
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Anim. Sci. , 31 March 2025
Sec. Animal Nutrition
Volume 6 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fanim.2025.1562527
 Peter A. Idowu*†
Peter A. Idowu*† Takalani J. Mpofu†
Takalani J. Mpofu† Aletta M. Magoro†
Aletta M. Magoro† Mamokoma C. Modiba†
Mamokoma C. Modiba† Khathutshelo A. Nephawe†
Khathutshelo A. Nephawe† Bohani Mtileni†
Bohani Mtileni†The poultry industry is continuously seeking strategies to improve chicken health, welfare, and productivity while minimizing the use of antibiotics. Probiotics, as a natural alternative, have gained considerable attention due to their ability to modulate the gut microbiota, enhance immune function, and improve productive performance. The aim of this article is to provide updated information on the importance of probiotics in chicken. To achieve this, a systematic review was conducted to synthesize current findings on the impact of probiotics on chicken gut microbiota composition, immune responses, behavior, productive traits, and meat quality using literature databases such as PubMed, CABI Abstract, Google Scholar, and ScienceDirect from April 2010. The PRISMA method was adopted, where 85 articles met the criteria for this review article after several exclusion criteria. The review stated that due to the influence of the intestinal microbial balance, probiotics promote beneficial bacterial populations, suppress pathogens, improve gut health, and enhance nutrient absorption, improving growth performance. Additionally, the immunomodulatory effects of probiotics help strengthen the chicken’s immune system, reducing disease susceptibility. Moreover, recent studies suggest that probiotics may positively influence chicken behavior, particularly by reducing stress, enhancing overall health, and improving welfare conditions. This review also addresses gaps in knowledge, highlighting areas where further research is needed to optimize probiotic use in poultry production systems. Understanding both the short- and long-term effects of probiotics on chicken health and performance will provide critical insights for developing sustainable strategies to boost poultry industry outcomes.
Chickens are considered monogastric, meaning they have a single-chambered stomach also known as the gastrointestinal tract (GIT) (Varastegani and Dahlan, 2014). The GIT of chickens is divided into three sections: the upper segment/gizzard, where food is broken into smaller units; the small intestine, which assists with digestion and nutrient absorption; and the large intestine, with the primary function to absorb water, dry out indigestible foods, and expel waste items (Borda-Molina et al., 2018). All these segments are populated with microbiota that aid in digestion and nutrient absorption (Borda-Molina et al., 2018). These microbiota form a symbiotic relationship with the chicken gut, which is essential for poultry health and production (Shang et al., 2018).
The activity of gut microbiota in digestion and absorption of nutrients is mostly through the process of breaking down complex nutrients into more digestible and absorbable forms in chickens (Apajalahti and Vienola, 2016).
Furthermore, microbiota sustain the wellbeing of chickens by regulating several physiological processes, such as immunity, metabolism, and nutrition (Diaz-Carrasco et al., 2019). As mentioned earlier, the majority of these microbiota are found in the glandular stomach/gizzard, ileum, cecum, and colon with different functions (Stanley et al., 2014). Chickens develop resistance to bacterial infections such as pathogenic Escherichia coli, Clostridium perfringens, and Salmonella spp. due to millions of microbiota colonization present in the gut such as Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Proteobacteria (Rychlik, 2020).
To maintain microbiota integrity, several probiotics have been used as dietary supplements with great therapeutic likelihood and capacity to reduce stress, emotions, and feeding habits, which in turn improves productivity. The recent definition of probiotics by the International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) stated that probiotics are “living microorganisms that give the host health benefits when given in the right proportion” (Salminen et al., 2021).
Probiotics, also known to be biofriendly agents or psychobiotics, are widely used as a dietary supplement to target the microbiome “community of microorganisms found in the GIT of chickens” (Puri et al., 2023). This approach is emerging as a promising therapeutic strategy for various diseases, heat stress modulators, productivity enhancers, and treatments for diseases in chickens.
The findings from several studies established that probiotics influence chicken’s behavioral patterns, immune cells and function, stress resistance, and productivity (Gadde et al., 2017; Jiang et al., 2022; Puri et al., 2023). Precisely, the actions of probiotics are influenced by the specificity of the probiotic strain, its concentration or dosage, and duration of use, as well as the host’s age and health condition among other factors.
Over the past few years, probiotics have gained significant attention and are considered as a safe and viable alternative to commercial antibiotics. This review highlights the importance of probiotics on chicken gut microbiota, immunity, behavior, and productive performance. It aims to provide insights into the current findings, mechanisms of action, blueprints of probiotics, and the growing necessity of probiotics as a crucial alternative to antibiotics in global poultry production.
This systematic review aimed to compile and critically analyze the available data on the use of probiotics in poultry, focusing on their impact on performance, immunity, behavior, and gut health in chickens (Figure 1). Relevant studies were identified through electronic search engines—PubMed, CABI Abstract, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar—using the following keywords: “(‘probiotics’ OR ‘probiotic supplements’ OR ‘Lactobacillus’ OR ‘Bacillus’ OR ‘Streptococcus’ OR ‘Bifidobacterium’)” AND “(‘gut microbiota’ OR ‘intestinal microbiota’)” AND “(‘chickens’ OR ‘broilers’ OR ‘layers’) AND “(‘immunity’ OR ‘immune response’) AND “(‘behavior’ OR ‘feeding behavior’)” AND “(‘productive performance’ OR ‘growth performance’).” The inclusion criteria were as follows: studies involving chickens—broilers, layers, and poultry in general (population); administration of probiotics as a supplement, either alone or in combination with other substances (intervention); studies that include a control group [placebo, no probiotics, or different probiotic doses (comparators)]; studies reporting the effects of probiotics on i) gut microbiota, ii) immunity, iii) behavior, and iv) productive performance (outcomes); studies using randomized controlled trials (RCTs), controlled trials, observational studies, cohort studies, and longitudinal studies (study design); articles written in the English language; and studies published from 2010 onward to capture the latest research developments (publication date). The exclusion criteria were studies conducted on other species. Also, conference abstracts; commentaries; reviews; studies that do not measure at least one of the four key outcomes (gut microbiota, immunity, behavior, or productivity). Studies on combinations of probiotics with antibiotics, the use of synbiotics, and the use of unspecified prebiotics and studies with significant biases as shown in Figure 1.
