- 1Department of Soil and Geological Sciences, College of Agriculture, Sokoine University of Agriculture, Morogoro, Tanzania
- 2Department of Crop Science and Horticulture, College of Agriculture, Sokoine University of Agriculture, Morogoro, Tanzania
Plastic waste in agriculture, particularly from polyethylene mulch, poses significant environmental challenges. Synthetic biodegradable mulch has emerged as a sustainable alternative, derived from renewable resources such as thermoplastic starch, polylactic acid, polyhydroxyalkanoates, and copolyesters. This review explores the benefits of synthetic biodegradable mulch, its environmental impact, and the policy landscape to support its adoption. A review of existing literature was conducted, focusing on three aspects: (1) the performance of synthetic biodegradable mulch in crop production and pest control, (2) the environmental, socioeconomic, and climate resilience compared to polyethylene mulch, and (3) the institutional policies that promote synthetic biodegradable mulch adoption. The analysis considered comparative data on yield, pest management, and sustainability metrics. Synthetic biodegradable mulch performs similarly or better than polyethylene mulch in various agricultural practices. It enhances crop yield, quality, and weed suppression, acts as a physical barrier against pests and diseases, reduces chemical usage, and aids in water and nutrient management. Moreover, synthetic biodegradable mulch offers environmental benefits by reducing plastic waste, microplastic pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change mitigation. While synthetic biodegradable mulch provides numerous advantages, adoption faces challenges such as high initial costs, farmer preferences, and the regulatory framework. Effective institutional policies and increased consumer demand could drive wider adoption, offering potential for improved livelihoods among small farmers while promoting environmental sustainability.
1 Introduction
Mulching, a well-established agricultural practice, involves directly applying materials onto soil surfaces for purposes such as safeguarding seedlings, minimizing evaporation, controlling weeds, and enhancing the aesthetic appeal of an area (Chalker-Scott, 2007; Mhlanga et al., 2021; Abbate et al., 2023). The mulches are instrumental in protecting delicate crops from adverse conditions caused by weather, pests, and weeds. Widely employed in agriculture, they are crucial tools for preventing crop yield loss (Mansoor et al., 2022). Mulching fosters economic and environmental sustainability by improving crop yields, reducing water usage, and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. This is achieved through decreased soil respiration and a diminished need for synthetic fertilizers, which typically have a high carbon footprint (Guo and Liu, 2022).
Mulching history dates back to around 500 BCE, with the earliest documented use of organic matter as a mulch film (Lightfoot, 1994). Over time, materials evolved from organic matter to stones, pebbles, and volcanic ash, particularly in arid regions during the 1600s (Mansoor et al., 2022). According to Mansoor et al. (2022), in the 1800s, straw was discovered as beneficial mulch for strawberry production. Throughout centuries, various naturally available materials have been experimented with and utilized for mulching based on climatic conditions in different parts of the world (Lightfoot, 1994). After the World War II, plastic was started to be used to avoid the high costs of glass, employed as a traditional material in greenhouses (Kasirajan and Ngouajio, 2012). The use of plastic mulch in agriculture, especially polyethylene, was commercialized in the late 1950s, marking a significant transformation in mulching practices (Kader et al., 2017). The negative effects of plastic mulching, including the creation of microplastics, led to the introduction of photodegradable and Oxo degradable plastics as alternatives to polyethylene in the 1980s. However, there is evidence that photo- and oxo-degradable plastic polymers do not degrade under field conditions and their generated microplastics (Steinmetz et al., 2016).
The international community has formulated a set of Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), with the objective of achieving various targets by 2030 (United Nations, 2015). Among these goals is ensuring access to food for all, increasing agricultural productivity, and attaining the eradication of hunger (Bizikova et al., 2020). One of the key objectives of these goals is to enhance agricultural productivity in a sustainable, manageable, and effective manner. The central focus is on increasing yields of food crops through the adoption of farming practices that are environmentally friendly and ecologically viable (Samphire et al., 2023). The use of mulching as a strategy to improve crop yield and prevent losses is a common practice in agriculture worldwide, and various materials have been used as mulch, each with its own advantages and disadvantages in the environment. Biodegradable plastic mulch, developed from fossil fuels, microorganisms, animals, and plants, is considered a viable option for mulching material (Sintim and Flury, 2017).
The industry-specific data on synthetic biodegradable mulch are categorized into three main areas: agriculture, environmental impact, and regulatory policies. In agriculture, this mulch is used to cover soil, reduce weeds, retain moisture, and boost crop yields, with common types including Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), Polylactic Acid (PLA), and starch-based films. These materials must meet standards like ASTM D6400 or EN 13432 for certification (Abbate et al., 2023; Hayes et al., 2012; Menossi et al., 2021). Although synthetic biodegradable mulch has a higher initial cost than conventional plastic mulch, it reduces long-term labor and disposal expenses (Mansoor et al., 2022). Synthetic biodegradable mulch is available on the market and is diverse and competitive with a large number of suppliers (Table 2). Environmentally, these mulches decompose into water, CO2, and biomass, significantly reducing plastic waste and the need for disposal (de Sadeleer and Woodhouse, 2023). This aligns with the increasing market growth driven by environmental awareness and regulations, especially in Europe and North America (Soylu and Kizildeniz, 2024; Mansoor et al., 2022). Regulatory policies play a crucial role, with government incentives supporting the adoption of biodegradable products, and compliance with biodegradability and environmental safety standards being essential for both manufacturers and farmers (Menossi et al., 2021).
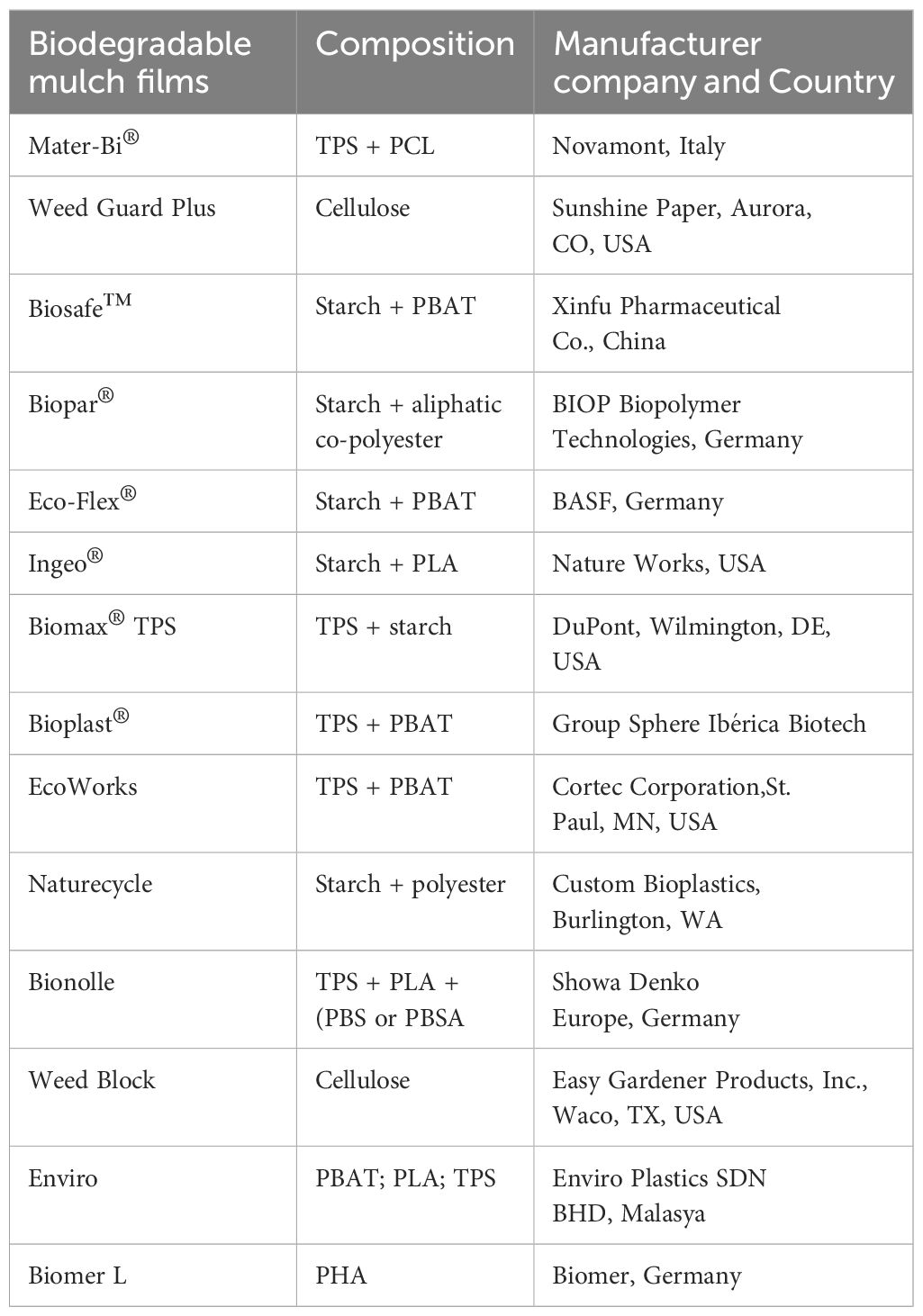
Table 2. Major players of biodegradable mulch polymers in Market (Serrano-Ruiz et al., 2018; Menossi et al., 2021; Mansoor et al., 2022; Campanale et al., 2023).
Biodegradable mulching materials originate from various sources, including food, animals, agriculture, and bio-based resources such as starch and cellulose (Samir et al., 2022). Synthetic biodegradable mulch is made from bio-based, fossil fuel-derived raw materials, or a combination of both. Bio-based polymers are classified into three categories: (1) those directly obtained from natural materials such as starch, thermoplastic starch, and cellulose; (2) those produced through chemical synthesis from biologically derived monomers, such as the synthetic polymerization of lactic acid to polylactic acid (Table 1); and (3) those produced by microorganisms, such as polyhydroxyalkanoates (Ghanbarzadeh and Almasi, 2013; Ghimire and Miles, 2020). Common raw materials for synthetic biodegradable mulch include thermoplastic starch due to its cost-effectiveness and wide application in products like mulch films (Miles et al., 2017). Notable bio-based polymers used in synthetic biodegradable mulches include polylactic acid and polyhydroxyalkanoates (Rajgadia and Debnath, 2023). Besides bio-based polymers, synthetic biodegradable mulch is also made from biodegradable aliphatic-aromatic copolyesters, such as PBAT (Jian et al., 2020). PBAT, a copolyester derived from butanediol (B), adipic acid (A), and terephthalic acid (T), offers a balance of flexibility, strength, and biodegradability, making it essential for producing biodegradable plastics and packaging materials (Jian et al., 2020).
According to Somanathan et al. (2022), the main material for mulching films is polyethylene plastic, which is a cause for environmental concern. These materials do not degrade under field conditions, leading to environmental concerns and the need for more effective and environmentally friendly mulching alternatives (Qiang et al., 2023; Rajgadia and Debnath, 2023). Synthetic, biodegradable mulch can be alternative solution, it consists of materials that are designed for a limited service life and are subject to regulated degradation into easy-to-dispose products (Peng et al., 2021). Synthetic, biodegradable mulch breaks down into carbon dioxide and water while contributing to microbial biomass and improving soil structure and fertility, promoting sustainable agriculture (Mola Ida et al., 2019; Tofanelli and Wortman, 2020; Bouzidi et al., 2023). In this process, resident microorganisms play a key role in facilitating the natural degradation of the plastic and provide a sustainable solution for disposal (Bandopadhyay et al., 2018; Di Mola et al., 2021). Compared to traditional polyethylene, synthetic biodegradable mulch provides environmental benefits by reducing microplastic accumulation, improving soil health, having similar mechanical properties to polyethylene, potentially requiring less labor for disposal, and potentially economically viable compared to plastic mulch (Miles et al., 2017; Cowan and Miles, 2018; Goldberger, 2018).
