Abstract
Introduction:
Pantoea dispersa is a Gram-negative bacterium generally considered as a plant pathogen and rarely causes human infections. To date, there have been 13 studies that have documented clinical infections linked to P. dispersa, with a primary emphasis on the initial identification of this pathogen. The genomic features and the mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of P. dispersa remain largely uninvestigated. In the present study, we describe a clinical infection caused by P. dispersa and provide the first genomic analysis of this bacterium.
Methods:
The bacterial strain designated A003 was isolated from blood samples. Preliminary identification of strain A003 was conducted using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) technology (VITEK® MS, bioMérieux, France). Biochemical and antimicrobial susceptibility assessments were carried out utilizing the VITEK-2 compact automated microbial analysis system (bioMérieux, France). Additionally, whole genome sequencing and subsequent analysis were performed to further elucidate the potential pathogenicity.
Results:
The bacterial isolate was cultured overnight at 35°C in a CO2-enriched environment on Columbia blood agar, resulting in the appearance of a white, smooth, Gram-negative rod-shaped bacterium with diameters ranging from 1 to 2 mm. Identification of strain A003 was achieved with a high confidence level of 99.9% as P. dispersa using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. The average nucleotide identity (ANI) value between strain A003 and the reference strain P. dispersa DSM 30073T was 98.08%, while the DNA–DNA hybridization (DDH) value was 84.10% (Formula 2) based on genome sequencing data, which further confirmed that A003 belonged to the P. dispersa species. Comprehensive analysis revealed the presence of 372 virulence factors, 15 antibiotic resistance genes, 222 carbohydrate-active enzymes, and 666 genes related to Type III secretion system (T3SS) effector proteins, as identified through the core databases of VFDB (Virulence Factors of Pathogenic Bacteria), CARD (Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database), CAZY (Carbohydrate-Active enZYmes Database), and T3SS. The virulence factors included type IV pili (TFP), type VI secretion system, flagella, iron uptake system, and ompA, which are implicated in bacterial pathogenicity. The antibiotic resistance profile indicated resistance to fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins, penams, macrolides, and aminoglycosides, as annotated by the CARD database.
Conclusion:
The draft genome sequenced represents the inaugural genomic sequence of P. dispersa derived from clinical sources. This advancement may enhance clinical practitioners’ comprehension of the organism’s clinical attributes and serve as a foundational resource for future research into its virulence, antibiotic resistance, and host–pathogen interactions.
Introduction
The genus Pantoea, a Gram-negative, flagellated, nonencapsulated, nonspore bacterium belonging to the family Erwiniaceae, was proposed as a novel family based on genomic phylogeny and taxonomy in 2016 (Adeolu et al., 2016); is wildly found in various natural environments, such as plants, water, and soil (Brady et al., 2008; Walterson and Stavrinides, 2015); and is generally considered as a plant pathogen. At present, Pantoea comprises 20 validly published and correctly named species, namely, Pantoea agglomerans, Pantoea allii, Pantoea ananatis, Pantoea anthophila, Pantoea brenneri, Pantoea coffeiphila, Pantoea conspicue, Pantoea cypripedii, Pantoea deleyi, Pantoea dispersa, Pantoea eucalypti, Pantoea eucrina, Pantoea leporis, Pantoea piersonii, Pantoea rodasii, Pantoea rwandensis, Pantoea septica, Pantoea stewartii, Pantoea vagans, and Pantoea wallisii, in the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN) database. Among these species, P. agglomerans is the most prominent species in causing human infections (Cruz et al., 2007; Dutkiewicz et al., 2016; Hassan et al., 2023), and a limited number of infections were attributed to P. dispersa, P. ananatis, and P. anthophila (Schmid et al., 2003; Manoharan et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2023).
The P. dispersa was first proposed as a novel species in 1989 (Gavini et al., 1989) and often isolated from plants. Previous studies have reported 13 clinical infections (Supplementary Table S1) caused by P. dispersa across various systems, including the respiratory, joint, hematologic, and digestive systems (Schmid et al., 2003; Barron et al., 2006; Mehar et al., 2013; Hagiya and Otsuka, 2014; Panditrao and Panditrao, 2018; Asai et al., 2019; Preis et al., 2022; Ruan et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2022; Ait Tamlihat et al., 2017; Adlan et al., 2023; San et al., 2024; Sak et al., 2024). These current studies only describe the preliminary identification of this pathogen; the genomic features and the mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of P. dispersa remain largely uninvestigated. In the present study, we describe a clinical infection caused by P. dispersa and provide the first genomic analysis of this bacterium.
Case presentation
A 40-year-old male patient was admitted to the emergency department of Sanya People’s Hospital with hematemesis, dizziness, and fatigue for 6 h on 19 June 2023. The patient had a long history of alcoholism. Results of the abdominal computed tomography performed at the People’s Hospital of Lingshui Li Autonomous County, Hainan Province showed cirrhosis (decompensated stage), splenomegaly, portal hypertension, and gastroesophageal venous dilation throughout. Physical examination during admission showed the following: a temperature of 36.5°C, a pulse of 116 beats/min, a respiration rate of 20 breaths/min, and a blood pressure of 138/78 mmHg. The patient was mentally tired and pale, showing acute illness and an anemic appearance. The skin of the whole body was slightly yellow, and liver palms could be seen.
Admission diagnosis was as follows: acute upper gastrointestinal bleeding, esophageal and gastric varices rupture bleeding, peptic ulcer with acute hemorrhagic anemia, decompensated stage of cirrhosis, portal hypertension, and chronic liver failure. The immediate blood tests showed the following: a total pH of 7.42, a lactic acid concentration of 3.80 mmol/L, a white blood cell (WBC) count of 5.52×109/L (67.6% neutrophils), an erythrocyte count of 2.72×1012/L (normal, 4.09–5.74×1012/L), a hemoglobin level of 99 g/L (normal, 131–172 g/L), a platelet count of 52×109/L (normal, 85–303×109/L), a prothrombin time (PT) of 17.10 s (normal, 9.80–13.20 s), and a fibrinogen level of 1.48 g/L (normal, 1.80–3.50 g/L). The liver function was very severely deranged: a serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase level of 128 U/L (normal, 15–40 U/L), a serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase level of 33 U/L (normal, 9–50 U/L), a total bilirubin level of 86.9 μmol/L (normal, 0–26 μmol/L), a direct bilirubin level of 54.8 μmol/L (normal, 0.3–6.8 μmol/L), an indirect bilirubin level of 32.1 μmol/L (normal, 1.7–17.0 μmol/L), and an albumin level of 25.2 g/L (normal, 40–55 g/L).
