
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Aging Neurosci., 09 April 2025
Sec. Parkinson’s Disease and Aging-related Movement Disorders
Volume 17 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2025.1488009
Background: Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a prevalent, disabling neurodegenerative disorder. Early diagnosis and treatment of PD remains challenging due to the absence of definitive diagnostic tests and the non-specificity of its clinical manifestations. Initial consultations for PD symptoms often involve specialists who are not specifically trained in PD. Consequently, it is imperative to assess the general knowledge regarding PD among these specialists to develop optimal educational strategies and enhance early recognition and diagnosis of PD.
Methods: We developed a questionnaire covering motor symptoms, non-motor symptoms, prodromal symptoms, risk factors and antiparkinsonian medications based on published guidelines, and conducted the web-based survey via Wenjuan xing (https://www.wjx.cn/) among physicians not specializing in PD in Guangdong Province, China.
Results: A total of 312 respondents, working in 28 diverse departments across 64 hospitals of three different categories, were eligible for data analysis. Notably, 95.2% of the respondents were aware of rest tremor as a motor symptom, yet only 76.9% recognized bradykinesia as a motor symptom. Regarding non-motor symptoms, erectile dysfunction, urinary dysfunction, restless legs, olfactory loss, orthostatic hypotension, rapid eye movement behavior disorder (RBD), lower back pain and diaphoresis, were recognized by less than 50% of the respondents. Additionally, with the exception of subthreshold parkinsonism or abnormal quantitative motor testing, prodromal symptoms such as excessive daytime somnolence, depression (± anxiety), olfactory loss, urinary dysfunction, RBD, and constipation were recognized by 36.5–48.7% of the respondents. First-degree relatives with PD received recognition from 86.5% of the respondents, whereas the remaining risk factors were recognized by 50–60% of the participants. Concerning protective factors for PD, recognition was limited to no more than 23%. Levodopa and dopamine releasers were the most widely recognized antiparkinsonian medications, while the recognition of other medications was below 70%. Variables such as medical degrees, professional titles, hospital categories, and education subjects contributed to statistical differences in PD knowledge.
Conclusion: Among non-PD specialists in south China, current knowledge regarding PD, including non-motor symptoms, prodromal symptoms, risk and protective factors, and antiparkinsonian medications, is relatively inadequate. This necessitates targeted education and training to improve their understanding and recognition of PD.
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a prevalent neurodegenerative condition, characterized by typical motor symptoms, such as akinesia, bradykinesia, tremor, rigidity, and postural instability. Additionally, patients with PD often exhibit various non-motor symptoms including constipation, olfactory dysfunction, depression, etc. (Postuma et al., 2015). Globally, PD affects an estimated 8.5 million individuals, with a reported age-standardized rate of prevalence at 0.106% in 2019, making it the second most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer’s Disease (Ou et al., 2021). Furthermore, in 2019, PD led to a global burden of 1.21 × 106 years lived with disability (Ou et al., 2021). In China specifically, the age-standardized incidence and prevalence rates for PD reached 2.43‰ and 2.457‰ in 2021, exceeding the global average and surpassing those of other G20 countries. Notably, the incidence and prevalence of PD in the southeast coastal regions of China were disproportionately higher than in other regions within the country (Xu et al., 2024).
Diagnosis of PD relies heavily on clinical manifestations and there are no definitive examinations (Postuma et al., 2015). Despite ongoing updates to diagnostic criteria, the accuracy of PD diagnosis is limited, ranging from 73.8 to 83.9% (Rizzo et al., 2016). Moreover, in prodromal or early stages of PD when classical motor symptoms have not been manifested, non-motor symptoms may become leading causes of hospital visits. However, the non-specificity of non-motor symptoms significantly results in misdiagnosis or underdiagnosis of PD in clinical practice (Greenland and Barker, 2018). Notably, a significant number of patients worldwide seek diagnosis from physicians not specialized in PD or movement disorders (Lim et al., 2022; 赵亚军, 龚继章, 葛许华, 2022), leading to a higher rate of PD diagnosis compared to specialists in this field (Tinelli et al., 2016; Virameteekul et al., 2023). Furthermore, PD diagnosis is typically confirmed when classical motor symptoms appear in a stage with substantial neurophysiological damage, at which point approximately 70% of dopamine neurons may have been lost (Murman, 2012). Intervention at this stage is often too late to delay disease progression or achieve neuroprotection. Therefore, early and timely diagnosis of PD based on non-motor symptoms in prodromal stage presents a valuable opportunity for early therapeutic intervention to alleviate symptoms, slow disease progression, improve quality of life and reduce long-term costs (Pagan, 2012; Soman et al., 2023; Tinelli et al., 2016).
Antiparkinsonian medications, including levodopa, dopamine agonists and monoamine oxidase type-B (MAO-B) inhibitors, etc., can significantly alleviate motor symptoms. Surprisingly, 76.7% of general practitioners (GPs) are not comfortable initiating antiparkinsonian medications primarily due to unfamiliarity with these medications (Lim et al., 2022). Notably, the exclusive dosage and duration of levodopa treatment may contribute to the occurrence of motor complications (Sun et al., 2020). Therefore, there is a need for preceding investigation into the general knowledge of antiparkinsonian medications before developing an educational strategy on the appropriate timing and strategy for prescribing antiparkinsonian medications.
