
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Aging, 28 February 2025
Sec. Genetics, Genomics and Epigenomics of Aging
Volume 6 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fragi.2025.1467639
This article is part of the Research TopicEpigenetic Regulation and Non-Histone Post-Translational Modification in AgingView all 4 articles
 Bowen Zhu1,2†
Bowen Zhu1,2† Dean Li1,2†
Dean Li1,2† Guojing Han3†
Guojing Han3† Xue Yao4
Xue Yao4 Hongqin Gu5
Hongqin Gu5 Tao Liu5
Tao Liu5 Linghua Liu5
Linghua Liu5 Jie Dai5
Jie Dai5 Isabella Zhaotong Liu6
Isabella Zhaotong Liu6 Yanlin Liang7
Yanlin Liang7 Jian Zheng8
Jian Zheng8 Zheming Sun9
Zheming Sun9 He Lin9
He Lin9 Nan Liu1
Nan Liu1 Haidong Yu5
Haidong Yu5 Meifang Shi5*
Meifang Shi5* Gaofang Shen10*
Gaofang Shen10* Zhaohui Hu11*
Zhaohui Hu11* Lefeng Qu3*
Lefeng Qu3*Estimation of chronological age is particularly informative in forensic contexts. Assessment of DNA methylation status allows for the prediction of age, though the accuracy may vary across models. In this study, we started with a carefully designed discovery cohort with more elderly subjects than other age categories, to diminish the effect of epigenetic drifting. We applied multiplexing and massive parallel sequencing of targeted DNA methylation, which let us to construct a model comprising 25 CpG sites with substantially improved accuracy (MAE = 2.279, R = 0.920). This model is further validated by an independent cohort (MAE = 2.204, 82.7% success (±5 years)). Remarkably, in a multi-center test using trace blood samples from forensic caseworks, the correct predictions (±5 years) are 91.7%. The nature of our analytical pipeline can easily be scaled up with low cost. Taken together, we propose a new age-prediction model featuring accuracy, sensitivity, high-throughput, and low cost. This model can be readily applied in both classic and newly emergent forensic contexts that require age estimation.
Forensic DNA phenotyping exploits not just genetic polymorphisms but also epigenetic modifications, i.e., DNA methylation, to draw a bio sketch of an unknown subject (Kayser, 2015). DNA methylation is a methyl group on the cytosine (C) followed by guanine (G) that is commonly referred to as CpG site, where the p stands for the phosphodiester bond between the two nucleotides. Studies have reported models that estimated chronological age from DNA methylation status, i.e., the ratio between methylated and non-methylated CpG forms (Bekaert et al., 2015a; 2015b; Jung et al., 2019). These models profiled DNA methylation by low-throughput assays, i.e., pyrosequencing or PCR-based SNaPshot, thus limiting their ability to handle a large quantity of samples (Lee et al., 2015; Zbieć-Piekarska et al., 2015). Although models that used massive parallel sequencing have been developed, their prediction accuracy varied, usually deviating above 3 years from the actual age (Naue et al., 2017; Vidaki et al., 2017; Aliferi et al., 2018).
Mounting evidence has associated aging and diseases with loss of fidelity due to epigenetic drift, which involves the accumulation of changes in an individual’s epigenome over time (Salameh et al., 2020; Wu et al., 2021; Alimohammadi et al., 2022). The currently available age-prediction models involved the use of five to eight selected CpG sites, and consequentially their actual performance could be perturbed by aging and pathophysiological conditions (Zbieć-Piekarska et al., 2015; Freire-Aradas et al., 2016; Jung et al., 2019). Indeed, a substantial decline of prediction accuracy in the elder population has been documented in previous models (Zbieć-Piekarska et al., 2015). Notably, regardless of human ethical groups and applicable body fluids, these models are converged on CpG islands of ELOVL2, FHL2, KLF14, miR29B2C, and TRIM59 genes (Zbieć-Piekarska et al., 2015; Cho et al., 2017; Freire-Aradas et al., 2018; Jung et al., 2019; Han et al., 2022), suggesting that these regions may harbor DNA methylation with changes being mostly consistent with the progression of age, and that additional age-related CpG sites within the regions might be used to improve the accuracy of age prediction.
In the present study, we aim to increase the prediction accuracy by diminishing the effect of epigenetic drift. Hence, we devised a discovery cohort by deliberately recruiting more aged human subjects than other age categories. Our rationale lies at the fact that older individuals tend to have stochastic and sometimes conflicting changes of methylation status, such that only the most age-related markers throughout life course and neighboring CpG sites could be used for the age-prediction tool. It’s important to highlight that we assessed the performance of the model with an independent validation cohort and a multi-center test using trace blood samples taken directly from the forensic casework. We demonstrate that multiplexing of target regions, when combined with massive parallel DNA sequencing, enables the prediction of chronological age from blood samples with substantially improved precision, sensitivity, ease of bulk processing, and low cost.
