
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Anim. Sci. , 13 March 2025
Sec. Animal Breeding and Genetics
Volume 6 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fanim.2025.1513876
Objective: Embryo death in the early stages, primarily caused by lethal alleles in the homozygous state, is one of the important challenges in dairy cattle breeding. The availability of large-scale genomic SNP data has proven to be a promising tool for identifying recessive genetic defects. This study was conducted to identify lethal alleles and genes causing embryo death in Holstein dairy cattle using omics data in genomic and transcriptomic level.
Methods: High-density Bovine770K SNP array genotypes of 3117 samples and whole-genome sequences (WGS) of 743 cows were utilized to identify lethal SNPs, defined as those markers significantly departing from Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium and lacking one of the homozygous genotypes.
Results: The potential candidate lethal SNPs are harbored by PARD3, BAHD1, FZD3, ERGIC2, IQCN, PROK1, PCTP, SH3GLB1, and RASSF5 genes, according to the ARS-UCD1.2 Bos taurus genome assembly. Transcriptome analysis showed that these genes are steadily expressed in the various embryonic tissues during different stages of embryo development, and therefore were considered as the potential candidate lethal genes. These genes play important roles in various biological processes of embryo development and prenatal survival ability in dairy cattle embryos. These genes contribute to the important embryo lethality-related mechanisms, including the regulation of cell polarity, placental development, phospholipid transport, and apoptosis.
Conclusion: The findings of this study provide insight into the complex molecular mechanisms of embryo mortality at the early stage of pregnancy caused by genes following the recessive inheritance model.
Reproduction is of economic importance in the livestock farming industry, and particularly in dairy cattle farms. Achievement of high reproductive performance in dairy cows (calving interval of 12 or 13 months with the first calf born at 24 months of age) requires a focus on management activities, especially during calving and the first 100 days following calving (Szenci, 2021). High embryonic mortality rates remain a major challenge in mammalian reproduction (Spencer, 2013). Embryonic deaths can occur at various stages of embryonic development, and much of the loss occurs early on (< day 16), shortly after fertilization. As a result, most pregnancies remain undiagnosed and the only sign of early mortality is reported to be reduced fertility (Spencer, 2013). Embryonic mortality, occurring before the 42nd day of pregnancy, significantly impacts the reproductive performance of cows. It is estimated that the extent of pregnancy loss in dairy cattle is 41 to 57%, with most occurring before day 16 when cows return to estrus due to early embryonic mortality and loss of corpus luteum (Spencer, 2013; Long, 2009; Noakes et al., 2001).
The factors involved in embryonic or fetal mortality are categorized into genetic, nutritional, endocrine, physiological, and environmental sources (Rani et al., 2018). There are several genetic factors and chromosomal abnormalities that lead to embryonic mortality (Perkel et al., 2015). Specifically, in terms of genetic factors, the primary cause of embryonic death is the lethal alleles in the homozygous state, which result in embryonic death (Jenko et al., 2019). Therefore, the homozygote genotypes of these loci may cause reproduction inefficiency and a substantial economic loss in dairy cattle breeding (Wu et al., 2019). Cole et al. (2016) stated that recessive lethal genes cause a significant economic loss (~ $11 million (mln) per year) due to reduced fertility and perinatal calf death in Holstein (~ $7,5 mln), Jersey ($2,9 mln), Ayrshire (~ $ 0.11 mln) and Brown Swiss (~ $ 0.233 mln) cattle population in the US. The wide use of a limited number of sires, with desirable economic traits, for artificial insemination in dairy cows has improved productivity, but it has also increased the risk of homozygosity in individuals and harmful alleles spread in the population (Mueller and Van Eenennaam, 2022). Traditionally, identifying genetic factors that cause embryonic defects or death involves tracking the common ancestors of affected animals using pedigree information (Wu et al., 2019). This approach requires phenotype information (affected and unaffected animals), and is not effective and efficient in identifying harmful genetic mutations even with very large sets of phenotypic and pedigree information (VanRaden et al., 2011). Additionally, this method is quite ineffective where the phenotype is not detectable, such as primary embryonic deaths. The lethal recessive alleles compromise embryonic survival and the alleles cause pre- or postnatal death in homozygous affected individuals (Derks et al., 2019). According to the recessive genetic inheritance model, the genes require two copies, one from each parent, to cause embryonic death. Therefore, the lethal recessive alleles that act prenatally may be distinguished from the lack of attendance of homozygous individuals in a population (Zhang et al., 2018). Thanks to advancing the genotyping technologies, the genome-wide SNP information can be used to identify loci that are common in the population but never occur in the homozygous state in living animals (Wu et al., 2019). This approach enables the identification of lethal alleles based on genomic information that collected from living animals, without any phenotype records required (VanRaden et al., 2011).
The occurrence of genetic bottlenecks due to domestication and breed formation has led to an increase in the frequency of harmful mutations and a decrease in genetic diversity in the gene pool of many domesticated breeds (Marsden et al., 2016; Bosse et al., 2019; Upperman et al., 2019). These processes lead to a reduction in genetic diversity, which increases the risk of drift and inbreeding in future generations of the population. Lethal mutations that have reached high frequencies are identified by deviation from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium and the absence of homozygous individuals for an allele (VanRaden et al., 2011). The identification and management of these alleles are crucial for the sustainability and productivity of the cattle breeding programs. This information can help to prevent the drift of these mutations to higher frequencies and improve the farm profitability by enhancing the fertility rates and reducing the occurrence of embryonic mortality. Therefore, the objective of this study was to identify embryonic lethal genes in the Holstein cattle population using genomic and transcriptomic information. Therefore, here we used population genetics methods to identify potentially lethal SNPs and transcriptomic data to investigate if genes harboring these SNPs show a steady expression levels across various embryonic tissues during different stages of embryo development.
Since, we haven’t interacted with the alive animals in this study and all the data were provided by the other researchers or were obtained from the public databases, therefore the approval by the animal ethics approval was not required.
In the present study, omics data in the levels of genome (SNP array genotypes and whole genome sequences data) and transcriptome (RNA-seq data) were used to identify potential lethal genes in Holstein dairy cattle. There are two approaches to study the early embryo lethal variants and genome regions, including variant- and haplotype-based detection. In this work, we applied population genomic methods to identify the lethal variants and genes following the procedure proposed by Todd et al. (2020). The flow chart of the consecutive steps of processing the data and applied approaches in this study is shown in Figure 1.
The SNP genotypes consisted of ≥ 617885 markers originated from three Holstein cattle populations (n=3117) genotyped by Illumina BovineHD 770K SNP BeadChip platform. Animals with more than 5% missing genotypes were excluded (n=180). SNPs with unknown position or located on sex chromosomes were filtered out. Also, only SNPs with ≥ 95% genotype call rate and minor allele frequency (MAF) ≥ 0.05 were retained. The quality control step was performed using PLINK v 1.9. Following the quality control step, the genotype information (> 559K SNPs) for 2937 individuals were available for further analysis. The number of samples and SNPs in raw data and after quality control step are shown in Tables 1, 2, respectively. The distribution of the SNPs over the chromosomes is summarized in Supplementary Table S1.
The whole genome sequence (WGS) data were obtained from Alemu et al. (2021), which is publicly free available. The data included 13,037,955 markers for 743 Holstein cattle. The whole process of generating the final Variant Call Format (VCF) file including DNA extraction, library preparation, reads alignment to the reference genome (Bos Taurus UMD 3.1), base quality calibration, variant calling and variant quality score recalibration have been described by Kadri et al. (2016). We selected 12,735,685 bi-allelic SNP located on autosomal chromosomes. After filtering out the SNPs with MAF (≥ 0.05), 4,279,775 SNPs for 743 sample remained for further analysis.