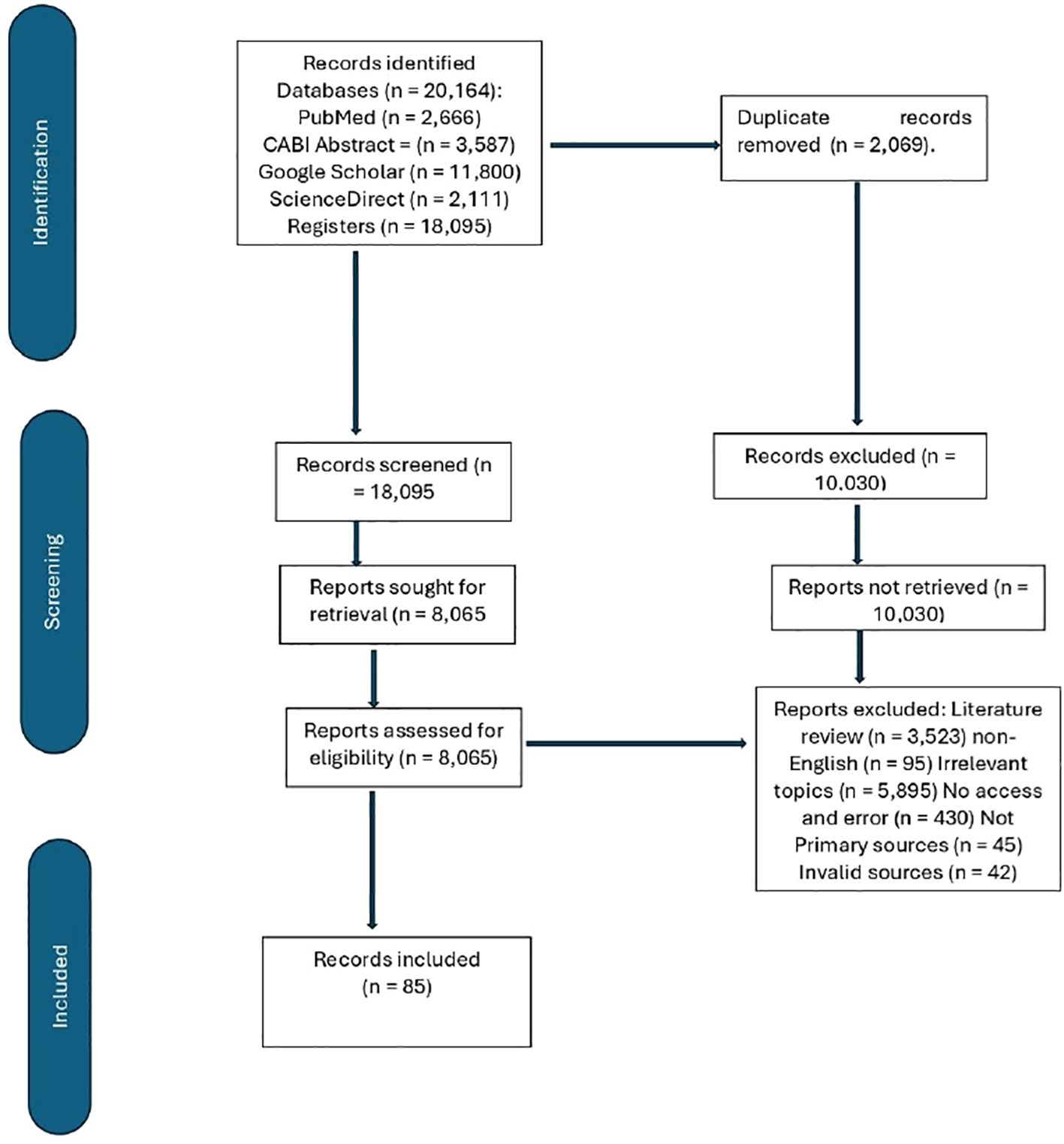
Figure 1. The PRISMA flowchart (Page et al., 2021).
Poultry production has become a major source of protein globally due to its accessibility, acceptance, and affordability (Idowu et al., 2019). However, poultry animals encounter challenges from environmental conditions and disease prevalence, which negatively affect their welfare and performance (Idowu et al., 2024). Traditionally, antibiotics have been used in commercial poultry production to enhance feed conversion, growth rates, and overall health, thereby increasing output and profitability. Nonetheless, the excessive use of antibiotics for prophylactic and nutritional purposes has raised concerns about antimicrobial resistance, prompting some countries to prohibit their use (Idowu et al., 2021; Summers et al., 2022).
In response to these challenges, many nations are exploring alternatives to antibiotics, with probiotics emerging as a promising option. Probiotics are living microorganisms that can serve as a substitute for antibiotics by enhancing the gastrointestinal microbiota of host animals when administered in appropriate quantities (Silva et al., 2020; Summers et al., 2022). Research indicates that probiotics can inhibit pathogen colonization, stimulate the immune system, and produce antimicrobial metabolites (Yadav and Jha, 2019). They also create an environment conducive to beneficial organisms by adhering to intestinal epithelium, which helps lower pH and neutralizes toxins (Rodjan et al., 2018). This results in improved nutrient absorption as probiotics increase the absorptive surface area of the intestinal mucosa (Martinez-Guryn et al., 2018).
Probiotics enhance nutrient absorption through several mechanisms. They colonize and adhere to the intestinal mucosa, particularly in the small intestine where villi maximize the surface area (Plaza-Diaz et al., 2019), fostering a beneficial habitat by interacting with the protective mucus layer (Plaza-Diaz et al., 2019). This adhesion is facilitated by surface molecules like mucus-binding proteins, enabling effective colonization and competition with pathogens (Collado et al., 2010).
Additionally, probiotics stimulate epithelial cell proliferation, promoting villi growth and enhancing nutrient absorption (Wang et al., 2017). They maintain gut barrier integrity by increasing mucus production and reinforcing tight junctions between epithelial cells. This ensures efficient nutrient uptake while blocking harmful substances (Collado et al., 2010; Wang et al., 2017). By reducing inflammation that can damage intestinal villi, probiotics support overall gut health and function in poultry.
The impact of probiotics on immune function and growth is also well-documented. Dong et al. (2012) observed that Lactobacillus strains enhanced T helper 1 (Th1) cytokine activity, while Bifidobacterium strains promoted anti-inflammatory immune responses. In terms of growth performance, Zaghari et al. (2020) demonstrated that Bacillus licheniformis supplementation (1 × 10⁹ CFU/g) at 0.5 g/kg significantly outperformed Bacillus subtilis in improving body weight gain (BWG) in chickens (2,580.70 g vs. 2,427.45 g). The B. licheniformis group also achieved a higher production efficiency factor (418.95 vs. 374.49), lower feed costs per kilogram of weight gain, and the highest return on investment. Additionally, B. licheniformis showed superior nutrient digestibility and significantly reduced ileal pH. Hossain et al. (2024) reported that lyophilized probiotic supplementation led to improved BWG, feed intake, and feed conversion ratio (FCR) compared to antibiotic-fed groups. In addition to these benefits, Xu et al. (2023) highlighted dynamic changes in gut microbiota composition during different laying periods, and Soumeh et al. (2021) found that Bacillus spp. reduced the levels of Bacteroides fragilis, a marker for antimicrobial resistance. This indicates the potential of probiotics to support performance and gut health in poultry farming.
Given the ban on antibiotics as growth promoters, the production and use of probiotics have garnered significant attention (Wan et al., 2019). However, the efficacy of probiotics can be influenced by factors such as age, nutrition, stress, and health status, all of which directly affect the gut microbiota’s physical and chemical composition, leading to dysbiosis and gastrointestinal issues (Shang et al., 2018; Rama et al., 2023). Furthermore, probiotics may be less effective under certain conditions: high temperatures can reduce the viability of live cultures (Ahmed et al., 2024); alkaline environments with high pH levels can hinder their effectiveness (Al-khalaifa et al., 2019); insufficient dietary fiber can impact their function (Singh et al., 2015); and the presence of antibiotics can diminish their efficacy (Jankowski et al., 2022). While some studies show that specific probiotics improve gut health and growth performance under stress, Cengiz et al. (2015) observed that they may not significantly reduce oxidative stress or chronic heat stress.
Therefore, to be effective, a probiotic must be non-pathogenic and non-toxic (Kesen and Aiyegoro, 2018), promote growth of gut microbiota such as Lactobacillus johnsonii BS15 (Wang et al., 2017), possess productive traits (Agustono et al., 2022), resist pathogenic diseases (Raheem et al., 2021; Rabetafika et al., 2023), and maintain a favorable gut environment by inhibiting low pH levels from stomach acids and organic compounds (Rodjan et al., 2018). As the poultry industry seeks sustainable solutions for improving animal health and productivity without relying on antibiotics, the role of probiotics becomes increasingly significant in ensuring the welfare and performance of poultry.
Probiotics are non-pathogenic bacteria that colonize and multiply in the chicken’s GIT while engulfing pathogenic bacteria (Rabetafika et al., 2023). They are known to enhance the secretion of digestive enzymes such as phytase, amylase, and protease for nutrient digestion and absorption (Bedford and Apajalahti, 2022). Probiotics exert their beneficial effects primarily through several mechanisms.
Probiotics compete with pathogenic bacteria for space and resources in the gut, thereby reducing the likelihood of infections. Rabetafika et al. (2023) emphasize that probiotics can effectively engulf pathogenic bacteria, enhancing gut health. Probiotics are known to stimulate the secretion of digestive enzymes such as phytase, amylase, and protease, which are crucial for nutrient digestion and absorption (Bedford and Apajalahti, 2022). This enzymatic activity improves the overall efficiency of feed utilization in chickens.
