- 1Clinic for Neuroradiology, University Hospital, Magdeburg, Germany
- 2Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, University Hospital, Magdeburg, Germany
- 3German Center for Mental Health (DZPG), Partner Site Halle-Jena-Magdeburg, Magdeburg, Germany
- 4Center for Intervention and Research on Adaptive and Maladaptive Brain Circuits Underlying Mental Health (C-I-R-C), Magdeburg, Germany
- 5Neuroradiologische Klinik, Katharinen-Hospital, Klinikum-Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany
- 6Stimulate Research Campus Magdeburg, Magdeburg, Germany
Background: Dementia can be caused by numerous different diseases that present variable clinical courses and reveal multiple patterns of brain atrophy, making its accurate early diagnosis by conventional examinative means challenging. Although highly accurate and powerful, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) currently plays only a supportive role in dementia diagnosis, largely due to the enormous volume and diversity of data it generates. AI-based software solutions/algorithms that can perform automated segmentation and volumetry analyses of MRI data are being increasingly used to address this issue. Numerous commercial and non-commercial software solutions for automated brain segmentation and volumetry exist, with FreeSurfer being the most frequently used.
Objectives: This Review is an account of the current situation regarding the application of automated brain segmentation and volumetry to dementia diagnosis.
Methods: We performed a PubMed search for “FreeSurfer AND Dementia” and obtained 493 results. Based on these search results, we conducted an in-depth source analysis to identify additional publications, software tools, and methods. Studies were analyzed for design, patient collective, and for statistical evaluation (mathematical methods, correlations).
Results: In the studies identified, the main diseases and cohorts represented were Alzheimer’s disease (n = 276), mild cognitive impairment (n = 157), frontotemporal dementia (n = 34), Parkinson’s disease (n = 29), dementia with Lewy bodies (n = 20), and healthy controls (n = 356). The findings and methods of a selection of the studies identified were summarized and discussed.
Conclusion: Our evaluation showed that, while a large number of studies and software solutions are available, many diseases are underrepresented in terms of their incidence. There is therefore plenty of scope for targeted research.
1 Introduction
According to the WHO, dementia is currently the seventh most common cause of death and one of the leading causes of disability and dependency among older people worldwide (World Health Organization, 2017). Furthermore, its incidence is likely to increase in coming years caused by aging populations. Accordingly, its early detection and prevention are matters of increasing urgency, necessitating methods for accurate diagnosis of the underlying disease. Diagnosis of dementia by clinical examination is often inconsistent and subject to inaccuracy. Additional biomarkers, such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and positron emission tomography (PET), are often not groundbreaking either. However, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) enables reliable and unambiguous classification of brain status.
Current high-resolution MRI is performed using magnetic field strengths of up to 7 Tesla, enabling excellent representations of brain tissue. However, the enormous amounts of image data generated present an obstacle to thorough analysis. An increasingly common method to address this obstacle is the use of computer software capable of automated MRI volumetry, whereby the volumes of specific anatomic brain regions are calculated using segmentation algorithms and detailed atlases.
Such segmentation tools enable a fully automated and objective assessment of brain atrophy. The results can confirm suspected diagnoses or provide differential diagnoses. Standardized use can also save time in radiological reporting.
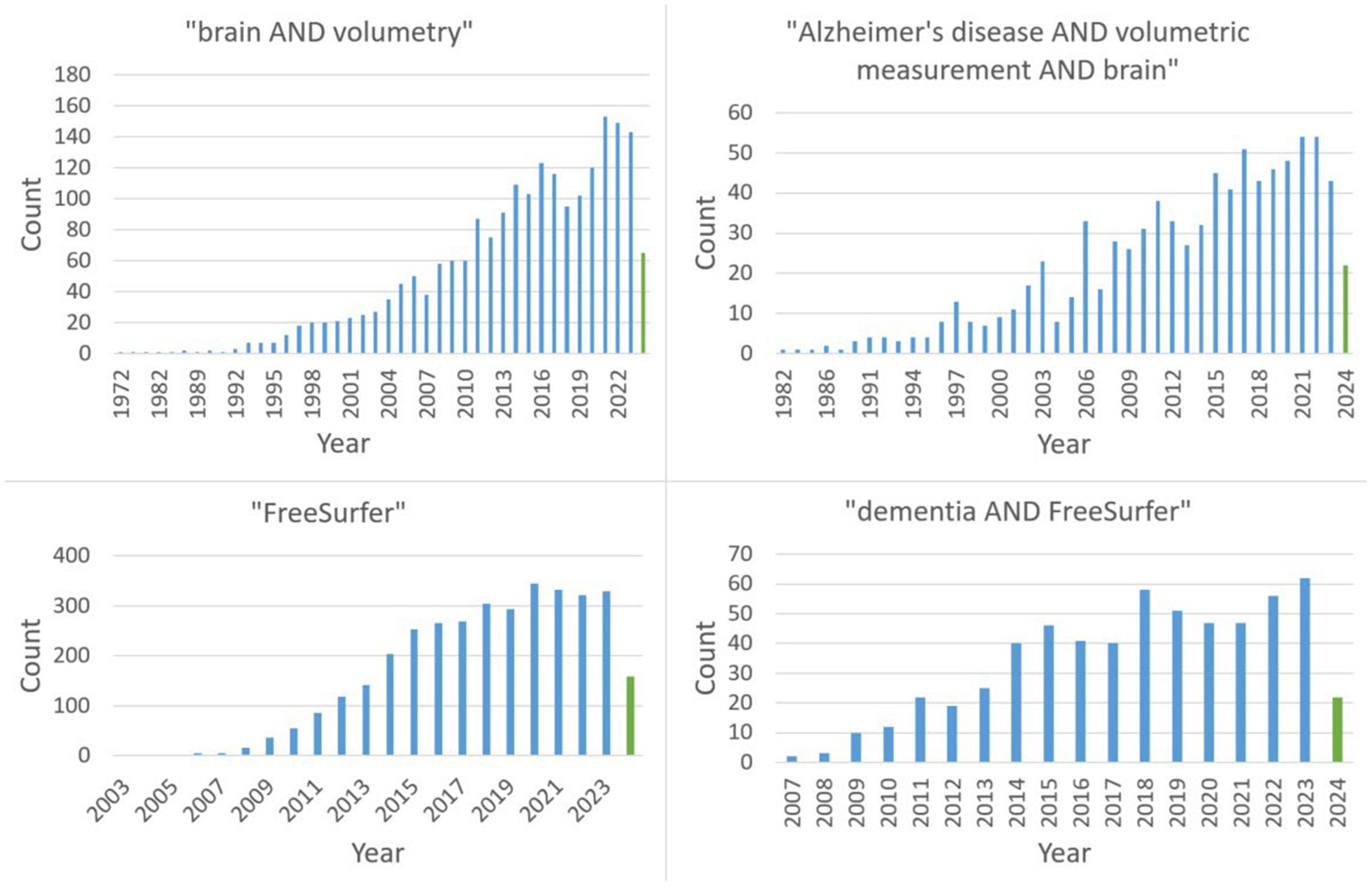
Currently, one of the first and most recognized software solutions is FreeSurfer, (Fischl, 2012) with 2,925 results being returned on PubMed using the search string “FreeSurfer.” It performs calculations lasting hours to days to produce robust and reliable results. For comparison, its “little brother” FastSurfer (Henschel et al., 2020) only returns 16 results on PubMed (search string “FastSurfer”).
The increasing prevalence of high-resolution sequences and 7-Tesla MRI could lead to problems for software solutions based on fixed-resolution or resolution-ignorant convolutional neural networks (CNNs). One possible solution is the new FastSurferVINN (Henschel et al., 2022). A slower high-resolution stream for FreeSurfer also exists (Zaretskaya et al., 2018). In any case, we are certain to see changes in the volumetry software used due to this trend in the next few years.
The aim of this review was to assess the status of automated volumetry in 2024 and identify recommendations, gaps, and opportunities within MR brain research. The focus was on FreeSurfer software and Alzheimer’s disease.
Even if global cortical surface area, thickness, and volume are not related to cognitive scores (Li et al., 2023), volumetric analysis is a useful tool to study and observe dementias. For instance, new Alzheimer medications based on antibodies against amyloid plaque can cause serious side effects leading to Amyloid-Related Imaging Abnormalities (ARIAs) or accelerated atrophy (Pinter et al., 2022), so for patients taking such medications, regular volumetric monitoring of the brain is essential (Withington and Turner, 2022; Van Dyck et al., 2023).
1.1 Search terms and included studies
The two major search terms were “dementia AND FreeSurfer” as well as “Alzheimer’s disease AND volumetric measurements AND brain.” Figure 1 reveals the continuing trend with a steady increase (with a possible plateau formation in the last years) in publications on PubMed regarding the search queries relevant to this review.
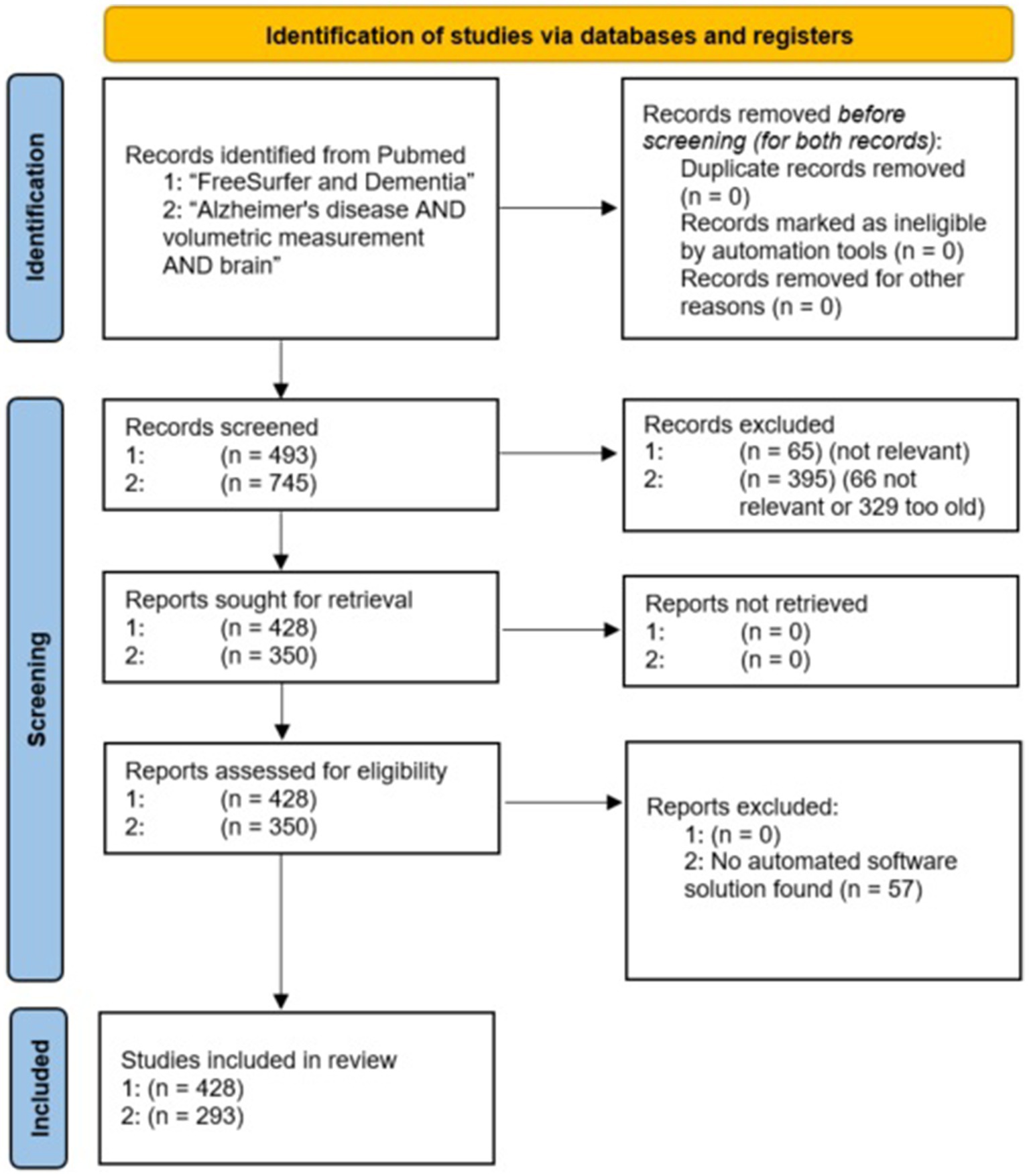
A PRISMA flow chart (Rethlefsen and Page, 2021) of the evaluated studies is shown in Figure 2. To reduce the risk of overlooking/underestimating relevant programs, we additionally performed a deep search for all software tools found.
2 Current state of the art
2.1 Evaluated dementias
A PubMed search on “FreeSurfer and Dementia” returned 493 results, 428 were included. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) was the most analyzed disease (40%), followed by mild cognitive impairment (MCI), frontotemporal dementia, and Parkinson’s disease (PD). Figure 3 illustrates the distribution of dementias evaluated using FreeSurfer.
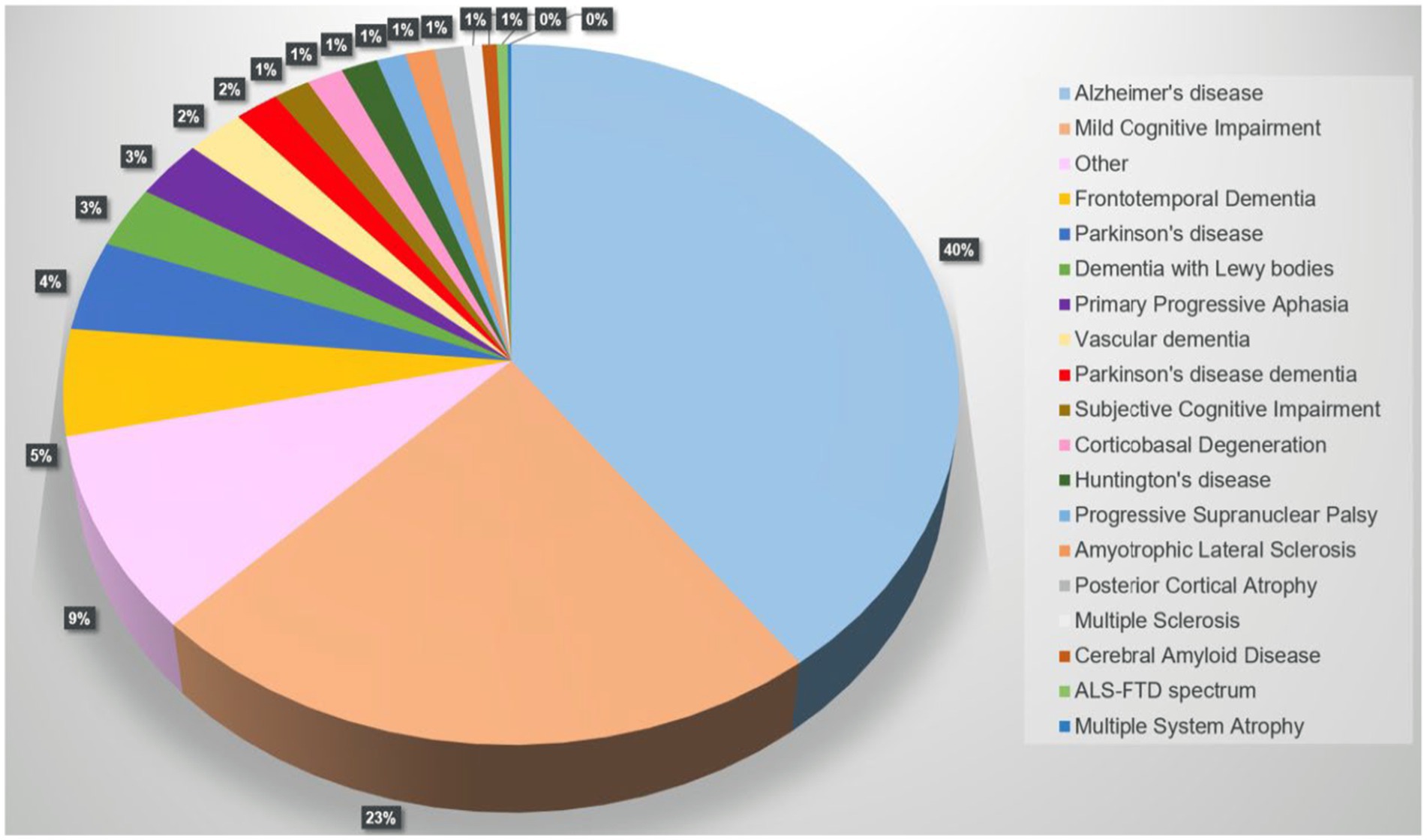
Figure 3. Pie chart showing the distribution of cohorts/diseases returned by the PubMed search “FreeSurfer and Dementia” (n = 428 of 493 studies, 01/01/2024).
