
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Anal. Sci., 05 March 2025
Sec. Biomedical Analysis and Diagnostics
Volume 5 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/frans.2025.1514381
A crucial step in drug discovery involves identifying active molecules, which depends on fast and efficient screening assay methods. Kallikreins a family of serine protease enzymes, play a pivotal role in biological fluids and tissues. Deregulated activity and expression of human KLKs have been implicated in various pathologies, so these enzymes constitute attractive biological targets for discovering molecules that can modulate their activity. The novelty of the present study is the IMER-pKLK-MB bioreactor resulting from immobilization of porcine pancreas kallikrein (pKLK) on magnetic beads which proved highly active and stable. For example, over 60% of IMER-pKLK-MB activity was maintained after it was incubated in 70% methanol. In addition, even after being stored for 11 months, IMER-pKLK-MB allowed for at least 10 consecutive cycles of activity, which attested to its excellent stability. Parameters such as KMapp and IC50 for leupeptin confirmed that the immobilized pKLK retained its ability to recognize both the substrate and reference inhibitor. We optimized an off-flow assay based on high-performance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS) and IMER-pKLK-MB to evaluate the inhibitory activity of some molecules toward pKLK. We also evaluated the kinetic parameter (KMapp = 81.2 ± 18 μmol.L−1) and qualified the method by using leupeptin as standard inhibitor (IC50 = 2.15 ± 0.4 μmol.L−1). The developed and qualified method proved an important and reliable approach for screening ligands and can be used to screen KLK inhibitors.
Identifying potentially active compounds is a critical step in drug discovery research and demands efficient screening assays. In this sense, an interesting approach is to develop analytical tools and assay strategies that allow enzyme inhibitors to be identified. Immobilized enzyme assays as an alternative to classic free enzyme assays offer advantages such as enhanced activity and stability in the assay conditions, allowing enzymes to be better handled and even reused in many screening cycles (de Moraes et al., 2019). Chromatographic supports such as magnetic particles (Trindade Ximenes et al., 2021; Vanzolini et al., 2015), Sepharose (de Carvalho et al., 2021), and silica gel microspheres (Li et al., 2019; Shi et al., 2015), have been used to prepare bioreactors for ligand screening assays. Such bioreactors can be employed to immobilize biomolecules by means of off-line or on-line approaches, resulting in different formats and applications (De Simone et al., 2019; Moraes et al., 2016; Girelli and Mattei, 2005; de Moraes et al., 2014). In general, the support must be inert and not retain biomolecules by adsorption (Hanefeld et al., 2013). Several enzyme immobilization methods have been described in the literature, and covalent reactions involving amino, carboxyl, or epoxide functional groups have been the most widely reported (Cao, 2006). Bioaffinity chromatography, employed at various stages of drug development, is based on an enzyme immobilized on a solid support. The support stabilizes the enzyme in the presence of organic solvents and temperature variations, allowing small amounts of the enzyme to be used and reused. In addition, immobilized enzymes can be applied in numerous assay formats, including continuous process reactors on-flow assays (de Moraes et al., 2019; De Simone et al., 2019; Girelli and Mattei, 2005; De Oliveira et al., 2022; Guo et al., 2019; Hou et al., 2020) or off-flow systems (Liu et al., 2024; Carvalho et al., 2022; Miranda de Souza Duarte-Filho et al., 2023; Wubshet et al., 2019) to screen new ligands fast. Moreover, bioaffinity chromatography allows the kinetics, thermodynamics, and affinity of a ligand to be rapidly characterized and is considered a high-throughput screening (HTS) technique.
Kallikreins (KLKs), a family of serine proteases involved in many crucial biological functions (Yousef and Diamandis, 2003; Prassas et al., 2015) comprise 15 types and are found in human tissues and organs (KLK-1 to KLK-15), human plasma (KLK1B), and venom of certain snakes (Prassas et al., 2015; Felicori et al., 2003). The KLK family is known for the role played by KLK1 in the kallikrein-kinin system and the use of KLK3 as a biomarker of prostate cancer (Prassas et al., 2015; Tan et al., 2015). However, over the past decade, great advances have been made toward understanding the localization, regulation, and physiological functions of most tissue KLKs (Prassas et al., 2015; Tan et al., 2015; Kryza et al., 2016; Stefanini et al., 2015). Among other functions, KLKs are directly involved in the inflammatory process cascade. Patients with COVID-19 may present pulmonary edema early in the disease. In recent studies, this has been suggested to occur due to a local vascular problem associated with activation of the bradykinin 1 (B1R) and 2 (B2R) receptors in endothelial cells in the lungs. SARS-C oV-2 enters the cell via angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) which, among other functions, is necessary to inactivate des-Arg9 bradykinin, a potent B1R ligand. Without ACE2 acting as gatekeeper to inactivate B1R ligands, the pulmonary environment is subject to local vascular leak, which culminates in angioedema. Therefore, it has been proposed that blocking B2R and inhibiting KLK activity may have an ameliorative effect on early COVID-19 and may even prevent acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) (van de Veerdonk et al., 2020). These associations have prompted research efforts to develop specific KLK inhibitors as therapeutic agents (Sotiropoulou and Pampalakis, 2012; Swedberg et al., 2010; Teixeira et al., 2011; de Souza et al., 2019). Researchers have been actively studying KLKs given that alterations in this enzyme family may lead to medical conditions such as cancer over time (Prassas et al., 2015). Due to structural similarities within the KLK family, in this study we have employed porcine pancreas KLK (pKLK) as a model enzyme to develop an active, stable, and applicable tool to screen KLK ligands. Studies have indicated that both human and porcine KLK can cleave peptides derived from human and bovine kininogen (Del Nery et al., 1999). Bearing in mind the advantages of enzyme immobilization and the growing search for KLK inhibitors, here we present an off-line assay based on pKLK immobilized on magnetic beads (MB) and MS detection to screen inhibitors of this enzyme. We will demonstrate that the IMER-pKLK-MB bioreactor is a valuable, stable, and reusable tool for off-line ligand screening, and that it can be integrated with an HPLC-MS method.
