
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Aging Neurosci. , 17 December 2024
Sec. Alzheimer's Disease and Related Dementias
Volume 16 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2024.1517965
This article is part of the Research Topic Current Chemical Approaches in Combating Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's Disease (AD) View all 5 articles
In recent years, mitochondrial transfer has emerged as a universal phenomenon intertwined with various systemic physiological and pathological processes. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a multifactorial disease, with mitochondrial dysfunction at its core. Although numerous studies have found evidence of mitochondrial transfer in AD models, the precise mechanisms remain unclear. Recent studies have revealed the dynamic transfer of mitochondria in Alzheimer’s disease, not only between nerve cells and glial cells, but also between nerve cells and glial cells. In this review, we explore the pathways and mechanisms of mitochondrial transfer in Alzheimer’s disease and how these transfer activities contribute to disease progression.
The authors reviewed scientific literature (PubMed, meeting abstracts, and websites) on mitochondrial transfer in AD. Numerous studies have found evidence and key role of mitochondrial transfer in AD models, and relevant publications are cited throughout the manuscript. In this review, the phenomenon of mitochondrial transfer is described in terms of its function under physiological and pathological conditions, including tissue homeostasis, damaged tissue repair, and dementia progression. Then, the mechanism of this process in AD is summarized, such as trigger factors and transfer pathways. In addition, various perspectives are explored to better understand the mysteries of cell-to-cell mitochondrial transport.
In the central nervous system (CNS), neuron function hinges extensively on mitochondrial integrity and activity. As a crucial powerhouse for cellular metabolism and tissue survival, mitochondria often adapt their morphology and position in response to various stressors and energy demands. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) represents one of the most prevalent forms of dementia worldwide, characterized by an incurable progression that typically results in the patient’s death. Recently, the mitochondrial cascade hypothesis has gained prominence, emphasizing the pivotal role of mitochondrial bioenergetics in AD (Swerdlow, 2018). This hypothesis posits that mitochondrial dysfunction is a preliminary and critical event that aggravates the pathological cascade (Sharma et al., 2021). While the question of whether mitochondrial-related changes contribute to AD’s development or are its consequence remains open, a clear association between mitochondrial dysfunction and AD has been extensively demonstrated.
Mitochondria can be spontaneous transferred intracellularly or intercellularly both in vivo and in vitro, by a process known as “mitochondrial transfer” (Chen et al., 2022). This phenomenon involves the incorporation of mitochondrial genes or mitochondria into recipient cells. Intercellular mitochondria transfer was initially documented by Koyanagi et al. (2005), and more recent research has underscored the significance in the CNS, particularly in the context of neurodegenerative diseases such as AD (Nitzan et al., 2019). Studies have reported decreased velocity and total travel distance of mitochondria in AD neuronal processes (Yu et al., 2016). However, the physiological nature and specific mechanisms underlying mitochondrial transfer remain unclear.
The study of mitochondrial transfer between and within cells has attracted increasing attention owing to the core functions of mitochondria in AD. This review provides an overview of mitochondrial dysfunction’s role in AD pathology, elucidates the primary mechanisms governing mitochondrial transfer among and within cells, and underscores the significance of this phenomenon. In doing so, it introduces fresh perspectives and potential targets for advancing AD treatment strategies.
Mitochondria are dynamic organelles that continually adapt their structure and metabolism to meet cellular demands. Their role is pivotal in preserving neurovascular function within the CNS, whether in physiological or pathophysiological states (Rutkai et al., 2019). In AD, mitochondrial dysfunction manifests through various facets, including reduced mitochondrial size (Wang et al., 2005), increased mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) damage, decreased synaptic adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels, impaired mtDNA expression, reduced mtDNA copies, increased oxidative damage, reduced mitochondrial axonal transport, and glucose hypometabolism (Sang et al., 2018). However, the source of these mitochondrial changes in AD remains debatable.
Aβ has been implicated in senile plaque formation and neuronal apoptosis, and it plays a crucial role in AD pathogenesis. An increasing body of evidence suggests that Aβ monomers and oligomers can inhibit axonal mitochondrial transport and interrupt the mitochondrial fusion/fission balance. For example, Guo et al. (2013) observed a significant 30–40% reduction in mitochondrial density and movement in axons exposed to 200 nM oligomeric Aβ, all without affecting cell viability. Additionally, studies (Devi et al., 2006) found that Amyloid Precursor Protein (APP) (full length or C-terminal fragment) and Aβ were associated with the mitochondrial membrane in AD human brains brain regions. This suggests that Aβ-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in AD occurs through both direct and indirect mechanisms, with early alterations in axonal mitochondrial transport preceding neuronal death. Conversely, excessive mitochondrial division also leads to Aβ-mediated neuropathological and cognitive decline (Qi et al., 2019). In other words, mitochondrial dysfunction may occur independently of Aβ and may be an upstream contributor to Aβ deposition in AD.
Apart from Aβ, overexpression and/or hyperphosphorylation of Tau has also been shown to disrupt both the distribution and localization of mitochondria in models and patient of AD. Tau is a hydrophobic protein that stabilizes the neuronal microtubules and regulates axonal transport. In the human AD brain, the distribution of mitochondria in neurites containing tau aggregates is disrupted in an age-dependent manner in the human AD brain (Kopeikina et al., 2011). Pérez et al. (2018) transfected a plasmid with different forms of Tau labeled with green fluorescent protein in Tau gene-knockout mice and found that cells expressing truncated Tau showed significantly lower optic atrophy 1 (OPA1) levels and mitochondrial fragmentation. Moreover, Tau inhibits mitochondrial Ca2+ efflux via the mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchanger, leading to mitochondrial depolarization in response to stimuli inducing Ca2+ signaling and cell death. Moreover, high concentrations of Tau protein can affect the dynamic balance between mitochondrial division and fusion, thus interfering with mitochondrial transport. Consequently, mitochondrial dynamics disorders arising from pathological changes due to abnormally expressed Tau protein plays an important role in AD pathogenesis. However, the mechanisms underlying the influence of the Tau protein on mitochondria warrant further exploration.
Interestingly, some studies have hypothesized that Aβ and Tau may interact to degrade mitochondrial dysfunction in AD (John and Reddy, 2021). The effects of Aβ species on mitochondrial movement is subject to the presence of Tau, with one study suggesting that Aβ mainly causes a complex IV defect, while Tau mainly affects complex I (Rhein et al., 2009). Another study found that compared with an AD mouse model with a single distinct pathology, the synergistic effects of both pathologies in a 3xTg-AD mouse model occur by impacting oxidative phosphorylation system (OXPHOS) (Kim and Mook-Jung, 2019). At present, knowledge regarding Aβ-tau synergy is still in its infancy, and many unknown factors remain, such as the different pathological causes and manifestations of mitochondrial damage in different models, which need further study.
Furthermore, abnormal secretion of apolipoprotein E4 (Reiman et al., 2004) and oxidative stress (Swomley and Butterfield, 2015) may also be related to a rise in ROS/RNS levels, leading to oxidation of mitochondrial proteins, lipids, and DNA. Thus, the relationship among the multiple mechanisms of mitochondrial dysfunction in AD is complex, with mechanisms potentially influencing each other (Figure 1). Excessive Aβ accumulation, abnormal forms of Tau protein, and Aβ-Tau interaction can individually or collectively disrupt mitochondrial axon transport, affecting nutrient delivery and synaptic information exchange. These disruptions may represent the primary contributors to learning and memory disorders.