Probiotic supplementation has been demonstrated to restore intestinal structures such as crypt depth and villus height, thereby enhancing nutrient absorption (Aruwa et al., 2021). Biswas et al. (2018) reported a significant increase in villus height, villus width, crypt depth, and the villus height-to-crypt depth ratio in broiler chickens on days 21 and 42 when their diet was supplemented with Lactobacillus acidophilus at 106 and 107 CFU/g. Similarly, in cases where excessive antibiotic use had compromised intestinal morphology, He et al. (2019) found that supplementing basal diets with a combination of probiotics, 500 mg/kg in phase 1 (days 0–21) and 300 mg/kg in phase 2 (days 21–42), containing B. subtilis (5 × 109 CFU/g), B. licheniformis (2.5 × 1010 CFU/g), and Saccharomyces cerevisiae (1 × 109 CFU/g) improved intestinal health. This was achieved by enhancing the villus height-to-crypt depth ratio, reinforcing the jejunal mucosal barrier, and optimizing intestinal structure. These findings highlight the potential of probiotic combinations to increase the absorptive surface area of the ileum and duodenum in broiler chickens. Several studies have consistently demonstrated that probiotics stimulate crypt cell proliferation in the small intestine, thereby supporting intestinal health (Cengiz et al., 2015; He et al., 2019; Chaudhari et al., 2020). A healthy intestinal structure is crucial for efficient nutrient absorption, maintaining gut integrity and promoting overall health and productivity in chickens. Probiotics are known to significantly influence the gut microbial landscape by enhancing microbial diversity, which correlates with improved gut health. This was demonstrated by Shahbaz et al. (2024), who isolated probiotic strains like Limosilactobacillus antri and Lactobacillus delbrueckii with resistance to bile salts and gastric acid, ensuring their viability in the gut. These probiotics not only promote a varied microbiota capable of outcompeting pathogens but also support essential physiological functions critical for intestinal homeostasis and overall chicken health (Diaz-Carrasco et al., 2019).
The adult chicken microbiota vary across different regions of the GIT. The crop is rich in lactic acid bacteria, particularly Lactobacillus, Enterococcus, and Gallibacterium. These bacteria aid in fermenting feed and producing beneficial byproducts like short-chain fatty acids, which are essential for energy metabolism (García-Amado et al., 2018). The presence of yeasts and potential pathogens can also be influenced by diet and health status. The gizzard microbiota are dominated by acid-tolerant bacteria such as Lactobacillus, contributing to feed grinding, though its microbial activity is limited compared to other segments (García-Amado et al., 2018). The small intestine is primarily populated by Lactobacillus, Enterococcus, E. coli, Bifidobacterium, and various yeast species. These microbiota adapt to dietary changes, facilitating nutrient absorption (Martinez-Guryn et al., 2018). Lastly, the cecal microbiota host a rich diversity of bacteria, including Lactobacillus, Clostridium, Faecalibacterium, Bacteroides, Prevotella, and some E. coli. These bacteria play critical roles in metabolic processes, such as converting uric acid to ammonia, which chickens utilize to produce amino acids like glutamine (Shang et al., 2018).
In certain situations, an imbalance in the normal gut microbiota of the small intestine may occur, either qualitatively or quantitatively. Specifically, beneficial microbes are reduced, while harmful or opportunistic microbes proliferate, disrupting gut health and overall wellbeing (Shang et al., 2018). This dysbiosis can result from environmental stressors, dietary imbalances, or selective breeding practices. It is associated with weakened intestinal barrier function such as thinning of the intestinal wall, decreased nutrient absorption, increased risk of bacterial translocation, and heightened inflammatory responses (Rama et al., 2023). Such an imbalance can promote the growth of pathogenic bacteria such as Salmonella and Campylobacter, which pose risks not only to chicken health but also to food safety (Shang et al., 2018).
To mitigate dysbiosis and enhance chicken health through probiotics, cost-effective feeding programs that include specific probiotic strains can help restore healthy gut microbiota composition under controlled conditions (Yadav and Jha, 2019). In addition, maintaining optimal climatic conditions and ensuring balanced nutrition are critical for preserving gut integrity and preventing dysbiosis.
Recent research highlights innovative probiotic application methods, such as in-ovo administration (Wishna-Kadawarage et al., 2024; Abdel-Moneim et al., 2020), which promotes early colonization of beneficial microbes in newly hatched chicks, enhancing their resistance to pathogenic colonization. Future studies should focus on identifying probiotic strains with superior pathogen resistance, nutrient bioavailability, and immune-modulating properties. Also, it is important to explore the interactions between probiotic strains and their metabolites, which can help in developing targeted formulations to optimize chicken health and productivity.
Probiotics are known to promote synergy between the innate and adaptive immune systems by interacting with various immune cells, including monocytes, dendritic cells, T and B lymphocytes, and macrophages. Lee et al. (2022) highlighted that probiotics such as Lactobacillus casei, L. acidophilus, and Streptococcus thermophilus enhance the activity of these immune cells, leading to improved immune responses. This interaction is facilitated by the regulation of gene expression and signaling pathways within host cells, underscoring the immunomodulatory abilities of probiotics (Gilad et al., 2011).
For instance, a study by Wishna-Kadawarage et al. (2024) observed the upregulation of the genes related to immune response—AVBD1, IL8, and FFAR2—in the spleen of chickens supplemented with Leuconostoc mesenteroides B/00288. Also, the study reported increased expression of energy (COX16), protein (mTOR), and lipid (CYP46A1) metabolism-related genes in the liver, with a dosage of 106 CFU per egg in a volume of 0.2 ml. This observation emphasizes how probiotics could influence both immune and metabolic pathways, presenting a dual benefit for health and productivity.
A study by Yan et al. (2018) observed a significant increase in the level of serum calcium level of broiler chicken exposed to B. subtilis on day 21. Table 1 shows some studies on the impact of probiotics on chicken immunity. Therefore, the potential influence of probiotics, particularly Bacillus subtilis, on calcium-dependent innate immune proteins like mannose-binding lectin remains unexplored and needs further research.
A study by Vitini et al. (2000) demonstrated that oral supplementation of L. casei, L. acidophilus, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, and S. thermophilus increases the number of intestinal IgA-producing cells. This supplementation also enhances the clonal expansion of B cells, which are crucial for antibody production.
The ability of probiotics to influence immunoglobulin levels is particularly relevant in chickens exposed to stressors, as observed by Deng et al. (2012) and Mohammed et al. (2024), where dietary inclusion of probiotics led to increased serum IgM levels by 0.25% following preslaughter stress. Also, a diet supplemented with Lactobacillus plantarum, L. acidophilus, Lactobacillus bulgaricus, L. rhamnosus, Bifidobacterium bifidum, S. thermophilus, Enterococcus faecium, Aspergillus oryzae, and Candida pintolopesii caused a 55% reduction in plasma CRP levels (Jankowski et al., 2022).
Wang et al. (2018a) observed that a basal diet with 1 × 106 colony-forming units significantly increased the serum levels of IgG and IgA on day 21 compared to the control group with no significant difference in IgM levels. Meanwhile, the basal diet with 1 × 105 group did not show any significant changes in immunoglobulin levels on day 21. This suggests that probiotic supplementation effectively mitigated inflammation associated with heat stress in broiler chickens. This is significant as high levels of inflammation can impair growth, feed efficiency, and overall health.
Conversely, Deng et al. (2012) found that the immunoglobulin levels in stressed laying hens exposed to B. licheniformis were reduced in the ileum and cecum, suggesting a complex interaction between stress and probiotic supplementation. Also, administration of 5 ml of MolaPlus microbes had no significant influence on the IgM antibody concentration (Khobondo et al., 2015). Administering probiotics containing E. faecium and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens to chickens at the early phase of life had no effect on the plasma levels of either IgY or IgA (Jankowski et al., 2022).
Therefore, stress-induced reductions in immunoglobulins such as IgA and IgM and the variable impacts of probiotics under stress conditions suggest the need for tailored formulations to address specific stressors like heat, feed deprivation, or transportation.
Probiotics also play a role in modulating cytokine production within the gut epithelium. They help maintain adequate pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, which are crucial for an effective immune response during stress. Abdelaziz et al. (2022) reported that lactobacilli-treated macrophages exhibited increased phagocytic activity and elevated nitric oxide production, indicating enhanced immune function under both normal and high-temperature conditions.
