
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Behav. Econ. , 19 March 2025
Sec. Health Behaviors
Volume 4 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/frbhe.2025.1541497
Introduction: Research consistently finds more workplace injuries occur on Mondays than on other weekdays. One hypothesis is that workers fraudulently claim that off-the-job weekend sprains and strains occurred at work on the Monday in order to receive workers' compensation.
Methods: We apply linear regression analysis to test this and competing hypotheses using data from New Zealand, where compensation is virtually identical whether or not an injury occurs at work.
Results: We still find that work claims, especially sprains and strains, occur disproportionately on Mondays, although less than in other jurisdictions. This suggests fraudulent claims in other countries are just one part of the story. Furthermore, we find work claims remain high on Tuesdays, and that workers' sprains and strains that occur off-the-job also disproportionately fall on Mondays. Sprains and strains treated at hospitals, which are not closed over the weekend, are also elevated on Mondays. However, Monday lost-time injuries are less severe than injuries on other days.
Discussion: Our findings are consistent with a physiological mechanism contributing to elevated Monday injury claims in New Zealand, but do not suggest doctors' offices being closed over the weekend, ergonomic explanations, or work being riskier on Mondays play important roles.
In 2017, the U.S. government spent $62 billion (0.3% of GDP) on workers' compensation benefits, highlighting the significant economic burden of workplace injury claims. A well-documented phenomenon in the literature is the “Monday Effect,” where workers' compensation claims for injuries are disproportionately higher on Mondays compared to other weekdays, particularly for hard-to-monitor injuries such as sprains and strains.1 This pattern has been attributed to moral hazard, where individuals may falsely report weekend injuries as occurring on Monday to access compensation benefits for which they would otherwise be ineligible (Hansen, 2016; Martin-Roman and Moral, 2016; Smith, 1990). Such behavior not only increases the costs of workers' compensation systems but also raises concerns about the design of policies aimed at mitigating fraudulent claims.
However, the extent to which the Monday Effect is driven by economic incentives vs. other factors—such as physiological or behavioral mechanisms—remains poorly understood. This gap in the literature is critical for policymakers seeking to design efficient and equitable compensation systems. To address this, we examine the Monday Effect in New Zealand, a unique setting with a universal no-fault accident compensation system that covers all injuries, regardless of where they occur, and provides equal compensation for work-related and non-work-related injuries. By design, this system minimizes moral hazard, offering a natural experiment to disentangle the economic, physiological, and behavioral drivers of the Monday Effect.
Using administrative data on the universe of accident claims in New Zealand from January 2001 to July 2018, we first document the persistence of the Monday Effect in this context where moral hazard should be minimized. We then test three alternative hypotheses for this finding: (1) physiological causes, where workers are more prone to injuries on Mondays due to reduced physical readiness after a weekend off (Butler et al., 2014; Campolieti and Hyatt, 2006; Card and McCall, 1996; Martin-Roman and Moral, 2016); (2) administrative frictions, where weekend closures of doctors' offices delay injury reporting until Monday; and (3) behavioral mechanisms, where individuals' lower pain thresholds or heightened stress levels on Mondays increase the likelihood of injury claims.2
Our empirical strategy leverages the unique features of the New Zealand system. First, we analyze injury claims by non-workers and off-the-job injuries, where physiological and incentive-based explanations are unlikely to apply. Second, we examine claims treated in public hospitals, which operate fully on weekends, to isolate the role of administrative frictions. Finally, we use data on injury severity to explore whether behavioral factors, such as lower pain thresholds or increased workplace stress on Mondays, contribute to the observed patterns.
We find robust evidence of a Monday Effect in New Zealand: 21.7% of weekday lost-time work injury claims occur on Mondays, with a slightly higher proportion (22.3%) for sprains and strains. Importantly, we find no Monday Effect for off-the-job or non-worker claims, and only a minimal effect for hospitalizations, suggesting that moral hazard plays a negligible role in this context. Instead, our results point to physiological and behavioral explanations. Sprains and strains are elevated on Mondays across all samples, and work injuries on Mondays are less severe than those on other weekdays, consistent with lower pain thresholds or reduced tolerance for discomfort at the start of the workweek. Additionally, we observe a declining trend in claims from Monday to Friday, mirroring patterns found in other countries (Fontaneda et al., 2024) and aligning with evidence that workers are less happy and more stressed at the beginning of the week (Pindek et al., 2021; Taylor, 2002) and that workplace incivility decreases during the week (Nicholson and Griffin, 2017).
Our findings make two key contributions to the literature. First, we demonstrate that fraudulent claims are not a significant driver of the Monday Effect in systems where moral hazard is minimized. Comparing our results to studies in the U.S. and Canada, we estimate that economic incentives explain at least half of the Monday Effect in traditional workers' compensation systems.3 This underscores the importance of policy interventions to reduce moral hazard in such settings. Second, we provide novel evidence that physiological and behavioral factors—such as the physical and psychological impact of the weekend—play a substantial role in shaping injury claims. These findings suggest that workplace policies aimed at improving employee wellbeing, such as flexible scheduling or stress-reduction programs, could mitigate the Monday Effect and reduce the economic burden of workers' compensation systems.
By shedding light on the interplay between economic incentives, physiological readiness, and behavioral responses, this study advances our understanding of the Monday Effect and offers actionable insights for policymakers and employers seeking to design more effective and equitable compensation systems.
Under the Accident Compensation Act 2002, everyone in New Zealand is entitled to comprehensive injury insurance cover, including tourists and the self-employed. Insurance coverage includes compensation for the costs of injury following an accident, such as medical treatment, lost wages and additional expenses where required (e.g., home help). When a person seeks treatment for an injury (e.g., visits a doctor, dentist, physiotherapist), the treatment provider will complete a form with information on initial diagnosis and ability to work (if relevant) and send it to the Accident Compensation Corporation (ACC) on the patient's behalf. Claims made under the scheme provide complete coverage of all injuries in New Zealand for which treatment has been provided by doctors, dentists and physiotherapists.4
Information on the accident date is recorded on the form. This information is usually recorded by the doctor following a discussion with the patient about when the injury happened and how it happened. To be eligible for compensation, an injury needs to be caused by a specific incident, so all accepted injury claims have an accident date. If treatment were to be delayed, for example due to weekend commitments, the accident date would differ from the date of treatment.