This study was conducted in the Chinese Han ethnic group. We collected 318 blood samples, including 254 samples aged 30–70 years from the community of Shanghai Baoshan District, 55 samples aged 20–70 years from Shanghai Chang Zheng Hospital, 9 samples aged 50–70 years from Shanghai Pu Nan Hospital. These samples comprised 180 females and 138 males. Healthy individuals were recruited according to standardized procedures, such as physical health, mental wellbeing, and social adaptation, at baseline and follow-up visits from past 5 years. All blood samples were collected in Blood Nucleic Acids Tubes (Thermo Fisher, catalog: 4342792) and stored at −80°C until use, avoiding repeated freezing and thawing of plasma to prevent DNA degradation and contamination. Blood samples were used within 30 days from the time of collection. In addition, dried bloodstains from forensic casework were provided by the public security from Beijing (n = 5), Yangzhou (n = 59), and Shanghai (n = 8). For these samples, clinical records were not available. Dried bloodstains were used within half a year from the time of collection. Written informed consent was obtained prior to sample collection from every participant after explaining the objectives and procedures of the study.
For isolation of total DNA, 300 μL of whole blood was mixed with 3 μL RNase A (200 ng/μL, ABclonal, Catalog: RM29870) and 20 μL Proteinase K Solution (Magen, catalog: D6310-03B) and incubated for 15 min at 37°C with shaking. Bloodstains were cut and mixed with 20 μL Proteinase K Solution and 400 μL Digestive Solution ATL (Magen, catalog: D6310-03B) and then processed according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Magen, catalog: D6310-03B). DNA concentration was measured using NanoDrop (Thermo Fisher).
Unmethylated cytosine was converted to uracil using the Bisulfite Conversion Kit (Singlera, catalog: EP110192). 200 ng- 1 μg of DNA was added with ddH2O to make up to 60 μL and then processed according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Singlera, catalog: EP110192).
Primers were designed by the website https://amplicondesign.dkfz.de/, with degenerate sequence as followings (R = A/G; Y=C/T): ELOVL2-F:5′- TACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTYGGTYGGGYGGYGATTTGTA-3’; ELOVL2-R: 5′- GACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCTACCCACCRAAACCCAACTAT-3’; miR29B2C-F: 5′- TACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTGTAAATATATAYGTGGGGGAAGAAGGG-3’; miR29B2C-R: 5′- GACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCTTAATAAAACCAAATTCTAAAACATTC-3’; TRIM59-F:5′- TACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTTATYGGTGGTTTGGGGGAGAG-3’; TRIM59-R:5′- GACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCTAACRACTTCCCRAAACAACRAATCTA-3’; KLF14-F:5′- TACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTYGGTTTTYGGTTAAGTTATGTTTAATAGT-3’; KLF14-R:5′-GACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCTCTACTACAACCCAAAAATTCC-3’; FHL2-F:5′- TACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCTTGTTTTTYGGGTTTTGGGAGTATAG-3’; FHL2-R:5′- GACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCTCACRTCCTAAAACTTCTCCAATCTCC-3’.
The concentration of each primer was 100 μM. 4 μL each of ELOVL2-F/R, 3 μL each of miR29B2C-F/R, 2.9 μL each of TRIM59-F/R, 13.5 μL each of TRIM59-F/R, 8.5 μL each of FHL2-F/R and ddH2O 36.2 μL o were mixed with ddH2O to make up to 100 μL of primer mix. Library pre-construction was performed using KAPA2G Fast Multiplex Mix (Roche, catalog: 2GFMPXKB). PCR reactions were carried out in a total volume of 25 μL, containing 10 ng of converted DNA, 1 μL of primer mix and 12.5 μL of 2X KAPA2G Fast Multiplex Mix and ddH2O. The PCR program operated with an initial denaturation step of 5 min at 95°C, amplification for 25cycles (denaturation for 15 s at 95°C, annealing for 15 s at 58°C and extension for 30 s at 72°C), and a final extension for 5 min at 72°C. The amplified pre-hybridized libraries were then purified using VAHTS DNA Clean Beads (Vazyme, catalog: N411-02) with a volume ratio of 0.9 for the first round of sorting (DNA Clean Beads: DNA) and 0.3 for the second round of sorting. The purified products were subjected to secondary amplification using TaKaRa Ex Taq (TaKaRa, catalog: RR53A) and adaptor-specific primer (F: AATGATACGGCGACCACCGAGATCTACACAGCGCTAGACACTCTTTCCCTACACGACGCTCTTCCGATCT; R: CAAGCAGAAGACGGCATACGAGATAACCGCGGGTGACTGGAGTTCAGACGTGTGCTCTTCCGATCT). PCR reactions were carried out in a total volume of 25 μL, containing10 μl of purified products, 2.5 μL of 10×Ex Taq Buffer, 2 μL of dNTP, 1 μL of TaKaRa Ex Taq, 1 µL each of adaptor-specific primer F/R and 8.4 µL of ddH2O. The PCR program operated with an initial denaturation step of 5 min at 95°C, amplification for 13cycles (denaturation for 15 s at 95°C, annealing for 15 s at 58°C and extension for 30 s at 72°C), and a final extension for 5 min at 72°C. VAHTS DNA Clean Beads was used for purification with a volume ratio of 0.7 for the first round of sorting (DNA Clean Beads: DNA) and 0.3 for the second round of sorting. The concentration of the final library was determined using Qubit 2.0 (Invitrogen) Libraries were sequenced on the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 system (paired end; 150 bp).
