
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Aging , 10 March 2025
Sec. Aging and the Immune System
Volume 6 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fragi.2025.1502746
This article is part of the Research Topic Immune Senescence: A Key Driver of Aging and Age-Related Disorders View all articles
Background: This research delved into the association between the systemic immune-inflammatory index (SII) and both all-cause and cancer-specific mortality among individuals aged 60 years and above in the United States during the period from 1999 to 2018, with follow-up extending until 31 December 2019. The data utilized was sourced from 4295 population-based participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES).
Methods: To analyze the relationship between SII and mortality, the study employed Cox proportional-risk models, restricted cubic spline curves, survival curves, and subgroup analyses.
Results: The average age of the participants was 70.7 (±7.6) years, the median follow-up duration was 131.7 (±59.8) months, and the all-cause mortality rate stood at 50.5%. Findings from the Cox regression model indicated that, after adjusting for covariates, SII was significantly and linearly related to all-cause mortality (hazard ratio HR = 1.31, 95% confidence interval CI = 1.15–1.48). Moreover, the relationship between SII and cancer mortality exhibited a U-shaped pattern. Results from the survival curves suggested that a higher SII was associated with an augmented risk of both all-cause mortality and cancer mortality.
Conclusion: There is a significant association between higher SII levels and increased risk of all-cause and cancer-specific mortality in the US population aged 60 years and older.
Chronic diseases and cancers have emerged as the primary culprits behind the high mortality rates among the elderly (Silva et al., 2023). As society steadily marches towards an ageing demographic, the incidence of these conditions among the senior population has witnessed an explosive upsurge. Projections indicate that by 2050, a full 20% of the global population will be 60 years old or older. Concomitantly, there will be a substantial hike in the incidence and mortality associated with age-related chronic diseases. Notably, the number of newly diagnosed cancer cases is anticipated to skyrocket to 35 million, and the death toll from cancer is projected to climb to 10 million (Fane et al., 2020; Bray et al., 2022). This not only poses a grave threat to the well-being of the elderly but also exerts a colossal burden on the economy and healthcare systems.
Inflammation is widely regarded as a pivotal endogenous factor in the ageing process, playing a crucial role in the development of chronic diseases and cancer (Li C. et al., 2023). SII serves as a key indicator of the body’s immune-inflammatory status. It is calculated by measuring neutrophils, platelets, and lymphocytes in peripheral blood samples (Feng et al., 2022). Clinically, it has been extensively employed to prognosticate the outcomes of various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, and sarcopenia (Tian et al., 2022; Ye et al., 2022; Han et al., 2023; Xie et al., 2024).
There is a significant increase in the incidence of chronic diseases and cancers among people over 60 years of age (Thomas et al., 2020; Fane et al., 2020). However, within the U.S. population aged 60 and older, the association between the SII and both all-cause and cancer mortality remains relatively under-investigated. Therefore, in this study, we harnessed data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) to thoroughly explore the relationship between the systemic immune-inflammatory status and mortality outcomes in this specific demographic.
The NHANES is a nationally representative survey executed by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). It utilizes stratified, multistage probability cluster sampling to evaluate the health and nutritional status of the non-institutionalized U.S. population (Li B. et al., 2023). For our study, we focused on individuals over 60 years of age from the NHANES 1999–2018 cycle. The NHANES study protocol received approval from the NCHS research ethics review board. Participants provided written informed consent upon enrollment. Our associated study conducted at Shangluo Central Hospital in Shangluo, China, was exempted by the institutional review board due to the use of publicly available, anonymized data, and informed consent was therefore waived (Yang et al., 2022). This study complied with the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) reporting guidelines.
Data were gathered from 19,087 individuals aged 60 years or older from the NHANES database, covering the period from 1999 to 2018. We applied the following exclusion criteria: individuals with missing SII data (n = 2,164) and those missing any other covariate values (n = 12,628). Ultimately, 4,295 participants were included in our study. A flowchart of the study data selection process is presented in Figure 1.
Complete blood cell counts were performed on samples according to the laboratory tests listed on the NHANES website (Chen Y. et al., 2023). The SII was calculated as the product of platelet count and neutrophil count divided by the lymphocyte count, expressed in ×109 cells/μl, consistent with previous studies (Hu et al., 2014).
All-cause mortality was determined from records obtained from the National Death Index (NDI) up to 31 December 2019, which were linked to the NHANES datasets. Cause-specific mortality was assessed using the 10th edition of the International Classification of diseases (ICD-10) codes; specifically, codes C00-C97 were employed to define cancer-related deaths (Cao et al., 2023).
