
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Aging Neurosci., 14 March 2025
Sec. Neurocognitive Aging and Behavior
Volume 17 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2025.1534824
This article is part of the Research TopicThe Open Challenges of Cognitive Frailty: Risk Factors, Neuropsychological Profiles and Psychometric Assessment for Healthy AgingView all 17 articles
 Yi Zhang1†
Yi Zhang1† Guifen Cheng1†
Guifen Cheng1† Ling Chen2
Ling Chen2 Xiaoxia Wang3
Xiaoxia Wang3 Lixia Lin1
Lixia Lin1 Qiao Huang3
Qiao Huang3 Jinhua Guo1
Jinhua Guo1 Bei Gong1
Bei Gong1 Tiemei Shen4*
Tiemei Shen4*Background and aims: As the country with the largest and fastest-aging older population worldwide, China has hosted an increasing number of regional investigations into disability among older adults. However, the prevalence of disabilities related to physical function and cognition in southern China remains unknown. This study aimed to assess the prevalence of and associated factors for cognitive and physical function impairment in individuals aged 60 years and older.
Methods: For this population-based cross-sectional study, a total of 5,603 participants were recruited between June 2021 and December 2022 using a multistage, stratified, cluster sampling procedure. Instruments, including a general questionnaire, basic and instrumental activities of daily living, the Chinese version of the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9), and the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7), were used to collect data through a WeChat mini program. Binary and multivariate logistic regression analyses were applied to explore the influencing factors.
Results: The prevalence of physical function and cognitive impairment among older adults was 37.3 and 31.0%, respectively. Multivariate regression analyses revealed that age, family income, education level, place of residence, medication type, annual physical examinations, weekly social activities, support from family or friends, hearing disorders, walking disorders, and depression were all associated with both physical function and cognitive impairment. Moreover, an increased risk of physical function impairment correlated with BMI, region, income source, smoking, and weekly exercise, while cognitive impairment was associated with the number of children, insurance type, coronary heart disease, and anxiety. Physical function (OR: 1.79, 95% CI: 1.49–2.16) and cognitive impairment (OR: 1.83, 95% CI: 1.51–2.21) were mutually influential in our study.
Conclusion: This study showed a high prevalence of various factors related to physical function and cognitive impairment. The results revealed that comprehensive and systematic prevention and control programs for disabilities should be developed to improve the quality of life for older adults.
With the growing trend of an aging population, China has gradually come to be regarded as having the largest elderly population worldwide, resulting in a substantial treatment-related economic burden for families and the healthcare system (Qiao et al., 2022; Han et al., 2022). According to the 7th national census in 2020, there were 26,402 million people aged 60 years or older in China, accounting for 18.7% of the total population, which was 5.4% higher than in 2010 (Statistic N B O, 2021). As a populous country experiencing rapid and significant aging, the health status of elderly individuals is concerning (Damluji et al., 2021; Han et al., 2022). Older adults face various physical and mental health issues, leading to lengthy durations of illness and a significant increase in the number of older adults with disabilities. Wang and Li (2020) reported that the estimated proportion of disabled older adults within the total population is rising year by year and is expected to reach 13.7% by 2050. Disability status not only affects the overall quality of life among older adults but also contributes to a greater demand for long-term care and associated costs, ultimately posing a substantial challenge to social care and medical security (Hsieh and Waite, 2019; Liao et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2022). Therefore, exploring the relationship between disability status and chronic diseases, the mechanisms and risk factors contributing to disability, and the establishment of prevention and treatment systems for disabilities has gradually become an important research topic in gerontology.
Disability status is a fundamental measure for assessing the functional capacity and health level of older adults (Wang and Li, 2020). The World Health Organization (WHO) and the Chinese disability classification standard define disability to encompass physical, visual, hearing, phonological, and cognitive impairment (Abdi et al., 2019).
The functional state used to define physical disability typically consists of activities of daily living (ADL), muscle strength, balance, and gait speed (Rajan et al., 2012). ADL assessment—which includes basic activities of daily living (BADL) and instrumental activities of daily living (IADL)—is regarded as a primary aspect widely used in previous studies (Wang et al., 2023; Rajan et al., 2012) to determine physical function or self-care ability among older adults due to its relatively simple and convenient nature.
BADLs refer to basic self-care activities, such as eating and dressing, that fulfill essential physiological requirements, while IADLs include more complex tasks that arise later and typically have a shorter duration than BADLs (Gold, 2012; Cornelis et al., 2019).
Cognitive impairment leading to dementia is a serious global public health concern, influenced by the growing number of older adults and recognized as a vital indicator for assessing disability (Inocian and Patalagsa, 2016). Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) represents an intermediate stage between normal cognition and dementia, and a growing body of research focused on risk management and interventions has focused on these individuals to prevent dementia (Tangalos and Petersen, 2018; Campbell et al., 2013). In the past 3 years, several studies have been conducted on the current circumstances of older adults with MCI or dementia, with estimated prevalence ranging from 1.2 to 23.2% (Xue et al., 2022; Teh et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2021; Vlachos et al., 2020) and nearly 15% in China (Deng et al., 2021; Jia et al., 2020).
Previous population-based regional studies investigated factors related to physical or cognitive function, such as age (Xue et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2018; Choi et al., 2019), education level (Xue et al., 2022; Jia et al., 2020; Goswami et al., 2019; Ravi et al., 2022), place of residence (Deng et al., 2021; Cheng et al., 2023; Chuang et al., 2021), illness state (Xue et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2021; Jia et al., 2020; Fuller-Thomson et al., 2022; Deckers et al., 2017), and mental problems (Freire et al., 2017; Desai et al., 2021; Kang et al., 2017). However, due to subjective characteristics or measuring approaches, there are still some controversies regarding the factors influencing disability. Moreover, these factors consistently change with social development, lifestyle, and regional environment.
China has the largest population of disabled and semi-disabled older adults in the world due to the increasing rate of deep aging. It is particularly important to explore and establish a long-term care service model and to conduct health function assessments for older adults with disabilities, from family and community settings to professional institutions, in order to promote long-term care services. There is a significant developmental gap between urban and rural areas in China, leading to major discrepancies in functional status among older adults in various institutions, including hospitals, communities, and nursing homes for the elderly. Surveys that capture regional characteristics regarding functional status and related factors among older adults are crucial to meeting diverse service needs. Although an increasing number of regional surveys targeting the prevalence of and factors influencing older adults with disabilities have been conducted nationwide in recent years, little is known about the prevalence of disability in the southern region. Furthermore, the definition of disability in most studies has been based on only a single aspect.
In view of the aforementioned variable factors related to disability and aiming to develop a more comprehensive understanding of the concept, we conducted a large cross-sectional study involving adults aged 60 years or older from approximately six cities in Guangdong Province, China. The aim was to explore the prevalence, associations, and influencing factors of disability related to physical function and cognitive impairment in older adults.
The present study’s hypotheses are as follows: First, there is a high incidence of physical or cognitive impairment in southern China. Second, both physical and cognitive impairments are associated with several factors, including sociodemographic, disease-related, behavior-related, and psychological factors. Finally, there is a significant relationship between physical and cognitive impairments.
We conducted a population-based observational cross-sectional study using a multistage, stratified, cluster-sampling procedure from June 2021 to December 2022.
The selection of study sites was divided into three stages. First, we selected 1–2 representative cities from the northern, southern, western, and eastern regions of Guangdong Province. Second, we chose 2–3 well-known or representative tertiary hospitals and one secondary hospital in the geriatric field. Given the significant discrepancy in functional states among hospitalized and non-hospitalized older adults, we included only those subjects who regularly attended outpatient follow-ups or utilized daily healthcare services. Third, we selected one community healthcare center and 60–70 families based on the community resident health files. Finally, we included 5,603 adults aged 60 years or older from 15 tertiary hospitals, six secondary hospitals, six community healthcare centers, and 350 families across six cities (Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Zhuhai, Foshan, Maoming, and Qingyuan). The inclusion criteria for participants were as follows: (1) aged≥60 years, (2) able to communicate normally without barriers, and (3) having provided informed consent for voluntary participation in this study. The exclusion criteria included: (1) having mental disorders or a history of mental disorders (e.g., depression and schizophrenia), (2) a diagnosis of dementia, (3) any acute diseases (e.g., myocardial infarction, and stroke), and (4) any conditions leading to limb movement disorders (e.g., trauma, surgery, and musculoskeletal diseases).
