
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Aging Neurosci., 12 February 2025
Sec. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Brain-aging
Volume 16 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2024.1454735
This article is part of the Research TopicTargeting the Aging Mitochondria: Mechanisms, Methods, and Therapeutic StrategiesView all 5 articles
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α (PGC-1α), which is highly expressed in the central nervous system, is known to be involved in the regulation of mitochondrial biosynthesis, metabolic regulation, neuroinflammation, autophagy, and oxidative stress. This knowledge indicates a potential role of PGC-1α in a wide range of functions associated with neurological diseases. There is emerging evidence indicating a protective role of PGC-1α in the pathogenesis of several neurological diseases. As such, a deeper and broader understanding of PGC-1α and its role in neurological diseases is urgently needed. The present review provides a relatively complete overview of the current knowledge on PGC-1α, including its functions in different types of neurons, basic structural characteristics, and its interacting transcription factors. Furthermore, we present the role of PGC-1α in the pathogenesis of various neurological diseases, such as intracerebral hemorrhage, ischemic stroke, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Huntington’s disease, and other PolyQ diseases. Importantly, we discuss some compounds or drug-targeting strategies that have been studied to ameliorate the pathology of these neurological diseases and introduce the possible mechanistic pathways. Based on the available studies, we propose that targeting PGC-1α could serve as a promising novel therapeutic strategy for one or more neurological diseases.
Mitochondria are vital organelles of eukaryotic cells that contain their own DNA.
In addition to ATP production, mitochondria play a crucial role in signaling and regulation across various pathways. Among these, calcium signaling stands out as a key mechanism through which mitochondria can regulate several cellular processes (Nunnari and Suomalainen, 2012). Mitochondrial biogenesis depends on the coordination between nuclear and mitochondrial DNA. The PPARγ coactivator-1 family (PGC-1) of transcription coactivators, including sirtuins and AMPK, is involved in regulating gene expression during mitochondrial biogenesis, as are mitochondrial transcription factor A (TFAM) and nuclear respiratory factors 1 and 2 (NRF1 and NRF2).
Neurons are high energy-demanding cells that require a tight regulation of Ca2+ to maintain their action potentials. Mitochondrial disorders have been reported in many neurological diseases. However, the exact mechanisms underlying the mitochondrial dysfunction vary between diseases. PGC-1α is conserved in eukaryotes and is particularly highly expressed in high-energy-consuming tissues and organs, such as brown adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, heart, liver, and brain. As a significant upstream molecule and downstream target of many vital pathways, PGC-1α is involved in the sophisticated crosstalk between neurons. In addition to acting as a master regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis (Jornayvaz and Shulman, 2010; Fan et al., 2024), PGC-1α also combats oxidative stress in neurons (Kong et al., 2010; Wang D. et al., 2022), protects against neuroinflammation (Ayasolla et al., 2005; Sun et al., 2024), functions as an upstream activator of neuro-autophagy (Tsunemi et al., 2012), and suppresses neuro-apoptosis (Wu et al., 2018). This review summarizes the current knowledge regarding the functions of PGC-1α in the brain and its role in neurological diseases, such as intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), ischemic stroke, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and Polyglutamine (PolyQ) diseases. We hope that this review will facilitate future exploration of neurological diseases and promote the possible use of PGC-1α agonists/inhibitors as a new therapeutic strategy.
PGC-1α is abundant in the brain, particularly in the cerebral cortex, striatum, globus pallidus, and substantia nigra (SN), whereas it is absent in the hypothalamus (Tritos et al., 2003). The abnormal distribution of PGC-1α in the central nervous system, to some extent, explains its diverse roles in the physiological functions of different cell types (Figure 1).
