
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Aging Neurosci., 29 January 2025
Sec. Alzheimer's Disease and Related Dementias
Volume 17 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2025.1535280
Genetic diversity in the apolipoprotein E (ApoE) gene has been identified as the major susceptibility genetic risk factor for sporadic Alzheimer’s disease (SAD). Specifically, the ApoEε4 allele is a significant risk factor for SAD, while ApoEε2 allele provides protection compared to the more common ApoEε3 allele. This review discusses the role of the ApoE in AD and other neurodegenerative disorders. ApoE, a cholesterol transport protein, influences several pathways involved in neurodegeneration, particularly in AD. Beyond its established role in amyloid β-protein (Aβ) metabolism and deposition, ApoE also impacts tau pathology, neurodegeneration, and the microglial response to AD. The review aims to provide an updated overview of ApoE’s diverse roles, emphasizing its involvement in Aβ clearance through ApoE receptors. It also covers ApoE’s influence in other neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s disease (PD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD), Huntington’s disease (HD), vascular dementia (VD), and multiple sclerosis (MS). New research highlights the interaction between ApoE and presenilin (PS), suggesting connections between familial AD (FAD) and SAD. The review also explores protective effects of ApoE mutations against AD and ApoE4-induced tauopathy, neurodegeneration, and neuroinflammation. The insights from this comprehensive update could indeed lead to new therapeutic strategies for neurodegenerative diseases.
Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) is a key genetic risk factor in the complex landscape of Alzheimer’s disease (AD), especially in its late-onset sporadic form. Genetic variation in the ApoE gene is a significant risk factor for late-onset AD, with the three primary ApoE allelic variants—ApoEε2, ApoEε3, and ApoEε4—being involved in about 95% of late-onset AD cases (Serrano-Pozo et al., 2021; Yamazaki et al., 2019). In late-onset AD, which occurs sporadically after the age of 65, the impairment of amyloid β-protein (Aβ) clearance mechanisms seems to be a primary factor in the accumulation of Aβ in the brain (Mawuenyega et al., 2010). Strong evidence from clinical and basic research indicates that among the three major ApoE allelic variants, the ApoEε4 allele is associated with an increased risk of AD (Corder et al., 1993; Saunders et al., 1993) while the ApoEε2 allele is linked to a decreased risk (Farrer et al., 1997; Corder et al., 1994) compared to the more common ApoEε3 allele (Bu, 2009; Liu et al., 2013). Clear evidence has shown that human ApoE2 knock-in (KI) mice exhibit a significant reduction in Aβ deposition compared to ApoE3-KI and ApoE4-KI mice (Holtzman et al., 2000; Li, 2019; Fagan et al., 2002). Additionally, ApoE2 has been found to lower Aβ oligomer levels more effectively than ApoE3 and ApoE4 (Hashimoto et al., 2012). Moreover, ApoE4 has a stronger stabilizing effect on Aβ oligomers than ApoE3 (Cerf et al., 2011). Conclusive evidence shows that ApoE4 contributes to the development of AD, likely through both a loss-of-function in neuroprotection and a gain-of-function in neurotoxicity, when compared to ApoE3 (Huang and Mucke, 2012; Kanekiyo et al., 2014). For instance, homocysteine, a known risk factor for AD, prevents ApoE3 from forming dimers and reduces its ability to produce HDL. This suggests that homocysteine impairs the clearance of amyloid-beta (Aβ) by affecting the function of ApoE3 (Minagawa et al., 2010). Individuals with the ApoEε4 allele of the ApoE gene not only have a higher risk of AD in a dose-dependent manner but also tend to experience an earlier age of onset (Liu et al., 2013; Kanekiyo et al., 2014; Sando et al., 2008). Indisputable evidence indicates that heterozygous carriers of the ApoEε4 allele have a 3–4-fold increased risk of developing late-onset AD, while homozygous carriers face a 9–15-fold higher risk (Farrer et al., 1997; Neu et al., 2017; Genin et al., 2011). The ApoEε2 allele reduces the risk of AD by approximately 0.6-fold (Corder et al., 1993; Holtzman et al., 2012). Among individuals with AD, the presence of ApoEε4 is also linked to an earlier age of disease onset (Corder et al., 1993; Sando et al., 2008). A meta-analysis reported an odds ratio (OR) of 0.621 for developing AD in individuals with one ApoEε2 allele and 3.68 for those with one ApoEε4 allele, compared to individuals homozygous for ApoEε3. In cognitively healthy individuals, the allele frequencies of ApoEε2, ApoEε3, and ApoEε4 are 7, 79, and 14%, respectively, whereas in AD patients, the frequencies are 4, 58, and 38%. These findings highlight that ApoEε4 significantly increases the risk of AD and lowers the age of onset in a dose-dependent manner (Yamazaki et al., 2019). Several in vitro and in vivo studies suggest that the ApoE4 protein isoform promotes amyloid pathology and disrupts various aspects of normal brain function, indicating a gain-of-function effect in neurotoxicity associated with ApoE4 (Liu et al., 2013). While the distinct effects of ApoE isoforms on amyloid pathology and Aβ metabolism have been confirmed at molecular, cellular, and organismal levels, the precise mechanisms remain not fully understood, and proposed mechanisms continue to be debated. Recent studies, however, have brought attention to pathways not dependent on Aβ that are differentially influenced by ApoE, such as tau-driven neurodegeneration (Shi et al., 2017), microglial responses, and the risks associated with dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) (Bras et al., 2014; Tsuang et al., 2013; Guerreiro et al., 2018), Parkinson’s disease dementia (PDD) (Tsuang et al., 2013; Huang et al., 2006; Irwin et al., 2012; Tropea et al., 2018) and the extent of TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) pathology in AD (Josephs et al., 2014; Wennberg et al., 2018; Yang et al., 2018).
In this review, we aim to explore the emerging connections between ApoE genotype and pathogenic proteins in individuals with AD and other neurodegenerative disorders. Moving beyond traditional viewpoints, we shed light on the multifaceted role of ApoE in its interaction with Aβ, elucidating the involvement of ApoE receptors in the clearance of Aβ. Our review entails the latest research findings on ApoE’s functions and its impact on AD, Parkinson’s disease (PD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD), Huntington’s disease (HD), vascular dementia (VD), and multiple sclerosis (MS), thus providing a fresh and insightful perspective on unraveling the mechanisms underlying neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, we review newly discovered ApoE functions and their close relationships with known cellular physiology and pathological processes. Through a comprehensive analysis of findings from multiple studies, this review underscores the multifaceted roles of ApoE and their implications in AD and other neurodegenerative conditions (Figure 1).
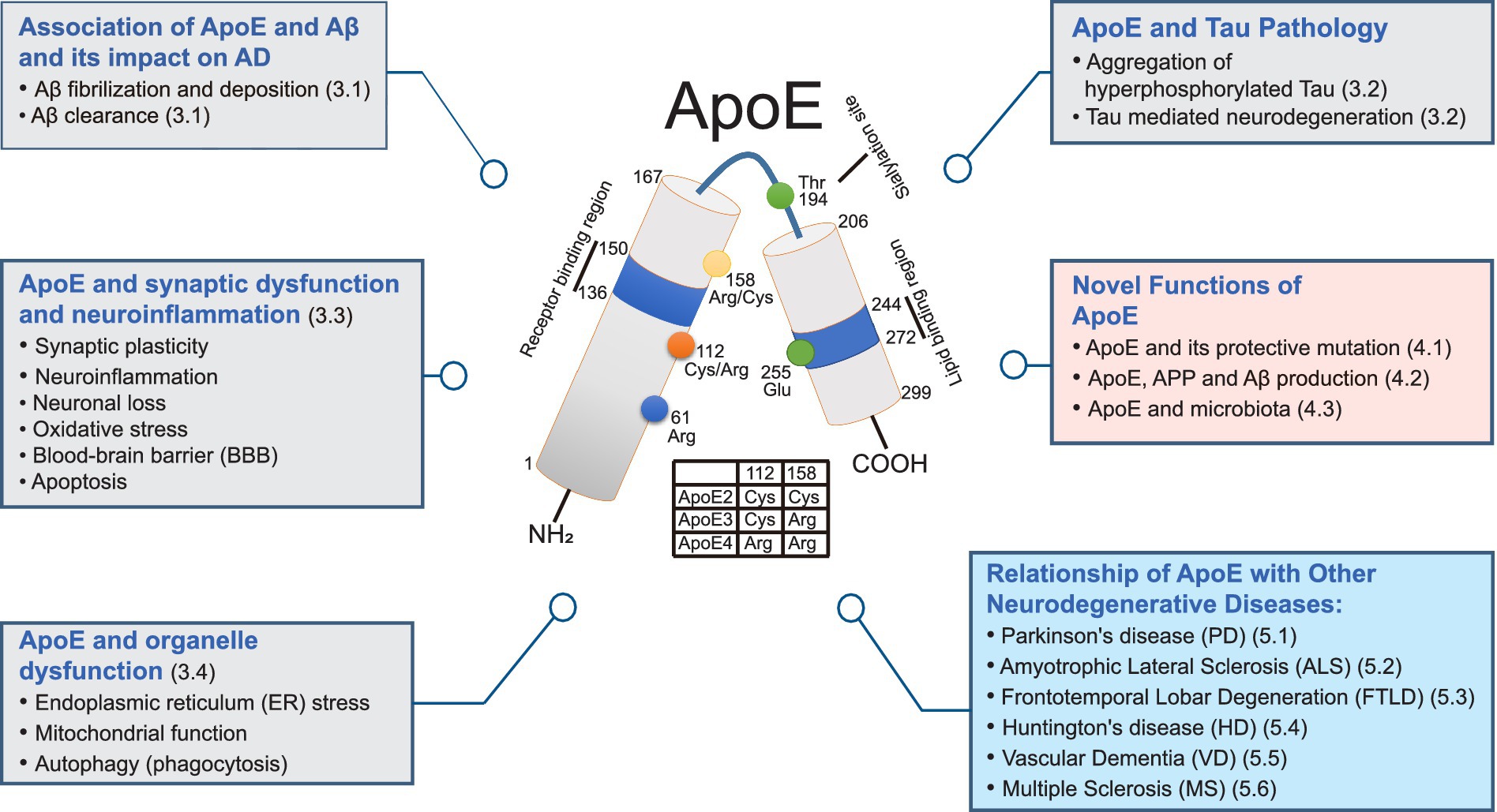
Figure 1. Multifaceted roles of ApoE in neurodegenerative disorders: a comprehensive diagram. This diagram illustrates the diverse functions of ApoE in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and other neurodegenerative disorders. Grey boxes represent functions associated with ApoE contributing to AD through Aβ fibrilization and deposition, Aβ clearance, aggregation of hyperphosphorylated tau, neuron loss, and organelle dysfunction. Pink boxes highlight novel functions of ApoE, indicating potential roles of ApoE and related mechanisms. Blue boxes depict the relationships between ApoE and other degenerative diseases. In the center, the illustration of structural and functional regions of ApoE are displayed. Human ApoE is a heavily glycosylated protein with 299 amino acid residues containing a receptor-binding region (residues 136–150) in the N-terminal domain (residues 1–167) and a lipid-binding region (residues 244–272) in the C-terminal domain (residues 206–299). Human ApoE exists three isoforms the ApoE2, ApoE3 and ApoE4 which are distinguished by the amino acid residues located at residues 112 and 158. ApoE2 isoform has Cys residues at both positions, ApoE3 isoform has a Cys residue at 112 and an Arg residue at 158, and apoE4 has Arg residues at both positions.
Human ApoE is a ~ 34 kDa glycoprotein composed of 299 amino acids and is part of the family of amphiphilic exchangeable lipoproteins (Mahley, 1988). The human ApoE gene is situated on chromosome 19q13.32 and consists of four exons and three introns (Das et al., 1985; Fernández-Calle et al., 2022). There are three primary ApoE alleles in humans: ApoEε2, ApoEε3, and ApoEε4. These alleles were first identified through the characterization of human ApoE polymorphisms using isoelectric focusing of plasma samples from patients with familial lipoprotein disorder type III hyperlipoproteinemia (Kanekiyo et al., 2014; Utermann et al., 1977). The ApoE isoforms encoded by the three gene alleles display distinct band patterns with specific isoelectric points: ApoE2 (pH 5.4), ApoE3 (pH 5.55), and ApoE4 (pH 6.1) (Utermann et al., 1977; Mahley and Rall, 2000). Studies indicate that the variability among the three major ApoE isoforms—ApoE2, ApoE3, and ApoE4—is attributable to genetic polymorphisms (Zannis and Breslow, 1981). Recent review studies have documented that human ApoE genotypes can be classified into six major types based on allelic variations: three homozygous genotypes (ApoE2/2, ApoE3/3, and ApoE4/4) and three heterozygous genotypes (ApoE2/3, ApoE2/4, and ApoE3/4) (Yamazaki et al., 2019; Chen et al., 2021). Complete amino acid sequencing has shown that the three ApoE gene alleles differ only at positions 112 and 158: ApoE2 has Cys112 and Cys158; ApoE3 has Cys112 and Arg158; and ApoE4 has Arg112 and Arg158 (Figure 1) (Rall et al., 1982; Weisgraber et al., 1981). However, these single amino acid polymorphisms significantly affect ApoE functionality, leading to isoform-specific variations in structure that influence its binding properties with lipids and receptors, as well as its propensity for oligomerization and stability (Yamazaki et al., 2019; Ruiz et al., 2005; Yamazaki et al., 2016; Hatters et al., 2006; Ma et al., 2018; Raulin et al., 2022). Therefore, understanding the differences between ApoE isoforms is crucial for elucidating its function.
The Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)-based model created from a monomeric mutant form of ApoE3, which has mutations in the C-terminal domain to prevent aggregation, provided the first complete view of ApoE’s full-length structure. However, the precise structure of native ApoE remains uncertain due to the protein’s tendency to aggregate (Chen et al., 2011). The human ApoE protein comprises two primary structural domains: an N-terminal domain and a C-terminal domain, connected by a flexible hinge region (Chen et al., 2011). The N-terminal domain (residues 1–167) includes the receptor-binding region (Wilson et al., 1991), while the C-terminal domain (residues 206–299) contains the lipid-binding region (Weisgraber, 1994). These domains are separated by the hinge region (residues 168–205) (Chen et al., 2011). X-ray crystallographic analyses (Wilson et al., 1991) and NMR-based working models (Sivashanmugam and Wang, 2009) have identified a four-helix bundle in the N-terminal domain of ApoE. The structure of the N-terminal domain in a monomeric mutant form of ApoE3 shows that Arg 61 forms a hydrogen bond with Thr 194, and Glu 255 forms a salt bridge with Lys 95 (Kanekiyo et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2011). In contrast, the N-terminal domain structure of ApoE4 shows that Arg 112 forms a salt bridge with Glu 109, causing Arg 61 to be exposed away from the four-helix bundle. In ApoE3, however, this side chain is buried, as revealed by X-ray crystallographic analyses (Dong et al., 1994). Consequently, it is predicted that Arg 61 in ApoE4 interacts with Glu 255, facilitating interactions between the N- and C-terminal domains (Mahley and Rall, 2000; Wilson et al., 1991; Mahley et al., 2009). Domain interaction is a unique structural characteristic of ApoE4 that sets it apart from ApoE2 and ApoE3. Unlike ApoE4, ApoE2 and ApoE3 lack domain interaction due to the presence of Cys-112 instead of Arg-112 (Raffai et al., 2001). The unique Cys-158 residue in ApoE2 disrupts the salt bridge between Arg-158 and Asp-154 and forms a new salt bridge between Arg-150 and Asp-154, leading to reduced affinity for the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) (Dong et al., 1994). This diminished binding to LDLR places ApoE2 homozygous individuals at a greater risk for type III hyperlipoproteinemia, a genetic disorder characterized by elevated plasma levels of cholesterol and triglycerides (Hatters et al., 2006). Although the NMR structure does not show domain-domain interactions in ApoE4, fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) analyses have indicated that such interactions are stronger in ApoE4 compared to ApoE3. Studies have also shown that the distance between Arg 61 and Glu 255 is closer in both lipid-free and phospholipid-bound ApoE4 (Hatters et al., 2005). Similarly, ApoE4-expressing neuronal cells also showed stronger domain-domain interaction by live cell imaging (Xu et al., 2004). Beyond these interactions, the single amino acid difference at position 112—Cys in ApoE3 and Arg in ApoE4—has a significant impact on the structure and functions of ApoE, particularly concerning AD pathways.
ApoE production and secretion are highly specific to particular cells and tissues (Fernández-Calle et al., 2022; Kockx et al., 2018). ApoE is primarily produced by hepatocytes and macrophages in the liver (Huang et al., 2004). Although ApoE does not cross the blood–brain barrier (BBB), it is abundantly expressed in the central nervous system (CNS) by astrocytes, microglia, vascular mural cells, and choroid plexus cells, and to a lesser extent in stressed neurons (Boyles et al., 1985; Xu et al., 2006; Aoki et al., 2003; Mahley and Huang, 2012a; Grubman et al., 2019; Kang et al., 2018). Furthermore, various cell types within the BBB, such as oligodendrocytes and pericytes can also produce ApoE to a lesser degree (Fernández-Calle et al., 2022; Bruinsma et al., 2010). In both astrocytes and microglia, ApoE2 is secreted to a greater extent than ApoE4 into the culture medium (Hasel and Liddelow, 2021). In primary cultures from human ApoE-targeted replacement (ApoE-TR) mice, astrocytes secreted at least six times more ApoE than microglia under basal conditions. ApoE2 astrocytes released more ApoE than ApoE4 astrocytes, though cellular ApoE levels were consistent across genotypes. Approximately 50–60% of total ApoE produced by astrocytes was secreted, regardless of genotype. While ApoE mRNA levels showed no significant differences among genotypes, ApoE4 astrocytes displayed a trend toward higher ApoE mRNA than ApoE2. In microglia, secreted ApoE2 was significantly higher than ApoE3 and ApoE4, and cellular ApoE levels were also greater in ApoE2 than in ApoE3 and ApoE4. The proportion of secreted ApoE relative to total ApoE in microglia was highest in ApoE2 (49%) and lowest in ApoE4 (30%). Notably, ApoE4 secretion was reduced in microglia (30%) compared to astrocytes (50%) (Lanfranco et al., 2021).
ApoE is produced and secreted through a classical secretory pathway: Initially, it is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), after which it undergoes post-translational glycosylation and sialylation in the Golgi network. Subsequently, it is transported to the plasma membrane and secreted (Figure 2) (Kockx et al., 2018; Kockx et al., 2007). Upon secretion from cells, ApoE mediates the uptake of cholesterol and phospholipids via interactions with transmembrane ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters, particularly ABCA1 and ABCG1, culminating in the assembly of lipoprotein particles (Hirsch-Reinshagen et al., 2004; Wahrle et al., 2004; Karten et al., 2006). ABCA1 and ABCG1 are predominantly expressed in neurons, glial cells, and macrophages, serving to facilitate the efflux of cholesterol to ApoE (Karasinska et al., 2013; Vance and Hayashi, 2010; Tarr and Edwards, 2008). The pivotal role of ApoE lies in the redistribution of cholesterol and phospholipids to neurons through its interaction with cell-surface ApoE receptors. Hence, to ensure proper functionality, ApoE necessitates both secretion and lipidation (Fernández-Calle et al., 2022). Additionally, prior studies have indicated that ApoE3 facilitates the efflux of cholesterol and phospholipids from both astrocytes and neurons more effectively than ApoE4. This distinction is attributed to the intramolecular domain interaction and intermolecular dimerization of ApoE3, which augment the generation of HDL-like particles, a characteristic not observed in ApoE4 (Figure 2) (Minagawa et al., 2009; Gong et al., 2002; Michikawa et al., 2000; Gong et al., 2007).
