- 1Department of Histology and Embryology, Medical School of Nantong University, Nantong, China
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Nantong, China
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a debilitating progressively neurodegenerative disease. The best-characterized hallmark of AD, which is marked by behavioral alterations and cognitive deficits, is the aggregation of deposition of amyloid-beta (Aβ) and hyper-phosphorylated microtubule-associated protein Tau. Despite decades of experimental progress, the control rate of AD remains poor, and more precise deciphering is needed for potential therapeutic targets and signaling pathways involved. In recent years, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and Akt have been recognized for their role in the neuroprotective effect of various agents, and glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3), a downstream enzyme, is also crucial in the tau phosphorylation and Aβ deposition. An overview of the function of PI3K/Akt pathway in the pathophysiology of AD is provided in this review, along with a discussion of recent developments in the pharmaceuticals and herbal remedies that target the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. In conclusion, despite the challenges and hurdles, cumulative findings of novel targets and agents in the PI3K/Akt signaling axis are expected to hold promise for advancing AD prevention and treatment.
1 Introduction
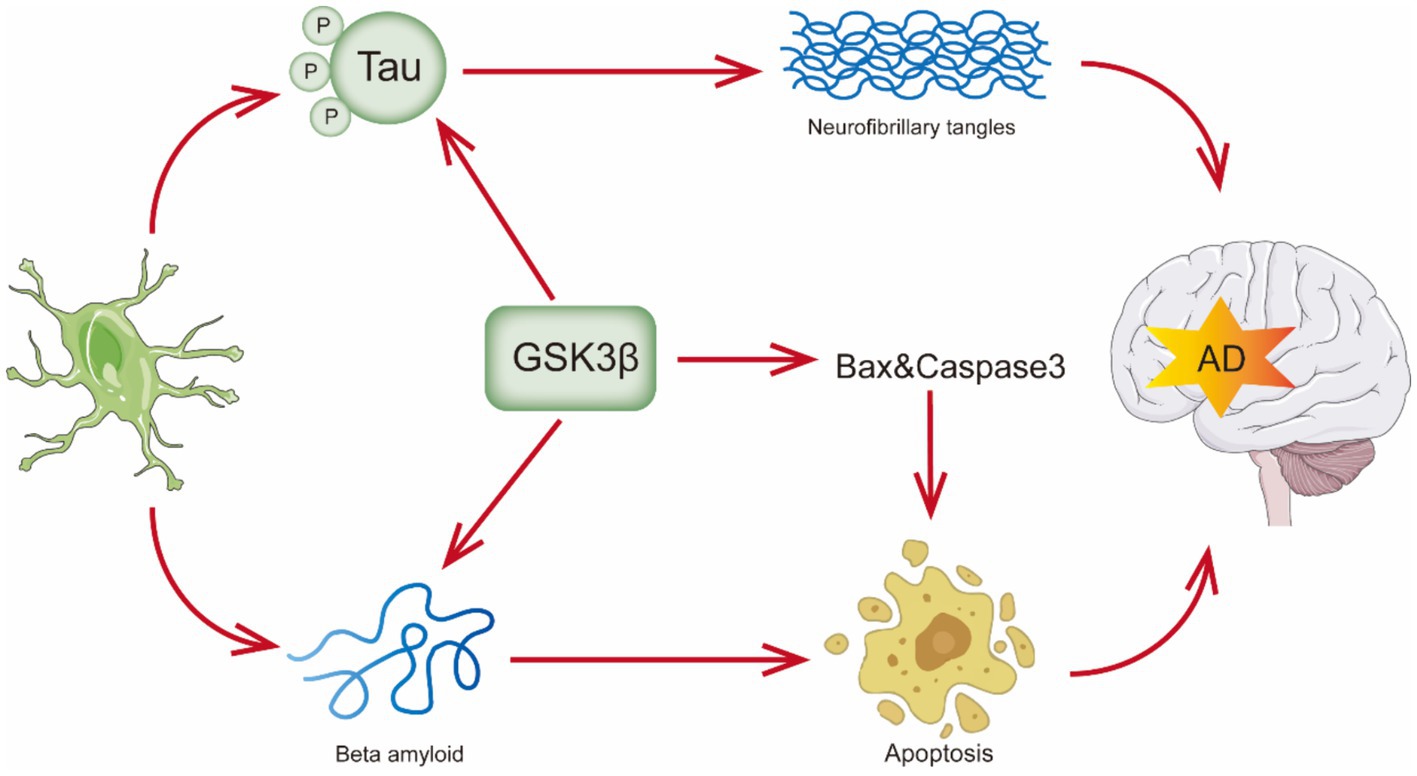
Progressive cognitive deficiencies, functional impairment, and behavioral abnormalities characterize AD. As it is well recognized, there are two pathological hallmarks of AD. The first is the buildup of senile plaques, which are composed of fibrils of amyloid-β peptide (Aβ), such as Aβ40 and Aβ42 in the central nervous system. Aβ plaque formation initiates with the aberrant cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) by β-secretase and γ-secretase, leading to the extracellular accumulation of Aβ, particularly the Aβ42 form. These peptides tend to aggregate and form plaques (Pichet Binette et al., 2024). The other pathological hallmark is the occurrence of intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), produced by hyperphosphorylation of Tau protein’s twisted filaments (also known as τ protein) (Kumar and Bansal, 2022; Shefa et al., 2019). (Figure 1) PHFs, or paired helical filaments, are composed of hyperphosphorylated tau protein, which is central to the formation of neurofibrillary tangles in AD (Meng et al., 2022). The tau protein found in PHF is always hyperphosphorylated and truncated, which contains all six tau isoforms, and recent studies have shed further light on the role of tau protein hyperphosphorylation in AD pathology, emphasizing its connection to cognitive deterioration and neurodegeneration (Li et al., 2020; Basheer et al., 2023). In addition to harming the quality of life for the elderly, AD causes a great deal of financial and psychological hardship for families, society, and even the global economy, with a projected $345 billion in costs in 2023 (Alzheimer’s and Dementia, 2023). By 2050, AD is projected to affect 152 million people worldwide (Cummings et al., 2019). Therefore, in the 21st century, AD is swiftly rising to the top of the list of diseases in terms of expense, mortality, and burden.
Over the past decades, researchers have focused substantial attention on the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, which is a key intracellular signaling pathway implicated in a range of essential cellular activities, and its physiological functions have progressively come to light. In neurons and various other cell types, PI3K and Akt are involved in key processes, particularly crucial within the central nervous system. Specifically, as upstream modulators such as insulin, growth factors, and cytokines activate the pathway, activated PI3K promotes intracellular production of second messengers PI(3,4)P2 and PIP3, which cause intracellular phosphatidylinositol-dependent kinase-l (PDK1) and inactive Akt to move to the inner surface of the plasma membrane (Jiang et al., 2022). PDK1 can phosphorylate and activate Akt, which subsequently inhibits its downstream molecule GSK3 (Figure 2). A large body of evidence supports the multiple roles of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in regulating oxidative stress (Jiao et al., 2022), autophagy (Zhang et al., 2023), inflammatory response (Meng et al., 2021), cell growth (Huang et al., 2021), cell differentiation (Liu F. et al., 2022), and cell cycle (Yuan et al., 2020). A wealth of evidence has confirmed the substantial involvement of all essential components of the PI3K/Akt pathway in the pathogenesis of AD. This review primarily focuses on recent studies regarding the functions of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in AD, as well as the role of pharmaceuticals and herbal remedies that influence this pathway. The figures in this manuscript were created using Adobe Illustrator 2020 (Adobe Systems Incorporated, San Jose, CA, United States).
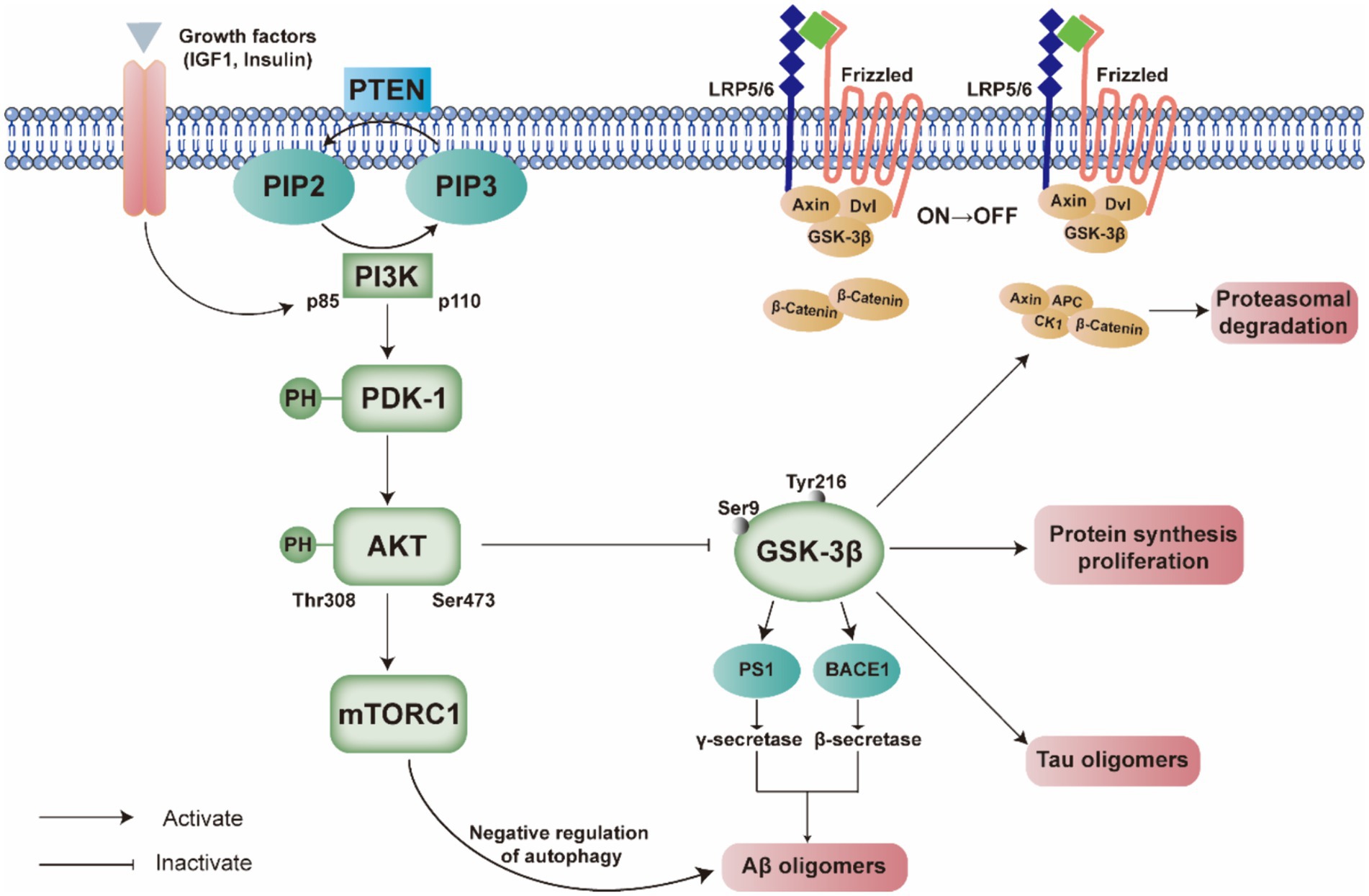
Figure 2. Comprehensive illustration of the interplay between the PI3K/PDK/Akt signaling pathway and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. This figure delineates the activation and regulation of key components within the pathway, such as PI3K p85 and p110 subunits, PDK-1, and AKT, and their downstream effects on molecules such as GSK-3β, mTORC1, and the Wnt signaling components. The legend emphasizes the reciprocal modulation between these signaling molecules and the formation of Aβ and Tau oligomers, which are hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. The pathway’s dysregulation is implicated in the disease’s progression, affecting protein synthesis, proliferation, and autophagy. The figure also highlights the negative feedback mechanisms involving PTEN and the serine/threonine phosphorylation of AKT.
2 The role of PI3K signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of AD
2.1 Different stages of AD and the selection of mouse model
In AD, the functions of PI3K and GSK3 vary by stage, underscoring the importance of stage-specific mouse models for research. Here, we describe the progression of AD through its different stages, along with the corresponding mouse models that reflect these stages (Figure 3). During the preclinical stage of AD, an intervention targeting the PI3K/Akt pathway and GSK3 early in the disease may help prevent or slow the advance of the disease. This strategy could be beneficial in the early and mild cognitive impairment stages when the pathological hallmarks of AD are initially emerging (Razani et al., 2021). During this stage, selecting mouse models that can simulate the initial deposition of Aβ and early phosphorylation of tau protein is crucial. For instance, transgenic mice carrying human APP and PS1 mutations typically exhibit Aβ deposition at an early age, reflecting the early pathological changes in AD (Yokoyama et al., 2022).
