
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Agron., 25 March 2025
Sec. Plant-Soil Interactions
Volume 7 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fagro.2025.1535871
Intercropping and phosphorus application are effective ways to increase crop yield and improve cultivated land quality. This study took the soil under the maize-peanut intercropping system which has been planted for 12 years as the research object, the physical, chemical, and electrochemical properties of soil, and crop yield under different planting patterns [sole-crop maize (SM), sole-crop peanut (SP), and maize-peanut intercropping (M/P)] and phosphorus application rates [P application (180 kg P2O5 ha−1) and no P application (0 kg P2O5 ha−1)] were studied. The results showed that intercropping increased soil aggregate stability, clay content, and gas phase ratio, P application further optimized the soil physical properties. At the same time, intercropping decreased soil pH and EC, increased soil organic carbon (SOC), total nitrogen (TN), and total phosphorus (TP) contents. P application increased soil pH, SOC, TN, TP, and EC. Compared with monoculture, intercropping increased the surface charge number (SCN) by 19.98%, specific surface area (SSA) by 44.34%, surface charge density (σ0) by 38.08, electric field strength (E0) by 38.22, and Zeta potential by 46.85%. P application further increased the SCN by 20.75%, SSA by 23.43%, σ0 by 67.82%, E0 by 67.13%, and Zeta potential by 15.51%. Maize-peanut intercropping increased the total crop yield of the intercropping system, the application of phosphate fertilizer further increased the yield of maize and peanut. The aggregate stability and nitrogen were significantly positively correlated with crop yield, and the carbon, phosphorus, and electrochemical properties were extremely significantly positively correlated with crop yield.
Intercropping refers to the planting pattern of two or more crops on the same land, which can intensively utilize resources such as light, temperature, water, and heat, and improve the yield of crops per unit area (Li et al., 2023a; Wang et al., 2024). Maize/peanut intercropping is a common intercropping pattern between grasses and legumes, which can fully leverage the dual advantages of crop marginal effects and peanut biological nitrogen fixation, not only solve the contradiction of land competition between grain and oil, but also effectively improve the utilization rate of resources and improve the soil ecological environment through compound planting pattern (Jiao et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2023).
Phosphorus (P), as one of the basic components of many biological compounds (such as phospholipids and nucleic acids), plays an important role in plant growth and metabolism. The content of available phosphorus in farmland soil is generally low. Applying phosphate fertilizer is not only the main means to alleviate the limitation of soil phosphorus and improve crop yield, but also the fundamental way to maintain and improve the level of soil phosphorus pools (Guo et al., 2023; Li et al., 2024). Maize and peanut are both phosphorus loving crops and are sensitive to the phosphorus content in the soil. The addition of phosphorus fertilizer can enhance the photosynthesis of crops, increase the accumulation of protein, improve the utilization rate of light energy, and promote the accumulation of dry matter and crop growth and development (Shi et al., 2020; An et al., 2023).
The electrochemical properties of soil surface are the basis of soil fertility and the key factors affecting crop growth and nutrient absorption, including surface charge number, specific surface area, surface charge density, surface electric field strength, etc. The soil surface carries charges, which can absorb and transfer various nutrient ions released by fertilizer, and can better reflect the fertility level, fertilizer retention ability and buffering ability of soil (Liu et al., 2022a; Ma et al., 2023; Zhou et al., 2024). The specific surface area of soil can reflect its adsorption and ion exchange capacity. A larger specific surface area can store nitrogen and provide nutrient support for crop growth (Jiang et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2021). The surface charge density and electric field strength of soil determine the cation adsorption strength of soil colloids, and the magnitude of soil ion adsorption strength is of great significance for the retention of effective nutrients in crops (Liu et al., 2020; Ali et al., 2023).
Compared with monoculture, long-term intercropping can increase the content of soil organic matter and change the basic physicochemical and electrochemical properties of soil (Jat et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2020). At the same time, the application of phosphate fertilizer can also promote the dissociation of hydroxyl group on the surface of soil colloids, and increase the charge amount of soil colloids (Lü et al., 2017; Luo et al., 2021). At present, there are many studies on soil physical and chemical properties, microbial properties, and photosynthetic performance under intercropping and phosphorus application (Qu et al., 2022; Zou et al., 2023; Wu et al., 2024), but there are few studies on soil surface electrochemical properties and crop yield under intercropping and phosphorus application. This study took the 12-year maize-peanut intercropping system as an example to study the soil physical, chemical, and electrochemical properties of soil, and crop yield under three planting patterns of sole-crop maize (SM), sole-crop peanut (SP), and maize-peanut intercropping (M/P), as well as two P levels of P application (180 kg P2O5 ha−1) and no P application (0 kg P2O5 ha−1). The purpose is to explore (1) the effects of different planting patterns and phosphorus application levels on soil physical, chemical, and electrochemical properties, (2) the effects of different planting patterns and phosphorus application levels on crop yield, (3) the relationship between crop yield and soil properties under different planting patterns and phosphorus application levels.
This experiment was conducted in Luoyang, Henan Province, China (33°35′N, 111°8′E) from 2010 to 2022. The experimental site is located in the temperate zone, belonging to the semi-humid and semi-arid continental monsoon climate, the average annual precipitation is 610 mm, the average annual evaporation is 2113 mm, and the average annual temperature is 13.6 °C. The soil in the experimental site is fluvo-aquic with medium soil texture. At the beginning of the experiment in 2010, the soil characteristics of 0-20 cm topsoil were as follows: pH, 7.33, bulk density, 1.35 g cm−3, organic carbon, 10.7 g kg−1, total nitrogen, 1.20 g kg−1, available phosphorus, 11.6 mg kg−1, available potassium, 223.8 mg kg−1.
Two-factor randomized block design was used in the experiment. Two factors were planting pattern and phosphorus application level. The planting patterns included sole-crop peanut (SP) (Arachis hypogaea L. cv. Huayu 16), sole-crop maize (SM) (Zea mays L. cv. Zhengdan 958), and maize intercropping with peanut (M/P) (combination of two rows of maize and four rows of peanut). The phosphorus application rates were set at 2 levels of 0 kg P2O5 ha−1 (P0) and 180 kg P2O5 ha−1 (P180). A total of 6 treatments, each treatment repeated 3 times, and there were 18 plots, each with an area of 60 m2 (6 m × 10 m). In sole cropping, the row spacing, plant spacing, and plant density for maize and peanut were 60 and 30 cm, 25 and 20 cm, 66 667 and 166 667 plants ha-1, respectively. In intercropping, the row spacing, plant spacing, and plant density for maize and peanut were 40 and 30 cm, 20 and 20 cm, 50 000 and 100 000 plants ha-1, respectively. In intercropping, the row spacing between maize and peanut was 35 cm.
Diammonium phosphate was adopted as the phosphate fertilizer and applied as the base fertilizer. Urea was used as nitrogen fertilizer, and 90 kg N ha−1 of basal fertilizer was applied to both monoculture and intercropping peanut at once. The nitrogen application rate for monoculture and intercropping maize was 180 kg N ha−1, divided into two applications according to a basal to topdressing ratio of 1:1. The topdressing was applied during the big bell stage of maize. Maize and peanut were planted at the same time in early June and harvested at the same time in early October.
Soil samples were collected after the crop was harvested in October 2022. Topsoil samples ranging from 0 to 20 cm were collected in each plot. In single cropping plot, three sub-samples were collected between crop rows in each plot with auger and mixed into one soil sample. In intercropping plot, three sub-samples were collected between two crop rows with auger and mixed into one soil sample. Then took the soil samples back to the laboratory and broke it into blocks with a diameter of about 10 mm according to its natural structure. Each sample was divided into two parts, one part was used to analyze the stability of soil aggregates, and the other part was used to analyze the physical, chemical, and electrochemical properties of soil.
Soil bulk density (BD) was analyzed by three cutting ring samples in 0-20 cm soil layers in each plot. Soil aggregate stability was determined by conventional wet sieving methods (Elliott, 1986). Mean weight diameter (MWD) was calculated as an index of soil aggregate stability as Equation 1. The particle size fraction (psf, sand: silt: clay) was measured by the Malvern laser particle size analyzer (MS3000). Soil solid-liquid-gas three-phase ratio (tpr, solid: liquid: gas) were determined by the conventional core method (Hao et al., 2020; Peng et al., 2020). Soil pH and electrical conductivity (EC) were measured by An HQ30d Protable Meter (HACTH, USA) [soil: water = 1: 2.5 (w/v)]. Soil organic carbon (SOC) content was determined by the potassium dichromate oxidation method (Lu, 2000). The total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) contents were determined by the Kjeldahl method and Mo-Sb colorimetric method, respectively (Lu, 2000). The zeta potentials and size distributions of soil colloid particles were analyzed using a ZetaPlus instrument (Brookhaven Instruments Corporation, USA), using the dynamic light scattering (DLS) method (Hong et al., 2021). Soil surface electrochemical properties were determined by the conjoint determination method of material surface properties established by Li et al. (2011). In short, first, washed approximately 100 g of soil with 500 mL 0.1 mol L-1 HCl to prepare an H+-saturated sample, and then washed repeatedly with deionized water until the solution contains no Cl-. Dried the H+-saturated soil sample at 60°C and passed it through a 0.25 mm sieve. Second, the 10 g H+-saturated soil sample (in triplicate) was transferred to the 150 ml triangular bottle, and the Ca(OH)2 and NaOH solution of the equal volume of 0.01 mol L−1 were added. After shaking for 24 hours, 0.1 mol L−1 HCl was dropped to adjust the pH of the suspension to 7. Third, centrifuged the suspension to collect the supernatant and measured the concentrations of Na+ and Ca2+ in the supernatant. Finally, the soil surface electrochemical properties were calculated by the following Equations 2–6 (Li et al., 2011; Yu et al., 2017).
where xi and wi mean the mean diameter (mm) and percentage (%) of each size aggregate fraction, respectively.
where
where φ0 (mV) is the surface potential, R (J K−1 mol−1) is the universal gas constant, T (K) is the absolute temperature, F (C mol−1) is the Faraday constant, Z is the charge of each ion species, βNa and βCa are the corresponding modification factors of Z for Na+ and Ca2+, respectively. c0Na (mol L−1) and c0Ca (mol L−1) are equilibrium Na+ and Ca2+ concentrations in the bulk solution, respectively. σ0 (C m−2) is the surface charge density, E0 (V m−1) is the surface electric field strength, SSA (m2 g−1) is the specific surface area, SCN (cmol kg−1) is the surface charge number, I (mol L−1) is the ionic strength, κ (dm−1) is the Debye-Hückel parameter.
