- 1School of Nursing, Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi, Guizhou, China
- 2Department of Nursing, Guizhou Provincial People’s Hospital, Guiyang, Guizhou, China
- 3School of Nursing, Guizhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Guiyang, Guizhou, China
Background: The presence of sarcopenia at the time of stroke may deteriorate the rehabilitation and functional outcomes. There is no consensus on the factors associated with stroke-related sarcopenia because previous studies produced inconsistent and disputed results. Therefore, we screened the possible risk factors by meta-analysis.
Methods: Studies published before March 2024 on risk factors with stroke-related sarcopenia were searched through PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, CINAHL, Cochrane Library, CNKI, Wan Fang, CBM, and VIP library databases. Two researchers independently screened the articles to extract the information and to evaluate their quality. Meta-analysis was then performed using Revman 5.4 software to determine the significant risk factors for patients with stroke-related sarcopenia.
Results: A total of 14 studies (n = 3,113) were selected to determine the following factors that were statistically significant in patients with stroke-related sarcopenia: Age (OR = 1.04; 95% CI: 1.02, 1.06; P < 0.0001), tube feeding (OR = 3.98; 95% CI: 2.12, 7.47; P < 0.0001), pre-stroke sarcopenia (OR = 1.84; 95% CI: 1.39, 2.43; P < 0.0001), atrial fibrillation (OR = 1.53; 95% CI: 1.15, 2.02; P = 0.003), NIHSS score (OR = 1.48; 95% CI: 1.21, 1.81; P = 0.0001), and osteoporosis (OR = 1.801; 95% CI: 58, 2.04; P < 0.00001). BMI (P = 0.71), FOIS (P = 0.80), time since stroke (P = 0.34), and calf circumference reduction (P = 0.48) were not identified as risk or protective factors after stroke (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Our results identified various risk factors for stroke-related sarcopenia which should be considered and studied by healthcare organizations and professionals to improve the health of stroke patients.
Systematic Review Registration: PROSPERO, Identifier CRD42024545757.
1 Introduction
The 2019 Global Burden of Disease (GBD) (GBD, 2019 Stroke Collaborators, 2021) declared stroke as the globe’s leading cause of death, and it ranks third when combined with disability. The number of strokes in rehabilitation departments usually ranges from 21% to 69% (Liu et al., 2020). Some of the affected patients experience reduced muscle mass on the paralyzed or healthy side, or even throughout the body with a concomitant decrease in muscle strength, presenting with stroke-related sarcopenia (SRS) (Li et al., 2020). With the progressively increasing aging process, the prevalence of sarcopenia is also increasing (Mas et al., 2020), ranging from 14% to 33% with a high prevalence of SRS (14%–54%).
Reportedly, the incidence of SRS not only increases the risk of further complications such as cognitive impairment, falls, functional decline, diabetes, and depression (Yuan and Larsson, 2023; Rodrigues et al., 2022; Izzo et al., 2021; Li Z. et al., 2022; Lisco et al., 2023) but also leads to the development of various metabolic disorders and increases the likelihood of cardiovascular disease (CVD) (Damluji et al., 2023). In addition, patients with SRS suffer from severe neurological damage, poor nutritional status, and lack of self-care ability (Nakanishi et al., 2021), which seriously affects their quality of life, thereby increasing the medical costs, which substantially impacts the medical burden of the family and the public health expenditure (Cui et al., 2023). Therefore, identifying the possible risk factors of SRS is essential for prognosis to reduce its associated adverse effects.
The established causes of sarcopenia are multifaceted and include ageing (Lisco et al., 2023), socio-demographic factors (Simsek et al., 2019), lifestyle (Bruyère et al., 2022), and multiple health conditions (Beaudart et al., 2014). However, previous studies have presented distinct findings on the factors associated with sarcopenia, sometimes with inconsistent and controversial results. Currently, no consensus on the factors associated with sarcopenia exists. Prevention of sarcopenia will be of special significance not only for improving the health of stroke patients but also for promoting public health.
Therefore, we systematically reviewed the factors associated with SRS through a meta-analysis to identify the significant factors and to support futuristic appropriate interventions to reduce sarcopenia and its negative effects, thereby improving the quality of life and health of stroke patients.
2 Materials and methods
This study followed the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyzes (PRISMA) (Page et al., 2021) and the Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (Stroup et al., 2000). Additionally, it has been registered with PROSPERO (No. CRD42024545757).
2.1 Search strategy
Two researchers independently searched the following databases from inception to March 2024: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, CINAHL, Cochrane Library, CNKI database, Wan Fang database, CBM databases, and VIP database. The search terms included stroke, cerebrovascular stroke, cerebrovascular disease, cerebrovascular accident, cerebral apoplexy, cerebral stroke, ischemic stroke, brain stroke, brain infarction, cerebral infarction, brain apoplexy, wind stroke, CVA, CVAs, cerebrovascular apoplexy, apoplexy, infarction, cerebrovascular stroke, brain vascular accident, acute stroke, cerebral arterial thrombosis, cerebral ischemic stroke, cerebral hemorrhage, intracerebral hemorrhage, hemorrhagic stroke, sarcopenia, sarcopeni*, muscle loss, muscle wast*, and muscle atroph*. To discover further research opportunities, we also screened the reference lists of the included articles. If necessary, we contact the authors to acquire supplementary information.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The following inclusion criteria were considered: (GBD, 2019 Stroke Collaborators, 2021) Observational study of alterations in stroke combined with sarcopenia (Liu et al., 2020); A clear description of the type of study and experimental methodology (Li et al., 2020); Accompanied by odds ratio (OR; 95% Confidence Interval or CI) data or could be transformed into OR (95% CI) data.