In China, both self-referral and GP-referral are available, resulting in non-PD specialists take significantly active involvement in the diagnosis and management of PD (Heping, 2021; Li et al., 2019). Consequently, early recognition and diagnosis of PD are challenging in real-world clinical practice in China. Additionally, healthcare system in China comprises a tertiary network, consisting of primary, secondary, and tertiary hospitals. Community-based primary hospitals and GPs, provide basic services for the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of common conditions. Secondary hospitals cater to a larger number of communities with comprehensive medical care, while tertiary hospitals offer specialized care for complicated cases (Heping, 2021). It has been reported that education and training of primary healthcare practitioners are inadequate (Li et al., 2020), highlighting the necessity to further explore the knowledge of PD among non-specialist healthcare professionals and promote PD education to reduce the potential misdiagnosis of PD. A comprehensive survey of PD knowledge among non-specialists healthcare professionals across various categories of hospitals would provide guidance for optimizing an education strategy and improving the quality of training for these physicians (Li et al., 2020).
Consequently, we designed a cross-sectional survey targeting physicians who are not specializing in PD. The objective of this survey was to evaluate the general knowledge of PD among non-PD specialists and to assess the barriers that hinder early diagnosis and appropriate treatment of PD in China.
The survey was conducted anonymously among non-PD specialists residing in Guangdong Province, China, utilizing a structured online questionnaire. The findings of this survey are reported in strict adherence to the Consensus-Based Checklist for Reporting of Survey Studies guidelines (Sharma et al., 2021).
The structured questionnaire was meticulously developed to investigate physicians’ knowledge pertaining to motor symptoms, non-motor symptoms, prodromal symptoms, risk factors and commonly prescribed antiparkinsonian medications.
The questionnaire was grounded in PD clinical diagnostic criteria (Clarke et al., 2016; Parkinson's Disease and movement Disorders Group NB, Chinese Medical Association, Parkinson's Disease and movement Disorders Professional Committee of Neurology Branch of Chinese Medical Doctor Association, 2016), research criteria for PD prodromal symptoms (Heinzel et al., 2019; 陈彪, 陈生弟, 刘疏影, 2019), treatment guidelines for PD (Grimes et al., 2019; Health NIf, Excellence C, 2017; 中华医学会神经病学分会帕金森病及运动障碍学组, 中国医师协会神经内科医师分会帕金森病及运动障碍学组, 2020), and related scholarly works (Kayis et al., 2023; Sun et al., 2020). It was initially drafted by Shaohua Lyu, with 56 questions covering demographic information, knowledge of PD involving motor symptoms, non-motor symptoms, prodromal symptoms, risk factors, protective factors and antiparkinsonian medications, as well as preferred treating methods in real-world clinical practice. Subsequently, it underwent a thorough review and approval process by five PD experts from Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine (GPHCM). Based on the feedback collected from a pre-testing pilot survey involving five non-PD physicians from GPHCM, language was polished to be plain and enhance the clarity of the items. Redundant questions were condensed for conciseness and questions related with real-world treating methods were removed from the final version as it is beyond the frame of research aim.
The final version comprises 44 questions specifically tailored to PD, respondents were asked to judge whether a given symptom belongs to motor symptom, non-motor symptom, prodromal symptom, risk and protective factor of PD, or a medicine belongs to antiparkinsonian medications (see Supplementary material 1 for more details). The questionnaire was made available as an electronic questionnaire on Wenjuan xing,1 a widely utilized online survey platform in China. This platform offers convenient access for data collection. Additionally, logic rules were carefully designed and implemented to streamline the question-answering process, compulsory response to each question was also implemented to minimize incomplete data.
The questionnaire can be accessed via https://www.wjx.cn/vm/mQJ5kge.aspx#.
Clinicians who do not specialize in PD and are employed within Guangdong Province were eligible to participate in the survey, regardless of their hospital category, department, educational qualifications, subjects studied, or professional titles. However, clinicians specializing in PD, nurses, physicians not actively engaged in clinical practice, and those not residing in Guangdong Province were excluded from participation.
Convenience sampling was employed to identify potential respondents during the survey. The minimum sample size was calculated to be 273, with a 90% confidence interval and a 5% error margin by the below formular:
Where n is the sample size, Z is the Z-score, p is the estimated proportion of an attribute that is present in the population, and E is the margin of error.
The online survey was actively promoted among the memberships of Guangdong Association of Integrative Chinese and Western Medicine, Guangdong Association of Traditional Chinese Medicine, and Guangdong Association of Medicine from November to December 2023. To ensure the accuracy and uniqueness of responses, measures were taken during the design stage to prevent duplicate or multiple participation through the incorporation of logic checks. Furthermore, additional data-checking was conducted to eliminate any potential instances of multiple participation, thereby safeguarding the integrity of the survey results.
The study was exempted from ethical review by the ethics committee of GPHCM (ZM2023-393), and conducted anonymously, adhering strictly to the principles outlined in the Helsinki Declaration (Goodyear et al., 2007). Confidential information, including names, contact details, and addresses, was not collected during the survey, ensuring the privacy and safety of all participants.
SPSS 26 (Corp, 2017) was utilized for data analysis. Continuous data were described using the mean and standardized deviation, and further comparisons were conducted using the Student’s t-test, where applicable. Categorical data was described by frequency and percentage, and further compared using the chi-square test. Furthermore, multiple regression analyses were conducted to identify demographic factors that result in differences of knowledge of PD.