All sequencing reads were processed with Trim Galore (v0.6.6) (Krueger, 2015) with the parameters “--nextseq 30 --paired” to remove the adapter sequences (AGATCGGAAGAGC) from NovaSeq-platforms and reads longer than 20 bp were kept. Reads that passed the quality control procedure were kept and mapped to the Homo sapiens genome (GRCh38) using bismark (v0.24.1) (Krueger and Andrews, 2011) with default parameters. Uniquely mapped read pairs were extracted using samtools (v1.17) (Li et al., 2009) Methylation level was extracted by bismark.
To develop an age prediction model, we employed elastic net regression. Age prediction was trained by regressing chronological age on methylation level using the discovery cohort (N = 191). To begin, we randomly split the discovery cohort into training (70%) and test (30%) sets with balanced ages. Model optimization including hyperparameter tuning was done by a grid search with leave-one-out cross-validation (LOOCV) based on training sets. Model performance was assessed on the test set, using several statistics including median absolute error (MAE), Pearson’s correlation coefficient and its associated p value. Furthermore, we performed a cross-validation scheme for arriving the least biased estimates of the accuracy of the aging clocks, consisting of leaving out a single sample from the regression, predicting age for that sample, and iterating over all samples on the discovery cohort. The best-tuned hyperparameter α was 0.01, and λ was 1.2. Above model training and hyperparameter tuning were performed with R packages caret (v6.0–93) and glmnet (v4.1–4).
To establish a discovery cohort, we collected 191 peripheral blood samples from volunteers of Chinese Han ethnicity at the Baoshan District community of Shanghai. We deliberately recruited more aged subjects equal to or older than 60 years compared to other age categories (Figure 1A; Supplementary Figure S1A). Our rationale lies at the fact that elderly individuals, due to medical history and age, may couple with epigenetic drifting that confounds DNA methylation status, such that only CpG sites that are mostly correlated with age could be selected. Different from previous reports that relied on low-throughput assay, we introduced multiplexing PCR reaction followed by massive parallel DNA sequencing, thereby allowing the assessment of all CpG sites from the select regions of ELOVL2, FHL2, KLF14, miR29B2C, and TRIM59 genes (Figure 1A). We consolidated the feasibility of the analytical pipeline. First, we performed PCR reaction to confirm the specificity of primer sets, as evidenced by single PCR products for each target region (Supplementary Figure S1B). Second, we subjected the product of multiplexed PCR reaction for high-throughput DNA sequencing. Sequence analysis demonstrated sufficient read counts, with minimally more than 1,000 for each region involved (Supplementary Figure S1C). Third, we assessed DNA methylation status for all target regions, revealing CpG sites that displayed discordant changes with age. Taken together, this data establishes that age-related CpG sites from target regions could be used to develop an aging prediction model.
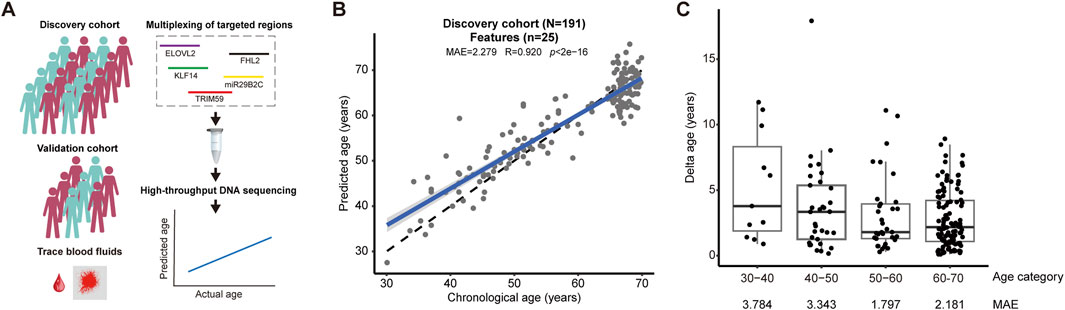
Figure 1. A new age-prediction model based on DNA methylation (A) We constructed an age-prediction model with a discovery cohort, which was consolidated by an independent validation cohort and a single-blind test using trace blood samples relevant to forensic casework (left panel). Our analytical pipeline was built on multiplexing of targeted DNA methylation from ELOVL2, FHL2, KLF14, miR29B2C, and TRIM59 gene, followed by high-throughput DNA methylation (right panel). (B) A new age-prediction model based on 25 CpG features was established using a discovery cohort consisting of 191 human subjects (MAE = 2.279, R = 0.920, p < 2e-16). (C) The accuracy of prediction shown as MAE in each age categories of the discovery cohort.