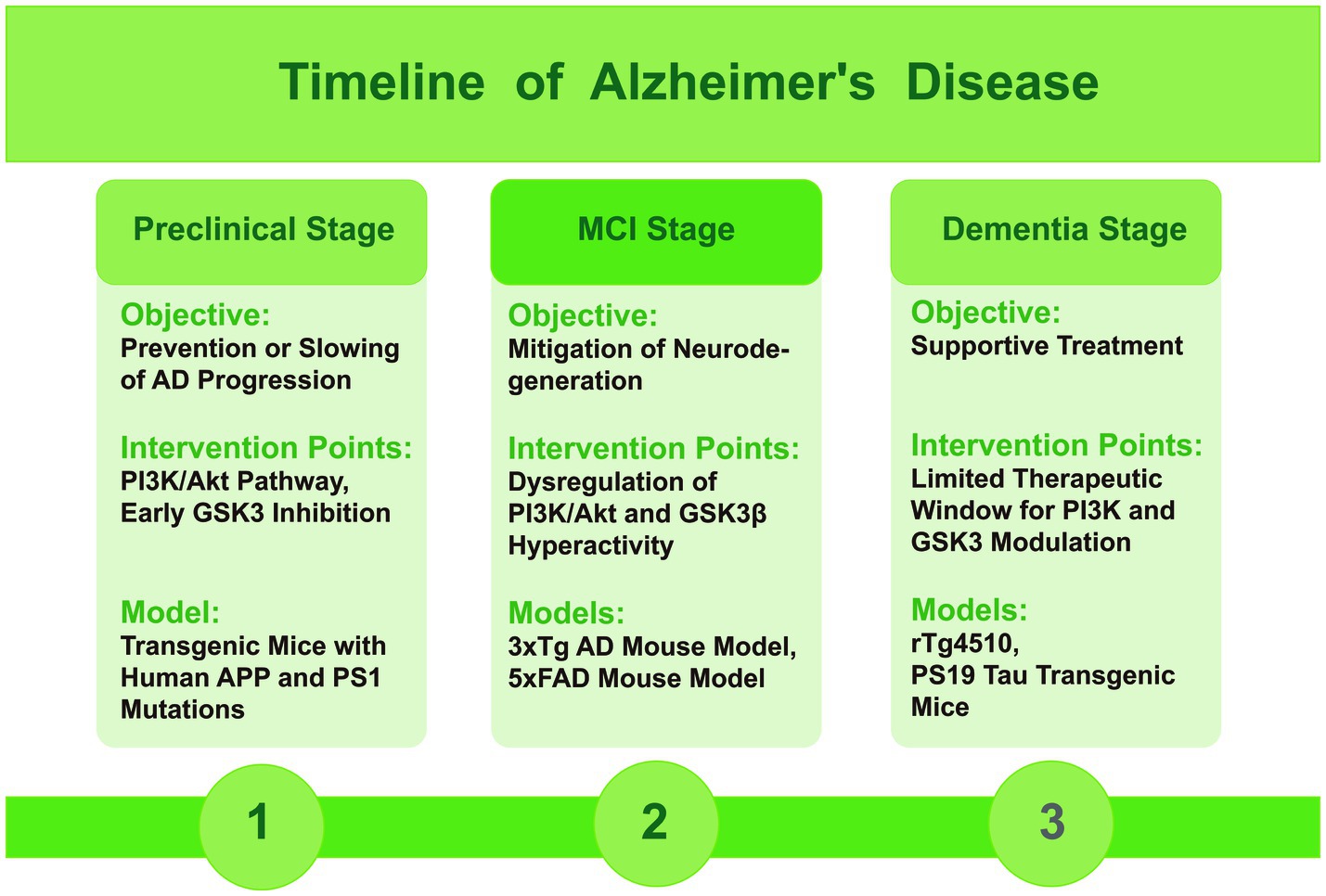
Figure 3. Timeline figure of Alzheimer’s disease, indicating the role of PI3K and GSK3 and mice models in different stages.
In the mild cognitive impairment (MCI) stage, as the disease progresses, the dysregulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling axis and the consequent hyperactivity of GSK3β contribute to the formation of toxic tau species and the accumulation of Aβ. Modulating these pathways at this stage may help to mitigate the ongoing neurodegeneration. During this stage, it is beneficial to choose mouse models that display pronounced Aβ plaques, NFTs, and cognitive decline. The triple-transgenic (3xTg) and 5xFAD mouse models are typical for this stage, showing a range of AD features such as plaque formation and abnormal tau protein (Götz et al., 2018).
In the dementia stage, the therapeutic window for modulating PI3K and GSK3 may be more limited, with treatment primarily focused on supportive care. While some studies suggest potential benefits of targeting these pathways, the overall effectiveness may be reduced due to the advanced neuronal damage and extensive plaque and tangle formation (Lauretti et al., 2020). During this stage, the selection should focus on mouse models that exhibit severe neurodegeneration and significant loss of cognitive function. Models such as the rTg4510 and PS19 tau transgenic mice, which express mutant tau protein, effectively simulate the formation of NFTs and associated neurodegeneration, aligning with the late-stage characteristics of AD (Jankowsky and Zheng, 2017).
2.2 PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and tau
As a microtubule-associated protein (MAP), Tau protein is enriched in axons and acts as a neurite microtubule stabilizer, regulating tubulin polymerization (Gabbouj et al., 2019). The two most common pathological indicators of AD related to tau pathology are hyperphosphorylated Tau and NFTs. AD etiology is significantly influenced by tau hyperphosphorylation, mainly at serine (Ser) or threonine (Thr), so molecules that reduce phospho-tau accumulation may represent an effective treatment strategy (Bloom, 2014). The degree of tau phosphorylation significantly influences its function and affinity for microtubules. Tau has over 85 different phospho-sites and its dephosphorylated form promotes microtubule assembly. However, phosphorylation reduces tau’s affinity for tubulin, leading to its detachment from the cytoskeleton and accumulation in the cytoplasm. This disruption of microtubules and loss of neuronal integrity ultimately result in NFT formation. Among more than three amino acid residues involved in abnormal tau phosphorylation, the phosphorylation of Thr-231 and Ser-396 is particularly responsible for enhanced NFT production (Rajput et al., 2020). Recent reports have shown that Aβ does not function as the only upstream molecule of tau, and Aβ removal alone is insufficient to reduce pathological tau deposition, suggesting that additional factors beyond amyloid contribute to downstream tau accumulation. In a word, tau pathology may occur independently of Aβ deposition, and studies targeting Aβ and tau should be performed simultaneously (Avgerinos et al., 2021; Oddo et al., 2003).
The extent of tau phosphorylation at specific sites is predominantly regulated by certain protein kinases and phosphatases. Notably, GSK3 and cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) have been identified as key protein kinases involved in tau hyperphosphorylation. Extensive data demonstrates that GSK3 plays a significant role in AD pathogenesis, impacting tau hyperphosphorylation, memory loss, intracellular Aβ accumulation, and inflammatory responses (Drewes et al., 1995; Wadhwa et al., 2020). The activation of GSK3 is not only intimately connected to the characteristic clinical alterations of both familial and sporadic AD, but it is also directly linked to cognitive impairment in the absence of AD pathology (King et al., 2014).
As the key kinase for tau protein hyperphosphorylation, GSK3 induces cytoskeletal instability, promotes tau aggregation, and leads to neuronal death. The subunits α and β are two isoforms of GSK3 in mammals, and each isoform, with ubiquitous distribution among cell types and tissues, is encoded by a separate gene and acts on different substrates (Soutar et al., 2010). It has been found that the catalytic domains of these two isoforms share similar biochemical characteristics and exhibit 98% amino acid sequence identity (Wadhwa et al., 2020). As a constitutively activated kinase, GSK3β was the first tau-related serine/threonine kinase to be identified, highly expressed in neuronal tissue, especially in the hippocampus, with its expression level increasing with age (Lee et al., 2006). Furthermore, GSK3 is regulated primarily by the inhibition of serine phosphorylation, a process mediated by different Ser/Thr kinases. In particular, phosphorylation at Ser-21 inhibits GSK3α, whereas phosphorylation at Ser-9 (Stambolic and Woodgett, 1994) inhibits GSK3β and phosphorylation at Tyr216 activates it (Jope et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2018). For GSK3β, there are two splice variants (Lin J. et al., 2020). At many AD-related sites, including Thr-181, Ser-199, Ser-202, Thr-205, Thr-212, Ser-214, Thr-217, Thr-231, Ser-396, and Ser-404, tau is phosphorylated by the active form of GSK3β. In AD brains, GSK3β also co-localizes with NFT (Liu et al., 2003; Tan et al., 2018).
Stimulation of the Wnt or insulin signaling pathways, which are negatively regulated by GSK3, has been observed to inhibit tau phosphorylation (Hoeflich et al., 2000). Upon stimulation by insulin, downstream target protein PI3K activity is elevated, subsequently leading to the activation of PDK1. AKT is activated when PDK1 phosphorylates PIP2 to PIP3. GSK3 is subsequently inhibited through the phosphorylation of serine 21 for GSK3α or serine 9 for GSK3β (Salkovic-Petrisic et al., 2006).
The Wnt signaling transduction cascade is initiated by Wnt, the evolutionarily conserved small glycoproteins. A canonical Wnt pathway can also regulate GSK3 activity. Inhibition of GSK3 activity by LiCl, the most prescribed medication for AD, is believed to act by emulating Wnt signaling (Ozbek et al., 2007). Deficits in canonical Wnt signaling have been linked to early stages of AD, including synapse loss and dysfunction (Marzo et al., 2016). In addition, defective Wnt signaling can also indirectly affect synapses, a process involving β-catenin activation (Folke et al., 2019) and microglial interference (Zheng et al., 2017).
The 19 isoforms of the Wnt protein family, a group of secreted glycoproteins, bind to lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) co-receptors and Frizzled receptors. It is well recognized that Wnt receptor activation results in signal transduction through at least three pathways: a canonical Wnt/β-catenin cascade, a non-canonical planar cell polarity pathway, and the Wnt/Ca2+ pathway (Palomer et al., 2019). The canonical Wnt pathway links expression of Wnt target genes, such as c-myc, cyclin D1, and Axin2 to cytosolic β-catenin, GSK3β, and CK1 (Nusse and Clevers, 2017). In the absence of Wnt signaling, the destruction complex consisting of GSK3α, GSK3β, casein kinase-1 (CK1), adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), and Axin breaks down β-catenin. Throughout the process of degradation, the amino-terminal region of β-catenin is sequentially phosphorylated by CK1 and GSK3, which enables ubiquitin E3 ligase to recognize it through β-transducing repeat-containing proteins (β-TrCP). It contributes to β-catenin ubiquitination and proteasomal breakdown (Tejeda-Muñoz and De Robertis, 2022). However, in the presence of Wnt signaling, the activity of GSK3β is inhibited, and degradation complex activity is suppressed. Therefore, the phosphorylation of β-catenin is also inhibited, thus protecting itself from degradation. Meanwhile, LRP5/6 is recruited to form a complex with the Wnt-bound Frizzled receptor. Subsequently, the Wnt-Fz-LRP6 complex induces the phosphorylation and activation of LRP6. Additionally, the recruitment of the scaffolding protein Disheveled (Dvl) and Axin to the membrane of the LRP signalosome, which contains several GSK3 phosphorylation sites, further reduces GSK3 activity. Dephosphorylated β-catenin increases the transcription of target proteins downstream that are controlled by TCF/LEF when it builds up in the cytoplasm and proceeds to the nucleus (Nusse and Clevers, 2017).
Tau tangles are associated with Wnt/β-catenin signaling, according to recent research. Decreased Wnt signaling generates tau hyperphosphorylation through increased GSK3β activity (Salcedo-Tello et al., 2014), reduction in β-catenin levels, β-catenin-dependent gene expression (Riise et al., 2015), loss of synapses, and memory impairment. Moreover, tau is dephosphorylated by protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) at several sites with varying degrees of efficiency. The activity of PP2A is markedly reduced in AD brains (Liu et al., 2005), and there was an association between PP2A activity and Wnt signaling in previous studies. In aged rats, PP2A activity decreases with suppression of Wnt signaling, suggesting that tau hyperphosphorylation is caused by the interaction and imbalance between GSK3β and PP2A activity (Salcedo-Tello et al., 2014). Our earlier studies have unambiguously demonstrated how GSK3β and PP2A cooperate to control tau phosphorylation. PP2A methylation is required to promote the dephosphorylation of tau and is modulated by GSK3β through leucine carboxyl methyltransferase 1 and protein phosphatase methylesterase-1. In turn, phosphorylation of GSK3β at Ser-9 is controlled by PP2A. Notably, PP2A and GSK3β dephosphorylate tau with a different preferred order of sites. As previous studies have indicated, the Ser-262/356 site, which is necessary for tau pathology, is PP2A but not the GSK3β site (Alonso et al., 2010). Targeting GSK3β may downregulate PP2A, which would enhance tau phosphorylation at PP2A-sensitive sites. As a result, PP2A is more recommended as a therapeutic target than GSK3β (Wang et al., 2015).
There are two recognized types of AD: the late-onset sporadic form (SAD) and the early-onset familial form (FAD). Mutations in the genes amyloid precursor protein (APP), presenilin-1 (PSEN1), or PSEN2 generate the dominantly inherited type of AD (FAD) (Hardy, 2017). Among them, both GSK3β and tau can co-immunoprecipitate with presenilin. The non-mutated presenilin-1 (PS1) gene can activate the PI3K/Akt signal transduction pathway, which leads to the increase of GSK3 phosphorylation level and inhibits its activity, resulting in the decrease in tau phosphorylation level catalyzed by GSK3, ultimately protecting cells and inhibiting apoptosis (Baki et al., 2004). While the mutant PS1, which is associated with FAD, can bind tightly to GSK3β, which leads to an improved ability of GSK3β to catalyze the phosphorylation of tau, resulting in tau hyperphosphorylation (Liu et al., 2004). Reports state that the non-mutated PS1 that initiates the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is greatly inhibited by the FAD-related mutant PS1. This, in turn, increases the activity of GSK3, which renders tau abnormally hyperphosphorylated (Haase et al., 2004). This is a potential pathogenesis whereby FAD mutations accelerate disease progression through secondary enhanced GSK3 activity. In human neurons, in addition to affecting tau phosphorylation through effects on GSK3, PS1 mutations also lead to tau accumulation through deregulation of the mammalian target of rapamycin 1 (mTORC1) signaling (Chong et al., 2022).
Several studies indicate that the GSK3β and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways are important targets for the treatment and prevention of AD, as well as for the protection against tauopathy. Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) is a transmembrane immunoglobulin superfamily receptor found exclusively on microglia in the central nervous system. Recent studies indicate that TREM2 improves the spatial cognitive capacity of APP/PS1 mice by preventing tau hyperphosphorylation at Ser-199, Ser-396, and Thr-205 and by suppressing neuronal death by activating PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signaling (Peng et al., 2023).
