
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Anim. Sci. , 26 March 2025
Sec. Animal Nutrition
Volume 6 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fanim.2025.1553829
 Tossaporn Incharoen1,2*
Tossaporn Incharoen1,2* Manatsanun Nopparatmaitree3
Manatsanun Nopparatmaitree3 Adisak Kongkeaw1
Adisak Kongkeaw1 Keatisak Soisuwan4
Keatisak Soisuwan4 Wirot Likittrakulwong5
Wirot Likittrakulwong5 Atichat Thongnum6
Atichat Thongnum6 Nima Norbu7
Nima Norbu7 Jigme Tenzin8
Jigme Tenzin8 Natphapat Supatsaraphokin9
Natphapat Supatsaraphokin9 Juan J. Loor10
Juan J. Loor10Introduction: Heat stress impairs broiler performance and exacerbates oxidative stress. Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) contains cannabidiol (CBD) and other bioactive compounds with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties, which may enhance health status and overall performance in broilers. This study aimed to investigate the effects of dietary micronized hemp fiber (MHF) supplementation on in vitro nutrient digestibility, cecal fermentation, antioxidant enzyme activity, lysosomal function, and productivity in finisher broilers reared under a thermal environment.
Methods: At 21 days of age, 210 broilers with uniform body weight were randomly allocated to three dietary treatments: a basal diet (CON), and diets supplemented with MHF at 0.75% (L-MHF) or 1.50% (H-MHF). Birds had ad libitum access to diets until 42 days of age.
Results: Compared with the CON, there was no effect (p > 0.05) of MHF supplementation on in vitro true digestibility of dry matter, organic matter, crude protein, ether extract, or gross energy. Similarly, gas production at various incubation times and the rate and extent of gas production from cecal fermentation did not differ (p > 0.05). However, cecal fermentation analysis revealed that total volatile fatty acid (VFA) concentrations, including acetic, propionic, and butyric acids, were significantly higher (p < 0.01) in the L-MHF and H-MHF groups. Microbiological analysis revealed increased (p < 0.01) total bacterial counts, lactic acid bacteria, and Enterococcus sp. populations, coupled with reduced E. coli counts in the L-MHF and H-MHF groups. There was a significant (p < 0.001) improvement in final body weight and average daily gain in the H-MHF group compared with the CON and L-MHF groups. Feed conversion ratio was lowest (p < 0.001) in the H-MHF group across all measured periods, while average daily feed intake remained unaffected (p > 0.05). Except for increased (p < 0.05) wing weight in the H-MHF group, dressing percentage or weight of major cuts did not differ (p > 0.05). Antioxidant enzyme activity was enhanced in the MHF-groups, with higher (p < 0.001) catalase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione peroxidase activities observed in the H-MHF and L-MHF groups. However, lysozyme activity was reduced (p < 0.05) in the H-MHF group.
Conclusion: Dietary supplementation with MHF improved in vitro cecal fermentation profiles, antioxidant capacity, and productivity metrics in finisher broilers under thermal stress. These findings underscore the potential of MHF as a functional feed additive in broiler production.
Heat stress in poultry, caused by elevated ambient temperatures, significantly impairs feed intake, nutrient utilization, and growth performance while exacerbating oxidative stress (Kpomasse et al., 2021; Goel, 2021). Oxidative stress is a critical factor leading to compromised growth and productivity in broilers. Nutritional strategies, particularly the incorporation of plant-derived bioactive compounds, have shown potential in alleviating the adverse effects of heat stress by enhancing intestinal health, improving nutrient digestibility, and supporting overall performance (Ivanova et al., 2024; Oni et al., 2024). Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.), a plant with a rich history of medicinal use, has garnered attention in animal nutrition due to its nutraceutical properties. It contains cannabinoids, including cannabidiol (CBD), and other bioactive compounds (Adesina et al., 2020; Ostapczuk et al., 2021). CBD is a key phytocannabinoid derived from various parts of the hemp plant such as flowers, leaves, and stems (Fallahi et al., 2022). Its pharmacological properties include antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anxiolytic, and immunomodulatory effects (Atalay et al., 2019; Wright et al., 2020). Konieczka et al. (2022) noted that CBD derived from hemp has garnered significant attention due to its ability to positively influence gut health and functionality. According to the findings of Kleinhenz et al. (2022), including hemp in the diets (5.5 mg/kg cannabidiolic acid) of male Holstein cattle resulted in a decrease in biomarkers related to inflammation and stress. The administration of hemp-CBD resulted in the upregulation of gene expression associated with gut barrier function and increased the activity of gut bacterial enzymes in broilers in response to a challenge with C. perfringens (Konieczka et al., 2020).
Hemp’s economic value has risen significantly due to its potential biomedical applications (Adesina et al., 2020). Hemp products, especially hemp seed oil, have gained popularity due to their high content of fatty acids and proteins, offering considerable benefits for human dietary applications and antimicrobial properties effective against bacterial and fungal pathogens (Ostapczuk et al., 2021; Meffo Kemda et al., 2024). The demand for hemp-based food has increased by 500% since 2017, driving more intensive agricultural practices and higher resource consumption across the supply chain (Sorrentino, 2021; Meffo Kemda et al., 2024). Typically, hemp seeds are harvested upon maturity, indicated by flower desiccation and seed head development. However, the by-products such as roots, leaves, desiccated seeds, and floral inflorescences are also collected, aligning with bio-green-circular economy principles to promote sustainable agricultural practices (Sopian et al., 2024; Meffo Kemda et al., 2024).
Recent advancements in hemp processing have enhanced the bioavailability of CBD and other cannabinoids by converting inactive cannabinoid acids into their active forms such as CBD, optimizing their physiological effects (Wang et al., 2016; Lima et al., 2022). Lima et al. (2022) reported that activated cannabinoids, such as CBD, may aid in regulating metabolism, alleviating stress, and potentially enhancing immune function, promoting improved health and growth in animals. These advancements support the inclusion of hemp by-products as sustainable feed ingredients or supplement for livestock (Tufarelli et al., 2023; Sopian et al., 2024). In addition, by promoting gut health and microbial balance, dietary fibers derived from hemp by-products may play an essential role in poultry nutrition. Fiber-rich diets improve intestinal morphology, enhance nutrient absorption, and support overall growth, particularly during the latter stages of broiler production (Jha and Mishra, 2021; Zhang et al., 2023). Soluble dietary fibers are rapidly fermented by gut microbiota, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that contribute to gut integrity and immune function (McRorie and McKeown, 2017; Guan et al., 2021). Such attributes may position hemp by-products as an optimal supplement in the formulation of sustainable feed solutions.
This study explored the potential to upcycle and add value to hemp by-products by manufacturing micronized hemp fiber (MHF) by reducing particle size and enhancing phytochemical compositions. Additionally, given the increasing demand for sustainable feeding, evaluating the efficacy of the MHF as a functional supplement under thermal stress conditions is crucial for improving broiler welfare and productivity. We hypothesized that dietary supplementation with MHF would enhance in vitro nutrient digestibility and cecal fermentation, and antioxidant activity, leading to improved growth performance in finisher broilers under thermal stress conditions. This research aimed to provide insights into the application of MHF in modern poultry feeding strategies, contributing to sustainable and efficient broiler management practices.
The hemp by-product consisting of leaves, inflorescences, shriveled seeds and stalks was obtained during the post-harvest processing stage and supplied by Hemp Pro Co. Ltd., Thailand.The materials were processed using a rotary grinder, passed through a 2.0 mm sieve, and classified as unmicronized hemp fiber (UHF). Subsequently, the UHF underwent a two-stage mechanical grinding process, with the first stage involving grinding through a 200-micrometer sieve, followed by a second stage using a 100-mesh (150-micron) screen. The sample was then heated in a hot air oven at 145°C for 10 minutes to induce decarboxylation reactions, which involve breaking a pro-carboxylic acid chain to activate the naturally occurring acid forms of the cannabinoids (Wang et al., 2016). Ultimately, the samples were then collected, stored in zip-lock plastic bags, and designated as MHF. Particle characteristics of the MHF were measured by stereo microscope (Figure 1A), light microscope (Figure 1B), and scanning electron microscope (Figure 1C). Quantitative contents of macronutrients and cannabinoids in the MHF are presented in Table 1.
