
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Astron. Space Sci., 05 March 2025
Sec. Extragalactic Astronomy
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fspas.2025.1560380
It remains challenging to systematically survey nearby diffuse dwarf galaxies and address the formation mechanism of this population distinguishing from regular ones. We carry out a pilot search for these galaxies in the COSMOS field using the deep HST/F814W imaging data. We report three diffuse dwarf galaxies satisfying the criteria: (1) redshift
The extremely low surface brightness (LSB) galaxies in the Universe provide crucial insights into galaxy formation and evolution, particularly concerning the role of dark matter and the mechanisms shaping diverse galaxy morphologies (e.g., Impey and Bothun, 1997; Bullock and Boylan-Kolchin, 2017). Ultra-diffuse galaxies (UDGs) are distinguished by their extremely low central surface brightness
UDGs have been found in a variety of environments, including galaxy clusters (e.g., van Dokkum et al., 2015a; Koda et al., 2015; Mihos et al., 2015; Muñoz et al., 2015; Martínez-Delgado et al., 2016; van der Burg et al., 2016; Román and Trujillo, 2017a; Janssens et al., 2017; Lee et al., 2017; Lee et al., 2020; Iodice et al., 2020; Wittmann et al., 2017; Janssens et al., 2019; Gannon et al., 2022; Venhola et al., 2022; La Marca et al., 2022a; b), groups (e.g., Smith Castelli et al., 2016; Merritt et al., 2016; Ordenes-Briceño et al., 2016; Trujillo et al., 2017; Román and Trujillo, 2017b; Shi et al., 2017; van der Burg et al., 2017; Müller et al., 2018; Greco et al., 2018b; Somalwar et al., 2020; Zaritsky et al., 2023; Jones et al., 2023) and the fields (e.g., Bellazzini et al., 2017; Leisman et al., 2017; Bennet et al., 2018; Prole et al., 2019; Barbosa et al., 2020; Fielder et al., 2024; Montes et al., 2024), as well as within cosmic void (Román et al., 2019) and associated with the large-scale structures (e.g., Román and Trujillo, 2017a; Shi et al., 2017). Accumulating observational evidence reveals that UDGs exhibit a diverse range of properties. They can be red and blue in color (e.g., Koda et al., 2015; Román and Trujillo, 2017a; Román and Trujillo, 2017b; Shi et al., 2017; Leisman et al., 2017), gas-poor and gas-rich in H I gas content (e.g., Trujillo et al., 2017; Kadowaki et al., 2017; Bellazzini et al., 2017; Papastergis et al., 2017; Spekkens and Karunakaran, 2018; Karunakaran et al., 2020; Karunakaran et al., 2024), and have prolate and oblate in geometry/intrinsic ellipticity distribution (Burkert, 2017). Some UDGs contain a high fraction of globular clusters (GCs) (e.g., Beasley et al., 2016; Beasley and Trujillo, 2016; Peng and Lim, 2016; van Dokkum et al., 2016; van Dokkum et al., 2017; van Dokkum et al., 2018b; Toloba et al., 2018; Lim et al., 2018; Marleau et al., 2024; Forbes et al., 2025), and many host a compact nucleus in their central regions (e.g., Yagi et al., 2016; Janssens et al., 2017; Lambert et al., 2024; Khim et al., 2024). These observations suggest that the UDG population, selected based on observational criteria, may be composed of different populations formed through different pathways. For instance, UDGs Dragonfly 44 and Dragonfly X1 are likely overwhelmingly dominated by dark matter and are considered as “failed” galaxies with massive halo (
Multiple formation scenarios have been proposed to account for the extended nature of UDGs. Galaxy collisions in dense environments are suggested as a mechanism for forming UDGs (Baushev, 2018), often leading to prolate rather than oblate morphologies (Burkert, 2017). Carleton et al. (2019) proposed that tidal stripping and heating are primary drivers of UDG formation in the dense environments. In less-dense environments, such as poor clusters and galaxy groups, the interaction of the interstellar medium (ISM) with the intra-cluster medium (ICM) is believed to play a pivotal role in shaping UDGs (Levy et al., 2007). On the other hand, Amorisco and Loeb (2016) contended that UDGs are predominantly dwarf galaxies with extremely high spins. Leisman et al. (2017) and Spekkens and Karunakaran (2018) reported that gas-rich UDGs tend to reside in halos of high angular momentum traced by H I line width, supporting the high-spin scenario (Amorisco and Loeb, 2016; Rong et al., 2017). Furthermore, gas outflow driven by strong feedback from supernovae and massive star winds in a star-forming galaxy is suggested to cause the expansion of dark matter and stellar disk, ultimately reshaping the galaxy into a faint and extended form (Di Cintio et al., 2017; Chan et al., 2018). In addition, Sales et al. (2020) suggested that UDG population is a mixture of normal LSB galaxies typically found in the low-density environments, along with a distinct population whose expansive size and LSB are a result of the impact of cluster tides (e.g., Tremmel et al., 2020).