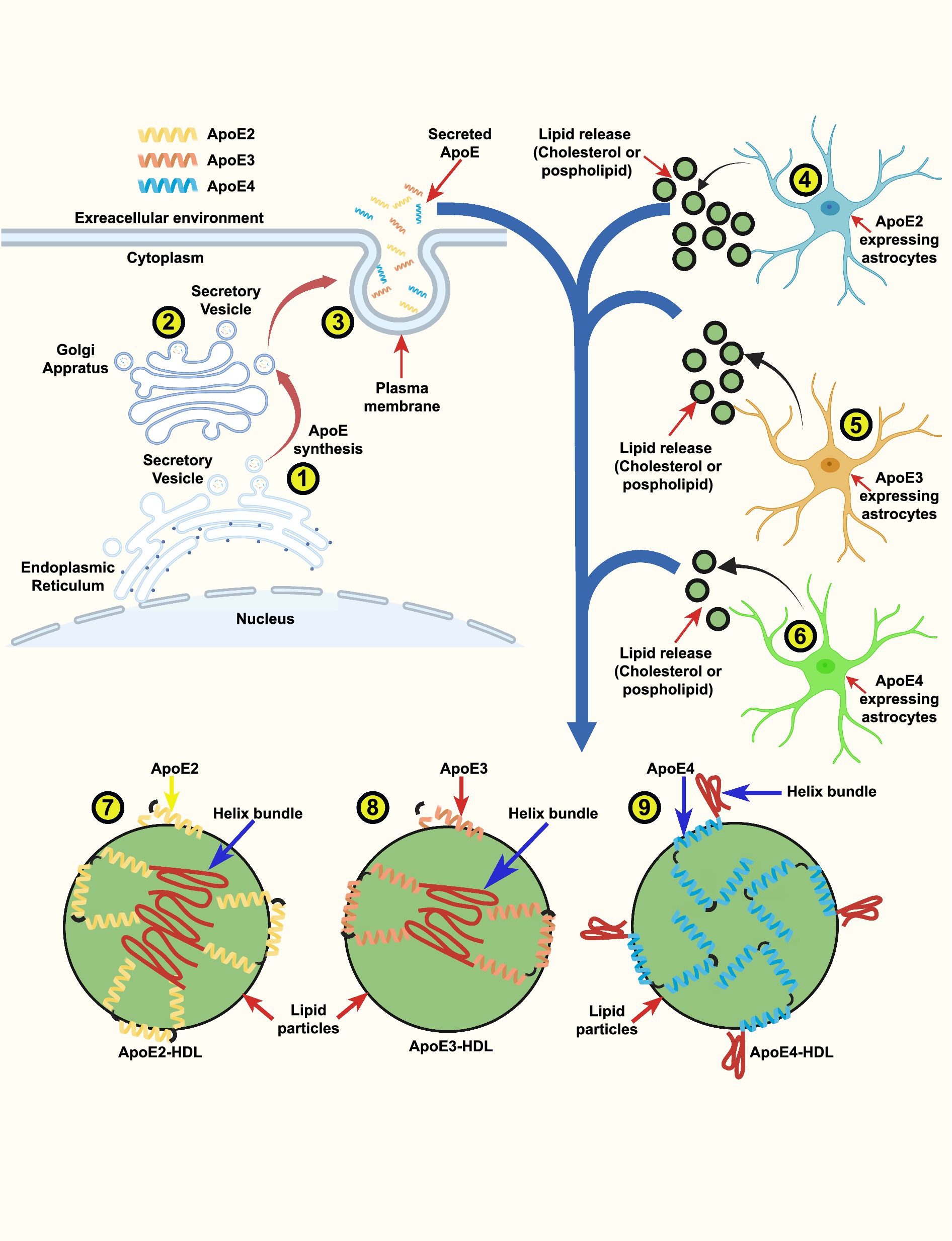
Figure 2. ApoE isoform-dependent lipid release from astrocytes and generation of ApoE-HDL particles: a schematic illustration. ApoE is vesicular protein that is produced and secreted through a classical secretory pathway. ApoE is synthesized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (1), after which it undergoes post-translational modification in the Golgi apparatus (2). Subsequently, it is transported to the plasma membrane and secreted to the extracellular environment (3). The amounts of lipid particles (cholesterol and phospholipids) release from (3) ApoE2-expressing astrocytes (4) ApoE3-expressing astrocytes and (5) from ApoE4-expressing astrocytes (6) derived from human ApoE2, ApoE3 and ApoE4 knock-in (KI) mouse brains. The release potency of lipid particles followed the rank order: ApoE2 > ApoE3 > ApoE4. To ensure proper functionality the secreted ApoE necessitates to bound to lipid particles to form ApoE-HDL. Model of ApoE lipid particles generated by ApoE2-, ApoE3- and ApoE4-expressing astrocytes. The intricate illustration indicate that ApoE2 has higher ApoE-HDL levels than ApoE3 and ApoE4 (7). ApoE3 has the ability to generate similarly sized ApoE lipid particles with a smaller number of ApoE molecules (8) than ApoE4 (9). Based on these findings, we propose a detailed sketch showing that one ApoE4-containing lipid particle contains ∼2-fold numbers of ApoE molecules (8) compared with an ApoE3-containing lipid particle (8).
ApoE3 and ApoE2 have a stronger attraction to high-density lipoproteins (HDL), while ApoE4 is often linked to very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) and low-density lipoproteins (LDL) (Dong et al., 1994; Hatters et al., 2006). The ApoE protein comprises two primary functional regions: the receptor-binding site (residues 136–150) within the N-terminal domain and the lipid-binding site (residues 244–272) within the C-terminal domain. NMR analysis of ApoE3 has elucidated that exposed hydrophobic residues result in the destabilization of the C-terminal domain, leading to the formation of a large exposed hydrophobic surface that facilitates the initial binding of lipids. However, it is noteworthy that several hydrophilic residues in the C-terminal domain are situated within the domain interface (Kanekiyo et al., 2014; Hatters et al., 2006). In ApoE4, the substitution of Arg 61 with Thr or Glu 255 with Ala induces a preference for HDL like that of ApoE3 (Dong et al., 1994; Hatters et al., 2006). Hence, it is likely that Arg 61, Glu 255, or their interaction is indispensable for VLDL preference in ApoE4. This implies that the distinct lipoprotein preference of ApoE4 increases plasma cholesterol levels, consequently elevating the risk of cardiovascular diseases, particularly atherosclerosis (Kanekiyo et al., 2014; Davignon et al., 1988).
Lipidated ApoE is internalized via ApoE receptors, specifically the LDL receptor (LDLR) family, which encompasses LDLR and LDLR-related protein 1 (LRP1) receptors (Yamazaki et al., 2019; Holtzman et al., 2012; Husain et al., 2021). LDLR is a member of the LRP family, composed of seven structurally similar transmembrane proteins, including LRP1, LRP1b, LRP2, LRP4, LRP8, VLDLR, and LDLR (May et al., 2007). LRPs and VLDLR bind to all forms of ApoE particles, with VLDLR also capable of binding to lipid-free ApoE, while LDLRs exhibit a higher affinity for lipidated ApoE particles (Bu, 2009; Ruiz et al., 2005). Genetic variations in ApoE directly influence its lipidation status in an isoform-specific manner (ApoE4 < ApoE3 < ApoE2) (Hubin et al., 2019; Morrow et al., 2000). The lipidation status of ApoE is instrumental in its receptor-binding properties, molecular stability, and functional integrity. Isoform disparities of ApoE markedly alter its composition and operation, consequently impacting its interaction with both lipids and receptors. Research indicates that ApoE3 possesses an increased ability, approximately 2.5 to 3.9-fold, to induce lipid efflux compared to ApoE4 (Minagawa et al., 2009). In a previous study, it was shown that ApoE2 has a binding affinity to LDLR that is more than 50 times weaker than the binding of ApoE3 or ApoE4 to this receptor (Hatters et al., 2006). This low binding propensity of ApoE2 for LDLR leads to impaired clearance of triglyceride-rich lipoprotein remnant particles, thereby contributing to the onset of type III hyperlipoproteinemia (Mahley, 1988; Phillips, 2014). On the other hand, ApoE4 has a higher binding affinity to VLDL particles compared to ApoE2 and ApoE3 (Hatters et al., 2006), which impairs the lipolytic processing of VLDL in the periphery. Consequently, ApoE4 exacerbates pro-atherogenic changes in lipoprotein distribution (Phillips, 2014). The lipidation state of ApoE significantly affects its physiological and pathological roles, and increasing ApoE lipidation has been suggested as a target for AD treatment (Lanfranco et al., 2020).
In addition, ApoE not only interacts with the LDLR family but also with cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPG) (Ji et al., 1993), either in its lipid-free or lipidated forms (Saito et al., 2003). This binding occurs through both the receptor-binding region in the N-terminal domain and the basic residues around Lys233 in the C-terminal domain (Saito et al., 2003). Additionally, LRP1 can form a complex with HSPG (Ji et al., 1993). In the HSPG/LRP1 uptake pathway, ApoE either binds initially to HSPG and is subsequently transferred to LRP1 for uptake, or it binds directly to the HSPG/LRP1 complex (Ji et al., 1993). The receptor-binding functionality of ApoE is isoform-dependent. ApoE3 and ApoE4 exhibit similar binding affinity to LDLR, whereas ApoE2 has a significantly lower affinity (Schneider et al., 1981). However, the reduced binding affinity of ApoE2 to LRP1 is less pronounced compared to LDLR (Kowal et al., 1990). Interestingly, there appear to be no substantial differences among ApoE isoforms in their capacity to bind to HSPG (Mahley and Rall, 2000). Moreover, the ApoE3-R136S mutation, also known as ApoE3 Christchurch (ApoE3-Ch), has recently gained attention for its significantly reduced heparin-binding ability (Arboleda-Velasquez et al., 2019). The ApoE3-Ch mutation strongly protects against early-onset AD, as evidenced by a homozygous index patient who developed only mild dementia much later in life than expected, highlighting the importance of studying rare ApoE variants in AD pathogenesis and protection (Arboleda-Velasquez et al., 2019). This mutation occurs in a region of ApoE that is critical for binding to lipoprotein receptors and HSPG (Mahley et al., 1999). Previous analyses revealed that ApoE4 exhibits a higher affinity for heparin compared to ApoE3 and ApoE2 (Yamauchi et al., 2008). HSPG is believed to promote Aβ aggregation and facilitate the neuronal uptake of extracellular tau, with ApoE binding potentially playing a key role in these processes (Rauch et al., 2018). A monoclonal antibody (1343A) was developed to target ApoE amino acids 130–143, including the R136S mutation, and demonstrated the ability to reduce the heparin-binding capacity of wild-type (WT) ApoE3 to levels similar to ApoE3-Ch in vitro. These findings suggest that targeting this specific region of ApoE with antibodies or other molecules, or modulating ApoE-HSPG interactions, may mimic the potentially protective effects associated with ApoE3-Ch (Arboleda-Velasquez et al., 2019).
Although the primary ApoE receptors include LDLR, LRP1, VLDLR, and ApoE receptor 2 (ApoER2), microglia and astrocytes also express a diverse collection of receptors. Microglia possess a variety of receptors, including those known as pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), which can detect stimuli of diverse origins. The key PRRs include toll-like receptors (TLRs), inflammasome-forming nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors (NLRs), the receptor for advanced glycation end-products (RAGE), and the triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) (Kigerl et al., 2014; Ulland and Colonna, 2018). In the brain, TREM2 is predominantly expressed by microglia (Ulland and Colonna, 2018), making it crucial to understand its microglia-associated functions and how they are influenced by the ApoE genotype under disease conditions. Typical TREM2 ligands include phosphatidylserine found in apoptotic cells, as well as glycolipids, sphingomyelin, and sulfatide present in damaged myelin. Additionally, other identified ligands for TREM2 include ApoE, clusterin (CLU/ApoJ), Aβ, phosphatidylinositol, and phosphatidylcholine (Ulland and Colonna, 2018; Gratuze et al., 2018). Another group of studies has emphasized the critical roles of TREM2 in the seeding and spreading of both Aβ and tau pathologies (Parhizkar et al., 2019; Leyns et al., 2019). In a seeding model involving intracerebral injection of Aβ-rich brain extracts from AD patients or aged APP mice, the absence of TREM2 resulted in an increased number of seeded amyloid plaques with reduced levels of microglia-derived ApoE deposition within the plaques in mouse brains (Parhizkar et al., 2019). Consistent with these findings, reduced ApoE levels in amyloid plaques were also observed in the brains of AD patients carrying various TREM2 loss-of-function variants (Parhizkar et al., 2019).
Although TREM2 can also be expressed in astrocytes, neurons, and oligodendrocytes, its primary and most critical role is as a microglial receptor essential for maintaining neuronal health (Kober et al., 2021). In vitro models have demonstrated that the Axl receptor acts as a potential regulator of ApoE homeostasis in astrocytes (Gratuze et al., 2018). Axl, along with Mer and Tyro3, belongs to the TAM receptor family (Lu and Lemke, 2001; Fourgeaud et al., 2016), which has long been associated with the phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells (Shinohara et al., 2010). In APP/PS1 mice lacking TAM receptors, the transcriptomic response to Aβ plaques was diminished, including the downregulation of genes involved in lipid metabolism, such as ApoE (Huang et al., 2021). Another receptor, LRP1, is a cell surface receptor involved in endocytosis and signal transduction. While it is expressed in microglia, it is also highly expressed in neurons and, to a lesser extent, in neuroblasts, radial glia, astrocytes, and oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs) (Auderset et al., 2016). In vitro studies using primary microglial cells have shown that LRP1 activation suppresses microglial activation by modulating the JNK and NF-κβ signaling pathways (Yang et al., 2016; Chuang et al., 2016). Additionally, LRP1 is thought to mediate ApoE’s effects on microglial inflammation (Pocivavsek et al., 2009). Microglia are also the primary source of the complement system component C1q. It has been demonstrated that all ApoE isoforms inhibit the classical complement cascade by binding to C1q with high affinity, thereby interfering with the early activation stages. The formation of C1q-ApoE complexes has been associated with cognitive decline, and suppression of complement protein C5 has been shown to reduce inflammation (Yin et al., 2019).
In humans, it has been found that the ApoE ε3 allele is the most common (77%), while the ApoEε2 allele is the least common (8%) (Mahley, 1988). There is strong evidence indicating that the ApoEε4 allele significantly increases the risk of AD (Yamazaki et al., 2019; Farrer et al., 1997) and decreases the age of disease onset (Corder et al., 1993; Sando et al., 2008) in a manner that depends on the number of alleles. The ApoEε4 allele is the most prominent genetic risk factor for AD, with an allele frequency of around 40% in AD patients compared to 15% in the general population (Farrer et al., 1997; Kanekiyo et al., 2014). The frequency of AD and the average age at clinical onset varies among ApoEε4 homozygotes (91% and 68 years of age), ApoEε4 heterozygotes (47% and 76 years of age), and ApoEε4 non-carriers (20% and 84 years) (Corder et al., 1993). ApoE is involved in various processes, including both Aβ-dependent and Aβ-independent pathways, which are differentially influenced by the specific ApoE isoforms. For example, the ApoE isoforms differ in their effects on Aβ accumulation and clearance. In contrast, the Aβ-independent roles of ApoE involve tau-related abnormalities, tau-driven neuronal damage, and microglial responses to AD-related conditions.
The relationship between the ApoE genotype and the pathological deposition of Aβ is isoform dependent (Raulin et al., 2022). Extensive evidence illustrates the isoform-dependent co-deposition of ApoE with Aβ in amyloid plaques (ApoE4 > ApoE3 > ApoE2) (Hashimoto et al., 2012; Namba et al., 1991). Notably, studies have consistently shown that ApoE4-TR mice exhibit elevated Aβ levels in both brain tissues and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) compared to ApoE3-TR mice (Bales et al., 2009; Holtzman et al., 2000). Furthermore, pathological analyses of post-mortem brain tissue from individuals with AD have revealed heightened intra-neuronal accumulation of Aβ in ApoE4 carriers (Christensen et al., 2010), plaque deposition in the brain parenchyma (Polvikoski et al., 1995; Schmechel et al., 1993; Tiraboschi et al., 2004), formation of neurotoxic Aβ oligomers (Koffie et al., 2012), and extensive cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) (Rannikmäe et al., 2014; Shinohara et al., 2016). Individuals who carry the ApoE2 gene variant exhibit reduced amyloid plaque numbers, less severe pathology, and maintained cognitive function (Serrano-Pozo et al., 2015). In murine models, it was observed that human ApoE4 knock-in (KI) mice display increased Aβ deposition compared to human ApoE3-KI mice (Holtzman et al., 2000), while human ApoE2 expressing mice showed a marked reduction in Aβ deposition (Fagan et al., 2002). The interaction of ApoE4 with oligomers and fibrils of Aβ has been found to impact the kinetics of amyloid aggregation, indicating that ApoE4 stabilizes soluble, cytotoxic oligomeric Aβ fragments, thereby enhancing fibril formation and promoting Aβ deposition (Garai et al., 2014). Furthermore, the overexpression of ApoE4 in murine models, where ApoE4 is conditionally induced in astrocytes, has been demonstrated to expedite the initial seeding of amyloid pathology, resulting in a significant increase in plaque deposition and an extended Aβ half-life in the brain (Liu et al., 2017). During the seeding stage in amyloid precursor protein (APP)/presenilin-21 (APP/PS1-21) animal models, the inhibition of ApoE4 with antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) results in the formation of larger Aβ plaques with reduced plaque-associated neuritic dystrophy (Huynh et al., 2017). In AD model mice overexpressing human mutant APP, the knockout of endogenous ApoE leads to a significant reduction in Aβ deposition in the brain, along with lowered Aβ40 and Aβ42 deposits, underscoring the substantial role of ApoE in Aβ fibril formation and amyloid deposition (Holtzman et al., 2000; Bales et al., 1999; Bales et al., 1997). Conversely, the complete absence of ApoE expression in AD mouse models (APP/PS1 mice) containing both APP and PS1 mutations enhances Aβ deposition and overall plaque size (Ulrich et al., 2018). Furthermore, studies have demonstrated the distinct impact of ApoE isoforms in mice. The mouse ApoE gene, situated on chromosome 7, exists as a single isoform and exhibits interactions like those of human ApoE3, with <40% similarity in the promoter regions (Raffai et al., 2001; Maloney et al., 2007). Consequently, mouse ApoE differs in functionality regarding Aβ clearance, neuroinflammation, and synaptic integrity. Notably, mouse ApoE significantly accelerates early Aβ deposition compared to human ApoE2 (and, to a lesser extent, ApoE3), indicating the protracted capacity of human ApoE2 and ApoE3 to impede Aβ conversion into fibrillar forms.(Fagan et al., 2002; Tai et al., 2017; Liao et al., 2015).
Studies have conducted an in-depth examination of the potential impact of ApoE isoforms on Aβ clearance. It has been observed that ApoE plays a crucial role in facilitating Aβ clearance in an isoform-dependent manner, with ApoE2 being more effective than ApoE3, and ApoE4 exhibiting the lowest efficiency. This facilitation is achieved through the activation of proteolytic degradation via endopeptidases such as neprilysin (NEP) and insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) (Saido and Leissring, 2012; Russo et al., 1998; Jiang et al., 2008). ApoE also enhances Aβ clearance through the activation of cellular uptake (phagocytosis) and subsequent degradation by brain parenchymal cells (neurons, astrocytes, and microglia), with its efficiency being ApoE isoform-dependent (Kiani, 2023; Koistinaho et al., 2004; Lin et al., 2018). The cellular uptake of Aβ by astrocytes and microglia likely represents a key pathway for Aβ clearance. When brain sections containing Aβ plaques from amyloid model mice were cultured with adult mouse astrocytes, the astrocytes internalized and degraded Aβ in a manner dependent on both ApoE and LRP1(Koistinaho et al., 2004). In microglia, soluble Aβ is likely internalized via fluid-phase macropinocytosis into lysosomes for degradation (Mandrekar et al., 2009), while Aβ aggregates interact with a multicomponent cell surface receptor complex and are internalized through phagocytosis (Bamberger et al., 2003). Neurons also contribute to Aβ clearance through uptake and lysosomal degradation (Li et al., 2012). Notably, neurons are at the highest risk of encountering Aβ in the brain, as Aβ is predominantly produced by neurons. The functional role of neurons in Aβ clearance depends on LRP1 function. A previous study demonstrated that when LRP1 is deleted exclusively in neurons in the adult mouse brain, the half-life of interstitial fluid (ISF) Aβ increases, leading to greater Aβ accumulation and pathology (Kanekiyo et al., 2013). Studies have also highlighted the influence of ApoE isoforms on other clearance pathways, such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) absorption into the circulatory and lymphatic systems, clearance via ISF bulk flow, as well as clearance through the BBB (Kanekiyo et al., 2014; Tarasoff-Conway et al., 2015). Furthermore, research findings indicate that ApoE4-TR mice exhibit Aβ40 aggregation in the peri-arterial drainage pathway following intracerebral injections, a phenomenon not observed in ApoE3-TR mice (Hawkes et al., 2012). An in vivo study has shown that ApoE2 and ApoE3, along with Aβ-ApoE2 and Aβ-ApoE3 complexes, are cleared at the BBB through both VLDLR and LRP1 at a significantly faster rate than Aβ-ApoE4 complexes (Deane et al., 2008). Before binding to the receptor, ApoE necessitates the generation of high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-like particles through its association with cholesterol and phospholipids. A study has shown that astrocytes expressing ApoE3 release 2.5 times more cholesterol than those expressing ApoE4 and that ApoE3 facilitates the creation of similarly sized HDL particles with a reduced number of ApoE3 molecules compared to ApoE4 (Figure 2) (Gong et al., 2002; Michikawa et al., 2000). However, ApoE may also hinder Aβ clearance by competitively binding with Aβ for receptors or by impeding Aβ clearance through the blood–brain barrier in an isoform-dependent manner (ApoE4 > ApoE3) (Yamazaki et al., 2019; Kanekiyo et al., 2014; Kanekiyo et al., 2013). Recently, a novel association between ApoE and PS has been discovered, linking the mechanisms associated with FAD and SAD. PS constitutes the primary core component of the γ-secretase complex, responsible for the proteolytic processing of APP to generate a series of amyloidogenic Aβ species (Bai et al., 2015). Most mutations in the PSEN1 and PSEN2 genes augment the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio, resulting in the early onset of FAD (Borchelt et al., 1996; Sun et al., 2017). We found that the absence of PS in fibroblasts leads to a complete cessation of ApoE secretion, accompanied by the nuclear translocation of ApoE from the cytosol (Islam et al., 2022). PS mutations and ApoE4 have long been considered to cause FAD and SAD by two independent mechanisms, abnormal Aβ generation and impaired Aβ clearance, respectively. Evidence suggests that PS mutations or altered γ-secretase activity play a role in Aβ clearance through the regulation of ApoE secretion. Consequently, enhancing ApoE levels by elevating PS function may augment Aβ clearance. These findings substantiate the notion that ApoE isoforms differentially govern Aβ deposition and clearance through their interaction with Aβ, indicating that the ApoE-Aβ interaction could serve as a promising target for therapeutic intervention during the early stages of the disease.