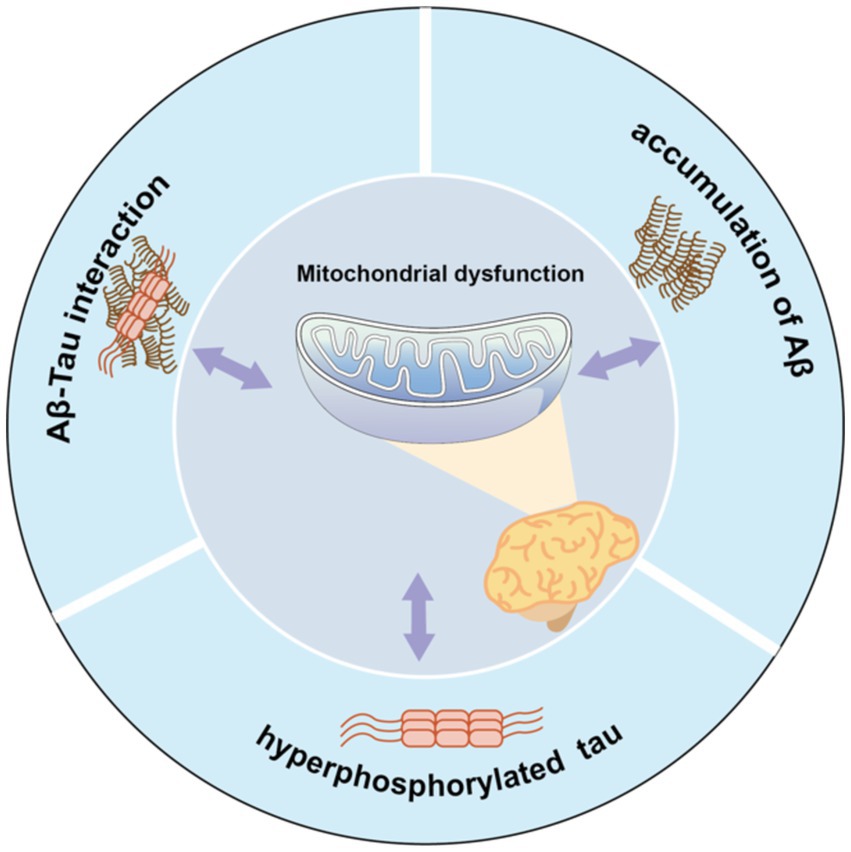
Figure 1. Mitochondrial dysfunction and pathological features form a vicious cycle in AD pathology. Aβ accumulation, Tau hyperphosphorylation, or Aβ-Tau interaction can all contribute to mitochondrial dysfunction, which in turn exacerbates abnormalities in all three, which further impair mitochondrial function.
Mitochondrial dysfunction and its associated pathological features form a vicious cycle in AD. Aβ accumulation, Tau hyperphosphorylation, or Aβ-Tau interaction can each instigate mitochondrial dysfunction. Consequently, these abnormalities collectively exacerbate the condition of all three factors, further impairing mitochondrial function.
Mitochondria are highly dynamic organelles that can move within and between subcellular compartments closely linked to neuroplasticity, such as synaptic terminals, dendrites, cell bodies, and axons, resulting in changes in their form, length, size and number, which in turn affect the energy, vitality, and even cell death. Researchers use cybrid cells with incorporated platelet mitochondria from AD or age-matched non-AD human subjects into mtDNA-depleted neuronal cells (SH-SY5Y) to prepare AD or non-AD hybrid cells, and found in non-AD cybrid cells; for instance, mitochondria are shorter and scattered along the differentiated neuronal processes, whereas in AD cells, the mitochondria are concentrated within the shortened processes (Yu et al., 2016). Du et al. (2021) observed a fission-pattern with fragmented and scattered mitochondria in AD cells as opposed to jointed and elongated mitochondria distributed in the differentiated normal non-AD cells. Consequently, the versatile and ever-changing nature of mitochondria underscores their dynamic nature, implying the possible existence of mitochondrial transfer in both in vivo and in vitro experiments. While the link between the phenotype and mitochondrial function is not always observed, under many conditions, actively respirating mitochondria are long and filamentous, while short, round fragmented mitochondria are often associated with pathological conditions.
The level of neuronal activity stands as a direct determinant of mitochondrial morphology and abundance during mitochondrial intracellular transfer. Neurons control the mobility, distribution, and clearance of mitochondria to maintain their energy balance and prevent oxidative stress. In mature neurons (Sheng, 2014), approximately 20–30% of axonal mitochondria exhibit motility, while roughly 15% undergo brief pausing or docking at synapses. Approximately 14% of motile mitochondria dynamically pass through presynaptic terminals, and their transport is modulated in response to physiological signals. This mobility allows mitochondria to adapt their metabolic state and function in response to changes in the external environment over time. Meanwhile, fission may be necessary for intercellular mitochondrial transfer (Zampieri et al., 2021) because smaller, non-elongated mitochondria are mor easily internalized by the recipient cell. Other researchers found that (Geng et al., 2023) astrocytes can deliver 300–1,100 nm mitochondrial particles. Moreover, transferred mitochondria lack a membrane potential, because dysfunctional mitochondria that lack a membrane potential are normally degraded or repaired by fusion with healthy mitochondrial networks (Phinney et al., 2015). Different conclusions may be related to different cell types, cell viability, and different cellular environments (Table 1).
Generally, intra- and inter-cellular mitochondrial transfer displays varying degrees of directional, saltatory, and bidirectional movement, and it is determined by several factors. Ruthel and Hollenbeck (2003) reported that intracellular mitochondrial transfer results from specific directed motility rather than bulk flow in the axoplasm or organelles. Other studies have demonstrated that the directionality of intracellular mitochondrial transfer is associated with cytoskeletal microfilaments in microvesicles of connected tubular structures (Ahmad et al., 2014; Yasuda et al., 2011). Additionally, Aβ protein concentration is also thought to affect the direction of intracellular mitochondrial transfer. Furthermore, low Aβ levels can impair anterograde transport while enhancing retrograde axonal mitochondrial movement by disrupting microtubule stability via decreased α-tubulin acetylation (Du et al., 2010; Wang et al., 2015). Moreover, hippocampal neurons treated with Aβ-derived diffusible ligands develop impaired axonal transport of mitochondria in both anterograde and retrograde directions (Wang et al., 2009).
Concerning the direction of intercellular mitochondrial transfer, Plotnikov et al. (2008) established that intercellular cytoplasmic transfer occurs in a nondirectional manner. Of course, some scholars believe that the direction of transfer is related to the cell state. In a typical intercellular mitochondrial transfer, recipient cells are characterized by elevated OXPHO needs and severely compromised mitochondrial functional (Marlein et al., 2019; Moschoi et al., 2016), while donor cells with proficient mitochondrial function are appropriately activated (Marlein et al., 2018). Although bidirectional mitochondrial transfer has occasionally been observed, the precise direction and mechanism of such transfer remain unclear.
In the brain, bidirectional mitochondrial transfer within neurons, between glia and other glial cells, and between glia and neurons has been observed; the delivered mitochondria are internalized and degraded (Davis et al., 2014) or even rescue signal transport (Liu et al., 2021). Although extracellular damaged mitochondria are injurious, transfer of functional mitochondria is protective. The ratio between damaged mitochondria and functional mitochondria in the extracellular milieu governs the outcome in neurons (Joshi et al., 2019). Mitochondrial transfer is a ubiquitous phenomenon associated with various physiological and pathological processes.
Mitochondrial dysfunction is an early and prominent feature of AD (Wang et al., 2014). The intracellular and intercellular transfer of mitochondria is involved in the mitochondrial quality control process and jointly maintains the mitochondrial homeostasis of local tissues or the whole body, which provides a promising therapeutic target for AD. Intracellular mitochondrial transfer, especially bidirectional mitochondrial transport within astrocytes, microglia, and neurons (Hayakawa et al., 2016; Lippert and Borlongan, 2019), is capable of eliminating damaged mitochondria or restoring healthy mitochondria and is necessary to meet the dynamic energy requirements of different regions of neurons. At the same time, intercellular mitochondrial transfer has also proved to be a biological event that cannot be ignored in the CNS. This transcellular transfer of mitochondria promotes the integration of the transferred mitochondria into the endogenous network of the recipient cell, participates in inflammatory or oxidative stress processes, regulates neuronal [Ca2+i] levels and health (Joshi et al., 2019; Padilla-Sánchez et al., 2020; English et al., 2020; Lampinen et al., 2022; Sun et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2020), contributes to changes in the bioenergy profile of the recipient cell and other functional properties, and exerts important implications in AD. One study verified that instead of degrading dysfunctional mitochondria through mitophagy, neurons in an AD mouse model transfer dysfunctional mitochondria to neighboring astrocytes (Lampinen et al., 2022), which contributes to neuronal mitochondrial homeostasis. English et al. (2020) have found that cisplatin-treated neurons acquire 35% more mitochondria than healthy neurons, and receptor neurons exhibit improved survival, mitochondrial membrane potential, and calcium homeostasis, in a Miro1-dependent manner. However, while the advantages of mitochondrial transfer are evident, the underlying process remains unclear. Typically, cellular stress or injury is a prerequisite for organelle transfer to occur. When mitochondrial function is relatively intact, mitochondrial transfer is rare (Islam et al., 2012), and it is triggered only when mitochondrial function is almost completely missing (such as when mtDNA is missing or when cells are exposed to mitochondrial inhibitors) (Berridge et al., 2016). Hence, the precise significance of mitochondrial exchange in the maintenance of tissue homeostasis remains unclear.