More observational efforts are eagerly demanded to determine the physical properties of UDGs for a better understanding of their origin. Notably, spectroscopic observations are crucial for revealing the properties of stellar populations, metallicity and kinematics. However, it is very expensive to obtain good-quality spectroscopic data for UDGs even with 10 m-class telescopes. To date, only
In this work, we systematically search for extremely LSB galaxies in the COSMOS field. The availability of pre-existing deep multiwavelength observations, spanning from the ultraviolet (UV) to the radio, enables us to delve into the properties of these galaxies in detail. In Section 2, we describe the selection of the three diffuse galaxies and the photometric data. Section 3 presents the photometry and analysis. finally, we discuss and summarize our results in Section 4. We adopt a cosmology with
We carry out a search for UDGs within the central
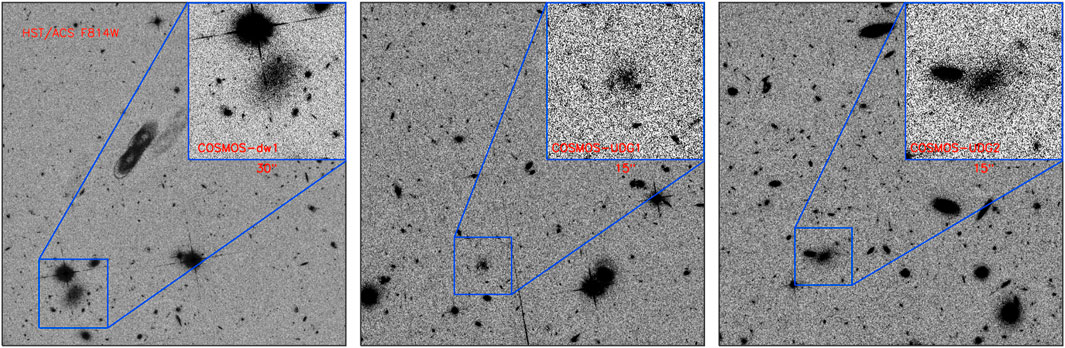
Figure 1. The HST/ACS F814W stamps of three COSMOS diffuse galaxies: COSMOS-dw1 (left), COSMOS-UDG1 (middle), and COSMOS-UDG2 (right). The size of the stamps is
The publicly-available multi-band mosaic science images of COSMOS are used to examine the broad properties of the selected UDGs, including Far-UV (FUV) and Near-UV (NUV) images from the Galaxy Evolution Explorer (GALEX) (Zamojski et al., 2007),
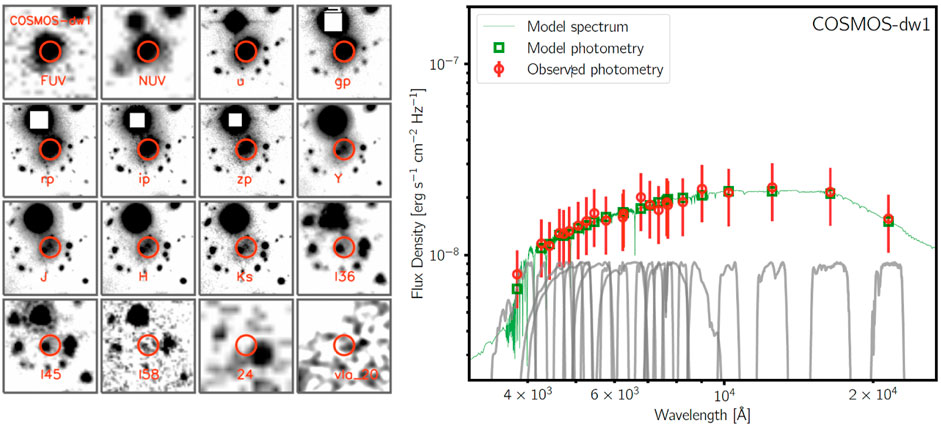
Figure 2. Left:The examples of multiwavelength science images of COSMOS-dw1. The size of each stamp is
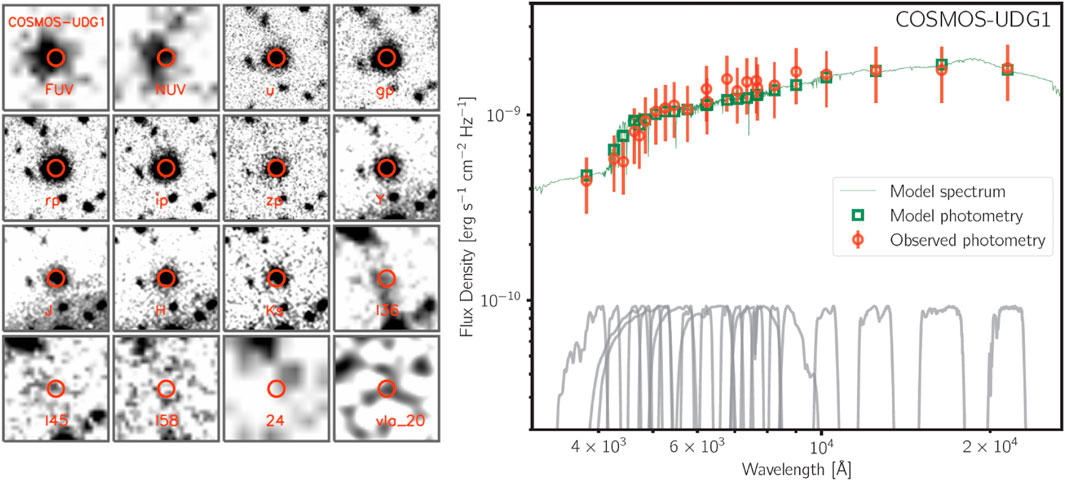
Figure 3. Left:The examples of multiwavelength science images of COSMOS-UDG1. The size of each stamp is
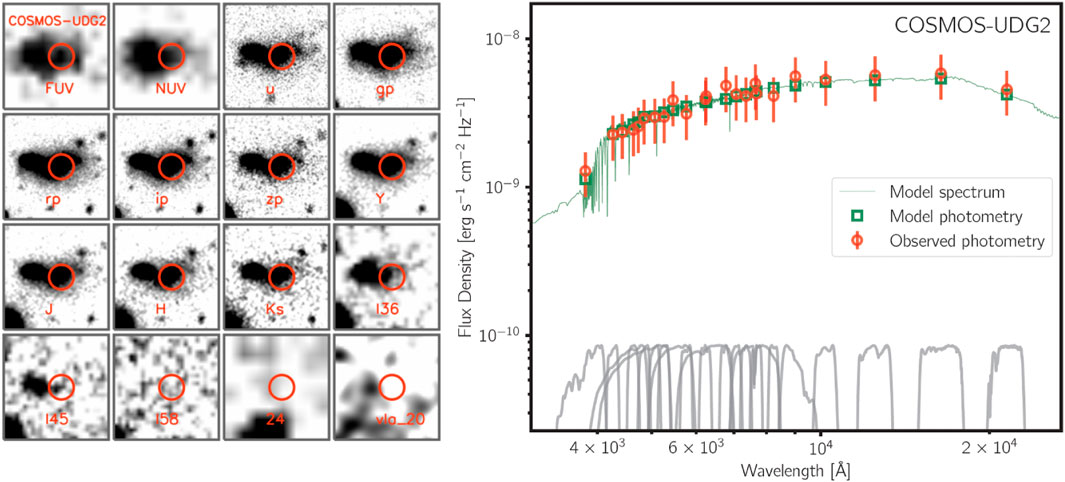
Figure 4. Left:The examples of multiwavelength science images of COSMOS-UDG2. The size of each stamp is
We construct aperture-matched SEDs from the FUV to the NIR for our three UDG targets. The three targets are very extended and removal of the blending fluxes from nearby sources is key to measuring their fluxes. The left panels in Figures 2–4 are the examples of mosaics in these three galaxies. Below we describe our processes to derive the aperture-matched photometry from the multi-band imaging data.
For each of our three targets, we cut stamp images of
We notice that the total magnitude in HST
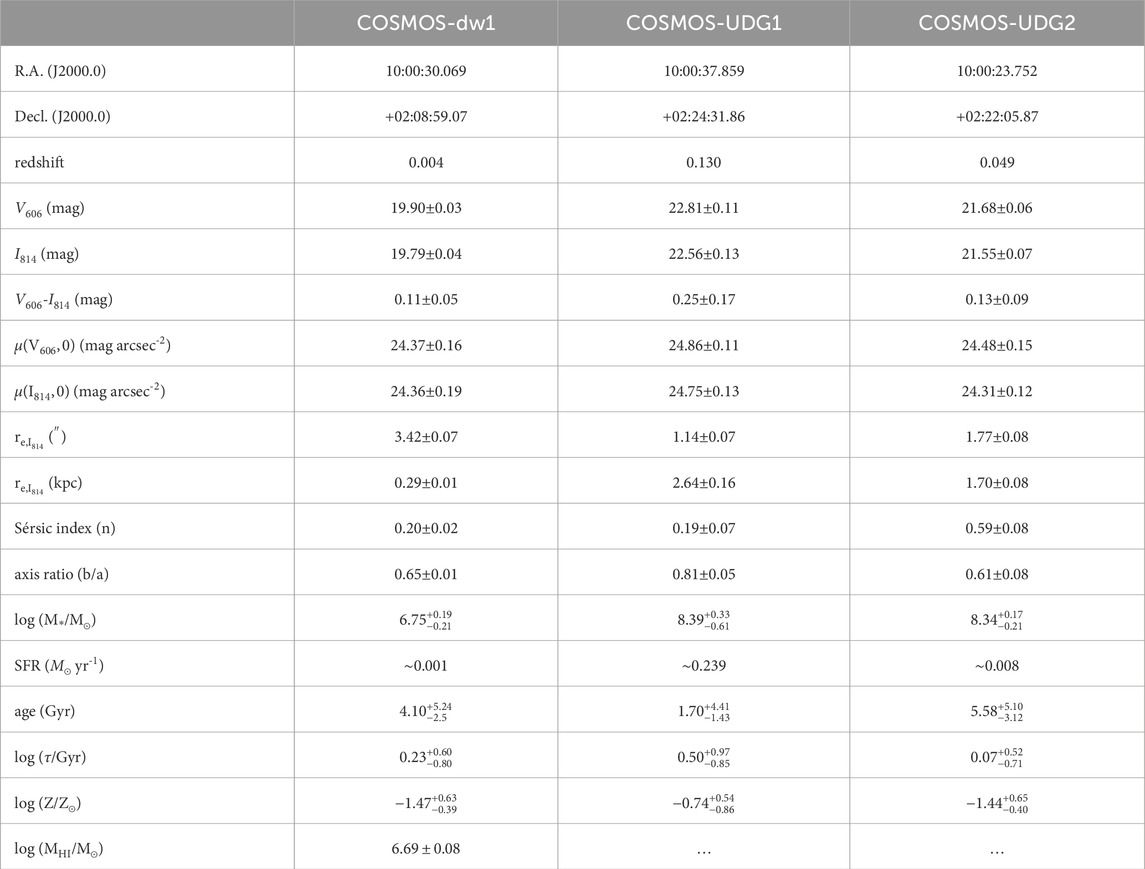
Table 1. The properties of COSMOS-dw1, COSMOS-UDG1 and COSMOS-UDG2. The parameters listed from top to bottom rows, refer to coordinates, redshift, magnitude in F606W/F814W, color, central surface brightness in F606W/F814W, effective radius in angular and physical size, Sérsic index (n), axis ratio (b/a), stellar mass log(
The Subaru optical images we used are already PSF-matched. We use a fixed aperture of radius two times the
We also examine the dust emission of our three galaxies using the deepest 850
Using the software Easy and Accurate Redshifts from Yale (EAZY) (Brammer et al., 2008), we can estimate photometric redshift (photo-
We constrain the star formation histories (SFHs) of these three galaxies using the SED fitting technique. The fitting is performed using Prospector (Leja et al., 2017; Leja et al., 2019), which uses the Flexible Stellar Population Synthesis (FSPS) package with fully Bayesian Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) code (Conroy et al., 2009). We use the default Stellar Population Synthesis (SPS) parameters in FSPS. For the SED modeling, we adopt the Chabrier (2003) IMF and the Calzetti et al. (2000) dust attenuation law. The delayed exponentially declining SFH (SFR
The best-fit models of these three galaxies with Prospector are shown in the right panels of the Figures 2–4. For COSMOS-dw1, we obtain stellar mass
In Figure 5, we show the stellar mass–metallicity relation (MZR) for these three COSMOS galaxies, compared to the relation found for the dwarfs (Kirby et al., 2013) and giant galaxies in the local Universe (Gallazzi et al., 2005). The MZR with large scatter appears to be continuous from low to high masses. Despite the large uncertainties of metallicity and stellar mass, COSMOS-dw1 obeys the MZR at the low mass end, COSMOS-UDG1 and COSMOS-UDG2 follow the MZR defined by normal dwarf galaxies. This suggests that stellar mass plays an important role in determining stellar metallicities, regardless of the size of a galaxy.