Based on the findings from the patient’s examination, the following medications were given: 4 vials of pantoprazole sodium powder for injection (40 mg per vial), 2 vials of potassium chloride injection (10% solution, 10 mL per vial), 6 vials of creatinine injection (100 mg in 2 mL per vial), 3 vials of thrombin powder (2,000 units per vial), 12 vials of octreotide injection (1 mL containing 0.1 mg per vial), and 8 vials of magnesium glycyrrhizinate isoglycyrrhizinate injection (10 mL containing 50 mg per vial). Despite these interventions, 3 days later, the patient’s symptoms of upper gastrointestinal bleeding showed no improvement. A complete blood count revealed a continued decline in erythrocyte, hemoglobin, and platelet levels, alongside an increase in prothrombin time and hypersensitive C-reactive protein levels (7.9 mg/L, with a normal range of 0–5.0 mg/L). The microbiology laboratory within the clinical laboratory department reported critical findings from blood cultures, identifying Gram-negative bacilli in both aerobic and anaerobic cultures. P. dispersa was ultimately identified, and the patient was treated with a combination of cefazoxime and ciprofloxacin as part of the anti-infective regimen. Unfortunately, the patient’s condition did not improve, and he subsequently exhibited signs of sepsis. Ultimately, the patient’s family requested his discharge from the hospital on 27 June 2023.
Materials and methods
Blood cultures
Blood samples from the patient were collected and transferred to the microbiology laboratory within the clinical laboratory department. Then, we performed two sets of blood cultures for the patient according to standard guidelines. The blood culture bottles that we used were BacT/Alert FN (BCBs) (bioMérieux) and incubated in the BacT/Alert 3D automated blood culture system (bioMérieux). Two blood cultures were both positive, and the broth was transferred to Columbia blood agar plates using a vaccination needle, and 10-μL bacterial circles were marked on it. The culture was incubated at 35°C with 5% CO2 and in anaerobic bags for 24 and 48 h, respectively, and for 2 to 8 h to check the growth of colonies on the medium.
Bacterial identification
The bacteria colonies with homogeneous morphology were observed on the Columbia blood agar plates. We selected the colonies and transferred them directly to the target plate, added a ready-to-use CHCA matrix, and fed the samples to VITEK® MS (bioMérieux, France), which is an automated mass spectrometry microbial identification system that uses matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) technology. The biochemical test was operated by a VITEK-2 GN card and loaded into the VITEK-2 compact (bioMérieux, France) automatic microbial analysis system. Antimicrobial susceptibility tests were performed on the isolate strains according to clinical and laboratory requirement standards for Enterobacteriaceae by the VITEK-2 automatic microbial system (bioMérieux, France).
Whole genome sequencing and analysis
The genome DNA was extracted from the overnight pure isolates using the TIANamp Bacteria DNA Kit (TIAGEN BIOTECH, China) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. The draft genome of the isolated strain was sequenced using the DNBSEQ platform at the Beijing Genomics Institute (Shenzhen, China). The paired-end libraries of 150:150 bp were generated, and an average size of 350-bp fragmented genome DNA was inserted for sequencing. Raw reads of low quality from paired-end sequencing (those with consecutive bases covered by fewer than five reads) were discarded. Then, the filtered sequenced reads were assembled using the SOAP de novo v1.05 software. Gene prediction was performed by glimmer3 (http://www.cbcb.umd.edu/software/glimmer) with Hidden Markov models. The genomic identity was assessed using average nucleotide identity (ANI) and DNA–DNA hybridization (DDH) metrics based on OrthoANIu (Lee et al., 2016) and GGDC (https://ggdc.dsmz.de/). The phylogenetic tree based on the 16S rRNA gene was constructed by MEGA X (Kumar et al., 2018). The functional annotation of the isolate’s genes was conducted utilizing the KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) (Kanehisa and Goto, 2000), COG (Clusters of Orthologous Groups) (Tatusov et al., 2000), and Swiss-Prot databases. The prediction of pathogenicity and drug resistance was performed by the core database of VFDB (Virulence Factors of Pathogenic Bacteria) (Chen et al., 2016), CARD (Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database) (Marchler-Bauer et al., 2013), and CAZY (Carbohydrate-Active enZYmes Database) (McArthur et al., 2013). Additionally, Type III secretion system (T3SS) effector proteins were identified using the Effective T3 tool (Arnold et al., 2009).
Results
The preliminary identification of Pantoea dispersa A003
The bacterial colonies appeared on Columbia blood agar after being cultured overnight at 35°C with 5% CO2. The colonies were white, smooth, and moist, and had diameters between 1 and 2 mm (Figure 1A). The Gram stain showed that the isolate was a Gram-negative rod bacterium (Figure 1B). We named the bacteria isolates as A003, and then we identified them by MALDI-TOF technology. The results showed that the isolated strain A003 was matched to P. dispersa with a high confidence level of 99.9% (Figure 1C). The antimicrobial susceptibility tests revealed that strain A003 was susceptible to almost all tested antibiotics (Table 1). The biochemical results are shown in Table 2 by testing with the VITEK-2 compact automatic microbial system.
Figure 1

Isolation and identification of Pantoea dispersa strain A003. (A) Bacterial colonies on Columbia blood agar at 35°C with 5% CO2 for 24 h. (B) Gram stain. (C) The spectrogram with protein molecular mass of the strain acquired by MALDI-TOF MS.
Table 1
| Antimicrobial agents | MIC (μg/mL) | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Ampicillin | ≤8 | S |
| Gentamicin | ≤1 | S |
| Amikacin | ≤4 | S |
| Ciprofloxacin | ≤0.06 | S |
| Ceftriaxone | ≤1 | S |
| Cefuroxime | ≤8 | S |
| Cefoxitin | ≤8 | S |
| Ampicillin/Sulbactam | ≤2/1 | S |
| Imipenem | ≤1 | S |
| Meropenem | ≤1 | S |
| Co-trimoxazole | ≤0.5/9.5 | S |
| Piperacillin/Tazobactam | ≤4/4 | S |
| Levofloxacin | ≤0.12 | S |
| Ceftazidime | ≤4 | S |
| Chloramphenicol | ≤8 | S |
| Cefoperazone/Sulbactam | =16/8 | S |
| Minocycline | ≤4 | S |
| Ticarcillin/Clavulanic acid | ≤4/2 | S |
The antimicrobial susceptibility test of Pantoea dispersa A003.
MIC, Minimum Inhibitory Concentration; S, sensitive; I, intermediate; R, resistant.