Previous research has indicated that the presence of ApoE4 significantly intensifies tau-induced neurodegeneration in a murine model of tauopathy (Shi et al., 2017). Conversely, the homozygous ApoE3-R136S mutation has been observed to mitigate ApoE4-triggered tau pathology, neurodegeneration, and neuroinflammation (Nelson et al., 2023). The ApoEε4 allele exerts influence on neurodegenerative conditions characterized by the presence of neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) comprised of hyperphosphorylated tau protein (Wang and Mandelkow, 2016). Numerous observations suggest a close association between ApoE4 and tau pathology with respect to neurodegeneration, while initial histopathological examinations have corroborated a link between ApoE4 protein and NFTs in AD brains (Huang et al., 2001; Rohn et al., 2012; Brecht et al., 2004). Prior research has shown that ApoE3 binds to tau more effectively than ApoE4 at regions responsible for aggregation into pathogenic NFTs. This suggests that ApoE3 may prevent tau phosphorylation and the formation of NFTs (Strittmatter et al., 1994). Studies have also demonstrated that mice expressing ApoE4 in tauopathy models exhibit more severe tau-induced neurodegeneration compared to other isoforms, while mice lacking ApoE are protected from this effect (Shi et al., 2017). Furthermore, eliminating ApoE4 derived from astrocytes has been found to offer protection against tau-driven neurodegeneration (Wang et al., 2021). In addition, ApoE4 prompts tau-mediated neurotoxicity through its interaction with the vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2), thereby impeding the transport of neurotransmitters into synaptic vesicles and ultimately leading to the degeneration of the locus coeruleus (Kang et al., 2021). Moreover, a recent study has indicated that reducing ApoE4 levels using antisense oligonucleotides in P301S/ApoE4 mice yields protective effects against tau pathology (Litvinchuk et al., 2021). Another study has demonstrated that ApoE4 exerts inhibitory effects on the Wnt signaling pathway by modulating LRP5/6 receptors, thereby leading to elevated GSK3 activity and facilitating tau phosphorylation (Caruso et al., 2006). In addition, ApoE4 has been shown to induce higher levels of tau phosphorylation in the presence of Aβ oligomers when compared to ApoE2 and ApoE3 (Hou et al., 2020). A recent genome-wide association study (GWAS) has suggested that ApoE2 distinctly attenuates the influence of the classical complement cascade on protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) activity, a pivotal tau phosphatase in the human brain. This finding implies that ApoE2 may offer protective effects against the risk of AD in contrast to ApoE4 (Jun et al., 2022). In contrast, the use of PET imaging in a human study revealed that individuals carrying the ApoE4 gene variant show significantly higher levels of tau deposition, even when there are no Aβ plaques present. Studies using human iPSC-derived cell types have indicated that the presence of neuronal ApoE4 leads to more extensive tau phosphorylation and cell death compared to ApoE3 (Therriault et al., 2020). Data from human iPSC-derived cell types have shown that neuronal ApoE4 promotes tau phosphorylation and cell death to a greater extent than ApoE3 (Wadhwani et al., 2019). Additionally, examination of postmortem human brains has shown that individuals with two copies of the ApoEε4 allele have higher levels of tau aggregates when Aβ is also present, in comparison to those with only one or no ApoEε4 alleles (Tiraboschi et al., 2004). However, this association is not observed in brains without Aβ (Farfel et al., 2016).
Synaptic dysfunction represents an early pathological hallmark of AD, preceding neurodegeneration and memory impairment, thereby culminating in cognitive decline and subsequent memory loss (Tzioras et al., 2023). Increasing evidence indicates that ApoE isoforms modulate synaptic function in an isoform-specific manner. Specifically, the ApoE3 isoform stimulates neurite outgrowth in both primary embryonic and adult cortical neurons and enhances neuronal sprouting within a developing organotypic hippocampal slice system (Nathan et al., 1994; Teter et al., 1999). In contrast, studies have demonstrated that ApoE4 exacerbates detrimental impacts on neurite outgrowth (Teter et al., 2002; Kim et al., 2014). Transgenic mouse models featuring neuronal overexpression of ApoE4 exhibited deficiencies in learning and vertical exploratory activity relative to those with neuronal overexpression of ApoE3 (Raber et al., 2000). A recent human study revealed that carriers of the ApoEε4 allele manifested significant synaptic loss in the medial temporal lobe compared to non-carriers, indicating the adverse effects of ApoE4 on synaptic function (He et al., 2024). Although ApoE2 has not been extensively studied, a particular study provided evidence that ApoE2 mitigated dendritic spine loss in the hippocampus of young APP transgenic mice (Lanz et al., 2003). Conversely, ApoE4 has been found to exacerbate Aβ plaque and tau burden, leading to heightened neuronal injury and synaptic dysfunction, which are closely linked with neuroinflammation. This observation implies that ApoE-mediated neuroinflammation may exacerbate tau and Aβ aggregation, as well as neurodegeneration (Yamazaki et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2023; Parhizkar and Holtzman, 2022).
A substantial body of literature suggests that ApoE is implicated in neuroinflammation, a pivotal characteristic of AD pathology. Microglia, frequently observed surrounding plaques in post-mortem brain tissue from individuals with AD, assume a central role in the immune response, as evidenced by pronounced reactive microgliosis (Song and Colonna, 2018). Interestingly, several studies have indicated that ApoE-null mice display a diminished microglial response to plaques, implying a potential regulatory role of ApoE in the microglial response to amyloid plaques (Ulrich et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2021; Krasemann et al., 2017). A recent study has reported that ApoE3 exhibits a higher capacity to stimulate a microglial response to injected Aβ compared to ApoE4. This effect may be mediated through the TREM2, which serves as an endogenous ligand of ApoE (Fitz et al., 2021). Notably, because of reduced lipidation and diminished affinity of ApoE4 for TREM2, ApoE4 has the potential to impede homeostatic microglial functions in comparison to other isoforms. This may lead to an acceleration of neuronal damage and disease progression (Fernandez et al., 2019). The targeting of ApoE-related neuroinflammation could represent a promising approach for the development of therapeutics for AD.
The decline in neuronal function represents a hallmark of advanced AD. The aggregation of Aβ and hyperphosphorylated tau, as well as neuroinflammation and synaptic dysfunction driven by ApoE, collectively contribute to progressive neurodegeneration (Yamazaki et al., 2019). Recent findings have demonstrated that the loss of ApoE function promotes neurodegeneration (Pankiewicz et al., 2021), highlighting the significant role of ApoE in neuronal loss. Additionally, a prior study has indicated that inhibiting endogenously synthesized cholesterol intensifies ApoE4-induced neuronal death (Michikawa and Yanagisawa, 1998). Therefore, gaining an understanding of the molecular mechanisms underpinning ApoE-mediated neuronal loss could potentially preserve neuronal function and decelerate disease progression.
Increased oxidative stress within neurons, attributed to an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants, results in lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation, and DNA damage, thus contributing to neurodegeneration in AD (Erekat, 2022). Research indicates a direct correlation between the degree of oxidative damage in the AD brain and the ApoE allele, with the order of potency being ApoE2 < ApoE3 < ApoE4 (Dose et al., 2016; Butterfield and Mattson, 2020). Furthermore, a study demonstrated that AD patients carrying the ApoEε4 allele display the most significant elevation of thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) signals in the hippocampus, indicating heightened lipid peroxidation, a characteristic feature of oxidative stress (Ramassamy et al., 2000). Mice lacking ApoE4, when exposed to oxidative stress, showed elevated glutathione and other antioxidants in the brain; however, in ApoE-null mice, the increased glutathione levels did not reduce the oxidative stress, supporting the hypothesis that ApoE deficiency is associated with oxidative impairment in the brain (Butterfield and Mattson, 2020; Shea et al., 2002).
BBB is a critical component for maintaining the brain’s microenvironment. Research has demonstrated that the compromise of the BBB serves as a biomarker of cognitive impairment in humans, particularly in the early stages of AD (Nation et al., 2019). BBB dysfunction leads to heightened neuroinflammation and exacerbates the pathology of AD (Brandl and Reindl, 2023). A prior study noted the impairment of tight junction (TJ) barrier function when the BBB was reconstituted with primary astrocytes from ApoE4-KI mice (ApoE4-BBB model) (Nishitsuji et al., 2011). A recent investigation has indicated that the ApoE4 variant, identified as the principal susceptibility gene for AD, precipitates dysfunction of the BBB and exacerbates cognitive impairment (Montagne et al., 2020). This finding suggests that the mitigation of ApoE4-associated cognitive decline, irrespective of AD pathology, may represent a viable therapeutic objective for individuals carrying the ApoEε4 allele.
Deregulated apoptosis, commonly known as programmed cell death, is recognized as a contributory element in neurodegenerative disorders, notably AD. Studies have evidenced that individuals with AD carrying the ApoE ε4/ε4 allele demonstrate heightened apoptosis and compromised synaptic integrity, thereby aggravating the loss of synapses and neurodegeneration (Zhao et al., 2020). Consequently, the modulation of ApoE represents a potential therapeutic strategy for addressing apoptosis and programmed cell death.
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is a cellular response to the accumulation of misfolded proteins in the ER. The involvement of ApoE in ER stress has been associated with the pathogenesis of AD. One study has revealed that domain interaction in ApoE4 induces ER stress and impairs astrocyte function in Arg-61 ApoE mice, a gene-targeted mouse model specific for domain interaction (Zhong et al., 2009). Another study has demonstrated that ApoE4 expression leads to macrophage dysfunction and promotes apoptosis through the induction of ER stress (Cash et al., 2012). The multifaceted impact of ApoE on cellular physiology is highlighted by its role in ER stress.
Mitochondrial dysfunction assumes a prominent role in neurodegenerative diseases, notably AD. Impaired mitochondria can evoke oxidative stress and energy deficits, culminating in neuronal damage, inflammation, accumulation of plaque-forming Aβ peptides, and cognitive decline (Qin et al., 2020). Notably, evidence suggests that mitochondrial dysfunction serves as a regulator of ApoE-dependent cellular processes in both healthy and pathological states by exerting influence on ApoE expression and secretion (Wynne et al., 2023). Investigations have revealed that the ApoE4 (1–272) fragment associates with mitochondrial complexes, thereby instigating neurodegeneration through its impact on neuronal mitochondrial function (Nakamura et al., 2009). Moreover, recent findings demonstrate a correlation between the ApoEε4 allele and compromised mitochondrial structure and function, oxidative stress, and synaptic integrity in the human brain, indicative of the potential for ApoE4 to precipitate neuronal damage (Yin et al., 2020).
ApoE facilitates the clearance of Aβ in a manner that is dependent on its isoform, with ApoE3 being more effective than ApoE4, by activating phagocytosis, which is a critical process for removing damaged organelles and protein aggregates (Koistinaho et al., 2004; Kanekiyo et al., 2013). A recent study has demonstrated that the expression of ApoE4 is associated with impaired autophagy and mitophagy in astrocytes (Eran and Ronit, 2022). This suggests that dysregulated autophagy may contribute to the accumulation of toxic Aβ aggregates, further exacerbating neurodegeneration in AD.
Recent advances in the understanding of ApoE have revealed its protective role against PS mutation-induced FAD and its involvement in the pathology of AD driven by ApoE. Moreover, the interactions between ApoE and PS, and the inhibitory effect of ApoE4 on γ-secretase activity have been elucidated. These discoveries suggest a common underlying mechanism shared between FAD and SAD. Furthermore, recent studies have uncovered the impact of ApoE isoforms on the expression of APP and the modulation of Aβ secretion, as well as the influence of gut microbiota on ApoE function.
Despite the heightened risk of AD onset by three to four times associated with the presence of the ApoE4 gene, certain protective mutations have been elucidated. Specifically, both the ApoE4-R251G mutation and a variant of ApoE3-V236E, known as the Jacksonville mutation, demonstrate protective attributes. These variants are linked to mitigated ApoE self-aggregation, facilitating lipid association and potentially reducing amyloid accumulation and toxicity (Figure 3) (Le Guen et al., 2022; Bu, 2022; Sepulveda-Falla, 2023). Additionally, the ApoE3-V236E variant is correlated with a decreased susceptibility to AD and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) (Figure 3) (Liu et al., 2021; Medway et al., 2014). Conversely, mutations such as L28P in ApoE4 (ApoE4-Freiburg) or ApoE3-R145C (ApoE3-Philadelphia) have been associated with an elevated risk of lipid disorders and cardiovascular diseases (Figure 3) (Orth et al., 1999; Abou Ziki et al., 2014). Furthermore, individuals homozygous for the ApoE3-Ch have exhibited resistance against aggressive forms of FAD associated with the PSEN1-E280A mutation (Figure 3) (Arboleda-Velasquez et al., 2019). Recent research has indicated that homozygosity for the ApoE3-R136S mutation can mitigate ApoE4-driven tau pathology, neurodegeneration, and neuroinflammation in mouse models of tauopathy and human induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC)-derived neuron models (Figure 3). In contrast, heterozygous carriers demonstrate partial protection against neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation but not against tau pathology (Nelson et al., 2023).
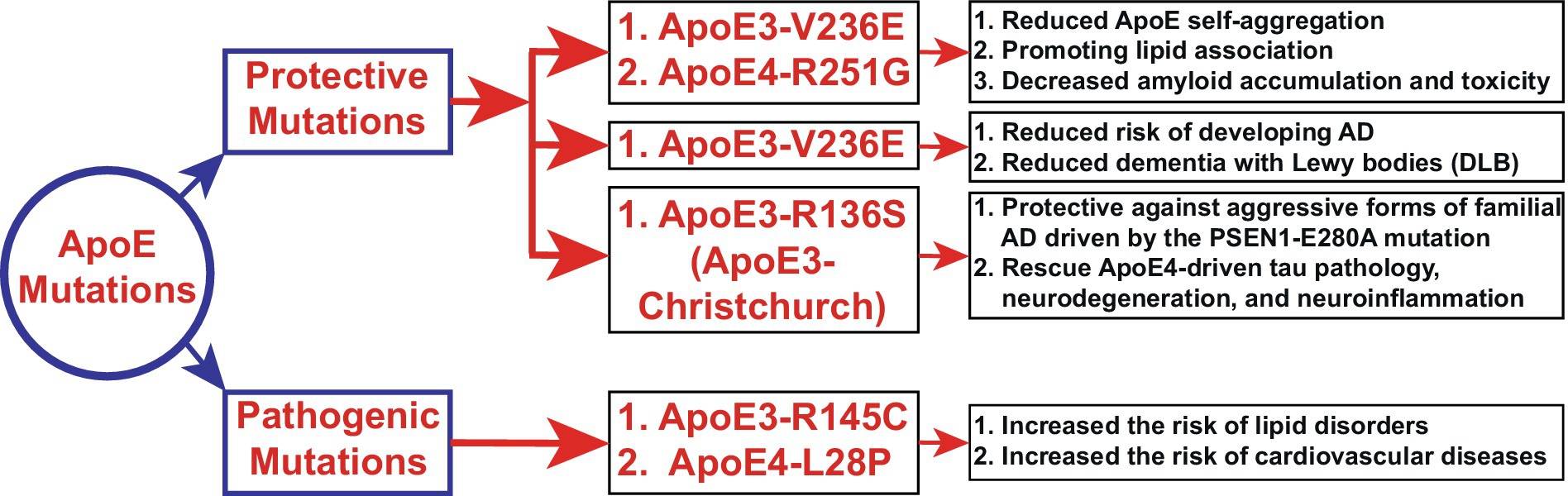
Figure 3. Novel functions of ApoE mutations (Section 4.1). The schematic diagram depicts the newly identified functions of ApoE3 and ApoE4 mutations. Polymorphism in the ApoE gene is the most significant risk factor for AD and other neurological disorders. Here, we elucidate the novel regulatory, protective, and pathogenic functions of ApoE mutations in AD and other neurodegenerative diseases. ApoE4 exerts toxic effects that are three to four times greater than those of ApoE3 in late-onset sporadic AD, leading to enhanced Aβ accumulation. However, the ApoE4-R251G mutation decreases amyloid accumulation and toxicity. On the other hand, ApoE3-R145C (ApoE3-Philadelphia) mutations have been associated with lipid disorders and cardiovascular diseases. Notably, most of the mutations shown here exert protective effects, suggesting that genetic mutations in ApoE3 or ApoE4 could be potential therapeutic strategies.
The generation of the Aβ peptide from APP represents a critical event in the pathogenesis of AD. Recent research indicates the involvement of ApoE in the processing of APP and subsequent Aβ generation. Specifically, ApoE, secreted by glial cells, has been shown to stimulate neuronal Aβ production, with ApoE4 exhibiting a greater potency in comparison to ApoE3 and ApoE2 (Huang et al., 2017). Furthermore, investigations involving human neurons derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) carrying the ApoEε4 allele have revealed elevated secretion levels of Aβ when compared to those harboring the ApoEε3 allele. This disparity in Aβ secretion may be attributed to augmented APP transcription or processing (Lin et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2018). Our recent investigation has revealed that intracellular ApoE4 significantly hinders Aβ40 production more than Aβ42 production, resulting in an elevated Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio due to its interaction with the γ-secretase complex. This discovery proposes a novel pathway through which intracellular ApoE4 contributes to the progression of SAD by impeding γ-secretase activity (Figure 4) (Sun et al., 2023).