Here, we summarize the functions of intercellular mitochondrial transfer in AD models (Table 2).
In recent years, the transportation of mitochondria within distinct cellular regions or between cells has garnered significance as a pivotal regulator of cellular health, but the mechanisms of intracellular and intercellular transfer may differ. Mitochondrial transfer through these different structures can lead to different functional outcomes for the recipient cells, i.e., functional mitochondrial acquisition, immune activation, or trans-mitophagy (Shanmughapriya et al., 2020). Therefore, a clear understanding of the mechanisms that mediate mitochondrial transfer will shed light on how this process is regulated and can be exploited for therapeutic purposes.
To meet different physiological needs, mitochondria are dynamically transported to specific cellular locations where they perform their functions. The intracellular transfer of mitochondria was first observed in neurons with long axons (Weiss and Mayr, 1971). The state of axon growth determines the proportion of mitochondria that are in motion or at rest: in the region of the active growth cone, the transition of mitochondria from motion to rest is reversed when axon growth is blocked. In addition, neuronal activity increases the mitochondrial transport in synapses. Within these neurons, mitochondria traverse from the cell body to provide energy for long-distance processing and return to the cell body afterward, exhibiting both anterograde (from the nucleus to mitochondria) and retrograde (from mitochondria to nucleus) motility as the classical mechanism of mitochondrial movement. The differences between the two types of intracellular mitochondrial motion patterns are shown in Figure 2 and Table 3.
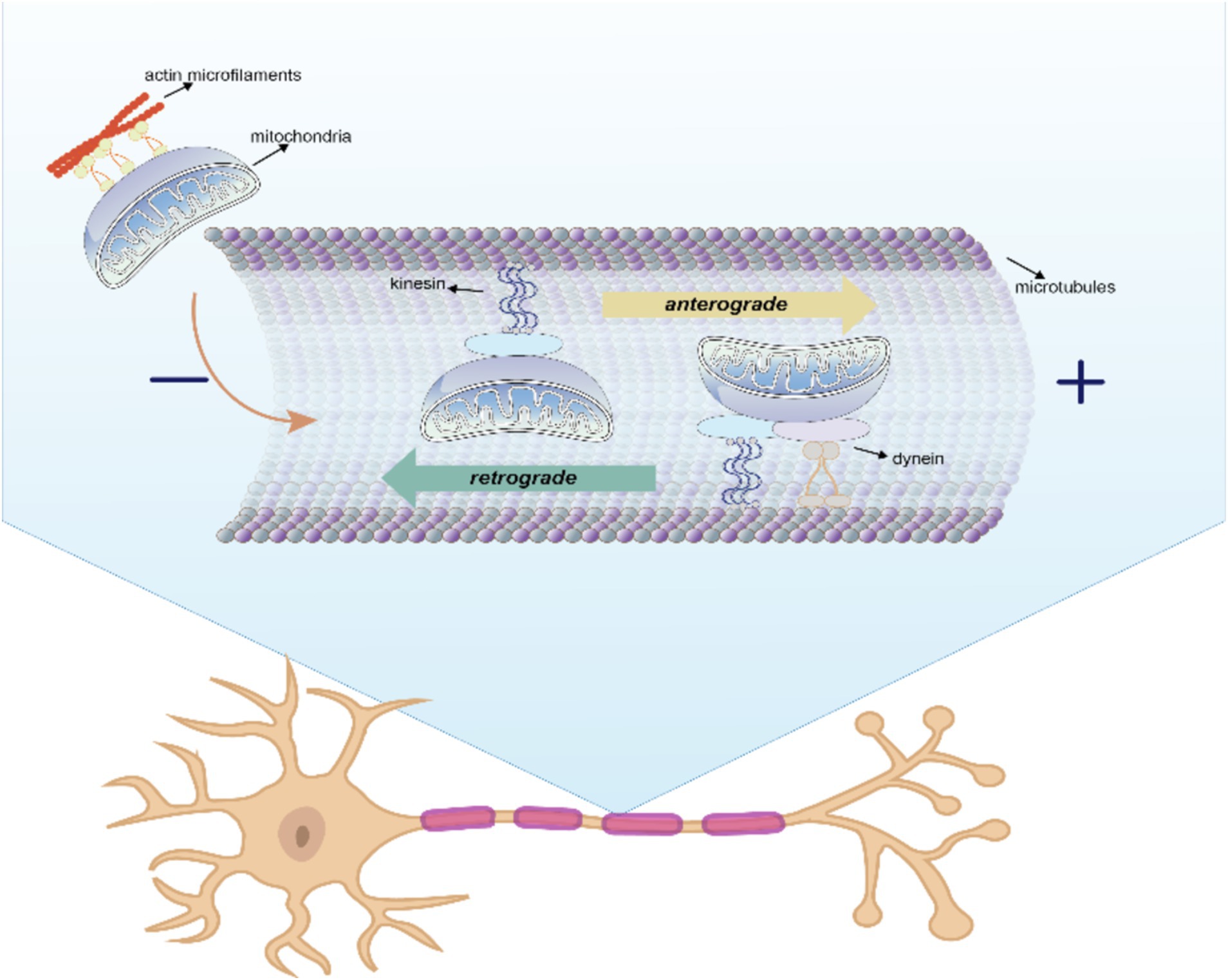
Figure 2. Anterograde and retrograde directions of intracellular mitochondrial movement. In this process, kinesin is responsible for moving mitochondria in an anterograde direction toward the nerve terminal, whereas kinesin and dynein move mitochondria in a retrograde direction toward the soma.
Kinesin is responsible for moving mitochondria in an anterograde direction toward the nerve terminal, whereas kinesin and dynein move mitochondria in a retrograde direction toward the soma (Seiler et al., 1999). Microtubules serve as rails for the long-range transport of mitochondria, whereas actin microfilaments in dendritic spines, growth cones, and synaptic buds are mainly used for docking and short-range movements (Hirokawa and Takemura, 2005). Intracellular locomotion of mitochondria is based on the interaction of motor and adapter proteins with the microtubule cytoskeleton to transport mitochondria across the neuron. An APP mouse model demonstrated impaired anterograde movement, while in presenilin-1 (PSEN1) and APP/PSEN1 mouse models (Trushina et al., 2012), both retrograde and anterograde transport were compromised. These findings strongly indicate the presence of intracellular mitochondrial transfer in AD.
Recently, a novel mechanism for mitochondrial movement, known as transcellular mitochondria transfer, has emerged (Shanmughapriya et al., 2020). In the context of AD, astrocytes play a crucial role in rescuing damaged neurons after cerebral ischemia by providing them with healthy mitochondria (Fiebig et al., 2019). Conversely, neurons release damaged mitochondria, which are then transferred to astrocytes for disposal and recycling. Moreover, the presence of extracellular particles containing mitochondria in conditioned media from rat cortical astrocytes has been confirmed through electron microscopy (Hayakawa et al., 2016). Transcellular mitochondrial transfer involves various structures and processes, including tunneling nanotubes (TNTs), membrane microvesicles (MVs), gap junctions, cell fusion, and mitochondrial expulsion, and it can lead to significant changes in various biological functions.
In 2004, Vandendriessche et al. (2020) first detected the movement of organelles between mammalian cells via TNTs. These TNTs consist of the cell membrane, F-actin, myosin, and tubulin. They serve as conduits for bidirectional movement of a wide range of substances, including small molecules, nearly all neurodegenerative proteins (including Tau (Tardivel et al., 2016) and Aβ (Dilna et al., 2021)), organelles, various ions, and even viral particles (Panasiuk et al., 2018). Therefore, the impact of intercellular TNTs is likely determined by both the transferred cargo and the types and states of connected cells.