Table 2
| Item | Value | Item | Value | Item | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APPA | – | ADO | – | PyrA | + |
| IARL | – | dCEL | + | BGAL | + |
| H2S | – | BNAG | + | AGLTp | – |
| dGLU | + | GGT | + | OFF | + |
| BGLU | – | dMAL | + | dMAN | + |
| dMNE | + | BXYL | – | BAIap | – |
| ProA | – | LIP | – | PLE | – |
| TyrA | + | URE | – | dSOR | – |
| SAC | + | dTAG | – | dTRE | + |
| CIT | + | MNT | – | 5KG | – |
| ILATk | + | AGLU | – | SUCT | + |
| NAGA | + | AGAL | – | PHOS | + |
| GlyA | – | ODC | – | LDC | – |
| IHISa | – | CMT | + | BGUR | – |
| O129R | + | GGAA | – | IMLTa | – |
| ELLM | – | ILATa | – |
The biochemical test of Pantoea dispersa A003.
The biochemical test was performed by the VITEK-2 compact automatic microbial analysis system.
+, positive; -, negative.
The whole genome sequencing of Pantoea dispersa A003
To further explore the genome characteristics and pathogenicity of the clinical isolate, we performed whole genome sequencing and analysis. The draft genome of P. dispersa A003 obtained 5,062,257 bp (N50, 229,566 bp) and assembled into 106 contigs with 57.41% GC content. The genome contained 4,823 genes, including 4,167 (86.39%) protein-coding genes, 69 tRNA genes, 8 rRNA (6 copies of 5S, 1 copy of 16S, and 1 copy of 23S rRNA) genes, 146 sRNA genes, and 276 tandem repeat sequences (Table 3). Furthermore, the full-length 16S rRNA gene sequence (1,515 bp) extracted from the newly sequenced genome had 99.54% similarities to the P. dispersa type strain DSM 30073 in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) nonredundant database by using the BLASTn program. The phylogenetic tree based on the 16S rRNA gene sequence, which was constructed using the neighbor-joining method by MEGA X, showed that the strain A003 was clustered with the P. dispersa type strain DSM 30073 with a high bootstrap value of 97% (Figure 2). The genome identification based on the OrthoANIu algorithm and DDH showed that the ANI value between strain A003 and P. dispersa DSM 30073T was 98.08%, and the DDH value was 84.10% (Formula 2), which further confirmed that the strain A003 belonged to the P. dispersa species. The results of gene function annotation revealed that 3,793 (78.64%) and 3,295 (68.31%) genes were annotated to COG and KEGG databases, respectively. The gene function subjected to COG classification was related to cellular processes, genetic information, and metabolism (Figure 3A). The KEGG annotation results showed that 198 genes were predicted to be associated with human diseases, mainly including cancer, infectious diseases, and drug resistance (Figure 3B).
Table 3
| Class | Number |
|---|---|
| Size (base) | 5,062,257 |
| G+C content (%) | 57.41 |
| Contigs | 106 |
| N50 (base) | 229,566 |
| Protein coding genes | 4,167 |
| Coding ratio (%) | 86.39 |
| tRNAs | 69 |
| rRNAs | 8 |
| sRNAs | 146 |
| Tandem repeat sequences | 276 |
The genome information of Pantoea dispersa A003.
Figure 2
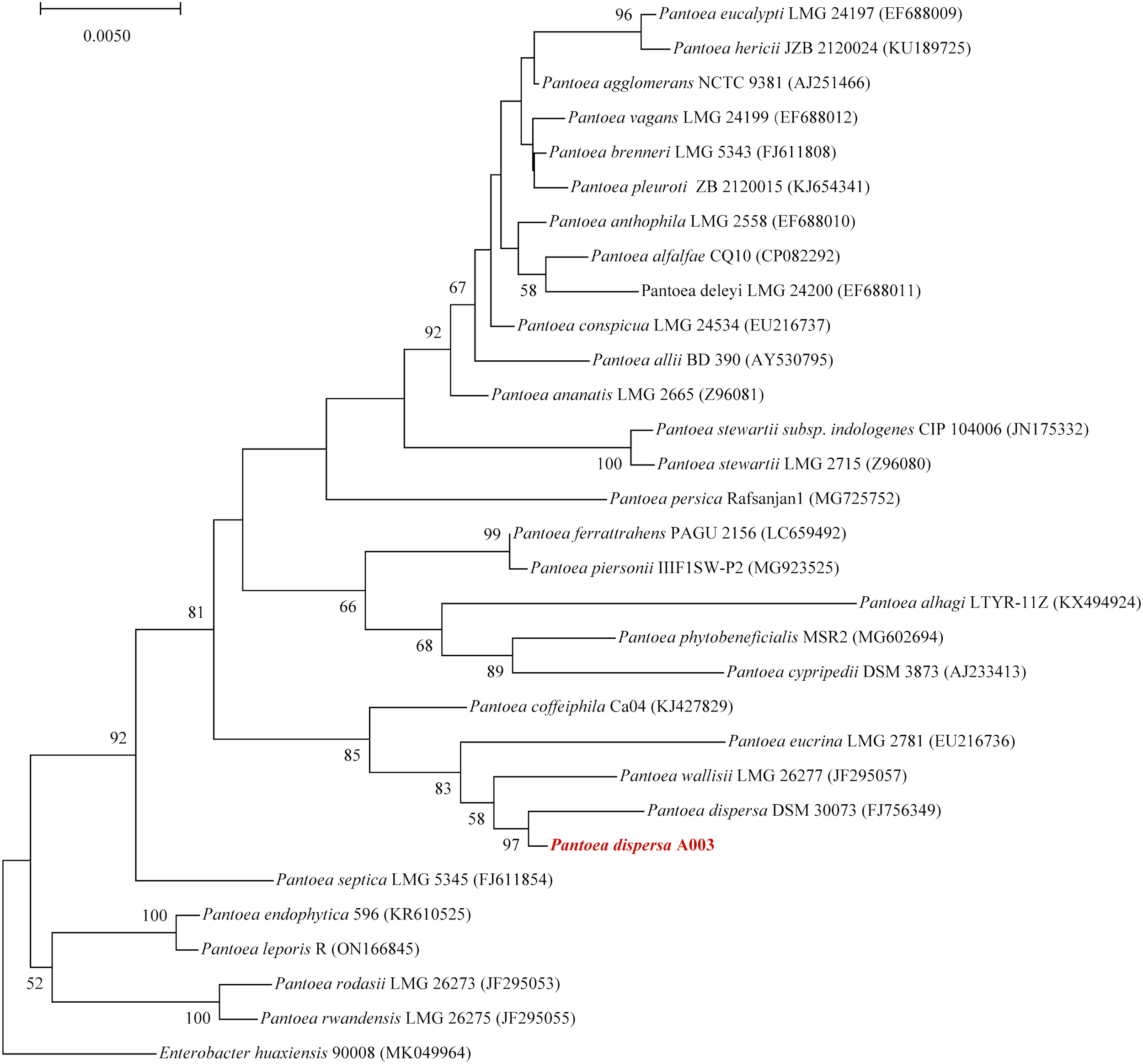
The phylogenetic tree based on the 16S rRNA gene sequence revealed the relationship between the Pantoea dispersa strain A003 (red arrow) and members of the genus Pantoea. The tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method, and Enterobacter huaxiensis 90008 was the outgroup. Bootstrap values (>50%) based on 1,000 replicates are shown at branch nodes.