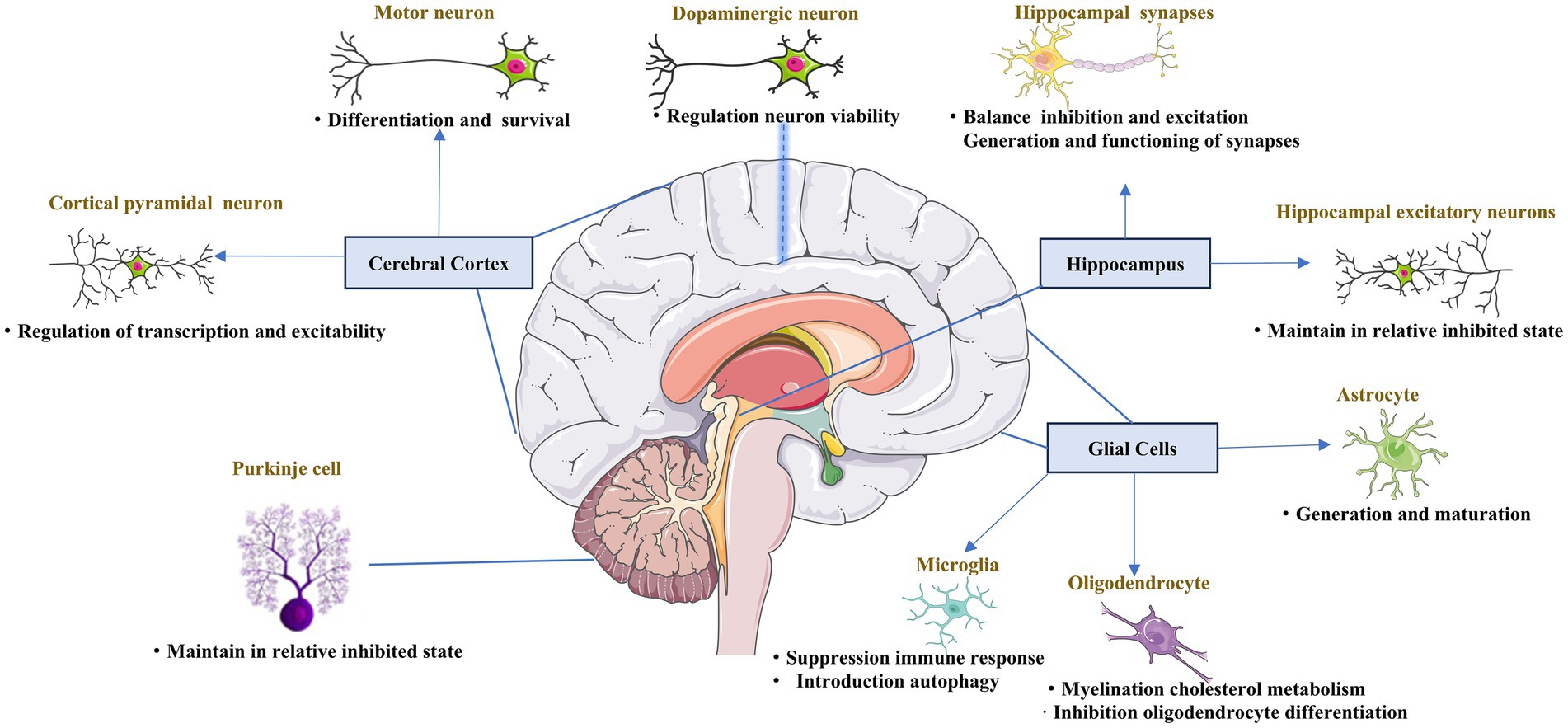
Figure 1. Role of PGC-1α in the central nervous system. The key role of PGC-1α in the maturation, differentiation, functioning, and survival of different neuron types across the central nervous system.
PGC-1α expression is enriched in GABAergic interneurons expressing parvalbumin and glutamatergic projection neurons, particularly those located in the cortical pyramidal layer V, which contains both inhibitory and excitatory neurons (Cowell et al., 2007; Lucas et al., 2010). Both glutamatergic and fast-spiking interneuron populations depend on PGC-1α. In neocortical and hippocampal excitatory neurons, PGC-1α was shown to impair calcium homeostasis, increase ROS levels, and maintain cells in a relatively inhibited state to balance the inhibition and excitation, as the deletion of PGC-1α from neocortical and hippocampal excitatory neurons caused enhanced glutamatergic transmission in the neocortex and hippocampus (McMeekin et al., 2020). Motor neurons abundantly express PGC-1α. And increasing in PGC-1α mRNA are accompanied by voltage-gated currents characteristic of excitable cells and action potential formation when differentiating human embryonic stem cells or human neural stem cells into motor neurons (O'Brien et al., 2015). Moreover, the survival of motor neurons was also found to increase after treatment with lactate to induce CNS-specific PGC-1α (Bayer et al., 2017). Furthermore, the function of PGC-1α in motor neurons was also verified in studies of ALS (Bayer et al., 2017; Mehta et al., 2021). Together, these results indicate that PGC-1α is vital for the differentiation and function of motor neurons in the cerebral cortex.