We constructed a new age-prediction model using the discovery cohort and a pipeline based on multiplexing of target regions and massive parallel DNA sequencing (Figure 1A). First, we assessed the ability of age-prediction by using reported CpG sites by Zbieć-Piekarska et al. (2015); Jung et al. (2019), respectively, and found that the use of limited CpG sites led to models with median absolute error (MAE) higher than 3 years and variance accountant for age (R) lower than 0.89 (Supplementary Figure S2). Second, we applied elastic net regression and cross-validation to construct a new age-prediction model that involved 25 CpG sites, including 2 from miR29B2C, 8 from FHL2, 5 from TRIM59, 9 from ELOVL2, and 1 from KLF14, respectively, with 18 new CpG features not being used by previous models (Table 1). This model demonstrated significantly improved accuracy with MAE as low as 2.279 (R = 0.920, p < 2e-16) (Figures 1B, C).
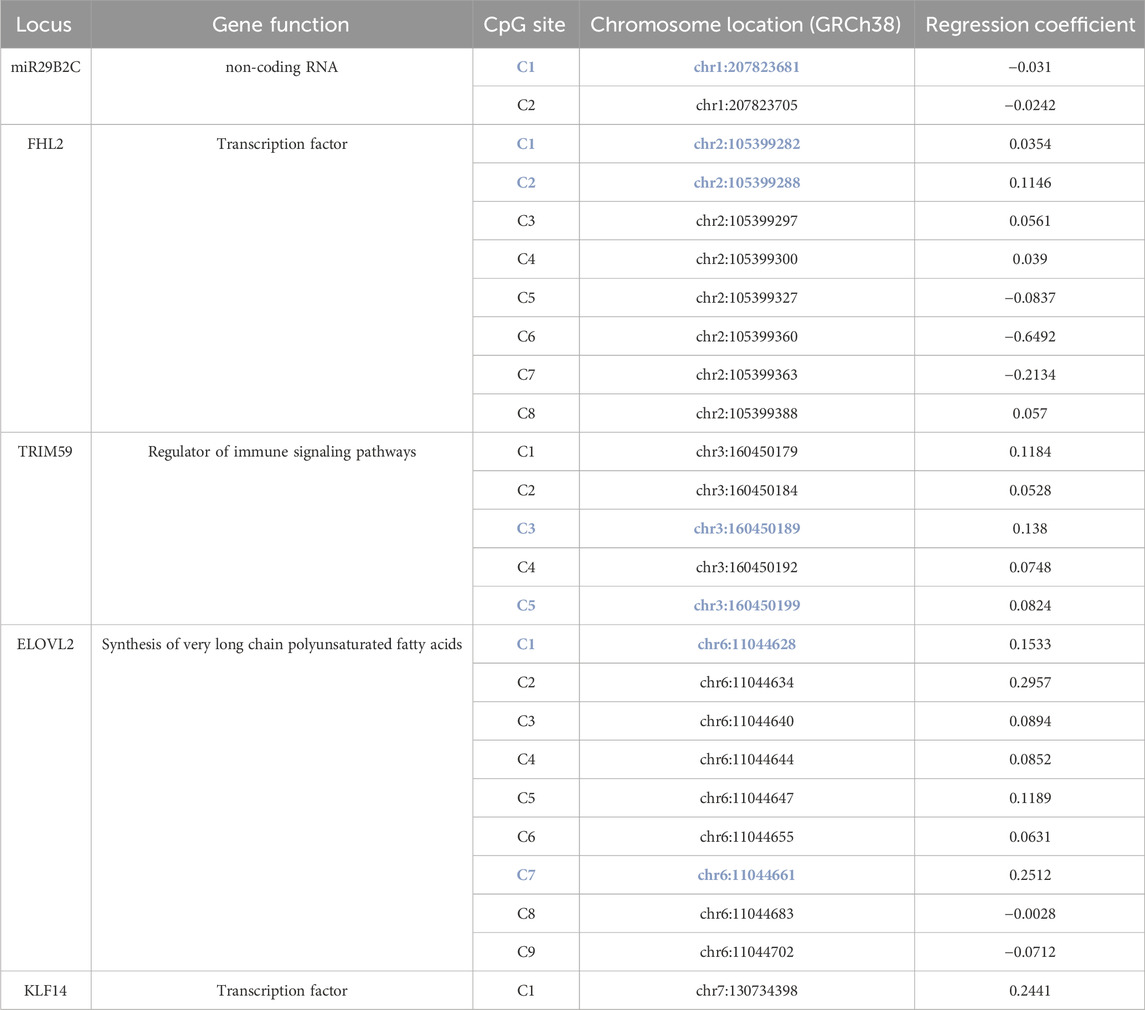
Table 1. A new age-prediction model based on 25 CpG sites A list of CpG sites used in the age-prediction model, including 2 from miR29B2C, 8 from FHL2, 5 from TRIM59, 9 from ELOVL2, and 1 from KLF14, respectively. CpG sites used by previous models were highlighted in bold blue.