Figure 3
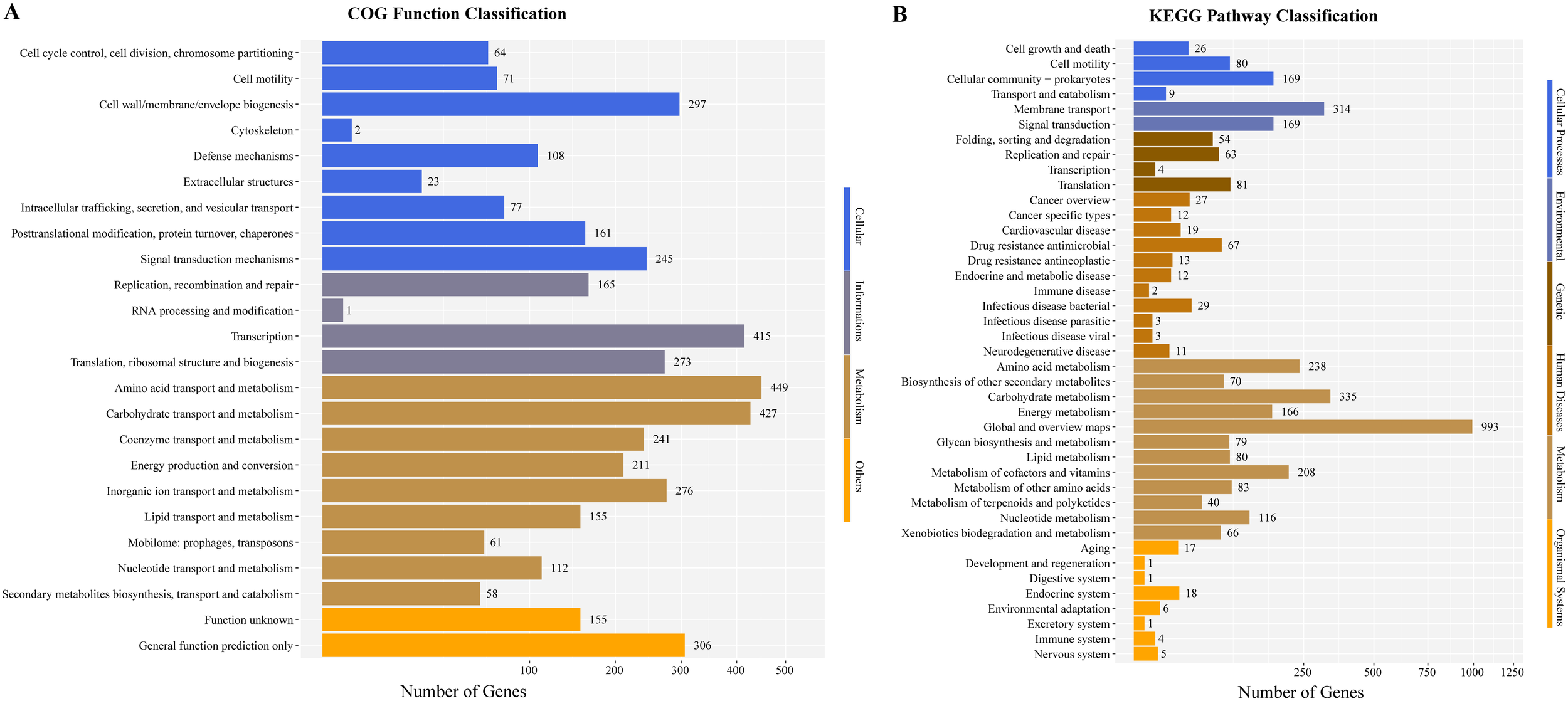
The gene function annotations of the Pantoea dispersa strain A003. (A) COG classification describes the properties of genes and gene products in four terms: cellular, genetic information, metabolism, and others. The X and Y axes indicate gene numbers and COG classification, respectively. (B) KEGG classification reveals the predicted gene involved in metabolic pathways and human disease. The X and Y axes indicate gene numbers and KEGG pathways, respectively.
The pathogenic prediction of Pantoea dispersa A003
We aligned the genome with the VFDB, CARD, and CAZY database to analyze the potential pathogenicity of strain A003. A total of 372 virulence factors were obtained through the core database of VFDB, which was divided into 14 categories. The highest number was related to nutritional/metabolic (86), followed by immune modulation (70) and motility (70) (Figure 4A). These virulence factors include type IV pili (TFP), type VI secretion system, flagella, iron uptake system, and ompA, which are associated with bacterial pathogenicity (Table 4). A total of 15 antibiotic resistance genes were predicated with the CARD database (Figure 4B), mainly related to antibiotic efflux and antibiotic inactivation. The drug resistance primarily includes fluoroquinolone antibiotic, cephalosporin, penam, macrolide antibiotic, and aminoglycoside antibiotic (Table 5). The carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation was carried out by the CAZY database, and glycoside hydrolases (GHs, 98) were highest, followed by glycosyl transferase (GTs, 89) (Figure 4C). Additionally, we performed the T3SS prediction, which has a close relationship with Gram-negative pathogens, and the 666 T3SS effector-related genes were detected.