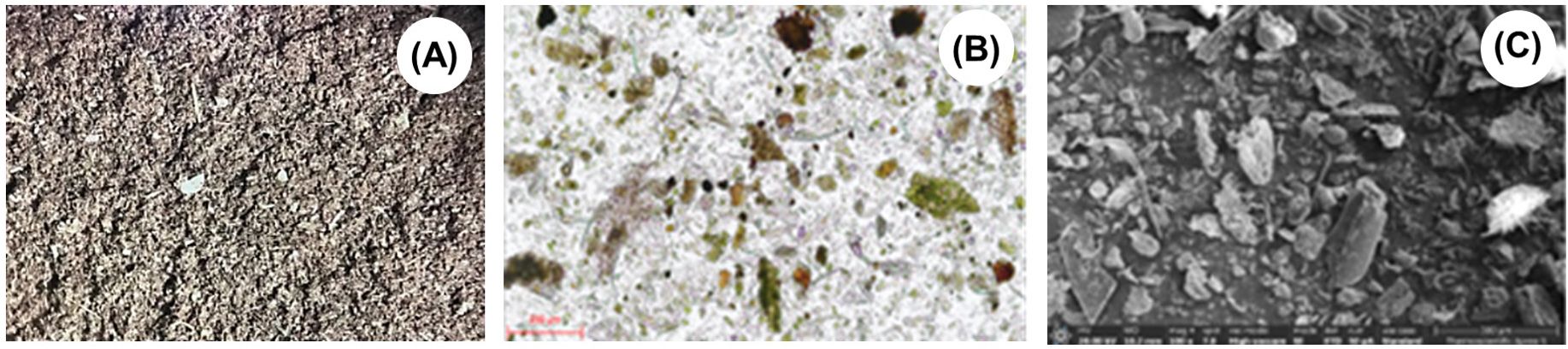

Figure 1. Particle characteristics of the MHF were measured by stereo microscope (A), light microscope (B), and scanning electron microscope (C).
The experiment was carried out in a completely randomized design with three dietary treatments, each consisting of five replicates using triplicates for each replication. The treatments consisted of a basal diet supplemented with MHF at levels of 0% (CON), 0.75% (Low level of micronized hemp fiber: L-MHF), and 1.50% (High level of micronized hemp fiber: H-MHF).
The experimental diets were standardized to deliver 19% crude protein (CP) and 3,000 kcal/kg metabolizable energy (ME). The dietary formulations were based on analyzed nutrient content in compliance with NRC (1994) specifications, as detailed in Table 2. The in vitro prediction of true nutrient digestibility involved a two-step process using enzymatic digestion. A series of feed samples of approximately 0.5 g of finely ground material (1 mm) were mixed with a pepsin solution containing 0.1 g porcine pepsin per 10 ml of a 0.2M HCl solution (pH 2.0). The pH was adjusted to 6.8 using either a 1M HCl or 1M NaOH solution. Subsequently, 1 mL of a freshly prepared pancreatin solution was added, consisting of 0.5 mg of pancreatin dissolved in 10 mL of a 0.2M phosphate buffer (pH 6.8). The nutritional composition (dry matter, organic matter, crude protein, crude fiber, ether extract, and gross energy) of broiler diets and digesta samples was analyzed according to AOAC (2016) methodologies. The in vitro prediction of true nutrient digestibility was calculated using the equation according to AOAC (2016). The in vitro digestibility coefficients were determined by calculating the difference between the initial sample values and the undigested residue values, with adjustments made for dry matter (DM) content based on a blank sample included in each experimental series according to Jezierny et al. (2010).
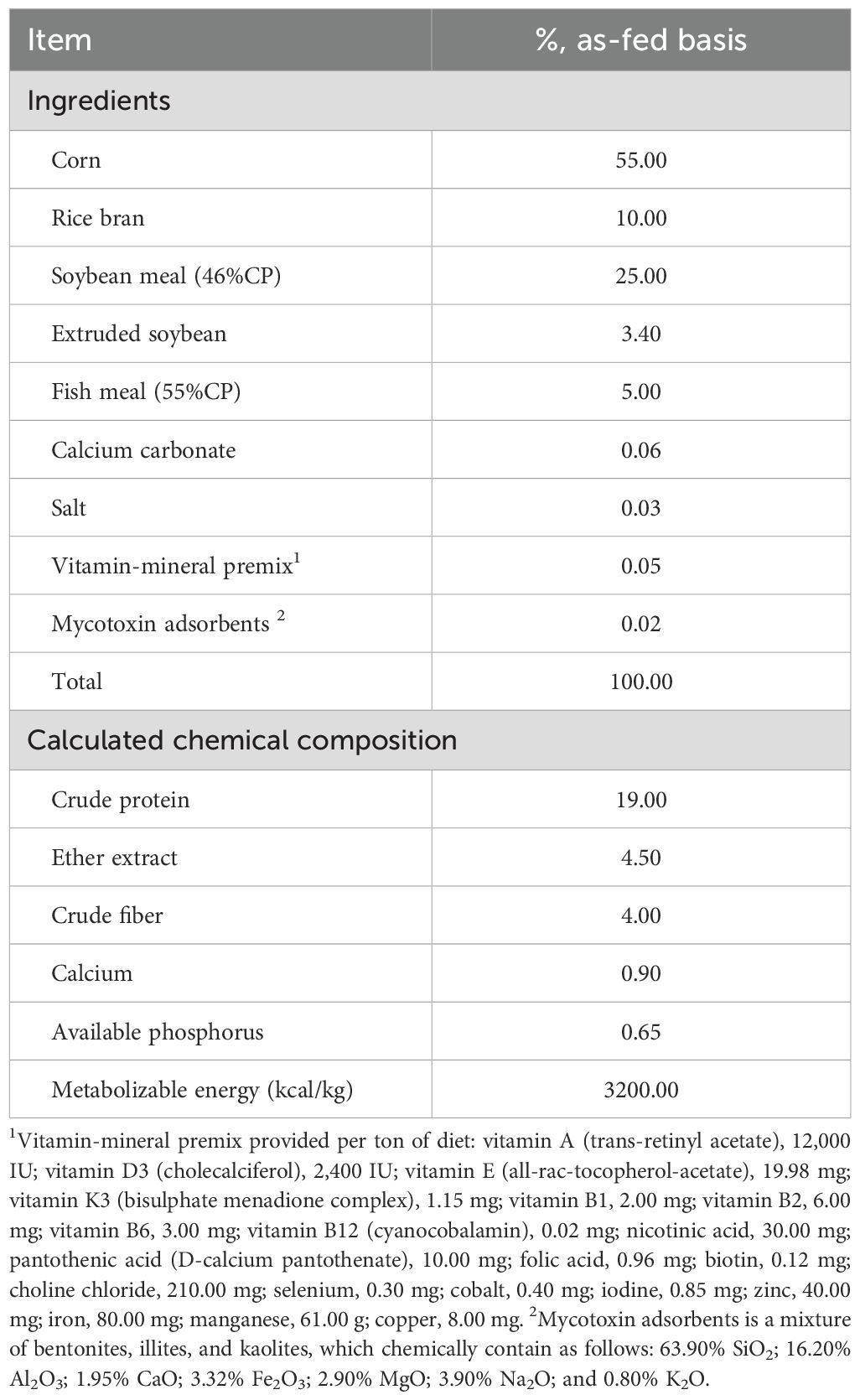
Table 2. Ingredients and calculated chemical composition of a basal diet (% as-fed basis unless stated otherwise).
The in vitro fermentations were set up in 100 mL serum bottles with rubber stoppers filled with 0.3 g of digesta after a two-step process using enzymatic digestion. Cecal samples were diluted at a ratio of 1:10 (w/w) in anaerobic phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; 0.1 mol/L, pH 7.4) before analysis. The Vian Levure (VL) sterile medium was prepared following a modified method adapted from Prayoonthien et al. (2018). All fermentation bottles were inoculated with 5 mL of cecal inoculum solution using a 5-mL syringe. Subsequently, 45 mL of VL sterile medium was added to each bottle to facilitate the fermentation process. For the ileum fermentation bottles, the pH was adjusted to between 5.60 and 5.83 (Gabriel et al., 2006). The media were flushed with carbon dioxide gas, and the in vitro fermentations were conducted at 42°C for 24 hours in an anaerobic chamber. Gas production content was collected after incubation for 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, and 24 h. Cumulative gas production data were calculated according to the equation of Ørskov and McDonald (1979).
where:
a = gas production from upper gut digestible fraction,
b = gas production from cecal fermentation fraction,
c = gas production rate constant for cecal fermentation fraction (b),
t = incubation time,
|a+b| = potential extent of gas production,
P = gas produced at time ‘t’.