This questionnaire was developed by researchers based on related previous studies (Qiao et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2018; Ding et al., 2015; Qin et al., 2022; Ramadass et al., 2018), and research content and was reviewed by two experts, Cui and Chen, prior to the pilot study. The evaluation of general information consisted of four main domains: (1) Demographic characteristics: age, sex, BMI, number of children, and more; (2) Behavioral habits: smoking, drinking, annual physical examinations, weekly social activities, and weekly exercise; (3) Family or social support: assistance from family or care from friends; and (4) Disease-related characteristics: cardiovascular or cerebrovascular diseases, hypertension, coronary heart disease, diabetes, type of medication, hearing disorders, vision disorders, and walking impairments. Participants were asked to indicate whether hearing, vision, or walking had an impact on the daily life of older adults, with three options: no effect, less effect, and obvious effect. The responses of “less effect” or “obvious effect” were deemed indicators of functional impairment in hearing, vision, or walking.
This was evaluated using an assessment of activities of daily living (ADLs). ADLs are defined as the essential activities required for daily life, reflecting the fundamental functions of individuals in medical institutions, communities, and families (Cornelis et al., 2019; De Vriendt et al., 2021). The assessment of ADLs is divided into basic activities of daily living (BADLs) and instrumental activities of daily living (IADLs). BADLs pertain to the critical movements and self-care tasks performed in hospitals or at home, which include eight items: eating, bathing, combing, dressing, controlling urination, managing excretion, walking, and ascending and descending stairs (Cornelis et al., 2019). IADLs refer to more complex activities than BADLs, such as those necessitating advanced skills and the use of tools performed within communities. These activities include seven items: shopping, cycling or riding, cooking, doing housework, washing clothes, making phone calls, and taking medication (De Vriendt et al., 2021; Bruderer-Hofstetter et al., 2022).
Each category is assessed on three levels: no assistance, partial assistance, and full assistance. Responses indicating anything other than “no assistance” for each category suggest functional impairment, which is considered a disability.
Cognitive impairment was evaluated using the Chinese version of the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), which has received authorization for its use (Wang and Zhang, 1989). This scale consists of 30 items across four dimensions: orientation, memory, attention and calculation, recall, and language. The sensitivity of this assessment for screening cognitive impairment reached up to 92.5% (Bo et al., 2018). This is the most common and widely used assessment worldwide, designed by Folstein in 1975 (Cockrell and Folstein, 1988). Each correct answer earns one point, while an incorrect or unclear response earns no points. The maximum score on the scale is 30 points, with lower scores indicating more severe cognitive impairment. The cutoff points for cognitive impairment were calculated based on education level: ≤19 points for illiterate individuals, ≤22 points for those with a primary school education, and ≤ 26 points for individuals with a secondary school education or above.
These symptoms were assessed using the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9). This questionnaire was used to assess the frequency of nine conditions over the past 2 weeks: displeasure, appetite changes, fatigue, feelings of worthlessness, guilt, decreased concentration, slow movements, restlessness, and suicidal tendencies (Kroenke et al., 2001). Each item is rated on a 4-point Likert scale, with total scores ranging from 0 to 27. Depressive symptoms are categorized into four levels: mild (5–9), moderate (10–14), moderate–severe (15–19), and severe (20–27).
This was measured using the Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 (GAD-7) questionnaire. This tool assessed the frequency of seven conditions over the 2 weeks: tension, uncontrollable worries, excessive worries, an inability to relax, akathisia, irritability, and foreboding (Löwe et al., 2008). Each question is evaluated on a 4-point Likert scale, with total scores ranging from 0 to 21. Depressive symptoms are categorized into four levels: mild (5–9), moderate (10–13), moderate–severe (14–18), and severe (19–21).
All procedures conducted in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee, the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments, or comparable ethical standards. The ethics committee of Guangdong Province People’s Hospital (KY-Z-2021-690-01). Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Data collection was conducted using the WeChat mini program called “Jingyice platform for the functional assessment of older adults.” First, we contacted the relevant leaders of selected hospitals and communities to obtain permission for the investigation. Specialized interviewers assigned to each hospital and community were responsible for collecting information in their specific research areas.
A door-to-door survey of families was conducted by interviewers from the respective communities. To ensure a uniform investigation process, online training on questionnaire interpretation and methods was organized, along with a preliminary survey held prior to the formal survey. Interviewers followed standardized instructions to present the study’s objectives and content and engaged in one-on-one, face-to-face dialogue to gather information after obtaining informed consent. Inquiries about family members or caregivers were allowed if participants were unable to communicate directly with interviewers due to speech or hearing disorders. Each data point was securely stored in a file accessible only to authorized personnel.
SPSS software version 26.0 was used to analyze the data. Descriptive statistics were employed to identify the distribution of the included factors. Means and standard deviations were used to describe continuous variables, while absolute values and percentages were used to express categorical variables. Independent-sample t-tests and chi-square tests were conducted to compare sex differences across each continuous and categorical variable, respectively. Univariate analysis was conducted through bivariate logistic regression to determine whether independent variables, including demographic characteristics, behavioral habits, social support, and disease-related factors, were associated with physical function impairment and cognitive impairment, with estimated odds ratios and 95% confidence intervals provided.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis was conducted to identify the influencing factors, treating the aforementioned variables as independent variables and physical-function impairment or cognitive impairment as dependent variables. A two-sided p-value < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
A total of 5,603 adults aged 60 years and older were enrolled in this survey, of whom 2,675 (47.4%) were men and 2,946 (52.6%) were women. The average age of the participants was 71.38 ± 7.65 old. The majority of the older adults lived in Guangdong Province during the survey, including 3,356 (59.9%) subjects living in Guangzhou or Shenzhen and 2,100 (37.5%) participants living in other cities within Guangdong.
The largest proportion of participants in this survey came from the rural population, which accounted for 41.5% of the total. Different levels of anxiety and depression symptoms were observed in 28.2 and 20.5% of subjects, respectively. A total of 2,089 participants aged 60 years or older exhibited a decline in physical function as measured via BADLs and IADLs, with a prevalence of 37.3%. Cognitive impairment, evaluated using the MMSE, was found in 1,378 participants aged 60 years or older, with a prevalence of 31.0%.
There was a significant difference between the sexes, including factors such as age, number of children, religion, living arrangements with children, monthly family income, source of income, education level, marital status, type of insurance, hypertension, coronary heart disease, alcohol consumption, smoking, care from family or friends, vision, walking ability, physical function impairment, and cognitive impairment. The general characteristics of the participants and the prevalence of disability are shown in Table 1.
As shown in Table 2, variables extracted through univariate analysis with statistical significance were included to establish a multivariate logistic regression. The results indicated that older age (OR: 1.06, 95% CI: 1.05, 1.07) and a higher BMI (OR: 1.03, 95% CI: 1.01, 1.05) were associated with an increased risk of physical function impairment. Older adults living in other cities in Guangdong, receiving income from children, being illiterate, and residing in large cities faced a higher risk of physical function impairment. A family monthly income between 2000 and 4,000¥ (OR: 1.40, 95% CI: 1.13, 1.72) or between 4,000 and 6,000¥ (OR: 1.51, 95% CI: 1.18, 1.92) was linked to an increased risk of physical function impairment. Regarding behavioral habits, older adults who had never smoked, had not received an annual physical examination in the past 10 years, and did not participate in weekly social activities were more likely to experience physical function impairment. In terms of family or social support, older adults not cared for by family or friends were at a greater risk of physical function impairment. For disease-related characteristics, taking multiple types of medication, having hearing disorders (OR: 1.24, 95% CI: 1.09, 1.43), and having impaired walking ability (OR: 6.35, 95% CI: 5.39, 7.45) were also correlated with a higher risk of physical function impairment. For psychological factors, older adults suffering from mild (OR: 1.58, 95% CI: 1.52, 2.00), moderate (OR: 3.46, 95% CI: 2.13, 5.61), or moderate–severe (OR: 3.94, 95% CI: 1.70, 9.12) depression showed an increasing risk of physical function impairment. The multivariate logistic regression analysis of risk factors for physical impairment among adults aged 60 years or older is presented in Table 3 and Figure 1.
