- 1Department of Agricultural Water Resources and Environment, Institute of Environment and Sustainable Development in Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Agriculture, Irrigation and Cooperatives, Kwimba District Council, Mwanza, Tanzania
- 3School of Materials, Energy, Water and Environmental Sciences, The Nelson Mandela African Institution of Science and Technology, Arusha, Tanzania
- 4School of Agriculture, Lovely Professional University, Punjab, India
Methods and procedures for measuring greenhouse gases vary in different aspects, which could dictate most of the decisions. Even within the same context of measurements, there are different techniques and procedures. This study presents a harmonized approach so that results from different studies are easily compared, and methods can be reproduced. The relevant literature on sampling has been discussed and used to establish consistency. The applied knowledge acquired during the two related field experiments, 2017-2018 and 2018-2019, has also been used to leverage the procedures. It was observed that the non-flow-through steady-state (closed or static chamber) method is the widely used method in the field for greenhouse gas measurements. Its chronological sampling’s main steps are anchor installation, upper part chamber placement, temperature recording, gas sample withdrawal, injecting the sample into the vial, flushing the syringe with air twice, upper chamber part removal from the anchor, and placement on the plot border beside the respective anchors. These leveraged procedures can ensure consistency in acquiring data for reliable results to help make informed decisions about greenhouse gas reductions.
1 Introduction
About 14% of the annual greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions are mainly from agriculture, and in developing countries, an additional 17% is induced through deforestation for the extension of agricultural land (Vermeulen et al., 2012; Pearson et al., 2017; Shakoor et al., 2020). The emissions are expected to mainly increase in developing countries from the current account of about three-quarters (Coady et al., 2019; Tubiello et al., 2021). It has also been reported that anthropogenic emissions globally, agricultural GHGs – methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) account for about 10 to 12% (Smith et al., 2008; Kasimir Klemedtsson et al., 2009; Eckard et al., 2010; Hu et al., 2012).
Increasing carbon sequestration in the soil and biomass can reduce agriculture`s contribution to climate change by 5.5 to 6.0 gigatons (Gt) of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2 eq) (Olander et al., 2013; Pant et al., 2023). Management practices trigger GHG emissions in agriculture; therefore, it is necessary to study the level of emissions in different agricultural management practices and bring forth the less emission practices yet provide optimal productivity. This can be of much importance to planners and policymakers in governing stakeholders toward efficient agricultural resource use and ensuring a resilient agricultural system (Olander et al., 2013). Due to these reasons, the quantification of GHGs has been of scientific attention for several years, and different methods have been developed and tested in various agricultural environmental conditions. These approaches are broadly grouped into micrometeorological and chamber categories (Denmead, 2008).
In the development, calibration, and validation of empirical and process-based models for quantification of GHG emissions at the farm scale and beyond, the chamber-based approach is the most used due to its adaptability, portability, cost-effectiveness regardless of the diverse agricultural environment and its surroundings (Sapkota et al., 2014). This method has been used for more than eight decades to estimate soil respiration (Peoples et al., 1995; Rochette and Eriksen-Hamel, 2008; Rochette et al., 2009). The chamber approach can quantify very small soil surface flux and applies to wide experimental objectives (Sapkota et al., 2014). More than 95% of the thousand published studies on the emission of N2O, in particular, used chamber methods (Venterea, 2013; Khalil et al., 2020). The chamber method can also be used for quantifying the impact of various treatments, but it has a few limitations regarding space coverage, time, and manual sampling. Due to the key aspects of chamber methodology, such as design, sampling frequency, storage time, and analytical procedures, the results from studies conducted by various researchers vary. However, they are from similar cropping systems and management practices. This makes it necessary to compare these studies and develop standard guidelines for manual chamber-based measurements. Despite improvements in measurement techniques, the manual chamber is the most widely used methodology at field plot scale, followed by automated. This study aimed to provide the leveraged procedures for sampling GHG emissions using the manual chamber method in field crops like rice, wheat, maize, chickpea, pineapple and other related crops or systems.
2 Materials and methods
To ensure precision for the desired location, the manual chamber anchor installation in the field is better placed right after the crop has been germinated. The chamber and components commonly use materials that do not react with GHGs or emit any contaminants, such as stainless steel, aluminum, polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polycarbonate, polyethylene, or polymethyl methacrylate, i.e., plexiglass, acrylic sheet (Parkin and Venterea, 2010; Clough and Nutbrown, 2012). To minimize internal heating from solar radiation, the preferred color is white or coated with a reflective material (Gorgolis and Karamanis, 2016). The components of the chamber include seals, tubing, septa, and vents (Clough et al., 2020). In the referenced experiment, the temperature was measured using a sensor probe (JM624, Jinming Instrument CO., LTD., Tianjin, China), inserted at the top of each chamber, and gas samples were analyzed using a gas chromatography system1 (Shimadzu CO., LTD., Kyoto, Japan), within 24 hours. The samples were kept in tightly sealed vials when the analysis was not conducted within 24 hours.
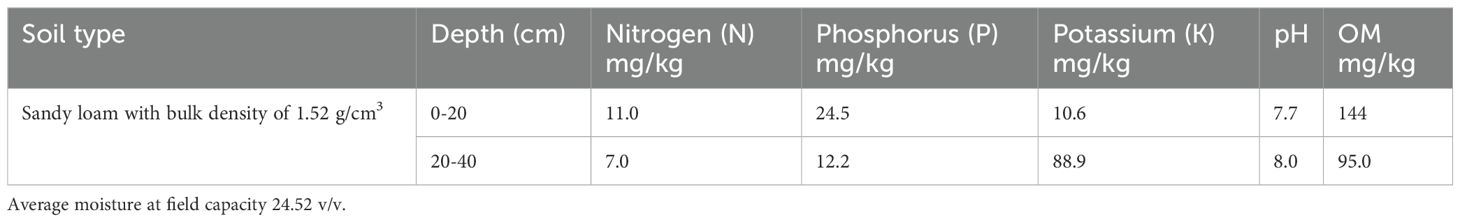
The soil physiochemical properties (Table 1) are from the referred wheat field experiment provided here for reference only.
