- 1Biomedical Research Centre, Qatar University, Doha, Qatar
- 2Sport Coaching Department, College of Sport Sciences, Qatar University, Doha, Qatar
- 3Department of Biomedical Sciences, College of Health Sciences, QU Health, Qatar University, Doha, Qatar
- 4College of Medicine, QU Health, Qatar University (QU), Doha, Qatar
- 5Heart hospital, Out-patient Department, Hamad Medical Corporation (HMC), Doha, Qatar
Introduction: Aging is a complex process marked by a gradual decline in physiological function and increased susceptibility to diseases. Telomere length is frequently regarded as one of the primary biomarkers of aging. Metabolic profiles are key features in longevity and have been associated with both age and age-related diseases. We previously reported an increase in the telomere length in healthy female subjects when Ramadan fasting was combined with physical training. This study aims to characterize the metabolic signature differentiating the combined effects of exercise and fasting from exercise alone and explore the correlations with the previously reported telomere length changes.
Methods: Twenty-nine young, non-obese, and healthy female subjects were previously randomized into two groups: one group followed a 4-week exercise program, while the other group followed the same 4-week exercise program but also fasted during Ramadan. Metabolic profiles were assessed pre- and post-intervention using untargeted metabolomics.
Results and Discussion: Our results showed a significant decrease in many lipid metabolites in the exercise-while-fasting group, particularly ceramides. Our study sheds light on the dynamic changes in lipid metabolism and its potential role in inflammation and age-related diseases, and contributes to the broader understanding of how lifestyle factors can influence cellular aging and metabolic health.
1 Introduction
In recent decades, research in aging has gained significant traction, driven by the understanding that aging is not merely a passive biological process but can be influenced by genetic and lifestyle factors. Telomere length is often considered one of the key biomarkers of aging. Metabolomics is a powerful tool that holds great significance in advancing our understanding of aging. It enables researchers to examine the influence of external factors, such as diet and physical activity on the aging process (Panyard et al., 2022). Notably, changes at the metabolic level are key features in longevity, and metabolic profiles have been associated with age and age-related diseases (van der Spek et al., 2019). Recent studies have developed novel metabolomic aging scores that predict mortality and disease risk more accurately than traditional metrics (Zhang et al., 2024). An increasing amount of research indicates that lipid metabolism plays a significant role in the aging process (Johnson and Stolzing, 2019; Pablo Palavicini and Han, 2021). Understanding these metabolic changes can help identify potential interventions and lifestyle modification aimed at enhancing health span.
Both exercise and intermittent fasting play vital roles in shaping the human metabolome through distinct yet complementary mechanisms. Exercise induces acute and chronic changes in metabolite concentrations, affecting energy metabolism, lipid metabolism, and amino acid metabolism (Pellegrino et al., 2022; Jaguri et al., 2023). On the other hand, intermittent fasting alters metabolic pathways by promoting fat oxidation and enhancing ketogenesis, which shifts the body’s energy source from carbohydrates to fats (Washburn et al., 2019; Madkour M. et al., 2023). The combination of exercise and intermittent fasting can yield synergistic effects, resulting in better metabolic health outcomes (Real-Hohn et al., 2018).
We previously reported (Almuraikhy et al., 2024), in a longitudinal study, that combining exercise with Ramadan fasting may be an effective tool for slowing down the aging process. In the exercise-while-fasting group, we observed a significant increase in the telomere length compared to the control group, which engaged in exercise alone and showed no notable change. Furthermore, our findings suggested that TNF-α and HDL may contribute to the observed variations in the telomere length, due to their opposing effects on inflammation and oxidative stress. The objective of this study is to use untargeted metabolomics analysis to characterize the metabolic signature that differentiated between the combined effects of exercise and fasting compared to the effect of exercise intervention only. By analyzing metabolites, we hope to uncover specific biochemical pathways influenced by this dual intervention that may not be evident through traditional clinical measures alone. The findings of this study will contribute to the growing body of knowledge on telomere biology and its interplay with metabolic factors.
2 Methods
2.1 Study participants
A total of 29 healthy female subjects aged between 20 and 30 years, categorized as lean or overweight (with a BMI ranging from 20 to less than 30), were selected from Qatar University students for this study. The research received approval from the Qatar University Institutional Review Board (QU-IRB 1798-EA/23). All participants gave their informed consent and underwent an initial medical assessment to identify any potential health issues and confirm their eligibility for the training program. The participants were divided into two randomized groups: the first group (n = 16), considered as the control group (4W), completed a 4-week exercise training program. The second group (4W + F), consisting of 13 participants, underwent a 4-week exercise training program while fasting for 14 h during Ramadan. Ramadan fasting is a form of intermittent fasting. This practice involves a daily fast that lasts from dawn until dusk, during which participants abstain from food, drink, and smoking. The training program, adhering to the American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) and American Heart association (AHA) recommendations (Samjoo et al., 2013; Marson et al., 2016; Battista et al., 2021; Kanaley et al., 2022), comprised aerobic exercises with progressive intensity. Exercise timing for both groups was in the afternoon period (1 to 3 p.m.). Anthropometric measurements and fasting blood samples were taken before and after intervention. Blood samples were collected by a licensed nurse between 8:00 a.m. and 12:00 p.m. during fasting. All samples were kept on ice, and the serum was separated within 1 hour after collection by centrifuging the blood for 15 min at 2500 rpm. For fasting blood glucose and lipid profile tests, the analyses were run immediately, and the remaining serum was aliquoted and stored at −80°C. Supplementary Table S1 provides an overview of participants in this study, grouped into (4W) and (4W + F), before and after intervention, respectively.