Lactic acid and volatile fatty acids were analyzed after 24 hours of in vitro fermentation. A 1 mL sample was centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 10 minutes at 4°C. The supernatant was collected and stored at -20°C for subsequent analysis of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and lactic acid. The concentrations of SCFAs, including acetate, propionate, and butyrate, as well as lactic acid, were analyzed using gas chromatography (GC; Agilent 7890B). A CP-Sil 5 CB column (0.32 mm × 25 m fused silica capillary column) and a flame-ionization detector (FID) were employed for the detection. Internal standards, 4-methylvaleric acid (Alfa Aesar, United Kingdom) for SCFAs and fumaric acid (Alfa Aesar, United Kingdom) for lactic acid, was used following the method described by Mookiah et al. (2014). The final concentrations of SCFAs and lactic acid were calculated using the modified method of Donalson et al. (2008).
The microbiological content was assessed simultaneously following in vitro fermentation, 5 mL solution samples were collected from the glass bottle with rubber seal cap and transferred into 45 mL of 0.85% NaCl solution. The samples were prepared for analysis using a ten-fold dilution method described by Gava et al. (2015). Microorganisms in the laboratory samples were quantified using culture techniques to measure total bacteria, lactic acid bacteria, Enterococcus, and E. coli, following the methods described by McDonald et al. (1983); Horn et al. (1996), and Schillinger and Holzapfel (2003). The microbial counts were then log-transformed (base 10) following the procedure described by Cengiz et al. (2015).
Three hundred one-day-old male Ross 308 broiler chicks were acquired from a local hatchery (Charoen Pokphand Foods PCL., Lamphun, Thailand), and transported to the research site via a controlled-environment truck. These chicks were immediately placed in a brooding zone with sterilized rice hull bedding. Throughout the pre-experimental phase, broilers had ad libitum access to a commercial starter diet containing 21% crude protein (CP) and 3,000 kcal/kg of metabolizable energy (ME), and clean drinking water. At 21 days old, a total of 210 birds with uniform weight was randomly separated into a completely randomized design with 3 dietary treatments, each with 10 replicates of 7 birds. The treatments were a basal diet (Table 2) supplemented with MHF at levels of 0% (CON), 0.75% (L-MHF), and 1.50% (H-MHF). Birds had ad libitum access to each experimental diet through 42 days of age. Animals’ health and biosecurity followed the standard recommendation based on Ross 308 management guidelines. Broilers were housed in a wire pen floored with disinfected rich hull as litter. Each pen was 120 × 60 cm2 and equipped with a nipple drinker and bulk feeder. All experimental birds were reared in the same tunnel-ventilated facility under daily cycling heat stress conditions over a 24 h period of 35 ± 4°C for 12 h, and 31 ± 4°C for 12 h. Relative humidity was held at approximately 70 ± 5% during the whole experimental period.
Body weights and residual feed in each pen were recorded weekly, and then calculations were performed to determine average daily gain (ADG), average daily feed intake (ADFI), and feed conversion ratio (FCR). At the completion of the feeding period, one bird was selected from each replication based on its average body weight from each group (n=10). Subsequently, the selected birds were subjected to an 8-hour fast, and the live body weight was individually measured using a commercial digital balance. Each bird was slaughtered by neck cutting, and its feathers were removed by an automatic plucking machine. Eviscerated carcasses were individually weighed and represented as carcass yield (g/100 g BW). Retailed meat cuts (breast, wings, and thighs + drumsticks) and edible visceral organs (liver without gall bladder, proventriculus, gizzard, and heart) were harvested and reported as g/100 g BW.
At 42 days old, 5 birds with uniform weight were selected from each treatment group for hematological analysis. A puncture was performed on each bird via the wing vein using sterile needles and syringes, and the blood was kept in blood collection tubes without anticoagulant solution. Subsequently, these samples were transferred to a centrifuge at 3,600 × g for 10 min at 4°C. The serum was taken and kept at -20°C until use. The activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), and catalase (CAT) in plasma were determined using colorimetric methods with a spectrophotometer. A modified approach was used to measure SOD activities using a commercial kit (ab65354; Abcam, Cambridge, UK), and the enzymatic activity was represented as the percent inhibition rate. The activity of GSH-Px (EC.1.11.1.9) was determined using assay kits (ab102530; Abcam, Cambridge, UK). The CAT activity (EC1.11.1.6) was analyzed using a commercial spectrophotometric kit (ab83464; Abcam, Cambridge, UK). All samples were measured in triplicate according to the manufacturer’s standard protocols. Lysosomal activity was conducted using a method previously described by Likittrakulwong et al. (2022) with slight modifications. A standard curve demonstrating the degree of lysis of the Gram-positive bacteria Micrococcus lysodeikticus by a known concentration of lysozyme standard was used to test lysosomal activity.
Data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a completely randomized design. The statistical model for in vitro nutrient digestibility and cecal fermentation was: yij = μ + Ti + ϵij, where yij = the observation (i = 1-3, j = 1-5), μ = the overall mean, Ti = the effect of treatment (i= MHF supplementation at levels of 0, 0.75 and 1.50%, and ϵij = the random error. While, the statistical model for in vivo experiment was: yij = μ + Ti + ϵij, where yij = the observation (i = 1-3, j = 1-10), μ = the overall mean, Ti = the effect of treatment (i= MHF supplementation at levels of 0, 0.75 and 1.50%, and ϵij = the random error. Statistical tests were performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) version 17.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, USA). The data are reported as group means with the standard error of the means (SEM). Duncan’s multiple range test was implemented to identify differences between the treatments. A significant effect of treatment was declared at p < 0.05.
Table 3 shows the in vitro true nutrient digestibility of a basal diet supplemented with MHF. The experimental results indicated that when compared with the CON diet, supplementation of MHF at both levels had no significant effect (p >0.05) on true nutrient digestibility of dry matter, organic matter, crude protein, ether extract, and gross energy.
Table 4 summarizes gas production and kinetic degradation of a basal diet supplemented with MHF derived from in vitro cecal fermentation by broiler microbiota. The data showed that gas production at various incubation times (4, 8, 12, 16, 20, and 24 hours) did not differ (p > 0.05) significantly among the dietary treatment groups L-MHF, H-MHF, and CON (Table 4; Figure 2). Furthermore, the experimental results indicated that supplementing the broiler diet with L-MHF and H-MHF had no significant impact on gas production at time ‘t’ or gas production from the upper gut digestible fraction. Similarly, when compared with the CON diet, no significant differences (p > 0.05) were observed in the gas production rate constant for the cecal fermentation fraction (b) or the potential extent of gas production.
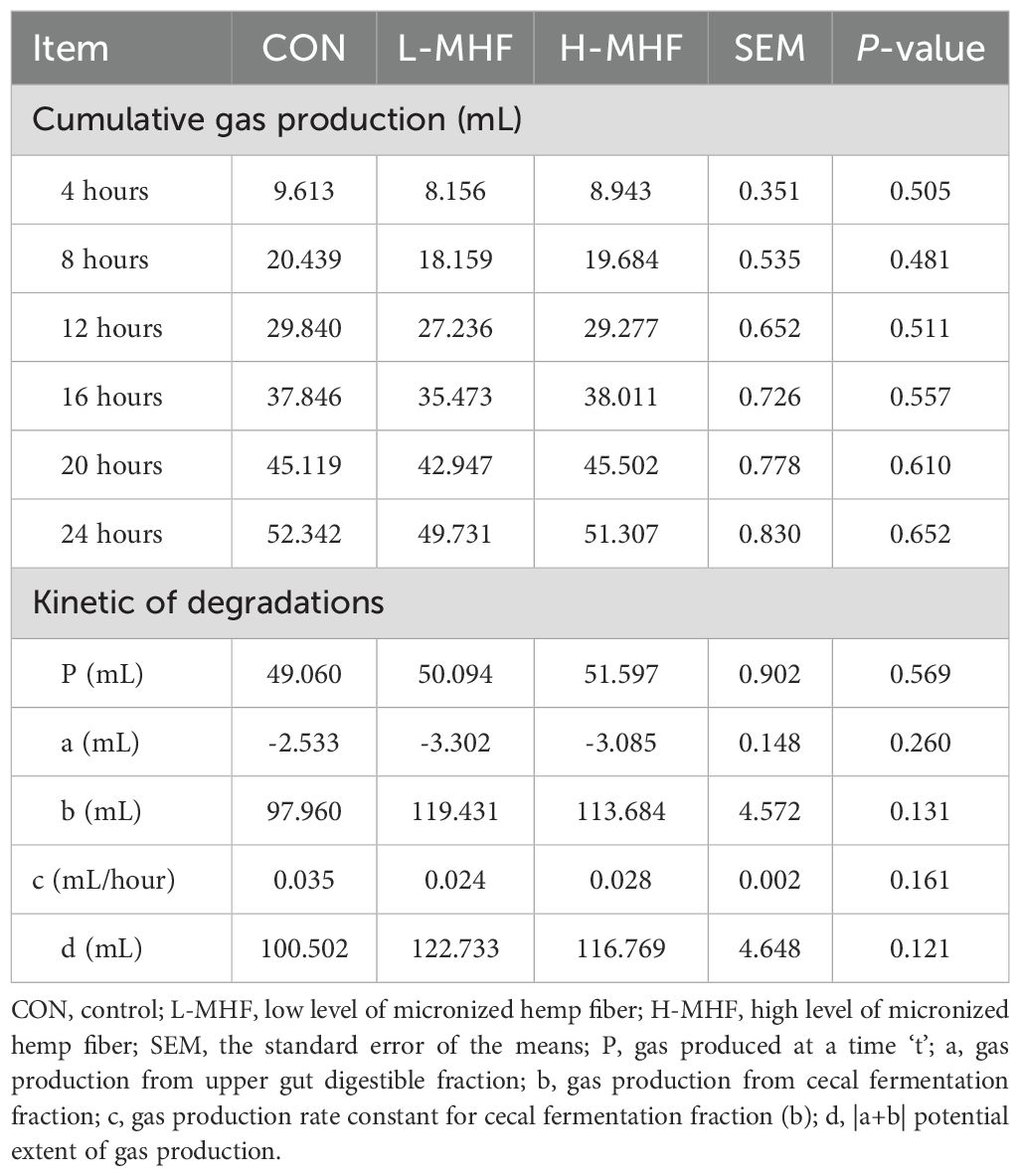
Table 4. Gas production and kinetic degradation of a basal diet supplemented with MHF derived from in vitro cecal fermentation by broiler microbiota.