2.1 Principles
The operating principle of the chamber method is the magnification of changes in the concentration of gas in the headspace, whereby restriction of the volume of air with gas exchange occurs (Denmead, 2008). The chamber method can be classified further into two categories (Rochette and Eriksen-Hamel, 2008): (i) open to the atmosphere (flow through or steady state) and (ii) closed to the atmosphere (non-flow-through or non-steady state). In a flow-through chamber, the difference in concentration between the air entering and leaving the headspace is measured, and a constant flow of outside air is maintained through the chamber’s headspace. Actual flux from the soil is calculated from the increase in concentration over time. The non-flow-through steady-state method, which is the most prominent method for GHG emission from the literature survey conducted, is commonly known as the static method (Bouwman et al., 2002; Rochette and Eriksen-Hamel, 2008; Clough et al., 2020).
2.2 Procedures
After the chamber is designed and constructed, an anchor should be inserted into the soil at least 8 cm deep during installation in the field, the remaining part being less than or equal to 5 cm close to the soil surface (Parkin and Venterea, 2010). During sampling, the chamber’s upper part should be placed and sealed onto the base using a water layer. After sampling, it should be removed until the next sampling day (Baram et al., 2022). Instead of using water, if necessary, the anchor and chamber upper part can be sealed using a rubber gasket (Parkin and Venterea, 2010). However, chamber anchors should not be removed except in cultivated systems; prior cultivation, planting, and fertilization, when removed, should be replaced at least 24 hours before sampling (Parkin and Venterea, 2010). The chamber environment should be checked regularly, ensuring similarity is maintained to reduce microclimate effects, possibly due to the permanent placement of chambers. In agricultural production systems, chamber placement and adaptation to the plants play an important role in flux determinations. If the main intention is to measure net trace gas flux from a particular production system, then ideally, some plants should be included inside the chambers during flux measurement; the object or context of the study acts as guidance as well.
To overcome a vertical gas concentration gradient during sampling (Parkin and Venterea, 2010), a gas sampling manifold should be used inside the chamber to draw headspace gas from four quadrants. Mixing headspace gas by pumping the syringe before sampling should be avoided, as it may cause pressure perturbations and/or excess dilution of headspace gas by entering outside air through the tube vent, as reported (Parkin and Venterea, 2010). Seedbed preparation can directly impact emissions. For example, row-cropping or raised bed planting cannot produce similar emissions, as inter-row gradients may lead to differences in soil, water, nutrient contents, and GHG emissions. Placing the chambers in rows and inter-row spaces/furrows is ideal. Otherwise, a larger chamber that considers both settings should be considered (Blanco-Canqui et al., 2008; Alexander, 2022).
Placement of the chamber on its base, headspace air cooling, or warming during sampling may create a pressure gradient (Davidson et al., 2002; Clough et al., 2020) or wind-driven turbulence. The venture effect may result from wind depressurizing the chamber by pulling air out of the chamber headspace, leading to the mass flow of the soil gases (Sapkota et al., 2014). The vent in the chamber close to the soil should be opened to correct the shortcomings. Sampling procedures should be consistent throughout the sampling season to minimize bias in the flux estimate and account for temporal and spatial variability of GHG emissions. Production and diffusion of gas can be impacted by compacting the soil by walking around for gas sampling and other measurements. Under moist soil that is eligible for compaction, it is recommended that the chamber be relocated periodically. The headspace gas sampling is done through a sampling port provision, which is inert, airtight, and made using butyl rubber septa. Sampling and storage work simultaneously start from the beginning of sampling and continue until analysis is undertaken. The gas samples from the chamber headspace are analyzed in the laboratory for trace gas concentration.
Site-specific diurnal variation studies can help establish the best time of day for sampling. Since soil temperature is influenced by surface residue retention, all plots should have a uniform amount of soil cover; otherwise, the mean daily temperature for the plots with more surface residue should be determined separately, and if possible, their sampling time should be rescheduled separately.
If gas-tight syringes are used for sample collection, gas samples can be stored in the syringes themselves for the short term, but it is expensive (Kammann et al., 2001; Capone, 2018; Harvey et al., 2020). However, this can be an expensive option. The glass vials (exetainers) sealed with rubber septa are mostly used for storing gases as they are non-reactive to greenhouse gases. Before sampling, the glass vial should be evacuated. This is mostly done through a vial evacuation manifold of the pump, vacuum gauge, valve, and needles. Alternatively, chamber headspace gas can be used to evacuate the vials by flushing four times backward and forward before sampling and then continuing with regular sampling (de Klein et al., 2003; Harvey et al., 2020). To avoid the incursion of ambient air into the vials during storage, vials can be over-pressurized by inserting a higher volume of gas sample than the actual size (Harvey et al., 2020). Proper storage should be followed after sampling to avoid contamination of the sample due to leakage; otherwise, analysis should be performed immediately. However, air-tight sealed samples can be stored for a longer period. Such as with butyl rubber containers stored at 10 ppm N2O for up to 126 days without significant loss in N2O concentration (Harvey et al., 2020).
The rate of change of trace gas concentration in the chamber headspace when its gradient is computed results in the fluxes estimates. Considering the available resources and linear increase of headspace gases over time, more than one sample at different intervals should be collected because the higher the number of samples, the better the flux estimate of a plot or station. Thus, to obtain a quality flux, Chadwick et al. (2014) suggested that four or more gas samples should be taken in one plot. By inserting a polypropylene syringe into the chamber septa and slowly removing the gas sample, an amount of 5-50 ml should be withdrawn, depending on the analytical method.