Moreover, probiotics have been shown to reduce the levels of acute-phase proteins such as C-reactive protein and ceruloplasmin in the blood, which are indicators of inflammation. This reduction may contribute to a more balanced immune response during periods of stress. Probiotics suppress pro-inflammatory cytokines like interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α), reducing inflammation and intestinal damage caused by pathogenic Salmonella while simultaneously enhancing interleukin (IL-10) expression, an anti-inflammatory cytokine essential for controlling excessive inflammation and maintaining immune balance (Raheem et al., 2021). The immunomodulatory properties of probiotics could therefore be a promising tool for enhancing disease resistance, particularly in poultry exposed to pathogenic stressors.
A study by Zaghari et al. (2020) observed higher IL-6 gene expression in broiler plasma supplemented with B. licheniformis than the control group. Also, Cao et al. (2013) observed a significant increase in IL-4 in the jejuna mucosa of broiler chicken supplemented with E. faecium. However, chicken supplemented with B. subtilis had no significant impact on cytokine expression as shown in Table 1.
Research indicates that probiotics can significantly improve antibody responses against diseases such as Newcastle disease (Alkhalf et al., 2010). Probiotic supplementation has been associated with higher Newcastle antibody titers compared to control groups. The beneficial effects of a diet containing lactobacilli spp. (L. casei Shirota, L. rhamnosus GG, L. plantarum NCIMB 8826, and L. reuteri NCIMB 11951) and Bifidobacteria spp. (Bifidobacterium longum SP 07/3 and B. bifidum MF 20/5) probiotics suggest that added bacteria enhance acquired immune responses. This is achieved by increasing microbial populations in the gastrointestinal tract, which stimulates the activation of T and B lymphocytes (Dong et al., 2012).
Wang et al. (2018a) observed a significant increase in the percentage of CD3+ and CD4+ T lymphocytes on days 21 and 42 in feed supplemented with a basal diet with 1 × 106 colony-forming units. Only at day 14, chicken supplemented with L. salivarius had significantly higher antibody titers to sheep red blood cell (Brisbin et al., 2011). However, in the same study, there was no significance in chicken supplemented with L. acidophilus and L. reuteri. Therefore, the inconsistent results between probiotic strains such as L. acidophilus and L. reuteri underline the need for comparative studies to determine which strains are most effective for specific immune functions.
While evidence supports the benefits of probiotics in poultry, outcomes can vary based on factors such as strain type, dosage, bird age, and environmental conditions. For instance, Alkhalf et al. (2010) emphasized that bird type (broilers vs. layers) and age (7, 28, or 42 weeks) could influence dosage requirements and administration intervals. Stress conditions also play a role; Deng et al. (2012) reported reduced immunoglobulin levels in the ileum and cecum of stressed laying hens exposed to B. licheniformis. This variability underscores the need for tailored probiotic strategies to optimize immune responses under different production conditions.
Probiotic supplementation has also been linked to improved development of immune organs such as the bursa of Fabricius through oral administration of L. casei, L. acidophilus, and Bifidobacterium (Zhang et al., 2021; Jankowski et al., 2022). Early administration of probiotics like E. faecium and B. amyloliquefaciens has been shown to modulate adaptive immunity, with a notable increase in CD3+Bu-1 (B cells) observed in the spleen and blood of 6-day-old chicks relative to controls (Jankowski et al., 2022). Additionally, reductions in acute-phase proteins such as C-reactive protein, ceruloplasmin, IL-6, and TNF were noted, suggesting an anti-inflammatory effect.
Probiotics also demonstrate potential for mitigating heat stress effects on immunity. Abdelaziz et al. (2022) reported that macrophages treated with L. acidophilus and Lactobacillus crispatus exhibited increased phagocytic activity and nitric oxide production under both normal and high-temperature conditions. These probiotics sustained macrophage function during heat stress by enhancing cytokine expression such as IL-1β, IL-12p40, and IL-18 while reducing TLR2 and TLR4 expression. This highlights their role in supporting immune function during environmental stressors.
In conclusion, probiotics offer significant potential for enhancing chicken immunity (Table 1) by improving antibody production, modulating cytokine responses, and supporting adaptive immunity under stress conditions. However, their effectiveness depends on factors such as strain specificity, dosage optimization, bird type, and environmental conditions. Future research should focus on long-term studies to refine probiotic strategies tailored to specific poultry production systems for maximum immunological benefits.
Probiotics have emerged as a significant factor influencing chicken behavior through their modulation of gut microbiota, which affects overall health and stress responses (Chen et al., 2021). This analysis synthesizes recent literature on the behavioral impacts of probiotics on chickens, focusing on aggression reduction, social interactions, and neurochemical influences.
Probiotics can significantly alter chicken behavior by improving gut health, enhancing nutrient absorption, and strengthening the immune system. Chickens supplemented with probiotics exhibit reduced aggressive behaviors such as feather pecking, anxiety, and cannibalism, leading to improved social interactions among birds (Figure 2). Jiang et al. (2022) found that such behavioral improvements are closely linked to better gut health and enhanced nutrient absorption, which collectively contribute to a more stable emotional state in chickens.
Environmental factors such as global warming can elevate stress levels in farm animals, negatively impacting their behavioral welfare. Shehata et al. (2021) highlighted that endocrine disturbances and immunosuppression are known to adversely affect chicken behavior. Probiotic supplementation may mitigate these stress-related behaviors by promoting a healthier gut microbiome, thereby enhancing resilience against environmental stressors. Also, probiotic supplementation may offer a solution to stress-induced behavioral issues in poultry farming, which could be critical for improving poultry welfare in the face of climate change.
Recent studies have explored the connection between gut health and feather pecking (FP) behaviors in laying hens. Mindus et al. (2021) demonstrated that feather peckers have a significantly lower abundance of beneficial Lactobacillus bacteria compared to non-peckers. The study also showed that hens supplemented with L. rhamnosus had a reduced incidence of severe feather pecking by 2.5-fold compared to the Placebo group in stressed birds. Furthermore, stressed hens in the L. rhamnosus group maintained more stable gut microbiota diversity over time than those in the control group. It can also be suggested that oral supplementation of L. rhamnosus might have led to the transfer of the bacteria to the feather cover through preening or pecking hereby altering the olfactory or taste characteristics of the feathers. This change may have encouraged gentler feather pecking and discouraged more harmful forms of feather pecking.
A study by Wang et al. (2018b) involved feeding male broiler chickens either a standard diet or one supplemented with 250 part per million concentration of the probiotic Bacillus subtilis, containing about 1.0 × 106 spores/g of feed, from day 1 to day 43. The probiotic supplementation was associated with positive behavioral effects, potentially enhancing welfare and reducing stress by influencing the central nervous system. This influence may lead to changes in behavior and emotional responses. Also, improved bone health could enhance mobility and reduce discomfort, contributing to better emotional well-being. The study found that broilers fed probiotics showed altered brain chemistry, with increased serotonin levels in the raphe nuclei and decreased dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the hypothalamus. Higher serotonin level promotes positive emotional traits like happiness, while reduced dopamine levels could affect motivation and behavior (Bacqué-Cazenave, et al., 2020). Hu et al. (2022) investigated the relationship between gut microbiota, aggression, and physiological homeostasis in inbred laying hen lines 63 and 72 that were diversely selected for Marek’s disease. The study observed that line 63 hens had higher central serotonin and tryptophan levels compared to line 72 hens. Also, line 63 hens showed lower plasma corticosterone levels, heterophil/lymphocyte ratios, and central norepinephrine levels, indicating a reduced stress response compared to line 72. The variations observed in serotonergic activity are linked to aggressive behaviors, with higher central tryptophan levels associated with reduced aggression and stress. This suggests that including probiotics in the diet could enhance serotoninergic function, helping to alleviate stress-related behaviors in chickens.
In this way, probiotics may not only improve physical health but also positively influence neurochemical processes that affect chicken behavior. More information about the impact of chicken behavior is shown in Table 2.