2.2 Metabolomics
Metabolomic profiling of serum samples from all participants was performed using Metabolon’s platform, according to standardized protocols (Al-Khelaifi et al., 2018). The Waters ACQUITY ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) instrument (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA) coupled to a Thermo Scientific Q-Exactive high resolution/accurate mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) interfaced with a heated electrospray ionization (HESI-II) source with the Orbitrap mass analyzer operated at 35,000 mass resolution. Details of the liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) techniques utilized in this study were previously described (Al-Khelaifi et al., 2018; Al-Sulaiti et al., 2024). Compounds were identified by comparing them to library entries of purified standards or recurrent unknown entities, using a database of over 3,300 commercially available purified standard compounds. Library matches for each compound were verified for each sample and corrected when necessary (Evans, 2014; Al-Sulaiti et al., 2019).
2.3 Statistical analysis
Metabolomics data on 1039 known and 259 unknown identities were batch-normalized (median-scaled) before imputation was performed for missing values using a minimum value across batches from the median-scaled data. The data were natural log-transformed prior to statistical analysis. Unknown metabolites were excluded from the downstream statistical steps. Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed to assess whether there is a significant difference between the before- and after-treatment groups (Supplementary Figure S1). The highest discriminant metabolites between the intervention groups were found using an OPLS-DA model. Univariate analysis was conducted using fold change and paired Student’s t-test. The p-values were adjusted using false discovery rate (FDR) correction. Functional enrichment analysis was performed on the FDR significant metabolites list from the univariate analysis using Fisher’s exact test and was followed by the FDR multiple testing correction method. The sub-pathways were previously predefined using Metabolon, and those with less than three top hits were dropped. The Δ(T/S) ratio, which captures the change in the telomere length before and after exercise, was previously calculated for the same subjects (Almuraikhy et al., 2024). A partial correlation network was constructed using a Gaussian graphical model (GGM) to explore the relationships between the significant metabolites before and after exercise and the Δ(T/S) ratio in the 4WF group. The network was based on significant correlations (p < 0.05).
3 Results
3.1 Multivariate analysis of metabolites differentiating (4W) and (4W + F) before and after intervention
Non-targeted metabolomics analysis was used to identify the metabolic signatures of participants in this study, grouped into (4W) and (4W + F) before and after intervention. OPLS-DA was used to identify the best distinguishing components before and after, as shown in Figures 1A, B. OPLS-DA revealed one predictive and two orthogonal components, with the discriminatory component accounting for 87% of the variance between before and after intervention in the (4W) group and 89.5% of the variance in the (4W + F) group. The loading plot (Figures 1C, D) displays metabolites responsible for differentiation, including diacylglycerols (DAGs), sphingomyelins (SMs), and phosphatidylcholines (PCs), which are common between both groups and ceramides only in the (4W + F) group.
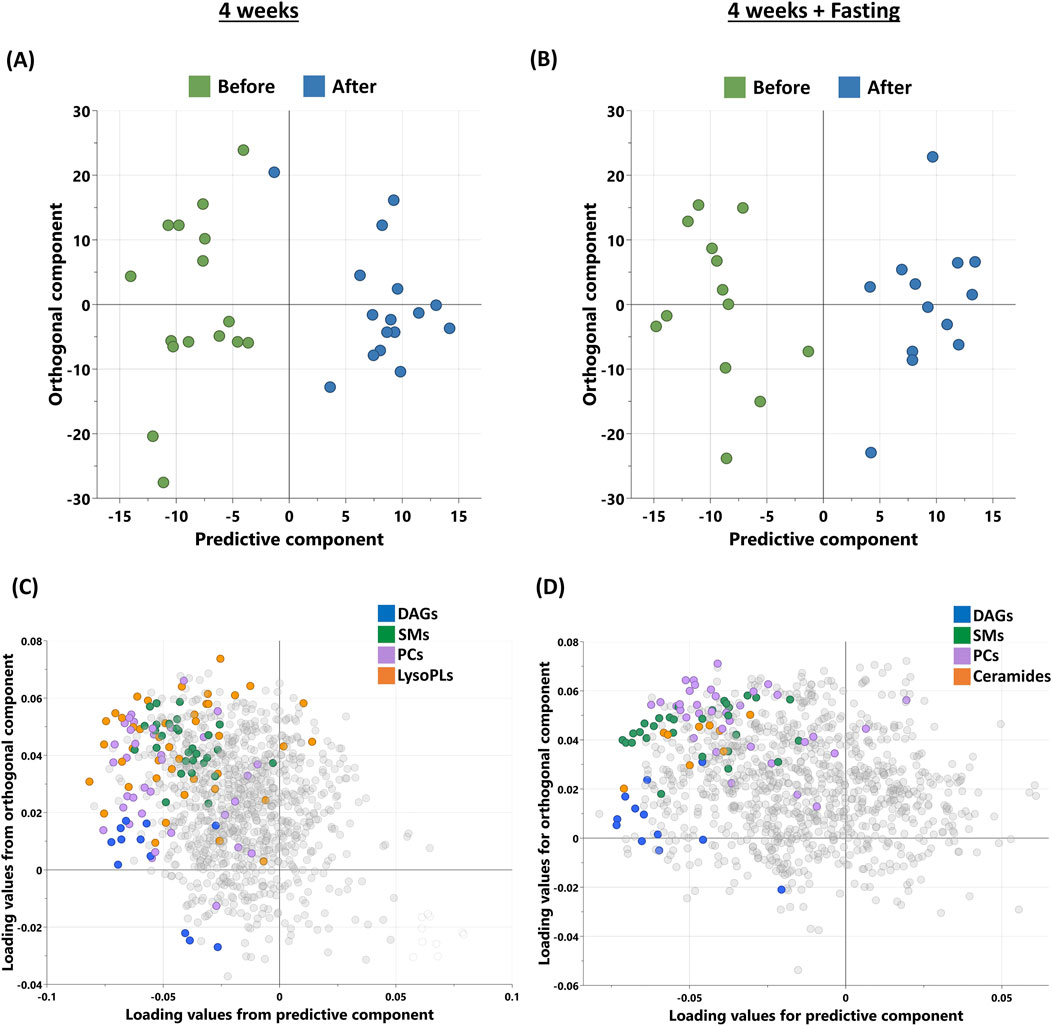
Figure 1. Metabolomics analysis of participants’ sera after 4 weeks of moderate physical training (n = 16) and 4 weeks training combined with fasting (n = 13). (A, B) OPLS-DA score plot of the participants before and after physical training in 4W (R2Y – 0.87, Q2 – 0.056) and 4W + F (R2Y – 0.895, Q2 – 0.331) groups, respectively. (C, D) Loading plots depicting the metabolites from significantly enriched pathways of the same. [DAGs, diacylglycerols; SMs, sphingomyelins; PCs, phosphatidylcholines; LysoPLs, lysophospholipids].