PGC-1α has heterogeneous functions in different nerve cells. Interneurons function to connect different types of CNS neurons, forming key nodes within brain neural circuitry. PGC-1α localizes in the nuclei of GABAergic interneurons, which form inhibitory synapses (Cowell et al., 2007). One study revealed that PGC-1α regulated inhibitory signaling via the control of the Ca2+–binding protein parvalbumin (Lucas et al., 2010), and the balance between inhibition and excitation of synapses in the hippocampus was also suggested to depend on sufficient levels of PGC-1α (Bartley et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2020). Moreover, PGC-1α upregulated the GABARα2 subunit in the hippocampus and frontal cortex, causing anxiety-like changes in the behavior of the mice (Vanaveski et al., 2021). Inhibitory signaling related to PGC-1α was also detected in Purkinje cells, the projection neurons in the cerebellum (Rosin et al., 2015). All these results demonstrate the essential function of PGC-1α in inhibitory signaling in the brain.
Dopaminergic neurons are localized in the midbrain. PGC-1α is essential for the proper functioning of dopaminergic neurons, and is involved in the regulation of their viability. Researchers found that PGC-1α-knockout adult mice lost dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra (Jiang et al., 2016). Further, in the presence of overexpressed α-synuclein, dopaminergic neurons lacking PGC-1α were more predisposed to degradation (Ciron et al., 2015). A few studies further showed that growth factors interact with PGC-1α to regulate its function via mitochondrial biogenesis, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation (Makela et al., 2014; Selvakumar et al., 2018; Fang et al., 2020). Several studies reported that PGC-1α was disadvantageous to dopaminergic neurons, as it might lead to developmental failures and the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons (Ciron et al., 2012; Clark et al., 2012). Together, the above information suggests that the levels of PGC-1α play a decisive role in whether it exerts protective or destructive effects.
Synapses are vital for ensuring the nutritional requirements of neurons, particularly in mitochondrial transport. PGC-1α is also engaged in the process of synaptogenesis, with research showing that PGC-1α is involved in the development of dendritic spines and the formation of synaptic connections in the brain (Cheng et al., 2012). PGC-1α also influences the postnatal functioning of synapses, preserving hippocampal synapses, and promoting the postnatal generation of excitatory synapses of astrocytes (Cheng et al., 2012; Zehnder et al., 2021). Furthermore, PGC-1α regulates neurotransmitter release via control of the expression of the calcium sensors synaptotagmin 2 and complexin 1 (Lucas et al., 2014). Thus, PGC-1α is considered essential for the generation and functioning of synapses.
Decrease in the level of PGC-1α was detected in regions affected by spinal cord injuries (SCI) compared to healthy tissue, suggesting that PGC-1α may be involved in the physiological functioning of the spinal cord (Hu et al., 2015). PGC-1α overexpression was found to decrease apoptosis in spinal cord neurons after SCI (Hu et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2017). Further studies in ALS mice showed that body-wide overexpression of PGC-1α decreased the degeneration of neuromuscular junctions (Liang et al., 2011). Activating PGC-1α ameliorated ischemic brain injury via PPARα-GOT1 axis by reducing the pyroptosis of endothelial cells, which was also reported (Wang et al., 2021). Microglial PGC-1α was found to be a promising therapeutic target for acute ischemic stroke by promoting autophagy and mitophagy through ULK1 and reducing NLRP3 activation (Han et al., 2021). Overall, these results suggest that PGC-1α may protect against spinal cord neuron failure, which is associated with the pathogenesis of many diseases, including ALS and stroke.