Porcine pancreas kallikrein (pKLK, 250 units) and amine-terminated magnetic particles (50 mg mL−1) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, United States). Buffer components and other chemicals were acquired from Sigma-Aldrich, Merck (Darmstadt, Germany), Synth (São Paulo, Brazil), or Acros (Geel, Belgium). The water used in all the preparations was obtained from a MILLI-Q® system (Millipore®, São Paulo, Brazil). All the chemicals and solvents used here were analytical or HPLC grade and were employed without any further purification.
The magnetic separator (model DynaMagTM-Spin Magnet) was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (São Paulo, SP, Brazil). Orbital Microplate shaker (IKA, model MS3 D, Staufen, Germany). HPLC-MS analyses were carried out on a high-performance liquid chromatography system (model NexeraXR) purchased from Shimadzu (Kyoto, Japan) and equipped with three LC 20ADXR pumps, an SIL-20A automatic injector, a DGU-20A degasser, a 10-port two-position high-pressure switching valve (Valco Instruments Co. Inc. Houston, United States), and a CBM-20A system controller. The HPLC system was coupled to an ion trap mass spectrometer (model AmaZon speed) acquired from Bruker Daltonics (Bremen) and equipped with an electrospray ionization source (ESI) interface. The system was controlled with the Bruker Compass Hystar software (version 4.5), and data were acquired and analyzed by using the Compass DataAnalysis software (version 4.3).
Porcine pancreas kallikrein (pKLK) was immobilized on the surface of amine-terminated magnetic beads (MBs). Briefly, 20 mg of MBs was washed three times with 1 mL of 100 mM KH2PO4 buffer, pH 7.0. After each wash, the MBs were magnetically separated by using a magnetic separator, and the supernatant was removed. Then, 1 mL of glutaraldehyde (5% in 100 mM KH2PO4 buffer, pH 7.0) was added to the MBs and incubated under smooth rotation at room temperature for 3 h. After that, the supernatant was removed, and the MBs were washed again three times with 1 mL of 25 mM KH2PO4 buffer, pH 8.0. Next, 400 μL of pKLK solution was added to the MBs and incubated under smooth rotation at 4°C for 16 h. After immobilization, the supernatant was removed, and IMER-pKLK-MB was washed three times with 100 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.0, and stored in the same buffer (20 mg mL−1) at 4°C until it was used.
After enzyme immobilization as described above, 100 μL of the supernatant was added to 100 μL of substrate Z-Phe-Arg-AMC (200 μM) and incubated for 15 min under agitation (800 rpm) at room temperature. Afterward, 5 μL of this solution was directly injected into the MS. Additionally, 100 μL of enzyme solution before the immobilization was incubated with 100 μL of substrate under the same conditions described above. Then, 5 μL of this solution was directly injected into MS. The ESI ionization parameters were as follows: positive ionization mode, SIM mode, capillary voltage = 4500 V, end plate voltage = 550 V, drying gas flow rate = 9 L·min−1, drying temperature = 275°C, and nebulizer pressure = 40 psi. The enzymatic reaction product, Z-Phe-Arg-OH, was monitored at m/z 456 [M + H]+. We evaluated the immobilization efficiency on the basis of immobilization yield (IY) by applying the following equation:
where A0 corresponds to the initial activity of the enzyme solution before immobilization, and Af corresponds to the activity of the supernatant solution after the immobilization procedure.
The LC-MS method was developed on the basis of a previous method described by Carvalho et al. (2022). LC analysis was carried out by using a Phenomenex Security Guard TM (model AJ04287) C18 micron guard cartridge (4.0 × 3.0 mm, Phenomenex, Torrance, California, EUA) connected to a 10-port/two-position valve in the LC-MS system to redirect the flow during pre-column cleaning to a waste line (Figure 1). The mobile phase consisted of water (solvent A and C) and methanol (solvent B); the injection volume was 5 µL. With the valve in position 1, the enzymatic reaction products were eluted from the trap column to the mass spectrometer with an initial mobile phase composed of 50% solvent B at a flow rate of 0.2 mL min−1. After 2.0 min, the valve was switched to position 2, and solvent B in the mobile phase was increased to 100% at a flow rate of 1.0 mL min−1, which was maintained until 5 min, to wash the column and to remove excess substrate. At 5.1 min, solvent B in the mobile phase was returned to 50% at a flow rate of 1.0 mL min−1 until 6.0 min. At 6.1 min, the valve was switched to position one again, under the initial condition. The total run time was 7 min. Pump C (solvent water) at a flow rate of 0.2 mL min−1 was used to deliver the mobile phase to the MS during the column washing step. All the analyses were performed at 21°C (controlled room temperature). The ESI ionization parameters were as follows: positive ionization mode, SIM mode, capillary voltage = 4,500 V, end plate voltage = 550 V, drying gas flow rate = 9 L min−1, drying temperature = 275°C, and nebulizer pressure = 40 psi. The enzymatic reaction product, Z-Phe-Arg-OH, was monitored at m/z 456 [M + H]+.