The agricultural industry has recognized the observable benefits of biodegradable mulches in reducing soil compaction and soil erosion, controlling nutrient consumption, increasing soil temperature, reducing fertilizer leaching, suppressing weed growth, increasing agricultural productivity and improving the quality of crops improve harvest (Sintim and Flury, 2017; Menossi et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022). The global market for synthetic biodegradable mulching films has been growing significantly, increasing from US$36 million in 2016 to US$53 million in 2021, with a compound annual growth rate of 8% (Business Research Insight, 2023). The market size was estimated at US$55 million in 2022 and is expected to reach US$74 million by 2031, growing at a compound annual growth rate of ~4% (Business Research Insight, 2023). This growth is driven by increasing demand for sustainable farming practices (Table 2). Europe and North America are the leading markets, with Asia-Pacific showing rapid growth due to heightened awareness and government support for sustainable agriculture (Business Research Insight, 2023). According to Business Research Insight (2023), biodegradable mulch market can be divided into four groups: based on plastic types, biodegradable plastics are categorized into thermoplastic starch and aliphatic-aromatic copolyester. Based on biodegradable composition, the market is divided into starch, starch blended with polylactic acid, and starch blended with polyhydroxyalkanoates. Additionally, based on the crops they cover, the market is divided into vegetables and fruits, grains and oilseeds, and plants and flowers. And also based on geographical regions, biodegradable mulch market categorized into North America, Europe, Latin America, Asia Pacific, and the Middle East and Africa. Factors leading to demand for synthetic biodegradable films include need for improved and sustainable ways to feed the growing population. For example, the synthetic biodegradable mulch market in Asia was noted to be growing rapidly, driven by the growing population (Sintim and Flury, 2017). To meet food demand, the use of synthetic, biodegradable mulch for crop production is important to increase productivity in small land areas (Miles et al., 2017).
The increasing demand for synthetic biodegradable mulch is also contributing to increased demand for starch due to the low cost and wide availability of starch, as well as its degradability upon contact with microbes in soil with harmless by-products (Sintim and Flury, 2017; Business Research Insight, 2023). Synthetic biodegradable mulch self-degrades and avoids disposal or reduces the cost of plastic like polyethylene. Marí et al. (2019) reported that the disposal costs of polyethylene film in certain regions of Spain were recorded differently for disposal (176.5 €/ha), landfill (186 €/ha) and recycling (192 €/ha). Other researchers reported that disposing of polyethylene mulch (excluding labor) costs up to $590 per hectare (Galinato and Walters, 2012; Miles et al., 2017). These economic challenges are likely to result in polyethylene mulch film waste accumulating or being processed in the field, and in some cases crop farmers abandoning it in rivers or rural areas (Menossi et al., 2021). These residues can also be burned outdoors and under unregulated conditions, contributing to an increase in greenhouse gas emissions (Menossi et al., 2021). In addition to the disadvantages associated with disposal, polyethylene mulch serves as a significant source of macro- and microplastic pollution in agricultural areas, resulting in soil and water pollution (Huang et al., 2020; Serrano et al., 2021). The use of biodegradable polymers brings environmental benefits by renewing raw materials, facilitating biodegradation, and reducing carbon dioxide emissions that contribute to global warming (Zhu and Wang, 2020).
Synthetic biodegradable bio-based mulch is required to meet specific compostability and biodegradability standards, such as ASTM D6400, ASTM D6868, European Standards (EN 13432), EN 14995, or ISO 17088. It must demonstrate at least 90% biodegradation relative to microcrystalline cellulose within two years in soil, verified through recognized test methods (ISO 17556 or ASTM D5988). Additionally, it needs to contain at least 80% bio-based content, determined using ASTM D6866 standards (NOSB, 2021). The practical implications of synthetic biodegradable mulch include several benefits. It saves labor by eliminating the need for mulch removal at the end of the growing season, thus reducing labor costs (Soylu and Kizildeniz, 2024; Mansoor et al., 2022). It also contributes to soil health by allowing organic matter to decompose and enrich the soil, aids in moisture retention by helping to retain soil moisture and reducing the need for frequent irrigation, and supports weed control by suppressing weed growth, thereby reducing the need for herbicides (Zhang et al., 2022). However, challenges exist as well. Performance can vary due to degradation rates that depend on environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and soil microorganisms. Additionally, market adoption faces hurdles, with farmers often hesitant to adopt this mulch due to higher costs and uncertain performance under different agricultural conditions (Goldberger et al., 2013).
The biggest challenge with synthetic biodegradable mulch is associated with the high initial market costs, including material prices, soil levelling machine, and installation costs (Ricker-Gilbert et al., 2014; Business Research Insight, 2023). The high installation costs have been noted as one of the key factors limiting their use, especially in developing countries (Business Research Insight, 2023). Although the market has significant potential in developing countries like India, the high acquisition cost has become a cause of concern for small farmers (Business Research Insight, 2023). The driving themes of this review include three main aspects: (1) exploring the potential of synthetic, biodegradable mulch in agriculture to improve the livelihoods of smallholder farmers; (2) Tapping into the socioeconomic frameworks that favor synthetic biodegradable mulch, taking into account differences that contribute to environmental sustainability and resilience to climate change; and (3) conduct a bench-based situational analysis of existing and viable institutional policies to enforce the sustainable use of synthetic biodegradable mulch.
2 Methods of literature search
This review followed the framework established by Page et al. (2020). To ensure scientific rigor and transparency, the review adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement protocol, as proposed by Moher, 2009.
This study identified relevant databases, including ScienceDirect, SCOPUS, Google Scholar, and PubMed, and developed search strategies to ensure the selection of peer-reviewed articles eligible for inclusion in indexed journals (Adams et al., 2016; Nassary et al., 2022), with studies sourced from these databases as well as some Grey Literature. Key search terms encompassed various aspects of synthetic biodegradable mulch, including its production, impact on crop productivity, potential, implications for livelihoods, relevance to smallholder farmers, pricing, market dynamics, policy considerations, environmental implications, impact on climate change, and effects on soil health. After eliminating duplicates and redundant sources, a total of 132 studies were included in the review (Figure 1).
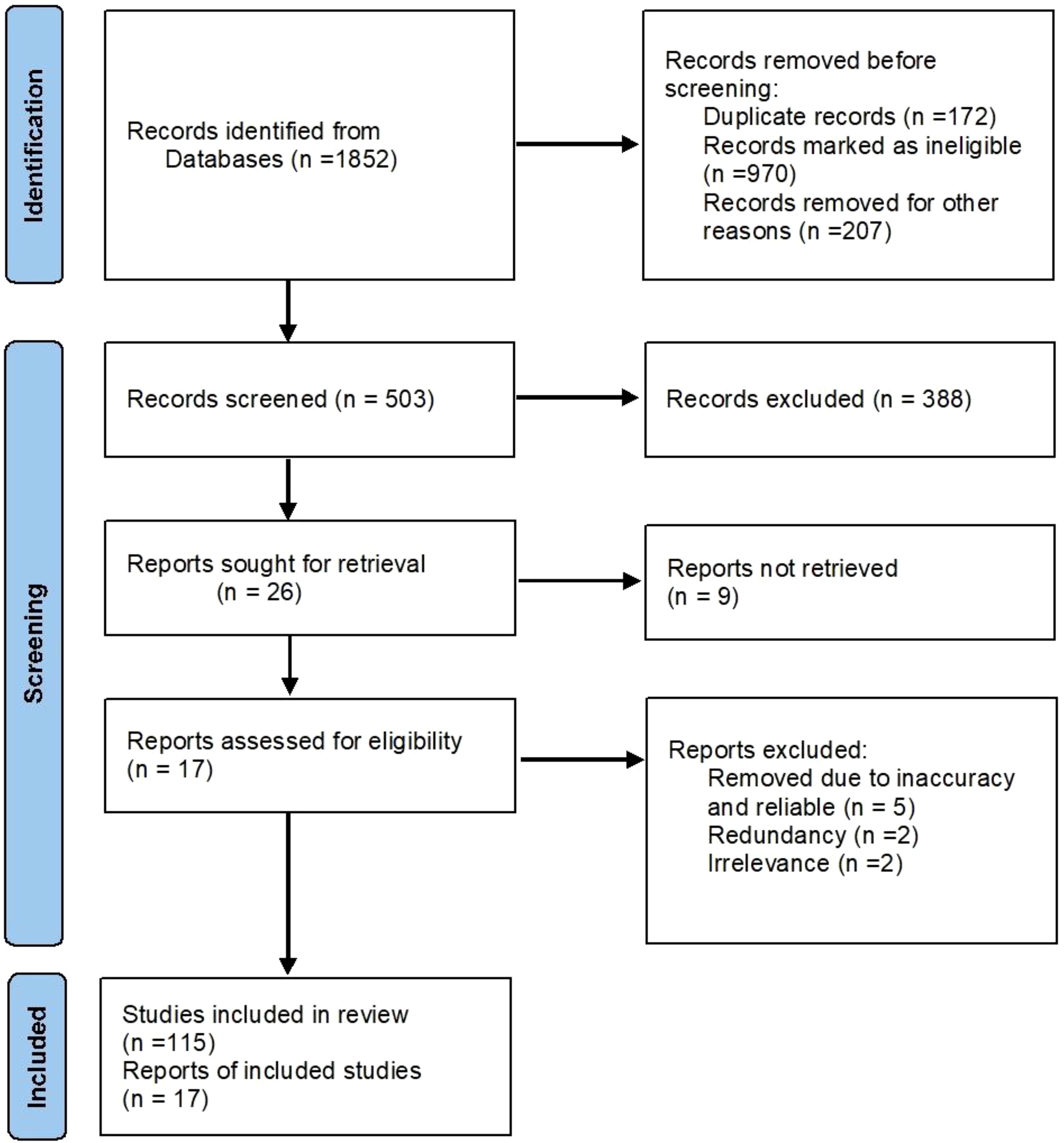
Figure 1. Schematic literature search route used in acquisition of appropriate articles. PRISMA Modified from PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for new systematic reviews of Page et al. (2020).