Initially, 348 physicians responded to our survey and completed the online questionnaire, and 312 questionnaires were deemed eligible for data analyses after throughout screening (Figure 1).
The survey comprises 312 respondents from 64 hospitals across 17 cities in Guangdong Province, with a mean age of 37.59 ± 6.82 years and 12.04 ± 7.74 years of clinical experience. The majority practiced in tertiary hospitals (74.36%), spanning 28 departments (93.27% non-neurology). Academic qualifications included master’s (52.56%), bachelor’s or lower (40.06%), and doctoral degrees (7.37%). Medical training backgrounds encompassed Chinese (41.67%), conventional (25.64%), and integrated medicine (32.69%). Professional titles comprised attending (41.67%), associate chief/chief (33.33%), and resident physicians (25%) (Supplementary file 2).
Table 1 provides a comprehensive overview of participants’ responses to motor, non-motor and prodromal symptoms, as well as risk factors and antiparkinsonian medications. Notably, rest tremor was the most widely recognized motor symptom (n = 297, 95.2%), followed by postural instability (n = 280, 89.7%) and rigidity (n = 275, 88.1%). Bradykinesia was the least acknowledged (n = 240, 76.9%).
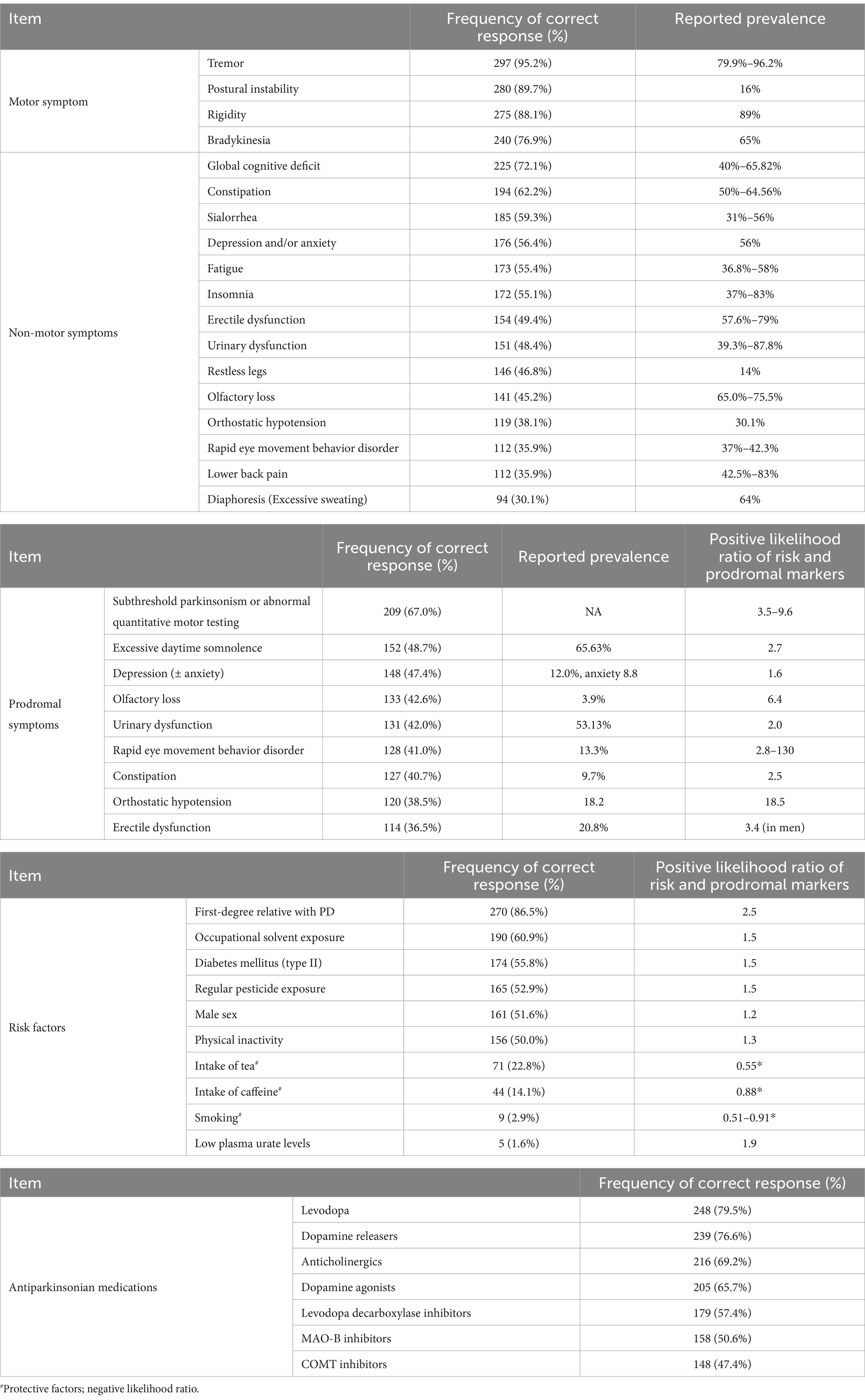
Table 1. Responses to motor, non-moto and prodromal symptoms, risk factors, and antiparkinsonian medications.