A doctors' certificate is required to certify that an injury requires time off work. ACC pays weekly compensation of 80% of pre-injury earnings (Accident Compensation Act 2002, sch 1 s32) regardless of where the injury occurred and who was at fault. This compensation is capped at an amount that is adjusted each year.5 There is a 1-week stand-down period for loss of earnings compensation. If the injury occurred at work, this excess is paid by the employer (Accident Compensation Act 2002, s97); if the injury occurred to a worker off the job, it is paid through sick leave or annual leave entitlements (Accident Compensation Corporation, 2025). This introduces a weak incentive for individuals to falsely report that off-the-job injuries that require time off work occurred at work.
On the other hand, New Zealand has an Accredited Employers Programme (AEP) whereby firms can apply to manage their employees work claims (or subcontract it to a third party), in exchange for an ACC levy reduction. Introduced in 2000, AEP is targeted to large firms—the requirement to pay for an onsite audit makes it is less appealing to smaller firms. ACC continues to manage off-the-job claims for the employees of AEP companies. For firms that are not part of AEP, a compulsory Experience Rating scheme was introduced in 2011.6 Both of these programs weakly incentivize firms to encourage employees to fraudulently claim that a work injury occurred off-the-job in order to avoid paying the claim costs.7
Accident compensation in New Zealand sits within a mixed private-public funding model for primary healthcare and a fully funded publicly provided secondary healthcare model. Primary health care services are funded through District Health Boards (DHBs). Funding is based on the number of people enrolled with a Primary Health Organization (PHOs), and the demographic composition of their enrolled population, rather than the number of visits (Ministry of Health, 2014), although general practitioners (GPs) retain the right to charge user fees (Ministry of Health, 2017).
Unlike primary health care, public hospitals are fully funded, and elective services are managed on a prioritization basis. Hospital treatment is free, irrespective of whether the person has an injury or illness. The hospital receives funding from ACC to cover the cost of treating injuries and from the DHB to cover the cost of treating other issues (e.g., illnesses). There are some private hospitals available for those willing to pay for non-urgent treatment. Although New Zealand has a private health insurance market, it is relatively small (The Treasury, 2014). In 2015, 71% of healthcare expenditure was funded by the government, nine percent through accident compensation insurance, five percent by voluntary private health insurance and 15% by user charges (OECD, 2017).
The data used in this paper come from the Integrated Data Infrastructure (IDI), an individual-level longitudinal data set managed by Statistics New Zealand. Individuals are linked between the data sets from different source agencies using deterministic and probabilistic linking. Most of the data sources are administrative and cover the full population. The main IDI data used here is all accepted accident compensation claims. The data cover the period January 2001 to July 2018. We exclude gradual process injury because, by definition, these types of injuries do not have a clear accident date. Sometimes there are multiple claims for the same accident and person. We assume that if an individual has multiple claims for an accident that occurred on the same day then it is the same accident. The claim with the highest amount of compensation paid-to-date is kept.
Consistent with the previous studies (Campolieti and Hyatt, 2006; Card and McCall, 1996), we exclude claims for injuries that occur on the weekend for most of our analysis, restricting analysis to the typical Monday-to-Friday working week. Our main analysis focuses on injuries that involve a week or more of time away from work, which we refer to as lost-time injuries. We focus on these injuries both to improve the comparability of our results with international findings and because we expect the claims information for these injuries to be more accurate, as when there are only medical costs to be paid, ACC only verifies minimal information about the claim (Statistics New Zealand, 2015).
We also use data on publicly funded hospital discharges to test whether there is a Monday Effect in injuries treated in hospitals. Privately funded hospital events have been excluded from this data because the available information is incomplete. Our hospital discharges data contain information on the start date of the hospital event and the type of injury. We focus on events with a start date between 2001 and 2017 and a primary diagnosis of an injury or a poisoning. Information on work status is not available in this data, so we restrict the hospitalisations sample to those of working age (15–64 years) to improve comparability with the worker samples.
We measure day of the week based on the accident date (as distinct from the treatment date or the claim acceptance date). Injuries are grouped into seven injury type categories: sprains and strains; cuts and lacerations; contusions; fractures; burns; dislocations; and other.8 Figure 1 displays the distribution of lost-time injuries for workers by the day of the week for work injuries (left hand panels) and off-the-job injuries (right hand panels). It shows work injuries are lowest on the weekend when fewer people work and off-the-job injuries are highest on the weekend when most workers are off work. Once we restrict our focus to weekdays, the highest proportion of work injuries occur on a Monday (21.7%), and the lowest proportion on a Friday (18.2%). This is equivalent to an excess of around 300 lost-time work claims on Mondays per year. For off-the-job injury, the highest proportion of injuries occurred on a Friday (21.9%), possibly alcohol-induced, with the second-highest number occurring on a Monday (19.9%).
