- 1College of Animal Science, Henan University of Science and Technology, Luoyang, China
- 2International Joint Laboratory of Animal Welfare and Healthy Breeding in Henan Province, Luoyang, China
Introduction: This study investigated the effects of Flammulina velutipes residue (FVR) on performance, antioxidant function, immunity, and intestinal flora of broilers.
Methods: A total of 192 one-day-old three-yellow chickens were divided into four groups of 48 chickens per group, 6 replicates per group and 8 chickens per replicate. The control group (CON) was fed a basal diet, while the remaining three groups were supplemented with FVR in the basal diet, adding 2%, 4% and 6% of the basal diet, respectively. The experiment lasted for 48 days. Blood samples were collected from the jugular vein on days 28 and 48 to determine serum biochemical indices. Caecum contents were collected on day 48 to assess flora diversity.
Results and discussion: No significant differences were observed in dry matter intake (DMI), average daily gain (ADG), or feed conversion ratio (FCR) between the 2% and 4% group and the CON. However, the 6% FRV group showed significantly reduced DMI and FCR. The FVR groups exhibited significantly increased levels of catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPC-PX) and total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), along with significantly decreased malondialdehyde (MDA) content. Additionally, serum interleukin-1 (IL-1) levels decreased, while immunoglobulin G (IgG), immunoglobulin A (IgA) and interleukin 10 (IL-10) levels significantly increased in the FVR groups. The caecal flora diversity test revealed that FVR altered the flora structure, with increased proportions of Bacteroides, Ruminococcus and Faecalibacterium in the 6% FVR groups. In conclusion, FVR can significantly enhance the antioxidant capacity and immunity of broilers and enrich the structure of intestinal flora. The impact on growth performance is limited and dosage-dependent. Further research is needed to optimize its use in poultry diets.
1 Introduction
Poultry feed, predominantly consisting of corn, soybean meal, and other grains, serves as the foundation of poultry farming and constitutes approximately one-third of the global food resources (Silver et al., 2021). By 2025, the consumption of animal-based food is projected to increase by 50% (McIntyre et al., 2009). Over the past few decades, the global population has grown significantly, reaching 7.43 billion in 2015, with food demand doubling and surpassing the Earth’s regenerative capacity (Staniškis, 2012; Michiel et al., 2021). Furthermore, the Food and Agriculture Organization estimates a 70% increase in global food demand by 2050 (Bruinsma, 2003). Given the continuous global population growth and climate change-induced food shortages, the conflict between feed resource supply and demand is intensifying, posing a significant threat to the sustainable development of poultry farming (Mottet and Tempio, 2017).
China, home to 20% of the world’s population but only 6% of its land area (Ziegler, 2006; Zhang, 2011), faces significant challenges. The rapid development of its poultry industry has dramatically increased food demand, particularly for grain, which has doubled, posing a substantial impact on the global food market and potentially leading to a food security crisis (Rosegrant et al., 2001; Trostle, 2008; Cao and Li, 2013; Chen and Nie, 2016).
As a producer of edible fungi, China boasts a diverse range of these resources (Falandysz, 2013; Yadav and Samadder, 2018), with an annual output of nearly 2 million tons that will continue to increase (Aida et al., 2009; Amin et al., 2014). Approximately 5 kg of residue is produced per kilogram of edible fungi (Lin et al., 2014; Zisopoulos et al., 2016). These residues are rich in proteins, vitamins, and trace elements (Medina et al., 2009; Zhu et al., 2012), cellulose and lignin, promoting food digestion (Fazaeli et al., 2014) and offering potential health benefits (Manila et al., 2000). As a foodborne mushroom, the Flammulina mushroom is deeply loved by Asian people because of its unique fragrance (Leifa et al., 2001; Ko et al., 2007; Jing et al., 2014). In addition, it contains various immune-active substances such as fungal ribosome inactivation protein (RIP) and fungal immunomodulatory protein (FIP), which deserve more attention. RIP from Flammulina velutifolia, with a molecular weight of 30 kDa, effectively inhibits tumor cells (Ng, 2006). FVPB2, a new polysaccharide from Flammulina vellum, enhances the immune response in mice, enabling B cells to induce high immunoglobulin (Ig) M and IgG levels (Wang et al., 2018). Polysaccharides extracted from Flammulina velutipes residue (FVR) also demonstrate strong antioxidant activity (Lin et al., 2016). Despite these benefits, edible mushroom residues are often discarded (Chiu et al., 1998; Williams et al., 2001).
Development and utilization of FVR and its rational use in broiler production will be conducive to increasing the diversity of feed, reducing the pressure of “human and animal competition for food”, and support the sustainable development of animal husbandry. The three-yellow chicken, a renowned breed in China for its meat and nutritional qualities, has been under-researched regarding the effects of FVR. The three-yellow chicken is typically raised for approximately 60–70 days to reach a market weight of 1.5–2.0 kg. This study examines the impact of varying FVR concentrations on the antioxidant activity, immunity, and intestinal flora of three-yellow chickens, evaluating the feasibility of incorporating FVR into their basal diet.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Treatments, experimental diet and management
One-day old three-yellow chickens were selected as the experimental subjects. A total of 192 healthy three-yellow chickens (96 males and 96 females) with similar body weight were purchased and randomly divided into four treatment groups, each comprising 48 chickens. Each treatment group comprised six replicates, with eight chickens per replicate. The control (CON) group was fed a basal diet, while the other three groups received FVR supplementation at levels of 2%, 4%, and 6% relative to the basal diet, respectively. The FVR used in this study was provided by the Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences. Before feeding, the residue was dried and crushed for inclusion in the diet. The entire experiment lasted 48 d.
FVR was derived from the residual material after the harvest. This material was utilized after being dried at 80°C. The nutritional composition was 90.40% dry matter, 9.63% crude protein, 0.20% crude fat, 17.20% crude fiber, 13.50% crude ash, 3.20% calcium, 0.38% total phosphorus, and 6.3% total amino acids.