Figure 4
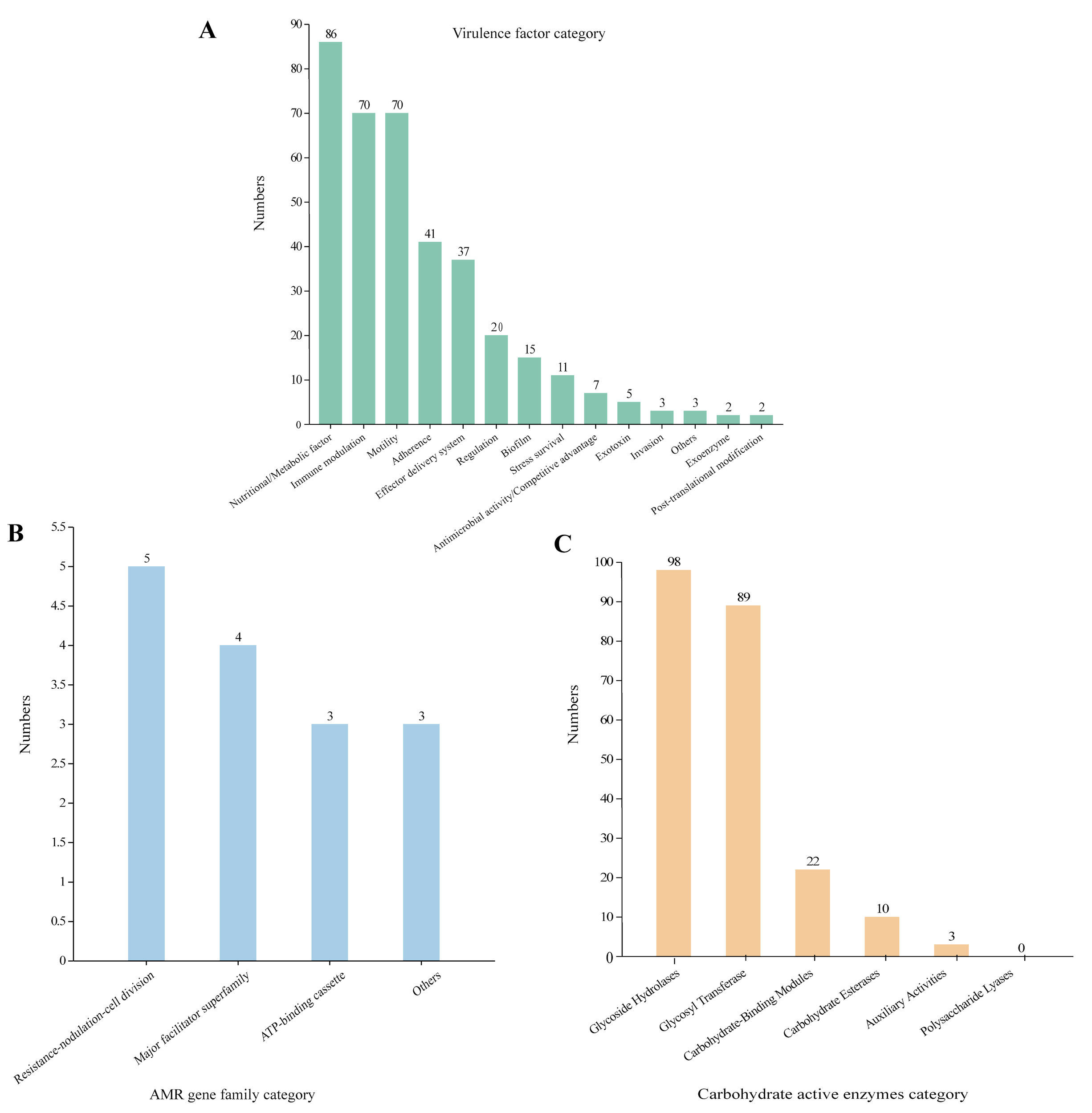
The pathogenic prediction of the Pantoea dispersa strain A003. (A) The virulence factors were predicted by the VFDB database. (B) The antibiotic resistance was predicted by the CARD database. (C) The carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation was performed through the CAZY database.
Table 4
| Virulence factor | Annotation | Numbers |
|---|---|---|
| Adherence | 41 | |
| pilL, pilM, pilN, pilO, pilP, pilQ, pilR, pilS, pilT, pilV, vfr, rpoN, tapQ, stjC, stbA, mrfF, lngT | Fimbrial [Type IV pili (TFP), Stj, Stb, mrf, lngT] | 21 |
| htpB, nmpC, hcpA, hcpB, hcpC | Hsp60, OmpD, HCP | 8 |
| Effector delivery system | 37 | |
| tssB (hsiB1/vipA), tssC, hcp1, tssE (hsiF1), tssF (hsiG1), tssG (hisH1), ClpV1, vgrG, tssK (vasE), tssL (dotU) | Type VI secretion system protein | 16 |
| Motility | 70 | |
| filA, fliC, fliD, fliE, fliF, fliG, fliH, fliI, fliJ, fliK, fliL,fliM, fliN, fliO, filp, fliQ, fliR, fliS, fliT, fliZ, flhA, flhB, flhC, flhD, flhE, flgA, flgB, flgC, flgD, flgE, flgF, flgG, flgH, flgI, flgJ, flgK, flgL, flgM, flgN, flmH, motA, motB, cheA, cheB, cheD, cheM, cheR, cheY, cheW, cheZ, tcyJ, nueA, tar, tsr | Flagella, peritrichous flagella, polar flagella | 70 |
| Iron uptake system | 15 | |
| Fur | Ferric iron uptake transcriptional regulator | 1 |
| fepB, fepC, fepG, entS, fes | Enterobactin transporter | 5 |
| fepA, pvuA | TonB-dependent siderophore receptor | 3 |
| fepD | Ferric siderophore ABC transporter permease | 3 |
| fbpC, hitC | Iron ABC transporter ATP-binding protein | 3 |
| Exotoxin | 5 | |
| hlyA, hlyIII, acpC, cysC1, argK | Hemolysin HlyA, hemolysin III, hemolysin/cytolysin, phytotoxin phaseolotoxin, | 5 |
| Invasion | 3 | |
| ompA | Outer membrane protein A | 2 |
| ail | attachment invasion locus protein | 1 |
The virulence factor profile of Pantoea dispersa A003.