Based on prior studies, the potential covariates considered in our analysis included age, sex, and race/ethnicity (categorized as non-Hispanic White, non-Hispanic Black, Mexican American, or other). Marital status was categorized as married/living with a partner or living alone, which included individuals who were never married, separated, divorced, or widowed. Educational attainment was divided into three categories: 9, 9–12, or >12 years of education. Lifestyle characteristics such as alcohol consumption and smoking were also included. Alcohol use was defined as consuming alcohol at least 12 times per year. Individuals who smoked ≥100 cigarettes in their lifetime were categorized as smokers (Lin et al., 2022). body mass index (BMI) was calculated as body weight (kg)/height (m2). Weight and height were measured at the Mobile Examination Center (Liu et al., 2022). Diagnoses of asthma and emphysema were based on participants affirmatively responding to NHANES questionnaire items asking if a doctor or other health professional had ever diagnosed them with these conditions (Salo et al., 2022). Stroke and cardiovascular diseases were considered if diagnosed by a physician. Diabetes was defined based on a physician’s diagnosis, a glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level >6.5%, fasting glucose levels ≥7.0 mmol/L, blood glucose levels ≥11.1 mmol/L during a random/2-h oral glucose tolerance test, or the use of diabetes medication or insulin (ElSayed et al., 2023). The NHANES website details the procedures for the collection of blood biochemicals. Measurements included platelets, neutrophils, lymphocytes, C-reactive protein (CRP), glycated hemoglobin, albumin, triglycerides, total cholesterol, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and urea nitrogen levels. These were all conducted on blood samples collected after at least 8 h of fasting, as outlined in the NHANES Detailed Laboratory Procedures (Mahemuti et al., 2023; Hong et al., 2023). The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated using the creatinine equation (Giavarina et al., 2021).
Participant characteristics are reported as means with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for continuous variables, and percentages with 95% CIs for categorical variables. For normally distributed data, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was utilized, while the Kruskal–Wallis test was applied to data with skewed distributions. Categorical variables are presented as proportions (%), and continuous variables as either means (standard deviation [SD]) or medians (interquartile range [IQR]), as appropriate. Differences between groups were evaluated using one-way ANOVA for normally distributed data, the Kruskal–Wallis test for skewed data, and the chi-squared test for categorical variables. Multifactorial Cox regression models were employed to analyze the association between SII and the risk of all-cause mortality or cancer death, providing estimated HRs and 95% CIs. Model 1 was adjusted for sociodemographic and lifestyle characteristics (age, sex, race/ethnicity, marital status, education, smoking and alcohol consumption status), and the NHANES cycle. Model 2 included adjustments for the factors in Model 1 plus HbA1c, albumin, CRP, TG, TC, ALT, AST, Cr, BUN, and eGFR. Model 3 further adjusted for factors in Model 2 and added asthma, emphysema, cardiovascular disease, stroke, and diabetes. SII values were categorized into four subgroups based on their quartiles. Survival curves were constructed using the Kaplan-Meier method, with the log-rank test employed to assess differences in survival. Additionally, to explore the dose-response relationship between SII and mortality, we utilized restricted cubic spline (RCS) regression with a likelihood ratio test for detecting non-linearity with multivariate adjustment.
To assess the stability of the association between SII values and cancer deaths, subgroup analyses were performed based on stratification variables, employing logistic regression models and likelihood ratio tests to evaluate interactions between subgroups. A priori calculation of statistical power was not conducted, as the sample size was derived entirely from available data. Analyses were conducted using R version 4.2.1 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) and Free Statistical Software version 1.92 (Beijing Free Clinical Medical Technology Co., Ltd.). All analyses were two-sided with a P-value threshold of less than 0.05 considered statistically significant. Data analysis took place between June and July 2024.
Of the 19,087 participants aged ≥60 years in the 1999–2018 NHANES, exclusions were made for those with missing SII data (n = 2,164) and those lacking values for other covariates (n = 12,628). Ultimately, 4,295 participants were included in the study (Figure 1).
The final sample consisted of 4,295 individuals aged 60 and older, with 50.3% being female and an average age of 70.7 (7.6) years. The median follow-up period was 131.7 (59.8) months, and the incidence of all-cause mortality was 50.5%. Table 1 presents the baseline characteristics of participants, categorized by quartiles of SII values. Generally, SII was higher in women, smokers, alcohol consumers, non-Hispanic whites, and those with higher educational attainment. Notably, higher SII levels were significantly associated with elevated levels of albumin, CRP, glutamine, urea nitrogen, and eGFR. Moreover, conditions such as emphysema and cardiovascular disease were also linked to increased SII values.