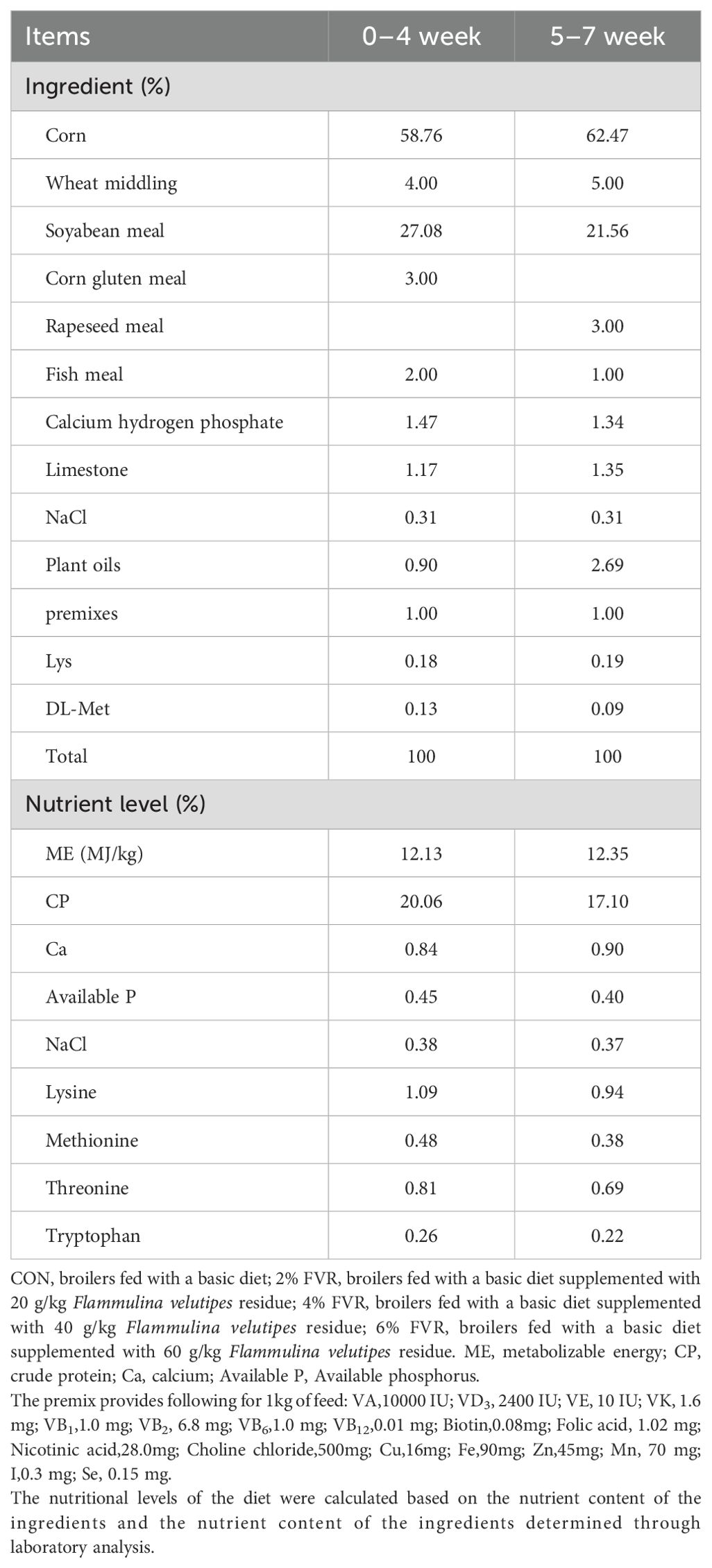
During the experiment, the chickens were raised in two-layer cages with eight chickens in each cage, and specially assigned individuals were responsible for feeding the chickens and maintaining natural ventilation in the cages. The dietary formulations and nutritional levels of the basic feed are presented in Table 1. The nutritional levels were formulated in accordance with standard poultry nutrition guidelines and were further refined based on data specific to local poultry breeds, including the three-yellow chicken. The experimental feed, consisting of a powdered mixture, was prepared on-site using a dedicated mixer and ingredients procured specifically for the study. Experimental animals were provided with ad libitum access to both feed and water throughout the trial period.
All animals experiment were conducted in accordance with the Guidelines for the Care and Use of Experimental Animals of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences and approved by the Review of Experimental Animal Welfare and Ethics of the Shanghai Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (SV-20230526- Y01).
2.2 Sample collection and analysis
Feed intake and weight were systematically recorded throughout the study periods. Feed intake was calculated the difference between the amount of feed provided and the amount of feed refused at each replicate. ADG was determined by starting weight and ending weight every periods. FCR was then calculated by dividing the total feed intake by the corresponding weight gain achieved during each specific period average daily.
One chicken was randomly selected from each replicate on 28 and 48 days. Blood was collected from the jugular vein, stored at 4°C overnight, and centrifuged at 8000g for 30 min. The upper serum was absorbed and stored at −80°C. Cecal contents of 2–3 g was collected aseptically on 48 day and frozen at −80 °C for microbial flora diversity detection.
According to the kit instructions (provided by Shanghai Yinuopai Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), the following serum antioxidant indices were determined: catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPC-PX), total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), and malondialdehyde (MDA); The serum immune indices were immunoglobulin A(IgA), Immunoglobulin G(IgG). The Serum inflammatory factors were interleukin-1 (IL-1), interleukin 10 (IL-10), and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α).
After first completing the genomic DNA extraction, the extracted genomic DNA was detected using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. For formal experiments, three replicates of each sample were mixed with the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products from the same sample and detected using 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. The PCR products were recovered by cutting glue using an E.Z.N.A. ® Gel Extraction Kit (Omega Bio-Tek, Guangzhou Feiyang Biological Engineering Co., LTD) and eluted with Tris HCl and 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. The abovementioned PCR sequencing region was 338F_806R, 338F(5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′), and 806R (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′). According to the preliminary quantitative results of electrophoresis, the PCR products were determined using QuantiFluor™ -ST blue fluorescence quantification system (Promega). Sequencing was performed using an Illumina’s MiSeq PE300 platform. The Flash (version 1.2.11) software was used for pair-end double-ended sequence splicing, and sequence quality was controlled and filtered simultaneously. Operational taxonomic unit (OTU) cluster and taxonomic analyses of species were performed after distinguishing the samples. Based on OTU cluster analysis results, α and β diversities were calculated, and the groups were compared. Differences in species at different levels in each group were analyzed using the Kruskal–Wallis H test.