The category “other” includes cohorts with less typical diseases or specific groups of interest in certain circumstances associated with suspected brain volume loss or fluctuations, such as HIV or Down syndrome. Supplementary Figure S1 shows the distribution of these entities. The results show that there is still a need for targeted research.
When it comes to the more common dementias, it is noticeable that the subgroupings are differently defined depending on the study. This makes a comparison, for example in the context of a meta-analysis, more difficult. More precise definitions appear to be necessary, e.g., for subgroups with mild cognitive impairment [e.g., MCI with PD or MCI before PD dementia (PDD)] or for classification into mild or severe symptoms. Table 1 shows a detailed breakdown of our PubMed search.
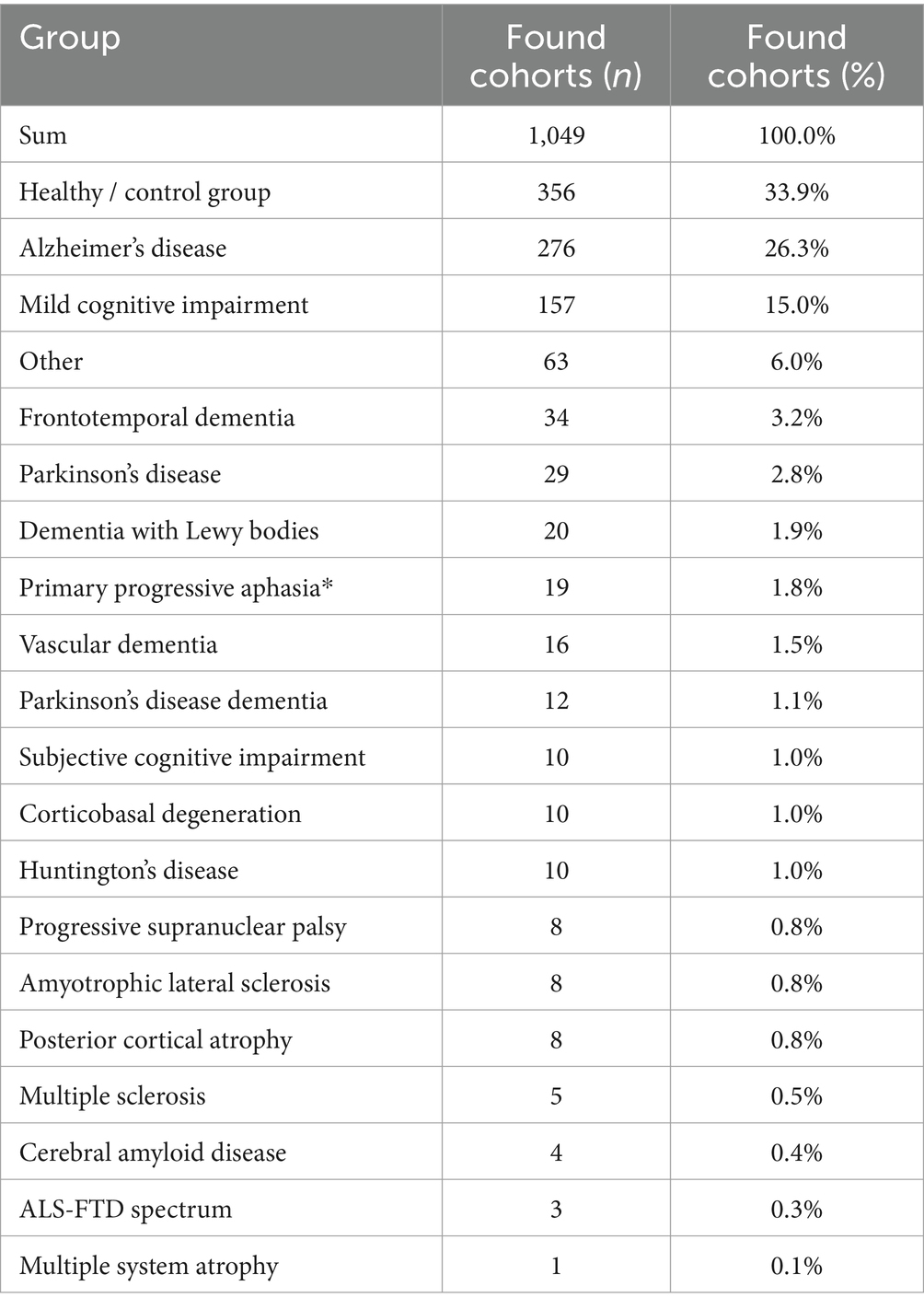
Table 1. Evaluated cohorts/diseases returned by the PubMed search “FreeSurfer and Dementia” (n = 428 of 493 studies, 01/01/2024).
While the number of Alzheimer’s cohorts examined dominates, individual dementias are significantly underrepresented in terms of incidence; particularly dementias in which no specific atrophy pattern is expected, such as vascular dementia (VD) or dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB).
2.2 Volumetric software
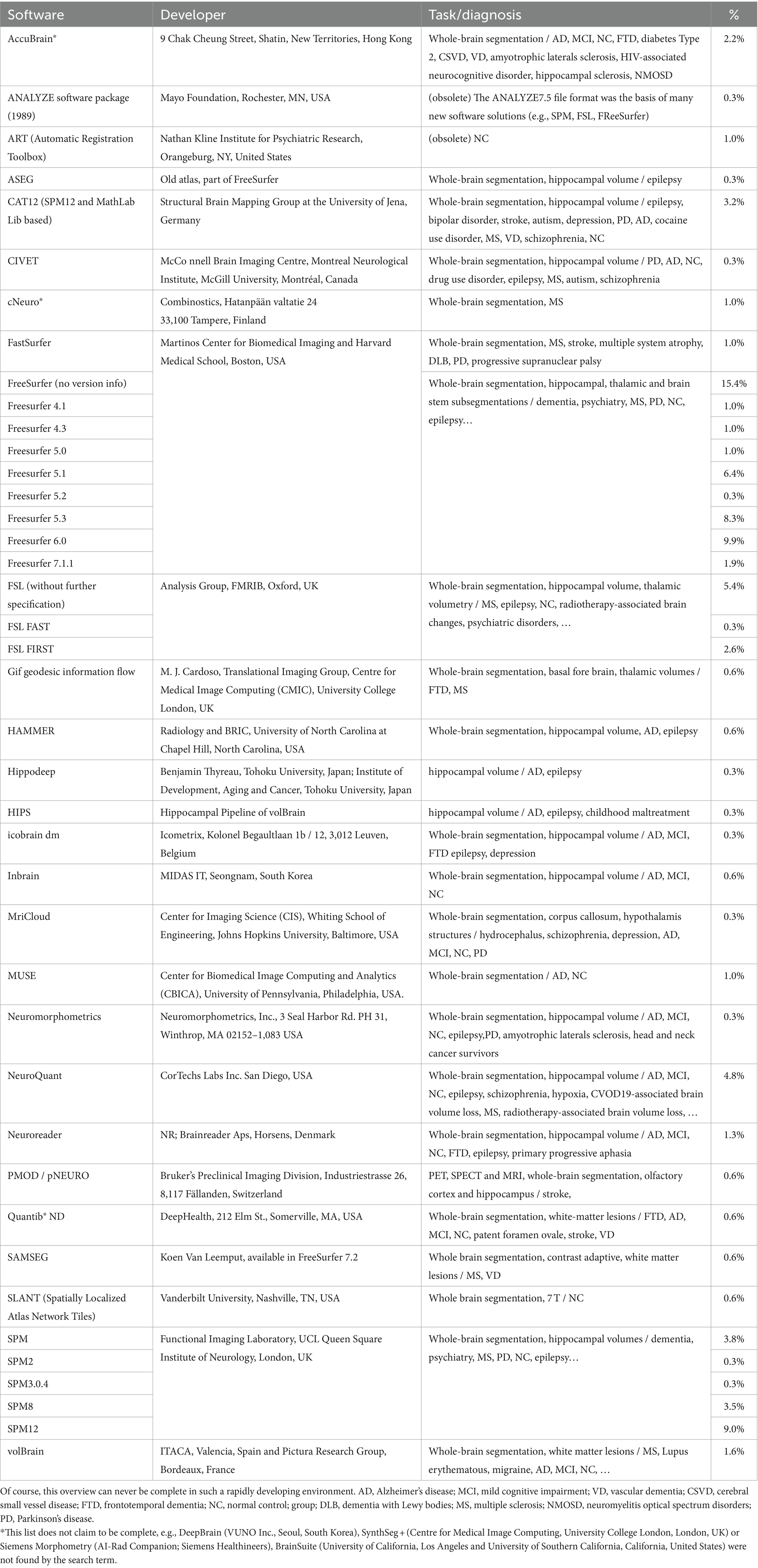
Since AD is the most studied dementia, we focused our search on this. A PubMed search on “Alzheimer’s disease AND volumetric measurement AND brain” revealed 745 results. The search revealed that FreeSurfer, SPM, and FSL are currently the most used software tools. Figure 4 demonstrates a pie chart of the mostly used tools. For a detailed list of software solutions see Table 2.
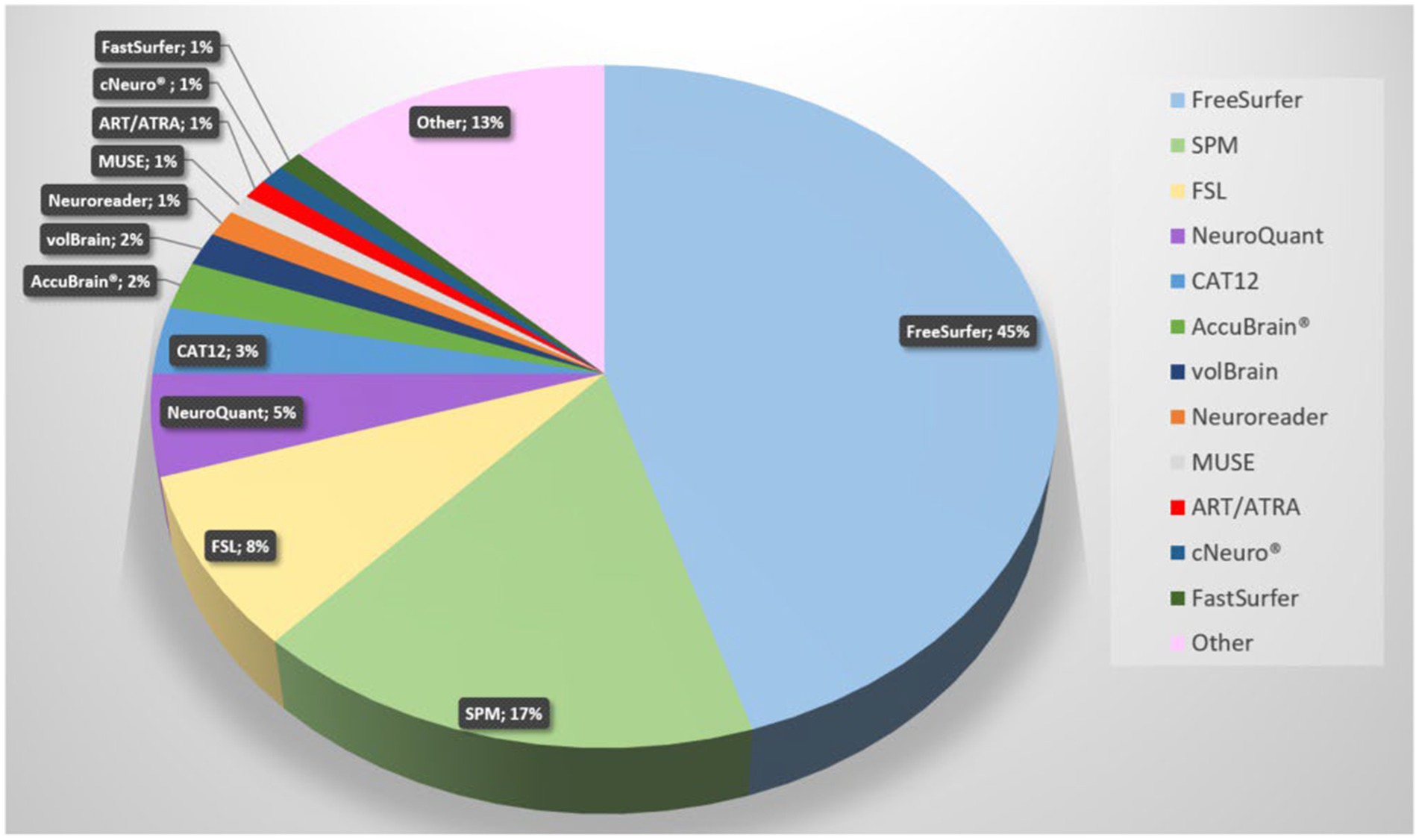
Figure 4. Pie chart of software solutions in reports retrieved from Pubmed with the search term “Alzheimer’s disease volumetric measurement brain” (most recent; descending). The newest 350 entries (from 2024 to 2015) were evaluated, 293 were included. All solutions with fewer than three entries are summarized under “Other”.
2.3 Performance assessment of the segmentation software
Several statistical parameters for the measurement of accuracy and quality of segmentation tools exist. Beside sensitivity, frequently used metrics are the dice similarity coefficient (Dice, 1945; Shamir et al., 2018) (0–1, higher better). the (Pompeiu-) Hausdorff distance (HD) (Birsan and Tiba, 2006) (in mm, lower better), and the mean average precision metric (mAP; 0–1, higher better) (Beitzel et al., 2009). A further development is the Modified or Robust Hausdorff Distance (MHD, HD95) (Huttenlocher et al., 1993), which is not sensitive to local outliers.
Often, manual segmentation (or another validated gold standard) is not used as a comparison segmentation to determine these values, but another automatic segmentation (e.g., FreeSurfer).
It is not yet clear whether these statistical values, which have been adopted from other areas for the segmentation algorithms, really allow a sufficient assessment, especially in brain tumor segmentation (Hoebel et al., 2024). Especially with FreeSurfer, it is difficult to find exact current parameteres due to the rapid development, and the metrics given are often limited to certain areas of the brain and types of MRI, e.g., hippocampal volume and 7-Tesla MRI (Hosseini et al., 2016; Schmidt et al., 2018; Li and Martinez, 2020). A comparison of white matter segmentations of FreeSurfer 6, FSL 5 and SPM 12, and revealed in simulated MRI following noise level dependant result: FreeSurfer (Dice index 0.88–0.90; HD 14–35 mm; MHD 4–6 mm); FSL (Dice index 0.89–0.96; HD 20–60 mm; MHD 3–22 mm); SPM (Dice index 0.87–0.94; HD 20–25 mm; MHD 4–9 mm) (Li and Martinez, 2020).
3 Tailor-made software solutions for the right question
3.1 The (“symmetric”) healthy or aged brain
Multiple software solutions have been developed for the segmentation and volumetry of the healthy or aged brain, e.g., FreeSurfer (Fischl, 2012), FastSurfer (Henschel et al., 2020), SAMSEG (as part of FreeSurfer) (Puonti et al., 2016; Cerri et al., 2023), NeuroQuant (Ross et al., 2012; Yim et al., 2021), SynthSeg (Billot et al., 2023), DeepBrain (Suh et al., 2020), volBrain (Manjón and Coupé, 2016), inBrain (Lee J. et al., 2021; Lee J. Y. et al., 2021), CAT-12 (Gaser et al., 2022), icobrain dm (Struyfs et al., 2020), FSL (Smith et al., 2004; Woolrich et al., 2009; Jenkinson et al., 2012) (with several segmentation tools), and Siemens Morphometry (Rahmani et al., 2023).