Articles with the following criteria were excluded: (GBD, 2019 Stroke Collaborators, 2021): Review articles, reviews, case reports, expert consensus, or guidelines (Liu et al., 2020); Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) scores <4 (Hu et al., 2021) or the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS)scores <6 (Fang et al., 2023); (Li et al., 2020) Articles with incomplete or unusable data (Mas et al., 2020); Studies where the diagnostic criteria for sarcopenia were not clearly reported.
2.3 Selection of articles
Initially, two researchers independently screened the title and abstract of articles, excluding those that did not meet the requirements. Next, the full texts of the relevant articles were obtained and read for further screening. Moreover, the two researchers cross-checked the articles. A third person may intervene if there is any remaining controversy during the screening procedure.
2.4 Data extraction
Two researchers read the articles to extract the basic information, study characteristics, and observation indicators, which were recorded using Excel sheets. Subsequently, the extracted data was cross-checked. In case of incomplete data, the corresponding author was requested to provide the missing information; however, the article was excluded if the data was unavailable.
2.5 Quality assessment
Various quality assessment methods were used according to the nature of the studies. The 9-point NOS scale was used to evaluate prospective cohort and case-control studies, and a score of >6 was regarded as a high-quality study. The AHRQ was used to evaluate cross-sectional studies, and those with scores of <4, 4–7, and above 7 were considered to be of low, moderate, and high qualities, respectively.
2.6 Statistical analysis