Figure 1. Schematic representation of the LC-MS system for monitoring the IMER-pKLK-MB activity. Source: Designed by the authors.
The mobile phase and method configuration are shown in Table 1.
The IMER-pKLK-MB off-line assay conditions were optimized. More specifically, the optimal AcNH4 concentration, pH, incubation temperature, incubation time, and IMER-pKLK-MB mass were determined.
AcNH4 was tested at 5 or 10 mmol.L−1, at pH 7.0, 8.0, 8.5, or 9.0, in triplicate. For this purpose, 0.5 mg of IMER-pKLK-MB (25 μL of the stock suspension) was added to a 0.5-mL conical microtube. IMER-pKLK-MB was washed three times with 200 μL of 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9.0, to remove the storage buffer. After each wash, IMER-pKLK-MB was separated by using a magnetic separator for 1 min, and the supernatant was removed. Following the washing procedure, 75 μL of 5 or 10 mmol.L−1 AcNH4 at pH 7.0, 8.0, 8.5, or 9.0, and 25 μL of 200 μmol.L−1 substrate solution (in AcNH4 and at the tested pH) were added to IMER-pKLK-MB. The suspension was homogenized by vortexing and incubated under agitation at room temperature for 5 min. After incubation, the supernatant of the enzymatic reaction was removed by using a magnetic separator and analyzed by the LC-MS method described above. For the LC-MS analysis, 25 μL of the enzymatic reaction supernatant and 25 μL of 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9.0, were added to a vial; the injected volume was 5 μL. To optimize the incubation temperature (10, 26, or 37°C), incubation time (5, 15, or 30 min), and IMER-pKLK-MB mass (0.1 or 0.5 mg, corresponding to 5 or 25 μL of the stock suspension, respectively), 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9.0, was used, and the procedure described above was followed.
The method was qualified on the basis of criteria outlined in the literature (Cassiano et al., 2009; Food and Drug Administration, 2001) The linearity of the method was assessed by constructing a calibration curve. For this purpose, 0.1 mg of IMER-pKLK-MB was incubated with the following final substrate concentrations (n = 3): 6, 10, 15, 30, or 50 μmol.L−1 in 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9.0, according to the procedure described above. Analyses were performed by using the LC-MS method described above. The curve was constructed by applying linear regression in Excel software, and the area of the product ion at m/z 456 [M + H]+ was plotted against substrate concentration. The selectivity of the method was evaluated by incubating IMER-pKLK-MB with buffer only, i.e., without substrate, under the same conditions described above. The lower limit of quantification (LLQ) and the limit of detection (LD) were assessed by incubating 0.1 mg of IMER-pKLK-MB with the following final substrate concentrations: 1, 6, 10, or 15 μmol.L−1. LLQ was defined as the lowest concentration that can produce precision expressed as relative standard deviation (RSD) of less than 20%, while LD was defined as the lowest concentration generating a signal greater than twice the baseline noise.
To determine KMapp, 0.1 mg of IMER-pKLK-MB (equivalent to 5 μL of the stock suspension) was added to a 0.5-mL conical microtube. IMER-pKLK-MB was washed three times with 200 μL of 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9, to remove the storage buffer. After each wash, IMER-pKLK-MB was magnetically separated by using a magnetic separator for 1 min, and the supernatant was discarded. Subsequently, IMER-pKLK-MB was incubated with 75 μL of 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9.0, and 25 μL of substrate at 1, 6, 10, 15, 30, 40, 50, 70, 200, or 300 μmol.L−1 in 5 mmol.L-1 AcNH4, pH 9.0. Each substrate concentration was tested in triplicate. The suspension was homogenized by vortexing and incubated under agitation at room temperature for 5 min. After incubation, the enzymatic reaction supernatant was removed by using a magnetic separator and analyzed by the LC-MS method described above. For the LC-MS analysis, 25 μL of the enzymatic reaction supernatant and 25 μL of 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9.0, were added to a vial; the injected volume was 5 μL. A curve was constructed by plotting the peak area of the product ion at m/z 456 [M + H]+ as a function of substrate concentration. Data were fitted by using nonlinear regression into a Michaelis-Menten plot, and KMapp was obtained with the GraphPad Prism 8.0 software.
Inhibition studies were carried out by using leupeptin as standard inhibitor. To determine the half maximum inhibitory concentration (IC50), 0.1 mg of IMER-pKLK-MB (equivalent to 5 μL of the stock suspension) was added to a 0.5-mL conical microtube. IMER-pKLK-MB was then washed three times with 200 μL of 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9.0, to remove the storage buffer. After each wash, IMER-pKLK-MB was magnetically separated using a magnetic separator for 1 min, and the supernatant was discarded. Next, IMER-pKLK-MB was incubated with 65 μL of 5 mM AcNH4, pH 9.0, 25 μL of 200 μmol.L−1 substrate (in 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9.0), and 10 μL of leupeptin at different concentrations. The final leupeptin concentration, tested in triplicate, was: 0.5, 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 40, 70, 100, 200, or 400 μmol.L−1. As control, the same assay was performed without adding leupeptin. The suspension was then homogenized by vortexing and incubated under agitation at room temperature for 5 min. After incubation, the enzymatic reaction supernatant was removed using a magnetic separator and analyzed by the LC-MS method described above. The enzymatic activity was monitored by quantifying the area of the product ion at m/z 456 [M + H]+. The enzymatic activities in the presence (Ai) and absence (A0) of leupeptin were compared, and the percentage of inhibition was calculated by employing the equation: %I = 100 - [(Ai/A0) × 100]. The inhibition curve was constructed by plotting the percentage inhibition versus the corresponding leupeptin concentration, and IC50 was determined from the curve built by plotting [leupeptin] versus % inhibition with the GraphPad Prism 5.0 software.