3.2 The “non-healthy” brain
Algorithms for the segmentation of the asymmetrical, unhealthy brain (tumor, stroke, traumatic brain injury) are not part of this review, but should be mentioned for completeness. In these cases, sometimes a more complex segmentation is needed, because symmetric approaches and atlases as described in the section above could fail.
One of the best known representatives is DeepMedic (Kamnitsas et al., 2017). Several hundred other approaches for the segmentation of brain tumors exist, many of which are compared annually in the BRATS challenge (Kazerooni et al., 2023), although validation and evaluation have also proven to be complicated. Recently, several new approaches based on generative adversarial networks (GANs) or U-Nets have been published, e.g., MMGan (Gao et al., 2023), nnUNetFormer (Guo et al., 2023), and multi-scale context UNet-like network (Qian et al., 2024).
Brain volume loss can also be detected in several diseases in younger patients, e.g., corpus callosum and thalamus volumes can decrease in patients with multiple sclerosis (Fujimori and Nakashima, 2024). However, for these studies it must always be noted that the accuracy of some segmentation algorithms may be reduced by the presence of multiple lesions (De Sitter et al., 2020).
4 Anatomic regions of interest
4.1 Cortex and white matter
The segmentation and volumetrization of cortex and white matter is the basis of all brain volume diagnostics. Brain volume loss occurs in both aging and dementia, but it is locally or globally accelerated in most central nervous system diseases, e.g., AD (Chwa et al., 2023) or PD (Jahanshahi A. et al., 2023). Therefore, most studies require a suitable control group of the same age.
In addition, it must be mentioned that brain volume also seems to depend on diet (Karstens et al., 2019; Bramen et al., 2023). For example, body mass index and hypothalamic volume are associated, and gray-matter-volume loss is described in anorexia nervosa, (Lyall et al., 2024) while minor physiological factors, like dehydration, blood pressure, caffeine levels, and circadian rhythm, do not seem to have any influence (Zahid et al., 2022).
However, there are slight differences between individual T1 sequences and MRI scanners, leading to slight shifts between gray and white matter volume. Therefore, this phenomenon can occur when analyzing the basal ganglia.
Individual software solutions also show differences from one another in (volume) calculations; for example, the voxel-based morphometry (VBM) results by SPM and FSL and the grey matter volume results by FSL, FreeSurfer, and SPM show dissimilarities (Rajagopalan and Pioro, 2015). In an ideal study, all patients would be scanned on the same scanner with the same sequence and should be analyzed with the same reliable software tool.
4.2 Thalamic nuclei
An additional FreeSurfer script contains a specific atlas and enables the fine segmentation of the thalamic nuclei (Iglesias et al., 2018). These scripts also work on FastSurfer segmentations, which use the same data structures. Many other approaches also exist (Su et al., 2019; Forno et al., 2023; Pfefferbaum et al., 2023; Vidal et al., 2024).
4.3 Brainstem and cerebellum
There is also an additional FreeSurfer script for this specific segmentation (Iglesias et al., 2015b), but it only offers a rough subdivision. For some diseases, such as progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), multiple system atrophy (MSA), and corticobasal syndrome, analysis of the brainstem is crucial (Brinia et al., 2023), but it is also atrophied in other dementias (Müller et al., 2023). Deep learning approaches are become more widely adopted here (Nigro et al., 2024). Some software solution can additionally analyze cerebellar hemispheres, e.g., volBrain. CerebNet (Faber et al., 2022) is compatible with FreeSurfer and FastSurfer and is able to measure cerebellar lobes.
4.4 Hippocampus
Since the hippocampus plays a crucial role in both AD and epilepsy, there are many approaches to its segmentation and volumetry in both dementia research and epilepsy research. Hippocampal volume can be used as early marker of dementia (Gentreau et al., 2023).
FreeSurfer provides a specific script (Iglesias et al., 2015a) for the segmentation of hippocampal subfields and the nuclei of the amygdala that supports T1-weighted and T2-weighted sequences.
An example of such a segmentation of a healthy brain/hippocampus is shown in Figure 5.
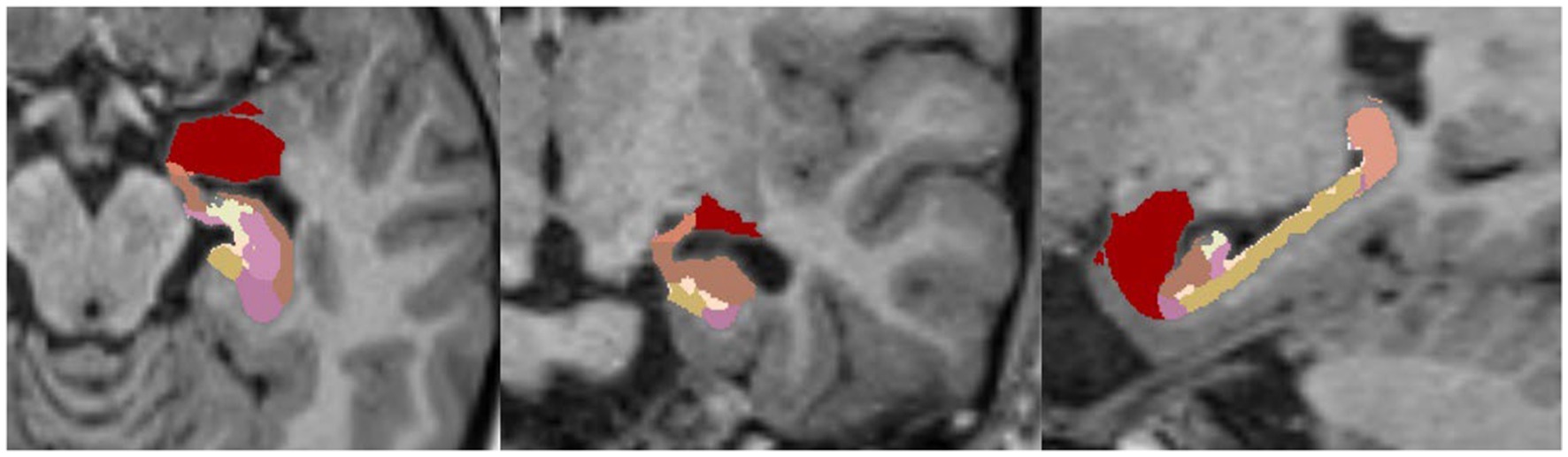
Figure 5. Example of FreeSurfer’s segmentation (HBT, Head Body Tail) of hippocampal subfields without nuclei of the amygdala in a 1.5-Tesla T1-MPRAGE sequence, transversal (left), coronary (middle) and sagittal (right).
Another popular approach is the automatic segmentation of hippocampal subfields (ASHS; https://www.nitrc.org/projects/ashs), which uses three-dimensional CNNs (Goubran et al., 2020). Several studies have compared the different algorithms in patients with AD (Mueller et al., 2018; Xie et al., 2018), or across lifespans (Bender et al., 2018).
4.5 Cerebral networks and connectomes
Atlas-based segmentations enable the design of connection models of the human brain. Such models can be designed using graph theory approaches, and several tools have been built, e.g., Brain Connectivity Toolbox (Rubinov and Sporns, 2010), eConnectome (He et al., 2011), BRAPH (Mijalkov et al., 2017), GRETNA (Wang et al., 2015), GAT (Hosseini et al., 2012), and GraphVar (Kruschwitz et al., 2015).
In the future, comparing the connectivity models of patients with dementia with those of healthy controls could reveal new disease concepts and causes of impairments.
5 Mild cognitive impairment (MCI)
MCI is defined as an intermediate state (or prodromal stage) between normal aging and dementia (Petersen et al., 1999) with a wide range of heterogeneous underlying pathophysiologies. Its prevalence in older (>80 years) patients is high (Campos et al., 2024). MCI does not necessarily convert into dementia. Subjects can recover from it. Diagnosis can be established using several tests, e.g., the Montreal cognitive assessment score (Nasreddine et al., 2005; Malek-Ahmadi and Nikkhahmanesh, 2024) or minimum mental state examination (Zaudig, 1992). Another category is subjective cognitive impairment (SCI), which describes a cognitive worsening that cannot be verified by standard tests (Garcia-Ptacek et al., 2014). Such patients are usually more educated and thus likely to pass the tests because they have a higher baseline cognitive level.
MCI (or SCI in some studies) is often examined as a comparison population. In many studies, it is not entirely clear which dementia the corresponding MCI will later develop into. In some studies, MCI is also divided into subgroups (MCI-AD, MCI-FTD, etc.) depending on the study design and protocol.
Aging, MCI, and AD are related with widespread cortical and subcortical atrophy and have overlapping atrophy patterns (Chwa et al., 2023). Therefore, brain changes in MCI are subtle and show as moderate atrophies of the hippocampus and amygdala (Qu et al., 2023) as well as hypometabolism (Bailly et al., 2015). A recent study found altered cortical and subcortical morphometry and asymmetries in SCI and MCI (Yang et al., 2023). A meta-analysis revealed that differentiation of MCI and AD using the whole hippocampus volume was not significantly worse than a hippocampal subfield analysis (Zhang J. et al., 2023), mainly because atrophy patterns are not restricted to specific subfields. Therefore, a precise differentiation should be made earlier, i.e., at the SCI stage.
Asymmetry of hippocampal subfields is often present in MCI and AD (Jahanshahi A. R. et al., 2023), but its diagnostic value is still a matter of debate (Singh et al., 2023).
A large Finnish study tried to prevent cognitive impairment with a 2-year multimodal intervention (diet, exercise, cognitive training, and vascular risk monitoring). They could not find significant differences between the intervention and control groups for regional brain volume changes (Stephen et al., 2019).
6 Dementias
6.1 Alzheimer’s disease
As revealed by our PubMed search “FreeSurfer and Dementia,” AD (Stoddart, 1913) is the most common (Stoeck et al., 2012) and best-researched dementia in terms of volumetric analysis. It represents an enormous global burden (Gauthier et al., 2022). The existence of several subtypes makes precise detection by MRI methods in some cases difficult or impossible, especially in patients with hippocampal sparing patterns or without atrophy (Ferreira et al., 2017). Another limiting factor is its potential co-existence with other diseases in older patients, e.g., vascular risk factors and carotid atherosclerosis are also associated with cortical volume loss (Cardenas et al., 2012), which supports the “double hit” theory for AD.
Even though the importance of volumetry is increasing, conventional visual radiologically ratings remain a valid and reliable alternative, e.g., the medial temporal lobe atrophy scale (Molinder et al., 2021) or the entorhinal cortex atrophy (ERICA) score (Enkirch et al., 2018).
In a study by Hari et al. (2023), morphometric analysis of medial temporal lobe subregions revealed a volume reduction of the entorhinal cortex as well as of the anterior amygdaloid area in the early stages of SCI-AD and MCI-AD, which partially correlates with the pathological findings of Braak, who found the origin of neurofibrillary (Tau) pathologies in the transentorhinal and entorhinal region (as well as the hippocampus) (Braak et al., 2006). So the medial temporal lobe remains the main target for early diagnoses, even if age-related and amyloid-beta-independent tau deposition is also observed in the frontal and parietal cortical regions (Wuestefeld et al., 2023).
A study in China emphasized the importance of the volume of the presubiculum in hippocampal subfield analysis and demonstrated that a specific volume loss is associated with memory decline during the early phase and progression of AD (Xiao et al., 2023).
FreeSurfer’s Bayesian longitudinal segmentation of hippocampal substructures (Iglesias et al., 2016) performed well in two large collectives for Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) (Mueller et al., 2005) and Minimal Interval Resonance Imaging in Alzheimer’s Disease (MIRIAD) (Malone et al., 2013). The sensitivity to distinguish between controls and patients with AD was increased. New atrophy patterns or differences in atrophy rates, e.g., in the right parasubiculum, left and right presubiculum, as wells as right subiculum, were found.
In some studies, commercial software tools, e.g., IcoBrain DM, performed partially better than FreeSurfer regarding volumetric errors, test–retest reliability, and diagnostic performance for AD (Wittens et al., 2021).
A standardized medial temporal atrophy volume ratio, which was calculated by QBraVo based on SPM8, revealed a good diagnostic performance for differentiation of AD and control group, as well as MCI and a control group (Ryu et al., 2022).
Resting-state functional connectivity and hippocampal radiomic features can also provide information about compensatory mechanisms and cognitive decline in the event of progressive volume loss of the hippocampus (Du et al., 2023).
Of course, Alzheimer’s disease spreads to many other areas of the brain over time, for example cortical thinning in the dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex and/or superior parietal cortex can be associated with a decline in cognitive-motor automaticity and task prioritization (Longhurst et al., 2023).
The complex division into multiple subclasses can be simplified using artificial intelligence methods. A study from Columbia demonstrated a possible classification of Alzheimer’s disease stages using deep learning (Mora-Rubio et al., 2023).
A method to handle the heterogeneity of AD atrophy patterns is normative modeling, with one study presenting a possible solution using multimodal variational autoencoders to identify such deviations (Kumar et al., 2023).
Another mathematical approach is the so-called graph theory, which defines the brain as a network of nodes and edges (connections), with pathologies corresponding to defects within this architecture. While the nodes usually represent specific segmented brain areas and their volumes, definition of their edges can vary from study to study, but often consists of correlations between brain areas. A study from Japan revealed left dominant morphometric changes of these networks in patients with AD (Maruoka et al., 2023). This method also enables the prognosis of epilepsy in patients with AD, as demonstrated in a study from Korea (Lee et al., 2023).
When considering Alzheimer’s disease, one should not forget that an inflammatory component is also suspected (Newcombe et al., 2018). Interestingly, a study from Japan found a negative correlation between inflammation values (high-sensitivity C-reactive protein) and disease progression (Zhang Y. et al., 2023).
White matter hyperintensities also play an important role in the AD and MCI spectrum. In a multicenter evaluation of automated segmentation algorithms using 3D fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequences, deep learning based (re-trained) algorithms performed well (Gaubert et al., 2023).
6.2 Frontotemporal dementia
Frontotemporal dementia or frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTD/FTLD) is a common cause of dementia in patients typically between 45–65 years (Galimberti and Scarpini, 2012). The most frequent phenotype is the behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD) (Rascovsky et al., 2011). Other subtypes are semantic variant PPA (svPPA) and non-fluent variant PPA (nfvPPA). Both sporadic and familial FTD exists. The genetic overlap of bvFTD with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) form a special variant called FTD-ALS.
Patients with FTD suffer from different symptoms, e.g., hoarding and obsessive-compulsive behaviors. A related study indicated associations of cortical atrophies of the left temporal lobe, the left insula and the anterior cingulate gyrus with hoarding, while obsessive-compulsive behaviors were associated with cortical decrease in the anterior cingulate, the bilateral hippocampus, and amygdala (Mitchell et al., 2019).
Neuropsychiatric symptoms are most common in FTD and are associated with cortical atrophies in cingulate, insular, and inferior frontal brain areas (Ozzoude et al., 2023). Lesion and/or atrophy of the medial and lateral ventral prefrontal cortex may also increase apathy and other inappropriate behaviors (Huey et al., 2015). Generally, apathy seems to be associated with volume loss of the ventral prefrontal cortex, the posterior cingulate cortex and the adjacent lateral cortex, as well as the superior temporal sulcus in both AD and FTD (Huey et al., 2016).
The association of CSF biomarkers and distinct brain atrophies is not yet sufficiently understood. However, cortical atrophies can be partially explained by levels of Aβ and 14–3-3 in AD, and neurofilament light chain and 14–3-3 in FTD (Falgàs et al., 2020).
The determination of ventricular volume as a simple follow-up parameter in FTD was suggested in a study from Tavares et al. (2019). In particular, the volume of the temporal horns often seems to provide an excellent follow-up parameter for several diseases (Erten-Lyons et al., 2006).