At the harvest stage of sole-crop maize (SM), intercropping maize (IM), sole-crop peanut (SP), intercropping peanut (IP), the yields of five-meter double row peanut and maize were measured randomly with three replicates. The weight of maize seed and peanut pod was measured after air-drying.
The intercropping advantage is measured by the land equivalent ratio (LER), and the formula is as Equation 7 (Mead and Willey, 1980):
where YIM and YIP represent the actual yields of intercropping maize and intercropping peanut, respectively, YSM and YSP represent the actual yields of monoculture maize and monoculture peanut, respectively. LER > 1 indicates intercropping advantage, LER < 1 indicates intercropping disadvantage.
Microsoft Excel 2013 and SPSS 22.0 software were used for statistical analysis of the experimental data, and Origin 2021 was used for plotting. Soil physical, chemical, and electrochemical properties, and crop yield were compared between different treatments using the one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a Tukey’s honest significant difference test. The Pearson coefficient test was used to measure the correlation between soil properties. Redundancy analysis (RDA) was carried out using the software of Canoco 5. Structural equation modeling (SEM) was used to analyze the direct and indirect effects of planting patterns and phosphate fertilizer application on soil electrochemical properties using AMOS 20.0 (AMOS Development, Spring House, U.S.A.).
The intercropping of maize and peanut and the application of phosphorus had a significant impact on soil physical properties (Figure 1). Intercropping and P application reduced soil BD compared to monoculture and no P application, but the difference was not significant (P > 0.05). Compared with SP and SM, M/P significantly increased soil MWD by 38.37% and 19.00%. Compared to P0, P180 significantly increased soil MWD by 19.42%. Compared with monoculture and no P application, intercropping and P application reduced sand (-6.04%-7.81% and -1.45%-11.80%) and silt contents (2.70-4.74% and -0.57%-1.84%) and increased clay content (1.87%-7.86% and 1.10%-4.92%). Intercropping and P application reduced the percentage of soil solid phase (0.64%-6.85% and -1.02%-2.22%) and increased the percentage of soil gas phase (3.90%-7.71% and 0.86%-5.55%) compared to monoculture and no phosphorus application. In addition, intercropping and P application had significant or extremely significant effects on MWD and particle size fraction (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01), the interaction effect between intercropping and P application had a significant impact on soil MWD, particle size fraction, and three-phase ratio (P < 0.05).
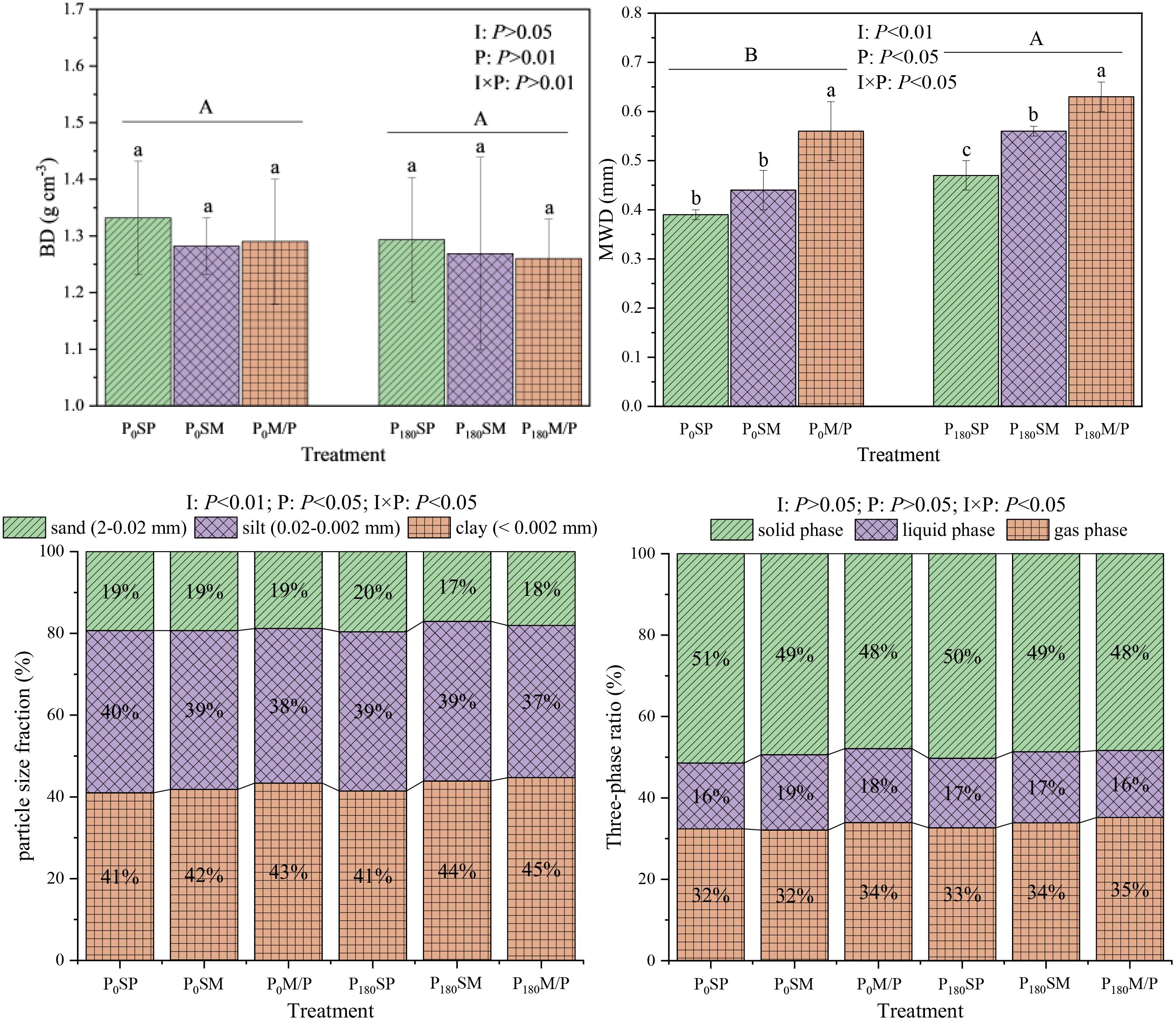
Figure 1. Soil physical properties under different planting patterns and phosphorus application rates. Different letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05. I, planting pattern; P, P level; I×P, planting pattern×P level.
The intercropping of maize and peanut and the application of phosphorus had a significant impact on soil chemical properties (Figure 2). Intercropping reduced soil pH compared to monoculture, but the difference was not significant (P > 0.05). Compared to SP and SM, M/P increased soil SOC by 0.95% and 2.94%, respectively. Under P0 level, the TN content of SP was the highest, which was significantly higher than that of SM and M/P by 6.15% and 3.74%. Under P180 level, M/P significantly increased TP content by 10.11% and 8.36% compared to SP and SM (P < 0.05). M/P significantly reduced soil EC by 11.43% and 7.41% compared to SP and SM (P < 0.05). Compared to P0, P180 significantly increased soil pH by 1.06% (P < 0.05), SOC by 5.61% (P < 0.05), TN by 13.92%, TP by 85.17%, and EC by 6.50% (P < 0.05). In addition, intercropping had a significant or extremely significant impact on soil pH, SOC, and EC (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01), while phosphorus application and the interaction between intercropping and phosphorus application had an extremely significant impact on soil pH, SOC, TN, TP, and EC% (P < 0.01).