3 Findings and discussion
3.1 Potential of synthetic biodegradable mulch in agriculture
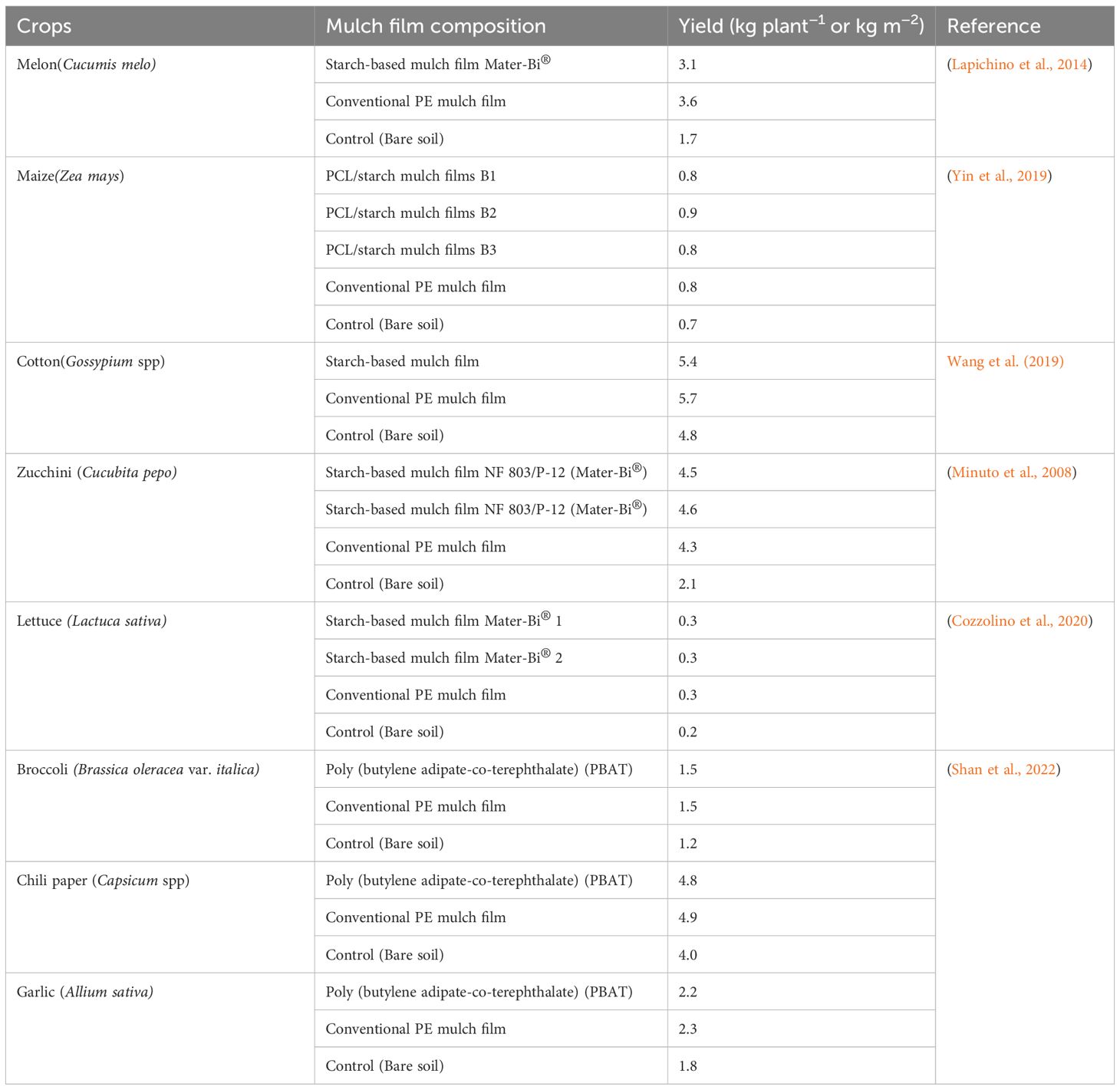
It is estimated that the world population will reach 10 billion by 2050, putting significant pressure on the agricultural sector due to increased demand for food (Hofmann et al., 2023). Climate change complicates matters further and poses challenges to food production (Food and Agriculture Organization, 2009). To address this issue, it is crucial to increase agricultural productivity, adopt sustainable practices and promote climate-resilient methods (Madrid et al., 2022). Synthetic biodegradable mulch provides numerous benefits for crop production by controlling weeds and insects, regulating soil temperature, and retaining soil moisture by reducing evaporation, minimizing soil erosion, preventing soil splashing, and improving the efficiency of nutrient use by plants (Menossi et al., 2021). According to Martín-Closas et al. (2017), the impacts of synthetic biodegradable mulch began in the late 1990s and were reported in Germany, Japan, Italy, Spain, France and other European countries that produced biodegradable mulch for their experiments. Synthetic biodegradable mulch was tested in the production of several crops, including horticultural crops like tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum), lettuces (Lactuca sativa), peppers (Capsicum spp), and Zucchini (Cucubita pepo) without significant differences reported in tomato between synthetic biodegradable mulch and polyethylene (Table 3).
Martín-Closas et al. (2008) found a significant increase in the number of fruits set per plant with synthetic biodegradable mulch and polyethylene (both 15 μm) compared to bare soil and paper mulch. The study conducted by Morra et al. (2021) discovered that Mater-Bi® (NOVAMONT) and Ecovio® (BASF) biodegradable mulches degraded completely but more slowly than paper mulch, leading to an improvement in soil quality. The use of biodegradable mulch resulted in a higher tomato yield and improvements in quality parameters relevant to the processing industry (Cowan, 2013; Sękara et al., 2019). According to Sękara et al. (2019), the parameters evaluated included fruit color, firmness, total soluble solids, titratable acidity, antioxidant activity, as well as the contents of ascorbic acid, polyphenols, flavonoids, and lycopene (Sękara et al., 2019).
Weed control stands out as one of the most valuable agronomic practices, according to Ngouajio et al. (2008), the optimal fresh tomato crop performance was achieved when weed control exceeded 85%. Massawe et al. (2023) reported a better performance of weed control by Novamont biodegradable mulch film compared to dead plant mulches in common beans production in Tanzania. Black synthetic biodegradable mulch is observed to be more effective than white and other colored synthetic biodegradable mulches (Schonbeck, 2012; Menossi et al., 2021). Olsen and Gounder (2001) reported that pepper was among the first crops evaluated for biodegradable mulching in Australia, and the yield was found to be equivalent to recycled brown paper (100 g m−2), synthetic biodegradable (black; 30 μm), and polyethylene mulch. Synthetic biodegradable mulch degrades rapidly in paper production due to its growth habit, which exposes the mulch to various environmental factors, compared to its use in tomato cultivation (Martín-Closas et al., 2017).
In a study evaluating the impact of biodegradable mulch on vegetable production, Waterer (2010) found that synthetic biodegradable mulch (15 μm) and polyethylene mulch (28 μm), whether black, clear, or infrared–IR-transmitting, had little effect on the yield, fruit quality, and maturity of peppers, without significant differences observed between them. A study conducted by González et al. (2003) in water melon (Cucumis melo) production demonstrated that the use of transparent or translucent synthetic biodegradable mulches resulted in fruit yields with high sugar content, comparable to clear polyethylene. In contrast, using black films water melon demonstrated poor performance (González et al., 2003). Another study by López-Marin et al. (2007) indicated a higher yield of Melon (Cucumis melo) with synthetic biodegradable mulch compared to polyethylene. This difference was attributed to the crop being spring–summer, requiring higher temperatures, clear mulch by allowing more sunlight to penetrate and reach the soil, leading to greater absorption of solar radiation and, consequently, a more significant warming effect on the underlying soil (Martín-Closas et al., 2017). Biodegradable mulches have also exhibited potential effects on cucurbit crops such as melons and cucumbers (Cucumis sativus), the study highlighted that using biodegradable mulching on melons, enhanced the quality of fruits and contributed to a 27.2%, 22.4%, and 24.6% increase in flavonoids (Cozzolino et al., 2023).
A study by Fontenot et al. (2021) in assessing biodegradable mulch duration and nutsedge suppression during late summer cucumber production indicated that biodegradable mulch performed comparably to polyethylene in terms of yield and quality. In the USA, various synthetic biodegradable mulches (grades NF0U/P and NF803/P; 12 and 15 μm) and polyethylene films did not show notable impact on water melon yield (Miles et al., 2007). Similarly, a study on zucchini (Cucubita pepo) by Minuto et al. (2008) reported comparable yields with synthetic biodegradable mulch (NF803/P; 12 and 15 μm) and polyethylene (50 μm) films. In a six-year study by Zhang et al. (2022) investigating the impacts of synthetic biodegradable mulch on soil physical, chemical, and biological properties, the findings revealed a non-significant difference in bulk density compared with polyethylene films. However, there was a notable decrease from 12 to 17% in the 10-20 cm soil depth (Zhang et al., 2022). Zhang et al. (2022) indicated that there was a significant increase in soil total nitrogen content by 15% to 28%, available phosphorus (64%) and exchangeable potassium (109%), but also synthetic biodegradable mulch was found to enhance microbial activities compared to both polyethylene and no mulch. Another study by Shan et al. (2022) on garlic (Allium sativa), chili pepper (Capsicum spp.), and broccoli (Brassica oleracea var.) observed insignificant differences in yield between synthetic biodegradable mulch and polyethylene mulch. Shan et al. (2022) indicated that both synthetic biodegradable mulch and polyethylene mulch were effective in maintaining higher exchangeable potassium contents in rhizosphere soil. Additionally, both types of mulch demonstrated significant effectiveness, with yield increases of 18% to 19%, 21% to 23%, and 26% to 30% for broccoli, chili pepper, and garlic, respectively. These increases reflected a significant improvement in smallholder farmers’ livelihoods, as they were able to sell more products in the market, resulting in higher income. It also improved food security in their communities and offered these farmers the opportunity to expand their operations or invest in other aspects of their livelihoods.
Synthetic biodegradable mulch has been reported to improve the rhizosphere microenvironment through the regulation of soil temperature and moisture (Abbate et al., 2023). The use of biodegradable and plastic film mulching can affect nitrogen uptake, distribution, and leaching in the soil, helping smallholder farmers manage nitrogen more effectively, leading to improved crop growth and reduced nutrient runoff (Wang et al., 2022; Samphire et al., 2023). Contrary to concerns about potential negative impacts, the results of a study by Zhang et al. (2022), coupled with Li et al. (2014) observations, suggest only a minor effect on soil quality. This implies that the long-term usage of synthetic biodegradable mulch does not degrade soil quality but, positively influences soil fertility (Samphire et al., 2023). The collective evidence explores the potential of synthetic biodegradable mulch as a sustainable choice in agriculture, improving the livelihoods of farmers by enhancing production, reducing environmental pollution, and overall contributing to soil health, benefiting smallholder farmers. This suggests that synthetic biodegradable mulch can be a promising alternative to polyethylene in agricultural production. Several crops have been grown using synthetic biodegradable mulch, which offers crop production benefits similar to polyethylene mulch but is designed to be incorporated into the soil after use, thereby eliminating waste and disposal challenges associated with polyethylene mulch use. Some of the crops researched with the use of synthetic biodegradable mulch and revealed a positive respond including maize, garlic, chili pepper, watermelon, broccoli, cotton, zucchini, and lettuce Table 4. Synthetic biodegradable mulch has been shown to enhance crop quality, save time for agricultural producers, and reduce labor costs (Moore and Wszelaki, 2016; Sintim and Flury, 2017).
Synthetic biodegradable mulch reportedly outperforms other dead plant mulches such as butterfly peas, corn husks and pimento grass in various aspects of growth parameters and yield parameters such as plant leaves, plant height, number of branches, and number of pods per plant and grain yield (Massawe et al., 2023). Synthetic biodegradable mulch manages to create favorable conditions for crops thanks to its superior performance attributed to its ability to effectively control weeds and conserve moisture by minimizing weed competition and maintaining optimal soil moisture. These combined benefits highlight the important role of synthetic biodegradable mulch in promoting better crop productivity by mitigating resource competition and creating an optimal growing environment.
Synthetic biodegradable mulch films act as a physical barrier, preventing direct contact between crops and potential pests or diseases (Kasirajan and Ngouajio, 2012; Sintim and Flury, 2017). Synthetic biodegradable mulch prevents the beating action of flushing drops which carry spores of different diseases (Kasirajan and Ngouajio, 2012). These spores attach themselves to foliage and shoots of the vulnerable plants, therefore synthetic biodegradable mulch reduce the chances of disease occurrence (Sintim and Flury, 2017). Some synthetic biodegradable mulch films are supplemented with antimicrobial properties, contributing to pest and disease control. For instance, a starch-based mulch film supplemented with linear polyvinyl alcohol and sodium propionate as an antimicrobial compound has demonstrated potential in managing pests and diseases (Menossi et al., 2021). Liang et al. (2020) reported that chitosan/hydroxypropyl methylcellulose pesticide mulch film allowed protection against root rot caused by the phytopathogens fungus Phytophthora sojae on soybean (Glycine max).