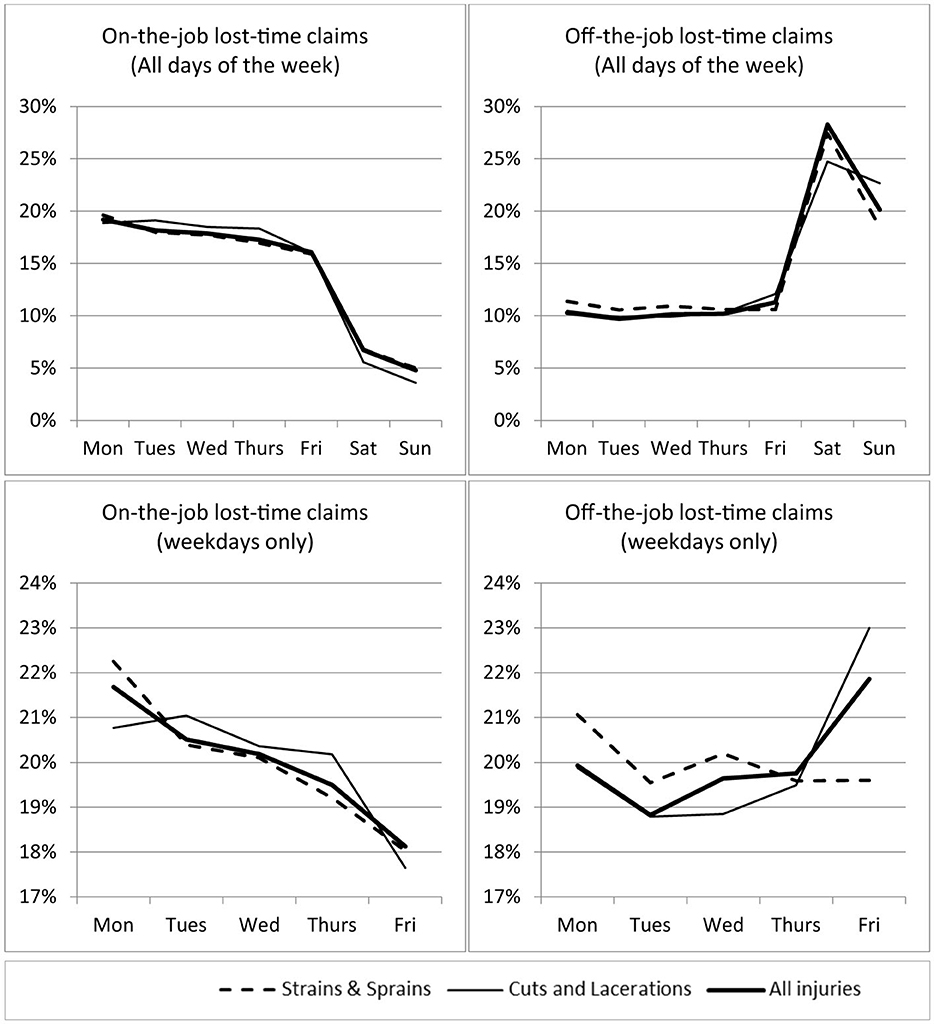
Figure 1. Distribution of lost-time injuries for workers by day of the week. “On-the-job lost-time claims” are injuries to workers that happened at work and resulted in more than a week off work; “off-the-job lost-time claims” are injuries that happened to workers during their leisure time and resulted in more than a week off work. Data have been confidentialized.
Figure 2 displays the weekday patterns for all injury claims, not just the lost-time injury subsample, and for hospitalisations. Including all claims does not change the pattern for work injury. For working-age non-workers, the highest proportion of weekday injuries occurs on a Wednesday, and the lowest on a Friday. For weekday hospitalisations of working age individuals, the highest proportion of injuries occurs on a Monday, followed by a Friday.
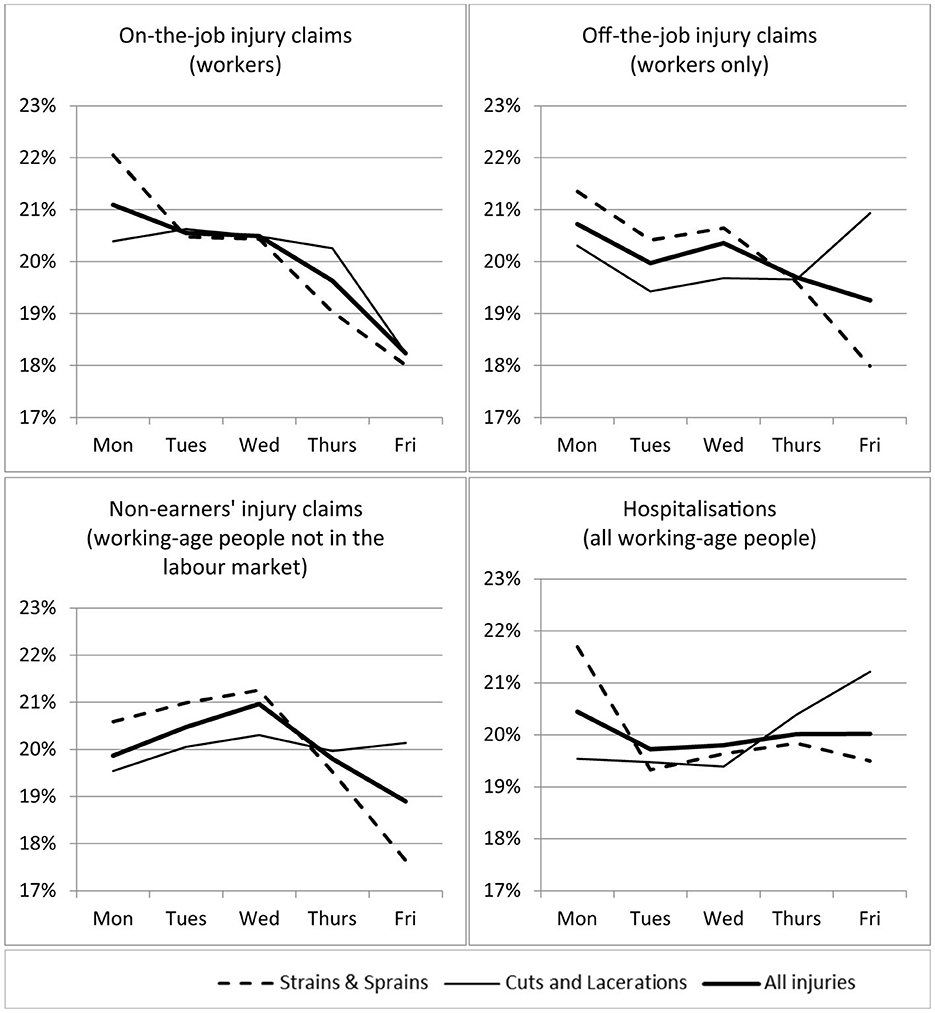
Figure 2. Distribution of all injuries by weekday and injury type. “On-the-job injury claims” are injuries to workers that happened at work; “off-the-job injury claims” are injuries that happened to workers during their leisure time; “Non-earners” injury claims' are injuries that happened to working-age people not in the labor market (aged 15–64); “hospitalisations” are all injuries where a working-age person was admitted to hospital (aged 15–64), irrespective of whether they are in the labor market. The data includes all injuries (claims and hospitalisations), those that resulted in time off work and those that did not. Data restricted to standard working weeks: exclude weekend injuries, the 2-week Christmas and New Year's Day period and weeks with a public holiday. Data have been confidentialized.