Genome-wide SNP data for each population was scanned for lethal SNPs which were defined as those: (1) are significantly deviated from the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, tested using test (p <7*10-8) using PLINK v 1.9, (2) lack of one of the homozygous genotypes, and (3) with ≥5 expected homozygote cows for the minor allele. Since the technical and systematic issues may affect the allele frequency, we considered only SNPs which were common in at least two populations, to avoid any unbiasedness. The same procedure was applied on WGS data for detecting the lethal variants in this dataset. In order to identify the lethal genes underlying the embryonic mortality in cattle, the genic variants were mapped on the last genome assembly (ARS-UCD1.2 Bos taurus). To achieve high-confidence results, we applied a narrow filtration on the genes harboring the resulted SNPs. Therefore, only those genes meeting all the following criteria were considered as potential candidate lethal genes: (1) harboring SNPs common in at least two populations, or genes which harbor a SNP from the chip array genotypes and ≥5 SNPs from the WGS data, (2) are annotated to the functions related to embryo mortality and development, and (3) have been expressed constantly over the early embryo stages.
The Bovine HD arrays and WGS positions, which were initially based on UMD3.1 genome assembly, were converted to ARS-UCD1.2 reference genome using UCSC liftOver online tool (https://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgLiftOver) with the default options. The genes harboring potential candidate lethal SNPs were explored using Ensembl Biomart online tool and the Ensembl genes 111 database. Also, the the Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor (VEP) online tool was used to check the mutation type within the gene (synonymous or non-synonymous). The comparative genomics tool in Ensembl was used to determine the orthologous genes in placental mammals’ species (n=103) and all species available on Ensemble database (n=214). Enrichment analyses of gene ontology terms, including biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF) categories were conducted using various bioinformatics platforms, ensemble (https://www.ensembl.org/Bos_taurus/Info/Index), Genecards (https://www.genecards.org/), NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), UniProt (https://www.uniprot.org/) and DAVID (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/) tools.
In order to explore the expression patterns of the genes of interest across the various stages of embryonic development, the publicly free available transcriptome data on NCBI were used. Two transcriptome data including RNA-seq of embryonic tissues (trophoblast, endoderm, and mesoderm, collected on 14, 15, and 18 days of embryo development; under project PRJNA230971) and RNA-seq of fetal stem cells (under project PRJNA718333) were investigated. These datasets had been generated employing standard protocols on the Hiseq 2000 platform, facilitated by the FastTrack service at Illumina. The gene expression analysis of all annotated genes was conducted using CLC Genomics Workbench (version: 8.5.1) QIAGEN Bioinformatics (https://www.qiagenbioinformatics.com/), including quality control of reads, filtering out unwanted reads, removing adapter contamination, and mapping reads to the Bos taurus ARS-UCD1.2 reference genome. Expression levels were quantified in the RPKM scale. Additionally, we utilized NGS-based transcriptome data of 10 studies available on cattle Genotype-Tissue Expression (cGTEx, http://cgtex.roslin.ed.ac.uk/) atlas to assess the expression level of the genes, measured by RNA-seq, in different tissues over various developmental stages of embryo. The accession number of these transcriptome data and sample size are given in Supplementary Table S2.
We also assessed the overlaps of the final gene list with identified QTLs underlying mortality related traits. To do this, the position of genes was inquired in Bovine QTL database available online at AnimalQTLdb (accessed in September 2024: https://www.animalgenome.org/cgi-bin/QTLdb/BT/index).
Utilizing population genetics procedures on SNP genotypes data, 11, 42 and 80 SNPs were identified in populations 1, 2 and 3, respectively (Table 3). The variants were distributed, not uniformly, over 25 chromosomes. There were no SNPs on BTA 12, BTA 22, BTA 24 and BTA 25. The number of identified variants varied between 1 SNP on BTA14 and BTA 26 to 18 SNPs (identified in all three population) on BTA 7. The distribution of the lethal variants identified in the populations over different autosomes are shown in Supplementary Figure S1.
The majority of the SNPs were identified only in one population, but the population had some SNPs in common. Around 6.7% of the lethal SNPs (n=6) were common among all the populations, indicating a high confidence level in their functional relevance to embryonic lethality. Figure 2 show the shared potential lethal variants among the studied populations, in Venn diagram. In the WGS dataset, 13,323 markers remained after applying the SNP discovery criteria, distributed across all 29 autosomes.
The distribution of the variants over the genome obtained by Ensemble Biomart showed that ≥43% of variants are located within intergenic regions. The distribution of the lethal variants of SNP array and WGS data over different functional annotation classes are presented in Supplementary Figures S2, S3, respectively. However, these SNPs are not functional variants, they can play an important role in survival-related gene expression. The intergenic region was initially referred to as junk DNA, but the further studies showed that they may regulate expression of the other genes through (de)methylation of the CpG islands (Madakashira and Sadler, 2017). Therefore, despite of their biological importance, due to lack of available information, the intergenic variants were not considered for the further steps.
The genic lethal variants located on 24 genes, which are listed in Table 4. Two genes harbor the common SNPs in three populations, while the SNPs located on 19 genes were common in two populations. The rest three genes harbor at least one variant of SNP chip data and 7 markers from WGS data.
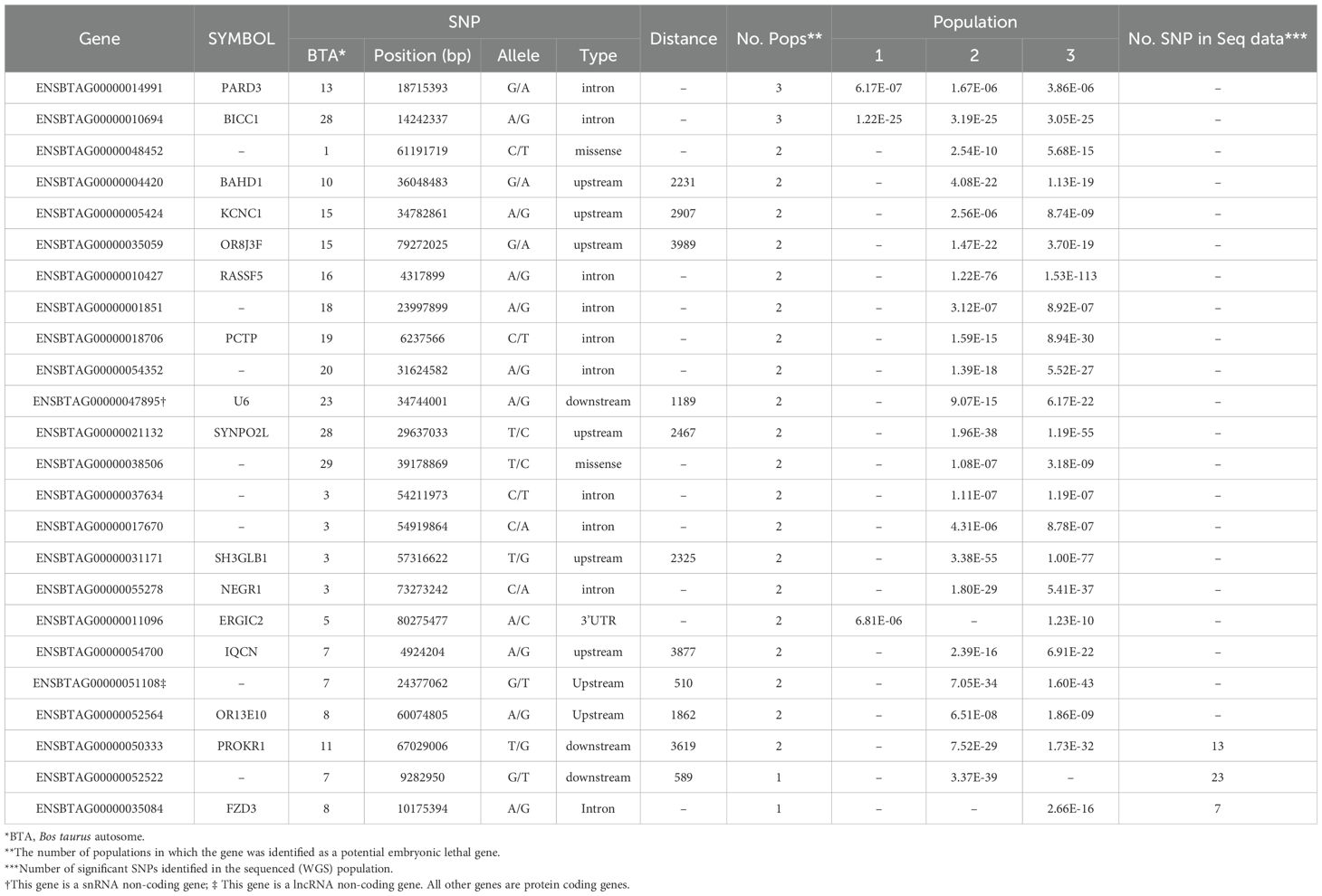
Table 4. List of the identified lethal genes harboring the lethal SNPs, along with the physical position of the SNP, variant type, distance of the SNP to the gene, and significant level of SNP in the populations.