Remarkably, sex hormones are fundamental to regulating the phosphorylation of tau, and the process is connected to both the GSK3β and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. It is widely recognized that in males, decreased testosterone level increases the risk of AD (Pike, 2017), while in females, decreased plasma testosterone correlates with significantly increased cerebrospinal fluid levels of phosphorylated tau (Sundermann et al., 2020). The function of testosterone in preventing tau hyperphosphorylation has been documented in recent animal studies. In an experiment conducted on 6- and 60-day-old male mice, testosterone was discovered to inhibit the interaction between tau and GSK3β in both cultured hippocampal neurons and neonatal mice, thereby attenuating the tau phosphorylation and cognitive impairment caused by sevoflurane (Yang et al., 2021). In male 3xTg-AD mice, testosterone and its active metabolite, dihydrotestosterone (DHT), significantly decreased phosphorylated tau while increasing the phosphorylation of Akt and GSK3β. This pathway is mediated through the androgen receptor (AR) (Lutshumba et al., 2023). However, while testosterone effectively reduces tau phosphorylation in vitro, clinical experimental results remain inconclusive. Clinical studies have shown that lower testosterone levels are linked to greater p-Tau levels in APOE4 carriers. The discrepancy in p-Tau levels between men and women was removed when testosterone was taken into consideration (Sundermann et al., 2020). However, testosterone therapy was reported to fail to improve cognitive function in elderly men (Snyder et al., 2018), which indicates that androgen is only one of the effective factors for neuroprotection, and therapies using testosterone to treat AD remain to be explored.
Estrogen has neuroprotective qualities in an array of in vitro and in vivo models, which are particularly significant in AD pathophysiology, apart from its essential role played in the reproductive system (Uddin et al., 2020). Previous studies have shown that 17β-Estradiol (E2) inhibited tau hyperphosphorylation by inhibiting the activation of the JNK/c-Jun/Dkk 1 pathway (Zhang et al., 2008). While in C57Bl6/J mice, GSK3β phosphorylation at the serine-9 site is inactivated when the 17β-estradiol pathway is activated, which, in turn, reduces Aβ accumulation as well as hyperphosphorylated tau (Goodenough et al., 2005). Therefore, therapies targeted at estrogen receptors are expected to offer a good clinical application. Belonging to the nuclear receptor superfamily, the estrogen receptor (ER) is a steroid hormone receptor that mediates the biological actions of estrogens and phytoestrogens. Some selective Erβ receptor agonists, such as gypenoside XVII and genistein, can improve the clinical symptoms of AD through ER-dependent activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway, inducing diminished oxidative stress and decreasing tau phosphorylation (Bagheri et al., 2011; Meng et al., 2014). Furthermore, it has been discovered that p-Tau (Thr-231, Ser-396)/Tau levels were much lower in PC12 cells treated with a combination of Aβ25-35 and naringin than in cells treated with Aβ25-35 alone (Qiu et al., 2023). These phytoestrogens, or estrogen analogs, produce potent estrogen-like effects and can avoid serious side effects caused by long-term estrogen use, such as breast cancer, uterine cancer, and thrombosis (Rozenberg et al., 2021; Zhang G. Q. et al., 2021; Abou-Ismail et al., 2020).
2.3 PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and Aβ
2.3.1 Modulation of Aβ by GSK3
The creation and buildup of extracellular Aβ, derived from the proteolytic processing of APP, serves as the main feature of AD. According to the timing of onset, AD is commonly classified into two basic types: late-onset AD (LOAD) and early-onset AD (EOAD). The former is usually diagnosed before the age of 65 years while the latter develops after the age of 65 years. EOAD is predominantly caused by the overproduction of three rare mutation genes: APP, PSEN1, and PSEN2 and is inherited by a dominant autosomal pattern, while the genetics of LOAD are much more complicated (Hardy, 2017). There are three major APP isoforms found in humans due to alternative splicing: APP695, APP751, and APP770, among which APP695 is found exclusively in neurons. There are two pathways to process APP, namely, amyloidogenic and non-amyloidogenic pathways. As the β-secretase enzyme in the former pathway, β-Site APP cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) cleaves extracellular domain of the transmembrane APP and releases a soluble APP fragment β. Then, γ-secretase cleavage occurs, and β- and γ-secretases cleave one another sequentially to generate full-length Aβ aggregates (mostly Aβ1-40/42), which are expected to develop into Aβ plaques. Nicastrin (NCT), anterior pharynx-deficient 1 (APH1), presenilin enhancer 2 (PEN-2), and presenilin (PSEN) make up the tetrameric protein complex known as γ-secretase (Escamilla-Ayala et al., 2020). In the latter pathway, APP is broken down by the α-secretase complex, which is comprised of ADAM-10 and-17 together with the γ-secretase, resulting in a truncated Aβ17-40/42 (P3) peptide, or broken down by β-secretase, resulting in a truncated Aβ1-16 peptide (Miranda et al., 2021; Khezri et al., 2023; Chow et al., 2010). Moreover, the most neurotoxic subgroups of Aβ42 oligomers, specifically the soluble ADDLs (Aβ-derived diffusible ligands), are known for their capacity to permeabilize cellular membranes, leading to cell dysfunction and death, which, in turn, contributes to the cognitive impairment associated with AD (Wen et al., 2018).
PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway has regulatory effects on Aβ. Chiang et al. illustrated that decreased PI3K activity can reverse Aβ42-mediated learning impairment in transgenic fly lines (Chiang et al., 2010). Investigators have also shown that overexpression of Akt significantly attenuated Aβ1-42-induced apoptosis, and its protective mechanisms include the activation of caspase-3 and JNK, downregulation of Bad and Bax, and upregulation of Bcl-xL and Bcl-w (Yin et al., 2011). In addition, Aβ1-42 was reported to increase Akt phosphorylation depending on the alpha (7) nicotinic receptor and NMDA receptor (Abbott et al., 2008). In drosophila, reduced Akt activity can mitigate Aβ-induced damage by modulating Notch activity, given that Notch is an intrinsic substrate of γ-secretase (Chen et al., 2019).
Previous studies suggested that the APP and PS1 are substrates of GSK3β, and during Aβ production, GSK3β plays a role by affecting β-secretase (Lauretti et al., 2020). BACE1 gene expression is activated by GSK3β, leading to increased β-secretase processing of APP and Aβ generation. Furthermore, GSK3β suppresses the γ-secretase complex and reduces α-secretase via PKC and ADAMs, which function as GSK3β substrates and ultimately affect Aβ synthesis (Saha et al., 2021; Pal et al., 2021). In 5 × FAD mice co-expressing mutant APP and presenilin-1, increased expression of GSK3 isoforms impedes Aβ clearance, increasing Aβ plaque formation and memory impairments. While L803-mts, the substrate-competitive GSK3 inhibitor restores lysosomal acidification, allowing Aβ to be cleared and mTOR to be reactivated (Avrahami et al., 2013). On the flip side, Aβ aggregation can induce GSK3β activity through Aβ-mediated neuroinflammation and oxidative stress; it can also increase GSK3β activity by preventing PI3K activation and subsequently preventing Akt activation (Townsend et al., 2007). In addition, specific Aβ antibodies have been shown to reduce GSK3β activity, suggesting an interaction between GSK3β and Aβ-peptide (Ma et al., 2006). However, considering the intricate mechanisms involved in Aβ formation and clearance, inhibiting GSK3β alone has limited effects on reducing the Aβ level. Additionally, as GSK3 activation results in tau hyperphosphorylation and neurofibrillary lesions, we propose that GSK3 could serve as a mediator in the interplay between the pathophysiology of NFT and amyloid plaques.
2.3.2 Modulation of Aβ by oxidative stress
Oxidative stress is well recognized as a contributor to the aging process and the development of a variety of neurological illnesses. It interacts with Aβ accumulation, resulting in a defect of mitochondrial respiratory complexes and eNOS deficiency, and is regulated by the PI3K/Akt pathway (Magrané et al., 2005). Metal ions in Aβ are crucial during oxidative stress. The accumulation of metal ions is among the main contributors to oxidative stress, including zinc, iron, and copper in Aβ, which can directly bind Aβ and encourage its aggregation. This is one of the characteristics of AD (Cheignon et al., 2018). Disruption of Fe and Cu homeostasis can lead to elevated levels of free or loosely bound ions, which may be reduced to Cu (I) or Fe(II) by biological reductants such as ascorbic acid or intracellular glutathione. Following a reaction with hydrogen peroxide or dioxygen, these compounds produce superoxide and hydroxyl radicals, respectively (Halliwell, 2006; Faller and Hureau, 2012).
Mitochondrial damage is an important pathway causing oxidative stress, leading to ROS surges including superoxide radical anion, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radical, which further increase mitochondrial respiratory chain damage. This process occurs early in AD, predating AD clinical symptoms and Aβ pathology (Tönnies and Trushina, 2017). Notably, the PI3K pathway affects mitochondrial injury through multiple pathways. When p-Akt (phosphorylated Akt) expression is significantly decreased, insulin fails to induce expression of GLUTs (glucose transporter) and promote glucose uptake, thereby disrupting glucose metabolism and consequently impairing mitochondrial aerobic respiration, which, in turn, augments ROS production. Furthermore, mitochondrial function affects Aβ processing. Studies have shown that oxidative stress caused by hydrogen peroxide raises the amount of Aβ deposited in brain arteries through the amyloidogenic pathway, potentially associating with the phosphorylation of p42/44 MAPK (Muche et al., 2017). As a result, Aβ oligomers that build up in the inner membrane or matrix reduce the respiratory chain complexes III and IV’s enzymatic activity (Caruso et al., 2019). Enzymes I, IV, and V of the mitochondrial complex exhibit increased activity when Aβ is injected into lateral ventricles using a bilateral intracerebroventricular route, as demonstrated by Garabadu and Verma (2019). However, this impact is considerably decreased by Exendin-4 through a PI3K/Akt-mediated mechanism.
Mitochondrial dysfunction not only causes increased ROS but also increases reactive nitrogen species (RNS), including nitric oxide (NO), and peroxynitrite (ONOO-) (Singh and Devasahayam, 2020). Previous research has indicated that eNOS(−/−) mice exhibit elevated levels of BACE1 activity and Aβ40 plaques compared to late middle-aged wild-type mice (Austin et al., 2013). Whereas recent research showed that compared with complete eNOS deficient (eNOS−/−) mice, APP/PS1/eNOS+/− mice showed more severe spatial working memory deficits. In fact, partial eNOS impairment contributes to an even higher rise in Aβ plaque in the brain by upregulating BACE1, downregulating insulin-degrading enzymes, and increasing immunoreactivity and microglial expression (Austin and Katusic, 2020; Linjuan et al., 2024).
Given that ENOS is downstream in the PI3K-Akt pathway, diseases stemming from ENOS damage can benefit from targeting this signaling system therapeutically. According to reports, exogenous hydrogen sulfide can activate the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway, protecting endothelial cells from damage caused by excessive hyperglycemia (Lin F. et al., 2020), and sulforaphane regulates eNOS activation via PI3K/Akt signaling in human endothelial cell. Furthermore, dietary supplements like as L-arginine and L-citrulline have been shown to be effective in enhancing nitric oxide production, suggesting that food therapy is a viable and essential alternative that warrants consideration in the control and avoidance of AD (Kiani et al., 2022).
2.3.3 Modulation of Aβ by autophagy
The preservation of neuronal morphology and homeostasis largely relies on autophagy, a prosurvival mechanism. Additionally, pathways involved in the degradation and clearance of abnormal protein products in cells also include the ubiquitin–proteasome system (UPS), microglial activation, and β-amyloid1–42-degrading enzyme releasing (Wang and Le, 2019). Through the equilibrium of these pathways, neuronal cells remove abnormal protein aggregates and maintain protein homeostasis (Yang and Zhang, 2023). The autophagy pathway involves proteins or organelles being transported to lysosomes for degradation via autophagosomes to form autolysosomes. An autophagosome develops in a distant axon of a neuron before moving retrogradely to merge with a lysosome in the soma. However, due to the anatomical characteristics of neurons, which feature highly polarized axons and dendritic compartments, the length of axons is much longer than that of the soma, and lysosomes are rarely distributed in distal axons. As a result, axonal autophagosomes must be transported over a long distance, which makes the autophagic function of neurons easily impaired, thus involved in various proteinopathies (Cason et al., 2022), including AD (Zhang Z. et al., 2021), Huntington’s disease (Kim et al., 2021), and Parkinson’s disease (Themistokleous et al., 2023). Premature autophagic vacuoles (AVs), which accumulate in dystrophic neuritis, have been seen in postmortem AD brains of animal models and patients. A substantial body of research has indicated that autophagy dysregulation can be seen in AD brains, particularly early in the pathogenesis (Li et al., 2017). Moreover, several investigations have demonstrated that the dysfunction of the autophagy–lysosome pathway may occur before the formation of NFTs or Aβ plaques (Ntsapi et al., 2018).
There are at least three well-recognized types of autophagy, known as chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), microautophagy, and macroautophagy, among which macroautophagy is considered as the major type and most associated with AD. As macroautophagy is activated, the unc-51-like kinase (ULK) and vacuolar protein-sorting 34 (VPS34) complexes initiate autophagosome formation, and the kinase activity of ULK promotes local production of PI3P (Zhang Z. et al., 2021). Meanwhile, the core subunit of the VPS34 complex, Beclin-1, decreases as AD progresses, and PI3P synthesis, catalyzed by the VPS34 complex, is downregulated in a similar way in AD brains (Yuan et al., 2022). In particular, abnormalities in autophagy lead to elevated γ-secretase activity, exacerbating Aβ buildup in the brain and causing amyloid processing of APP.
The primary downstream target of PI3K-Akt signaling, mTOR, is responsible for the control of autophagy. As a serine/threonine kinase, mTOR controls transcription, protein synthesis, cell division, growth, and autophagy. In particular, mTOR can consolidate and sustain memory function by boosting both synaptic plasticity and protein synthesis in dendrites and synapses through the formation of two multiprotein complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2 (Querfurth and Lee, 2021). In mouse AD models, synaptic density and plasticity can be restored by using Akt or PI3K activators to stimulate the insulin/mTOR pathway (Yi et al., 2018). Additionally, TORC1 is a crucial negative regulator of autophagy, meaning that autophagy is induced by negative regulation of mTORC1 and suppressed by activated mTORC1. Recent evidence suggests that mTORC1 inhibition, both in vivo and in vitro, can reduce amyloid secretion via neuronal autophagy induction (Benito-Cuesta et al., 2021). On the one hand, dysregulated mTOR activation can exacerbate Aβ generation and deposition, either by inhibiting Aβ clearance or by increasing Aβ generation via pathways such as insulin resistance (Luchsinger, 2008). On the other hand, injection of naturally secreted Aβ into the rat brain has been reported to increase mTOR signaling and activity (Davoody et al., 2024).