Among the transported cargoes that have been described, the mitochondrion appears to be the most frequently reported organelle that can be unidirectionally or bidirectionally transferred via TNTs (Driscoll et al., 2022). Accumulating evidence suggests that the intracellular accumulation of damaged mitochondria can induce the biogenesis of TNT-based mitochondrial transfer (Torralba et al., 2016) in AD (Valappil et al., 2022). However, the mechanisms by which TNTs precisely target recipient cells remain elusive. While the transport of mitochondria via TNTs is well defined, the directionality of mitochondrial transfer and other factors essential for initiating and promoting TNT formation in AD are not fully understood. On the contrary, other research argues against this notion, finding that the inhibiting TNTs did not impact mitochondrial transfer, despite the frequent observation of mitochondria within these structures.
EVs are bilayer membranous structures derived from the endosomal system or shed from the plasma membrane, and they serve as crucial carriers for mitochondrial transport. EVs are found in different types based on their origin, size, and molecular composition, including exosomes (30–100 nm in diameter), MVs (100 nm–1 μm in diameter) and apoptotic bodies (1–2 μm), depending on their origin, size, and molecular constitution (van Niel et al., 2018; Sardar Sinha et al., 2018). They contain cellular proteins, nucleic acids, and organelles that can reach all parts of the body through the circulation and other body fluids due to differences in mitochondrial pressure. Evidence indicates that various cell types, such as astrocytes, neurons (Vandendriessche et al., 2020), mesenchymal stem cells (Phinney et al., 2015), epithelial cells, immune cells (Hosseinkhani et al., 2018), and hepatocytes (Cai et al., 2017), release EVs, which play a pivotal role in intercellular communication during numerous pathophysiological processes (Iraci et al., 2016).
Although the mechanisms by which mitochondrial proteins or mtDNA are loaded into EVs remain unknown, mitochondrial components have been detected in EVs. Three different types of extracellular mitochondrial contents within EVs have been reported: free mtDNA, functional mitochondria, and mitochondrial content (Amari and Germain, 2021). MV-mediated mitochondrial transfer enhances macrophage function by improving mitochondrial bioenergetics. Several studies have clearly highlighted the harmful role of EVs in the pathogenesis of AD (Aulston et al., 2019; Winston et al., 2016). One study found that neuronal- and astrocytic-origin-enriched EVs from plasma and human cells were carriers of AD pathogenic proteins (Nogueras-Ortiz et al., 2020). Specifically, small EVs spread mitochondrial particles, mitochondria (Li et al., 2020), and toxic proteins (Sardar Sinha et al., 2018), inducing neuronal loss and contributing to neuroinflammation and AD progression.
Gap junctions are plasma membrane channels composed of connexins that transfer molecules of up to 1,000 Daltons (Ishikawa et al., 2012), including nutrients, metabolites, second messengers, cations, anions, and whole mitochondria (Norris, 2021) between cells. Norris (2021) found that mitochondria and endosomes are incorporated into double-membrane vesicles, called connexosomes or annular gap junctions, that form as a result of gap junction internalization. This process may facilitate not only the transfer of mitochondria, but also the release of small molecules from the enclosed mitochondria into the receiving cell cytosol.
It is hypothesized that neuronal and glial gap junctions play a role in propagating neuronal damage in AD models (Pechlivanidou et al., 2022). In older 5XFAD mice (Angeli et al., 2020), connectivity of astrocyte-oligodendrocyte gap junctions decreases, and the expression of gap junctions protein connexin 43 (Cx43) appears to shift, favoring astrocyte-astrocyte gap junctions and/or hemichannels, which could impair oligodendrocyte homeostasis and myelination. Recent studies (Berridge et al., 2016) indicate that Cx43, which mediates the connection between mitochondrial particles and the plasma membrane to form channels, is required for mitochondrial transfer. When gap junctions are inhibited, the benefits of respiratory capacity and ATP synthesis rapidly decline (Li et al., 2019).
Mitochondrial extrusion is another possible mechanism by which naked mitochondria or mitochondrial components are transferred from one cell to another. The mechanism of recognition and extrusion of such damaged mitochondrial components seems to involve the protein Parkin (Crewe et al., 2021). Increasing evidence suggests that the ejection of damaged mitochondria plays an important role in maintaining intracellular mitochondrial quality. This process occurs during developmental processes, inflammatory activation (Liu et al., 2021), or in post-mitotic cells (Lyamzaev et al., 2022) when mitochondria become unfit to remain in the cells. For example, HeLa cells extruded fragmented mitochondria for extracellular mitoptosis under reactive oxygen species (ROS) stress (Lyamzaev et al., 2008). Notably, intact actin and tubulin cytoskeletons and mitochondrial fragmentation are prerequisites for mitochondrial extrusion (Nakajima et al., 2008).
Mitochondrial extrusion is a phenomenon that occurs in response to tumor necrosis factor α-induced cell death (Nakajima et al., 2008); this process occurs both in vitro and in vivo and involves the formation of cytoplasmic vacuoles originating in the plasma membrane—these vacuoles engulf fragmented mitochondria and expel them into the extracellular space, contributing to AD induction (König and McBride, 2024). Potential mechanisms include selective packing into mitochondrial-derived vesicles (MDVs) or autophagosomes before ejection into extracellular spaces, or direct transportation via a mitocytosis-like process (Fan et al., 2022). The mechanisms underlying the ejection of damaged mitochondria in AD are not yet fully understood.
Cell fusion is a process in which two or more individual cells fuse their plasma membranes, sharing organelles and cytosolic compounds, while their individual nuclei remain intact. This process can be triggered by injury and inflammation (Aguilar et al., 2013). Cell fusion plays a crucial role in several physiological and pathological processes (Lee and Chen, 2019), including mitochondrial transfer. Acquistapace et al. (2011) co-cultured human adipose stem cells with mouse cardiomyocytes and found that F-actin junctions were formed between the cells, indicating that mitochondria participate in the recovery of cell function through partial cell fusion. Similarly, Spees et al. (2006) demonstrated that cells could acquire exogenous mitochondria but not exogenous nuclei, indicating that complete cell fusion is unlikely. However, these findings do not definitively rule out the possibility of cell fusion followed by selective loss of the donor cell nuclei. Mitochondria may use TNT to exchange damaged mtDNA for incomplete fusion between two cells under oxidative stress (Guo et al., 2023). Further investigation is needed to determine whether AD cells undergo mitochondrial transfer through complete or partial fusion (Spees et al., 2006).
Endocytosis is a fundamental cellular process that facilitates active transport across the plasma membrane into cells (Wei et al., 2018). Endocytosed mitochondria are typically found in close proximity to the endogenous mitochondrial network, which is usually located apical to the contractile apparatus (Cowan et al., 2017). Recent reports have suggested that the clathrin-mediated endocytic pathway is one of the main mechanisms of AD (Treusch et al., 2011). However, HepG2 cells can engulf mitochondria via cellular extensions, but clathrin-mediated endocytosis, caveolae-dependent endocytosis, lipid rafts, and other endocytosis mechanisms do not involve interactions with cellular extensions (Kesner et al., 2016). Inhibitors of macrophage phagocytosis may block mitochondrial transfer (Jackson et al., 2016). Nevertheless, understanding regarding how endocytosis specifically regulates mitochondrial transcellular transfer in the context of AD remains limited.
In summary, several hypotheses have been proposed to explain the specific mechanisms underlying mitochondrial transfer (Table 4). Of note, these mechanisms may not be entirely independent from one another. For example, the gap junction protein Cx43 is an important regulator of both TNT formation and function. Moreover, gap junctions and TNTs share some compositional similarities, but they serve distinct functions due to differences in the range of connectivity and the size of molecules they transport. Gap junctions facilitate short-range intercellular interactions, allowing for the transfer of molecules up to 1.2 kDa (Ariazi et al., 2017), whereas TNTs mediate long-range intercellular interactions, allowing greater material transfer. Mitochondrial transfer can occur through either partial or complete cell fusion, often facilitated by TNT formation. Diaphragms are present at TNT-cell junctions, requiring transported substances to pass through this membrane to enter target cells. Additionally, this process may involve cellular endocytosis (Bittins and Wang, 2017). Whether the combination of these communication mechanisms such as TNTs and gap junctions holds significance remains unclear, and clear research evidence or conclusions regarding potential differences in the efficiency and efficacy of different transfer modes is lacking. Therefore, further research is necessary to comprehensively understand the interconnections between these mechanisms and their respective contributions to mitochondrial transfer.