The most well-known function of glia in adults is controlling the formation of myelin sheaths around axons, which allows for the rapid conduction of signals essential for nervous system function (Jessen, 2004; Ludwig and Das, 2022). Glia also maintains appropriate concentrations of ions and neurotransmitters in the neuronal environment. There is an increasing body of evidence to indicate that glial cells also function as essential regulators of the formation, maintenance, and function of synapses, which are the key functional units of the nervous system (Hughes, 2021). The primary glial cell types in the CNS are astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Astrocytes in the CNS regulate synapse formation and maintain the efficacy of synapses. PGC-1α was suggested to be important for the maturation of astrocytes (Zehnder et al., 2021). In neuronal models constructed from differentiated iPSCs, the activation of mitochondrial biogenesis was linked to upregulation of PGC-1α and the neuronal to glial fate decision switch (Augustyniak et al., 2019). Research further showed that deletion of PGC-1α resulted in the extended proliferation and hindered astrocyte morphogenesis (Zehnder et al., 2021). The central function of oligodendrocytes is to generate myelin, which is an extended membrane from the cell that wraps tightly around axons. Indeed, research reported that there is a considerable increase in PGC-1α during myelination in rat brain (Cowell et al., 2007). PGC-1α also plays several roles in myelination by regulating MBP expression and cholesterol metabolism in oligodendrocytes (Xiang et al., 2011). Activation of PGC-1α by exercise has been shown to be linked to the enhancement of myelin thickness (Jensen et al., 2018). In one in vitro study, PGC-1α was shown to be involved in the protection of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs) under inflammatory conditions.
As a transcriptional coactivator, PGC-1α contains several domains with various functions. PGC-1 coactivators exert their transcriptional regulatory function by binding to a variety of transcription factors and nuclear receptors that recognize specific sequences on target genes (Villena, 2015). The amino-terminal region of PGC-1α contains a highly conserved activation domain that serves as a surface for the recruitment of histone acetyltransferase proteins. This domain also contains several leucine-rich LXXL motifs, also termed NR boxes, which drive a coactivator signature essential for interactions with multiple types of other transcription factors and nuclear receptors (Monsalve et al., 2000). The carboxy-terminal contains a well-conserved RNA recognition motif (RRM), which is involved in the binding of both RNA and single-stranded DNA. Short serine/arginine-rich stretches, called RS domains, are also located at the N-terminal of the RRM motif in PGC-1α (Monsalve et al., 2000), and they play an important role in mRNA splicing, although their role in disease is unclear. The C-terminal region of PGC-1α also has a binding site for host cell factor (HCF), also known as DHDY, which synergizes with HCF to regulate the cell cycle and enhance the transcriptional activity of PGC-1α (Lin et al., 2002). Finally, several binding sites for other coregulators, including MEF-2C, yin yang-1 (YY1), PPARγ, forkhead box O1 (FoxO1), mediator complex subunit 1 (MED1), and BRG1-associated factor 60a, are also located in the C-terminal region of PGC-1α (Villena, 2015; Ma et al., 2018; Xin et al., 2018). The intermediate connector is a multiunit complex that is required for transcription (Figure 2).

Figure 2. Structure of PGC-1α. The amino-terminal region of PGC-1α functions as the surface for the recruitment of histone acyltransferase proteins. This domain contains several LXXL motifs (NR boxes), acting as coactivator signature essential for interactions with multiple types of other transcription factors and nuclear receptors. The carboxy-terminal contains RRM, which act as binding site of RNA and single-stranded DNA. The binding site for host cell factor, DHDY, synergizes with HCF to regulate the cell cycle and enhance the transcriptional activity of PGC-1α. Another RS domain plays an important role in mRNA splicing.
Neurons are high-energy-demanding cells, whereas PGC-1α is abundantly expressed in the CNS. Many studies of the role of PGC-1α in neurological diseases, such as ICH, ischemic stroke, AD, PD, ALS and PolyQ diseases, have been conducted. The main pathogenesis of these disorders included mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, autophagy, etc. (Figure 3). Therefore, we review the main roles and pathways of PGC-1α in neurological diseases below.