2.3 Statistical analysis
All data were preliminarily sorted using EXCEL 2010, and SPSS 26.0. was used to test the significance between different groups using one-way analysis of variance and Duncan’s multiple comparison test. The results were expressed as means ± SD. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05. The GraphPad Prism 9.5 software was used for mapping.
3 Results and discussion
3.1 Growth performance
The results of performance are shown in Table 2. The results indicated that the low-dose addition of FVR (2%) tended to increase dry matter intake compared to the control group, although this difference was not statistically significant. There was no significant difference in average daily weight gain between the control and low-dose groups. The feed conversion ratio (FCR) was higher in the low-dose group than in the control group, but not significant, indicating a potential decrease in feed conversion efficiency. Conversely, the high-dose addition of FVR (6%) significantly reduced body weight at 48 days of age (P<0.05). Additionally, dry matter intake was significantly lower in the high-dose group during both the 29 to 48 days period and the entire 1 to 48 days period (P<0.05). The high-dose group also exhibited a significantly increased FCR during both the 29 to 48 days and 1 to 48 days periods, indicating reduced feed conversion efficiency (P<0.05).
3.2 Blood serum antioxidant capacity
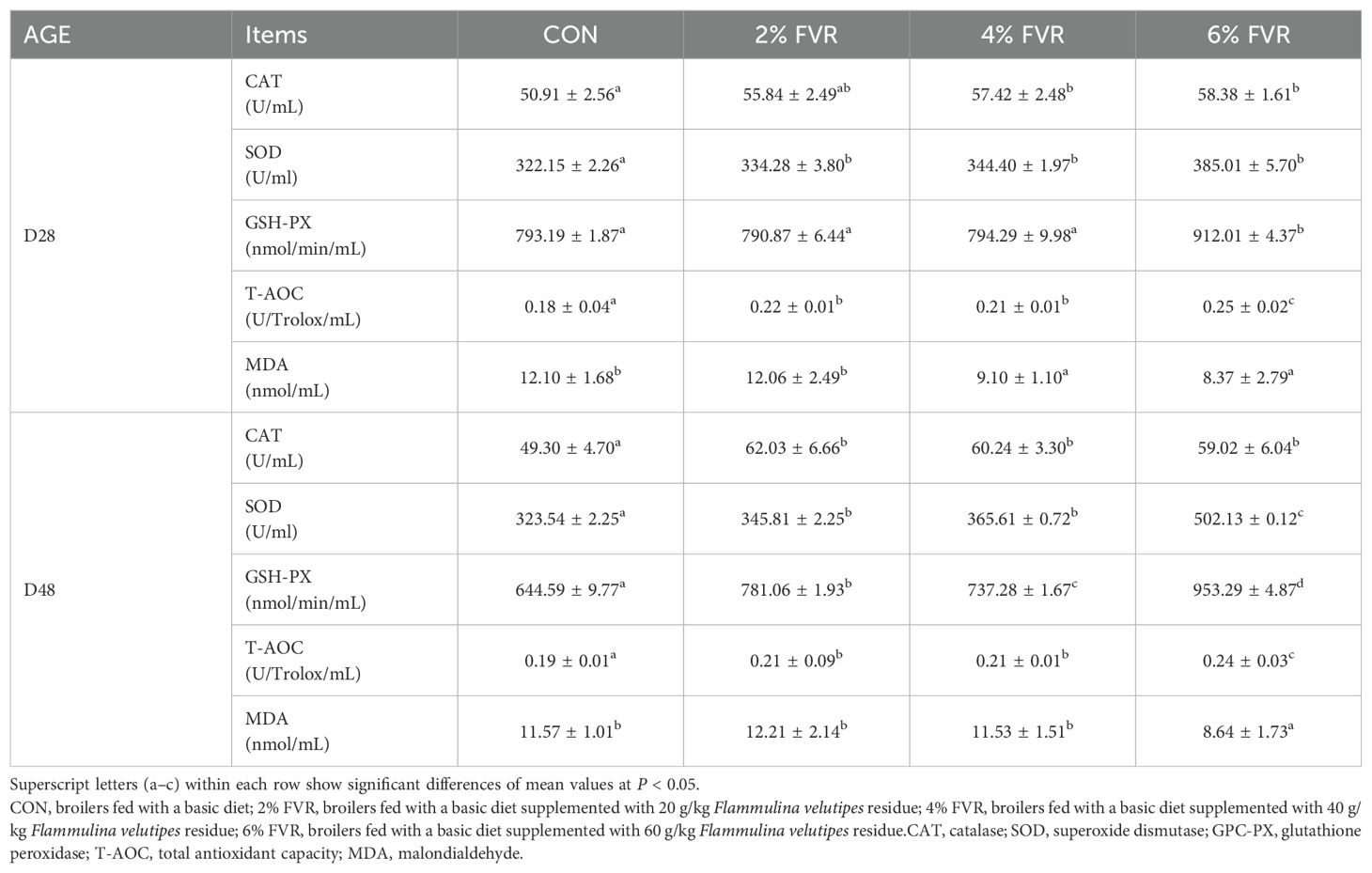
As shown in Table 3, the serum antioxidant content of broilers added with FVR was significantly changed compared with that in the CON group. On D28, serum CAT levels in the 4% and 6% FVR groups were significantly higher than those in the control group (P<0.05), whereas the 2% FVR group showed no significant difference. By D48, all experimental groups demonstrated significantly elevated serum CAT levels compared to the control group (P<0.05). Throughout the experimental period, SOD levels in the experimental groups consistently remained significantly higher than those in the control group (P<0.05). On D28, serum GSH-PX levels in the 6% FVR group were significantly higher than those in the control group (P<0.05). By D48, GSH-PX levels in all experimental groups exceeded those in the control group (P<0.05). During the trial period, T-AOC in the 2% and 4% FVR groups was significantly higher than that in the control group (P<0.05), while the 6% FVR group exhibited an extremely significant increase (P<0.01). On D28, serum MDA levels in the 4% and 6% FVR groups were significantly lower than those in the control group (P<0.05). By D48, MDA levels in the 2% and 4% FVR groups showed a significant reduction (P<0.05), while the 6% FVR group exhibited an extremely significant decrease compared to the control group (P<0.01).
