an indicator of arthritis progression. The difference between the values that were recorded at normal condition and after arthritis induction showed the swelling of the knee at different times, Figure 5A. In comparison to the negative control, all the groups showed significant joint swelling at 95% significance level, at days 7 and 14, respectively (following 1 and 2 weeks of antigen injection). On day 21, 1 week apart from the treatment beginning, a significant reduction in the knee swelling was recorded at the same level of significance. Furthermore, the knee swelling through all the treated groups was significantly lower than the positive control group (p < 0.05).
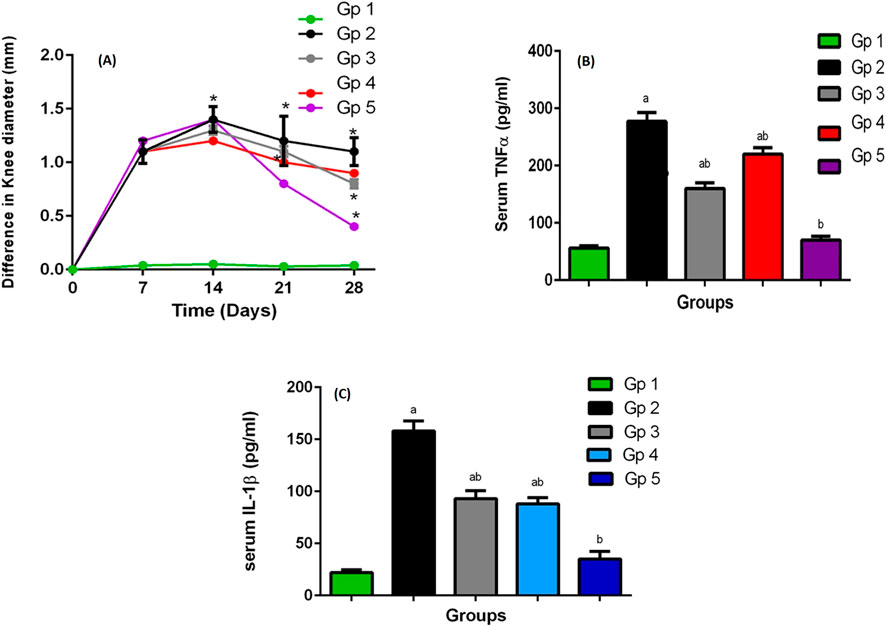
Figure 5. (A) The knee swelling for GP1 (negative control), GP2 (positive control), GP3 (Blank SMIOMPs), GP4 (DCN aqueous dispersion), and GP5 (optimized DCN loaded SMIOMPs (F6)), (B) The rat’s plasma TNF-α levels, (C) The rat’s plasma IL-1b levels. a Significantly different from negative control group at p < 0.05, * or b Significantly different from positive control group at p < 0.05, ab Significantly different from both negative and positive control group at p < 0.05.
At day 28, 1 week apart from receiving the treatment second dose, the treatment anti-edematous activity was clearly revealed, where the knee swelling of the groups was significantly reduced in the treated groups compared to the untreated ones; moreover, the difference among the treated groups became clearer. Results showed that the knee swelling degree followed the order: group 5 (treated with optimized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs (F6)) < group 4 (treated with DCN aqueous dispersion) < group 3 (treated with blank SMIOMPs) p < 0.05. The results were in accordance with the likely good effect of the selected formulation (F6).
Plasma interleukin 1-beta (IL-1b) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) that represent the main proinflammatory cytokines, were significantly increased in the affected joint having large contribution to OA pathogenesis. Further, induction of other inflammatory mediators production, such as prostaglandins and cycloxygenase-2 from synovial cells was done by these cytokines leading to more cartilage inflammation and deterioration (Stannus et al., 2010; Kany et al., 2019). TNF-α and IL-1b serum levels, greatly elevated in such inflammatory condition, could be decreased by the correct utilization of anti-inflammatory agents; accordingly, they are regarded as appropriate markers for evaluation of synovial inflammatory disorders and pharmacological activity of actives (Larsson et al., 2015). Results of the plasma levels of TNF-α and IL-1b in rats measured following 4 weeks of OA induction are graphically illustrated in Figures 5B,C. The levels of TNF-α and IL-1b in the arthritic group (group 2) were elevated significantly (277 pg/mL for TNF-α and 158 pg/mL for IL-1b) relative to their levels in the treated groups (groups 3–5). A great correlation between TNF-α and IL-1b plasma levels and the knee swelling results was observed; the levels of such inflammatory markers followed the same order as the knee swelling degree. The superiority of the optimized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs (F6) was confirmed via achieving lowest serum levels (70 pg/mL for TNF-α and 45 pg/mL for IL-1b) over both blank SMIOMPs and the aqueous dispersion of DCN. The magnetic behavior of the iron oxide microparticles could be a major contributing factor to the observed superior performance. Such behavior allows for the direction of the particles by the external magnetic field enabling targeted delivery of DCN directly to the affected knee joint. This facilitates localized treatment while minimizing side effects (Tursunkulov et al., 2013). In addition, the controlled and prolonged release of the dug through the magnetic field could enhance the therapeutic efficacy with consequent improved outcomes (Hagit et al., 2010). It is worthy to note that localization of the iron oxide magnetic microparticles in the affected joint could generate localized heat when exposed to an alternating magnetic field; the developed magnetic hyperthermia could effectively aid in promoting cartilage regeneration and reducing inflammation through cellular and molecular signaling pathways (Abenojar et al., 2016; Guan et al., 2024).