Table 5
| Gene name | AMR gene family | Drug class | Resistance mechanism | % identity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| msbA | ATP-binding cassette (ABC) antibiotic efflux pump | Nitroimidazole antibiotic | Antibiotic efflux | 88.28 |
| adeF | Resistance-nodulation-cell division (RND) antibiotic efflux pump | Fluoroquinolone antibiotic, tetracycline antibiotic | Antibiotic efflux | 60.19 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae KpnE | Major facilitator superfamily (MFS) antibiotic efflux pump | Macrolide antibiotic, aminoglycoside antibiotic, cephalosporin, tetracycline antibiotic, peptide antibiotic, rifamycin antibiotic | Antibiotic efflux | 71.79 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae KpnF | Major facilitator superfamily (MFS) antibiotic efflux pump | Macrolide antibiotic, aminoglycoside antibiotic, cephalosporin, tetracycline antibiotic, peptide antibiotic, rifamycin antibiotic | Antibiotic efflux | 75.73 |
| lmrD | ATP-binding cassette (ABC) antibiotic efflux pump | Lincosamide antibiotic | Antibiotic efflux | 100 |
| Escherichia coli ampH | ampC-type beta-lactamase | Cephalosporin, penam | Antibiotic inactivation | 72.49 |
| emrR | Major facilitator superfamily (MFS) antibiotic efflux pump | Fluoroquinolone antibiotic | Antibiotic efflux | 80.7 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae KpnH | Major facilitator superfamily (MFS) antibiotic efflux pump | Macrolide antibiotic, fluoroquinolone antibiotic, aminoglycoside antibiotic, carbapenem, cephalosporin, penam, peptide antibiotic | Antibiotic efflux | 88.38 |
| amrB | Resistance-nodulation-cell division (RND) antibiotic efflux pump | Aminoglycoside antibiotic | Antibiotic efflux | 100 |
| adeF | Resistance-nodulation-cell division (RND) antibiotic efflux pump | Fluoroquinolone antibiotic, tetracycline antibiotic | Antibiotic efflux | 41.87 |
| smeE | Resistance-nodulation-cell division (RND) antibiotic efflux pump | Macrolide antibiotic, fluoroquinolone antibiotic, tetracycline antibiotic, phenicol antibiotic | Antibiotic efflux | 100 |
| CRP | Resistance-nodulation-cell division (RND) antibiotic efflux pump | Macrolide antibiotic, fluoroquinolone antibiotic | Antibiotic efflux | 99.52 |
| abcA | ATP-binding cassette (ABC) antibiotic efflux pump | Cephalosporin, penam, peptide antibiotic | Antibiotic efflux | 100 |
| AAC(3)-IV | AAC(3) | Aminoglycoside antibiotic | Antibiotic inactivation | 100 |
| Haemophilus influenzae PBP3 | Penicillin-binding protein mutations conferring resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics | Cephalosporin, cephamycin, penam | Antibiotic target alteration | 54.08 |
The antibiotic resistance gene profile of Pantoea dispersa A003 by the CARD database.
Discussion
Considering the previous cases, we find that P. dispersa can be isolated from different types of patients, such as neonates and adults, as well as immunocompromised and immunocompetent patients. In addition, P. dispersa can cause infection of different systems, such as the respiratory, joint, blood, digestive, and skin. Infections caused by P dispersa are more likely to occur in immunocompromised patients and usually present with high fever and infection-related symptoms. In our study, P. dispersa A003 was isolated from a 40-year-old male patient with a severe immune deficit according to his history of liver cirrhosis and blood routine results, which were consistent with some previous cases. However, the patient did not have a high fever or obvious infection-related symptoms. Because of the scarcity of P. dispersa infection, its clinical features remain unclear and may decrease the accuracy of clinical identification. Additionally, previously reported cases showed that P. dispersa infection may cause bloodstream infection (BSI) after admission (Hagiya and Otsuka, 2014; Panditrao and Panditrao, 2018; Ruan et al., 2022), indicating that the clinical staff should pay more attention to P. dispersa with the increase and gravity of nosocomial BSI.
Importantly, in the reported cases, most were detected by MALDI-TOF, and half of them were identified by 16S rRNA gene sequencing, which only provides a preliminary identification of the bacteria species. In our study, we performed genome sequencing and obtained the first clinically sourced genome sequence of P. dispersa. The analysis of the A003 genome data led to the identification of several virulence factors, such as the genes associated with the TFP, T6SS, flagella, iron uptake system, ompA, and secretion of toxins such as hemolysin. These virulence genes may play a role in niche adaptation, colonization, and pathogenesis in a wide range of hosts.
TFP, which are thin filaments covalently anchored to the bacterial cell wall and extend toward the environment, can mediate an array of essential tasks, including cell adhesion, motility, aggregation, and the secretion of proteolytic enzymes and colonization factors, and have been found in human pathogens, such as Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae (Craig et al., 2019; Pelicic, 2008; Craig and Li, 2008). T6SS is a versatile protein secretion machinery that can target eukaryotic cells, which is essential for entry and multiplication within host macrophages (Clemens et al., 2018). T6SS was shown in human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa and V. cholerae, which functions as a delivery apparatus of bacterial toxins into the host cells (Pukatzki et al., 2006; Mougous et al., 2006). Moreover, we also detected the gene hcp, which is regarded as one of the secreted effectors of T6SS, and it forms a tube in the outer component of the T6SS apparatus. The genes vgrG and ClpV were also detected, which facilitate the translocation of effector proteins to mediate microbe–host interactions and enables a new T6SS complex to be reassembled from the released subunits (Cianfanelli et al., 2016; Ho et al., 2014). Flagella are typically regarded as significant virulence factors that can facilitate motility and chemotaxis, allowing bacteria to travel to more favorable environments (Duan et al., 2013; Nakamura and Minamino, 2019). Iron is an important element for survival and colonization by bacteria since it plays a crucial role in the electron transport chain to produce energy. Iron acquisition systems are used by bacteria to scavenge iron from the environment under iron-restricted conditions (Andrews et al., 2003; Krewulak and Vogel, 2008). Therefore, successful competition for iron is crucial for pathogenicity. In the iron uptake category, we detected the genes encoding proteins related to iron uptake and transport, including ferric iron uptake transcriptional regulator (fur), enterobactin transporter (fepB, fepC, fepG, entS, and fes), TonB-dependent siderophore receptor (fepA and pvuA), ferric siderophore ABC transporter permease (fepD), and iron ABC transporter ATP-binding protein (fbpC and hitC). These siderophore systems could be an essential genetic determinant for the growth, virulence, and potential pathogenicity of P. dispersa A003. Additionally, we also found the gene ompA, which plays an essential role in bacterial adhesion, invasion, and intracellular survival along with evasion of host defenses or stimulators of pro-inflammatory cytokine production (Confer and Ayalew, 2013). The A003 strain also harbored genes involved in hemolysis. These genes code for extracellular cytotoxic proteins, which are known virulence factors that target cell membranes, causing erythrocyte lysis (Vandenesch et al., 2012). Furthermore, we identified 666 genes associated with T3SS effectors, which are essential for the pathogenicity of various Gram-negative bacteria, including E. coli, Salmonella, Shigella, and Yersinia (Ruano-Gallego et al., 2021). Taken together, all these virulence genes detected in A003 could be an essential genetic determinant for the growth, virulence, and potential pathogenicity of P. dispersa A003. Moreover, the carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation was carried out by the CAZY database, and glycoside hydrolases (GHs, 98) were the highest, followed by glycosyl transferase (GTs, 89), which may play important roles in the pathogenicity of many bacteria (St John et al., 2023; Hashimoto et al., 2007).