3.2 Univariate analysis of metabolites differentiating between before and after 4 weeks training
Paired Student’s t-test revealed FDR (≤0.05) significant changes in the (4W) group before and after exercise, as indicated in Table 1. Results showed a decrease in diacylglycerols, lysophospholipids, and acylcarnitines in this group. Dot-plot boxplots of the top significant metabolites are depicted in Supplementary Figure S2. Volcano plots showing all the increased and decreased metabolites post-exercise are shown in Supplementary Figure S4A.
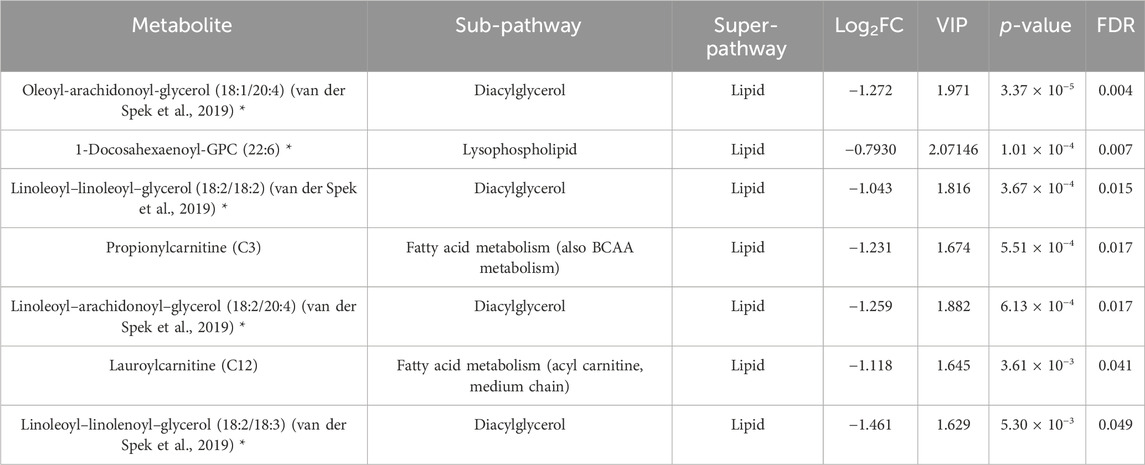
Table 1. Results from the paired Student’s t-test showing metabolites differentiating the exercise group before and after intervention. (*) indicates a compound that has not been officially confirmed based on a standard but that Metabolon is confident in its identity.
3.3 Univariate analysis of metabolites differentiating between before and after 4 weeks training while fasting
Paired Student’s t-test revealed FDR (≤0.05) significant changes in the (4W + F) group before and after exercise, as indicated in Table 2. Results showed a decrease in diacylglycerols, acylcarnitines, ceramides, and one kynurenine metabolite in this group. Dot-plot boxplots of the top significant metabolites are depicted in Supplementary Figure S3. Volcano plots showing all the increased and decreased metabolites post-exercise are shown in Supplementary Figure S4B.