The use of black synthetic biodegradable mulch films can be effective in suppressing most weeds, leading to reduced labor and other costs associated with weed management (Schonbeck, 2012; Martín-Closas et al., 2017; Menossi et al., 2021). It contributes to improved growing conditions for the crop, enhancing its competitiveness against weeds (Martín-Closas et al., 2017; Menossi et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2022). More on that, synthetic biodegradable mulch films play a role in nutrient management in the soil, indirectly contributing to pest and disease management. For example, they can improve nitrogen management, ultimately reducing the incidence of pests and diseases (Kasirajan and Ngouajio, 2012). Proactive nutrient management plays a critical role in protecting plants from pests and diseases. By reducing the stress levels of plants, these practices improve their ability to effectively fight various pathogens (Dutta et al., 2017). Also plants develop resistance to weed infestation and other harmful pests. As a result, there is less dependence on fungicides, insecticides and herbicides (Dutta et al., 2017). This approach not only promotes healthier plant growth, but also contributes to sustainable agricultural practices by minimizing chemical use. The reduced use of such chemicals will be in favor of small holder farmers in the sense that no funds will be incurred with non-use of chemicals that will compromise beneficial soil organisms’ population, activity and the environment (Chalker-Scott, 2007).
3.2 Socioeconomic and environmental implications of synthetic biodegradable mulch
Polyethylene mulch, valued for its low cost, ease of application, and durability, is projected to experience a 6.5% annual growth rate, reaching a $15.7 billion market value by 2026 (Madrid et al., 2022). Despite its immediate benefits, the long-term consequences of polyethylene mulch use pose adverse effects on society and the environment due to its non-degradable nature, taking hundreds of years to undergo changes (Ghatge et al., 2020). Madrid et al. (2022) also highlight its ability to adsorb pesticides, concentrating them in the soil. The plastic material, adsorbs pesticides through partitioning, which can influence the persistence of the pesticides in soil and water (Wang et al., 2020). Proper disposal is crucial to prevent plastic accumulation, but removal poses challenges, being labor-intensive and expensive (Galinato and Walters, 2012; Miles et al., 2017). Disposal methods like landfill contribute to environmental harm, generating micro- and nano-plastics and toxic by-products (Ohtake et al., 1998; Hakkarainen and Albertsson, 2004; Yu and Flury, 2020). The socioeconomic impact of these mulch is illustrated in Figure 2.
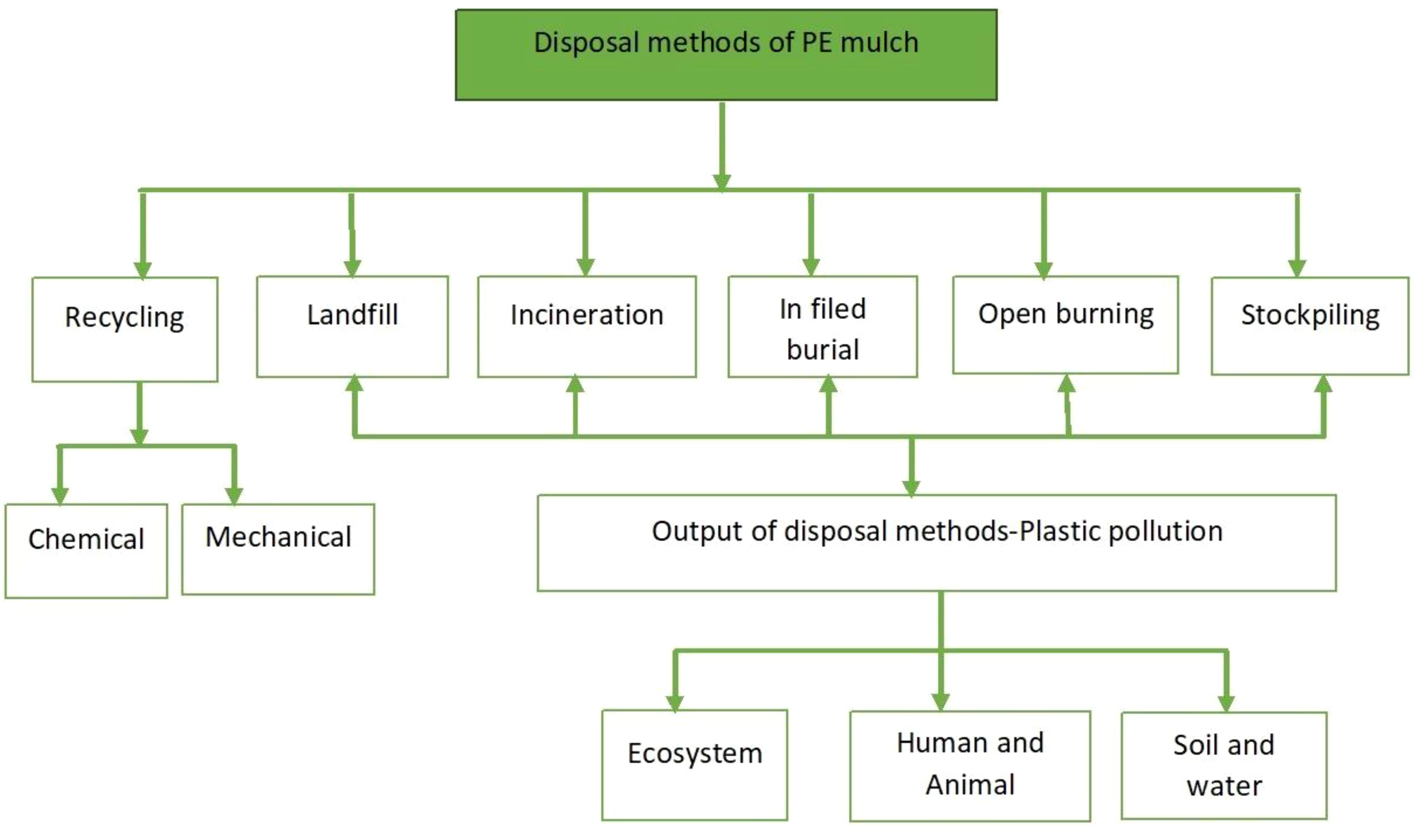
Figure 2. Schematic diagram disposal pathways of used plastic agricultural mulch; adopted and modified from Madrid et al. (2022).
In contrast, synthetic biodegradable mulch is designed for tillage into the soil, facilitating biodegradation by microorganisms and reducing plastic waste, environmental impacts, and labor costs compared to polyethylene mulch (Hayes et al., 2019; Madrid et al., 2022). However, the adoption of synthetic biodegradable mulch is influenced by socioeconomic factors, such as relative initial pricing and labor costs, affecting the net profit for crop growers (Galinato et al., 2020; Velandia et al., 2020). A study conducted by Hao et al. (2024) in Northern China finds that while biodegradable mulch film offers environmental benefits, it requires ongoing subsidies to remain viable. The net benefit for biodegradable film is around $314 per hectare, which is lower than that of conventional plastic mulch. In contrast, another analysis by Long (2023) in the U.S. demonstrates that biodegradable mulch leads to significant cost savings through water conservation (up to 25% savings), increased crop yields (about 20%), and reduced herbicide costs. These factors offset the higher initial investment, making biodegradable mulch economically viable, especially for larger operations. Johansson (2018) emphasizes that although biodegradable mulches have higher initial costs, they eliminate the need for post-harvest disposal, which offsets some of these expenses over time. Therefore, the cost-benefit analysis of biodegradable mulch reveals its potential for economic savings through reduced labor and disposal costs, improved crop yields, and alignment with sustainable agricultural practices. These factors contribute to a favorable economic outlook for farmers considering the switch from traditional plastic mulch to biodegradable alternatives.
Despite benefits of using biodegradable mulches, still its use faces some challenges. These include farmers’ willingness (Chen et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2020). A study by Chen et al. (2021) in China found that the adoption of synthetic biodegradable mulch is influenced by economic and social factors such as farmers’ education level and the effectiveness of mulch film on productivity, as well as agronomic factors. The extensive use of polyethylene mulches in agriculture has resulted in the pervasive issue of white pollution, significantly impacting the quality and safety of cultivated land and the rural environment (Zeng et al., 2013). Microplastics have been identified as a significant contributor to ecological damage and agricultural pollution (Yu et al., 2022). They exert a profound influence on soil physicochemical properties, microbial communities, and crop growth. Microplastics serve as carriers for the transfer of heavy metals or organic pollutants to organisms, as highlighted in the research conducted by Wu et al. (2023). Hofmann et al. (2023) emphasize that plastic mulch films alone contribute to approximately 50% of the total mass of agricultural plastics. Discarded plastic fragments persist in farm landscapes post-crop cycle, and the residues are often scattered across fields, land, irrigation areas, and drainage zones (Sajjad et al., 2022). This results in soil pollution and marine environmental degradation through runoff (Zeng et al., 2013; Jambeck et al., 2015). Incinerating leftover plastic can produce organic pollutants, such as furan and dioxins, contributing to air pollution (Jayasekara et al., 2005). The accumulation of plastic waste in the soil adversely affects soil porosity and structure, impeding water movement and hindering root penetration and nutrient uptake by plants (Nawaz et al., 2016; Hu et al., 2020; Li C et al., 2021).
It was reported that the residual amount of plastic film mulch in China reached 900 kg·hm-2, with root length decreasing by 33.7%, resulting in a 22% decrease in cotton yield (Zumilaiti et al., 2017). A study by Gao et al. (2021) reveals alarming statistics from China, where the average amount of plastic film mulch residue on cropland was 34.0 kg·hm-2 and reached a maximum of 317.4 kg·hm-2. Huang et al. (2023) reported that the annual consumption of plastic films for mulching or greenhouse purposes in China was about 2.5 × 106 tons. About 2 × 107 hectares of agricultural land in China is covered with mulch (Sa’adu and Farsang, 2023). Consequently, the accumulation of polyethylene mulch residues is identified as a significant factor in the presence of microplastics and this accumulation alters the nature, function and biodiversity of the soil ecosystem, thereby affecting smallholder farmers’ livelihoods (Li et al., 2020). This highlights the urgent need for sustainable solutions to address the problem of microplastic pollution in agricultural practices (Chah et al., 2022). The environmental concerns arise from the accumulation of macro and micro plastics in the soil after mulch use, in short-term studies, microbioplastic residues have similar effects on soil properties as non-biodegradable residues (Fojt et al., 2022). The size, shape and polymer composition of microbioplastic from different sources have different effects on soil properties. Macro-sized particles have greater effects on soil bulk density, porosity and hydraulic conductivity than micro-sized particles (Campanale et al., 2023). To understand the long-term impacts, a detailed study of the degradation of bioplastics, particularly synthetic biodegradable mulch, is critical. According to Menossi et al. (2021), synthetic, biodegradable mulch based on polysaccharide bio composites completely breaks down in the soil and improves soil structure, lowers pH and increases nutrient availability. Abbate et al. (2023) reported that synthetic biodegradable mulch can be completely degraded by abiotic factors such as UV light, wind, precipitation and other mechanical stresses. The biotic factors include microbes and can occur in four main stages of biodegradation consisting of fragmentation into small pieces, depolymerization (the splitting of the polymer chains into oligomers, dimers and monomers), assimilation and mineralization. During assimilation and mineralization, molecules such as CO2, N2, CH4 and H2O are released into the soil (Abbate et al., 2023).
The lack of specific standard tests for the biodegradability of synthetic, biodegradable mulch in unmanaged natural environments represents a challenge. Existing standards such as the European standard EN 17033:2018 and the American standard ISO 17556-2019 focus on achieving ≥90% biodegradation of polymeric feedstock within two years (Hayes and Flury, 2018; Dentzman and Hayes, 2019). However, due to climate and location variations, these standards may not accurately reflect the true biodegradability of synthetic biodegradable mulch in natural soil environments (Sintim et al., 2020). So assessing degradation of synthetic biodegradable mulch using thermal time is more effective than using calendar days, particularly under field conditions (Dharmalingam et al., 2015). Despite challenges, synthetic biodegradable mulch holds promise as a sustainable alternative in agriculture, provided it can match the performance of traditional polyethylene mulch and degrade into environmentally safe constituents (Miles et al., 2017).