PTEN, a lipid phosphatase and protein tyrosine phosphatase, dephosphorylates and changes PI3K-generated PIP3 into PIP2, inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway (Hodges et al., 2018). Research has indicated that the ionophore alborixin can block the PI3K/Akt pathway by binding to PTEN, suppressing mTOR, which subsequently triggers autophagy and eliminates Aβ (Wani et al., 2019). Drugs that directly target proteins associated with the mTOR signaling pathway confer an immense potential for application in AD treatment. However, given the role of mTOR pathway in several vital biological processes, there is a risk of toxicity for patients due to the prolonged inhibition of mTOR by drugs such as rapamycin. Therefore, finding targets for new AD drugs that are more precise than existing drugs is needed, such as p70S6K1/2 and other mTOR-dependent effectors (Caccamo et al., 2015).
3 The therapeutic possibility of the modulation of PI3K/Akt/GSK3β in AD
Drug treatment is an important option for AD patients; however, only a few medications are authorized for use in therapeutic settings, such as galantamine, memantine, donepezil, rivastigmine, and the Chinese herb extract huperzine A. Given the function of the PI3K-Akt pathway in AD, several synthetic and natural modulators, ranging from chemicals to herbs, have been shown to alleviate the symptoms of this degenerative condition in various in vivo and in vitro models. Among these modulators, natural products can be classified into saponins, phenylpropanoids, flavonoids, non-flavonoid polyphenols, and others. Many of these compounds are derived from traditional Chinese medicine, offering increased safety and reduced toxicity in therapeutic applications, thus holding significant potential as future drug candidates. When comparing natural herbal inhibitors with commercially available GSK3B inhibitors, it is important to consider their origin and accessibility, with natural herbal inhibitors often being more readily available, especially in regions where traditional medicine is prevalent. They are known for their multi-target action, which could potentially overcome drug resistance in cancer cells, in contrast to the targeted, single-focus approach of commercial inhibitors (Yoshino and Ishioka, 2015). Although natural herbal inhibitors are generally perceived as having fewer side effects due to their holistic approach and historical use, they may lack the stringent safety assessments that accompany the development of commercial inhibitors, which are often synthetic and could have unforeseen side effects. In terms of clinical research and evidence base, commercial inhibitors are typically backed by extensive studies validating their safety and efficacy, whereas natural herbal inhibitors, despite their long use in traditional medicine, often lack this level of scientific validation and clinical trial support (Thapa et al., 2023).
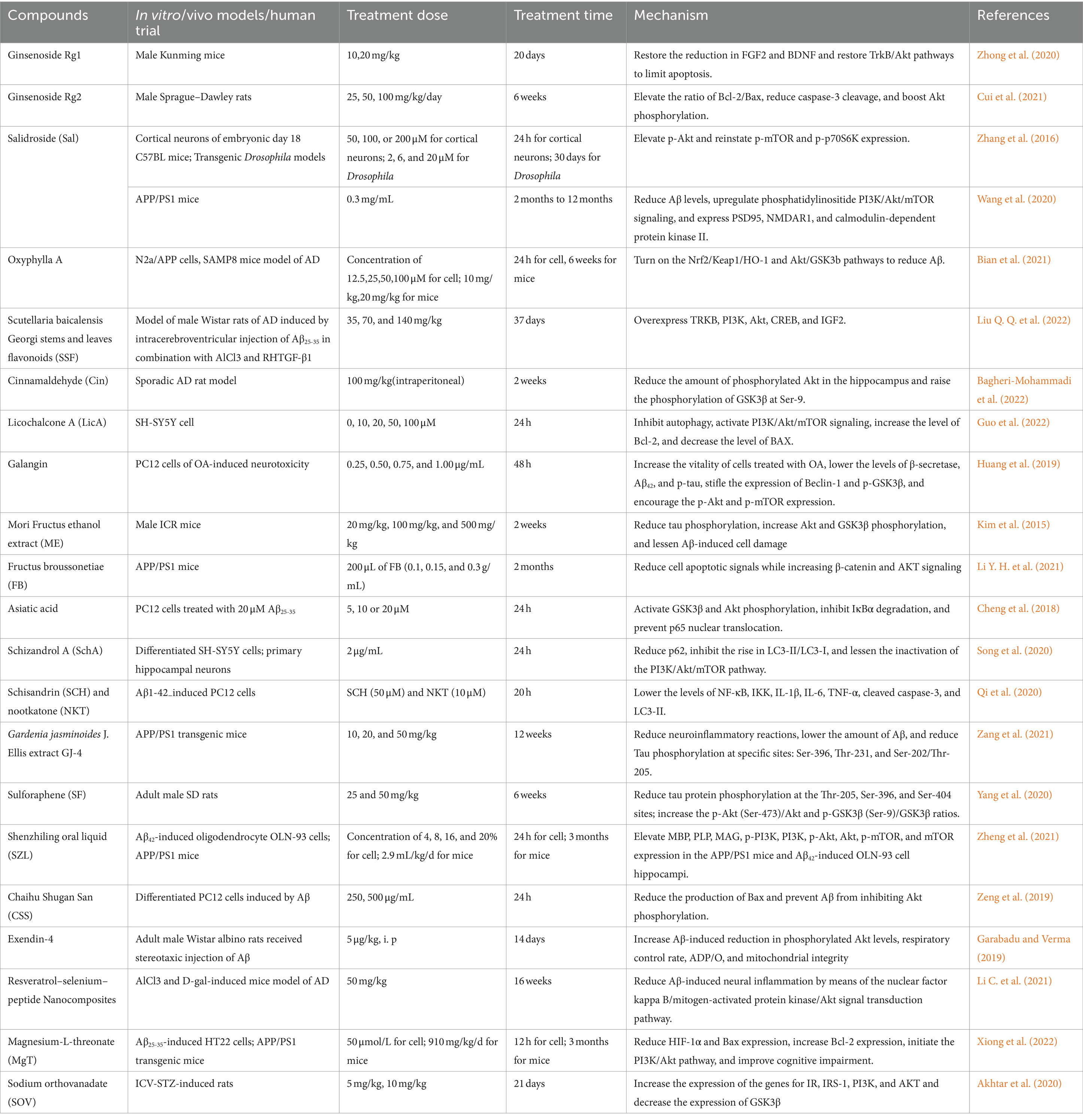
However, the action mechanism, molecular targets, and, most importantly, clinical efficiency of many novel modulators remain to be further studied. In the following part of this article, some important modulators of PI3K/Akt/GSK3β are discussed, and Table 1 offers a summary for readers of the experimental cell, animals, dosage, and duration utilized in studies using natural and synthetic drugs.
Ginsenoside Rd, belonging to saponins, is the active compound in Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer, which is famous for its effects to reduce neurological damage in neurodegenerative diseases through several pathways, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptosis (Chen Y. Y. et al., 2022). Researchers have demonstrated that Ginsenoside Rd. acts through estrogen receptor α (ERα) to affect the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways, increasing sAPPα levels and decreasing extracellular Aβ in OVX rats (Yan et al., 2017). According to research on aging mice given D-galactose and AlCl3, ginsenoside Rg1 reverts the aging-induced decrease in FGF2 and BDNF, stimulates the TrkB/Akt pathways in the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus, and ultimately prevents apoptosis (Zhong et al., 2020). Yang et al. also demonstrated how Rg1 modulates the GSK3β/Wnt signaling pathway to decrease Tau protein phosphorylation, Aβ1-42 deposition, and BACE1 expression in AD tree shrews (Yang et al., 2022). Additional research has verified that ginsenoside Rg2 reduces cognitive impairment caused by Aβ25-35, raises the Bcl-2/Bax ratio, and prevents the rat model of caspase-3 cleavage by initiating the PI3K/Akt pathway (Cui et al., 2021). Regarding preclinical and clinical trials, existing evidence focused on combination treatment and dietary supplements of ginseng or red ginseng as a whole, instead of its specific components, indicating that more high-quality clinical trials remain to be conducted (Li J. et al., 2021).
Salidroside (Sal) is a bioactive compound derived from Rhodiola rosea L, a valuable medicinal plant. It was reported to exhibit neuroprotective activities, notably against AD, through a range of mechanisms including antioxidant defense, apoptosis regulation, and modulation of amyloid-beta levels via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Additionally, it enhances cognitive function by affecting p-GSK3β and p-tau, inhibits neuroinflammation and apoptosis via the SIRT1/NF-κB pathway, protects against excitotoxicity, and regulates amyloid precursor protein processing (Zhong et al., 2018). In particular, Sal has not yet shown any detectable toxicity or deleterious effects in acute trials or other toxicity investigations (Zhang X. et al., 2021). According to earlier studies, Sal works as a novel therapeutic drug for cardiovascular diseases by inhibiting platelet activity via the Akt/GSK3β signaling pathway (Wei et al., 2020). According to research by Zhu et al. on the neuroprotective benefits of sal for aging models, Sal increases the production of the telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) protein through the PI3K/Akt pathway. The TERT protein, as the catalytic subunit of telomerase, plays a crucial role in maintaining telomere length, which is inherently linked to cellular aging. By increasing TERT expression, salidroside helps to slow the rate of telomere shortening, thereby delaying the cellular aging process (Zhu et al., 2021). These results align with similar studies in the AD model. Sal may enhance PC12 cell survival and proliferation by activating the ERK1/2 and Akt signaling pathways, according to prior in vitro research (Liao et al., 2019). Additionally, the researchers showed that Sal raises the expression of PSD95, NMDAR1, and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II and reduces the levels of both soluble and insoluble Aβ via upregulating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in an experiment to assess its neuroprotective effects on APP/PS1 mice (Wang et al., 2020). In a study on the Drosophila model, the results are similar to Zhang et al. (2016). In particular, natural Sal is present in very low concentrations, necessitating the use of synthesized products as backups in clinical settings (Zhang X. et al., 2021).
Curcumin, belonging to flavonoids, is the major compound of turmeric, which is an herb native to southern Asia, mainly extracted from the rhizome of Curcuma longa. Curcumin has been extensively examined for its remarkable capacity to alter AD pathogenesis through multiple mechanisms, including reducing the formation and neurotoxicity of Aβ and tau. However, the implication of the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway in these processes has not been illustrated in detail (Tang and Taghibiglou, 2017; Reddy et al., 2018). Recent reviews pointed out that two significant signaling pathways, PI3K/Akt/GSK3 and PI3K/Akt/CREB/BDNF, mediate the main mechanisms of curcumin neuroprotection, namely antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic functions (Kandezi et al., 2020). Researchers have demonstrated that curcumin improves memory recall impairment in scopolamine-induced mouse models by restoring Akt and GSK dephosphorylation (SoukhakLari et al., 2018). Wang et al. have shown how exosomes produced from cells primed with curcumin prevent Tau protein phosphorylation by triggering the Akt/GSK3β pathway, which alleviates symptoms in the AD rat model. It is widely recognized that the low bioavailability of curcumin hinders its therapeutic effects, while exo-cur boasts highly effective BBB-crossing, offering a solution to this problem (Wang et al., 2019). Vorinostat, also known as suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA), is an FDA-approved histone deacetylase inhibitor. Silibinin, a naturally occurring flavonolignan, has been recognized for its hepatoprotective and antioxidant properties. Studies focused on combination therapy, revealing that curcumin, vorinostat, and silibinin together alter the Akt/MDM2/p53 pathway, shielding PC12 cells from the toxicity caused by Aβ25–35 (Meng et al., 2019). Recent clinical trials appear to be positive as well. Dietary supplementation with curcumin has shown that it reduces circulating levels of islet amyloid polypeptide (IAPP) and GSK3β, significantly alleviating insulin resistance. IAPP is a hormone that, when misfolded, forms toxic amyloid deposits in pancreatic islets, contributing to beta cell dysfunction and a key pathological feature of type 2 diabetes (Thota et al., 2020). However, the reduction in circulating levels of risk molecules is still far from the improvement of clinical symptoms and more convincing evidence is required.
Oxyphylla A is a recently identified compound extracted from Alpinia oxyphylla, a plant employed historically to treat brain-related disorders and also referred to as Yi Zhi in Chinese herbal medicine. Bian et al. demonstrated how oxyphylla A acts as a neuroprotective agent in N2a/APP cells and SAMP8 mice by lowering the expression levels of APP, Aβ1-40, and Aβ1-42 and inhibiting oxidative stress through Nrf2 activation via the Akt/GSK3β pathway (Bian et al., 2021). Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi stems and leaves flavonoids (SSF) is a component with multi-pharmacological neuroprotective activities, extracted from the stems and leaves of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi. A previous in vivo investigation found that by upregulating the PI3K-Akt-CREB signaling pathway and the mRNA and protein expressions of TRKB, PI3K, Akt, CREB, and IGF2, SSF may enhance cognitive impairment and neurogenesis in AD model rats (Liu Q. Q. et al., 2022). Recent investigations have indicated that the main ingredient in cinnamon, cinnamaldehyde (Cin), has dose-dependent neuroprotective properties. Recent research indicates that Cin selectively triggers caspase-3 activation, hippocampal IRS-1/Akt/GSK3β signaling disruption, and Aβ aggregation. This results in improved AD symptoms in the sporadic AD rat model, which is comparable to insulin (3 mU/ICV) therapy (Bagheri-Mohammadi et al., 2022). Licochalcone A (LicA), as a dietary and herbal flavonoid extracted from the root of Glycyrrhiza glabra, was reported to have quite a few biological activities, including protective effect against Aβ peptide. In the experiment to test the neuroprotective effects of Sal on SH-SY5Y cells, Guo et al. illustrated that LicA significantly reduces Aβ25-35-induced autophagy and elevates anti-apoptotic protein levels along with PI3K, Akt, and mTOR activation. Galangin, as a natural flavonol that is an important active component of Alpinia officinarum, has been considered useful in treating or delaying AD. Galangin has been shown to decrease β-secretase and acetylated H3 in the promoter regions of β-secretase in SH-SY5Y cells (Zeng et al., 2015). Furthermore, Huang et al. showed that in okadaic acid-induced PC12 cells, galanin could suppress autophagy through the Akt/GSK3β/mTOR pathway by raising p-Akt and p-mTOR and decreasing p-GSK3β levels (Huang et al., 2019).