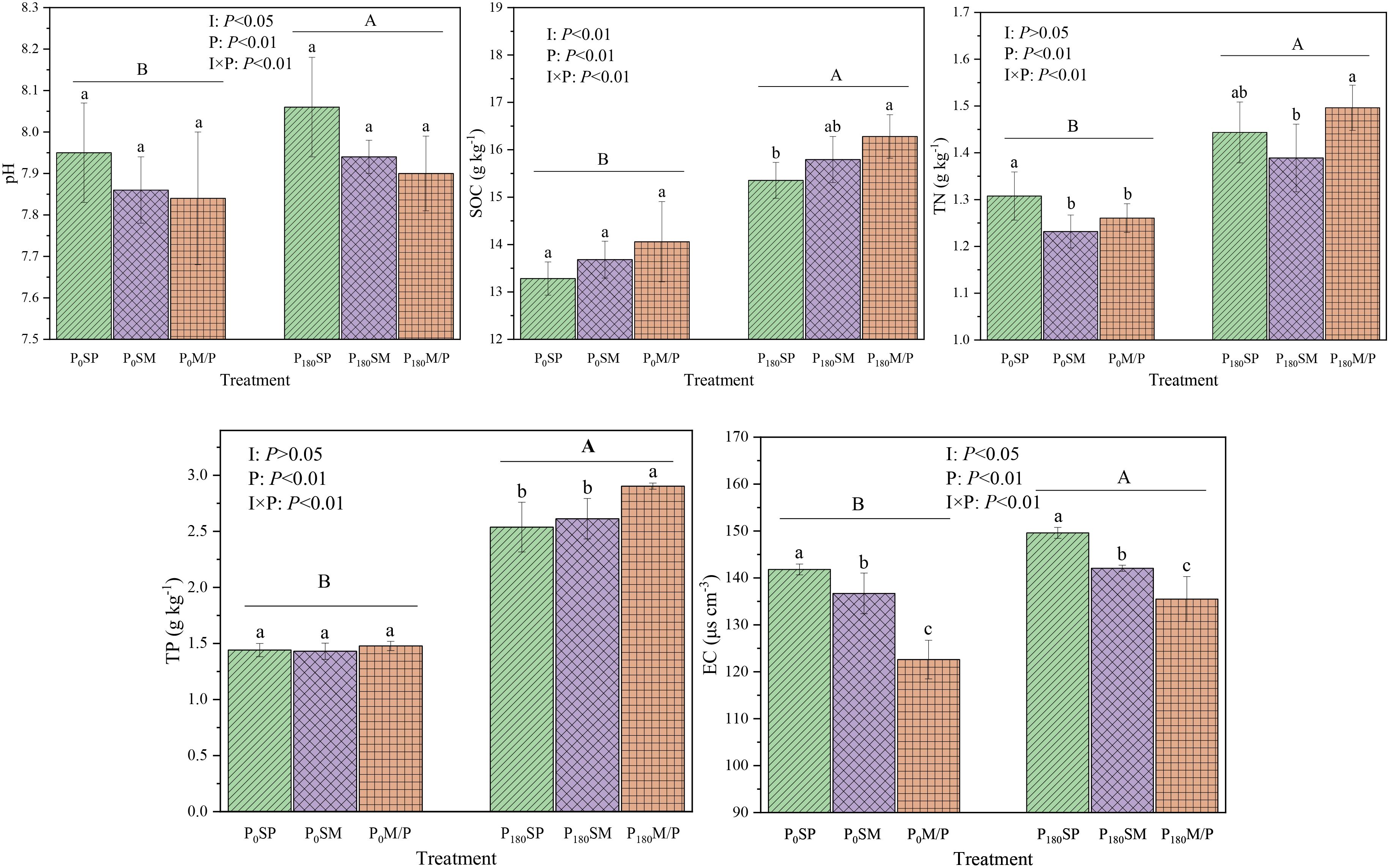
Figure 2. Soil chemical properties under different planting patterns and phosphorus application rates. Different letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05. I, planting pattern; P, P level; I×P, planting pattern×P level.
The intercropping of maize and peanut and the application of phosphorus had a significant impact on soil electrochemical properties (Figure 3). Compared to SP and SM, M/P increased soil SCN by 27.89% and 12.07%, respectively. Compared to P0, P180 significantly increased soil SCN by 20.75% (P < 0.05). M/P significantly increased SSA by 60.90% and 27.78% compared to SP and SM (P < 0.05). P180 significantly increased SSA content by 23.43% compared to P0 (P < 0.05). Compared to SP and SM, M/P increased σ0 by 43.85% and 32.30%, respectively. Compared to P0, P180 significantly increased σ0 by 67.82% (P < 0.05). Compared to SP and SM, M/P increased E0 by 37.95% and 38.48%, respectively. Compared to P0, P180 significantly increased E0 by 67.13% (P < 0.05). Under P0 level, M/P significantly increased φ0 by 15.29% and 9.13% compared to SP and SM. Under P180 level, there was no significant difference in φ0 between different treatments (P > 0.05). P180 significantly increased φ0 by 10.52% compared to P0. In addition, the interaction between intercropping and phosphorus application had an extremely significant impact on soil SCN, SSA, σ0, E0, and φ0 (P < 0.01).
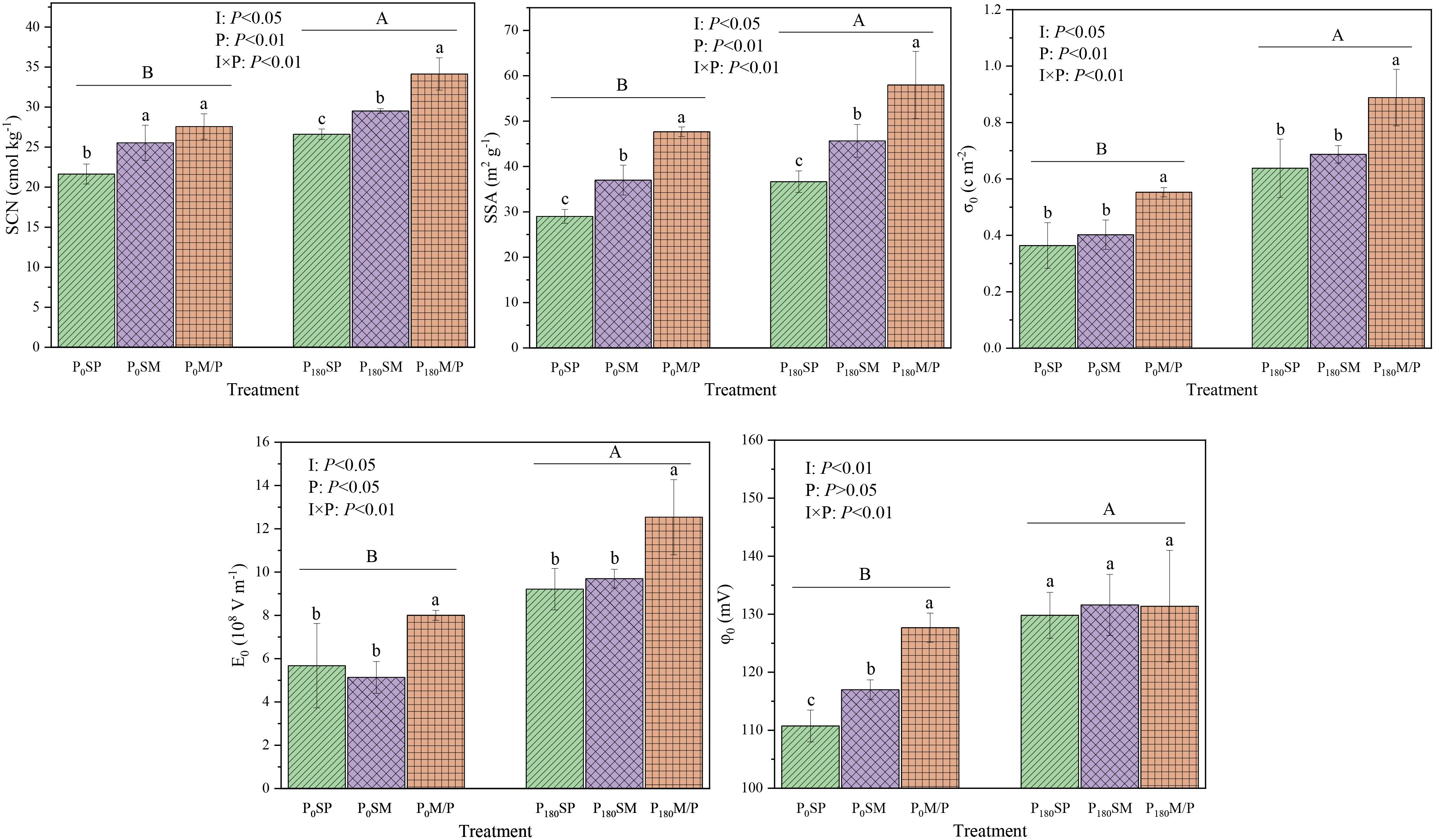
Figure 3. Soil electrochemical properties under different planting patterns and phosphorus application rates. Different letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05. I, planting pattern; P, P level; I×P, planting pattern×P level.
Figure 4 shows the Zeta potential under different planting patterns and phosphorus application rates. Compared to SP and SM, M/P increased Zeta potential by 41.10% and 11.49%, respectively. Compared to P0, P180 significantly increased Zeta potential by 15.51%.

Figure 4. Zeta potential under different planting patterns and phosphorus application rates. Different letters indicate significant differences at P < 0.05. I, planting pattern; P, P level; I×P, planting pattern×P level.
Figure 5 shows the soil particle size distribution under different planting patterns and phosphorus application rates. Under P0 level, the main distribution range of soil particle size was 400-2000 nm, and under P180 level, the main distribution range of soil particle size was 300-3000 nm. The average effective particle sizes of P0SP, P0SM, P0M/P, P180SP, P180SM, and P180M/P were 476, 762, 1220, 892, 557, and 1428 nm, respectively.