To determine the operational stability of IMER-pKLK-MB, 0.5 mg of IMER-pKLK-MB (equivalent to 25 μL of the stock suspension) in a 0.5-mL conical microtube was subjected to 10 consecutive analysis cycles. IMER-pKLK-MB was then washed three times with 200 μL of 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9.0, to remove the storage buffer. After each wash, IMER-pKLK-MB was separated using a magnetic separator for 1 min, and the supernatant was discarded. Following the washing procedure, 75 μL of 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9.0, and 25 μL of 200 μmol.L-1 substrate solution (in 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9.0) were added to IMER-pKLK-MB. The suspension was homogenized by vortexing and incubated under agitation at room temperature for 5 min. After incubation, the enzymatic reaction supernatant was removed by using the magnetic separator and analyzed by the HPLC-MS method described above, immediately after the reaction had ended. To analyze the enzymatic activity, 25 μL of the enzymatic reaction supernatant and 25 μL of 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9.0, were added to a vial. The injected volume was 5 μL. To initiate a new reaction cycle, IMER-pKLK-MB was washed three times with 5 mmol.L-1 AcNH4, pH 9, and the reaction procedure was restarted.
The storage stability of IMER-pKLK-MB was assessed by measuring its activity over time. The procedure and HPLC-MS method described above were followed. The evaluation periods included 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, and 11 months after immobilization. A specific aliquot was set aside and used exclusively for this study.
Compared to assays using enzymes in solution, assays with enzymes immobilized on magnetic particles are particularly useful for conducting ligand screening studies in an optimized manner. In this context, assays based on immobilized enzymes coupled with HPLC-MS systems have emerged as a promising alternative to colorimetric screening assays in microplates. In this study, we developed an off-line assay that couples HPLC-MS with pKLK-immobilized magnetic particles as an alternative method for ligand screening. The immobilization of pKLK was successful, resulting in a highly active bioreactor (IMER-pKLK-MB) with an immobilization efficiency of 97%.
Figure 2 shows the chromatograms of the reaction products recorded for the enzyme solution containing either the free enzyme or the supernatant after the enzyme immobilization. The product at m/z 456 [M + H]+ was monitored. The solution remaining after enzyme immobilization did not produce any reaction product.
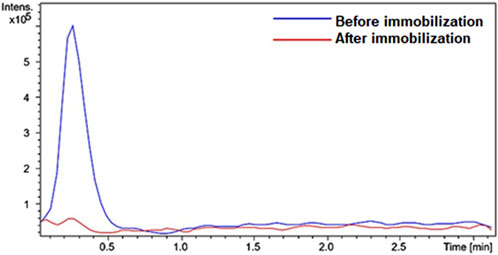
Figure 2. Overlap of peaks in the extracted ion chromatograms recorded for IMER-pKLK-MB activity. The HPLC-MS conditions are described in the experimental section. Source: Designed by the authors.
We developed the HPLC-MS method to analyze reaction products while preventing ionic suppression or contamination of the ionization source by the substrate. To achieve this, we employed a C18 pre-column as a trap column, which effectively separated the products from the substrate and allowed only the products to enter the mass spectrometer, while the substrate was retained on the stationary phase. A 10-port, two-position switching valve was used for this purpose. In position 1, the reaction products are eluted from the trap column and transferred to the mass spectrometer using a methanol mobile phase (1:1, v/v), as detailed in Table 1. Changing the valve to position two allows excess substrate to be removed by washing the pre-column with mobile phase of increasing strength, containing up to 100% solvent B. We evaluated the enzymatic activity by integrating the area of the extracted ion chromatograms (EIC) for the product Z-Phe-Arg-OH, at m/z 456 [M + H]+, which showed a more intense signal compared to the other product (AMC, at m/z 176 with [M + H]+). Scheme 1 illustrates the catalytic reaction involving pKLK.
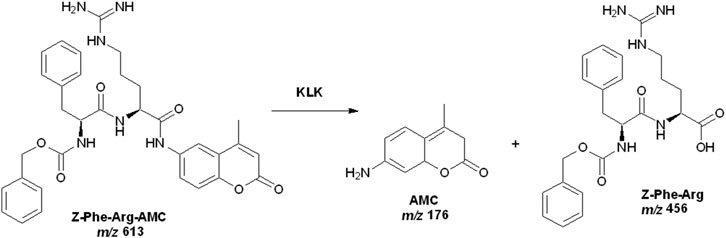
Scheme 1. Catalytic reaction involving pKLK and the substrate Z-Phe-Arg-AMC. Source: Designed by the authors.
Figure 3 displays the chromatogram obtained when we analyzed the IMER-pKLK-MB activity by using the developed LC-MS method. By applying the method, we successfully separated the reaction products from the substrate and effectively removed most of the substrate from the system, thereby minimizing potential issues related to ionic suppression resulting in a fast analysis that lasted only 6 min.