A machine learning approach has shown good differentiation between FTD and other dementias using FreeSurfer segmentation, numerous clinical and MRI data (De Francesco et al., 2023). Differentiation of AD and FTD appears to be possible through the reduced cortical thickness in the posterior cingulate gyrus, which seems to be characteristic of typical and atypical AD, but not FTD (Lehmann et al., 2010). In one study, FTD patients had a more selective loss in frontal cortex and in anterior parts of the temporal lobes compared with AD patients (Möller et al., 2016).
A longitudinal FreeSurfer study of Alzheimer’s disease and behavioral-variant frontotemporal dementia revealed that, at follow-up, patients with AD demonstrate a pronounced cortical volume loss in the inferior parietal and posterior cingulate cortex, while patients with bvFTD show a greater volume loss in the striatum (Landin-Romero et al., 2017).
A (multi-level) hierarchical classification algorithm of AD versus FTD (and bvFTD versus PPA, and nfvPPA versus svPPA) revealed distinct discriminative areas for each comparison using machine learning and demonstrated an overall accuracy of 75.8% (Kim et al., 2019). A study from Barcelona, which tried to distinguish control, AD, and FTD groups using support vector machines, showed an accuracy of 82% in distinguishing the control and FTD groups, and 63% in distinguishing the AD and FTD groups (the accuracy improves to 75% after adding longitudinal data) (Pérez-Millan et al., 2023a; Pérez-Millan et al., 2023b).
White matter hyperintensities and cortical atrophy are associated with a loss of empathy (Ozzoude et al., 2022). Emotional decline in bvFTD could be triggered by an atrophy of the right pregenual anterior cingulate cortex (Sturm et al., 2013). In 2023, a study revealed significant atrophies of the frontotemporal cortex and the bilateral anterior-dorsal thalamus in sporadic bvFTD (Jakabek et al., 2023). Some patients with bvFTD suffer from extrapyramidal symptoms, which could be caused by brainstem atrophy (Heikkinen et al., 2022).
Repeat expansion within C9orf72 is the most common genetic cause of FTD, which especially seems to be associated with gray matter changes (Popuri et al., 2018), a thalamic atrophy (Bonham et al., 2023) and a loss of brain stem white matter (Pérez-Millan et al., 2023a; Pérez-Millan et al., 2023b). Dyslexia susceptibility genes play an important role in frontotemporal dementia as well and are associated with specific local cortical thickness reduction (Paternicó et al., 2016). In svFTD and nfvPPA, different patterns of cortical atrophy are observed (Rohrer et al., 2009). The rate of brain volume loss in FTD varies depending on the mutation, as demonstrated for MAPT and GRN (Whitwell et al., 2011). Pre-symptomatic mutation carriers could be useful for disease monitoring (Borrego-Écija et al., 2021).
Cortical thinning and regional prefrontal cortical atrophy has also been observed in patients with ALS-FTD (Schuster et al., 2014; Ratti et al., 2021).
6.3 Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB)
Although DLB is the second most common dementia of the elderly (>65 years) (Walker et al., 2015), it seems to be one of the least scientifically understood diseases. One review revealed a lack of detailed understanding of its clinical course, neuropathology, genetic factors, and molecular mechanism (Outeiro et al., 2019). MRI is still only a supportive marker in the diagnostic pathway (McKeith et al., 2017, 2020).
Studies have reported focal pronounced atrophies of the substantia innominata (Hanyu et al., 2007) and the insula (Tisserand et al., 2024). A low hippocampal volume is also associated with a risk of DLB in patients with MCI (Kantarci et al., 2016). But DLB shows significantly larger hippocampal volumes than AD and MCI (Mak et al., 2014, 2017). Atrophy of extra-hippocampal structures linked to visual functions were found in patients with DLB as well (Delli Pizzi et al., 2016). DLB subgroups with psychiatric and cognitive onset showed different atrophy patterns (Hansen et al., 2022) of the substantia innominate. The caudate nucleus appears to be relatively unaffected by global atrophy (Khadhraoui et al., 2022), while the brainstem also atrophies at the same rate (Müller et al., 2023). Gray matter atrophy is associated with decrease in dual task gait in DLB (Subotic et al., 2023).
More prospective and longitudinal studies for the evaluation of MRI (especially volumetric analyzes), FDG-PET, biomarkers, and clinical tools are needed (Hansen et al., 2023a,b; Burgio et al., 2024).
6.4 Parkinson’s disease dementia (PDD)
To begin with, a distinction must be made between PD, PD-MCI, and PDD. The worse the cognitive state, the more advanced atrophy is to be expected. A meta-analysis of patients with PD revealed a regional atrophy that mainly manifests in the gray matter (He et al., 2020), but with several limitations. Another study (Říha et al., 2022) reported patients with PD show an accelerated volume loss of the hippocampal, which could be a marker for a dementia conversion (Low et al., 2019). Hippocampal subfield analysis revealed significantly smaller volumes in patients with PD-MCI than in patients with PD but without cognitive impairment (Becker et al., 2021). Additionally, a pronounced cortical thinning was found in PD patients with MCI compared with those without (Mak et al., 2015). A study from Singapore revealed pronounced baseline atrophy of the thalamus and progressive atrophies of thalamus, caudate nucleus, presubiculum, and cornu ammonis 1–3 (Foo et al., 2017). Dopamine loss may support the development of cortical atrophies (Sampedro et al., 2019).
In a four-year follow-up study, cortical thinning was correlated with impairment in visuospatial and visuoperceptual performance (Garcia-Diaz et al., 2018b), while another study found a link between poor test performance and a pronounced cortex atrophy of the lateral temporo-parietal regions (Garcia-Diaz et al., 2018a).
An association of white matter hyperintensities with global brain atrophy and cognitive impairment has been reported (Chen et al., 2020). A mild midbrain atrophy was found in 20% of PD patients (Sako et al., 2023). A more pronounced atrophy of the corpus callosum was found in patients with PDD than in PD and PD-MCI (Goldman et al., 2017). Left-sided olfactory amygdala volume reduction is not only associated with hyposmia but with cognitive impairment in patients with PD and can also predict a possible shift to PDD (Ay et al., 2023). The cortical atrophy of PDD is less severe than that in AD or DLB (Colloby et al., 2020). An asymmetric course with an early left-sided atrophy and late right-hemisphere involvement was revealed in a study from the USA (Claassen et al., 2016).
Therefore, MR volumetry can potentially play a role in the early detection of progression from PD to PDD (Trufanov et al., 2013).
6.5 Vascular dementia (VD)
White matter lesions can be visually assessed better in T2-or FLAIR-weighted images than in T1-weighted sequences, which are usually required by segmentation algorithms. The classic Fazekas score (Fazekas et al., 1987) is still used today to simplify assessments, but it has long since ceased to be suitable for fine classification and follow-up monitoring. While Fazekas 0 and 1 are usually not considered VD, a score of 2 can describe early VD, while a score of 3 can represent classic VD. However, there is no fine granular classification in the score, which is needed to describe a progressive disease.
The reasons for such lesions are diverse and range from stroke, arterial hypertension (Sierra, 2014), atrial fibrillation, arteriosclerosis (Kim et al., 2014), and carotid stenosis to rarer diseases of large and small vessels (Chojdak-Łukasiewicz et al., 2021) to genetic diseases such as CADASIL (Kalimo et al., 1999) and CARASIL (Müller et al., 2020). Vitamin D insufficiency is also linked with white matter lesions (Annweiler et al., 2015). Subcortical ischemic vascular dementia (SIVD) is a term that describes a disease with the typical subcortical MR lesions in order to separate it from other causes, like large infarctions (Chui, 2007).
Volumetric approaches, which are significantly more suitable, show an association of measured global lesion volumes with this Fazekas Score (Andere et al., 2022). A combination of T1-and T2-weighted sequences is probably the most accurate way to determine such lesion volumes, otherwise adapted normalizations and metrics are recommended (Valdés Hernández et al., 2017).
A high lesion load must be viewed as a possible cause of dementia (or as secondary or mixed dementia), especially in old people (Jellinger and Attems, 2010). Especially, frontal white matter hyperintensities could have a strong impact in cognitive impairment of older adults (Boutzoukas et al., 2021).
Another reason for neuropsychiatric deterioration in addition to the lesion itself can be the induced focal thinning in connected cortical regions (Duering et al., 2012). Furthermore, a high lesion load has been associated with hippocampal atrophy in mild cognitive impairment in a study from Sweden (Eckerström et al., 2011). A study from China reported cognitive deterioration with abnormalities in the brain network between hippocampal subfields and the whole cerebral cortex (Wang et al., 2018). Silent micro infarction may also play a crucial role (Knopman et al., 2015).
Besides FreeSurfer, several other white matter tools exists, e.g., Brain Intensity AbNormality Classification Algorithm (BIANCA, part of FSL) (Griffanti et al., 2016) and UBO Detector (Jiang et al., 2018). However, the right choice of sequence and segmentation algorithm is essential (Hotz et al., 2022).
A study revealed an association between cortical volume and cognitive impairment in patients with white matter lesions using FreeSurfer (Liu et al., 2021). In addition to the information provided by volumetry, MR perfusion (e.g., arterial spin labelling) can also detect brain areas with reduced blood flow in vascular diseases (Gyanwali et al., 2022).
Stroke-dependent severe neurocognitive decline appears in approx. 10% of patients up to 3 months after stroke (Aamodt et al., 2021). In the years after a stroke, a progressive ipsilateral brain volume reduction has also been observed (Salah Khlif et al., 2022).
Hippocampal lesions may explain memory deficits in patients with VD (He et al., 2022). Hippocampal subfield volumetry via FreeSurfer revealed a significant volume reduction of the left hippocampus, left subiculum, presubiculum, and the right CA4/dentate gyrus in patients with vascular lesions and MCI (Li et al., 2016). Another reason fot such memory impairments could be cortical thinning in the precuneus and medial temporal lobe (Chen et al., 2021).
Regarding white matter lesions, deep learning may be a promising solution to specifically classify, monitor, and evaluate these lesions. A study using VUNO Med-DeepBrain (9F, 479, Gangnam-daero, Seocho-gu, Seoul, Korea) and FLAIR images demonstrated the successful classification via the Fazekas scale and could distinguish non-SVID from SVID (Joo et al., 2022). The main architecture of most deep learning solutions is actually still CNN based (Dong and Hayashi, 2024).
6.6 Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA)
The accumulation of amyloid β (Aβ) in the vascular walls of intracranial (micro-) vessels defines CAA as a form of VD (Wang et al., 2024). These deposits can lead to (atypical) brain hemorrhages. CAA patients are usually significantly older and a overlaps with other dementias exist. This may be the reason why no significant subcortical atrophy has been observed in some studies (Chen et al., 2023). However, most studies suggest that CAA also leads to cortical thinning (Subotic et al., 2021). A large study demonstrated significant losses of whole cortical volume as well as bilateral hippocampus, amygdala, thalamus, left caudate and right putamen volumes in patients with positive amyloid status (Ten Kate et al., 2018).
In patients with amnestic MCI, the amyloid status can be predicted by hippocampal volume, grey matter volume, or the ratio of hippocampal volume and whole brain volume (Kang et al., 2020).
6.7 Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP)
PSP as a rare atypical parkinsonism with vertical gaze, pseudobulbar palsy, and dementia (Steele, 1964). Volumes of the thalamus, mesencephalon, and caudate nucleus are significantly reduced in PSP (Coughlin and Litvan, 2020). A study revealed an association of gait characteristics in PSP and volumetric changes using FreeSurfer (Chatterjee et al., 2023). The mild pontine atrophy compared to the pronounced mesencephalic volume loss is used as a diagnostic criterion by many indices along with “neuroradiologic signs” on MRI (Slowinski et al., 2008; Hussl et al., 2010; Mittal et al., 2017; Cui et al., 2020; Lupascu et al., 2023). Additionally, volume loss has been observed in the frontal lobe, particularly the superior frontal gyrus (Worker et al., 2014).
Despite a detailed fine segmentation of the brain stem, deep learning methods could improve the early detection of patients (Nigro et al., 2024).
6.8 Multiple system atrophy (MSA)
MSA is a rare synucleinopathy, characterized by α-synuclein-positive cytoplasmic deposits. It presents with Parkinsonism and is challenging to diagnose for both neurologists and neuroradiologist (Goh et al., 2023). It is separated into Parkinsonian (MSA-P) and cerebellar (MSA-C) subtypes; atrophies of the putamen, middle cerebellar peduncles, pons, and cerebellum are described. However, a study did not detect significant volume reductions in cortical morphology for MSA compared with that for PD and control groups (Worker et al., 2014).
In addition to detailed brain stem segmentation, a deep learning approach also shows promise for the future detection of this disease.
6.9 Alcohol dementia/alcohol use disorder
A common secondary disease that also leads to cortical atrophy and can be a disruptive factor is alcohol addiction. The expected volume losses are in the left ventral diencephalon, left inferior and middle temporal gyrus, left caudate nucleus, brain stem, and cerebellum (Squeglia et al., 2014). Interestingly, one study here even describes a possible regional recovery of brain volume during abstinence (Durazzo et al., 2023). Additionally, a thickness reduction of the occipitotemporal cortex and an association with apathy was reported (Yang et al., 2020). Hippocampal atrophies, particularly of the subiculum, CA1, molecular layer, and hippocampal tail, have also been observed (Sawyer et al., 2020).
6.10 Other dementias
Other forms of dementia are very rare and only poorly investigated using MR morphometric methods. An exception is diseases with a specific atrophy pattern. These include also mixed etiologies, for example, semantic-variant primary progressive aphasia (svPPA) and posterior cortical atrophy (PCA) (Fazlollahi et al., 2023), which are subtypes of FTD, corticobasal degeneration and AD, respectively.
Even diseases that are not primarily referred to as dementia can present this as a secondary consequence. The most prominent example is multiple sclerosis. Besides the thalamic changes, the cortical thickness is significantly reduced in older patients with multiple sclerosis and cognitive impairment (Jakimovski et al., 2023). An association between whole brain volume and disability exists as well (Moridi et al., 2022).
A study revealed a cortical involvement in idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus (Bianco et al., 2022). This form of dementia is also suitable for segmentation algorithms. In addition to calculating the volume of the ventricles, a measurement of the areas “compressed” by the increase in CSF is also of interest but remains underresearched.
7 Discussion
There are similar reviews about brain segmentation (Singh and Singh, 2021) or hippocampal segmentation software (Zhang J. et al., 2023). Our review provides an up-to-date status of the software and dementias researched so far with a focus on FreeSurfer. It makes it possible to discover numerous gaps in research and to focus specifically on a question that has not yet been researched.
Even if numerous commercial and non-commercial software solutions for automated brain segmentation and volumetry exist, FreeSurfer seems to be currently the most frequently used. There are many reasons for this. In addition to the extensive functions for almost all questions and diagnosis, regular updates are also offered. The accuracy of the tool is sufficient. Since it has been around for a long time, there is a wide acceptance and validation. In addition, it is free and there is a large open source community that is constantly adapting the extensive documentation. FreeSurfer is compatible with many other tools (e.g., FastSurfer, CerebNet).
There are still numerous gaps in research. Be it the few publications in the area of Lewy Body Dementia, which has only been sparsely researched, or the multiple atrophy patterns in Alzheimer’s disease, which are still not fully understood. Many diseases are underrepresented, measured by the percentage ratio of entries found compared to the prevalence of the disease. There are also only a few longitudinal studies that have been conducted using the same protocols and MRI devices. The many new artifacts in clinical application in 7 T MRI will also influence the segmentation algorithms.
Increasing comorbidities and mixed dementias in old age, as well as the normal level of physiological brain involution, are areas of research that will occupy us for decades to come.
In addition to volumetry and nuclear-medicinal examinations, there are also new possibilities for quantification in MRI using T1-and T2-mappings (Gräfe et al., 2022; Müller et al., 2022) or quantitative susceptibility mapping (Li et al., 2024). Improvement from 3 to 7-Tesla scanning also promises more accurate diagnostics.