Mori Fructus (Morus alba L. fruit, mulberry) was believed to exert neuroprotective effects in several models in recent years, including AD. Researchers have examined the neuroprotective qualities of Mori Fructus ethanol extract (ME) in rat primary hippocampus cells in response to Aβ-induced toxicity. ME prevented Aβ25–35-induced cell damage both in vitro and in vivo. This protective effect was mediated by activation of GSK3β and Akt and results in the reduction in tau phosphorylation and apoptosis in mouse models induced by the toxicity of Aβ25–35 (Kim et al., 2015). In addition, pharmacological and clinical studies suggest Chinese herbal medicine Fructus broussonetiae (FB) may be a possible medication for AD therapy. In the experiment to test the neuroprotective effects of FB on APP/PS1 mice, Li et al. demonstrated that FB exerted anti-AD effects both in vivo and in vitro, and the in vitro experiment revealed that cells treated with FB had elevated levels of both AKT and β-catenin signaling (Li Y. H. et al., 2021). Research has indicated that asiatic acid (AA), a naturally occurring pentacyclic triterpene derived from Centella asiatica, may aid in lowering the concentration of Aβ in the AD brain. Through regulating PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signaling, AA has been shown to protect differentiated PC12 cells against Aβ25–35-induced apoptosis and tau protein hyperphosphorylation (Cheng et al., 2018). Moreover, the berries of the Chinese plant Schisandra chinensis yield Schizandrol A (SchA), a naturally occurring active ingredient. Prior research has shown that SchA acts as an antioxidant and regulates DNA methylation to ameliorate Aβ1–40-induced cell survival and cognitive impairment (Zhang et al., 2015; Hu et al., 2012). According to Song et al., autophagy suppression mediated by the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is responsible for attenuating over-activated autophagy in Aβ1-42-induced neurons by SchA, in their experiment on human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells (Song et al., 2020). Nootkatone (Nkt) is extracted from sesquiterpenes in Alpinia oxyphylla, and recent studies indicate that Sch and NKT may work in concert. According to Qi et al., treating Aβ1–42-induced PC12 cells with Nkt and Sch stimulated the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/mTOR pathway, resulting in a neuroprotective effect (Qi et al., 2020). It has been shown that GJ-4 (crocin richments), which is isolated from Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis, targets neuroinflammation and oxidative stress, boosting the cognition of mice treated with Aβ25-35 (Zhang et al., 2020). Multiple targets of GJ-4 have been shown in recent investigations, including the Aβ level, tau hyperphosphorylation, and neuroinflammatory reactions. In studies using APP/PS1 transgenic mice, GJ-4 was demonstrated to ameliorate cognitive impairments by preventing neuroinflammation through the PI3K/Akt pathway (Zang et al., 2021). Furthermore, sulforaphane (SF), among the main isothiocyanates found in Raphani Semen, has been demonstrated to possess neuroprotective qualities in AD mouse models. Zhu et al., in their study on adult male SD rats and BV-2 cells, pointed out that SF improved cognitive impairments induced by streptozotocin (STZ) in rats and decreased the AD pathology via modifying the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway (Yang et al., 2020).
The utilization of multi-target pharmaceutical methods is essential in the pharmacotherapy of AD. A considerable literature has grown and supported that traditional Chinese medicines (TCM) contain various components that can prevent or relieve moderate to mild AD through many mechanisms. TCM compound formulations have a special benefit in treating AD as they have multi-target capabilities. Among them, many of the herbal decoctions and formulas act by triggering the PI3K-Akt pathway. Theoretically, there are multiple roles of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, so modifications in PI3K activity may result in side effects, which is a negative feature for therapeutical treatments. However, considering the complex components of TCM, side effects are not significant in real experiments. For example, 10 Chinese herbs make up Shenzhiling oral liquid (SZL), a combination used in TCM. Recent investigations state that serum containing SZL has approximately 126 active chemicals, ranging from phenols to phenolic acids. Moreover, SZL treatment was shown by Zheng et al. to exert neuroprotective functions in APP/PS1 mice by reducing Aβ42 and Aβ40 accumulation in the hippocampi. During this process, the expression of the PI3K/Akt–mTOR signaling pathway has been upregulated (Zheng et al., 2021). Moreover, it has been shown that the 152 active ingredients in Chaihu Shugan San (CSS) can help ameliorate the cognitive impairment linked to AD. According to earlier research, CSS can suppress the production of Bax and prevent inhibitory effect of Aβ on Akt phosphorylation (Zeng et al., 2019).
Natural herbal inhibitors offer a diverse range of options due to their origins in various plants, which may provide a broader spectrum of selectivity for treatment. They are known for their multi-target mechanisms of action, potentially overcoming drug resistance in cancer cells that can develop against single-target inhibitors. These natural inhibitors may also present lower toxicity and fewer side effects, making them safer alternatives to synthetic compounds in some cases.
The cost-effectiveness of natural herbal inhibitors could make them more accessible to patients who might not be able to afford commercially available drugs. Additionally, certain natural compounds have demonstrated immunomodulatory effects that could enhance the immune response of the body to cancer, offering new therapeutic strategies.
However, despite their potential benefits, natural herbal inhibitors face challenges in clinical application, such as standardization, quality control, stability, and long-term safety. While some natural components such as curcumin and resveratrol have shown promise in modulating immune checkpoints in laboratory and animal models, further clinical studies are needed to confirm their efficacy and safety in treating diseases related to GSK3β.
As a GLP-1 agonist, exendin-4 was reported to exhibit neuroprotective activity. Exendin-4 has been shown to reduce levels of Aβ and cholinergic dysfunction in memory-sensitive brain areas of AD rat models, and the action was mediated by the PI3K/Akt pathway (Garabadu and Verma, 2019). In particular, resveratrol (Res) also has neuroprotective properties, and in recent research, it was indicated that a small Resselenium–peptide nanocomposite improves cognitive disorder through various mechanisms, one of which is via preventing Akt from being phosphorylated in brains of AD model mice (Li C. et al., 2021). Evidence abounds that the concentration of some cations in the brain is decreased in AD patients, such as magnesium. As a result, magnesium-L-threonate (MgT), a new magnesium compound, has been applied recently for its capacity to increase brain magnesium levels and reduce degenerative alterations associated with AD. Xiong et al. demonstrated that, in Aβ25-35-treated HT22 cells and APP/PS1 mouse hippocampus, MgT treatment exerts neuroprotective benefits against oxidative stress and hippocampal neuronal injury and activates the PI3K/Akt pathway as well (Xiong et al., 2022).
As stated earlier, GSK3β inhibitors are utilized in the treatment of AD because GSK3β is crucial to the pathogenesis of the disease. Lithium has a well-established ability to reduce AD pathogenesis by preventing tau phosphorylation due to its GSK3β inhibitory effects (Haussmann et al., 2021). In terms of clinical efficacy, several recent meta-analyses showed that lithium can successfully enhance cognitive functions in AD patients. According to Shinji et al., there were no appreciable variations in CSF biomarkers between the GSK3β inhibitor and placebo therapy groups. That can be the result of the individual heterogeneity and an inadequate sample size of the group (Matsunaga et al., 2015; Matsunaga et al., 2019). In addition to the many investigations conducted on lithium, we notice that in the past year, several new GSK3β inhibitors have been found, synthesized, and produced. In experiments on the HEK293-Tau P301L cell-based model and okadaic acid-induced mouse model, Liu et al. (2023) demonstrated that ZDWX-25, as a harmine derivative, can inhibit both GSK3β and DYRK1A, reducing phosphorylation of multiple Tau epitopes. Synthetic and semi-synthetic GSK3β inhibitors, including 17 β-carboline-1,2,3-triazole hybrids (compound 21), oxazole-4-carboxamide/butylated hydroxytoluene hybrids (compound KWLZ-9e), 1,2,4-thiadiazolidine-3,5-dione derivatives (compound 10a), novel coumarin derivatives (compound 30), and novel α-carboline derivatives (compound ZCH-9), exhibit remarkable anti-AD and therapeutic benefits (Liu et al., 2022a; Luo et al., 2023; Dong et al., 2023; Liu et al., 2022b; Chen H. et al., 2022). The drug development strategies focusing on designing inhibitors for single targets based on molecular docking and other technologies represent a future trend in AD treatment.
4 Conclusion and future directions
It is well established that PI3K and Akt possess crucial effects on the physiological functions of cells in both the central nervous system and other somatic cells, from neurons and microglia to the myocardium. With insulin, growth factors, and cytokines as upstream modulators and mTOR, GSK3, and FoxO as downstream molecules, PI3K and Akt consist of the whole signaling pathway, maintaining cell homeostasis, and regulating survival, metabolism, apoptosis, inflammation, autophagy, and cytoskeleton remodeling. Abound experimental data within the past decades supported the linkage between the PI3K signaling pathway and AD, the former modulating the pathology of AD including Aβ deposition and tau protein tangles majorly through affecting various processes including inflammation, oxidative stress, cholinergic neurotransmission, synaptic plasticity, and autophagy. Significantly, AD is associated with aberrantly elevated levels of GSK3β, whose inhibitors seem to have intriguing promise as AD treatments. Natural and synthetic modulators are listed in Table 1.
While the genetic determinants of the PI3K pathway are complex and not fully elucidated, the potential influence of expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) or allele-specific QTL (aQTL) on the variability of gene expression within this pathway is gaining attention. In particular, a recent genome-wide association study (GWAS) has identified 4,166 single nucleotide variants associated with the expression of 85 genes involved in the PI3K/Akt pathway, highlighting the significant role of eQTLs in modulating gene expression within this critical cellular pathway. The study, which utilized mRNA expression data from lymphoblastoid cell lines of 373 Europeans and their genotypes at nearly 6 million nucleotide variants, revealed 73 eQTLs associated with the expression of multiple genes. These eQTLs include variants for genes encoding collagen type I alpha 1 (COL1A1), integrin alpha 11 (ITGA11), and type IV collagen molecules, suggesting a complex regulatory network influenced by genetic variation. Furthermore, the identification of eQTLs in regulatory regions, such as the promoter of the palladin (PALLD) gene and an enhancer of cadherin related family member 3 (CDHR3) gene, points toward a direct impact of these genetic variants on gene expression. This could potentially affect critical cellular processes, including cell adhesion and cytoskeletal organization (Ryu and Lee, 2017). This evidence underscores the importance of considering eQTLs and aQTLs in future studies aiming to dissect the genetic control of the PI3K pathway and its implications in cancer susceptibility and therapy response. By integrating these findings with functional genomics approaches, we can expect to uncover a deeper understanding of the regulatory mechanisms governing the PI3K pathway and identify novel therapeutic targets.
The present review emphasizes that the targets mentioned are valuable to research not only in animal models but also in preclinical and clinical trials, and combinations of multi-target therapeutics and more precise delivery methods, apart from oral administration, are awaiting further exploration.
Author contributions
JP: Writing – review & editing. QY: Writing – review & editing.YaW: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Conceptualization. SC: Writing – review & editing. CL: Writing – review & editing, Data curation. YoW: Writing – review & editing. JS: Writing – original draft, Investigation. RY: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. We acknowledge the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82101455), Nantong 14th Five-Year Plan for Science, Education and Health Project (NTCXTD48), Nantong Civic Science, Technology Project of China (MS2023045), Jiangsu Provincial Medical Innovation Center (CXZX202212), Jiangsu Provincial Research Hospital (YJXYY202204), and Higher school in Jiangsu Province College Students’ Practice Innovation Training Programs (202410304124Y).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
Aβ, Amyloid-beta; ADDLs, Amyloid β-derived diffusible ligands; AD, Alzheimer’s disease; AKT, Protein kinase B; APP, Amyloid precursor protein; ApoE, Apolipoprotein E; BACE1, β-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; Bax, Bcl-2-associated X protein; CNS, Central nervous system; CREB, cAMP response element-binding protein; CSS, Chaihu-Shugan-San; ERK, Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; FAD, Familial Alzheimer’s disease; FoxO, Forkhead box O; GABA, Gamma-aminobutyric acid; GSK3β, Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; HIF-1α, Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha; IAPP, Islet amyloid polypeptide; IGF-1, Insulin-like growth factor 1; iNOS, Inducible nitric oxide synthase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; mTOR, Mechanistic target of rapamycin; MAPK, Mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB, Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NMDAR, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; NOS, Nitric oxide synthase; PDK1, Phosphatidylinositol-dependent kinase-1; PI3K, Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PIP2, Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate; PTEN, Phosphatase and tensin homolog; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; SAD, Sporadic Alzheimer’s disease; SF, Sulforaphene; TGF-β, Transforming growth factor beta; TREM2, Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2.