Figure 2. In vitro cecal gas production in different incubation times of a basal diet supplemented with MHF (CON, control; L-MHF, low level of micronized hemp fiber; H-MHF, high level of micronized hemp fiber).
Table 5 displays concentrations of lactic acid, volatile fatty acids, and microbial counts from in vitro cecal fermentation by broiler microbiota of a basal diet supplemented with MHF. The levels of total lactic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, and butyric acid among the treatments were significantly different (p < 0.01), with the L-MHF and H-MHF groups showing higher values compared with the CON group. Moreover, the H-MHF group had the highest total volatile fatty acid (VFA) levels when compared with the L-MHF and CON groups (p < 0.01). The results from microbiological analysis of in vitro cecal fermentation by broiler microbiota revealed that the H-MHF group had a higher (p < 0.01) total bacterial count compared with the CON group. Additionally, lactic acid bacteria and Enterococcus sp. counts in the L-MHF and H-MHF groups were significantly higher (p < 0.01) than those in the CON group, which positively contributed to inhibiting harmful microorganisms. The data clearly showed that compared with the CON group the E. coli counts in the L-MHF and H-MHF groups were significantly lower (p < 0.01).
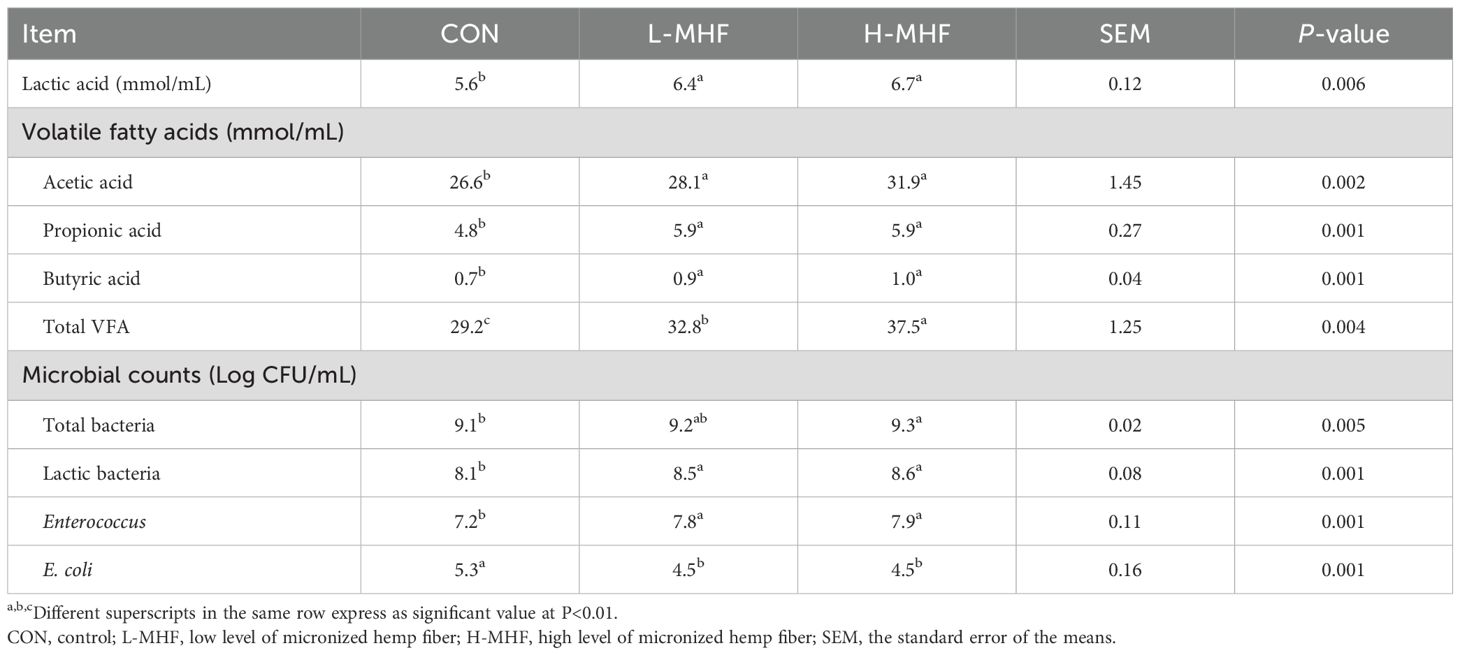
Table 5. Concentrations of lactic acid, volatile fatty acids, and microbial counts of a basal diet supplemented with MHF derived from in vitro cecal fermentation by broiler microbiota.
Table 6 presents the growth performance and economic benefit return of broilers fed a basal diet supplemented with the MHF during 21 to 42 days of age. At 21 days old, the initial body weight was not statistically significant among the groups. However, the final body weight among the treatments was significant (p < 0.001), with the H-MHF group having the highest weight gain compared with CON and L-MHF birds. The average daily gain during the overall period was significantly increased (p < 0.001) in the H-MHF group compared with other treatments. Conversely, there was no significant difference (p > 0.05) in average daily feed intake among the treatments. Despite this, the feed conversion ratio was lowest (p < 0.001) in the H-MHF group during 21 to 28 d, 29 to 35 d, or when calculated throughout the whole experimental period.