7.1 AI-based software/algorithms
Many of the methods mentioned, such as FreeSurfer, are based on neural networks and are formally already AI software. Nevertheless, other AI algorithms can additionally be applied to all the methods mentioned, potentially facilitating new discoveries in the field. In particular, when networking multiple different data, such as clinical information (Noroozi et al., 2024), electroencephalogram (Carrarini et al., 2024), CSF biomarkers and MR imaging data, enormous advantages can arise from AI approaches. Of course, as the number of data to be processed increases, so does the computing power and time required.
However, a major problem remains the diversity of data, MR sequences, and scanners, which make uniform, large, multi-center data analysis difficult. Here, too, the advantage of neural networks could become apparent, as they already include a very efficient normalization of the data.
Besides the brain, the liver is another organ where segmentation using AI can deliver promising results (Zhang et al., 2024), e.g., universal models like segment anything model (SAM), MedSAM and SAMed2D in hepatocellular carcinoma (Saha and Van Der Pol, 2024).
7.2 Limitations
Today, neurodegenerative disorders that progress to dementia are often identified solely from a clinical perspective (Tahami Monfared et al., 2023), without considering the underlying biological substrate, such as the CSF biomarker profile. This is an important (disturbing) factor that can also lead to incorrect diagnoses and inclusions or exclusions within many studies. In the case of small deviations in median brain volumes for some diseases, such misclassifications could also influence the validity of studies.
Due to the heterogeneity of the diseases and the software tools used, it seems almost impossible to conduct a homogeneous PubMed search in this research area. Many programs are only used for individual diseases and are specifically adapted for them, while a universal solution for whole brain volumetry with specialization in certain regions using additional scripts/apps, such as those offered by FreeSurfer, has not yet been fully adopted by the research community.
We therefore concentrated on the FreeSurfer results. Accordingly, a certain bias in the searches with an emphasis on the results in favor of FreeSurfer and Alzheimer’s disease is to be expected.
To reduce the potential of underrepresentation of certain dementia types and overlooking relevant software tools, we performed a deep search on all software tools found. Nevertheless, there remains a certain residual risk of having overlooked or underestimated software solutions.
In addition, we did not perform a detailed evaluation of accuracy and reliability, as the latter in particular was often not available and the sensitivity/specificity data often referred to specific comparisons of two patient cohorts, which were, however, often defined differently in the studies. This significant variability in study protocols affects result comparability, and therefore, a detailed evaluation of the accuracy and reliability of segmentation tools is almost impossible.
8 Conclusion
Automated brain segmentation and volumetry could enable earlier and more reliable dementia diagnosis than other approaches. It can also clarify and objectify the radiological findings. However, the method is not yet widely established. There is also a lack of studies proving its high diagnostic accuracy. In everyday clinical practice, MR volumetry still plays little role in smaller hospitals and is mainly carried out by university institutions for research and validation purposes. The importance of automated evaluation in diagnostics will continue to increase in the coming years. Nevertheless, the clinical picture, CSF biomarkers and PET will remain important.
Author contributions
EK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. TN-J: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. HH: Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. DB: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. SM: Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. We acknowledge support by the Open Access Publication fund of medical faculty of the Otto-von-Guericke-University Magdeburg.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnagi.2024.1459652/full#supplementary-material
References
Aamodt, E. B., Schellhorn, T., Stage, E., Sanjay, A. B., Logan, P. E., Svaldi, D. O., et al. (2021). Predicting the emergence of major neurocognitive disorder within three months after a stroke. Front. Aging Neurosci. 13:705889. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.705889
Andere, A., Jindal, G., Molino, J., Collins, S., Merck, D., Burton, T., et al. (2022). Volumetric white matter Hyperintensity ranges correspond to Fazekas scores on brain MRI. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 31:106333. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2022.106333
Annweiler, C., Bartha, R., Karras, S. N., Gautier, J., Roche, F., and Beauchet, O. (2015). Vitamin D and white matter abnormalities in older adults: a quantitative volumetric analysis of brain MRI. Exp. Gerontol. 63, 41–47. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2015.01.049
Ay, U., Yıldırım, Z., Erdogdu, E., Kiçik, A., Ozturk-Isik, E., Demiralp, T., et al. (2023). Shrinkage of olfactory amygdala connotes cognitive impairment in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Cogn. Neurodyn. 17, 1309–1320. doi: 10.1007/s11571-022-09887-y
Bailly, M., Destrieux, C., Hommet, C., Mondon, K., Cottier, J.-P., Beaufils, E., et al. (2015). Precuneus and cingulate cortex atrophy and Hypometabolism in patients with Alzheimer’s Disease and mild cognitive impairment: MRI and 18 F-FDG PET quantitative analysis using FreeSurfer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 1–8. doi: 10.1155/2015/583931
Becker, S., Granert, O., Timmers, M., Pilotto, A., Van Nueten, L., Roeben, B., et al. (2021). Association of Hippocampal Subfields, CSF biomarkers, and cognition in patients with Parkinson Disease without dementia. Neurology 96, e904–e915. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000011224
Beitzel, S. M., Jensen, E. C., and Frieder, O. (2009). “MAP” in Encyclopedia of database systems. eds. L. Liu and M. T. Özsu (Boston, MA: Springer US), 1691–1692. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-39940-9_492
Bender, A. R., Keresztes, A., Bodammer, N. C., Shing, Y. L., Werkle-Bergner, M., Daugherty, A. M., et al. (2018). Optimization and validation of automated hippocampal subfield segmentation across the lifespan. Hum. Brain Mapp. 39, 916–931. doi: 10.1002/hbm.23891
Bianco, M. G., Quattrone, A., Sarica, A., Vescio, B., Buonocore, J., Vaccaro, M. G., et al. (2022). Cortical atrophy distinguishes idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus from progressive supranuclear palsy: a machine learning approach. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 103, 7–14. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2022.08.007
Billot, B., Greve, D. N., Puonti, O., Thielscher, A., Van Leemput, K., Fischl, B., et al. (2023). SynthSeg: segmentation of brain MRI scans of any contrast and resolution without retraining. Med. Image Anal. 86:102789. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2023.102789
Birsan, T., and Tiba, D. (2006). “One hundred years since the introduction of the set distance by Dimitrie Pompeiu” in System modeling and optimization. eds. F. Ceragioli, A. Dontchev, H. Futura, K. Marti, and L. Pandolfi (Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers), 35–39. doi: 10.1007/0-387-33006-2_4
Bonham, L. W., Geier, E. G., Sirkis, D. W., Leong, J. K., Ramos, E. M., Wang, Q., et al. (2023). Radiogenomics of C9orf72 expansion carriers reveals global transposable element Derepression and enables prediction of thalamic atrophy and clinical impairment. J. Neurosci. 43, 333–345. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1448-22.2022
Borrego-Écija, S., Sala-Llonch, R., Van Swieten, J., Borroni, B., Moreno, F., Masellis, M., et al. (2021). Disease-related cortical thinning in presymptomatic granulin mutation carriers. NeuroImage Clin. 29:102540. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102540
Boutzoukas, E. M., O’Shea, A., Albizu, A., Evangelista, N. D., Hausman, H. K., Kraft, J. N., et al. (2021). Frontal white matter Hyperintensities and executive functioning performance in older adults. Front. Aging Neurosci. 13:672535. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.672535
Braak, H., Alafuzoff, I., Arzberger, T., Kretzschmar, H., and Del Tredici, K. (2006). Staging of Alzheimer disease-associated neurofibrillary pathology using paraffin sections and immunocytochemistry. Acta Neuropathol. 112, 389–404. doi: 10.1007/s00401-006-0127-z
Bramen, J. E., Siddarth, P., Popa, E. S., Kress, G. T., Rapozo, M. K., Hodes, J. F., et al. (2023). Impact of eating a carbohydrate-restricted diet on cortical atrophy in a cross-section of amyloid positive patients with Alzheimer’s Disease: a small sample study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 96, 329–342. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230458
Brinia, M.-E., Kapsali, I., Giagkou, N., and Constantinides, V. C. (2023). Planimetric and volumetric brainstem MRI markers in progressive Supranuclear palsy, multiple system atrophy, and Corticobasal syndrome. A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Neurol. Int. 16, 1–19. doi: 10.3390/neurolint16010001
Burgio, M. I., Veronese, N., Sarà, D., Saccaro, C., Masnata, R., Vassallo, G., et al. (2024). Markers for the detection of Lewy body disease versus Alzheimer’s disease in mild cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 36:60. doi: 10.1007/s40520-024-02704-y
Campos, A. C. B. F., Teixeira, I. G., De Souza Moraes, N., De Jesus Cadorin, I., Morelli, P. M., Lidio, A. V., et al. (2024). Prevalence of cognitive impairment and associated factors in older people. J. Affect. Disord. 355, 283–289. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.03.072
Cardenas, V. A., Reed, B., Chao, L. L., Chui, H., Sanossian, N., DeCarli, C. C., et al. (2012). Associations among vascular risk factors, carotid atherosclerosis, and cortical volume and thickness in older adults. Stroke 43, 2865–2870. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.659722
Carrarini, C., Nardulli, C., Titti, L., Iodice, F., Miraglia, F., Vecchio, F., et al. (2024). Neuropsychological and electrophysiological measurements for diagnosis and prediction of dementia: a review on machine learning approach. Ageing Res. Rev. 100:102417. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102417
Cerri, S., Greve, D. N., Hoopes, A., Lundell, H., Siebner, H. R., Mühlau, M., et al. (2023). An open-source tool for longitudinal whole-brain and white matter lesion segmentation. NeuroImage Clin. 38:103354. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2023.103354
Chatterjee, K., Paul, S., Banerjee, R., Choudhury, S., Tiwari, M., Basu, P., et al. (2023). Characterizing gait and exploring neuro-morphometry in patients with PSP-Richardson’s syndrome and vascular parkinsonism. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 113:105483. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2023.105483
Chen, C.-H., Khnaijer, M. K., Beaudin, A. E., McCreary, C. R., Gee, M., Saad, F., et al. (2023). Subcortical volumes in cerebral amyloid angiopathy compared with Alzheimer’s disease and controls. Front. Neurosci. 17:1139196. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1139196
Chen, L., Song, J., Cheng, R., Wang, K., Liu, X., He, M., et al. (2021). Cortical thinning in the medial temporal lobe and Precuneus is related to cognitive deficits in patients with subcortical ischemic vascular Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 12:614833. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.614833
Chen, H. M., Zhang, M. M., and Wang, Y. L. (2020). Association of age-related white matter hyperintensity with brain atrophy and cognitive impairment in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 100, 3397–3401. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20200519-01588
Chojdak-Łukasiewicz, J., Dziadkowiak, E., Zimny, A., and Paradowski, B. (2021). Cerebral small vessel disease: a review. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 30, 349–356. doi: 10.17219/acem/131216
Chui, H. C. (2007). Subcortical ischemic vascular dementia. Neurol. Clin. 25, 717–740. doi: 10.1016/j.ncl.2007.04.003
Chwa, W. J., Lopez, O. L., Longstreth, W. T., Dai, W., and Raji, C. A. (2023). Longitudinal patterns of brain changes in a community sample in relation to aging and cognitive status. J. Alzheimers Dis. 94, 1035–1045. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230080
Claassen, D. O., McDonell, K. E., Donahue, M., Rawal, S., Wylie, S. A., Neimat, J. S., et al. (2016). Cortical asymmetry in Parkinson’s disease: early susceptibility of the left hemisphere. Brain Behav. 6:e00573. doi: 10.1002/brb3.573
Colloby, S. J., Watson, R., Blamire, A. M., O’Brien, J. T., and Taylor, J.-P. (2020). Cortical thinning in dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson disease dementia. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 54, 633–643. doi: 10.1177/0004867419885165
Coughlin, D. G., and Litvan, I. (2020). Progressive supranuclear palsy: advances in diagnosis and management. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 73, 105–116. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2020.04.014
Cui, S.-S., Ling, H.-W., Du, J.-J., Lin, Y.-Q., Pan, J., Zhou, H.-Y., et al. (2020). Midbrain/pons area ratio and clinical features predict the prognosis of progressive Supranuclear palsy. BMC Neurol. 20:114. doi: 10.1186/s12883-020-01692-6
De Francesco, S., Crema, C., Archetti, D., Muscio, C., Reid, R. I., Nigri, A., et al. (2023). Differential diagnosis of neurodegenerative dementias with the explainable MRI based machine learning algorithm MUQUBIA. Sci. Rep. 13:17355. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43706-6
De Sitter, A., Verhoeven, T., Burggraaff, J., Liu, Y., Simoes, J., Ruggieri, S., et al. (2020). Reduced accuracy of MRI deep grey matter segmentation in multiple sclerosis: an evaluation of four automated methods against manual reference segmentations in a multi-center cohort. J. Neurol. 267, 3541–3554. doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-10023-1
Delli Pizzi, S., Franciotti, R., Bubbico, G., Thomas, A., Onofrj, M., and Bonanni, L. (2016). Atrophy of hippocampal subfields and adjacent extrahippocampal structures in dementia with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 40, 103–109. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2016.01.010
Dice, L. R. (1945). Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26, 297–302. doi: 10.2307/1932409
Dong, C., and Hayashi, S. (2024). Deep learning applications in vascular dementia using neuroimaging. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 37, 101–106. doi: 10.1097/YCO.0000000000000920
Du, Y., Zhang, S., Qiu, Q., Zhang, J., Fang, Y., Zhao, L., et al. (2023). The effect of hippocampal radiomic features and functional connectivity on the relationship between hippocampal volume and cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Psychiatr. Res. 158, 382–391. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2023.01.024
Duering, M., Righart, R., Csanadi, E., Jouvent, E., Hervé, D., Chabriat, H., et al. (2012). Incident subcortical infarcts induce focal thinning in connected cortical regions. Neurology 79, 2025–2028. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3182749f39
Durazzo, T. C., Stephens, L. H., and Meyerhoff, D. J. (2023). Regional cortical thickness recovery with extended abstinence after treatment in those with alcohol use disorder. Alcohol 114, 51–60. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2023.08.011
Eckerström, C., Olsson, E., Klasson, N., Bjerke, M., Göthlin, M., Jonsson, M., et al. (2011). High white matter lesion load is associated with hippocampal atrophy in mild cognitive impairment. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 31, 132–138. doi: 10.1159/000323014
Enkirch, S. J., Traschütz, A., Müller, A., Widmann, C. N., Gielen, G. H., Heneka, M. T., et al. (2018). The ERICA score: an MR imaging–based visual scoring system for the assessment of entorhinal cortex atrophy in Alzheimer Disease. Radiology 288, 226–333. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018171888
Erten-Lyons, D., Howieson, D., Moore, M. M., Quinn, J., Sexton, G., Silbert, L., et al. (2006). Brain volume loss in MCI predicts dementia. Neurology 66, 233–235. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000194213.50222.1a
Faber, J., Kügler, D., Bahrami, E., Heinz, L.-S., Timmann, D., Ernst, T. M., et al. (2022). CerebNet: a fast and reliable deep-learning pipeline for detailed cerebellum sub-segmentation. NeuroImage 264:119703. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119703
Falgàs, N., Ruiz-Peris, M., Pérez-Millan, A., Sala-Llonch, R., Antonell, A., Balasa, M., et al. (2020). Contribution of CSF biomarkers to early-onset Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia neuroimaging signatures. Hum. Brain Mapp. 41, 2004–2013. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24925
Fazekas, F., Chawluk, J., Alavi, A., Hurtig, H., and Zimmerman, R. (1987). MR signal abnormalities at 1.5 T in Alzheimer’s dementia and normal aging. Am. J. Roentgenol. 149, 351–356. doi: 10.2214/ajr.149.2.351
Fazlollahi, A., Lee, S., Coleman, F., McCann, E., Cloos, M. A., Bourgeat, P., et al. (2023). Increased resolution of structural MRI at 3T improves estimation of regional cortical degeneration in individual dementia patients using surface thickness maps. J. Alzheimers Dis. 95, 1253–1262. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230030
Ferreira, D., Verhagen, C., Hernández-Cabrera, J. A., Cavallin, L., Guo, C.-J., Ekman, U., et al. (2017). Distinct subtypes of Alzheimer’s disease based on patterns of brain atrophy: longitudinal trajectories and clinical applications. Sci. Rep. 7:46263. doi: 10.1038/srep46263
Foo, H., Mak, E., Yong, T. T., Wen, M. C., Chander, R. J., Au, W. L., et al. (2017). Progression of subcortical atrophy in mild Parkinson’s disease and its impact on cognition. Eur. J. Neurol. 24, 341–348. doi: 10.1111/ene.13205
Forno, G., Saranathan, M., Contador, J., Guillen, N., Falgàs, N., Tort-Merino, A., et al. (2023). Thalamic nuclei changes in early and late onset Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Res. Neurobiol. 4:100084. doi: 10.1016/j.crneur.2023.100084
Fujimori, J., and Nakashima, I. (2024). Early-stage volume losses in the corpus callosum and thalamus predict the progression of brain atrophy in patients with multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 387:578280. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2023.578280
Galimberti, D., and Scarpini, E. (2012). Genetics of frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Front. Neurol. 3:52. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2012.00052
Gao, L., Li, J., Zhang, R., Bekele, H. H., Wang, J., Cheng, Y., et al. (2023). MMGan: a multimodal MR brain tumor image segmentation method. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 17:1275795. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2023.1275795
Garcia-Diaz, A. I., Segura, B., Baggio, H. C., Marti, M. J., Valldeoriola, F., Compta, Y., et al. (2018a). Structural brain correlations of visuospatial and Visuoperceptual tests in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 24, 33–44. doi: 10.1017/S1355617717000583
Garcia-Diaz, A. I., Segura, B., Baggio, H. C., Uribe, C., Campabadal, A., Abos, A., et al. (2018b). Cortical thinning correlates of changes in visuospatial and visuoperceptual performance in Parkinson’s disease: a 4-year follow-up. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 46, 62–68. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.11.003
Garcia-Ptacek, S., Cavallin, L., Kåreholt, I., Kramberger, M. G., Winblad, B., Jelic, V., et al. (2014). Subjective cognitive impairment subjects in our clinical practice. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. Extra 4, 419–430. doi: 10.1159/000366270
Gaser, C., Dahnke, R., Thompson, P. M., Kurth, F., and Luders, E., and Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2022). CAT–A computational anatomy toolbox for the analysis of structural MRI data. Neuroscience 13:giae049. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giae049
Gaubert, M., Dell’Orco, A., Lange, C., Garnier-Crussard, A., Zimmermann, I., Dyrba, M., et al. (2023). Performance evaluation of automated white matter hyperintensity segmentation algorithms in a multicenter cohort on cognitive impairment and dementia. Front. Psych. 13:1010273. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1010273
Gauthier, S., Webster, C., Servaes, S., Morais, J., and Rosa-Neto, P. (2022). World Alzheimer report 2022: life after diagnosis: navigating treatment, care and support. Available at: https://www.alzint.org/u/World-Alzheimer-Report-2022.pdf (Accessed May 01, 2024).