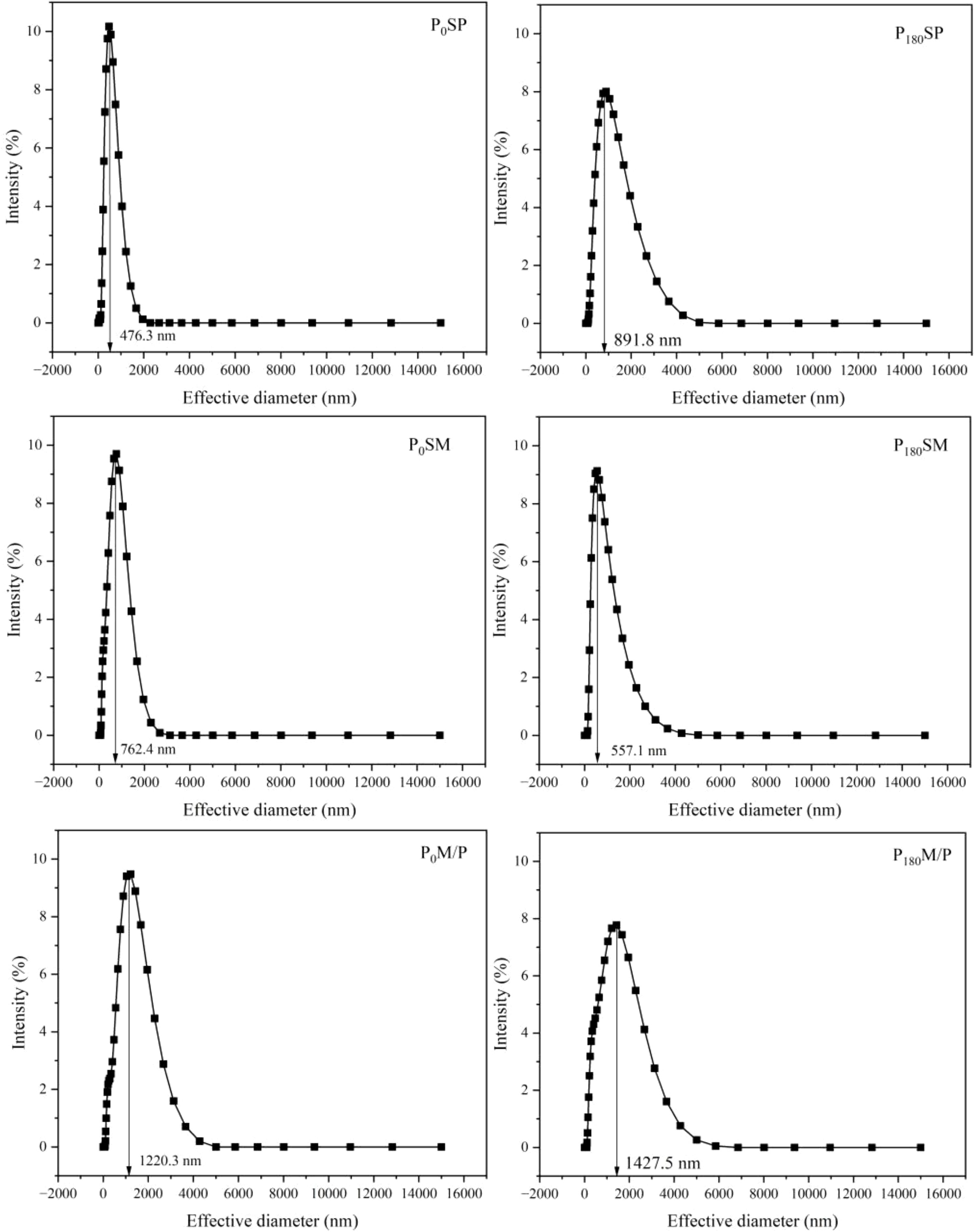
Figure 5. Soil particle size distribution under different planting patterns and phosphorus application rates.
Figure 6 shows the redundancy analysis (RDA) of soil electrochemical properties and basic physicochemical properties. The first and second axes accounted for 82.33% and 6.93% of the total variance, respectively. There were differences in soil properties under different planting patterns and phosphorus fertilizer application. Soil P, C, and MWD (F=37.5, P=0.001; F=18.6, P=0.001; F=8.4, P=0.018) were the main factors affecting soil surface electrochemical properties, which explained 42.8%, 26.7%, and 12.6% of the variation of electrochemical properties, respectively (Table 1).
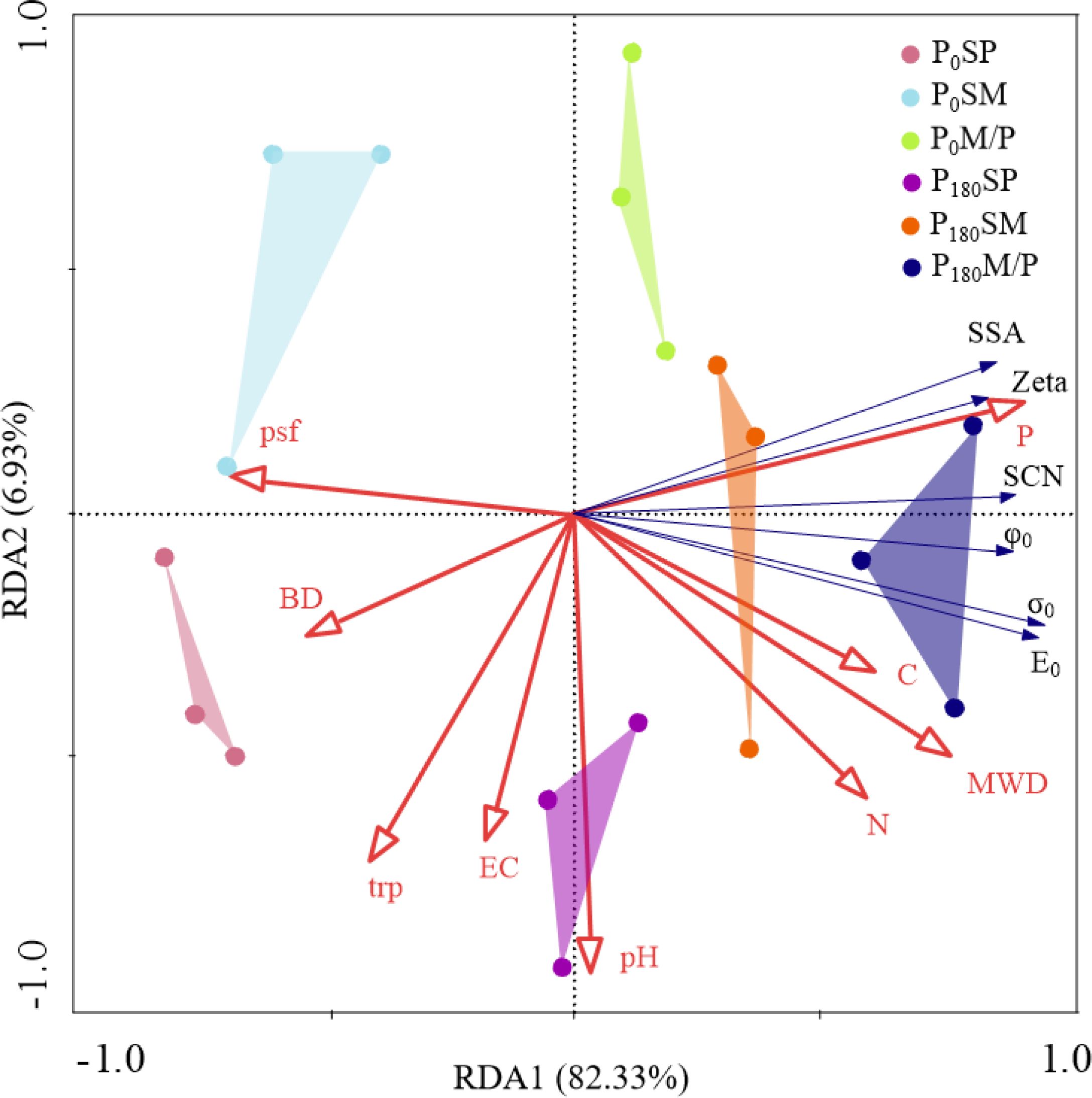
Figure 6. Redundancy analysis (RDA) of soil electrochemical properties and basic physicochemical properties. BD, bulk density. MWD, mean weight diameter. psf, particle size fraction (sand: silt: clay). tpr, solid-liquid-gas three-phase ratio. EC, electric conductivity. SCN, surface charge number. SSA, specific surface area. σ0, surface charge density. E0, electric field strength. φ0, surface potential.
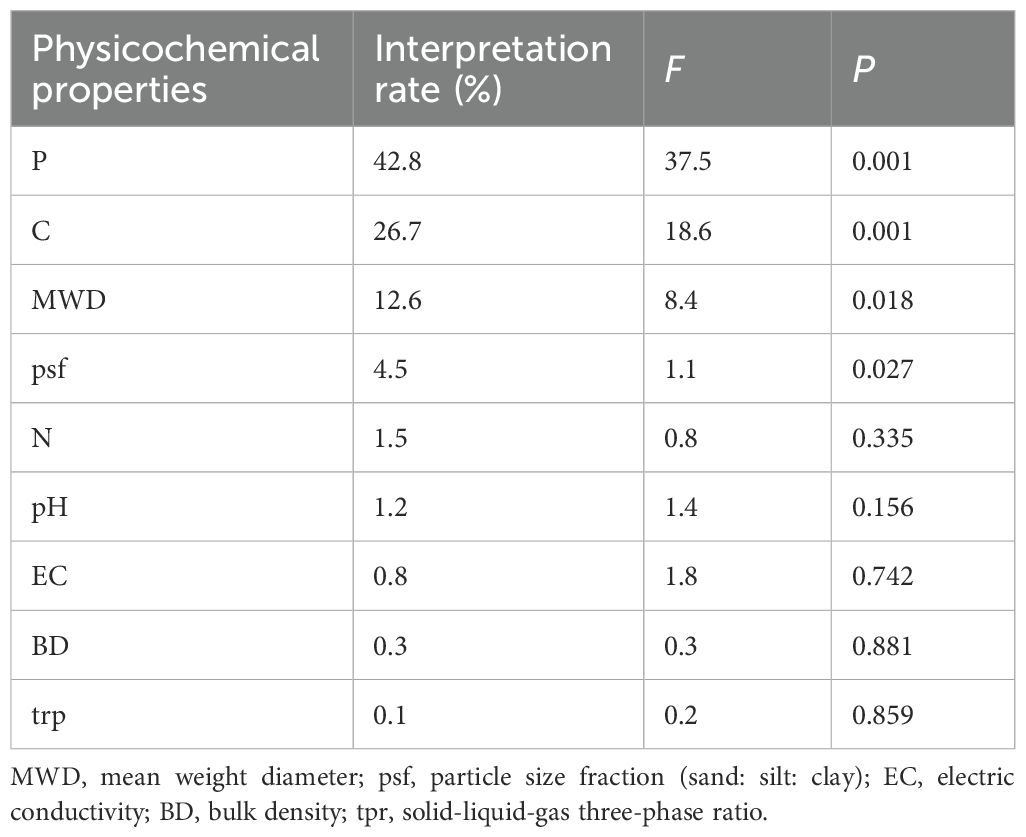
Table 1. Interactions between soil basic physicochemical properties and surface electrochemical properties.