The field wheat crop was subjected to 3 irrigation treatments (0 mm, 40 mm and 120 mm) and 2 different nitrogen rates (157.5 Nkg and 315 Nkg) with 3 replications in the referred experiment. Thus, 6 x 3 randomized complete block design (RCBD) in a split-plot arrangement with 18 treatment combinations. Whereby irrigation factor came under main plot (Block 1 to Block 3) and nitrogen factor with the two doses under sub-plots on each irrigation treatment as per Figure 1.
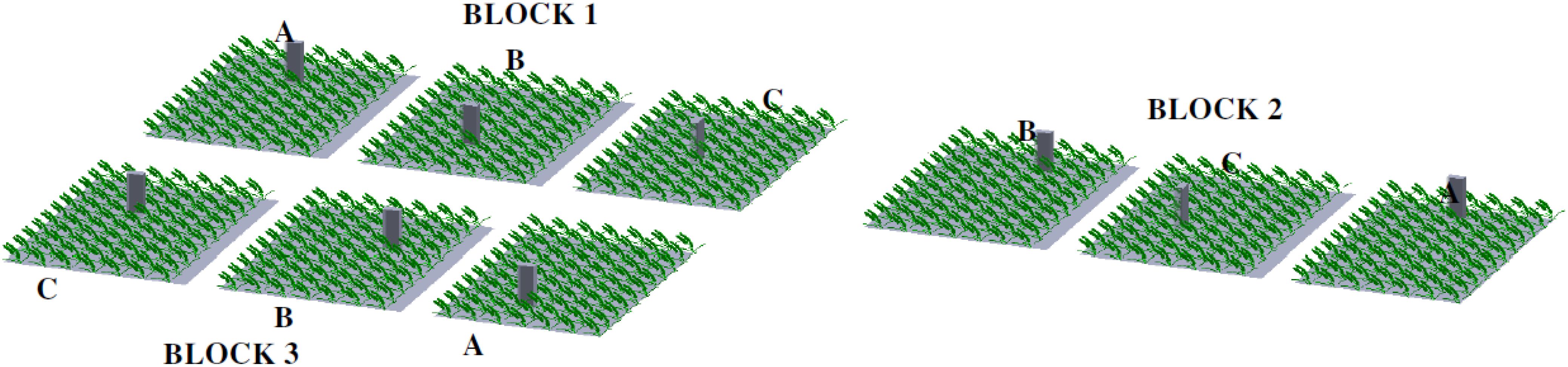
Figure 1. A schematic diagram illustrating the collection of gas samples through a manual chamber in a wheat field. (A) 0 - irrigation (B) 1 - irrigation (C) 3 - irrigation.
Sampling was conducted between 8:00 and 12:00 am local time for all treatments to measure GHG emissions using the field’s manual closed chamber method (Zhao et al., 2009). The gas samples were drawn from chambers with 100 ml nylon syringes through a three-way stopcock attachment at 0, 15, 30, and 45 minutes. In each of the 18 plots, chamber anchors were permanently placed right after wheat germination, and sampling was performed immediately. The chamber’s upper parts were laid along the plot border beside each anchor. A few minutes before sampling, vials and syringes were placed at each sampling spot, and temperature probes were installed permanently at the top of each chamber’s upper part. The detailed leveraged systematic sampling procedures for trace gas flux sampling were used (Parkin and Venterea, 2010), and our field experience is as follows;
Take one (1) ambient air gas sample (from the air)
a) Place all chamber upper parts on their anchors (vent facing downwind).
b) Start the stopwatch.
c) Sample gas at time equal to zero (t = 0) at the 1st plot only.
d) Start sampling at 1st plot when stopwatch time is at 15min.
e) Record temperature (T1).
f) Withdraw three (3) samples of 10 ml gas.
g) Inject the sampled gases into the glass vial, which has been previously evacuated and sealed with a butyl rubber septum for storage.
h) Flush the syringe with air twice.
i) Proceed to 2nd chamber.
j) Record the temperature (T2).
k) Withdraw three (3) sample of 10 ml gas.
l) Inject the sample into the vial.
m) Flush the syringe with air twice.
n) Repeat the procedure letter e to h consecutively for plots (anchors) from 3rd to 18th within the shortest time possible.
o) When 18 plots are completed, do not remove the chambers from the anchor; wait for the stopwatch to reach 30 minutes, then start the next round.
p) Repeat from letter d to n with sampling times at 30 minutes (t2 = 30 min) and 45 minutes (t3 = 45 min) for all the plots.
q) After all plots have been done with t1, t2, and t3, remove the upper part chambers and place them on the plot border beside the respective anchors until the next sampling day.
r) Collect all the sampled gases into a general cool container and carry them to the laboratory for analysis.
