- Department of Accounting, University of Sri Jayewardenepura, Nugegoda, Sri Lanka
Animal welfare is a critical concern for the food industry, and companies must take responsibility for managing their policies and procedures to ensure the welfare of farm animals. However, many companies fail to prioritize animal welfare in their reporting. This study applies the theory of planned behavior to examine how behavioral factors—such as attitude, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, and awareness of farm animal welfare—influence the intentions of individuals involved in sustainability reporting to include farm animal welfare disclosures in the sustainability reports of listed food companies in Sri Lanka. This study focuses on individuals involved in the sustainability reporting process of publicly listed food companies in the Colombo Stock Exchange. Out of 124 companies which were engaged in the food sector as derived from GICS industry classification index, the study identified 61 companies by isolating companies having a farm animal footprint along its’ supply chain which involved an individual analysis of the products offered by the company. The survey approach was used for this study with 110 self-administered questionnaires being distributed among individuals in the designations of CFOs, Directors, Managers, Accountants, assistant managers, Accounts assistants/executives and associates. Data were analyzed using structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). The findings reveal that only perceived behavioral control and subjective norms have a significant positive impact on the intention to adopt farm animal welfare disclosure practices among those engaged in the sustainability reporting process of listed food companies. This study is important because it highlights the need for standardized guidelines and mandatory regulations for animal welfare reporting in Sri Lanka, offering insights for policymakers and institutions to improve sustainability practices and establish stringent farm animal welfare reporting standards.
1 Introduction
Farm Animal Welfare (FAW) is a crucial socially relevant issue for businesses in the food industry (identified as a “business issue”), including retailers, food services, manufacturers, processors, and producers, owing to changes in public attitudes on animal care and the size of the livestock industry (Amos et al., 2021). This business issue is increasingly getting the public spotlight since over a five-year period, it has been calculated that the number of farm animals raised for food climbed from 60 billion annually to slightly over 70 billion, with livestock accounting for most of the agricultural land usage (McLaren and Appleyard, 2020). Also, with the population expected to expand to 9.8 billion people by 2050, there is a further expectant rise in demand (McLaren and Appleyard, 2020). This demand increases the need for feed, forage, water, and land which puts pressure on farmers to expand their farming methods, raising moral and ethical issues related to FAW (McLaren and Appleyard, 2022). Further it must be noted that for the first time a resolution tying animal welfare and sustainability was approved by the United Nations Environment Assembly on 2nd March 2022. The resolution on the link between animal welfare, the environment, and sustainable development was approved after being supported by seven member states. This action is seen as historic and may serve as a spark for broad government action to safeguard animals and, indirectly, the environment (United Nations Environment Assembly of the United Nations Environment Programme, 2022). Therefore, it is formidable that FAW is linked to sustainability and is expected to be a major component of sustainability-related literature in the future.
Further, the fact that investors increasingly believe that the issue of FAW is potentially relevant to the creation of long-term investment value in the food sector and that FAW is a relevant consideration when forming views on the strategic positioning of companies in the food sector strengthens the case that FAW is a significant business issue. Investors seek assurance that the companies they invest in have thoroughly evaluated the risks and opportunities related to farm animal welfare and have implemented effective policies and processes to address these challenges. Analyzing a company’s farm animal welfare practice and performance offers valuable insights into the quality of its management and risk management process (Amos et al., 2021). Thus, food firms should be held accountable for FAW because their operational and managerial methods and operations have an important impact on the wellbeing and welfare of farmed animals. The dedication of a single business can have a significant impact on animal welfare, especially if the dedication is demonstrated through actual behavior. This isn’t merely to be identified as a matter of ethical concern. There are evoking commercial reasons for food corporations to be concerned about FAW, including rules and regulations on animal welfare, organizational pressures from entities promoting animal welfare and wellbeing, and brand and market potential for companies with greater FAW standards (Sullivan et al., 2017).
To counter this issue, the Business Benchmark on Farm Animal Welfare (BBFAW) provides a disclosure framework that any food company can use to publish their FAW disclosures (Amos et al., 2021). The BBFAW is thought to be crucial in encouraging food companies’ FAW disclosure policies (Amos et al., 2021). Accountants in the Asia Pacific region, which includes Sri Lanka, severely underreport company performance and impact on FAW compared to the rest of the world where no food company in this region represent tier 1 and tier 2 companies according to BBFAW impact rankings which is a ranking system made to assist investors and other stakeholders in determining whether businesses are improving the welfare of the animals they use in their supply chain and to provide important information regarding the efficiency of their management systems on FAW (Amos et al., 2021).
Regardless of the importance of FAW, it is still heavily under-represented in the context of companies, and corporate disclosures are thought to enhance animal welfare significantly. However, food companies hardly ever disclose information about animal welfare (Leslie and Sunstein, 2007). Even when food corporations do disclose information about farm animal care, it is often with very little detail with the quality of reporting tending to be limited (Amos et al., 2021). “Steps should be taken to promote disclosure so as to fortify market processes and to promote democratic discussion of the treatment of animals,” claim Leslie and Sunstein (2007). Previous research and studies on sustainability reporting (SR) focused primarily on CSR, sustainability disclosures, disclosures on intellectual capital, and Integrated reporting disclosure practice.
Thus, there is a gap in the literature regarding the disclosure of FAW and its potential determinants from an accountant’s perspective. As a result, the behavioral aspects of people who engage in SR that affect FAW disclosure practices have rarely been studied in previous work. Therefore, this study aims to bridge this gap, by analyzing the behavioral determinants that affect the adoption of FAW disclosure practices of listed food companies in Sri Lanka, using TPB. This study’s main goal is to examine behavioral factors such as the influence of attitude, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, and awareness of FAW that affects the intention to adopt FAW disclosures by individuals engaged in the SR process of the listed food companies in Sri Lanka.
1.1 Sri Lanka, a developing nation, as the research context
In this study, Sri Lanka has been taken as the country of interest because, as a multi-religious country, the business issue of farm animal cruelty and welfare in the food industry affects the societal values of Sri Lanka as a whole. For example, since economic, cultural, and religious considerations have a role in how Sri Lanka’s livestock and meat business develops, religious and cultural values have an impact on how the country promotes and consumes meat and animal byproducts (Alahakoon et al., 2016).
The idea of animal welfare has a long history in Sri Lanka. According to the “Mahawansa,” a chronicle of the history of Sri Lanka, the country’s ancient monarchs erected veterinary facilities and hired veterinary doctors to care for animals, particularly cattle, in most communities. Due to the tight association that has existed between man and domesticated cattle, paying special attention to cattle was necessary since the early days of history in Sri Lanka (Ediriweera et al., 2010). Ancient Sri Lankans were honorable people who adhered to Buddhist teachings by respecting all living things. Following his conversion to Buddhism, King Devanampiya Tissa [r.247–207 BCE] established the first animal sanctuary in history and partially forbade hunting. Under the reign of King Kassapa III (r. 725–31), Voharika Tissa (r. 201-23), Sila-kala (r. 518–31), Agga Bodhi IV (r. 658–74), and King Amanda Gamini (r. 20–30), hunting and animal killing was practically outlawed. Ibn Battuta, an Arab explorer who lived in the 14th century, wrote that he met a Muslim of Sri Lankan descent who had his arms amputated by a monarch as retribution for killing a cow (Mos, 2016). Thus, the preservation of animal rights was of much importance in this Buddhist nation since ancient times.
Further, from a legislative standpoint, a legal milestone has been achieved in Sri Lanka on the 23rd of March 2022, when the cabinet passed and gazetted the bill on animal welfare, to scrutinize animal abuse stringently while ensuring proper welfare practices for farmed animals. Any act of animal cruelty can now directly be taken up in court as opposed to the prior law where a complaint must first be made to the Police. This regulatory action increases scrutiny of animal treatment at farms, thus increasing the level of accountability of the food industry in Sri Lanka, which deals with farm animals in their production and in their supply chain (Parliament of the democratic socialist republic of Sri Lanka, 2022).
Moreover, the Sri Lankan meat industry is facing growing market competition from competitive alternative products such as cultured meat, where a study carried out on perceptions of cultured meat among the Sri Lankan community found that 75% of the population was fascinated in welcoming the concept of cultured meat and that respondents had an understanding of the benefits of cultured meat in terms of animal welfare, environmental aspects, and the nation’s food security (Chandimala et al., 2022). Based on these factors, FAW is a growing business issue in Sri Lanka where companies engaged in the food industry are more accountable to the interests of the society in terms of corporate disclosures and practices. Consumers stand to benefit significantly from listed companies disclosing their farm animal welfare practices. Increased transparency enables consumers to make informed purchasing decisions aligned with their ethical values. It also holds companies accountable, driving them toward more humane and sustainable practices. Enhanced animal welfare is often linked to improved food safety and quality, providing consumers with healthier products. Moreover, such disclosures help build trust between companies and consumers, strengthening brand loyalty and promoting a more socially responsible food industry.