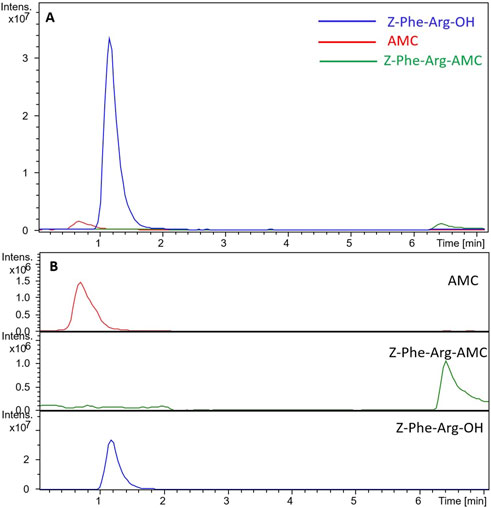
Figure 3. Chromatograms obtained during analysis of IMER-pKLK-MB activity (A) Superposition of the substrate and reaction product chromatograms (B) Separate chromatograms of the substrate and reaction products. Source: Designed by the authors.
Buffer conditions influence the enzymatic activity. As illustrated in Figure 4A, unfavorable buffer concentration or pH causes the enzymatic activity to be reduced. Additionally, during LC-MS analyses, using low buffer concentration enhances sensitivity and reduces ionic suppression by the matrix (García-Moreno et al., 1991). Here, we achieved optimal IMER-pKLK-MB activity by using 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4 and pH 9.0.
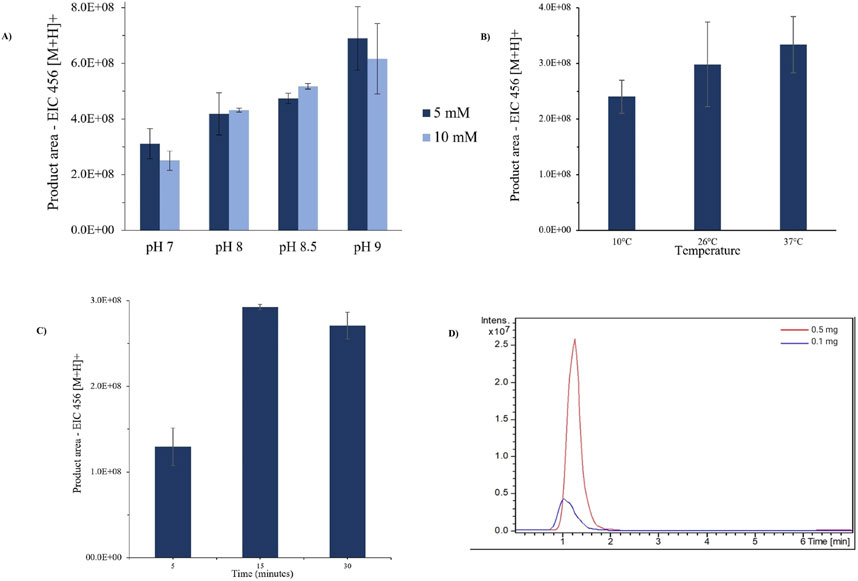
Figure 4. (A) Effect of AcNH4 buffer conditions on IMER-pKLK-MB activity. (B) Effect of temperature on IMER-pKLK-MB activity. (C) Effect of incubation time on IMER-pKLK-MB activity (D) Effect of IMER-pKLK-MB mass on IMER activity. Source: Designed by the authors.
The IMER-pKLK-MB activity increased slightly, but not significantly, upon rising temperatures, as shown in Figure 4B. Therefore, we selected the room temperature to conduct further assays given that the temperature in the laboratory was approximately 26°C. This temperature was sufficient to maintain the enzymatic activity and dismissed additional temperature control, thereby simplifying the experimental procedure.
Longer incubation yielded a greater amount of reaction product, with significant difference between incubation times of 5 and 15 min, as shown in Figure 4C. However, even at 5 min, the amount of product was more than sufficient for detection in the mass spectrometer. To avoid exceeding the MS detection limits, we diluted the reaction solution 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9.0, at a 50:50 v/v ratio, before analysis.
We found that 0.1 mg of IMER-pKLK-MB was sufficient to obtain a measurable product area within 5 min of reaction, as illustrated in Figure 4D. Therefore, we employed 0.1 mg of IMER-pKLK-MB hereafter, which ensured that the method was sensitive, and that the available resources were effectively used.
We established the assay protocol on the basis of the previously optimized conditions. In a 0.5-mL conical microtube, we added 0.1 mg of IMER-pKLK-MB (equivalent to 5 μL of the stock suspension). We washed IMER-pKLK-MB three times with 200 μL of 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9, to remove the storage buffer. After each wash, we magnetically separated IMER-pKLK-MB by using a magnetic separator for 1 min and discarded the supernatant. Subsequently, we added 75 μL of 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9, and 25 μL of 200 μmol.L−1 substrate solution (in 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9.0) to IMER-pKLK-MB. We homogenized the suspension by vortexing and incubated it under agitation at room temperature for 5 min. After incubation, we removed the enzymatic reaction supernatant by using a magnetic separator and analyzed it by the LC-MS method (Table 1). To analyze the enzymatic activity, we added 25 μL of the enzymatic reaction solution and 25 μL of 5 mmol.L−1 AcNH4, pH 9.0 to a vial. The injection volume was 5 μL.