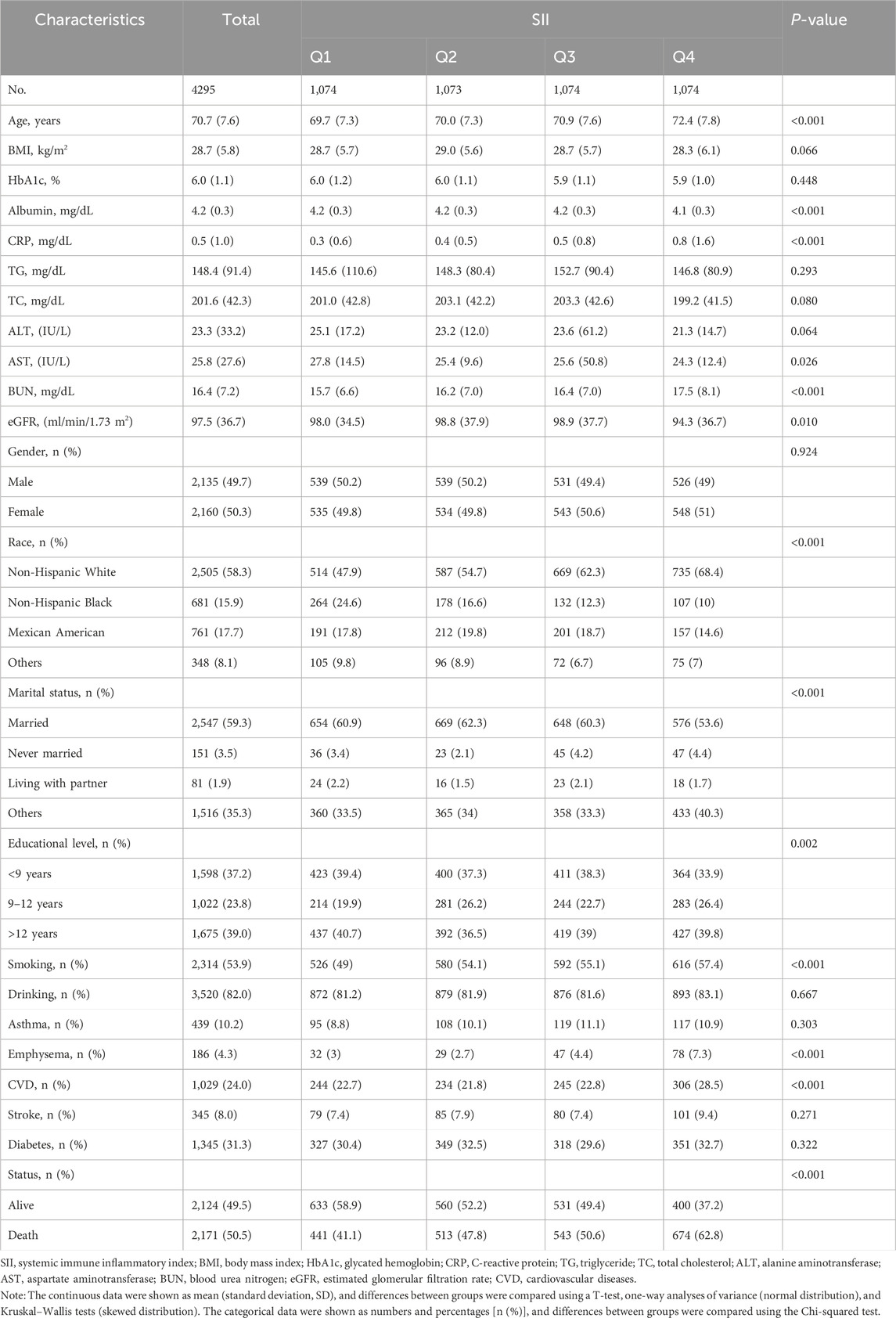
Table 1. General characteristics of the participants from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999–2018 cycles.
The results of the Cox regression models, as presented in Table 2, indicate that SII was significantly associated with the risk of all-cause mortality (HR = 1.73, 95% CI = 1.54–1.95) in the unadjusted model. This association remained robust and statistically significant after multivariate adjustments in model 1 (HR = 1.40, 95% CI = 1.24–1.59), model 2 (HR = 1.31, 95% CI = 1.16–1.49), and model 3 (HR = 1.31, 95% CI = 1.15–1.48). In contrast, the association between SII and cancer death, though significant in the unadjusted model (HR = 1.52, 95% CI = 1.19–1.95), showed reduced stability and was not statistically significant across the adjusted models: model 1 (HR = 1.31, 95% CI = 1.02–1.68), model 2 (HR = 1.24, 95% CI = 0.96–1.60), and model 3 (HR = 1.23, 95% CI = 0.95–1.59). The RCS results revealed a linear relationship between SII and all-cause mortality, with increasing SII values correlating with higher mortality risk, whereas a U-shaped relationship was observed between SII and cancer mortality (Figures 2A, B). Threshold analysis indicated that the HR for the risk of cancer death for participants with an SII <504.52 was 0.998 (95% CI: 0.997 to 0.999, P = 0.037) (Table 3). For those with an SII ≥504.52, the HR was 1.004 (95% CI: 1.002 to 1.007, P = 0.003), suggesting that a higher SII was associated with an increased risk of cancer death. Survival curves indicated that patients with an SII >725.33 had a worse prognosis compared to other groups during the follow-up period, P < 0.001 on the log-rank test) (Figures 3A, B).
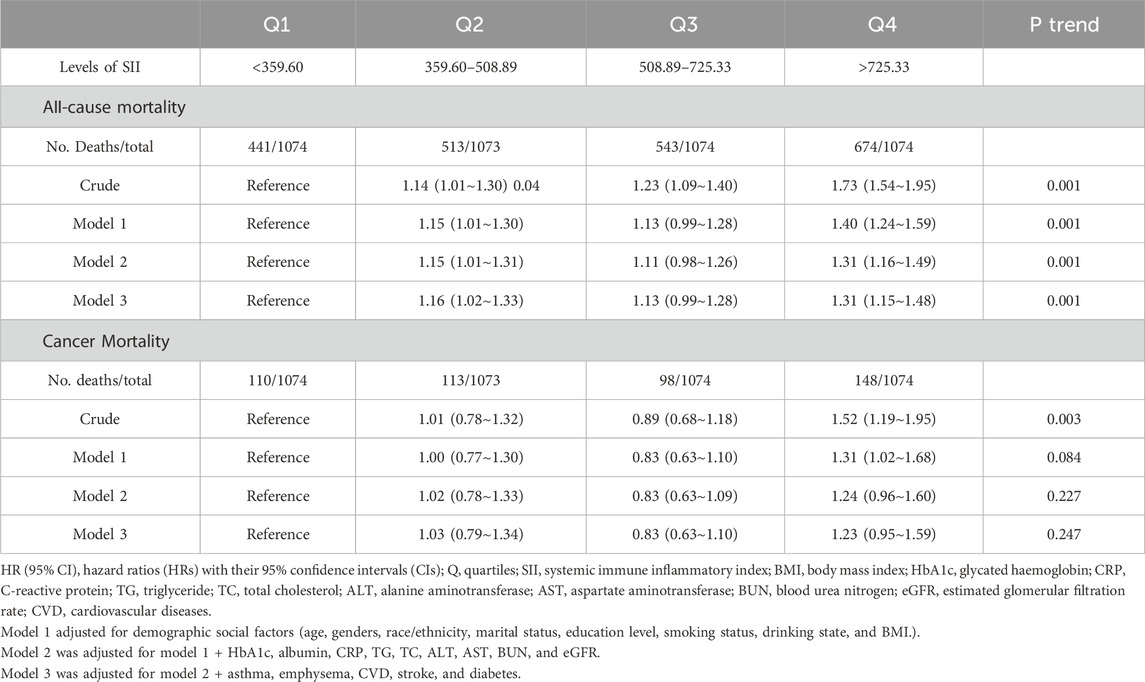
Table 2. HRs (95% Cis) for all-cause and cancer mortality based on SII quartiles in American 60 years and older.