Extracted data were subjected to meta-analysis using Revman 5.4, and count data were expressed as OR and their 95% CI. The heterogeneity of the included articles was estimated using the I2 and Cochran’s Q statistics. Heterogeneity was significant when I2 ≥ 50 and analyzed using a random-effects model while a fixed-effects model was used when I2 < 50% or heterogeneity was non-significant. The publication bias was assessed using visual funnel plots. Specifically, the asymmetrically distributed funnel plots indicated no publication bias, and vice-versa (Sterne and Egger, 2001). Sensitivity analyses were performed by sequentially eliminating the individual studies to determine the reliability and stability of the findings.
3 Results
3.1 Search results
A total of 4,912 articles were retrieved of which 3,579 were selected after removing duplicates. Further, based on the titles and abstracts, we selected 1,292 studies for full-text assessment. Ultimately, 1,278 articles were excluded and 14 were included. The flowchart of literature screening is shown in Figure 1.
3.2 Basic characteristics of included articles
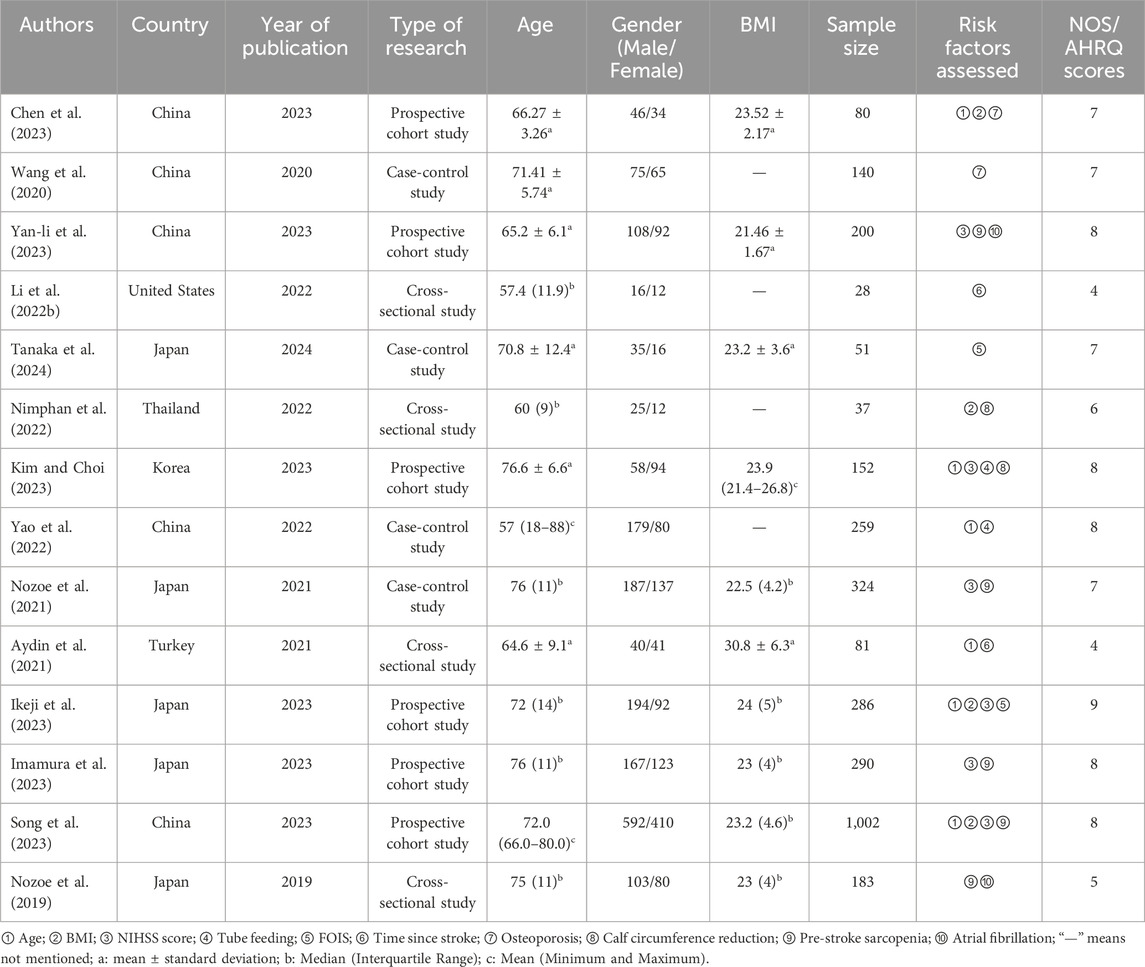
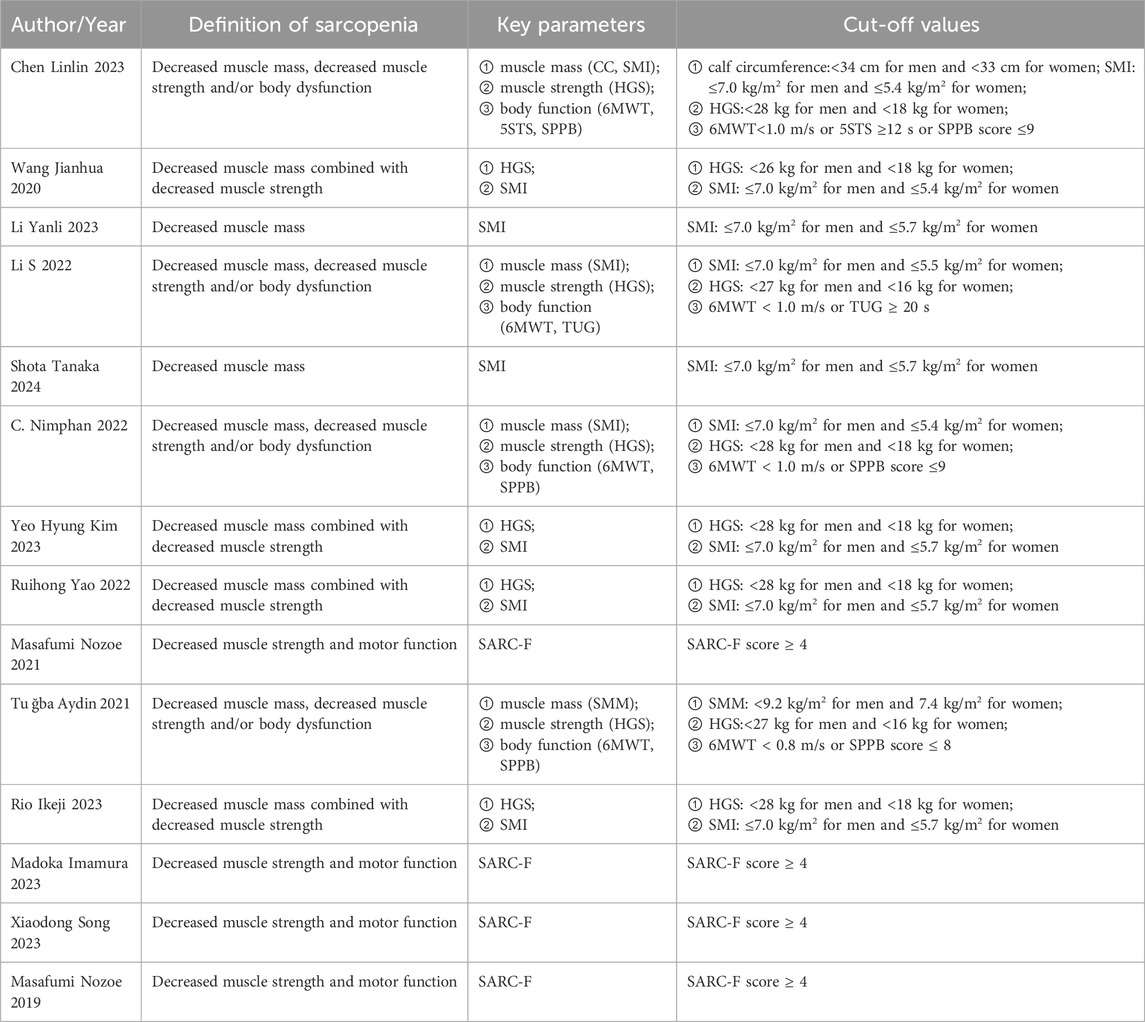
The meta-analysis included three Chinese and 11 English articles. The final selection comprised six prospective cohort studies, four cross-sectional studies, and four case-control studies, with a total sample size of 3,113 cases. The NOS scores of prospective cohort and case-control studies ranged from 7 to 9, indicating a high quality. The AHRQ scores of four cross-sectional studies ranged from 4 to 6, indicating a moderate quality. The overall score indicated that the article quality included in this study was relatively high. (Table 1). In addition, we summarized the diagnostic parameters and corresponding cut-off values for the included articles in Table 2.
3.3 Meta-analysis results
3.3.1 Age
Six studies (Chen et al., 2023; Kim and Choi, 2023; Yao et al., 2022; Aydin et al., 2021; Ikeji et al., 2023; Song et al., 2023) reported the effect of age on SRS with <50% heterogeneity between articles (I2 = 37%, P = 0.18); however, slight heterogeneity was observed within acceptable limits. The fixed-effects model analyses showed that patients with SRS were notably older than those without SRS (OR = 1.04; 95% CI: 1.02, 1.06; P < 0.0001, see Figure 2A).
