
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol., 14 December 2023
Sec. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
Volume 11 - 2023 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2023.1335918
This article is a correction to:
The Fabrication of a Gellan Gum-Based Hydrogel Loaded With Magnesium Ions for the Synergistic Promotion of Skin Wound Healing
A Corrigendum on
The fabrication of a gellan gum-based hydrogel loaded with magnesium ions for the synergistic promotion of skin wound healing
by Li W, Jian X, Zou Y, Wu L, Huang H, Li H, Hu D and Yu B (2021). Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 9:709679. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.709679
In the published article, there was an error in Affiliation 2. Instead of “Gungdong provincial engineering technology research center for sports assistive devices, Guangzhou Sport University, Guangzhou, China.”, it should be “Guangdong Provincial Engineering Technology Research Center for Sports Assistive Devices, Guangzhou Sport University, Guangzhou, China.”
In the published article, there was an error in the order of “Graphical Abstract, Scheme 1, and Figure 1”, and in the legend for “Scheme 1, Figure 1” as published. The corrected order and legend appears below.
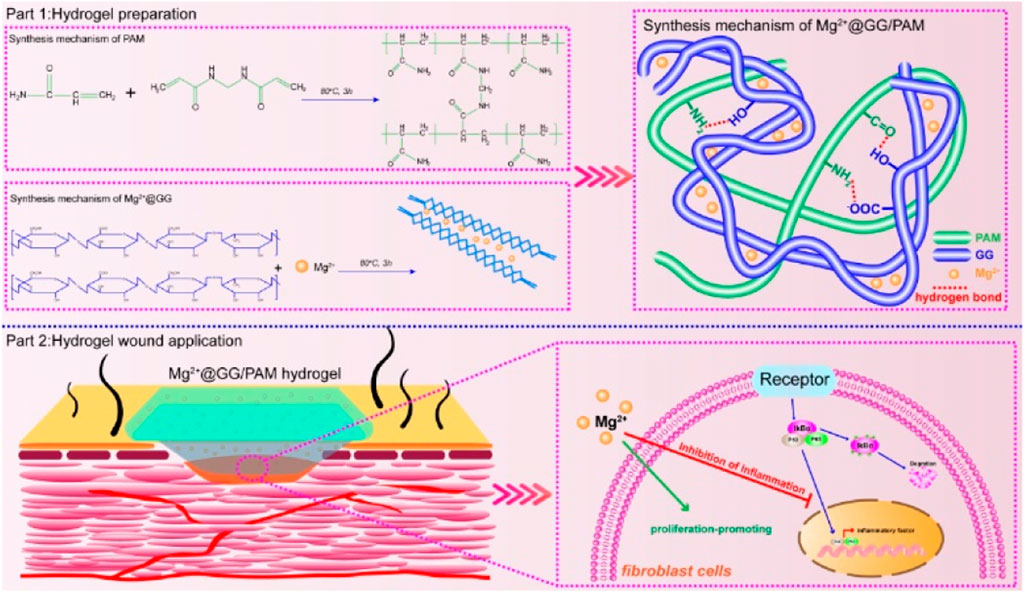
SCHEME 1. Schematic illustration of synthesis procedure for Mg2+@GG/PAM hydrogel and the repair mechanism of Mg2+ ions from Mg2+@GG/PAM hydrogel in the burn wound.

FIGURE 1. Characterization of Mg2+@GG/PAM hydrogel (A) SEM (B) FT-IR (C) EDS analysis (D) TGA (E) Water vapor transmission rate (F–G) Swelling ratio.
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 6 as published. The corrected Figure 6 and its caption appear below.
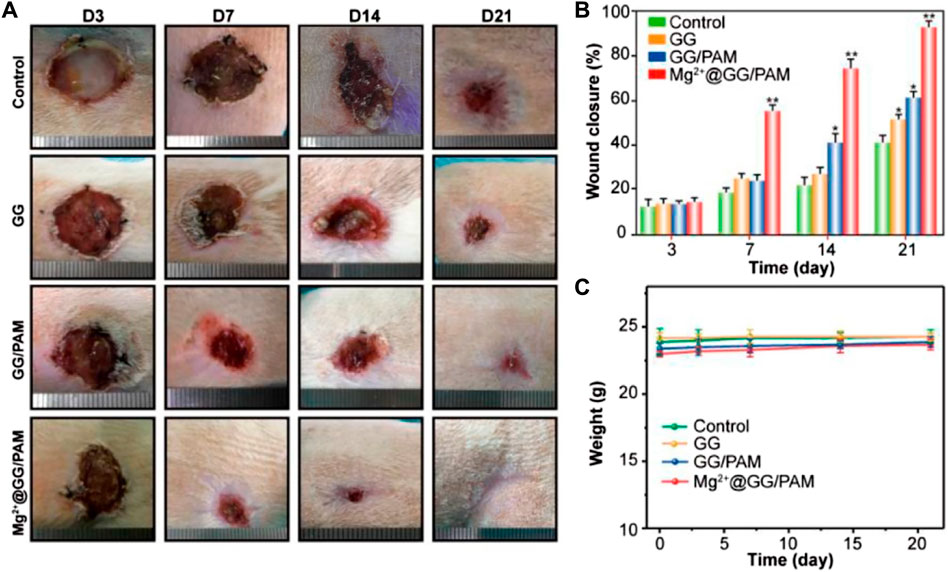
FIGURE 6. Macroscopic observation (A), statistical analysis (B), and weight changes (C) of wound healing process at 3, 7, 14, and 21 days, after treatment with PBS (control), GG, GG/PAM, and Mg2+@GG/PAM. The values are represented as mean ± SD (n = 6). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs control.
The authors apologize for these error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: gellan gum, magnesium ion, polyacrylamide, skin wounds, hydrogel
Citation: Li W, Jian X, Zou Y, Wu L, Huang H, Li H, Hu D and Yu B (2023) Corrigendum: The fabrication of a gellan gum-based hydrogel loaded with magnesium ions for the synergistic promotion of skin wound healing. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 11:1335918. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1335918
Received: 09 November 2023; Accepted: 16 November 2023;
Published: 14 December 2023.
Edited and reviewed by:
Martijn van Griensven, Maastricht University, NetherlandsCopyright © 2023 Li, Jian, Zou, Wu, Huang, Li, Hu and Yu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dandan Hu, Z3VvaGRkQDEyNi5jb20=; Bo Yu, Mjg2NzcwNTc1NEBxcS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.