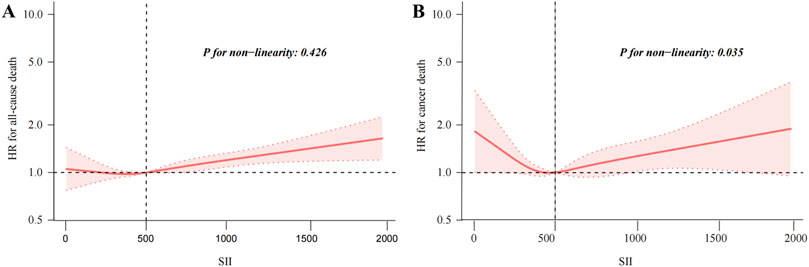
Figure 2. Restricted cubic spline fitting for the association between SII with mortality. Association of SII levels with the all-cause (A), and cancer mortality (B).
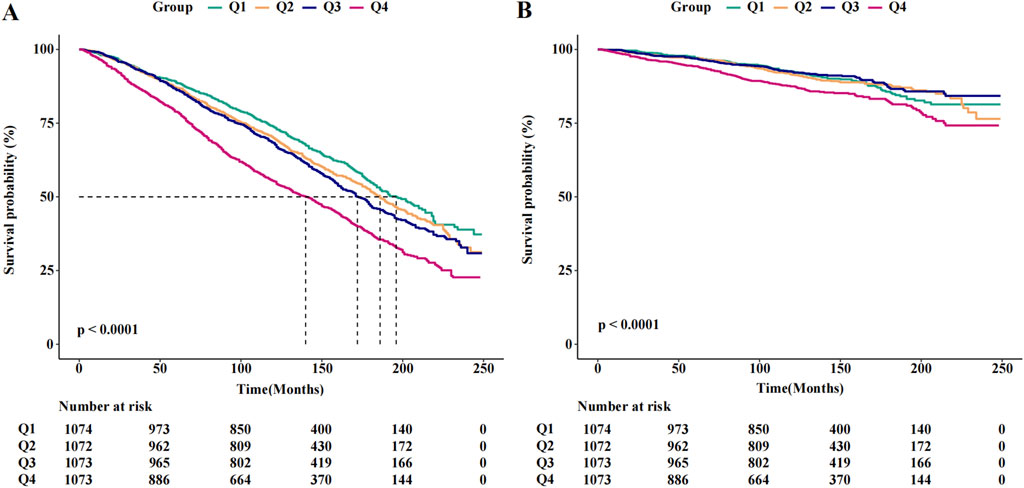
Figure 3. The Kaplan-Meier curves for 20-year occurrence of (A) all-cause and (B) cancer mortality, by quartiles of SII.
Subgroup analysis, after adjusting for age, sex, body mass index, CRP, creatinine clearance, and diabetes, revealed an interaction between SII and body mass index in the subgroup analysis of SII and all-cause mortality (p < 0.05). In the subgroup analysis of SII and cancer mortality, the relationship between SII and cancer mortality was stable, with no significant interaction between subgroups (p > 0.05), and the difference was not statistically significant (Supplementary Figure A, B)
The results of the study showed an association between SII and the risk of all-cause and cancer mortality even after adjustment for multifactorial modelling. SII was linearly associated with all-cause mortality and U-shaped with cancer mortality, and survival curve analyses showed an increased risk of all-cause and cancer deaths in the group with higher levels of SII (> 725.33). In addition, we found that in the subgroup analysis of SII with all-cause mortality, the results showed an interaction between SII and body mass index (P < 0.05). This may be related to the higher risk of dying from cardiovascular disease in individuals with higher body mass index. However, in the subgroup analysis of SII and cancer mortality, there was no interaction between subgroups (P > 0.05).