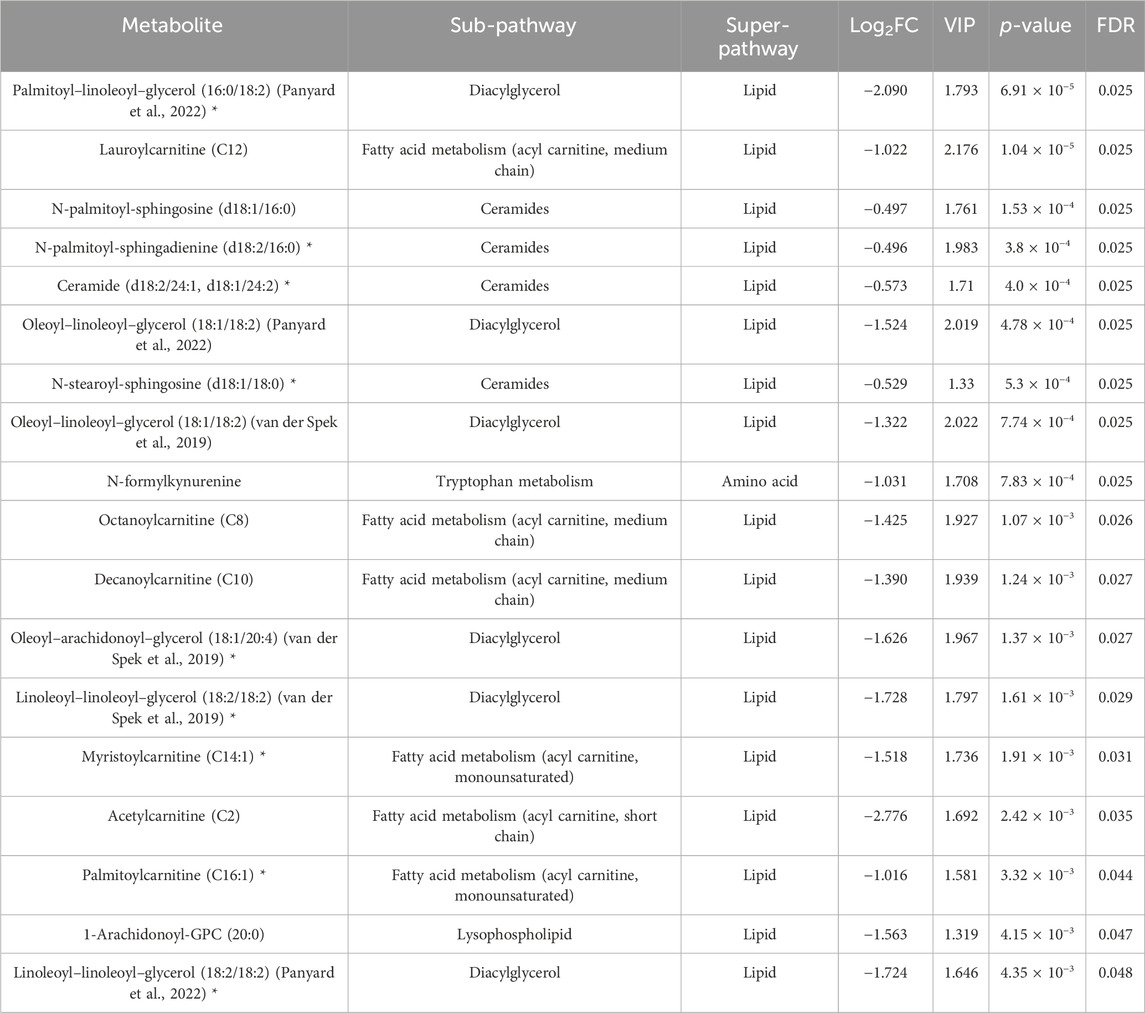
Table 2. Results from the paired Student’s t-test showing metabolites differentiating the exercise-while-fasting group before and after intervention. (*) indicates a compound that has not been officially confirmed based on a standard but that metabolon is confident in its identity.
3.4 Functional enrichment analysis of metabolites differentiating between before and after intervention in (4W) and (4W + F) groups
The results of functional enrichment analyses (Figure 2) indicated significant differences in sphingomyelins, phosphatidylcholines, lysophospholipids, diacylglycerol, acetylcholines, and acylcarnitines in both groups, whereas the exercise-while-fasting group showed a significant difference in ceramides.
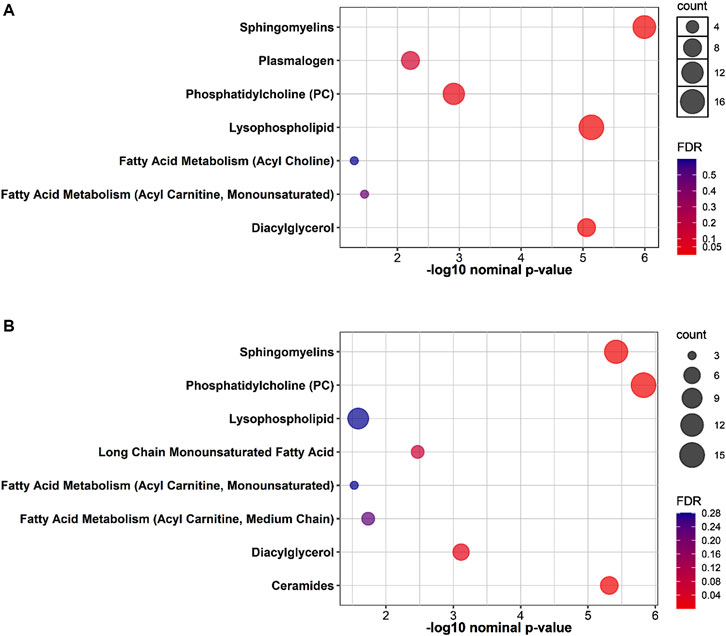
Figure 2. Plots showing the results of metabolite set enrichment analysis using Fisher’s exact test for (A): 4W group and (B): 4W + F group.
3.5 Partial correlation network in the 4W + F group
To reveal key metabolic interactions influenced by exercise in the 4WF group, a partial correlation network was created using a GGM to investigate the relationships between the significant metabolites before and after exercise with the difference in the T/S ratio in the 4WF group. Figure 3 shows that the Δ(T/S) ratio is strongly and negatively correlated with ceramides.
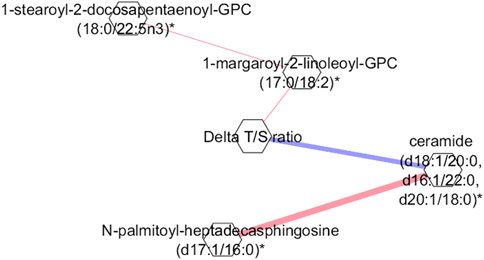
Figure 3. Gaussian graphical model (GGM) representing the partial correlations between the Δ(T/S) ratio and the metabolites in the 4W + F group. Red color indicates positive correlation. Blue color indicates negative correlation. Each node corresponds to a metabolite, and the edges indicate partial correlations, with the thickness of the edges reflecting the strength of these correlations.