Thus, this study aims to examine the influence of attitude on FAW, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, and awareness of FAW on the intention of individuals engaged in the SR process to adopt FAW disclosures in sustainability reporting processes of listed food companies in Sri Lanka. Whereas previous research has predominantly centered on constructing theoretical frameworks for integrating animals into SR frameworks with a primary focus on European and US companies, there is limited understanding regarding participants’ intentions to embrace FAW disclosure practices considering such research findings (Vinnari and Vinnari, 2022). Hence, examining individuals’ intention to adopt FAW disclosure methods is forward-looking and addresses a gap in the limited accounting literature. This study is a pioneer in examining the behavioral determinants of farm animal welfare disclosure practices, where this paper would have implications for policymakers in developing a more stringent set of standards related to sustainability issues around the world. Further, the study incorporates an extended version of the theory of planned behavior where it integrates multi-theoretical perspectives which adds to its theoretical significance. Accordingly, the following hypotheses were formulated in the study, with a detailed explanation provided in section 3.2, Hypotheses development.
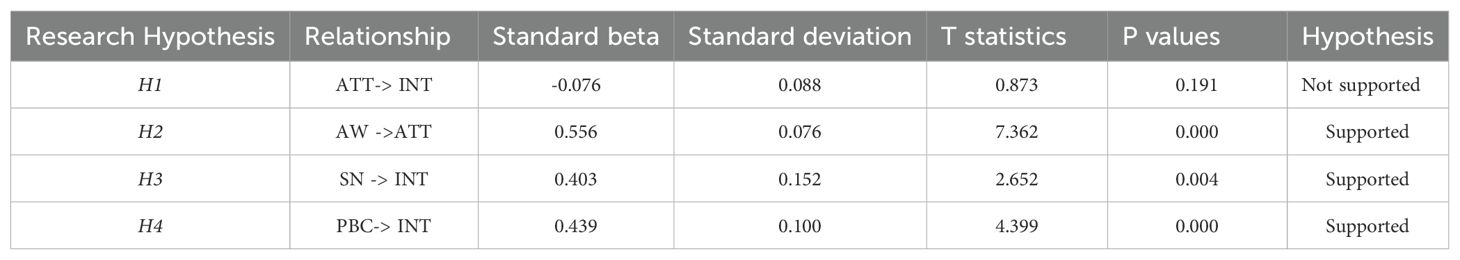
Hypothesis 1 (H1): There is a significant relationship between attitude on Farm Animal Welfare and the intention to adopt Farm Animal Welfare disclosures by individuals engaged in the sustainability reporting process of food companies.
Hypothesis 2 (H2): There is a significant relationship between awareness of Farm Animal Welfare and attitude on Farm Animal Welfare of individuals engaged in the sustainability reporting process of food companies.
Hypothesis 3 (H3): There is a significant relationship between subjective norms on Farm Animal Welfare and the intention to adopt Farm Animal Welfare disclosures by individuals engaged in the sustainability reporting process of food companies.
Hypothesis 4 (H4): There is a significant relationship between perceived behavioral control on Farm Animal Welfare disclosure practices and the intention to adopt Farm Animal Welfare disclosures by individuals engaged in the sustainability reporting process of food companies.
From a stakeholder perspective, particularly investors, it becomes clear that with sufficient interest and pressure, they can influence the management of listed food companies to incorporate FAW disclosures into their reporting. This aligns with the findings of this study, which demonstrate that social norms, including investor expectations, positively impact companies’ intentions to adopt FAW disclosures. By doing so, investors can gain assurance that the companies they invest in have fully considered the risks and opportunities associated with FAW and have implemented effective policies and processes to address these challenges (Amos et al., 2021). Based on the other findings of this study which states that awareness of FAW and Perceived Behavioral Control on FAW disclosure practices influences the intention of those engaged in SR in listed companies to adopt FAW disclosure practices, the policy makers would be made aware that more awareness programs on FAW responsibilities of companies and stringent disclosure frameworks on FAW reporting would encourage companies in adopting FAW related strategies, related risk management processes and frameworks, performance metrices in relation to progress towards FAW and ultimately, proper disclosure practices on FAW.
The population of this study includes the individuals engaged in the SR process in public listed food companies in the Colombo Stock Exchange. The list of companies engaged in the food sector were derived from GICS industry classification index and by isolating companies uniquely having a farm animal footprint along its’ supply chain which involved an individual analysis of the products offered by the company. The survey approach was used for this study and to achieve the goals of the research, the data were tested using structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). The findings indicate that perceived behavioral control and subjective norms have a significant positive influence on the intention to adopt FAW disclosure practices by those engaged in the SR process of listed food companies, with perceived behavioral control being the strongest predictor. The attitude towards FAW did not have a significant influence on the intention to adopt FAW disclosure practices.
The rest of this paper is structured as follows: Section 2 provides the theoretical background. Section 3 reviews related literature on FAW disclosures and their behavioral determinants, while also developing the research hypotheses. Section 4 outlines the research methodology. Section 5 presents the study’s results, followed by a discussion in Section 6. Section 7 addresses the study’s limitations, and Section 8 concludes the paper.
2 Theoretical background
The theory of planned behavior (TPB) is applied as the theoretical background of this paper to explain what factors affect the intention of individuals involved in the SR process to incorporate FAW disclosures in sustainability reporting of listed food companies in Sri Lanka.
According to the TPB, the behavioral intention to perform or refrain from performing a particular activity can predict, explain, or influence the actual performance of that behavior. The behavioral intention can be predicted, explained, or impacted by the behavioral antecedents of attitude, perceived behavioral control and subjective norms (Ajzen and Fishbein, 1980). In the context of FAW disclosures, attitude refers to the individual’s positive or negative evaluation of incorporating FAW into sustainability reports, which can be influenced by their personal beliefs about the ethical and business implications of animal welfare. Perceived behavioral control reflects the individual’s belief in their ability to influence or control the inclusion of FAW disclosures, shaped by factors such as company resources, policies, or regulatory frameworks. Subjective norms represent the social pressures or expectations from stakeholders, including investors, consumers, and peers, regarding the importance of FAW. Together, these factors determine the individual’s intention to include FAW disclosures in corporate sustainability reports.
Further, to increase the prediction power of the original TPB model, many psychologists have proposed adding new constructs (Yazdanpanah and Forouzani, 2015). Hence, an additional construct, which is awareness of FAW have been added to the conceptual framework based on the work of Lidfors et al. (2022), where the results of the study which investigated pet owners’ knowledge, attitudes, and practices regarding animal care in Ethiopia showed a significant positive relationship between respondents’ awareness (knowledge) and attitude toward animal welfare.
3 Literature review
3.1 Literature review
The subject of animal welfare disclosures is significant, but the body of existing literature on the subject is lacking. Covering the years of 2012 and 2013, Sullivan et al. (2017) investigated the disclosure practices of the biggest food companies in the globe. They discovered that, compared to year 2012, sample companies’ disclosure standards on animal welfare improved in the year 2013. However, only a small portion of the sample companies published extensive animal welfare policies, suggesting that many companies do not consider animal welfare to be a significant business concern and do not disclose this kind of information to stakeholders and public.
Further, through a content analysis, Reis and Molento (2020) investigated the frequency of animal welfare disclosure in the annual reports from 2007 to 2016 of two significant multinationals engaged in meat processing in Brazil. To gauge the frequency of animal welfare disclosure, they measured the number of phrases that mentioned animal welfare activities. According to their findings, annual reports’ page counts and frequency of animal welfare disclosure have both risen over time. However, it was discovered that there was no correlation between the frequency of animal welfare reporting and the length of such reports.
It has been noted that limited studies have been carried out on determinants of animal welfare disclosure practices, but closely related studies include biodiversity and species protection disclosures (Sun et al., 2021). For example, whether board gender diversity affects the volume of biodiversity disclosures by European corporations was the subject of a study by (Haque and Jones, 2020), Haque and Jones (2020). They discovered that boards with more female directors disclose more information about biodiversity. The scope of biodiversity disclosures is also favorably impacted by the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) framework and the EU strategy plan on biodiversity covering the period of 2011 to 2020. On the same note, Hassan et al. (2020) investigated the factors influencing the top 200 Fortune Global firms’ disclosure practices for biodiversity and species protection. According to their findings, companies that are Big-four audited, receive environmental awards, operate in the red/amber sector, are in developing nations, have partnerships with biodiversity organizations, and publish specific biodiversity-related terms in their reports tend to exhibit higher levels of disclosure regarding their practices for protecting biodiversity and species.
The literature review clearly demonstrates a lack of studies on animal welfare disclosure practices, leaving room for more in-depth research into animal welfare disclosures and its potential determinants. Research specific to the animal agricultural sector is lacking as well. Because there are so little studies on reporting animal welfare, this paper adds to the body of knowledge already in existence. The research aim being to examine the factors affecting the intention of individuals engaged in the SR process of listed food companies in Sri Lanka to adopt FAW disclosure practices.
3.2 Hypotheses development
This research examines a range of possible explanatory behavioral factors influencing the intention of individuals engaged in the sustainability reporting of listed food companies of Sri Lanka to adopt FAW disclosures. Therefore, this study is exploratory in nature. This study is based on variables derived from TPB and is focused on four behavioral factors which have been proven significant in previous sustainability reporting studies. These variables are, attitude on farm animal welfare (ATT), social norms on farm animal welfare (SN), perceived behavioral control on FAW disclosure practices (PBC), and awareness of FAW (AW).