The IMER-pKLK-MB activity as a function of substrate concentration revealed a Michaelian-type curve. This behavior indicates that the IMER-pKLK-MB activity exhibits a hyperbolic dependence on substrate concentration, thus following Michaelis-Menten kinetics. In previous studies by our group, we found that free pKLK in solution has KMapp of 23.5 ± 3.3 μmol.L−1 (de Carvalho et al., 2021). We found that IMER-pKLK-MB has KMapp of 81.2 ± 18 μmol. L−1 (Figure 5), so immobilized pKLK can still recognize its substrate.
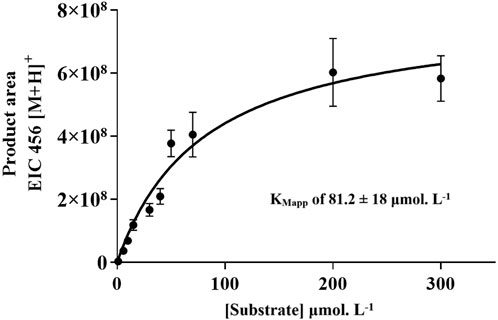
Figure 5. IMER-pKLK-MB activity upon varying substrate concentration: Michaelian curve for determining KMapp. Source: Designed by the authors.
To validate the assay as a tool to screening inhibitors, we selected the reference inhibitor leupeptin. Previous studies identified that leupeptin has IC50 of 1.62 ± 0.18 μM for the free enzyme in solution and 0.13 ± 0.01 μM for IMER-KLK-Sepharose-NHS, determined through fluorescence detection assays (de Carvalho et al., 2021). Here, we obtained IC50 of 2.15 ± 0.4 μmol.L−1 concerning IMER-pKLK-MB inhibition by leupeptin. The IC50 values vary when the test conditions are modified, so it is a relative comparison parameter (Holdgate et al., 2018). Thus, pKLK immobilization did not affect its ability to recognize the inhibitor Figure 6.

Figure 6. Dose-response curve plot of inhibition percentage for IMER-pKLK-MB in the presence of leupeptin. Source: Designed by the authors.
IMER-pKLK-MB kept its high activity even after 10 consecutive analysis cycles, as illustrated in Figure 7A. This finding indicates that the analytical method was robust, that pKLK was not significantly lost during the washing steps, that immobilization was successful, and that pKLK was securely anchored to the support.
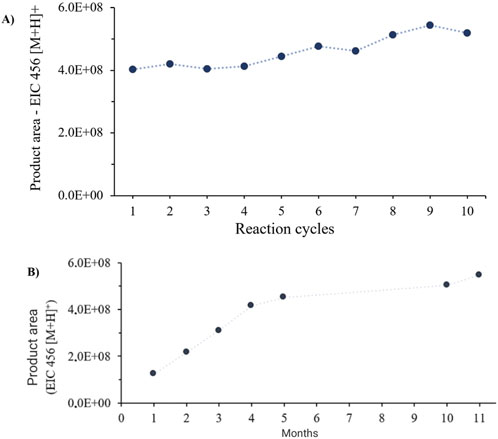
Figure 7. (A) IMER-pKLK-MB activity over 10 consecutive analysis cycles. (B) IMER-pKLK-MB activity along time. Source: Designed by the authors.
Evaluation of the storage stability of IMER-pKLK-MB revealed it was highly stable in 100 mM Tris-HCl buffer at pH 8.0 even after 11 months elapsed since it was immobilized. These results indicate that immobilization effectively preserved the IMER-pKLK-MB activity over an extended period. Additionally, we observed that the IMER-pKLK-MB activity increased during the first months following immobilization probably because pKLK was adapting to its new environment and adjusting its active conformation in the immobilized state. However, after this initial period, the IMER-pKLK-MB activity remained at a high level, which means that the immobilized enzyme sustained (Figure 7B). These results highlight one of the main advantages of immobilized enzymes: their reuse in multiple reaction cycles, which provides both economic and environmental benefits.
We assessed the linearity of the method by constructing a calibration curve in which we plotted the product area as a function of substrate concentration. The calibration curve demonstrated a linear response for substrate concentrations ranging from 1 to 50 μmol.L−1. The regression equation was y = 3606771.127x + 5817619.093; the coefficient of determination (R2) was 0.999 (n = 3). The RSD values for the curve construction were less than 19% for all triplicates. We confirmed that the method was selective by noting the absence of a detectable signal for the product at m/z at 456 [M + H]+ with when we incubated only the buffer with IMER-pKLK-MB under the same assay conditions. The limit of detection (LD) and lower limit of quantification (LLQ) were 1 and 6 μmol.L-1, respectively. On the basis of literature parameters, the developed method proved adequate for monitoring the IMER-pKLK-MB activity.
Compared to traditional kallikrein activity assays that use the enzyme in solution with fluorimetric detection, the proposed method offers several advantages. It allows for enzyme reuse, reducing costs and increasing storage stability, and is effective in the presence of organic solvents. This is particularly beneficial for ligand screening applications, as it enables testing of a broader range of samples, including those that are insoluble in aqueous solutions. Additionally, samples that present fluorescence can interfere with fluorimetric assays, leading to false positives (Simeonov, 2018). This issue is avoided by using mass spectrometry, which offers high selectivity, sensitivity, and efficiency.