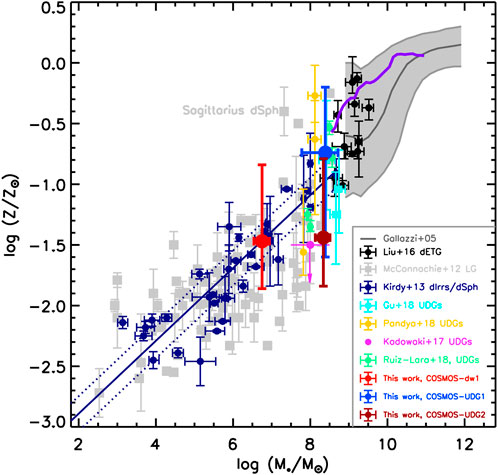
Figure 5. The stellar mass-metallicity relation. The black solid points are the early-type galaxies (ETGs) in Virgo (Liu et al., 2016), dwarf galaxies in and around the Local group are shown in gray solid squares (McConnachie, 2012), and local group dIrrs/dSphs from Kirby et al. (2013) are shown in dark blue solid points, the blue solid line shows the least-squares line, and the dotted lines are the rms about the best fit. MZR relation could extend to the massive galaxies (Gallazzi et al., 2005), as shown the gray solid curves. The purple solid line is the MZR relation of star-forming galaxies with stellar masses ranging between
We present the physical properties of three nearby diffuse galaxies identified in the central region of the COSMOS field, which is covered by the 3D-HST/CANDELS survey. The primary uncertainty in our analysis is the distances of the three diffuse galaxies. The photometric redshifts derived from the broadband SEDs affirm that these objects are nearby, with redshifts
Obtaining accurate distance estimates for the ultra-faint and diffuse objects in local Universe is critical to derive correct galaxy physical properties. Polzin et al. (2021) applied the surface brightness fluctuation (SBF) method to COSMOS-dw1 and measured a distance of
COSMOS-dw1 exhibits a blue color with
The dynamical mass
The MZR of galaxies offers profound insights into their star formation and chemical enrichment histories. The relatively low scatter in this relation, particularly at the low-mass end (e.g., Kirby et al., 2013), poses a challenge to explain. This relationship is intricately tied to the complex dynamics involving reionization, star formation, gas inflow, outflow, and recycling processes (e.g., Ma et al., 2016).
Recently, numerous researches have unveiled the stellar population properties of some UDGs through optical spectra and multiwavelength photometric data in different environments. These studies have demonstrated the diverse stellar populations of UDGs across different environments. Specifically, UDGs in clusters (e.g., Coma and Virgo) identified by optical spectroscopy are intermediate-to-old age (
We examine the environments around the three galaxies, and find that COSMOS-dw1, COSMOS-UDG1 and COSMOS-UDG2 do not have obvious luminous companions, suggesting that all three galaxies reside in the low-density environments. In comparison to UDGs in galaxy clusters (e.g., Kadowaki et al., 2017; Gu et al., 2018; Ruiz-Lara et al., 2018; Buzzo et al., 2022), COSMOS-UDG1 shows younger age and higher metallicity, whereas COSMOS-UDG2 is younger but metal-poor. These observations imply that the relative young ages of COSMOS-UDG1 and COSMOS-UDG2 may be associated with their low-density environment (Martínez-Delgado et al., 2016; Trujillo et al., 2017; Pandya et al., 2018). A possible explanation is that COSMOS-UDG1 have relatively massive halos, more metals can be locked, and finally reproduce the metal-rich galaxies. Besides, the non-universal initial mass function (IMF) may provide the constrains (Ferré-Mateu et al., 2013). Interestingly, the gray squares in Figure 5 show the Sagittarius (Sr) dwarf spheroidal (dSph) galaxy, a satellite galaxy in the Milky way, exhibits a relatively high metallicity ([Fe
COSMOS-UDG1 and COSMOS-UDG2 belong to the dwarf galaxies with large size, and their diffuse nature potentially may be governed by internal mechanisms. UDGs are the extended dwarf galaxies with high spin angular momentum (Amorisco and Loeb, 2016; Rong et al., 2017), and strong feedback from supernova or massive stars driven gas outflow, dark matter halo and stellar disks expansion, and reproduce low luminosity and extended galaxies (Di Cintio et al., 2017; Chan et al., 2018). Furthermore, some UDGs may be tidal disturbed dwarf galaxies and some present tidal feature associated with galaxy mergers (Merritt et al., 2016; Greco et al., 2018a). From the deep multiwavelength imaging, the three COSMOS galaxies we identified appear to be no tidal structures. The multiwavelength photometric data can help constrain the properties of these three galaxies, and we look forward to spatially resolving these diffuse galaxies in subsequent work to understand their formation mechanisms.
We summarize our results as follows:
(1) We conducted a search for a low-mass LSB galaxies (COSMOS-dw1) and two new UDGs (COSMOS-UDG1 and COSMOS-UDG2) within the central region of the COSMOS field, and examine their properties using the existing multiwavelength data. We present their UV-to-IR SEDs built through our careful PSF- and aperture-matched photometry. The spec-
(2) SED fitting reveals that these three galaxies exhibit different physical properties. COSMOS-dw1 is a quenched low-mass galaxy with a stellar mass of
(3) Interestingly, COSMOS-dw1 contains atomic gas with an H
(4) Despite the significant uncertainties in metallicity measurements, COSMOS-dw1 aligns with the MZR at the low mass end, while COSMOS-UDG1 and COSMOS-UDG2 broadly follow the MZR established by typical dwarf galaxies. This suggests that stellar mass may be a crucial factor in determining stellar metallicities.
Taken together, the detection of low-luminosity LSB galaxies and UDGs in the COSMOS field indicate that UDGs can indeed be found in random fields. These extreme LSB galaxies identified so far are just the tip of the iceberg. In the future, more unknown LSB galaxies and UDGs could be discovered through multiwavelength imaging facilitated by space- (e.g., Euclid, CSST and Roman) (e.g., Zhan, 2011; Montes et al., 2023; Euclid Collaboration et al., 2024) and ground-based (e.g., LSST and WFST) telescopes with a wide field-of-view capabilities (e.g., Robertson et al., 2017; Shi et al., 2018; Martin et al., 2022; Breivik et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2023). By combining these observations with spectroscopic analysis, the real natures of UDGs and LSB structures can be fully unveiled.