3.9 Histopathological evaluation
Modified-Mankin score system was used to assess the tibiofemoral articular cartilage degree of inflammation, Table 3. Inflammation was assigned to a score system starting from 0 to 14 according to modified Mankin grading ranging from 0 (minimum score) to 14 (maximal score) referring to normal cartilage and osteoarthritic model, respectively. Group 2 representing the positive control group had the highest score of 10, while group 5 (receiving DCN-loaded SMIOMPs) had the lowest score of 3.5. In addition, assessment of microscopic histopathological changes was done by using H&E stains, Figure 6.
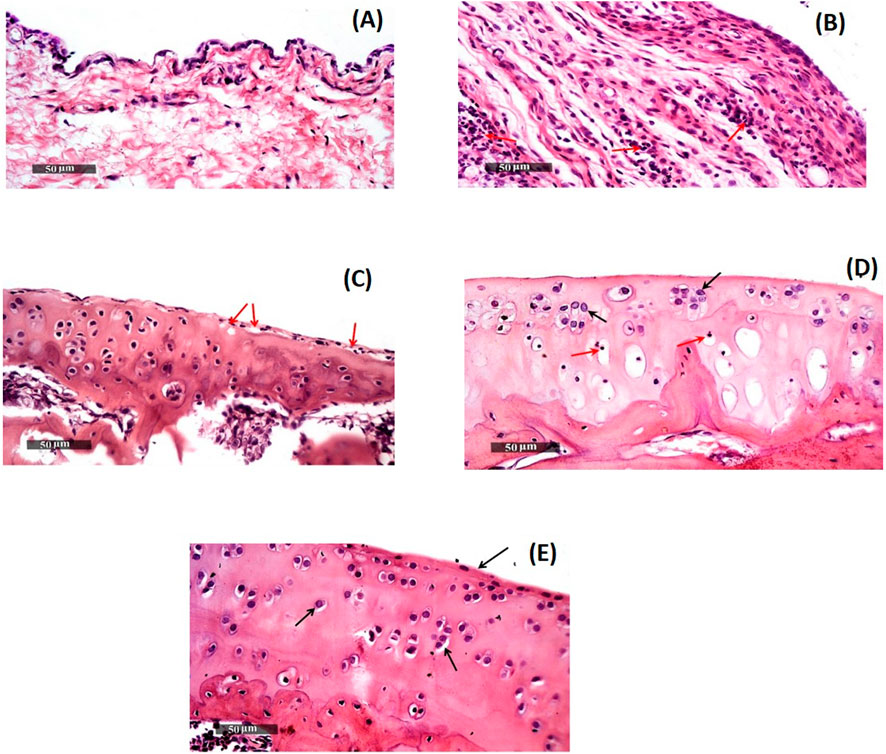
Figure 6. Morphological features of (A) GP.1 negative control, (B)GP.2 positive control, (C) GP.3 Blank SMIOMPs, (D) DCN aqueous dispersion, and (E) GP.5 Optimized DCN-loaded SMIOMPs (F6). Figure 6D is adopted from our previous work (Eladawy et al., 2021).
Group 1 (negative control, mean Mankin score of 0.5) samples showed normal histological features of cartilages covered with hyaline and had intact smooth articular surfaces, all over cartilage zones with large vesicular intact nuclei and well organized apparent intact chondrocytes (Arrows). Uninjured synovial membranes were noticed with normal vasculatures and minimal records of infiltrates of inflammatory cells, Figure 6A.
Group 2 (positive control, mean Mankin score of 10) samples revealed subchondral congested blood vessels (dashed arrow) together with significant reduction of chondrocytes and large areas of cartilaginous surface fissures and erosions (star) with many necrotic and degenerated changes (red arrow). Many infiltrates of inflammatory cells in synovial membranes (red arrow, Figure 6B) with covering epithelium showing slight focal hyperplasia.