In this study, we focused on coding genes with functionality on embryo development in cattle. The constant expression of a gene during the developmental stages of the embryo can indicate the gene's importance for embryo survival and development. Therefore, the genes which are steadily expressed during different stage of embryo growth and development were considered as potential embryo lethal genes. The expression level of the genes of interest obtained from 12 RNA-seq analysis, available on cGTX, are shown in Figure 3. These expression pattern have been shown as the cumulative percentage of the samples (%) of each study where the gene is expressed. The results showed that 10 genes are expressed in almost all the samples of these studies. Two studies, PRJNA432600 and PRJNA243569, were specifically evaluated due to different stages of the embryo development and diverse tissue samples including PRJNA432600 (stem cells and blastocyst stage; Supplementary Table S3) and PRJNA243569 (blastocyst, elongated embryo, hatched embryo, implantation and maternal recognition of pregnancy). The results are shown in Figure 4, which confirm the results of the former transcriptome analysis, indicating that these 10 genes are expressed in at least in one tissue of all samples of these studies, and additionally in ≥60% of the samples in all these studies, regardless the tissue. The expression level of the potential candidate lethal genes in different stages of development of embryo are given in Table 5. However, the expression level of the genes varied in different tissues or stages, but all the genes are constantly expressed during the developmental stages including blastocyst, elongated embryo, hatched embryo, implantation and pregnancy. The early developmental stages of the embryo are critical for the establishment of pregnancy in cow. Particularly, the peri-implantation stages that occur on days 7, 10, 13, 16 and 19 of pregnancy (Mamo et al., 2011). Therefore, the continued expression of a gene during the peri-implantation stages might be a sign of critical function of the gene in embryo growth and development. In the PRJNA243569 study, the gene expression has been studied at 7, 10, 13, 16 and 19 days of pregnancy, which are crucial for bovine embryo development. All the genes showed a steady expression pattern during the aforementioned stages, with a small fluctuation. The expression analysis of the genes in another study (PRJNA432600), during the stages of blastocyst and bovine embryonic stem cells (bESC) also showed that all the genes except for IQCN and PROKR1 are expressed in both stages. The lower expression level (or lack of expression of these two genes) in the later study (PRJNA432600) compared to the former study (PRJNA243569) may be due to sample preparation or technical issues, and/or a small sample size (2 samples) in the blastocyst stage.
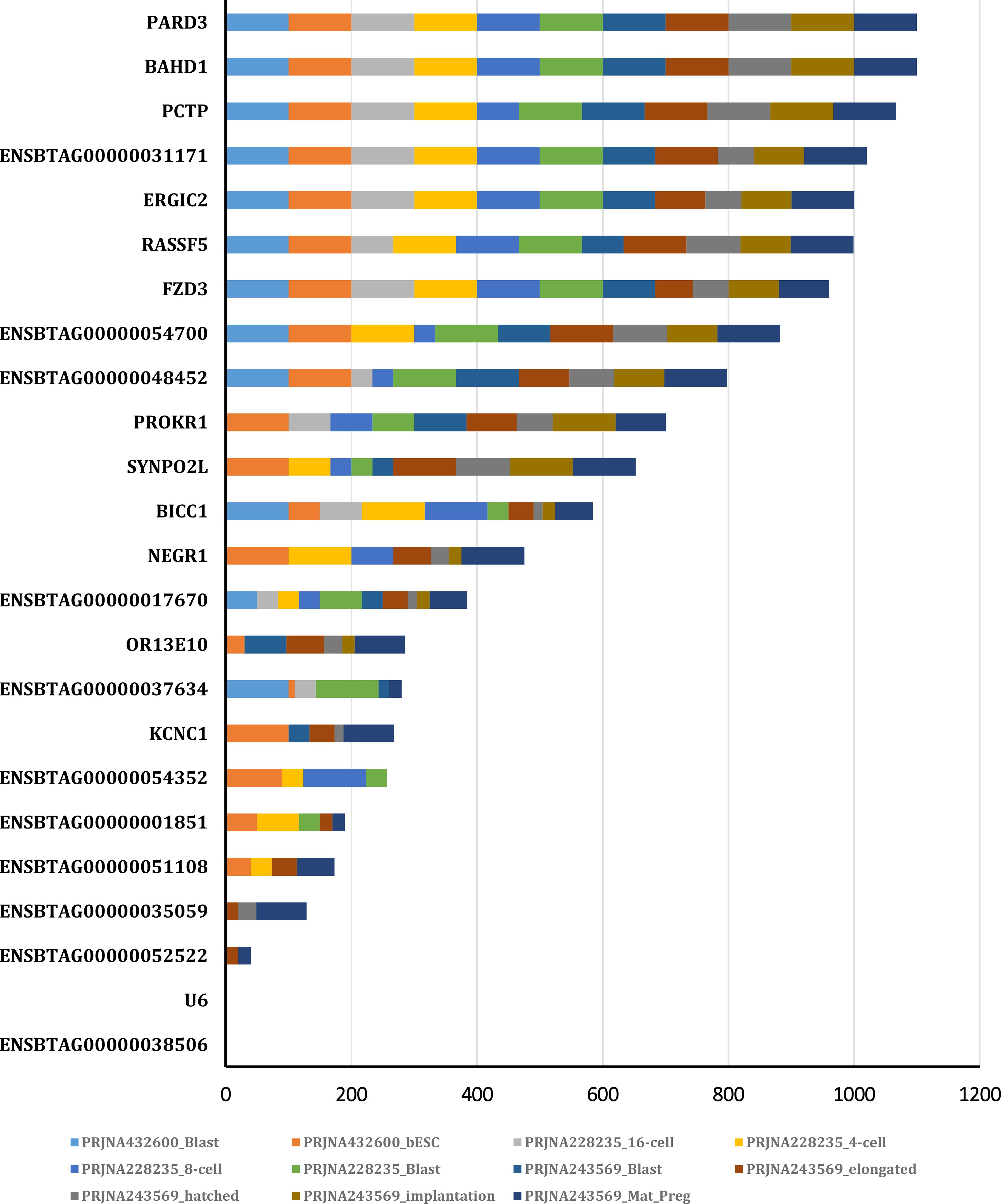
Figure 4. The expression pattern of the genes in different stages of embryo development obtained from PRJNA432600 and PRJNA243569 projects.