4 Discussion
Changes at the metabolic level are crucial factors influencing longevity. Exercising while fasting may be an effective tool for slowing down the aging rate and contribute to overall wellbeing. The aim of this research is to identify and characterize the distinct metabolic signatures that emerged from the combined effects of exercise and fasting, in contrast to the effects of exercise alone. Analyzing these metabolites allows us to pinpoint the specific biochemical and metabolic changes induced by the combination of exercise and fasting. These unique metabolites may serve as potential biomarkers or targets for further investigations.
Our results showed a significant reduction in many ceramides and their derivatives in the exercise-while-fasting group only. Moreover, our GGM showed a strong negative correlation between the telomere length and ceramides. Ceramides are a type of sphingolipids that play a crucial role in regulating various cellular responses, such as senescence, apoptosis, and, more recently, autophagy (Hannun and Obeid, 2011). Kazmirczak et al. (2023) showed that intermittent fasting is effective in the attenuation of ceramide accumulation. However, Madkour et al. demonstrated a decrease in many sphingolipids, but not ceramides, upon Ramadan intermittent fasting (Madkour M. I. et al., 2023). The effects of exercise on ceramides are complex and depend on various factors such as the exercise duration, type, intensity, and the metabolic status of the individuals. Carrard et al. (2021) and Tan-Chen et al. (2020) reported in their reviews that while regular exercise is associated with a reduction in plasma ceramide levels, acute exercise may lead to a transient increase in the concentrations of these metabolites. However, Bergman et al. (2015) showed that chronic exercise training does not change plasma ceramide levels. This suggests that the notable reduction in ceramide levels observed in our study may result from the combined effects of exercise and fasting.
Interestingly, a close connection between ceramide levels and aging has been revealed (Mencarelli and Martinez–Martinez, 2013), and ceramides have been shown to be as one of the key upstream regulators of telomerase activity (Sundararaj et al., 2004a). Notably, C18-ceramide, generated by the enzyme ceramide synthase 1, has been found to downregulate the expression of telomerase (Wooten-Blanks et al., 2007). Relatedly, Laurila et al. reported an accumulation of ceramides in the skeletal muscle upon aging (Laurila et al., 2022). Moreover, treatment with exogenous ceramides was demonstrated to cause a rapid shortening of the telomere length (Sundararaj et al., 2004b) and trigger a senescent-like phenotype in young cells (Venable and Yin, 2009). Our previous research (Almuraikhy et al., 2024) indicated that TNF-α and HDL might play a role in the observed variations in the telomere length due to their contrasting impacts on inflammation and oxidative stress. Interestingly, ceramides were found to be inversely correlated with HDL (Meeusen et al., 2018), and TNF-α was demonstrated to induce and accelerate ceramide production (Hernández-Corbacho et al., 2015; Chaurasia et al., 2020). Reducing ceramide levels through exercise combined with fasting or blocking its effects on telomeres may be a promising anti-aging strategy. More research is needed to fully elucidate the mechanisms by which ceramides regulate telomere biology and influence the aging process.
Our results also showed a reduction in acylcarnitines and phosphatidylcholine in both groups; however, the reduction appears to be more pronounced in the exercise-while-fasting group. Recent studies suggest that aging may contribute to the generation of carnitine metabolites (Lo et al., 2023; Huguenard et al., 2023). Moreover, acylcarnitines and phosphatidylcholines were associated, among other metabolites, with a shorter telomere length (van der Spek et al., 2019; Subedi et al., 2023). Markedly, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1C, the enzyme responsible for the formation of acylcarnitines, was shown to play a role in regulating cellular senescence and telomere length (Wang et al., 2020). Intriguingly, acylcarnitines have been reported to induce the secretion of TNF-α among other inflammatory cytokines (Enooku et al., 2019) and that the energy metabolism pattern of immune cells is determined by the availability of acylcarnitines, directing the activation of immune cell toward a pro-inflammatory phenotype (Dambrova et al., 2022; Rutkowsky et al., 2014). However, phosphatidylcholines are generally recognized for their anti-inflammatory properties (Treede et al., 2007). This paradoxical decrease in phosphatidylcholines could be related to their use as an energy source during fasting and exercise or may reflect alterations in membrane composition rather than just inflammatory status. This highlights the need for future comprehensive studies, which could provide a deeper understanding of the complex metabolic and inflammatory responses to fasted exercise and their potential relation with aging.
Our results showed a decrease in lysophospholipids and diacylglycerols in both groups, with a more marked decrease in the 4W group. Lysophospholipids are critical for maintaining mitochondrial membrane integrity and function, while diacylglycerols are crucial lipid molecules that play a significant role in cellular signaling and metabolism. Interestingly, research identified a significant downregulation of lysophospholipid levels in older adults (Pan et al., 2023). Additionally, overexpression of diacylglycerol lipase in model organisms has been linked to extended lifespans and enhanced resistance to oxidative stress (Lin et al., 2014). Our findings indicate that the 4W + F group exhibited a lesser impact on lysophospholipid and diacylglycerols levels compared to the 4W group. This observation suggests that fasting may confer a protective effect on the levels of these lipids.
The univariate analysis showed a significant decrease in N-formylkynurenine only in the exercise-while-fasting group. N-formylkynurenine is a metabolite in the kynurenine pathway, which is involved in the degradation of tryptophan. Strikingly, N-formylkynurenine was found to increase with age (Refaey et al., 2017). Moreover, TNF-α was shown to play a crucial role in directing tryptophan metabolism toward the kynurenine pathway, thereby increasing levels of kynurenine and its metabolites, including N-formylkynurenine (Okamoto et al., 2023). Despite these insights, there remains a notable gap in the literature concerning the relationship between N-formylkynurenine with both exercise and fasting, highlighting an important area for future research.