3.3 Blood serum immunoglobulin and inflammatory factors
As illustrated in Figures 1A–D, serum immunoglobulin levels indicated no significant change in IgA in the FVR groups compared with that in the CON group at 28 days, and IgA levels in the 6% FVR groups were significantly higher than those in the CON group at 48 days and increased in the 2% and 4% FVR groups (P<0.05). At 28 d and 48 d, the IgG levels in the 6% FVR groups were significantly higher than those in the CON group (P<0.05). As presented in Figures 1E–J, the levels of inflammatory factors changed. The FVR groups demonstrated lower serum IL-1 contents than the CON group at 48 days. The content of IL-10 in the 4% FVR and 6% FVR groups significantly increased compared to that in the CON group (P<0.05). For TNF-α activity, no significant change was observed between groups.
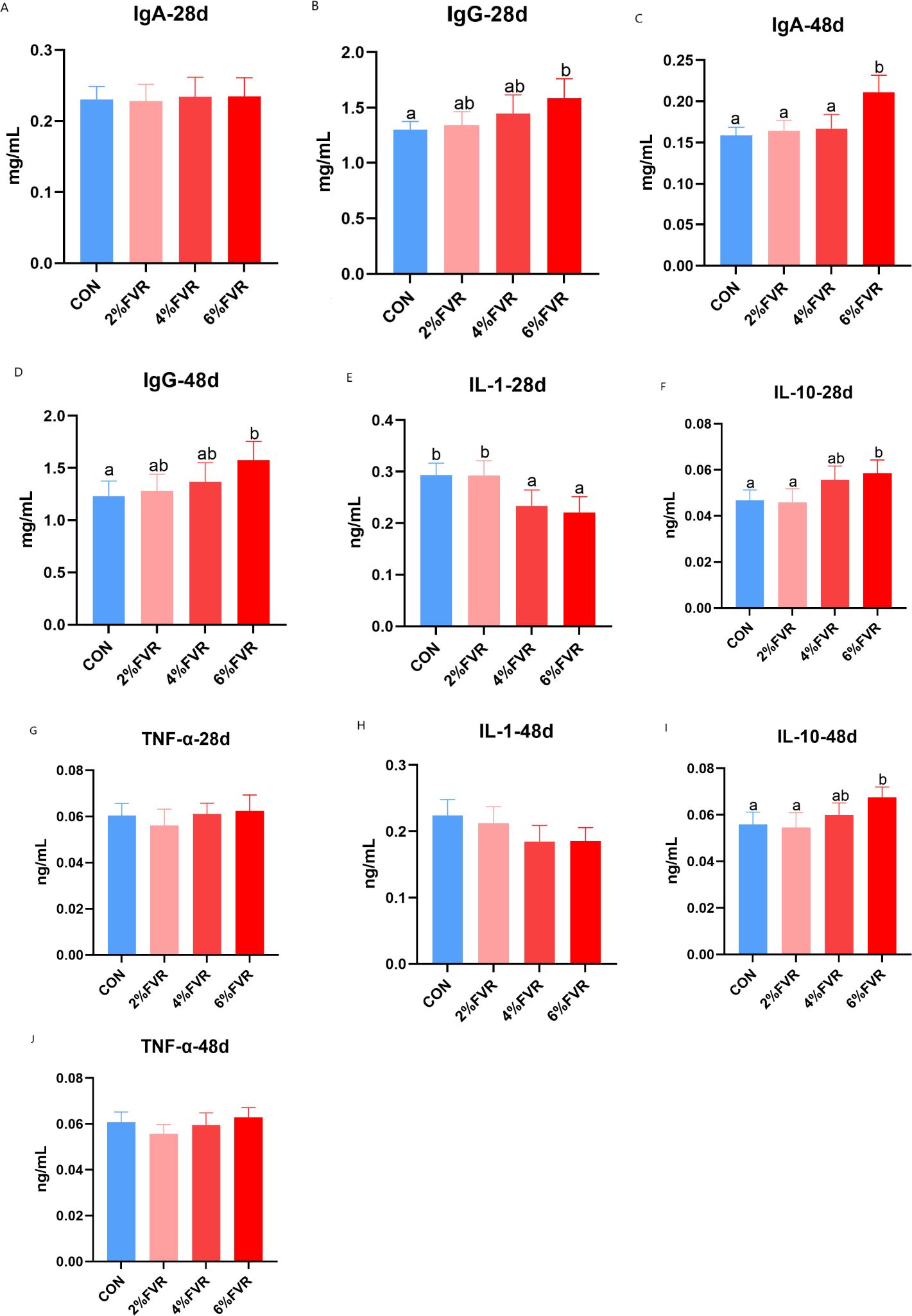
Figure 1. Effects of Flammulla velutipes residue on serum immunoglobulin and inflammatory factors of broilers. (A, B) IgA and IgG content in d28; (C, D) IgA and IgG content in d48; (E–G) IL-1, IL-10 and INF-α content in d28; (H–J) IL-1, IL-10 and INF-α content in d48. Lower-case letters show significant differences of mean values at P < 0.05.
3.4 Cecal microbiota of broilers
As presented in Figure 2A, the Venn plot demonstrates 1249 OTUs in the four groups, with 84, 49, 110 and 66 OTUs unique to the CON, 2% FVR and 4% FVR, and 6% FVR, respectively. Based on α diversity, Ace, Chao, Shannon, and Simson indices changed in Figures 2B–E, although the difference was not significant (P>0.05). Assessing β-diversity as in Figures 2F, G, the microbial composition was slightly altered at the genus and phylum level (P>0.05). The dominant flora of each group was further analyzed at the phylum and genus level. At the phylum level, Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes were the dominant bacteria. As in Figures 2H, I, Firmicutes were upregulated in 2% and 4% FVR groups, and the proportion of Bacteroidetes was significantly upregulated in 6% FVR groups (P<0.05). At the genus level, Bacteroides and Lactobacillus accounted for a high proportion (Figures 2H, I). The total proportion of Bacteroides and Lactobacillus in the FVR groups decreased, whereas those of other bacteria were upregulated, including Ruminococcus and Faecalibacterium, which were slightly upregulated. However, Bacteroides was significantly upregulated in the 6% FVR groups (P<0.05).