Table 2 shows the yield of maize and peanut under monoculture and intercropping and different phosphorus application rates. Overall, the yield of SM was the highest, significantly higher than that of IM, and the yield of SP was significantly higher than that of IP. The yield of maize was higher than that of peanut. The yield of maize and peanut under P180 was significantly higher than that under P0. Planting method, phosphorus levels, and their interaction had significant effects on crop yield. LER values ranged from 1.23 to 1.46 with an average of 1.32. LER value > 1, showing intercropping advantage.
Figure 7 shows the relationship between crop yield and soil properties. Soil BD was significantly negatively correlated with MWD and σ0 (P < 0.01). Soil MWD was significantly positively correlated with psf, SCN, SSA, σ0 and φ0 (P < 0.01), and significantly negatively correlated with EC (P < 0.01). Soil psf was significantly negatively correlated with SSA and σ0 (P < 0.01), and significantly positively correlated with EC (P < 0.01). Soil trp was significantly positively correlated with pH (P < 0.01). C was significantly positively correlated with P, SCN, SSA, φ0, E0, and σ0 (P < 0.01), and significantly negatively correlated with EC (P < 0.01). N was significantly positively correlated with P, σ0, and E0 (P < 0.01). P was significantly positively correlated with SCN, σ0, E0, and φ0 (P < 0.01). EC was significantly negatively correlated with SCN, σ0, and E0 (P < 0.01). There was a significantly positive correlation among SCN, SSA, σ0, E0, and φ0 (P < 0.01). Crop yield was significantly positively correlated with C, P, SCN, SSA, σ0, E0, φ0, and Zeta potential (P < 0.01).
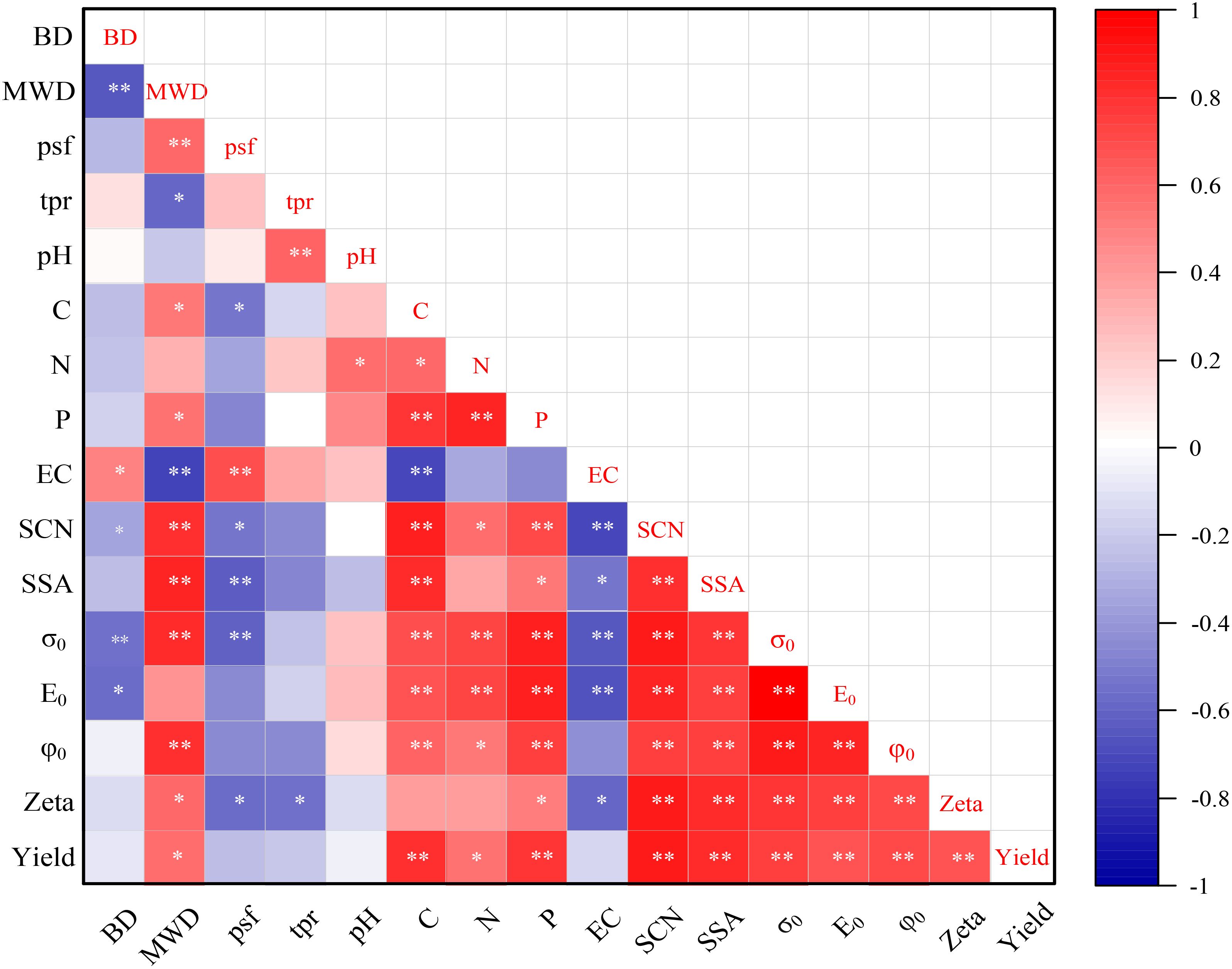
Figure 7. Relationship between crop yield and soil properties. ** and * indicating statistical significance at levels of P < 0.01 and P < 0.05, respectively.
The interaction among planting patterns, phosphorus application, soil properties, and crop yield was analyzed by structural equation model (SEM). As can be seen from Figure 8, planting patterns had significant positive effects on soil physical (P < 0.001), chemical (P < 0.01), and electrochemical properties (P < 0.01). Phosphorus application had significant negative effects on soil physical properties (P < 0.001) and electrochemical properties (P < 0.01), and significant positive effects on soil chemical properties (P < 0.001). At the same time, planting patterns and phosphorus application also had positive effects on soil electrochemical properties through indirect effects on soil physical and chemical properties. Soil physical (P < 0.01), chemical (P < 0.01), and electrochemical properties (P < 0.001) had significant positive effects on crop yield, and the electrochemical properties had the greatest effect on crop yield, with a correlation coefficient of 0.76.
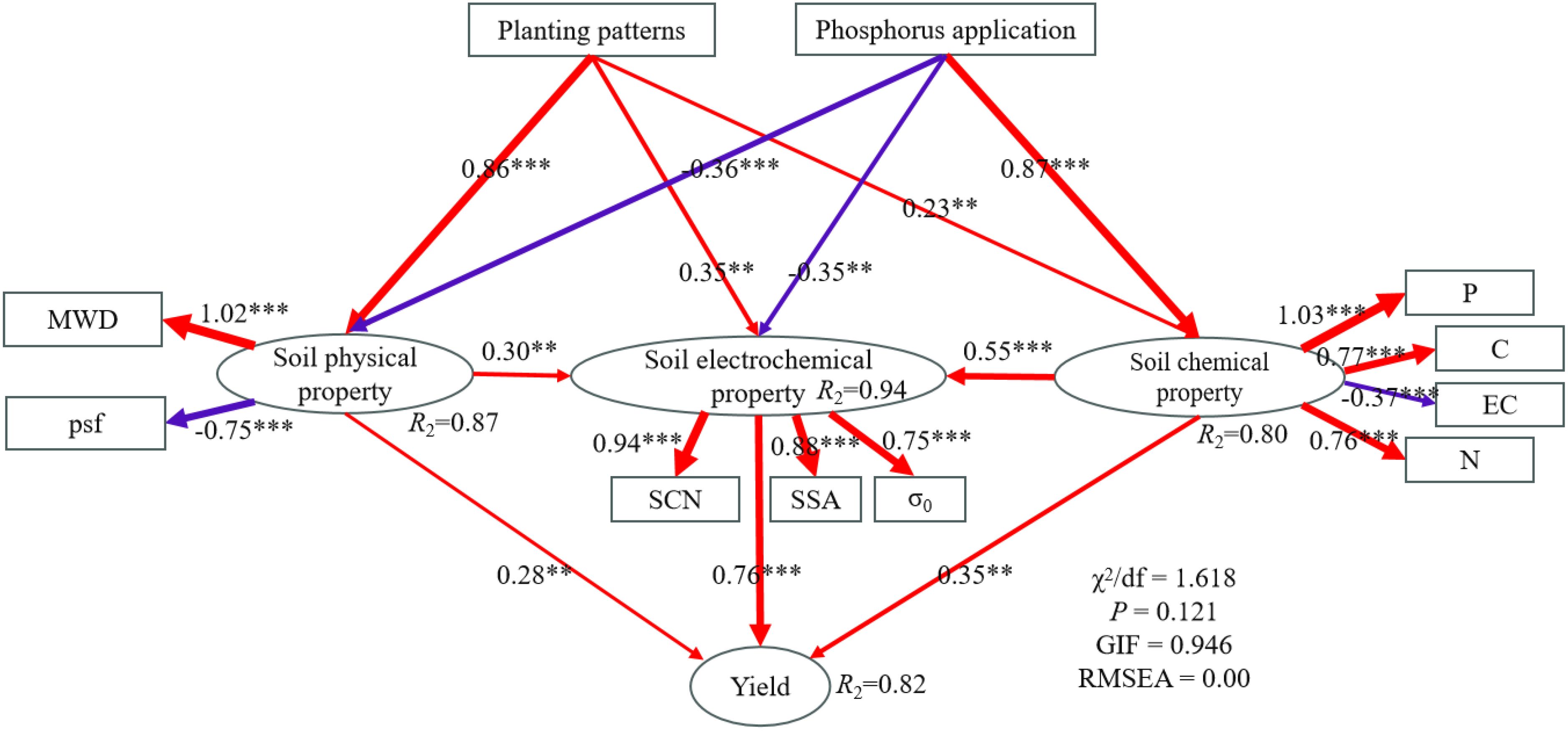
Figure 8. Structural equation modeling (SEM) of the associations among planting patterns, phosphorus application, and soil properties. The red and blue lines represent positive and negative pathways, respectively. Numbers on the arrowed lines and thickness of arrows indicate normalized path coefficient. ** Significant at P < 0.01. *** Significant at P < 0.001. R2 beside the latent variables are the coefficients of determination. Model fitness details (χ2/df, P, GIF, RMSEA) are shown in the figure.