Mitochondrial transfer represents a mode of intracellular and intercellular communication that is widespread among organisms. A considerable body of evidence suggests that movement of mitochondria, both between cells and within individual cells, is a phenomenon observed in mammalian cells both in laboratory settings and in living organisms, occurring under various physiological and pathological conditions. These findings have significantly expanded understanding of mitochondrial transfer. Intracellular and intracellular mitochondrial transfer have different triggering factors, and both contribute to AD pathogenesis. Nevertheless, another connection is also present. Intercellular mitochondrial transfer, a continuation of intracellular mitochondrial transport increases the mtDNA content of the recipient cells and restores their capacity for respiration and survival (Liu et al., 2022).
Dendrites and an axon form a highly polarized structure along the direction of impulse propagation in neurons, which is the basis of intracellular mitochondrial movement (Hirokawa et al., 2010). The intracellular motion of mitochondria is bidirectional, and the direction changes frequently. These movements are regulated by a range of different signals and mechanisms that determine the movement of mitochondria in neurons. Intracellular transport is essential for neuronal development, function, and survival. This intercellular exchange of mitochondria can provide an exogenous mitochondrial source, playing a dynamic role in cellular and tissue responses to CNS injuries. It appears to be essential for the maintenance and restoration of homeostasis within the organism (Wei et al., 2018). Nonetheless, several intricate mechanisms remain to be elucidated. These include the precise processes governing the fusion of TNTs with the target cell membrane, the reception of signals by surrounding cells, the release of EVs, the endocytosis of EVs by target cells, the role of gap junctions and the cytoskeleton in TNTs and EVs, the accurate regulation of mitochondrial transfer mediated by microtubules and microfilaments, and the pathways by which mitochondria are internalized after their release from donor cells and subsequent contact with recipient cells. These areas require further investigation.
Notably, mitochondrial transfer in AD is a bidirectional process, with some transfers proving beneficial for cell survival, while others may potentially exert toxicity on the recipient cells. Despite the growing body of research concerning mitochondrial transfer in AD, many questions remain unanswered. For example, the frequency of this phenomenon in vivo remains uncertain, and there is a need to discern whether the exchange of mitochondria observed in vitro is merely an artifact of cell culture conditions. Additionally, understanding the degree of cellular damage required to initiate intercellular mitochondrial transfer is crucial. Furthermore, the impact of mitochondrial transfer or transplantation on mitochondrial homeostasis within recipient cells has yet to be comprehensively described in the existing literature. Devoting increased attention to evaluating both the quantity and quality of transferred mitochondria and their subsequent effects on mitochondrial homeostasis during transplantation is imperative. Addressing these unresolved issues necessitates further dedicated research efforts.
Mitochondrial dysfunction stands as a pivotal contributor to AD pathogenesis. Consequently, intracellular and intercellular mitochondrial transfer may be an effective target for the treatment of AD. Restoring mitochondrial function and preserving damaged mitochondria play crucial roles in treating brain injury. Facilitating intercellular mitochondrial transfer through mechanisms such as accelerating neuronal release or enhancing astrocytic phagocytosis holds the potential to be a valuable therapeutic strategy for future AD treatments.
YW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XD: Visualization, Writing – original draft. HG: Writing – review & editing. JH: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. ML: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the Beijing Natural Science Foundation Project (grant no. 7222297), Science and technology Innovation Project of China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences (grant no. CI2021A01402), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 81904194 and 82074509).
The authors would like to express their sincerest gratitude to all the staff of the Department of Geriatrics at Xiyuan Hospital including doctors, nurses and administrators.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
AD, Alzheimer’s disease; Aβ, amyloid-β; APP, amyloid precursor protein; CNS, central nervous system; Cx43, connexin 43; EV, extracellular vesicle; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; TNTs, Tunneling nanotubes.
Acquistapace, A., Bru, T., Lesault, P. F., Figeac, F., Coudert, A. E., le Coz, O., et al. (2011). Human mesenchymal stem cells reprogram adult cardiomyocytes toward a progenitor-like state through partial cell fusion and mitochondria transfer. Stem Cells 29, 812–824. doi: 10.1002/stem.632
Aguilar, P. S., Baylies, M. K., Fleissner, A., Helming, L., Inoue, N., Podbilewicz, B., et al. (2013). Genetic basis of cell-cell fusion mechanisms. Trends Genet. 29, 427–437. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2013.01.011
Ahmad, T., Mukherjee, S., Pattnaik, B., Kumar, M., Singh, S., Kumar, M., et al. (2014). Miro1 regulates intercellular mitochondrial transport & enhances mesenchymal stem cell rescue efficacy. EMBO J. 33, 994–1010. doi: 10.1002/embj.201386030
Amari, L., and Germain, M. (2021). Mitochondrial extracellular vesicles - origins and roles. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 14:767219. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.767219
Angeli, S., Kousiappa, I., Stavrou, M., Sargiannidou, I., Georgiou, E., Papacostas, S. S., et al. (2020). Altered expression of glial gap junction proteins Cx43, Cx30, and Cx47 in the 5XFAD model of Alzheimer's disease. Front. Neurosci. 14:582934. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.582934
Ariazi, J., Benowitz, A., De Biasi, V., Den Boer, M. L., Cherqui, S., Cui, H. F., et al. (2017). Tunneling nanotubes and gap junctions-their role in long-range intercellular communication during development, health, and disease conditions. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 10:333. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00333
Aulston, B., Liu, Q., Mante, M., Florio, J., Rissman, R. A., and Yuan, S. H. (2019). Extracellular vesicles isolated from familial Alzheimer's disease neuronal cultures induce aberrant tau phosphorylation in the wild-type mouse brain. J. Alzheimers Dis. 72, 575–585. doi: 10.3233/jad-190656
Berridge, M. V., Schneider, R. T., and McConnell, M. J. (2016). Mitochondrial transfer from astrocytes to neurons following ischemic insult: guilt by association? Cell Metab. 24, 376–378. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.08.023
Bittins, M., and Wang, X. (2017). TNT-induced phagocytosis: tunneling nanotubes mediate the transfer of pro-phagocytic signals from apoptotic to viable cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 232, 2271–2279. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25584
Cai, Y., Xu, M. J., Koritzinsky, E. H., Zhou, Z., Wang, W., Cao, H. X., et al. (2017). Mitochondrial DNA-enriched microparticles promote acute-on-chronic alcoholic neutrophilia and hepatotoxicity. J. Insight 2:92634. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.92634
Calkins, M. J., and Reddy, P. H. (2011). Amyloid beta impairs mitochondrial anterograde transport and degenerates synapses in Alzheimer's disease neurons. BBA-Mol. Basis Dis. 1812, 507–513. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.01.007
Cereghetti, G. M., and Scorrano, L. (2006). The many shapes of mitochondrial death. Oncogene 25, 4717–4724. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209605
Chakraborty, R., Nonaka, T., Hasegawa, M., and Zurzolo, C. (2023). Tunnelling nanotubes between neuronal and microglial cells allow bi-directional transfer of α-Synuclein and mitochondria. Cell Death Dis. 14:329. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05835-8
Chen, E. L., Chen, Z., Chen, L. X., and Hu, X. L. (2022). Platelet-derived respiratory-competent mitochondria transfer to mesenchymal stem cells to promote wound healing via metabolic reprogramming. Platelets 33, 171–173. doi: 10.1080/09537104.2021.1961717
Cheng, Y., Liu, P., Zheng, Q., Gao, G., Yuan, J., Wang, P., et al. (2018). Mitochondrial trafficking and processing of telomerase RNA TERC. Cell Rep. 24, 2589–2595. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.08.003