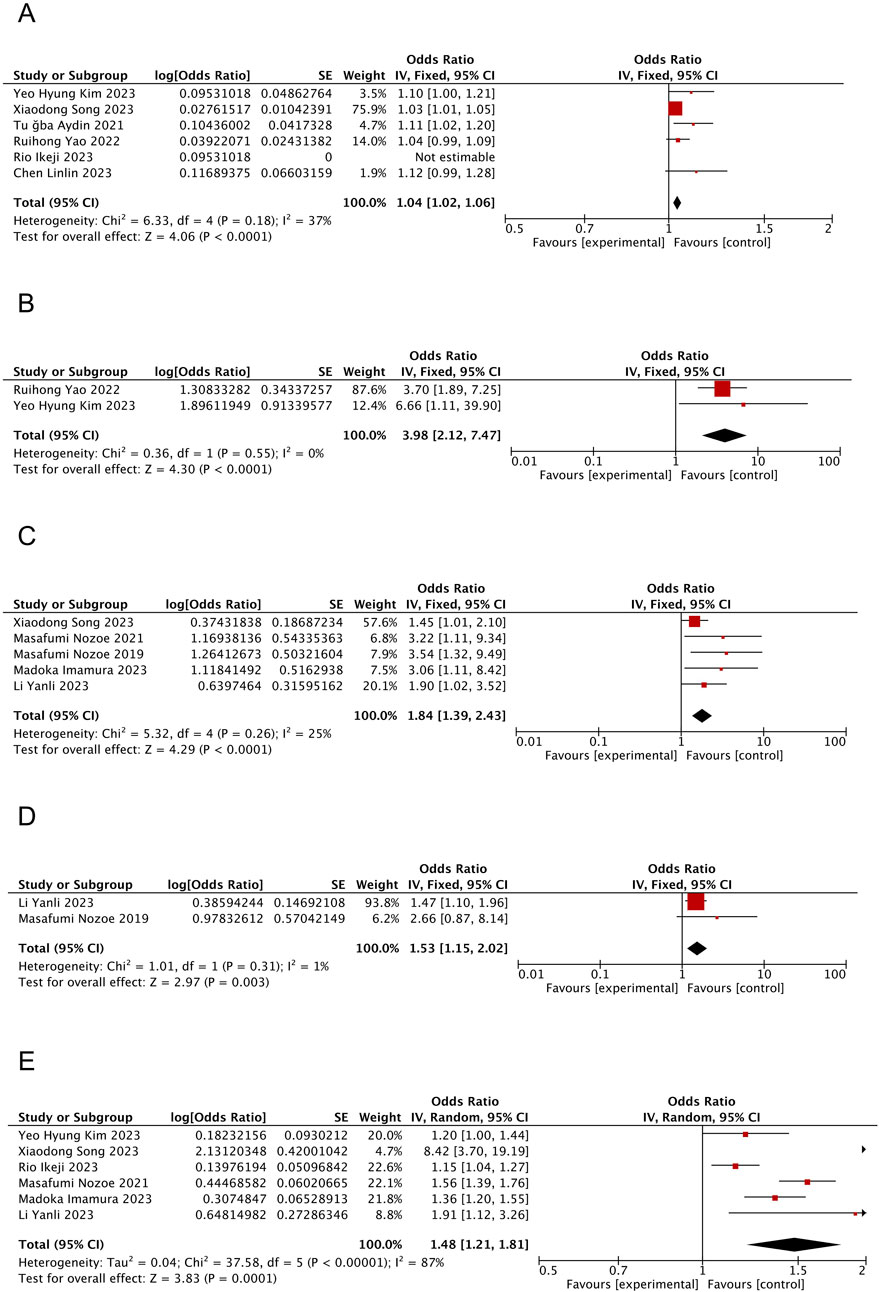
Figure 2. Forest plot of the meta-analysis results. (A) Forest plot of age factors; (B) Forest plot of tube feeding factors; (C) Forest plot of pre-stroke sacopenia factors; (D) Forest plot of atrial fibrillation factors; (E) Forest plot of NIHSS score factors.
3.3.2 Tube feeding
Two studies (Kim and Choi, 2023; Yao et al., 2022) reported the effect of tube feeding on SRS with no heterogeneity between articles (I2 = 0%, P = 0.55). Moreover, the fixed-effects model analysis suggested tube feeding as an influential factor in patients with SRS (OR = 3.98; 95% CI: 2.12, 7.47; P < 0.0001, see Figure 2B).
3.3.3 Pre-stroke sarcopenia
Five studies (Yan-li et al., 2023; Nozoe et al., 2021; Imamura et al., 2023; Song et al., 2023; Nozoe et al., 2019) reported the effect of pre-stroke sarcopenia on SRS with slight but acceptable heterogeneity between articles (<50%; I2 = 25%, P = 0.26). Moreover, the fixed-effects model analyses showed that patients having sarcopenia before stroke were relatively more prone to experience SRS (OR = 1.84; 95% CI: 1.39, 2.43; P < 0.0001, see Figure 2C).
3.3.4 Atrial fibrillation
Two studies (Yan-li et al., 2023; Nozoe et al., 2019) reported the effect of AF on SRS, with no heterogeneity between articles (I2 = 1%, P = 0.31), and fixed-effects model analyses revealed a higher tendency of patients with comorbid AF to develop SRS (OR = 1.53; 95% CI: 1.15, 2.02; P = 0.003, see Figure 2D).
3.3.5 NIHSS score
Six studies (Yan-li et al., 2023; Kim and Choi, 2023; Nozoe et al., 2021; Ikeji et al., 2023; Imamura et al., 2023; Song et al., 2023) reported the effect of NIHSS score on the incidence of SRS on admission, with >50% heterogeneity between articles (I2 = 87%, P < 0.00001). The results from the random-effects model demonstrated significantly higher NIHSS scores among patients with SRS compared to those without SRS (OR = 1.48; 95% CI: 1.21, 1.81; P = 0.0001, see Figure 2E).