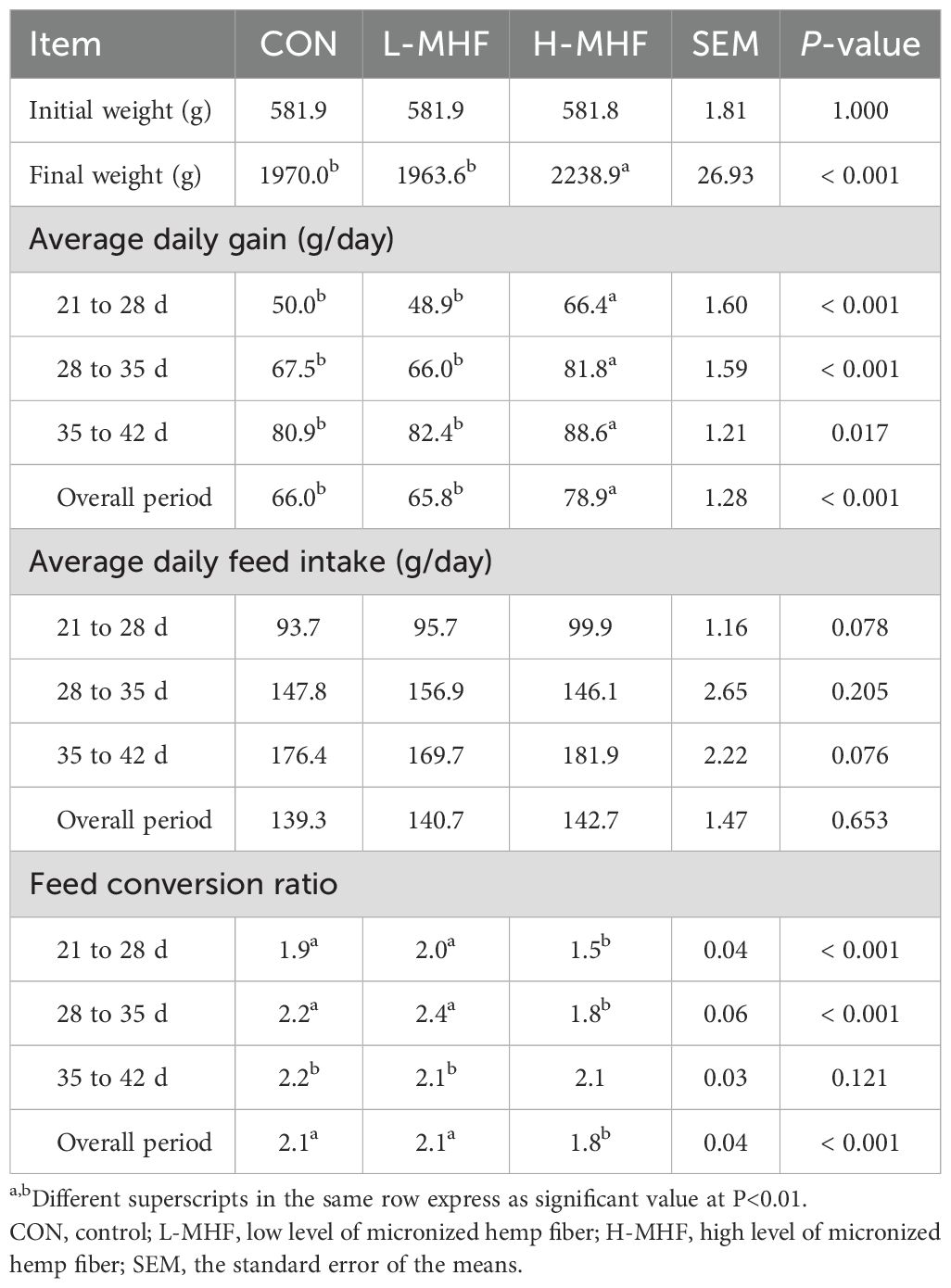
Table 6. Growth performance of broilers fed a basal diet supplemented with the MHF during 21 to 42 days of age.
The carcass characteristics of broilers fed a basal diet with MHF during 21 to 42 days of age are shown in Table 7. There was no significant different difference in dressing, wings, and thighs+drumsticks (p > 0.05). However, the wing was significantly larger and heavier (p < 0.05) in the diet supplemented with the H-MHF. The edible visceral organs in the treatment groups did not differ significantly (p > 0.05). Surprisingly, the weight of the proventriculus, gizzard, and heart were lower (p > 0.05) in the diet supplemented with H-MHF. Thus, overall, the results indicated only modest difference in carcass weight with supplemental MHF.
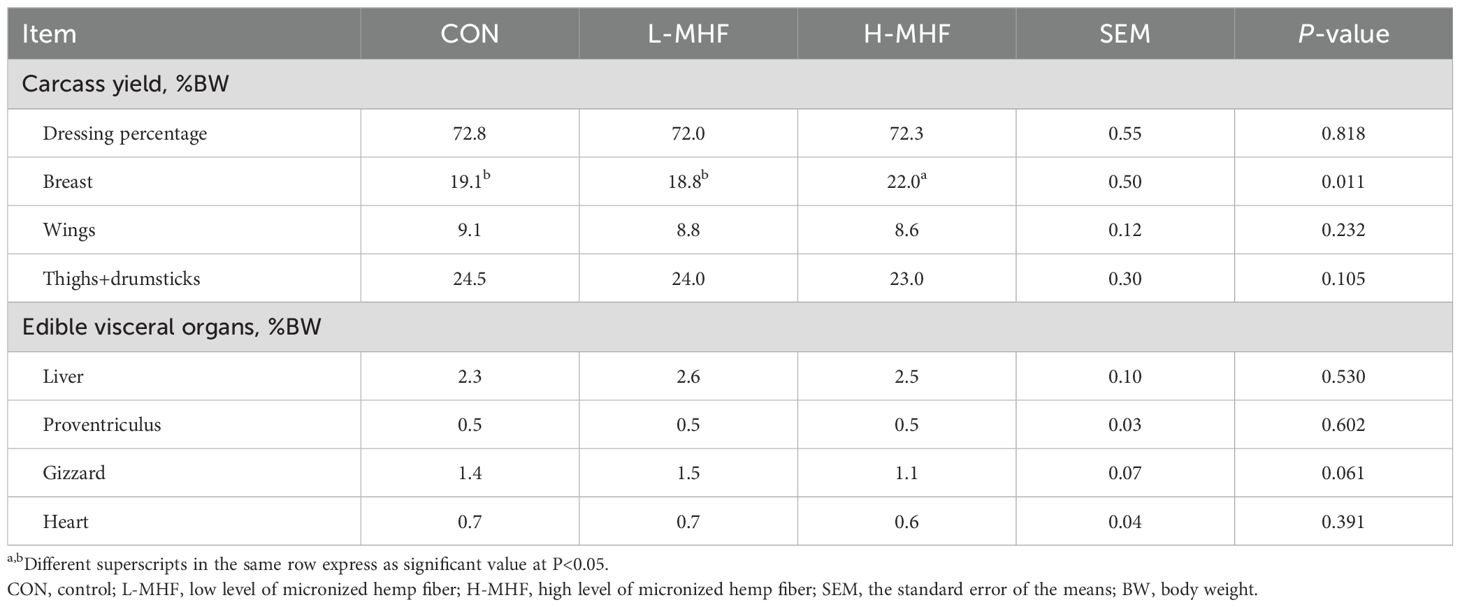
Table 7. Carcass characteristic of broilers fed a basal diet supplemented with the MHF during 21 to 42 days of age.
Figure 3 shows the antioxidant activities of SOD, GSH-Px, and CAT of broilers fed a basal diet supplemented with MHF during 21 to 42 days of age. The CAT activity was significantly different between diets supplemented with MHF and control (p < 0.001). The highest (p < 0.001) CAT and SOD activities were observed in the diet supplemented with H-MHF followed by L-MHF and the lowest in the control. The GSH-Px activity was significantly different with the MHF supplemented diets with highest (p < 0.001) activity in the L-MHF followed by H-MHF diet, and the lowest activity in the control. In addition, the lysozyme activity was lowest (p < 0.05) in the H-MHF and highest in the control (Figure 4). Thus, these results indicate important benefits of supplementation with MHF. Although MHF decreased lysozyme activity and may impact immunity, this effect could be counteracted by the increase in the other antioxidant enzymes.
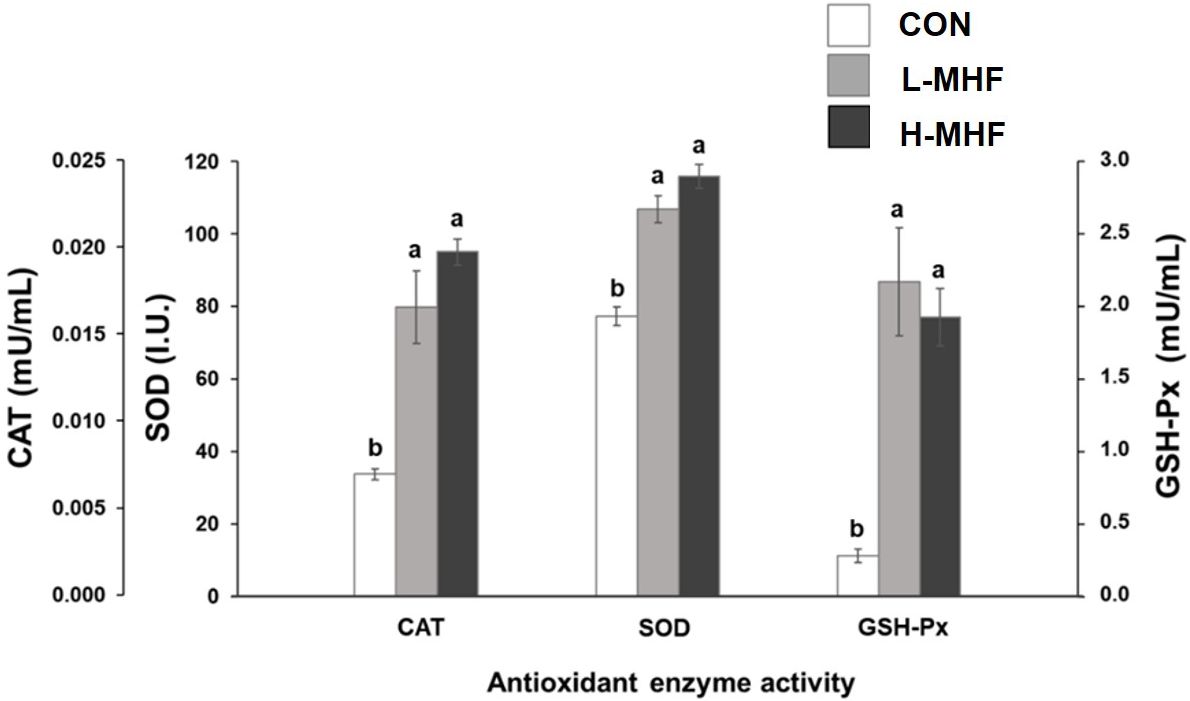
Figure 3. Antioxidant enzyme activities (CAT, catalase; SOD, superoxide dismutase; GSH-Px, glutathione peroxidase) of broilers fed a basal diet supplemented with the MHF during 21 to 42 days of age (CON, control; L-MHF, low level of micronized hemp fiber; H-MHF, high level of micronized hemp fiber). The data represent the means ± SE of 5 replicates. a,bEach bar with different letters denotes a significant difference (P < 0.001).