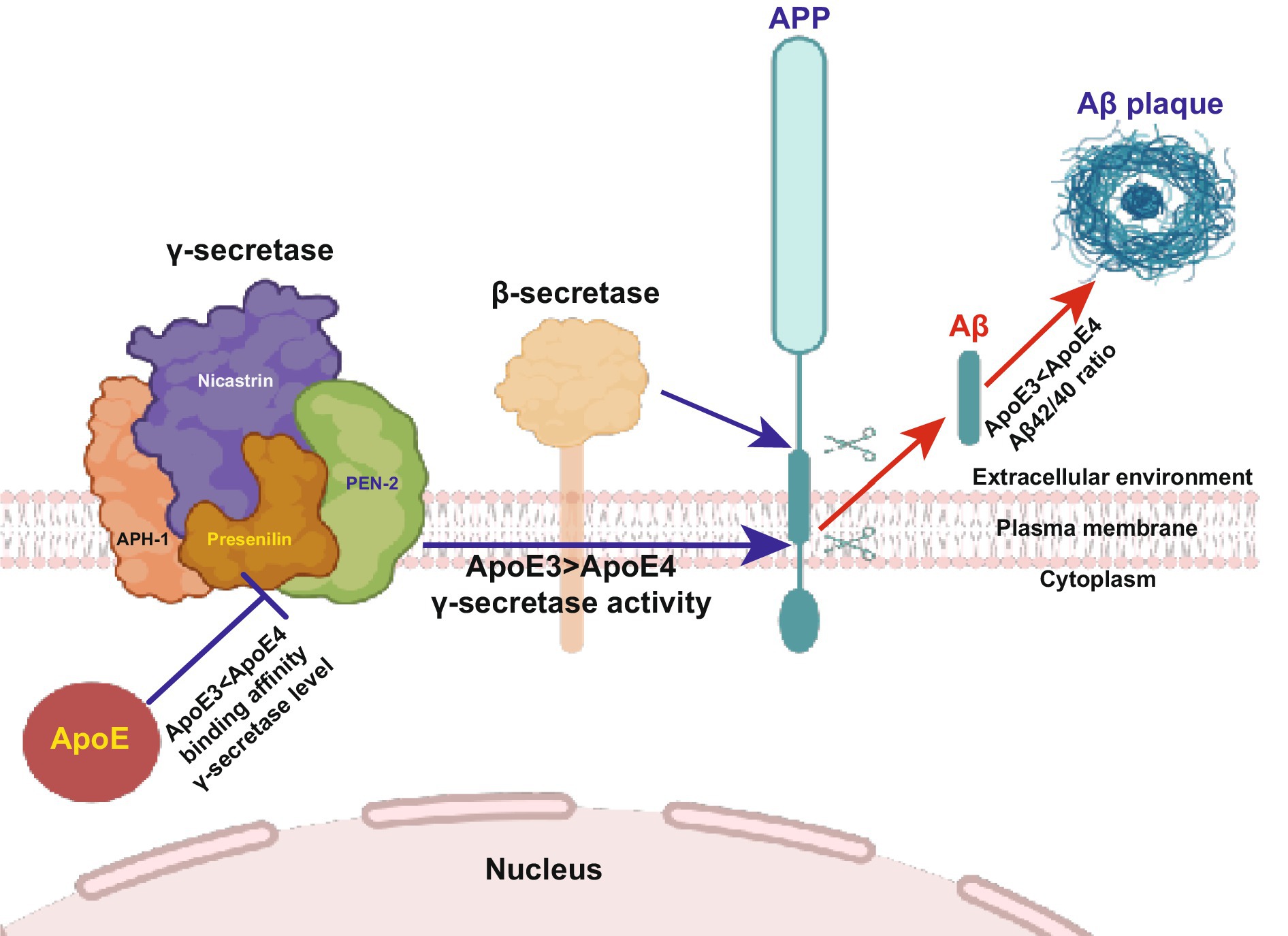
Figure 4. Higher binding affinity of ApoE4 to the γ-secretase complex inhibits γ-secretase activity (Section 4.2). Familial mutations in PS lead to impaired γ-secretase activity and altered Aβ production, resulting in a substantially increased Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio. Here, we illustrate the novel functions of ApoE in Aβ production. This finding elucidates the involvement of ApoE in the formation and activity of the γ-secretase complex. ApoE4 suppresses γ-secretase activity and increases the Aβ42/Aβ40 ratio compared to ApoE3, suggesting that Aβ production and γ-secretase activity are regulated by ApoE in an isoform-dependent manner. This study reveals a novel connection between ApoE and PS, the most important causative molecules in sporadic and familial Alzheimer’s disease, respectively. The diagram is sourced from Sun et al. (2023).
ApoE-mediated neuroinflammation is understood to play a pivotal role in tau-mediated neurodegeneration, and there is evidence that the gut microbiota exerts control over neuroinflammation in an ApoE genotype-dependent manner. A study conducted on a genetically modified mouse model of tauopathy, expressing human ApoE isoforms, revealed a decrease in gliosis, tau pathology, and neurodegeneration. This reduction was influenced by both sex (male > female) and specific ApoE isoforms (ApoE3 > ApoE4). These findings unveiled a substantial interplay between microbiota composition, neuroinflammation, and tau-mediated neurodegeneration (Figure 5) (Seo et al., 2023). Several studies have underscored the increasing significance of the gut microbiome in impacting AD pathology through its influence on metabolism and immune function. Notably, insulin supplementation has been demonstrated to enhance metabolism, resulting in heightened levels of beneficial microbiota and reduced neuroinflammation, particularly in ApoE4 mouse models (Hoffman et al., 2019). Moreover, the presence of the ApoEε4 allele has been associated with modified levels of gut microbiota in AD patients. Consequently, directing interventions toward the microbiota may constitute an efficacious therapeutic strategy for AD individuals bearing the ApoEε4 allele (Hou et al., 2021). These collective findings elucidate a multifaceted interplay between the ApoE genotype, gut microbiota, neuroinflammation, and AD pathology, consequently delineating potential therapeutic trajectories targeting microbiota-related mechanisms in AD.
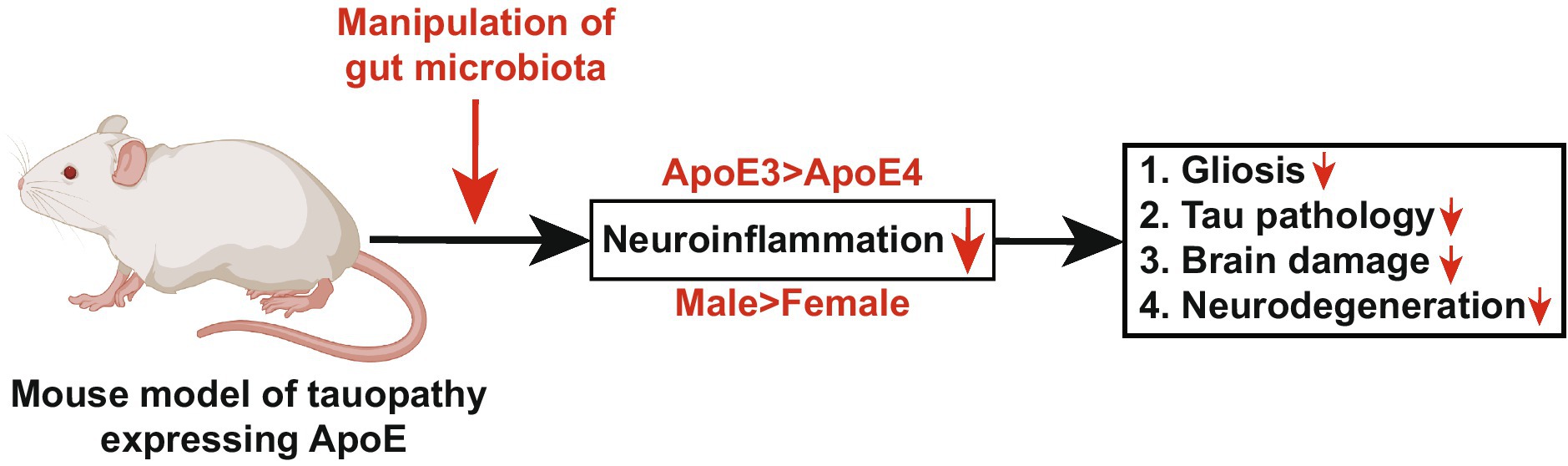
Figure 5. Manipulation of gut microbiota in a mouse model of tauopathy expressing human ApoE attenuates neurodegeneration (Section 4.3). This diagram illustrates the role of ApoE and gut microbiota in controlling neurodegeneration. The progression of tau-mediated neurodegeneration is regulated by ApoE-driven neuroinflammation, and emerging evidence suggests that gut microbiota regulates neuroinflammation in an ApoE-genotype-dependent manner. In this study, we demonstrated that a genetically modified mouse model of tauopathy expressing human ApoE isoforms, manipulated by gut microbiota, exhibited reduced gliosis, tau pathology, brain damage, and neurodegeneration in a sex- and ApoE-isoform-dependent manner. This finding reveals a novel mechanism linking gut microbiota, ApoE-mediated neuroinflammation, and tau-driven neurodegeneration. The diagram is sourced from Seo et al. (2023).
Numerous studies have demonstrated the multifaceted impact of ApoE alleles on neurodegenerative diseases. Our research delves into the diverse roles of ApoE across diseases such as PD, ALS, FTLD, HD, VD and MS, offering new insights into its multifaceted significance.
PD is the second most prevalent neurodegenerative disorders, characterized by the accumulation of protein aggregates known as Lewy Bodies (LBs) within brain cells. These LBs primarily consist of α-synuclein along with other proteins and lipids, making their composition highly complex (Calabresi et al., 2023; Burré et al., 2018; Vázquez-Vélez and Zoghbi, 2021; Emamzadeh, 2017). It is hypothesized that cholesterol-rich domains, such as lipid rafts, may act as focal points for α-synuclein aggregation. Additionally, cholesterol is believed to regulate α-synuclein binding to structures resembling synaptic vesicles, potentially initiating aggregation processes (Sarchione et al., 2021). Recent research has uncovered elevated levels of ApoE, a lipid transport protein, in the cerebrospinal fluid of individuals in early stages of PD. This finding suggests that α-synuclein might facilitate its movement between neurons by interacting with ApoE, which is involved in lipid transport mechanisms (Paslawski et al., 2019). Moreover, studies indicate that high levels of fatty acids can induce α-synuclein aggregation, contributing to LB formation (Erskine et al., 2021). In the context of fatty acids (FAs), harmful forms can be generated in hyperactive neurons and transferred to astrocyte lipid droplets via ApoE-positive lipid particles. Within astrocytes, these FAs undergo mitochondrial beta-oxidation for detoxification (Ioannou et al., 2019). However, pathogenic α-synuclein has been implicated in impairing astrocyte mitochondria function (Braidy et al., 2013). This dysfunction can disrupt FA metabolism in astrocytes, potentially leading to neuronal damage from toxic FAs and exacerbating the progression of PD (Braidy et al., 2013). In summary, disruptions in FA metabolism mediated by astrocyte mitochondria dysfunction may contribute to the pathogenesis and progression of PD, highlighting potential targets for therapeutic interventions.
Recent studies have highlighted the role of ApoE variants in PD and related cognitive decline. Cognitive decline appears to progress more rapidly in PD patients carrying ApoE4 variants compared to single variant carriers (Jo et al., 2021). In vitro studies investigating different ApoE isoforms have shown that ApoE4 increases α-synuclein aggregation more than other isoforms, which may exacerbate disease progression (Emamzadeh, 2016). Additionally, research conducted in Spain indicated that the ApoEε4 allele is more prevalent in familial PD but less common in sporadic PD compared to control groups, suggesting a potential risk association in individuals with specific genetic backgrounds (Blázquez et al., 2006). However, other studies have reported conflicting findings regarding ApoE genotypes and PD risk (Federoff et al., 2012; Multhammer et al., 2014).
Clinical and genetic evidence points to variants in the ApoE gene as significant risk factors for LBD and the onset of dementia in PD patients (Kaivola et al., 2022; Pankratz et al., 2006). Specifically, ApoE4 variants are associated with more severe LB pathology independent of AD pathology (Dickson et al., 2018; van Steenoven et al., 2020). ApoE4 also increases the risk of PD-related dementia and may lead to earlier symptom onset. Animal studies have further demonstrated that ApoE4 influences α-synuclein pathology and exacerbates its detrimental effects, suggesting a role in impairing α-synuclein clearance and promoting neuroinflammation (Zhao et al., 2020; Davis et al., 2020). These processes could contribute to neuronal dysfunction and degeneration in LBD. The relationship between ApoE and PD is complex and likely involves interactions with other genetic and environmental factors. Further research is crucial to elucidate the precise mechanisms underlying the association between ApoE variants and PD susceptibility and progression.
ALS is a devastating neurodegenerative disease that affects upper and lower motor neurons in the brain and spinal cord, leading to progressive muscle weakness, stiffness, and eventual paralysis (Mead et al., 2023; Longinetti and Fang, 2019; Kim et al., 2020). ALS can occur sporadically or in familial forms, with mutations in genes like superoxide-dismutase1 (SOD1) and TDP-43 being common causes that result in nerve cell degeneration and death (Jeon et al., 2019; Brown et al., 2021; Tziortzouda et al., 2021). The ApoE gene, crucial for lipid transport and metabolism, is well-established as a genetic risk factor for AD, with the ApoEε4 allele notably linked to increased susceptibility (Fernández-Calle et al., 2022; Verghese et al., 2011). However, its role in ALS remains less clear. Studies exploring the ApoEε4 allele association with ALS risk or disease progression have produced inconsistent findings. In ALS, TDP43 pathology is prevalent in nearly all sporadic cases, affecting 90 to 95% of patients (Oiwa et al., 2023). Recent research indicates a potential interplay between ApoE genotype and TDP-43 pathology in ALS. Overexpression of TDP-43 can lead to motor deficits, neuronal loss, and gliosis in the motor cortex, with these effects being most severe in ApoE2 mice. Additionally, observations from human postmortem brain samples suggest an association between the ApoEε2 allele and more pronounced TDP-43 pathology, implying that genetic factors such as ApoE genotype may influence the progression and severity of ALS pathology (Meneses et al., 2023).
Recent research has indicated a potential link between mitochondrial dysfunction and ApoE expression and secretion in ALS (Wynne et al., 2023). This suggests that mitochondrial impairment may influence ApoE levels, which could in turn contribute to the neurodegenerative processes observed in ALS. Moreover, lipid dysregulation or lipid cacostasis is one of the pathological hallmarks of ALS, contributing to neurodegeneration (González De Aguilar, 2019; Dodge et al., 2020). In addition to mitochondrial dysfunction, lipid dysregulation is another hallmark of ALS pathology (Abdel-Khalik et al., 2017). Studies have reported defective cholesterol metabolism in the brains of ALS patients and abnormal lipid droplet accumulation in astrocytes, particularly in regions like the motor cortex and spinal cord (Chaves-Filho et al., 2019). These lipidomic findings underscore the importance of lipid homeostasis in ALS pathophysiology and suggest that disruptions in lipid metabolism may exacerbate neurodegeneration. Despite these insights, the precise mechanisms through which ApoE and lipid dysregulation contribute to ALS remain complex and multifaceted. Ongoing research continues to investigate these genetic factors and their interactions with mitochondrial function and lipid metabolism in ALS, aiming to uncover novel therapeutic targets for this devastating disease.
FTLD comprises a spectrum of neurodegenerative disorders primarily affecting the frontal and temporal lobes, resulting in progressive changes in behavior, personality, language, and motor function (Mann and Snowden, 2017; Grossman et al., 2023). These disorders are characterized by the accumulation of different protein aggregates, including tau, TDP-43, or fused in sarcoma (FUS) proteins, depending on the specific subtype of FTLD (Riku et al., 2022; Irwin et al., 2015). The impact of ApoE polymorphism on FTLD has been a subject of scientific investigation, but findings have been inconsistent and contradictory across different populations. For instance, in the Dutch population, ApoEε4 allele has been associated with an increased risk of FTLD (Stevens et al., 1997). Conversely, studies in German patients have reported a negative association between ApoE polymorphism and FTLD risk (Riemenschneider et al., 2002). A comprehensive meta-analysis encompassing Caucasian and Asian populations concluded that ApoEε4 allele serves as a genetic risk factor for FTLD (Su et al., 2017). However, GWAS on FTLD have not consistently validated a positive association with the ApoE gene (Ferrari et al., 2014; Girard and Rouleau, 2014). Unlike its well-established role in AD, where ApoEε4 allele significantly increases risk, the influence of ApoEε4 allele on FTLD risk appears to be less pronounced. Research indicates that the presence of the ApoEε4 allele does not substantially elevate the risk of FTLD as it does with AD. This discrepancy underscores the complexity of genetic and molecular factors underlying FTLD and necessitates further investigation to elucidate the precise relationship between ApoE and FTLD pathogenesis.
HD is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder caused by a genetic mutation involving the huntingtin gene (HTT), characterized by motor dysfunction, cognitive decline, and psychiatric symptoms (Margolis et al., 2001; van der Burg et al., 2009). Research in both human subjects and animal models has highlighted significant alterations in cholesterol metabolism as a pivotal early event in HD pathogenesis (Trushina et al., 2006; del Toro et al., 2010; Boussicault et al., 2016; Kacher et al., 2022). Astrocytes, specialized glial cells in the brain, play a crucial role in maintaining cholesterol homeostasis, which becomes disrupted in HD. This disruption manifests through the decreased expression of genes involved in cholesterol biosynthesis and transport, leading to reduced levels and impaired secretion of ApoE lipoproteins (Valenza et al., 2010; Valenza et al., 2015). ApoE is vital for transporting lipids and aiding in repair processes within the brain. A deficiency in ApoE exacerbates the impact of reduced cholesterol availability on neurons, potentially contributing to the observed neuronal dysfunction and degeneration in HD. Additionally, HD models display a decrease in ApoE expression (Kacher et al., 2022) and mitochondrial genes (Intihar et al., 2019), indicating a potential link to impaired cholesterol metabolism and mitochondrial function. ApoE proteins play critical roles in cellular pathways associated with mitochondrial function (Lee et al., 2023). Disruptions in these interactions, particularly in the context of HD, could exacerbate mitochondrial dysfunction and contribute to disease progression. Therefore, there is growing interest in exploring strategies to modify ApoE expression or function as a potential therapeutic approach to mitigate mitochondrial dysfunction in HD. This could involve innovative techniques such as gene therapy, small molecule interventions targeting ApoE pathways, or other approaches aimed at restoring mitochondrial health in affected cells.
VD is a prevalent cause of dementia after AD, resulting from brain damage due to compromised blood flow. This condition accounts for approximately 15% of dementia cases (O'Brien and Thomas, 2015). VD shares a 20–30% prevalence of dementia along with other pathologies, manifesting in impaired reasoning, planning, judgment, memory, and other cognitive processes (Jellinger, 2013). Studies have identified similar pathological features between VD and AD, inclusive of neurofibrillary tangles, amyloid plaques, white-matter lesions, and CAA. ApoE represents a significant risk factor for VD, with meta-analyses demonstrating heightened susceptibility to VD in individuals with the ApoEε4 allele compared to those with the ApoEε3 allele (Yin et al., 2012). Recent investigations suggest that ApoE4 exacerbates advanced-stage vascular and neurodegenerative disorders in aged AD mice, leading to BBB breakdown, diminished cerebral blood flow, neuronal loss, and behavioral deficits independently of Aβ (Montagne et al., 2021). Thus, the presence of ApoE polymorphism in VD patients may establish a potential connection between VD and AD and elevate the risk for VD.
MS represents a prevalent autoimmune disorder affecting the central nervous system within the young adult population aged 18–40 years (Jakimovski et al., 2024). Recent pathophysiological insights underscore the significance of the genetic linkage between the chromosome 19q13 region and MS (Sawcer et al., 2002; Giau et al., 2015). The association between ApoE genotype and MS susceptibility remains ambiguous, although a study has suggested that both the ApoEε2 and ApoEε4 alleles may exert substantial effects on MS susceptibility (Lill et al., 2012). Furthermore, investigations have proposed that the presence of the ApoEε4 allele in MS patients may contribute to disease progression, leading to heightened brain damage, exacerbated cognitive dysfunction, and augmented disease severity (Parmenter et al., 2006; Shi et al., 2008; Oliveri et al., 1999; Sahebari et al., 2023). Additionally, it has been reported that MS patients carrying the ApoEε4 allele demonstrate deficits in verbal memory (Shi et al., 2008; Koutsis et al., 2007). Consequently, the influence of ApoE4 on MS pathogenesis appears predominantly adverse.
Extensive research on AD has spurred inquiries into therapeutic approaches targeting amyloid aggregates, a defining feature of the disease. Notable avenues of interest involve pharmacotherapies such as aducanumab and lecanemab, which possess a specific affinity for amyloid plaques. While these pharmaceuticals have been subjected to clinical trials, further investigation is imperative to ascertain their long-term safety and efficacy (Raulin et al., 2022; Sperling et al., 2011; Sevigny et al., 2016). Some studies demonstrated that ApoE4 homozygotes have a very high risk for Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) with both aducanumab and lecanemab and many providers do not administer these medications in ApoE4 homozygote carriers for this reason (Sperling et al., 2012; VandeVrede et al., 2020). Additionally, it remains to be explored whether the ApoE genotype influences the safety and efficacy of these therapies. Current therapeutic strategies for AD also concentrate on modulating ApoE levels and lipidation status, targeting ApoE’s structural attributes, and its interactions with Aβ. Recognized for its pivotal role in lipid transportation and preservation of synaptic homeostasis, ApoE presents itself as a viable therapeutic target for AD. Evidence suggests that augmenting ApoE levels or enhancing its lipidation could prove advantageous in AD treatment. Notably, in murine models of amyloid pathology, ligands of liver X receptor (LXR) and retinoid X receptor (RXR) have demonstrated the capability to enhance the transcription and secretion of all ApoE isoforms, thereby mitigating Aβ deposition and reinstating cognitive function (Yamazaki et al., 2019; Fernández-Calle et al., 2022). Additionally, ABCA1, which is transcriptionally regulated by LXR and is crucial for cholesterol efflux and HDL formation, is affected by the self-aggregation of ApoE4, which reduces ABCA1 membrane recycling and leads to decreased lipidation of ApoE4 particles (Fernández-Calle et al., 2022; Rawat et al., 2019).