The genome data and results showed that the A003 genome carried out 15 antibiotic resistance genes conferring resistance to clinically important antibiotics, including fluoroquinolone, cephalosporin, penam, macrolide, and aminoglycoside. However, the antimicrobial susceptibility tests revealed that strain A003 was susceptible to almost all test antibiotics, which could be due to the poor concordance between bacterial resistance genotype and phenotype. In addition, another reason may be the scarcity of the P. dispersa clinical infection. The antibiotic resistance gene result suggested that the clinical staff should pay more attention to P. dispersa with the increasing drug resistance of clinical Gram-negative bacteria.
In conclusion, we report a clinical infection case of P. dispersa isolated from a 40-year-old male patient with liver cirrhosis and gastric varicose hemorrhage. The clinical isolate was identified and analyzed using MALDI-TOF MS and whole genome sequencing. The clinical phenotype and pathogenesis of P. dispersa infections remain largely unknown due to the relatively limited number of documented cases; the current cases may indicate an emerging pathogen in medical practice and deserve the attention of clinicians. The draft genome obtained in this study represents the first clinically sourced genome sequence of P. dispersa. This resource could assist clinical staff in better understanding the organism’s clinical characteristics and provide a foundation for further investigations into its virulence factors, antibiotic resistance, and host–pathogen interactions.
Statements
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, PRJNA1086653.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Medical Ethics Committee of the Sanya People’s Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The human blood samples used in this study were collected from patients in our hospital during normal diagnosis and treatment. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
LW: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Investigation, Conceptualization. XW: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Formal analysis. SC: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. SZ: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Investigation. LX: Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Investigation. XZ: Writing – review & editing, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization. LD: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Investigation, Formal analysis, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the fund of the innovation platform for Academicians of Hainan Province.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fbrio.2024.1445804/full#supplementary-material
References
1
AdeoluM.AlnajarS.NaushadS.GuptaR. S. (2016). Genome-based phylogeny and taxonomy of the ‘Enterobacteriales’: proposal for Enterobacterales ord. nov. divided into the families Enterobacteriaceae, Erwiniaceae fam. nov., Pectobacteriaceae fam. nov., Yersiniaceae fam. nov., Hafniaceae fam. nov., Morganellaceae fam. nov., and Budviciaceae fam. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.66, 5575–5599. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.001485
2
AdlanM. T. A.AnuradhaP. R.MasuraM. Y.AzslynnaA. M.AhneezA. H. (2023). A case series of complicated pantoea dispersa bacteremia: is pantoea species another pandora’s box? Int. J. Infect. Dis.130, S153. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2023.04.378
3
Ait TamlihatY.BoubienC.DaunayC.DulacT.Le CoustumierA. (2017). Pantoea dispersa cause rare de choc septique, à propos d’un cas et revue de la littérature. Médecine Intensive Réanimation26, 330–334. doi: 10.1007/s13546-017-1290-z
4
AndrewsS. C.RobinsonA. K.Rodríguez-QuiñonesF. (2003). Bacterial iron homeostasis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev.27, 215–237. doi: 10.1016/S0168-6445(03)00055-X
5
ArnoldR.BrandmaierS.KleineF.TischlerP.HeinzE.BehrensS.et al. (2009). Sequence-based prediction of type III secreted proteins. PloS Pathog.5, e1000376. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000376
6
AsaiN.KoizumiY.YamadaA.SakanashiD.WatanabeH.KatoH.et al. (2019). Pantoea dispersa bacteremia in an immunocompetent patient: a case report and review of the literature. J. Med. Case Rep.13, 33. doi: 10.1186/s13256-019-1969-z
7
BarronD. T.EadesA. A.KaneJ. (2006). A pseudo outbreak of pantoea dispersa in total joint replacement procedures. Am. J. Infection Control34, E104. doi: 10.1016/j.ajic.2006.05.286
8
BradyC.CleenwerckI.VenterS.VancanneytM.SwingsJ.CoutinhoT. (2008). Phylogeny and identification of Pantoea species associated with plants, humans and the natural environment based on multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA). Syst. Appl. Microbiol.31, 447–460. doi: 10.1016/j.syapm.2008.09.004
9
ChenL.ZhengD.LiuB.YangJ.JinQ. (2016). VFDB 2016: hierarchical and refined dataset for big data analysis–10 years on. Nucleic Acids Res.44, D694–D697. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1239
10
CianfanelliF. R.Alcoforado DinizJ.GuoM.De CesareV.TrostM.CoulthurstS. J. (2016). VgrG and PAAR proteins define distinct versions of a functional type VI secretion system. PloS Pathog.12, e1005735. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005735
11
ClemensD. L.LeeB. Y.HorwitzM. A. (2018). The francisella type VI secretion system. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol.8, 121. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2018.00121
12
ConferA. W.AyalewS. (2013). The OmpA family of proteins: roles in bacterial pathogenesis and immunity. Vet. Microbiol.163, 207–222. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.08.019
13
CraigL.ForestK. T.MaierB. (2019). Type IV pili: dynamics, biophysics and functional consequences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol.17, 429–440. doi: 10.1038/s41579-019-0195-4
14
CraigL.LiJ. (2008). Type IV pili: paradoxes in form and function. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol.18, 267–277. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2007.12.009
15
CruzA. T.CazacuA. C.AllenC. H. (2007). Pantoea agglomerans, a plant pathogen causing human disease. J. Clin. Microbiol.45, 1989–1992. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00632-07
16
DuanQ.ZhouM.ZhuL.ZhuG. (2013). Flagella and bacterial pathogenicity. J. Basic Microbiol.53, 1–8. doi: 10.1002/jobm.201100335
17
DutkiewiczJ.MackiewiczB.Kinga LemieszekM.GolecM.MilanowskiJ. (2016). Pantoea agglomerans: a mysterious bacterium of evil and good. Part III. Deleterious effects: infections of humans, animals and plants. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med.23, 197–205. doi: 10.5604/12321966.1203878
18
GaviniF.MergaertJ.BejiA.MielcarekC.IzardD.KerstersK.et al. (1989). Transfer of Enterobacter agglomerans (Beijerinck 1888) Ewing and Fife 1972 to Pantoea gen. nov. as Pantoea agglomerans comb, nov. and Description of Pantoea dispersa sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.39, 337–345. doi: 10.1099/00207713-39-3-337
19
HagiyaH.OtsukaF. (2014). Pantoea dispersa bacteremia caused by central line-associated bloodstream infection. Braz. J. Infect. Dis.18, 696–697. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2014.06.006