Probiotic supplementation in poultry diets has garnered significant attention due to its potential to enhance growth performance, egg production, and overall health in chickens (Paz et al., 2019; Agustono et al., 2022). This analysis synthesizes findings from various studies to highlight the effects of probiotics on chicken growth metrics, egg quality, and the underlying mechanisms involved (Table 3). Probiotics have been shown to improve chicken growth performance significantly. Studies indicate that dietary supplementation can lead to enhanced body weight, average daily weight gain, and improved FCRs. Specifically, probiotics can improve FCR by approximately 5%–6%, which is influenced by factors such as dosage, type of probiotic, and farming systems. For instance, L. casei, L. acidophilus, and Bifidobacterium lactis have been associated with increased intestinal villus height, thereby enhancing nutrient absorption (Zhang et al., 2022). In support of this, Agustono et al. (2022) confirmed that probiotics enhance feed efficiency by improving gut health and nutrient intake.
Moreover, a review of multiple studies indicated that different strains of probiotics can yield varying results based on their specific properties and the health status of the chickens (Huang et al., 2023; Qiu et al., 2021; Mazanko et al., 2022; Paz et al., 2019; Agustono et al., 2022). However, Olnood et al. (2015) found no significant impact of adding Lactobacillus spp. at a concentration of 106 CFU/g to the feed on weight gain, feed intake, or FCR in broiler chickens at 6 weeks of age. The discrepancies in these findings can be the result of inclusion rates that are lower than the commonly recommended 108 CFU/g for commercial probiotic feed additives and limited fermentation capacity. Therefore, a probiotic’s capacity depends on factors such as the appropriate concentration level and adequate fermentation. Further understanding the influence of environmental factors, such as temperature, humidity, and diet composition, on the activity of probiotics performance is needed, and identifying how these variables interact with probiotics will help refine supplementation strategies to improve poultry productivity.
Probiotics also positively influence egg production and quality. Studies have demonstrated that dietary supplementation can lead to increased egg production rates, improved eggshell quality, and enhanced egg weight. This is attributed to the improved digestibility of calcium and phosphorus, which are the key components in eggshell formation (Carvalho et al., 2023). For example, research involving Clostridium butyricum and Brevibacillus strains showed significant improvements in egg quality parameters such as eggshell strength and albumen height (Obianwuna et al., 2022). Additionally, probiotics like L. acidophilus have been shown to enhance yolk color intensity by increasing carotenoid absorption (Carvalho et al., 2023). Another study found that probiotic supplementation significantly improved egg quality metrics such as yolk pH and yolk index (Carvalho et al., 2022). These findings suggest that probiotics not only contribute to higher egg production but also enhance the nutritional profile of the eggs produced. Conversely, feed supplemented with Bacillus mesentericus TO-A, C. butyricum TO-A, and Streptococcus faecalis T-110 had no significance on the height of the thick albumen (egg white) surrounding the yolk in relation to the egg’s weight (Inatomi, 2016). These contrasting results may stem from variations in the ability of probiotics to enhance protein synthesis and facilitate the transfer of water from the yolk. More impacts of probiotics on chicken productive traits are presented in Table 3.
Generally, despite the positive outcomes associated with probiotic supplementation, it is essential to note that not all probiotics produce uniform results. The effectiveness of probiotics can vary based on several factors. Different probiotic strains exhibit distinct effects on growth performance and health. Dosage, which is the amount of probiotic administered, plays a critical role in determining its efficacy. Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and diet composition can influence how well probiotics perform in enhancing chicken health. Given the variability in probiotic efficacy, further research is needed to explore the cost-effectiveness of different probiotic strains in commercial poultry production as well as the optimal inclusion rates for various types of probiotics and the long-term impacts on chicken health and productivity.
Research on probiotics in poultry has highlighted several important gaps and areas for future exploration. One key development is formulating probiotics tailored to specific poultry types (broilers vs. layers) and production conditions, which could optimize health outcomes. Understanding how probiotics produce metabolites that modulate immune responses could enhance chicken immunity and overall health. Future studies should also explore the effects of combining different probiotic strains to identify the most effective formulations.
Novel delivery methods, such as in-ovo administration, may improve gut microbiota and immune system development early in life, leading to better health and productivity. Identifying probiotics that support immune function under heat stress is vital as climate change impacts poultry farming. Research on probiotics’ effects on vaccine efficacy, particularly for diseases like Newcastle disease, is also needed to improve vaccination strategies.
In terms of chicken behavior, further research is required to understand the link between gut health and behavioral changes such as aggression and anxiety. Exploring the long-term effects of probiotics on stress behavior and how environmental factors like heat and overcrowding influence their effectiveness is crucial. Identifying probiotic strains that promote positive social interactions and reduce negative behaviors will improve poultry welfare.
Assessing the long-term impact of probiotics on chicken health and productivity is essential for determining their cost-effectiveness in commercial production. Future studies should also examine how probiotics influence egg quality, focusing on mechanisms like protein synthesis and water transfer in eggs. By addressing these gaps, research can enhance our understanding of probiotics’ role in improving poultry health, behavior, and productivity.
One of the strengths of this systematic review is the rigorous methodology used to identify and evaluate relevant studies. The literature search was conducted across multiple reputable databases, including PubMed, CABI Abstract, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar, which increases the likelihood of capturing a comprehensive range of relevant studies. Furthermore, the study adhered to predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria, focusing on high-quality research, such as randomized controlled trials (RCTs), controlled trials, and observational studies, thereby enhancing the reliability of the findings. The review specifically examined the impact of probiotics on gut microbiota, immunity, behavior, and productivity in chickens, providing a focused and structured analysis of these critical areas. Additionally, limiting the selection to studies published from 2010 onward ensures that the findings are based on recent advancements in probiotic research.
Despite these strengths, there are several limitations to consider. First, while multiple databases were searched, other relevant databases or sources of gray literature were not included, which may have led to the omission of some relevant studies. Second, only articles written in English were considered, potentially excluding valuable research published in other languages. Third, studies involving combinations of probiotics with antibiotics, synbiotics, or unspecified prebiotics were excluded, which may limit the generalizability of the results to real-world poultry production scenarios where such combinations are commonly used. Lastly, inherent biases in the included studies, such as variations in probiotic strains, dosages, and study conditions, may have influenced the findings, though efforts were made to minimize these biases through strict inclusion criteria.
This systematic review highlights the significant impact of various probiotic strains on chicken gut microbiota, immunity, behavior, and productivity. Probiotics such as Lactobacillus (L. acidophilus, L. casei, L. rhamnosus, L. plantarum, L. reuteri, L. salivarius, L. delbrueckii), Bacillus (B. subtilis, B. licheniformis, B. amyloliquefaciens), Bifidobacterium (B. bifidum, B. longum), Enterococcus (E. faecium), Clostridium butyricum, Brevibacillus, S. thermophilus, S. cerevisiae, and L. mesenteroides play a crucial role in maintaining gut health, improving nutrient absorption, and reducing the colonization of harmful pathogens such as Salmonella and C. perfringens.
These probiotics not only enhance digestion and feed efficiency but also have immunomodulatory effects, increasing immunoglobulin (IgA, IgM, and IgG) levels, cytokine expression (IL-6, IL-4, IL-10), and T-cell activation (CD3+, CD4+), leading to improved disease resistance. Furthermore, probiotics like L. rhamnosus and B. subtilis have been linked to reduced stress and aggression, promoting better welfare by modulating neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine.
In terms of productive traits, L. casei, L. acidophilus, B. subtilis, and B. licheniformis have been found to enhance body weight gain, FCR, egg production, and eggshell quality, making them viable alternatives to antibiotic growth promoters. However, the effectiveness of probiotics varies based on strain specificity, dosage, environmental conditions, and administration method.
To optimize probiotic use in poultry farming, future research should focus on strain selection, combination formulations, and novel delivery methods such as in-ovo administration. Overall, probiotics offer a sustainable and effective approach to improving poultry health, welfare, and productivity while reducing reliance on antibiotics in poultry production.