IMER-pKLK-MB displays high activity and stability even after being stored for 11 months. It also exhibits excellent operational stability, which allowed it to be reused for at least 10 consecutive cycles of activity. IMER-pKLK-MB proved remarkably stable in the presence of organic solvents—60% and 10% activity was recovered after it was incubated in 70% and 100% methanol for 15 min, respectively. Additionally, the KMapp and IC50 parameters regarding leupeptin confirmed that IMER-pKLK-MB can still recognize both the substrate and the reference inhibitor. The developed LC-MS method proved suitable and reliable for monitoring the IMER-pKLK-MB activity, effectively overcoming ion suppression and contamination of the ESI source caused by the substrate.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
CR: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing–original draft. CC: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Visualization, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by the São Paulo State Foundation (FAPESP grants 2019/05363-0, 2022/00432-7 and 2014/50299-5), and by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) Grants 307108/2021-0. This study was partially financed by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior, Brazil (CAPES), Finance Code 001.
CR and CC acknowledge the Sao Paulo State Research Foundation (FAPESP), CNPq (307108-2021-0), and CAPES Fellowship. The content of the manuscript has previously appeared in the dissertation/master’s thesis of CR (Rocha, 2023).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Carvalho, D. R., De Laurentino, B. B., Rocha, C. L., Kool, J., Somsen, G., Amstalden van Hove, E., et al. (2022). Activity assay based on the immobilized enzyme kallikrein and mass spectrometry. Front. Anal. Sci. 2, 1. doi:10.3389/frans.2022.1018115
Cassiano, N. M., Barreiro, J. C., Martins, L. R. R., Oliveira, R. V., and Cass, Q. B. (2009). Validação em métodos cromatográficos para análises de pequenas moléculas em matrizes biológicas. Quim Nova 32, 1021–1030. doi:10.1590/S0100-40422009000400033
de Carvalho, D. R., Farias Ximenes, V., Groppo, M., and Cardoso, C. L. (2021). Ligand screening assay for the enzyme kallikrein immobilized on NHS-activated Sepharose. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 199, 114026. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2021.114026
Del Nery, E., Chagas, J. R., Juliano, M. A., Juliano, L., and Prado, E. S. (1999). Comparison of human and porcine tissue kallikrein substrate specificities. Immunopharmacology 45, 151–157. doi:10.1016/s0162-3109(99)00077-6
de Moraes, M. C., Cardoso, C. L., and Cass, Q. B. (2019). Solid-supported proteins in the liquid chromatography domain to probe ligand-target interactions. Front. Chem. 7, 752. doi:10.3389/fchem.2019.00752
de Moraes, M. C., Vanzolini, K. L., Cardoso, C. L., and Cass, Q. B. (2014). New trends in LC protein ligand screening. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 87, 155–166. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2013.07.021
De Oliveira, P. C. O., Lessa, R. C., Ceroullo, M. S., Wegermann, C. A., and De Moraes, M. C. (2022). Onflow enzymatic inhibitor screening: the emerging success of liquid chromatographybased assays. Front. Anal. Sci. 2, 1. doi:10.3389/frans.2022.1004113
De Simone, A., Naldi, M., Bartolini, M., Andrisano, V., and Davani, L. (2019). Immobilized enzyme reactors: an overview of applications in drug discovery from 2008 to 2018. Chromatographia 82, 425–441. doi:10.1007/s10337-018-3663-5
de Souza, A. S., Pacheco, B. D. C., Pinheiro, S., Muri, E. M. F., Dias, L. R. S., Lima, C. H. S., et al. (2019). 3-Acyltetramic acids as a novel class of inhibitors for human kallikreins 5 and 7. Rev. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 29, 1094–1098. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.02.031
Felicori, L., Souza, C. T., Velarde, D. T., Magalhaes, A., Almeida, A. P., Figueiredo, S., et al. (2003). Kallikrein-like proteinase from bushmaster snake venom. Expr. Purif. 30, 32–42. doi:10.1016/s1046-5928(03)00053-6
Food and Drug Administration (2001). FDA guidance for industry: bioanalytical method validation. US department of Health and human Services, Food and drug administration. Rockville, MD: Center for Drug Evaluation and Research.