Furthermore, in a mouse model of amyloid pathology, AAV-mediated human ApoE gene expression revealed that the presence of the ApoEε4 allele exacerbated synaptic loss and Aβ deposition, while the ApoEε2 allele expression in the same model led to a reduction in brain Aβ levels (Yamazaki et al., 2019; Hudry et al., 2013). Deletion of the gene encoding ABCA1, responsible for lipidating ApoE in the CNS, resulted in an increase in Aβ deposition (Wahrle et al., 2005) Conversely, overexpression of ABCA1 resulted in a decrease in Aβ deposition (Wahrle et al., 2008) in amyloid mouse models, suggesting that increasing ApoE lipidation can reduce Aβ pathology. Various studies have demonstrated that ApoE immunotherapy targeting ApoE-mediated plaque formation, using anti-mouse ApoE antibody HJ6.3 and/or anti-human ApoE antibody HAE-4, induced a significant reduction in Aβ deposition in a mouse model of amyloid pathology (Kim et al., 2012; Liao et al., 2018). Additionally, treatment with peptides bearing characteristics similar to native ApoE has shown promise in reducing Aβ deposition (Vitek et al., 2012; Handattu et al., 2013), tau hyperphosphorylation (Ghosal et al., 2013), and glial activation in mouse models of amyloid pathology. However, the potential impact of these findings on human subjects requires further exploration (Yamazaki et al., 2019).
The targeted modification of ApoE4 structural properties using PH002, an inhibitor of intracellular domain interaction of ApoE4, has demonstrated a reduction in ApoE4 fragmentation and its associated effects on Aβ production, tau phosphorylation, and GABAergic neuron degeneration in human iPSC-derived neurons (Wang et al., 2018; Mahley and Huang, 2012b). ApoE4, due to its pathological conformation compared to ApoE3 and ApoE2, is considered the primary risk factor for SAD. Consequently, the conversion of ApoE4 to ApoE3 or ApoE2 represents a promising therapeutic approach for AD treatment. Studies have indicated that editing the ApoEε4 allele to the ApoEε3 allele via gene-editing technologies leads to a reduction in ApoE fragmentation, Aβ production, tau phosphorylation, and GABAergic neuron degeneration in iPSC-derived neurons, suggesting that the detrimental effects of ApoE4 could be alleviated through gene editing (Yamazaki et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2018). Inhibition of the interaction between ApoE and Aβ demonstrates potential benefits in mitigating Aβ pathology. Administration of the synthetic peptide Aβ12–28P, structurally akin to the ApoE binding site on full-length Aβ, has exhibited a reduction in insoluble tau accumulation in AD mouse models (Liu et al., 2014). Additionally, it has led to diminished brain Aβ buildup, coupled with concurrent ApoE co-deposition within Aβ plaques and neuritic degeneration in amyloid mouse models characterized by ApoE2-TR and ApoE4-TR backgrounds (Pankiewicz et al., 2014).
The targeting of ApoE receptors presents a promising therapeutic approach for mitigating Aβ pathology. It is firmly established that the clearance of Aβ in the brain is, in part, facilitated by ApoE receptors, namely LDLR and LRP1 (Bu, 2009; Kanekiyo et al., 2014; Zhao et al., 2018). Research has demonstrated that the upregulation of LDLR augments Aβ clearance, leading to a significant reduction in Aβ deposition in murine models of amyloid pathology (Kim et al., 2009). Moreover, the clinical exploration of fluvastatin, a compound for AD therapy, suggests its potential in diminishing Aβ deposition and/or enhancing Aβ clearance, potentially through the augmentation of LRP1 expression (Shinohara et al., 2010). Nevertheless, further investigation is imperative to fully elucidate the role of ApoE in mediating Aβ clearance via ApoE receptors.
Recently, a rare ApoE variant, ApoE3-Ch, was found to protect against both early-onset AD and in late onset AD (Nelson et al., 2023). This variant has gained significant attention in the AD field, as its homozygosity was associated with remarkable resistance to a severe form of familial AD linked to the PSEN1-E280A mutation (Arboleda-Velasquez et al., 2019). Individuals carrying two copies of this rare allele exhibited significantly reduced tau pathology and neurodegeneration, along with preserved glucose metabolism and cognitive function (Arboleda-Velasquez et al., 2019). Additionally, ApoE3-Ch/ApoE3-Ch astrocytes were shown to effectively mitigate tau propagation in iPSC-derived neurons (Murakami et al., 2024). Studies in a humanized APOE3-Ch knock-in mouse model, crossed with an Aβ plaque-depositing model, demonstrated that ApoE3-Ch alters microglial responses and suppresses Aβ-induced tau seeding and spreading (Chen et al., 2024). Furthermore, the homozygous ApoE4-R136S mutation (ApoE4-Ch) was shown to rescue ApoE4-driven tau pathology, neurodegeneration, and neuroinflammation in tauopathy mouse models and human iPSC-derived neurons carrying human ApoE4 with either homozygous or heterozygous R136S mutations in late-onset AD. While the heterozygous ApoE4-Ch mutation partially protected against ApoE4-driven neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation, it did not prevent tau pathology. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing revealed that the ApoE4-Ch mutation increased protective cell populations and reduced disease-associated populations in a gene dose-dependent manner (Nelson et al., 2023). These findings highlight the potential of the ApoE-Ch mutation to protect against ApoE4-driven AD pathologies, offering a promising target for therapeutic development against AD.
This review examines the correlation between the diverse functions of ApoE and its role in the development of various neurodegenerative conditions, including AD, PD, ALS, FTLD, HD, VD, and MS. The three primaries human ApoE polymorphisms, ApoE2, ApoE3, and ApoE4, exhibit differential effects on Aβ clearance and aggregation within the brain. Additionally, they play distinct roles in redistributing cholesterol and phospholipids to neurons through their interaction with cell-surface ApoE receptors. These polymorphisms also influence glucose metabolism, neuronal signaling, and neuroinflammation. ApoE is also pivotal in tau pathology, tau-mediated neurodegeneration, and the microglial response to AD-related pathologies. Recent investigations have shed light on novel functions of ApoE, notably its interaction with presenilin, the protective role of ApoE mutations against AD, and the ApoE4-driven tau pathology and neurodegeneration. Furthermore, ApoE isoforms, particularly ApoE4, demonstrate involvement in α-synuclein aggregation, TDP-43 and FUS-induced neurodegeneration, HTT gene regulation, MS susceptibility, and disruption of BBB. ApoE also governs vascular health, an area of significance given the strong association between vascular pathology and neurodegenerative diseases. Accordingly, the comprehensive study of ApoE and its multifaceted functions may unveil novel strategies for early disease risk identification. Emphasizing the link between ApoE and the risk of pathogenesis in various neurodegenerative diseases is imperative for human disease diagnosis, risk assessment, prevention, and treatment. Despite persistent challenges, ongoing ApoE research instills optimism for pioneering therapeutic interventions capable of attenuating or arresting the progression of neurodegenerative diseases.
Our team undertook an exhaustive literature review focusing on the multifunctionality of ApoE in neurodegenerative disorders. Employing systematic keyword searches and delving into highly referenced classical articles within databases such as PubMed and ScienceDirect allowed us to comprehensively cover recent research. Our primary objective was to select recent publications to acquire the most current insights into ApoE’s diverse roles in various neurodegenerative disorders. Prioritizing classical articles with substantial citations provided a robust theoretical basis for our review, facilitating a thorough exploration of ApoE’s involvement. Genetic variation data was sourced from AlzForum URL.1 This approach to literature review was designed to offer substantial support for our study, thus enriching the overall understanding of ApoE’s multifunctionality within the realm of neurodegenerative disorders.
SI: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. AN: Investigation, Writing – original draft. YS: Resources, Writing – original draft. MM: Writing – review & editing. KZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research C 19K07846 and 22K07352 (to KZ) and by the Grant-in-Aid for JSPS fellows 23KF0156 (to KZ) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, Japan. The grants-in-aid from “The 24th General Assembly of the Japanese Association of Medical Sciences” (to KZ), the Daiko Foundation (to KZ), the Hirose International Scholarship Foundation (to KZ), and the Hori Sciences and Arts Foundation (to KZ). SI was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) as an FY 2023 JSPS fellow from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, Japan.
We are thankful to all the members of the Department of Neuro-Oncology, Institute of Brain Science, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Nagoya City University, for their feedback on the manuscript. We are also thankful to BioRender (biorender.com) for the resources used to create the figures in the manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
AD, Alzheimer’s disease; Aβ, Amyloid β-protein; ApoE, Apolipoprotein E; APP, Amyloid precursor protein; SAD, Sporadic Alzheimer’s disease; FAD, Familial Alzheimer’s disease; PD, Parkinson’s disease; ALS, Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; FTLD, Frontotemporal lobar degeneration; HD, Huntington’s disease; VD, Vascular dementia; MS, Multiple sclerosis; LB, Lewy bodies; DLB, Dementia with Lewy bodies; PDD, Parkinson’s disease dementia; TDP-43, TAR DNA-binding protein 43; NMR, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance; FRET, Fluorescence resonance energy transfer; EPR, Electron paramagnetic resonance; BBB, Blood–brain barrier; CNS, Central nervous system; ER, Endoplasmic reticulum; HDL, High density lipoprotein; VLDL, Very low-density lipoprotein; LDL, Low-density lipoprotein; TR, Targeted replacement; PS, Presenilin; NEP, Neprilysin; IDE, Insulin-degrading enzyme; CSF, Cerebrospinal fluid; ISF, Interstitial fluid; NFTs, Neurofibrillary tangles; VMAT2, Vesicular monoamine transporter 2; GWAS, Genome-wide association study; PP2A, Protein phosphatase 2A; TREM2, Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2; TBARS, Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances; TJ, Tight junction; FAs, Fatty acids; SOD1, Superoxide-dimutase1; LXR, Ligands of liver X receptor; RXR, Retinoid X receptor; TR, Targeted-replacement; ARIA, Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities; ABCA1, ATP-binding cassette transporter A1.
Abdel-Khalik, J., Yutuc, E., Crick, P. J., Gustafsson, J. Å., Warner, M., Roman, G., et al. (2017). Defective cholesterol metabolism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Lipid Res. 58, 267–278. doi: 10.1194/jlr.P071639
Abou Ziki, M. D., Strulovici-Barel, Y., Hackett, N. R., Rodriguez-Flores, J. L., Mezey, J. G., Salit, J., et al. (2014). Prevalence of the apolipoprotein E Arg145Cys dyslipidemia at-risk polymorphism in African-derived populations. Am. J. Cardiol. 113, 302–308. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.09.021
Aoki, K., Uchihara, T., Sanjo, N., Nakamura, A., Ikeda, K., Tsuchiya, K., et al. (2003). Increased expression of neuronal apolipoprotein E in human brain with cerebral infarction. Stroke 34, 875–880. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000064320.73388.C6
Arboleda-Velasquez, J. F., Lopera, F., O’Hare, M., Delgado-Tirado, S., Marino, C., Chmielewska, N., et al. (2019). Resistance to autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease in an APOE3 Christchurch homozygote: a case report. Nat. Med. 25, 1680–1683. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0611-3
Auderset, L., Cullen, C. L., and Young, K. M. (2016). Low density lipoprotein-receptor related protein 1 is differentially expressed by neuronal and glial populations in the developing and mature mouse central nervous system. PLoS One 11:e0155878. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155878
Bai, X. C., Yan, C., Yang, G., Lu, P., Ma, D., Sun, L., et al. (2015). An atomic structure of human γ-secretase. Nature 525, 212–217. doi: 10.1038/nature14892
Bales, K. R., Liu, F., Wu, S., Lin, S., Koger, D., DeLong, C., et al. (2009). Human APOE isoform-dependent effects on brain beta-amyloid levels in PDAPP transgenic mice. J. Neurosci. 29, 6771–6779. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0887-09.2009
Bales, K. R., Verina, T., Cummins, D. J., du, Y., Dodel, R. C., Saura, J., et al. (1999). Apolipoprotein E is essential for amyloid deposition in the APP(V717F) transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 15233–15238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.26.15233
Bales, K. R., Verina, T., Dodel, R. C., du, Y., Altstiel, L., Bender, M., et al. (1997). Lack of apolipoprotein E dramatically reduces amyloid beta-peptide deposition. Nat. Genet. 17, 263–264. doi: 10.1038/ng1197-263
Bamberger, M. E., Harris, M. E., McDonald, D. R., Husemann, J., and Landreth, G. E. (2003). A cell surface receptor complex for fibrillar beta-amyloid mediates microglial activation. J. Neurosci. 23, 2665–2674. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-07-02665.2003
Blázquez, L., Otaegui, D., Sáenz, A., Paisán-Ruiz, C., Emparanza, J. I., Ruiz-Martinez, J., et al. (2006). Apolipoprotein E epsilon4 allele in familial and sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurosci. Lett. 406, 235–239. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.07.037
Borchelt, D. R., Thinakaran, G., Eckman, C. B., Lee, M. K., Davenport, F., Ratovitsky, T., et al. (1996). Familial Alzheimer's disease-linked presenilin 1 variants elevate Abeta1-42/1-40 ratio in vitro and in vivo. Neuron 17, 1005–1013. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(00)80230-5
Boussicault, L., Alves, S., Lamazière, A., Planques, A., Heck, N., Moumné, L., et al. (2016). CYP46A1, the rate-limiting enzyme for cholesterol degradation, is neuroprotective in Huntington's disease. Brain 139, 953–970. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv384
Boyles, J. K., Pitas, R. E., Wilson, E., Mahley, R. W., and Taylor, J. M. (1985). Apolipoprotein E associated with astrocytic glia of the central nervous system and with nonmyelinating glia of the peripheral nervous system. J. Clin. Invest. 76, 1501–1513. doi: 10.1172/JCI112130
Braidy, N., Gai, W. P., Xu, Y. H., Sachdev, P., Guillemin, G. J., Jiang, X. M., et al. (2013). Uptake and mitochondrial dysfunction of alpha-synuclein in human astrocytes, cortical neurons and fibroblasts. Transl. Neurodegener. 2:20. doi: 10.1186/2047-9158-2-20
Brandl, S., and Reindl, M. (2023). Blood–brain barrier breakdown in neuroinflammation: current in vitro models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:12699. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612699
Bras, J., Guerreiro, R., Darwent, L., Parkkinen, L., Ansorge, O., Escott-Price, V., et al. (2014). Genetic analysis implicates APOE, SNCA and suggests lysosomal dysfunction in the etiology of dementia with Lewy bodies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 23, 6139–6146. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu334
Brecht, W. J., Harris, F. M., Chang, S., Tesseur, I., Yu, G. Q., Xu, Q., et al. (2004). Neuron-specific apolipoprotein e4 proteolysis is associated with increased tau phosphorylation in brains of transgenic mice. J. Neurosci. 24, 2527–2534. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4315-03.2004
Brown, C. A., Lally, C., Kupelian, V., and Flanders, W. D. (2021). Estimated prevalence and incidence of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and SOD1 and C9orf72 genetic variants. Neuroepidemiology 55, 342–353. doi: 10.1159/000516752
Bruinsma, I. B., Wilhelmus, M. M. M., Kox, M., Veerhuis, R., de Waal, R. M. W., and Verbeek, M. M. (2010). Apolipoprotein E protects cultured pericytes and astrocytes from D-Abeta(1-40)-mediated cell death. Brain Res. 1315, 169–180. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.12.039
Bu, G. (2009). Apolipoprotein E and its receptors in Alzheimer's disease: pathways, pathogenesis and therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 10, 333–344. doi: 10.1038/nrn2620
Bu, G. (2022). APOE targeting strategy in Alzheimer's disease: lessons learned from protective variants. Mol. Neurodegener. 17:51. doi: 10.1186/s13024-022-00556-6
Burré, J., Sharma, M., and Südhof, T. C. (2018). Cell biology and pathophysiology of α-Synuclein. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 8:a024091. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a024091
Butterfield, D. A., and Mattson, M. P. (2020). Apolipoprotein E and oxidative stress in brain with relevance to Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 138:104795. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104795
Calabresi, P., di Lazzaro, G., Marino, G., Campanelli, F., and Ghiglieri, V. (2023). Advances in understanding the function of alpha-synuclein: implications for Parkinson's disease. Brain 146, 3587–3597. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad150
Caruso, A., Motolese, M., Iacovelli, L., Caraci, F., Copani, A., Nicoletti, F., et al. (2006). Inhibition of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway by apolipoprotein E4 in PC12 cells. J. Neurochem. 98, 364–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03867.x
Cash, J. G., Kuhel, D. G., Basford, J. E., Jaeschke, A., Chatterjee, T. K., Weintraub, N. L., et al. (2012). Apolipoprotein E4 impairs macrophage efferocytosis and potentiates apoptosis by accelerating endoplasmic reticulum stress. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 27876–27884. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.377549
Cerf, E., Gustot, A., Goormaghtigh, E., Ruysschaert, J. M., and Raussens, V. (2011). High ability of apolipoprotein E4 to stabilize amyloid-β peptide oligomers, the pathological entities responsible for Alzheimer's disease. FASEB J. 25, 1585–1595. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-175976
Chaves-Filho, A. B., Pinto, I. F. D., Dantas, L. S., Xavier, A. M., Inague, A., Faria, R. L., et al. (2019). Alterations in lipid metabolism of spinal cord linked to amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 9:11642. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48059-7
Chen, J., Li, Q., and Wang, J. (2011). Topology of human apolipoprotein E3 uniquely regulates its diverse biological functions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 14813–14818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1106420108
Chen, Y., Song, S., Parhizkar, S., Lord, J., Zhu, Y., Strickland, M. R., et al. (2024). APOE3ch alters microglial response and suppresses Aβ-induced tau seeding and spread. Cell 187, 428–445. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.11.029
Chen, Y., Strickland, M. R., Soranno, A., and Holtzman, D. M. (2021). Apolipoprotein E: structural insights and links to Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. Neuron 109, 205–221. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.10.008
Christensen, D. Z., Schneider-Axmann, T., Lucassen, P. J., Bayer, T. A., and Wirths, O. (2010). Accumulation of intraneuronal Abeta correlates with ApoE4 genotype. Acta Neuropathol. 119, 555–566. doi: 10.1007/s00401-010-0666-1
Chuang, T. Y., Guo, Y., Seki, S. M., Rosen, A. M., Johanson, D. M., Mandell, J. W., et al. (2016). LRP1 expression in microglia is protective during CNS autoimmunity. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 4:68. doi: 10.1186/s40478-016-0343-2
Corder, E. H., Saunders, A. M., Risch, N. J., Strittmatter, W. J., Schmechel, D. E., Gaskell, P. C. Jr., et al. (1994). Protective effect of apolipoprotein E type 2 allele for late onset Alzheimer disease. Nat. Genet. 7, 180–184. doi: 10.1038/ng0694-180
Corder, E. H., Saunders, A. M., Strittmatter, W. J., Schmechel, D. E., Gaskell, P. C., Small, G. W., et al. (1993). Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science 261, 921–923. doi: 10.1126/science.8346443
Das, H. K., McPherson, J., Bruns, G. A., Karathanasis, S. K., and Breslow, J. L. (1985). Isolation, characterization, and mapping to chromosome 19 of the human apolipoprotein E gene. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 6240–6247. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)88963-3
Davignon, J., Gregg, R. E., and Sing, C. F. (1988). Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis 8, 1–21. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.8.1.1
Davis, A. A., Inman, C. E., Wargel, Z. M., Dube, U., Freeberg, B. M., Galluppi, A., et al. (2020). APOE genotype regulates pathology and disease progression in synucleinopathy. Sci. Transl. Med. 12:3069. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aay3069
Deane, R., Sagare, A., Hamm, K., Parisi, M., Lane, S., Finn, M. B., et al. (2008). apoE isoform-specific disruption of amyloid beta peptide clearance from mouse brain. J. Clin. Invest. 118, 4002–4013. doi: 10.1172/JCI36663
del Toro, D., Xifró, X., Pol, A., Humbert, S., Saudou, F., Canals, J. M., et al. (2010). Altered cholesterol homeostasis contributes to enhanced excitotoxicity in Huntington's disease. J. Neurochem. 115, 153–167. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06912.x
Dickson, D. W., Heckman, M. G., Murray, M. E., Soto, A. I., Walton, R. L., Diehl, N. N., et al. (2018). APOE ε4 is associated with severity of Lewy body pathology independent of Alzheimer pathology. Neurology 91, e1182–e1195. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000006212
Dodge, J. C., Jensen, E. H., Yu, J., Sardi, S. P., Bialas, A. R., Taksir, T. V., et al. (2020). Neutral lipid Cacostasis contributes to disease pathogenesis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurosci. 40, 9137–9147. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1388-20.2020
Dong, L. M., Wilson, C., Wardell, M. R., Simmons, T., Mahley, R. W., Weisgraber, K. H., et al. (1994). Human apolipoprotein E. Role of arginine 61 in mediating the lipoprotein preferences of the E3 and E4 isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 22358–22365. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(17)31797-0
Dose, J., Huebbe, P., Nebel, A., and Rimbach, G. (2016). APOE genotype and stress response - a mini review. Lipids Health Dis. 15:121. doi: 10.1186/s12944-016-0288-2
Emamzadeh, F. N. (2016). Alpha-synuclein structure, functions, and interactions. J. Res. Med. Sci. 21:29. doi: 10.4103/1735-1995.181989
Emamzadeh, F. N. (2017). Role of Apolipoproteins and α-Synuclein in Parkinson's disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 62, 344–355. doi: 10.1007/s12031-017-0942-9
Eran, S., and Ronit, P. K. (2022). APOE4 expression is associated with impaired autophagy and mitophagy in astrocytes. Neural Regen. Res. 17, 777–778. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.322452