Previous studies have reported significant associations between SII and the prognosis of chronic diseases and cancer (Ye et al., 2023; Tian et al., 2022; Nakamoto et al., 2023). Among Americans with hypertension, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and adult frailty, SII demonstrated a U-shaped relationship with both all-cause and cancer mortality. When SII was treated as a categorical variable, it was consistently associated with all-cause mortality after multi-model adjustment. Nevertheless, the relationship between SII and cancer mortality varied. SII was significantly associated with cancer mortality in the cardiovascular disease and frailty populations (Xiao et al., 2023; Zheng et al., 2023). In the hypertension and type 2 diabetes populations, SII was not significantly associated with the risk of cancer mortality (Cao et al., 2023; Chen C. et al., 2023). Additionally, SII showed a J-shaped relationship with all-cause mortality in patients with non - alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and osteoarthritis (Zhou et al., 2024; Zhao et al., 2023), and a linear rather than U-shaped relationship in the sarcopenia and chronic renal failure populations (Zeng et al., 2024; Tang et al., 2024). These studies have shown that the relationship between SII and the risk of all-cause mortality and cancer mortality varies between populations. In our study, we found a linear relationship between elevated SII and all-cause mortality and a U-shaped relationship between SII and cancer mortality in the US population aged 60 years and older. This adds to our understanding of the relationship between SII and mortality risk in populations.
To further investigate the association between SII and cancer mortality, we explored a number of factors that influence the association with cancer mortality, such as female, age, higher body mass index, higher CRP, creatinine clearance, and diabetes. Consistent with previous studies, we found an association between SII and cancer mortality in female participants, which may be attributed to the higher risk of breast, uterine and ovarian cancers in this group (Zhou et al., 2023; Extermann et al. 2023; Huang et al. 2019; Mao et al. 2023). In older populations, there is an association between SII and mortality risk, which may be related to chronic inflammation, impaired immune function and increased cancer risk ( Li et al., 2021). In obese populations, SII is positively correlated with the percentage of body fat distribution in obese individuals (body mass index >30 kg/m2), and overweight and obesity may increase the risk of all-cause and cancer mortality (Liu et al., 2024; Molina-Montes et al., 2021). Both SII and CRP can be used to reflect the body’s inflammation level, and clinical studies have found that higher CRP potentially increases the risk of cancer mortality (Wulaningsih et al., 2016). Previous studies have shown that the relationship between SII and creatinine clearance and cancer mortality is unclear. (Zhai et al., 2024) found that the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) tended to be lower in patients with a high SII group in immunoglobulin A (IgA) nephropathy, and that elevated SII was associated with a poor prognosis in diabetic nephropathy and IgA nephropathy (Guo et al., 2022). In contrast, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and targeted therapies can cause acute kidney injury with decreased creatinine clearance, which increases the risk of cancer mortality (Jagieła et al., 2021). In diabetic populations, elevated SII is positively associated with diabetes (Nie et al., 2023), and previous studies have confirmed the association between diabetes and the risk of cancer mortality (Pearson-Stuttard et al., 2021; Yeh et al., 2018).
Low-grade systemic inflammation is a characteristic of aging, with a significant correlation between chronic inflammation and cardiovascular, metabolic, and cancer diseases (Vasto et al., 2009). The morbidity and mortality of most chronic diseases increase with age, particularly in individuals over 60 years old (Prince et al., 2015). The SII is used to evaluate the body’s immune level and inflammatory status through the ratio of neutrophils and platelets to lymphocytes (Hang et al., 2022). Neutrophils play a crucial role in maintaining immune function and in the pathogenesis of diseases. The elimination of pathogenic microorganisms, mediation of tissue damage, and aseptic inflammation are mediated by the release of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Simultaneously, NETs can interact with P-selectin to activate platelets, promote thrombosis, and lead to organ damage (Hidalgo et al., 2022). Moreover, neutrophil extracellular traps can induce the production of autoimmune complexes that exacerbate autoimmune diseases and participate in the inflammatory response to induce tumors and promote cancer progression (Mutua et al., 2021). Lymphocytes, classified into T-lymphocytes, B-lymphocytes, and natural killer cells, maintain the body’s immune function through cellular and humoral immunity (Yazicioglu et al., 2024). Activated lymphocytes can also cause tissue damage and organ dysfunction by releasing mitochondrial danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which mediate the inflammatory response to pathogens (Faas et al., 2020). The heterogeneity, differentiation, and proliferation of lymphocytes are relevant to the development of infectious diseases, chronic inflammation, tumors, and autoimmune diseases (Sun et al., 2023; Chapman et al., 2022). Platelets are not only essential for hemostasis but are also intricately involved in the body’s inflammatory response, thrombosis, cancer occurrence, and metastasis. They also interact with neutrophils and lymphocytes and participate in the systemic immune-inflammatory response (Mandel et al., 2022). In the elderly population (especially those with chronic comorbidities), high levels of inflammation are commonly observed. Meanwhile, the immune system undergoes immune senescence with age, and immune cell senescence acquires an inflammatory senescence - associated secretory phenotype (SASP), which further induces immune cell senescence and immune deterioration, leading to an imbalance in the body’s immune-inflammation levels (Karanth et al., 2021; Saavedra et al., 2023). Inflammation and immune aging cause an increase in immune- inflammation levels. High SII promotes the development of chronic inflammation and cancer and is closely related to the poor prognosis of many diseases (Benz et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2023).
The current study has some limitations. First, while the analysis utilized a large sample from NHANES and accounted for relevant covariates, the study population was restricted to individuals aged 60 years or older in the United States, which limits its generalizability to other demographics. Second, the SII results were based on a single measurement; the absence of data from multiple repeated measurements might not accurately represent the long-term immune-inflammatory status, potentially underestimating the association. Third, the reliance on self-reported data for conditions like asthma, emphysema, and stroke could introduce memory bias. Finally, given the observational nature of our study, we could not establish a causal relationship between SII and mortality outcomes.