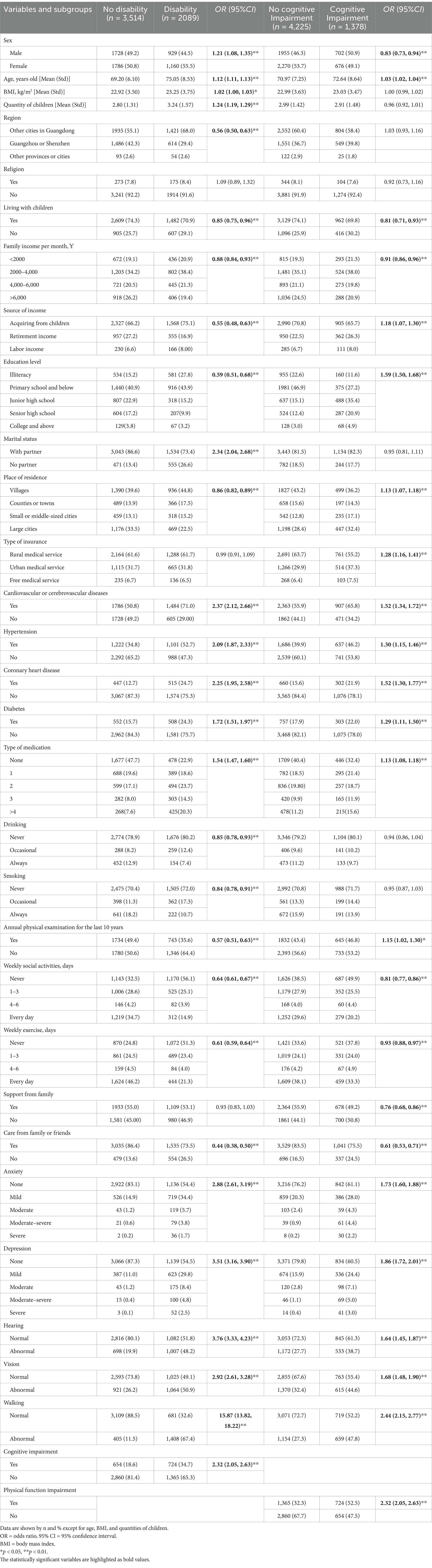
Table 2. Univariate analysis of influencing factors for physical function or cognitive impairment (n = 5,603).
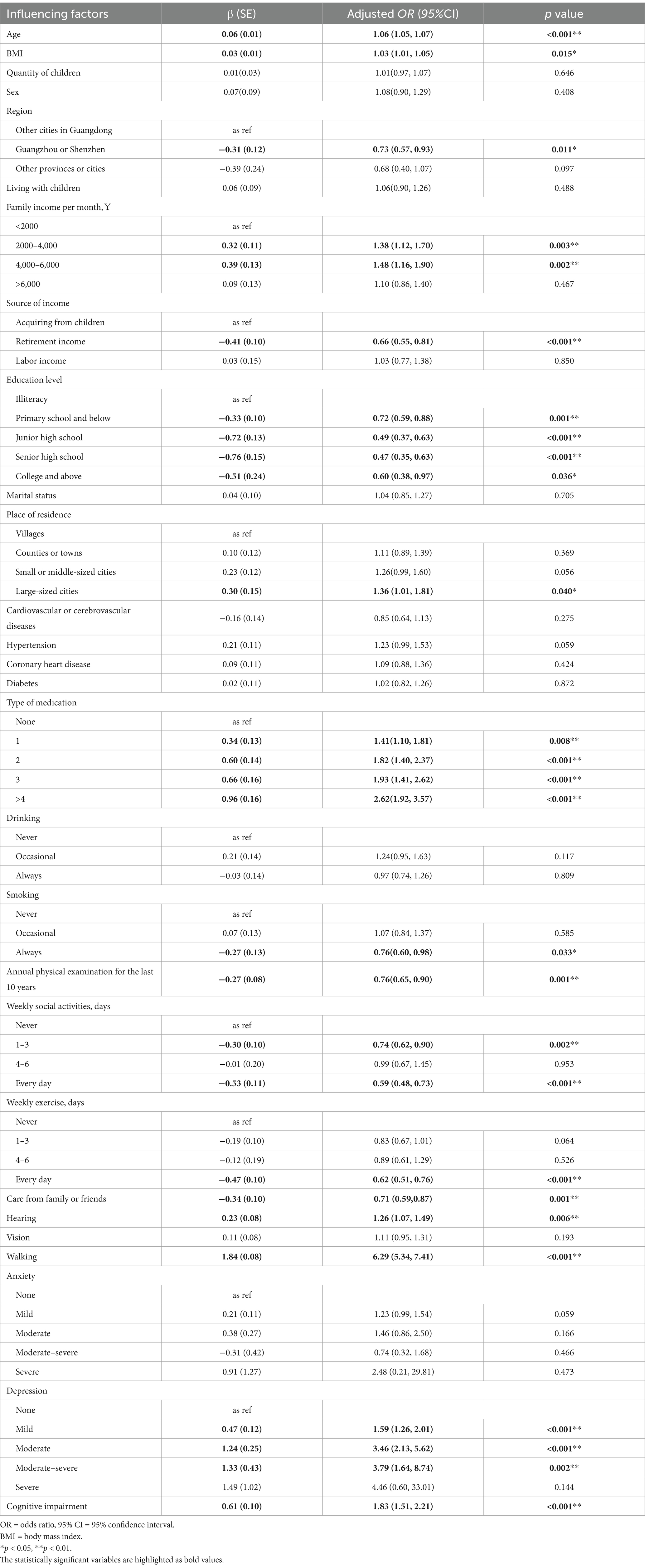
Table 3. Multivariate logistic regression analysis of influencing factors for physical function impairment (n = 5,603).
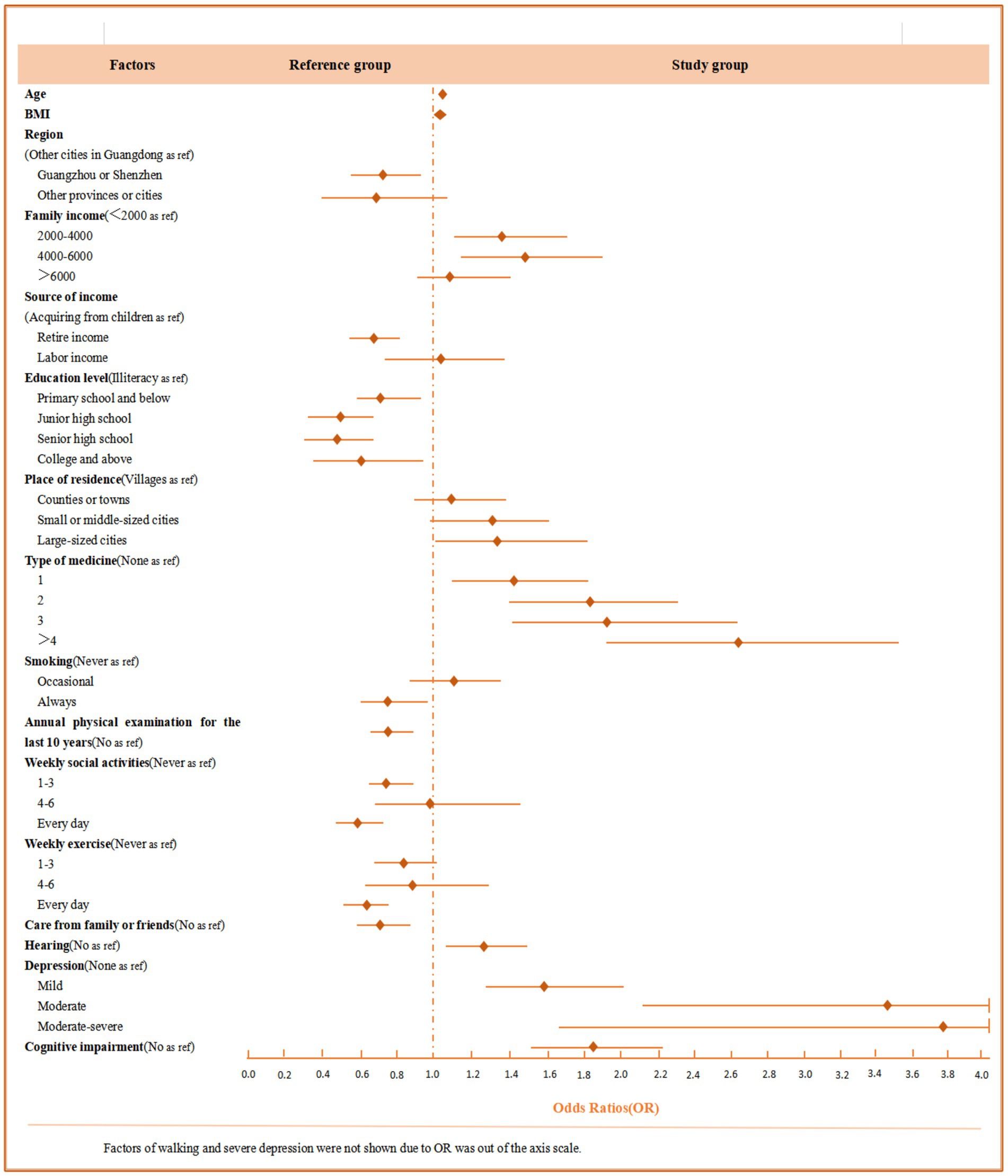
Figure 1. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) for factors that are statistically significant in relation to physical function impairment.