Here, we have measured the structure parameters of COSMOS-dw1, COSMOS-UDG1 and COSMOS-UDG2 using both 1D Sérsic and 2D Sérsic fitting methods. The structure properties obtained are summarized in Table 2. Figures 6–8 depict the 1D surface brightness profiles and 2D Sérsic fitting results for COSMOS-dw1, COSMOS-UDG1 and COSMOS-UDG2, respectively. In the upper panels of Figures 7, 8, the blue and red points and curves represent the results from the F606W and F814W filters, respectively. The bottom panels of these figures show, from left to right, the original image, the model, and the residual image for each galaxy. The axial ratios (b/a) of these three diffuse galaxies are greater than 0.5, indicating that they exhibit an ellipsoidal shape. Their Sérsic indices
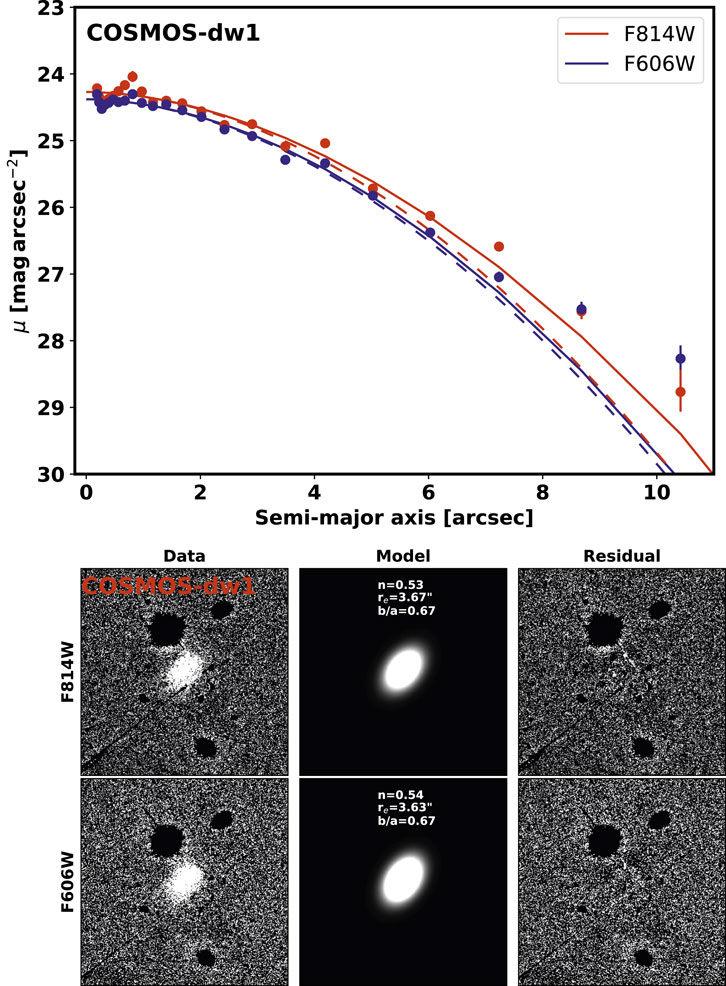
Figure 6. The 1D surface brightness profile (Upper panel) and 2D Sérsic fitting (Bottom panel) of COSMOS-dw1. The size of each stamp is
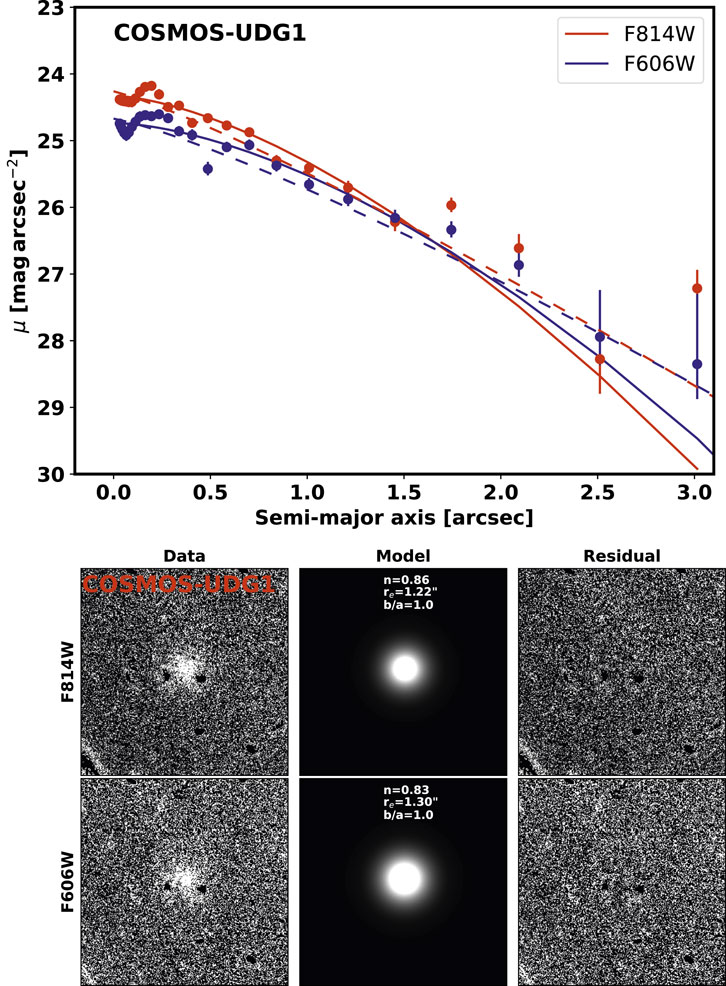
Figure 7. The 1D surface brightness profile (Upper panel) and 2D Sérsic fitting (Bottom panel) of COSMOS-UDG1. The size of each stamp is
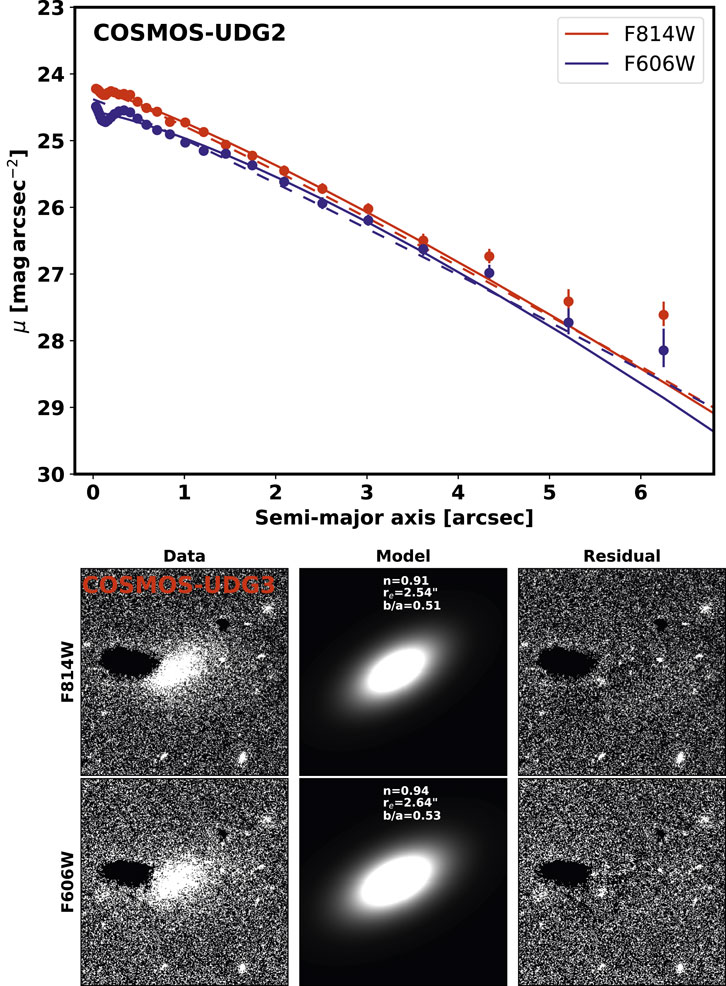
Figure 8. The 1D surface brightness profile (Upper panel) and 2D Sérsic fitting (Bottom panel) of COSMOS-UDG2. The size of each stamp is
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
DS: Methodology, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, Funding acquisition, Visualization, Investigation, Software. XZ: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing–review and editing, Visualization. ZP: Writing–review and editing, Formal Analysis, Visualization. YL: Visualization, Writing–review and editing. HD: Visualization, Writing–review and editing. QH: Visualization, Writing–review and editing. XL: Visualization, Writing–review and editing. QW: Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work is supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2023YFA1608100), Scientific Research Foundation for High-level Talents of Anhui University of Science and Technology (2024yjrc104), the National Science Foundation of China (12303015 and 12173088), and the National Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20231106).
We thank the referees for the valuable and helpful comments and suggestions, which improve our manuscript. We acknowledgment support from Anhui University of Science and Technology and China Manned Space Project.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Amorisco, N. C., and Loeb, A. (2016). Ultradiffuse galaxies: the high-spin tail of the abundant dwarf galaxy population. Ultradiffuse galaxies high-spin tail Abund. dwarf galaxy Popul. 459, L51–L55. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slw055
Amorisco, N. C., Monachesi, A., Agnello, A., and White, S. D. M. (2018). The globular cluster systems of 54 Coma ultra-diffuse galaxies: statistical constraints from HST data, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 475, 4235–4251. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty116
Barbosa, C. E., Zaritsky, D., Donnerstein, R., Zhang, H., Dey, A., Mendes de Oliveira, C., et al. (2020). One hundred SMUDGes in S-plus: ultra-diffuse galaxies flourish in the field, Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser., 247, 46. doi:10.3847/1538-4365/ab7660
Baushev, A. N. (2018). Galaxy collisions as a mechanism of ultra diffuse galaxy (UDG) formation. Galaxy collisions as a Mech. ultra diffuse galaxy (UDG) Form. 60, 69–73. doi:10.1016/j.newast.2017.10.008
Beasley, M. A., Romanowsky, A. J., Pota, V., Navarro, I. M., Martinez Delgado, D., Neyer, F., et al. (2016). An overmassive dark halo around an ultra-diffuse galaxy in the virgo cluster Astrophys. J. Lett., 819, L20. doi:10.3847/2041-8205/819/2/L20
Beasley, M. A., and Trujillo, I. (2016). Globular clusters indicate that ultra-diffuse galaxies are dwarfs, Astrophys. J., 830, 23. doi:10.3847/0004-637X/830/1/23
Bellazzini, M., Belokurov, V., Magrini, L., Fraternali, F., Testa, V., Beccari, G., et al. (2017). Redshift, metallicity size two Ext. dwarf Irregul. galaxies a link between dwarf Irregulars ultra diffuse galaxies? 467, 3751–3758. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx236
Bennet, P., Sand, D. J., Zaritsky, D., Crnojević, D., Spekkens, K., and Karunakaran, A. (2018). Evidence for ultra-diffuse galaxy “formation” through galaxy interactions. “Formation” through Galaxy Interact. 866, L11. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aadedf
Bertin, E. (2011). “Automated morphometry with SExtractor and PSFEx,”. . Editors I. N. Evans, A. Accomazzi, D. J. Mink, and A. H. Rots (Astronomical Society of the Pacific Conference Series), 442, 435.