Erekat, N. S. (2022). Apoptosis and its therapeutic implications in neurodegenerative diseases. Clin. Anat. 35, 65–78. doi: 10.1002/ca.23792
Erskine, D., Koss, D., Korolchuk, V. I., Outeiro, T. F., Attems, J., and McKeith, I. (2021). Lipids, lysosomes and mitochondria: insights into Lewy body formation from rare monogenic disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 141, 511–526. doi: 10.1007/s00401-021-02266-7
Fagan, A. M., Watson, M., Parsadanian, M., Bales, K. R., Paul, S. M., and Holtzman, D. M. (2002). Human and murine ApoE markedly alters a beta metabolism before and after plaque formation in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 9, 305–318. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.2002.0483
Farfel, J. M., Yu, L., de Jager, P. L., Schneider, J. A., and Bennett, D. A. (2016). Association of APOE with tau-tangle pathology with and without β-amyloid. Neurobiol. Aging 37, 19–25. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.09.011
Farrer, L. A., Cupples, L. A., Haines, J. L., Hyman, B., Kukull, W. A., Mayeux, R., et al. (1997). Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. JAMA 278, 1349–1356. doi: 10.1001/jama.1997.03550160069041
Federoff, M., Jimenez-Rolando, B., Nalls, M. A., and Singleton, A. B. (2012). A large study reveals no association between APOE and Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 46, 389–392. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.02.002
Fernandez, C. G., Hamby, M. E., McReynolds, M. L., and Ray, W. J. (2019). The role of APOE4 in disrupting the homeostatic functions of astrocytes and microglia in aging and Alzheimer's disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 11:14. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00014
Fernández-Calle, R., Konings, S. C., Frontiñán-Rubio, J., García-Revilla, J., Camprubí-Ferrer, L., Svensson, M., et al. (2022). APOE in the Bullseye of neurodegenerative diseases: impact of the APOE genotype in Alzheimer's disease pathology and brain diseases. Mol. Neurodegener. 17:62. doi: 10.1186/s13024-022-00566-4
Ferrari, R., Hernandez, D. G., Nalls, M. A., Rohrer, J. D., Ramasamy, A., Kwok, J. B. J., et al. (2014). Frontotemporal dementia and its subtypes: a genome-wide association study. Lancet Neurol. 13, 686–699. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70065-1
Fitz, N. F., Nam, K. N., Wolfe, C. M., Letronne, F., Playso, B. E., Iordanova, B. E., et al. (2021). Phospholipids of APOE lipoproteins activate microglia in an isoform-specific manner in preclinical models of Alzheimer's disease. Nat. Commun. 12:3416. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23762-0
Fourgeaud, L., Través, P. G., Tufail, Y., Leal-Bailey, H., Lew, E. D., Burrola, P. G., et al. (2016). TAM receptors regulate multiple features of microglial physiology. Nature 532, 240–244. doi: 10.1038/nature17630
Garai, K., Verghese, P. B., Baban, B., Holtzman, D. M., and Frieden, C. (2014). The binding of apolipoprotein E to oligomers and fibrils of amyloid-β alters the kinetics of amyloid aggregation. Biochemistry 53, 6323–6331. doi: 10.1021/bi5008172
Genin, E., Hannequin, D., Wallon, D., Sleegers, K., Hiltunen, M., Combarros, O., et al. (2011). APOE and Alzheimer disease: a major gene with semi-dominant inheritance. Mol. Psychiatry 16, 903–907. doi: 10.1038/mp.2011.52
Ghosal, K., Stathopoulos, A., Thomas, D., Phenis, D., Vitek, M. P., and Pimplikar, S. W. (2013). The apolipoprotein-E-mimetic COG112 protects amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain-overexpressing animals from Alzheimer's disease-like pathological features. Neurodegener Dis 12, 51–58. doi: 10.1159/000341299
Giau, V. V., Bagyinszky, E., An, S. S., and Kim, S. Y. (2015). Role of apolipoprotein E in neurodegenerative diseases. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 11, 1723–1737. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S84266
Girard, S. L., and Rouleau, G. A. (2014). Genome-wide association study in FTD: divide to conquer. Lancet Neurol. 13, 643–644. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70070-5
Gong, J. S., Kobayashi, M., Hayashi, H., Zou, K., Sawamura, N., Fujita, S. C., et al. (2002). Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) isoform-dependent lipid release from astrocytes prepared from human ApoE3 and ApoE4 knock-in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 29919–29926. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M203934200
Gong, J. S., Morita, S. Y., Kobayashi, M., Handa, T., Fujita, S. C., Yanagisawa, K., et al. (2007). Novel action of apolipoprotein E (ApoE): ApoE isoform specifically inhibits lipid-particle-mediated cholesterol release from neurons. Mol. Neurodegener. 2:9. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-2-9
González De Aguilar, J. L. (2019). Lipid biomarkers for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 10:284. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00284
Gratuze, M., Leyns, C. E. G., and Holtzman, D. M. (2018). New insights into the role of TREM2 in Alzheimer's disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 13:66. doi: 10.1186/s13024-018-0298-9
Grossman, M., Seeley, W. W., Boxer, A. L., Hillis, A. E., Knopman, D. S., Ljubenov, P. A., et al. (2023). Frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 9:40. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00447-0
Grubman, A., Chew, G., Ouyang, J. F., Sun, G., Choo, X. Y., McLean, C., et al. (2019). A single-cell atlas of entorhinal cortex from individuals with Alzheimer's disease reveals cell-type-specific gene expression regulation. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 2087–2097. doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0539-4
Guerreiro, R., Ross, O. A., Kun-Rodrigues, C., Hernandez, D. G., Orme, T., Eicher, J. D., et al. (2018). Investigating the genetic architecture of dementia with Lewy bodies: a two-stage genome-wide association study. Lancet Neurol. 17, 64–74. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30400-3
Handattu, S. P., Monroe, C. E., Nayyar, G., Palgunachari, M. N., Kadish, I., van Groen, T., et al. (2013). In vivo and in vitro effects of an apolipoprotein e mimetic peptide on amyloid-β pathology. J. Alzheimers Dis. 36, 335–347. doi: 10.3233/JAD-122377
Hasel, P., and Liddelow, S. A. (2021). Isoform-dependent APOE secretion modulates neuroinflammation. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 17, 265–266. doi: 10.1038/s41582-021-00483-y
Hashimoto, T., Serrano-Pozo, A., Hori, Y., Adams, K. W., Takeda, S., Banerji, A. O., et al. (2012). Apolipoprotein E, especially apolipoprotein E4, increases the oligomerization of amyloid β peptide. J. Neurosci. 32, 15181–15192. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1542-12.2012
Hatters, D. M., Budamagunta, M. S., Voss, J. C., and Weisgraber, K. H. (2005). Modulation of apolipoprotein E structure by domain interaction: differences in lipid-bound and lipid-free forms. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 34288–34295. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M506044200
Hatters, D. M., Peters-Libeu, C. A., and Weisgraber, K. H. (2006). Apolipoprotein E structure: insights into function. Trends Biochem. Sci. 31, 445–454. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2006.06.008
Hatters, D. M., Zhong, N., Rutenber, E., and Weisgraber, K. H. (2006). Amino-terminal domain stability mediates apolipoprotein E aggregation into neurotoxic fibrils. J. Mol. Biol. 361, 932–944. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.06.080
Hawkes, C. A., Sullivan, P. M., Hands, S., Weller, R. O., Nicoll, J. A. R., and Carare, R. O. (2012). Disruption of arterial perivascular drainage of amyloid-β from the brains of mice expressing the human APOE ε4 allele. PLoS One 7:e41636. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041636
He, K., Li, B., Wang, J., Wang, Y., You, Z., Chen, X., et al. (2024). APOE ε4 is associated with decreased synaptic density in cognitively impaired participants. Alzheimers Dement. 20, 3157–3166. doi: 10.1002/alz.13775
Hirsch-Reinshagen, V., Zhou, S., Burgess, B. L., Bernier, L., McIsaac, S. A., Chan, J. Y., et al. (2004). Deficiency of ABCA1 impairs apolipoprotein E metabolism in brain. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 41197–41207. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407962200
Hoffman, J. D., Yanckello, L. M., Chlipala, G., Hammond, T. C., McCulloch, S. D., Parikh, I., et al. (2019). Dietary inulin alters the gut microbiome, enhances systemic metabolism and reduces neuroinflammation in an APOE4 mouse model. PLoS One 14:e0221828. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221828
Holtzman, D. M., Bales, K. R., Tenkova, T., Fagan, A. M., Parsadanian, M., Sartorius, L. J., et al. (2000). Apolipoprotein E isoform-dependent amyloid deposition and neuritic degeneration in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 2892–2897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.050004797
Holtzman, D. M., Fagan, A. M., Mackey, B., Tenkova, T., Sartorius, L., Paul, S. M., et al. (2000). Apolipoprotein E facilitates neuritic and cerebrovascular plaque formation in an Alzheimer's disease model. Ann. Neurol. 47, 739–747. doi: 10.1002/1531-8249(200006)47:6<739::AID-ANA6>3.0.CO;2-8
Holtzman, D. M., Herz, J., and Bu, G. (2012). Apolipoprotein E and apolipoprotein E receptors: normal biology and roles in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2:a006312. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006312
Hou, T. T., Han, Y. D., Cong, L., Liu, C. C., Liang, X. Y., Xue, F. Z., et al. (2020). Apolipoprotein E facilitates amyloid-β oligomer-induced tau phosphorylation. J. Alzheimers Dis. 74, 521–534. doi: 10.3233/JAD-190711
Hou, M., Xu, G., Ran, M., Luo, W., and Wang, H. (2021). APOE-ε4 carrier status and gut microbiota Dysbiosis in patients with Alzheimer disease. Front. Neurosci. 15:619051. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.619051
Huang, X., Chen, P., Kaufer, D. I., Tröster, A. I., and Poole, C. (2006). Apolipoprotein E and dementia in Parkinson disease: a meta-analysis. Arch. Neurol. 63, 189–193. doi: 10.1001/archneur.63.2.189
Huang, Y., Happonen, K. E., Burrola, P. G., O’Connor, C., Hah, N., Huang, L., et al. (2021). Microglia use TAM receptors to detect and engulf amyloid β plaques. Nat. Immunol. 22, 586–594. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00913-5
Huang, Y., Liu, X. Q., Wyss-Coray, T., Brecht, W. J., Sanan, D. A., and Mahley, R. W. (2001). Apolipoprotein E fragments present in Alzheimer's disease brains induce neurofibrillary tangle-like intracellular inclusions in neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 8838–8843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.151254698
Huang, Y., and Mucke, L. (2012). Alzheimer mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Cell 148, 1204–1222. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.040
Huang, Y., Weisgraber, K. H., Mucke, L., and Mahley, R. W. (2004). Apolipoprotein E: diversity of cellular origins, structural and biophysical properties, and effects in Alzheimer's disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 23, 189–204. doi: 10.1385/JMN:23:3:189
Huang, Y. A., Zhou, B., Wernig, M., and Südhof, T. C. (2017). ApoE2, ApoE3, and ApoE4 differentially stimulate APP transcription and Aβ secretion. Cell 168, 427–441. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.044
Hubin, E., Verghese, P. B., van Nuland, N., and Broersen, K. (2019). Apolipoprotein E associated with reconstituted high-density lipoprotein-like particles is protected from aggregation. FEBS Lett. 593, 1144–1153. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13428
Hudry, E., Dashkoff, J., Roe, A. D., Takeda, S., Koffie, R. M., Hashimoto, T., et al. (2013). Gene transfer of human Apoe isoforms results in differential modulation of amyloid deposition and neurotoxicity in mouse brain. Sci. Transl. Med. 5:212ra161. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3007000
Husain, M. A., Laurent, B., and Plourde, M. (2021). APOE and Alzheimer's disease: from lipid transport to physiopathology and therapeutics. Front. Neurosci. 15:630502. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.630502
Huynh, T. V., Liao, F., Francis, C. M., Robinson, G. O., Serrano, J. R., and Jiang, H. (2017). Age-dependent effects of apoE reduction using antisense oligonucleotides in a model of β-amyloidosis. Neuron 96, 1013–1023. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.11.014
Intihar, T. A., Martinez, E. A., and Gomez-Pastor, R. (2019). Mitochondrial dysfunction in Huntington's disease; interplay between HSF1, p53 and PGC-1α transcription factors. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 13:103. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00103
Ioannou, M. S., Jackson, J., Sheu, S. H., Chang, C. L., Weigel, A. V., Liu, H., et al. (2019). Neuron-astrocyte metabolic coupling protects against activity-induced fatty acid toxicity. Cell 177, 1522–1535. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.04.001
Irwin, D. J., Cairns, N. J., Grossman, M., McMillan, C. T., Lee, E. B., van Deerlin, V. M., et al. (2015). Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: defining phenotypic diversity through personalized medicine. Acta Neuropathol. 129, 469–491. doi: 10.1007/s00401-014-1380-1
Irwin, D. J., White, M. T., Toledo, J. B., Xie, S. X., Robinson, J. L., van Deerlin, V., et al. (2012). Neuropathologic substrates of Parkinson disease dementia. Ann. Neurol. 72, 587–598. doi: 10.1002/ana.23659
Islam, S., Sun, Y., Gao, Y., Nakamura, T., Noorani, A. A., Li, T., et al. (2022). Presenilin is essential for ApoE secretion, a novel role of Presenilin involved in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. J. Neurosci. 42, 1574–1586. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2039-21.2021
Jakimovski, D., Bittner, S., Zivadinov, R., Morrow, S. A., Benedict, R. H. B., Zipp, F., et al. (2024). Multiple sclerosis. Lancet 403, 183–202. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)01473-3
Jellinger, K. A. (2013). Pathology and pathogenesis of vascular cognitive impairment-a critical update. Front. Aging Neurosci. 5:17.
Jeon, G. S., Shim, Y. M., Lee, D. Y., Kim, J. S., Kang, M. J., Ahn, S. H., et al. (2019). Pathological modification of TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with SOD1 mutations. Mol. Neurobiol. 56, 2007–2021. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1218-2
Ji, Z. S., Brecht, W. J., Miranda, R. D., Hussain, M. M., Innerarity, T. L., and Mahley, R. W. (1993). Role of heparan sulfate proteoglycans in the binding and uptake of apolipoprotein E-enriched remnant lipoproteins by cultured cells. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 10160–10167. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)82186-X
Jiang, Q., Lee, C. Y. D., Mandrekar, S., Wilkinson, B., Cramer, P., Zelcer, N., et al. (2008). ApoE promotes the proteolytic degradation of Abeta. Neuron 58, 681–693. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2008.04.010
Jo, S., Kim, S. O., Park, K. W., Lee, S. H., Hwang, Y. S., and Chung, S. J. (2021). The role of APOE in cognitive trajectories and motor decline in Parkinson's disease. Sci. Rep. 11:7819. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86483-w
Josephs, K. A., Whitwell, J. L., Weigand, S. D., Murray, M. E., Tosakulwong, N., Liesinger, A. M., et al. (2014). TDP-43 is a key player in the clinical features associated with Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 127, 811–824. doi: 10.1007/s00401-014-1269-z
Jun, G. R., You, Y., Zhu, C., Meng, G., Chung, J., Panitch, R., et al. (2022). Protein phosphatase 2A and complement component 4 are linked to the protective effect of APOE ɛ2 for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 18, 2042–2054. doi: 10.1002/alz.12607
Kacher, R., Mounier, C., Caboche, J., and Betuing, S. (2022). Altered cholesterol homeostasis in Huntington's disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 14:797220. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.797220
Kaivola, K., Shah, Z., Chia, R., International LBD Genomics ConsortiumBlack, S. E., Gan-Or, Z., et al. (2022). Genetic evaluation of dementia with Lewy bodies implicates distinct disease subgroups. Brain 145, 1757–1762. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab402
Kanekiyo, T., Cirrito, J. R., Liu, C. C., Shinohara, M., Li, J., Schuler, D. R., et al. (2013). Neuronal clearance of amyloid-β by endocytic receptor LRP1. J. Neurosci. 33, 19276–19283. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3487-13.2013
Kanekiyo, T., Xu, H., and Bu, G. (2014). ApoE and Aβ in Alzheimer's disease: accidental encounters or partners? Neuron 81, 740–754. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.01.045
Kang, S. S., Ahn, E. H., Liu, X., Bryson, M., Miller, G. W., Weinshenker, D., et al. (2021). ApoE4 inhibition of VMAT2 in the locus coeruleus exacerbates tau pathology in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 142, 139–158. doi: 10.1007/s00401-021-02315-1
Kang, S. S., Ebbert, M. T. W., Baker, K. E., Cook, C., Wang, X., Sens, J. P., et al. (2018). Microglial translational profiling reveals a convergent APOE pathway from aging, amyloid, and tau. J. Exp. Med. 215, 2235–2245. doi: 10.1084/jem.20180653
Karasinska, J. M., de Haan, W., Franciosi, S., Ruddle, P., Fan, J., Kruit, J. K., et al. (2013). ABCA1 influences neuroinflammation and neuronal death. Neurobiol. Dis. 54, 445–455. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2013.01.018
Karten, B., Campenot, R. B., Vance, D. E., and Vance, J. E. (2006). Expression of ABCG1, but not ABCA1, correlates with cholesterol release by cerebellar astroglia. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 4049–4057. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508915200
Kiani, L. (2023). ApoE attracts microglia to amyloid-β plaques. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 19:639. doi: 10.1038/s41582-023-00885-0
Kigerl, K. A., de Rivero Vaccari, J. P., Dietrich, W. D., Popovich, P. G., and Keane, R. W. (2014). Pattern recognition receptors and central nervous system repair. Exp. Neurol. 258, 5–16. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2014.01.001
Kim, J., Castellano, J. M., Jiang, H., Basak, J. M., Parsadanian, M., Pham, V., et al. (2009). Overexpression of low-density lipoprotein receptor in the brain markedly inhibits amyloid deposition and increases extracellular a beta clearance. Neuron 64, 632–644. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.11.013
Kim, J., Eltorai, A. E. M., Jiang, H., Liao, F., Verghese, P. B., Kim, J., et al. (2012). Anti-apoE immunotherapy inhibits amyloid accumulation in a transgenic mouse model of Aβ amyloidosis. J. Exp. Med. 209, 2149–2156. doi: 10.1084/jem.20121274
Kim, G., Gautier, O., Tassoni-Tsuchida, E., Ma, X. R., and Gitler, A. D. (2020). ALS genetics: gains, losses, and implications for future therapies. Neuron 108, 822–842. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.08.022
Kim, J., Yoon, H., Basak, J., and Kim, J. (2014). Apolipoprotein E in synaptic plasticity and Alzheimer's disease: potential cellular and molecular mechanisms. Mol. Cells 37, 767–776. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2014.0248
Kober, D. L., Stuchell-Brereton, M. D., Kluender, C. E., Dean, H. B., Strickland, M. R., Steinberg, D. F., et al. (2021). Functional insights from biophysical study of TREM2 interactions with apoE and Aβ1-42. Alzheimers Dement. 17, 475–488. doi: 10.1002/alz.12194
Kockx, M., Guo, D. L., Huby, T., Lesnik, P., Kay, J., Sabaretnam, T., et al. (2007). Secretion of apolipoprotein E from macrophages occurs via a protein kinase a and calcium-dependent pathway along the microtubule network. Circ. Res. 101, 607–616. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.157198
Kockx, M., Traini, M., and Kritharides, L. (2018). Cell-specific production, secretion, and function of apolipoprotein E. J. Mol. Med. 96, 361–371. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1632-y
Koffie, R. M., Hashimoto, T., Tai, H. C., Kay, K. R., Serrano-Pozo, A., Joyner, D., et al. (2012). Apolipoprotein E4 effects in Alzheimer's disease are mediated by synaptotoxic oligomeric amyloid-β. Brain 135, 2155–2168. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws127
Koistinaho, M., Lin, S., Wu, X., Esterman, M., Koger, D., Hanson, J., et al. (2004). Apolipoprotein E promotes astrocyte colocalization and degradation of deposited amyloid-beta peptides. Nat. Med. 10, 719–726. doi: 10.1038/nm1058
Koutsis, G., Panas, M., Giogkaraki, E., Potagas, C., Karadima, G., Sfagos, C., et al. (2007). APOE epsilon4 is associated with impaired verbal learning in patients with MS. Neurology 68, 546–549. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000254468.51973.44
Kowal, R. C., Herz, J., Weisgraber, K. H., Mahley, R. W., Brown, M. S., and Goldstein, J. L. (1990). Opposing effects of apolipoproteins E and C on lipoprotein binding to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 10771–10779. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)87014-4
Krasemann, S., Madore, C., Cialic, R., Baufeld, C., Calcagno, N., el Fatimy, R., et al. (2017). The TREM2-APOE pathway drives the transcriptional phenotype of dysfunctional microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Immunity 47, 566–581. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.08.008
Lanfranco, M. F., Ng, C. A., and Rebeck, G. W. (2020). ApoE Lipidation as a therapeutic target in Alzheimer's disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21:336. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176336
Lanfranco, M. F., Sepulveda, J., Kopetsky, G., and Rebeck, G. W. (2021). Expression and secretion of apoE isoforms in astrocytes and microglia during inflammation. Glia 69, 1478–1493. doi: 10.1002/glia.23974
Lanz, T. A., Carter, D. B., and Merchant, K. M. (2003). Dendritic spine loss in the hippocampus of young PDAPP and Tg2576 mice and its prevention by the ApoE2 genotype. Neurobiol. Dis. 13, 246–253. doi: 10.1016/S0969-9961(03)00079-2
Le Guen, Y., Belloy, M. E., Grenier-Boley, B., De Rojas, I., Castillo-Morales, A., Jansen, I., et al. (2022). Association of Rare APOE missense variants V236E and R251G with risk of Alzheimer disease. JAMA Neurol. 79, 652–663. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2022.1166
Lee, E. G., Leong, L., Chen, S., Tulloch, J., and Yu, C. E. (2023). APOE locus-associated mitochondrial function and its implication in Alzheimer's disease and aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:10440. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310440
Leyns, C. E. G., Gratuze, M., Narasimhan, S., Jain, N., Koscal, L. J., Jiang, H., et al. (2019). TREM2 function impedes tau seeding in neuritic plaques. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 1217–1222. doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0433-0
Li, Z. (2019). New APOE-related therapeutic options for Alzheimer’s disease. AIP Conf. Proc. 2058:020002.