Table 1 displays summary statistics for the sample of work lost-time injuries, off-the-job lost-time injuries and working-age non-worker injuries.9 The average number of compensated days for work injury (100.4) is higher than that found in other countries because injuries with less than a week off work are excluded here.10 The average number of compensated days for a work injury is 99.3 for Monday injuries and 100.7 for injuries that occurred on other weekdays. The values are slightly lower for off-the-job injuries: 82.1 for Monday injuries and 84.1 for other weekday injuries.
We begin by testing whether, as is observed internationally, weekday lost-time work injuries are disproportionately likely to be reported to occur on Mondays, overall and for each injury type. If injury risk per hour of work are constant throughout the week, then the proportion of weekday workplace injuries that occurred on Monday will be equal to the proportion of weekday hours worked on Mondays. We thus use one-sided t-tests to test whether more than 20 percent of weekday workplace lost-time injuries occur on a Monday. Finding a Monday Effect here could indicate workers genuinely have higher injury rates on Mondays, or that they misreport injuries as disproportionately occurring on Mondays.
Table 2 presents the results of our t-tests and the comparable results from other jurisdictions estimated in prior studies. Workers in New Zealand who sustain off-the-job injuries have very little incentive to misreport these as work injuries because access to and cost of healthcare is identical for work and off-the-job injuries, and compensation for the two differs only for the first week of lost work time. We find that 21.7% of weekday lost-time work injuries in New Zealand occur on a Monday (with a 95% confidence interval of 21.5 to 21.8%), and this percentage is statistically significantly >20%. However, it is economically and statistically significantly smaller than the 23.0% (with 95% confidence interval of 22.7 to 23.3%) found in Minnesota (Card and McCall, 1996) and the 24.7% (with 95% confidence interval of 24.3 to 25.1%) found in Ontario (Campolieti and Hyatt, 2006). This suggests that the fraudulent claims theory may explain half or more of the Monday Effect in countries where there are incentives to make fraudulent workers' compensation claims, but it is not the full story.
We next conduct t-tests for whether injuries overall or strains and sprains in particular are disproportionately likely to occur on each weekday. The ease with which injuries can be misreported or faked depends a lot of the type of injury. Strains and sprains are easier to misreport than are other types of injury, because delaying seeking medical attention for them is less costly and they are more easily concealed. Furthermore, the fact sprains and strains are harder to diagnose makes them more liable to be both misreported and faked. A larger Monday Effect for strains and sprains than for injures in general would therefore be consistent with misreported or faked injuries.
These results are shown in Table 2. We find that 22.3% of weekday sprains and strains in New Zealand occur on a Monday, a higher proportion than any other day. This magnitude of Monday Effect is more than twice as large as for any other injury type, though cuts and lacerations, dislocations, fractures, and contusions also have a higher likelihood of occurring on a Monday than on other days. Burns are less likely to happen on a Monday (17.9%). These values are all statistically significantly different to 20%. The lower fraction of Monday burns is common to Ontario and Minnesota, but in these two jurisdictions dislocations have the largest Monday Effect (though the number of observations for dislocations is low in Ontario).
The first panel of Table 3 looks at whether lost-time work injuries overall, lost-time work sprains and strains (“sprains”), and other lost-time work injuries (“non-sprains”) are more likely to occur on each individual day of the week. Studying the pattern of injuries across each day of the week allows us to distinguish whether any higher injury rate on Mondays is specific to Mondays or whether it is an “early in the week” phenomenon. A Monday Effect driven by fraudulent claims, impairment, or the closure of doctors' offices over the weekend should not carry over to above-average claims on a Tuesday; if dissatisfaction drives a Monday Effect, Tuesdays might also have elevated rates of claims. Weeks with a public holiday are excluded from these tables to improve comparability of the weekdays.
We find that these injuries overall are also elevated on Tuesdays, though to a smaller extent than on Mondays. In fact, the fraction of weekday injuries falls steadily through the week, with Monday, Tuesday, and Wednesday work injuries all statistically significantly higher than 20%. Strains and sprains are similarly downward sloping, again with Tuesday injuries elevated. Lost-time work injuries other than strains and sprains reflect the same pattern as injuries overall, decreasing steadily through the week with Monday, Tuesday, and Wednesday injuries all statistically significantly higher than 20%. Fontaneda et al. (2024) finds the same pattern for Spain. All work injury claims, shown in Appendix Table A1, have a similar pattern over the week to lost-time work injury claims.11
We next repeat these tests for lost-time off-the-job injuries to workers and all injury claims by non-workers. If fraudulent claims, ergonomics, or higher work risk drive a Monday effect in work claims, we would not expect to see a similar Monday effect for the off-the-job injuries of workers. However, if doctors' office closures, worker impairment, or higher dissatisfaction drive a Monday effect in work claims, we would expect to see a similar Monday effect in the off-the-job claims of workers. Non-workers' claims will also not be affected by fraudulent claims, ergonomics, or higher work risk, and may not be affected by higher dissatisfaction on Mondays.
The second panel of Table 3 examines off-the-job lost-time injuries. The population at risk here is the same, workers, but the causes of the injuries differ. We find that off-the-job lost-time injuries as a whole are most likely to occur on a Friday (21.9%), many of which are likely to be alcohol-related. Even within the days Monday to Thursday, off-the-job lost-time injuries do not show the same downward-sloping pattern Mondays, Wednesdays, and Thursdays have relatively similar numbers of injuries, and Tuesdays have fewer. However, off-the-job lost-time sprains and strains are more likely to occur on a Monday (21.1%). Off-the-job lost-time non-sprains follow the same pattern as injuries overall, with a highest proportion of injuries occurring on a Friday (23.2%).12
The final panel of Table 3 presents results for non-worker injuries. Non-workers are a heterogeneous group that includes people such as students, tourists, beneficiaries, and stay-at-home parents. We find no evidence of a Monday Effect overall for non-workers, though Monday strains and sprains are slightly elevated. The broader pattern is elevated and rising injuries from Monday through Wednesday, and fewer injuries on Thursday and Friday.
We next use linear probability regressions to test whether Monday injuries are more likely to be of each type relative to the injuries that occur on other weekdays, with a particular interest in whether they are more likely to be sprains or strains.13 This approach allows us to control for individual characteristics including, in the case of work injuries, industry and occupation. We can thus test whether Monday work injuries are disproportionately likely to be strains or sprains relative to work injuries in the same occupation and industry that occur on other days of the week.