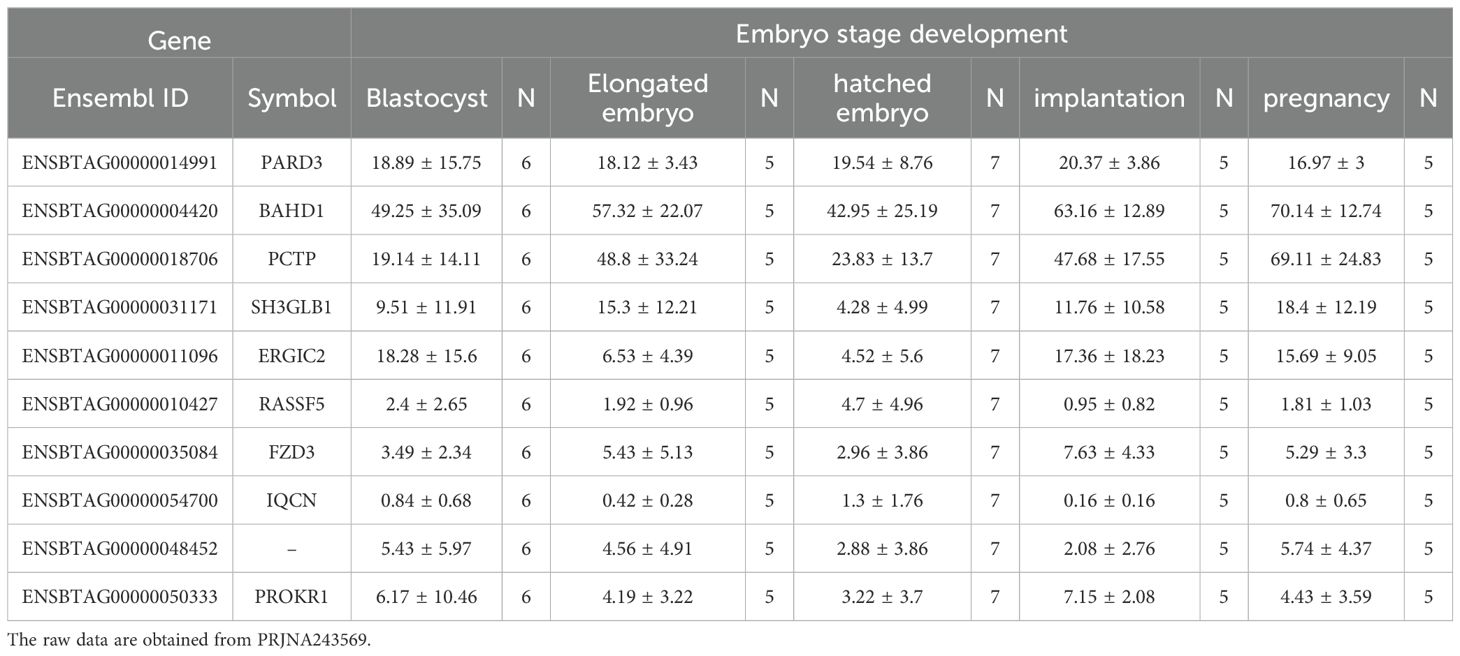
Table 5. The expression level (TPM) of the potential candidate lethal genes in different stages of development of embryo.
Elucidation of genetic factors involving in molecular function and biological process related to embryo growth and survival provides valuable insights into the complicated mechanisms of embryogenesis and embryo development. In this study, we found a novel gene (ENSBTAG00000048452) to be an important genetic factor for embryo lethality in dairy cattle. This gene has not been annotated in cattle genome and there is no much information about its function and biological role. We also discovered that PARD3, BAHD1, ERGIC2, FZD3, IQCN, PROK1, PCTP, SH3GLB1, and RASSF5 play significant roles in various critical biological processes related to bovine embryo development. The role of these genes in the cell including molecular function, cellular component and biological process as well as the results of comparative genomics are summarized in Table 6. According the bioinformatic databases uses for gene ontology, these genes are involved in some important molecular functions in the cell including protein, lipid, phosphatidylinositol and chromatin binding, transcription cis-regulatory region binding, phosphatidylcholine transporter activity and transmembrane signaling receptor activity. The protein coded by these genes can be found in cytoplasm, nucleus, nucleoplasm and microtubule as well as membrane of the cell, plasma, Golgi and endoplasmic reticulum. Additionally, they have critical roles in the very important biological process in cell like cell division and regulation of mitotic cell cycle, heterochromatin formation, establishment of cell polarity, regulation of autophagy and apoptotic process, transport of phospholipid and lipid, as well as signal transduction and signaling pathway. Comparative genomic analysis showed that all these genes are highly conserved in all animal species as well as in placental mammal species (Table 6). Based on our comprehensive literature reviewed, some vital functions have been reported for these potential candidate lethal genes, mainly in embryo development in mouse and human.
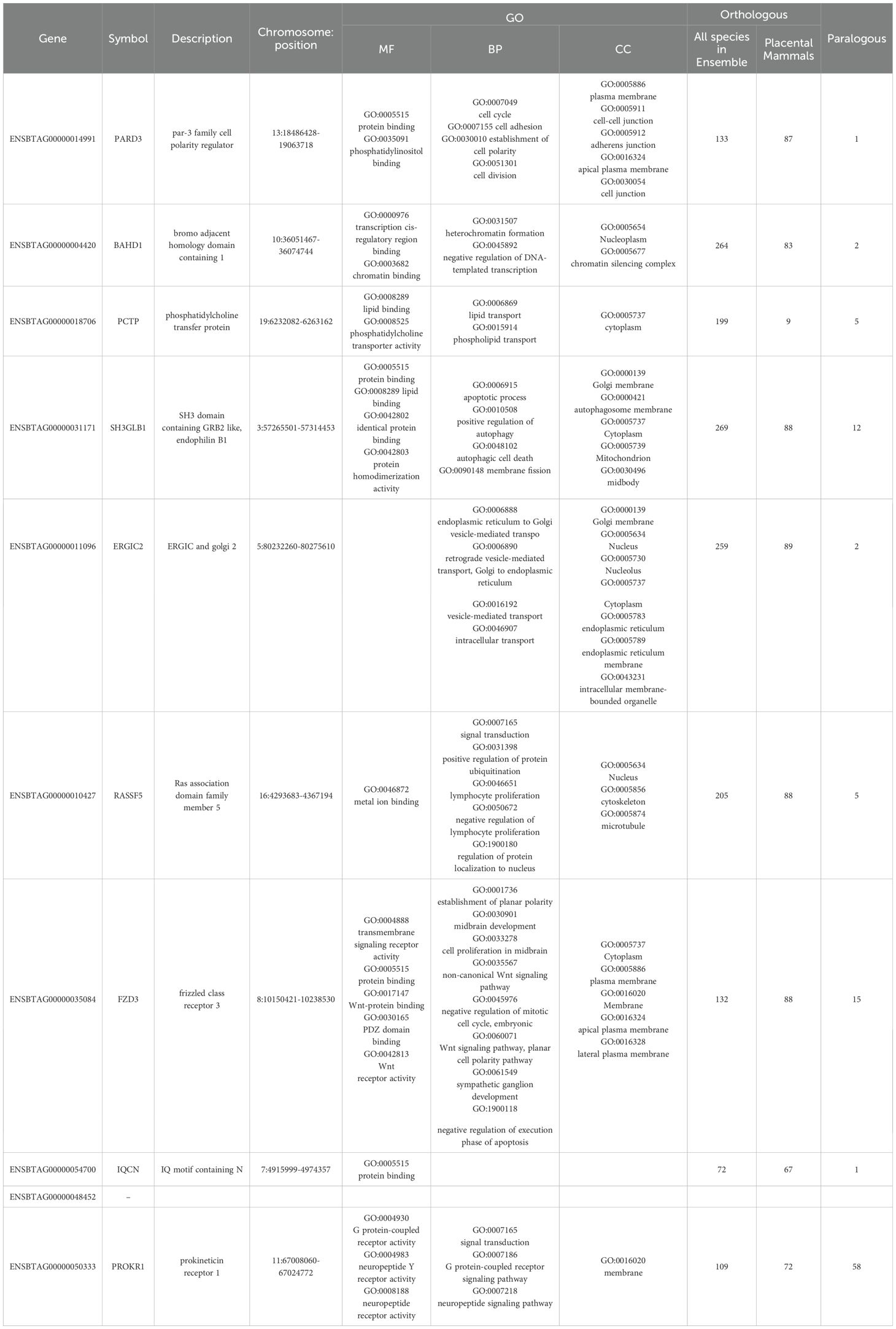
Table 6. List of the identified potential candidate lethal gene associated with early embryonic mortality.