Cowan, D. B., Yao, R. A., Thedsanamoorthy, J. K., Zurakowski, D., del Nido, P. J., and McCully, J. D. (2017). Transit and integration of extracellular mitochondria in human heart cells. Sci. Rep. 7:17450. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17813-0
Crewe, C., Funcke, J. B., Li, S., Joffin, N., Gliniak, C. M., Ghaben, A. L., et al. (2021). Extracellular vesicle-based interorgan transport of mitochondria from energetically stressed adipocytes. Cell Metab. 33, 1853–1868. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2021.08.002
Davis, C. H. O., Kim, K. Y., Bushong, E. A., Mills, E. A., Boassa, D., Shih, T., et al. (2014). Transcellular degradation of axonal mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111, 9633–9638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1404651111
Devi, L., Prabhu, B., Galati, D. F., Avadhani, N., and Anandatheerthavarada, H. (2006). Accumulation of amyloid precursor protein in the mitochondrial import channels of human Alzheimer's disease brain is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. J. Neurosci. 26, 9057–9068. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1469-06.2006
Dilna, A., Deepak, K. V., Damodaran, N., Kielkopf, C. S., Kagedal, K., Ollinger, K., et al. (2021). Amyloid-β induced membrane damage instigates tunneling nanotube-like conduits by p21-activated kinase dependent actin remodulation. BBA-Mol. Basis Dis. 1867:166246. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166246
Driscoll, J., Gondaliya, P., and Patel, T. (2022). Tunneling nanotube-mediated communication: a mechanism of intercellular nucleic acid transfer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:5487. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105487
Du, H., Guo, L., Yan, S. Q., Sosunov, A. A., McKhann, G. M., and Yan, S. S. (2010). Early deficits in synaptic mitochondria in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 18670–18675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1006586107
Du, F., Yu, Q., and Yan, S. S. (2021). PINK1 activation attenuates impaired neuronal-like differentiation and synaptogenesis and mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease trans-mitochondrial Cybrid cells. J. Alzheimers Dis. 81, 1749–1761. doi: 10.3233/jad-210095
English, K., Shepherd, A., Uzor, N. E., Trinh, R., Kavelaars, A., and Heijnen, C. J. (2020). Astrocytes rescue neuronal health after cisplatin treatment through mitochondrial transfer. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 8:36. doi: 10.1186/s40478-020-00897-7
Fan, Q., Maejima, Y., Wei, L., Nakagama, S., Shiheido-Watanabe, Y., and Sasano, T. (2022). The pathophysiological significance of "mitochondrial ejection" from cells. Biomol. Ther. 12:1770. doi: 10.3390/biom12121770
Fiebig, C., Keiner, S., Ebert, B., Schäffner, I., Jagasia, R., Lie, D. C., et al. (2019). Mitochondrial dysfunction in astrocytes impairs the generation of reactive astrocytes and enhances neuronal cell death in the cortex upon Photothrombotic lesion. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 12:40. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00040
Geng, Z., Guan, S., Wang, S. Q., Yu, Z. X., Liu, T. C., Du, S. A., et al. (2023). Intercellular mitochondrial transfer in the brain, a new perspective for targeted treatment of central nervous system diseases. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 29, 3121–3135. doi: 10.1111/cns.14344
Guo, X. D., Can, C., Liu, W. C., Wei, Y. H., Yang, X. Y., Liu, J. T., et al. (2023). Mitochondrial transfer in hematological malignancies. Research 11:89. doi: 10.1186/s40364-023-00529-x
Guo, L., Du, H., Yan, S. Q., Wu, X. P., McKhann, G. M., Chen, J. X., et al. (2013). Cyclophilin D deficiency rescues axonal mitochondrial transport in Alzheimer's neurons. PLoS One 8:54914. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054914
Han, J., Park, H., Maharana, C., Gwon, A. R., Park, J., Baek, S. H., et al. (2021). Alzheimer's disease-causing presenilin-1 mutations have deleterious effects on mitochondrial function. Theranostics 11, 8855–8873. doi: 10.7150/thno.59776
Hayakawa, K., Esposito, E., Wang, X., Terasaki, Y., Liu, Y., Xing, C., et al. (2016). Transfer of mitochondria from astrocytes to neurons after stroke. Nature 535, 551–555. doi: 10.1038/nature18928
Hirai, K., Aliev, G., Nunomura, A., Fujioka, H., Russell, R. L., Atwood, C. S., et al. (2001). Mitochondrial abnormalities in Alzheimer's disease. Rapid Commun. 21, 3017–3023. doi: 10.1523/jneurosci.21-09-03017.2001
Hirokawa, N., Niwa, S., and Tanaka, Y. (2010). Molecular motors in neurons: transport mechanisms and roles in brain function, development, and disease. Neuron 68, 610–638. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2010.09.039
Hirokawa, N., and Takemura, R. (2005). Molecular motors and mechanisms of directional transport in neurons. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6, 201–214. doi: 10.1038/nrn1624
Hosseinkhani, B., Kuypers, S., van den Akker, N. M. S., Molin, D. G. M., and Michiels, L. (2018). Extracellular vesicles work as a functional inflammatory mediator between vascular endothelial cells and immune cells. Front. Immunol. 9:1789. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01789
Iraci, N., Leonardi, T., Gessler, F., Vega, B., and Pluchino, S. (2016). Focus on extracellular vesicles: physiological role and signalling properties of extracellular membrane vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17:171. doi: 10.3390/ijms17020171
Ishikawa, E. T., Gonzalez-Nieto, D., Ghiaur, G., Dunn, S. K., Ficker, A. M., Murali, B., et al. (2012). Connexin-43 prevents hematopoietic stem cell senescence through transfer of reactive oxygen species to bone marrow stromal cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 9071–9076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1120358109
Islam, M. N., Das, S. R., Emin, M. T., Wei, M., Sun, L., Westphalen, K., et al. (2012). Mitochondrial transfer from bone-marrow-derived stromal cells to pulmonary alveoli protects against acute lung injury. Nat. Med. 18, 759–765. doi: 10.1038/nm.2736
Jackson, M. V., Morrison, T. J., Doherty, D. F., McAuley, D. F., Matthay, M. A., Kissenpfennig, A., et al. (2016). Mitochondrial transfer via tunneling nanotubes is an important mechanism by which mesenchymal stem cells enhance macrophage phagocytosis in the in vitro and in vivo models of ARDS. Stem Cells 34, 2210–2223. doi: 10.1002/stem.2372
Jain, R., Begum, N., Tryphena, K. P., Singh, S. B., Srivastava, S., Rai, S. N., et al. (2023). Inter and intracellular mitochondrial transfer: future of mitochondrial transplant therapy in Parkinson's disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 159:114268. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114268
John, A., and Reddy, P. H. (2021). Synaptic basis of Alzheimer’s disease: focus on synaptic amyloid beta, P-tau and mitochondria. Ageing Res. Rev. 65:101208. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101208
Joshi, A. U., Minhas, P. S., Liddelow, S. A., Haileselassie, B., Andreasson, K. I., Dorn, G. W., et al. (2019). Fragmented mitochondria released from microglia trigger A1 astrocytic response and propagate inflammatory neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 22:1635. doi: 10.1038/s41593-019-0486-0
Kesner, E. E., Saada-Reich, A., and Lorberboum-Galski, H. (2016). Characteristics of mitochondrial transformation into human cells. Sci. Rep. 6:26057. doi: 10.1038/srep26057
Kim, D. K., and Mook-Jung, I. (2019). The role of cell type-specific mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. BMB Rep. 52, 679–688. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2019.52.12.282
König, T., and McBride, H. M. (2024). Mitochondrial-derived vesicles in metabolism, disease, and aging. Cell Metab. 36, 21–35. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2023.11.014
Kopeikina, K. J., Carlson, G. A., Pitstick, R., Ludvigson, A. E., Peters, A., Luebke, J. I., et al. (2011). Tau accumulation causes mitochondrial distribution deficits in neurons in a mouse model of tauopathy and in human Alzheimer's disease brain. Am. J. Pathol. 179, 2071–2082. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.07.004
Koyanagi, M., Brandes, R. P., Haendeler, J., Zeiher, A. M., and Dimmeler, S. (2005). Cell-to-cell connection of endothelial progenitor cells with cardiac myocytes by nanotubes - a novel mechanism for cell fate changes? Circ. Res. 96, 1039–1041. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.0000168650.23479.0c
Lampinen, R., Belaya, I., Saveleva, L., Liddell, J. R., Rait, D., Huuskonen, M. T., et al. (2022). Neuron-astrocyte transmitophagy is altered in Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 170:105753. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105753
Lee, D. M., and Chen, E. H. (2019). Drosophila myoblast fusion: invasion and resistance for the ultimate union. Annu. Rev. Genet. 53, 67–91. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120116-024603