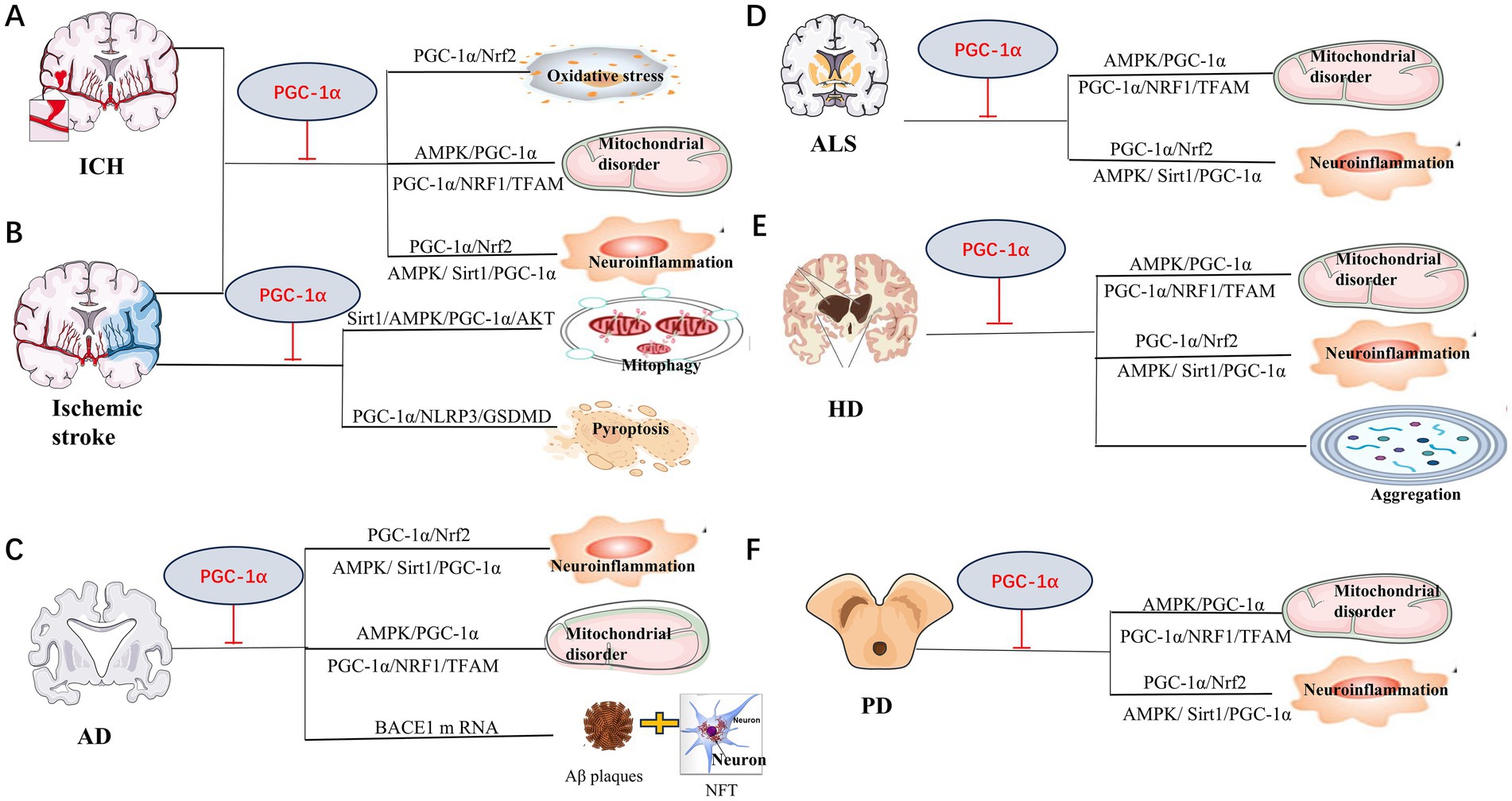
Figure 3. Mechanisms of PGC-1α involved in neurological diseases. Mitochondrial disorder, neuroinflammation and oxidative stress are the main pathway for PGC-1α amelioration of neurological disorders in Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) (A), ischemic stroke (B), Alzheimer’s disease (AD) (C), Huntington disease (HD) (D), Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) (E) and Parkinson’s disease (PD) (F). Repair of mitochondria mediated by PGC-1α plays a crucial role in the protection against ICH injury. Recent study also demonstrated that pyroptosis was another vital process for ischemic stroke. Study suggest that PGC-1α preventing ischemic stroke via reducing pyroptosis. PGC-1α could also suppress BACE1 mRNA, which is important for generation of Aβ, to protect AD. In HD, PGC-1α was also found to decrease aberrant aggregation and turnover of mutant HTT. The specific pathways as shown.
Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) is a life-threatening disease of global importance, with poor prognosis and few efficient treatment options (Cordonnier et al., 2018). Previous reports indicate that the mortality rate among ICH patients is approximately 40% within one month (van Asch et al., 2010). ICH accounts for 10–30% of all strokes, affecting more than one million people every year worldwide (Feigin et al., 2003). The pathology of ICH involves mechanical disruption following initial bleeding and oxidative stress, inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neuronal death (Aronowski and Zhao, 2011; Yu et al., 2019). Abundant evidence supports the hypothesis that mitochondrial dysfunction occurs after ICH (Wu et al., 2020; Li et al., 2021), which is reportedly linked with both structural and functional disorders (Zhou et al., 2017; Xu et al., 2019). By injecting autologous arterial blood into rat brains, researchers found that the level of PGC-1α increases significantly at 1 h after ICH injury, reaching a peak at 72 h (You et al., 2016). Studies in an ICH rat model showed that treatment with PGC-1α siRNAs significantly decreased ATP concentration, the number of mitochondria, mitochondrial proteins, and mitochondrial DNA, increased brain water content, and led to the formation of mitochondrial myelin layer structures (Zhou et al., 2017). The activation or overexpression of PGC-1α after ICH injury promoted mitochondrial biogenesis and mitochondrial-related ROS metabolism, reduced mitochondrial dysfunction, inhibited mitochondrial-dependent cell death, and prevented the further occurrence of secondary brain injury (You et al., 2016; Zhou et al., 2017; Jin et al., 2022). Further studies showed that PGC-1α alleviated mitochondrial dysfunction and secondary brain injury following ICH via AMPK- PGC-1α pathway (Yu et al., 2019). Studies in recent years also demonstrated that PGC-1α involvement in mitochondrial biogenesis and antioxidative capability is protective for mice following ICH (Zhang et al., 2024).
More than 80% of strokes are ischemic and caused by an occlusion of cerebral arteries (Lapchak and Zhang, 2017). Lack of blood supply results in neurons being deprived of necessary glucose and oxygen (OGD), which finally triggers pathophysiological processes including excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, and cell death. Though the introduction of tissue plasminogen activator for the acute treatment of ischemic was achieved (Yoshimura et al., 2018), development of neuroprotective agents for treating ischemia outside of the current narrow therapeutic window is still much more vital. There is significant experimental evidence supporting the roles of mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress as determinants of neuronal death, as well as endogenous protective mechanisms after stroke (St-Pierre et al., 2006; Yin et al., 2008; Chen et al., 2010). Several studies reveal that PGC1-α contributes to neuronal survival (St-Pierre et al., 2006; Chen et al., 2011). ROS plays a crucial role in the fate of neurons, as well as in damage progression following ischemic stroke (Mattiasson et al., 2003). PGC-1α is a master regulator of the mitochondrial proteins SOD2 and UCP2. UCP2 and SOD2 are vital ROS-detoxifying proteins found in mitochondria. Studies revealed that the upregulation of UCP2 decreases ROS and neuronal loss in the brain tissue after cerebral ischemia (Mattiasson et al., 2003; Chen et al., 2006; Deierborg et al., 2008). All the above information demonstrates that PGC1-α protects neurons from ischemic stroke by improving mitochondrial function. Advances in neuroscience have prompted further exploration of the mechanisms by which PGC-1α provides protection. Pyroptosis, a type of programmed cell death has been demonstrated to be involved in ischemic stroke in recent years (Zhang et al., 2019). And, study found that medioresinol, a PGC-1α activator, ameliorated the pyroptosis of endothelial cells and ischemic brain injury via PPARα-GOT1 axis (Wang et al., 2021). Neferine, a bisbenzylisoquinoline alkaloids extracted from Plumula Nelumbinis.
was also found to benefit ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting pyroptosis, reducing mitochondrial oxidative stress, ameliorates endothelial inflammation via regulation of PGC-1α/NLRP3/GSDMD signaling pathway (Zheng et al., 2024). Mitophagy, which is beneficial in ischemic stroke, was also triggered by USP18/FTO via the SIRT6/AMPK/PGC-1α/AKT pathway in recent studies (Song et al., 2024). Studies have revealed that neuroinflammation and immune responses occur minutes to hours after stroke (Fu et al., 2015). PGC-1α in microglia could also protect against the ischemic brain injury by suppressing neuroinflammation (Wang et al., 2018; Han et al., 2021). Further, changes in the level of PGC-1α after stroke are reported for decades (Valerio et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2014). Therefore, targeting PGC-1α is a promising therapeutic strategy for ischemic stroke. Compounds and drugs targeting PGC-1α that have been explored for improving ischemic stroke in past decades are also collected (Table 1).