For each type of injury, the regressions we run take the form:
where InjuryTypeidt is an indicator variable denoting the type of injury reported by person i on day of the week d in year t, Mondaydt is an indicator for whether the injury occurred on a Monday (or the Tuesday after a Monday public holiday),14 Xidt are controls for a limited set of individual characteristics (including industry grouping and occupation in the case of work injuries),15 and the αt are year fixed effects. We run the regression separately for work injuries involving lost time, injuries to workers that occurred off the job and involved lost time, all work injuries, all injuries to workers that occurred off the job, and injuries to non-workers. We report standard errors clustered at the individual level to allow for arbitrary correlation within individuals over time.
Table 4 displays the results for each injury type (excluding “other” injuries) and each category of claim. Each coefficient presented is the coefficient on the Monday dummy from a separate regression as described in equation six. Each column represents a different sample of claims: work lost-time injuries; off-the-job lost-time injuries; all work injuries; all off-the-job injuries; and all working-age non-worker injuries.
For every claim category, sprains and strains make up a greater proportion of injuries on a Monday than on other weekdays after controlling for other characteristics. The estimate for work lost-time sprains and strains is a statistically significant 1.8 percentage points, which is smaller than the 2.6 percentage points found in Ontario by Campolieti and Hyatt, 2006.16 All off-the-job injury claims and non-worker injury claims have similar estimates at 1.9 and 1.8 percentage points, respectively; lost-time off-the-job injury claims and all work injury claims have higher estimates of 2.3 and 2.9 percentage points, respectively. The Monday coefficient results for all other injury types and claim categories are negative, or very small in magnitude and not statistically significant. It is stark that almost other types of injuries are less likely to occur on Mondays, which means that the “oversupply” of strains and sprains comes from an even distribution of an “undersupply” across other categories. The only exceptions are “fractures” that occur off the job. These results support the idea that there may be something about Mondays that increases the risk of sprains and strains more generally rather than being caused by something specific to work.17
To look at whether the results relate to doctors' offices being closed in the weekend, we investigate whether there is a Monday Effect in public hospitalization data, since hospitals are open seven days a week. The top panel of Table 5 shows the proportion of injury hospitalisations for working-age people that occur on a Monday is 20.4 percent. This is statistically significantly above 20 percent, but not as high as the 21.7 percent found for lost-time work injuries. The proportion of strains and sprains in the hospitalisations data that occur on a Monday is higher, at 21.7 percent, but again is lower than the 22.3 percent found for lost-time work strains and sprains.
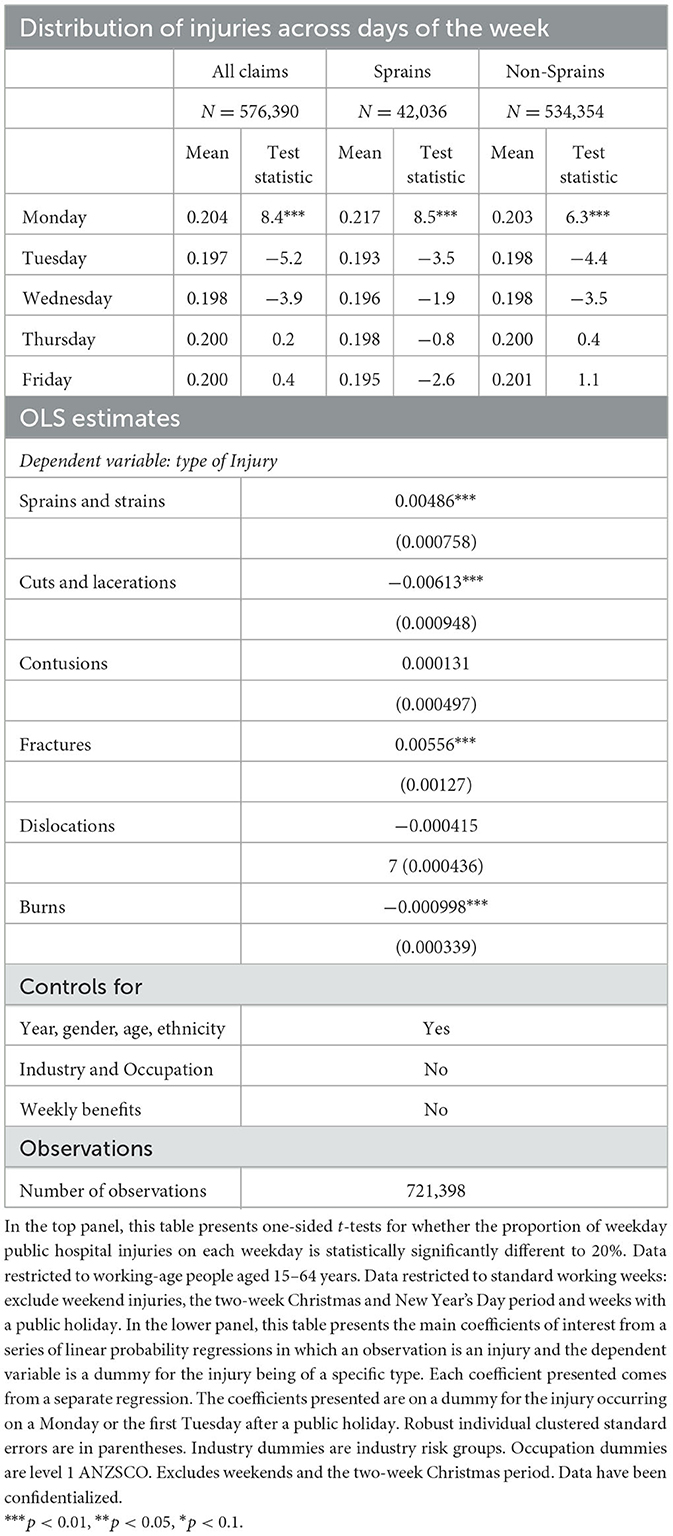
Table 5. Public hospital data on injuries for working-age people: Distribution of injuries across days of the week and OLS estimates of injury types disproportionately common on Mondays.