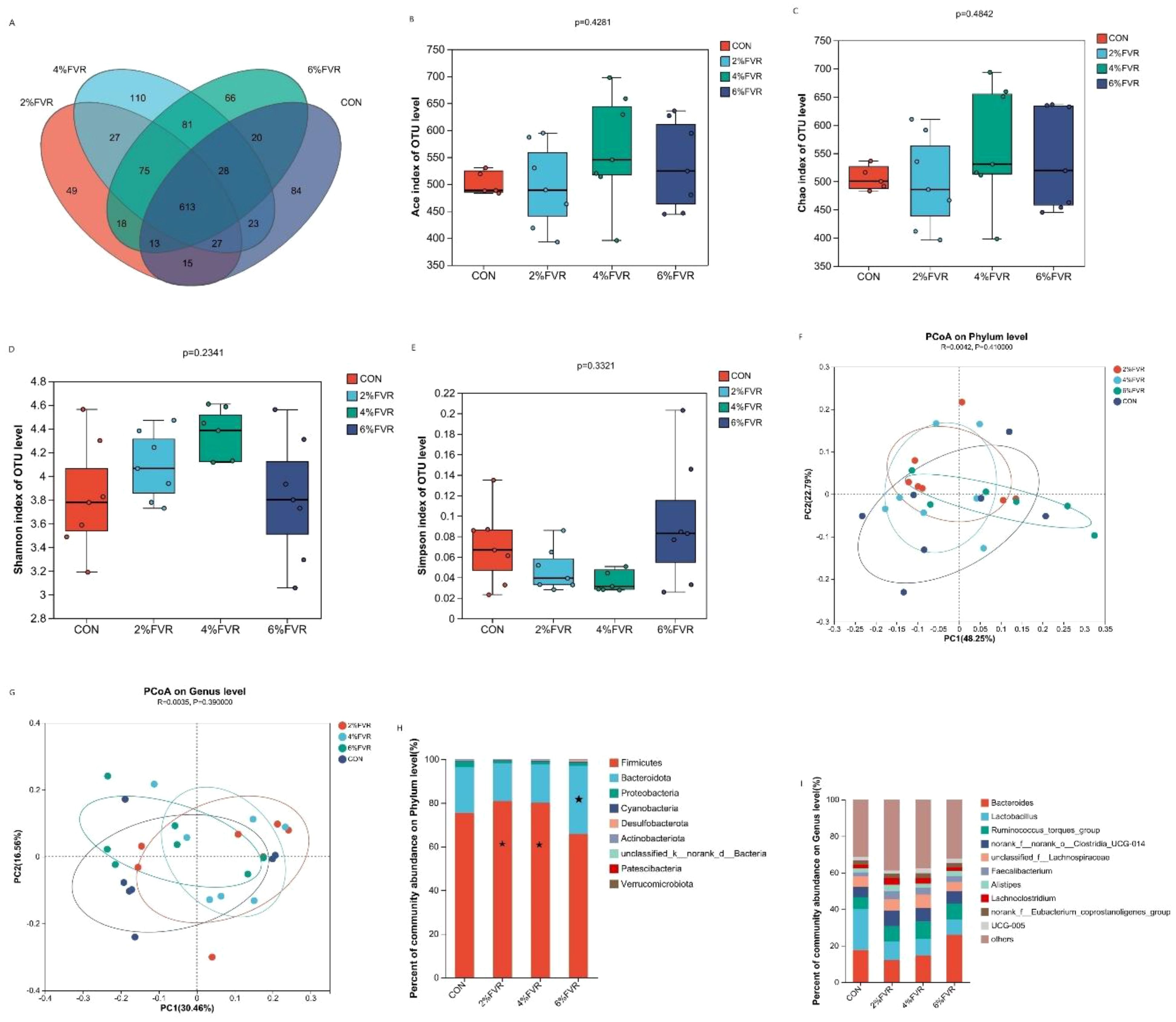
Figure 2. Effect of Flammulla velutipes residue on cecal microbiota of broilers. (A) Venn diagram of broilers cecal microbiota in different treatments: (B) Ace index; (C) Chao index; (D) Shannon index; (E) Simpson index of OUT level of broilers cecal microbiota. (F, G) β-diversity (PCoA) on Phylum level and Genus level. (H, I) relative abundance of bacteria at the phylum and genus levels. * indicates significant differences (P<0.05).
4 Discussion
In animal production, growth performance is a critical determinant of economic benefits. Key indicators such as ADG and FCR are often researched to optimize feeding strategies. Studies have shown that dietary supplementation with certain mushrooms can improve these performance metrics. For instance, higher body weight gain and lower FCR were observed in broilers fed a 2% level of Agaricus bisporus mushroom (Giannenas et al., 2010). In our research, the addition of FVR at low doses (2%, 4%) did not significantly affect the growth performance of broiler. These findings align with previous research by Hassan et al. (2020) and Mahfuz et al. (2020), who observed similar results. The limited impact of FVR at low doses could be attributed to the nutrient composition and bioactive substances in the residue. Flammulina velutipes mycelium produces cellulolytic enzymes during growth, which break down fibrous structures, releasing nutrients that aid in digestion and absorption. The presence of phenolic compounds and glucans in mushrooms enhances antioxidant capacity in animals. However, the active substances in fungal residue are limited, which might explain the negligible effect on broiler chickens’ production performance when FVR is used in small quantities. The experiment revealed that a high dose of FVR (6%) significantly reduced body weight, dry matter intake, and feed conversion efficiency. These adverse effects are likely due to the lower protein content and higher levels of indigestible fiber and crude ash in the fungal residue compared to the basal diet. The direct addition of high doses of FVR diluted the overall nutrient content, inhibiting dry matter intake and thus negatively impacting growth performance. These findings suggest that while FVR has potential as a feed ingredient, careful consideration of its dosage and nutrient content is essential to avoid negative impacts on broiler performance.