3.3.6 Others
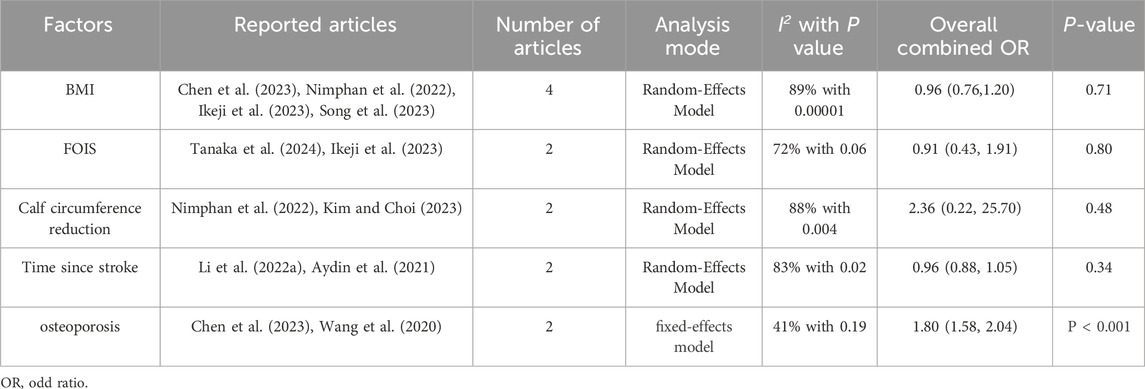
The combined effect values of the factors calculated by the software revealed that osteoporosis influenced SRS (P < 0.05) whereas the effect of the remaining factors remained uncertain (P > 0.05, see Table 3).
3.4 Heterogeneity investigation and sensitivity analysis
Significant heterogeneity was observed between the six studies that reported the effect of NIHSS score; however, we sequentially excluded these studies individually to explore the source of heterogeneity but the heterogeneity persisted. This indicated the reliability and stability of the results. Moreover, different characteristics of the patients, such as the course and severity of the disease may have contributed to the heterogeneity.
3.5 Publication bias
The results of the study demonstrated that the heterogeneity of the NIHSS scores was >50%; therefore, we performed a funnel plot analysis of the publication bias to visually observe the signs of asymmetry in the funnel plot (see Figure 3A). Next, a trim and fill method was employed to correct the bias and to obtain the adjusted symmetrical funnel plot (see Figure 3B), thereby reporting a low risk of publication bias in the present review.
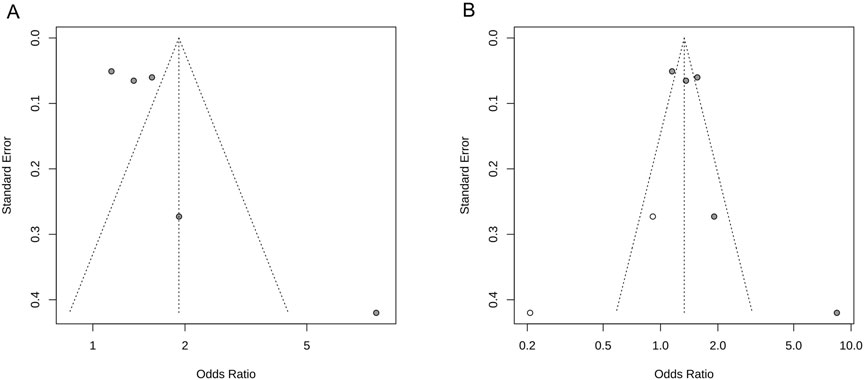
Figure 3. NIHSS score funnel plot. (A) Funnel plot of publication bias; (B) Adjusted funnel plot of publication bias.
4 Discussion
Stroke is associated with the highest rate of disability in adults (Hacke et al., 2004). At 90 days from the onset, one-fourth of stroke survivors will experience severe motor impairment (Li et al., 2014). Although the brain is the damaged organ in stroke, the skeletal muscle is the primary cause of disability. A reduction in the number of motor units in the affected limb can be observed as early as 4 h after the stroke (Harris et al., 2001). The results showed that the risk factors associated with SRS included age, tube feeding, pre-stroke sarcopenia, AF, and NIHSS score.
According to the definition and earlier findings, sarcopenia becomes more likely as one gets older. Notably, age is an important independent predictor of strength changes (Hughes et al., 2001). A longitudinal study (Delmonico et al., 2009) investigated age-related changes in muscle mass, muscle strength, and body composition discovered that older adults experienced a progressive decline in strength and muscle mass regardless of changes in muscle mass or body weight. In addition, fat accumulation within skeletal muscles worsens with age, no matter how weight changes. Although past research has suggested that age-related changes in muscle number and mass may lead to sarcopenia, further physiological research is needed to elucidate the potential mechanisms driving the development of probable sarcopenia with age in stroke patients (Clark and Manini, 2010).
Our results suggested that tube feeding after stroke was a risk factor for the development of sarcopenia. Some stroke patients need to be fed by nasogastric tube due to dysphagia or unconsciousness at the start of their stroke. The size and location of the stroke lesion are directly related to dysphagia which may lead to swallowing-related muscle atrophy, particularly in patients with large stroke lesions. This result was consistent with a recent study that found dysphagia to be the most significant risk factor for stroke-related sarcopenia among patients undergoing rehabilitation (Yao et al., 2022). Dysphagia after stroke increases the initial stroke severity (Arnold et al., 2016). Prolonged nasogastric tube feeding may indicate severe malnutrition, further leading to loss of muscle mass and strength. Moreover, infections that impact muscle catabolism, such as aspiration pneumonia, can lead to diminished muscular strength. Thus, various factors and outcomes work together to predispose a patient to sarcopenia.
Pre-stroke sarcopenia was significantly associated with stroke prognosis. Specifically, 18% of the elderly with acute stroke had pre-stroke sarcopenia, an independent predictor of poor prognosis (Nozoe et al., 2019). A previous study showed (Ryan et al., 2017) that patients with pre-stroke sarcopenia were mostly females, had longer hospital stays and experienced higher rates of poor prognosis and prior strokes than those without sarcopenia. A possible explanation could be the decreased muscular function in patients with pre-stroke sarcopenia, making it difficult to move their arms or legs, thereby aggravating the sarcopenia symptoms and leading to severe paralysis.