References
Abbott, J. J., Howlett, D. R., Francis, P. T., and Williams, R. J. (2008). Abeta(1-42) modulation of Akt phosphorylation via alpha7 nachR and Nmda receptors. Neurobiol. Aging 29, 992–1001. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.01.003
Abou-Ismail, M. Y., Citla Sridhar, D., and Nayak, L. (2020). Estrogen and thrombosis: a bench to bedside review. Thromb. Res. 192, 40–51. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.05.008
Akhtar, A., Bishnoi, M., and Sah, S. P. (2020). Sodium orthovanadate improves learning and memory in intracerebroventricular-streptozotocin rat model of Alzheimer's disease through modulation of brain insulin resistance induced tau pathology. Brain Res. Bull. 164, 83–97. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.08.001
Alonso, A. D., Di Clerico, J., Li, B., Corbo, C. P., Alaniz, M. E., Grundke-Iqbal, I., et al. (2010). Phosphorylation of tau at Thr212, Thr231, and Ser262 combined causes neurodegeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 30851–30860. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.110957
Alzheimer’s and Dementia (2023). 2023 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 19, 1598–1695. doi: 10.1002/alz.13016
Austin, S. A., and Katusic, Z. S. (2020). Partial loss of endothelial nitric oxide leads to increased cerebrovascular beta amyloid. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 40, 392–403. doi: 10.1177/0271678X18822474
Austin, S. A., Santhanam, A. V., Hinton, D. J., Choi, D. S., and Katusic, Z. S. (2013). Endothelial nitric oxide deficiency promotes Alzheimer's disease pathology. J. Neurochem. 127, 691–700. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12334
Avgerinos, K. I., Ferrucci, L., and Kapogiannis, D. (2021). Effects of monoclonal antibodies against amyloid-β on clinical and biomarker outcomes and adverse event risks: a systematic review and meta-analysis of phase iii Rcts in Alzheimer's disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 68:101339. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2021.101339
Avrahami, L., Farfara, D., Shaham-Kol, M., Vassar, R., Frenkel, D., and Eldar-Finkelman, H. (2013). Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 ameliorates β-amyloid pathology and restores lysosomal acidification and mammalian target of rapamycin activity in the Alzheimer disease mouse model: in vivo and in vitro studies. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 1295–1306. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.409250
Bagheri, M., Joghataei, M. T., Mohseni, S., and Roghani, M. (2011). Genistein ameliorates learning and memory deficits in amyloid β(1-40) rat model of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 95, 270–276. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2010.12.001
Bagheri-Mohammadi, S., Askari, S., Alani, B., Moosavi, M., and Ghasemi, R. (2022). Cinnamaldehyde regulates insulin and Caspase-3 signaling pathways in the sporadic Alzheimer's disease model: involvement of hippocampal function via Irs-1, Akt, and Gsk-3β phosphorylation. J. Mol. Neurosci. 72, 2273–2291. doi: 10.1007/s12031-022-02075-x
Baki, L., Shioi, J., Wen, P., Shao, Z., Schwarzman, A., Gama-Sosa, M., et al. (2004). Ps1 activates Pi3K thus inhibiting Gsk-3 activity and tau overphosphorylation: effects of fad mutations. EMBO J. 23, 2586–2596. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600251
Basheer, N., Smolek, T., Hassan, I., Liu, F., Iqbal, K., Zilka, N., et al. (2023). Does modulation of tau hyperphosphorylation represent a reasonable therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer's disease? From preclinical studies to the clinical trials. Mol. Psychiatry 28, 2197–2214. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02113-z
Benito-Cuesta, I., Ordóñez-Gutiérrez, L., and Wandosell, F. (2021). Ampk activation does not enhance autophagy in neurons in contrast to Mtorc1 inhibition: different impact on β-amyloid clearance. Autophagy 17, 656–671. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1728095
Bian, Y., Chen, Y., Wang, X., Cui, G., Ung, C. O. L., Lu, J. H., et al. (2021). Oxyphylla a ameliorates cognitive deficits and alleviates neuropathology via the Akt-Gsk3β and Nrf2-Keap1-ho-1 pathways in vitro and in vivo murine models of Alzheimer's disease. J. Adv. Res. 34, 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.09.002
Bloom, G. S. (2014). Amyloid-β and tau: the trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol. 71, 505–508. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.5847
Caccamo, A., Branca, C., Talboom, J. S., Shaw, D. M., Turner, D., Ma, L., et al. (2015). Reducing ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 expression improves spatial memory and synaptic plasticity in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurosci. 35, 14042–14056. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2781-15.2015
Caruso, G., Spampinato, S. F., Cardaci, V., Caraci, F., Sortino, M. A., and Merlo, S. (2019). β-Amyloid and oxidative stress: perspectives in drug development. Curr. Pharm. Des. 25, 4771–4781. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666191209115431
Cason, S. E., Mogre, S. S., Holzbaur, E. L. F., and Koslover, E. F. (2022). Spatiotemporal analysis of axonal autophagosome-lysosome dynamics reveals limited fusion events and slow maturation. Mol. Biol. Cell 33:ar123. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E22-03-0111
Cheignon, C., Tomas, M., Bonnefont-Rousselot, D., Faller, P., Hureau, C., and Collin, F. (2018). Oxidative stress and the amyloid beta peptide in Alzheimer's disease. Redox Biol. 14, 450–464. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.10.014
Chen, Y. R., Li, Y. H., Hsieh, T. C., Wang, C. M., Cheng, K. C., Wang, L., et al. (2019). Aging-induced Akt activation involves in aging-related pathologies and Aβ-induced toxicity. Aging Cell 18:e12989. doi: 10.1111/acel.12989
Chen, Y. Y., Liu, Q. P., An, P., Jia, M., Luan, X., Tang, J. Y., et al. (2022). Ginsenoside Rd: a promising natural neuroprotective agent. Phytomedicine 95:153883. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153883
Chen, H., Yu, C., Liu, W., Zhu, C., Jiang, X., Xu, C., et al. (2022). Discovery of novel α-carboline derivatives as glycogen synthase kinase-3β inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Pharm (Weinheim) 355:e2200156. doi: 10.1002/ardp.202200156
Cheng, W., Chen, W., Wang, P., and Chu, J. (2018). Asiatic acid protects differentiated Pc12 cells from Aβ(25-35)-induced apoptosis and tau hyperphosphorylation via regulating Pi3K/Akt/Gsk-3β signaling. Life Sci. 208, 96–101. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.07.016
Chiang, H. C., Wang, L., Xie, Z., Yau, A., and Zhong, Y. (2010). Pi3 kinase signaling is involved in Abeta-induced memory loss in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107, 7060–7065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909314107
Chong, C. M., Tan, Y., Tong, J., Ke, M., Zhang, K., Yan, L., et al. (2022). Presenilin-1 F105C mutation leads to tau accumulation in human neurons via the Akt/mtorc1 signaling pathway. Cell Biosci. 12:131. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00874-8
Chow, V. W., Mattson, M. P., Wong, P. C., and Gleichmann, M. (2010). An overview of app processing enzymes and products. NeuroMolecular Med. 12, 1–12. doi: 10.1007/s12017-009-8104-z
Cui, J., Shan, R., Cao, Y., Zhou, Y., Liu, C., and Fan, Y. (2021). Protective effects of ginsenoside Rg2 against memory impairment and neuronal death induced by Aβ25-35 in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 266:113466. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113466
Cummings, J. L., Tong, G., and Ballard, C. (2019). Treatment combinations for Alzheimer's disease: current and future pharmacotherapy options. J. Alzheimers Dis. 67, 779–794. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180766
Davoody, S., Asgari Taei, A., Khodabakhsh, P., and Dargahi, L. (2024). Mtor signaling and Alzheimer's disease: what we know and where we are? CNS Neurosci. Ther. 30:e14463. doi: 10.1111/cns.14463
Dong, Y., Lu, J., Zhang, S., Chen, L., Wen, J., Wang, F., et al. (2023). Design, synthesis and bioevaluation of 1,2,4-thiadiazolidine-3,5-dione derivatives as potential Gsk-3β inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Bioorg. Chem. 134:106446. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106446
Drewes, G., Trinczek, B., Illenberger, S., Biernat, J., Schmitt-Ulms, G., Meyer, H. E., et al. (1995). Microtubule-associated protein/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase (p110mark). A novel protein kinase that regulates tau-microtubule interactions and dynamic instability by phosphorylation at the Alzheimer-specific site serine 262. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 7679–7688
Escamilla-Ayala, A., Wouters, R., Sannerud, R., and Annaert, W. (2020). Contribution of the presenilins in the cell biology, structure and function of γ-secretase. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 105, 12–26. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.02.005
Faller, P., and Hureau, C. (2012). A bioinorganic view of Alzheimer's disease: when misplaced metal ions (re)direct the electrons to the wrong target. Chemistry 18, 15910–15920. doi: 10.1002/chem.201202697
Folke, J., Pakkenberg, B., and Brudek, T. (2019). Impaired Wnt signaling in the prefrontal cortex of Alzheimer's disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 56, 873–891. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1103-z
Gabbouj, S., Ryhänen, S., Marttinen, M., Wittrahm, R., Takalo, M., Kemppainen, S., et al. (2019). Altered insulin signaling in Alzheimer's disease brain - special emphasis on Pi3K-Akt pathway. Front. Neurosci. 13:629. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00629
Garabadu, D., and Verma, J. (2019). Exendin-4 attenuates brain mitochondrial toxicity through Pi3K/Akt-dependent pathway in amyloid beta (1-42)-induced cognitive deficit rats. Neurochem. Int. 128, 39–49. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2019.04.006
Goodenough, S., Schleusner, D., Pietrzik, C., Skutella, T., and Behl, C. (2005). Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta links neuroprotection by 17beta-estradiol to key Alzheimer processes. Neuroscience 132, 581–589. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.12.029
Götz, J., Bodea, L. G., and Goedert, M. (2018). Rodent models for Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 19, 583–598. doi: 10.1038/s41583-018-0054-8
Guo, J., Xue, J., Ding, Z., Li, X., Wang, X., and Xue, H. (2022). Activated phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin signal and suppressed autophagy participate in protection offered by Licochalcone a against amyloid-β peptide fragment 25-35-induced injury in Sh-Sy5Y cells. World Neurosurg. 157, e390–e400. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2021.10.098
Haase, C., Stieler, J. T., Arendt, T., and Holzer, M. (2004). Pseudophosphorylation of tau protein alters its ability for self-aggregation. J. Neurochem. 88, 1509–1520. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02287.x
Halliwell, B. (2006). Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: where are we now? J. Neurochem. 97, 1634–1658. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03907.x
Hardy, J. (2017). The discovery of Alzheimer-causing mutations in the app gene and the formulation of the "amyloid cascade hypothesis". FEBS J. 284, 1040–1044. doi: 10.1111/febs.14004
Haussmann, R., Noppes, F., Brandt, M. D., Bauer, M., and Donix, M. (2021). Lithium: a therapeutic option in Alzheimer's disease and its prodromal stages? Neurosci. Lett. 760:136044. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2021.136044
Hodges, S. L., Reynolds, C. D., Smith, G. D., Jefferson, T. S., Nolan, S. O., and Lugo, J. N. (2018). Molecular interplay between hyperactive mammalian target of rapamycin signaling and Alzheimer's disease neuropathology in the ns-Pten knockout mouse model. Neuroreport 29, 1109–1113. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001081
Hoeflich, K. P., Luo, J., Rubie, E. A., Tsao, M. S., Jin, O., and Woodgett, J. R. (2000). Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in cell survival and Nf-kappaB activation. Nature 406, 86–90. doi: 10.1038/35017574
Hu, D., Cao, Y., He, R., Han, N., Liu, Z., Miao, L., et al. (2012). Schizandrin, an antioxidant lignan from Schisandra chinensis, ameliorates Aβ1-42-induced memory impairment in mice. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2012:721721. doi: 10.1155/2012/721721
Huang, M., Duan, W., Chen, N., Lin, G., and Wang, X. (2021). Synthesis and antitumor evaluation of Menthone-derived pyrimidine-urea compounds as potential Pi3K/Akt/mtor signaling pathway inhibitor. Front. Chem. 9:815531. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.815531
Huang, L., Lin, M., Zhong, X., Yang, H., and Deng, M. (2019). Galangin decreases p-tau, Aβ42 and β-secretase levels, and suppresses autophagy in okadaic acid-induced Pc12 cells via an Akt/Gsk3β/mtor signaling-dependent mechanism. Mol. Med. Rep. 19, 1767–1774. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.9824
Jankowsky, J. L., and Zheng, H. (2017). Practical considerations for choosing a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 12:89. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0231-7
Jiang, Q., Zhang, X., Dai, X., Han, S., Wu, X., Wang, L., et al. (2022). S6K1-mediated phosphorylation of Pdk1 impairs Akt kinase activity and oncogenic functions. Nat. Commun. 13:1548. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28910-8
Jiao, W., Hao, J., Xie, Y., Meng, M., and Gao, W. (2022). Ezh2 mitigates the cardioprotective effects of mesenchymal stem cell-secreted exosomes against infarction via Hmga2-mediated Pi3K/Akt signaling. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 22:95. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02533-9
Jope, R. S., Yuskaitis, C. J., and Beurel, E. (2007). Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (Gsk3): inflammation, diseases, and therapeutics. Neurochem. Res. 32, 577–595. doi: 10.1007/s11064-006-9128-5
Kandezi, N., Mohammadi, M., Ghaffari, M., Gholami, M., Motaghinejad, M., and Safari, S. (2020). Novel insight to neuroprotective potential of curcumin: a mechanistic review of possible involvement of mitochondrial biogenesis and Pi3/Akt/Gsk3 or Pi3/Akt/Creb/Bdnf signaling pathways. Int J Mol Cell Med 9, 1–32. doi: 10.22088/IJMCM.BUMS.9.1.1
Khezri, M. R., Yousefi, K., Esmaeili, A., and Ghasemnejad-Berenji, M. (2023). The role of Erk1/2 pathway in the pathophysiology of Alzheimer's disease: An overview and update on new developments. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 43, 177–191. doi: 10.1007/s10571-022-01191-x
Kiani, A. K., Bonetti, G., Medori, M. C., Caruso, P., Manganotti, P., Fioretti, F., et al. (2022). Dietary supplements for improving nitric-oxide synthesis. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 63, E239–e245. doi: 10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2022.63.2S3.2766
Kim, A., Lalonde, K., Truesdell, A., Gomes Welter, P., Brocardo, P. S., Rosenstock, T. R., et al. (2021). New avenues for the treatment of Huntington's disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:8363. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168363