Among the reported non-motor symptoms, global cognitive deficit ranked highest with 225 (72.1%) respondents recognizing it. Other commonly recognized symptoms include constipation (n = 192, 62.2%), sialorrhea (n = 185, 59.3%), anxiety (n = 176, 56.4%), fatigue (n = 173, 55.4%) and insomnia (n = 172, 55.1%). Notably, less than half of the respondents recognized non-motor symptoms such as erectile dysfunction, urinary dysfunction, restless legs, olfactory loss, orthostatic hypotension, RBD, lower back pain and diaphoresis.
Subthreshold parkinsonism or abnormal quantitative motor testing emerged as the sole prodromal symptom recognized by over 50% of respondents. Other prodromal features including excessive daytime somnolence (n = 152, 48.7%), depression (± anxiety) (n = 148, 47.4%), olfactory loss (n = 133, 42.6%), urinary dysfunction (n = 131, 42.0%), RBD (n = 128, 41%), and constipation (n = 127, 40.7%), were recognized by <50%.
First-degree familial PD history was the most recognized risk factor 270 (86.5%). Other risk factors recognized by over 50% of respondents include occupational solvent exposure (n = 190, 60.9%), diabetes mellitus (n = 174, 55.8%), regular pesticide exposure (n = 165, 52.9%), male sex (n = 161, 51.6%) and physical inactivity (n = 156, 50%). Prospective factors, like smoking, intake of tea and caffeine, were less recognized by respondents, with only 71 (22.8%), 44 (14.1%) and 9 (2.9%) respondents recognizing them, respectively. Notably, a mere 5 (1.6%) respondents identified low plasma urate level as a risk factor for PD.
In terms of antiparkinsonian medications commonly used in current clinical practice, levodopa stands out as the most familiar to respondents, with 248 (79.5%) acknowledging it. Dopamine releasers (n = 239, 76.6%), anticholinergics (n = 216, 69.2%), and dopamine agonists (n = 205, 65.7%) also enjoy widespread recognition. Conversely, MAO-B inhibitors and catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors are less familiar by the respondents, with frequencies of 158 (50.6%) and 148 (47.4%), respectively.
Comparison of PD knowledge regarding motor, non-motor and prodromal symptoms, risk factors and antiparkinsonian medications was conducted across education qualifications, professional titles, categories of hospitals and education subjects. The findings of these comparisons are presented in Tables 2–5, respectively.
Among respondents holding different medical degrees, statistically significant differences were observed only in the recognition of specific risk factors. Notably, those with a master’s degree demonstrated a lower rate of identifying constipation as a risk factor compared to those with a bachelor’s degree (28.8% vs. 46.9%, p = 0.029). In addition, respondents with doctoral degrees were less likely to identify diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for PD, compared to those with master’s degrees (45.1% vs. 61.3%) or bachelor’s degrees (45.1% vs. 60.8%) (p = 0.032) (Table 2).
In the context of professional titles, chief or associate chief physicians outperformed residents in recognizing bradykinesia (83.7% vs. 66.7%, p = 0.028) and anticholinergics (75.0% vs. 57.7%, p = 0.038). Attendings demonstrated higher awareness of familial PD risk (93.1% vs. 79.5%, p = 0.01) and medications (levodopa: 83.8% vs. 67.9%; dopamine agonists: 73.1% vs. 55.1%, p < 0.03) than residents (Table 3).
Respondents from tertiary hospitals recognized insomnia as a non-motor symptom less than secondary hospital peers (50.4% vs. 80%, p = 0.003), though no other symptom or medication differences were significant (Table 4).
By education background, respondents majoring conventional medicine recognized constipation as a prodromal symptom less than those studying Chinese medicine (28.8% vs. 46.9%, p = 0.029). Interestingly, those pursuing integrated medicine showed significantly reduced awareness of diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for PD, with only 45.1% recognizing it as such, contrasted to respondents majoring in either Chinese medicine (60.8%) or conventional medicine (61.3%) (p = 0.032) (Table 5).
Multiple regression analyses were conducted to identify potential relationships between demographic factors and correct response to knowledge of PD. All surveyed items related to PD knowledge, including motor symptoms, non-motor symptoms, prodromal symptoms, risk and protective factors, and antiparkinsonian medications, were initially considered as dependent variables. Regression analyses that were successfully constructed and met the statistical criteria for inclusion can be found in Supplementary file 3.
The results indicate that, as age increases, the physicians seem to be less aware of rigidity as a motor symptom but know more about PD risk factors like the first-degree relative with PD and physical inactivity. Compared to physicians working outside neurology department, those working in neurology departments were more aware of non-motor symptoms like constipation, orthostatic hypotension, urinary dysfunction, olfactory loss, lower back pain, RBD and diaphoresis, prodromal symptom of constipation, protective factors of consumption of tea and caffeine, risk factors of first-degree relative with PD and low plasma urate levels. Categories of hospitals result in differences in knowing insomnia as a non-motor symptom. Professional titles lead to differences in knowing risk factors of first-degree relatives with PD and physical inactivity, antiparkinsonian medication of levodopa and dopamine agonists. In addition, medical practice experience contributes to different knowledge of physical inactivity as a risk factor, while education subjects contribute to differences of knowing diabetes mellitus as a risk factor.
The cross-sectional survey encompassed 312 respondents working in diverse departments across 64 hospitals of varying levels in 17 cities. These respondents boasted a range of educational qualifications and professional titles, spanning different medical specialities. This diversity in demographic information not only enhances the representativeness of the respondents but also contributes to the increased generalizability of our findings.