3.3 Climate resilience with synthetic biodegradable mulch
Smallholder farmers’ vulnerability to climate change is indeed influenced by critical resources such as water, the availability, accessibility, and management of water resources play a crucial role in determining how resilient these farmers are to the impacts of climate change (Marie Chimi et al., 2023). The effective implementation of comprehensive soil and water conservation practices involves the integration of conservation agricultural methods and the adoption of smart farming practices (Danish et al., 2023). The approach enhances sustainability by mitigating soil erosion, preserving water resources, and promoting ecologically sound farming techniques, collectively contributing to the overall health and resilience of agricultural ecosystems (Marie Chimi et al., 2023; Yeleliere et al., 2023). Synthetic biodegradable mulch contributes to climate change resilience and improves the livelihood of smallholder farmers through weed control, reduces soil erosion, conserves soil moisture, and enhances soil nutrient status, which are all essential for sustainable agriculture (Iqbal et al., 2020). The materials allow for earlier planting and harvesting of crops due to increased soil temperature, improve the quality of the harvest, and provide a market benefit to farmers (de Sadeleer and Woodhouse, 2023).
Synthetic biodegradable mulch films offer a significant advantage in arid agricultural regions by enhancing water use efficiency, averaging a 9.5% increase (Thakur and Kumar, 2021). This benefit is particularly valuable for smallholder farmers facing water scarcity or drought conditions, as it helps conserve moisture and improve crop growth. In a study by Deng et al. (2019a), the use of synthetic biodegradable mulch led to a notable increase in maize biomass at harvest, with a 25% to 33% rise over three years from 2015 to 2017. This demonstrates the suitability of degradable mulch films, primarily consisting of PBAT, for large-scale adoption in arid regions. Deng et al. (2019b) also investigated the effects of biodegradable mulch films on cotton and maize in arid areas, revealing a significant increase in water use efficiency by 65–73%, which resulted in improved crop yields and positively impacted smallholder farmers’ livelihoods. Studies show that synthetic biodegradable mulch reduces soil water evaporation by 25% to 50% compared to bare soil. Additionally, several studies indicate that synthetic biodegradable mulch saves between 2% and 35% of soil moisture, depending on climatic conditions and the crop grown (Li Q et al., 2021; Jia et al., 2020; Zhang et al., 2019; Alamro et al., 2019). This results in savings of up to $978 per acre per season. Synthetic biodegradable mulch influences micro-climatic conditions by moderating soil temperature, compared to bare soil, mulched areas exhibit slower cooling and more gradual warming, potentially due to the albedo effect (Menossi et al., 2021). Notably, Moreno and Moreno (2008) found that biodegradable mulch, particularly those primarily composed of PBAT, induces lower temperatures than black polyethylene mulch. This could be attributed to the prevention of water exchange between air and soil, leading to reduction in latent heat flux (Menossi et al., 2021). Consequently, the modification of soil temperature by synthetic biodegradable mulch proves beneficial for crop growth, contributing to higher yields and improved harvest quality, ultimately aiding in the adaptation to climate change and improving the livelihood of the small holder farmers in tropical hot environments.
3.4 Policy enforcement for the sustainable use of synthetic biodegradable mulch
In the context of sustainable agriculture, institutional policies play an important role in shaping the impact of synthetic biodegradable mulch across its lifecycle, from production to application and disposal. Effective policies are essential for promoting environmentally responsible manufacturing practices, ensuring alignment with sustainability goals (Table 5). For instance, the National Organic Program (NOP) in the USA mandates that synthetic biodegradable mulch must be free from genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and excluded methods in feedstock, thereby prohibiting materials like polyvinyl chloride and oxo-degradable mulches. Similar regulations are enforced by entities such as the Canadian General Standard Board (Kim, 2022; Madrid et al., 2022). In 2022, the European Commission introduced a policy framework for sustainable biobased, biodegradable, and compostable plastics, endorsed by European Bioplastics (European Bioplastics, 2023). This framework highlights the role of biobased plastics in advancing EU climate goals, while industrially compostable plastics enhance waste recycling, also, a clear communication and certification prevent green washing. Bioplastics contribute to circularity, climate objectives, reduce environmental impact, microplastic accumulation, aid soil health, and foster a greener future (European Bioplastics, 2023). The EU has established standards like EN 13432 to facilitate organic recycling of compostable plastics (European Bioplastics, 2021). However, petroleum-based biodegradable mulch is currently permitted for organic producers without strict biobased ingredient requirements. Plans for mulch review in 2024 could lead to regulatory changes in EU policy (European Bioplastics, 2021).
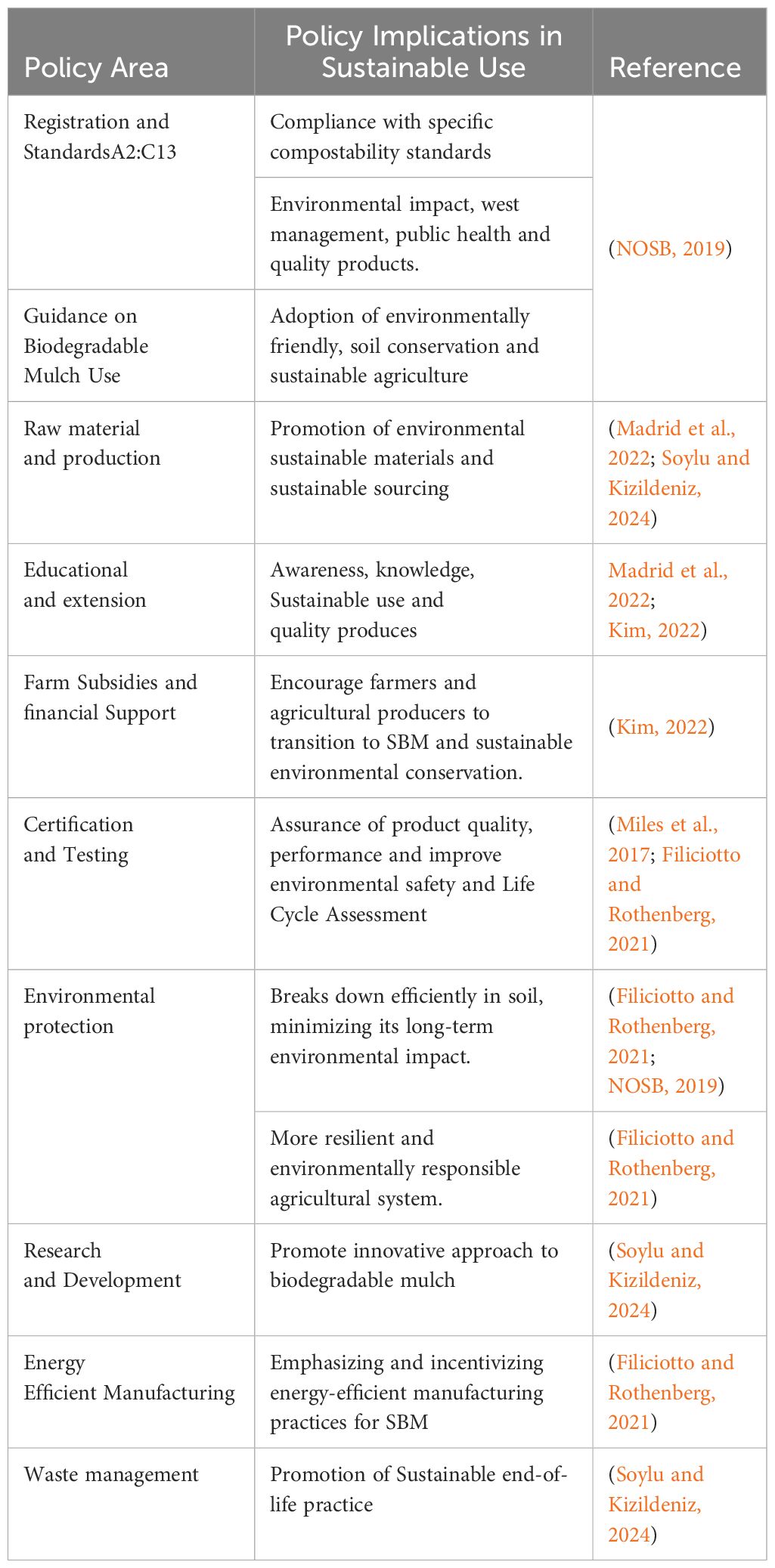
Table 5. Outline of policy implications in sustainable use of synthetic biodegradable mulch for improving smallholder farming system.
In Asia, particularly China, Japan, and India, there is a significant uptake of biodegradable mulch films in organic farming, driven by a shift toward eco-friendly options and environmental regulations (Filiciotto and Rothenberg, 2021). Africa, typical example by Rwanda’s ban on single-use plastics, shows increasing interest in biodegradable plastics (Babayemi et al., 2019; Filiciotto and Rothenberg, 2021). However, detailed policy information for Asian and African countries on the use of synthetic biodegradable mulch is limited. The European Union’s regulatory framework for biodegradable and bio-based plastics may influence adoption in these regions (Filiciotto and Rothenberg, 2021). Despite the details of specific policies, in African countries are not readily available. The increasing awareness of the harmful effects of plastic pollution and the need for sustainable farming practices suggests a potential for the adoption of biodegradable mulch materials in the region (Babayemi et al., 2019). Overall, the trend towards biodegradable mulch materials reflects a global move towards sustainability in agriculture, driven by environmental concerns and the search for eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastic mulch films. Incentivizing farmers to adopt synthetic biodegradable mulch, governments and organizations can offer financial incentives like subsidies or tax credits, helping offset initial transition costs from conventional plastic mulch (Kim, 2022). However, challenges such as varying degradation rates depending on environmental conditions and regulatory hurdles from institutions like the National Organic Program can pose obstacles for farmers (Goldberger et al., 2013). Addressing these challenges through financial incentives, educational outreach, and technical assistance can encourage wider adoption of synthetic biodegradable mulch, contributing to a more sustainable agricultural system (Madrid et al., 2022). Also, establishing a rigorous certification and testing procedure is crucial to ensure that synthetic biodegradable mulch adheres to defined compostability and biodegradability standards (Miles et al., 2017). This approach fosters confidence in the product, motivating farmers to embrace its use, while also ensuring that breakdown products pose no toxicity or persistent environmental presence, being fully assimilated by the soil (Corbin et al., 2013). Institutions can play a crucial role in promoting the sustainable use of synthetic biodegradable mulch through educational outreach programs aimed at informing growers about its benefits and proper usage (Madrid et al., 2022; Kim, 2022). Therefore, effective policies for promoting environmentally responsible manufacturing and application practices of synthetic biodegradable mulch and its sustainable use can include a combination of strategies, including certification standards, regulatory compliance, incentives and subsidies, research and development, education and awareness, environmental protection, sustainable sourcing and raw materials, waste management, and energy-efficient manufacturing. These policies are essential for ensuring that manufacturing processes and application align with sustainability goals and contribute to a more eco-friendly environmentally and sustainable future.
4 Conclusions and future scope
Mulching practices offer an essential benefits, including conserving soil moisture, enhancing soil nutrient status, controlling erosion, suppressing weed growth, improving microbial activities, and moderating soil temperature, they reduce soil water losses, protect against temperature extremes, and improve soil structure by increasing aeration and aggregating soil particles. Synthetic biodegradable mulch plays an important role in fostering both economic and environmental sustainability, through enhances crop yields, reduces water usage, and lowers greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, synthetic biodegradable mulch provides comparable or superior benefits to traditional polyethylene mulch which is commonly used, in terms of crop yield, quality, and protection, and mitigating plastic waste, soil pollution, and disposal costs. Its use significantly enhances soil fertility, water use efficiency, and nutrient management, thereby contributing to soil and water conservation, climate change resilience, and the livelihoods of smallholder farmers, surpassing other widely used mulches like polyethylene.