Li, B., Liu, J. H., Gu, G. J., Han, X., Zhang, Q., and Zhang, W. (2020). Impact of neural stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles on mitochondrial dysfunction, sirtuin 1 level, and synaptic deficits in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurochem. 154, 502–518. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15001
Li, H., Wang, C., He, T., Zhao, T., Chen, Y. Y., Shen, Y. L., et al. (2019). Mitochondrial transfer from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to motor neurons in spinal cord injury rats via gap junction. Theranostics 9, 2017–2035. doi: 10.7150/thno.29400
Lippert, T., and Borlongan, C. V. (2019). Prophylactic treatment of hyperbaric oxygen treatment mitigates inflammatory response via mitochondria transfer. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 25, 815–823. doi: 10.1111/cns.13124
Liu, D. L., Gao, Y. S., Liu, J., Huang, Y. G., Yin, J. H., Feng, Y. Y., et al. (2021). Intercellular mitochondrial transfer as a means of tissue revitalization. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 6:65. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00440-z
Liu, Z., Sun, Y., Qi, Z., Cao, L., and Ding, S. (2022). Mitochondrial transfer/transplantation: an emerging therapeutic approach for multiple diseases. Cell Biosci. 12:66. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00805-7
Lyamzaev, K. G., Nepryakhina, O. K., Saprunova, V. B., Bakeeva, L. E., Pletjushkina, O. Y., Chernyak, B. V., et al. (2008). Novel mechanism of elimination of malfunctioning mitochondria (mitoptosis): formation of mitoptotic bodies and extrusion of mitochondrial material from the cell. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1777, 817–825. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.03.027
Lyamzaev, K. G., Zinovkin, R. A., and Chernyak, B. (2022). Extrusion of mitochondria: garbage clearance or cell-cell communication signals? J. Cell. Physiol. 237, 2345–2356. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30711
Marlein, C. R., Piddock, R. E., Mistry, J. J., Zaitseva, L., Hellmich, C., Horton, R. H., et al. (2019). CD38-driven mitochondrial trafficking promotes bioenergetic plasticity in multiple myeloma. Cancer Res. 79, 2285–2297. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-18-0773
Marlein, C. R., Zaitseva, L., Piddock, R. E., Raso-Barnett, L., Scott, M. A., Ingham, C. J., et al. (2018). PGC-1α driven mitochondrial biogenesis in stromal cells underpins mitochondrial trafficking to leukemic blasts. Leukemia 32, 2073–2077. doi: 10.1038/s41375-018-0221-y
Martín-Maestro, P., Gargini, R., García, E., Perry, G., Avila, J., and García-Escudero, V. (2017). Slower dynamics and aged mitochondria in sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017:9302761. doi: 10.1155/2017/9302761
Mattenberger, Y., James, D. I., and Martinou, J. C. (2003). Fusion of mitochondria in mammalian cells is dependent on the mitochondrial inner membrane potential and independent of microtubules or actin. FEBS Lett. 538, 53–59. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(03)00124-8
Miller, K. E., and Sheetz, M. P. (2004). Axonal mitochondrial transport and potential are correlated. J. Cell Sci. 117, 2791–2804. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01130
Moschoi, R., Imbert, V., Nebout, M., Chiche, J., Mary, D., Prebet, T., et al. (2016). Protective mitochondrial transfer from bone marrow stromal cells to acute myeloid leukemic cells during chemotherapy. Blood 128, 253–264. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-07-655860
Nakajima, A., Kurihara, H., Yagita, H., Okumura, K., and Nakano, H. (2008). Mitochondrial extrusion through the cytoplasmic vacuoles during cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 24128–24135. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M802996200
Niescier, R. F., Kwak, S. K., Joo, S. H., Chang, K. T., and Min, K. T. (2016). Dynamics of mitochondrial transport in axons. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 10:123. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00123
Nitzan, K., Benhamron, S., Valitsky, M., Kesner, E. E., Lichtenstein, M., Ben-Zvi, A., et al. (2019). Mitochondrial transfer ameliorates cognitive deficits, neuronal loss, and gliosis in Alzheimer's disease mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 72, 587–604. doi: 10.3233/jad-190853
Nogueras-Ortiz, C. J., Mahairaki, V., Delgado-Peraza, F., Das, D., Avgerinos, K., Eren, E., et al. (2020). Astrocyte- and neuron-derived extracellular vesicles from Alzheimer's disease patients effect complement-mediated neurotoxicity. Cells 9:1618. doi: 10.3390/cells9071618
Norris, R. P. (2021). Transfer of mitochondria and endosomes between cells by gap junction internalization. Traffic 22, 174–179. doi: 10.1111/tra.12786
Nygren, J. M., Liuba, K., Breitbach, M., Stott, S., Thorén, L., Roell, W., et al. (2008). Myeloid and lymphoid contribution to non-haematopoietic lineages through irradiation-induced heterotypic cell fusion. Nat. Cell Biol. 10, 584–592. doi: 10.1038/ncb1721
Padilla-Sánchez, S. D., Navarrete, D., Caicedo, A., and Teran, E. (2020). Circulating cell-free mitochondrial DNA levels correlate with body mass index and age. BBA-Mol. Basis Dis. 1866:165963. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165963
Panasiuk, M., Rychlowski, M., Derewonko, N., and Bienkowska-Szewczyk, K. (2018). Tunneling nanotubes as a novel route of cell-to-cell spread of herpesviruses. J. Virol. 92:18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00090-18
Pechlivanidou, M., Kousiappa, I., Angeli, S., Sargiannidou, I., Koupparis, A. M., Papacostas, S. S., et al. (2022). Glial gap junction pathology in the spinal cord of the 5xFAD mouse model of early-onset Alzheimer's disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:5597. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415597
Pérez, M. J., Vergara-Pulgar, K., Jara, C., Cabezas-Opazo, F., and Quintanilla, R. A. (2018). Caspase-cleaved tau impairs mitochondrial dynamics in Alzheimer's disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 55, 1004–1018. doi: 10.1007/s12035-017-0385-x
Phinney, D. G., Di Giuseppe, M., Njah, J., Sala, E., Shiva, S., St Croix, C. M., et al. (2015). Mesenchymal stem cells use extracellular vesicles to outsource mitophagy and shuttle microRNAs. Nat. Commun. 6:8472. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9472
Plotnikov, E. Y., Khryapenkova, T. G., Vasileva, A. K., Marey, M. V., Galkina, S. I., Isaev, N. K., et al. (2008). Cell-to-cell cross-talk between mesenchymal stem cells and cardiomyocytes in co-culture. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 12, 1622–1631. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2007.00205.x
Qi, Z. H., Huang, Z., Xie, F., and Chen, L. X. (2019). Dynamin-related protein 1: a critical protein in the pathogenesis of neural system dysfunctions and neurodegenerative diseases. J. Cell. Physiol. 234, 10032–10046. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27866
Reiman, E. M., Chen, K., Alexander, G. E., Caselli, R. J., Bandy, D., Osborne, D., et al. (2004). Functional brain abnormalities in young adults at genetic risk for late-onset Alzheimer's dementia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 284–289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2635903100
Ren, X., Keeney, J. T. R., Miriyala, S., Noel, T., Powell, D. K., Chaiswing, L., et al. (2019). The triangle of death of neurons: oxidative damage, mitochondrial dysfunction, and loss of choline-containing biomolecules in brains of mice treated with doxorubicin. Advanced insights into mechanisms of chemotherapy induced cognitive impairment ("chemobrain") involving TNF-α. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 134, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.12.029
Rhein, V., Song, X., Wiesner, A., Ittner, L. M., Baysang, G., Meier, F., et al. (2009). Amyloid-beta and tau synergistically impair the oxidative phosphorylation system in triple transgenic Alzheimer's disease mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 20057–20062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0905529106
Ruthel, G., and Hollenbeck, P. J. (2003). Response of mitochondrial traffic to axon determination and differential branch growth. Rapid Commun. 23, 8618–8624. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-24-08618.2003
Rutkai, I., Merdzo, I., Wunnava, S. V., Curtin, G. T., Katakam, P. V., and Busija, D. W. (2019). Cerebrovascular function and mitochondrial bioenergetics after ischemia-reperfusion in male rats. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 39, 1056–1068. doi: 10.1177/0271678x17745028