Additionally, the results of our meta-analysis revealed AF was one of the significant factors. Although CVD causes muscle wasting (Proietti et al., 2022), studies on the association between AF and decompensation remain limiting (Ochi et al., 2010; Sato et al., 2020). The association between sarcopenia and AF may be due to several underlying mechanisms, particularly those associated with aging. These include changes in the cardiac conduction system, such as increased interstitial fibrosis, loss of atrial cardiomyocytes, and alterations in the distribution and function of ion channels, which may predispose individuals to AF (Pugh and Wei, 2001). In addition, AF may cause heart palpitations, fatigue and breathing difficulties, all of which can result in reduced mobility and sarcopenia (Shim et al., 2024).
Consistent with our study, a higher NIHSS score was substantially related to the risk of sarcopenia upon discharge (Kim and Choi, 2023). A prospective study reported baseline NIHSS scores as excellent predictors of post-stroke functional outcomes (Rost et al., 2016). A potential reason for this relationship could be that the severity of the stroke increases the incidence of disability, eventually leading to a reduced ability to contract on the hemiplegic and non-hemiplegic sides (García-Hermoso et al., 2018). Since patients suffering from severe stroke are more prone to develop sarcopenia, further research is necessary to elucidate the factors resulting in loss of muscle strength on the non-hemiplegic side, such as inflammation, malnutrition, and disability. Presumably, neurological factors such as insufficient nerve activation, as well as muscular factors like muscle fiber atrophy and the infiltration of fat cells leading to a decrease in overall muscle mass, work in conjunction to initiate the development of sarcopenia (Manini and Clark, 2012).
In this study, the relationship between BMI and SRS was not statistically significant, which contradicts a prior survey of potential sarcopenia among old-aged stroke survivors in the Malaysian community, where a higher BMI was strongly correlated with a lower risk of possible sarcopenia irrespective of age (Wong et al., 2022). This discrepancy may be attributed to the differences in the populations studied. Moreover, interrelationships between musculoskeletal disorders often caused by impaired gene regulation, endocrine frameworks, and close mechanical interactions (Wong et al., 2022; Kawao and Kaji, 2015; Karasik and Kiel, 2008; Laurent et al., 2016) often exist together.
5 Strengths and limitations
This study presented some significant findings as follows. As far as we know, this is the first systematic review and meta-analysis of risk factors for stroke-associated sarcopenia. In addition, we utilized comprehensive databases, including nine Chinese and English databases. Moreover, we employed a dual review process to improve the comprehensiveness of our findings.
Nevertheless, some limitations of the study should be acknowledged in future studies. Firstly, a high degree of heterogeneity was observed in the NIHSS scores, probably due to population, age, gender, and disease severity, or due to unavoidable heterogeneity associated with the meta-analyses of cross-sectional surveys. Secondly, the lack of standardization in the diagnostic criteria and assessment tools for SRS used in the source studies introduced measurement bias and compromised the reliability of our findings.
6 Conclusion
Age, tube feeding, pre-stroke sarcopenia, AF, NIHSS score, and osteoporosis are significant risk factors in patients with SRS. Moreover, BMI, FOIS, time since stroke, and calf circumference reduction are neither risk nor protective factors after stroke.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
HY: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. JL: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. LX: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft. YL: Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing–original draft. SL: Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft. QW: Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [grant numbers 72364005].
Acknowledgments
We thank Bullet Edits Limited for the linguistic editing and proofreading of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Arnold, M., Liesirova, K., Broeg-Morvay, A., Meisterernst, J., Schlager, M., Mono, M.-L., et al. (2016). Dysphagia in acute stroke: incidence, burden and impact on clinical outcome. PLoS One 11 (2), e0148424. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0148424
Aydin, T., Kesiktaş, F. N., Oren, M. M., Erdogan, T., Ahisha, Y. C., Kizilkurt, T., et al. (2021). Sarcopenia in patients following stroke: an overlooked problem. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 44 (3), 269–275. doi:10.1097/MRR.0000000000000487
Beaudart, C., Rizzoli, R., Bruyère, O., Reginster, J.-Y., and Biver, E. (2014). Sarcopenia: burden and challenges for public health. Arch. Public Health 72 (1), 45. doi:10.1186/2049-3258-72-45
Bruyère, O., Reginster, J.-Y., and Beaudart, C. (2022). Lifestyle approaches to prevent and retard sarcopenia: a narrative review. Maturitas 161, 44–48. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2022.02.004
Chen, L., Xueping, Da, and Ma, S. Construction of risk factors and prediction model for secondary sarcopenia in elderly stroke patients. ournal Chin. J Gerontology (2023) 43(20):4981–4983. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2023.20.034
Clark, B. C., and Manini, T. M. (2010). Functional consequences of sarcopenia and dynapenia in the elderly. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 13 (3), 271–276. doi:10.1097/MCO.0b013e328337819e
Cui, H., Wang, Z., Wu, J., Liu, Y., Zheng, J., Xiao, W., et al. (2023). Chinese expert consensus on prevention and intervention for elderly with sarcopenia (2023). Aging Med. Milt. 6 (2), 104–115. doi:10.1002/agm2.12245
Damluji, A. A., Alfaraidhy, M., AlHajri, N., Rohant, N. N., Kumar, M., Al Malouf, C., et al. (2023). Sarcopenia and cardiovascular diseases. Circulation 147 (20), 1534–1553. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.064071