The results of the multivariate logistic regression analysis of risk factors for cognitive impairment are shown in Table 4 and Figure 2. For demographic characteristics, older age was associated with a higher risk of cognitive impairment (OR: 1.02 95% CI: 1.01–1.03), as was having fewer children. Education level also played a significant role, with a higher risk observed among those with primary school (OR: 1.75, 95%CI: 1.40–2.22), junior high school (OR: 11.59, 95% CI: 8.96–15.00), senior high school (OR: 8.71, 95% CI: 6.57–11.56), or college education (OR: 7.14, 95%CI: 4.70–10.86). Additionally, older adults with a family income of <2000¥ and those relying on rural medical services had a higher risk of cognitive impairment. Living in small or middle-sized cities (OR: 1.49, 95%CI: 1.19–1.87) or large cities (OR: 1.68, 95% CI: 1.38–2.05) was related to an increased risk compared to those living in villages.
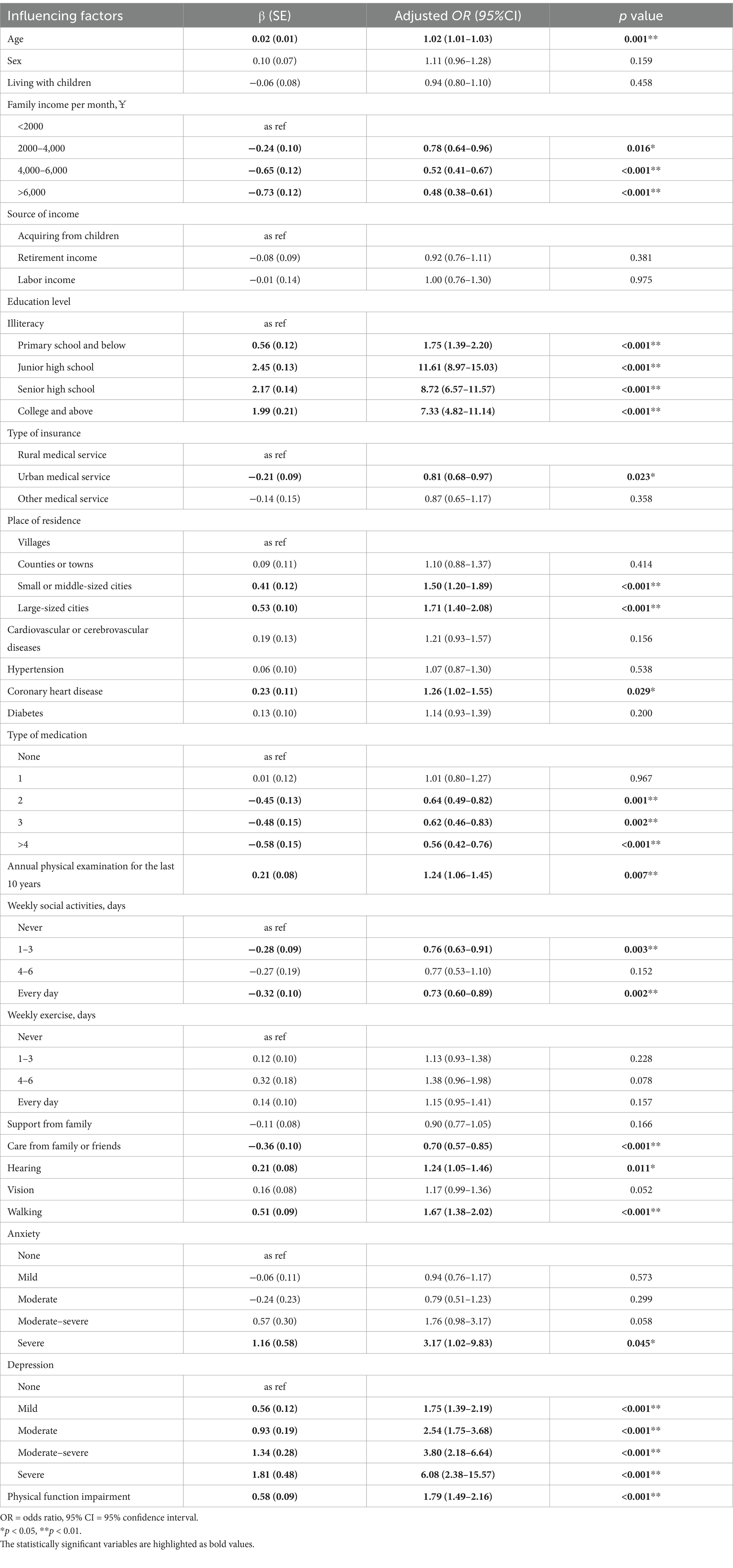
Table 4. Multivariate logistic regression analysis of influencing factors for cognitive impairment (n = 5,603).
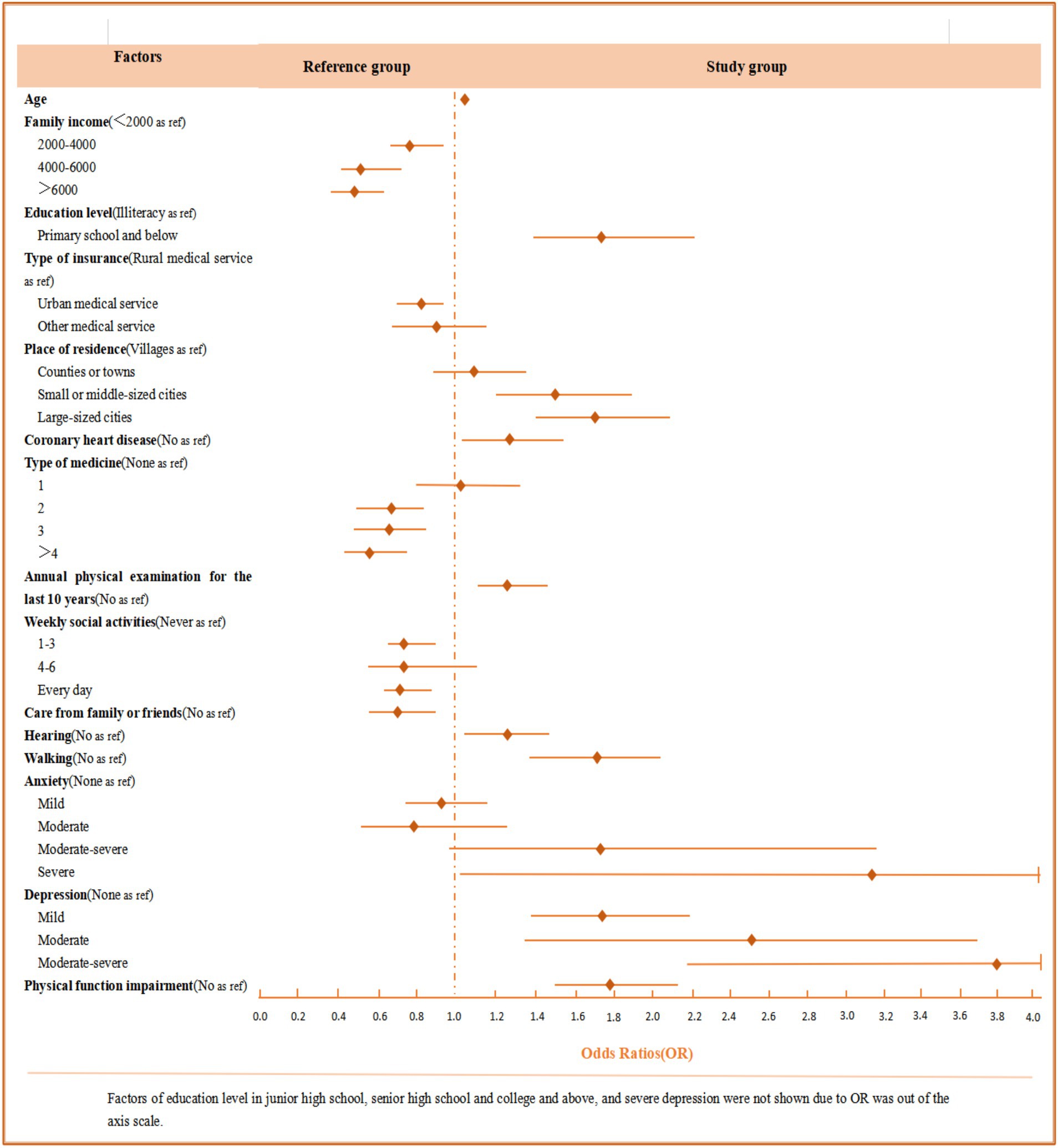
Figure 2. Odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) for factors that are statistically significant regarding cognitive impairment.