Sang, S., Pan, X., Chen, Z., Zeng, F., Pan, S., Liu, H., et al. (2018). Thiamine diphosphate reduction strongly correlates with brain glucose hypometabolism in Alzheimer’s disease, whereas amyloid deposition does not. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 10:26. doi: 10.1186/s13195-018-0354-2
Sardar Sinha, M., Ansell-Schultz, A., Civitelli, L., Hildesjö, C., Larsson, M., Lannfelt, L., et al. (2018). Alzheimer's disease pathology propagation by exosomes containing toxic amyloid-beta oligomers. Acta Neuropathol. 136, 41–56. doi: 10.1007/s00401-018-1868-1
Seiler, S., Plamann, M., and Schliwa, M. (1999). Kinesin and dynein mutants provide novel insights into the roles of vesicle traffic during cell morphogenesis in Neurospora. Curr. Biol. 9, 779–7S1. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(99)80360-1
Shanmughapriya, S., Langford, D., and Natarajaseenivasan, K. (2020). Inter and intracellular mitochondrial trafficking in health and disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 62:101128. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2020.101128
Sharma, V. K., Singh, T. G., and Mehta, V. (2021). Stressed mitochondria: a target to intrude Alzheimer's disease. Mitochondrion 59, 48–57. doi: 10.1016/j.mito.2021.04.004
Sheng, Z. H. (2014). Mitochondrial trafficking and anchoring in neurons: new insight and implications. J. Cell Biol. 204, 1087–1098. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201312123
Spees, J. L., Olson, S. D., Whitney, M. J., and Prockop, D. J. (2006). Mitochondrial transfer between cells can rescue aerobic respiration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 1283–1288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0510511103
Sun, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., Tu, J., Wang, X. J., Su, X. D., et al. (2012). Tunneling-nanotube direction determination in neurons and astrocytes. Cell Death Dis. 3:e438. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2012.177
Swerdlow, R. H. (2018). Mitochondria and mitochondrial cascades in Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 62, 1403–1416. doi: 10.3233/jad-170585
Swomley, A. M., and Butterfield, D. A. (2015). Oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment: evidence from human data provided by redox proteomics. Arch. Toxicol. 89, 1669–1680. doi: 10.1007/s00204-015-1556-z
Takenaga, K., Koshikawa, N., and Nagase, H. (2021). Intercellular transfer of mitochondrial DNA carrying metastasis-enhancing pathogenic mutations from high- to low-metastatic tumor cells and stromal cells via extracellular vesicles. BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 22:52. doi: 10.1186/s12860-021-00391-5
Tardivel, M., Begard, S., Bousset, L., Dujardin, S., Coens, A., Melki, R., et al. (2016). Tunneling nanotube (TNT)-mediated neuron-to neuron transfer of pathological tau protein assemblies. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 4:4. doi: 10.1186/s40478-016-0386-4
Torralba, D., Baixauli, F., and Sánchez-Madrid, F. (2016). Mitochondria know no boundaries: mechanisms and functions of intercellular mitochondrial transfer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 4:107. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2016.00107
Treusch, S., Hamamichi, S., Goodman, J. L., Matlack, K. E. S., Chung, C. Y., Baru, V., et al. (2011). Functional links between Aβ toxicity, endocytic trafficking, and Alzheimer's disease risk factors in yeast. Science 334, 1241–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.1213210
Trushina, E., Nemutlu, E., Zhang, S., Christensen, T., Camp, J., Mesa, J., et al. (2012). Defects in mitochondrial dynamics and Metabolomic signatures of evolving energetic stress in mouse models of familial Alzheimer's disease. PLoS One 7:e32737. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0032737
Unuma, K., Aki, T., Funakoshi, T., Hashimoto, K., and Uemura, K. (2015). Extrusion of mitochondrial contents from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated cells: involvement of autophagy. Autophagy 11, 1520–1536. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2015.1063765
Valappil, D. K., Mini, N. J., Dilna, A., and Nath, S. (2022). Membrane interaction to intercellular spread of pathology in Alzheimer's disease. Front. Neurosci. 16:936897. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.936897
van Niel, G., D'Angelo, G., and Raposo, G. (2018). Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 213–228. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.125
Vandendriessche, C., Bruggeman, A., Van Cauwenberghe, C., and Vandenbroucke, R. E. (2020). Extracellular vesicles in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease: small entities with large consequences. Cells 9:2485. doi: 10.3390/cells9112485
Wada, K. I., Hosokawa, K., Ito, Y., and Maeda, M. (2017). Quantitative control of mitochondria transfer between live single cells using a microfluidic device. Biol. Open. 6, 1960–1965. doi: 10.1242/bio.024869
Wang, X., Su, B., Fujioka, H., and Zhu, X. (2008). Dynamin-like protein 1 reduction underlies mitochondrial morphology and distribution abnormalities in fibroblasts from sporadic Alzheimer's disease patients. Am. J. Pathol. 173, 470–482. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.071208
Wang, X. L., Su, B., Zheng, L., Perry, G., Smith, M. A., and Zhu, X. W. (2009). The role of abnormal mitochondrial dynamics in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurochem. 109, 153–159. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.05867.x
Wang, Z. X., Tan, L., and Yu, J. T. (2015). Axonal transport defects in Alzheimer's disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 51, 1309–1321. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8810-x
Wang, X., Wang, W., Li, L., Perry, G., Lee, H. G., and Zhu, X. (2014). Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1842, 1240–1247. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.10.015
Wang, J., Xiong, S., Xie, C., Markesbery, W. R., and Lovell, M. A. (2005). Increased oxidative damage in nuclear and mitochondrial DNA in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 93, 953–962. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03053.x
Wei, Z. Y., Su, W. F., Lou, H. F., Duan, S. M., and Chen, G. (2018). Trafficking pathway between plasma membrane and mitochondria via clathrin-mediated endocytosis. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 539–548. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjy060
Weiss, P. A., and Mayr, R. (1971). Neuronal organelles in neuroplasmic ("axonal") flow. Symp. Pathol. Axons Axonal Flow 5, 187–197. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-47449-1_24
Winston, C. N., Goetzl, E. J., Akers, J. C., Carter, B. S., Rockenstein, E. M., Galasko, D., et al. (2016). Prediction of conversion from mild cognitive impairment to dementia with neuronally derived blood exosome protein profile. Alzheimers Dement. 3, 63–72. doi: 10.1016/j.dadm.2016.04.001
Yasuda, K., Khandare, A., Burianovskyy, L., Maruyama, S., Zhang, F., Nasjletti, A., et al. (2011). Tunneling nanotubes mediate rescue of prematurely senescent endothelial cells by endothelial progenitors: exchange of lysosomal pool. Aging 3, 597–608. doi: 10.18632/aging.100341
Yu, Q., Fang, D., Swerdlow, R. H., Yu, H. Y., Chen, J. X., and Yan, S. S. (2016). Antioxidants rescue mitochondrial transport in differentiated Alzheimer's disease trans-mitochondrial Cybrid cells. J. Alzheimers Dis. 54, 679–690. doi: 10.3233/jad-160532
Zampieri, L. X., Silva-Almeida, C., Rondeau, J. D., and Sonveaux, P. (2021). Mitochondrial transfer in Cancer: a comprehensive review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:245. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063245
Zhang, Z., Sheng, H., Liao, L., Xu, C., Zhang, A., Yang, Y., et al. (2020). Mesenchymal stem cell-conditioned medium improves mitochondrial dysfunction and suppresses apoptosis in Okadaic acid-treated SH-SY5Y cells by extracellular vesicle mitochondrial transfer. J. Alzheimers Dis. 78, 1161–1176. doi: 10.3233/jad-200686
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, mitochondrial transfer, mitochondrial dysfunction, neuroprotection, AD treatment
Citation: Wei Y, Du X, Guo H, Han J and Liu M (2024) Mitochondrial dysfunction and Alzheimer’s disease: pathogenesis of mitochondrial transfer. Front. Aging Neurosci. 16:1517965. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1517965
Received: 27 October 2024; Accepted: 04 December 2024;
Published: 17 December 2024.
Edited by:
Prasenjit Mondal, Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School, United StatesReviewed by:
Minhong Neenah Huang, Mayo Clinic, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Wei, Du, Guo, Han and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yun Wei, d2VpeXVuXzA5MTNAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Meixia Liu, bGl1bWVpeGlhMjAwNEAxMjYuY29t
†These authors share first authorship
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.