García-Moreno, M., Havsteen, B. H., Varón, R., and Rix-Matzen, H. (1991). Evaluation of the kinetic parameters of the activation of trypsinogen by trypsin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1080 (2), 143–147. doi:10.1016/0167-4838(91)90141-l
Girelli, A. M., and Mattei, E. (2005). Application of immobilized enzyme reactor in on-line high performance liquid chromatography: a review. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 819, 3–16. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2005.01.031
Guo, J., Lin, H., Wang, J., Lin, Y., Zhang, T., and Jiang, Z. (2019). Recent advances in bio-affinity chromatography for screening bioactive compounds from natural products. J. Pharm. Biom. Anal. 165, 182–197. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2018.12.009
Hanefeld, U., Cao, L., and Magner, E. (2013). Enzyme immobilisation: fundamentals and application. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 6211–6212. doi:10.1039/c3cs90042h
Holdgate, G. A., Meek, T. D., and Grimley, R. L. (2018). Mechanistic enzymology in drug discovery: a fresh perspective. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 17 (2), 115–132. doi:10.1038/nrd.2017.219
Hou, X., Sun, M., Bao, T., Xie, X., Wei, F., and Wang, S. (2020). Recent advances in screening active components from natural products based on bioaffinity techniques. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 10, 1800–1813. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2020.04.016
Kryza, T., Silva, M. L., Loessner, D., Heuzé-Vourc’h, N., and Clements, J. A. (2016). The kallikreinrelated peptidase family: dysregulation and functions during cancer progression. Biochimie 122, 283–299. doi:10.1016/j.biochi.2015.09.002
Li, D., Xu, L., Qi, J., and Yu, B. (2019). Screening and analysis of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors from the complex matrix: a case study to illustrate the important effect of immobilized enzyme activity in magnetic ligand fishing. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 175, 112795. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2019.112795
Liu, H., Wang, J., Yang, S., Li, Z., Song, M., Zhang, X., et al. (2024). A magnetic beads-based ligand fishing method for rapid discovery of monoterpene indoles as monoamine oxidase in review a inhibitors from Hunteria zeylanica. J. Chromatogr. A 10, 1722. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2024.464896
Miranda de Souza Duarte-Filho, L. A., Ortega de Oliveira, P. C., Yanaguibashi Leal, C. E., de Moraes, M. C., and Picot, L. (2023). Ligand fishing as a tool to screen natural products with anticancer potential. J. Sep. Sci. 46, e2200964. doi:10.1002/jssc.202200964
Moraes, M. C., Cardoso, C. L., Seidl, C., Moaddel, R., Cass, Q. B., and de Moraes, M. C. (2016). Targeting anti-cancer active compounds: affinity-based chromatographic assays. Curr. Pharm. Des. 22 (39), 5976–5987. doi:10.2174/1381612822666160614080506
Prassas, I., Eissa, A., Poda, G., and Diamandis, E. P. (2015). Unleashing the therapeutic potential of human kallikrein-related serine proteases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 14, 183–202. doi:10.1038/nrd4534
Rocha, C. L. (2023). Imobilização de calicreína para aplicação na triagem de ligantes. [dissertation/master´s thesis]. Ribeirão Preto (SP): Faculty of Philosophy, Sciences and Letters of Ribeirão Preto - University of São Paulo SP.
Shi, Q., Chen, J., Wang, Y., Li, Z., Li, X., Sun, C., et al. (2015). Immobilization of cyclooxygenase-2 on silica gel microspheres: optimization and characterization. Molecules 20, 19971–19983. doi:10.3390/molecules201119670
Sotiropoulou, G., and Pampalakis, G. (2012). Targeting the kallikrein-related peptidases for drug development. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 33, 623–634. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2012.09.005
Stefanini, A. C. B., da Cunha, B. R., Henrique, T., and Tajara, E. H. (2015). Involvement of kallikrein related peptidases in normal and pathologic processes. Dis. Markers 2015, 946572. doi:10.1155/2015/946572
Swedberg, J. E., De Veer, S. J., and Harris, J. M. (2010). Natural and engineered kallikrein inhibitors: an emerging pharmacopoeia. Biol. Chem. 391, 357–374. doi:10.1515/BC.2010.037
Tan, X., Soualmia, F., Furio, L., Renard, J. F., Kempen, I., Qin, L., et al. (2015). Toward the first class of suicide inhibitors of kallikreins involved in skin diseases. J. Med. Chem. 58, 598–612. doi:10.1021/jm500988d
Teixeira, T. S. P., Freitas, R. F., Abrahão, O., Devienne, K. F., De Souza, L. R., Blaber, S. I., et al. (2011). Biological evaluation and docking studies of natural isocoumarins as inhibitors for human kallikrein 5 and 7. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 21, 6112–6115. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2011.08.044
Trindade Ximenes, I. A., de Oliveira, P. C. O., Wegermann, C. A., and de Moraes, M. C. (2021). Magnetic particles for enzyme immobilization: a versatile support for ligand screening. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 204, 114286. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2021.114286
van de Veerdonk, F. L., Netea, M. G., van Deuren, M., Van Der Meer, J. W. M., de Mast, Q., Brü Ggemann, R. J., et al. (2020). Kallikrein-kinin blockade in patients with Covid-19 to prevent acute respiratory distress syndrome. Elife 9, e57555. doi:10.7554/eLife.57555
Vanzolini, K. L., Vieira, LCCC, Corrêa, A. G., Moaddel, R., and Cass, Q. B. (2015). Acetylcholinesterase immobilized on modified magnetic beads as a tool for screening a compound library. Microchim. Acta 182, 2209–2213. doi:10.1007/s00604-015-1562-0
Wubshet, S. G., Liu, B., Kongstad, K. T., Böcker, U., Petersen, M. J., Li, T., et al. (2019). Combined magnetic ligand fishing and high-resolution inhibition profiling for identification of αglucosidase inhibitory ligands: a new screening approach based on complementary inhibition and affinity profiles. Talanta 1, 279–287. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2019.03.047
Keywords: kallikrein, activity assay, immobilized enzyme, HPLC-MS, screening assay
Citation: Rocha CL and Cardoso CL (2025) Kallikrein immobilized on magnetic beads for activity-based assays using mass spectrometry. Front. Anal. Sci. 5:1514381. doi: 10.3389/frans.2025.1514381
Received: 20 October 2024; Accepted: 10 February 2025;
Published: 05 March 2025.
Edited by:
Rishi Kumar Jaiswal, University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences, United StatesReviewed by:
Mark C. Chappell, Wake Forest University, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Rocha and Cardoso. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Carmen Lúcia Cardoso, Y2NjYXJkb3NvQGZmY2xycC51c3AuYnI=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.