The lower panel of Table 5 presents regression analysis that tests whether the probability an injury hospitalization is each particular injury type is higher if it occurred on a Monday, controlling for individual characteristics. For strains and sprains, the coefficient on Monday for injuries requiring hospitalization is substantially smaller than for the other types of claims discussed previously, but it is positive and statistically significant (0.5 percentage points). The Monday coefficient for fractures is positive and similar in magnitude to that for sprains and strains; for all other injury types, the Monday coefficient is close to zero or negative. These results do not suggest that doctors' office hours are an important driver of the increased proportion of sprains and strains on Mondays, though we cannot rule out that they have some effect.
If excess Monday strains and sprains are not the result of misrepresentation or faking, they could occur because workers are more likely to be injured on a Monday, or because workers are more likely to seek treatment conditional on severity (and thus appear in our data) if the injury occurred on a Monday. If the latter were the case, we would expect the average severity of reported Monday accidents to be lower than the severity of accidents that occurred on other days.
To attempt to distinguish between these hypotheses, we run two regressions relating to injury severity by day of the week. First, we regress a dummy for a work injury being a lost-time injury on a Monday dummy and controls. Second, we limit the sample to lost-time work injuries and regress the log number of days of loss of earnings compensation paid on a Monday dummy and controls. The coefficients on the Monday variables tell us whether Monday injuries are less likely to be lost-time injuries, and whether lost-time Monday injuries involve less lost work time than injuries on other days. We repeat this analysis for off-the-job injury claims. In each case, we run the regressions separately for all injuries and for the sub-sample of sprains and strains. Significant effects in the case of strains and sprains would suggest more treatment of low-severity strains and sprains that occur on a Monday contributes to the excess strains and sprains we observe on a Monday.18
Table 6 displays the results for work and off-the-job claims. Work injury claims on a Monday are 0.3 percentage points (2.7%) more likely to be lost-time claims than are claims on other weekdays, while off-the-job injury claims on a Monday are 0.1 percentage points (2.6%) less likely to be lost-time claims. Both results are small but statistically significantly different from zero. The coefficients on Monday for sprains and strains are small and not statistically significant for the samples of injuries that occur at work and that occur off the job. Looking at the duration of time off work for lost-time claims, the coefficient on Monday is negative and statistically significant in the work injury regression that pools all injury types, and the magnitude of the coefficient suggests injuries that occur on Monday and involve lost time involve 3.5 percent fewer days off work than injuries that occur on other days. The coefficient is similarly negative and significant in the regressions that limit the sample to sprains and strains. In the equivalent regressions for off-the-job injuries the coefficient on Monday tends to be even more negative.
Overall, these regressions provide evidence that Monday lost-time injury claims, both those that occur at work and those that occur off the job for workers, tend to be less severe than injury claims that occur on other days of the week.
The main focus of the previous literature on the Monday Effect has been on the idea that workers fraudulently claim that leisure injuries that occurred over the weekend were work injuries in order to access better healthcare or compensation for lost earnings. In New Zealand, healthcare access and cost are exactly the same regardless of whether the injury occurred at work or not, and compensation for lost earnings differs for only the first week. While the first week differential introduces a small incentive to fraudulently claim leisure injuries to be work injuries, this explanation is inconsistent with two of our empirical results: elevated claims on Tuesdays and elevated Monday claims for off-the-job sprains and strains. As such, this mechanism is unlikely to be a substantial driver of the Monday Effect we find here. Moreover, the magnitude of excess Monday injuries in New Zealand, 1.7%, is substantially lower than that found in prior studies of Ontario (4.7%) and Minnesota (3.0%), where such incentives are stronger. Fraudulent claims may help explain the difference.
Another previously discussed hypothesis is ergonomics: people need time to warm up after a weekend off work, so they are more likely to strain themselves at work on a Monday. A related hypothesis is that work is more dangerous on a Monday. Both these hypotheses are work-specific, meaning that, if they drove the Monday Effect, we should not see a higher proportion of claims on a Monday for off-the-job and non-workers' injury. We should also not see a higher rate of claims on Tuesdays. In fact, we do observe elevated strains and strains on Mondays for both off-the-job injuries and non-workers' injuries, and we also observe elevated work injuries in general, and strains and sprains specifically, on Tuesdays. Ergonomics and higher work risk on Mondays are therefore unlikely to be the main drivers of the Monday Effect in New Zealand.
Turning to alternative hypotheses, we do not find evidence that the Monday Effect occurs because doctors' offices are closed on the weekend, as we also find higher numbers of injuries in hospitals on Mondays. Further, since we use accident date rather than treatment date for the analysis, this does not reflect a treatment delay due to weekend commitments. On the other hand, we find support for the idea that the Monday Effect is caused by the impact of the weekend on individuals' physiological state. This could be because individuals are fatigued or hungover from weekend activities or because pain thresholds for seeking treatment are lower earlier in the week. We find supporting evidence for both mechanisms: injury rates decline throughout the week, while injury severity is lower on a Monday.
A limitation of this study is that we do not have data on hours worked by day of the week. Only limited data on this in New Zealand is available. It is known that about 63 percent of workers in New Zealand usually work all hours at standard times (between 7 a.m. and 7 p.m. Monday to Friday; Statistics New Zealand, 2008) and that Retail Trade and Agriculture, Forestry and Fishing industries have a higher proportion of people working on the weekend (Callister and Dixon, 2001). New Zealand Time Use Survey data from the 1990s indicate that the highest number of hours worked on average occurs on a Tuesday (7.9 h) and the lowest on a Friday (7.5 h), with 19.1 percent of all paid weekday work time occurring on a Monday (Callister and Dixon, 2001). We do not have any reason to believe that this pattern has changed over this period. Given this evidence, it seems unlikely that proportionally more injuries and strains and sprains occur on Monday because people are more likely to be working.
We make a unique contribution to the literature by looking at whether the Monday Effect in workers' compensation persists within a broader accident compensation scheme and whether off-the-job injuries, non-workers' injuries, and hospitalisations also exhibit a Monday Effect. We find that not only is the Monday Effect for strains and sprains present in the work claims data, but it is also present for off-the-job injury claims, non-worker injury claims, and injury hospitalisations. Work and off-the-job injuries on Mondays are also found to be less severe as measured by average days off work.
Unlike in the USA and Canada, the New Zealand compensation system is such that it is less likely to be susceptible to people claiming an off-the-job injury from the weekend as happening at work on the Monday. This means the Monday Effect found here is unlikely to be a result of fraudulently claiming of off-the-job injuries as occurring at work. The magnitude of the results for New Zealand are smaller than that found elsewhere (Campolieti and Hyatt, 2006; Card and McCall, 1996). This lends support to the conclusion of Martin-Roman and Moral (2016) that, in countries with an incentive to claim weekend injuries as Monday work injuries, the fraudulent claims theory is part of the explanation, but is not the full story.