However, it is worth noting that approximately three-quarters of the respondents come from tertiary hospitals, whereas the estimated ratio of tertiary hospitals to other hospitals in Guangdong province stands at around 1: 4. Intriguingly, despite this preponderance, we found no statistical differences among hospital categories in relation to the surveyed issues, with the exception of non-motor symptom of insomnia. Therefore, the preponderance of respondents from tertiary hospitals did not significantly hamper the generalizability of our findings to primary and secondary hospitals.
Nevertheless, the fact that respondents primarily from tertiary hospitals, which are expected to demonstrate superior medical knowledge, displayed limited awareness of PD knowledge, underscores a broader issue of low PD knowledge awareness across hospitals in Guangdong Province. This observation is particularly concerning as tertiary hospitals are often considered the leaders in medical research and education. The limited PD knowledge among these respondents suggests that there is a need for more widespread and targeted educational efforts to enhance PD awareness and understanding across all levels of hospitals in Guangdong Province.
Bradykinesia stands as the most defining clinical features of PD (Ling et al., 2012), serving as the cornerstone for diagnosing the condition among its four motor symptoms (Postuma et al., 2015). Nevertheless, it was discovered to the least recognized among these symptoms. Notably, resident physicians demonstrated a significant lack of awareness regarding bradykinesia as a motor symptom of PD, compared to (associate) chief physicians, likely due to their fewer years of clinical practice. This low awareness of bradykinesia aligns with findings from a prior survey in Shanghai, China, which revealed that bradykinesia tend to take longer to be diagnosed compared to tremor (朱莹莹 et al., 2015).
Unsurprisingly, tremor emerged as the most recognized motor symptom, constant with a prior report (Zach et al., 2015). It is estimated that an average of 79.9% of individuals with PD exhibit tremors, yet notably, up to 19.9% do not (Gupta et al., 2020). It is important to highlight that tremor can also manifest in other conditions, such as essential tremor (Pan and Kuo, 2022), thereby emphasizing the significance of a thorough differential diagnosis.
The multiple regression analysis indicated that rigidity was less recognized as a motor symptom among physicians as their age increased. This could be attributed to the fact that rigidity can also arise from normal aging or arthritis (Ertan et al., 1999), leading to confusion in differential diagnosis.
It has been documented that over 90% of patients with PD manifest at least one non-motor symptom in the early stages (Frucht, 2004), and no PD patient is exempt from these non-motor symptoms throughout the course of their illness (Carroll et al., 2021; Chaudhuri et al., 2021; Gulunay et al., 2020). The high prevalence of non-motor symptoms underscores their significance in the early detection, recognition and diagnosis of PD.
However, our survey indicates that non-PD specialists often fail to adequately recognize these non-motor symptoms. Even the most common non-motor symptom, such as constipation, insomnia, fatigue, drooling, depression and anxiety, are reported to be under-recognized and undertreated by physicians, despite their widespread prevalence (American Parkinson Disease Association, 2023; Garrison et al., 2021; Miller et al., 2019; Shulman et al., 2002). The lack of recognition may stem from the non-specific and inclusive nature of symptoms like excessive sweating and pain, while symptoms like RBD and restless legs are less frequently encountered.
Interestingly, we found that physicians from tertiary hospitals were less aware of insomnia as a non-motor symptom, compared to those from secondary hospitals. This may be attributed to the high level of specialization in tertiary hospitals, which could result in a narrower focus and a lack of knowledge across multiple disciplines (王宇朋, 王萍, 2021; 韩笑, 王瑞, 2022). In addition, it was not surprising that non-PD specialists from neurology department know better about non-motor symptoms when compared to those not working in neurology departments, after taking all demographic information into consideration.
The widespread under-recognition of non-motor symptoms indicates a gap in knowledge about PD among non-PD specialists and highlight the necessity of education and training. Enhancing the awareness and understanding of non-motor symptoms among these specialists is crucial for improving diagnostic accuracy and facilitating timely therapeutic interventions (Shulman et al., 2002).
Prodromal PD refers to the preclinical stage, during which individuals do not yet fulfill the diagnostic criteria for PD but exhibit signs and symptoms. Prodromal symptoms predict an increased risk of developing motor symptoms and a future diagnosis of PD (Postuma et al., 2015). Notably, most prodromal symptoms are non-motor and significantly impact the quality of life of individuals in both the prodromal stage and those who have progressed to motor-PD. Consequently, the early detection and management of these prodromal symptoms are crucial for providing optimal care (Mantri and Morley, 2018; Plouvier et al., 2014).
It is noteworthy that less than half of non-PD specialists are aware of most prodromal symptoms, excluding subthreshold parkinsonism, despite their high predictive value for developing PD. This includes symptoms such as RBD. The under-awareness of prodromal symptoms may be attributed to their non-specific nature, or relatively low prevalence. Interestingly, surveyed physicians with a master’s degree demonstrated less awareness of constipation as a prodromal symptom compared to those with a bachelor or doctoral degrees. Furthermore, physicians trained in western medicine demonstrated less awareness of constipation as a prodromal symptom than those with an education history in Chinese medicine. However, after controlling all surveyed demographic information, these differences got insignificant.