3.2.1 Relationship between attitude on farm animal welfare and intention of individuals to engage in farm animal welfare disclosure practices
A study on the behavioral factors influencing Australian cotton producers’ intentions to embrace Environmental Management Accounting methods was conducted by Tashakor et al. (2019). The results show that attitude and perceived behavioral control have a substantial direct influence on farmers’ intention to adopt Environmental Management Accounting practices. Further, in a study by Chen et al. (2020), the main factors influencing managers’ intentions to use Environmental Accounting practices in Sri Lanka are examined where the TPB is used in this study to conceptualize the causes of managers’ intentions to use Environmental Accounting techniques. The PLS-SEM findings showed that managers’ intentions are greatly influenced by their attitude toward Environmental Accounting procedures. The above arguments generate the first hypothesis for this study:
Hypothesis 1 (H1). There is a significant relationship between attitude on Farm Animal Welfare and the intention to adopt Farm Animal Welfare disclosures by individuals engaged in the sustainability reporting process of food companies.
3.2.2 Relationship between awareness of farm animal welfare and attitude towards farm animal welfare
The foundation of Ajzen’s TPB model is the idea that three predetermined antecedents—attitude, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control—principally control a person’s behavioral intention (Ajzen and Fishbein, 2005). To increase the prediction power of the original TPB model, many psychologists have proposed adding new constructs (Yazdanpanah and Forouzani, 2015). Similar ideas have been put up to broaden the TPB framework by adding additional constructs or changing the direction of the variables already included in Ajzen’s model (Perugini and Bagozzi, 2001).
In this study, awareness is considered as the individuals’ ability to directly know, perceive, feel or to be conscious of events or happenings in his or her immediate environment (Kazaure, 2019) (Kazaure, 2019). The literature on the influence of awareness on attitude has been consistent as per the studies conducted by Suárez-Cáceres et al. (2021) which revealed that in Spain and Latin America, consumers’ attitudes of aquaponic goods were highly influenced by their level of awareness. Further, Amit Kumar (2021) carried out an investigation of the modified/extended TPB model, which sought to validate the traditional TPB model and the predictability of green consumer behavior. Three separate constructs (Eco-purchasing attitude, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control) plus the independent green buying behavior made up the four constructs of the traditional TPB model in the study. It was found that green purchasing behavior was significantly impacted by all three independent variables. The findings further demonstrated that attitudes toward green products are directly and significantly influenced by environmental and health awareness which was taken as an additional construct.
Therefore, it is proposed here that the positive or negative attitude of individuals engaged in the SR process of companies depend on the level of knowledge and awareness on FAW of the individual. These arguments generate the next hypothesis for this study:
Hypothesis 2 (H2). There is a significant relationship between awareness of Farm Animal Welfare and attitude on Farm Animal Welfare of individuals engaged in the sustainability reporting process of food companies.
3.2.3 Relationship between subjective norms on farm animal welfare and intention of individuals to engage in farm animal welfare disclosure practices
In a 2013 study, Läpple and Kelley (2013) used the TPB to account for social factors and technical limitations when examining Irish farmers’ decisions to switch to organic agricultural practices. The study’s findings indicate that subjective norms, as well as a farmer’s abilities and resources, are factors that limit the adoption of organic agricultural practices. It seems that farmers are hesitant to act in a way that other people find objectionable. Thus, it is deemed reasonable to test the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 3 (H3). There is a significant relationship between subjective norms on Farm Animal Welfare and the intention to adopt Farm Animal Welfare disclosures by individuals engaged in the sustainability reporting process of food companies.
3.2.4 Relationship between perceived behavioral control on FAW disclosure practices and intention of individuals to engage in farm animal welfare disclosure practices
A study on the behavioral factors influencing Australian cotton producers’ intentions to embrace Environmental Management Accounting methods was conducted by Tashakor et al. (2019). The results show that attitude and perceived behavioral control have a substantial direct influence on farmers’ intention to adopt Environmental Management Accounting practices. Furthermore, the research indicates that while attitude and subjective norms influences the intention of more environmentally conscious farmers, perceived behavioral control mostly determines the intention of less environmentally conscientious farmers. This study offers crucial insights on how attitude, subjective norms, and perceived behavioral control influence farmers’ decisions to adopt Environmental Management Accounting techniques. Thus, it is deemed reasonable to test the following hypothesis:
Hypothesis 4 (H4). There is a significant relationship between perceived behavioral control on Farm Animal Welfare disclosure practices and the intention to adopt Farm Animal Welfare disclosures by individuals engaged in the sustainability reporting process of food companies.
4 Methodology
A study by Thoradeniya et al. (2015) stated that there is a lack of correlation between the intention and actual behavior in non-listed companies mainly based on the expectation that they are less likely to be aware of SR than listed companies, as there is no mandatory SR for companies operating in Sri Lanka. Further, Thoradeniya et al. (2015) states that evidence from the study suggests a comparatively stronger relationship between intentions and behavior when it comes to SR in listed companies as opposed to non-listed companies. Thus, this study focuses solely on the listed companies assuming that there is a significant relationship between the manager’s intention and the actual reporting behavior.
As per the BBFAW report (Amos et al., 2021), the FAW disclosures of the top 150 listed food companies in the world have been assessed and ranked as per an impact rating system. These top 150 food companies have been sub-classified as food retailers and wholesalers, food producers and restaurant and bars, all of whom who has potential to use farm animals as a part of their supply chain, using the ICB (Industry Classification Benchmark) introduced by Dow Jones. Thus, basing off on this classification by BBFAW, this study too, focuses on Sri Lanka’s food companies listed in the Colombo Stock Exchange, identified through the Global Industry Classification Standard industry classification index (GICS). Therefore, the population of this study includes the individuals engaged in the SR process in public listed food companies of Sri Lanka in the Colombo Stock Exchange. The list of companies engaged in the food sector were derived from GICS. The total list of food companies amounted to 124. From this selection of companies, a further filtration process was carried out to isolate companies uniquely having a farm animal footprint along its’ supply chain. This is because, as per the IFRS S1 standard on General requirements for disclosure of sustainability-related financial information, sustainability-related information of a company is inextricably linked to the interactions between the company and its stakeholders throughout the value chain, where the company should be held accountable to FAW across its value chain (Sustainability Disclosure Standard International Sustainability Standards Board, 2023). This filtration process involved an individual analysis of the products offered by the company to assess the use of farmed animals in its supply chain. For example, the hotel and restaurant business related companies were selected because they use poultry, cattle, and other farmed products in its operations. The filtered companies belonged to the GICS categories of beverage, food and tobacco, food & staples retailing and materials. This filtration process allowed the identification of 61 companies which utilized farm animals along its supply chain.
A survey approach was used for this study, where the sampling frame involved all the individuals engaged in the sustainability reporting process of the selected sample of entities. Most entities involved only one member within the finance team who was dedicated to SR while some others had elaborate sustainability-related reporting teams with sustainability champions allocated to each business unit. Thus, data was collected using a self-administered questionnaire where a total of 110 self-administrated questionnaires were distributed through social media platforms, personal mails, and contacts to Chief Financial Officers (CFOs), finance directors, finance managers, accountants and sustainability reporting executives who are directly involved in the sustainability reporting process of the entity. The distribution and collection process took three weeks to complete. Ultimately, 89 questionnaires were returned (80.91%) out of which only 71 questionnaires (64.55%) were valid for further analysis due to outliers and irrelevant respondents, and incomplete responses. To identify the relationship between the behavioral factors, the data was tested using structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) using SMART-PLS 4.0 software.
4.1 Structure of the questionnaire
The self-administered questionnaire was labeled as ‘Factors affecting the intention to adopt farm animal welfare disclosures in the sustainability reporting process of the company.’ which was divided into five subsections based on the variables. The variables are namely, Attitude on Farm Animal Welfare, Awareness of Farm Animal Welfare, Social Norms on Farm Animal Welfare, Perceived Control factors affecting the adoption of Farm Animal Welfare disclosure practices and Intention of individuals engaged in the sustainability reporting process of listed food companies to adopt Farm Animal Welfare disclosure practices. Please refer Appendix A for the survey questions attributed to the variables.
To measure Attitude on Farm Animal Welfare, 12 statements were presented. These statements were scaled and phrased using semantic differential scales based on a 7-point Likert scale. These statements were adapted from the studies of Sawang and Kivits (2014); Singh et al. (2021); Tashakor et al. (2019) and Thoradeniya et al. (2015).
To measure the Awareness of Farm Animal Welfare, 14 statements were presented. These statements were scaled and phrased using semantic differential scales based on a 7-point Likert scale. These statements were adapted from the studies of Lidfors et al. (2022); Pulina et al. (2022) and the BBFAW Report (Amos et al., 2021).
To measure the Social Norms on Farm Animal Welfare, 10 statements were presented. These statements were scaled and phrased using semantic differential scales based on a 7-point Likert scale. These statements were adapted from the studies of Kashif et al. (2017); Läpple and Kelley (2013); Tashakor et al. (2019) and Thoradeniya et al. (2015).