Regarding, Group 3 (receiving SMIOMPs, mean Mankin score of 7.5), 50% of samples showed focal areas of separation and fissures of superficial articular cartilage (red arrow) with mild mononuclear inflammatory cells infiltrates in synovial membranes, Figure 6C.
Samples of group 4 (rats IA injected with 0.5 mL of the DCN aqueous dispersion, mean Mankin score of 4) samples, Figure 6D (Eladawy et al., 2021), showed relatively smooth, intact articular surfaces without any changes (black arrow) with blood vessels congestion (star). Synovial membranes revealed few scattered infiltrates of inflammatory cells (red arrow) with degenerative changes appeared as focal areas and deeper cartilaginous zones showed pyknotic nuclei (red arrow).
Group 5 (receiving optimized SMIOMPs F6, mean Mankin score of 3.5) showed well organized apparent intact histological features, normal cartilages covered with hyaline and chondrocytes showing large vesicular intact nuclei (Arrows), and the smooth articular surfaces were also intact. Samples demonstrated intact synovial membranes with normal vasculatures and minimal infiltrates of inflammatory cells, Figure 6E.
These results showed that DCN-loaded SMIOMPs has the ability to improve the knee swelling results, in addition to reducing plasma levels of proinflammatory mediators, demonstrating the marked chondrogenic impact of the optimized formulation. Such findings suggest that DCN-loaded SMIOMPs could promote marked healing effect in case of OA inflammation via suppressing inflammation, as well as promoting the repair of tissues by virtue of the advantages of the magnetic iron oxide microparticles as previously discussed.
4 Conclusion
In the current study, intra-articular injectable SMIOMPs loaded with DCN were successfully formulated via using iron salts, and surface modified with natural polymer (CS or CO). Full factorial design was successfully employed for optimizing the proposed formulation. Statistical analysis revealed that using 2 M FeCL3 and 1 M FeSO4 in presence of 33% ammonia solution led to the production of SMIOMPs with the minimized size, maximized absolute ZP and EE% with overall desirability of 0.951. Further in vivo study showed that the optimized formulation obviously improved the swelling of rats’ knees. Therefore, this DCN-loaded SMIOMPs could be considered as an appropriate alternative for DCN oral treatment.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Research ethical committee, Faculty of Pharmacy, Cairo, Egypt. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
NA: Conceptualization, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing–original draft. NM: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. SB-E: Software, Visualization, Validation, Funding acquisition, Writing–review and editing. RS: Conceptualization, Methodology, Formal analysis, Project administration, Validation, Writing–original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research work was funded by the Institutional Fund Projects under grant no. (IFPIP: 726-249-1443). The authors gratefully acknowledge technical and financial support provided by the Ministry of Education and King Abdulaziz University, DSR, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2024.1439085/full#supplementary-material
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S1 | Line charts for the effect of (A) FeCL3 concentration, (B) surface modifier type, and (C) surface modifier and interaction plots for the interaction between (D) FeCL3 molar concentration and surface modifier type, (E) FeCL3 molar concentration and surface modifier concentration, and (F) surface modifier concentration and surface modifier type on the EE%.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S2 | Line charts for the effect of (A) FeCL3 concentration, (B) surface modifier type, and (C) surface modifier on PS.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S3 | Line chart (A) for the effect of surface modifier type and interaction plots for the interaction between (B) FeCL3 molar concentration and surface modifier type and (C) surface modifier concentration and surface modifier type on the PDI.
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE S4 | Line charts for the effect of (A) FeCL3 concentration, (B) surface modifier type, and (C) surface modifier and interaction plots for the interaction between (D) FeCL3 molar concentration and surface modifier type, (E) FeCL3 molar concentration and surface modifier concentration, and (F) surface modifier concentration and surface modifier type on the absolute ZP.