Modifiable risk factors and protective measures, including tea and coffee consumption, smoking habits, physical activity, exposure to solvents and pesticides, as well as plasma urate levels, can significantly influence the development and progression of PD (Belvisi et al., 2020). Nevertheless, it has been observed that surveyed physicians lack sufficient awareness of these factors. This limited understanding among physicians may stem from insufficient medical education focused on non-PD specialists, potentially contributing to unfavorable outcomes in disease progression.
Twenty percent of the surveyed physicians remain unaware of levodopa as an antiparkinsonian medication, despite being the first-line treatment choice (Health NIf, Excellence C, 2017; Waller et al., 2021). In addition, COMT inhibitors are the least well-known medication, despite having a long history of clinical use since 1998 (First COMT inhibitor approved for Parkinson's disease, 1998). Moreover, several antiparkinsonian medications including levodopa, anticholinergics and dopamine agonists, are less familiar to resident physicians, potentially due to their limited clinical experience. These findings may explain the GPs’ lack of confidence in prescribing antiparkinsonian medications (Lim et al., 2022). Inappropriate utilization of antiparkinsonian medications can lead to motor complications, side effects, and negatively impact the progression of PD (Connolly and Lang, 2014). Therefore, it is imperative to enhance knowledge of PD medications among non-PD specialists.
The survey reveals insufficient knowledge of PD diagnosis and treatment, involving prodroma symptom, non-motor symptoms, risk and protective factors, and antiparkinsonian medications, among non-PD specialists. It has been established that the scarcity of specialized physicians in primary and secondary hospitals is a significant obstacle to early diagnosis of PD (Li et al., 2019). Moreover, education, training and qualifications among physicians in China’s primary care system has also been widely documented (Li et al., 2017). Our results underscore the urgent need for specialized education and training for non-PD specialists to enhance early and timely diagnosis, as well as appropriate management strategies of the disease (徐静, 2015). The effects of specialized education and training in improving diagnostic accuracy and efficiency can be proposed to be evaluated in future research.
A significant limitation of this study is its generalizability. Firstly, as the survey was conducted solely in south China, the findings may not be fully applicable to physicians residing in other regions of China. Secondly, given the disparities in healthcare systems between China and other nations, the conclusions drawn from this study may not be directly transferable to non-PD specialists practicing in countries with different healthcare frameworks. Nonetheless, given China’s substantial contribution to the global PD burden and the representativeness of its healthcare challenges among low- and middle-income countries, the findings may still hold relevance for similar contexts. The study’s emphasis on fundamental clinical challenges—such as patient education, multidisciplinary coordination, and resource limitations—may offer valuable perspectives for practitioners in comparable settings. Finally, the convenience sampling method employed in this research may also constrain the generalizability of the results to a broader population. Despite these limitations, the findings provide a foundational understanding of the challenges faced by physicians in managing PD within resource-constrained environments, underscoring the need for context-specific strategies to optimize care delivery.
The knowledge of PD non-motor symptoms, prodromal symptoms, risk and protective factors, as well as antiparkinsonian medications, was relatively inadequate among non-PD specialists in south China. To improve the quality of healthcare for PD patients in this region, it is imperative to develop targeted education and training strategies aimed at enhancing the knowledge of PD among non-PD specialists.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because no identifiable information was collected in this study.
SL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. ZM: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. JS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Writing – review & editing. QS: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (no. 2019YFC1708601), the Specific Fund of State Key Laboratory of Dampness Syndrome of Chinese Medicine (SZ2021ZZ14), National Traditional Chinese Medicine Clinical Outstanding Talents Training Program for QS, and Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine for SL (YN2023MS13).
The authors extend gratitude to the respondents for their participation in this study. Additionally, we acknowledged the contribution of Wenjuan xing for providing technical support in conduction of this survey.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2025.1488009/full#supplementary-material
COMT, catechol-O-methyltransferase; PD, Parkinson’s disease; GP, general practitioner; GPHCM, Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Chinese Medicine; MAO-B, monoamine oxidase type-B; RBD, rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder.
American Parkinson Disease Association. (2023). Understanding weakness in Parkinson’s disease. Available online at: https://www.apdaparkinson.org/article/understanding-weakness-parkinsons-disease/
Belvisi, D., Pellicciari, R., Fabbrini, G., Tinazzi, M., Berardelli, A., and Defazio, G. (2020). Modifiable risk and protective factors in disease development, progression and clinical subtypes of Parkinson's disease: what do prospective studies suggest? Neurobiol. Dis. 134:104671. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104671
Carroll, V., Rossiter, R., and Blanchard, D. (2021). Non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Austral. J. Gen. Pract. 50, 812–817. doi: 10.31128/AJGP-07-21-6093
Chaudhuri, J. R., Mridula, K. R., and Bandaru, V. S. (2021). Prevalence of non-motor symptoms in Parkinson’s disease: a study from South India. Turk. J. Neurol. 27, 52–57. doi: 10.4274/tnd.2021.52993
Clarke, C. E., Patel, S., Ives, N., Rick, C. E., Woolley, R., Wheatley, K., et al. (2016). Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of physiotherapy and occupational therapy versus no therapy in mild to moderate Parkinson’s disease: a large pragmatic randomised controlled trial (PD REHAB), appendix 1, UK Parkinson’s disease society brain Bank diagnostic criteria. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library.