To measure the perceived behavioral control, 14 statements were presented. These statements were scaled and phrased using semantic differential scales based on a 7-point Likert scale. These statements were adapted from the studies of Despotović et al. (2019); Läpple and Kelley (2013); Sawang and Kivits (2014); Singh et al. (2021); Tashakor et al. (2019) and Thoradeniya et al. (2015).
To measure the intention of individuals engaged in the sustainability reporting process of listed food companies to adopt Farm Animal Welfare disclosure practices, 9 statements were presented. These statements were scaled and phrased using semantic differential scales based on a 7-point Likert scale. These statements were adapted from the studies of Singh et al. (2021); Tashakor et al. (2019), the BBFAW Report (Amos et al., 2021) and Thoradeniya et al. (2015).
The questions were based on data gathered throughout the literature review to ensure they were indicative of the internationally accepted perspectives on TPB. The review of literature is expected to provide a basis for content, convergent, discriminant and nomological validity (Hair et al., 2010). During the validation process of the questionnaire, copies of the questionnaire were given to certain academics and professionals for further insight and development. These professionals involved researchers whose expertise lies in sustainability reporting and in veterinary science specializing in farm animal health and production.
5 Results of the study
5.1 Diagnostic tests (PLS measurement results for the outer model)
The reliability of the constructs was tested by computing scores of Cronbach’s alpha. The indicator reliability was assessed with factor loadings and almost all the indicators were well above the cut-off limit of 0.5. The range of scores for all five constructs were between 0.874 and 0.963, which met the criteria recommended by Hair et al. (2010). Internal consistency of constructs was assessed through the utilization of Composite Reliability (CR) for each construct. The CR score for each construct surpassed the recommended limit of 0.7, indicating that it is adequate (Hair et al., 2010).
Anderson and Gerbing (1988) and Dunn et al. (1994) have suggested evaluating convergent validity by examining the statistical significance of standardized factor loadings. Wei and Nguyen (2020) reported support for convergent validity with an acceptable overall model fit, and all the standardized factor loadings in the model were statistically significant and higher than 0.5. Stevens (2002) suggested that the value of a factor loading should be greater than 0.4 for interpretation purposes, whereas Hair et al. (2010) argued that all standardized factor loadings should be at least 0.5. In this study, all standardized factor loadings are above the limit of 0.5, which provides support for convergent validity with an acceptable overall model fit. In addition to examining the standardized factor loadings, Yu et al. (2021) and Zahoor et al. (2022) have employed the Fornell and Larcker (1981) criterion for assessing convergent validity. Fornell and Larcker (1981) suggested that convergent validity is established when a latent construct accounts for no less than half of the variance in its associated indicators. They proposed using the average variance extracted (AVE) to represent the average amount of variance that a construct explains in its indicators relative to the overall variance of its indicators. Thus, the AVE should not be lower than 0.5 to demonstrate an acceptable level of convergent validity, meaning that the latent construct explains no less than 50% of the indicator variance (Fornell and Larcker, 1981). As represented in Table 1, the AVE is above the minimum threshold of 0.5 which demonstrates an acceptable level of convergent validity (Hair et al., 2010). Table 1 presents summary statistics of the variables.
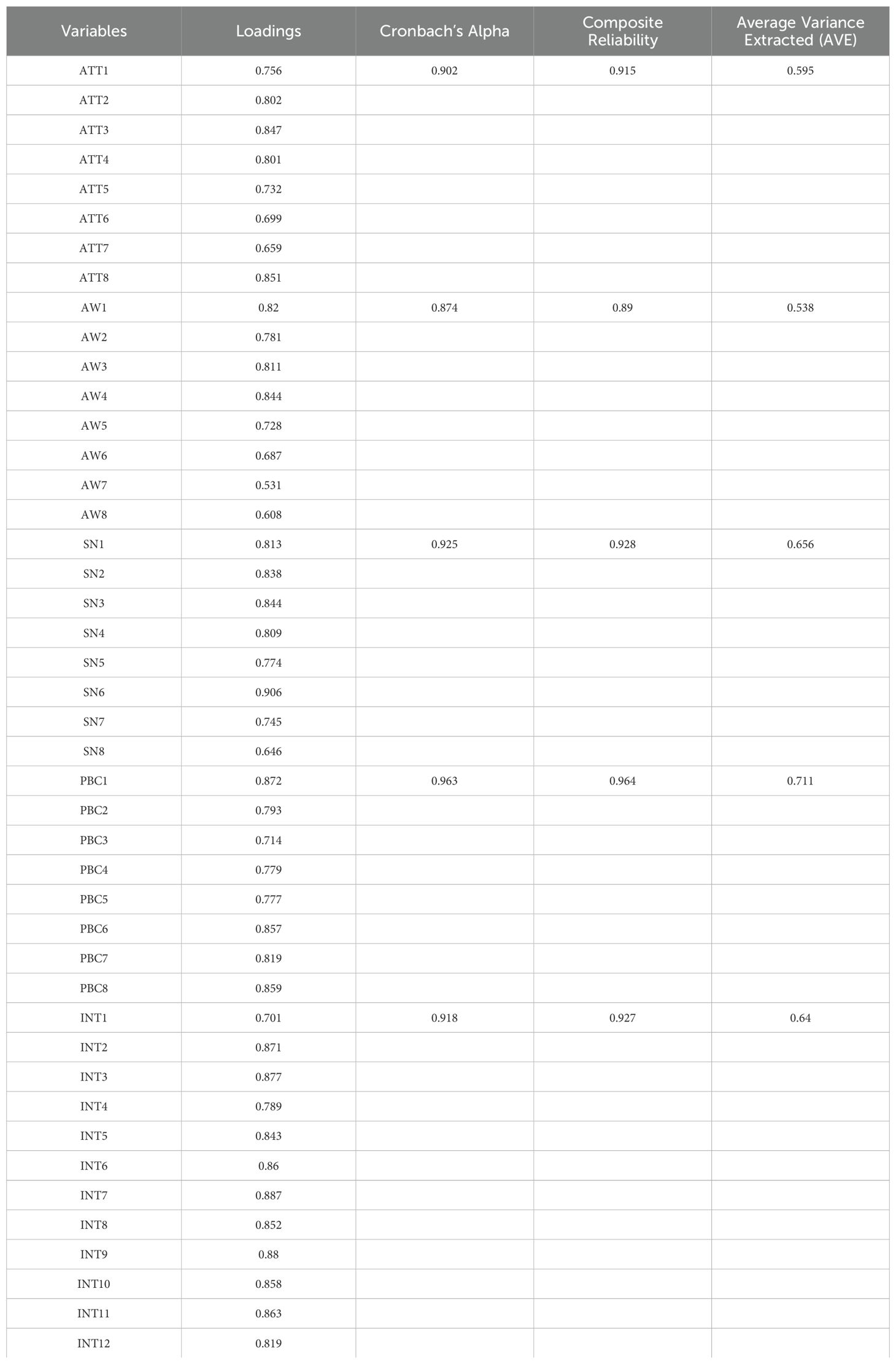
Table 1. Factor loadings, Cronbach’s alpha, composite reliability, average variance extracted (AVE).
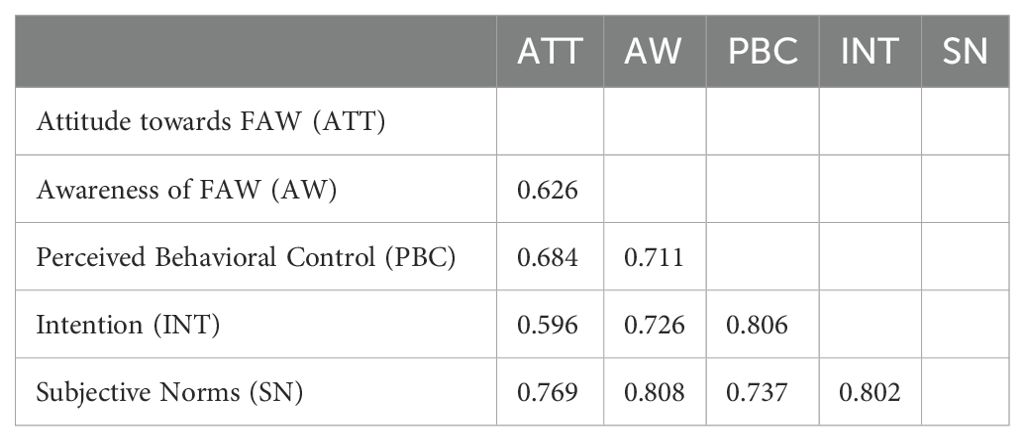
Discriminant validity was assessed by using the Heterotrait-Monotrait ratio. To qualify for discriminant validity, the correlation between the latent variables, as measured by the Heterotrait-Monotrait ratio, must not be greater than 0.9 (Henseler et al., 2015). As presented in Table 2 there is no correlation between the latent constructs exceeding the value of 0.9. Therefore, it signifies a valid discriminant validity amongst the constructs.
All things considered, the model performs well and is suitable for examining the paths connected to these variables’ relevance.