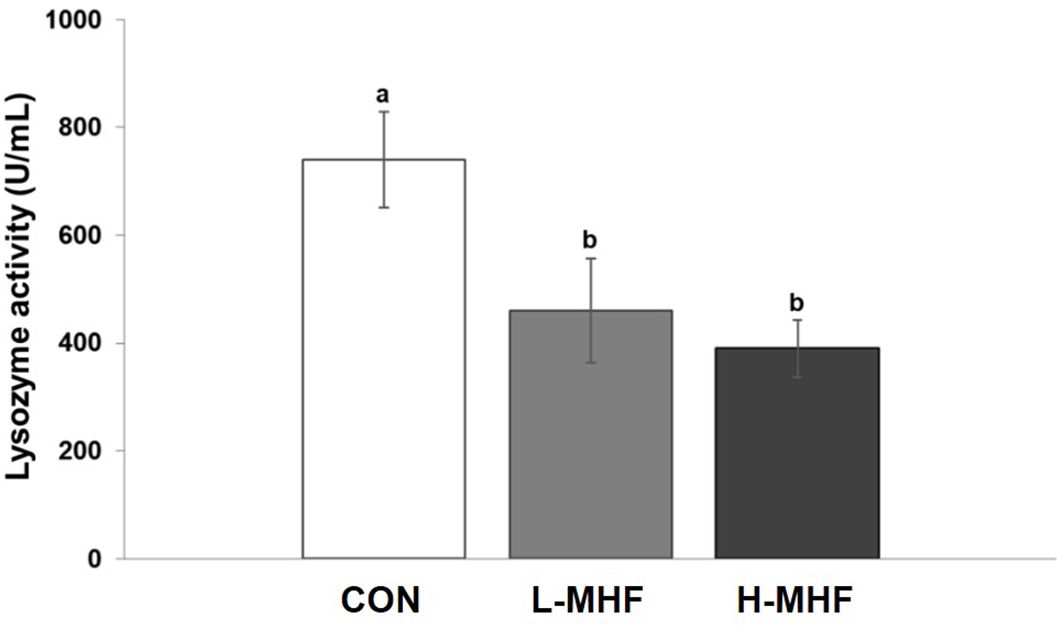
Figure 4. Lysosomal activity of broilers fed a basal diet supplemented with the MHF during 21 to 42 days of age (CON, control; L-MHF, low level of micronized hemp fiber; H-MHF, high level of micronized hemp fiber). The data represent the means ± SE of 5 replicates. a,bEach bar with different letters denotes a significant difference (P < 0.05).
Although the supplementation of MHF did not significantly influence the in vitro true nutrient digestibility, incorporating MHF into the diet has the potential to enhance in vitro cecal fermentation activity by broiler microbiota. Its impact on cecal fermentation suggests a potential prebiotic effect. Additionally, the increase in lactic acid bacteria and Enterococcus spp., coupled with a reduction in E. coli counts, suggests that MHF fosters a more favorable gut microbial balance. This could be due to the soluble fiber fraction in MHF, which serves as a fermentable substrate for beneficial bacteria, promoting competitive exclusion of harmful pathogens. Furthermore, the acidic environment created by VFAs inhibits the growth of harmful pathogens, such as Salmonella and E. coli, while promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria (Walugembe et al., 2015; Palamidi et al., 2023). As a result, a significant increasing in lactic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, and total VFA production was observed in MHF-fed birds. These metabolites are known to improve gut health by lowering pH and inhibiting pathogenic bacteria. Regarding to short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), particularly butyrate, are known to enhance intestinal integrity, reduce inflammation, and provide an energy source for epithelial cells, thereby promoting efficient nutrient absorption (Singh and Kim, 2021; Chandrasekaran et al., 2024). Similarly, Li et al. (2022) observed that dietary fiber supplementation led to promoting acid-producing bacteria and SCFAs, which positively activated AMPK pathway-related genes through the gut-liver axis.
The role of fiber in modulating intestinal morphology, nutrient absorption, and the gut microbiota in broilers has been highlighted in studies by Tejeda and Kim (2021). On the other hand, Walugembe et al. (2015) reported that an increase in dietary fiber led to an elevation in the cecal levels of SCFA, which in turn influenced positively the use of nutrients and general intestinal health in fattening chickens. Similarly, Okrathok et al. (2023) reported that modified dietary fiber in the form of cassava pulp improved cecal microbial populations and the production of SCFA. Ali et al. (2022) observed that the microbial fermentation of dietary fibers leads to the production of SCFA, promoting a healthy intestinal environment in the animal. In this study, the analysis of the nutritive value of MHF revealed that it contained 36.36% dietary fiber, comprising 4.75% soluble dietary fiber and 31.61% insoluble dietary fiber. Because modern broiler feed formulations are deliberately designed with a restricted crude fiber content, the incorporation of MHF into these diets could help achieve an optimal fiber composition. The recommended ratio of soluble to insoluble fiber should range from 30:70 to 40:60 (soluble:insoluble) (Amerah et al., 2009). The present findings suggest that incorporating MHF into broiler diets could serve as a functional strategy to improve cecal fermentation, microbial population, and in consequence growth performance. Additionally, previous studies have demonstrated that dietary fiber supplementation, when optimally balanced between soluble and insoluble fractions, enhances feed efficiency and weight gain in broilers (Jiménez-Moreno et al., 2016; Sabour et al., 2019). Sadeghi et al. (2015) reported that dietary fiber sources with a balanced combination in broiler diet resulted in enhanced immunological function. Lactobacillus populations were significantly elevated in broilers consuming fiber-supplemented diets, which corresponded with superior growth performance and enhanced humoral immune responses (Sabour et al., 2019). In addition, the inclusion of organic acids and fiber sources can improve intestinal performance and health (Adewole et al., 2021). Dietary supplementation with moderate quantities of insoluble fiber, specifically the incorporation of oat or sunflower hulls into low-fiber formulations, resulted in enhanced growth performance parameters in broiler chickens (Jiménez-Moreno et al., 2016). Dietary inclusion of insoluble fiber up to 4% maintains the performance, nutrient metabolism and improves the development of the proventriculus and gizzard in slow-growing broilers (Oliveira et al., 2024). Furthermore, Incharoen et al. (2010) stated that dietary fiber derived from ginger by-product stimulated the intestinal development and function resulting in enhanced growth performance of broiler chickens.
Antioxidant enzyme activities such as GSH-Px, SOD, and CAT, serve as crucial biomarkers for assessing redox reactions and oxidative stress (Gusti et al., 2021). Oke et al. (2024) found that the antioxidant enzymes GPX, SOD, and CAT play a protective role in alleviating oxidative stress caused by environmental challenges such as high temperatures in broilers. Based on our experimental results, the supplementation of the MHF in broiler feed formulations demonstrated significant potential as an approach to upregulate antioxidant enzyme activity. Additionally, it was observed that MHF supplementation led to a reduction in lysosomal activity levels in the serum of broilers. These findings indicated that the observed antioxidant effects may be linked to the bioactive compounds present in MHF, particularly cannabinoids. Several previous studies have described the potential of hemp CBD to significantly influence redox reactions and oxidative stress in broiler chickens, owing to its bioactive properties, particularly its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects (Sopian et al., 2024; Hassan et al., 2023). The CBD antioxidant properties can be attributed to their ability to modulate oxidative stress in chickens. Bień et al. (2024) reported a reduction in oxidative stress markers after CBD supplementation during a lipopolysaccharide challenge, which illustrated the potential of CBD to combat oxidative damage in chickens. In addition, the immunostimulatory and antibacterial effects observed by Balenović et al. (2024) and Hassan et al. (2023) further support the idea that CBD can improve general health in poultry, especially by enhancing the immune response. The CBD can influence several biochemical pathways in experimental birds. Szkopek et al. (2024) reported an interaction between receptors activated by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) and CBD in the intestine, which could significantly contribute to improving intestinal health and nutrient absorption. In addition, Konieczka et al. (2022) observed that the combination of CBD and nano-selenium reduced degenerative changes in the muscle of animals infected with C. perfringens, which underlines the potential of cannabinoids to improve health and muscle performance. Regarding our study, the results obtained indicated that it is likely the improved growth performance of the broilers reared under thermal stress was due to the bioactive compounds present in the micronized hemp fiber, with an emphasis on the cannabinoids (as presented in Table 1).