2.3 Specifications
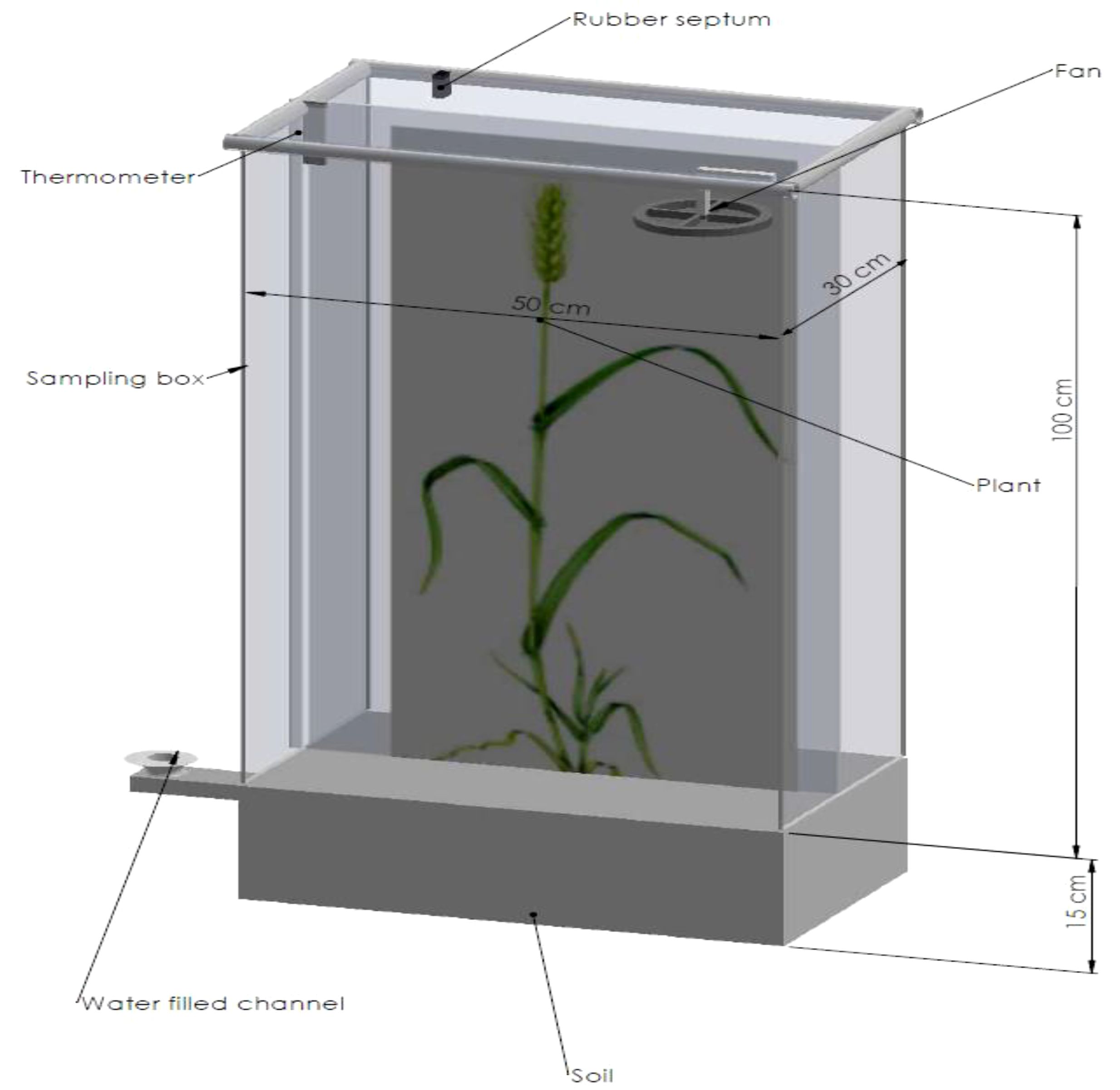
The main chamber is divided into two parts (Baram et al., 2022). The upper part should have an appropriate height and size to cover at least 175 cm2 according to the crops to be included; this will maximize flux detection and minimize perturbation of the environmental variables (Pihlatie et al., 2013; Sapkota et al., 2014). It should be noted that as chamber height increases, temperature, humidity, and gas concentration as environmental variables sensitivity get reduced (Fang et al., 2010; Li et al., 2010; Both et al., 2015). The dimensions of the chambers used in the study for winter wheat in North China were suggested by Fang et al. (2010) and Li et al. (2010). The fabrication of chambers can be done locally, provided the basic construction requirements are met. This can help reduce costs and still obtain satisfactory results (Friedrich and Gustafson, 2007; Jain et al., 2015). Selecting the appropriate size of the chamber, number, place to install, time of the day to take samples, and sampling frequency reduces the temporal and spatial variability of fluxes. Figure 2 is the ideal representation of a rectangular manual chamber.
Including plants may increase chamber height, resulting in reduced sensitivity. To improve this, the chamber closure period can be extended. The time of closure is essential for flux estimate; the longer the time, the better it is; for a chamber with a maximum height of 20 cm, a closure of 30 to 40 minutes was recommended (Alves et al., 2012; Chadwick et al., 2014; Charteris et al., 2020; Martins et al., 2021). Generally, the chamber height to closure time ratio should be ≥ 40 cm per hour (Rochette and Eriksen-Hamel, 2008). Apart from the plant’s height, another reason for the possibility of increasing chamber height is the headspace at the crop canopy for fans, which have been used to mix air in closed chambers to overcome possible bias from vertical gas concentration gradients (Clough et al., 2020).
The period of the day when the GHG emissions are expected to be at their peak is the best time to compare the short-term emissions differences among the treatments. Between 9 a.m. and 12 p.m. in April, the maximum CO2 emissions from maize and chickpeas in Northwest India were observed (Sapkota et al., 2014). However, daily flux is measured by using points in time measurement, and the ideal time for measurement could be the time of the day when the flux is determined to be equal to its daily mean. This is because soil temperature controls the GHG emissions from soil (Dalal et al., 2008; Livesley et al., 2010; Schaufler et al., 2010). The average daily flux can be attained when the soil temperature in the plough layer is close to its daily mean temperature (Laville et al., 2011). In New Delhi, India, several studies have suggested that the time between 10 am and 12 noon reflects the diurnal mean range (DMR) average (Parihar et al., 2018).