Li, J., Kanekiyo, T., Shinohara, M., Zhang, Y., LaDu, M. J., Xu, H., et al. (2012). Differential regulation of amyloid-β endocytic trafficking and lysosomal degradation by apolipoprotein E isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 44593–44601. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.420224
Liao, F., Li, A., Xiong, M., Bien-Ly, N., Jiang, H., Zhang, Y., et al. (2018). Targeting of nonlipidated, aggregated apoE with antibodies inhibits amyloid accumulation. J. Clin. Invest. 128, 2144–2155. doi: 10.1172/JCI96429
Liao, F., Zhang, T. J., Jiang, H., Lefton, K. B., Robinson, G. O., Vassar, R., et al. (2015). Murine versus human apolipoprotein E4: differential facilitation of and co-localization in cerebral amyloid angiopathy and amyloid plaques in APP transgenic mouse models. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 3:70. doi: 10.1186/s40478-015-0250-y
Lill, C. M., Liu, T., Schjeide, B. M. M., Roehr, J. T., Akkad, D. A., Damotte, V., et al. (2012). Closing the case of APOE in multiple sclerosis: no association with disease risk in over 29 000 subjects. J. Med. Genet. 49, 558–562. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2012-101175
Lin, Y. T., Seo, J., Gao, F., Feldman, H. M., Wen, H. L., Penney, J., et al. (2018). APOE4 causes widespread molecular and cellular alterations associated with Alzheimer's disease phenotypes in Human iPSC-derived brain cell types. Neuron 98:1294. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.06.011
Litvinchuk, A., Huynh, T. P. V., Shi, Y., Jackson, R. J., Finn, M. B., Manis, M., et al. (2021). Apolipoprotein E4 reduction with antisense oligonucleotides decreases neurodegeneration in a Tauopathy model. Ann. Neurol. 89, 952–966. doi: 10.1002/ana.26043
Liu, S., Breitbart, A., Sun, Y., Mehta, P. D., Boutajangout, A., Scholtzova, H., et al. (2014). Blocking the apolipoprotein E/amyloid β interaction in triple transgenic mice ameliorates Alzheimer's disease related amyloid β and tau pathology. J. Neurochem. 128, 577–591. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12484
Liu, C. C., Liu, C. C., Kanekiyo, T., Xu, H., and Bu, G. (2013). Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: risk, mechanisms and therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 9, 106–118. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2012.263
Liu, C. C., Murray, M. E., Li, X., Zhao, N., Wang, N., Heckman, M. G., et al. (2021). APOE3-Jacksonville (V236E) variant reduces self-aggregation and risk of dementia. Sci. Transl. Med. 13:eabc9375.
Liu, C. C., Zhao, N., Fu, Y., Wang, N., Linares, C., Tsai, C. W., et al. (2017). ApoE4 accelerates early seeding of amyloid pathology. Neuron 96, 1024–1032. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.11.013
Longinetti, E., and Fang, F. (2019). Epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: an update of recent literature. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 32, 771–776. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000730
Lu, Q., and Lemke, G. (2001). Homeostatic regulation of the immune system by receptor tyrosine kinases of the tyro 3 family. Science 293, 306–311. doi: 10.1126/science.1061663
Ma, Q., Zhao, Z., Sagare, A. P., Wu, Y., Wang, M., Owens, N. C., et al. (2018). Blood-brain barrier-associated pericytes internalize and clear aggregated amyloid-β42 by LRP1-dependent apolipoprotein E isoform-specific mechanism. Mol. Neurodegener. 13:57. doi: 10.1186/s13024-018-0286-0
Mahley, R. W. (1988). Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science 240, 622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935
Mahley, R. W., and Huang, Y. (2012a). Apolipoprotein e sets the stage: response to injury triggers neuropathology. Neuron 76, 871–885. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.11.020
Mahley, R. W., and Huang, Y. (2012b). Small-molecule structure correctors target abnormal protein structure and function: structure corrector rescue of apolipoprotein E4-associated neuropathology. J. Med. Chem. 55, 8997–9008. doi: 10.1021/jm3008618
Mahley, R. W., Huang, Y., and Rall, S. C. Jr. (1999). Pathogenesis of type III hyperlipoproteinemia (dysbetalipoproteinemia). Questions, quandaries, and paradoxes. J. Lipid Res. 40, 1933–1949. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2275(20)32417-2
Mahley, R. W., and Rall, S. C. (2000). Apolipoprotein E: far more than a lipid transport protein. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 1, 507–537. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.1.1.507
Mahley, R. W., Weisgraber, K. H., and Huang, Y. (2009). Apolipoprotein E: structure determines function, from atherosclerosis to Alzheimer's disease to AIDS. J. Lipid Res. 50, S183–S188. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R800069-JLR200
Maloney, B., Ge, Y. W., Alley, G. M., and Lahiri, D. K. (2007). Important differences between human and mouse APOE gene promoters: limitation of mouse APOE model in studying Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurochem. 103, 1237–1257. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04831.x
Mandrekar, S., Jiang, Q., Lee, C. Y. D., Koenigsknecht-Talboo, J., Holtzman, D. M., and Landreth, G. E. (2009). Microglia mediate the clearance of soluble Abeta through fluid phase macropinocytosis. J. Neurosci. 29, 4252–4262. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5572-08.2009
Mann, D. M. A., and Snowden, J. S. (2017). Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: pathogenesis, pathology and pathways to phenotype. Brain Pathol. 27, 723–736. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12486
Margolis, R. L., O'Hearn, E., Rosenblatt, A., Willour, V., Holmes, S. E., Franz, M. L., et al. (2001). A disorder similar to Huntington's disease is associated with a novel CAG repeat expansion. Ann. Neurol. 50, 373–380. doi: 10.1002/ana.1312
Mawuenyega, K. G., Sigurdson, W., Ovod, V., Munsell, L., Kasten, T., Morris, J. C., et al. (2010). Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. Science 330:1774. doi: 10.1126/science.1197623
May, P., Woldt, E., Matz, R. L., and Boucher, P. (2007). The LDL receptor-related protein (LRP) family: an old family of proteins with new physiological functions. Ann. Med. 39, 219–228. doi: 10.1080/07853890701214881
Mead, R. J., Shan, N., Reiser, H. J., Marshall, F., and Shaw, P. J. (2023). Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a neurodegenerative disorder poised for successful therapeutic translation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 22, 185–212. doi: 10.1038/s41573-022-00612-2
Medway, C. W., Abdul-Hay, S., Mims, T., Ma, L., Bisceglio, G., Zou, F., et al. (2014). ApoE variant p.V236E is associated with markedly reduced risk of Alzheimer's disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 9:11. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-9-11
Meneses, A. D., Koga, S., Li, Z., O'Leary, J., Li, F., Chen, K., et al. (2023). APOE2 exacerbates TDP-43 related toxicity in the absence of Alzheimer pathology. Ann. Neurol. 93, 830–843. doi: 10.1002/ana.26580
Michikawa, M., Fan, Q. W., Isobe, I., and Yanagisawa, K. (2000). Apolipoprotein E exhibits isoform-specific promotion of lipid efflux from astrocytes and neurons in culture. J. Neurochem. 74, 1008–1016. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0741008.x
Michikawa, M., and Yanagisawa, K. (1998). Apolipoprotein E4 induces neuronal cell death under conditions of suppressed de novo cholesterol synthesis. J. Neurosci. Res. 54, 58–67. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19981001)54:1<58::AID-JNR7>3.0.CO;2-G
Minagawa, H., Gong, J. S., Jung, C. G., Watanabe, A., Lund-Katz, S., Phillips, M. C., et al. (2009). Mechanism underlying apolipoprotein E (ApoE) isoform-dependent lipid efflux from neural cells in culture. J. Neurosci. Res. 87, 2498–2508. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22073
Minagawa, H., Watanabe, A., Akatsu, H., Adachi, K., Ohtsuka, C., Terayama, Y., et al. (2010). Homocysteine, another risk factor for Alzheimer disease, impairs apolipoprotein E3 function. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 38382–38388. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.146258
Montagne, A., Nation, D. A., Sagare, A. P., Barisano, G., Sweeney, M. D., Chakhoyan, A., et al. (2020). APOE4 leads to blood–brain barrier dysfunction predicting cognitive decline. Nature 581, 71–76. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2247-3
Montagne, A., Nikolakopoulou, A. M., Huuskonen, M. T., Sagare, A. P., Lawson, E. J., Lazic, D., et al. (2021). APOE4 accelerates advanced-stage vascular and neurodegenerative disorder in old Alzheimer’s mice via cyclophilin A independently of amyloid-β. Nat. Aging 1, 506–520. doi: 10.1038/s43587-021-00073-z
Morrow, J. A., Segall, M. L., Lund-Katz, S., Phillips, M. C., Knapp, M., Rupp, B., et al. (2000). Differences in stability among the human apolipoprotein E isoforms determined by the amino-terminal domain. Biochemistry 39, 11657–11666. doi: 10.1021/bi000099m
Multhammer, M., Michels, A., Zintl, M., Mendoza, M. C., and Klünemann, H. H. (2014). A large ApoE ε4/ε4 homozygous cohort reveals no association with Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurol. Belg. 114, 25–31. doi: 10.1007/s13760-013-0223-5
Murakami, R., Watanabe, H., Hashimoto, H., Kashiwagi-Hakozaki, M., Hashimoto, T., and Karch, C. M. (2024). Inhibitory roles ofApolipoprotein EChristchurch astrocytes in curbing tau propagation using Human pluripotent stem cell-derived models. J. Neurosci. 44:e1709232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1709-23.2024
Nakamura, T., Watanabe, A., Fujino, T., Hosono, T., and Michikawa, M. (2009). Apolipoprotein E4 (1–272) fragment is associated with mitochondrial proteins and affects mitochondrial function in neuronal cells. Mol. Neurodegener. 4:35. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-4-35
Namba, Y., Tomonaga, M., Kawasaki, H., Otomo, E., and Ikeda, K. (1991). Apolipoprotein E immunoreactivity in cerebral amyloid deposits and neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease and kuru plaque amyloid in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain Res. 541, 163–166. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91092-F
Nathan, B. P., Bellosta, S., Sanan, D. A., Weisgraber, K. H., Mahley, R. W., and Pitas, R. E. (1994). Differential effects of apolipoproteins E3 and E4 on neuronal growth in vitro. Science 264, 850–852. doi: 10.1126/science.8171342
Nation, D. A., Sweeney, M. D., Montagne, A., Sagare, A. P., D’Orazio, L. M., Pachicano, M., et al. (2019). Blood-brain barrier breakdown is an early biomarker of human cognitive dysfunction. Nat. Med. 25, 270–276. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0297-y
Nelson, M. R., Liu, P., Agrawal, A., Yip, O., Blumenfeld, J., Traglia, M., et al. (2023). The APOE-R136S mutation protects against APOE4-driven tau pathology, neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. Nat. Neurosci. 26, 2104–2121. doi: 10.1038/s41593-023-01480-8
Neu, S. C., Pa, J., Kukull, W., Beekly, D., Kuzma, A., Gangadharan, P., et al. (2017). Apolipoprotein E genotype and sex risk factors for Alzheimer disease: a meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 74, 1178–1189. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.2188
Nishitsuji, K., Hosono, T., Nakamura, T., Bu, G., and Michikawa, M. (2011). Apolipoprotein E regulates the integrity of tight junctions in an isoform-dependent manner in an in vitro blood-brain barrier model. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 17536–17542. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.225532
O'Brien, J. T., and Thomas, A. (2015). Vascular dementia. Lancet 386, 1698–1706. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00463-8
Oiwa, K., Watanabe, S., Onodera, K., Iguchi, Y., Kinoshita, Y., Komine, O., et al. (2023). Monomerization of TDP-43 is a key determinant for inducing TDP-43 pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Sci. Adv. 9:eadf6895. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adf6895
Oliveri, R. L., Cittadella, R., Sibilia, G., Manna, I., Valentino, P., and Gambardella, A. (1999). APOE and risk of cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 100, 290–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1999.tb00398.x
Orth, M., Weng, W., Funke, H., Steinmetz, A., Assmann, G., Nauck, M., et al. (1999). Effects of a frequent Apolipoprotein E isoform, ApoE4Freiburg(Leu28→pro), on lipoproteins and the prevalence of coronary artery disease in whites. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 19, 1306–1315. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.19.5.1306
Pankiewicz, J. E., Guridi, M., Kim, J., Asuni, A. A., Sanchez, S., Sullivan, P. M., et al. (2014). Blocking the apoE/Aβ interaction ameliorates Aβ-related pathology in APOE ε2 and ε4 targeted replacement Alzheimer model mice. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2:75.
Pankiewicz, J. E., Lizińczyk, A. M., Franco, L. A., Diaz, J. R., Martá-Ariza, M., and Sadowski, M. J. (2021). Absence of Apolipoprotein E is associated with exacerbation of prion pathology and promotes microglial neurodegenerative phenotype. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 9:157. doi: 10.1186/s40478-021-01261-z
Pankratz, N., Byder, L., Halter, C., Rudolph, A., Shults, C. W., Conneally, P. M., et al. (2006). Presence of an APOE4 allele results in significantly earlier onset of Parkinson's disease and a higher risk with dementia. Mov. Disord. 21, 45–49. doi: 10.1002/mds.20663
Parhizkar, S., Arzberger, T., Brendel, M., Kleinberger, G., Deussing, M., Focke, C., et al. (2019). Loss of TREM2 function increases amyloid seeding but reduces plaque-associated ApoE. Nat. Neurosci. 22, 191–204. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0296-9
Parhizkar, S., and Holtzman, D. M. (2022). APOE mediated neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Semin. Immunol. 59:101594. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2022.101594
Parmenter, B. A., Shucard, J. L., Benedict, R. H., and Shucard, D. W. (2006). Working memory deficits in multiple sclerosis: comparison between the n-back task and the paced auditory serial addition test. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 12, 677–687. doi: 10.1017/S1355617706060826
Paslawski, W., Zareba-Paslawska, J., Zhang, X., Hölzl, K., Wadensten, H., Shariatgorji, M., et al. (2019). α-Synuclein-lipoprotein interactions and elevated ApoE level in cerebrospinal fluid from Parkinson's disease patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 116, 15226–15235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1821409116
Phillips, M. C. (2014). Apolipoprotein E isoforms and lipoprotein metabolism. IUBMB Life 66, 616–623. doi: 10.1002/iub.1314
Pocivavsek, A., Mikhailenko, I., Strickland, D. K., and Rebeck, G. W. (2009). Microglial low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 modulates c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation. J. Neuroimmunol. 214, 25–32. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2009.06.010
Polvikoski, T., Sulkava, R., Haltia, M., Kainulainen, K., Vuorio, A., Verkkoniemi, A., et al. (1995). Apolipoprotein E, dementia, and cortical deposition of beta-amyloid protein. N. Engl. J. Med. 333, 1242–1248. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199511093331902
Qin, L., Zhu, X., and Friedland, R. P. (2020). ApoE and mitochondrial dysfunction. Neurology 94, 1009–1010. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009569
Raber, J., Wong, D., Yu, G. Q., Buttini, M., Mahley, R. W., Pitas, R. E., et al. (2000). Apolipoprotein E and cognitive performance. Nature 404, 352–354. doi: 10.1038/35006165
Raffai, R. L., Dong, L. M., Farese, R. V. Jr., and Weisgraber, K. H. (2001). Introduction of human apolipoprotein E4 "domain interaction" into mouse apolipoprotein E. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 11587–11591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.201279298
Rall, S. C. Jr., Weisgraber, K. H., and Mahley, R. W. (1982). The complete amino acid sequence. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 4171–4178. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)34702-1
Ramassamy, C., Averill, D., Beffert, U., Theroux, L., Lussier-Cacan, S., Cohn, J. S., et al. (2000). Oxidative insults are associated with apolipoprotein E genotype in Alzheimer's disease brain. Neurobiol. Dis. 7, 23–37. doi: 10.1006/nbdi.1999.0273
Rannikmäe, K., Kalaria, R. N., Greenberg, S. M., Chui, H. C., Schmitt, F. A., and Samarasekera, N. (2014). APOE associations with severe CAA-associated vasculopathic changes: collaborative meta-analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 85, 300–305. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2013-306485
Rauch, J. N., Chen, J. J., Sorum, A. W., Miller, G. M., Sharf, T., See, S. K., et al. (2018). Tau internalization is regulated by 6-O Sulfation on Heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs). Sci. Rep. 8:6382. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24904-z
Raulin, A. C., Doss, S. V., Trottier, Z. A., Ikezu, T. C., Bu, G., and Liu, C. C. (2022). ApoE in Alzheimer's disease: pathophysiology and therapeutic strategies. Mol. Neurodegener. 17:72. doi: 10.1186/s13024-022-00574-4
Rawat, V., Wang, S., Sima, J., Bar, R., Liraz, O., Gundimeda, U., et al. (2019). ApoE4 alters ABCA1 membrane trafficking in astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 39, 9611–9622. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1400-19.2019
Riemenschneider, M., Diehl, J., Müller, U., Förstl, H., and Kurz, A. (2002). Apolipoprotein E polymorphism in German patients with frontotemporal degeneration. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 72, 639–641. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.72.5.639
Riku, Y., Yoshida, M., Iwasaki, Y., Sobue, G., Katsuno, M., and Ishigaki, S. (2022). TDP-43 Proteinopathy and Tauopathy: do they have Pathomechanistic links? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:5755. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415755
Rohn, T. T., Catlin, L. W., Coonse, K. G., and Habig, J. W. (2012). Identification of an amino-terminal fragment of apolipoprotein E4 that localizes to neurofibrillary tangles of the Alzheimer's disease brain. Brain Res. 1475, 106–115. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2012.08.003
Ruiz, J., Kouiavskaia, D., Migliorini, M., Robinson, S., Saenko, E. L., Gorlatova, N., et al. (2005). The apoE isoform binding properties of the VLDL receptor reveal marked differences from LRP and the LDL receptor. J. Lipid Res. 46, 1721–1731. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M500114-JLR200
Russo, C., Angelini, G., Dapino, D., Piccini, A., Piombo, G., Schettini, G., et al. (1998). Opposite roles of apolipoprotein E in normal brains and in Alzheimer's disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 15598–15602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.26.15598
Sahebari, S. S., Naseri, A., and Talebi, M. (2023). The association of ApoE genotype and cognitive impairment in multiple sclerosis (MS): a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 80:105217. doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2023.105217
Saido, T., and Leissring, M. A. (2012). Proteolytic degradation of amyloid β-protein. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2:a006379. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a006379
Saito, H., Dhanasekaran, P., Nguyen, D., Baldwin, F., Weisgraber, K. H., Wehrli, S., et al. (2003). Characterization of the heparin binding sites in human apolipoprotein E. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 14782–14787. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M213207200
Sando, S. B., Melquist, S., Cannon, A., Hutton, M. L., Sletvold, O., Saltvedt, I., et al. (2008). APOE epsilon 4 lowers age at onset and is a high risk factor for Alzheimer's disease; a case control study from Central Norway. BMC Neurol. 8:9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2377-8-9
Sarchione, A., Marchand, A., Taymans, J. M., and Chartier-Harlin, M. C. (2021). Alpha-Synuclein and lipids: the elephant in the room? Cells 10:2452. doi: 10.3390/cells10092452
Saunders, A. M., Strittmatter, W. J., Schmechel, D., Pericak-Vance, M. A., Joo, S. H., Rosi, B. L., et al. (1993). Association of apolipoprotein E allele epsilon 4 with late-onset familial and sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 43, 1467–1472. doi: 10.1212/WNL.43.8.1467
Sawcer, S., Maranian, M., Setakis, E., Curwen, V., Akesson, E., Hensiek, A., et al. (2002). A whole genome screen for linkage disequilibrium in multiple sclerosis confirms disease associations with regions previously linked to susceptibility. Brain 125, 1337–1347. doi: 10.1093/brain/awf143
Schmechel, D. E., Saunders, A. M., Strittmatter, W. J., Crain, B. J., Hulette, C. M., Joo, S. H., et al. (1993). Increased amyloid beta-peptide deposition in cerebral cortex as a consequence of apolipoprotein E genotype in late-onset Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 9649–9653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9649
Schneider, W. J., Kovanen, P. T., Brown, M. S., Goldstein, J. L., Utermann, G., Weber, W., et al. (1981). Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia. Abnormal binding of mutant apoprotein E to low density lipoprotein receptors of human fibroblasts and membranes from liver and adrenal of rats, rabbits, and cows. J. Clin. Invest. 68, 1075–1085. doi: 10.1172/JCI110330
Seo, D. O., O’Donnell, D., Jain, N., Ulrich, J. D., Herz, J., Li, Y., et al. (2023). ApoE isoform- and microbiota-dependent progression of neurodegeneration in a mouse model of tauopathy. Science 379:eadd1236.