References
Abdelhakeem, E., El-Nabarawi, M., and Shamma, R. (2021). Effective ocular delivery of eplerenone using nanoengineered lipid carriers in rabbit model. Int. J. Nanomedicine 16, 4985–5002. doi:10.2147/IJN.S319814
Abenojar, E. C., Wickramasinghe, S., Bas-Concepcion, J., and Samia, A. C. S. (2016). Structural effects on the magnetic hyperthermia properties of iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 26, 440–448. doi:10.1016/J.PNSC.2016.09.004
Alangari, A., Alqahtani, M. S., Mateen, A., Kalam, M. A., Alshememry, A., Ali, R., et al. (2022). Retracted: iron oxide nanoparticles: preparation, characterization, and assessment of antimicrobial and anticancer activity. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022. doi:10.1155/2022/1562051
Ali, A., Zafar, H., Zia, M., ul Haq, I., Phull, A. R., Ali, J. S., et al. (2016). Synthesis, characterization, applications, and challenges of iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 9, 49–67. doi:10.2147/NSA.S99986
Alibeigi, S., and Vaezi, M. R. (2008). Phase transformation of iron oxide nanoparticles by varying the molar ratio of Fe2+:Fe3+. Chem. Eng. Technol. 31, 1591–1596. doi:10.1002/CEAT.200800093
Allen, K. D., Adams, S. B., and Setton, L. A. (2010). Evaluating intra-articular drug delivery for the treatment of osteoarthritis in a rat model. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 16, 81–92. doi:10.1089/TEN.TEB.2009.0447
Ataide, J. A., Gérios, E. F., Cefali, L. C., Fernandes, A. R., Teixeira, M. do C., Ferreira, N. R., et al. (2019). Effect of polysaccharide sources on the physicochemical properties of bromelain–chitosan nanoparticles. Polymers 11, 1681. doi:10.3390/POLYM11101681
Aziz, D. E., Abdelbary, A. A., and Elassasy, A. I. (2018). Fabrication of novel elastosomes for boosting the transdermal delivery of diacerein: statistical optimization, ex-vivo permeation, in-vivo skin deposition and pharmacokinetic assessment compared to oral formulation. Drug Deliv. 25, 815–826. doi:10.1080/10717544.2018.1451572
Balestrieri, F., Magrì, A. D., Magrì, A. L., Marini, D., and Sacchini, A. (1996). Application of differential scanning calorimetry to the study of drug-excipient compatibility. Thermochim. Acta 285, 337–345. doi:10.1016/0040-6031(96)02904-8
Cardoso, V. S., Quelemes, P. V., Amorin, A., Primo, F. L., Gobo, G. G., Tedesco, A. C., et al. (2014). Collagen-based silver nanoparticles for biological applications: synthesis and characterization. J. Nanobiotechnology 12, 36–39. doi:10.1186/preaccept-1204601670134438
Cheung, R. C. F., Ng, T. B., Wong, J. H., and Chan, W. Y. (2015). Chitosan: an update on potential biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Mar. Drugs 13, 5156–5186. doi:10.3390/MD13085156
Comblain, F., Rocasalbas, G., Gauthier, S., and Henrotin, Y. (2017). Chitosan: a promising polymer for cartilage repair and viscosupplementation. Biomed. Mater Eng. 28, S209–S215. doi:10.3233/BME-171643
Cui, A., Li, H., Wang, D., Zhong, J., Chen, Y., and Lu, H. (2020a). Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies. EClinicalMedicine 29-30, 100587–100630. doi:10.1016/J.ECLINM.2020.100587
Cui, L., Zhang, J., Zou, J., Yang, X., Guo, H., Tian, H., et al. (2020b). Electroactive composite scaffold with locally expressed osteoinductive factor for synergistic bone repair upon electrical stimulation. Biomaterials 230, 119617. doi:10.1016/J.BIOMATERIALS.2019.119617
Da Costa Martins, R., Gamazo, C., and Irache, J. M. (2009). Design and influence of gamma-irradiation on the biopharmaceutical properties of nanoparticles containing an antigenic complex from Brucella ovis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 37, 563–572. doi:10.1016/J.EJPS.2009.05.002
Dasari, A., Xue, J., and Deb, S. (2022). Magnetic nanoparticles in bone tissue engineering. Nanomaterials 12, 757. doi:10.3390/NANO12050757
Dhakar, R. C., Dutta Maurya, S., and Saluja, V. (2012). From formulation variables to drug entrapment efficiency of microspheres: a technical review introduction. J. Drug Deliv. & Ther. Available at: http://jddtonline.info (Accessed February 15, 2024).