Par-3 Family Cell Polarity Regulator (PARD3), as member of the PARD family, plays crucial roles in asymmetric cell division and directing polarized cell growth (Cui et al., 2022). Studies have highlighted its involvement in key signaling pathways such as MAPK and Hippo, contributing to follicle growth and development in sheep (Wang et al., 2023a), morula formation during mouse embryonic development (Pfeffer, 2018), and the polarization process of mammalian embryonic blastomeres (Negrón-Pérez and Hansen, 2018). Additionally, research focused on carcass traits and gene networks has underscored PARD3's significant role in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism (Zhang et al., 2020). Notably, Cole et al. (2011) through a genome-wide analysis of predicted transmissibility (PTA) identified 5 QTLs (QTL IDs in AnimalQTLdb: 46882, 46852, 46866, 46835, and 46838), overlapping with the PARD3 gene, to be associated with stillbirth in Holstein cattle.
Bromodomain Adjacent Homology Domain-Containing Protein 1 (BAHD1) encodes a pivotal protein for chromatin organization and gene silencing, thereby contributing to cell differentiation and maintenance of homeostasis in mammals (Zhao et al., 2016). The Bromo Adjacent Homology (BAH) domain is essential for its function, facilitating gene silencing by mediating interactions with specific combinations of histones, such as H3K27me3 (Currie et al., 2024). Disruption of this interaction through point mutation leads to chromatin remodeling and increased histone acetylation at Polycomb gene targets. Mice with dysfunctional mutations in this pathway exhibits severe embryonic instability, thereby underscoring its critical role in normal embryo development (Fan et al., 2021).
In humans, Bierne et al. (2009) proposed that BAHD1 acts as a silencer by linking heterochromatin factors (e.g., HP1, MBD1, and HDAC5) to DNA-bound transcription factors (e.g., SP1), thereby functioning as a tumor suppressor through the silencing of cancer-related genes (e.g., IGF2). Studies in mice have shown that BAHD1 plays a crucial role in fetal growth and placental development. Lakisic et al. (2016) demonstrated that BAHD1-/- embryos exhibited structural changes in the placenta, including reduced weight and smaller placentas, with notable reductions in the junctional and cardio-fetal areas essential for nutrient exchange between the mother and fetus. Additionally, there was a decrease in the number of trophoblast glycogen (GC) cells, which is crucial for providing glucose for photo-placenta development.
Furthermore, Salilew-Wondim et al. (2018) suggested that BAHD1 is involved in DNA methylation in bovine embryos due to exposure conditions. They studied three groups of bovine embryos produced in vivo but cultured in vitro at different stages (2-, 8-, and 16-cell) and measured gene methylation and expression at the blastocyst stage. The authors reported that BAHD1 was one of the 28 (2%) genes differentially methylated and expressed in all groups. Additionally, BAHD1 exhibited a negative correlation between DNA methylation patterns and expression level, showing hyper-methylation but downregulation of mRNA expression in all blastocyst groups, likely due to suboptimal culture conditions.
Endoplasmic Reticulum-Golgi Intermediate Compartment Protein 2 (ERGIC2) is fundamental in early secretion pathways, particularly in the trafficking pathway responsible for transporting proteins, lipids, and other newly translated molecules. Located in the intermediate compartment of the endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi apparatus, ERGIC2 plays a crucial role in modulating ER-to-Golgi transport (Moreau et al., 2011). Additionally, Yu et al. (2014) reported that ERGIC2 is essential for efficient Wnt protein secretion and signaling. In their study, knocking down ERGIC2 in Xenopus through morpholino injection into two-cell embryos resulted in lethality before gastrulation, highlighting its indispensable role in embryonic growth (Yu et al., 2014).
Frizzled class receptor 3 (FZD3) plays a pivotal role in orchestrating various cellular processes, embryonic and postnatal development, particularly in the nervous and integumentary systems (Millar et al., 1999; Deardorff et al., 2001; Stuebner et al., 2010). Seigfried et al. (2017) stated that deficiency in FZD3 leads to severe developmental abnormalities, including impaired regulation of angiogenesis and disrupted neural tube closure. Deletion or absence of FZD3 has resulted in embryonic lethality and impedes neural tube closure (Kemp et al., 2007). Moreover, FZD3 has been reported to be involved in midbrain morphogenesis and cell migration (Stuebner et al., 2010), highlighting its crucial role in embryonic development, particularly in neural tube closure and organogenesis. The FZD3 regulates critical processes during embryonic development and the pre-implantation uterine environment in various species, including cattle, sheep, mice, and humans. High expression of FZD3 is observed in early gastrulation-stage bovine embryos, indicating its crucial role in embryonic tissue patterning and differentiation (Pfeffer et al., 2017). In general, FZD3 acts as a critical component of the Wnt signaling pathway, wherein Wnt proteins bind to Frizzled receptors (e.g., FZD3). It is essential for embryonic development and tissue homeostasis (Pan et al., 2022) and regulates various aspects of organogenesis, including nephrogenesis processes such as differentiation, proliferation, and morphogenesis (Cizelsky et al., 2014). In cattle, FZD3 participates in these pathways to regulate embryonic development and angiogenesis under hypoxic conditions (Verma et al., 2018).
IQ Motif Containing Nucleoporin (IQCN) is required to facilitate proper acrosome attachment during spermatogenesis (Dai et al., 2022). Dysfunction leads to fertilization failure, highlighting its significance in reproductive processes (Dai et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2023b). Wang et al. (2023b) reported that homozygous frameshift variants of this gene cause dysfunction in sperm, leading to male infertility in humans and mice. This dysfunctionality is mediated by abnormalities in the sperm oocyte activating factor PLCζ and head deformity. In a study on mice, Dai et al. (2022) showed that Iqcn-knockout (Iqcn-/-) mice can survive and grow, but are not fertile due to abnormal acrosome structures. From this study, it can be deduced that this gene does not directly cause embryo lethality. Since this gene is protein-coding and located on an autosome (chromosome 7), it likely has functions in ova as well. Moreover, the effect of the homozygous status of this gene on ova function, similar to its effect on sperm, remains unclear. To our knowledge, there are no published reports in this regard; therefore, further investigations into the function of this gene in bovine semen, ova, zygotes, and embryos are highly recommended.