Kim, H. G., Park, G., Lim, S., Park, H., Choi, J. G., Jeong, H. U., et al. (2015). Mori Fructus improves cognitive and neuronal dysfunction induced by beta-amyloid toxicity through the Gsk-3β pathway in vitro and in vivo. J. Ethnopharmacol. 171, 196–204. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.05.054
King, M. K., Pardo, M., Cheng, Y., Downey, K., Jope, R. S., and Beurel, E. (2014). Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibitors: rescuers of cognitive impairments. Pharmacol. Ther. 141, 1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.07.010
Kumar, M., and Bansal, N. (2022). Implications of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt (Pi3K-Akt) pathway in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 59, 354–385. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02611-7
Lauretti, E., Dincer, O., and Praticò, D. (2020). Glycogen synthase kinase-3 signaling in Alzheimer's disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Cell Res. 1867:118664. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118664
Lee, S. J., Chung, Y. H., Joo, K. M., Lim, H. C., Jeon, G. S., Kim, D., et al. (2006). Age-related changes in glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (Gsk3beta) immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of rats. Neurosci. Lett. 409, 134–139. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.09.026
Li, J., Huang, Q., Chen, J., Qi, H., Liu, J., Chen, Z., et al. (2021). Neuroprotective potentials of Panax ginseng against Alzheimer's disease: a review of preclinical and clinical evidences. Front. Pharmacol. 12:688490. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.688490
Li, Y. H., Jin, Y., Wang, X. S., Chen, X. L., Chen, H. B., Xu, J., et al. (2021). Neuroprotective effect of Fructus broussonetiae on app/Ps1 mice via upregulation of Akt/β-catenin signaling. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 27, 115–124. doi: 10.1007/s11655-019-3178-4
Li, J., Li, Y., Liu, M., and Xie, S. (2020). Modified heptapeptide from tau binds both tubulin and microtubules. Thorac Cancer 11, 2993–2997. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13643
Li, Q., Liu, Y., and Sun, M. (2017). Autophagy and Alzheimer's disease. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 37, 377–388. doi: 10.1007/s10571-016-0386-8
Li, C., Wang, N., Zheng, G., and Yang, L. (2021). Oral Administration of Resveratrol-Selenium-Peptide Nanocomposites Alleviates Alzheimer's disease-like pathogenesis by inhibiting Aβ aggregation and regulating gut microbiota. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 46406–46420. doi: 10.1021/acsami.1c14818
Liao, Z. L., Su, H., Tan, Y. F., Qiu, Y. J., Zhu, J. P., Chen, Y., et al. (2019). Salidroside protects Pc-12 cells against amyloid β-induced apoptosis by activation of the Erk1/2 and Akt signaling pathways. Int. J. Mol. Med. 43, 1769–1777. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4088
Lin, J., Song, T., Li, C., and Mao, W. (2020). Gsk-3β in Dna repair, apoptosis, and resistance of chemotherapy, radiotherapy of cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Cell Res. 1867:118659. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118659
Lin, F., Yang, Y., Wei, S., Huang, X., Peng, Z., Ke, X., et al. (2020). Hydrogen sulfide protects against high glucose-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury through activating Pi3K/Akt/enos pathway. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 14, 621–633. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S242521
Linjuan, S., Chengfu, L. I., Jiangang, L., Nannan, L. I., Fuhua, H., Dandan, Q., et al. (2024). Efficacy of Sailuotong on neurovascular unit in amyloid precursor protein/presenilin-1 transgenic mice with Alzheimer's disease. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 44, 289–302. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240203.007
Liu, F., Chen, G. D., and Fan, L. K. (2022). Knockdown of Pdx1 enhances the osteogenic differentiation of Adscs partly via activation of the Pi3K/Akt signaling pathway. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 17:107. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02825-4
Liu, Q. Q., Ding, S. K., Zhang, H., and Shang, Y. Z. (2022). The molecular mechanism of Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi stems and leaves flavonoids in promoting neurogenesis and improving memory impairment by the Pi3K-Akt-Creb signaling pathway in rats. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 25, 919–933. doi: 10.2174/1386207324666210506152320
Liu, F., Grundke-Iqbal, I., Iqbal, K., and Gong, C. X. (2005). Contributions of protein phosphatases Pp1, Pp2A, Pp2B and Pp5 to the regulation of tau phosphorylation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 22, 1942–1950. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04391.x
Liu, X., Lai, L. Y., Chen, J. X., Li, X., Wang, N., Zhou, L. J., et al. (2023). An inhibitor with Gsk3β and Dyrk1A dual inhibitory properties reduces tau hyperphosphorylation and ameliorates disease in models of Alzheimer's disease. Neuropharmacology 232:109525. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2023.109525
Liu, W., Tian, L., Wu, L., Chen, H., Wang, N., Liu, X., et al. (2022a). Discovery of novel β-carboline-1,2,3-triazole hybrids as AchE/Gsk-3β dual inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease treatment. Bioorg. Chem. 129:106168. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106168
Liu, W., Wu, L., Liu, W., Tian, L., Chen, H., Wu, Z., et al. (2022b). Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel coumarin derivatives as multifunctional ligands for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 242:114689. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114689
Liu, S. J., Zhang, J. Y., Li, H. L., Fang, Z. Y., Wang, Q., Deng, H. M., et al. (2004). Tau becomes a more favorable substrate for Gsk-3 when it is prephosphorylated by Pka in rat brain. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 50078–50088. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406109200
Liu, S. J., Zhang, A. H., Li, H. L., Wang, Q., Deng, H. M., Netzer, W. J., et al. (2003). Overactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by inhibition of phosphoinositol-3 kinase and protein kinase C leads to hyperphosphorylation of tau and impairment of spatial memory. J. Neurochem. 87, 1333–1344. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02070.x
Luchsinger, J. A. (2008). Adiposity, hyperinsulinemia, diabetes and Alzheimer's disease: an epidemiological perspective. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 585, 119–129. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.02.048
Luo, Z., Li, S., Zhang, Y., Yin, F., Luo, H., Chen, X., et al. (2023). Oxazole-4-carboxamide/butylated hydroxytoluene hybrids with Gsk-3β inhibitory and neuroprotective activities against Alzheimer's disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 256:115415. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115415
Lutshumba, J., Wilcock, D. M., Monson, N. L., and Stowe, A. M. (2023). Sex-based differences in effector cells of the adaptive immune system during Alzheimer's disease and related dementias. Neurobiol. Dis. 184:106202. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106202
Ma, Q. L., Lim, G. P., Harris-White, M. E., Yang, F., Ambegaokar, S. S., Ubeda, O. J., et al. (2006). Antibodies against beta-amyloid reduce Abeta oligomers, glycogen synthase kinase-3beta activation and tau phosphorylation in vivo and in vitro. J. Neurosci. Res. 83, 374–384. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20734
Magrané, J., Rosen, K. M., Smith, R. C., Walsh, K., Gouras, G. K., and Querfurth, H. W. (2005). Intraneuronal beta-amyloid expression downregulates the Akt survival pathway and blunts the stress response. J. Neurosci. 25, 10960–10969. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1723-05.2005
Marzo, A., Galli, S., Lopes, D., Mcleod, F., Podpolny, M., Segovia-Roldan, M., et al. (2016). Reversal of synapse degeneration by restoring Wnt signaling in the adult Hippocampus. Curr. Biol. 26, 2551–2561. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.07.024
Matsunaga, S., Fujishiro, H., and Takechi, H. (2019). Efficacy and safety of glycogen synthase kinase 3 inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 69, 1031–1039. doi: 10.3233/JAD-190256
Matsunaga, S., Kishi, T., Annas, P., Basun, H., Hampel, H., and Iwata, N. (2015). Lithium as a treatment for Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 48, 403–410. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150437
Meng, J., Li, Y., Zhang, M., Li, W., Zhou, L., Wang, Q., et al. (2019). A combination of curcumin, vorinostat and silibinin reverses Aβ-induced nerve cell toxicity via activation of Akt-Mdm2-p53 pathway. PeerJ 7:e6716. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6716
Meng, X., Wang, M., Sun, G., Ye, J., Zhou, Y., Dong, X., et al. (2014). Attenuation of Aβ25-35-induced parallel autophagic and apoptotic cell death by gypenoside Xvii through the estrogen receptor-dependent activation of Nrf2/are pathways. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 279, 63–75. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2014.03.026
Meng, Y., Yin, Q., Ma, Q., Qin, H., Zhang, J., Zhang, B., et al. (2021). Fxii regulates the formation of deep vein thrombosis via the Pi3K/Akt signaling pathway in mice. Int. J. Mol. Med. 47:4920. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.4920
Meng, J. X., Zhang, Y., Saman, D., Haider, A. M., De, S., Sang, J. C., et al. (2022). Hyperphosphorylated tau self-assembles into amorphous aggregates eliciting Tlr4-dependent responses. Nat. Commun. 13:2692. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30461-x
Miranda, A., Montiel, E., Ulrich, H., and Paz, C. (2021). Selective secretase targeting for Alzheimer's disease therapy. J. Alzheimers Dis. 81, 1–17. doi: 10.3233/JAD-201027
Muche, A., Arendt, T., and Schliebs, R. (2017). Oxidative stress affects processing of amyloid precursor protein in vascular endothelial cells. PLoS One 12:e0178127. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178127
Ntsapi, C., Lumkwana, D., Swart, C., Du Toit, A., and Loos, B. (2018). New insights into autophagy dysfunction related to amyloid Beta toxicity and neuropathology in Alzheimer's disease. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 336, 321–361. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2017.07.002
Nusse, R., and Clevers, H. (2017). Wnt/β-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell 169, 985–999. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.05.016
Oddo, S., Caccamo, A., Shepherd, J. D., Murphy, M. P., Golde, T. E., Kayed, R., et al. (2003). Triple-transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease with plaques and tangles: intracellular Abeta and synaptic dysfunction. Neuron 39, 409–421. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(03)00434-3
Ozbek, U., Kandilci, A., Van Baal, S., Bonten, J., Boyd, K., Franken, P., et al. (2007). Set-can, the product of the t(9;9) in acute undifferentiated leukemia, causes expansion of early hematopoietic progenitors and hyperproliferation of stomach mucosa in transgenic mice. Am. J. Pathol. 171, 654–666. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060934
Pal, D., Mukherjee, S., Song, I. H., and Nimse, S. B. (2021). Gsk-3 inhibitors: a new class of drugs for Alzheimer's disease treatment. Curr. Drug Targets 22, 1725–1737. doi: 10.2174/1389450122666210114095307
Palomer, E., Buechler, J., and Salinas, P. C. (2019). Wnt signaling deregulation in the aging and Alzheimer's brain. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 13:227. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00227
Peng, X., Guo, H., Zhang, X., Yang, Z., Ruganzu, J. B., Yang, Z., et al. (2023). Trem2 inhibits tau hyperphosphorylation and neuronal apoptosis via the Pi3K/Akt/Gsk-3β signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro. Mol. Neurobiol. 60, 2470–2485. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03217-x
Pichet Binette, A., Gaiteri, C., Wennström, M., Kumar, A., Hristovska, I., Spotorno, N., et al. (2024). Proteomic changes in Alzheimer disease associated with progressive Aβ plaque and tau tangle pathologies. Nat. Neurosci. 2024:1737. doi: 10.1038/s41593-024-01737-w
Pike, C. J. (2017). Sex and the development of Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 95, 671–680. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23827
Qi, Y., Cheng, X., Gong, G., Yan, T., Du, Y., Wu, B., et al. (2020). Synergistic neuroprotective effect of schisandrin and nootkatone on regulating inflammation, apoptosis and autophagy via the Pi3K/Akt pathway. Food Funct. 11, 2427–2438. doi: 10.1039/C9FO02927C
Qiu, Q., Lei, X., Wang, Y., Xiong, H., Xu, Y., Sun, H., et al. (2023). Naringin protects against tau hyperphosphorylation in Aβ (25-35)-injured Pc12 cells through modulation of Er, Pi3K/Akt, and Gsk-3β signaling pathways. Behav. Neurol. 2023:1857330. doi: 10.1155/2023/1857330
Querfurth, H., and Lee, H. K. (2021). Mammalian/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mtor) complexes in neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurodegener. 16:44. doi: 10.1186/s13024-021-00428-5
Rajput, M. S., Nirmal, N. P., Rathore, D., and Dahima, R. (2020). Dimethyl fumarate mitigates Tauopathy in Aβ-induced neuroblastoma Sh-Sy5Y cells. Neurochem. Res. 45, 2641–2652. doi: 10.1007/s11064-020-03115-x
Razani, E., Sigaroodi, A. P., Azar, A. S., Zoghi, A., Bavarsad, M. S., and Bashash, D. (2021). The PI3K/Akt signaling axis in Alzheimer’s disease: a valuable target to stimulate or suppress? Cell Stress Chaperones. 26, 871–887. doi: 10.1007/s12192-021-01231-3
Reddy, P. H., Manczak, M., Yin, X., Grady, M. C., Mitchell, A., Tonk, S., et al. (2018). Protective effects of Indian spice curcumin against amyloid-β in Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 61, 843–866. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170512
Riise, J., Plath, N., Pakkenberg, B., and Parachikova, A. (2015). Aberrant Wnt signaling pathway in medial temporal lobe structures of Alzheimer's disease. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 122, 1303–1318. doi: 10.1007/s00702-015-1375-7
Rozenberg, S., Di Pietrantonio, V., Vandromme, J., and Gilles, C. (2021). Menopausal hormone therapy and breast cancer risk. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 35:101577. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2021.101577
Ryu, D., and Lee, C. (2017). Expression quantitative trait loci for Pi3K/Akt pathway. Medicine (Baltimore) 96:e5817. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005817
Saha, S., Pal, D., and Nimse, S. B. (2021). Recent advances in the discovery of Gsk-3 inhibitors from synthetic origin in the treatment of neurological disorders. Curr. Drug Targets 22, 1437–1462. doi: 10.2174/1389450122666210120143953
Salcedo-Tello, P., Hernández-Ortega, K., and Arias, C. (2014). Susceptibility to Gsk3β-induced tau phosphorylation differs between the young and aged hippocampus after Wnt signaling inhibition. J. Alzheimers Dis. 39, 775–785. doi: 10.3233/JAD-130749