Further, other factors like rainfall and farm operations such as tillage, fertilization, and irrigation greatly influence GHG emissions. For instance, after soil disturbance, rainfall, or irrigation and fertilization, nitrous oxide emissions, in particular, peaks are observed and can last from a few hours to a few weeks (Bouwman et al., 2002). When no event influences emissions and normal growing season, gas sampling can be done once a week, while after events, that influence should be taken more frequently (Sass et al., 1992; Kallenbach et al., 2010). In the referred experiment, one week before and until the emission drops to its daily mean, the measurements were taken daily. This ensured that the interpolation of the pre- and post-event emissions was reliable and did not underestimate or overestimate emissions.
3 Results and discussion
Soil gas flux can also be affected by fan speed, position, and mixing rate; thus, further data are required, especially on the systematic evaluation of systems containing tall plants to establish best practices (Clough et al., 2020). Generally, stable isotope techniques are the most accurate methods for measuring GHGs as they allow process-specific quantification but require sophisticated and expensive equipment (Mumu et al., 2024). Another aspect of GHG assessment accuracy is using high-quality known standards; this ensures accuracy and comparability between laboratories (Harvey et al., 2020). An ideal single standard protocol for all three major GHGs (CO2, CH4, and NO2), from chamber design to data reporting, would be a consolidation of present knowledge from the best practices (Fiedler et al., 2022). Estimating differences between treatments and exploring systems dynamics over systems over seasons or years using a comprehensive experimental design is essential in conforming to established guidelines (Collier et al., 2014). Moreover, where fluxes are exceptionally spatially variable, such that heterogeneous agricultural landscapes like woody grazed pastures, deploying more chambers with fewer headspace samples per chamber may be beneficial (Charteris et al., 2020). Similarly, increasing chamber sampling frequency will improve accuracy and reduce the uncertainty of temporally interpolated N2O for flux induced due to irrigation or freeze-thaw cycles. The detailed substantiated protocols and recommendations focused on manual chamber method are presented in Table 2.
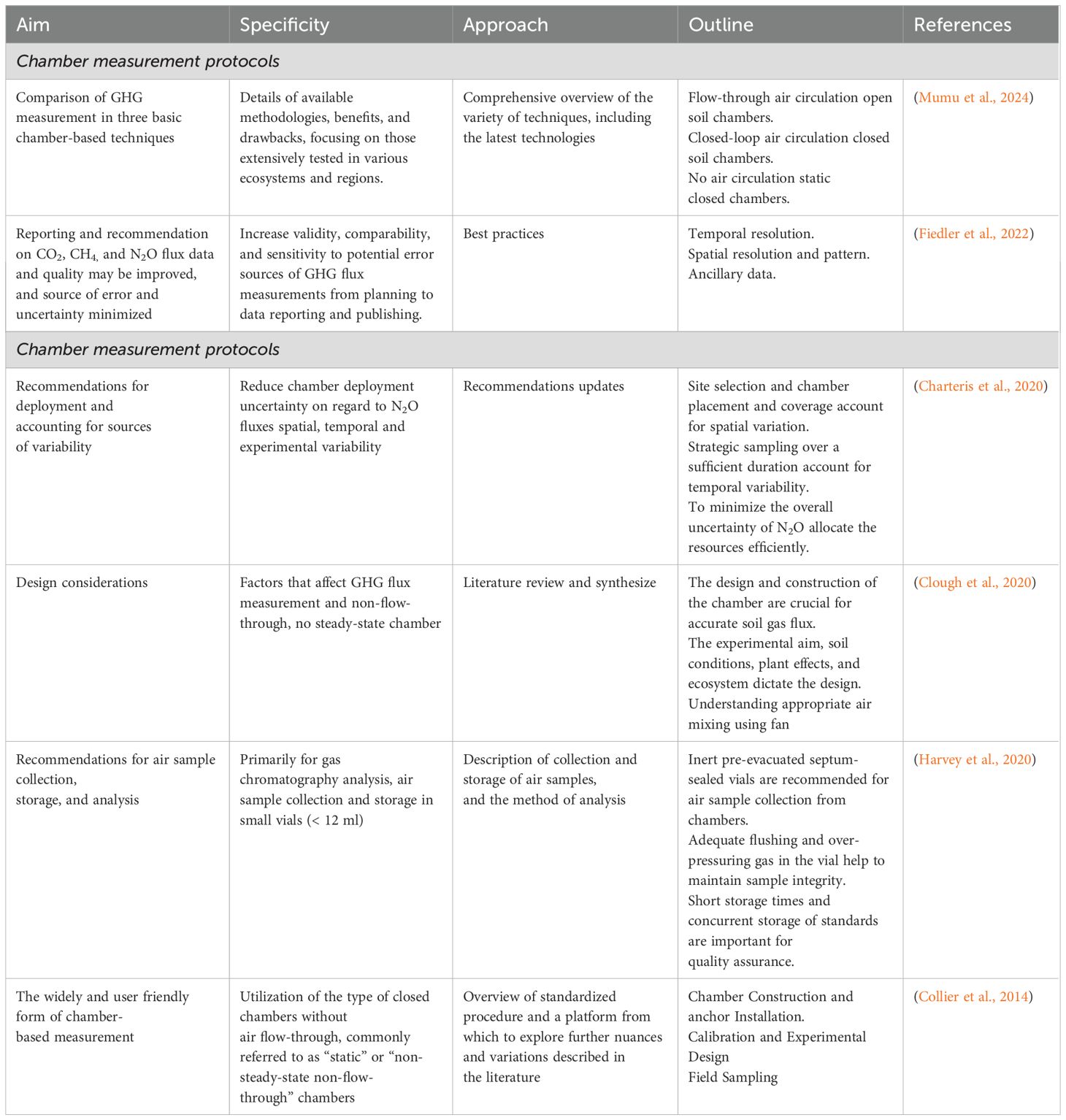
Table 2. Literature highlight on measurements of GHGs emissions using static manual chamber methodology.