Gentreau, M., Maller, J. J., Meslin, C., Cyprien, F., Lopez-Castroman, J., and Artero, S. (2023). Is hippocampal volume a relevant early marker of dementia? Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 31, 932–942. doi: 10.1016/j.jagp.2023.05.015
Goh, Y. Y., Saunders, E., Pavey, S., Rushton, E., Quinn, N., Houlden, H., et al. (2023). Multiple system atrophy. Pract. Neurol. 23, 208–221. doi: 10.1136/pn-2020-002797
Goldman, J. G., Bledsoe, I. O., Merkitch, D., Dinh, V., Bernard, B., and Stebbins, G. T. (2017). Corpus callosal atrophy and associations with cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease. Neurology 88, 1265–1272. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003764
Goubran, M., Ntiri, E. E., Akhavein, H., Holmes, M., Nestor, S., Ramirez, J., et al. (2020). Hippocampal segmentation for brains with extensive atrophy using three-dimensional convolutional neural networks. Hum. Brain Mapp. 41, 291–308. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24811
Gräfe, D., Simion, S.-H., Rosolowski, M., Merkenschlager, A., Frahm, J., Voit, D., et al. (2022). Brain deposition of gadobutrol in children—a cross-sectional and longitudinal MRI T1 mapping study. Eur. Radiol. 33, 4580–4588. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-09297-y
Griffanti, L., Zamboni, G., Khan, A., Li, L., Bonifacio, G., Sundaresan, V., et al. (2016). BIANCA (brain intensity AbNormality classification algorithm): a new tool for automated segmentation of white matter hyperintensities. NeuroImage 141, 191–205. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.07.018
Guo, S., Chen, Q., Wang, L., Wang, L., and Zhu, Y. (2023). nnUnetFormer: an automatic method based on nnUnet and transformer for brain tumor segmentation with multimodal MR images. Phys. Med. Biol. 68:245012. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ad0c8d
Gyanwali, B., Tan, C. S., Petr, J., Escobosa, L. L. T., Vrooman, H., Chen, C., et al. (2022). Arterial spin-labeling parameters and their associations with risk factors, cerebral small-vessel Disease, and etiologic subtypes of cognitive impairment and dementia. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 43, 1418–1423. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7630
Hansen, N., Bouter, C., Müller, S. J., van Riesen, C., Khadhraoui, E., Ernst, M., et al. (2023a). New insights into potential biomarkers in patients with mild cognitive impairment occurring in the prodromal Stage of dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain Sci. 13:242. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13020242
Hansen, N., Müller, S. J., Khadhraoui, E., Ernst, M., Riedel, C. H., Wiltfang, J., et al. (2023b). Psychiatric onset of prodromal dementia with Lewy bodies: current insights into neuroimaging tools. J. World Fed. Soc. Biol. 5, 1–22. doi: 10.1080/15622975.2023.2191008
Hansen, N., Müller, S. J., Khadhraoui, E., Riedel, C. H., Langer, P., Wiltfang, J., et al. (2022). Metric magnetic resonance imaging analysis reveals pronounced substantia-innominata atrophy in dementia with Lewy bodies with a psychiatric onset. Front. Aging Neurosci. 14:815813. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.815813
Hanyu, H., Shimizu, S., Tanaka, Y., Hirao, K., Iwamoto, T., and Abe, K. (2007). MR features of the substantia innominata and therapeutic implications in dementias. Neurobiol. Aging 28, 548–554. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2006.02.009
Hari, E., Kurt, E., Ulasoglu-Yildiz, C., Bayram, A., Bilgic, B., Demiralp, T., et al. (2023). Morphometric analysis of medial temporal lobe subregions in Alzheimer’s disease using high-resolution MRI. Brain Struct. Funct. 228, 1885–1899. doi: 10.1007/s00429-023-02683-2
He, B., Dai, Y., Astolfi, L., Babiloni, F., Yuan, H., and Yang, L. (2011). eConnectome: a MATLAB toolbox for mapping and imaging of brain functional connectivity. J. Neurosci. Methods 195, 261–269. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2010.11.015
He, M., Li, Y., Zhou, L., Li, Y., Lei, T., Yan, W., et al. (2022). Relationships between memory impairments and hippocampal structure in patients with subcortical ischemic vascular Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 14:823535. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.823535
He, H., Liang, L., Tang, T., Luo, J., Wang, Y., and Cui, H. (2020). Progressive brain changes in Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis of structural magnetic resonance imaging studies. Brain Res. 1740:146847. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2020.146847
Heikkinen, S., Cajanus, A., Katisko, K., Hartikainen, P., Vanninen, R., Haapasalo, A., et al. (2022). Brainstem atrophy is linked to extrapyramidal symptoms in frontotemporal dementia. J. Neurol. 269, 4488–4497. doi: 10.1007/s00415-022-11095-x
Henschel, L., Conjeti, S., Estrada, S., Diers, K., Fischl, B., and Reuter, M. (2020). FastSurfer - a fast and accurate deep learning based neuroimaging pipeline. NeuroImage 219:117012. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117012
Henschel, L., Kügler, D., and Reuter, M. (2022). FastSurferVINN: building resolution-independence into deep learning segmentation methods—a solution for HighRes brain MRI. NeuroImage 251:118933. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.118933
Hoebel, K. V., Bridge, C. P., Ahmed, S., Akintola, O., Chung, C., Huang, R. Y., et al. (2024). Expert-centered evaluation of deep learning algorithms for brain tumor segmentation. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 6:e220231. doi: 10.1148/ryai.220231
Hosseini, S. M. H., Hoeft, F., and Kesler, S. R. (2012). GAT: a graph-theoretical analysis toolbox for analyzing between-group differences in large-scale structural and functional brain networks. PLoS One 7:e40709. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040709
Hosseini, M.-P., Nazem-Zadeh, M.-R., Pompili, D., Jafari-Khouzani, K., Elisevich, K., and Soltanian-Zadeh, H. (2016). Comparative performance evaluation of automated segmentation methods of hippocampus from magnetic resonance images of temporal lobe epilepsy patients: comparative performance evaluation of automated segmentation of hippocampus. Med. Phys. 43, 538–553. doi: 10.1118/1.4938411
Hotz, I., Deschwanden, P. F., Liem, F., Mérillat, S., Malagurski, B., Kollias, S., et al. (2022). Performance of three freely available methods for extracting white matter hyperintensities: FREESURFER, UBO detector, and BIANCA. Hum. Brain Mapp. 43, 1481–1500. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25739
Huey, E. D., Lee, S., Brickman, A. M., Manoochehri, M., Griffith, E., Devanand, D. P., et al. (2015). Neuropsychiatric effects of neurodegeneration of the medial versus lateral ventral prefrontal cortex in humans. Cortex 73, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2015.08.002
Huey, E. D., Lee, S., Cheran, G., Grafman, J., and Devanand, D. P. (2016). Brain regions involved in arousal and reward processing are associated with apathy in Alzheimer’s Disease and frontotemporal dementia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 55, 551–558. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160107
Hussl, A., Mahlknecht, P., Scherfler, C., Esterhammer, R., Schocke, M., Poewe, W., et al. (2010). Diagnostic accuracy of the magnetic resonance parkinsonism index and the midbrain-to-pontine area ratio to differentiate progressive supranuclear palsy from Parkinson’s disease and the Parkinson variant of multiple system atrophy: diagnostic accuracy of the MRPI and the m/p-ratio. Mov. Disord. 25, 2444–2449. doi: 10.1002/mds.23351
Huttenlocher, D. P., Klanderman, G. A., and Rucklidge, W. J. (1993). Comparing images using the Hausdorff distance. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 15, 850–863. doi: 10.1109/34.232073
Iglesias, J. E., Augustinack, J. C., Nguyen, K., Player, C. M., Player, A., Wright, M., et al. (2015a). A computational atlas of the hippocampal formation using ex vivo, ultra-high resolution MRI: application to adaptive segmentation of in vivo MRI. NeuroImage 115, 117–137. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.04.042
Iglesias, J. E., Insausti, R., Lerma-Usabiaga, G., Bocchetta, M., Van Leemput, K., Greve, D. N., et al. (2018). A probabilistic atlas of the human thalamic nuclei combining ex vivo MRI and histology. NeuroImage 183, 314–326. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.08.012
Iglesias, J. E., Van Leemput, K., Augustinack, J., Insausti, R., Fischl, B., and Reuter, M. (2016). Bayesian longitudinal segmentation of hippocampal substructures in brain MRI using subject-specific atlases. NeuroImage 141, 542–555. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.07.020
Iglesias, J. E., Van Leemput, K., Bhatt, P., Casillas, C., Dutt, S., Schuff, N., et al. (2015b). Bayesian segmentation of brainstem structures in MRI. NeuroImage 113, 184–195. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.02.065
Jahanshahi, A., Ghareaghaji, N., Hassanpour, S., Vafadar, A., Mousavi, S., and Khezerloo, D. (2023). Cortical gray matter and cerebral white matter atrophy and asymmetry in Parkinson’s disease patients with normal cognitive precede. Int. J. Neurosci. 6, 1–6. doi: 10.1080/00207454.2023.2294260
Jahanshahi, A. R., Naghdi Sadeh, R., and Khezerloo, D. (2023). Atrophy asymmetry in hippocampal subfields in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Exp. Brain Res. 241, 495–504. doi: 10.1007/s00221-022-06543-z
Jakabek, D., Power, B. D., Spotorno, N., Macfarlane, M. D., Walterfang, M., Velakoulis, D., et al. (2023). Structural and microstructural thalamocortical network disruption in sporadic behavioural variant frontotemporal dementia. NeuroImage Clin. 39:103471. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2023.103471
Jakimovski, D., Zivadinov, R., Weinstock, Z., Fuchs, T. A., Bartnik, A., Dwyer, M. G., et al. (2023). Cortical thickness and cognition in older people with multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 270, 5223–5234. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-11945-2
Jellinger, K. A., and Attems, J. (2010). Prevalence of dementia disorders in the oldest-old: an autopsy study. Acta Neuropathol. 119, 421–433. doi: 10.1007/s00401-010-0654-5
Jenkinson, M., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E. J., Woolrich, M. W., and Smith, S. M. (2012). FSL. NeuroImage 62, 782–790. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.09.015
Jiang, J., Liu, T., Zhu, W., Koncz, R., Liu, H., Lee, T., et al. (2018). UBO detector – a cluster-based, fully automated pipeline for extracting white matter hyperintensities. NeuroImage 174, 539–549. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.03.050
Joo, L., Shim, W. H., Suh, C. H., Lim, S. J., Heo, H., Kim, W. S., et al. (2022). Diagnostic performance of deep learning-based automatic white matter hyperintensity segmentation for classification of the Fazekas scale and differentiation of subcortical vascular dementia. PLoS One 17:e0274562. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274562
Kalimo, H., Viitanen, M., Amberla, K., Juvonen, V., Marttila, R., Pöyhönen, M., et al. (1999). CADASIL: hereditary disease of arteries causing brain infarcts and dementia. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 25, 257–265. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2990.1999.00198.x
Kamnitsas, K., Ledig, C., Newcombe, V. F. J., Simpson, J. P., Kane, A. D., Menon, D. K., et al. (2017). Efficient multi-scale 3D CNN with fully connected CRF for accurate brain lesion segmentation. Med. Image Anal. 36, 61–78. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2016.10.004
Kang, K. M., Sohn, C.-H., Byun, M. S., Lee, J. H., Yi, D., Lee, Y., et al. (2020). Prediction of amyloid positivity in mild cognitive impairment using fully automated brain segmentation software. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 16, 1745–1754. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S252293
Kantarci, K., Lesnick, T., Ferman, T. J., Przybelski, S. A., Boeve, B. F., Smith, G. E., et al. (2016). Hippocampal volumes predict risk of dementia with Lewy bodies in mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 87, 2317–2323. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003371
Karstens, A. J., Tussing-Humphreys, L., Zhan, L., Rajendran, N., Cohen, J., Dion, C., et al. (2019). Associations of the Mediterranean diet with cognitive and neuroimaging phenotypes of dementia in healthy older adults. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 109, 361–368. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy275
Kazerooni, A. F., Khalili, N., Liu, X., Haldar, D., Jiang, Z., Anwar, S. M., et al. (2023). The brain tumor segmentation (BraTS) challenge 2023: focus on pediatrics (CBTN-CONNECT-DIPGR-ASNR-MICCAI BraTS-PEDs). ArXiv. 2305.17033v7. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.2305.17033
Khadhraoui, E., Müller, S. J., Hansen, N., Riedel, C. H., Langer, P., Timäeus, C., et al. (2022). Manual and automated analysis of atrophy patterns in dementia with Lewy bodies on MRI. BMC Neurol. 22:114. doi: 10.1186/s12883-022-02642-0
Kim, T. H., Choi, J. W., Roh, H. G., Moon, W.-J., Moon, S. G., Chun, Y. I., et al. (2014). Atherosclerotic arterial wall change of non-stenotic intracracranial arteries on high-resolution MRI at 3.0T: correlation with cerebrovascular risk factors and white matter hyperintensity. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 126, 1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2014.08.010
Kim, J. P., Kim, J., Park, Y. H., Park, S. B., Lee, J. S., Yoo, S., et al. (2019). Machine learning based hierarchical classification of frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroImage Clin. 23:101811. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101811
Knopman, D. S., Griswold, M. E., Lirette, S. T., Gottesman, R. F., Kantarci, K., Sharrett, A. R., et al. (2015). Vascular imaging abnormalities and cognition: mediation by cortical volume in nondemented individuals: atherosclerosis risk in communities-neurocognitive study. Stroke 46, 433–440. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.114.007847
Kruschwitz, J. D., List, D., Waller, L., Rubinov, M., and Walter, H. (2015). GraphVar: a user-friendly toolbox for comprehensive graph analyses of functional brain connectivity. J. Neurosci. Methods 245, 107–115. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2015.02.021
Kumar, S., Payne, P. R. O., and Sotiras, A. (2023). “Normative modeling using multimodal variational autoencoders to identify abnormal brain volume deviations in Alzheimer’s disease” in Medical imaging 2023: Computer-aided diagnosis. eds. K. M. Iftekharuddin and W. Chen (San Diego, US: SPIE), 1.