Although research indicates that the single-gene T/S ratio method yields reliable and reproducible results when executed correctly (Martin-Ruiz et al., 2015), we recognize that our study’s assessment of the telomere length was limited to the T/S ratio derived from a single reference gene. This represents a notable limitation in our research. It is essential to emphasize that the fasting duration is standardized for all participants throughout Ramadan. This intentional decision aims to maintain uniformity in fasting times and ensure compliance among everyone involved. Although participants were encouraged to follow a balanced diet, they were not required to adhere to a specific, predetermined dietary plan. This lack of a defined dietary regimen may be viewed as an additional limitation to our study, potentially influencing their metabolic profiles. The relatively short duration of this study is another limitation. A longer follow-up period would have allowed us to observe potential long-term changes in metabolite profiles and assess the stability of the observed effects over time. Additionally, it is important to acknowledge that the metabolite changes reported in this study were not confirmed or validated using a secondary analytical method. Future studies should consider employing complementary techniques. Moreover, it is crucial to recognize that, although we can speculate on the possible connections between the observed metabolic changes and variations in the telomere length, the existing evidence remains preliminary. Currently, it does not establish any causal relationship, and further research is necessary to deepen our understanding of this connection.
5 Conclusion
Our study demonstrates that the combination of exercise and fasting leads to significant metabolic alterations, particularly a notable reduction in ceramide levels, which may play a crucial role in promoting longevity and overall health. This synergistic approach not only affects ceramide metabolism but also influences other key metabolites, such as acylcarnitines, lysophospholipids, diacylglycerol, and phosphatidylcholine, underscoring the relationship between metabolism, inflammation, and cellular vitality. By identifying specific metabolites as potential biomarkers, our research paves the way for targeted interventions that may further promote healthy aging and longevity. Future comprehensive studies could offer deeper insights into the complex metabolic and inflammatory responses to fasted exercise and their complex relationship with aging.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Qatar University (QU-IRB 1798-EA/23) and have received expedited review according to the Qatar Ministry of Public Health (MoPH) regulations. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
SA: writing–original draft. KN: writing–original draft. NA: software and writing–original draft. MS: data curation and writing–review and editing. HA-A: investigation and writing–review and editing. HA-S: investigation and writing–review and editing. SB: investigation and writing–review and editing. AA: investigation and writing–review and editing. ME: funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, and writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by Qatar University (grant number IRCC-2022-467) (ME).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Qatar University Research Office for funding this work. They also thank the physical education department of the College of Education and Biomedical Center of Qatar University for supporting the project and the Al Esraa Medical Center for performing clinical trait measurements.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Al-Khelaifi, F., Diboun, I., Donati, F., Botrè, F., Alsayrafi, M., Georgakopoulos, C., et al. (2018). A pilot study comparing the metabolic profiles of elite-level athletes from different sporting disciplines. Sports Med. Open 4, 2–15. doi:10.1186/s40798-017-0114-z
Almuraikhy, S., Sellami, M., Naja, K., Al-Amri, H. S., Anwardeen, N., Aden, A., et al. (2024). Joint effects of exercise and ramadan fasting on telomere length: implications for cellular aging. Biomedicines 12 (6), 1182. doi:10.3390/biomedicines12061182
Al-Sulaiti, H., Anwardeen, N., Bashraheel, S. S., Naja, K., and Elrayess, M. A. (2024). Alterations in choline metabolism in non-obese individuals with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolites 14 (8), 457. doi:10.3390/metabo14080457
Al-Sulaiti, H., Diboun, I., Agha, M. V., Mohamed, F. F. S., Atkin, S., Dömling, A. S., et al. (2019). Metabolic signature of obesity-associated insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. J. Transl. Med. 17 (1), 348. doi:10.1186/s12967-019-2096-8
Battista, F., Ermolao, A., van Baak, M. A., Beaulieu, K., Blundell, J. E., Busetto, L., et al. (2021). Effect of exercise on cardiometabolic health of adults with overweight or obesity: focus on blood pressure, insulin resistance, and intrahepatic fat-A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 22 (Suppl. 4), e13269. doi:10.1111/obr.13269
Bergman, B. C., Brozinick, J. T., Strauss, A., Bacon, S., Kerege, A., Bui, H. H., et al. (2015). Serum sphingolipids: relationships to insulin sensitivity and changes with exercise in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 309 (4), E398–E408. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00134.2015
Carrard, J., Gallart-Ayala, H., Weber, N., Colledge, F., Streese, L., Hanssen, H., et al. (2021). How ceramides orchestrate cardiometabolic health-an ode to physically active living. Metabolites 11 (10), 675. doi:10.3390/metabo11100675
Chaurasia, B., Talbot, C. L., and Summers, S. A. (2020). Adipocyte ceramides—the nexus of inflammation and metabolic disease. Front. Immunol. 11, 576347. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.576347
Dambrova, M., Makrecka-Kuka, M., Kuka, J., Vilskersts, R., Nordberg, D., Attwood, M. M., et al. (2022). Acylcarnitines: nomenclature, biomarkers, therapeutic potential, drug targets, and clinical trials. Pharmacol. Rev. 74 (3), 506–551. doi:10.1124/pharmrev.121.000408
Enooku, K., Nakagawa, H., Fujiwara, N., Kondo, M., Minami, T., Hoshida, Y., et al. (2019). Altered serum acylcarnitine profile is associated with the status of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and NAFLD-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 10663. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-47216-2
Evans, A. M. (2014). High resolution mass spectrometry improves data quantity and quality as compared to unit mass resolution mass spectrometry in high-throughput profiling metabolomics. 4(2): 1.