Soil physical properties are the foundation of soil fertility and have a significant impact on crop gas exchange and root development (Burrell et al., 2016; Yang et al., 2021). This study found that intercropping could reduce soil bulk density compared to monoculture (Figure 1), this was mainly due to the dense distribution of crop roots under intercropping pattern, which helped loosen the soil and reduce soil bulk density (Li et al., 2020). Soil aggregates is a reservoir of soil nutrients, and its stability is related to soil nutrient supply capacity. Intercropping and phosphorus application could improve soil aggregate stability, which was consistent with the results reported by Garland et al. (2017) and Zan et al. (2023). Intercropping could increase the stability of soil aggregates because the intercropping pattern has a more developed crop root system, which made it easier for the soil to form larger particle size aggregates through root entanglement and consolidation (Seidel et al., 2017). At the same time, intercropping increased the interaction between roots of different crops, and promoted the increase of root exudates and microbial activity. Polysaccharides and other organic complexes secreted by plant roots and fungal hyphae promoted the bonding of soil particles and microaggregates, which was conducive to the transformation of microaggregates into macroaggregates (Tian et al., 2019). Additionally, the application of phosphate fertilizer increased the complexation of aluminum and calcium with phosphate in soil, and the complexation product was a good cementitious substance, which promoted the formation of aggregates (Du et al., 2022).
Intercropping and phosphorus application also increased soil clay content and reduced sand content (Figure 1), indicating that intercropping and phosphorus application were beneficial to soil cohesion, optimize soil texture, and improve particle composition. At the same time, intercropping and phosphorus application changed the soil three-phase ratio, that was, increased soil gas phase ratio and decreased soil solid phase ratio. This was mainly because intercropping and phosphorus application promoted crop root growth, established a good physical structure in the cultivated layer, reduced soil bulk density and compaction, increased porosity and moisture content, resulting in the change of soil three-phase ratio (Moura et al., 2021).
Soil chemical properties reflect the potential ability of soil to supply nutrients to plant roots and are closely related to the nutritional status of plants (Deiss et al., 2020). In this study, intercropping reduced soil pH compared to monoculture (Figure 2), which was related to the interaction between roots in the intercropping system inducing changes in root secretion of H+ and OH- (Wang et al., 2015). The decrease of soil pH in the intercropping can promote the activation of some insoluble nutrients in the soil, which can improve the nutritional status of crops and promote crop growth. Intercropping increased the soil organic carbon content, because the roots in the intercropping system was developed, and the number of roots and their secretions in the soil increased, resulting in an increase in the input of organic carbon in the soil, and thus increased the soil organic carbon content (Jat et al., 2019). Phosphorus application not only promoted the growth and development of aboveground parts of crops, but also promoted the growth of crop roots, resulting in an increase in the number of stubble returned to the field and thereby increasing the organic carbon content in the soil (Mahmoud et al., 2019). In addition, it was found that at P0 level, the total nitrogen content of monoculture peanut was significantly higher than that of monoculture maize and maize-peanut intercropping. This was because the rhizobia in peanut roots have a nitrogen fixing effect, which in turn increases the nitrogen content in the soil.
Compared with monoculture, intercropping increased the total phosphorus content in the soil. This was because intercropping promoted the root growth of maize and peanut, significantly increased root dry weight, root crown ratio, and root length, and changed the distribution of roots in different levels of soil, thereby promoting the increase of soil nutrients (Jiao et al., 2021). Compared with not applying phosphorus fertilizer, the total phosphorus content in the soil significantly increased after applying phosphorus fertilizer. This might be due to the fact that an appropriate amount of phosphorus fertilizer promoted root growth, increased root exudates, and led to more root exudates and residues entering the soil (Du et al., 2022). Moreover, the application of phosphorus fertilizer is the main reason for the increase in soil phosphorus content. Soil electrical conductivity is an indicator that reflects the concentration of electrolytes in the soil and also characterizes the concentration of soil salt ions (Liu et al., 2019). Within an appropriate range, a higher soil electrical conductivity indicates more available nutrients for plant utilization in the soil. Intercropping reduced soil electrical conductivity, because intercropping increased soil porosity, water content, and other characteristics, increased nutrient absorption, and allows some salt to be absorbed, resulting in a decrease in soil electrical conductivity (Su et al., 2022).
The electrochemical properties of soil surface affect a series of physical and chemical processes, such as soil fertility, nutrient uptake, element migration, and soil structural stability (Li et al., 2013; Hu et al., 2015). Surface charge number is one of the factors affecting cation exchange capacity, and it is also the key to affect the absorption of nutrients by crops (Yu et al., 2017). This study found that intercropping increased the amount of soil surface charge (Figure 3), because the crop root density and root exudates were high under intercropping conditions, while substances such as sugars and organic acids secreted by roots entered the soil and were adsorbed due to strong complexation, thus increasing the amount of soil surface charge (Farhangi-Abriz and Ghassemi-Golezani, 2023). The application of phosphate fertilizer also increased the amount of charge, because when phosphorus entered the soil, it would promote the dissociation of hydroxyl groups on the surface of soil colloids, resulting in an increase in the amount of negative charge of soil colloids (Lü et al., 2017). The specific surface area of soil is an important site for adsorption reaction and ion exchange in soil, which is closely related to the ability of soil to maintain and supply nutrients and water for crops (Bayat et al., 2015). Intercropping and phosphorus application increased soil specific surface area, which indicated that intercropping and phosphorus application could improve soil adsorption and ion exchange capacity, and store more nutrients for crop growth.
Surface charge density of soil particles refers to the number of charges per unit area of soil particles. The higher the charge density, the greater the ion adsorption capacity (Liu et al., 2022b). Intercropping and phosphorus application increased the surface charge density of soil particles, indicating that intercropping and phosphorus application increased the amount of charge per unit area and the ability of soil to retain nutrient ions. It was found that intercropping and phosphorus application increased the Zeta potential (Figure 4), because intercropping and phosphorus application increased the content of soil organic matter, and soil organic matter (mainly humus) could generate variable negative charge through the dissociation of its functional groups, which led to the increase of Zeta potential absolute value (Li et al., 2023b).
In this study, under different planting patterns and phosphorus application rates, MWD and particle size fraction in soil physical properties are the main factors affecting soil electrochemical properties (SSA and SCN) (Figure 6, Table 2). MWD affects the electrochemical properties of soil because the more stable the aggregates are, the stronger the ability of soil to hold charges, and the organic carbon is not easy to mineralize (Even and Cotrufo, 2024). In the particle size composition of soil, clay has a large specific surface area, and its main components are layered silicate clay minerals and oxides, which the soil surface negatively charged by isomorphism displacement and hydroxyl ion dissociation, respectively (Liu et al., 2020). Therefore, the increase of clay content can increase the value of soil electrochemical properties. While the sand particles are mostly primary minerals, whose specific surface is smaller and can provide fewer ion exchange sites, the increase of its content in soil will decrease the value of electrochemical properties (Chen et al., 2019).
As is well known, due to the valence state of phosphorus itself, it inevitably participates in the adsorption, fixation, and certain exchange reactions on the surface of soil colloids in the soil. The reactions may also affect and alter the release of hydroxyl groups on the surface of soil colloids, causing changes in the types and quantities of charges carried on the surface of soil colloids (Luo et al., 2021). Intercropping and phosphorus application can also affect the electrochemical properties of soil by increasing the content of soil organic matter, because organic matter can produce variable negative charges through the dissociation of its functional groups, which increases the amount of soil surface charges (Yu et al., 2017). Moreover, organic matter is composed of three-dimensional polymer phases and has a high internal surface area (Liu et al., 2020). Therefore, the higher the content of soil organic matter, the greater the specific surface area of soil. Intercropping and phosphorus application change the pH value of soil (Figure 2). In addition to directly affecting the variable charge properties and quantity, soil pH can also affect the electrochemical properties of soil colloid through ion morphology, competitive adsorption, precipitation dissolution, coordination and other reactions (Xu et al., 2017; Bian et al., 2021).
Long-term rational intercropping can improve the biodiversity and ecological environment of farmland, increase crop yield, and maintain the stability of crop yield. The results of this study indicated that although the yield of each crop in the intercropping system decreased, the total crop yield of the intercropping system was higher than that of the monoculture, and the land equivalent ratio (LER) was greater than 1 (Table 2). LER is the main indicator for evaluating the efficiency of land use. LER greater than 1 indicates that intercropping systems have certain intercropping advantages, and land use efficiency increases (Yu et al., 2015). In this study, the LER of the maize-peanut intercropping system was greater than 1 (Table 2), indicating that the intercropping of maize and peanut showed obvious yield advantages and improved land productivity. This result was consistent with the research findings of Feng et al. (2020), who found that the land equivalent ratio of maize-soybean intercropping system was 1.23-1.57, it also indicated that intercropping had significant yield advantages. In addition, compared with no phosphorus fertilizer, the application of phosphorus fertilizer could increase the yield of maize and peanut (Table 2).