20
HashimotoW.ItohT.MaruyamaY.MikamiB.MurataK. (2007). Hydration of vinyl ether groups by unsaturated glycoside hydrolases and their role in bacterial pathogenesis. Int. Microbiol.10, 233–243. doi: 10.2436/20.1501.01.32
21
HassanD.SaleemN.HaneefM.KhanM.AzizM.UsmanM. (2023). Pantoea agglomerans: A rare infectious outbreak affecting maintenance hemodialysis patients in a tertiary care hospital. Semin. Dial. 37, 172–177. doi: 10.1111/sdi.13182
22
HoB. T.DongT. G.MekalanosJ. J. (2014). A view to a kill: the bacterial type VI secretion system. Cell Host Microbe15, 9–21. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.11.008
23
KanehisaM.GotoS. (2000). KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res.28, 27–30. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.27
24
KrewulakK. D.VogelH. J. (2008). Structural biology of bacterial iron uptake. Biochim. Biophys. Acta1778, 1781–1804. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2007.07.026
25
KumarS.StecherG.LiM.KnyazC.TamuraK. (2018). MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol.35, 1547–1549. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msy096
26
LeeI.Ouk KimY.ParkS. C.ChunJ. (2016). OrthoANI: An improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.66, 1100–1103. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.000760
27
ManoharanG.LalithaP.JeganathanL. P.DsilvaS. S.PrajnaN. V. (2012). Pantoea ananatis as a cause of corneal infiltrate after rice husk injury. J. Clin. Microbiol.50, 2163–2164. doi: 10.1128/JCM.06743-11
28
Marchler-BauerA.ZhengC.ChitsazF.DerbyshireM. K.GeerL. Y.GeerR. C.et al. (2013). CDD: conserved domains and protein three-dimensional structure. Nucleic Acids Res.41, D348–D352. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1243
29
McArthurA. G.WaglechnerN.NizamF.YanA.AzadM. A.BaylayA. J.et al. (2013). The comprehensive antibiotic resistance database. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.57, 3348–3357. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00419-13
30
MeharV.YadavD.SanghviJ.GuptaN.SinghK. (2013). Pantoea dispersa: an unusual cause of neonatal sepsis. Braz. J. Infect. Dis.17, 726–728. doi: 10.1016/j.bjid.2013.05.013
31
MougousJ. D.CuffM. E.RaunserS.ShenA.ZhouM.GiffordC. A.et al. (2006). A virulence locus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa encodes a protein secretion apparatus. Science312, 1526–1530. doi: 10.1126/science.1128393
32
NakamuraS.MinaminoT. (2019). Flagella-driven motility of bacteria. Biomolecules9, 279. doi: 10.3390/biom9070279
33
PanditraoM.PanditraoM. (2018). Pantoea dispersa: Is it the Next Emerging “Monster” in our Intensive Care Units? A Case Report and Review of Literature. Anesth. Essays Res.12, 963–966. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_147_18
34
PelicicV. (2008). Type IV pili: e pluribus unum? Mol. Microbiol.68, 827–837. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06197.x
35
PreisS.SchröderK.BiedermannT.ZinkA. (2022). Folliculitis caused by Pantoea dispersa as a souvenir from a self-discovery excursion in bat caves. JAAD Case Rep.25, 15–17. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2022.05.009
36
PukatzkiS.MaA. T.SturtevantD.KrastinsB.SarracinoD.NelsonW. C.et al. (2006). Identification of a conserved bacterial protein secretion system in Vibrio cholerae using the Dictyostelium host model system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A.103, 1528–1533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510322103
37
RuanX. L.QinX.LiM. (2022). Nosocomial bloodstream infection pathogen Pantoea dispersa: a case report and literature review. J. Hosp Infect.127, 77–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2022.06.011
38
Ruano-GallegoD.Sanchez-GarridoJ.KozikZ.Núñez-BerruecoE.Cepeda-MoleroM.Mullineaux-SandersC.et al. (2021). Type III secretion system effectors form robust and flexible intracellular virulence networks. Science371, eabc9531. doi: 10.1126/science.abc9531
39
SakY. H.HawC. Y.ChanY. Q. (2024). Pantoea dispersa peritoneal dialysis catheter-related infection. BMJ Case Rep.17, e260878. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2024-260878
40
SanE. V.Mohamed SukurS.Abdul HameedA.P. RadhakrishnanA. (2024). Disseminated Lodderomyces elongisporus and Pantoea dispersa: A Rare Dual Infection in an Immunocompromised Patient. Cureus16, e58985. doi: 10.7759/cureus.58985
41
SchmidH.SchubertS.WeberC.BognerJ. R. (2003). Isolation of a Pantoea dispersa-like strain fron a 71-year-old woman with acute myeloid leukemia and multiple myeloma. Infection31, 66–67. doi: 10.1007/s15010-002-3024-y
42
St JohnA.PeraultA. I.GiacomettiS. I.SommerfieldA. G.DumontA. L.LaceyK. A.et al. (2023). Capsular polysaccharide is essential for the virulence of the antimicrobial-resistant pathogen enterobacter hormaechei. mBio14, e0259022. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02590-22
43
TatusovR. L.GalperinM. Y.NataleD. A.KooninE. V. (2000). The COG database: a tool for genome-scale analysis of protein functions and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res.28, 33–36. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.33
44
VandeneschF.LinaG.HenryT. (2012). Staphylococcus aureus hemolysins, bi-component leukocidins, and cytolytic peptides: a redundant arsenal of membrane-damaging virulence factors? Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol.2, 12. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00012
45
WaltersonA. M.StavrinidesJ. (2015). Pantoea: insights into a highly versatile and diverse genus within the Enterobacteriaceae. FEMS Microbiol. Rev.39, 968–984. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuv027
46
YangY.HuH.ZhouC.ZhangW.YuY.LiuQ.et al. (2022). Characteristics and accurate identification of Pantoea dispersa with a case of spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma in China: A case report. Med. (Baltimore)101, e28541. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000028541
47
ZhangY.FanY.ZhanY.WangH.LiX.WangH.et al. (2023). Genomic characterization of Pantoea anthophila strain UI705 causing urinary tract infections in China. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol.13, 1208473. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1208473
Summary
Keywords
Pantoea dispersa, blood culture, MALDI-TOF MS, whole genome sequencing (WGS), clinical infection
Citation
Wang L, Wang X, Chen S, Zhong S, Xu L, Zhu X and Dong L (2024) Genomic characterization of Pantoea dispersa A003 isolated from a clinical patient. Front. Bacteriol. 3:1445804. doi: 10.3389/fbrio.2024.1445804
Received
11 June 2024
Accepted
02 October 2024
Published
25 October 2024
Volume
3 - 2024
Edited by
Zhuo Ma, Albany College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences, United States
Reviewed by
Shifu Aggarwal, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, United States
Itziar Chapartegui-González, Karolinska Institutet (KI), Sweden
Updates
Copyright
© 2024 Wang, Wang, Chen, Zhong, Xu, Zhu and Dong.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lingzhi Dong, 18234505042@163.com; Xiong Zhu, zhuxiong6@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.