Prokineticin receptor 1 (PROK1) plays a pivotal role in regulating endometrial angiogenesis and secretory function during the estrous cycle and early gestation. Its heightened expression is linked with monocyte recruitment, crucial for successful pregnancy establishment (Baryla et al., 2023). PROK1's involvement spans various species, as evidenced by its increased expression during the mid-luteal phase in pigs, humans, and cattle. Notably, its expression dynamics differ in the late luteal phase, suggesting a role in monocyte recruitment to the regressing corpus luteum (Baryla et al., 2023). In Spanish beef cattle, PROK1 is emerged as a fertility-related gene (González-Rodríguez et al., 2016).
During implantation and early placentation, PROK1 mRNA expression undergoes dynamic changes across species. In humans and mice, mRNA levels peak during early pregnancy, whereas in pigs, upregulation occurs in trophoblasts during implantation and early placentation (Hoffmann et al., 2007).
Phosphatidylcholine Transfer Protein (PCTP), also known as StARD2, is an important member of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein-related transfer (START) domain superfamily (Kanno et al., 2007a, b). This family encompasses proteins involved in lipid transfer and metabolism, with PCTP facilitating the transfer of phospholipids, especially phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho), between cellular membranes. The evolutionarily conserved START domain, to which PCTP belongs, underscores its functional importance across species (Schrick et al., 2004). STARD2, with its minimal START domain structure, functions as a cytosolic phosphatidylcholine transfer protein and crucial for phospholipid trafficking between membranes (Soccio et al., 2002). Studies have highlighted PCTP's significance in various biological processes. The PCTP gene overlaps with quantitative trait loci (QTLs) associated with stillbirth reported by Cole et al. (2011) in Holstein dairy cattle, indicating its role in reproductive health. Additionally, PCTP's expression throughout mice embryo development stages suggests its involvement in cell growth and differentiation (Geijtenbeek et al., 1996).
The SH3 Domain-Containing GRB2-Like Protein 1 (SH3GLB1) gene encodes a multifunctional protein, also known as endophilin B1, which drives membrane curvature. This protein plays a role in apoptosis, a process involving dying cells characterized by cytoplasmic shrinkage, membrane blebbing, chromatin condensation, and fragmentation into membrane-bound vesicles or apoptotic bodies (Peterson et al., 2015). Additionally, SH3GLB1 contributes to regulating molecular pathways associated with spermatogenesis and male fertility (Henderson et al., 2011; Peterson et al., 2015). SH3GLB1 activity is crucial in the early development of the auditory, cardiovascular, and muscular systems in zebrafish. Therefore, abnormal SH3GLB1 function might lead to imbalanced mitophagy (Gao et al., 2023). Furthermore, SH3GLB1 acts as a pivotal tumor suppressor, essential for preventing chromosomal instability and suppressing resistance to apoptosis (Takahashi et al., 2013). Deficiency in SH3GLB1 could result in embryonic lethality and/or misregulated lymphoma cell homing through up-regulation of the expression of the Mcl-1 gene (Moshnikova et al., 2006).
Ras Association Domain Family Member 5 (RASSF5), also known as novel Ras effector 1 (NORE1), belongs to the Ras-association domain family and serves as a crucial regulator of cellular homeostasis. It exerts its functions through growth suppression and regulation of apoptosis (Moshnikova et al., 2006). RASSF5 plays multifaceted roles in cellular processes and is thus act as an essential player in maintaining cellular homeostasis. Its predominant cytoplasmic localization allows it to interact with cytoskeletal proteins, thereby participating in microtubule stabilization and potentially regulating mitosis. Furthermore, RASSF5's interaction with KRAS highlights its unique role in Ras-induced pro-apoptotic pathways, distinguishing it from other RASSF family members. The existence of multiple isoforms of RASSF5, generated through alternative splicing or promoter usage, underscores its diverse functions in cellular regulation, including cellular motility, cell cycle control, apoptosis, stability of microtubules, and adaptive immune defense (Ehrkamp et al., 2013).
Park et al. (2010) observed significant protection from TNF-α-mediated apoptosis of the liver in mice due to the inactivation of RASSF5. They concluded that RASSF5 acts as a tumor suppressor and plays a direct role in the activation of the proapoptotic kinase Mst1 after TNF-α stimulation. Moreover, RASSF5 and RASSF1 are homologous and play similar roles in regulating early embryonic differentiation in mice.
In the current study, omics data in genome and transcriptome levels were used to identify the potential candidate genes contributing to embryo lethality in Holstein dairy cattle. Through a rigorous analysis of several genes, including PARD3, BAHD1, ERGIC2, IQCN, FZD3, PROK1, PCTP, SH3GLB1, and RASSF5, were identified, all of which play crucial roles in various biological processes related to embryo development and prenatal survival. Despite being understudied in livestock, particularly in dairy cattle, their conservation among mammals suggests similar functions in cattle. Our findings provided a new information on the complex molecular mechanisms underlying embryo mortality in the early stages of pregnancy, particularly highlighting the importance of genes with a recessive inheritance model. These genes are involved in crucial functions such as regulation of cell polarity, phospholipid transport, apoptosis, cell division, and signaling pathways associated with embryo rejection or structural abnormalities, reflecting their significance in embryo lethality-related mechanisms. These findings shed light on the genetic factors underlying embryonic mortality in cattle, supporting the development genomic-based selective breeding programs to improve reproductive efficiencies and farm profitability. Given the limited knowledge about the functions of these genes in livestock species, further investigation, particularly in cattle is strongly recommended to enhance our understanding of their roles in farm animals.
The original contributions presented in the study are publicly available. The publicly available RNA-seq datasets analyzed in this study can be found here: NCBI, accession PRJNA230971 and PRJNA718333. The gene expression data are available on the Cattle Genotype-Tissue Expression (cGTEx) database (http://cgtex.roslin.ed.ac.uk/).