Bertin, E., and Arnouts, S. (1996). SExtractor: software for source extraction, Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. Ser., 117, 393–404. doi:10.1051/aas:1996164
Brammer, G. B., van Dokkum, P. G., and Coppi, P. (2008). Eazy: a fast, public photometric redshift code. ApJ 686, 1503–1513. doi:10.1086/591786
Breivik, K., Connolly, A. J., Ford, K. E. S., Jurić, M., Mandelbaum, R., Miller, A. A., et al. (2022). From data to software to science with the rubin observatory LSST. arXiv e-prints. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2208.02781
Bullock, J. S., and Boylan-Kolchin, M. (2017). Small-scale challenges to the λcdm paradigm. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 55, 343–387. doi:10.1146/annurev-astro-091916-055313
Burkert, A. (2017). The geometry and origin of ultra-diffuse ghost galaxies. Galaxies 838, 93. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aa671c
Buttitta, C., Iodice, E., Doll, G., Hartke, J., Hilker, M., Forbes, D. A., et al. (2025). “Looking into the faintEst WIth MUSE (LEWIS): exploring the nature of ultra-diffuse galaxies in the Hydra-I cluster II,” in Stellar kinematics and dynamical masses. arXiv e-prints , arXiv:2501.16190. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2501.16190
Buzzo, M. L., Forbes, D. A., Brodie, J. P., Romanowsky, A. J., Cluver, M. E., Jarrett, T. H., et al. (2022). The stellar populations of quiescent ultra-diffuse galaxies from optical to mid-infrared spectral energy distribution fitting, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 517, 2231–2250. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac2442
Buzzo, M. L., Forbes, D. A., Jarrett, T. H., Marleau, F. R., Duc, P.-A., Brodie, J. P., et al. (2024a). Constraining the stellar populations of ultra-diffuse galaxies in the MATLAS survey using spectral energy distribution fitting, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 529, 3210–3234. doi:10.1093/mnras/stae564
Buzzo, M. L., Forbes, D. A., Jarrett, T. H., Marleau, F. R., Duc, P.-A., Brodie, J. P., et al. (2024b). The multiple classes of ultra-diffuse galaxies: can we tell them apart? Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 536, 2536–2557. doi:10.1093/mnras/stae2700
Calzetti, D., Armus, L., Bohlin, R. C., Kinney, A. L., Koornneef, J., and Storchi-Bergmann, T. (2000). The dust content and opacity of actively star-forming galaxies. Galaxies 533, 682–695. doi:10.1086/308692
Carleton, T., Errani, R., Cooper, M., Kaplinghat, M., Peñarrubia, J., and Guo, Y. (2019). The formation of ultra-diffuse galaxies in cored dark matter haloes through tidal stripping and heating, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 485, 382–395. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz383
Casey, C. M., Chen, C.-C., Cowie, L. L., Barger, A. J., Capak, P., Ilbert, O., et al. (2013). Characterization of scuba-2 450m and 850m selected galaxies in the cosmos field. MNRAS 436, 1919–1954. doi:10.1093/mnras/stt1673
Chabrier, G. (2003). Galactic stellar and substellar initial mass function. Publ. Astronomical Soc. Pac. 115, 763–795. doi:10.1086/376392
Chan, T. K., Kereš, D., Wetzel, A., Hopkins, P. F., Faucher-Giguère, C. A., El-Badry, K., et al. (2018). The origin of ultra diffuse galaxies: stellar feedback and quenching. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 478, 906–925. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty1153
Chilingarian, I. V., Afanasiev, A. V., Grishin, K. A., Fabricant, D., and Moran, S. (2019). Internal dynamics and stellar content of nine ultra-diffuse galaxies in the coma cluster prove their evolutionary link with dwarf early-type galaxies*. Galaxies 884, 79. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab4205
Chou, M.-Y., Majewski, S. R., Cunha, K., Smith, V. V., Patterson, R. J., Martínez-Delgado, D., et al. (2007). A 2MASS all-sky view of the Sagittarius dwarf galaxy. V. Variation of the metallicity distribution function along the Sagittarius stream. V. Var. Metallicity Distribution Funct. along Sagittarius Stream 670, 346–362. doi:10.1086/522483
Conroy, C., Gunn, J. E., and White, M. (2009). The propagation of uncertainties in stellar population synthesis modeling. i. the relevance of uncertain aspects of stellar evolution and the initial mass function to the derived physical properties of galaxies. ApJ 699, 486–506. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/699/1/486
Di Cintio, A., Brook, C. B., Dutton, A. A., Macciò, A. V., Obreja, A., and Dekel, A. (2017). NIHAO – XI. Formation of ultra-diffuse galaxies by outflows. Form. ultra-diffuse galaxies by outflows 466, L1–L6. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slw210
Emsellem, E., van der Burg, R. F. J., Fensch, J., Jeřábková, T., Zanella, A., Agnello, A., et al. (2019). The ultra-diffuse galaxy NGC 1052-DF2 with MUSE: I. Kinematics of the stellar body. Kinemat. stellar body 625, A76. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201834909
Euclid Collaboration Mellier, Y., Acevedo Barroso, J. A., Achúcarro, A., Adamek, J., et al. (2024). Euclid. I. Overview of the Euclid mission. arXiv e-prints , arXiv:2405.13491. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2405.13491
Ferré-Mateu, A., Alabi, A., Forbes, D. A., Romanowsky, A. J., Brodie, J., Pandya, V., et al. (2018). Origins of ultradiffuse galaxies in the Coma cluster – II. Constraints from their stellar populations. Constraints their stellar populations 479, 4891–4906. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty1597
Ferré-Mateu, A., Gannon, J. S., Forbes, D. A., Buzzo, M. L., Romanowsky, A. J., and Brodie, J. P. (2023). The star formation histories of quiescent ultra-diffuse galaxies and their dependence on environment and globular cluster richness, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 526, 4735–4754. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad3102
Ferré-Mateu, A., Vazdekis, A., and de la Rosa, I. G. (2013). The impact of a non-universal Initial Mass Function on the star formation histories of early-type galaxies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 431, 440–454. doi:10.1093/mnras/stt193
Fielder, C., Jones, M. G., Sand, D. J., Bennet, P., Crnojević, D., Karunakaran, A., et al. (2024). All puffed up: exploring ultra-diffuse galaxy origins through galaxy interactions, Astron. J., 168, 212. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ad74f6
Forbes, D. A., Buzzo, M. L., Ferre-Mateu, A., Romanowsky, A. J., Gannon, J., Brodie, J. P., et al. (2025). Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 536, 1217–1225. doi:10.1093/mnras/stae2675
Foster, L. M., Taylor, J. E., and Blakeslee, J. P. (2024). Testing the surface brightness fluctuation method on dwarf galaxies in the COSMOS field, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 527, 1656–1673. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad3235
Gallazzi, A., Charlot, S., Brinchmann, J., White, S. D. M., and Tremonti, C. A. (2005). The ages and metallicities of galaxies in the local universe. Mon. Notices R. Astronomical Soc. 362, 41–58. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.09321.x
Gannon, J. S., Ferré-Mateu, A., Forbes, D. A., Brodie, J. P., Buzzo, M. L., and Romanowsky, A. J. (2024). A catalogue and analysis of ultra-diffuse galaxy spectroscopic properties. Mon. Notices R. Astronomical Soc. 531, 1856–1869. doi:10.1093/mnras/stae1287
Gannon, J. S., Forbes, D. A., Romanowsky, A. J., Ferré-Mateu, A., Couch, W. J., Brodie, J. P., et al. (2022). Ultra-diffuse galaxies in the perseus cluster: comparing galaxy properties with globular cluster system richness, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 510, 946–958. doi:10.1093/mnras/stab3297
Geach, J. E., Dunlop, J. S., Halpern, M., Smail, I., van der Werf, P., Alexander, D. M., et al. (2016). The scuba-2 cosmology legacy survey: 850 m maps, catalogues and number counts. MNRAS 465, 1789–1806. doi:10.1093/mnras/stw2721
Greco, J. P., Greene, J. E., Price-Whelan, A. M., Leauthaud, A., Huang, S., Goulding, A. D., et al. (2018a). Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. Nihon. Tenmon. Gakkai., 70, S19. doi:10.1093/pasj/psx051
Greco, J. P., Greene, J. E., Strauss, M. A., Macarthur, L. A., Flowers, X., Goulding, A. D., et al. (2018b). Illuminating low surface brightness galaxies with the hyper suprime-cam survey. Survey 857, 104. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aab842