Maize-peanut intercropping and phosphate fertilizer application affected crop yield by changing soil physical, chemical, and electrochemical properties (Figures 7, 8). In soil physical properties, aggregate stability was positively correlated with crop yield. This results align with the findings of Yang et al. (2024). Stable soil aggregate structure can provide a favorable soil environment for crop growth, regulate soil permeability, increase soil temperature, promote root penetration and development, thereby improving crop yield and quality (Tian et al., 2019). The planting pattern and phosphorus fertilizer application also affected crop yield by changing the soil three-phase ratio and particle size fraction. The different proportions of soil solid-liquid-gas three phases directly affect the ventilation, water permeability, water supply and water retention of soil, and also affect the acidity and alkalinity of soil and the absorption efficiency of nutrients, thus affecting crop yield (Zhou et al., 2023). The particle size fraction of soil directly affects the ability of soil to retain water and fertilizer and the growth of crops (Jiang et al., 2024).
Maize-peanut intercropping and phosphate fertilizer application increased crop yield by increasing soil nutrient contents. Soil organic matter has a significant impact on crop growth and soil carbon cycling, promoting stable soil aggregate structure, enhancing water and fertilizer retention capacity, and microbial activity, which is beneficial for the growth of maize and peanut roots and nutrient supply (Li et al., 2021; Wu et al., 2021). As an important element, nitrogen can participate in the physiological and metabolic activities of crops, promote the accumulation of organic matter in crops, ensure the development of various organs of crops, and thus improve crop yield and quality (Zhang et al., 2025). Phosphorus application can increase the available phosphorus content in soil, which is beneficial for improving the leaf area index, photosynthetic substance accumulation, and growth rate of maize and peanut, and enhancing the photosynthetic capacity of maize and peanut (Jiao et al., 2021; An et al., 2023; Zan et al., 2023). Electrical conductivity is an important parameter for evaluating soil fertility and one of the key factors for crop growth (Liu et al., 2024). Different crops have different requirements for soil conductivity, and too high or too low conductivity will hinder the growth of maize and peanut.
The electrochemical properties of soil have a significant impact on the yield of maize and peanut. The quantity and properties of soil surface charges directly affect the adsorption performance of soil and the effectiveness of nutrients. The electric field formed by soil surface charges can affect root growth and nutrient absorption. The quantity and properties of soil surface charges also affect microbial activity, which in turn affects the decomposition of organic matter and nutrient cycling (Yu et al., 2017). Specific surface area is one of the important indicators for evaluating soil texture and water management capacity. Due to the large surface area of soil particles, the soil can adsorb and retain more water, which is crucial for plant growth and development. The specific surface area is closely related to the nutrient cycling and fertility of the soil. Due to the large surface area of soil particles, soil can adsorb and store relatively more nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (Bayat et al., 2015). Zeta potential also has a significant impact on the availability of soil nutrients. It can affect the cation exchange capacity (CEC) in soil, which in turn affects the release and absorption of nutrients, ultimately affecting the nutritional status of plants (Farhangi-Abriz and Ghassemi-Golezani, 2023).
Maize-peanut intercropping and phosphorus application have effects on soil physical, chemical, electrochemical properties, and crop yield. Intercropping and phosphorus application decreased soil bulk density, increased soil aggregate stability, and increased soil clay content and gas phase ratio. At the same time, intercropping and phosphorus application increased soil SOC, TN, and TP contents, while intercropping decreased soil pH and EC. Intercropping and phosphorus application increased the soil surface charge number, specific surface area, surface charge density, electric field strength, and Zeta potential, optimizing soil electrochemical properties. Maize-peanut intercropping increased the total crop yield of the intercropping system and improved land productivity. The application of phosphate fertilizer further increased the yield of maize and peanut. The physical, chemical, and electrochemical properties of soil had a significant positive impact on crop yield, with electrochemical properties having the greatest positive effect on crop yield.
The data analyzed in this study is subject to the following licenses/restrictions: Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Requests to access these datasets should be directed to Rentian Ma, MTM3MTEwNTYyNUBxcS5jb20=.
RM: Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. NY: Investigation, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft. SZ: Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing. TK: Formal Analysis, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. NJ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the PhD Startup Foundation of Henan University of Science and Technology (13480107) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32401971).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Ali W., Hussain S., Chen J., Hu F., Liu J., He Y., et al. (2023). Cover crop root derived organic carbon influences aggregate stability through soil internal forces in a clayey red soil. Geoderma 429, 116271. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2022.116271
An R., Yu R., Xing Y., Zhang J., Bao X., Lambers H., et al. (2023). Enhanced phosphorus-fertilizer-use efficiency and sustainable phosphorus management with intercropping. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 43, 57. doi: 10.1007/s13593-023-00916-6
Bayat H., Ebrahimi E., Ersahin S., Hepper E., Singh D., Amer A., et al. (2015). Analyzing the effect of various soil properties on the estimation of soil specific surface area by different methods. Appl. Clay Sci. 116, 129–140. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.07.035
Bian F., Zhong Z., Li C., Zhang X., Gu L., Huang Z., et al. (2021). Intercropping improves heavy metal phytoremediation efficiency through changing properties of rhizosphere soil in bamboo plantation. J. Hazard. 416, 125898. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125898
Burrell D., Zehetner F., Rampazzo N., Wimmer B., Soja G. (2016). Long-term effects of biochar on soil physical properties. Geoderma 282, 96–102. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.07.019
Chen X., Wu J., Opoku-Kwanowaa Y. (2019). Effects of organic wastes on soil organic carbon and surface charge properties in primary saline-alkali soil. Sustainability 11, 7088. doi: 10.3390/su11247088
Deiss L., Kleina G., Moraes A., Franzluebbers A., Motta A., Dieckow J., et al. (2020). Soil chemical properties under no-tillage as affected by agricultural trophic complexity. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 71, 1090–1105. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12869
Du J., liu K., Huang J., Han T., Zhang L., Anthonio C., et al. (2022). Organic carbon distribution and soil aggregate stability in response to long-term phosphorus addition in different land-use types. Soil Till. Res. 215, 105195. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2021.105195
Elliott E. (1986). Aggregate structure and carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in native and cultivated soils. Soil Sci. Soc Am. J. 50, 627–633. doi: 10.2136/sssaj1986.03615995005000030017x
Even R., Cotrufo F. (2024). The ability of soils to aggregate, more than the state of aggregation, promotes protected soil organic matter formation. Geoderma 442, 116760. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2023.116760
Farhangi-Abriz S., Ghassemi-Golezani K. (2023). Improving electrochemical characteristics of plant roots by biochar is an efficient mechanism in increasing cations uptake by plants. Chemosphere 313, 137365. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.137365
Feng L., Raza M., Shi J., Ansar M., Titriku J., Meraj T. (2020). Delayed maize leaf senescence increases the land equivalent ratio of maize soybean relay intercropping system. Eur. J. Agron 118, 126092. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2020.126092
Garland G., Bünemann E., Oberson A., Frossard E., Six J. (2017). Plant-mediathizospheric interactions in maied rhizospheric interactions in maize-pigeon pea intercropping enhance soil aggregation and organic phosphorus storage. Plant Soil 415, 1–19. doi: 10.1007/s11104-016-3145-1
Guo Y., Wang Z., Li J. (2023). Coupling effects of phosphate fertilizer type and drip fertigation strategy on soil nutrient distribution, maize yield and nutrient uptake. Agr. Water Manage. 290, 108602. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2023.108602
Hao H., Wei Y., Cao D., Guo Z., Shi Z. (2020). Vegetation restoration and fine roots promote soil infiltrability in heavy-textured soils. Soil Till. Res. 198, 104542. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2019.104542
Hong Z., Bish D., Chang E., Yu Y., Dong Y., Zhao W., et al. (2021). Effect of paddy cultivation on the surface electrochemical properties of different-sized particles of a Gleysol. J. Plant Nutt. Soil Sci. 184, 471–478. doi: 10.1002/jpln.202100086
Hu F., Xu C., Li H., Li S., Yu Z., Li Y., et al. (2015). Particles interaction forces and their effects on soil aggregates breakdown. Soil Till. Res. 147, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2014.11.006
Jat H., Datta A., Choudhary M., Yadav A., Choudhary V., Sharma P., et al. (2019). Effects of tillage, crop establishment and diversification on soil organic carbon, aggregation, aggregate associated carbon and productivity in cereal systems of semi-arid Northwest India. Soil Till. Res. 190, 128–138. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2019.03.005
Jiang F., Xue X., Zhang L., Zuo Y., Zhang H., Zheng W., et al. (2024). Soil wind erosion, nutrients, and crop yield response to conservation tillage in North China: A field study in a semi-arid and wind erosion region after 9 years. Field Crops Res. 316, 109508. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2024.109508
Jiang X., Ma Y., Yuan J., Wright A. L., Li H. (2011). Soil particle surface electrochemical property effects on abundance of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and ammonia-oxidizing archaea, NH4+ activity, and net nitrification in an acid soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 43, 2215–2221. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.07.014
Jiao N., Wang J., Ma C. (2021). The importance of aboveground and belowground interspecific interactions in determining crop growth and advantages of peanut/maize intercropping. Crop J. 9, 1460–1469. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2020.12.004
Li H., Hou J., Liu X., Li R., Zhu H., Wu L. (2011). Combined determination of specific surface area and surface charge properties of charged particles from a single experiment. Soil Sci. Soc Am. J. 75, 2128–2135. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2010.0301
Li P., Jia L., Chen Q., Zhang H., Deng J., Lu J., et al. (2024). Adaptive evaluation for agricultural sustainability of different fertilizer management options for a green manure-maize rotation system: Impacts on crop yield, soil biochemical properties and organic carbon fractions. Sci. Total Environ. 908, 168170. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.168170
Li S., Li H., Xu C., Huang X., Xie D., Ni J. (2013). Particle interaction forces induce soil particle transport during rainfall. Soil. Sci. Soc Am. J. 77, 1563–1571. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2013.01.0009
Li C., Stomph T., Makowski D., Li H., Zhang C., Zhang F., et al. (2023a). The productive performance of intercropping. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 120, e2201886120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2201886120
Li X. F., Wang Z. G., Bao X. G., Sun J. H., Yang S. C., Wang P., et al. (2021). Long-term increased grain yield and soil fertility from intercropping.Nat. Sustain 4, 943–950. doi: 10.1038/s41893-021-00767-7
Li S., Wang B., Zhang X., Wang H., Yi Y., Huang X., et al. (2023b). Soil particle aggregation and aggregate stability associated with ion specificity and organic matter content. Geoderma 429, 116285. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2022.116285
Li H., Zhu N., Wang S., Gao M., Xia L., Kerr P., et al. (2020). Dual benefits of long-term ecological agricultural engineering: Mitigation of nutrient losses and improvement of soil quality. Sci. Total Environ. 721, 137848. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137848
Liu Z., Gao C., Yan Z., Shao L., Chen S., Niu J., et al. (2024). Effects of long-term saline water irrigation on soil salinity and crop production of winter wheat-maize cropping system in the North China Plain: A case study. Agr. Water Manage. 303, 109060. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2024.109060
Liu X., Tang Y., Li H., Wu L. (2019). Effects of interactions between soil particles and electrolytes on saturated hydraulic conductivity. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 71, 190–203. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12855
Liu Z., Wang H., Cao S., Sun Z., Wang N., Zhang Z., et al. (2022b). Variation characteristics of particle surface electrochemical properties during the improvement of reclaimed soil from hollow village in loess area. Sustainability 14, 11527. doi: 10.3390/su141811527
Liu J., Wang Z., Hu F., Xu C., Ma R., Zhao S. (2020). Soil organic matter and silt contents determine soil particle surface electrochemical properties across a long-term natural restoration grassland. Catena 190, 104526. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2020.104526
Liu J., Yang Y., Zheng Q., Su X., Liu J., Zhou Z. (2022a). Effects of soil surface electrochemical properties on soil detachment regulated by soil types and plants. Sci. Total Environ. 834, 154991. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.154991
Lu R. (2000). Soil agrochemical analysis (Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press).