PI: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TM: Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. AM: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. MM: Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. KN: Funding acquisition, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. BM: Funding acquisition, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors declare that the financial support was received from the Department of Animal Sciences, Faculty of Animal Science, Tshwane University of Technology, Pretoria, South Africa.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abdelaziz K., Nixon T., Joye A., Hassan H., Alizadeh M., Sharif S., et al. (2022). Modulation of functional activity of heat-stressed chicken macrophages by poultry-derived probiotic lactobacilli. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 104 (3), 301– 312. doi: 10.1139/cjas-2023-0124
Abdel-Moneim A. M., Elbaz A. M., Khidr R. E., Badri F. B. (2020). Effect of in ovo inoculation of Bifidobacterium spp. on growth performance, thyroid activity, ileum histomorphometry, and microbial enumeration of broilers. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 12, 873–882. doi: 10.1007/s12602-019-09613-x
Agustono B., Lokapirnasari W. P., Yunita M. N., Kinanti R. N., Cesa A. E., Windria S. (2022). Efficacy of dietary supplementary probiotics as substitutes for antibiotic growth promoters during the starter period on growth performances, carcass traits, and immune organs of male layer chicken. Vet. World 15, 324. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2022.324-330
Ahmed T., Hashem M. A., Afrin A., Lahiry A., Rahman S., Bungo T., et al. (2024). Effects of fasting on heat-stressed broiler chickens: part I-growth performance, meat quality, gut histomorphological and microbial responses. bioRxiv 2024.09.08.611910. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.08.611910
Alkhalf A., Alhaj M., Al-Homidan I. (2010). Influence of probiotic supplementation on immune response of broiler chicks. Egyptian Poult. Sci. 30, 271–280. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235419794_Influence_of_probiotic_supplementation_on_immune_response_of_broiler_chicks (Accessed October 12, 2024).
Al-Khalaifa H., Al-Nasser A., Al-Surayee T., Al-Kandari S., Al-Enzi N., Al-Sharrah T., et al. (2019). Effect of dietary probiotics and prebiotics on the performance of broiler chickens. Poultry Sci. 98 (10), 4465–4479. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez282
Apajalahti J., Vienola K. (2016). Interaction between chicken intestinal microbiota and protein digestion. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 221, 323–330. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2016.05.004
Aruwa C. E., Pillay C., Nyaga M. M., Sabiu S. (2021). Poultry gut health–microbiome functions, environmental impacts, microbiome engineering and advancements in characterization technologies. J. Anim. Sci. Biotech. 12, 1–5. doi: 10.1186/s40104-021-00640-9
Asgari F., Madjd Z., Falak R., Bahar M. A., Nasrabadi M. H., Raiani M., et al. (2016). Probiotic feeding affects t cell populations in blood and lymphoid organs in chickens. Beneficial Microbes 7 (5), 669–676. doi: 10.3920/BM2016.0014
Bai S. P., Wu A. M., Ding X. M., Lei Y., Bai J., Zhang K. Y., et al. (2013). Effects of probiotic-supplemented diets on growth performance and intestinal immune characteristics of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 92, 663–670. doi: 10.3382/ps.2012-02813
Bacqué-Cazenave J., Bharatiya R., Barrière G., Delbecque J. P., Bouguiyoud N., Di Giovanni G., et al. (2020). Serotonin in animal cognition and behavior. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (5), 1649.doi: 10.3390/ijms21051649
Bavananthasivam J., Alizadeh M., Astill J., Alqazlan N., Matsuyama-Kato A., Shojadoost B., et al. (2021). Effects of administration of probiotic lactobacilli on immunity conferred by the herpesvirus of Turkeys vaccine against challenge with a very virulent Marek’s disease virus in chickens. Vaccine 39, pp.2424–2433. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.03.046
Bedford M. R., Apajalahti J. H. (2022). The role of feed enzymes in maintaining poultry intestinal health. J. Sci. Food Agric. 102, 1759–1770. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.11670
Biswas A., Junaid N., Kumawat M., Qureshi S., Mandal A. B. (2018). Influence of dietary supplementation of probiotics on intestinal histo-morphometry, blood chemistry and gut health status of broiler chickens. South Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 48 (5), 968–976. doi: 10.4314/sajas.v48i5.17
Borda-Molina D., Seifert J., Camarinha-Silva A. (2018). Current perspectives of the chicken gastrointestinal tract and its microbiome. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 16, 131–139. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2018.03.002
Brisbin J. T., Gong J., Orouji S., Esufali J., Mallick A. I., Parvizi P., et al. (2011). Oral treatment of chickens with lactobacilli influences elicitation of immune responses. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 18, 1447–1455. doi: 10.1128/cvi.05100-11
Cao G. T., Zeng X. F., Chen A. G., Zhou L., Zhang L., Xiao Y. P., et al. (2013). Effects of a probiotic, Enterococcus faecium, on growth performance, intestinal morphology, immune response, and cecal microflora in broiler chickens challenged with Escherichia coli K88. Poult. Sci. 92, 2949–2955. doi: 10.3382/ps.2013-03366
Carvalho C. L., Andretta I., Galli G. M., Bastos Stefanello T., Camargo N. D., Mendes R. E., et al. (2023). Dietary supplementation with β-mannanase and probiotics as a strategy to improve laying hen performance and egg quality. Front. Vet. Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.985947
Carvalho C. L., Andretta I., Galli G. M., Stefanello T. B., Camargo N. D. O. T., Marchiori M., et al. (2022). Effects of dietary probiotic supplementation on egg quality during storage. Poultry 1, 180–192. doi: 10.3390/poultry1030016
Cengiz Ö., Köksal B. H., Tatlı O., Sevim Ö., Ahsan U., Üner A. G., et al. (2015). Effect of dietary probiotic and high stocking density on the performance, carcass yield, gut microflora, and stress indicators of broilers. Poul. Sci. 94, 2395–2403. doi: 10.3382/ps/pev194
Chaudhari A. A., Lee Y., Lillehoj H. S. (2020). Beneficial effects of dietary supplementation of Bacillus strains on growth performance and gut health in chickens with mixed coccidiosis infection. Vet. Parasitol. 277, 109009. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2019.109009
Chen S., Liu J., Luo S., Xing L., Li W., Gong L. (2024). The Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens SC06 on Behavior and Brain Function in Broilers Infected by Clostridium perfringens. Animals 14, 1547. doi: 10.3390/ani14111547
Chen S., Luo S., Yan C. (2021). Gut microbiota implications for health and welfare in farm animals: a review. Animals 12, 93. doi: 10.3390/ani12010093
Collado M. C., Gueimonde M., Salminen S. (2010). Probiotics in adhesion of pathogens: mechanisms of action. In Bioactive foods in promoting health. Academic Press. 353–370. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-374938-3.00023-2
Deng W., Dong X. F., Tong J. M., Zhang Q. (2012). The probiotic Bacillus licheniformis ameliorates heat stress-induced impairment of egg production, gut morphology, and intestinal mucosal immunity in laying hens. Poult. Sci. 91, 575–582. doi: 10.3382/ps.2010-01293
Diaz-Carrasco J. M., Casanova N. A., Fernández Miyakawa M. E. (2019). Microbiota, gut health, and chicken productivity: what is the connection? Microorganisms 7, 374. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7100374
Dong H., Rowland I., Yaqoob P. (2012). Comparative effects of six probiotic strains on immune function in vitro. Br. J. Nutr. 108, 459–470. doi: 10.1017/S0007114511005824
Fathi M., Al-Homidan I., Al-Dokhail A., Ebeid T., Abou-Emera O., Alsagan A. (2018). Effects of dietary probiotic (Bacillus subtilis) supplementation on productive performance, immune response and egg quality characteristics in laying hens under high ambient temperature. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 17 (3), 804–814. doi: 10.1080/1828051X.2018.1425104
Gadde U., Oh S. T., Lee Y. S., Davis E., Zimmerman N., Rehberger T., et al. (2017). The effects of direct-fed microbial supplementation, as an alternative to antibiotics, on growth performance, intestinal immune status, and epithelial barrier gene expression in broiler chickens. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 9, 397–405. doi: 10.1007/s12602-017-9275-9
Garcia-Amado M. A., Michelangeli F., Gueneau P., Perez M. E., Dominguez-Bello M. G. (2017). Bacterial detoxification of saponins in the crop of the avian foregut fermenter Opisthocomus hoazin. J. Anim. Feed Sci. 16 (2), 82–85. Available online at: https://www.jafs.com.pl/pdf-74460-11031?filename=Bacterial%20detoxification.pdf (Accessed February 9, 2024).