Gu, M., Conroy, C., Law, D., van Dokkum, P., Yan, R., Wake, D., et al. (2018). Low metallicities and old ages for three ultra-diffuse galaxies in the coma cluster, Astrophys. J., 859, 37. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aabbae
Heywood, I., Ponomareva, A. A., Maddox, N., Jarvis, M. J., Frank, B. S., Adams, E. A. K., et al. (2024). Mightee-hi: deep spectral line observations of the cosmos field. Mon. Notices R. Astronomical Soc. 534, 76–96. doi:10.1093/mnras/stae2081
Impey, C., and Bothun, G. (1997). Low surface brightness. Galaxies 35, 267–307. doi:10.1146/annurev.astro.35.1.267
Iodice, E., Cantiello, M., Hilker, M., Rejkuba, M., Arnaboldi, M., Spavone, M., et al. (2020). The first detection of ultra-diffuse galaxies in the Hydra I cluster from the VEGAS survey. first Detect. ultra-diffuse galaxies Hydra I Clust. VEGAS Surv. 642, A48. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202038523
Iodice, E., Hilker, M., Doll, G., Mirabile, M., Buttitta, C., Hartke, J., et al. (2023). Looking into the faintEst WIth MUSE (LEWIS): exploring the nature of ultra-diffuse galaxies in the Hydra-I cluster. I. Project description and preliminary results. 679, A69. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202347129
Janssens, S., Abraham, R., Brodie, J., Forbes, D., Romanowsky, A. J., and van Dokkum, P. (2017). Ultra-diffuse and ultra-compact galaxies in the frontier fields cluster abell 2744, Astrophys. J. Lett., 839, L17. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa667d
Janssens, S. R., Abraham, R., Brodie, J., Forbes, D. A., and Romanowsky, A. J. (2019). The distribution of ultra-diffuse and ultra-compact galaxies in the frontier fields, Astrophys. J., 887, 92. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab536c
Jones, M. G., Verdes-Montenegro, L., Moldon, J., Damas Segovia, A., Borthakur, S., Luna, S., et al. (2023). Disturb. diffuse, or just missing? A Glob. study H I content Hickson compact groups 670, A21. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202244622
Kadowaki, J., Zaritsky, D., and Donnerstein, R. L. (2017). Spectroscopy of ultra-diffuse galaxies in the coma cluster, Astrophys. J. Lett., 838, L21. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa653d
Karunakaran, A., Motiwala, K., Spekkens, K., Zaritsky, D., Donnerstein, R. L., and Dey, A. (2024). Systematically measuring ultradiffuse galaxies. VII. The H i survey overview. VII. H I Surv. Overv. 975, 91. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ad77cf
Karunakaran, A., Spekkens, K., Zaritsky, D., Donnerstein, R. L., Kadowaki, J., and Dey, A. (2020). Systematically measuring ultradiffuse galaxies in H i: results from the pilot survey, Astrophys. J., 902, 39. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/abb464
Khim, D. J., Zaritsky, D., Lambert, M., and Donnerstein, R. (2024). Properties of nuclear star clusters in low surface brightness galaxies. Galaxies 168, 45. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ad4ed3
Kirby, E. N., Cohen, J. G., Guhathakurta, P., Cheng, L., Bullock, J. S., and Gallazzi, A. (2013). The universal stellar mass-stellar metallicity relation for dwarf. Galaxies 779, 102. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/779/2/102
Koda, J., Yagi, M., Yamanoi, H., and Komiyama, Y. (2015). Astrophys. J., 807, L2. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/807/1/L2
Kravtsov, A. (2024). On the dark matter content of ultra-diffuse galaxies. Open J. Astrophysics 7, 117. doi:10.33232/001c.127487
Laigle, C., McCracken, H. J., Ilbert, O., Hsieh, B. C., Davidzon, I., Capak, P., et al. (2016). The cosmos2015 catalog: exploring the 1 < z < 6 universe with half a million galaxies, Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser., 224, 24. doi:10.3847/0067-0049/224/2/24
La Marca, A., Iodice, E., Cantiello, M., Forbes, D. A., Rejkuba, M., Hilker, M., et al. (2022a). Galaxy populations in the Hydra I cluster from the VEGAS survey. II. ultra-diffuse galaxy Popul. 665, A105. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202142367
La Marca, A., Peletier, R., Iodice, E., Paolillo, M., Choque Challapa, N., Venhola, A., et al. (2022b). Galaxy populations in the Hydra I cluster from the VEGAS survey: I. Optical properties of a large sample of dwarf galaxies. Opt. Prop. a large sample dwarf galaxies 659, A92. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202141901
Lambert, M., Khim, D. J., Zaritsky, D., and Donnerstein, R. (2024). Systematically measuring ultra-diffuse galaxies (SMUDGes). VI. Nuclear star clusters. Vi. Nucl. Star. Clust. 167, 61. doi:10.3847/1538-3881/ad0f25
Lee, J. H., Kang, J., Lee, M. G., and Jang, I. S. (2020). The nature of ultra-diffuse galaxies in distant massive galaxy clusters: a370 in the hubble frontier fields, Astrophys. J., 894, 75. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab8632
Lee, M. G., Kang, J., Lee, J. H., and Jang, I. S. (2017). Detection of a large population of ultradiffuse galaxies in massive galaxy clusters: abell S1063 and abell 2744, Astrophys. J., 844, 157. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aa78fb
Leisman, L., Haynes, M. P., Janowiecki, S., Hallenbeck, G., Józsa, G., Giovanelli, R., et al. (2017). (Almost) dark galaxies in the ALFALFA survey: isolated H i-bearing ultra-diffuse galaxies. Galaxies 842, 133. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aa7575
Leja, J., Johnson, B. D., Conroy, C., van Dokkum, P., Speagle, J. S., Brammer, G., et al. (2019). An older, more quiescent universe from panchromatic SED fitting of the 3D-HST survey. Survey 877, 140. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab1d5a
Leja, J., Johnson, B. D., Conroy, C., van Dokkum, P. G., and Byler, N. (2017). Deriving physical properties from broadband photometry with prospector: description of the model and a demonstration of its accuracy using 129 galaxies in the local universe, Astrophys. J., 837, 170. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aa5ffe
Levy, L., Rose, J. A., van Gorkom, J. H., and Chaboyer, B. (2007). The effect of cluster environment on galaxy evolution in the pegasus I cluster, Astron. J., 133, 1104–1124. doi:10.1086/510723
Lilly, S. J., Le Fèvre, O., Renzini, A., Zamorani, G., Scodeggio, M., Contini, T., et al. (2007). zCOSMOS: a large VLT/VIMOS redshift survey covering 0 <z< 3 in the COSMOS field, Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser., 172, 70–85. doi:10.1086/516589
Lim, S., Peng, E. W., Côté, P., Sales, L. V., den Brok, M., Blakeslee, J. P., et al. (2018). The globular cluster systems of ultra-diffuse galaxies in the coma cluster, Astrophys. J., 862, 82. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aacb81
Liu, Y., Peng, E. W., Blakeslee, J., Côté, P., Ferrarese, L., Jordán, A., et al. (2016). Evidence for the rapid formation of low-mass early-type galaxies in dense. Environments 818, 179. doi:10.3847/0004-637X/818/2/179
Ma, X., Hopkins, P. F., Faucher-Giguère, C.-A., Zolman, N., Muratov, A. L., Kereš, D., et al. (2016). The origin and evolution of the galaxy mass–metallicity relation, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 456, 2140–2156. doi:10.1093/mnras/stv2659
Marleau, F. R., Duc, P.-A., Poulain, M., Müller, O., Lim, S., Durrell, P. R., et al. (2024). Dwarf galaxies in the MATLAS Survey: hubble Space Telescope observations of the globular cluster systems of 74 ultra-diffuse galaxies. Dwarf galaxies MATLAS Surv. Hubble Space Telesc. observations Globul. Clust. Syst. 74 ultra-diffuse galaxies 690, A339. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202449617
Martin, G., Bazkiaei, A. E., Spavone, M., Iodice, E., Mihos, J. C., Montes, M., et al. (2022). Preparing for low surface brightness science with the Vera C. Rubin Observatory: characterization of tidal features from mock images. Rubin Observatory Charact. tidal Featur. mock images 513, 1459–1487. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac1003
Martínez-Delgado, D., Läsker, R., Sharina, M., Toloba, E., Fliri, J., Beaton, R., et al. (2016). Astron. J., 151, 96. doi:10.3847/0004-6256/151/4/96
McCracken, H. J., Capak, P., Salvato, M., Aussel, H., Thompson, D., Daddi, E., et al. (2010). The COSMOS-WIRCam NEAR-INFRARED imaging survey. I.BzK-SELECTED passive and STAR-FORMING galaxy candidates ATz- 1.4. BzK-Selected Passive Star-Forming Galaxy Candidates A. T. z gsim 1.4 708, 202–217. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/708/1/202
McCracken, H. J., Milvang-Jensen, B., Dunlop, J., Franx, M., Fynbo, J. P. U., Le Fèvre, O., et al. (2012). UltraVISTA: a new ultra-deep near-infrared survey in COSMOS. UltraVISTA a new ultra-deep near-infrared Surv. COSMOS 544, A156. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219507