In conclusion, our investigation revealed that dietary MHF supplementation enhances in vitro cecal fermentation dynamics of broiler microbiota. Supplementation of MHF at a 1.5% inclusion rate can enhance overall growth performance parameters. Collectively, these findings indicate that dietary incorporation of 1.5% MHF benefits overall productivity, potentially through the stimulation of antioxidant mechanisms. The observed beneficial effects may have arisen from the synergistic interaction between the fiber components and phytochemical constituents of MHF. However, while MHF enhanced antioxidant activity, its long-term effects on immune function and gut health require further investigation. Future research should explore its practical application in large-scale poultry production and assess regulatory considerations.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The animal study was approved by The Naresuan University Agricultural Animal Care and Use Committee (approval ID: 66 01 003). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements, adhering to the Ethical Guidelines for Animal Experimentation established by the National Research Council of Thailand.
TI: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MN: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. AK: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. KS: Visualization, Writing – original draft. WL: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. AT: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. NN: Visualization, Writing – original draft. JT: Validation, Writing – original draft. NS: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. JL: Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The authors declare that this study received funding from the Firstly Tech Co. Ltd., Thailand (Grant number R2564A043). The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication. Also, this work was partially supported by Reinventing University Program 2024, The Ministry of Higher Education, Science, Research and Innovation (MHESI), Thailand (Grant number R2567A143).
We gratefully acknowledge Hemp Pro Co. Ltd., Thailand, for providing the hemp by-product samples used in this study. Authors extend our gratitude for the invaluable support of the Reinventing University Program 2024 and the Division of Research and Innovations, Naresuan University. We also thank the Faculty of Agriculture, Natural Resources and Environment, Naresuan University for providing the experimental facilities.
NS is a director at Firstly Tech Co. Ltd.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Adesina I., Bhowmik A., Sharma H., Shahbazi A. (2020). A review on the current state of knowledge of growing conditions, agronomic soil health practices and utilities of hemp in the United States. Agriculture 10, 129. doi: 10.3390/agriculture10040129
Adewole D. I., Oladokun S., Santin E. (2021). Effect of organic acids–essential oils blend and oat fiber combination on broiler chicken growth performance, blood parameters, and intestinal health. Anim. Nutri. 7, 1039–1051. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2021.02.001
Ali Q., Ma S., La S., Guo Z., Liu B., Gao Z., et al. (2022). Microbial short-chain fatty acids: a bridge between dietary fibers and poultry gut health—a review. Anim. Biosci. 35, 1461–1478. doi: 10.5713/ab.21.0562
Amerah A. M., Ravindran V., Lentle R. G. (2009). Influence of insoluble fibre and whole wheat inclusion on the performance, digestive tract development and ileal microbiota profile of broiler chickens. Br. Poult. Sci. 50, 366–375. doi: 10.1080/00071660902865901
AOAC (2016). Association of Official Analytical Chemists. In: Official methods of analysis of AOAC International. 20th Edition (Benjamin Franklin Station, Washington DC: AOAC International).
Atalay S., Jarocka-karpowicz I., Skrzydlewskas E. (2019). Antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties of cannabidiol. Antioxid. (Basel). 9, 21. doi: 10.3390/antiox9010021
Balenović M., Janječić Z., Savić V., Kasap A., Popović M., Šimpraga B., et al. (2024). Immunostimulatory and antibacterial effects of Cannabis sativa l. leaves Broilers. Anim. 14, 1159. doi: 10.3390/ani14081159
Bień D., Michalczuk M., Jóźwik A., Matuszewski A., Konieczka P. (2024). Effects of extracton growth performance, meat physicochemical properties, and oxidative status in chickens challenged with and lipopolysaccharide. Anim. Sci. Pap. Rep. 42, 81–108. doi: 10.2478/aspr-2023-0024
Cengiz Ö., Köksal B. H., Tatlı O., Sevim Ö., Ahsan U., Üner P. A., et al. (2015). Effect of dietary probiotic and high stocking density on the performance, carcass yield, gut microflora, and stress indicators of broilers. Poult. Sci. 94, 2395–2403. doi: 10.3382/ps/pev194
Chandrasekaran P., Weiskirchen S., Weiskirchen R. (2024). Effects of probiotics on gut microbiota: an overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 6022. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116022
Donalson L. M., Kim W. K., Chalova V. I., Herrera P., McReynolds J. L., Gotcheva V. G., et al. (2008). In vitro fermentation response of laying hen cecal bacteria to combinations of fructooligosaccharide prebiotics with alfalfa or a layer ration. Poult. Sci. 87, 1263–1275. doi: 10.3382/ps.2007-00179
Fallahi S., Bobak Ł., Opaliński S. (2022). Hemp in animal diets—cannabidiol. Animals 12, 2541. doi: 10.3390/ani12192541
Gabriel I. L., Mallet S. G., Mallet S., Guillot J. F. (2006). Microflora of the digestive tract: critical factors and consequences for poultry. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 62, 499–511. doi: 10.1017/S0043933906001115
Gava M. S., Moraes L. B., Carvalho D., Chitolina G. Z., Fallavena L. C. B., Moraes H. L. S., et al. (2015). Determining the best sectioning method and intestinal segment for morphometric analysis in broilers. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Avic. 17, (2) 145–149. doi: 10.1590/1516-635x1702145-150
Goel A. (2021). Heat stress management in poultry. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 105, 1136–1145. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13496
Guan Z. W., Yu E. Z., Feng Q. (2021). Soluble dietary fiber, one of the most important nutrients for the gut microbiota. Molecules 26, 6802. doi: 10.3390/molecules26226802
Gusti A. M. T., Qusti S. Y., Alshammari E. M., Toraih E. A., Fawzy M. S. (2021). Antioxidants-related superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), glutathione-s-transferase (GST), and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) gene variants analysis in an obese population: a preliminary case-control study. Antioxid. (Basel) 10, 595. doi: 10.3390/antiox10040595
Hassan F. U., Liu C., Mehboob M., Bilal R. M., Arain M. A., Siddique F., et al. (2023). Potential of dietary hemp and cannabinoids to modulate immune response to enhance health and performance in animals: opportunities and challenges. Front. Immunol. 14. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1285052
Horn K. G., Gedris C. A., Rodney K. M. (1996). Selective isolation of vancomycin-resistant enterococci. J. Clin. Microbiol. 34, 924–927. doi: 10.1128/jcm.34.4.924-927.1996
Incharoen T., Yamauchi K., Thongwittaya N. (2010). Intestinal villus histological alterations in broilers fed dietary dried fermented ginger. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 94, e130–e137. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0396.2010.00994.x
Ivanova S., Sukhikh S., Popov A., Shishko O., Nikonov I., Kapitonova E., et al. (2024). Medicinal plants: A source of phytobiotics for the feed additives. J. Agric. Food Res. 16, 101172. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2024.101172
Jezierny D., Mosenthin R., Sauer N., Eklund M. (2010). In vitro prediction of standardised ileal crude protein and amino acid digestibilities in grain legumes for growing pigs. Animal 4 4, 1987–1996. doi: 10.1017/S1751731110001114
Jha R., Mishra P. (2021). Dietary fiber in poultry nutrition and their effects on nutrient utilization, performance, gut health, and on the environment: a review. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 12, 51. doi: 10.1186/s40104-021-00576-0
Jiménez-Moreno E., de-Coca-Sinova A., González-Alvarado J. M., Mateos G. G. (2016). Inclusion of insoluble fiber sources in mash or pellet diets for young broilers. 1. Effects on growth performance and water intake. Poult. Sci. 95, 41–52. doi: 10.3382/ps/pev309
Kleinhenz M. D., Weeder M., Montgomery S., Martin M., Curtis A., Magnin G., et al. (2022). Short term feeding of industrial hemp with a high cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) content increases lying behavior and reduces biomarkers of stress and inflammation in Holstein steers. Sci. Rep. 12, 3683. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07795-z