Gilad O., Svensson B., Viborg A. H., Stuer-Lauridsen B., Jacobsen S. (2011). The extracellular proteome of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis BB-12 reveals proteins with putative roles in probiotic effects. Proteomics 11, 2503–2514. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201000716
Guo M., Wu F., Hao G., Qi Q., Li R., Li N., et al. (2017). Bacillus subtilis improves immunity and disease resistance in rabbits. Front. Immunol. 8. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00354
He T., Long S., Mahfuz S., Wu D., Wang X., Wei X., et al. (2019). Effects of probiotics as antibiotics substitutes on growth performance, serum biochemical parameters, intestinal morphology, and barrier function of broilers. Animals 9 (11), 985. doi: 10.3390/ani9110985
Hossain M. T., Sardar D., Afsana S., Datta M., Habib M. A. (2024). Comparative analysis between multi-strain probiotics and antibiotic as starter feed supplement of poultry on growth performance, serum metabolites and meat quality. Veterinary Anim. Sci. 24, 100346. doi: 10.1016/j.vas.2024.100346
Huang C., Yue Q., Sun L., Di K., Yang D., Hao E., et al. (2023). Restorative effects of lactobacillus rhamnosus LR-32 on the gut microbiota, barrier integrity, and 5-HT metabolism in reducing feather-pecking behavior in laying hens with antibiotic-induced dysbiosis. Front. Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1173804
Hu J., Johnson T. A., Zhang H., Cheng H. W. (2022). The microbiota–gut–brain axis: gut microbiota modulates conspecific aggression in diversely selected laying hens. Microorganisms 10, 1081. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10061081
Idowu P. A., Idowu A. P., Zishiri O. T., Mpofu T. J., Veldhuizen E. J., Nephawe K. A., et al. (2021). Activity of mannose-binding lectin on bacterial-infected chickens—a review. Animals 11, 787. doi: 10.3390/ani11030787
Idowu P. A., Mpayipheli M., Muchenje V. (2019). A survey study on productive and reproductive performance of indigenous poultry. Am. J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 14, 33–39. doi: 10.3844/ajavsp.2019.33.39
Idowu P. A., Mpofu T. J., Zishiri O. T., Adelabu O. A., Nephawe K. A., Mtileni B. (2024). Molecular detection and genetic characterization of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and Mycoplasma synoviae in selected chicken breeds in South Africa. BMC Infect. Dis. 24, 562. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09437-3
Inatomi T. (2016). Laying performance, immunity and digestive health of layer chickens fed diets containing a combination of three probiotics. Sci. Postprint 1, e00058. Available at: http://www.spp-j.com/spp/1-2/spp.2016.03A0001sthash.hmTJkuQC.dpbs (Accessed October 12, 2024).
Jankowski J., Tykałowski B., Stępniowska A., Konieczka P., Koncicki A., Matusevičius P., et al. (2022). Immune parameters in chickens treated with antibiotics and probiotics during early life. Animals 12, 1133. doi: 10.3390/ani12091133
Jiang S., Hu J. Y., Cheng H. W. (2022). The impact of probiotic Bacillus subtilis on injurious behavior in laying hens. Animals 12, 870. doi: 10.3390/ani12070870
Kesen M. A., Aiyegoro O. A. (2018). Beneficial characteristics and evaluation criteria of probiotics. Int. J. Food Biosci. 1, 19–26. Available at: https://www.innovationinfo.org/articles/IJFB-1-106.pdf (Accessed October 12, 2024).
Khobondo J. O., Ogore P. B., Atela J. A., Onjoro P. S., Ondiek J. O., Kahi A. (2015). The effects of dietary probiotics on natural IgM antibody titers of Kenyan indigenous chicken. Livestock Res. Rural Dev. 27, 27–30. Available at: https://www.lrrd.cipav.org.co/lrrd27/11/khob27230.html (Accessed October 9, 2024).
Larsberg F., Sprechert M., Hesse D., Loh G., Brockmann G. A., Kreuzer-Redmer S. (2023). Probiotic Bacillus strains enhance T cell responses in chicken. Microorganisms 11, 269. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11020269
Lee J. Y., Tsolis R. M., Bäumler A. J. (2022). The microbiome and gut homeostasis. Science 377, eabp9960. doi: 10.1126/science.abp9960
Liu X., Cao G., Qiu K., Dong Y., Hu C. (2023). Lactobacillus plantarum decreased ammonia emissions through modulating cecal microbiota in broilers challenged with ammonia. Animals 13, 2739. doi: 10.3390/ani13172739
Liu X., Peng C., Qu X., Guo S., Chen J. F., He C., et al. (2019). Effects of Bacillus subtilis C-3102 on production, hatching performance, egg quality, serum antioxidant capacity and immune response of laying breeders. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 103, 182–190. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13022
Martinez-Guryn K., Hubert N., Frazier K., Urlass S., Musch M. W., Ojeda P., et al. (2018). Small intestine microbiota regulate host digestive and absorptive adaptive responses to dietary lipids. Cell Host Microbe 23, 458–469. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2018.03.011
Mazanko M. S., Popov I. V., Prazdnova E. V., Refeld A. G., Bren A. B., Zelenkova G. A., et al. (2022). Beneficial effects of spore-forming Bacillus probiotic bacteria isolated from poultry microbiota on broilers’ health, growth performance, and immune system. Front. Vet. Sci. 9. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.877360
Mindus C., van Staaveren N., Bharwani A., Fuchs D., Gostner J. M., Kjaer J. B., et al. (2021). Ingestion of Lactobacillus rhamnosus modulates chronic stress-induced feather pecking in chickens. Sci. Rep. 11, 17119. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96615-x
Mohammed A. R., El-Said E. I., Abd ElAal S. F., Kamal R. M. (2024). Screening of antibiogram, virulence factors, and biofilm production of Staphylococcus aureus and the bio-control role of some probiotics as alternative antibiotics. Open Vet. J. 14, 176. doi: 10.5455/ovj.2024.v14.i1.16
Obianwuna U. E., Qiu K., Chang X. Y., Zhang H. J., Wang J., Qi G. H., et al. (2022). Enhancing egg production and quality by the supplementation of probiotic strains (Clostridium and Brevibacillus) via improved amino acid digestibility, intestinal health, immune response, and antioxidant activity. Front. Microbiol. 13. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.987241
Olnood C. G., Beski S. S., Choct M., Iji P. A. (2015). Novel probiotics: Their effects on growth performance, gut development, microbial community and activity of broiler chickens. Anim. Nutr. 1, 184–191. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2015.07.003
Page M. J., McKenzie J. E., Bossuyt P. M., Boutron I., Hoffmann T. C., Mulrow C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. bmj 372. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
Paz I.C.D.L.A., de Lima Almeida I. C., de la Vega L. T., Milbradt E. L., Borges M. R., Chaves G. H. C., et al. (2019). Productivity and well-being of broiler chickens supplemented with probiotic. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 28, 930–942. doi: 10.3382/japr/pfz054
Plaza-Diaz J., Ruiz-Ojeda F. J., Gil-Campos M., Gil A. (2019). Mechanisms of action of probiotics. Adv. Nutr. 10, S49–S66. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmy063
Popov I. V., Skripkin V. S., Mazanko M. S., Epimakhova E. E., Prazdnova E. V., Dilekova O. V., et al. (2024). Effects of spore-forming Bacillus probiotics on growth performance, intestinal morphology, and immune system of broilers housed on deep litter. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 33, 100396. doi: 10.1016/j.japr.2023.100396
Puri P., Singh R., Sharma J. (2023). Micro-/bio-/nano-/syn-encapsulations and co-treatments of bioactive microbial feed supplementation in augmenting finfish health and aquaculture nutrition: a review. Beneficial Microbes. 14 (3), 281–302. doi: 10.3920/bm2022.0087
Qiu K., Li C. L., Wang J., Qi G. H., Gao J., Zhang H. J., et al. (2021). Effects of dietary supplementation with bacillus subtilis, as an alternative to antibiotics, on growth performance, serum immunity, and intestinal health in broiler chickens. Front. Nutr. 8. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.786878
Rabetafika H. N., Razafindralambo A., Ebenso B., Razafindralambo H. L. (2023). Probiotics as antibiotic alternatives for human and animal applications. Encyclopedia 3, 561–581. doi: 10.3390/encyclopedia3020040