Ebadi, M., Bullo, S., Buskaran, K., Hussein, M. Z., Fakurazi, S., and Pastorin, G. (2021). Dual-functional iron oxide nanoparticles coated with polyvinyl alcohol/5-fluorouracil/zinc-aluminium-layered double hydroxide for a simultaneous drug and target delivery system. Polymers 13, 855. doi:10.3390/POLYM13060855
Eladawy, N. O., Morsi, N. M., and Shamma, R. N. (2021). Diacerein-loaded hyaluosomes as a dual-function platform for osteoarthritis management via intra-articular injection: in vitro characterization and in vivo assessment in a rat model. Pharmaceutics 13, 765. doi:10.3390/PHARMACEUTICS13060765
El-Gogary, R. I., Khattab, M. A., and Abd-Allah, H. (2020). Intra-articular multifunctional celecoxib loaded hyaluronan nanocapsules for the suppression of inflammation in an osteoarthritic rat model. Int. J. Pharm. 583, 119378. doi:10.1016/J.IJPHARM.2020.119378
Elsherif, N. I., Al-Mahallawi, A. M., Abdelkhalek, A. A., and Shamma, R. N. (2021). Investigation of the potential of nebivolol hydrochloride-loaded chitosomal systems for tissue regeneration: in vitro characterization and in vivo assessment. Pharmaceutics 13, 700. doi:10.3390/PHARMACEUTICS13050700
El Zaafarany, G. M., Awad, G. A. S., Holayel, S. M., and Mortada, N. D. (2010). Role of edge activators and surface charge in developing ultradeformable vesicles with enhanced skin delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 397, 164–172. doi:10.1016/J.IJPHARM.2010.06.034
Fan, D., Wang, Q., Zhu, T., Wang, H., Liu, B., Wang, Y., et al. (2020). Recent advances of magnetic nanomaterials in bone tissue repair. Front. Chem. 8, 745. doi:10.3389/FCHEM.2020.00745
Farahmandjou, M., and Soflaee, F. (2015). Synthesis and characterization of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles by simple Co-precipitation method. Phys. Chem. Res. 3, 191–196. doi:10.22036/PCR.2015.9193
Franconetti, A., Carnerero, J. M., Prado-Gotor, R., Cabrera-Escribano, F., and Jaime, C. (2019). Chitosan as a capping agent: insights on the stabilization of gold nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 207, 806–814. doi:10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2018.12.046
Frank, L. A., Onzi, G. R., Morawski, A. S., Pohlmann, A. R., Guterres, S. S., and Contri, R. V. (2020). Chitosan as a coating material for nanoparticles intended for biomedical applications. React. Funct. Polym. 147, 104459. doi:10.1016/J.REACTFUNCTPOLYM.2019.104459
Garthe, O. M., Kothawade, P. S., and Mahajan, V. R. (2013). Solubility enhancement of diacerein by solid dispersion technique. Int. J. Pharm. Res. & Allied Sci. 2, 47–55. Available at: www.ijpras.com (Accessed April 18, 2024).
Gmitrov, J., Ohkubo, C., and Okano, H. (2002). Effect of 0.25 T static magnetic field on microcirculation in rabbits. Bioelectromagnetics 23, 224–229. doi:10.1002/BEM.10007
Goldie, I., and Nachemson, A. (1970). Synovial ph in rheumatoid knee joints: II. The effect of local corticosteroid treatment. Acta Orthop. 41, 354–362. doi:10.3109/17453677008991521
Guan, W., Gao, H., Liu, Y., Sun, S., and Li, G. (2024). Application of magnetism in tissue regeneration: recent progress and future prospects. Regen. Biomater. 11, rbae048. doi:10.1093/RB/RBAE048
Gupta, A. K., and Gupta, M. (2005). Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26, 3995–4021. doi:10.1016/J.BIOMATERIALS.2004.10.012
Hagit, A., Soenke, B., Johannes, B., and Shlomo, M. (2010). Synthesis and characterization of dual modality (CT/MRI) core-shell microparticles for embolization purposes. Biomacromolecules 11, 1600–1607. doi:10.1021/bm100251s
Hartmann, P., Butt, E., Fehér, Á., Szilágyi, Á. L., Jász, K. D., Balázs, B., et al. (2018). Electroporation-enhanced transdermal diclofenac sodium delivery into the knee joint in a rat model of acute arthritis. Drug Des. Devel Ther. 12, 1917–1930. doi:10.2147/DDDT.S161703
Howard, D., Buttery, L. D., Shakesheff, K. M., and Roberts, S. J. (2008). Tissue engineering: strategies, stem cells and scaffolds. J. Anat. 213, 66–72. doi:10.1111/J.1469-7580.2008.00878.X
Huang, W., Tsui, C. P., Tang, C. Y., and Gu, L. (2018). Effects of compositional tailoring on drug delivery behaviours of silica xerogel/polymer core-shell composite nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 8, 13002. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-31070-9
Ignjatović, N. L., Sakač, M., Kuzminac, I., Kojić, V., Marković, S., Vasiljević-Radović, D., et al. (2018). Chitosan oligosaccharide lactate coated hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as a vehicle for the delivery of steroid drugs and the targeting of breast cancer cells. J. Mater Chem. B 6, 6957–6968. doi:10.1039/C8TB01995A