There is a significant association between higher SII levels and increased risk of all-cause and cancer-specific mortality in the US population aged 60 years and older.
These survey data are free and publicly available, and can be downloaded directly from the NHANES website (https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/default.aspx) by users and researchers worldwide.
The studies involving humans were approved by NHANES Institutional Review Board (IRB), NCHS Research Ethics Review Board (ERB),NCHS Ethics Review Board. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
WL: Data curation, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. YG: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Project administration, Investigation, Writing–original draft. LL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. YZ: Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. XT: Conceptualization, Data curation, Project administration, Resources, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HL: Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
We thank Jie LL, PhD (Department of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Chinese PLA General Hospital) for his helpful review and comments regarding the manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fragi.2025.1502746/full#supplementary-material
Benz, E., Wijnant, S. R. A., Trajanoska, K., Arinze, J. T., de Roos, E. W., de Ridder, M., et al. (2022). Sarcopenia, systemic immune-inflammation index and all-cause mortality in middle-aged and older people with COPD and asthma: a population-based study. ERJ Open Res.8, 00628–02021. doi:10.1183/23120541.00628-2021
Bray, F., Laversanne, M., Sung, H., Me, J. F., Siegel, R. L., Soerjomataram, I., et al. (2022). Global cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 74C, 229–263. doi:10.3322/caac.21834
Cao, Y., Li, P., Zhang, Y., Qiu, M., Li, J., Ma, S., et al. (2023). Association of systemic immune inflammatory index with all-cause and cause-specific mortality in hypertensive individuals: results from NHANES. Front. Immunol. 14, 1087345. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1087345
Chapman, N. M., and Chi, H. (2022). Metabolic adaptation of lymphocytes in immunity and disease. Immunity. 55, 14–30. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2021.12.012
Chen, C., Chen, Y., Gao, Q., and Wei, Q. (2023). Association of systemic immune inflammatory index with all-cause and cause-specific mortality among individuals with type 2 diabetes. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 23, 596. doi:10.1186/s12872-023-03638-5
Chen, Y., Huang, R., Mai, Z., Chen, H., Zhang, J., Zhao, L., et al. (2023). Association between systemic immune-inflammatory index and diabetes mellitus: mediation analysis involving obesity indicators in the NHANES. Front. Public Health. 11, 1331159. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2023.1331159
ElSayed, N. A., Aleppo, G., Aroda, V. R., Bannuru, R. R., Brown, F. M., et al. (2023). 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of care in diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. 46 (Suppl. 1), S19–S40. doi:10.2337/dc23-S002
Extermann, M., Al-Jumayli, M., Sam, C., and Kish, J. A. (2023). Oncogeriatric developments. Gerontology. 69, 1045–1055. doi:10.1159/000531559
Faas, M. M., and de Vos, P. (2020). Mitochondrial function in immune cells in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1866, 165845. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165845
Fane, M., and Weeraratna, A. T. (2020). How the ageing microenvironment influences tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 20, 89–106. doi:10.1038/s41568-019-0222-9
Feng, L., Xu, R., Lin, L., and Liao, X. (2022). Effect of the systemic immune-inflammation index on postoperative complications and the long-term prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer: a Retrospective cohort study. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 13, 2333–2339. doi:10.21037/jgo-22-716
Giavarina, D., Husain-Syed, F., and Ronco, C. (2021). Clinical implications of the new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Nephron. 145, 508–512. doi:10.1159/000516638
Guo, W., Song, Y., Sun, Y., Du, H., Cai, Y., You, Q., et al. (2022). Systemic immune-inflammation index is associated with diabetic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: evidence from NHANES 2011-2018. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 13, 1071465. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.1071465
Han, J., Yang, L., Lou, Z., and Zhu, Y. (2023). Association between systemic immune-inflammation index and systemic inflammation response index and outcomes of acute ischemic stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 26, 655–662. doi:10.4103/aian.aian_85_23
Hang, W., Luo, J., Wen, J., and Jiang, M. (2022). The relationship between systemic immune inflammatory index and prognosis of patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Front. Surg. 9. doi:10.3389/fsurg.2022.898304
Hidalgo, A., Libby, P., Soehnlein, O., Aramburu, I. V., Papayannopoulos, V., and Silvestre-Roig, C. (2022). Neutrophil extracellular traps: from physiology to pathology. Cardiovasc Res. 118, 2737–2753. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvab329
Hong, C., Zhu, H., Zhou, X., Zhai, X., Li, S., Ma, W., et al. (2023). Association of blood urea nitrogen with cardiovascular diseases and all-cause mortality in USA adults: results from NHANES 1999–2006. Nutrients. 15, 461. doi:10.3390/nu15020461
Hu, B., Yang, X. R., Xu, Y., Sun, Y. F., Sun, C., Guo, W., et al. (2014). Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 20, 6212–6222. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0442