Despite its potential, synthetic biodegradable mulch faces some barriers to widespread adoption, high initial costs, particularly compared to polyethylene mulch, may discourage farmers, particularly those in developing countries with limited financial resources. The lack of awareness and knowledge about synthetic biodegradable mulch among farmers, consumers, and policymakers also affects its demand and supply. Unclear standards and regulations create confusion and uncertainty regarding synthetic biodegradable mulch quality, performance, and safety. Inadequate research and development limit synthetic biodegradable mulch innovation and improvement in terms of biodegradability, durability, functionality, and diversity. A well-designed policy framework can be imperative to promote the sustainable use of synthetic biodegradable mulch without adverse environmental implications. This can include providing financial incentives and support for farmers and manufacturers, conducting educational programs, developing certification and testing systems, and investing in research and development. Collaborative efforts involving regulatory agencies, industry, academia, and government are essential to ensure sustainable manufacturing and application practices for Synthetic biodegradable mulch.
The synthetic biodegradable mulch holds a significant potential to enhance smallholder farmer’s livelihoods and contribute to environmental sustainability and climate change resilience, and further research and innovation are indeed crucial to optimize the application and adoption of synthetic biodegradable mulch, research area, including the economic, degradability in different environment and raw materials of synthetic biodegradable mulch as a beneficial choice for farmers. The results will provide evidence of the importance of sustainable use of synthetic biodegradable mulch and improve farmer’s livelihoods, and promote its sustainability use.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
AR: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. EN: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. FR: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. BM: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. SN: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The authors acknowledge material and financial support from the FoodLAND project. FoodLAND has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement (GA No 862802). The views and opinions expressed in this publication are the sole responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the European Commission. We thank all the FoodLAND partners and field staff for their support when doing this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abbate C., Scavo A., Pesce G. R., Fontanazza S., Restuccia A., Mauromicale G. (2023). Soil bioplastic mulches for agroecosystem sustainability: A comprehensive review. Agric. (Switzerland) 13 (1), 197. doi: 10.3390/agriculture13010197
Adams J., Hillier-Brown F. C., Moore H. J., Lake A. A., Araujo-Soares V., White M., et al. (2016). Searching and synthesising ‘grey literature’ and ‘grey information’ in public health: critical reflections on three case studies. Systematic Rev. 5, 164. doi: 10.1186/s13643-016-0337-y
Alamro M., Mahadeen A., Mohawesh O. (2019). Effect of degradable mulch on tomato growth and yield under field conditions. Bulgarian J. Agric. Sci. 25, 1122–1132. doi: 10.22620/bjas.2019.25.080
Alliedmarketresearch. (2021). Starch-blended biodegradable polymer market size,share, compititive land scape and trend analysis report, by application: global opportunity analysis and industrial forecast, 2021-2030.
Babayemi J. O., Nnorom I. C., Osibanjo O., Weber R. (2019). Ensuring sustainability in plastics use in Africa: consumption, waste generation, and projections. Environ. Sci. Europe 31 (1), 36. doi: 10.1186/s12302-019-0254-5
Bandopadhyay S., Martin-Closas L., Pelacho A. M., DeBruyn J. M. (2018). Biodegradable plastic mulch films: impacts on soil microbial communities and ecosystem functions. Front. Microbiol. 9. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00819
Bizikova L., Jungcurt S., McDougal K., Tyler S. (2020). How can agricultural interventions enhance contribution to food security and SDG 2.1. Global Food Secur. 26, 100450. doi: 10.1016/j.gfs.2020.100450
Bouzidi S., Ben ayed E., Tarrés Q., Delgado-Aguilar M., Boufi S. (2023). Processing polymer blends of mater-bi® and poly-L-(Lactic acid) for blown film application with enhanced mechanical strength. Polymers 15 (1), 153. doi: 10.3390/polym15010153
Business Research Insight (2023). Biodegradable mulch film market size, share, Growth, and Industry analysis by the type (starch based, starch blended with PLA and other application (fruits and vegetables, grain, horticultural and others) Regional insights and forecast to 2031. Available online at: https://www.businessresearchinsights.com/market-reports/biodegradable-mulch-film-market-102119. (Accessed January 26, 2024).
Campanale C., Galafassi S., Di Pippo F., Pojar I., Massarelli C., Uricchio V. F. (2023). A critical review of biodegradable plastic mulch films in agriculture: Definitions, scientific background and potential impacts. Trac Trends Analytical Chem. 170, 117391. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2023.117391
Chah C. N., Banerjee A., Gadi V. K., Sekharan S., Katiyar V. (2022). A systematic review on bioplastic-soil interaction: Exploring the effects of residual bioplastics on the soil geoenvironment. Sci. Total Environ. 851, 158311. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.158311
Chalker-Scott L. (2007). Impact of mulches on landscape plants and the environment—A review. J. Environ. Horticulture 25, 239–249. doi: 10.24266/0738-2898-25.4.239
Chen J., Chen X., Guo J., Zhu R., Liu M., Kuang X., et al. (2021). Agricultural, ecological, and social insights: residual mulch film management capacity and policy recommendations based on evidence in Yunnan Province, China. Sustainability 13, 4. doi: 10.3390/su13041603
Chen K. J., Galinato S. P., Marsh T. L., Tozer P. R., Chouinard H. H. (2020). Willingness to pay for attributes of biodegradable plastic mulches in the agricultural sector. HortTechnology 30, 437–447. doi: 10.21273/HORTTECH04518-20
Corbin A., Miles C., Cowan J., Moore-Kucera J., Inglis D. (2013). Current and future prospects for biodegradable plastic mulch in certified organic production systems. Available online at: https://eorganic.org/node/8260. (Accessed January 27, 2024).
Cowan J. S. (2013). The use of biodegradable mulch for tomato and broccoli production: Crop yield and quality, mulch deterioration, and growers’ perceptions. (Pullman, WA: Washington State University).
Cowan J., Miles C. (2018). Impact of biodegradable plastic mulch on specialty crop production. Available online at: http://vegetables.wsu.edu/MulchReport07. (Accessed May 19, 2023).
Cozzolino E., Di Mola I., Ottaiano L., Bilotto M., Petriccione M., Ferrara E., et al. (2023). Assessing yield and quality of melon (Cucumis melo L.) improved by biodegradable mulching film. Plants (Basel Switzerland) 12 (1), 219. doi: 10.3390/plants12010219
Cozzolino E., Giordano M., Fiorentino N., El-Nakhel C., Pannico A., Di Mola I., et al. (2020). Appraisal of biodegradable mulching films and vegetal-derived biostimulant application as eco-sustainable practices for enhancing lettuce crop performance and nutritive value. Agronomy. 10 (3), 427. doi: 10.3390/agronomy10030427
Danish S., Ali H., Datta R. (2023). Introductory Chapter: Smart Farming. Eds. Danish S., Ali H., Datta R. (London, UK: IntechOpen). Ch. 1. doi: 10.5772/intechopen.111561
Deng L., Meng X., Yu R., Wang Q. (2019a). Assessment of the effect of mulch film on crops in the arid agricultural region of China under future climate scenarios. Water 11 (9), 1819. doi: 10.3390/w11091819
Deng L., Yu Y., Zhang Y., Wang Q. (2019b). The effects of biodegradable mulch film on the growth, yield, and water use efficiency of cotton and maize in an arid region. Sustainability 11, 7039. doi: 10.3390/su11247039
Dentzman K., Hayes D. (2019). The role of standards for use biodegradable plastic mulches: truth and myths. Available online at: https://ag.tennessee.Edu/biodegradablemulch/Documents/Standards%20Factsheet%20Formatted%20revised%2015Jan2019.pdf. (Accessed February 12, 2024).
de Sadeleer I., Woodhouse A. (2023). Environmental impact of biodegradable and non-biodegradable agricultural mulch film: A case study for Nordic conditions. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 28 (1), 137–149. doi: 10.1007/s11367-023-02253-y
Dharmalingam S., Hayes D. G., Wadsworth L. C., Dunlap R. N. (2015). Analysis of the time course of degradation for fully biobased nonwoven agricultural mulches in compost-enriched soil. Textile Res. J. 86, 1343–1355. doi: 10.1177/0040517515612358
Di Mola I., Ventorino V., Cozzolino E., Ottaiano L., Romano I., Duri L. G., et al. (2021). Biodegradable mulching vs traditional polyethylene film for sustainable solarization: Chemical properties and microbial community response to soil management. Appl. Soil Ecol. 163, 103921. doi: 10.1016/J.APSOIL.2021.103921
Dutta B., Langston D. B., Luo X., Carlson S., Kichler J., Gitaitis R. (2017). A Risk Assessment Model for Bacterial Leaf Spot of Pepper (Capsicum annuum), Caused by Xanthomonas euvesicatoria, Based on Concentrations of Macronutrients, Micronutrients, and Micronutrient Ratios. Phytopathology® 107, 1331–1338. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-05-17-0187-R
European Bioplastics (2021).Renewable feedstock. Available online at: https://www.european-bioplastics.org/bioplastics/feedstoc. (Accessed January 28, 2024).
European Bioplastics (2023).Eu policy framework on biobased, biodegrad- able and compostable plastics. Available online at: www.european-bioplastics.org. (Accessed January 28, 2024).
Filiciotto L., Rothenberg G. (2021). Biodegradable plastics: standards, policies, and impacts. ChemSusChem 14, 56–72. doi: 10.1002/cssc.202002044
Fojt J., Denková P., Brtnický M., Holátko J., Řezáčová V., Pecina V., et al. (2022). Influence of poly-3-hydroxybutyrate micro-bioplastics and polyethylene terephthalate microplastics on the soil organic matter structure and soil water properties. Environ. Sci. Technol. 56, 10732–10742. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.2c01970
Fontenot K., Kirk-Ballard H., Coker C. E., Strahan R., Bacas I., Ely R. M. (2021). Assessing biodegradable mulch duration and nutsedge suppression during late summer cucumber production in mississippi and louisiana. Horticulturae 7 (9), 290. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae7090290
Food and Agriculture Organization (2009). Global agriculture towards 2050 (00153 Rome, Italy: Agricultural Development Economics Division Economic and Social Development Department Viale delle Terme di Caracalla). Available at: https://www.fao.org/fileadmin/templates/wsfs/docs/Issues_papers/HLEF2050_Global_Agriculture.pdf.
Galinato S. P., Velandia M., Ghimire S. (2020). Economic feasibility of using alternative plastic mulches: case study for pumpkin in western WA. Available online at: https://pubs.extension.wsu.edu/economic-feasibility-of-using-alternative-plastic-mulches-a-pumpkin-case-study-in-western-washington. (Accessed December 18, 2023).
Galinato S., Walters T. W. (2012). Cost Estimates of Producing Strawberries in a High Tunnel in Western Washington (Pullman, WA: Washington State University Ex), 1–8. Available at: http://cru.cahe.wsu.edu/CEPublications/FS093E/FS093E.pdf. FS093E.
Gao X. H., Xie D., Yang C. (2021). Effects of a PLA/PBAT biodegradable film mulch as a replacement of polyethylene film and their residues on crop and soil environment. Agric. Water Manage. 255, 107053. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2021.107053
Ghatge S., Yang Y., Ahn J. H., Hur H. G. (2020). Biodegradation of polyethylene: a brief review. Appl. Biol. Chem. 63, 1–14. doi: 10.1186/s13765-020-00511-3
Ghimire S., Miles C. (2020). Soil-Biodegradable Mulches: Course Lecture. Soil-biodegradable Mulches in Agriculture (Washington State University Extension). Available at: https://s3.wp.wsu.edu/uploads/sites/2181/2021/11/2.-long-lecture_presenter-notes.pdf.