Hannun, Y. A., and Obeid, L. M. (2011). Many ceramides. J. Biol. Chem. 286 (32), 27855–27862. doi:10.1074/jbc.R111.254359
Hernández-Corbacho, M. J., Canals, D., Adada, M. M., Liu, M., Senkal, C. E., Yi, J. K., et al. (2015). Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα)-induced ceramide generation via ceramide synthases regulates loss of focal adhesion kinase (FAK) and programmed cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 290 (42), 25356–25373. doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.658658
Huguenard, C. J. C., Cseresznye, A., Darcey, T., Nkiliza, A., Evans, J. E., Hazen, S. L., et al. (2023). Age and APOE affect L-carnitine system metabolites in the brain in the APOE-TR model. Front. Aging Neurosci. 14, 1059017. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2022.1059017
Jaguri, A., Al Thani, A. A., and Elrayess, M. A. (2023). Exercise metabolome: insights for health and performance. Metabolites 13 (6), 694. doi:10.3390/metabo13060694
Johnson, A. A., and Stolzing, A. (2019). The role of lipid metabolism in aging, lifespan regulation, and age-related disease. Aging Cell 18 (6), e13048. doi:10.1111/acel.13048
Kanaley, J. A., Colberg, S. R., Corcoran, M. H., Malin, S. K., Rodriguez, N. R., Crespo, C. J., et al. (2022). Exercise/physical activity in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a consensus statement from the American College of Sports medicine. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc 54 (2), 353–368. doi:10.1249/MSS.0000000000002800
Kazmirczak, F., Hartweck, L. M., Vogel, N. T., Mendelson, J. B., Park, A. K., Raveendran, R. M., et al. (2023). Intermittent fasting activates AMP-kinase to restructure right ventricular lipid metabolism and microtubules. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 8 (3), 239–254. doi:10.1016/j.jacbts.2022.12.001
Laurila, P.-P., Wohlwend, M., Imamura de Lima, T., Luan, P., Herzig, S., Zanou, N., et al. (2022). Sphingolipids accumulate in aged muscle, and their reduction counteracts sarcopenia. Nat. Aging 2 (12), 1159–1175. doi:10.1038/s43587-022-00309-6
Lin, Y. H., Chen, Y. C., Kao, T. Y., Lin, Y. C., Hsu, T. E., Wu, Y. C., et al. (2014). Diacylglycerol lipase regulates lifespan and oxidative stress response by inversely modulating TOR signaling in Drosophila and C. elegans. Aging Cell 13 (4), 755–764. doi:10.1111/acel.12232
Lo, C.-J., Lin, C. M., Fan, C. M., Tang, H. Y., Liu, H. F., Ho, H. Y., et al. (2023). Plasma acylcarnitine in elderly Taiwanese: as biomarkers of possible sarcopenia and sarcopenia. BMC Geriatr. 23 (1), 769. doi:10.1186/s12877-023-04485-x
Madkour, M., Giddey, A. D., Soares, N. C., Semreen, M. H., Bustanji, Y., Zeb, F., et al. (2023a). Ramadan diurnal intermittent fasting is associated with significant plasma metabolomics changes in subjects with overweight and obesity: a prospective cohort study. Front. Nutr. 9, 1008730. doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.1008730
Madkour, M. I., Islam, M. T., Tippetts, T. S., Chowdhury, K. H., Lesniewski, L. A., Summers, S. A., et al. (2023b). Ramadan intermittent fasting is associated with ameliorated inflammatory markers and improved plasma sphingolipids/ceramides in subjects with obesity: lipidomics analysis. Sci. Rep. 13 (1), 17322. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-43862-9
Marson, E. C., Delevatti, R. S., Prado, A. K. G., Netto, N., and Kruel, L. F. M. (2016). Effects of aerobic, resistance, and combined exercise training on insulin resistance markers in overweight or obese children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prev. Med. 93, 211–218. doi:10.1016/j.ypmed.2016.10.020
Martin-Ruiz, C. M., Baird, D., Roger, L., Boukamp, P., Krunic, D., Cawthon, R., et al. (2015). Reproducibility of telomere length assessment: an international collaborative study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 44 (5), 1673–1683. doi:10.1093/ije/dyu191
Meeusen, J. W., Donato, L. J., Bryant, S. C., Baudhuin, L. M., Berger, P. B., and Jaffe, A. S. (2018). Plasma ceramides. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, Vasc. Biol. 38 (8), 1933–1939. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311199
Mencarelli, C., and Martinez–Martinez, P. (2013). Ceramide function in the brain: when a slight tilt is enough. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 70 (2), 181–203. doi:10.1007/s00018-012-1038-x
Okamoto, N., Hoshikawa, T., Honma, Y., Chibaatar, E., Ikenouchi, A., Harada, M., et al. (2023). Effect modification of tumor necrosis factor-α on the kynurenine and serotonin pathways in major depressive disorder on type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur. Archives Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 274, 1697–1707. doi:10.1007/s00406-023-01713-8
Pablo Palavicini, J., and Han, X. (2021). “Chapter 18 - lipidomics of aging,” in Handbook of the biology of aging. Ninth Edition (Academic Press), 391–404.