Regarding behavior habits, older adults who had undergone annual physical examinations over the last decade (OR: 1.23, 95%CI: 1.05–1.44) and those who did not participate in weekly social activities were more likely to develop cognitive impairment. In terms of family or social support, older adults who were not cared for by family or friends were at a higher risk of cognitive impairment. Several health conditions were also found to be significantly associated with cognitive impairment, such as coronary heart disease (OR: 1.26, 95% CI: 1.03–1.55), hearing disorders (OR: 1.24 95% CI: 1.05–1.47), and impaired walking ability (OR: 1.67, 95% CI: 1.30–2.02). Furthermore, older adults who did not take any medication were more likely to experience cognitive impairment than those taking two or more types of medication. Regarding psychological factors, the results revealed that risk factors significantly associated with cognitive impairment were severe anxiety (OR: 3.16, 95% CI: 1.02–9.81) and depression. Moreover, as shown in Tables 3, 4, we found that physical function impairment (OR: 1.79, 95%CI: 1.49–2.16) and cognitive impairment (OR: 1.83, 95% CI: 1.51–2.21) were independent risk factors for each other among older adults.
We found that physical function impairment existed in nearly one-third of subjects in the total population, with a prevalence of 37.3%. This result was similar to the data from Vásquez et al. (2022), who studied 3,050 older adults in the Hispanic Established Populations for Epidemiologic Study, and Farías-Antúnez et al. (2018), who investigated 1,451 older adults in Brazil. However, this rate of disability was significantly lower than that reported in a nationwide population-based longitudinal survey of healthy aging, which randomly selected participants from 22 provinces in China (Hou et al., 2019).
The prevalence of disability in the above study was more than half of the total number of individuals in both urban and rural areas. This is likely because the average age of the older adults included in our survey was generally younger. Moreover, several native regional studies close to Guangdong Province have reached similar results. For example, one population-based study (Chen et al., 2018) conducted in Guangxi Province involving 2,300 adults aged 60 years or older indicated that the disability rates, measured with ADL and IADL, were 43.4 and 42.4%, respectively.
A similar conclusion was reached in another study conducted in the northeastern rural areas of India that involved a community-based population (Medhi et al., 2021). The likely reason is that the urban and rural distribution in our study was almost balanced, whereas a higher proportion of participants in the aforementioned studies resided in rural areas.
The discrepancy in the evaluation criteria for BADL or IADL in the two studies may also lead to inconsistent results. To make the results more accurate and representative, future multicenter, large-scale epidemiological investigations should focus on uniform distributions of age and region during sampling and consistency of measurement methods.
The overall cognitive impairment rate in our study was 31%. This result supports the proportion of surveys conducted for representative older adults from Brazil (34.0%) (Brigola et al., 2020). However, many population-based cross-sectional studies carried out in different countries, such as Spain (Lara et al., 2016), Italy (Caffò et al., 2022), Mexico (Givan et al., 2022), Japan (Saw et al., 2020), and Korea (Lee et al., 2022), all showed a lower cognitive impairment rate. Nationwide data from China, based on samples of 46,011 (Jia et al., 2020), 21,732 (Qi et al., 2021), and 3,768 (Qin et al., 2022) in 2018, also showed prevalence rates of 15.0, 17.8, and 22.4%, respectively, which were significantly lower than those of our study. A similar result was observed in other epidemiological studies in eastern (Ding et al., 2015) and northern China (Jiang et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2019).
Qin et al. (2022) also analyzed regional prevalence and found that the rate of cognitive impairment among older adults in the southwest region was 29.9%, the highest among all regions. These data are closely aligned with our results. The differences by country or region may be related to complex factors such as race, lifestyle, economic level, and medical practices. All findings suggest that southern China should be a major focus for preventing and controlling cognitive impairment or dementia. Further studies should emphasize developing interventions and management systems that consider regional characteristics.
The results of our study’s multivariate logistic regression analysis indicated that age, family income, education level, type of medication, physical examination, social activities, support from family or friends, hearing ability, walking, and depression were all associated with both physical function and cognitive impairment. There was broad consensus linking older age to disability, whether in terms of body or cognition (Chen et al., 2018; Goswami et al., 2019; Ramadass et al., 2018).
We also confirmed this view in previous studies. The possible reason may be that older adults often experience several irreversible declines in organic functions and degenerative changes, such as Alzheimer’s disease, as they age, which can directly impair self-care and daily living abilities. High family income was recognized as a significant protective factor against cognitive impairment in our study, aligning with most published research on (Danielewicz et al., 2019; Philibert et al., 2013) the relationship between socioeconomic status or income and the incidence of disability. This phenomenon may be explained by the fact that older adults with low family incomes often lack sufficient financial resources and social support to cope with increased healthcare burdens, have less access to medical services for chronic disease management, and experience restricted interaction with their social networks, which contributes to the development of functional disorders (Bowling and Stafford, 2007; Zeng et al., 2010; Vaughan et al., 2016). There was a significant difference in the prevalence of physical and cognitive impairments among older adults with varying education levels. A higher level of education was linked to a reduced risk of physical function impairment, while the opposite was observed for cognitive impairment.
Previous studies (Goswami et al., 2019; Ravi et al., 2022) tended to support the viewpoint that education level is a protective factor, as individuals with more education have greater access to resources and knowledge for health-related services, enhancing their ability to manage diseases. However, in our study, more educated older adults exhibited a higher risk of cognitive impairment, which is inconsistent with the majority of studies (Xue et al., 2022; Liu et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2020) investigating the relationship between cultural features and disability.
However, the findings of Godinho et al. (2022) are consistent with our findings, which may be explained by complex neuropathologic theories and structural and functional changes in brain features due to aging. Further research into mechanistic exploration is needed to better interpret this relationship.
Our study found a positive association between medication use and physical function impairment, which aligns with previous findings (Chen et al., 2018; Medhi et al., 2021). Unfortunately, the opposite result was observed regarding cognitive aspects. One possible reason could be that older adults taking multiple types of medication may have various chronic diseases, leading them to seek medical assistance more frequently; thus, they might detect and manage the risk and early stages of cognition-related issues sooner.
Although the habit of undergoing regular physical examinations is beneficial for health promotion, the results of our study indicated that having an annual physical examination for the past 10 years was associated with a higher risk of cognitive impairment. We clarified that this phenomenon differed from conventional findings, as older adults who usually participate in physical examinations may have more health issues, which can lead to an increased risk of negative emotions or mental health problems, thereby accelerating cognitive decline (Freire et al., 2017; Desai et al., 2021).
The findings in our study also indicated that the effect of spiritual level support on disability, whether physical or cognitive, was more significant than that of material support, which highlighted the potential value of disability interventions based on psychological theories.