Connolly, B. S., and Lang, A. E. (2014). Pharmacological treatment of Parkinson disease: a review. JAMA 311, 1670–1683. doi: 10.1001/jama.2014.3654
Ertan, S., Fresko, I., Apaydin, H., Ozekmekçi, S., and Yazici, H. (1999). Extrapyramidal type rigidity in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 38, 627–630
First COMT inhibitor approved for Parkinson's disease (1998). First COMT inhibitor approved for Parkinson's disease. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 55:524. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/55.6.524
Frucht, S. J. (2004). Parkinson disease: an update. Neurologist 10, 185–194. doi: 10.1097/01.nrl.0000131146.08278.a5
Garrison, C., Bishop, K., Taber, S., Ho, H., Jose, I., Khemani, P., et al. (2021). Insomnia: an Underrecognized nonmotor symptom in Parkinson disease. J. Nurse Pract. 17, 815–818. doi: 10.1016/j.nurpra.2021.03.004
Goodyear, M. D., Krleza-Jeric, K., and Lemmens, T. (2007). The declaration of Helsinki. Br. Med. J. 335, 624–625. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39339.610000.BE
Greenland, J. C., and Barker, R. A. (2018). “The differential diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease” in Parkinson’s disease: pathogenesis and clinical aspects. eds. T. B. Stoker and J. C. Greenland (Brisbane (AU): Codon Publications).
Grimes, D., Fitzpatrick, M., Gordon, J., Miyasaki, J., Fon, E. A., Schlossmacher, M., et al. (2019). Canadian guideline for Parkinson disease. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 191, E989–E1004. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.181504
Gulunay, A., Cakmakli, G. Y., Yon, M. I., Ulusoy, E. K., and Karakoc, M. (2020). Frequency of non-motor symptoms and their impact on the quality of life in patients with Parkinson's disease: a prospective descriptive case series. Psychogeriatrics 20, 206–211. doi: 10.1111/psyg.12489
Gupta, D. K., Marano, M., Zweber, C., Boyd, J. T., and Kuo, S. H. (2020). Prevalence and relationship of rest tremor and action tremor in Parkinson's disease. Tremor. Other Hyperkinet. Mov. (N Y) 10:58. doi: 10.5334/tohm.552
Heinzel, S., Berg, D., Gasser, T., Chen, H., Yao, C., and Postuma, R. B. (2019). Update of the MDS research criteria for prodromal Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. 34, 1464–1470. doi: 10.1002/mds.27802
Heping, D. L. (2021). “China’s 3-tier hospital system: gaps and challenges” in Hospital management Asia.
Kayis, G., Yilmaz, R., Arda, B., and Akbostancı, M. C. (2023). Risk disclosure in prodromal Parkinson's disease - a survey of neurologists. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 106:105240. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2022.105240
Li, X., Krumholz, H. M., Yip, W., Cheng, K. K., De Maeseneer, J., Meng, Q., et al. (2020). Quality of primary health care in China: challenges and recommendations. Lancet 395, 1802–1812. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30122-7
Li, X., Lu, J., Hu, S., Cheng, K. K., De Maeseneer, J., Meng, Q., et al. (2017). The primary health-care system in China. Lancet 390, 2584–2594. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33109-4
Li, G., Ma, J., Cui, S., He, Y., Xiao, Q., Liu, J., et al. (2019). Parkinson’s disease in China: a forty-year growing track of bedside work. Transl. Neurodegener. 8:22. doi: 10.1186/s40035-019-0162-z
Lim, I. C. Z. Y., Saffari, S. E., and Neo, S. (2022). A cross-sectional study of knowledge and practices in the management of patients with Parkinson’s disease amongst public practice-based general practitioners and geriatricians. BMC Health Serv. Res. 22:91. doi: 10.1186/s12913-022-07503-7
Ling, H., Massey, L. A., Lees, A. J., Brown, P., and Day, B. L. (2012). Hypokinesia without decrement distinguishes progressive supranuclear palsy from Parkinson's disease. Brain 135, 1141–1153. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws038
Mantri, S, and Morley, JF. (2018). Prodromal and early Parkinson's disease diagnosis - earlier diagnosis may lead to earlier and more effective treatments. Practical Neurology [Internet]. Available online at: https://practicalneurology.com/articles/2018-may/prodromal-and-early-parkinsons-disease-diagnosis
Miller, N., Walshe, M., and Walker, R. W. (2019). Sialorrhea in Parkinson’s disease: prevalence, impact and management strategies. Res. Rev. Parkinson. 9, 17–28. doi: 10.2147/JPRLS.S177409
Murman, D. L. (2012). Early treatment of Parkinson's disease: opportunities for managed care. Am. J. Manag. Care 18, S183–S188
Ou, Z., Pan, J., Tang, S., Duan, D., Yu, D., Nong, H., et al. (2021). Global trends in the incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability of Parkinson's disease in 204 countries/territories from 1990 to 2019. Front. Public Health 9:776847. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.776847
Pagan, F. L. (2012). Improving outcomes through early diagnosis of Parkinson's disease. Am. J. Manag. Care 18, S176–S182
Pan, M.-K., and Kuo, S.-H. (2022). Essential tremor: clinical perspectives and pathophysiology. J. Neurol. Sci. 435:120198. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2022.120198
Parkinson's Disease and movement Disorders Group NB, Chinese Medical Association, Parkinson's Disease and movement Disorders Professional Committee of Neurology Branch of Chinese Medical Doctor Association (2016). Diagnostic criteria for Parkinson's disease in China (2016) 中国帕金森病的诊断标准(2016版) [published in Chinese]. Chin. J. Neurol. 4, 268–271.