We validated the new model in an independent validation cohort comprising 127 subjects. This experiment showed that our model could reach 2.204 for MAE (R = 0.963, p < 2e-16) (Figure 2A). When the maximum difference between predicted and actual age was set as 5 years, we observed 82.7% successful predictions for the entire cohort (Figure 2B), and notably 89.6% success for the age category between 50 and 60 (Figure 2B).
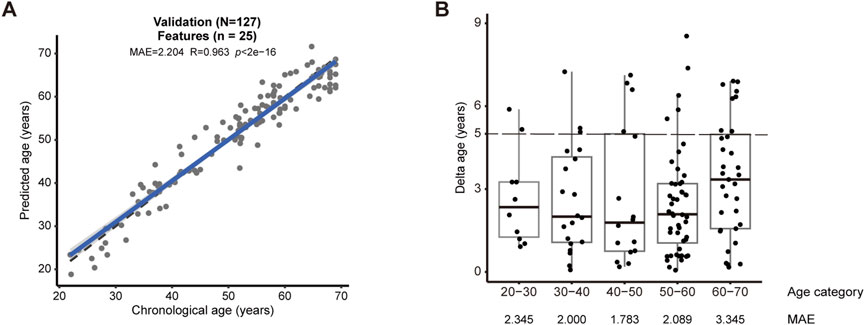
Figure 2. Validation by an independent cohort (A) The validation cohort consisting of 127 human subjects confirmed the accuracy of the model (MAE = 2.204, R = 0.963, p < 2e-16). (B) The accuracy of prediction in each age category of the validation cohort. Successful prediction could reach 82.7%, when the deviation between predicted versus actual age was set as 5 years (dashed lines). MAE was shown for each age categories.
We attested the model with trace blood samples that were practically relevant to the crime scenes in the real world. We initiated a multi-center test using dried bloodstains from forensic casework provided by public security from Beijing (n = 5), Yangzhou (n = 59), and Shanghai (n = 8) (Figure 3A). Without prior knowledge of age, our model could reach 1.965 for MAE (R = 0.949, p < 2.2e-16) (Figure 3A). Notably, when the maximum difference between the predicted and actual age was set as 5 years, our data demonstrated 91.7% success (Figure 3B). Comparatively, our new model has improved accuracy than previous age-prediction tools also based on massive parallel sequencing technique (Supplementary Table S1). Significantly, this result illustrates the ability of our model, together with the streamlined analytical pipeline, to handle trace blood samples, strongly supporting its readiness in forensic application.
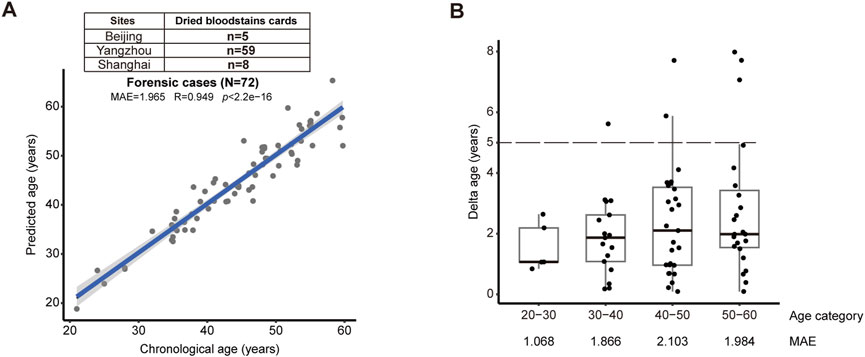
Figure 3. Validation by trace blood samples from forensic casework (A) The validation cohort consisting of 72 dried bloodstains subjects confirmed the accuracy of the model (MAE = 1.965, R = 0.949, p < 2.2e-16). (B) Successful prediction could reach 91.6% from bloodstains and trace blood fluids, when the deviation between predicted versus actual age was set as 5 years (dashed lines). MAE was shown for each age categories.
Estimation of age is informative in many forensic contexts, e.g., classically used in investigative leads for crime scenes (Phillips, 2015). The demand of this application is now rapidly growing in age categorization of illegal immigrants as well as asylum seekers in which context valid identification documents are usually missing (Schmeling et al., 2016). Thus far, forensically practical age-prediction models have been established by the assessment of DNA methylation status, known as epigenetic clock (Hannum et al., 2013; Horvath, 2013; Florath et al., 2014). The currently available models involve the use of 5-8 CpG sites and low-throughput analytical platforms, e.g., pyrosequencing (Weidner et al., 2014; Bekaert et al., 2015b; 2015a; Huang et al., 2015). In the present study, we apply multiplexing of target regions followed by high-throughput DNA sequencing. Trained by a carefully designed aging cohort, we propose a new epigenetic clock model that includes 25 age-related CpG sites.