Salkovic-Petrisic, M., Tribl, F., Schmidt, M., Hoyer, S., and Riederer, P. (2006). Alzheimer-like changes in protein kinase B and glycogen synthase kinase-3 in rat frontal cortex and hippocampus after damage to the insulin signalling pathway. J. Neurochem. 96, 1005–1015. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03637.x
Shefa, U., Jeong, N. Y., Song, I. O., Chung, H. J., Kim, D., Jung, J., et al. (2019). Mitophagy links oxidative stress conditions and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 14, 749–756. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.249218
Singh, E., and Devasahayam, G. (2020). Neurodegeneration by oxidative stress: a review on prospective use of small molecules for neuroprotection. Mol. Biol. Rep. 47, 3133–3140. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05354-1
Snyder, P. J., Bhasin, S., Cunningham, G. R., Matsumoto, A. M., Stephens-Shields, A. J., Cauley, J. A., et al. (2018). Lessons from the testosterone trials. Endocr. Rev. 39, 369–386. doi: 10.1210/er.2017-00234
Song, L., Yao, L., Zhang, L., Piao, Z., and Lu, Y. (2020). Schizandrol a protects against Aβ(1-42)-induced autophagy via activation of Pi3K/Akt/mtor pathway in Sh-Sy5Y cells and primary hippocampal neurons. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 393, 1739–1752. doi: 10.1007/s00210-019-01792-2
Soukhaklari, R., Moezi, L., Pirsalami, F., Ashjazadeh, N., and Moosavi, M. (2018). Curcumin ameliorates scopolamine-induced mice memory retrieval deficit and restores hippocampal p-Akt and p-Gsk-3β. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 841, 28–32. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.10.012
Soutar, M. P., Kim, W. Y., Williamson, R., Peggie, M., Hastie, C. J., Mclauchlan, H., et al. (2010). Evidence that glycogen synthase kinase-3 isoforms have distinct substrate preference in the brain. J. Neurochem. 115, 974–983. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06988.x
Stambolic, V., and Woodgett, J. R. (1994). Mitogen inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta in intact cells via serine 9 phosphorylation. Biochem. J. 303, 701–704. doi: 10.1042/bj3030701
Sundermann, E. E., Panizzon, M. S., Chen, X., Andrews, M., Galasko, D., and Banks, S. J. (2020). Sex differences in Alzheimer's-related tau biomarkers and a mediating effect of testosterone. Biol. Sex Differ. 11:33. doi: 10.1186/s13293-020-00310-x
Tan, Z., Chen, Y., Xie, W., Liu, X., Zhu, Y., and Zhu, Y. (2018). Nimodipine attenuates tau phosphorylation at Ser396 via miR-132/Gsk-3β pathway in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 819, 1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.10.027
Tang, M., and Taghibiglou, C. (2017). The mechanisms of action of curcumin in Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 58, 1003–1016. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170188
Tejeda-Muñoz, N., and De Robertis, E. M. (2022). Wnt, Gsk3, and macropinocytosis. Subcell. Biochem. 98, 169–187. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-94004-1_9
Thapa, R., Gupta, G., Bhat, A. A., Almalki, W. H., Alzarea, S. I., Kazmi, I., et al. (2023). A review of glycogen synthase Kinase-3 (Gsk3) inhibitors for cancers therapies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 253:127375. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127375
Themistokleous, C., Bagnoli, E., Parulekar, R., and Muqit, M. M. K. (2023). Role of autophagy pathway in Parkinson's disease and related genetic neurological disorders. J. Mol. Biol. 435:168144. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168144
Thota, R. N., Rosato, J. I., Dias, C. B., Burrows, T. L., Martins, R. N., and Garg, M. L. (2020). Dietary supplementation with curcumin reduce circulating levels of glycogen synthase kinase-3β and islet amyloid polypeptide in adults with high risk of type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer's disease. Nutrients 12, 1032–1043. doi: 10.3390/nu12041032
Tönnies, E., and Trushina, E. (2017). Oxidative stress, synaptic dysfunction, and Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 57, 1105–1121. doi: 10.3233/JAD-161088
Townsend, M., Mehta, T., and Selkoe, D. J. (2007). Soluble Abeta inhibits specific signal transduction cascades common to the insulin receptor pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 33305–33312. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M610390200
Uddin, M. S., Rahman, M. M., Jakaria, M., Rahman, M. S., Hossain, M. S., Islam, A., et al. (2020). Estrogen signaling in Alzheimer's disease: molecular insights and therapeutic targets for Alzheimer's dementia. Mol. Neurobiol. 57, 2654–2670. doi: 10.1007/s12035-020-01911-8
Wadhwa, P., Jain, P., and Jadhav, H. R. (2020). Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (Gsk3): its role and inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 20, 1522–1534. doi: 10.2174/1568026620666200516153136
Wang, Y., and Le, W. D. (2019). Autophagy and ubiquitin-proteasome system. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1206, 527–550. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-0602-4_25
Wang, H. B., Li, T., Ma, D. Z., and Zhi, H. (2018). Erα36 gene silencing promotes tau protein phosphorylation, inhibits cell proliferation, and induces apoptosis in human neuroblastoma Sh-Sy5Y cells. FASEB J. 2018:fj201701386. doi: 10.1096/fj.201701386
Wang, H., Li, Q., Sun, S., and Chen, S. (2020). Neuroprotective effects of Salidroside in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 40, 1133–1142. doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-00801-w
Wang, H., Sui, H., Zheng, Y., Jiang, Y., Shi, Y., Liang, J., et al. (2019). Curcumin-primed exosomes potently ameliorate cognitive function in ad mice by inhibiting hyperphosphorylation of the tau protein through the Akt/Gsk-3β pathway. Nanoscale 11, 7481–7496. doi: 10.1039/C9NR01255A
Wang, Y., Yang, R., Gu, J., Yin, X., Jin, N., Xie, S., et al. (2015). Cross talk between Pi3K-Akt-Gsk-3β and Pp2A pathways determines tau hyperphosphorylation. Neurobiol. Aging 36, 188–200. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.07.035
Wani, A., Gupta, M., Ahmad, M., Shah, A. M., Ahsan, A. U., Qazi, P. H., et al. (2019). Alborixin clears amyloid-β by inducing autophagy through Pten-mediated inhibition of the Akt pathway. Autophagy 15, 1810–1828. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1596476
Wei, G., Xu, X., Tong, H., Wang, X., Chen, Y., Ding, Y., et al. (2020). Salidroside inhibits platelet function and thrombus formation through Akt/Gsk3β signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 12, 8151–8166. doi: 10.18632/aging.103131
Wen, J., Fang, F., Guo, S. H., Zhang, Y., Peng, X. L., Sun, W. M., et al. (2018). Amyloid β-derived diffusible ligands (Addls) induce abnormal autophagy associated with Aβ aggregation degree. J. Mol. Neurosci. 64, 162–174. doi: 10.1007/s12031-017-1015-9
Xiong, Y., Ruan, Y. T., Zhao, J., Yang, Y. W., Chen, L. P., Mai, Y. R., et al. (2022). Magnesium-L-threonate exhibited a neuroprotective effect against oxidative stress damage in Ht22 cells and Alzheimer's disease mouse model. World J Psychiatry 12, 410–424. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i3.410
Yan, X., Hu, G., Yan, W., Chen, T., Yang, F., Zhang, X., et al. (2017). Ginsenoside Rd promotes non-amyloidogenic pathway of amyloid precursor protein processing by regulating phosphorylation of estrogen receptor alpha. Life Sci. 168, 16–23. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2016.11.002
Yang, Y., Liang, F., Gao, J., Dong, Y., Zhang, Y., Yang, G., et al. (2021). Testosterone attenuates sevoflurane-induced tau phosphorylation and cognitive impairment in neonatal male mice. Br. J. Anaesth. 127, 929–941. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2021.08.028
Yang, W., Liu, Y., Xu, Q. Q., Xian, Y. F., and Lin, Z. X. (2020). Sulforaphene ameliorates Neuroinflammation and Hyperphosphorylated tau protein via regulating the Pi3K/Akt/Gsk-3β pathway in experimental models of Alzheimer's disease. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020:4754195. doi: 10.1155/2020/4754195
Yang, Y., Wang, L., Zhang, C., Guo, Y., Li, J., Wu, C., et al. (2022). Ginsenoside Rg1 improves Alzheimer's disease by regulating oxidative stress, apoptosis, and neuroinflammation through Wnt/Gsk-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 99, 884–896. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.14041
Yang, J., and Zhang, C. (2023). Targeting the autophagy-lysosomal pathway in Huntington disease: a pharmacological perspective. Front. Aging Neurosci. 15:1175598. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1175598
Yi, J. H., Baek, S. J., Heo, S., Park, H. J., Kwon, H., Lee, S., et al. (2018). Direct pharmacological Akt activation rescues Alzheimer's disease like memory impairments and aberrant synaptic plasticity. Neuropharmacology 128, 282–292. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.10.028
Yin, G., Li, L. Y., Qu, M., Luo, H. B., Wang, J. Z., and Zhou, X. W. (2011). Upregulation of Akt attenuates amyloid-β-induced cell apoptosis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 25, 337–345. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-110104
Yokoyama, M., Kobayashi, H., Tatsumi, L., and Tomita, T. (2022). Mouse models of Alzheimer's disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 15:912995. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2022.912995
Yoshino, Y., and Ishioka, C. (2015). Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta induces apoptosis and mitotic catastrophe by disrupting centrosome regulation in cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 5:13249. doi: 10.1038/srep13249
Yuan, M., Wang, Y., Huang, Z., Jing, F., Qiao, P., Zou, Q., et al. (2022). Impaired autophagy in amyloid-beta pathology: a traditional review of recent Alzheimer's research. J. Biomed. Res. 37, 30–46. doi: 10.7555/JBR.36.20220145
Yuan, L., Yu, L., Zhang, J., Zhou, Z., Li, C., Zhou, B., et al. (2020). Long non-coding Rna H19 protects H9c2 cells against hypoxia-induced injury by activating the Pi3K/Akt and Erk/p38 pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 21, 1709–1716. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.10978
Zang, C., Liu, H., Shang, J., Yang, H., Wang, L., Sheng, C., et al. (2021). Gardenia jasminoides J. Ellis extract Gj-4 alleviated cognitive deficits of app/Ps1 transgenic mice. Phytomedicine 93:153780. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153780
Zeng, H., Huang, P., Wang, X., Wu, J., Wu, M., and Huang, J. (2015). Galangin-induced down-regulation of Bace1 by epigenetic mechanisms in Sh-Sy5Y cells. Neuroscience 294, 172–181. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.02.054
Zeng, Q., Li, L., Siu, W., Jin, Y., Cao, M., Li, W., et al. (2019). A combined molecular biology and network pharmacology approach to investigate the multi-target mechanisms of Chaihu Shugan san on Alzheimer's disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 120:109370. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109370
Zhang, G. Q., Chen, J. L., Luo, Y., Mathur, M. B., Anagnostis, P., Nurmatov, U., et al. (2021). Menopausal hormone therapy and women's health: An umbrella review. PLoS Med. 18:e1003731. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003731
Zhang, R., Deng, X., Liu, Q., Zhang, X., Bai, X., Weng, S., et al. (2023). Global research trends and hotspots of Pi3K/Akt signaling pathway in the field of osteoarthritis: a bibliometric study. Medicine (Baltimore) 102:e33489. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033489
Zhang, M., Huo, D. S., Cai, Z. P., Shao, G., Wang, H., Zhao, Z. Y., et al. (2015). The effect of Schizandrol A-induced Dna methylation on Sh-Sy5yab 1-40 altered neuronal cell line: a potential use in Alzheimer's disease. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 78, 1321–1327. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2015.1085942
Zhang, Z., Liu, H., Zhao, Z., Zang, C., Ju, C., Li, F., et al. (2020). Gj-4 alleviates Aβ(25-35)-induced memory dysfunction in mice through protecting the neurovascular unit. Biomed. Pharmacother. 127:110131. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110131
Zhang, Q. G., Wang, R., Khan, M., Mahesh, V., and Brann, D. W. (2008). Role of Dickkopf-1, an antagonist of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway, in estrogen-induced neuroprotection and attenuation of tau phosphorylation. J. Neurosci. 28, 8430–8441. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2752-08.2008
Zhang, B., Wang, Y., Li, H., Xiong, R., Zhao, Z., Chu, X., et al. (2016). Neuroprotective effects of salidroside through Pi3K/Akt pathway activation in Alzheimer's disease models. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 10, 1335–1343. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S99958
Zhang, X., Xie, L., Long, J., Xie, Q., Zheng, Y., Liu, K., et al. (2021). Salidroside: a review of its recent advances in synthetic pathways and pharmacological properties. Chem. Biol. Interact. 339:109268. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2020.109268
Zhang, Z., Yang, X., Song, Y. Q., and Tu, J. (2021). Autophagy in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis: therapeutic potential and future perspectives. Ageing Res. Rev. 72:101464. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2021.101464
Zheng, H., Jia, L., Liu, C. C., Rong, Z., Zhong, L., Yang, L., et al. (2017). Trem2 promotes microglial survival by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J. Neurosci. 37, 1772–1784. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2459-16.2017
Zheng, M., Liu, Z., Mana, L., Qin, G., Huang, S., Gong, Z., et al. (2021). Shenzhiling oral liquid protects the myelin sheath against Alzheimer's disease through the Pi3K/Akt-mtor pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 278:114264. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114264
Zhong, Z., Han, J., Zhang, J., Xiao, Q., Hu, J., and Chen, L. (2018). Pharmacological activities, mechanisms of action, and safety of salidroside in the central nervous system. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 12, 1479–1489. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S160776
Zhong, S. J., Wang, L., Gu, R. Z., Zhang, W. H., Lan, R., and Qin, X. Y. (2020). Ginsenoside Rg1 ameliorates the cognitive deficits in D-galactose and AlCl(3)-induced aging mice by restoring Fgf2-Akt and Bdnf-TrkB signaling axis to inhibit apoptosis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 17, 1048–1055. doi: 10.7150/ijms.43979
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, PI3K, tau protein, amyloid-β, Akt, GSK3
Citation: Pan J, Yao Q, Wang Y, Chang S, Li C, Wu Y, Shen J and Yang R (2024) The role of PI3K signaling pathway in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 16:1459025. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1459025
Edited by:
Jianhua Shi, Harvard Medical School, United StatesReviewed by:
Ravinder Gulia, University of California, Irvine, United StatesKarina Hernández Ortega, National Autonomous University of Mexico, Mexico
Copyright © 2024 Pan, Yao, Wang, Chang, Li, Wu, Shen and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianhong Shen, dHlzamhAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Riyun Yang, eWFuZ3JpeXVueXhAMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Jingying Pan
Jingying Pan Qi Yao
Qi Yao Yankai Wang
Yankai Wang Suyan Chang1
Suyan Chang1 Yongjiang Wu
Yongjiang Wu Riyun Yang
Riyun Yang