Delmonico, M. J., Harris, T. B., Visser, M., Park, S. W., Conroy, M. B., Velasquez-Mieyer, P., et al. (2009). Longitudinal study of muscle strength, quality, and adipose tissue infiltration. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 90 (6), 1579–1585. doi:10.3945/ajcn.2009.28047
Fang, P., Zhou, J., Xiao, X., Yang, Y., Luan, S., Liang, Z., et al. (2023). The prognostic value of sarcopenia in oesophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 14 (1), 3–16. doi:10.1002/jcsm.13126
García-Hermoso, A., Cavero-Redondo, I., Ramírez-Vélez, R., Ruiz, J. R., Ortega, F. B., Lee, D.-C., et al. (2018). Muscular strength as a predictor of all-cause mortality in an apparently healthy population: a systematic review and meta-analysis of data from approximately 2 million men and women. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 99 (10), 2100–2113.e5. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2018.01.008
GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators (2021). Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurology 20 (10), 795–820. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00252-0
Hacke, W., Donnan, G., Fieschi, C., Kaste, M., von Kummer, R., Broderick, J. P., et al. (2004). Association of outcome with early stroke treatment: pooled analysis of ATLANTIS, ECASS, and NINDS rt-PA stroke trials. Lancet 363 (9411), 768–774. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)15692-4
Harris, M. L., Polkey, M. I., Bath, P. M., and Moxham, J. (2001). Quadriceps muscle weakness following acute hemiplegic stroke. Clin. Rehabil. 15 (3), 274–281. doi:10.1191/026921501669958740
Hu, S., Pan, N., Liu, C., Wang, Y., and Zhang, T. (2021). Age matching is essential for the study of cerebrospinal fluid sTREM2 levels and alzheimer’s disease risk: a meta-analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 13, 775432. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2021.775432
Hughes, V. A., Frontera, W. R., Wood, M., Evans, W. J., Dallal, G. E., Roubenoff, R., et al. (2001). Longitudinal muscle strength changes in older adults: influence of muscle mass, physical activity, and health. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 56 (5), B209–B217. doi:10.1093/gerona/56.5.b209
Ikeji, R., Nozoe, M., Yamamoto, M., Seike, H., Kubo, H., and Shimada, S. (2023). Sarcopenia in patients following stroke: prevalence and associated factors. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 233, 107910. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2023.107910
Imamura, M., Nozoe, M., Kubo, H., and Shimada, S. (2023). Association between premorbid sarcopenia and neurological deterioration in patients with acute ischemic stroke. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 224, 107527. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2022.107527
Izzo, A., Massimino, E., Riccardi, G., and Della Pepa, G. (2021). A narrative review on sarcopenia in type 2 diabetes mellitus: prevalence and associated factors. Nutrients 13 (1), 183. doi:10.3390/nu13010183
Karasik, D., and Kiel, D. P. (2008). Genetics of the musculoskeletal system: a pleiotropic approach. J. Bone Mineral Res. 23 (6), 788–802. doi:10.1359/jbmr.080218
Kawao, N., and Kaji, H. (2015). Interactions between muscle tissues and bone metabolism: interactions between muscle and bone. J. Cell Biochem. 116 (5), 687–695. doi:10.1002/jcb.25040
Kim, Y. H., and Choi, Y.-A. (2023). Prevalence and risk factors of possible sarcopenia in patients with subacute stroke. PLoS One 18 (9), e0291452. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0291452
Laurent, M. R., Dubois, V., Claessens, F., Verschueren, S. M. P., Vanderschueren, D., Gielen, E., et al. (2016). Muscle-bone interactions: from experimental models to the clinic? A critical update. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 432, 14–36. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2015.10.017
Li, S., Gonzalez-Buonomo, J., Ghuman, J., Huang, X., Malik, A., Yozbatiran, N., et al. (2022b). Aging after stroke: how to define post-stroke sarcopenia and what are its risk factors? Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 58 (5), 683–692. doi:10.23736/S1973-9087.22.07514-1
Li, W., Yue, T., and Liu, Y. (2020). New understanding of the pathogenesis and treatment of stroke-related sarcopenia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 131, 110721. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110721
Li, X., Shin, H., Zhou, P., Niu, X., Liu, J., and Rymer, W. Z. (2014). Power spectral analysis of surface electromyography (EMG) at matched contraction levels of the first dorsal interosseous muscle in stroke survivors. Clin. Neurophysiol. 125 (5), 988–994. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2013.09.044
Li, Z., Tong, X., Ma, Y., Bao, T., and Yue, J. (2022a). Prevalence of depression in patients with sarcopenia and correlation between the two diseases: systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 13 (1), 128–144. doi:10.1002/jcsm.12908
Lisco, G., Disoteo, O. E., De Tullio, A., De Geronimo, V., Giagulli, V. A., Monzani, F., et al. (2023). Sarcopenia and diabetes: a detrimental liaison of advancing age. Nutrients 16 (1), 63. doi:10.3390/nu16010063
Liu, J., Shi, Z., Bai, R., Zheng, J., Ma, S., Wei, J., et al. (2020). Temporal, geographical and demographic trends of stroke prevalence in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 8 (21), 1432. doi:10.21037/atm-19-4342
Manini, T. M., and Clark, B. C. (2012). Dynapenia and aging: an update. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 67 (1), 28–40. doi:10.1093/gerona/glr010
Mas, M. F., González, J., and Frontera, W. R. (2020). Stroke and sarcopenia. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 8 (4), 452–460. doi:10.1007/s40141-020-00284-2
Nakanishi, N., Okura, K., Okamura, M., Nawata, K., Shinohara, A., Tanaka, K., et al. (2021). Measuring and monitoring skeletal muscle mass after stroke: a review of current methods and clinical applications. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 30 (6), 105736. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.105736