According to Bain et al. (2005), CO2 fluxes exceeded a factor of 2 in response to wind events for vented chambers. Xu et al. (2006) presented a new vent design to avoid overestimating CO2 fluxes under windy conditions due to the venture effect. The timing of measurements and sampling frequency affect the flux. According to Parkin (2008), sampling once every 21 days yielded estimates within - 40 to + 60% of the actual cumulative flux. However, manual chambers daily overestimated seasonal N2O and CH4 fluxes by 18 to 31% because diurnal variation in fluxes was not accounted for; on the other hand, automated chambers reduced soil moisture due to unchanged chamber position (Yao et al., 2009). When sampling CH4 between 1800 and 0800 hr, intervals < 7 days (Wood et al., 2013), measurements yielded ± 10% deviation, and for N2O was 50% when sampling at 2000 hr. Changing the position is recommended to avoid soil moisture reduction when using an automated chamber, and diurnal variations should be accounted for when using a manual chamber.
4 Conclusion
Greenhouse gas emission sampling must be optimized to minimize the uncertainties in flux estimation arising from temporal and spatial variation. Currently, resources are most limited when the number of chambers and sampling frequencies are to be increased to account for spatial and temporal variability. Optimization can be achieved through the verified methods and recommendations in each GHG emissions sampling context. For example, taking at least three samples in each chamber for adequate quality assessment of the calculated flux, sampling each round within the shortest time possible before the next round. Also, change the sampling route, starting from first to last and vice versa on each day or for each round, to minimize temporal variation. Accurate GHG measurement can help policymakers make informed decisions and policies on greenhouse gas reduction.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
TM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. LX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. MM: Validation, Writing – review & editing. RG: Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The study was supported by the China National Key Research and Development Program (2023YFD1900503).
Acknowledgments
The authors greatly acknowledge Abdallah Ally Abdallah for drawing Figures 1 and 2. The authors gratefully acknowledge the in-kind support from the institutions or partners of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, and individuals consulted at all stages of the study. The Institute of Environmental and Sustainable Development in Agriculture (IEDA) hosted the research trials and provided its laboratory space for analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
- ^ https://www.shimadzu.com/an/products/gas-chromatography/application-specific-system-gc/transformer-oil-gas-analysis/index.html
References
Alexander J. R. (2022). Management Considerations for Maize in Kura Clover Living Mulch. St. Paul, MN, USA: University of Minnesota.
Alves B. J. R., Smith K. A., Flores R. A., Cardoso A. S., Oliveira W. R. D., Jantalia C. P., et al. (2012). Selection of the most suitable sampling time for static chambers for the estimation of daily mean N2O flux from soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 46, 129–135. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.11.022
Bain W. G., Hutyra L., Patterson D. C., Bright A. V., Daube B. C., Munger J. W., et al. (2005). Wind-induced error in the measurement of soil respiration using closed dynamic chambers. Agric. For. Meteorol. 131, 225–232. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2005.06.004
Baram S., Bar-Tal A., Gal A., Friedman S. P., Russo D. (2022). The effect of static chamber base on N 2 O flux in drip irrigation. Biogeosciences 19, 3699–3711. doi: 10.5194/bg-19-3699-2022
Blanco H., Lal R. (2008). Cropping systems. Principles of soil conservation and management (New York: Springer) 167169, 165–193. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-8709-7
Both A.-J., Benjamin L., Franklin J., Holroyd G., Incoll L. D., Lefsrud M. G., et al. (2015). Guidelines for measuring and reporting environmental parameters for experiments in greenhouses. Plant Methods 11, 1–18. doi: 10.1186/s13007-015-0083-5
Bouwman A. F., Boumans L. J. M., Batjes N. H. (2002). Emissions of N2O and NO from fertilized fields: Summary of available measurement data. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 16, 1–6. doi: 10.1029/2001GB001811
Capone D. G. (2018). Determination of nitrogenase activity in aquatic samples using the acetylene reduction procedure. In Handbook of methods in aquatic microbial ecology (CRC Press), 621–631.
Chadwick D. R., Cardenas L., Misselbrook T. H., Smith K. A., Rees R. M., Watson C. J., et al. (2014). Optimizing chamber methods for measuring nitrous oxide emissions from plot-based agricultural experiments. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 65, 295–307. doi: 10.1111/ejss.2014.65.issue-2
Charteris A. F., Chadwick D. R., Thorman R. E., Vallejo A., de Klein C. A. M., Rochette P., et al. (2020). Global Research Alliance N2O chamber methodology guidelines: Recommendations for deployment and accounting for sources of variability. J. Environ. Qual. 49, 1092–1109. doi: 10.1002/jeq2.20126
Clough T. J., Rochette P., Thomas S. M., Pihlatie M., Christiansen J. R., Thorman R. E. (2020). Global Research Alliance N2O chamber methodology guidelines: Design considerations. J. Environ. Qual. 49, 1081–1091. doi: 10.1002/jeq2.20117
Coady M. D., Parry I., Le N.-P., Shang B. (2019). Global fossil fuel subsidies remain large: An update based on country-level estimates. Int. Monetary Fund. doi: 10.5089/9781484393178.001
Collier S. M., Ruark M. D., Oates L. G., Jokela W. E., Dell C. J. (2014). Measurement of greenhouse gas flux from agricultural soils using static chambers. Journal of visualized experiments: JoVE (90), 52110. doi: 10.3791/52110
Dalal R. C., Allen D. E., Livesley S. J., Richards G. (2008). Magnitude and biophysical regulators of methane emission and consumption in the Australian agricultural, forest, and submerged landscapes: a review. Plant Soil 309, 43–76. doi: 10.1007/s11104-007-9446-7
Davidson E. A., Savage K., Verchot L. V., Navarro R. (2002). Minimizing artifacts and biases in chamber-based measurements of soil respiration. Agric. For. Meteorol. 113, 21–37. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1923(02)00100-4
de Klein C. A. M., Barton L., Sherlock R. R., Li Z., Littlejohn R. P. (2003). Estimating a nitrous oxide emission factor for animal urine from some New Zealand pastoral soils. Soil Res. 41, 381–399. doi: 10.1071/SR02128
Denmead O. T. (2008). Approaches to measuring fluxes of methane and nitrous oxide between landscapes and the atmosphere. Plant Soil 309, 5–24. doi: 10.1007/s11104-008-9599-z
Eckard R. J., Grainger C., De Klein C. A. M. (2010). Options for the abatement of methane and nitrous oxide from ruminant production: A review. Livestock Sci. 130, 47–56. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2010.02.010
Fang H. J., Yu G. R., Cheng S. L., Zhu T. H., Wang Y. S., Yan J. H., et al. (2010). Effects of multiple environmental factors on CO 2 emission and CH 4 uptake from old-growth forest soils. Biogeosciences 7, 395–407. doi: 10.5194/bg-7-395-2010
Fiedler J., Fuß R., Glatzel S., Hagemann U., Huth V., Jordan S., et al. (2022). Measurement of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide fluxes between 1–70. doi: 10.23689/fidgeo-5422
Friedrich T., Gustafson D. (2007). Conservation agriculture: synergies of resource-conserving technologies in rice-based systems. Articulos Gen.