Edible fungi contain numerous active substances (Meng et al., 2018) with antioxidative properties and tumor-inhibiting abilities (Muszyń et al., 2018). Polysaccharides, the most abundant macromolecules present in edible fungi, significantly scavenge hydroxyl and superoxide anion free radicals (Lin et al., 2014). By influencing the Keap1-Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway, these polysaccharides regulate antioxidant enzyme expression and enhance the body antioxidant capacity (Lin et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2020). Li et al. (2018) reported that polysaccharides can increase the expression of Nrf2 and ARE in cyclophosphamide-treated mouse testicular tissue, reduce Keap1 expression, and promote antioxidant enzyme production. These polysaccharides also regulate apoptosis pathway genes expression and promote antioxidant production, thereby mitigating oxidative damage. Additionally, polysaccharides from sea buckthorn increase SOD activity in mice by inhibiting BAX expression (Chen et al., 2020). Polyphenols in edible fungi act as natural antioxidants, clearing free radicals and quenching reactive oxygen species. Wang et al. (2012) found that sesquiterpenoids from Flammulinella magnolia prevent lipid peroxidation by chelating OH− with Fe2+ or Cu2+ in the polyphenol ring, thus reducing oxidative stress. Feeding FVR to broilers significantly increased antioxidant enzyme activity in the serum and decreased harmful products, highlighting the role of bioactive substances in FVR. However, the specific antioxidant effects of edible mushroom residues require further elucidation.
Additionally, the immune capacities of livestock and poultry should not be ignored, and the concentration of immune factors is an important index for measuring poultry immunity (Criste et al., 2020). FVR supplementation significantly increased IgG and IgA contents in serum of 48-day-old broilers, decreased IL-1 levels, and increased IL-10 levels, which had positive effects on the immunity of broilers. Active substances of edible fungi are known to enhance macrophage phagocytosis and stimulate the release of cytokines such as NO, TNF-α, and IL-6 (Guo et al., 2023). Among them, edible polysaccharide regulates the secretion and expression of cytokines and other factors through nuclear factor-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinases signaling pathways, thereby exerting its immunomodulatory activity (Wu et al., 2019). In addition, edible fungi contain various active proteins, the most common of which are lectins (12–190 kDa) and FIP (12.7 kDa), which are involved in various physiological functions such as anticancer, antiviral, antibacterial, and immune regulation (Ng and Wang, 2004). Polypeptides from mycelium of Pleurotus eryngii have been demonstrated to inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells (cervical, breast, and stomach cancer cells) while promoting the proliferation of macrophages (Ana-1 cells), TNF-α, and IL-6 and expression of TLR2 and TLR4 (Sun et al., 2017).
The gut microbiota plays an important role in nutrient digestion, metabolism, maintenance of intestinal barrier function, and immune development (Fu et al., 2021). Active substances of edible fungi, which can regulate the structure and diversity of the intestinal microbial community and affect the production of short-chain fatty acids in the intestine and intestinal barrier to exert benefits (Zhao et al., 2018). According to the results of the fecal microflora diversity analysis, FVR affected the regulation of intestinal microflora and its number. Firmicutes and Bacteroides constitute was the main of microbial communities at the phylum level (Ahir et al., 2010), and Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes were the dominant bacteria in this study, consistent with the results of previous studies (Choi et al., 2014). However, in contrast to that in the CON group, the abundance of Bacteroidetes significantly increased at the phylum and genus levels in the 6% FVR groups. However, Bacteroidetes promote the production of short-chain fatty acids during biological metabolism, maintain intestinal environmental stability, and effectively prevent inflammation (Zhang et al., 2019). Bacteroidetes also respond significantly to changes in the intestinal environment (Flint and Duncan, 2014). This indicates that the intestinal environment is changed by the addition of FVR, which makes the above-mentioned immunity improvement in broilers feasible. Other studies have demonstrated that Bacteroides can increase the relative abundance of plant polysaccharides through degradation them (Tamura et al., 2017). In addition, at the genus level, while the total proportion of Bacteroides and Lactobacillus decreased in the FVR groups, the proportion of other beneficial bacterial genera, such as Ruminococcus and Faecalibacterium, increased. Ruminococcus is known to be one of the most efficient bacterial genera for decomposing carbohydrates, and can degrade and ferment cellulose and hemicellulose. Fibers can further increase the viscosity of the digestive fluid and thickness of the mucous layer, reduce the number of mucus-degrading bacteria, and increase the number of cellulose-degrading bacteria, which are considered a line of defense against pathogens in the intestinal tract (La Reau and Suen, 2018). Ruminococcus is a probiotic that can enhance the overall immunity and growth indices of cultured fish (Gayed et al., 2021). As a member of Firmicutes, Faecalibacterium plays an important role in promoting the production of butyrate in the intestine, anti-inflammation, maintenance of bacterial enzyme activity, and protection of the digestive system from intestinal pathogens. Farhadfar et al. (2021) have reported that Faecalibacterium is actively involved in the metabolism of the host and regulates the intestinal immune system, oxidative stress, and colon cell metabolism through butyrate production. The addition of FVR has been demonstrated to increase the diversity of cecal flora and increase the number of beneficial bacteria.
5 Conclusion
Our results demonstrate that supplement 2% or 4% FVR to three-yellow chickens has no significant effect on performance, but supplement 6% FVR can reduce performance of broiler. But supplement FVR can improve antioxidant capacity and immunity, change intestinal probiotic flora to a certain extent, and enrich the diversity of intestinal flora.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.
Ethics statement
The animal study was approved by Review of Experimental Animal Welfare and Ethics of the Shanghai Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (SV-20230526- Y01). The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
YL: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DL: Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Resources, Writing – review & editing. PC: Data curation, Resources, Software, Writing – review & editing. YM: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. KD: Resources, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing. NL: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported the Program for International S&T Cooperation Projects of Henan (232102521012), the Science Foundation for Expat Scientist Studio for Animal Stress and Health Breeding of Henan Province (GZS2021006), and the Key Scientific Research Foundation of the Higher Education Institutions of Henan Province (22A230001).
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the help from The Shanghai Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, offers laboratory animal sites and services.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Ahir V. B., Koringa P. G., Bhatt V. D., Ramani U. V., Tripathi A. K., Singh K. M., et al. (2010). Metagenomic analysis of poultry gut microbes. Indian J. Poult. Sci. 45, 111–114.
Aida F., Shuhaimi M., Yazid M., Maaruf A. G. (2009). Mushroom as a potential source of prebiotics: a review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 20, 567–575. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2009.07.007
Amin M. Z., Harun A., Wahab M. A. (2014). Status and potential of mushroom industry in Malaysia. Econ Technol. Manag. Rev. 9b, 103–111. Available at: http://etmr.mardi.gov.my/Content/ETMR%20Vol.9b%20(2014)/Vol9b_2_.pdf.
Bruinsma J. (2003). World agriculture: towards 2015/2030-An FAO perspective (London: FAO/Earthscan), 432.