Goldberger J. R. (2018). AFHVS presidential address: agriculture in the plastic age. Agr. Hum. Val. 35, 899–904. doi: 10.1007/s10460-018-9889-x
Goldberger J. R., Inglis D. A., Jones R. E., Miles C. A., Wallace R. W. (2013). Barriers and bridges to the adoption of biodegradable plastic mulches for US specialty crop production. Renewable Agric. Food Syst. 30, 143–153. doi: 10.1017/S1742170513000276
González A., López J., Rodríguez R., Martín P., Bañón S., Fernández J. A., et al. (2003). Behaviour of biodegradable film for mulching in open-air melon cultivation in SE Spain. Ktbl- schrift 414, 71–77. doi: 10.5555/20033186607
Guo C., Liu X. (2022). Effect of soil mulching on agricultural greenhouse gas emissions in China: A meta-analysis. PloS One 17, e0262120. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262120
Hakkarainen M., Albertsson A. C. (2004). Environmental degradation of polyethylene. Adv. Polym. Sci. 169, 177–200. doi: 10.1007/b13523
Hao A., Yin C., Léonard A., Dogot T. (2024). Cost–benefit analysis of mulch film management and its policy implications in northern China. Agriculture 14 (7), 1081. doi: 10.3390/agriculture14071081
Hayes D. G., Anunciado M. B., DeBruyn J. M., Bandopadhyay S., Schaeffer S., English M., et al. (2019). Biodegradable Plastic Mulch Films for Sustainable Specialty Crop Production BT - Polymers for Agri-Food Applications. Ed. Gutiérrez T. J. (Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing), 183–213. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-19416-1_11
Hayes D. G., Dharmalingam S., Wadsworth L. C., Leonas K. K., Miles C., Inglis D. A. (2012). “Biodegradable agricultural mulches derived from biopolymers,” in Degradable Polymers and Materials: Principles and Practice (2nd Edition), vol. 1114. (Washington, D.C., USA: American Chemical Society), 13–201. doi: 10.1021/bk-2012-1114.ch013
Hayes D. G., Flury M. (2018). Summary and assessment of EN 17033: A new standard for biodegradable plastic mulch films. Available online at: https://ag.tennessee.edu/biodegradablemulch/Documents/EU%20regs%20factsheet.pdf. (Accessed February 12, 2024).
Hofmann T., Ghoshal S., Tufenkji N., Adamowski J. F., Bayen S., Chen Q., et al. (2023). Plastics can be used more sustainably in agriculture. Commun. Earth Environ. 4, 1–11. doi: 10.1038/s43247-023-00982-4
Hu Q., Li X. Y., Goncalves J. M., Shi H. B., Tian T., Chen N. (2020). Effects of residual plastic-film mulch on field corn growth and productivity. Sci. Total Environ. 729, 138901. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138901
Huang Y., Liu Q., Jia W., Yan C., Wang J. (2020). Agricultural plastic mulching as a source of microplastics in the terrestrial environment. Environ. pollut. 260, 114096. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114096
Huang F., Zhang Q., Wang L., Zhang C., Zhang Y. (2023). ). Are biodegradable mulch films a sustainable solution to microplastic mulch film pollution? A biogeochemical perspective. J. Hazardous Materials 459, 132024. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.132024
Iqbal R., Raza M. A. S., Valipour M., Saleem M. F., Zaheer M. S., Ahmad S., et al. (2020). Potential agricultural and environmental benefits of mulches—a review. Bull. Natl. Res. Centre 44, 75. doi: 10.1186/s42269-020-00290-3
Jambeck J. R., Geyer R., Wilcox C., Siegler T. R., Perryman M., Andrady A., et al. (2015). Marine pollution. Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Sci. (New York N.Y.) 347, 768–771. doi: 10.1126/science.1260352
Jayasekara R., Harding I., Bowater I., Lonergan G. (2005). Biodegradability of a selected range of polymers and polymer blends and standard methods for assessment of biodegradation. J. Polymers Environ. 13, 231–251. doi: 10.1007/s10924-005-4758-2
Jia H., Wang Z., Zhang J., Li W., Ren Z., Jia Z., et al. (2020). Effects of biodegradable mulch on soil water and heat conditions, yield and quality of processing tomatoes by drip irrigation. J. Arid Land 12, 1–18. doi: 10.1007/s40333-020-0108-4
Jian J., Xiangbin Z., Xianbo H. (2020). An overview on synthesis, properties and applications of poly (butylene-adipate-co-terephthalate)–PBAT. Advanced Ind. Eng. Polymer Res. 3, 19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.aiepr.2020.01.001
Johansson E. M. V. (2018). Analysing costs for bio-based materials in agriculture. Available online at: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:169842217. (Accessed August 19, 2024).
Kader M. A., Senge M., Mojid M. A., Ito K. (2017). Recent advances in mulching materials and methods for modifying soil environment. Soil Tillage Res. 168, 155–166. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2017.01.001
Kasirajan S., Ngouajio M. (2012). Polyethylene and biodegradable mulches for agricultural applications: a review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 32, 501–529. doi: 10.1007/s13593-011-0068-3
Kim R. (2022). To mulch or not to mulch: problems with plastic mulch and how to address them, 42 J. Nat’l ass’n admin. L. Judiciary 1. Available online at: https://digitalcommons.pepperdine.edu/naalj/vol42/iss2/1. (Accessed February 11, 2024).
Lapichino G., Mustazza G., Sabatino L., D’Anna F. (2014). Polyethylene and biodegradable starch-based positively affect winter melon production in Sicily. Acta Hortic. 1015, 225–231. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2014.1015.25
Li R., Li L., Zhang Y., Yang J., Tu C., Zhou Q., et al. (2020). Uptake and accumulation of microplastics in cereal plant wheat. Chin. Sci. Bul. 65, 2120–2127. doi: 10.1360/TB-2020-0030
Li C., Moore-Kucera J., Lee J., Corbin A., Brodhagen M., Miles C., et al. (2014). Effects of biodegradable mulch on soil quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 79, 59–69. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2014.02.012
Li Q., Sugihara T., Shibusawa S., Li M. (2021). A case study on water use efficiency in extreme water-saving cultivation of tomato plants. Eur. J. Hortic. Sci. 86, 556–566. doi: 10.17660/eJHS.2021/86.5.11
Li C., Sun M., Xu X., Zhang L. (2021). Characteristics and influencing factors of mulch film use for pollution control in China: Microcosmic evidence from smallholder farmers. Resources Conserv. Recycling 164, 105222. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.105222
Liang W., Zhao Y., Xiao D Cheng J., Zhao J. (2020). A biodegradable water-triggered chitosan/hydroxypropyl methylcellulose pesticide mulch film for sustained control of Phytophthora sojae in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). J. Clean Prod 245, 118943. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118943
Lightfoot D. R. (1994). Morphology and ecology of lithic-mulch agriculture. Geographical Rev. 84, 172–185. doi: 10.2307/215329
Long A. (2023). The economics of mulch film: cost-benefit analysis. Available online at: https://aneuma.com/the-economics-of-mulch-film-cost-benefit-analysis. (Accessed August 19, 2024).
López-Marin J., Gonzalez Benavente-Garcia A., Fernandez J., Bañón S. (2007). Behaviour of biodegradable films used for mulching in melon cultivation. Acta Hortic. 747, 125–130. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2007.747.13
Madrid B., Wortman S., Hayes D. G., DeBruyn J. M., Miles C., Flury M., et al. (2022). End-of-life management options for agricultural mulch films in the United States—A review. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 6. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2022.921496
Mansoor Z., Tchuenbou-Magaia F., Kowalczuk M., Adamus G., Manning G., Parati M., et al. (2022). Polymers use as mulch films in agriculture—A review of history, problems and current trends. Polymers 14 (23), 5062. doi: 10.3390/polym14235062
Marí A. I., Pardo G., Cirujeda A., Martínez Y. (2019). Economic evaluation of biodegradable plastic films and paper mulches used in open-air grown pepper (Capsicum annum L.) Crop. Agronomy 9, 36. doi: 10.3390/agronomy9010036
Marie Chimi P., Armand Mala W., Ngamsou Abdel K., Louis Fobane J., Manga Essouma F., Hermann Matick J., et al. (2023). Vulnerability of family farming systems to climate change: The case of the forest-savannah transition zone, Centre Region of Cameroon. Res. Globalization 7, 100138. doi: 10.1016/j.resglo.2023.100138
Martín-Closas L., Bach A., Pelacho A. M. (2008). Biodegradable mulching in an organic tomato production system. Acta Hortic. 767, 267–274. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2008.767.28
Massawe B. H., Moisan L., Semu T., Nchimbi-Msolla S. (2023). Effects of biodegradable mulch films in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) performance: On-station trials. Tanzania J. Agric. Sci. 22 (2), 161–168.
Menossi M., Cisneros M., Alvarez V. A., Casalongué C. (2021). Current and emerging biodegradable mulch films based on polysaccharide bio-composites. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 41, (4). doi: 10.1007/s13593-021-00685-0
Mhlanga B., Ercoli L., Pellegrino E., Onofri A., Thierfelder C. (2021). The crucial role of mulch to enhance the stability and resilience of cropping systems in southern Africa. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 41, 29. doi: 10.1007/s13593-021-00687-y
Miles C., DeVetter L., Ghimire S., Hayes D. G. (2017). Suitability of biodegradable plastic mulches for organic and sustainable agricultural production systems. HortScience 52, 10–15. doi: 10.21273/hortsci11249-16
Miles C., Nelson L., Reed J. (2007). Alternatives to plastic mulch in vegetable production systems. HortScience 42, 899–900. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/296111767_Alternatives_to_Plastic_Mulch_in_Vegetable_Production_Systems.
Miles C., Wallace R., Wszelaki A., Martin J., Cowan J., Walters T., et al. (2012). Deterioration of potentially biodegradable alternatives to black plastic mulch in three tomato production regions. HortScience 47, 1270–1277. doi: 10.21273/hortsci.47.9.1270
Minuto G., Pisi L., Tinivella F., Bruzzone C., Guerrini S., Versari M., et al. (2008). Weed control with biodegradable mulch in vegetable crops. Acta Hortic. 801, 291–298. doi: 10.17660/ActaHortic.2008.801.29
Moher D., Liberati A., Tetzlaff J., Altman D. G., PRISMA Group (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann. Internal Med. 151, 264–9,W64. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135
Mola Ida D., Eugenio C., Lucia O., Luigi Giuseppe D., Riccardo R., Patrizia S., et al. (2019). The effect of novel biodegradable films on agronomic performance of zucchini squash grown under open-field and greenhouse conditions. AJCS 13, 1835–2707. doi: 10.21475/ajcs.19.13.11.p1796
Moore J., Wszelaki A. (2016). Plastic mulch in fruit and vegetable production: challenges for disposal. Available online at: https://ag.tennessee.edu/biodegradablemulch/Documents/Plastic%20Mulch%20in%20Fruit%20and%20Vegetable%20Production_12_20factsheet.pdf. (Accessed February 26, 2024).
Moreno M. M., Moreno A. (2008). Effect of different biodegradable and polyethylene mulches on soil properties and production in a tomato crop. Sci. Hortic. 116, 256–263. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2008.01.007
Moreno M. M., Moreno A., Mancebo I. (2009). Comparison of different mulch materials in a tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) crop. Spanish J. ofAgricultural Res. 7, 454–464. doi: 10.5424/sjar/2009072-1500
Morra L., Cozzolino E., Salluzzo A., Modestia F., Bilotto M., Baiano S., et al. (2021). Plant growth, yields and fruit quality of processing tomato (Solanum lycopersicon L.) as affected by the combination of biodegradable mulching and digestate. Agronomy 11 (1), 100. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11010100
Nassary E. K., Msomba B. H., Masele W. E., Ndaki P. M., Kahangwa C. A. (2022). Exploring urban green packages as part of Nature-based Solutions for climate change adaptation measures in rapidly growing cities of the Global South. J. Environ. Manage. 310, 114786. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114786
Nawaz A., Lal R., Shrestha R. K., Farooq M. (2016). Mulching affects soil properties and greenhouse gas emissions under long-Term no-Till and plough-Till systems in alfisol of central Ohio. Land Degrad. Dev. 28, 673–681. doi: 10.1002/ldr.2482
Ngouajio M., Auras R., Fernandez R. T., Rubino M., Counts J. W., Kijchavengkul T. (2008). Field performance of aliphatic-aromatic copolyester biodegradable mulch films in a fresh market tomato production system. HortTechnology Hortte 18, 605–610. doi: 10.21273/horttech.18.4.605
Nogueira R., Bhalerao A., Banerjeep R. (2018). Cost effective production of polyhydroxyalkanoate biopolymers using mixed microbial culture and industry waste water: an ecofriendly approach. Journal of Bioprocessing & Biotechniques 8, 1–8. doi: 10.4172/2090-4541-c4059/api
NOSB (2019). Biodegradable Biobased Mulch Film In response to a recommendation of the National Organic Standards Board (NOSB), biodegradable biobased mulch film. Available online at: https://www.ams.usda.gov/sites/default/files/media/2019MemoBiobasedMulchReport.pdf. (Accessed January 26, 2024).