Over the last few years, some researchers have conducted large-scale population-based observational studies (Fuller-Thomson et al., 2022; Borges et al., 2021)and a longitudinal study (He et al., 2023) that explored the relationship between sensory disorders and cognitive impairment, which indicated that hearing disorders are an independent influencing factor on cognitive impairment. Our findings also align with this result. The reason for the observed correlation between sensory function and cognitive impairment may relate to potential mechanisms based on several hypotheses regarding internal effects, such as sensory deprivation (Lin et al., 2014; Nixon et al., 2019)and resource allocation (Nixon et al., 2019), or external effects, such as social disengagement (Fuller-Thomson et al., 2022). Unfortunately, there is no evidence to determine whether the relationship between sensory disorders and cognitive impairment is causal, nor to clarify the exact mechanisms, which require further longitudinal studies with large sample sizes or basic research for confirmation.
However, it may be necessary to pay particular attention to older adults with age-related sensory disorders, identify them, and provide early interventions to mitigate cognitive decline. Our study also suggested that elderly adults with walking disorders had a higher risk of impairments in physical and cognitive function. One systematic review (Binotto et al., 2018) included 49 studies that considered gait speed as a predictor of physical frailty and health indicators, showing a potential correlation between walking problems and disability that is consistent with our study.
The results of our study showed a significant association between psychological factors, such as anxiety and depression, and cognitive impairment. There is a broad consensus that psychological distress is an independent predictor of cognitive health (Freire et al., 2017; Desai et al., 2021). Therefore, investigating coping strategies for stress and developing intervention networks based on the social-psychological aspects of cognitive health among older adults may gradually become a key direction for future studies. Interestingly, we also found that depression was a contributing factor to physical function impairment. While this finding aligns with numerous previous studies (Kang et al., 2017; Taş et al., 2007), the connection between these two variables remains debatable (Duba et al., 2012) and merits further discussion.
In addition to the factors mentioned above, the opposite result obtained in our study, that smoking was a protective factor against disability, was unusual compared to most studies addressing the negative effects of unhealthy lifestyles on diseases (Ravi et al., 2022; Ramadass et al., 2018; Medhi et al., 2021). This may be explained by the complex relationship between praxeology or psychology and diseases, but further studies are needed to investigate the validity of this result.
Interestingly, our study’s additional findings demonstrated that older adults with physical function impairment faced an increased risk of cognitive impairment; conversely, cognitive impairment also accelerated the progression of physical disability. Most published studies (Kiiti et al., 2019; Chong et al., 2015; Boyle et al., 2010; Shimada et al., 2013) suggest a strong link between physical and cognitive impairment, indicating that the association is bidirectional. Longitudinal studies (Chong et al., 2015; Boyle et al., 2010) have confirmed that physical function impairment or frailty is a predictor of cognitive decline among people with mild cognitive impairment and is associated with a higher risk of dementia.
Cognitive impairment is a potentially modifiable risk factor for physical disability in aging, impacting self-care and mobility. Therefore, interventions designed to slow or manage the progression of physical function impairment may be crucial in preventing cognitive impairment or dementia; conversely, the reverse strategy is also possible.
Our findings suggest that comprehensive interventions be implemented for screening and preventing disability to support healthy aging in China. The implications for public health policy and the medical system include the following: First, governments and healthcare administrations should pay more attention to regional discrepancies in disability, improve screening measures for older adults, and provide social security and healthcare services that meet health requirements. Second, healthcare managers must conduct early assessments and monitor functional status, developing intervention strategies for various functional impairments based on the characteristics of older adults, with the aim of delaying the disabling process. Finally, interventions related to physical and cognitive training for older adults should encompass the entire continuum of disease management and offer more accessible platforms and opportunities for family involvement, as this may effectively promote the reasonable allocation of medical resources.
To the best of our knowledge, this was the first large-scale population-based cross-sectional survey on the incidence of physical and cognitive impairment among older adults in the southern region of China. We collected comprehensive information on older adults via a digital platform, analyzed the prevalence of physical and cognitive impairment, and investigated the factors influencing disability. However, this study has certain limitations. First, as a cross-sectional study, it cannot verify the causal association between the included factors and physical function or cognitive impairment. Second, physical function can be classified in ways other than by BADL or IADL, such as muscle strength, balance, and gait speed, but we did not perform other measurements beyond the method of questionnaires due to restrictions on instruments and the population base. Third, the MMSE is merely a cognitive screening tool and cannot clarify the diagnosis of cognitive impairment and its subtypes. Further studies need to use more nuanced measures to assess cognitive function across various domains, thereby verifying the conclusions of the present study. Finally, some results of this study might be biased because older adults with hearing or vision loss cannot complete the survey themselves and require assistance from caregivers or family members, which may introduce subjective opinions from proxy respondents affecting the data. Participants’ ability to recall past information may also lead to inaccurate results.
The findings from this population-based cross-sectional study in Guangdong Province demonstrated a high incidence rate of disability in terms of physical dysfunction and cognitive impairment. Numerous influencing factors related to age, family income, education level, type of medication, physical examination, social activities, support from family or friends, hearing or walking disorders, and depression were linked to declines in physical or cognitive function. Physical dysfunction was significantly correlated with cognitive impairment among older adults.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
The studies involving humans were approved by the ethics committee of Guangdong Province People’s Hospital (KY-Z-2021-690-01). They were conducted in accordance with local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
YZ: Conceptualization, Software, Data curation, Methodology, Writing -original draft. GC: Investigation, Methodology, Writing -original draft. LC: Data curation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. XW: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. LL: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – review & editing. QH: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JG: Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft. BG: Investigation, Software, Writing – review & editing. TS: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by National Key R&D Program of China (Grant number: 2020YFC2008500), and Nursing Research Program of Guangdong Province People’s Hospital(grant number: DFJH2023006).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2025.1534824/full#supplementary-material
Abdi, S., Spann, A., Borilovic, J., de Witte, L., and Hawley, M. (2019). Understanding the care and support needs of older adults: a scoping review and categorisation using the WHO international classification of functioning, disability and health framework (ICF). BMC Geriatr. 19:195. doi: 10.1186/s12877-019-1189-9
Binotto, M. A., Lenardt, M. H., and Rodríguez-Martínez, M. (2018). Physical frailty and gait speed in community elderly: a systematic review. Rev. Esc. Enferm. U.S.P. 52:e3392. doi: 10.1590/s1980-220x2017028703392
Bo, Z. Y., Kuang, W. H., Wang, Y., Chen, G., Xiong, Q. R., and Qiu, P. Y. (2018). Cognitive impairments and associated factors in community-dwelling elderly in Chengdu, Sichuan. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 49, 759–764. doi: 10.13464/j.scuxbyxb.2018.05.014
Borges, K., Resende, L. M., and Couto, E. (2021). Hearing function, perception of disability (handicap) and cognition in the elderly: a relation to be elucidated. Codas 33:e20200150. doi: 10.1590/2317-1782/20202020150
Bowling, A., and Stafford, M. (2007). How do objective and subjective assessments of neighbourhood influence social and physical functioning in older age? Findings from a British survey of ageing. Soc. Sci. Med. 64, 2533–2549. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2007.03.009