SR: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft. AS: Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. SG: Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Authors are thankful to the Prof. Holly Neibergs for generously sharing the data.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fanim.2025.1513876/full#supplementary-material
Alemu S. W., Kadri N. K., Harland C., Faux P., Charlier C., Caballero A., et al. (2021). An evaluation of inbreeding measures using a whole-genome sequenced cattle pedigree. Hered 126, 410–423. doi: 10.1038/s41437-020-00383-9
Baryla M., Goryszewska-Szczurek E., Kaczynski P., Balboni G., Waclawik A. (2023). Prokineticin 1 is a novel factor regulating porcine corpus luteum function. Sci. Rep. 13, 5085. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-32132-3.+
Bermingham M. L., Bishop S. C., Woolliams J. A., Pong-Wong R., Allen A. R., McBride S. H., et al. (2014). Genome-wide association study identifies novel loci associated with resistance to bovine tuberculosis. Hered 112, 543–551. doi: 10.1038/hdy.2013.137
Bierne H., Tham T. N., Batsche E., Dumay A., Leguillou M., Kernéis-Golsteyn S., et al. (2009). Human BAHD1 promotes heterochromatic gene silencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 13826–13831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0901259106
Bosse M., Megens H. J., Derks M. F., de Cara Á.M., Groenen M. A. (2019). Deleterious alleles in the context of domestication, inbreeding, and selection. Evol. Appl. 12, 6–17. doi: 10.1111/eva.12691
Cizelsky W., Tata A., Kühl M., Kühl S. J. (2014). The Wnt/JNK signaling target gene alcam is required for embryonic kidney development. Dev 141, 2064–2074. doi: 10.1242/dev.107938
Cole J. B., Null D. J., VanRaden P. M. (2016). Phenotypic and genetic effects of recessive haplotypes on yield, longevity, and fertility. J. Dairy Sci. 99, 7274–7288. doi: 10.3168/jds.2015-10777
Cole J. B., Wiggans G. R., Ma L., Sonstegard T. S., Lawlor T. J., Crooker B. A., et al. (2011). Genome-wide association analysis of thirty-one production, health, reproduction and body conformation traits in contemporary US Holstein cows. BMC Genom. 12, 1–7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-408
Cui R., Chen D., Li N., Cai M., Wan T., Zhang X., et al. (2022). PARD3 gene variation as candidate cause of nonsyndromic cleft palate only. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 26, 4292–4304. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17452
Currie M. A., Behrouzi R., Moazed D. (2024). “The BAH domain: A versatile histone modification reader,” in Chromatin Readers in Health and Disease (Ottawa, ON, Canada: Academic Press), 13–30. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-823376-4.00006-9
Dai J., Li Q., Zhou Q., Zhang S., Chen J., Wang Y., et al. (2022). IQCN disruption causes fertilization failure and male infertility due to manchette assembly defect. EMBO Mol. Med. 14, e16501. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.19.3655
Deardorff M. A., Tan C., Saint-Jeannet J. P., Klein P. S. (2001). A role for frizzled 3 in neural crest development. Dev 128 (19), 3655–3663. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.19.3655
Derks M. F., Gjuvsland A. B., Bosse M., Lopes M. S., Van son M., Harlizius B., et al. (2019). Loss of function mutations in essential genes cause embryonic lethality in pigs. PloS Genet. 15, e1008055. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008055
Ehrkamp A., Herrmann C., Stoll R., Heumann R. (2013). Ras and rheb signaling in survival and cell death. Cancers 5, 639–661. doi: 10.3390/cancers5020639
Fan H., Guo Y., Tsai Y. H., Storey A. J., Kim A., Gong W., et al. (2021). A conserved BAH module within mammalian BAHD1 connects H3K27me3 to Polycomb gene silencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, 4441–4455. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab210
Gao X., Wang W., Xu J., Huang S., Yang K., Yang J., et al. (2023). Characterization of SH3GLB1 in the auditory system and its potential role in mitophagy. Genes. Dis. 11, 101018. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.05.017
Geijtenbeek B. H., Smith T., Borst A. J., Wirtz K. W. (1996). cDNA cloning and tissue-specific expression of the phosphatidylcholine transfer protein gene. J. Biochem. 316, 49–55. doi: 10.1042/bj3160049
González-Rodríguez A., Munilla S., Mouresan E. F., Cañas-Álvarez J. J., Díaz C., Piedrafita J., et al. (2016). On the performance of tests for the detection of signatures of selection: a case study with the Spanish autochthonous beef cattle populations. Genet. Sel. Evol. 48, 1–2. doi: 10.1186/s12711-016-0258-1
Henderson H., Macleod G., Hrabchak C., Varmuza S. (2011). New candidate targets of protein phosphatase-1c-gamma-2 in mouse testis revealed by a differential phosphoproteome analysis. Int. J. Androl. 34, 339–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2010.01085.x
Hoffmann P., Feige J. J., Alfaidy N. (2007). Placental expression of EG-VEGF and its receptors PKR1 (prokineticin receptor-1) and PKR2 throughout mouse gestation. Placenta 28, 1049–1058. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2007.03.008
Jenko J., McClure M. C., Matthews D., McClure J., Johnsson M., Gorjanc G., et al. (2019). Analysis of a large dataset reveals haplotypes carrying putatively recessive lethal and semi-lethal alleles with pleiotropic effects on economically important traits in beef cattle. Genet. Sel. Evol. 51, 1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12711-019-0452-z
Kadri N. K., Harland C., Faux P., Cambisano N., Karim L., Coppieters W., et al. (2016). Coding and noncoding variants in HFM1, MLH3, MSH4, MSH5, RNF212, and RNF212B affect recombination rate in cattle. Genome Res. 26, 1323–1332. doi: 10.1101/gr.204214.116
Kanno K., Wu M. K., Agate D. S., Fanelli B. J., Wagle N., Scapa E. F., et al. (2007a). Interacting proteins dictate function of the minimal START domain phosphatidylcholine transfer protein/StarD2. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 30728–30736. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M703745200
Kanno K., Wu M. K., Scapa E. F., Roderick S. L., Cohen D. E. (2007b). Structure and function of phosphatidylcholine transfer protein (PC-TP)/StarD2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 1771, 654–662. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2007.04.003
Kemp C. R., Hendrickx M., Willems E., Wawrzak D., Métioui M., Leyns L. (2007). The roles of Wnt signaling in early mouse development and embryonic stem cells. Func. Dev. Embryo. 1, 1–13.
Kiser J. N., Clancey E., Moraes J. G., Dalton J., Burns G. W., Spencer T. E., et al. (2019b). Identification of loci associated with conception rate in primiparous Holstein cows. BMC Genom. 20, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6203-2
Kiser J. N., Keuter E. M., Seabury C. M., Neupane M., Moraes J. G., Dalton J., et al. (2019a). Validation of 46 loci associated with female fertility traits in cattle. BMC Genom. 20, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5935-3
Lakisic G., Lebreton A., Pourpre R., Wendling O., Libertini E., Radford E. J., et al. (2016). Role of the BAHD1 chromatin-repressive complex in placental development and regulation of steroid metabolism. PloS Genet. 12, e1005898. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005898
Long S. (2009). Abnormal development of the conceptus and its consequences. Arthur’s Vet. Reprod. Obstet. 8, 119–143.