Inam, M. A., Khan, R., Park, D. R., Lee, Y. W., and Yeom, I. T. (2018). Removal of Sb(III) and Sb(V) by ferric chloride coagulation: implications of Fe solubility. Water 10, 418. doi:10.3390/W10040418
Jamshaid, T., Neto, E. T. T., Eissa, M. M., Zine, N., Kunita, M. H., El-Salhi, A. E., et al. (2016). Magnetic particles: from preparation to lab-on-a-chip, biosensors, microsystems and microfluidics applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 79, 344–362. doi:10.1016/J.TRAC.2015.10.022
Jauch, P., Weidner, A., Riedel, S., Wilharm, N., Dutz, S., and Mayr, S. G. (2020). Collagen–iron oxide nanoparticle based ferrogel: large reversible magnetostrains with potential for bioactuation. Multifunct. Mater. 3, 035001. doi:10.1088/2399-7532/ABAA2D
Jiang, W., Lai, K. L., Hu, H., Zeng, X. B., Lan, F., Liu, K. X., et al. (2011). The effect of [Fe3+]/[Fe2+] molar ratio and iron salts concentration on the properties of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles in the water/ethanol/toluene system. J. Nanoparticle Res. 13, 5135–5145. doi:10.1007/s11051-011-0495-8
Kamel, R., Salama, A. H., and Mahmoud, A. A. (2016). Development and optimization of self-assembling nanosystem for intra-articular delivery of indomethacin. Int. J. Pharm. 515, 657–668. doi:10.1016/J.IJPHARM.2016.10.063
Kanai, S., Taniguchi, N., Kanai, S., and Taniguchi, N. (2012). Efficacy of static magnetic field for pain of adjuvant arthritis rats. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 3, 511–515. doi:10.4236/ABB.2012.324067
Kany, S., Vollrath, J. T., and Relja, B. (2019). Cytokines in inflammatory disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20, 6008. doi:10.3390/IJMS20236008
Kianfar, E. (2021). Magnetic nanoparticles in targeted drug delivery: a review. J. Supercond. Nov. Magnetism 34 (7 34), 1709–1735. doi:10.1007/S10948-021-05932-9
Küçüktürkmen, B., Öz, U. C., and Bozkir, A. (2017). In situ hydrogel formulation for intra-articular application of diclofenac sodium-loaded polymeric nanoparticles. Turk J. Pharm. Sci. 14, 56–64. doi:10.4274/TJPS.84803
Lagrow, A. P., Besenhard, M. O., Hodzic, A., Sergides, A., Bogart, L. K., Gavriilidis, A., et al. (2019). Unravelling the growth mechanism of the co-precipitation of iron oxide nanoparticles with the aid of synchrotron X-Ray diffraction in solution. Nanoscale 11, 6620–6628. doi:10.1039/C9NR00531E
Larsson, S., Englund, M., Struglics, A., and Lohmander, L. S. (2015). Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in synovial fluid are associated with progression of radiographic knee osteoarthritis in subjects with previous meniscectomy. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 23, 1906–1914. doi:10.1016/J.JOCA.2015.05.035
León-López, A., Morales-Peñaloza, A., Martínez-Juárez, V. M., Vargas-Torres, A., Zeugolis, D. I., and Aguirre-Álvarez, G. (2019). Hydrolyzed collagen-sources and applications. Molecules 24, 4031. doi:10.3390/MOLECULES24224031
Liu, H., Ma, Y., Wang, M., Li, D., and Pan, H. (2016). Physicochemical properties, characterization, and antioxidant activity of sodium ferric gluconate complex. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 22, 639–646. doi:10.3136/fstr.22.639
Liu, K., Zhang, D., and Wang, W. (2021). Nanoparticle-based drug delivery system—a target strategy for osteoarthritis treatment. J. Nanomater 2021, 1–15. doi:10.1155/2021/4064983
Liu, Z., Liu, J., Cui, X., Wang, X., Zhang, L., and Tang, P. (2020). Recent advances on magnetic sensitive hydrogels in tissue engineering. Front. Chem. 8, 124. doi:10.3389/FCHEM.2020.00124
Maguire, C. M., Rösslein, M., Wick, P., and Prina-Mello, A. (2018). Characterisation of particles in solution - a perspective on light scattering and comparative technologies. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater 19, 732–745. doi:10.1080/14686996.2018.1517587
Marycz, K., Kornicka, K., and Röcken, M. (2018). Static magnetic field (SMF) as a regulator of stem cell fate - new perspectives in regenerative medicine arising from an underestimated tool. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 14, 785–792. doi:10.1007/S12015-018-9847-4
Materón, E. M., Miyazaki, C. M., Carr, O., Joshi, N., Picciani, P. H. S., Dalmaschio, C. J., et al. (2021). Magnetic nanoparticles in biomedical applications: a review. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 6, 100163. doi:10.1016/J.APSADV.2021.100163