Plouvier, A. O., Hameleers, R. J., van den Heuvel, E. A., Bor, H. H., Olde Hartman, T. C., Bloem, B. R., et al. (2014). Prodromal symptoms and early detection of Parkinson's disease in general practice: a nested case-control study. Fam. Pract. 31, 373–378. doi: 10.1093/fampra/cmu025
Postuma, R. B., Berg, D., Stern, M., Poewe, W., Olanow, C. W., Oertel, W., et al. (2015). MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. 30, 1591–1601. doi: 10.1002/mds.26424
Rizzo, G., Copetti, M., Arcuti, S., Martino, D., Fontana, A., and Logroscino, G. (2016). Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of Parkinson disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 86, 566–576.
Sharma, A., Minh Duc, N. T., Luu Lam Thang, T., Nam, N. H., Ng, S. J., Abbas, K. S., et al. (2021). A consensus-based checklist for reporting of survey studies (CROSS). J. Gen. Intern. Med. 36, 3179–3187. doi: 10.1007/s11606-021-06737-1
Shulman, L. M., Taback, R. L., Rabinstein, A. A., and Weiner, W. J. (2002). Non-recognition of depression and other non-motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 8, 193–197. doi: 10.1016/S1353-8020(01)00015-3
Soman, K., Nelson, C. A., Cerono, G., Goldman, S. M., Baranzini, S. E., and Brown, E. G. (2023). Early detection of Parkinson’s disease through enriching the electronic health record using a biomedical knowledge graph. Front. Med. 10:10. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1081087
Sun, B., Wang, T., Li, N., and Qiao, J. (2020). Analysis of motor complication and relative factors in a cohort of Chinese patients with Parkinson's disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2020, 1–7. doi: 10.1155/2020/8692509
Tinelli, M., Kanavos, P. G., and Grimaccia, F. (2016). The value of early diagnosis and treatment in Parkinson’s disease: a literature review of the potential clinical and socioeconomic impact of targeting unmet needs in Parkinson’s disease.
Virameteekul, S., Revesz, T., Jaunmuktane, Z., Warner, T. T., and De Pablo-Fernández, E. (2023). Clinical diagnostic accuracy of Parkinson's disease: where do we stand? Mov. Disord. 38, 558–566. doi: 10.1002/mds.29317
Waller, S., Williams, L., Morales-Briceño, H., and Fung, V. (2021). The initial diagnosis and management of Parkinson’s disease. Austral. J. Gen. Pract. 50, 793–800.
Xu, T., Dong, W., Liu, J., Yin, P., Wang, Z., Zhang, L., et al. (2024). Disease burden of Parkinson's disease in China and its provinces from 1990 to 2021: findings from the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 46:101078. doi: 10.1016/j.lanwpc.2024.101078
Zach, H., Dirkx, M., Bloem, B. R., and Helmich, R. C. (2015). The clinical evaluation of Parkinson's tremor. J. Parkinsons Dis. 5, 471–474. doi: 10.3233/JPD-150650
徐静 (2015). The effect of health education in patients with Parkinson's disease [published in Chinese] 帕金森病患者健康教育效果调查. 中国卫生标准管理China Health Stand Manag. 16, 27–28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9316.2015.16.021
朱莹莹,, 万赢,, 罗懿,, 李艳,, 君杰施,, 魏雅荣,, et al. (2015). Potential influencing factors of time from onset to clinical diagnosis and misdiagnosis rate of Parkinson's patients in Shanghai [published in Chinese] 影响上海地区帕金森病患者诊断时程及临床误诊率的相关因素分析. Chin J Neurol中华神经科杂志 11, 995–999. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2015.11.013
赵亚军, 龚继章, 葛许华 (2022). Role of community physicians in early diagnosis of Parkinson's disease [published in Chinese] 全科医生在帕金森病早期诊断及社区管理中的作用. 中华全科医师杂志. Chin. Gen. Pract. 3, 296–300. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn114798-20210928-00733
陈彪, 陈生弟, 刘疏影 (2019). Diagnostic criteria for prodromal Parkinson's disease: an expert consensus in China [published in Chinese] 帕金森病前驱期诊断研究标准中国专家共识. 中华老年医学杂志. 38, 825–831. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-9026.2019.08.001
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease, web-based survey, motor symptoms, non-motor symptoms, prodromal symptoms, risk factors, antiparkinsonian medications
Citation: Lyu S, Li Z, Mao Z, Sun J, Zheng C and Su Q (2025) Knowledge of Parkinson’s disease among non-PD specialists: a web-based survey in South China. Front. Aging Neurosci. 17:1488009. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1488009
Received: 29 August 2024; Accepted: 27 March 2025;
Published: 09 April 2025.
Edited by:
Wenquan Zou, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, ChinaReviewed by:
Lucia Muntean, Paracelsus Elena Klinik Kassel, GermanyCopyright © 2025 Lyu, Li, Mao, Sun, Zheng and Su. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chunye Zheng, MTYwMjE2NTlAcXEuY29t; Qiaozhen Su, MTA2NDU2OTUxNEBxcS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.