5.2 Descriptive analysis
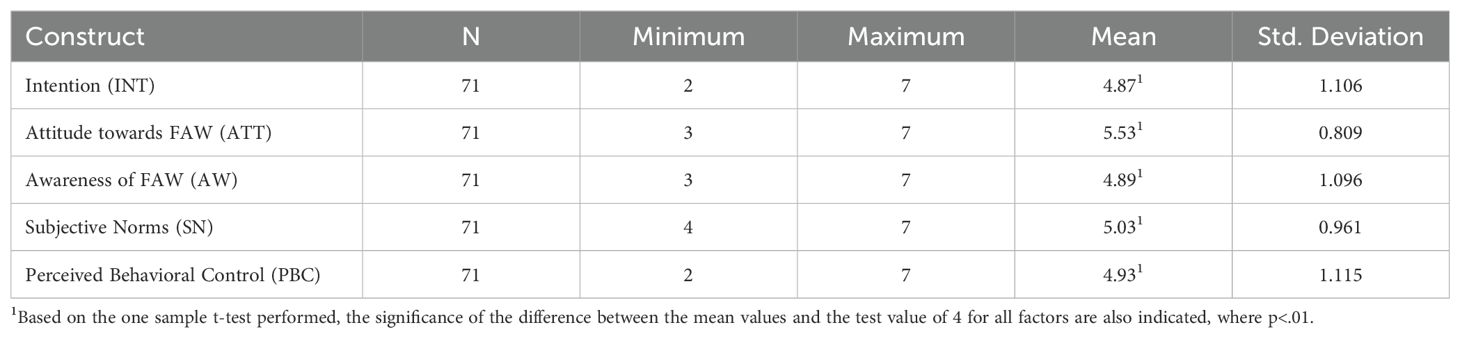
The descriptive statistics of the behavioral factors affecting INT are presented in Table 3. Considering the overall mean values of AW and PBC, they are approximately neutral on a 7-point Likert scale which is ranging from 1 – 7 giving an early indication that the respondents are neutral in their AW and PBC with a mean value of 4.89 and 4.93 respectively, in a seven-point Likert scale. Further, it can be noted that the respondents have a somewhat positive ATT and SN, based on the average values denoted. One sample t-test has been performed to measure if there is a significant difference between the mean values and the mid-value which is represented in Table 4.
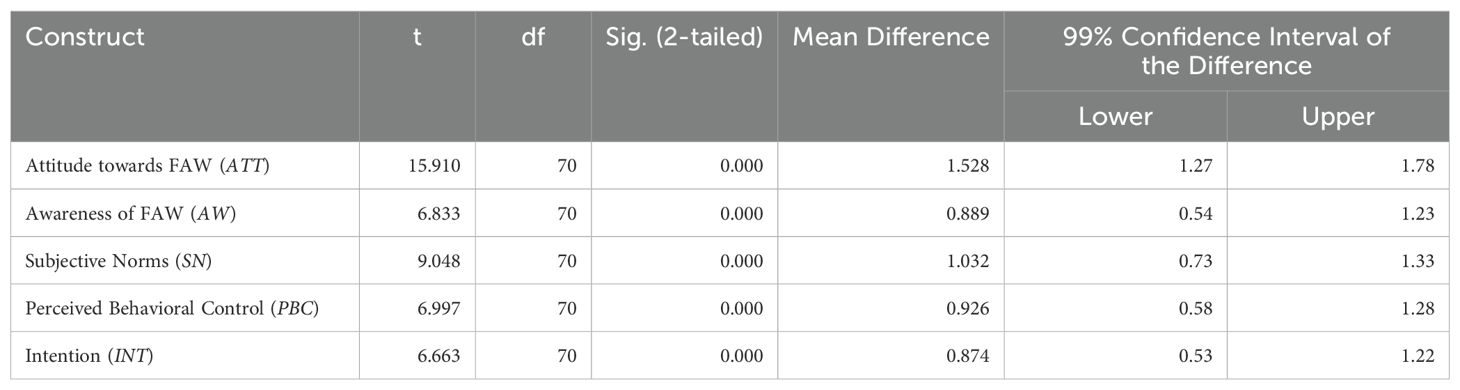
Table 4. One sample t-test denoting a significant difference between the mean values and the test value of 4.
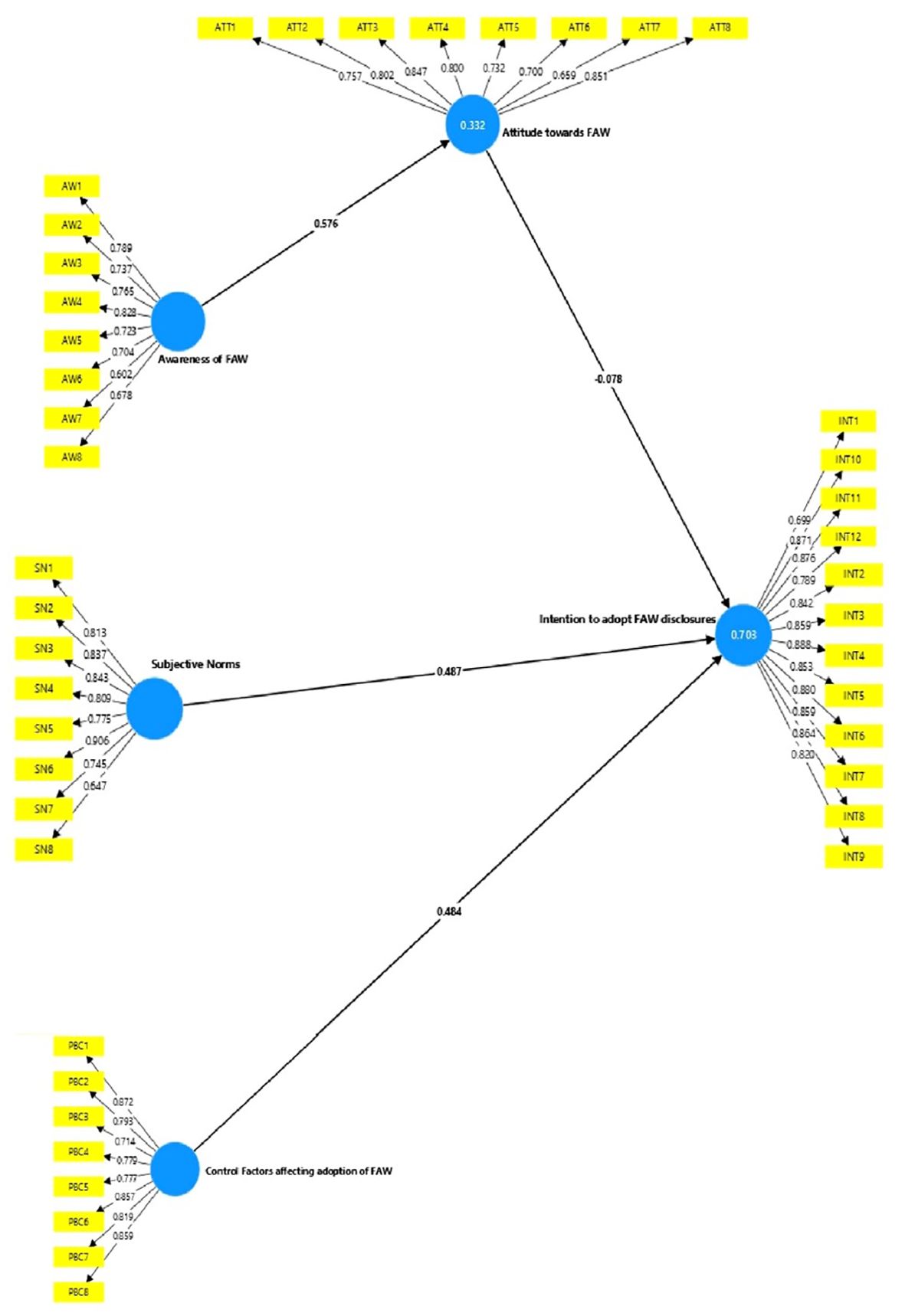
5.3 The structural model
The calculated path coefficients for the structural model are shown in Figures 1, 2 along with a description of them. The structural model depicts the research framework’s hypothesized paths.
The correlations between the latent variables of the structural model, known as the path coefficients, determine the degree of a relationship between an independent and dependent variable while balancing the impacts of all other independent variables (Hair et al., 2010). The hypotheses that were created in this study were verified using the path coefficient which is presented in Table 5.