Konieczka P., Szkopek D., Kinsner M., Fotschki B., Juśkiewicz J., Banach J. (2020). Cannabis-derived cannabidiol and nanoselenium improve gut barrier function and affect bacterial enzyme activity in chickens subjected to C. perfringens challenge. Vet. Res. 51, 141. doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-00863-0
Konieczka P., Szkopek D., Kinsner M., Kowalczyk P., Michalczuk M., Bień D., et al. (2022). Cannabidiol and nano-selenium increase microvascularization and reduce degenerative changes in superficial breast muscle in C. perfringens-infected chickens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24, 237. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010237
Kpomasse C. C., Oke O. E., Houndonougbo F. M., Tona K. (2021). Broiler production challenges in the tropics: A review. Vet. Med. Sci. 7, 831–842. doi: 10.1002/vms3.435
Li Y., Xia D., Chen J., Zhang X., Wang H., Huang L., et al. (2022). Dietary fibers with different viscosity regulate lipid metabolism via ampk pathway: roles of gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acid. Poult. Sci. 101, 101742. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101742
Likittrakulwong W., Poolprasert P., Hanthongkul W., Roytrakul S. (2022). Effects of intramuscular injections of vitamins AD3E and C in combination on fertility, immunity, and proteomic and transcriptomic analyses of dairy cows during early gestation. BioTech 11, 20. doi: 10.3390/biotech11020020
Lima T. M., Santiago N. R., Alves E. C. R., Chaves D. S. A., Visacri M. B. (2022). Use of cannabis in the treatment of animals: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 23, 25–38. doi: 10.1017/S1466252321000189
McDonald L. C., Hackney C. R., Ray B. (1983). Enhanced recovery of injured Escherichia coli by compounds that degrade hydrogen peroxide or block its formation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 45, 360–365. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.360-365.1983
McRorie J. W. Jr., McKeown N. M. (2017). Understanding the physics of functional fibers in the gastrointestinal tract: an evidence-based approach to resolving enduring misconceptions about insoluble and soluble fiber. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 117, 251–264. doi: 10.1016/j.jand.2016.09.021
Meffo Kemda M., Marchi. M., Nerim E., Marchettini N., Niccolucci V. (2024). Environmental impact assessment of hemp cultivation and its seedbased food products. Front. Environ. Sci. 12. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1342330
Mookiah S., Sieo C. C., Ramasamy K., Abdullah N., Ho Y. W. (2014). Effects of dietary prebiotics, probiotic and synbiotics on performance, caecal bacterial populations and caecal fermentation concentrations of broiler chickens. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 94, 341–348. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.6365
National Research Council (1994). Nutrient requirement of poultry. 9th Edn (Washington, DC: National Academy Press).
Oke O. E., Akosile O. A., Oni A. I., Opowoye I. O., Ishola C. A., Adebiyi J. O., et al (2024). Oxidative stress in poultry production. Poult. Sci. 103, 104003. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104003
Okrathok S., Sirisopapong M., Mermillod P., Khempaka S. (2023). Modified dietary fiber from cassava pulp affects the cecal microbial population, short-chain fatty acid, and ammonia production in broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 102, 102265. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102265
Oliveira N. R., Santos F. R., Sousa Silva M. R., Rissato I. S., Roque G. C., Silva C. M., et al. (2024). Dietary levels of soluble and insoluble fibre sources for young slow-growing broilers. Czech J. Anim. Sci. 69, 139–154. doi: 10.17221/84/2023-CJAS
Oni A. I., Adeleye O. O., Adebowale T. O., Oke O. E. (2024). The role of phytogenic feed additives in stress mitigation in broiler chickens. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 108, 81–98. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13869
Ørskov E. R., McDonald I. (1979). The estimation of protein degradability in the rumen from incubation measurements weighted according to rate of passage. J. Agric. Sci. 92, 499–503. doi: 10.1017/S0021859600063048
Ostapczuk K., Apori S. O., Estrada G., Tian F. (2021). Hemp growth factors and extraction methods effect on antimicrobial activity of hemp seed oil: A systematic review. Separations 8, 183. doi: 10.3390/separations810018
Palamidi I., Paraskeuas V. V., Mountzouris K. C. (2023). Dietary and phytogenic inclusion effects on the broiler chicken cecal ecosystem. Front. Anim. Sci. 3. doi: 10.3389/fanim.2022.1094314
Prayoonthien P., Nitisinprasert S., Keawsompong S. (2018). In vitro fermentation of copra meal hydrolysate by chicken microbiota. 3 Biotech. 8, 41. doi: 10.1007/s13205-017-1058-1
Sabour S., Tabeidian S. A., Sadeghi G. (2019). Dietary organic acid and fiber sources affect performance, intestinal morphology, immune responses and gut microflora in broilers. Anim. Nutr. 5, 156–162. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2018.07.004
Sadeghi A., Toghyani M., Gheisari A. (2015). Effect of various fiber types and choice feeding of fiber on performance, gut development, humoral immunity, and fiber preference in broiler chicks. Poult. Sci. 94, 2734–2743. doi: 10.3382/ps/pev292
Schillinger U., Holzapfel W. H. (2003). Chapter 8 Culture media for lactic acid bacteria. Progr. Industr. Microbiol. 37, 127–140. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6352(03)80011-5
Singh A. K., Kim W. K. (2021). Effects of dietary fiber on nutrients utilization and gut health of poultry: A review of challenges and opportunities. Anim. (Basel). 11, 181. doi: 10.3390/ani11010181
Sopian Y., Sartsook A., Arjin C., Lumsangkul C., Sringarm K., Sivapirunthep P., et al. (2024). Dietary supplementation of Cannabis sativa residues in broiler chickens affects performance, carcass characteristics, intestinal morphology, blood biochemistry profile, and oxidative stability. Poult. Sci. 103, 104117. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104117
Sorrentino G. (2021). Introduction to emerging industrial applications of cannabis (Cannabis sativa L.). Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei. 32, 233–243. doi: 10.1007/s12210-021-00979-1
Szkopek D., Mendel M., Kinsner M., Fotschki B., Juśkiewicz J., Kozłowski K., et al. (2024). Interaction between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and cannabidiol in the gut of chickens applied to different challenge conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 11398. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111398
Tejeda O. J., Kim W. K. (2021). Role of dietary fiber in poultry nutrition; review. Anim. (Basel). 11, 461. doi: 10.3390/ani11020461
Tufarelli V., Losacco C., Tedone L., Passantino L., Tarricone S., Laudadio V., et al. (2023). Hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) cake as sustainable dietary additive in slow-growing broilers: effects on performance, meat quality, oxidative stability and gut health. Vet. Q. 43, 1–12. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2023.2260448
Walugembe M., Hsieh J. C. F., Koszewski N. J., Lamont S. J., Persia M. E., Rothschild M. F. (2015). Effects of dietary fiber on cecal short-chain fatty acid and cecal microbiota of broiler and laying-hen chicks. Poult. Sci. 94, 2351–2359. doi: 10.3382/ps/pev242
Wang M., Wang Y. H., Avula B., Radwan M. M., Wanas A. S., Van Antwerp, et al. (2016). Decarboxylation study of acidic cannabinoids: a novel approach using ultra-high-performance supercritical fluid chromatography/photodiode array-mass spectrometry. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 1, 262–271. doi: 10.1089/can.2016.0020
Wright M., Di Ciano P., Brands B. (2020). Use of cannabidiol for the treatment of anxiety: a short synthesis of pre-clinical and clinical evidence. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 5, 191–196. doi: 10.1089/can.2019.0052
Keywords: micronized hemp fiber, broiler productivity, in vitro nutrient digestibility, cecal fermentation, antioxidant enzyme activity, thermal stress
Citation: Incharoen T, Nopparatmaitree M, Kongkeaw A, Soisuwan K, Likittrakulwong W, Thongnum A, Norbu N, Tenzin J, Supatsaraphokin N and Loor JJ (2025) Dietary micronized hemp fiber enhances in vitro nutrient digestibility and cecal fermentation, antioxidant enzyme, lysosomal activity, and productivity in finisher broilers reared under thermal stress. Front. Anim. Sci. 6:1553829. doi: 10.3389/fanim.2025.1553829
Received: 31 December 2024; Accepted: 18 February 2025;
Published: 26 March 2025.
Edited by:
Michael D. Flythe, United States Department of Agriculture, United StatesReviewed by:
Sohail Ahmad, University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, PakistanCopyright © 2025 Incharoen, Nopparatmaitree, Kongkeaw, Soisuwan, Likittrakulwong, Thongnum, Norbu, Tenzin, Supatsaraphokin and Loor. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tossaporn Incharoen, dG9zc2Fwb3JuaUBudS5hYy50aA==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.