Nimphan, C., Laosuwan, K., Saengsuwan, J., and Vichiansiri, R. (2022). Prevalence a and predictive factors for sarcopenia in chronic stroke patients:A preliminary study. Eur. Stroke J. 7 (1), 345. doi:10.1177/23969873221087559
Nozoe, M., Kanai, M., Kubo, H., Yamamoto, M., Shimada, S., and Mase, K. (2019). Prestroke sarcopenia and stroke severity in elderly patients with acute stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 28 (8), 2228–2231. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.05.001
Nozoe, M., Kubo, H., Kanai, M., and Yamamoto, M. (2021). Relationships between pre-stroke SARC-F scores, disability, and risk of malnutrition and functional outcomes after stroke-A prospective cohort study. Nutrients 13 (10), 3586. doi:10.3390/nu13103586
Ochi, M., Kohara, K., Tabara, Y., Kido, T., Uetani, E., Ochi, N., et al. (2010). Arterial stiffness is associated with low thigh muscle mass in middle-aged to elderly men. Atherosclerosis 212 (1), 327–332. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.05.026
Page, M. J., McKenzie, J. E., Bossuyt, P. M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T. C., Mulrow, C. D., et al. (2021). The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372, n71. doi:10.1136/bmj.n71
Proietti, M., Romiti, G. F., Raparelli, V., Diemberger, I., Boriani, G., Dalla Vecchia, L. A., et al. (2022). Frailty prevalence and impact on outcomes in patients with atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 1,187,000 patients. Ageing Res. Rev. 79, 101652. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2022.101652
Pugh, K. G., and Wei, J. Y. (2001). Clinical implications of physiological changes in the aging heart. Drugs Aging 18 (4), 263–276. doi:10.2165/00002512-200118040-00004
Rodrigues, F., Domingos, C., Monteiro, D., and Morouço, P. (2022). A review on aging, sarcopenia, falls, and resistance training in community-dwelling older adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19 (2), 874. doi:10.3390/ijerph19020874
Rost, N. S., Bottle, A., Lee, J.-M., Randall, M., Middleton, S., Shaw, L., et al. (2016). Stroke severity is a crucial predictor of outcome: an international prospective validation study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 5 (1), e002433. doi:10.1161/JAHA.115.002433
Ryan, A. S., Ivey, F. M., Serra, M. C., Hartstein, J., and Hafer-Macko, C. E. (2017). Sarcopenia and physical function in middle-aged and older stroke survivors. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 98 (3), 495–499. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2016.07.015
Sato, R., Akiyama, E., Konishi, M., Matsuzawa, Y., Suzuki, H., Kawashima, C., et al. (2020). Decreased appendicular skeletal muscle mass is associated with poor outcomes after ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 27 (12), 1278–1287. doi:10.5551/jat.52282
Shim, G. Y., Kim, M., and Won, C. W. (2024). Cross-sectional and longitudinal association between atrial fibrillation and sarcopenia: findings from the Korean frailty and aging cohort study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 15 (1), 434–441. doi:10.1002/jcsm.13401
Simsek, H., Meseri, R., Sahin, S., Kilavuz, A., Bicakli, D. H., Uyar, M., et al. (2019). Prevalence of sarcopenia and related factors in community-dwelling elderly individuals. Saudi Med. J. 40 (6), 568–574. doi:10.15537/smj.2019.6.23917
Song, X., Chen, X., Bai, J., and Zhang, J. (2023). Association between pre-stroke sarcopenia risk and stroke-associated infection in older people with acute ischemic stroke. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 10, 1090829. doi:10.3389/fmed.2023.1090829
Sterne, J. A., and Egger, M. (2001). Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: guidelines on choice of axis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 54 (10), 1046–1055. doi:10.1016/s0895-4356(01)00377-8
Stroup, D. F., Berlin, J. A., Morton, S. C., Olkin, I., Williamson, G. D., Rennie, D., et al. (2000). Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) group. JAMA 283 (15), 2008–2012. doi:10.1001/jama.283.15.2008
Tanaka, S., Yamauchi, K., Hayashi, Y., Kumagae, K., Goto, K., Harayama, E., et al. (2024). Factors influencing the reduction in quadriceps muscle thickness in the paretic limbs of patients with acute stroke. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 60, 173–178. doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2024.01.019
Wang, J., Mei, F., and Qiao, A. (2020). Effects of sarcopenia on neurological function and quality of life in patients with cerebral infarction and its risk factors. Chin. J. General Pract. 19 (9), 824–828. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn114798-20200207-00086
Wong, H. J., Harith, S., Lua, P. L., and Ibrahim, K. A. (2022). Possible sarcopenia and its association with nutritional status, dietary intakes, physical activity and health-related quality of life among older stroke survivors. Ann. Geriatr. Med. Res. 26 (2), 162–174. doi:10.4235/agmr.22.0033
Yan-li, L. I., Bin, M. U., and Wen-jie, YANG (2023). The effect of early sarcopenia screening on the prognosis and rehabilitation of stroke patients. J. Hebei Med. Univ. 44 (6), 635–639. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1007-3205.2023.06.003
Yao, R., Yao, L., Rao, A., Ou, J., Wang, W., Hou, Q., et al. (2022). Prevalence and risk factors of stroke-related sarcopenia at the subacute stage: a case control study. Front. Neurol. 13, 899658. doi:10.3389/fneur.2022.899658
Keywords: stroke, sarcopenia, risk factors, systematic review, meta-analysis
Citation: Yan H, Li J, Xian L, Li Y, Li S and Wen Q (2025) Risk factors of stroke-related sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Aging 6:1452708. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1452708
Received: 21 June 2024; Accepted: 14 January 2025;
Published: 31 January 2025.
Edited by:
Joana Reis, Instituto Politécnico de Viana do Castelo, PortugalReviewed by:
Tan Wang, University of Pennsylvania, United StatesNobuaki Sasai, Suzuka University of Medical Science, Japan
Copyright © 2025 Yan, Li, Xian, Li, Li and Wen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Juan Li, Njk0ODA3MDU1QHFxLmNvbQ==
 Huan Yan
Huan Yan Juan Li2*
Juan Li2* Yujie Li
Yujie Li