Sepulveda-Falla, D. (2023). Resistant and resilient mutations in protection against familial Alzheimer’s disease: learning from nature. Mol. Neurodegener. 18:36. doi: 10.1186/s13024-023-00626-3
Serrano-Pozo, A., Das, S., and Hyman, B. T. (2021). APOE and Alzheimer's disease: advances in genetics, pathophysiology, and therapeutic approaches. Lancet Neurol. 20, 68–80. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(20)30412-9
Serrano-Pozo, A., Qian, J., Monsell, S. E., Betensky, R. A., and Hyman, B. T. (2015). APOEε2 is associated with milder clinical and pathological Alzheimer disease. Ann. Neurol. 77, 917–929. doi: 10.1002/ana.24369
Sevigny, J., Chiao, P., Bussière, T., Weinreb, P. H., Williams, L., Maier, M., et al. (2016). The antibody aducanumab reduces Aβ plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Nature 537, 50–56. doi: 10.1038/nature19323
Shea, T. B., Rogers, E., Ashline, D., Ortiz, D., and Sheu, M. S. (2002). Apolipoprotein E deficiency promotes increased oxidative stress and compensatory increases in antioxidants in brain tissue. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 33, 1115–1120. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(02)01001-8
Shi, Y., Yamada, K., Liddelow, S. A., Smith, S. T., Zhao, L., Luo, W., et al. (2017). ApoE4 markedly exacerbates tau-mediated neurodegeneration in a mouse model of tauopathy. Nature 549, 523–527. doi: 10.1038/nature24016
Shi, J., Zhao, C. B., Vollmer, T. L., Tyry, T. M., and Kuniyoshi, S. M. (2008). APOE epsilon 4 allele is associated with cognitive impairment in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 70, 185–190. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000264004.62612.44
Shinohara, M., Murray, M. E., Frank, R. D., Shinohara, M., DeTure, M., Yamazaki, Y., et al. (2016). Impact of sex and APOE4 on cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 132, 225–234. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1580-y
Shinohara, M., Sato, N., Kurinami, H., Takeuchi, D., Takeda, S., Shimamura, M., et al. (2010). Reduction of brain beta-amyloid (Abeta) by fluvastatin, a hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitor, through increase in degradation of amyloid precursor protein C-terminal fragments (APP-CTFs) and Abeta clearance. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 22091–22102. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.102277
Sivashanmugam, A., and Wang, J. (2009). A unified scheme for initiation and conformational adaptation of human apolipoprotein E N-terminal domain upon lipoprotein binding and for receptor binding activity. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 14657–14666. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M901012200
Song, W. M., and Colonna, M. (2018). The identity and function of microglia in neurodegeneration. Nat. Immunol. 19, 1048–1058. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0212-1
Sperling, R. A., Jack, C. R. Jr., Black, S. E., Frosch, M. P., Greenberg, S. M., Hyman, B. T., et al. (2011). Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities in amyloid-modifying therapeutic trials: recommendations from the Alzheimer's Association research roundtable workgroup. Alzheimers Dement. 7, 367–385. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.05.2351
Sperling, R., Salloway, S., Brooks, D. J., Tampieri, D., Barakos, J., Fox, N. C., et al. (2012). Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities in patients with Alzheimer's disease treated with bapineuzumab: a retrospective analysis. Lancet Neurol. 11, 241–249. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(12)70015-7
Stevens, M., van Duijn, C. M., de Knijff, P., van Broeckhoven, C., Heutink, P., Oostra, B. A., et al. (1997). Apolipoprotein E gene and sporadic frontal lobe dementia. Neurology 48, 1526–1529. doi: 10.1212/WNL.48.6.1526
Strittmatter, W. J., Saunders, A. M., Goedert, M., Weisgraber, K. H., Dong, L. M., Jakes, R., et al. (1994). Isoform-specific interactions of apolipoprotein E with microtubule-associated protein tau: implications for Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 11183–11186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11183
Su, W. H., Shi, Z. H., Liu, S. L., Wang, X. D., Liu, S., and Ji, Y. (2017). Updated meta-analysis of the role of APOE ε2/ε3/ε4 alleles in frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Oncotarget 8, 43721–43732. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17341
Sun, Y., Islam, S., Gao, Y., Nakamura, T., Zou, K., and Michikawa, M. (2023). Apolipoprotein E4 inhibits γ-secretase activity via binding to the γ-secretase complex. J. Neurochem. 164, 858–874. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15750
Sun, L., Zhou, R., Yang, G., and Shi, Y. (2017). Analysis of 138 pathogenic mutations in presenilin-1 on the in vitro production of Aβ42 and Aβ40 peptides by γ-secretase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 114, E476–e485.
Tai, L. M., Balu, D., Avila-Munoz, E., Abdullah, L., Thomas, R., Collins, N., et al. (2017). EFAD transgenic mice as a human APOE relevant preclinical model of Alzheimer's disease. J. Lipid Res. 58, 1733–1755. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R076315
Tarasoff-Conway, J. M., Carare, R. O., Osorio, R. S., Glodzik, L., Butler, T., Fieremans, E., et al. (2015). Clearance systems in the brain-implications for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 11, 457–470. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2015.119
Tarr, P. T., and Edwards, P. A. (2008). ABCG1 and ABCG4 are coexpressed in neurons and astrocytes of the CNS and regulate cholesterol homeostasis through SREBP-2. J. Lipid Res. 49, 169–182. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M700364-JLR200
Teter, B., Xu, P. T., Gilbert, J. R., Roses, A. D., Galasko, D., and Cole, G. M. (1999). Human apolipoprotein E isoform-specific differences in neuronal sprouting in organotypic hippocampal culture. J. Neurochem. 73, 2613–2616. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1999.0732613.x
Teter, B., Xu, P. T., Gilbert, J. R., Roses, A. D., Galasko, D., and Cole, G. M. (2002). Defective neuronal sprouting by human apolipoprotein E4 is a gain-of-negative function. J. Neurosci. Res. 68, 331–336. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10221
Therriault, J., Benedet, A. L., Pascoal, T. A., Mathotaarachchi, S., Chamoun, M., Savard, M., et al. (2020). Association of Apolipoprotein E ε4 with medial temporal tau independent of amyloid-β. JAMA Neurol. 77, 470–479. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.4421
Tiraboschi, P., Hansen, L. A., Masliah, E., Alford, M., Thal, L. J., and Corey-Bloom, J. (2004). Impact of APOE genotype on neuropathologic and neurochemical markers of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 62, 1977–1983. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000128091.92139.0F
Tropea, T. F., Xie, S. X., Rick, J., Chahine, L. M., Dahodwala, N., Doshi, J., et al. (2018). APOE, thought disorder, and SPARE-AD predict cognitive decline in established Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. 33, 289–297. doi: 10.1002/mds.27204
Trushina, E., Singh, R. D., Dyer, R. B., Cao, S., Shah, V. H., Parton, R. G., et al. (2006). Mutant huntingtin inhibits clathrin-independent endocytosis and causes accumulation of cholesterol in vitro and in vivo. Hum. Mol. Genet. 15, 3578–3591. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl434
Tsuang, D., Leverenz, J. B., Lopez, O. L., Hamilton, R. L., Bennett, D. A., Schneider, J. A., et al. (2013). APOE ε4 increases risk for dementia in pure synucleinopathies. JAMA Neurol. 70, 223–228. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.600
Tzioras, M., McGeachan, R. I., Durrant, C. S., and Spires-Jones, T. L. (2023). Synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 19, 19–38. doi: 10.1038/s41582-022-00749-z
Tziortzouda, P., Van Den Bosch, L., and Hirth, F. (2021). Triad of TDP43 control in neurodegeneration: autoregulation, localization and aggregation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 22, 197–208. doi: 10.1038/s41583-021-00431-1
Ulland, T. K., and Colonna, M. (2018). TREM2 - a key player in microglial biology and Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 14, 667–675. doi: 10.1038/s41582-018-0072-1
Ulrich, J. D., Ulland, T. K., Mahan, T. E., Nyström, S., Nilsson, K. P., Song, W. M., et al. (2018). ApoE facilitates the microglial response to amyloid plaque pathology. J. Exp. Med. 215, 1047–1058. doi: 10.1084/jem.20171265
Utermann, G., Hees, M., and Steinmetz, A. (1977). Polymorphism of apolipoprotein E and occurrence of dysbetalipoproteinaemia in man. Nature 269, 604–607. doi: 10.1038/269604a0
Valenza, M., Leoni, V., Karasinska, J. M., Petricca, L., Fan, J., Carroll, J., et al. (2010). Cholesterol defect is marked across multiple rodent models of Huntington's disease and is manifest in astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 30, 10844–10850. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0917-10.2010
Valenza, M., Marullo, M., di Paolo, E., Cesana, E., Zuccato, C., Biella, G., et al. (2015). Disruption of astrocyte-neuron cholesterol cross talk affects neuronal function in Huntington's disease. Cell Death Differ. 22, 690–702. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.162
van der Burg, J. M., Björkqvist, M., and Brundin, P. (2009). Beyond the brain: widespread pathology in Huntington's disease. Lancet Neurol. 8, 765–774. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70178-4
van Steenoven, I., Koel-Simmelink, M. J. A., Vergouw, L. J. M., Tijms, B. M., Piersma, S. R., Pham, T. V., et al. (2020). Identification of novel cerebrospinal fluid biomarker candidates for dementia with Lewy bodies: a proteomic approach. Mol. Neurodegener. 15:36. doi: 10.1186/s13024-020-00388-2
Vance, J. E., and Hayashi, H. (2010). Formation and function of apolipoprotein E-containing lipoproteins in the nervous system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1801, 806–818. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.02.007
VandeVrede, L., Gibbs, D. M., Koestler, M., la Joie, R., Ljubenkov, P. A., Provost, K., et al. (2020). Symptomatic amyloid-related imaging abnormalities in an APOE ε4/ε4 patient treated with aducanumab. Alzheimer Dementia Diag. Assessment Dis. Monitor. 12:e12101. doi: 10.1002/dad2.12101
Vázquez-Vélez, G. E., and Zoghbi, H. Y. (2021). Parkinson's disease genetics and pathophysiology. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 44, 87–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-100720-034518
Verghese, P. B., Castellano, J. M., and Holtzman, D. M. (2011). Apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer's disease and other neurological disorders. Lancet Neurol. 10, 241–252. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70325-2
Vitek, M. P., Christensen, D. J., Wilcock, D., Davis, J., van Nostrand, W. E., Li, F. Q., et al. (2012). APOE-mimetic peptides reduce behavioral deficits, plaques and tangles in Alzheimer's disease transgenics. Neurodegener Dis 10, 122–126. doi: 10.1159/000334914
Wadhwani, A. R., Affaneh, A., van Gulden, S., and Kessler, J. A. (2019). Neuronal apolipoprotein E4 increases cell death and phosphorylated tau release in Alzheimer disease. Ann. Neurol. 85, 726–739. doi: 10.1002/ana.25455
Wahrle, S. E., Jiang, H., Parsadanian, M., Hartman, R. E., Bales, K. R., Paul, S. M., et al. (2005). Deletion of Abca1 increases Abeta deposition in the PDAPP transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 43236–43242. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M508780200
Wahrle, S. E., Jiang, H., Parsadanian, M., Kim, J., Li, A., Knoten, A., et al. (2008). Overexpression of ABCA1 reduces amyloid deposition in the PDAPP mouse model of Alzheimer disease. J. Clin. Invest. 118, 671–682. doi: 10.1172/JCI33622
Wahrle, S. E., Jiang, H., Parsadanian, M., Legleiter, J., Han, X., Fryer, J. D., et al. (2004). ABCA1 is required for normal central nervous system ApoE levels and for lipidation of astrocyte-secreted apoE. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 40987–40993. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407963200
Wang, Y., and Mandelkow, E. (2016). Tau in physiology and pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 5–21. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2015.1
Wang, C., Najm, R., Xu, Q., Jeong, D. E., Walker, D., Balestra, M. E., et al. (2018). Gain of toxic apolipoprotein E4 effects in human iPSC-derived neurons is ameliorated by a small-molecule structure corrector. Nat. Med. 24, 647–657. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0004-z
Wang, C., Xiong, M., Gratuze, M., Bao, X., Shi, Y., Andhey, P. S., et al. (2021). Selective removal of astrocytic APOE4 strongly protects against tau-mediated neurodegeneration and decreases synaptic phagocytosis by microglia. Neuron 109, 1657–1674. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.03.024
Weisgraber, K. H. (1994). Apolipoprotein E: structure-function relationships. Adv. Protein Chem. 45, 249–302. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3233(08)60642-7
Weisgraber, K. H., Rall, S. C. Jr., and Mahley, R. W. (1981). Cysteine-arginine interchanges in the amino acid sequence of the apo-E isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 256, 9077–9083. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)52510-8
Wennberg, A. M., Tosakulwong, N., Lesnick, T. G., Murray, M. E., Whitwell, J. L., Liesinger, A. M., et al. (2018). Association of Apolipoprotein E ε4 with transactive response DNA-binding protein 43. JAMA Neurol. 75, 1347–1354. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2018.3139
Wilson, C., Wardell, M. R., Weisgraber, K. H., Mahley, R. W., and Agard, D. A. (1991). Three-dimensional structure of the LDL receptor-binding domain of human apolipoprotein E. Science 252, 1817–1822. doi: 10.1126/science.2063194
Wynne, M. E., Ogunbona, O., Lane, A. R., Gokhale, A., Zlatic, S. A., Xu, C., et al. (2023). APOE expression and secretion are modulated by mitochondrial dysfunction. eLife 12:e85779. doi: 10.7554/eLife.85779.sa0
Xu, Q., Bernardo, A., Walker, D., Kanegawa, T., Mahley, R. W., and Huang, Y. (2006). Profile and regulation of apolipoprotein E (ApoE) expression in the CNS in mice with targeting of green fluorescent protein gene to the ApoE locus. J. Neurosci. 26, 4985–4994. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5476-05.2006
Xu, Q., Brecht, W. J., Weisgraber, K. H., Mahley, R. W., and Huang, Y. (2004). Apolipoprotein E4 domain interaction occurs in living neuronal cells as determined by fluorescence resonance energy transfer. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 25511–25516. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M311256200
Yamauchi, Y., Deguchi, N., Takagi, C., Tanaka, M., Dhanasekaran, P., Nakano, M., et al. (2008). Role of the N- and C-terminal domains in binding of apolipoprotein E isoforms to heparan sulfate and dermatan sulfate: a surface plasmon resonance study. Biochemistry 47, 6702–6710. doi: 10.1021/bi8003999
Yamazaki, Y., Painter, M. M., Bu, G., and Kanekiyo, T. (2016). Apolipoprotein E as a therapeutic target in Alzheimer's disease: a review of basic research and clinical evidence. CNS Drugs 30, 773–789. doi: 10.1007/s40263-016-0361-4
Yamazaki, Y., Zhao, N., Caulfield, T. R., Liu, C. C., and Bu, G. (2019). Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: pathobiology and targeting strategies. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 15, 501–518. doi: 10.1038/s41582-019-0228-7
Yang, L., Liu, C. C., Zheng, H., Kanekiyo, T., Atagi, Y., Jia, L., et al. (2016). LRP1 modulates the microglial immune response via regulation of JNK and NF-κB signaling pathways. J. Neuroinflammation 13:304. doi: 10.1186/s12974-016-0772-7
Yang, H. S., Yu, L., White, C. C., Chibnik, L. B., Chhatwal, J. P., Sperling, R. A., et al. (2018). Evaluation of TDP-43 proteinopathy and hippocampal sclerosis in relation to APOE ε4 haplotype status: a community-based cohort study. Lancet Neurol. 17, 773–781. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30251-5
Yin, C., Ackermann, S., Ma, Z., Mohanta, S. K., Zhang, C., Li, Y., et al. (2019). ApoE attenuates unresolvable inflammation by complex formation with activated C1q. Nat. Med. 25, 496–506. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0336-8
Yin, Y. W., Li, J. C., Wang, J. Z., Li, B. H., Pi, Y., Yang, Q. W., et al. (2012). Association between apolipoprotein E gene polymorphism and the risk of vascular dementia: a meta-analysis. Neurosci. Lett. 514, 6–11. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.02.031
Yin, J., Reiman, E. M., Beach, T. G., Serrano, G. E., Sabbagh, M. N., Nielsen, M., et al. (2020). Effect of ApoE isoforms on mitochondria in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 94, e2404–e2411. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009582
Zannis, V. I., and Breslow, J. L. (1981). Human very low density lipoprotein apolipoprotein E isoprotein polymorphism is explained by genetic variation and posttranslational modification. Biochemistry 20, 1033–1041. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a059
Zhang, W., Xiao, D., Mao, Q., and Xia, H. (2023). Role of neuroinflammation in neurodegeneration development. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 8:267. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01486-5
Zhao, N., Attrebi, O. N., Ren, Y., Qiao, W., Sonustun, B., Martens, Y. A., et al. (2020). APOE4 exacerbates α-synuclein pathology and related toxicity independent of amyloid. Sci. Transl. Med. 12:1809. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aay1809
Zhao, J., Fu, Y., Yamazaki, Y., Ren, Y., Davis, M. D., Liu, C. C., et al. (2020). APOE4 exacerbates synapse loss and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease patient iPSC-derived cerebral organoids. Nat. Commun. 11:5540. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19264-0
Zhao, N., Liu, C. C., Qiao, W., and Bu, G. (2018). Apolipoprotein E, receptors, and modulation of Alzheimer's disease. Biol. Psychiatry 83, 347–357. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.03.003
Keywords: apolipoprotein E, Alzheimer’s disease, amyloid-β (Aβ), Parkinson’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, neurodegenerative diseases
Citation: Islam S, Noorani A, Sun Y, Michikawa M and Zou K (2025) Multi-functional role of apolipoprotein E in neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Aging Neurosci. 17:1535280. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1535280
Received: 27 November 2024; Accepted: 13 January 2025;
Published: 29 January 2025.
Edited by:
Wei-Jye Lin, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, ChinaReviewed by:
Celia Giulietta Fernandez, Recursion Pharmaceuticals, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Islam, Noorani, Sun, Michikawa and Zou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Kun Zou, a3Vuem91QG1lZC5uYWdveWEtY3UuYWMuanA=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.