Madakashira B. P., Sadler K. C. (2017). DNA methylation, nuclear organization, and cancer. Front. Genet. 8. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2017.00076
Mamo S., Mehta J. P., McGettigan P., Fair T., Spencer T. E., Bazer F. W., et al. (2011). RNA sequencing reveals novel gene clusters in bovine conceptuses associated with maternal recognition of pregnancy and implantation. Biol. Reprod. 85, 1143–1151. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.111.092643
Marsden C. D., Ortega-Del-Vecchyo D., O’Brien D. P., Taylor J. F., Ramirez O., Vilà C., et al. (2016). Bottlenecks and selective sweeps during domestication have increased deleterious genetic variation in dogs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 113, 152–157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1512501113
Millar S. E., Willert K., Salinas P. C., Roelink H., Nusse R., Sussman D. J., et al. (1999). WNT signaling in the control of hair growth and structure. Dev. Biol. 207, 133–149. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1998.9140
Moreau D., Kumar P., Wang S. C., Chaumet A., Chew S. Y., Chevalley H., et al. (2011). Genome-wide RNAi screens identify genes required for ricin and PE intoxications. Dev. Cell 21, 231–244. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2011.06.014
Moshnikova A., Frye J., Shay J. W., Minna J. D., Khokhlatchev A. V. (2006). The growth and tumor suppressor NORE1A is a cytoskeletal protein that suppresses growth by inhibition of the ERK pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 8143–8152. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M511837200
Mueller M. L., Van Eenennaam A. L. (2022). Synergistic power of genomic selection, assisted reproductive technologies, and gene editing to drive genetic improvement of cattle. CABI Agric. Biosci. 3, 13. doi: 10.1186/s43170-022-00080-z
Negrón-Pérez V. M., Hansen P. J. (2018). Role of yes-associated protein 1, angiomotin, and mitogen-activated kinase kinase 1/2 in development of the bovine blastocyst. Biol. Reprod. 98, 170–183. doi: 10.1093/biolre/iox172
Noakes D. E., Parkinson T. J., England G. C. W., Arthur G. H. (Eds.) (2001). “Chapter 4 - Abnormal development of the conceptus and its consequences,” in Arthur’s Veterinary Reproduction and Obstetrics, Eighth Edition (W. B. Saunders, Oxford), 119–143. doi: 10.1016/B978-070202556-3.50008-6
Pan C., Wang S., Yang C., Hu C., Sheng H., Xue X., et al. (2022). Genome-wide identification and expression profiling analysis of Wnt family genes affecting adipocyte differentiation in cattle. Sci. Rep. 12, 489. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-04468-1
Park J., Im Kang S., Lee S. Y., Zhang X. F., Kim M. S., Beers L. F., et al. (2010). Tumor suppressor ras association domain family 5 (RASSF5/NORE1) mediates death receptor ligand-induced apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 35029–35038. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.165506
Perkel K. J., Tscherner A., Merrill C., Lamarre J., Madan P. (2015). The ART of selecting the best embryo: A review of early embryonic mortality and bovine embryo viability assessment methods. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 82, 822–838. doi: 10.3906/vet-1907-123
Peterson J. S., Timmons A. K., Mondragon A. A., McCall K. (2015). The end of the beginning: cell death in the germline. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 114, 93–119. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.07.025
Pfeffer P. L. (2018). Building principles for constructing a mammalian blastocyst embryo. Biol 7, 41. doi: 10.3390/biology7030041
Pfeffer P. L., Smith C. S., Maclean P., Berg D. K. (2017). Gene expression analysis of bovine embryonic disc, trophoblast and parietal hypoblast at the start of gastrulation. Zygote 25, 265–278. doi: 10.1017/S0967199417000090
Rani P., Dutt R., Singh G., Chandolia R. K. (2018). Embryonic mortality in cattle-A review. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 7, 1501–1516. doi: 10.20546/ijcmas.2018.707.177
Salilew-Wondim D., Saeed-Zidane M., Hoelker M., Gebremedhn S., Poirier M., Pandey H. O., et al. (2018). Genome-wide DNA methylation patterns of bovine blastocysts derived from in vivo embryos subjected to in vitro culture before, during or after embryonic genome activation. BMC Genom. 19, 1–9. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4826-3
Schrick K., Nguyen D., Karlowski W. M., Mayer K. F. (2004). START lipid/sterol-binding domains are amplified in plants and are predominantly associated with homeodomain transcription factors. Genome Biol. 5, 1–16. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-6-r41
Seigfried F. A., Cizelsky W., Pfister A. S., Dietmann P., Walther P., Kühl M., et al. (2017). Frizzled 3 acts upstream of Alcam during embryonic eye development. Dev. Biol. 426, 69–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2017.04.004
Soccio R. E., Adams R. M., Romanowski M. J., Sehayek E., Burley S. K., Breslow J. L. (2002). The cholesterol-regulated StarD4 gene encodes a StAR-related lipid transfer protein with two closely related homologues, StarD5 and StarD6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 99, 6943–6948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.052143799
Spencer T. E. (2013). Early pregnancy: Concepts, challenges, and potential solutions. Anim. Front. 3, 48–55. doi: 10.2527/af.2013-0033
Stuebner S., Faus-Kessler T., Fischer T., Wurst W., Prakash N. (2010). Fzd3 and Fzd6 deficiency results in a severe midbrain morphogenesis defect. Dev. Dynam. 239, 246–260. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22127
Szenci O. (2021). Recent possibilities for the diagnosis of early pregnancy and embryonic mortality in dairy cows. Anim. (Basel) 11, p.1666. doi: 10.3390/ani11061666
Takahashi Y., Young M. M., Serfass J. M., Hori T., Wang H. G. (2013). Sh3glb1/Bif-1 and mitophagy: acquisition of apoptosis resistance during Myc-driven lymphomagenesis. ATG 9, 1107–1109. doi: 10.4161/auto.24817
Todd E. T., Thomson P. C., Hamilton N. A., Ang R. A., Lindgren G., Viklund Å., et al. (2020). A genome-wide scan for candidate lethal variants in Thoroughbred horses. Sci. Rep. 10, 13153. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68946-8
Upperman L. R., Kinghorn B. P., MacNeil M. D., Van Eenennaam A. L. (2019). Management of lethal recessive alleles in beef cattle through the use of mate selection software. Genet. Sel. Evol. 51, 1–16. doi: 10.1186/s12711-019-0477-3
VanRaden P. M., Olson K. M., Null D. J., Hutchison J. L. (2011). Harmful recessive effects on fertility detected by absence of homozygous haplotypes. J. Dairy Sci. 94, 6153–6161. doi: 10.3168/jds.2011-4624
Verma P., Sharma A., Sodhi M., Thakur K., Kataria R. S., Niranjan S. K., et al. (2018). Transcriptome analysis of circulating PBMCs to understand mechanism of high-altitude adaptation in native cattle of Ladakh region. Sci. Rep. 8, 7681. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-25736-7
Wang J., Chen H., Zhang Y., Jiang S., Zeng X., Shen H. (2023a). Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed circRNAs in the ovaries of low-and high-fertility sheep. Animals 13, 236. doi: 10.3390/ani13020236
Wang Y., Chen G., Tang Z., Mei X., Lin C., Kang J., et al. (2023b). Loss-of-function mutations in IQCN cause male infertility in humans and mice owing to total fertilization failure. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 29, gaad018. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gaad018
Wu X., Mesbah-Uddin M., Guldbrandtsen B., Lund M. S., Sahana G. (2019). Haplotypes responsible for early embryonic lethality detected in Nordic Holsteins. J. Dairy Sci. 102, 11116–11123. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-16651
Yu J., Chia J., Canning C. A., Jones C. M., Bard F. A., Virshup D. M. (2014). WLS retrograde transport to the endoplasmic reticulum during Wnt secretion. Dev. Cell 29, 277–291. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.03.016
Zhang C., MacNeil M. D., Kemp R. A., Dyck M. K., Plastow G. S. (2018). Putative loci causing early embryonic mortality in duroc swine. Front. Genet. 9. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00655
Zhang F., Wang Y., Mukiibi R., Chen L., Vinsky M., Plastow G., et al. (2020). Genetic architecture of quantitative traits in beef cattle revealed by genome wide association studies of imputed whole genome sequence variants: I: feed efficiency and component traits. BMC Genom. 21, 1–22. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6362-1
Keywords: embryonic lethality, genomic, Holstein dairy cattle, recessive alleles, transcriptomic
Citation: Rezaei S, Shadparvar AA, Baneh H and Ghovvati S (2025) Genome-wide scanning for candidate lethal genes associated with early embryonic mortality in Holstein dairy cattle. Front. Anim. Sci. 6:1513876. doi: 10.3389/fanim.2025.1513876
Received: 19 October 2024; Accepted: 13 February 2025;
Published: 13 March 2025.
Edited by:
Juliana Petrini, Clinica do Leite Ltda, BrazilReviewed by:
Vinicius Henrique Da Silva, University of São Paulo (ESALQ-USP), BrazilCopyright © 2025 Rezaei, Shadparvar, Baneh and Ghovvati. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Abdol Ahad Shadparvar, c2hhZEBndWlsYW4uYWMuaXI=
†ORCID: Somayeh Rezaei, orcid.org/0009-0003-8349-3014
Abdol Ahad Shadparvar, orcid.org/0000-0003-3575-5406
Hasan Baneh, orcid.org/0000-0003-2437-6005
Shahrokh Ghovvati, orcid.org/0000-0002-2016-2184
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.