Boyle, P. A., Buchman, A. S., Wilson, R. S., Leurgans, S. E., and Bennett, D. A. (2010). Physical frailty is associated with incident mild cognitive impairment in community-based older persons. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 58, 248–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02671.x
Brigola, A. G., Ottaviani, A. C., Carvalho, D., Oliveira, N. A., Souza, É. N., and SCI, P. (2020). Association between cognitive impairment and criteria for frailty syndrome among older adults. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 78, 2–8. doi: 10.1590/0004-282x20190138
Bruderer-Hofstetter, M., Gorus, E., Cornelis, E., Meichtry, A., and de Vriendt, P. (2022). Influencing factors on instrumental activities of daily living functioning in people with mild cognitive disorder - a secondary investigation of cross-sectional data. BMC Geriatr. 22:791. doi: 10.1186/s12877-022-03476-8
Caffò, A. O., Spano, G., Tinella, L., Lopez, A., Ricciardi, E., Stasolla, F., et al. (2022). The prevalence of amnestic and non-amnestic mild cognitive impairment and its association with different lifestyle factors in a south Italian elderly population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:3097. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19053097
Campbell, N. L., Unverzagt, F., LaMantia, M. A., Khan, B. A., and Boustani, M. A. (2013). Risk factors for the progression of mild cognitive impairment to dementia. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 29, 873–893. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2013.07.009
Chen, S., Qin, J., Li, Y., Wei, Y., Long, B., Cai, J., et al. (2018). Disability and its influencing factors among the elderly in a county, Guangxi Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 15:1967. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15091967
Cheng, G. R., Liu, D., Huang, L. Y., Han, G. B., Hu, F. F., Wu, Z. X., et al. (2023). Prevalence and risk factors for subjective cognitive decline and the correlation with objective cognition among community-dwelling older adults in China: results from the Hubei memory and aging cohort study. Alzheimers Dement. 19, 5074–5085. doi: 10.1002/alz.13047
Choi, Y. S., Kim, M. J., Lee, G. Y., Seo, Y. M., Seo, A. R., Kim, B., et al. (2019). The association between frailty and disability among the elderly in rural areas of Korea. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 16:2481. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16142481
Chong, M. S., Tay, L., Chan, M., Lim, W. S., Ye, R., Tan, E. K., et al. (2015). Prospective longitudinal study of frailty transitions in a community-dwelling cohort of older adults with cognitive impairment. BMC Geriatr. 15:175. doi: 10.1186/s12877-015-0174-1
Chuang, Y. F., Liu, Y. C., Tseng, H. Y., Lin, P. X., Li, C. Y., Shih, M. H., et al. (2021). Urban-rural differences in the prevalence and correlates of mild cognitive impairment in community-dwelling older adults in Taiwan: the EMCIT study. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 120, 1749–1757. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2021.03.005
Cockrell, J. R., and Folstein, M. F. (1988). Mini-mental state examination (MMSE). Psychopharmacol. Bull. 24, 689–692
Cornelis, E., Gorus, E., Van Schelvergem, N., and De Vriendt, P. (2019). The relationship between basic, instrumental, and advanced activities of daily living and executive functioning in geriatric patients with neurocognitive disorders. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 34, 889–899. doi: 10.1002/gps.5087
Damluji, A. A., Chung, S. E., Xue, Q. L., Hasan, R. K., Walston, J. D., Forman, D. E., et al. (2021). Physical frailty phenotype and the development of geriatric syndromes in older adults with coronary heart disease. Am. J. Med. 134, 662–671.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.09.057
Danielewicz, A. L., D'Orsi, E., and Boing, A. F. (2019). Contextual income and incidence of disability: results of EpiFloripa elderly cohort. Rev. Saude Publica 53:11. doi: 10.11606/S1518-8787.2019053000659
De Vriendt, P., Cornelis, E., Cools, W., and Gorus, E. (2021). The usefulness of evaluating performance of activities in daily living in the diagnosis of mild cognitive disorders. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:11623. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182111623
Deckers, K, Schievink, S, Rodriquez, M, Van Oostenbrugge, RJ, MPJ, BoxtelVan, FRJ, Verhey, et al. Coronary heart disease and risk for cognitive impairment or dementia: systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. (2017). 12:e184244, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184244
Deng, Y., Zhao, S., Cheng, G., Yang, J., Li, B., Xu, K., et al. (2021). The prevalence of mild cognitive impairment among Chinese people: a Meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology 55, 79–91. doi: 10.1159/000512597
Desai, R., Whitfield, T., Said, G., John, A., Saunders, R., Marchant, N. L., et al. (2021). Affective symptoms and risk of progression to mild cognitive impairment or dementia in subjective cognitive decline: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 71:101419. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2021.101419
Ding, D., Zhao, Q., Guo, Q., Meng, H., Wang, B., Luo, J., et al. (2015). Prevalence of mild cognitive impairment in an urban community in China: a cross-sectional analysis of the Shanghai aging study. Alzheimers Dement. 11, 300–309. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2013.11.002
Duba, A. S., Rajkumar, A. P., Prince, M., and Jacob, K. S. (2012). Determinants of disability among the elderly population in a rural south Indian community: the need to study local issues and contexts. Int. Psychogeriatr. 24, 333–341. doi: 10.1017/S1041610211001669
Farías-Antúnez, S., Lima, N. P., Bierhals, I. O., Gomes, A. P., Vieira, L. S., and Tomasi, E. (2018). Disability relating to basic and instrumental activities of daily living: a zopulation-based study with elderly in Pelotas, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, 2014. Epidemiol. Serv. Saude 27:e2017290. doi: 10.5123/S1679-49742018000200005
Freire, A., Pondé, M. P., Liu, A., and Caron, J. (2017). Anxiety and depression as longitudinal predictors of mild cognitive impairment in older adults. Can. J. Psychiatr. 62, 343–350. doi: 10.1177/0706743717699175
Fuller-Thomson, E., Nowaczynski, A., and MacNeil, A. (2022). The association between hearing impairment, vision impairment, dual sensory impairment, and serious cognitive impairment: findings from a population-based study of 5.4 million older adults. J Alzheimers Dis Rep 6, 211–222. doi: 10.3233/ADR-220005
Givan, A., Downer, B., Chou, L. N., and al Snih, S. (2022). Cognitive impairment and low physical function among older Mexican Americans: findings from a 20-year follow-up(☆). Ann. Epidemiol. 70, 9–15. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2022.03.006
Godinho, F., Maruta, C., Borbinha, C., and Pavão Martins, I. (2022). Effect of education on cognitive performance in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Appl. Neuropsychol. Adult 29, 1440–1449. doi: 10.1080/23279095.2021.1887191
Gold, D. A. (2012). An examination of instrumental activities of daily living assessment in older adults and mild cognitive impairment. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 34, 11–34. doi: 10.1080/13803395.2011.614598
Goswami, A. K., Kalaivani, M., Nongkynrih, B., Kant, S., and Gupta, S. K. (2019). Disability and its association with sociodemographic factors among elderly persons residing in an urban resettlement colony, New Delhi, India. PLoS One 14:e222992. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0222992
Han, G., Han, J., Han, K., Chung, T. Y., Na, K. S., and Lim, D. H. (2022). Relationships among visual acuity, risk of acute myocardial infarction, and stroke: a nationwide cohort study in South Korea. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 29, 57–69. doi: 10.1080/09286586.2021.1893340
Han, Y., Zhang, L., and Fang, Y. (2022). Multidimensional disability evaluation and confirmatory analysis of older adults in a home-based Community in China. Front. Public Health 10:899303. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.899303
He, Y., Song, W., Jiang, X., Wang, C., Zhou, Y., Lu, B., et al. (2023). Longitudinal association between visual disability and cognitive function among middle-aged and older adults in China. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 107, 1025–1030. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2021-320026
Hou, C., Ma, Y., Yang, X., Tao, L., Zheng, D., Liu, X., et al. (2019). Disability transitions and health expectancies among elderly people aged 65 years and over in China: a Nationwide longitudinal study. Aging Dis. 10, 1246–1257. doi: 10.14336/AD.2019.0121
Hsieh, N., and Waite, L. (2019). Disability, psychological well-being, and social interaction in later life in China. Res. Aging 41, 362–389. doi: 10.1177/0164027518824049
Inocian, E., and Patalagsa, J. G. (2016). Cognitive impairment in older adults living in the community. Nurs Older adults 28, 25–30. doi: 10.7748/nop.28.2.25.s21
Jia, L., Du, Y., Chu, L., Zhang, Z., Li, F., Lyu, D., et al. (2020). Prevalence, risk factors, and management of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 60 years or older in China: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Public Health 5, e661–e671. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30185-7
Jiang, F., Kong, F., and Li, S. (2021). The association between social support and cognitive impairment among the urban elderly in Jinan, China. Healthcare (Basel) 9:1443. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9111443