Gorgolis G., Karamanis D. (2016). Solar energy materials for glazing technologies. Solar Energy Mater. Solar Cells 144, 559–578. doi: 10.1016/j.solmat.2015.09.040
Harvey M. J., Sperlich P., Clough T. J., Kelliher F. M., McGeough K. L., Martin R. J., et al. (2020). Global Research Alliance N2O chamber methodology guidelines: Recommendations for air sample collection, storage, and analysis. J. Environ. Qual. 49, 1110–1125. doi: 10.1002/jeq2.20129
Hu Z., Lee J. W., Chandran K., Kim S., Khanal S. K. (2012). Nitrous oxide (N2O) emission from aquaculture: a review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46, 6470–6480. doi: 10.1021/es300110x
Jain N., Bhatia A., Pathak H., Gupta N., Sharma D. K., Kaushik R. (2015). Greenhouse gas emission and global warming. Introduction to environmental sciences, 379–411.
Kallenbach C. M., Rolston D. E., Horwath W. R. (2010). Cover cropping affects soil N2O and CO2 emissions differently depending on type of irrigation. Agricult. Ecosyst. Environ. 137, 251–260. doi: 10.1016/j.agee.2010.02.010
Kammann C., Grünhage L., Jäger H. (2001). A new sampling technique to monitor concentrations of CH4, N2O and CO2 in air at well-defined depths in soils with varied water potential. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 52, 297–303. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2389.2001.00380.x
Kasimir Klemedtsson Å., Weslien P., Klemedtsson L. (2009). Methane and nitrous oxide fluxes from a farmed Swedish Histosol. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 60, 321–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.2009.01124.x
Khalil M. I., Islam S. F., O’Neill M., Osborne B. (2020). Measuring and quantifying greenhouse gas emissions from agricultural activities. In Climate change and agriculture (Burleigh Dodds Science Publishing), 195–272.
Laville P., Lehuger S., Loubet B., Chaumartin F., Cellier P. (2011). Effect of management, climate and soil conditions on N2O and NO emissions from an arable crop rotation using high temporal resolution measurements. Agric. For. Meteorol. 151, 228–240. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2010.10.008
Li F., Zhang H., Jia L., Bareth G., Miao Y., Chen X. (2010). Estimating winter wheat biomass and nitrogen status using an active crop sensor. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 16, 1221–1230.
Livesley S. J., Dougherty B. J., Smith A. J., Navaud D., Wylie L. J., Arndt S. K. (2010). Soil-atmosphere exchange of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide in urban garden systems: impact of irrigation, fertiliser and mulch. Urban Ecosyst. 13, 273–293. doi: 10.1007/s11252-009-0119-6
Martins M. R., Sarkis L. F., Guareschi R. F., Santos C. A., Sant’Anna S. A. C., Zaman M., et al. (2021). A simple and easy method to measure ammonia volatilization: accuracy under field conditions. Pedosphere 31, 255–264. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0160(20)60077-7
Mumu N. J., Ferdous J., Müller C., Ding W. (2024). Methodological progress in the measurement of agricultural greenhouse gases. Carbon Manage. 15 (1), 2366527. doi: 10.1080/17583004.2024.2366527
Olander L., Wollenberg E., Tubiello F., Herold M. (2013). Advancing agricultural greenhouse gas quantification. Environ. Res. Lett. 8, 11002. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/8/1/011002
Pant D., Shah K. K., Sharma S., Bhatta M., Tripathi S., Pandey H. P., et al. (2023). Soil and ocean carbon sequestration, carbon capture, utilization, and storage as negative emission strategies for global climate change. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 23, 1421–37. doi: 10.1007/s42729-023-01215-5
Parihar C. M., Parihar M. D., Sapkota T. B., Nanwal R. K., Singh A. K., Jat S. L., et al. (2018). Long-term impact of conservation agriculture and diversified maize rotations on carbon pools and stocks, mineral nitrogen fractions and nitrous oxide fluxes in inceptisol of India. Sci. Total Environ. 640, 1382–1392. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.05.405
Parkin T. B. (2008). Effect of sampling frequency on estimates of cumulative nitrous oxide emissions. Journal of environmental quality 37(4), 1390–1395. doi: 10.2134/jeq2007.0333
Parkin T. B., Venterea R. T. (2010). “USDA-ARS GRACEnet Project Protocols chapter 3,” in Chamber-Based Trace Gas Flux Measurements (Washington DC: United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service), vol. 4.