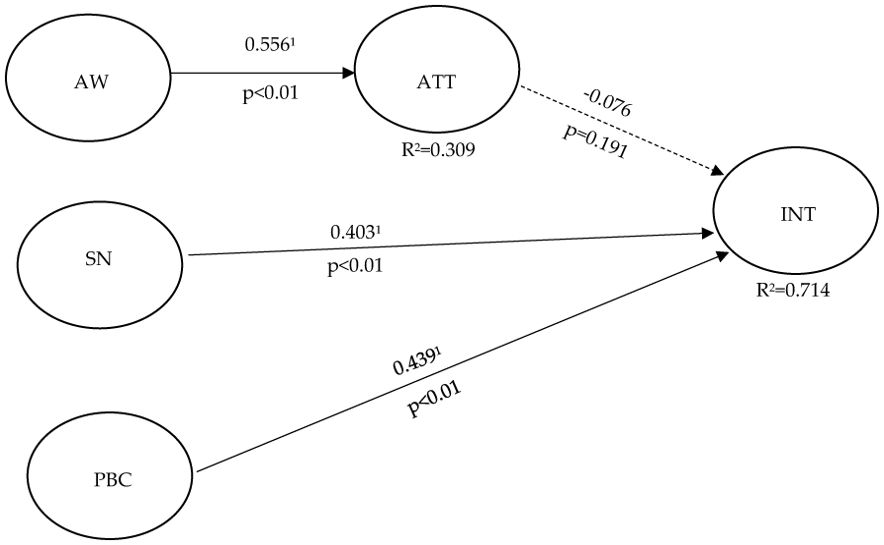
H1 posited a significant relationship between ATT and INT to adopt FAW disclosures by individuals engaged in the sustainability reporting process of food companies. However, the analysis does not support this hypothesis, as the path coefficient is negative (-0.076) and the p-value (0.191) is not statistically significant (since it is greater than the conventional threshold of 0.05). The negative path coefficient indicates that, rather than positively influencing intention, the attitude toward FAW might have a weak or possibly inverse effect, but more importantly, this effect is not significant. This means that attitude does not play a meaningful role in influencing the intention to adopt FAW disclosures, according to this data.
H2 posits that there is a significant relationship between FAW awareness and attitude towards FAW (ATT). The analysis provides strong empirical support for this hypothesis, revealing that an increase in FAW awareness leads to a significant positive shift in attitudes toward FAW. Specifically, the path coefficient of 0.556 (p<0.01) indicates a substantial effect size, demonstrating that as individuals become more aware of FAW issues, their attitudes toward improving or supporting FAW initiatives become more favorable. The high significance level (p<0.01) underscores the robustness of this relationship, implying that the observed correlation is not due to random chance. This suggests that raising awareness about FAW plays a critical role in shaping positive perceptions and behaviors, likely because increased knowledge highlights ethical concerns, societal implications, and personal responsibilities related to animal welfare, prompting more supportive attitudes.
H3, based on the TPB, predicts a positive relationship between SN and the intention (INT) to adopt FAW disclosures among individuals involved in sustainability reporting within food companies. The analysis, with a significant standardized path coefficient of 0.403 (p<0.01), supports this hypothesis, indicating that perceived social pressure from stakeholders, such as regulators, peers, and consumers, positively influences the intention to adopt FAW disclosures. This effect is expected to strengthen further with the recent UN resolution linking animal welfare to sustainability, which will likely increase societal expectations for ethical practices. As these external pressures intensify, companies are more likely to adopt FAW disclosures to meet stakeholder demands, align with international standards, and safeguard their reputational integrity.
H4 predicted a positive relationship between PBC and the INT to adopt FAW disclosures by individuals involved in the SR process of food companies. The analysis, with a significant path coefficient of 0.439 (p<0.01), confirms this hypothesis, indicating that the more control individuals perceive they have over implementing FAW disclosures, the more likely they are to act on this intention. This suggests that when people feel empowered with the necessary resources, time, and organizational support, their willingness to adopt FAW disclosures increases. Consequently, enhancing PBC is crucial for encouraging greater adoption of FAW reporting.
6 Discussion
In the context of Sri Lanka, this study looked at the intentions of individuals engaged in SR process to embrace FAW disclosure procedures in the sustainability reporting process. During the procedure, a structured questionnaire was developed backed by prior literature and was administered in Sri Lanka. To achieve the goals of the research, a total of four hypotheses were created and tested using structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). The data, measurement model, and structural model all demonstrated good fits.
The findings of the PLS analysis show that the individual’s intention to adopt FAW disclosure practices are likely influenced by their perceptions of whether the external and internal parties and stakeholders of the company and themselves approve of FAW disclosure practices and their perception of the resource accessibility and the absence of obstacles that would prevent the adoption of FAW disclosure practices. The significant relationships between INT and its three antecedent variables which are ATT, SN and PBC are comparable to those of Raab et al. (2018) and Sobaih and Elshaer (2023). However, the results are contrary to Glandon’s (Glandon, 2003) finding of a non-significant relationship in the case of perceived behavioral control and intention as well as the findings of Thoradeniya et al. (2015) which posits a significant relationship between attitude and intention. In addition, Ajzen (1991) suggests that compared to the other categories, attitude seems to be a higher predictor of intention, whereas these results reveal that in the context of sustainability reporting and animal welfare disclosures, attitude does not have strong determinative power over the intention to adopt FAW disclosure practices, and that PBC is the strongest predictor and determinant of INT for listed food companies. So, in contrast to previous research, the results show that, when examining listed companies in the context of a developing nation like Sri Lanka, stakeholders’ perceptions of pressure, resource availability, and constraints matter more than the companies’ own attitudes when determining whether to engage in FAW disclosure practices.
H2 evaluates whether AW has an impact on ATT and H2 was supported with a positive relationship. It was identified to be the most significant predictor in the study. This finding is consistent with the studies of Shah et al. (2021); Saleh et al. (2020); Mohiuddin et al. (2018); Amit Kumar (2021); Metzger (2015) and Suárez-Cáceres et al. (2021), where each of these studies have introduced a new construct, namely, “awareness” or “knowledge” into the model of TPB and have proven that this construct has a significant relationship with the construct of Attitude. This result indicates that the individuals engaged in the SR process of listed food companies in Sri Lanka have awareness of the cruelty and consequences of animal handling and on FAW, which positively affects their attitude towards FAW. The more aware they are on the concept of animal welfare and the consequences of corporate actions on animals, the more positive their attitude on FAW. Awareness influences attitude by enhancing an individual’s understanding of the consequences of their actions. In Sri Lanka’s food industry, awareness of the impact of corporate actions on animals increases sensitivity toward FAW issues. As people become more knowledgeable about animal welfare concerns, they are more likely to develop favorable attitudes toward adopting FAW disclosures. This aligns with the positive relationship seen in other studies, reinforcing the idea that knowledge shapes ethical perspectives and positive attitudes.
H3 evaluates whether SN has an impact on INT and H3 was supported with a positive relationship. It is the second-most significant predictor out of all the other variables. According to Madden et al. (1992), this prediction is consistent with the fact that the more the individual feels that referent groups think that the individual should engage in such behavior, it is more likely that the individual would intend to engage in such behavior. Since Sri Lanka consists of a collectivism culture as per Niles (1998), the individuals would act on their intention which is highly influenced by their friends’, family members’, or colleagues’ perceptions of the concept of FAW. As a multi-religious country, the business issue of farm animal cruelty and welfare in the food industry affects the societal values of Sri Lanka as a whole. For example, since economic, cultural, and religious considerations all have a role in how Sri Lanka’s livestock and meat business develops, religious and cultural values have an impact on how the country promotes and consumes meat and animal byproducts (Alahakoon et al., 2016). Subjective norms are beliefs about how significant others (e.g., family, colleagues, society) perceive the behavior in question. Sri Lanka’s collectivist culture places strong emphasis on communal values and societal expectations, meaning individuals are highly influenced by social pressure when forming intentions. Given the multi-religious and socially interconnected nature of Sri Lanka, societal and cultural norms surrounding animal welfare play a major role in shaping individuals’ intentions to embrace FAW disclosure practices. Thus, individuals are expected to adhere to the societal norms when intending to adopt FAW disclosure practices in food companies.
H4 evaluates whether PBC has an impact on INT and H4 was supported with a positive relationship. These results are consistent with Despotović et al. (2019); Läpple and Kelley (2013); Raab et al. (2018); Tashakor et al. (2019) and Thoradeniya et al. (2015) where they found that PBC is significantly influencing the behavioral intention of adopting environmental accounting practices, sustainability reporting and other environmental related reporting measures. These results suggest that while individuals engaged in the SR process of listed food companies of Sri Lanka are highly driven by the perceptions of internal and external stakeholders regarding FAW, their willingness to act is primarily driven by the resources available to the company to carry out FAW disclosure practices such as the expertise of FAW, knowledge, skills, conditions, and facilities as well as competent employees. As per the results of this study, PBC has the highest effect on the intention to adopt FAW disclosure practices. This would also be because 64.79% of the respondents were of the positions of CEO, CFO, Managing Director, Finance Director, Senior Manager, Manager, Finance Manager, Accounting Manager, Assistant Manager, Assistant General Manager – Finance, where these individuals have a degree of control over the adoption process of new disclosure practices of the organization. Also, it seems that knowledge, skills, and financial ability are necessities and that without them, it is difficult for individuals to adopt FAW disclosure practices.
Further, it is to be noted that although AW stimulates the individual’s ATT, the results of the current research showed that this was not enough to have a significant effect on their intention to adopt FAW disclosure practices. Individual’s ATT did not significantly affect their intention to adopt FAW disclosure practices.
7 Implications of the study
Regulatory bodies, including the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB) under the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) and the Business Benchmark on Farm Animal Welfare (BBFAW), stand to benefit from the findings of this study. By identifying key factors that influence sustainability reporting practices, particularly regarding FAW, policymakers can create stringent standards related to sustainability worldwide. From a Sri Lankan context, the government and legislative bodies can utilize the study’s insights to establish stronger statutory requirements for companies involved with farm animals in their supply chains. Predicting individual behavior toward FAW reporting will help introduce more comprehensive regulations, ensuring ethical conduct and accountability in managing FAW.