Kang, H. J., Bae, K. Y., Kim, S. W., Shin, H. Y., Shin, I. S., Yoon, J. S., et al. (2017). Impact of anxiety and depression on physical health condition and disability in an elderly Korean population. Psychiatry Investig. 14, 240–248. doi: 10.4306/pi.2017.14.3.240
Kiiti, B. M., Oiring, D. C. C. N., Silva, S. S. A., Yassuda, M., Cesari, M., and Aprahamian, I. (2019). The relationship between physical frailty and mild cognitive impairment in the elderly: a systematic review. J. Frailty Aging 8, 192–197. doi: 10.14283/jfa.2019.29
Kroenke, K., Spitzer, R. L., and Williams, J. B. (2001). The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 16, 606–613. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.2001.016009606.x
Lara, E., Koyanagi, A., Olaya, B., Lobo, A., Miret, M., Tyrovolas, S., et al. (2016). Mild cognitive impairment in a Spanish representative sample: prevalence and associated factors. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 31, 858–867. doi: 10.1002/gps.4398
Lee, W. T., Lim, S. S., Yoon, J. H., and Won, J. U. (2022). Association between changes in the regularity of working hours and cognitive impairment in middle-aged and older Korean workers: the Korean longitudinal study of aging, 2008-2018. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:4161. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19074161
Liao, J., Wang, Q., Huang, J. L., and Wei, Y. M. (2022). Urban-rural difference in the costs of disability and its effects on poverty among people with disabilities in China. Front. Public Health 10:989540. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.989540
Lin, F. R., Ferrucci, L., An, Y., Goh, J. O., Doshi, J., Metter, E. J., et al. (2014). Association of hearing impairment with brain volume changes in older adults. NeuroImage 90, 84–92. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.12.059
Liu, L. Y., Lu, Y., Shen, L., Li, C. B., Yu, J. T., Yuan, C. R., et al. (2021). Prevalence, risk and protective factors for mild cognitive impairment in a population-based study of Singaporean elderly. J. Psychiatr. Res. 145, 111–117. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2021.11.041
Löwe, B., Decker, O., Müller, S., Brähler, E., Schellberg, D., Herzog, W., et al. (2008). Validation and standardization of the generalized anxiety disorder screener (GAD-7) in the general population. Med. Care 46, 266–274. doi: 10.1097/MLR.0b013e318160d093
Medhi, G. K., Visi, V., Bora, P. J., Sarma, J., Borah, P., Mahanta, J., et al. (2021). A community-based study on functional disability and its associated factors among elderly individuals in a rural setting in northeastern India. Cureus 13:e13309. doi: 10.7759/cureus.13309
Nixon, G. K., Sarant, J. Z., and Tomlin, D. (2019). Peripheral and central hearing impairment and their relationship with cognition: a review. Int. J. Audiol. 58, 541–552. doi: 10.1080/14992027.2019.1591644
Philibert, M. D., Pampalon, R., Hamel, D., and Daniel, M. (2013). Interactions between neighborhood characteristics and individual functional status in relation to disability among Québec urbanites. Disabil. Health J. 6, 361–368. doi: 10.1016/j.dhjo.2013.02.004
Qi, S., Sun, Y., Yin, P., Zhang, H., and Wang, Z. (2021). Mobile phone use and cognitive impairment among elderly Chinese: a National Cross-Sectional Survey Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:5695. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18115695
Qiao, R., Jia, S., Zhao, W., Xia, X., Su, Q., Hou, L., et al. (2022). Prevalence and correlates of disability among urban-rural older adults in Southwest China: a large, population-based study. BMC Geriatr. 22:517. doi: 10.1186/s12877-022-03193-2
Qin, F., Luo, M., Xiong, Y., Zhang, N., Dai, Y., Kuang, W., et al. (2022). Prevalence and associated factors of cognitive impairment among the elderly population: a nationwide cross-sectional study in China. Front. Public Health 10:1032666. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1032666
Rajan, K. B., Hebert, L. E., Scherr, P., Dong, X., Wilson, R. S., Evans, D. A., et al. (2012). Cognitive and physical functions as determinants of delayed age at onset and progression of disability. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 67, 1419–1426. doi: 10.1093/gerona/gls098
Ramadass, S., Rai, S. K., Gupta, S. K., Kant, S., Wadhwa, S., Sood, M., et al. (2018). Prevalence of disability and its association with sociodemographic factors and quality of life in a rural adult population of northern India. Natl. Med. J. India 31, 268–273. doi: 10.4103/0970-258X.261179
Ravi, J., Kuzhali, S., and Ramamoorthy, P. (2022). Prevalence of disability among the elderly people in an urban slum of Chennai - a cross-sectional study. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 11, 7763–7768. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1022_22
Saw, Y. M., Saw, T. N., Than, T. M., Khaing, M., Soe, P. P., Oo, S., et al. (2020). Cognitive impairment and its risk factors among Myanmar elderly using the revised Hasegawa's dementia scale: a cross-sectional study in Nay Pyi Taw, Myanmar. PLoS One 15:e236656. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236656
Shimada, H., Makizako, H., Doi, T., Yoshida, D., Tsutsumimoto, K., Anan, Y., et al. (2013). Combined prevalence of frailty and mild cognitive impairment in a population of elderly Japanese people. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 14, 518–524. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2013.03.010
Statistic N B O. Bulletin of the 7th National Population Census(No.5): Age composition of the population [EB/OL]. (2021). Available online at:http://www.stats.gov.cn/tjsj/zxfb/202105/t20210510_1817181.html.
Tangalos, E. G., and Petersen, R. C. (2018). Mild cognitive impairment in geriatrics. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 34, 563–589. doi: 10.1016/j.cger.2018.06.005
Taş, U., Verhagen, A. P., Bierma-Zeinstra, S. M., et al. (2007). Incidence and risk factors of disability in the elderly: the Rotterdam study. Prev. Med. 44, 272–278. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2006.11.007
Teh, W. L., Abdin, E., Vaingankar, J. A., Shafie, S., Jeyagurunathan, A., Yunjue, Z., et al. (2021). Prevalence, lifestyle correlates, and psychosocial functioning among multi-ethnic older adults with mild cognitive impairment in Singapore: preliminary findings from a 10/66 population study. Yale J. Biol. Med. 94, 73–83
Vásquez, E., Gadgil, M. A., Zhang, W., and Angel, J. L. (2022). Diabetes, disability, and dementia risk: results from the Hispanic established populations for the epidemiologic studies of the elderly (H-EPESE). Int. J. Soc. Psychiatry 68, 1462–1469. doi: 10.1177/00207640211037722
Vaughan, M., LaValley, M. P., AlHeresh, R., and Keysor, J. J. (2016). Which features of the environment impact community participation of older adults? A systematic review and Meta-analysis. J. Aging Health 28, 957–978. doi: 10.1177/0898264315614008
Vlachos, G. S., Kosmidis, M. H., Yannakoulia, M., Dardiotis, E., Hadjigeorgiou, G., Sakka, P., et al. (2020). Prevalence of mild cognitive impairment in the elderly population in Greece: results from the HELIAD study. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 34, 156–162. doi: 10.1097/WAD.0000000000000361
Wang, L. Y., Feng, M., Hu, X. Y., and Tang, M. L. (2023). Association of daily health behavior and activity of daily living in older adults in China. Sci. Rep. 13:19484. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44898-7
Wang, J., and Li, T. (2020). The age pattern of disability in China and prediction of future disability population. Population J. 4, 362–398.
Wang, J., Xiao, L. D., Wang, K., Luo, Y., and Li, X. (2020). Cognitive impairment and associated factors in rural elderly in North China. J. Alzheimers Dis. 77, 1241–1253. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200404
Wang, Z., and Zhang, M. (1989). Application of the Chinese version ofMini-mental state examination (MMSE). J Shanghai Psychiatry 7, 108–111.
Xue, J., Jiao, Y., Wang, J., and Chen, S. (2022). The incidence and burden of risk factors for mild cognitive impairment in older rural Chinese persons. Gerontol Geriatr Med 8:1682809665. doi: 10.1177/23337214221114559
Zeng, Y., Gu, D., Purser, J., Hoenig, H., and Christakis, N. (2010). Associations of environmental factors with elderly health and mortality in China. Am. J. Public Health 100, 298–305. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2008.154971
Zhang, Y., Guan, Y., Shi, Z., Yue, W., Liu, S., Liu, S., et al. (2019). Sex differences in the prevalence of and risk factors for cognitive impairment no dementia among the elderly in a rural area of northern China: a population-based cross-sectional study. Neuroepidemiology 52, 25–31. doi: 10.1159/000493141
Keywords: physical function, cognitive impairment, older adults, a population-based regional cross-sectional study, prevalence and related factors
Citation: Zhang Y, Cheng G, Chen L, Wang X, Lin L, Huang Q, Guo J, Gong B and Shen T (2025) Prevalence and related factors of physical function and cognitive impairment among older adults: a population-based regional cross-sectional study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 17:1534824. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1534824
Received: 26 November 2024; Accepted: 27 February 2025;
Published: 14 March 2025.
Edited by:
Simone Varrasi, University of Catania, ItalyReviewed by:
Krystel Ouaijan, Saint George Hospital University Medical Center, LebanonCopyright © 2025 Zhang, Cheng, Chen, Wang, Lin, Huang, Guo, Gong and Shen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Tiemei Shen, bWVpcm1laXJzaGVuQDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.