Pearson T. R. H., Brown S., Murray L., Sidman G. (2017). Greenhouse gas emissions from tropical forest degradation: an underestimated source. Carbon Balance Manage. 12, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13021-017-0072-2
Peoples M. B., Freney J. R., Mosier A. R. (1995). Minimizing gaseous losses of nitrogen. Nitrogen Fertil. Environ., 565–602.
Pihlatie M. K., Christiansen J. R., Aaltonen H., Korhonen J. F. J., Nordbo A., Rasilo T., et al. (2013). Comparison of static chambers to measure CH4 emissions from soils. Agric. For. Meteorol. 171, 124–136. doi: 10.1016/j.agrformet.2012.11.008
Rochette P., Angers D. A., Chantigny M. H., MacDonald J. D., Gasser M.-O., Bertrand N. (2009). Reducing ammonia volatilization in a no-till soil by incorporating urea and pig slurry in shallow bands. Nutrient Cycling Agroecosys. 84, 71–80. doi: 10.1007/s10705-008-9227-6
Rochette P., Eriksen-Hamel N. S. (2008). Chamber measurements of soil nitrous oxide flux: are absolute values reliable? Soil Sci. Soc. America J. 72, 331–342. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2007.0215
Sapkota T. B., Rai M., Singh L. K., Gathala M. K., Jat M. L., Sutaliya J. M., et al. (2014). Greenhouse gas measurement from smallholder production systems: guidelines for static chamber method. International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi, India. p. 18.
Sass R. L., Fisher F. M., Wang Y. B., Turner F. T., Jund M. F. (1992). Methane emission from rice fields: the effect of floodwater management. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 6, 249–262. doi: 10.1029/92GB01674
Schaufler G., Kitzler B., Schindlbacher A., Skiba U., Sutton M. A., Zechmeister-Boltenstern S. (2010). Greenhouse gas emissions from European soils under different land use: effects of soil moisture and temperature. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 61, 683–696. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.2010.01277.x
Shakoor A., Ashraf F., Shakoor S., Mustafa A., Rehman A., Altaf M. M. (2020). Biogeochemical transformation of greenhouse gas emissions from terrestrial to atmospheric environment and potential feedback to climate forcing. Environ. Sci. pollut. Res. 27, 38513–38536. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10151-1
Smith P., Martino D., Cai Z., Gwary D., Janzen H., Kumar P., et al. (2008). Greenhouse gas mitigation in agriculture. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B: Biol. Sci. 363, 789–813. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2007.2184
Tubiello F. N., Rosenzweig C., Conchedda G., Karl K., Gütschow J., Xueyao P., et al. (2021). Greenhouse gas emissions from food systems: building the evidence base. Environ. Res. Lett. 16, 65007. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/ac018e
Venterea R. T. (2013). Theoretical comparison of advanced methods for calculating nitrous oxide fluxes using non-steady state chambers. Soil Sci. Soc. America J. 77, 709–720. doi: 10.2136/sssaj2013.01.0010
Vermeulen S. J., Campbell B. M., Ingram J. S. I. (2012). Climate change and food systems. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 37, 195–222. doi: 10.1146/annurev-environ-020411-130608
Wood J. D., Gordon R. J., Wagner-Riddle C. (2013). Biases in discrete CH4 and N2O sampling protocols associated with temporal variation of gas fluxes from manure storage systems. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 171, 295–305.
Xu L., Furtaw M. D., Madsen R. A., Garcia R. L., Anderson D. J., McDermitt D. K. (2006). On maintaining pressure equilibrium between a soil CO2 flux chamber and the ambient air. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 111(D8). doi: 10.1029/2005JD006435
Yao Z., Zheng X., Xie B., Liu C., Mei B., Dong H., et al. (2009). Comparison of manual and automated chambers for field measurements of N2O, CH4, CO2 fluxes from cultivated land. Atmos. Environ. 43, 1888–1896. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2008.12.031
Keywords: gas chromatography, in-situ, quantification, accuracy, greenhouse gases reduction
Citation: Mazengo TER, Zhong X, Liu X, Mwema MF and Gill R (2024) Non-flow-through static (closed chamber) method for sampling of greenhouse gases in crop production systems. Front. Agron. 6:1464495. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2024.1464495
Received: 14 July 2024; Accepted: 25 November 2024;
Published: 23 December 2024.
Edited by:
Rajiv Kumar Srivastava, Texas A and M University, United StatesReviewed by:
Ali Yetgin, Toros Agri Industry and Trade Co. Inc., TürkiyeKanu Murmu, Bidhan Chandra Krishi Viswavidyalaya, India
Subrat Kumar Behera, Orissa University of Agriculture and Technology, India
Copyright © 2024 Mazengo, Zhong, Liu, Mwema and Gill. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoying Liu, bGl1eGlhb3lpbmdAY2Fhcy5jbg==
†ORCID: Tumaini Erasto Robert Mazengo, orcid.org/0000-0002-3283-1007
Liu Xiaoying, orcid.org/0000-0003-4593-3114
Mwema Felix Mwema, orcid.org/0009-0007-1084-2497
Rubina Gill, orcid.org/0000-0002-2888-785X
Xuili Zhong, orcid.org/0000-0002-3298-4855
 Tumaini Erasto Robert Mazengo
Tumaini Erasto Robert Mazengo Xiuli Zhong1†
Xiuli Zhong1† Xiaoying Liu
Xiaoying Liu Rubina Gill
Rubina Gill