Epigenetic DNA methylation is one of the hallmarks of aging, laying critical foundation for its application to estimate the chronological age of human subjects. However, it is well-known that stochastic changes in DNA methylation occur with age, smoking habit, alcoholic consumption, and disease situations (Johansson et al., 2013; Hagerty et al., 2016; Spólnicka et al., 2018b; 2018a; Yang et al., 2019). Consequently, an age-related increase in interindividual variability and reciprocally a decline in accuracy have been reported in many age-prediction models based on biomarkers of DNA methylation (Bekaert et al., 2015a; 2015b; Zbieć-Piekarska et al., 2015; Park et al., 2016). Hence, we designed a training cohort by deliberately recruiting more elderly subjects than other age categories, such that our model could be built with CpG sites that are mostly consistent with the progression of age. Presumably, the accuracy of age prediction could be substantially improved by increasing the number of DNA methylation loci. As such, we focus on 5 genomic regions with CpG sites therein repeatedly used by various early models (Zbieć-Piekarska et al., 2015; Freire-Aradas et al., 2018; Jung et al., 2019; Woźniak et al., 2021; Aliferi et al., 2022; Han et al., 2022). By high-throughput DNA sequencing, we can obtain profiles of all DNA methylation loci from which we construct a new model comprising 25 CpG sites. Despite increased number of DNA methylation loci, our pipeline has been simplified by multiplexing of these 5 target regions. Moreover, the nature of our analytical pipeline, by measuring the ratios between methylated and non-methylated CpG from high-throughput sequencing, with minimally 1000 read counts for each region, supports the consistency and robustness of the result. Empowered by this new model, we could predict age with a success rate of 82.7% (±5 years) in an independent validation cohort and a success rate of 91.7% (±5 years) in a multi-center test using dried bloodstains taken from real world forensic casework.
Compared to the early models based on low-throughput assay, we apply high-throughput sequencing, together with multiplexing of target regions, thus allowing bulk processing of large volume of samples. This ability is of paramount urgency, given the exponentially increasing casework of illegal immigrants and asylum seekers resulted from geographic conflict. Moreover, another issue to consider is cost. It is important to note that the cost for massive parallel DNA sequencing has been significantly reduced, especially feasible for batch testing. Taken together, we propose a new age-prediction model featuring substantially improved accuracy, sensitivity, ease of bulk processing, and low cost.
In this study, we propose a new age-prediction model, when combined with multiplexing of targeted DNA methylation and massive parallel sequencing, that has substantially improved accuracy, ability to handle trace blood samples, ease of large-scale application, and low cost. To conclude, this model can be readily applied in both classic and newly emergent forensic contexts that require the estimation of chronological age.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/, GSE267985.
The studies involving humans were approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Shanghai Chang Zheng Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
BZ: Investigation, Writing–original draft. DL: Investigation, Writing–original draft. GH: Investigation, Writing–original draft. XY: Investigation, Writing–original draft. HG: Investigation, Writing–original draft. TL: Investigation, Writing–original draft. LL: Investigation, Writing–original draft. JD: Investigation, Writing–original draft. IL: Investigation, Writing–original draft. YL: Investigation, Writing–original draft. JZ: Investigation, Writing–original draft. ZS: Investigation, Writing–original draft. HL: Investigation, Writing–original draft. NL: Writing–review and editing. HY: Writing–review and editing. MS: Writing–review and editing. GS: Writing–review and editing. LQ: Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (8237020490) to LQ, innovative clinical research project of the Chang Zheng Hospital, Naval Medical University (2020YLCYJ-Z09) to LQ, clinical research projects initiated by investigators in exemplary research award (2023YJBF-FH04) to LQ, the Shanghai Key Laboratory of Aging Studies (19DZ2260400) to NL, the National Key Research and Development Project of China (2018YFC2000203, 2018YFC2000204) and to MS, and an open project grant of Institute of Forensic Science of China (2021FGKFKT02) to XY.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fragi.2025.1467639/full#supplementary-material