Mizutani, N., Iwasaki, T., Watano, S., Yanagida, T., Tanaka, H., and Kawai, T. (2008). Effect of ferrous/ferric ions molar ratio on reaction mechanism for hydrothermal synthesis of magnetite nanoparticles. Bull. Mater. Sci. 31, 713–717. doi:10.1007/s12034-008-0112-3
Nafee, N., Zewail, M., and Boraie, N. (2018). Alendronate-loaded, biodegradable smart hydrogel: a promising injectable depot formulation for osteoporosis. J. Drug Target 26, 563–575. doi:10.1080/1061186X.2017.1390670
Neogi, T. (2013). The epidemiology and impact of pain in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 21, 1145–1153. doi:10.1016/J.JOCA.2013.03.018
Nguyen, D. T., Nguyen, N. M., Vu, D. M., Tran, M. D., and Ta, V. T. (2021). On-demand release of drug from magnetic nanoparticle-loaded alginate beads. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2021, 1–7. doi:10.1155/2021/5576283
Oprenyeszk, F., Sanchez, C., Dubuc, J. E., Maquet, V., Henrist, C., Compère, P., et al. (2015). Chitosan enriched three-dimensional matrix reduces inflammatory and catabolic mediators production by human chondrocytes. PLoS One 10, e0128362. doi:10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0128362
Pauli, C., Whiteside, R., Heras, F. L., Nesic, D., Koziol, J., Grogan, S. P., et al. (2012). Comparison of cartilage histopathology assessment systems on human knee joints at all stages of osteoarthritis development. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 20, 476–485. doi:10.1016/J.JOCA.2011.12.018
Petit, A., Redout, E. M., van de Lest, C. H., de Grauw, J. C., Müller, B., Meyboom, R., et al. (2015). Sustained intra-articular release of celecoxib from in situ forming gels made of acetyl-capped PCLA-PEG-PCLA triblock copolymers in horses. Biomaterials 53, 426–436. doi:10.1016/J.BIOMATERIALS.2015.02.109
Pochapski, D. J., Carvalho Dos Santos, C., Leite, G. W., Pulcinelli, S. H., and Santilli, C. V. (2021). Zeta potential and colloidal stability predictions for inorganic nanoparticle dispersions: effects of experimental conditions and electrokinetic models on the interpretation of results. Langmuir 37, 13379–13389. doi:10.1021/ACS.LANGMUIR.1C02056
Prasanna Mallick, S., Prasad Panda, S., Gayatri, A., Kunaal, Y., Naresh, C., Kumar Suman, D., et al. (2021). Chitosan oligosaccharide based hydrogel: an insight into the mechanical. Drug Deliv. Antimicrob. Stud. 11, 10293–10300. doi:10.33263/BRIAC113.1029310300
Rose, J. C., Cámara-Torres, M., Rahimi, K., Köhler, J., Möller, M., and De Laporte, L. (2017). Nerve cells decide to orient inside an injectable hydrogel with minimal structural guidance. Nano Lett. 17, 3782–3791. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b01123
Rostamnezhad, M., Mireskandari, K., Rouini, M. R., Ansari, S., Darabi, M., and Vatanara, A. (2023). Screening of cyclodextrins in the processing of buserelin dry powders for inhalation prepared by spray freeze-drying. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 13, 772–783. doi:10.34172/APB.2023.086
Sacco, P., Furlani, F., Marzo, G.De, Marsich, E., Paoletti, S., and Donati, I. (2018). Concepts for developing physical gels of chitosan and of chitosan derivatives. Gels 4, 67. doi:10.3390/GELS4030067
Shipko, F. J., and Douglas, D. L. (1956). Stability of ferrous hydroxide precipitates. J. Phys. Chem. 60, 1519–1523. doi:10.1021/J150545A011
Stannus, O., Jones, G., Cicuttini, F., Parameswaran, V., Quinn, S., Burgess, J., et al. (2010). Circulating levels of IL-6 and TNF-α are associated with knee radiographic osteoarthritis and knee cartilage loss in older adults. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 18, 1441–1447. doi:10.1016/J.JOCA.2010.08.016
Sulistyaningsih, T., Santosa, S. J., Siswanta, D., and Rusdiarso, B. (2017). Synthesis and characterization of magnetites obtained from mechanically and sonochemically assissted Co-precipitation and reverse Co-precipitation methods. Int. J. Mater. Mech. Manuf. 5, 16–19. doi:10.18178/IJMMM.2017.5.1.280
Taherian, A., Esfandiari, N., and Rouhani, S. (2021). Breast cancer drug delivery by novel drug-loaded chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Cancer Nanotechnol. 12, 15–20. doi:10.1186/s12645-021-00086-8
Tóth, I. Y., Veress, G., Szekeres, M., Illés, E., and Tombácz, E. (2015). Magnetic hyaluronate hydrogels: preparation and characterization. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 380, 175–180. doi:10.1016/J.JMMM.2014.10.139
Trivedi, D., and Jana, S. (2019). Solid state characterization of the consciousness energy healing treated ferrous sulphate. J. Nutr. Health Sci. Available at: https://www.academia.edu/39995971/Solid_State_Characterization_of_the_Consciousness_Energy_Healing_Treated_Ferrous_Sulphate (Accessed April 18, 2024).