Merritt, A., van Dokkum, P., Danieli, S., Abraham, R., Zhang, J., Karachentsev, I. D., et al. (2016). The dragonfly nearby galaxies survey. II. Ultra-Diffuse Galaxies near Elliptical Galaxy NGC 833, 168. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/833/2/168
Michałowski, M. J., Dunlop, J. S., Koprowski, M. P., Cirasuolo, M., Geach, J. E., Bowler, R. A. A., et al. (2017). The scuba-2 cosmology legacy survey: the nature of bright submm galaxies from 2 deg2 of 850-m imaging. MNRAS 469, 492–515. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx861
Mihos, J. C., Durrell, P. R., Ferrarese, L., Feldmeier, J. J., Côté, P., Peng, E. W., et al. (2015). Astrophys. J., 809, L21. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/809/2/L21
Mihos, J. C., Harding, P., Feldmeier, J. J., Rudick, C., Janowiecki, S., Morrison, H., et al. (2017). The burrell schmidt deep Virgo survey: tidal debris, galaxy halos, and diffuse intracluster light in the Virgo cluster. Astrophys. J. 834, 16. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/834/1/16
Momcheva, I. G., Brammer, G. B., van Dokkum, P. G., Skelton, R. E., Whitaker, K. E., Nelson, E. J., et al. (2016). The 3d-hst survey: hubble space telescope wfc3/g141 grism spectra, redshifts, and emission line measurements for -100,000 galaxies. 000 Galaxies 225, 27. doi:10.3847/0067-0049/225/2/27
Montes, M., Annibali, F., Bellazzini, M., Borlaff, A. S., Brough, S., Buitrago, F., et al. (2023). Optimizing roman’s high latitude wide area survey for low surface brightness astronomy. doi:10.48550/arXiv.2306.09414
Montes, M., Infante-Sainz, R., Madrigal-Aguado, A., Román, J., Monelli, M., Borlaff, A. S., et al. (2020). The galaxy “missing dark matter” NGC 1052-DF4 is undergoing tidal disruption. NGC 1052-DF4 is Undergoing Tidal Disrupt. 904, 114. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/abc340
Montes, M., Trujillo, I., Karunakaran, A., Infante-Sainz, R., Spekkens, K., Golini, G., et al. (2024). An almost dark galaxy with the mass of the Small Magellanic Cloud. 681, A15. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202347667
Müller, O., Jerjen, H., and Binggeli, B. (2018). The Leo-I group: new dwarf galaxy and ultra diffuse galaxy candidates. Leo-I group new dwarf galaxy ultra diffuse galaxy candidates 615, A105. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201832897
Muñoz, R. P., Eigenthaler, P., Puzia, T. H., Taylor, M. A., Ordenes-Briceño, Y., Alamo-Martínez, K., et al. (2015). Astrophys. J., 813, L15. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/813/1/L15
Ogiya, G. (2018). Tidal stripping as a possible origin of the ultra diffuse galaxy lacking dark matter. Tidal stripping as a possible Orig. ultra diffuse galaxy lacking dark matter 480, L106–L110. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/sly138
Ordenes-Briceño, Y., Taylor, M. A., Puzia, T. H., Muñoz, R. P., Eigenthaler, P., Georgiev, I. Y., et al. (2016). Faint dwarf galaxies in hickson compact group 90, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 463, 1284–1290. doi:10.1093/mnras/stw2066
Pan, H., Jarvis, M. J., Zhu, M., Ma, Y.-Z., Santos, M. G., Ponomareva, A. A., et al. (2024). Deep extragalactic H i survey of the COSMOS field with FAST, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 534, 202–214. doi:10.1093/mnras/stae2054
Pandya, V., Romanowsky, A. J., Laine, S., Brodie, J. P., Johnson, B. D., Glaccum, W., et al. (2018). The stellar populations of two ultra-diffuse galaxies from optical and near-infrared photometry, Astrophys. J., 858, 29. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aab498
Papastergis, E., Adams, E. A. K., and Romanowsky, A. J. (2017). HI content Isol. ultra-diffuse galaxies A sign multiple Form. mechanisms? 601, L10. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201730795
Peng, C. Y., Ho, L. C., Impey, C. D., and Rix, H.-W. (2002). Detailed structural decomposition of galaxy images, Astron. J., 124, 266–293. doi:10.1086/340952
Peng, C. Y., Ho, L. C., Impey, C. D., and Rix, H.-W. (2010). Detailed decomposition of galaxy images. II. Beyond Axisymmetric Models 139, 2097–2129. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/139/6/2097
Peng, E. W., and Lim, S. (2016). A rich globular cluster system in dragonfly 17: are ultra-diffuse galaxies pure stellar halos?* Astrophys. J. Lett., 822, L31. doi:10.3847/2041-8205/822/2/L31
Piña, P. E. M., Fraternali, F., Adams, E. A. K., Marasco, A., Oosterloo, T., Oman, K. A., et al. (2019). Off the baryonic tully–Fisher relation: a population of baryon-dominated ultra-diffuse galaxies. Astrophysical J. Lett. 883, L33. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab40c7
Polzin, A., van Dokkum, P., Danieli, S., Greco, J. P., and Romanowsky, A. J. (2021). A recently quenched isolated dwarf galaxy outside of the local group environment, Astrophys. J. Lett., 914, L23. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac024f
Prole, D. J., van der Burg, R. F. J., Hilker, M., and Davies, J. I. (2019). Observational properties of ultra-diffuse galaxies in low-density environments: field UDGs are predominantly blue and star forming, 488, 2143–2157. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz1843
Robertson, B. E., Banerji, M., Cooper, M. C., Davies, R., Driver, S. P., Ferguson, A. M. N., et al. (2017). Large synoptic survey telescope galaxies science roadmap. arXiv e-prints. arXiv:1708.01617. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1708.01617
Román, J., Beasley, M. A., Ruiz-Lara, T., and Valls-Gabaud, D. (2019). Discovery of a red ultra-diffuse galaxy in a nearby void based on its globular cluster luminosity function, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 486, 823–835. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz835
Román, J., and Trujillo, I. (2017a). Spatial distribution of ultra-diffuse galaxies within large-scale structures. scale Struct. 468, 703–716. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx438
Román, J., and Trujillo, I. (2017b). Ultra-diffuse galaxies outside clusters: clues to their formation and evolution, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 468, 4039–4047. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx694
Rong, Y., Guo, Q., Gao, L., Liao, S., Xie, L., Puzia, T. H., et al. (2017). A Universe of ultradiffuse galaxies: theoretical predictions from ΛCDM simulations, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 470, 4231–4240. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx1440
Rong, Y., Zhu, K., Johnston, E. J., Zhang, H.-X., Cao, T., Puzia, T. H., et al. (2020). Lessons on star-forming ultra-diffuse galaxies from the stacked spectra of the sloan digital sky survey. Survey 899, L12. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aba8aa
Ruiz-Lara, T., Beasley, M. A., Falcón-Barroso, J., Román, J., Pinna, F., Brook, C., et al. (2018). Spectroscopic characterization of the stellar content of ultra-diffuse galaxies, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 478, 2034–2045. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty1112
Sales, L. V., Navarro, J. F., Peñafiel, L., Peng, E. W., Lim, S., and Hernquist, L. (2020). The formation of ultradiffuse galaxies in clusters, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 494, 1848–1858. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa854
Sanders, D. B., Salvato, M., Aussel, H., Ilbert, O., Scoville, N., Surace, J. A., et al. (2007). S-COSMOS: the spitzer legacy survey of the hubble space telescope ACS 2 deg 2 COSMOS field I: survey strategy and first analysis, Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser., 172, 86–98. doi:10.1086/517885
Schinnerer, E., Smolčić, V., Carilli, C. L., Bondi, M., Ciliegi, P., Jahnke, K., et al. (2007). The vla-cosmos survey. ii. source catalog of the large project. ApJS 172, 46–69. doi:10.1086/516587
Shen, Z., Bowman, W. P., van Dokkum, P., Abraham, R. G., Pasha, I., Keim, M. A., et al. (2024). First results from the dragonfly ultrawide survey: the largest 11 quenched diffuse dwarf galaxies in 3100 deg2 with spectroscopic confirmation, Astrophys. J., 976, 75. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ad84e2
Shen, Z., Danieli, S., van Dokkum, P., Abraham, R., Brodie, J. P., Conroy, C., et al. (2021). A tip of the red giant branch distance of 22.1 ± 1.2 Mpc to the dark matter deficient galaxy NGC 1052–DF2 from 40 orbits of hubble space telescope imaging, Astrophys. J. Lett., 914, L12. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac0335