Our findings suggest that the remaining part of the Monday effect is an externality caused by the existence of weekends. It appears that individuals are either fatigued from weekend activities or have lower pain thresholds earlier in the week, and this is what causes an elevated level of injury claims on Monday both at and away from work.
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because the results in this paper are not official statistics, they have been created for research purposes from the Integrated Data Infrastructure (IDI), managed by Statistics New Zealand. The opinions, findings, recommendations, and conclusions expressed in this paper are those of the authors, not Statistics NZ, the Accident Compensation Corporation or WorkSafe New Zealand. Access to the anonymised data used in this study was provided by Statistics NZ in accordance with security and confidentiality provisions of the Statistics Act 1975. Only people authorized by the Statistics Act 1975 are allowed to see data about a particular person, household, business, or organization, and the results in this paper have been confidentialized to protect these groups from identification. Careful consideration has been given to the privacy, security, and confidentiality issues associated with using administrative and survey data in the IDI. Further detail can be found in the Privacy impact assessment for the Integrated Data Infrastructure available from www.stats.govt.nz. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to https://www.stats.govt.nz/integrated-data/integrated-data-infrastructure.
MP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. IS: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SS: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was completed as part of a PhD in Economics by Michelle Poland at the University of Otago. It was undertaken with funding from the Macandrew-Stout Postgraduate Scholarship in Economics; University of Otago Postgraduate Publishing Bursary; WorkSafe New Zealand; and Marsden Grant 12-UOO-067, Mind the gap? Worker productivity and pay gaps between similar workers in New Zealand.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frbhe.2025.1541497/full#supplementary-material
1. ^There are a number of papers showing this finding for the US (Brogmus, 2007; Butler et al., 2014; Card and McCall, 1996; Hansen, 2016; Smith, 1990), Canada (Campolieti and Hyatt, 2006; Choi et al., 1996; Mason, 1979), Spain (Martin-Roman and Moral, 2016) and Australia (Wigglesworth, 2006).
2. ^Psychosocial risk factors have been found to be associated with musculoskeletal pain in the workplace (Bernal et al., 2015; Lang et al., 2012). Taylor (2002) finds that people surveyed on a Friday have higher levels of self-reported job satisfaction compared to those interviewed earlier in the week. This could be because of higher levels of stress earlier in the week which are associated with lower pain thresholds.
3. ^The scale of potential moral hazard also appears to be stable in regards to other health related policy changes. For example, Dong (2022) finds no impact of recreational marijuana sales legalization on Monday work injury claims in the US.
4. ^Private health insurance coverage does not overlap accident insurance, rather it provides additional coverage to complement that provided by ACC.
5. ^The gross maximum rate of weekly compensation payable in 2017/18 was NZ$1,940.75 per week (applied from 1 July 2017 to 31 June 2018) (Accident Compensation Corporation, 2023).
6. ^Small firms are eligible for a no claims discount while larger firms are eligible for an ACC levy discount or penalty, depending on how their claims history compares to similar firms.
7. ^This could be done unintentionally by introducing injury prevention incentives such as no- claims bonuses for work teams or intentionally by explicitly asking this of workers.
8. ^Claims are assigned to injury type based on the first two digits of the primary diagnosis code.
9. ^Non-workers' are not entitled to loss of earnings compensation so there are no “lost-time” claims for this group.
10. ^ACC starts paying weekly compensation one week from the day of the first doctor visit for treatment. There is no information available in the claims data for time off work if the person requires less than a week off.
11. ^The differences when all work injury claims are considered are that the proportion of non-sprains on a Thursday is also statistically significantly higher than 20% and the proportion of non-sprains on a Monday is lower than that on Tuesday and Wednesday.
12. ^Extending the sample to all off-the-job injuries, as shown in Appendix Table A1, we find a small Monday Effect for all injuries, consisting of an “early in the week” pattern for strains and sprains, and a higher proportion of non-sprains on a Friday (20.9%) and a lower proportion on a Tuesday (19.4%).
13. ^This approach assumes that injuries are independently realized (e.g., if I have a higher likelihood of receiving a sprain, then I do not have a different likelihood of receiving other injuries). While this seems unlikely in practice, this assumption will only impact our results if this correlation varies by the day of the week, which seems unlikely.
14. ^We include Tuesdays after a public holiday Monday in the Monday variable because they are the first day back at work after several days off, and thus any mechanisms that drive higher rates of reported injuries on Mondays are likely to apply to these days as well.
15. ^Gender, age, self-reported ethnicity combination; for example, if a person reports that he is Māori and NZ European he is coded to a “Māori and New Zealand European” category. Where the number of observations with an ethnicity combination is fewer than 100, the individuals are coded to an “Other” category. For work injuries, we also include controls industry risk group and occupation fixed effects. Industries are placed in three groups based on risk of harm. Group 1 contains the high-risk industries of Agriculture, Forestry and Fishing; Mining, Manufacturing; Electricity, Gas, Water and Waste Supplies; Construction; and Transport, Postal and Warehousing. Group 2 contains the medium risk industries of Public Administration and Safety; Education and Training; Healthcare and Social Assistance; and Arts and Recreation. All other industries are in Group 3. For lost-time injuries, we include average weekly benefits as a proxy for weekly earnings.
16. ^Adding industry risk group interactions with the Monday variable produces interaction coefficients that are small and not statistically different from zero, indicating that the Monday Effect results are not industry risk group specific.
17. ^These results are robust to removing weeks with a public holiday; including weekends in the data and adding dummy variables for each day of the week (omitting Wednesdays); excluding industries likely to have a large proportion of the workforce working on the weekends: Agriculture, Forestry and Fishing, Retail Trade, and Accommodation and Food Services. See Appendix Table A2 for the results of these robustness checks. The results are also broadly consistent when the samples of work and off-the-job injury claims are extended from lost-time claims to all claims.