Lü C., Yan D., He J., Zhou B., Li L., Zheng Q. (2017). Environmental geochemistry significance of organic phosphorus: an insight from its adsorption on iron oxides. Appl. Geochem. 84, 52–60. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.05.026
Luo C., Wen S., An S., Lu Y., Du Y. (2021). Phosphate alters the compositional characteristics of humic acid adsorbed onto goethite. J. Soils Sediment. 21, 3352–3366. doi: 10.1007/s11368-021-02973-4
Ma R., Hu F., Xu C., Liu J., Yu Z., Liu G., et al. (2023). Vegetation restoration enhances soil erosion resistance through decreasing the net repulsive force between soil particles. Catena 226, 10708. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2023.107085
Mahmoud E., Ibrahim M., Abd El-Rahman L., Khader A. (2019). Effects of biochar and phosphorus fertilizers on phosphorus fractions, wheat yield and microbial biomass carbon in Vertic Torrifluvents. Commun. Soil Sci. Plan. 50, 362–372. doi: 10.1080/00103624.2018.1563103
Mead R., Willey R. (1980). The concept of a ‘land equivalent ratio’and advantages in yields from intercropping. Exp. Agric. 16, 217–228. doi: 10.1017/S0014479700010978
Moura M., Silva B., Mota P., Borghi E., Resende A., Acua-Guzman S., et al. (2021). Soil management and diverse crop rotation can mitigate early-stage no-till compaction and improve least limiting water range in a ferralsol. Agr. Water Manage. 243, 106523. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2020.106523
Peng X., Dai Q., Ding G., Shi D., Li C. J., Research T. (2020). Impact of vegetation restoration on soil properties in near-surface fissures located in karst rocky desertification regions. Soil Till. Res. 200, 104620. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2020.104620
Qu J., Li L., Wang Y., Yang J., Zhao X. (2022). Effects of rape/common vetch intercropping on biomass, soil characteristics, and microbial community diversity. Fron. Environ. Sci. 10, 947014. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.947014
Seidel E., Reis W., Mottin M., Fey E., Schneider A., Sustakowski M. (2017). Evaluation of aggregate distribution and selected soil physical properties under maize jack bean intercropping and gypsum rates. Acad. Journals 12, 1209–1216. doi: 10.5897/AJAR2016.11642
Shi Q., Pang J., Yong J. W. H., Bai C., Guilherme Pereira C., Song Q., et al. (2020). Phosphorus-fertilisation has differential effects on leaf growth and photosynthetic capacity of Arachis hypogaea L. Plant Soil 447, 99–116. doi: 10.1007/s11104-019-04041-w
Su K., Mu L., Zhou T., Kamran M., Yang H. (2022). Intercropped alfalfa and spring wheat reduces soil alkali-salinity in the arid area of northwestern China. Plant Soil 499, 275–292. doi: 10.1007/s11104-022-05846-y
Tian X., Wang C., Bao X., Wang P., Li X., Yang S., et al. (2019). Crop diversity facilitates soil aggregation in relation to soil microbial community composition driven by intercropping. Plant Soil 436, 173–192. doi: 10.1007/s11104-018-03924-8
Wang Z., Bao X., Li X. (2015). Intercropping maintains soil fertility in terms of chemical properties and enzyme activities on a timescale of one decade. Plant Soil. 391, 265–282. doi: 10.1007/s11104-015-2428-2
Wang N., Wang T., Chen Y., Wang M., Lu Q., Wang K., et al. (2024). Microbiome convergence enables siderophore-secreting-rhizobacteria to improve iron nutrition and yield of peanut intercropped with maize. Nat. Commun. 15, 839. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45207-0
Wang Q., Wen J., Wen Y., Zhang Y., Zhang N., Wang Y., et al. (2021). Alteration of soil-surface electrochemical properties by organic fertilization to reduce dissolved inorganic nitrogen leaching in paddy fields. Soil Till. Res. 209, 104956. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2021.104956
Wu H., Chen S., Huang Z., Huang T., Tang X., He L., et al. (2024). Effects of intercropping and nitrogen application on soil fertility and microbial communities in peanut rhizosphere soil. Agronomy 14, 635. doi: 10.3390/agronomy14030635
Wu P., Zhao G., Liu F., Ahmad S., Fan T. L., Li S. Z., et al. (2021). Agronomic system for stabilizing wheat yields and enhancing the sustainable utilization of soil: a 12-year in-situ rotation study in a semi-arid agro-ecosystem. J. Clean. Prod. 329, 129768. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129768
Xu C., Li J., Xu R., Hong Z. (2017). Sorption of organic phosphates and its effects on aggregation of hematite nanoparticles in monovalent and bivalent solutions. Environ. Sci. pollut. R. 24, 7197–7207. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-8382-1
Yang Y., Wu J., Zhao S., Mao Y., Zhang J., Pan X., et al. (2021). Impact oflong-term sub-soiling tillage on soil porosity and soil physicalproperties in the soil profile. Land Degrad. Dev. 32, 2892–2905. doi: 10.1002/ldr.v32.10
Yang J., Zhou Y., Ye X., Liu E., Sun S., Ren X., et al. (2024). Continuous ridge-furrow film mulching enhances maize root growth and crop yield by improving soil aggregates characteristics in a semiarid area of China: An eight-year field experiment. Plant Soil 499, 173–191. doi: 10.1007/s11104-023-05953-4
Yu Y., Stomph T., Makowski D., van der Werf W. (2015). Temporal niche differentiation increases the land equivalent ratio of annual intercrops: A meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 184, 133–144. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2015.09.010
Yu Z., Zhang J., Zhang C., Xin X., Li H. (2017). The coupling effects of soil organic matter and particle interaction forces on soil aggregate stability. Soil Till. Res. 174, 251–260. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2017.08.004
Zan Z., Jiao N., Ma R., Wang J., Wang Y., Ning T., et al. (2023). Long-term maize intercropping with peanut and phosphorus application maintains sustainable farmland productivity by improving soil aggregate stability and P availability. Agronomy 13, 2846. doi: 10.3390/agronomy13112846
Zhang X., Wang Z., Wang Y., Tian X., He K., Chen Z., et al. (2025). Contribution of nitrogen to main cereal crops yield and the key drivers in China. Resour. Conser. Recy. 212, 107995. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2024.107995
Zhao X., Hao C., Zhang R., Jiao N., Tian J., Lambers H., et al. (2023). Intercropping increases soil macroaggregate carbon through root traits induced microbial necromass accumulation, Soil Biol. Biochem 185, 109146. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2023.109146
Zhou X., Wang Q., Zhang D., Mak-Mensah E., Zhao X., Xu Y., et al. (2023). Effects of ridge-furrow rainwater harvesting with biochar application on soil physical properties and alfalfa fodder yield in semiarid region in China. J. Soils Sediment. 23, 1008–1022. doi: 10.1007/s11368-022-03361-2
Zhou Z., Yang Y., Yang Y., Chang B., Yang X., Cao G., et al. (2024). Electrochemical mechanisms of Robinia pseudoacacia restoration affecting the interfacial reaction of base cations in loess hilly areas. Catena 243, 108143. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2024.108143
Keywords: intercropping system, phosphatic fertilizer, surface charge number, specific surface area, zeta potential
Citation: Ma R, Yu N, Zhao S, Kou T and Jiao N (2025) Effects of long-term maize/peanut intercropping and phosphorus application on soil surface electrochemical properties and crop yield. Front. Agron. 7:1535871. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2025.1535871
Received: 28 November 2024; Accepted: 11 March 2025;
Published: 25 March 2025.
Edited by:
Tariq Aziz, Faisalabad, PakistanReviewed by:
Ping Liao, Yangzhou University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Ma, Yu, Zhao, Kou and Jiao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Rentian Ma, MTM3MTEwNTYyNUBxcS5jb20=; Nianyuan Jiao, bmlhbnl1YW5qaWFvQGhhdXN0LmVkdS5jbg==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.