Huang, H., Liu, Q., Zhu, L., Zhang, Y., Lu, X., Wu, Y., et al. (2019). Prognostic value of preoperative systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with cervical cancer. Sci. Rep. 9, 3284. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-39150-0
Jagieła, J., Bartnicki, P., and Rysz, J. (2021). Nephrotoxicity as a complication of chemotherapy and immunotherapy in the treatment of colorectal cancer, melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22, 4618. doi:10.3390/ijms22094618
Karanth, S. D., Washington, C., Cheng, T. Y. D., Zhou, D., Leeuwenburgh, C., and Braithwaite, D., (2021). Inflammation in relation to sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity among older adults living with chronic comorbidities: results from the national health and nutrition examination survey 1999–2006. Nutrients. 13, 3957. doi:10.3390/nu13113957
Li, H., Wu, X., Bai, Y., Wei, W., Li, G., Fu, M., et al. (2021). Physical activity attenuates the associations of systemic immune-inflammation index with total and cause-specific mortality among middle-aged and older populations. Sci. Rep. 11, 12532. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-91324-x
Li, B., Chen, L., Hu, X., Tan, T., Yang, J., Bao, W., et al. (2023). Association of serum uric acid with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 46, 425–433. doi:10.2337/dc22-1339
Li, X., Li, C., Zhang, W., Wang, Y., Qian, P., and Huang, H. (2023). Inflammation and aging: signaling pathways and intervention therapies. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 8 , 239. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01502-8
Lin, W. T., Kao, Y. H., Li, M. S., Luo, T., Lin, H. Y., Lee, C. H., et al. (2022). Sugar-sweetened beverages intake, abdominal obesity, and inflammation among US adults without and with prediabetes-an NHANES study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 20, 681. doi:10.3390/ijerph20010681
Liu, Q., Kang, Y., and Yan, J. (2022). Association between overall dietary quality and constipation in American adults: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 22, 1971. doi:10.1186/s12889-022-14360-w
Liu, Y. Y., Ruan, G. T., Ge, Y. Z., Li, Q. Q., Zhang, Q., Zhang, X., et al. (2023). Systemic inflammation with sarcopenia predicts survival in patients with gastric cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 149, 1249–1259. doi:10.1007/s00432-022-03925-2
Liu, X., Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Sang, Y., Chai, Y., Zhang, L., et al. (2024). Systemic immunity-inflammation index is associated with body fat distribution among U.S. Adults: evidence from national health and nutrition examination survey 2011-2018. BMC Endocr. Disord. 24, 189. doi:10.1186/s12902-024-01725-y
Mahemuti, N., Jing, X., Zhang, N., Liu, C., Li, C., Cui, Z., et al. (2023). Association between systemic immunity-inflammation index and hyperlipidemia: a population-based study from the NHANES (2015–2020). Nutrients. 15, 1177. doi:10.3390/nu15051177
Mandel, J., Casari, M., Stepanyan, M., Martyanov, A., and Deppermann, C. (2022). Beyond hemostasis: platelet innate immune interactions and thromboinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23, 3868. doi:10.3390/ijms23073868
Mao, H., and Yang, F. (2023). Prognostic significance of systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis. Front. Oncol. 13, 1193962. doi:10.3389/fonc.2023.1193962
Molina-Montes, E., Ubago-Guisado, E., Petrova, D., Amiano, P., Chirlaque, M. D., Agudo, A., et al. (2021). The role of diet, alcohol, BMI, and physical activity in cancer mortality: summary findings of the EPIC study. Nutrients. 13, 4293. doi:10.3390/nu13124293
Mutua, V., and Gershwin, L. J. (2021). A review of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in disease: potential anti-NETs therapeutics. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 61, 194–211. doi:10.1007/s12016-020-08804-7
Nakamoto, S., Ohtani, Y., Sakamoto, I., Hosoda, A., Ihara, A., and Naitoh, T. (2023). Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts tumor recurrence after radical resection for colorectal cancer. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 261, 229–238. doi:10.1620/tjem.2023.J074
Nie, Y., Zhou, H., Wang, J., and Kan, H. (2023). Association between systemic immune-inflammation index and diabetes: a population-based study from the NHANES. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 14, 1245199. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1245199
Pearson-Stuttard, J., Papadimitriou, N., Markozannes, G., Cividini, S., Kakourou, A., Gill, D., et al. (2021). Type 2 diabetes and cancer: an umbrella review of observational and mendelian randomization studies. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 30, 1218–1228. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-20-1245
Prince, M. J., Wu, F., Guo, Y., Gutierrez Robledo, L. M., O’Donnell, M., Sullivan, R., et al. (2015). The burden of disease in older people and implications for health policy and practice. Lancet. 385, 549–562. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61347-7
Saavedra, D., Añé-Kourí, A. L., Barzilai, N., Caruso, C., Cho, K. H., Fontana, L., et al. (2023). Aging and chronic inflammation: highlights from a multidisciplinary workshop. Immun. Ageing. 20, 25. doi:10.1186/s12979-023-00352-w
Salo, P. M., Mendy, A., Wilkerson, J., Molsberry, S. A., Feinstein, L., London, S. J., et al. (2022). Serum antioxidant vitamins and respiratory morbidity and mortality: a pooled analysis. Respir. Res. 23, 150. doi:10.1186/s12931-022-02059-w