18. ^Using this test to draw conclusions about whether injury rates are higher or treatment thresholds are lower on Mondays requires two assumptions. First, we must assume the distribution of injury severities, conditional on an injury occurring but not limiting the sample to injuries that result in a claim, is the same for injuries occurring on each day of the week. Second, we must assume that any psychological mechanism that lowers the treatment threshold for Monday injuries does not also result in a different length of lost-time for an injury of the same severity.
Accident Compensation Corporation (2023). Official Information Act Request, Reference: GOV-025143. Available at: https://www.acc.co.nz/assets/oia-responses/inflationary-increases-to-long-term-weekly-compensation-oia-response-GOV-025143_redacted.pdf
Accident Compensation Corporation (2025). How Payments Work. Available at: https://www.acc.co.nz/im-injured/financial-support/weekly-compensation/how-payments-work (accessed February 27, 2025).
Bernal, D., Campos-Serna, J., Tobias, A., Vargas-Prada, S., and Benavides, F. G. (2015). Work-related psychosocial risk factors and musculoskeletal disorders in hospital nurses and nursing aides: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 52, 635–648. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2014.11.003
Brogmus, G. (2007). Day of the week lost time occupational injury trends in the US by gender and industry and their implications for work scheduling. Ergonomics 50, 446–474. doi: 10.1080/00140130601133826
Butler, R. J., Kleinman, N., and Gardner, H. H. (2014). I don't like Mondays: explaining monday work injury claims. Ind. Labor Relations Rev. 67, 762–783. doi: 10.1177/00197939140670S312
Callister, P., and Dixon, S. (2001). New Zealanders' Working Time and Home Work Patterns: Evidence from the Time Use Survey. Available online at: https://web.archive.org/web/20170925085838/http://thehub.superu.govt.nz/project/new-zealanders-working-time-and-home-work-patterns-evidence-new-zealand-time-use-survey
Campolieti, M., and Hyatt, D. E. (2006). Further evidence on the “monday effect” in workers' compensation. ILR Rev. 59, 438–450. doi: 10.1177/001979390605900306
Card, D., and McCall, B. P. (1996). Is workers' compensation covering uninsured medical costs? Evidence from the “monday effect”. ILR Rev. 49, 690–706. doi: 10.1177/001979399604900407
Choi, B. C., Levitsky, M., and Lloyd, R. D. (1996). Patterns and risk factors for sprains and strains in Ontario, Canada 1990: an analysis of the workplace health and safety agency data base. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 38, 379–389. doi: 10.1097/00043764-199604000-00016
Dong, X. (2022). Recreational marijuana sales legalization and monday work injury claims. B.E. J. Econ. Anal. Policy. 22, 99–121. doi: 10.1515/bejeap-2021-0105
Fontaneda I. Camino López M. A. González Alcántara O. J. Greiner B. A. (2024), The “weekday effect”: a decrease in occupational accidents from monday to friday—an extension of the “monday effect”. Biomed. Res. Int. 2024:4792081. 10.1155/2024/4792081
Hansen, B. (2016). California's 2004 workers' compensation reform: costs, claims, and contingent workers. ILR Rev. 69, 173–198. doi: 10.1177/0019793915605507
Lang, J., Ochsmann, E., and Kraus, T. (2012). Psychosocial work stressors as antecedents of musculoskeletal problems: a systematic review and meta-analysis of stability-adjusted longitudinal studies. Soc. Sci. Med. 75, 1163–1174. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2012.04.015
Martin-Roman, A. L., and Moral, A. (2016). Moral hazard in monday claim filing: evidence from spanish sick leave insurance. B.E. J. Econ. Anal. Policy 16, 437–476. doi: 10.1515/bejeap-2014-0035
Mason, K. (1979). Accident patterns by time-of-day and day-of-week of injury occurrence. J. Occup. Accid 2, 159–176. doi: 10.1016/0376-6349(79)90006-3
Ministry of Health. (2014). Capitation Funding. Available online at: https://web.archive.org/web/20141108080622/http://www.health.govt.nz/our-work/primary-health-care/primary-health-care-subsidies-and-services/capitation-funding (accessed July 08, 2014).
Ministry of Health. (2017). Visiting a Doctor. Available online at: https://web.archive.org/web/20170618143325/https://www.health.govt.nz/your-health/services-and-support/health-care-services/visiting-doctor (accessed June 28, 2017).
Nicholson, T., and Griffin, B. (2017). Thank goodness it's friday: weekly pattern of workplace incivility. Anxiety Stress Coping. 30, 1–14. doi: 10.1080/10615806.2016.1192150
OECD. (2017). Health at a Glance 2017: OECD Indicators. Paris. Available online at: http://dx.doi.org/10.1787/health_glance-2017-en
Pindek, S., Zhou, Z. E., Kessler, S. R., Krajcevska, A., and Spector, P. E. (2021). Workdays are not created equal: job satisfaction and job stressors across the workweek. Hum. Relations 74, 1447–1472. doi: 10.1177/0018726720924444
Smith, R. S. (1990). “Mostly on monday: is workers' compensation covering off-the-job injuries?” in Benefits, Costs, and Cycles in Workers' Compensation (Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands), 115–127. doi: 10.1007/978-94-009-2179-5_5
Statistics New Zealand. (2015). IDI Data Dictionary: ACC injury claims data (June 2015 edition). Wellington. Available online at: www.stats.govt.nz
Taylor, M. P. (2002). “Tell me why I don't like mondays: investigating day of the week effects on job satisfaction and psychological wellbeing,” in Working Papers of the Institute for Social and Economic Research, paper 2002–22. Colchester: University of Essex.
The Treasury. (2014). Briefing to Incoming Minister: Health. Wellington, New Zealand: The Treasury.Available online at: http://www.treasury.govt.nz/publications/briefings/2014-health
Keywords: I13, J38, Monday effect, workplace injuries, workers compensation, accidents, incentives, I18
Citation: Poland M, Sin I and Stillman S (2025) Why are there more accidents on Mondays? Economic incentives, ergonomics or externalities. Front. Behav. Econ. 4:1541497. doi: 10.3389/frbhe.2025.1541497
Received: 07 December 2024; Accepted: 11 February 2025;
Published: 19 March 2025.
Edited by:
Luca Corazzini, University of Milano-Bicocca, ItalyReviewed by:
Marco Bertoni, University of Padua, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Poland, Sin and Stillman. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Steven Stillman, c3RldmVuLnN0aWxsbWFuQHVuaWJ6Lml0
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.