Landin-Romero, R., Kumfor, F., Leyton, C. E., Irish, M., Hodges, J. R., and Piguet, O. (2017). Disease-specific patterns of cortical and subcortical degeneration in a longitudinal study of Alzheimer’s disease and behavioural-variant frontotemporal dementia. NeuroImage 151, 72–80. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.03.032
Lee, D. A., Lee, H., Kim, S. E., and Park, K. M. (2023). Brain networks and epilepsy development in patients with Alzheimer disease. Brain Behav. 13:e3152. doi: 10.1002/brb3.3152
Lee, J., Lee, J. Y., Oh, S. W., Chung, M. S., Park, J. E., Moon, Y., et al. (2021). Evaluation of reproducibility of brain Volumetry between commercial software, Inbrain and established research purpose method. J. Clin. Neurol. 17:307. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2021.17.2.307
Lee, J. Y., Oh, S. W., Chung, M. S., Park, J. E., Moon, Y., Jeon, H. J., et al. (2021). Clinically available software for automatic brain Volumetry: comparisons of volume measurements and validation of Intermethod reliability. Korean J. Radiol. 22, 405–414. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2020.0518
Lehmann, M., Rohrer, J. D., Clarkson, M. J., Ridgway, G. R., Scahill, R. I., Modat, M., et al. (2010). Reduced cortical thickness in the posterior cingulate gyrus is characteristic of both typical and atypical Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 20, 587–598. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-1401
Li, C., Buch, S., Sun, Z., Muccio, M., Jiang, L., Chen, Y., et al. (2024). In vivo mapping of hippocampal venous vasculature and oxygenation using susceptibility imaging at 7T. NeuroImage 291:120597. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2024.120597
Li, X., Li, D., Li, Q., Li, Y., Li, K., Li, S., et al. (2016). Hippocampal subfield volumetry in patients with subcortical vascular mild cognitive impairment. Sci. Rep. 6:20873. doi: 10.1038/srep20873
Li, X., and Martinez, J. (2020). “Quantitative comparison of white matter segmentation for brain MR images” in Advances in computer vision. eds. K. Arai and S. Kapoor (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 639–647.
Li, W.-X., Yuan, J., Han, F., Zhou, L.-X., Ni, J., Yao, M., et al. (2023). White matter and gray matter changes related to cognition in community populations. Front. Aging Neurosci. 15:1065245. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1065245
Liu, Y., Hu, A., Chen, L., Li, B., Zhang, M., Xi, P., et al. (2021). Association between cortical thickness and distinct vascular cognitive impairment and dementia in patients with white matter lesions. Exp. Physiol. 106, 1612–1620. doi: 10.1113/EP089419
Longhurst, J. K., Sreenivasan, K. R., Kim, J., Cummings, J. L., John, S. E., Poston, B., et al. (2023). Cortical thickness is related to cognitive-motor automaticity and attention allocation in individuals with Alzheimer’s disease: a regions of interest study. Exp. Brain Res. 241, 1489–1499. doi: 10.1007/s00221-023-06618-5
Low, A., Foo, H., Yong, T. T., Tan, L. C. S., and Kandiah, N. (2019). Hippocampal subfield atrophy of CA1 and subicular structures predict progression to dementia in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 90, 681–687. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2018-319592
Lupascu, N., Lupescu, I. C., Caloianu, I., Naftanaila, F., Glogojeanu, R. R., Sirbu, C. A., et al. (2023). Imaging criteria for the diagnosis of progressive Supranuclear palsy: supportive or mandatory? Diagnostics 13:1967. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13111967
Lyall, A. E., Breithaupt, L., Ji, C., Haidar, A., Kotler, E., Becker, K. R., et al. (2024). Lower region-specific gray matter volume in females with atypical anorexia nervosa and anorexia nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 57, 951–966. doi: 10.1002/eat.24168
Mak, E., Gabel, S., Su, L., Williams, G. B., Arnold, R., Passamonti, L., et al. (2017). Multi-modal MRI investigation of volumetric and microstructural changes in the hippocampus and its subfields in mild cognitive impairment, Alzheimer’s disease, and dementia with Lewy bodies. Int. Psychogeriatr. 29, 545–555. doi: 10.1017/S1041610216002143
Mak, E., Su, L., Williams, G. B., Firbank, M. J., Lawson, R. A., Yarnall, A. J., et al. (2015). Baseline and longitudinal grey matter changes in newly diagnosed Parkinson’s disease: ICICLE-PD study. Brain 138, 2974–2986. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv211
Mak, E., Su, L., Williams, G. B., and O’Brien, J. T. (2014). Neuroimaging characteristics of dementia with Lewy bodies. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 6:18. doi: 10.1186/alzrt248
Malek-Ahmadi, M., and Nikkhahmanesh, N. (2024). Meta-analysis of Montreal cognitive assessment diagnostic accuracy in amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Front. Psychol. 15:1369766. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1369766
Malone, I. B., Cash, D., Ridgway, G. R., MacManus, D. G., Ourselin, S., Fox, N. C., et al. (2013). MIRIAD—public release of a multiple time point Alzheimer’s MR imaging dataset. NeuroImage 70, 33–36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.12.044
Manjón, J. V., and Coupé, P. (2016). volBrain: an online MRI brain Volumetry system. Front. Neuroinform. 10:30. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2016.00030
Maruoka, H., Hattori, T., Hase, T., Takahashi, K., Ohara, M., Orimo, S., et al. (2023). Aberrant morphometric networks in Alzheimer’s disease have hemispheric asymmetry and age dependence. Eur. J. Neurosci. 59, 1332–1347. doi: 10.1111/ejn.16225
McKeith, I. G., Boeve, B. F., Dickson, D. W., Halliday, G., Taylor, J.-P., Weintraub, D., et al. (2017). Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: fourth consensus report of the DLB consortium. Neurology 89, 88–100. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004058
McKeith, I. G., Ferman, T. J., Thomas, A. J., Blanc, F., Boeve, B. F., Fujishiro, H., et al. (2020). Research criteria for the diagnosis of prodromal dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology 94, 743–755. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009323
Mijalkov, M., Kakaei, E., Pereira, J. B., Westman, E., and Volpe, G., and for the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2017). BRAPH: a graph theory software for the analysis of brain connectivity. PLoS One 12:e0178798. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178798
Mitchell, E., Tavares, T. P., Palaniyappan, L., and Finger, E. C. (2019). Hoarding and obsessive–compulsive behaviours in frontotemporal dementia: clinical and neuroanatomic associations. Cortex 121, 443–453. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2019.09.012
Mittal, S., Rakshith, K., Misri, Z., Pai, S., and Shenoy, N. (2017). Humming bird sign, a significant sign. Neurol. India 65, 673–674. doi: 10.4103/neuroindia.NI_45_17
Molinder, A., Ziegelitz, D., Maier, S. E., and Eckerström, C. (2021). Validity and reliability of the medial temporal lobe atrophy scale in a memory clinic population. BMC Neurol. 21:289. doi: 10.1186/s12883-021-02325-2
Möller, C., Hafkemeijer, A., Pijnenburg, Y. A. L., Rombouts, S. A. R. B., Van Der Grond, J., Dopper, E., et al. (2016). Different patterns of cortical gray matter loss over time in behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 38, 21–31. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.10.020
Mora-Rubio, A., Bravo-Ortíz, M. A., Quiñones Arredondo, S., Saborit Torres, J. M., Ruz, G. A., and Tabares-Soto, R. (2023). Classification of Alzheimer’s disease stages from magnetic resonance images using deep learning. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 9:e1490. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1490
Moridi, T., Stawiarz, L., McKay, K. A., Ineichen, B. V., Ouellette, R., Ferreira, D., et al. (2022). Association between brain volume and disability over time in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. J. Exp. Transl. Clin. 8:205521732211442. doi: 10.1177/20552173221144230
Mueller, S. G., Weiner, M. W., Thal, L. J., Petersen, R. C., Jack, C. R., Jagust, W., et al. (2005). Ways toward an early diagnosis in Alzheimer’s disease: the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI). Alzheimers Dement. 1, 55–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2005.06.003
Mueller, S. G., Yushkevich, P. A., Das, S., Wang, L., Van Leemput, K., Iglesias, J. E., et al. (2018). Systematic comparison of different techniques to measure hippocampal subfield volumes in ADNI2. NeuroImage Clin. 17, 1006–1018. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2017.12.036
Müller, S. J., Khadhraoui, E., Allam, I., Argyriou, L., Hehr, U., Liman, J., et al. (2020). CARASIL with coronary artery disease and distinct cerebral microhemorrhage: a case report and literature review. Clin. Transl. Neurosci. 4:2514183X2091418. doi: 10.1177/2514183X20914182
Müller, S. J., Khadhraoui, E., Hansen, N., Jamous, A., Langer, P., Wiltfang, J., et al. (2023). Brainstem atrophy in dementia with Lewy bodies compared with progressive supranuclear palsy and Parkinson’s disease on MRI. BMC Neurol. 23:114. doi: 10.1186/s12883-023-03151-4
Müller, S. J., Khadhraoui, E., Voit, D., Riedel, C. H., Frahm, J., and Ernst, M. (2022). First clinical application of a novel T1 mapping of the whole brain. Neuroradiol. J. 35, 684–691. doi: 10.1177/19714009221084244
Nasreddine, Z. S., Phillips, N. A., Bédirian, V., Charbonneau, S., Whitehead, V., Collin, I., et al. (2005). The Montreal cognitive assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 53, 695–699. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.53221.x
Newcombe, E. A., Camats-Perna, J., Silva, M. L., Valmas, N., Huat, T. J., and Medeiros, R. (2018). Inflammation: the link between comorbidities, genetics, and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflammation 15:276. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1313-3
Nigro, S., Filardi, M., Tafuri, B., Nicolardi, M., De Blasi, R., Giugno, A., et al. (2024). Deep learning–based approach for brainstem and ventricular MR Planimetry: application in patients with progressive Supranuclear palsy. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 6:e230151. doi: 10.1148/ryai.230151
Noroozi, M., Gholami, M., Sadeghsalehi, H., Behzadi, S., Habibzadeh, A., Erabi, G., et al. (2024). Machine and deep learning algorithms for classifying different types of dementia: a literature review. Appl. Neuropsychol. Adult 1–15, 1–15. doi: 10.1080/23279095.2024.2382823
Outeiro, T. F., Koss, D. J., Erskine, D., Walker, L., Kurzawa-Akanbi, M., Burn, D., et al. (2019). Dementia with Lewy bodies: an update and outlook. Mol. Neurodegener. 14:5. doi: 10.1186/s13024-019-0306-8
Ozzoude, M., Varriano, B., Beaton, D., Ramirez, J., Adamo, S., Holmes, M. F., et al. (2023). White matter hyperintensities and smaller cortical thickness are associated with neuropsychiatric symptoms in neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular diseases. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 15:114. doi: 10.1186/s13195-023-01257-y
Ozzoude, M., Varriano, B., Beaton, D., Ramirez, J., Holmes, M. F., Scott, C. J. M., et al. (2022). Investigating the contribution of white matter hyperintensities and cortical thickness to empathy in neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular diseases. GeroScience 44, 1575–1598. doi: 10.1007/s11357-022-00539-x
Paternicó, D., Manes, M., Premi, E., Cosseddu, M., Gazzina, S., Alberici, A., et al. (2016). Frontotemporal dementia and language networks: cortical thickness reduction is driven by dyslexia susceptibility genes. Sci. Rep. 6:30848. doi: 10.1038/srep30848
Pérez-Millan, A., Borrego-Écija, S., Van Swieten, J. C., Jiskoot, L., Moreno, F., Laforce, R., et al. (2023a). Loss of brainstem white matter predicts onset and motor neuron symptoms in C9orf72 expansion carriers: a GENFI study. J. Neurol. 270, 1573–1586. doi: 10.1007/s00415-022-11435-x
Pérez-Millan, A., Contador, J., Juncà-Parella, J., Bosch, B., Borrell, L., Tort-Merino, A., et al. (2023b). Classifying Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia using machine learning with cross-sectional and longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging data. Hum. Brain Mapp. 44, 2234–2244. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26205
Petersen, R. C., Smith, G. E., Waring, S. C., Ivnik, R. J., Tangalos, E. G., and Kokmen, E. (1999). Mild cognitive impairment: clinical characterization and outcome. Arch. Neurol. 56:303. doi: 10.1001/archneur.56.3.303
Pfefferbaum, A., Sullivan, E. V., Zahr, N. M., Pohl, K. M., and Saranathan, M. (2023). Multi-atlas thalamic nuclei segmentation on standard T1-WEIGHED MRI with application to normal aging. Hum. Brain Mapp. 44, 612–628. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26088
Pinter, N. K., Ganji, S., Johnson, B., Huijbers, W., Ajtai, B., Dorn, R., et al. (2022). A standardized protocol for detection of amyloid related imaging Abnormality (ARIA) on 3T Philips magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Alzheimers Dement. 18:e065618. doi: 10.1002/alz.065618
Popuri, K., Dowds, E., Beg, M. F., Balachandar, R., Bhalla, M., Jacova, C., et al. (2018). Gray matter changes in asymptomatic C9orf72 and GRN mutation carriers. NeuroImage Clin. 18, 591–598. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.02.017
Puonti, O., Iglesias, J. E., and Van Leemput, K. (2016). Fast and sequence-adaptive whole-brain segmentation using parametric Bayesian modeling. NeuroImage 143, 235–249. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.09.011
Qian, L., Wen, C., Li, Y., Hu, Z., Zhou, X., Xia, X., et al. (2024). Multi-scale context UNet-like network with redesigned skip connections for medical image segmentation. Comput. Methods Prog. Biomed. 243:107885. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2023.107885
Qu, H., Ge, H., Wang, L., Wang, W., and Hu, C. (2023). Volume changes of hippocampal and amygdala subfields in patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neurol. Belg. 123, 1381–1393. doi: 10.1007/s13760-023-02235-9
Rahmani, F., Jindal, S., Raji, C. A., Wang, W., Nazeri, A., Perez-Carrillo, G. G., et al. (2023). Validity assessment of an automated brain morphometry tool for patients with De novo memory symptoms. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 44, 261–267. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A7790
Rajagopalan, V., and Pioro, E. P. (2015). Disparate voxel based morphometry (VBM) results between SPM and FSL softwares in ALS patients with frontotemporal dementia: which VBM results to consider? BMC Neurol. 15:32. doi: 10.1186/s12883-015-0274-8
Rascovsky, K., Hodges, J. R., Knopman, D., Mendez, M. F., Kramer, J. H., Neuhaus, J., et al. (2011). Sensitivity of revised diagnostic criteria for the behavioural variant of frontotemporal dementia. Brain 134, 2456–2477. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr179
Ratti, E., Domoto-Reilly, K., Caso, C., Murphy, A., Brickhouse, M., Hochberg, D., et al. (2021). Regional prefrontal cortical atrophy predicts specific cognitive-behavioral symptoms in ALS-FTD. Brain Imaging Behav. 15, 2540–2551. doi: 10.1007/s11682-021-00456-1
Rethlefsen, M. L., and Page, M. J. (2021). PRISMA 2020 and PRISMA-S: common questions on tracking records and the flow diagram. J. Med. Libr. Assoc. 110, 253–257. doi: 10.5195/jmla.2022.1449
Říha, P., Brabenec, L., Mareček, R., Rektor, I., and Rektorová, I. (2022). The reduction of hippocampal volume in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 129, 575–580. doi: 10.1007/s00702-021-02451-8
Rohrer, J. D., Warren, J. D., Modat, M., Ridgway, G. R., Douiri, A., Rossor, M. N., et al. (2009). Patterns of cortical thinning in the language variants of frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Neurology 72, 1562–1569. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181a4124e