Cao Y., Li D. (2013). Impact of increased demand for animal protein products in Asian countries: Implications on global food security. Anim. Front. 3, 48–55. doi: 10.2527/af.2013-0024
Chen T., Song T., Sun X. (2020). Regulatory effect of angelica sinensis polysaccharide on bcl-2/bax/caspase-3 signal pathway in spleen of rats with radiation injury. J. Biobased Mater Bioenergy 14, 579–583. doi: 10.1166/jbmb.2020.1994
Chen Y., Nie F. (2016). “Analysis of China’s Food Supply and Demand Balance and Food Security,” in Food Security and Industrial Clustering in Northeast Asia. New Frontiers in Regional Science: Asian Perspectives. Eds. Kiminami L., Nakamura T. (Springer, Tokyo), 47–59. doi: 10.1007/978-4-431-55282-6_4
Chiu S. W., Ching M. L., Fong K. L., Moore D. (1998). Spent oyster mushroom substrate performs better than many mushroom mycelia in removing the biocide pentachlorophenol. Mycol. Res. 102, 1553–1562. doi: 10.1017/S0953756298007588
Choi J. H., Kim G. B., Cha C. J. (2014). Spatial heterogeneity and stability of bacterial community in the gastrointestinal tracts of broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 93, 1942–1950. doi: 10.3382/ps.2014-03974
Criste A., Urcan A. C., Corcionivoschi N. (2020). Avian IgY antibodies, ancestors of mammalian antibodies–production and application. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 25, 1311–1319. doi: 10.25083/rbl/25.2/1311.1319
Falandysz J. (2013). On published data and methods for selenium in mushrooms. Food Chem. 138, 242–250. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.10.046
Farhadfar N., Gharaibeh R. Z., Lyon D., Whitlock J. A., Murthy H. S., Weaver M. T., et al. (2021). Microbiota phylogenic analysis revealed decreased abundance of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium, in patients with chronic graft-versus-host disease. Hematology/oncol. Stem Cell Ther. 14, 263–265. doi: 10.1016/j.hemonc.2021.03.004
Fazaeli H., Shafyee-Varzeneh H., Farahpoor A., Moayyer A. (2014). Recycling of mushroom compost wheat straw in the diet of feedlot calves with two physical forms. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 3, 65. doi: 10.1007/s40093-014-0065-z
Flint H. J., Duncan S. H. (2014). “Bacteroides, Prevotella,” in Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed. Eds. Batt C. A., Tortorello M. L. (Academic Press, Elsevier).
Fu J., Wang T., Cheng Y., Cheng Y., Wang F., Jin M., et al. (2021). Clostridium butyricum ZJU-F1 benefits the intestinal barrier function and immune response associated with its modulation of gut microbiota in weaned piglets. Cells 10, 527. doi: 10.3390/cells10030527
Gayed M. A., Elabd H., Tageldin M., Abbass A. (2021). Probiotic Zado®(Ruminococcus Flavefaciens) boosts hematology, immune, serum proteins, and growth profiles in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. Rep. 2, 100021. doi: 10.1016/j.fsirep.2021.100021
Giannenas I., Pappas I. S., Mavridis S., Kontopidis G., Skoufos J., Kyriazakis I., et al. (2010). Performance and antioxidant status of broiler chickens supplemented with dried mushrooms (Agaricus bisporus) in their diet. Poult. Sci. 89, 303–311. doi: 10.3382/ps.2009-00207
Guo Q., Liang S. G., Xiao Z. C., Ge C. R. (2023). Research progress on extraction technology and biological activity of polysaccharides from edible fungi: A review. Food Rev. Int. 39, 4909–4940. doi: 10.1080/87559129.2022.2039182
Hassan R. A., Shafi M. E., Attia K. M., Assar M. H.. (2020). Influence of oyster mushroom waste on growth performance, immunity and intestinal morphology compared with antibiotics in broiler chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 7. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00333
Jing P., Zhao S. J., Lu M. M., Cai Z., Pang J., Song L. H. (2014). Multiple-fingerprint analysis for investigating quality control of Flammulina velutipes fruiting body polysaccharides. J. Agric. Food Chem. 62, 12128–12133. doi: 10.1021/jf504349r
Ko W. C., Liu W. C., Tsang Y. T., Hsieh C. W.. (2007). Kinetics of winter mushrooms (Flammulina velutipes) microstructure and quality changes during thermal processing. J. Food Eng. 81, 587–598. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2006.12.009
La Reau A. J., Suen G. (2018). The Ruminococci: key symbionts of the gut ecosystem. J. Microbiol. 56, 199–208. doi: 10.1007/s12275-018-8024-4
Leifa F., Pandey A., Soccol C. R. (2001). Production of Flammulina velutipes on coffee husk and coffee spent-ground. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 44, 205–212. doi: 10.1590/S1516-89132001000200015
Li S., Song Z., Liu T. (2018). Polysaccharide from Ostrea rivularis attenuates reproductive oxidative stress damage via activating Keap1-Nrf2/ARE pathway. Carbohydr. Polym. 186, 321–331. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.01.075
Lin L., Cui F. Y., Zhang J. J., Gao X. (2016). Antioxidative and renoprotective effects of residue polysaccharides from Flammulina velutipes. Carbohydr. Polym. 146, 388–395. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.03.071
Lin Y., Ge X., Li Y. (2014). Solid-state anaerobic co-digestion of spent mushroom substrate with yard trimmings and wheat straw for biogas production. Biores. Technol. 169, 468–474. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.07.020
Mahfuz S., He T., Ma J., Liu H., Long Q., Shang Q., et al (2020). Mushroom (Flammulina velutipes) stem residue on growth performance, meat quality, antioxidant status and lipid metabolism of broilers. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 19, 803–812. doi: 10.1080/1828051X.2020.1797545
Manila P., Suonpaa K., Piironen V. (2000). Functional properties of edible mushrooms. Nutrition 16, 694–696. doi: 10.1016/S0899-9007(00)00341-5
McIntyre B. D., Herren H. R., Wakhungu J., Watson R. (2009). IAASTD-International Assessment of Agricultural Knowledge, Science and Technology for Development. Global Report (Washington, DC: Island Press).