Shi, D. D., Zheng, X. Z., Zhao, H. B., Lou, Z., Wang, H. R., Qian, Y., et al. (2018). A study of detector response and filter optimization for the wide field survey telescope. Acta Astron. Sin. 59, 22. doi:10.15940/j.cnki.0001-5245.2018.03.001
Shi, D. D., Zheng, X. Z., Zhao, H. B., Pan, Z. Z., Li, B., Zou, H., et al. (2017). Deep imaging of the HCG 95 field. I. Ultra-Diffuse galaxies. I. Ultra-diffuse Galaxies 846, 26. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aa8327
Smith Castelli, A. V., Faifer, F. R., and Escudero, C. G. (2016). Stellar systems in the direction of the Hickson Compact Group 44: I. Low surface brightness galaxies. Low. Surf. Bright. galaxies 596, A23. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201628969
Somalwar, J. J., Greene, J. E., Greco, J. P., Huang, S., Beaton, R. L., Goulding, A. D., et al. (2020). Hyper suprime-cam low surface brightness galaxies. II. A hubble space telescope study of the globular cluster systems of ultradiffuse galaxies in groups*. A Hubble Space Telesc. Study Globul. Clust. Syst. Ultradiffuse Galaxies Groups 902, 45. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/abb1b2
Spekkens, K., and Karunakaran, A. (2018). Atomic gas in blue ultra diffuse galaxies around hickson compact groups. Astrophys. J. 855, 28. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aa94be
Taniguchi, Y., Scoville, N., Murayama, T., Sanders, D. B., Mobasher, B., Aussel, H., et al. (2007). The cosmic evolution survey (COSMOS): Subaru observations of the HST cosmos field. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 172, 9–28. doi:10.1086/516596
Toloba, E., Lim, S., Peng, E., Sales, L. V., Guhathakurta, P., Mihos, J. C., et al. (2018). Dark matter in ultra-diffuse galaxies in the Virgo cluster from their globular cluster populations. Astrophys. J. Lett. 856, L31. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aab603
Tremmel, M., Wright, A. C., Brooks, A. M., Munshi, F., Nagai, D., and Quinn, T. R. (2020). The formation of ultradiffuse galaxies in the RomulusC galaxy cluster simulation. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 497, 2786–2810. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa2015
Trujillo, I., Beasley, M. A., Borlaff, A., Carrasco, E. R., Di Cintio, A., Filho, M., et al. (2019). A distance of 13 Mpc resolves the claimed anomalies of the galaxy lacking dark matter. matter 486, 1192–1219. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz771
Trujillo, I., Roman, J., Filho, M., and Sánchez Almeida, J. (2017). The nearest ultra diffuse galaxy: UGC 2162. Astrophys. J. 836, 191. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aa5cbb
van der Burg, R. F. J., Hoekstra, H., Muzzin, A., Sifón, C., Viola, M., Bremer, M. N., et al. (2017). The abundance of ultra-diffuse galaxies from groups to clusters. UDGs are Relat. more common more massive haloes 607, A79. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201731335
van der Burg, R. F. J., Muzzin, A., and Hoekstra, H. (2016). The abundance and spatial distribution of ultra-diffuse galaxies in nearby galaxy clusters. 590, A20. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201628222
van Dokkum, P., Abraham, R., Brodie, J., Conroy, C., Danieli, S., Merritt, A., et al. (2016). A high stellar velocity dispersion and -100 globular clusters for the ultra-diffuse galaxy dragonfly. Astrophys. J. Lett. 44, L6. doi:10.3847/2041-8205/828/1/L6
van Dokkum, P., Abraham, R., Romanowsky, A. J., Brodie, J., Conroy, C., Danieli, S., et al. (2017). Extensive globular cluster systems associated with ultra diffuse galaxies in the coma cluster. Astrophys. J. Lett. 844, L11. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa7ca2
van Dokkum, P., Brammer, G., Momcheva, I., Skelton, R. E., and Whitaker, K. E. (2013). 3D-HST data release v3.0: extremely deep spectra in the UDF and WFC3 mosaics in the 3D-HST/CANDELS fields. arXiv e-prints , arXiv:1305.2140. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1305.2140
van Dokkum, P., Danieli, S., Abraham, R., Conroy, C., and Romanowsky, A. J. (2019). A second galaxy missing dark matter in the NGC 1052 group. Astrophys. J. Lett. 874, L5. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab0d92
van Dokkum, P., Danieli, S., Cohen, Y., Merritt, A., Romanowsky, A. J., Abraham, R., et al. (2018a). A galaxy lacking dark matter. , 555, 629–632. doi:10.1038/nature25767
van Dokkum, P., Danieli, S., Cohen, Y., Romanowsky, A. J., and Conroy, C. (2018b). The distance of the dark matter deficient galaxy NGC 1052-DF2. Astrophys. J. Lett. 864, L18. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aada4d
van Dokkum, P., Shen, Z., Keim, M. A., Trujillo-Gomez, S., Danieli, S., Dutta Chowdhury, D., et al. (2022). A trail of dark-matter-free galaxies from a bullet-dwarf collision, 605, 435–439. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04665-6
van Dokkum, P. G., Abraham, R., Merritt, A., Zhang, J., Geha, M., and Conroy, C. (2015a). “Forty-seven Milky way-sized,”. Astrophys. J. 798. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/798/2/L45
van Dokkum, P. G., Romanowsky, A. J., Abraham, R., Brodie, J. P., Conroy, C., Geha, M., et al. (2015b). Spectroscopic confirmation of the existence of large. Diffuse Galaxies Coma Clust. 804, L26. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/804/1/L26
Venhola, A., Peletier, R. F., Salo, H., Laurikainen, E., Janz, J., Haigh, C., et al. (2022). The fornax deep survey with the VST. XII. Low Surf. Bright. dwarf galaxies Fornax Clust. 662, A43. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202141756
Villaume, A., Romanowsky, A. J., Brodie, J., van Dokkum, P., Conroy, C., Forbes, D. A., et al. (2022). Spatially resolved stellar spectroscopy of the ultra-diffuse galaxy dragonfly 44. iii. evidence for an unexpected star formation history under conventional galaxy evolution processes. Astrophysical J. 924, 32. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac341e
Wang, T., Liu, G., Cai, Z., Geng, J., Fang, M., He, H., et al. (2023). Science with the 2.5-meter wide field survey telescope (WFST). Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astronomy 66, 109512. doi:10.1007/s11433-023-2197-5
Wittmann, C., Lisker, T., Ambachew Tilahun, L., Grebel, E. K., Conselice, C. J., Penny, S., et al. (2017). A population of faint low surface brightness galaxies in the Perseus cluster core. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 470, 1512–1525. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx1229
Yagi, M., Koda, J., Komiyama, Y., and Yamanoi, H. (2016). Catalog of ultra-diffuse galaxies in the coma clusters from Subaru imaging data. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 225, 11. doi:10.3847/0067-0049/225/1/11
Zahid, H. J., Kudritzki, R.-P., Conroy, C., Andrews, B., and Ho, I. T. (2017). Stellar absorption line analysis of local star-forming galaxies: the relation between stellar mass, metallicity. Dust Attenuation, Star Form. Rate 847, 18. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aa88ae
Zamojski, M. A., Schiminovich, D., Rich, R. M., Mobasher, B., Koekemoer, A. M., Capak, P., et al. (2007). Deep GALEX imaging of the COSMOS HST field: a first look at the morphology of z - 0.7 star-forming galaxies. 7 Star-forming Galaxies 172, 468–493. doi:10.1086/516593
Zaritsky, D., Donnerstein, R., Dey, A., Karunakaran, A., Kadowaki, J., Khim, D. J., et al. (2023). Systematically measuring ultra-diffuse galaxies (SMUDGes). V. The complete SMUDGes catalog and the nature of ultradiffuse galaxies. V. Complete SMUDGes Catalog Nat. Ultradiffuse Galaxies 267, 27. doi:10.3847/1538-4365/acdd71
Keywords: galaxy formation, galaxy evolution, COSMOS field, ultra-diffuse galaxies, dwarf galaxies, extragalactic astronomy
Citation: Shi DD, Zheng XZ, Pan Z, Luo Y, Deng H, Hua Q, Luo X and Wu Q (2025) Searching for nearby diffuse dwarf galaxies in the COSMOS field. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 12:1560380. doi: 10.3389/fspas.2025.1560380
Received: 14 January 2025; Accepted: 12 February 2025;
Published: 05 March 2025.
Edited by:
Mauro D’Onofrio, University of Padua, ItalyReviewed by:
Daniela Bettoni, Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova (INAF), ItalyCopyright © 2025 Shi, Zheng, Pan, Luo, Deng, Hua, Luo and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dong Dong Shi, ZGRzaGlAYXVzdC5lZHUuY24=; Xian Zhong Zheng, eHp6aGVuZ0BzanR1LmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.