Aliferi, A., Ballard, D., Gallidabino, M. D., Thurtle, H., Barron, L., and Syndercombe Court, D. (2018). DNA methylation-based age prediction using massively parallel sequencing data and multiple machine learning models. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 37, 215–226. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2018.09.003
Aliferi, A., Sundaram, S., Ballard, D., Freire-Aradas, A., Phillips, C., Lareu, M. V., et al. (2022). Combining current knowledge on DNA methylation-based age estimation towards the development of a superior forensic DNA intelligence tool. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 57, 102637. doi:10.1016/J.FSIGEN.2021.102637
Alimohammadi, M., Makaremi, S., Rahimi, A., Asghariazar, V., Taghadosi, M., and Safarzadeh, E. (2022). DNA methylation changes and inflammaging in aging-associated diseases. Epigenomics 14, 965–986. doi:10.2217/EPI-2022-0143
Bekaert, B., Kamalandua, A., Zapico, S. C., Van de Voorde, W., and Decorte, R. (2015a). A selective set of DNA-methylation markers for age determination of blood, teeth and buccal samples. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. Suppl. Ser. 5, e144–e145. doi:10.1016/j.fsigss.2015.09.058
Bekaert, B., Kamalandua, A., Zapico, S. C., Van De Voorde, W., and Decorte, R. (2015b). Improved age determination of blood and teeth samples using a selected set of DNA methylation markers. Epigenetics 10, 922–930. doi:10.1080/15592294.2015.1080413
Cho, S., Jung, S. E., Hong, S. R., Lee, E. H., Lee, J. H., Lee, S. D., et al. (2017). Independent validation of DNA-based approaches for age prediction in blood. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 29, 250–256. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2017.04.020
Florath, I., Butterbach, K., Müller, H., Bewerunge-hudler, M., and Brenner, H. (2014). Cross-sectional and longitudinal changes in DNA methylation with age: an epigenome-wide analysis revealing over 60 novel age-associated CpG sites. Hum. Mol. Genet. 23, 1186–1201. doi:10.1093/HMG/DDT531
Freire-Aradas, A., Phillips, C., Girón-Santamaría, L., Mosquera-Miguel, A., Gómez-Tato, A., Casares de Cal, M. Á., et al. (2018). Tracking age-correlated DNA methylation markers in the young. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 36, 50–59. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2018.06.011
Freire-Aradas, A., Phillips, C., Mosquera-Miguel, A., Girón-Santamaría, L., Gómez-Tato, A., Casares De Cal, M., et al. (2016). Development of a methylation marker set for forensic age estimation using analysis of public methylation data and the Agena Bioscience EpiTYPER system. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 24, 65–74. doi:10.1016/J.FSIGEN.2016.06.005
Hagerty, S. L., Bidwell, L. C., Harlaar, N., and Hutchison, K. E. (2016). An exploratory association study of alcohol use disorder and DNA methylation. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 40, 1633–1640. doi:10.1111/ACER.13138
Han, X., Xiao, C., Yi, S., Li, Y., Chen, M., and Huang, D. (2022). Accurate age estimation from blood samples of Han Chinese individuals using eight high-performance age-related CpG sites. Int. J. Leg. Med. 136, 1655–1665. doi:10.1007/S00414-022-02865-3
Hannum, G., Guinney, J., Zhao, L., Zhang, L., Hughes, G., Sadda, S. V., et al. (2013). Genome-wide methylation profiles reveal quantitative views of human aging rates. Mol. Cell 49, 359–367. doi:10.1016/J.MOLCEL.2012.10.016
Horvath, S. (2013). DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell types. Genome Biol. 14, R115. doi:10.1186/GB-2013-14-10-R115
Huang, Y., Yan, J., Hou, J., Fu, X., Li, L., and Hou, Y. (2015). Developing a DNA methylation assay for human age prediction in blood and bloodstain. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 17, 129–136. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2015.05.007
Johansson, Å., Enroth, S., and Gyllensten, U. (2013). Continuous aging of the human DNA methylome throughout the human lifespan. PLoS One 8, e67378. doi:10.1371/JOURNAL.PONE.0067378
Jung, S. E., Lim, S. M., Hong, S. R., Lee, E. H., Shin, K. J., and Lee, H. Y. (2019). DNA methylation of the ELOVL2, FHL2, KLF14, C1orf132/MIR29B2C, and TRIM59 genes for age prediction from blood, saliva, and buccal swab samples. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 38, 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2018.09.010
Kayser, M. (2015). Forensic DNA Phenotyping: predicting human appearance from crime scene material for investigative purposes. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 18, 33–48. doi:10.1016/J.FSIGEN.2015.02.003
Krueger, F. (2015). Trim galore - google 学术搜索 516 (517), 517. Available at: https://scholar.google.com.hk/scholar?hl=zh-CN&as_sdt=0,5&cluster=12747908586058570640 (Accessed March 22, 2024).