Pan, Y., Liu, P., Li, S., Li, B., Li, Y., and Ma, L. (2023). Lysophospholipids and branched chain amino acids are associated with aging: a metabolomics-based study of Chinese adults. Eur. J. Med. Res. 28 (1), 58. doi:10.1186/s40001-023-01021-w
Panyard, D. J., Yu, B., and Snyder, M. P. (2022). The metabolomics of human aging: advances, challenges, and opportunities. Sci. Adv. 8 (42), eadd6155. doi:10.1126/sciadv.add6155
Pellegrino, J. K., Anthony, T. G., Gillies, P., and Arent, S. M. (2022). The exercise metabolome: acute aerobic and anaerobic signatures. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 19 (1), 603–622. doi:10.1080/15502783.2022.2115858
Real-Hohn, A., Navegantes, C., Ramos, K., Ramos-Filho, D., Cahuê, F., Galina, A., et al. (2018). The synergism of high-intensity intermittent exercise and every-other-day intermittent fasting regimen on energy metabolism adaptations includes hexokinase activity and mitochondrial efficiency. PLoS One 13 (12), e0202784. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0202784
Refaey, M. E., McGee-Lawrence, M. E., Fulzele, S., Kennedy, E. J., Bollag, W. B., Elsalanty, M., et al. (2017). Kynurenine, a tryptophan metabolite that accumulates with age, induces bone loss. J. Bone Min. Res. 32 (11), 2182–2193. doi:10.1002/jbmr.3224
Rutkowsky, J. M., Knotts, T. A., Ono-Moore, K. D., McCoin, C. S., Huang, S., Schneider, D., et al. (2014). Acylcarnitines activate proinflammatory signaling pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 306 (12), E1378–E1387. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00656.2013
Samjoo, I. A., Safdar, A., Hamadeh, M. J., Raha, S., and Tarnopolsky, M. A. (2013). The effect of endurance exercise on both skeletal muscle and systemic oxidative stress in previously sedentary obese men. Nutr. Diabetes 3 (9), e88. doi:10.1038/nutd.2013.30
Subedi, P., Palma-Gudiel, H., Fiehn, O., Best, L. G., Lee, E. T., Howard, B. V., et al. (2023). Lipidomics profiling of biological aging in American Indians: the strong Heart family study. Geroscience 45 (1), 359–369. doi:10.1007/s11357-022-00638-9
Sundararaj, K. P., Wood, R. E., Ponnusamy, S., Salas, A. M., Szulc, Z., Bielawska, A., et al. (2004a). Rapid shortening of telomere length in response to ceramide involves the inhibition of telomere binding activity of nuclear glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J. Biol. Chem. 279 (7), 6152–6162. doi:10.1074/jbc.M310549200
Sundararaj, K. P., Wood, R. E., Ponnusamy, S., Salas, A. M., Szulc, Z., Bielawska, A., et al. (2004b). Rapid shortening of telomere length in response to ceramide involves the inhibition of telomere binding activity of nuclear glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J. Biol. Chem. 279 (7), 6152–6162. doi:10.1074/jbc.M310549200
Tan-Chen, S., Guitton, J., Bourron, O., Le Stunff, H., and Hajduch, E. (2020). Sphingolipid metabolism and signaling in skeletal muscle: from physiology to physiopathology. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 11, 491. doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.00491
Treede, I., Braun, A., Sparla, R., Kühnel, M., Giese, T., Turner, J. R., et al. (2007). Anti-inflammatory effects of phosphatidylcholine. J. Biol. Chem. 282 (37), 27155–27164. doi:10.1074/jbc.M704408200
van der Spek, A., Broer, L., Draisma, H. H. M., Pool, R., Albrecht, E., Beekman, M., et al. (2019). Metabolomics reveals a link between homocysteine and lipid metabolism and leukocyte telomere length: the ENGAGE consortium. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 11623. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-47282-6
Venable, M. E., and Yin, X. (2009). Ceramide induces endothelial cell senescence. Cell Biochem. Funct. 27 (8), 547–551. doi:10.1002/cbf.1605
Wang, Y., Yu, T., Zhou, Y., Wang, S., Zhou, X., Wang, L., et al. (2020). Carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1C contributes to progressive cellular senescence. Aging (Albany NY) 12 (8), 6733–6755. doi:10.18632/aging.103033
Washburn, R. L., Cox, J. E., Muhlestein, J. B., May, H. T., Carlquist, J. F., Le, V. T., et al. (2019). Pilot study of novel intermittent fasting effects on metabolomic and trimethylamine N-oxide changes during 24-hour water-only fasting in the FEELGOOD trial. Nutrients 11 (2), 246. doi:10.3390/nu11020246
Wooten-Blanks, L. G., Song, P., Senkal, C. E., and Ogretmen, B. (2007). Mechanisms of ceramide-mediated repression of the human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter via deacetylation of Sp3 by histone deacetylase 1. Faseb J. 21 (12), 3386–3397. doi:10.1096/fj.07-8621com
Keywords: aging, telomere length, metabolomics, fasting, exercise
Citation: Almuraikhy S, Naja K, Anwardeen N, Sellami M, Al-Amri HS, Al-Sulaiti H, Bashraheel SS, Aden AA and Elrayess MA (2024) Metabolic signatures of combined exercise and fasting: an expanded perspective on previous telomere length findings. Front. Aging 5:1494095. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2024.1494095
Received: 10 September 2024; Accepted: 05 November 2024;
Published: 20 November 2024.
Edited by:
Jianhua Zhang, University of Alabama at Birmingham, United StatesReviewed by:
Juan Pablo Palavicini, The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, United StatesSilvienne Catherine Sint Jago, University of Alabama at Birmingham, United States
Copyright © 2024 Almuraikhy, Naja, Anwardeen, Sellami, Al-Amri, Al-Sulaiti, Bashraheel, Aden and Elrayess. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mohamed A. Elrayess, bS5lbHJheWVzc0BxdS5lZHUucWE=
 Shamma Almuraikhy
Shamma Almuraikhy Khaled Naja
Khaled Naja Najeha Anwardeen
Najeha Anwardeen Maha Sellami
Maha Sellami Hadaia Saleh Al-Amri2
Hadaia Saleh Al-Amri2 Haya Al-Sulaiti
Haya Al-Sulaiti Sara S. Bashraheel
Sara S. Bashraheel Mohamed A. Elrayess
Mohamed A. Elrayess