Medina E., Paredes C., Pérez-Murcia M. D., Bustamante M. A., Moral R. (2009). Spent mushroom substrates as component of growing media for germination and growth of horticultural plants. Biores. Technol. 100, 4227–4232. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.03.055
Meng Y., Yan J. M., Yang G., Han Z., Tai G. H., Cheng H. R., et al. (2018). Structural characterization and macrophage activation of a hetero-galactan isolated from Flammulina velutipes. Carbohydr. Polym. 183, 207–218. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.12.017
Michiel D., Morley T., Rau M. L., Saghai Y. (2021). A meta-analysis of projected global food demand and population at risk of hunger for the period 2010–2050. Nat. Food 2, 494–501. doi: 10.1038/s43016-021-00322-9
Mottet A., Tempio G. (2017). Global poultry production: current state and future outlook and challenges. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 73, 245–256. doi: 10.1017/S0043933917000071
Muszyń B., Agata G. K., Katarzyna K., Gdula-qrgasinska J. (2018). Anti-inflammatory properties of edible mushrooms: A review. Food Chem. 243, 373–381. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.09.149
Ng T. B. (2006). “Fungal Ribosome Inactivating Proteins,” in Handbook of Biologically Active Peptides. Ed. Kastin A. J. (Academic Press), 145–149. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-369442-3.X5001-6
Ng T. B., Wang H. X. (2004). Flammin and velin: new ribosome inactivating polypeptides from the mushroom Flammulina velutipes. Peptides 25, 929–933. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2004.03.007
Rosegrant M. W., Paisner M. S., Meijer S., Witcover J. (2001). Global Food Projections to 2020: Emerging Trends and Alternative Futures (Washington, DC: International Food Policy Research Institute).
Silver W. L., Perez T., Mayer A., Jones A. R. (2021). The role of soil in the contribution of food and feed. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 376, 20200181. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2020.0181
Staniškis J. K. (2012). Sustainable consumption and production: how to make it possible. Clean Techn Environ. Policy 14, 1015–1022. doi: 10.1007/s10098-012-0535-9
Sun Y. N., Hu X. L., Li W. X. (2017). Antioxidant, antitumor and immunostimulatory activities of the polypeptide from Pleurotus eryngii mycelium. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 97, 323–330. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.043
Tamura K., Hemsworth G. R., Déjean G. (2017). Molecular mechanism by which prominent human gut Bacteroidetes utilize mixed-linkage beta-glucans, major health-promoting cereal polysaccharides. Cell Rep. 21, 417–430. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.09.049
Trostle R. (2008). Global Agricultural Supply and Demand: Factors Contributing to the Recent Increase in Food Commodity Prices (United States Department of Agriculture), 30. International Agriculture and Trade Outlook. https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/GOVPUB-A93-PURL-gpo10109/pdf/GOVPUB-A93-PURL-gpo10109.pdf.
Wang S. J., Li Y. X., Bao L., Han J. J., Yang X. L., Li H. R., et al. (2012). Eryngiolide A, a cytotoxic macrocyclic diterpenoid with an unusual cyclododecane core skeleton produced by the edible mushroom Pleurotus eryngii. Org. Lett. 14, 3672–3675. doi: 10.1021/ol301519m
Wang W. H., Zhang J. S., Feng T. (2018). Structural elucidation of a polysaccharide from Flammulina velutipes and its immunomodulation activities on mouse B lymphocytes. Sci. Rep. 8, 3120. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21375-0
Williams B. C., McMullan J. T., McCahey S. (2001). An initial assessment of spent mushroom compost as a potential energy feedstock. Biores. Technol. 79, 227–230. doi: 10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00073-6
Wu Q., Liu L. T., Wang X. Y. (2020). Lycium barbarum polysaccharides attenuate kidney injury in septic rats by regulating Keap1-Nrf2/ARE pathway. Life Sci. 242, 117240. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117240
Wu Y. J., Wei Z. X., Zhang F. M., Linhardt R. J., Sun P. L., Zhang A. Q. (2019). Structure, bioactivities and applications of the polysaccharides from Tremella fuciformis mushroom: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 121, 1005–1010. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.117
Yadav P., Samadder S. R. (2018). A critical review of the life cycle assessment studies on solid waste management in Asian countries. J. Clean Prod. 185, 492–515. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.298
Zhang J. H. (2011). China’s success in increasing per capita food production. J. Exp. Bot. 62, 3707–3711. doi: 10.1093/jxb/err132
Zhang H., Wang Q., Liu S., Huo D., Zhao J., Zhang L., et al. (2019). Genomic and metagenomic insights into the microbial community in the regenerating intestine of the sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Front. Microbiol. 10. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.01165
Zhao R. Q., Yang W. J., Pei F., Zhao L., Hu Q. (2018). In vitro fermentation of six kinds of edible mushrooms and its effects on fecal microbiota composition. LWT 96, 627–635. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.06.012
Zhu H., Sheng K., Yan E., Qiao J., Lv F. (2012). Extraction, purification and antibacterial activities of a polysaccharide from spent mushroom substrate. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 50, 840–843. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2011.11.016
Ziegler E. H. (2006). China’s cities, globalization, and sustainable development: comparative thoughts on urban planning, energy, and environmental policy. Wash U Glob Stud. Law Rev. 5, 295–322.
Keywords: Flammulina velutipes residue, performance, antioxidant, immunity, cecal flora
Citation: Li Y, Liu D, Li W, Zhao L, Cao P, Ma Y, Ding K, Zhang C and Liu N (2025) Optimizing Flammulina velutipes residue use: impact on health metrics and performance in three-yellow chickens. Front. Anim. Sci. 5:1458762. doi: 10.3389/fanim.2024.1458762
Received: 03 July 2024; Accepted: 26 December 2024;
Published: 06 February 2025.
Edited by:
Anusorn Cherdthong, Khon Kaen University, ThailandReviewed by:
Chompunut Lumsangkul, National Chung Hsing University, TaiwanJessada Rattanawut, Prince of Songkla University, Thailand
Copyright © 2025 Li, Liu, Li, Zhao, Cao, Ma, Ding, Zhang and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ning Liu, bmluZ2xpdTY4QDE2My5jb20=
 Yuanxiao Li
Yuanxiao Li Dan Liu1
Dan Liu1 Yanbo Ma
Yanbo Ma Ke Ding
Ke Ding Cai Zhang
Cai Zhang