Krueger, F., and Andrews, S. R. (2011). Bismark: a flexible aligner and methylation caller for Bisulfite-Seq applications. Bioinformatics 27, 1571–1572. doi:10.1093/BIOINFORMATICS/BTR167
Lee, H. Y., Jung, S. E., Oh, Y. N., Choi, A., Yang, W. I., and Shin, K. J. (2015). Epigenetic age signatures in the forensically relevant body fluid of semen: a preliminary study. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 19, 28–34. doi:10.1016/J.FSIGEN.2015.05.014
Li, H., Handsaker, B., Wysoker, A., Fennell, T., Ruan, J., Homer, N., et al. (2009). The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25, 2078–2079. doi:10.1093/BIOINFORMATICS/BTP352
Naue, J., Hoefsloot, H. C. J., Mook, O. R. F., Rijlaarsdam-Hoekstra, L., van der Zwalm, M. C. H., Henneman, P., et al. (2017). Chronological age prediction based on DNA methylation: massive parallel sequencing and random forest regression. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 31, 19–28. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2017.07.015
Park, J. L., Kim, J. H., Seo, E., Bae, D. H., Kim, S. Y., Lee, H. C., et al. (2016). Identification and evaluation of age-correlated DNA methylation markers for forensic use. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 23, 64–70. doi:10.1016/J.FSIGEN.2016.03.005
Phillips, C. (2015). Forensic genetic analysis of bio-geographical ancestry. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 18, 49–65. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2015.05.012
Salameh, Y., Bejaoui, Y., and El Hajj, N. (2020). DNA methylation biomarkers in aging and age-related diseases. Front. Genet. 11, 171. doi:10.3389/fgene.2020.00171
Schmeling, A., Dettmeyer, R., Rudolf, E., Vieth, V., and Geserick, G. (2016). Forensic age estimation: methods, certainty, and the law. Dtsch. Arztebl Int. 113, 44–50. doi:10.3238/ARZTEBL.2016.0044
Spólnicka, M., Pośpiech, E., Pepłońska, B., Zbieć-Piekarska, R., Makowska, P. A., Pięta, A., et al. (2018a). DNA methylation in ELOVL2 and C1orf132 correctly predicted chronological age of individuals from three disease groups. Int. J. Leg. Med. 132, 1–11. doi:10.1007/S00414-017-1636-0
Spólnicka, M., Zbieć-Piekarska, R., Karp, M., Machnicki, M. M., Własiuk, P., Makowska, Ż., et al. (2018b). DNA methylation signature in blood does not predict calendar age in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia but may alert to the presence of disease. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 34, e15–e17. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2018.02.004
Vidaki, A., Ballard, D., Aliferi, A., Miller, T. H., Barron, L. P., and Syndercombe Court, D. (2017). DNA methylation-based forensic age prediction using artificial neural networks and next generation sequencing. Forensic Sci. Int. Genet. 28, 225–236. doi:10.1016/j.fsigen.2017.02.009
Weidner, C. I., Lin, Q., Koch, C. M., Eisele, L., Beier, F., Ziegler, P., et al. (2014). Aging of blood can be tracked by DNA methylation changes at just three CpG sites. Genome Biol. 15, R24. doi:10.1186/GB-2014-15-2-R24
Woźniak, A., Heidegger, A., Piniewska-Róg, D., Pośpiech, E., Xavier, C., Pisarek, A., et al. (2021). Development of the VISAGE enhanced tool and statistical models for epigenetic age estimation in blood, buccal cells and bones. Aging (Albany NY) 13, 6459–6484. doi:10.18632/AGING.202783
Wu, J., Liu, L. lin, Cao, M., Hu, A., Hu, D., Luo, Y., et al. (2021). DNA methylation plays important roles in retinal development and diseases. Exp. Eye Res. 211, 108733. doi:10.1016/J.EXER.2021.108733
Yang, Y., Gao, X., Just, A. C., Colicino, E., Wang, C., Coull, B. A., et al. (2019). Smoking-related DNA methylation is associated with DNA methylation phenotypic age acceleration: the veterans affairs normative aging study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16, 2356. doi:10.3390/IJERPH16132356
Keywords: DNA methylation, age-prediction model, multiplexing, massive parallel sequencing, targeted region
Citation: Zhu B, Li D, Han G, Yao X, Gu H, Liu T, Liu L, Dai J, Liu IZ, Liang Y, Zheng J, Sun Z, Lin H, Liu N, Yu H, Shi M, Shen G, Hu Z and Qu L (2025) Multiplexing and massive parallel sequencing of targeted DNA methylation to predict chronological age. Front. Aging 6:1467639. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1467639
Received: 20 July 2024; Accepted: 04 February 2025;
Published: 28 February 2025.
Edited by:
Weiwei Dang, Baylor College of Medicine, United StatesReviewed by:
Ravi Shankar Singh, The University of Utah, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Zhu, Li, Han, Yao, Gu, Liu, Liu, Dai, Liu, Liang, Zheng, Sun, Lin, Liu, Yu, Shi, Shen, Hu and Qu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Meifang Shi, c21mMTg5MzA3MjE4NjBAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Gaofang Shen, MTI4NDY3MjAzOEBxcS5jb20=; Zhaohui Hu, MDYxMTA0MTQwQGZ1ZGFuLmVkdS5jbg==; Lefeng Qu, cXVsZWZlbmdAc21tdS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.