Ross, D. E., Ochs, A. L., Seabaugh, J. M., DeMark, M. F., Shrader, C. R., Marwitz, J. H., et al. (2012). Progressive brain atrophy in patients with chronic neuropsychiatric symptoms after mild traumatic brain injury: a preliminary study. Brain Inj. 26, 1500–1509. doi: 10.3109/02699052.2012.694570
Rubinov, M., and Sporns, O. (2010). Complex network measures of brain connectivity: uses and interpretations. NeuroImage 52, 1059–1069. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.10.003
Ryu, D.-W., Hong, Y. J., Cho, J. H., Kwak, K., Lee, J.-M., Shim, Y. S., et al. (2022). Automated brain volumetric program measuring regional brain atrophy in diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease dementia. Brain Imaging Behav. 16, 2086–2096. doi: 10.1007/s11682-022-00678-x
Saha, A., and Van Der Pol, C. B. (2024). Liver observation segmentation on contrast-enhanced MRI: SAM and MedSAM performance in patients with probable or definite hepatocellular carcinoma. Can. Assoc. Radiol. J. :08465371241250215. doi: 10.1177/08465371241250215
Sako, W., Suda, A., Taniguchi, D., Kamagata, K., Shindo, A., Ogawa, T., et al. (2023). Midbrain atrophy in pathologically diagnosed Lewy body disease and clinically diagnosed Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 454:120821. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2023.120821
Salah Khlif, M., Egorova-Brumley, N., Bird, L. J., Werden, E., and Brodtmann, A. (2022). Cortical thinning 3 years after ischaemic stroke is associated with cognitive impairment and APOE ε4. NeuroImage Clin. 36:103200. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103200
Sampedro, F., Marín-Lahoz, J., Martínez-Horta, S., Pagonabarraga, J., and Kulisevsky, J. (2019). Dopaminergic degeneration induces early posterior cortical thinning in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 124, 29–35. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2018.11.001
Sawyer, K. S., Adra, N., Salz, D. M., Kemppainen, M. I., Ruiz, S. M., Harris, G. J., et al. (2020). Hippocampal subfield volumes in abstinent men and women with a history of alcohol use disorder. PLoS One 15:e0236641. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236641
Schmidt, M. F., Storrs, J. M., Freeman, K. B., Jack, C. R., Turner, S. T., Griswold, M. E., et al. (2018). A comparison of manual tracing and FreeSurfer for estimating hippocampal volume over the adult lifespan. Hum. Brain Mapp. 39, 2500–2513. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24017
Schuster, C., Kasper, E., Dyrba, M., Machts, J., Bittner, D., Kaufmann, J., et al. (2014). Cortical thinning and its relation to cognition in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol. Aging 35, 240–246. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.07.020
Shamir, R. R., Duchin, Y., Kim, J., Sapiro, G., and Harel, N. (2018). Continuous Dice Coefficient: a Method for Evaluating Probabilistic Segmentations. bioRxiv. doi: 10.1101/306977
Sierra, C. (2014). Essential hypertension, cerebral white matter pathology and ischemic stroke. Curr. Med. Chem. 21, 2156–2164. doi: 10.2174/0929867321666131227155140
Singh, S., Malo, P. K., Mensegere, A. L., and Issac, T. G. (2023). Letter to editor: atrophy asymmetry in hippocampal subfields in patients with Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Exp. Brain Res. 241:2205. doi: 10.1007/s00221-023-06673-y
Singh, M. K., and Singh, K. K. (2021). A review of publicly available automatic brain segmentation methodologies, machine learning models, recent advancements, and their comparison. Ann. Neurosci. 28, 82–93. doi: 10.1177/0972753121990175
Slowinski, J., Imamura, A., Uitti, R. J., Pooley, R. A., Strongosky, A. J., Dickson, D. W., et al. (2008). MR imaging of brainstem atrophy in progressive supranuclear palsy. J. Neurol. 255, 37–44. doi: 10.1007/s00415-007-0656-y
Smith, S. M., Jenkinson, M., Woolrich, M. W., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E. J., Johansen-Berg, H., et al. (2004). Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. NeuroImage 23, S208–S219. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.051
Squeglia, L. M., Rinker, D. A., Bartsch, H., Castro, N., Chung, Y., Dale, A. M., et al. (2014). Brain volume reductions in adolescent heavy drinkers. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 9, 117–125. doi: 10.1016/j.dcn.2014.02.005
Steele, J. C. (1964). Progressive Supranuclear palsy: a heterogeneous degeneration involving the brain stem, basal ganglia and cerebellum with vertical gaze and pseudobulbar palsy Nuchal Dystonia and Dementia. Arch. Neurol. 10, 333–359. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460160003001
Stephen, R., Liu, Y., Ngandu, T., Antikainen, R., and Hulkkonen, J. (2019). Brain volumes and cortical thickness on MRI in the Finnish geriatric intervention study to prevent cognitive impairment and disability (FINGER). Alzheimers Res. Ther. 11:53. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0506-z
Stoddart, W. H. (1913). Presbyophrenia (Alzheimer’s Disease). Proc. R. Soc. Med. 6, 13–14. doi: 10.1177/003591571300601702
Stoeck, K., Sanchez-Juan, P., Gawinecka, J., Green, A., Ladogana, A., Pocchiari, M., et al. (2012). Cerebrospinal fluid biomarker supported diagnosis of Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease and rapid dementias: a longitudinal multicentre study over 10 years. Brain 135, 3051–3061. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws238
Struyfs, H., Sima, D. M., Wittens, M., Ribbens, A., Pedrosa De Barros, N., Phan, T. V., et al. (2020). Automated MRI volumetry as a diagnostic tool for Alzheimer’s disease: validation of icobrain dm. NeuroImage Clin. 26:102243. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102243
Sturm, V. E., Sollberger, M., Seeley, W. W., Rankin, K. P., Ascher, E. A., Rosen, H. J., et al. (2013). Role of right pregenual anterior cingulate cortex in self-conscious emotional reactivity. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 8, 468–474. doi: 10.1093/scan/nss023
Su, J. H., Thomas, F. T., Kasoff, W. S., Tourdias, T., Choi, E. Y., Rutt, B. K., et al. (2019). Thalamus optimized multi atlas segmentation (THOMAS): fast, fully automated segmentation of thalamic nuclei from structural MRI. NeuroImage 194, 272–282. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.03.021
Subotic, A., Gee, M., Nelles, K., Ba, F., Dadar, M., Duchesne, S., et al. (2023). Gray matter loss relates to dual task gait in Lewy body disorders and aging. J. Neurol. 271, 962–975. doi: 10.1007/s00415-023-12052-y
Subotic, A., McCreary, C. R., Saad, F., Nguyen, A., Alvarez-Veronesi, A., Zwiers, A. M., et al. (2021). Cortical thickness and its association with clinical cognitive and Neuroimaging markers in cerebral amyloid Angiopathy. J. Alzheimers Dis. 81, 1663–1671. doi: 10.3233/JAD-210138
Suh, C. H., Shim, W. H., Kim, S. J., Roh, J. H., Lee, J.-H., Kim, M.-J., et al. (2020). Development and Validation of a Deep Learning–Based Automatic Brain Segmentation and Classification Algorithm for Alzheimer Disease Using 3D T1-Weighted Volumetric Images. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 41, 2227–2234. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A6848
Tahami Monfared, A. A., Phan, N. T. N., Pearson, I., Mauskopf, J., Cho, M., Zhang, Q., et al. (2023). A systematic review of clinical practice guidelines for Alzheimer’s Disease and strategies for future advancements. Neurol. Ther. 12, 1257–1284. doi: 10.1007/s40120-023-00504-6
Tavares, T. P., Mitchell, D. G. V., Coleman, K., Shoesmith, C., Bartha, R., Cash, D. M., et al. (2019). Ventricular volume expansion in presymptomatic genetic frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 93, e1699–e1706. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008386
Ten Kate, M., Redolfi, A., Peira, E., Bos, I., Vos, S. J., Vandenberghe, R., et al. (2018). MRI predictors of amyloid pathology: results from the EMIF-AD multimodal biomarker discovery study. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 10:100. doi: 10.1186/s13195-018-0428-1
Tisserand, A., Blanc, F., Mondino, M., Muller, C., Durand, H., Demuynck, C., et al. (2024). Who am I with my Lewy bodies? The insula as a core region of the self-concept networks. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 16:85. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01447-2
Trufanov, A. G., Odinak, M. M., Litvinenko, I. V., Rezvantsev, M. V., and Voronkov, L. V. (2013). Early diagnosis of dementia with the help of MR-morphometry in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Voen. Med. Zh. 334, 29–34.
Valdés Hernández, M. D. C., Chappell, F. M., Muñoz Maniega, S., Dickie, D. A., Royle, N. A., Morris, Z., et al. (2017). Metric to quantify white matter damage on brain magnetic resonance images. Neuroradiology 59, 951–962. doi: 10.1007/s00234-017-1892-1
Van Dyck, C. H., Swanson, C. J., Aisen, P., Bateman, R. J., Chen, C., Gee, M., et al. (2023). Lecanemab in early Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 388, 9–21. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2212948
Vidal, J. P., Danet, L., Péran, P., Pariente, J., Bach Cuadra, M., Zahr, N. M., et al. (2024). Robust thalamic nuclei segmentation from T1-weighted MRI using polynomial intensity transformation. Brain Struct. Funct. 229, 1087–1101. doi: 10.1007/s00429-024-02777-5
Walker, Z., Possin, K. L., Boeve, B. F., and Aarsland, D. (2015). Lewy body dementias. Lancet 386, 1683–1697. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00462-6
Wang, L., Liu, Q., Yue, D., Liu, J., and Fu, Y. (2024). Cerebral amyloid Angiopathy: an undeniable small vessel Disease. J. Stroke 26, 1–12. doi: 10.5853/jos.2023.01942
Wang, J., Wang, X., Xia, M., Liao, X., Evans, A., and He, Y. (2015). GRETNA: a graph theoretical network analysis toolbox for imaging connectomics. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 9:386. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00386
Wang, X., Yu, Y., Zhao, W., Li, Q., Li, X., Li, S., et al. (2018). Altered whole-brain structural covariance of the hippocampal subfields in subcortical vascular mild cognitive impairment and amnestic mild cognitive impairment patients. Front. Neurol. 9:342. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00342
Whitwell, J. L., Weigand, S. D., Gunter, J. L., Boeve, B. F., Rademakers, R., Baker, M., et al. (2011). Trajectories of brain and hippocampal atrophy in FTD with mutations in MAPT or GRN. Neurology 77, 393–398. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e318227047f
Withington, C. G., and Turner, R. S. (2022). Amyloid-related imaging abnormalities with anti-amyloid antibodies for the treatment of dementia due to Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 13:862369. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.862369
Wittens, M. M. J., Sima, D. M., Houbrechts, R., Ribbens, A., Niemantsverdriet, E., Fransen, E., et al. (2021). Diagnostic performance of automated MRI Volumetry by icobrain dm for Alzheimer’s Disease in a clinical setting: a REMEMBER study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 83, 623–639. doi: 10.3233/JAD-210450
Woolrich, M. W., Jbabdi, S., Patenaude, B., Chappell, M., Makni, S., Behrens, T., et al. (2009). Bayesian analysis of neuroimaging data in FSL. NeuroImage 45, S173–S186. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.10.055
Worker, A., Blain, C., Jarosz, J., Chaudhuri, K. R., Barker, G. J., Williams, S. C. R., et al. (2014). Cortical thickness, surface area and volume measures in Parkinson’s Disease, multiple system atrophy and progressive Supranuclear palsy. PLoS One 9:e114167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114167
World Health Organization (2017). Global action plan on the public health response to dementia 2017–2025. Geneva: World Health Organization.
Wuestefeld, A., Pichet Binette, A., Berron, D., Spotorno, N., Van Westen, D., Stomrud, E., et al. (2023). Age-related and amyloid-beta-independent tau deposition and its downstream effects. Brain 146, 3192–3205. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad135
Xiao, Y., Hu, Y., and Huang, K.The Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (2023). Atrophy of hippocampal subfields relates to memory decline during the pathological progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 15:1287122. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1287122
Xie, L., Shinohara, R. T., Ittyerah, R., Kuijf, H. J., Pluta, J. B., Blom, K., et al. (2018). Automated multi-atlas segmentation of hippocampal and Extrahippocampal subregions in Alzheimer’s Disease at 3T and 7T: what atlas composition works best? J. Alzheimers Dis. 63, 217–225. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170932
Yang, J., Liang, L., Wei, Y., Liu, Y., Li, X., Huang, J., et al. (2023). Altered cortical and subcortical morphometric features and asymmetries in the subjective cognitive decline and mild cognitive impairment. Front. Neurol. 14:1297028. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1297028
Yang, K., Yang, Q., Niu, Y., Fan, F., Chen, S., Luo, X., et al. (2020). Cortical thickness in alcohol dependent patients with apathy. Front. Psych. 11:364. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00364
Yim, Y., Lee, J. Y., Oh, S. W., Chung, M. S., Park, J. E., Moon, Y., et al. (2021). Comparison of automated brain volume measures by NeuroQuant vs. Freesurfer in patients with mild cognitive impairment: effect of slice thickness. Yonsei. Med. J. 62, 255–261. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2021.62.3.255
Zahid, U., Hedges, E. P., Dimitrov, M., Murray, R. M., Barker, G. J., and Kempton, M. J. (2022). Impact of physiological factors on longitudinal structural MRI measures of the brain. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 321:111446. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2022.111446
Zaretskaya, N., Fischl, B., Reuter, M., Renvall, V., and Polimeni, J. R. (2018). Advantages of cortical surface reconstruction using submillimeter 7 T MEMPRAGE. NeuroImage 165, 11–26. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.09.060
Zaudig, M. (1992). A new systematic method of measurement and diagnosis of “mild cognitive impairment” and dementia according to ICD-10 and DSM-III-R criteria. Int. Psychogeriatr. 4, 203–219. doi: 10.1017/S1041610292001273
Zhang, P., Gao, C., Huang, Y., Chen, X., Pan, Z., Wang, L., et al. (2024). Artificial intelligence in liver imaging: methods and applications. Hepatol. Int. 18, 422–434. doi: 10.1007/s12072-023-10630-w
Zhang, Y., Tatewaki, Y., Nakase, T., Liu, Y., Tomita, N., Thyreau, B., et al. (2023). Impact of hs-CRP concentration on brain structure alterations and cognitive trajectory in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 15:1227325. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1227325
Keywords: dementia, FreeSurfer, segmentation, volumetry, review
Citation: Khadhraoui E, Nickl-Jockschat T, Henkes H, Behme D and Müller SJ (2024) Automated brain segmentation and volumetry in dementia diagnostics: a narrative review with emphasis on FreeSurfer. Front. Aging Neurosci. 16:1459652. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1459652
Edited by:
Thomas Van Groen, University of Alabama at Birmingham, United StatesReviewed by:
Minhong Neenah Huang, Mayo Clinic, United StatesFederico Paolini Paoletti, University of Perugia, Italy
Copyright © 2024 Khadhraoui, Nickl-Jockschat, Henkes, Behme and Müller. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Eya Khadhraoui, ZXlhLmtoYWRocmFvdWlAbWVkLm92Z3UuZGU=
 Eya Khadhraoui
Eya Khadhraoui Thomas Nickl-Jockschat
Thomas Nickl-Jockschat Hans Henkes
Hans Henkes Daniel Behme
Daniel Behme Sebastian Johannes Müller
Sebastian Johannes Müller