In Sri Lanka, although animal welfare is deeply ingrained in society, FAW practices are not heavily publicized within business sectors. Many food businesses have inadequately managed FAW and have failed to communicate these efforts effectively to the public and stakeholders. This study contributes to the development of FAW reporting in Sri Lanka by highlighting the need for transparency and accountability. It offers practical recommendations for addressing significant animal welfare issues, reminding senior managers and policymakers of the importance of FAW in both operational practices and long-term strategic planning.
Empirically, this study addresses a gap in the literature, as previous research on sustainability reporting has largely concentrated on corporate social responsibility (CSR), sustainability, intellectual capital, and integrated reporting (IR) disclosures. There has been little empirical research on FAW disclosure or its determinants, particularly in the context of developing economies like Sri Lanka. Previous studies have focused on the theoretical inclusion of animals in sustainability frameworks, such as the BBFAW, primarily in European and U.S. companies. The current research contributes to sustainability literature by focusing on FAW disclosure practices in the Sri Lankan food industry and examining participants’ intentions to adopt these practices in the future, filling a void in accounting research.
Theoretically, this study builds on existing models by incorporating an extended version of the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB). The research integrates awareness as a factor influencing the intention to adopt FAW disclosure practices and introduces attitude as a mediating variable between awareness and behavioral intention. This multi-theoretical framework enriches the conceptual model and deepens the understanding of how individuals engaged in sustainability reporting are influenced by FAW awareness. This contributes to the ongoing theoretical discourse around behavioral intention and sustainability practices, positioning the study as an important addition to both FAW and broader sustainability literature.
8 Conclusion
This study aimed to investigate and comprehend the ways in which various psychological elements impact people’s behavioral intention to embrace FAW disclosure policies in food companies that are listed in Sri Lanka. That is, to comprehend how people’s intentions to implement FAW disclosure practices in the workplace are influenced by their personal attitudes toward FAW, awareness of the concept of FAW, how they perceive the social pressure that external and internal stakeholders place on the organization (subjective norm), and how they feel like they have influence over the FAW disclosure decision (perceived behavioral control). The study employed Ajzen’s Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB), a widely recognized framework in the psychology field, to gain a deeper understanding of the motivations behind behavioral intentions to disclose FAW. While the hypothesis positing a significant relationship between attitude and intention was not supported—indicating that attitude may have a weak or negative effect—strong empirical support was found for the positive impact of FAW awareness on attitude. Additionally, the research demonstrated that subjective norms positively influence intention, suggesting that social pressures from stakeholders enhance the likelihood of adopting FAW disclosures, particularly in light of recent global resolutions linking animal welfare to sustainability. Lastly, a positive relationship was confirmed between perceived behavioral control and intention, indicating that individuals who feel empowered and supported are more inclined to adopt FAW disclosure practices. Overall, the findings underscore the importance of awareness, social pressure, and perceived control in driving the intention to enhance animal welfare reporting within the food industry.
Because farm animals are utilized by people as food and clothing, they have a strong relationship with humans (Sun et al., 2021). However, Sri Lankan food companies are still seen to be in the infancy stage of farm animal welfare reporting and transparency of business operations relating to its’ farm animals, especially the companies in the food industry (Amos et al., 2021). In Sri Lanka, animal welfare is grounded in society, but business practices on FAW are not heavily publicized. Many food businesses have not managed FAW well, and they have not fully informed society and other stakeholders about how they manage FAW. Using this study, companies where animals are used extensively in their supply chain can discover and explore new paths to broaden and enhance the commitment of the management by re-exploring their role in the realm of sustainability reporting, reporting issues and responsibility towards inculcating greater awareness and knowledge of FAW and its relative benefits. This study offers some recommendations for dealing with the country’s serious animal welfare issues. Firstly, a set of guidelines for reporting on animal welfare by companies can be issued by established standard-setting institutions to provide a clear set of guidelines to those engaged in sustainability reporting of listed food companies. Thus, designing a guideline for reporting animal welfare that is unique to Sri Lanka is necessary. Secondly, laying the foundations of an organization similar to BBFAW in Sri Lanka would be beneficial in both improving disclosure procedures on animal welfare and assessing how well businesses are doing with regard to farm animal welfare (Sun et al., 2021). It further needs to be noted that sustainability reporting in Sri Lanka is voluntary (Thoradeniya et al., 2015). Thus, it inherently means animal welfare reporting is voluntary as well. Therefore, the Sri Lankan government should enforce laws requiring mandatary animal welfare reporting of food companies which would provide guidance to individuals engaged in the sustainability reporting process of food companies which would enhance a sense of control and consequently more inclination towards adoption of FAW reporting as per the findings of the study.
Prior research on sustainability reporting has mostly been on integrated reporting transparency, sustainability, corporate social responsibility (CSR), and intellectual capital. This suggests that there is a gap in the literature because there is no empirical research on animal welfare disclosures and its potential determinants. The study contributes to the sustainability reporting literature by examining FAW disclosure practices in the Sri Lankan food industry. Previous studies mainly focused on developing theoretical frameworks to include animals in sustainability reporting frameworks (such as the BBFAW framework) (Vinnari and Vinnari, 2022). The study’s findings add to the current body of research on SR from a developing country’s viewpoint, with an emphasis on the psychological factors that encourage corporate reporters to pursue FAW disclosure practices. Additionally, little is known about the participants’ future plans to adopt FAW disclosure practices based on the outcomes of such research. Therefore, the study of people’s intention to adopt FAW disclosure methods is more future-focused and fills a void in the extremely restricted accounting literature.
This study has some limitations whereas this research focuses only on sustainability reporting intentions in publicly listed food companies of Sri Lanka, which effectively excludes employees in private sectors and small-scale farms. It does not consider companies dealing with animal-related products, such as fur in cosmetics and fashion. Also, the findings cannot be applied globally, as the research is limited to the Sri Lankan context, making it less valuable for those seeking information about developed nations, thus, future research could analyze data by using an international sample to enhance the generalizability of the study.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
No human or animal studies are presented in the manuscript. Therefore, no ethical approval was obtained for this study.
Author contributions
SS: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. IM: Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fanim.2024.1476959/full#supplementary-material
References
Ajzen I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behav. Hum. Decision Processes 50, 179–211. doi: 10.1016/0749-5978(91)90020-T
Ajzen I., Fishbein M. (1980). Understanding Attitudes and Predicting Social Behavior. (the University of Michigan: Prentice-Hall).
Ajzen I., Fishbein M. (2005). The influence of attitudes on behavior. Handb. Attitudes 173, 173–221.
Alahakoon A. U., Jo C., Jayasena D. D. (2016). An overview of meat industry in Sri Lanka: A comprehensive review. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. doi: 10.5851/kosfa.2016.36.2.137
Amit Kumar G. (2021). Framing a model for green buying behavior of Indian consumers: From the lenses of the theory of planned behavior. J. Cleaner Production 295. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.126487
Amos N., Sullivan R., Romanowicz B., van de Weerd H. (2021). The Business Benchmark on Farm Animal Welfare Report 2021 (Sheffield: Greenleaf Publishing).
Anderson J. C., Gerbing D. W. (1988). Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. psychol. Bull. 103, 411–423. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.103.3.411
Chandimala U. R., Gunathilake D. M. C. C., Vidanapathirana N. P., Rifnas L. M. (2022). Perception of cultured meat among Sri Lankan community. J. Agro-Technology Rural Sci. 1, 21. doi: 10.4038/atrsj.v1i2.33
Chen X., Weerathunga P. R., Nurunnabi M., Kulathunga K.M.M.C.B., Samarathunga W. H. M. S. (2020). Influences of behavioral intention to engage in environmental accounting practices for corporate sustainability: Managerial perspectives from a developing country. Sustainability (Switzerland) 12. doi: 10.3390/su12135266
Despotović J., Rodić V., Caracciolo F. (2019). Factors affecting farmers’ adoption of integrated pest management in Serbia: An application of the theory of planned behavior. J. Cleaner Production 228, 1196–1205. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.149
Dunn S. C., Seaker R. F., Waller M. A. (1994). Latent variables in business logistics research: scale development and validation. J. Business Logistics.
Ediriweera E., Nanayakkara N., Kalawana O., Sugathadasa Y. (2010). A review on traditional veterinary medical practices in Sri Lanka with special reference to cattle diseases. Trop. Agric. Res. Extension 13, 56–62.
Fornell C., Larcker D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Marketing Res. 18, 39–50. doi: 10.2307/3151312
Glandon T. A. (2003). “Edi adoption: controls in a changing environment,” in Advances in Management Accounting (Leeds: Emerald Group Publishing Limited). doi: 10.1016/S1474-7871(02)11012-4
Hair J. F. J., Black W. C., Babin B. J., Anderson R. E. (2010). Multivariate Data Analysis (New York: Pearson).