Silva, N., Rajado, A. T., Esteves, F., Brito, D., Apolónio, J., Roberto, V. P., et al. (2023). Measuring healthy ageing: current and future tools. Biogerontology. 24, 845–866. doi:10.1007/s10522-023-10041-2
Sun, L., Su, Y., Jiao, A., Wang, X., and Zhang, B. (2023). T cells in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 8, 235. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01471-y
Tang, R., Chen, J., Zhou, Q., Deng, J., Zhan, X., Wang, X., et al. (2024). Association between systemic immune inflammation index and all-cause mortality in incident peritoneal dialysis-treated CKD patients: a multi-center retrospective cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 25, 8. doi:10.1186/s12882-023-03451-4
Thomas, S. A., Qiu, Z., Chapman, A., Liu, S., and Browning, C. J. (2020). Editorial: chronic illness and ageing in China. Front. Public Health. 8, 104. doi:10.3389/fpubh.2020.00104
Tian, B. W., Yang, Y. F., Yang, C. C., Yan, L. J., Ding, Z. N., et al. (2022). Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of cancer immunotherapy: systemic review and meta-analysis. Immunotherapy. 14, 1481–1496. doi:10.2217/imt-2022-0133
Vasto, S., Carruba, G., Lio, D., Colonna-Romano, G., Di Bona, D., Candore, G., et al. (2009). Inflammation, ageing and cancer. Mech. Ageing Dev. 130, 40–45. doi:10.1016/j.mad.2008.06.003
Wulaningsih, W., Holmberg, L., Ng, T., Rohrmann, S., and Van Hemelrijck, M. (2016). Serum leptin, C-reactive protein, and cancer mortality in the NHANES III. Cancer Med. 5, 120–128. doi:10.1002/cam4.570
Xiao, S., Wang, Z., Zuo, R., Zhou, Y., Yang, Y., Chen, T., et al. (2023). Association of systemic immune inflammation index with all-cause, cardiovascular disease, and cancer-related mortality in patients with cardiovascular disease: a cross-sectional study. J. Inflamm. Res. 16, 941–961. doi:10.2147/JIR.S402227
Xie, S., and Wu, Q. (2024). Association between the systemic immune-inflammation index and sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. . 19, 314. doi:10.1186/s13018-024-04808-7
Yang, S., Li, S.-Z., Guo, F.-Z., Zhou, D. X., Sun, X. F., and Tai, J. D. (2022). Association of sleep duration with chronic constipation among adult men and women: findings from the national health and nutrition examination survey (2005-2010). Front. Neurol. 13, 903273. doi:10.3389/fneur.2022.903273
Yazicioglu, Y. F., Mitchell, R. J., and Clarke, A. J. (2024). Mitochondrial control of lymphocyte homeostasis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 161–162, 42–53. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2024.03.002
Ye, Z., Hu, T., Wang, J., Xiao, R., Liao, X., Liu, M., et al. (2022). Systemic immune-inflammation index as a potential biomarker of cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Cardiovasc Med. 9, 933913. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2022.933913
Ye, C., Yuan, L., Wu, K., Shen, B., and Zhu, C. (2023). Association between systemic immune-inflammation index and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a population-based study. BMC Pulm. Med. 23, 295. doi:10.1186/s12890-023-02583-5
Yeh, H. C., Golozar, A., Brancati, F. L., Cowie, C. C., Casagrande, S. S., and Menke, A., (2018). Cancer and diabetes. Diabetes in America. 3rd edition.
Zeng, Q. Y., Qin, Y., Shi, Y., Mu, X. Y., Huang, S. J., Yang, Y. H., et al. (2024). Systemic immune-inflammation index and all-cause and cause-specific mortality in sarcopenia: a study from national health and nutrition examination survey 1999-2018. Front. Immunol. 15, 1376544. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1376544
Zhai, Y., Sun, S., Zhang, W., and Tian, H. (2024). The prognostic value of the systemic immune inflammation index in patients with IgA nephropathy. Ren. Fail. 46, 2381613. doi:10.1080/0886022X.2024.2381613
Zhang, S., and Ni, W. (2023). High systemic immune-inflammation index is relevant to osteoporosis among middle-aged and older people: a cross-sectional study. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 11, e992. doi:10.1002/iid3.992
Zhao, E., Cheng, Y., Yu, C., Li, H., and Fan, X. (2023). The systemic immune-inflammation index was non-linear associated with all-cause mortality in individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Med. 55, 2197652. doi:10.1080/07853890.2023.2197652
Zheng, Z., Luo, H., and Xue, Q. (2023). U-shaped association of systemic immune-inflammation index levels with cancer-related and all-cause mortality in middle-aged and older individuals with frailty. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 116, 105228. doi:10.1016/j.archger.2023.105228
Zhou, Y., Guo, X., Shen, L., Liu, K., Sun, Q., Wang, Y., et al. (2023). Predictive significance of systemic immune-inflammation index in patients with breast cancer: a retrospective cohort study. Onco Targets Ther. 16, 939–960. doi:10.2147/OTT.S434193
Keywords: SII, mortality, cancer, inflammation, NHANES
Citation: Lu W, Gong Y, Liu L, Zhang Y, Tian X and Liu H (2025) Association of systemic immune-inflammatory index with all-cause and cancer mortality in Americans aged 60 years and older. Front. Aging 6:1502746. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1502746
Received: 27 September 2024; Accepted: 28 January 2025;
Published: 10 March 2025.
Edited by:
Xingchun Gao, Xi’an Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Pingze Zhang, Yale University, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Lu, Gong, Liu, Zhang, Tian and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wangfeng Lu, bHV3YW5nZmVuZ3NsQDEyNi5jb20=; Huanxian Liu, aHVhbnhpYW5fbGl1QDEyNi5jb20=
†ORCID: Wangfeng Lu, orcid.org/0000-0001-9750-7788; Huanxian Liu, orcid.org/0000-0002-6356-2938
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.