Raheem A., Liang L., Zhang G., Cui S. (2021). Modulatory effects of probiotics during pathogenic infections with emphasis on immune regulation. Front. Immunol. 12. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.616713
Rama E. N., Bailey M., Kumar S., Leone C., den Bakker H. C., Thippareddi H., et al. (2023). Characterizing the gut microbiome of broilers raised under conventional and no antibiotics ever practices. Poult. Sci. 102, 102832. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102832
Rodjan P., Soisuwan K., Thongprajukaew K., Theapparat Y., Khongthong S., Jeenkeawpieam J., et al. (2018). Effect of organic acids or probiotics alone or in combination on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, enzyme activities, intestinal morphology and gut microflora in broiler chickens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 102, e931–e940. doi: 10.1111/jpn.12858
Rychlik I. (2020). Composition and function of chicken gut microbiota. Animals 10, 103. doi: 10.3390/ani10010103
Salminen S., Collado M. C., Endo A., Hill C., Lebeer S., Quigley E. M., et al. (2021). The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 18, 649–667. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00440-6
Shahbaz F., Muccee F., Shahab A., Safi S. Z., Alomar S. Y., Qadeer A. (2024). Isolation and in vitro assessment of chicken gut microbes for probiotic potential. Front. Microbiol. 15. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1278439
Shang Y., Kumar S., Oakley B., Kim W. K. (2018). Chicken gut microbiota: importance and detection technology. Front. Vet. Sci. 5. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2018.00254
Shehata A. M., Paswan V. K., Attia Y. A., Abdel-Moneim A. M., Abougabal M. S., Sharaf M., et al. (2021). Managing gut microbiota through in ovo nutrition influences early-life programming in broiler chickens. Animals 11, 3491. doi: 10.3390/ani11123491
Silva D. R., Sardi J. D., de Souza Pitangui N., Roque S. M., da Silva A. C., Rosalen P. L. (2020). Probiotics as an alternative antimicrobial therapy: Current reality and future directions. J. Funct. Foods 73, 104080. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.104080
Singh A. K., Berrocoso J. D., Dersjant-Li Y., Awati A., Jha R. (2015). Effect of supplemental multi-enzymes and direct-fed microbial on nutrients digestibility in broilers fed low and high fiber diets. Poult. Sci. 94 (9). Availabl online at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280570689_Effect_of_supplemental_multi-enzymes_and_direct_fed_microbial_on_nutrients_digestibility_in_broilers_fed_low_and_high_fiber_diets (Accessed October 12, 2024).
Soroko M., Zaborski D. (2020). Investigation of the effects of probiotic, bacillus subtilis on stress reactions in laying hens using infrared thermography. PloS One 15 (6), e0234117. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234117
Soumeh E. A., Cedeno A. D. R. C., Niknafs S., Bromfield J., Hoffman L. C. (2021). The efficiency of probiotics administrated via different routes and doses in enhancing production performance, meat quality, gut morphology, and microbial profile of broiler chickens. Animals 11 (12), 3607. doi: 10.3390/ani11123607
Stanley D., Hughes R. J., Moore R. J. (2014). Microbiota of the chicken gastrointestinal tract: influence on health, productivity and disease. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 98, 4301–4310. doi: 10.1007/s00253-014-5646-2
Summers J., Turner B., Tillman N. (2022). Effects of feeding a probiotic blend on live performance of broiler chickens from 0 to 49 days of age. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 31, 100273. doi: 10.1016/j.japr.2022.100273
Varastegani A., Dahlan I. (2014). Influence of dietary fiber levels on feed utilization and growth performance in poultry. J. Anim. Prod. Adv. 4, 422–429. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/A-Varastegani/publication/327895220_Fiber_in_Poultry/links/5babe9f5299bf13e604f9782/Fiber-in-Poultry.pdf (Accessed September 9, 2024).
Vitini E., Alvarez S., Medina M., Medici M., De Budeguer M. V., Perdigon G. (2000). Gut mucosal immunostimulation by lactic acid bacteria. Biocell. Off. J. Sociedades Latinoamericanas Microscopia Electronica 24, 223–232. Available online at: https://ri.conicet.gov.ar/bitstream/handle/11336/57246/CONICET_Digital_Nro.91fd511e-f84e-4aa6-abcb-ea416fff4e08_A.pdf?sequence=2&isAllowed=y (Accessed December 1, 2024).
Wan M. L., Forsythe S. J., El-Nezami H. (2019). Probiotics interaction with foodborne pathogens: a potential alternative to antibiotics and future challenges. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 59, 3320–3333. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1490885
Wang H., Ni X., Qing X., Liu L., Xin J., Luo M., et al. (2018a). Probiotic Lactobacillus johnsonii BS15 improves blood parameters related to immunity in broilers experimentally infected with subclinical necrotic enteritis. Front. Microbiol. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00049
Wang W. C., Yan F. F., Hu J. Y., Amen O. A., Cheng H. W. (2018b). Supplementation of Bacillus subtilis-based probiotic reduces heat stress-related behaviors and inflammatory response in broiler chickens. J. Anim. Sci. 96 (5), 1654–1666.
Wang H., Ni X., Qing X., Zeng D., Luo M., Liu L., et al. (2017). Live probiotic Lactobacillus johnsonii BS15 promotes growth performance and lowers fat deposition by improving lipid metabolism, intestinal development, and gut microflora in broilers. Front. Microbiol. 8. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01073
Wishna-Kadawarage R. N., Połtowicz K., Hickey R. M., Siwek M. (2024). Modulation of gene expression in immune-related organs by in ovo stimulation with probiotics and prophybiotics in broiler chickens. J. Appl. Genet. 66 (1), 195–205. doi: 10.1007/s13353-024-00891-y
Xu H., Lu Y., Li D., Yan C., Jiang Y., Hu Z., et al. (2023). Probiotic mediated intestinal microbiota and improved performance, egg quality and ovarian immune function of laying hens at different laying stage. Front. Microbiol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1041072
Yadav S., Jha R. (2019). Strategies to modulate the intestinal microbiota and their effects on nutrient utilization, performance, and health of poultry. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 10, 1–1. doi: 10.1186/s40104-018-0310-9
Yan F. F., Wang W. C., Cheng H. W. (2018). Bacillus subtilis-based probiotic improved bone mass and altered brain serotoninergic and dopaminergic systems in broiler chickens. J. Funct. Foods 49, 501–509. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2018.09.017
Zaghari M., Sarani P., Hajati H. (2020). Comparison of two probiotic preparations on growth performance, intestinal microbiota, nutrient digestibility and cytokine gene expression in broiler chickens. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 48, 166–175. doi: 10.1080/09712119.2020.1754218
Zhang L., Wang Y., Zhang R., Jia H., Liu X., Zhu Z. (2022). Effects of three probiotics and their interactions on the growth performance of and nutrient absorption in broilers. PeerJ 10, e13308. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13308
Keywords: chicken, immunity, gut microbiota, supplementation, stress, poultry production, antimicrobial resistance, chicken behavior
Citation: Idowu PA, Mpofu TJ, Magoro AM, Modiba MC, Nephawe KA and Mtileni B (2025) Impact of probiotics on chicken gut microbiota, immunity, behavior, and productive performance—a systematic review. Front. Anim. Sci. 6:1562527. doi: 10.3389/fanim.2025.1562527
Received: 17 January 2025; Accepted: 21 February 2025;
Published: 31 March 2025.
Edited by:
Assar Ali Shah, Jiangsu University, ChinaReviewed by:
Ravikanth Reddy Poonooru, University of Missouri, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Idowu, Mpofu, Magoro, Modiba, Nephawe and Mtileni. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Peter A. Idowu, YXlvZGVqaWlkb3d1b2x1QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
†ORCID: Peter Ayodeji Idowu, orcid.org/0000-0002-0227-3171
Takalani J. Mpofu, orcid.org/0000-0003-4688-0413
Aletta Magoro, orcid.org/0000-0002-3230-3167
Mamokoma C. Modiba, orcid.org/0000-0003-0141-9703
Khathutshelo A. Nephawe, orcid.org/0000-0002-4181-3134
Bohani Mtileni, orcid.org/0000-0001-5126-598X
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.