Haque F., Jones M. J. (2020). European firms’ corporate biodiversity disclosures and board gender diversity from 2002 to 2016. Br. Accounting Rev. 52. doi: 10.1016/j.bar.2020.100893
Hassan A. M., Roberts L., Atkins J. (2020). Exploring factors relating to extinction disclosures: What motivates companies to report on biodiversity and species protection? Business Strategy Environ. 29, 1419–1436. doi: 10.1002/bse.2442
Henseler J., Ringle C. M., Sarstedt M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Marketing Sci. 43, 115–135. doi: 10.1007/s11747-014-0403-8
Kashif M., Zarkada A., Thurasamy R. (2017). The moderating effect of religiosity on ethical behavioural intentions: An application of the extended theory of planned behaviour to Pakistani bank employees. Personnel Rev. 46, 429–448. doi: 10.1108/PR-10-2015-0256
Kazaure M. A. (2019). Extending the theory of planned behavior to explain the role of awareness in accepting Islamic health insurance (takaful) by microenterprises in northwestern Nigeria. J. Islamic Accounting Business Res. 10, 607–620. doi: 10.1108/JIABR-08-2017-0113
Läpple D., Kelley H. (2013). Understanding the uptake of organic farming: Accounting for heterogeneities among Irish farmers. Ecol. Economics 88, 11–19. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2012.12.025
Leslie J., Sunstein C. R. (2007). Animal Rights without Controversy Vol. 70 (North Carolina: Duke University School of Law).
Lidfors L. M., Gonçalves Titto C., Brazil P., Neethirajan S., Alemayehu G. (2022). Animal welfare knowledge, attitudes, and practices among livestock holders in Ethiopia. Front. Veterinary Sci. 9.
Madden T. J., Ellen P. S., Ajzen I. (1992). A comparison of the theory of planned behavior and the theory of reasoned action. Pers. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 18, 3–9. doi: 10.1177/0146167292181001
McLaren J., Appleyard T. (2020). Improving accountability for farm animal welfare: the performative role of a benchmark device. Accounting Auditing Accountability J. 33, 32–58. doi: 10.1108/AAAJ-06-2017-2955
McLaren J., Appleyard T. (2022). Social movements, identity and disruption in organizational fields: Accounting for farm animal welfare. Crit. Perspect. Accounting 84. doi: 10.1016/j.cpa.2021.102310
Metzger M. (2015). Knowledge of the animal welfare act and animal welfare regulations influences attitudes toward animal research. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 54, 70–75.
Mohiuddin M., Al Mamun A., Ali Syed F., Mehedi Masud M., Su Z. (2018). Environmental knowledge, awareness, and business school students’ Intentions to purchase green vehicles in emerging countries. doi: 10.3390/su10051534
Mos S. (2016).Reinstating animal rights in Sri Lanka. In: Buddhist Door Global. Available online at: https://www.buddhistdoor.net/features/reinstating-animal-rights-in-sri-lanka/ (Accessed 8 September 2024).
Niles F. S. (1998). Individualism-Collectivism Revisited The constructs individualism-collectivism (I-C) have been ex-tensively researched and seem to have been generally accepted as. Cross-Cultural Res. 32, 315–341. doi: 10.1177/106939719803200401
Parliament of the democratic socialist republic of Sri Lanka (2022). Animal welfare bill, the department of government printing, Sri Lanka (Colombo, Sri Lanka: Sri Lanka).
Perugini M., Bagozzi R. P. (2001). The role of desires and anticipated emotions in goal-directed behaviours: Broadening and deepening the theory of planned behaviour. Br. J. Soc. Psychol. 40, 79–98. doi: 10.1348/014466601164704
Pulina G., Carta S., Pulino D., Spanu S., Deriu R., Mazzette A. (2022). Farm animal welfare: A survey of the opinion of farmers and consumers in Sardinia. Anim. - Open Space 1, 100020. doi: 10.1016/j.anopes.2022.100020
Raab C., Baloglu S., Chen Y. S. (2018). Restaurant managers’ Adoption of sustainable practices: an application of institutional theory and theory of planned behavior. J. Foodservice Business Res. 21, 154–171. doi: 10.1080/15378020.2017.1364591
Reis G. G., Molento C. F. M. (2020). Emerging market multinationals and international corporate social responsibility standards: bringing animals to the fore. J. Business Ethics 166, 351–368. doi: 10.1007/s10551-019-04144-5
Saleh R. M., Anuar M. M., Al-Swidi A. K., Omar K. (2020). The effect of awareness, knowledge and cost on intention to adopt green building practices. Int. J. Environ. Sustain. Dev. 19, 33–58. doi: 10.1504/IJESD.2020.105468
Sawang S., Kivits R. A. (2014). Greener workplace: Understanding senior management’s adoption decisions through the Theory of Planned Behaviour. Australas. J. Environ. Manage. 21, 22–36. doi: 10.1080/14486563.2013.848418
Shah S. K., Zhongjun T., Sattar A., XinHao Z. (2021). Consumer’s intention to purchase 5G: Do environmental awareness, environmental knowledge and health consciousness attitude matter? Technol. Soc. 65, 101563. doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101563
Singh G., Sharma S., Sharma R., Dwivedi Y. K. (2021). Investigating environmental sustainability in small family-owned businesses: Integration of religiosity, ethical judgment, and theory of planned behavior. Technological Forecasting Soc. Change 173. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2021.121094
Sobaih A. E. E., Elshaer I. A. (2023). Risk-taking, financial knowledge, and risky investment intention: expanding theory of planned behavior using a moderating-mediating model. Mathematics 11. doi: 10.3390/math11020453
Stevens J. P. (2002). Applied Multivariate Statistics for the Social Sciences. 4th Ed (Mahwah, NJ, US: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers).
Suárez-Cáceres G. P., Fernández-Cabanás V. M., Lobillo-Eguíbar J., Pérez-Urrestarazu L. (2021). Consumers’ knowledge, attitudes and willingness to pay for aquaponic products in Spain and Latin America. Int. J. Gastronomy Food Sci. 24, 100350. doi: 10.1016/j.ijgfs.2021.100350
Sullivan R., Amoss N., van de weerd H. A. (2017). Corporate reporting on farm animal welfare: An evaluation of global food companies’ discourse and disclosures on farm animal welfare. Animals 7. doi: 10.3390/ani7030017
Sun Y., Ip P. S., Jones M., Wang J. J., An Y. (2021). Determinants of animal welfare disclosure practices: Evidence from China. Sustainability (Switzerland) 13, 1–16. doi: 10.3390/su13042200
Sustainability Disclosure Standard International Sustainability Standards Board (2023). General Requirements for Disclosure of Sustainability-Related Financial Information IFRS S1 IFRS ®. (State of Delaware, United States of America: The International Financial Reporting Standards Foundation).
Tashakor S., Appuhami R., Munir R. (2019). Environmental management accounting practices in Australian cotton farming: The use of the theory of planned behaviour. Accounting Auditing Accountability J. 32, 1175–1202. doi: 10.1108/AAAJ-04-2018-3465
Thoradeniya P., Lee J., Tan R., Ferreira A. (2015). Sustainability reporting and the theory of planned behaviour. Accounting Auditing Accountability J. 28, 1099–1137. doi: 10.1108/AAAJ-08-2013-1449
United Nations Environment Assembly of the United Nations Environment Programme (2022). Animal Welfare-Environment-Sustainable Development Nexus (Nairobi: UN Environment Programme).
Vinnari E., Vinnari M. (2022). Making the invisibles visible: Including animals in sustainability (and) accounting. Crit. Perspect. Accounting 82. doi: 10.1016/j.cpa.2021.102324
Wei Z., Nguyen Q. T. K. (2020). Chinese service multinationals: the degree of internationalization and performance. Manage. Int. Rev. 60, 869–908. doi: 10.1007/s11575-020-00434-7
Yazdanpanah M., Forouzani M. (2015). Application of the theory of planned behaviour to predict Iranian students’ Intention to purchase organic food. J. Cleaner Production 107, 342–352. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2015.02.071
Yu M., Lin H., Wang G., Liu Y., Zheng X. (2021). Is too much as bad as too little? The S-curve relationship between corporate philanthropy and employee performance. Asia Pacific J. Manage. 39. doi: 10.1007/s10490-021-09775-9
Keywords: attitudes, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, awareness, intention to adopt farm animal welfare disclosures
Citation: Samaraweera S and Manawadu I (2024) Factors affecting the intention to adopt farm animal welfare disclosures in sustainability reporting: evidence from listed food companies in Sri Lanka. Front. Anim. Sci. 5:1476959. doi: 10.3389/fanim.2024.1476959
Received: 06 August 2024; Accepted: 28 October 2024;
Published: 20 November 2024.
Edited by:
Muhammad Khalilur Rahman, Universiti Malaysia Kelantan, MalaysiaReviewed by:
Sohail Ahmad, University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, PakistanKuldeep Singh, Gati Shakti Vishwavidyalya, India
Copyright © 2024 Samaraweera and Manawadu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Saviesha Samaraweera, c2F2aWVzaGFzYW1hcmF3ZWVyYUBnbWFpbC5jb20=
 Saviesha Samaraweera
Saviesha Samaraweera Isuru Manawadu
Isuru Manawadu