Tursunkulov, O., Allabergenov, B., Abidov, A., Jeong, S.-W., and Kim, S. (2013). Synthesis, characterization and functionalization of the coated iron oxide nanostructures. J. Korean Powder Metallurgy Inst. 20, 180–185. doi:10.4150/KPMI.2013.20.3.180
Ursescu, M., Măluţan, T., and Ciovică, S. (2009). Iron gall inks influence on papers’ thermal degradation ftir spectroscopy applications. Eur. J. Sci. Theol. 5, 71–84.
Üstündaǧ-Okur, N., Gökçe, E. H., Bozbiyik, D. I., Eǧrilmez, S., Özer, Ö., and Ertan, G. (2014). Preparation and in vitro–in vivo evaluation of ofloxacin loaded ophthalmic nano structured lipid carriers modified with chitosan oligosaccharide lactate for the treatment of bacterial keratitis. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 63, 204–215. doi:10.1016/J.EJPS.2014.07.013
Veeman, D., Sai, M. S., Sureshkumar, P., Jagadeesha, T., Natrayan, L., Ravichandran, M., et al. (2021). Additive manufacturing of biopolymers for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: an overview, potential applications, advancements, and trends. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2021, 1–20. doi:10.1155/2021/4907027
Veliks, V., Ceihnere, E., Svikis, I., and Aivars, J. (2004). Static magnetic field influence on rat brain function detected by heart rate monitoring. Bioelectromagnetics 25, 211–215. doi:10.1002/BEM.10186
Wahyuni, S., Wibowo, K. R. P., Prakoso, H. T., and Bintang, M.Siswanto (2021). Chitosan-Ag nanoparticle antifungal activity against Fusarium sp., causal agent of wilt disease on chili. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 948, 012064. doi:10.1088/1755-1315/948/1/012064
Wang, T., Xie, W., Ye, W., and He, C. (2019). Effects of electromagnetic fields on osteoarthritis. Biomed. & Pharmacother. 118, 109282. doi:10.1016/J.BIOPHA.2019.109282
Wu, S., Sun, A., Zhai, F., Wang, J., Xu, W., Zhang, Q., et al. (2011). Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles synthesis from tailings by ultrasonic chemical co-precipitation. Mater Lett. 65, 1882–1884. doi:10.1016/J.MATLET.2011.03.065
Yang, J., Xiao, Y., Tang, Z., Luo, Z., Li, D., Wang, Q., et al. (2020a). The negatively charged microenvironment of collagen hydrogels regulates the chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Mater Chem. B 8, 4680–4693. doi:10.1039/D0TB00172D
Yang, Y. N., Lu, K. Y., Wang, P., Ho, Y. C., Tsai, M. L., and Mi, F. L. (2020b). Development of bacterial cellulose/chitin multi-nanofibers based smart films containing natural active microspheres and nanoparticles formed in situ. Carbohydr. Polym. 228, 115370. doi:10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2019.115370
Yin, J., Huang, Y., Gao, G., Nong, L., Xu, N., and Zhou, D. (2018). Changes and significance of inflammatory cytokines in a rat model of cervical spondylosis. Exp. Ther. Med. 15, 400–406. doi:10.3892/ETM.2017.5418
Zhang, Y., Sun, Y., Yang, X., Hilborn, J., Heerschap, A., and Ossipov, D. A. (2014). Injectable in situ forming hybrid iron oxide-hyaluronic acid hydrogel for magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery. Macromol. Biosci. 14, 1249–1259. doi:10.1002/MABI.201400117
Keywords: diacerein, iron oxide microparticles, osteoarthritis, intra-articular injection, rat model, factorial design
Citation: Ali NA, Morsi NM, Badr-Eldin SM and Shamma RN (2024) Diacerein-loaded surface modified iron oxide microparticles (SMIOMPs): an emerging magnetic system for management of osteoarthritis via intra-articular injection. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 12:1439085. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1439085
Received: 01 June 2024; Accepted: 07 October 2024;
Published: 28 October 2024.
Edited by:
Otto Carl Wilson, The Catholic University of America, United StatesReviewed by:
Asif Nawaz, Gomal University, PakistanSharanabasava V. Ganachari, KLE Technological University, India
Copyright © 2024 Ali, Morsi, Badr-Eldin and Shamma. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rehab N. Shamma, cmVoYWIuc2hhbW1hQHBoYXJtYS5jdS5lZHUuZWc=
 Nouran Abdelmageed Ali
Nouran Abdelmageed Ali Nadia M. Morsi1
Nadia M. Morsi1 Shaimaa M. Badr-Eldin
Shaimaa M. Badr-Eldin Rehab N. Shamma
Rehab N. Shamma