NOSB (2021). Biodegradable Biobased Mulch Film In response to a recommendation of the National Organic Standards Board (NOSB), biodegradable biobased mulch film. Available online at: https://www.ams.usda.gov/sites/default/files/media/CSBiodegradBiobasedFinalRec.pdf. (Accessed January 26, 2024).
Ohtake Y., Kobayashi T., Asabe H., Murakami N. (1998). Studies on biodegradation of LDPE-observation of LDPE films scattered in agricultural fields or in garden soil. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 60, 79–84. doi: 10.1016/S0141-3910(97)00032-3
Olsen J., Gounder R. (2001). Alternatives to polyethylene mulch film — a field assessment of transported materials in capsicum (Capsicum annuum L.). Anim. Production Sci. 41, 93–103. doi: 10.1071/EA00077
Page M. J., McKenzie J. E., Bossuyt P. M., Boutron I., Hoffmann T. C., Mulrow C. D., et al. (2020). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021 372, n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
Peng X., Dong K., Wu Z., Wang J., Wang Z. (2021). A review on emerging biodegradable polymers for environmentally benign transient electronic skins. J. Materials Sci. 56, 16765–16789. doi: 10.1007/s10853-021-06323-0
Qiang L., Hu H., Li G., Xu J., Cheng J., Wang J., et al. (2023). Plastic mulching, and occurrence, incorporation, degradation, and impacts of polyethylene microplastics in agroecosystems. Ecotoxicology Environ. Saf. 263, 115274. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.115274
Rajgadia N., Debnath M. (2023). Biodegradable mulch utilizing bioplastic biopolymer polyhydroxyalkanoates. Materials Today: Proc. 79, 411–419. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2022.12.167
Ricker-Gilbert J., Jumbe C., Chamberlin J. (2014). How does population density influence agricultural intensification and productivity? Evidence Malawi. Food Policy 48, 114–128. doi: 10.1016/j.foodpol.2014.02.006
Sękara A., Pokluda R., Cozzolino E., Del Piano L., Cuciniello A., Caruso G. (2019). Plant growth, yield, and fruit quality of tomato affected by biodegradable and nondegradable mulches. Hortic. Sci. 46, 138–145. doi: 10.17221/218/2017-hortsci
Sa’adu I., Farsang A. (2023). Plastic contamination in agricultural soils: a review. Environ. Sci. Europe 35, 13. doi: 10.1186/s12302-023-00720-9
Sajjad M., Huang Q., Khan S., Khan M. A., Liu Y., Wang J., et al. (2022). Microplastics in the soil environment: A critical review. Environ. Technol. Innovation 27, 102408. doi: 10.1016/j.eti.2022.102408
Samir A., Ashour F. H., Hakim A. A. A., Bassyouni M. (2022). Recent advances in biodegradable polymers for sustainable applications. NPJ Materials Degradation 6, 68. doi: 10.1038/s41529-022-00277-7
Samphire M., Chadwick D. R., Jones D. L. (2023). Biodegradable plastic mulch films increase yield and promote nitrogen use efficiency in organic horticulture. Front. Agron. 5. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2023.1141608
Schonbeck M. (2012). Synthetic mulching materials for weed management; oregon state university, virginia association for biological farming. Available online at: https://eorganic.org/node/4872. (Accessed January 23, 2024).
Serrano R. H., Martin-Closas L., Pelacho A. M. (2021). Biodegradable plastic mulches: impact on the agricultural biotic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 750, 141228. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141228
Serrano-Ruiz H., Martín-Closas L., Pelacho A. M. (2018). Application of an in vitro plant ecotoxicity test to unused biodegradable mulches. Polymer Degradation Stability 158, 102–110. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2018.10.016
Shan X., Zhang W., Dai Z., Li J., Mao W., Yu F., et al. (2022). Comparative analysis of the effects of plastic mulch films on soil nutrient, yields and soil microbiome in three vegetable fields. Agronomy 12 (2), 506. doi: 10.3390/agronomy12020506
Sintim H. Y., Bary A. I., Hayes D. G., Wadsworth L. C., Anunciado M. B., English M. E., et al. (2020). In situ degradation of biodegradable plastic mulch films in compost and agricultural soils. Sci. Total Environ. 727, 138668. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138668
Sintim H., Flury M. (2017). Is biodegradable plastic mulch the solution to agriculture’s plastic problem? Environ. Sci. Technol. 51, 1068–1069. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b06042
Somanathan H., Sathasivam R., Sivaram S., Mariappan Kumaresan S., Muthuraman M. S., Park S. U. (2022). An update on polyethylene and biodegradable plastic mulch films and their impact on the environment. Chemosphere 307, 135839. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135839
Soylu E., Kizildeniz T. (2024). Innovative approach of biodegradable mulches in sustainable agriculture for crop production and environmental conservation. Bio Web Conferences 85, 01060. doi: 10.1051/bioconf/20248501060
Steinmetz Z., Wollmann C., Schaefer M., Buchmann C., David J., Tröger J., et al. (2016). Plastic mulching in agriculture. Trading short-term agronomic benefits for long-term soil degradation? Sci. Total Environ. 550, 690–705. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.01.153
Thakur M., Kumar R. (2021). Mulching: Boosting crop productivity and improving soil environment in herbal plants. J. Appl. Res. Medicinal Aromatic Plants 20, 100287. doi: 10.1016/j.jarmap.2020.100287
Tofanelli M. B. D., Wortman S. E. (2020). Benchmarking the agronomic performance of biodegradable mulches against polyethylene mulch film: A meta-analysis. Agronomy 10 (10), 1618. doi: 10.3390/agronomy10101618
United Nations (2015). Sustainable development; department of economic and social affairs. Available online at: https://sdgs.un.org/goals. (Accessed January 12, 2024).
Velandia M., Galinato S. P., Wszelaki A. (2020). Economic evaluation of biodegradable plastic films in Tennessee pumpkin production. Agronomy 10, 51. doi: 10.3390/agronomy10010051
Wang F., Gao J., Zhai W., Liu D., Zhou Z., Wang P. (2020). The influence of polyethylene microplastics on pesticide residue and degradation in the aquatic environment. J. Hazardous Materials 394, 122517. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122517
Wang K., Wang C., Chen M., Misselbrook T., Kuzyakov Y., Soromotin A., et al. (2022). Effects of plastic film mulch biodegradability on nitrogen in the plant-soil system. Sci. Total Environ. 833, 155220. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.155220
Wang Z., Wu Q., Fan B., Zhang J., Li W., Zheng X., et al. (2019). Testing biodegradable films as alternatives to plastic films in enhancing cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) yield under mulched drip 53 Page 26 of 27 Agron. Sustain. Dev., (2021) 41: 53 irrigation. Soil Tillage Res. 192, 196–205. doi: 10.1016/j.still.2019.05.004
Waterer D. (2010). Evaluation of biodegradable mulches for production of warm-season vegetable crops. Can. J. Plant Sci. 90, 737–743. doi: 10.4141/CJPS10031
Wellenreuther C., Wolf A., Zander N. (2021). Cost structure of bio-based plastics: A Monte-Carlo-analysis for PLA (Issue 197). Hamburgisches WeltWirtschaftsInstitut (HWWI). Available online at: https://hdl.handle.net/10419/235600.
Wu Z., Zheng Y., Sui X., Zhang Z., Wang E., Liu Y., et al. (2023). Comparative analysis of the effects of conventional and biodegradable plastic mulching films on soil-peanut ecology and soil pollution. Chemosphere 334, 139044. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2023.139044
Yeleliere E., Antwi-Agyei P., Guodaar L. (2023). Farmer’s response to climate variability and change in rainfed farming systems: Insight from lived experiences of farmers. Heliyon 9, e19656. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19656
Yin M., Li Y., Fang H., Chen P. (2019). Biodegradable mulching film with an optimum degradation rate improves soil environment and enhances maize growth. Agric. Water Manag 216, 127–137. doi: 10.1016/j.agwat.2019.02.004
Yu Y., Flury M. (2020). Current understanding of subsurface transport of micro- and nanoplastics in soil. Vadose Zone J. 20, 20108. doi: 10.1002/vzj2.20108
Yu H., Zhang Y., Tan W., Zhang Z. (2022). Microplastics as an emerging environmental pollutant in agricultural soils: effects on ecosystems and human health. Front. Environ. Sci. 10. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.855292
Zeng L. S., Zhou Z. F., Shi Y. X. (2013). Environmental problems and control ways of plastic film in agricultural production. Appl. Mechanics Materials 295–298, 2187–2190. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.295-298.2187
Zhang H., DeVetter L. W., Scheenstra E., Miles C. (2020). Weed pressure, yield, and adhesion of soil-biodegradable mulches with pie pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo). HortScience 55, 1014–1021. doi: 10.21273/hortscI15017-20
Zhang M., Xue Y., Jin T., Zhang K., Li Z., Sun C., et al. (2022). Effect of long-term biodegradable film mulch on soil physicochemical and microbial properties. Toxics 2022 10, 129. doi: 10.3390/toxics10030129
Zhang X., You S., Tian Y., Li J. (2019). Comparison of plastic film, biodegradable paper and bio-based film mulching for summer tomato production: Soil properties, plant growth, fruit yield and fruit quality. Scientia Hortic. 249, 38–48. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2019.01.037
Zhu J., Wang C. (2020). Biodegradable plastics: Green hope or green washing. Mar. pollut. Bull. 161, 111774. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111774
Zumilaiti T., Tao L., Wang L., Wang J., Li J., Tang Q. (2017). Effects of plastic film residues on soil nitrogen content, root distribution, and cotton yield during the long-term continuous cropping of cotton. Cotton Sci. 29, 374–384. doi: 10.11963/1002-7807.zmlttegtqx.20170602
Keywords: conservation agricultural practices, bio-based products, improved livelihoods, smallholder farming systems, synthetic biodegradable mulch
Citation: Ramadhani AM, Nassary EK, Rwehumbiza FB, Massawe BHJ and Nchimbi-Msolla S (2024) Potentials of synthetic biodegradable mulch for improved livelihoods on smallholder farmers: a systematic review. Front. Agron. 6:1454060. doi: 10.3389/fagro.2024.1454060
Received: 24 June 2024; Accepted: 02 September 2024;
Published: 23 September 2024.
Edited by:
Saif Ullah, University of Agriculture, Faisalabad, PakistanReviewed by:
Umair Riaz, Muhammad Nawaz Shareef University of Agriculture, PakistanAsif Naeem, Nuclear Institute for Agriculture and Biology, Pakistan
Copyright © 2024 Ramadhani, Nassary, Rwehumbiza, Massawe and Nchimbi-Msolla. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ahamed Mwarabu Ramadhani, bXdhcmFidWFAZ21haWwuY29t
 Ahamed Mwarabu Ramadhani
Ahamed Mwarabu Ramadhani Eliakira Kisetu Nassary
Eliakira Kisetu Nassary Filbert B. Rwehumbiza1
Filbert B. Rwehumbiza1 Susan Nchimbi-Msolla
Susan Nchimbi-Msolla