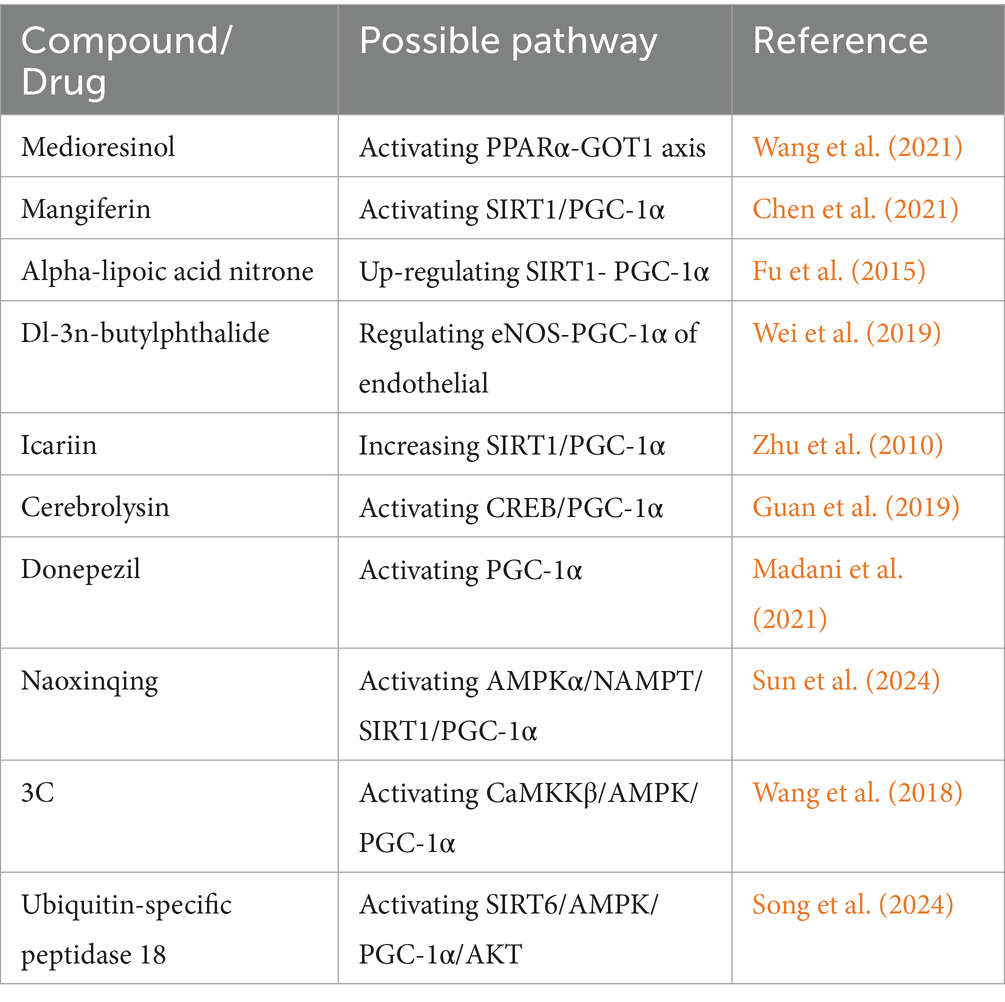
Table 1. Compounds and drugs which have been found to improve ischemic stroke in past decade studies.
Close to 50 million people worldwide are currently suffering from dementia, including AD, whose prevalence is estimated to surpass 100 million by 2050. AD, a progressive neurodegenerative disease, is the most common form of dementia (Blennow et al., 2006; Alzheimer's Association, 2016). Age, family history, apolipoprotein E ɛ4 genotype, hypertension, obesity, diabetes, traumatic brain injury, hyperlipidemia, and low education level are all considered risk factors for AD (Blennow et al., 2006; Alzheimer's Association, 2016). Synaptic dysfunction, neurotransmitter imbalance, neuroinflammation, infection, gut microbiome disruption, genetic mutations, oxidative stress, and autophagy are all potential pathogenic factors influencing AD (Crews and Masliah, 2010; Barage and Sonawane, 2015; Ferreira-Vieira et al., 2016; De-Paula et al., 2018; Giau et al., 2018; Ashraf et al., 2019; Khan et al., 2020). Aggregation of Aβ peptides in neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) of hyperphosphorylated Tau protein are pathological features of AD (Amemori et al., 2015). Generation of Aβ depends on the sequential proteolytic cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP) by β-secretase 1 (BACE1) and the γ-secretase complex (Hardy and Selkoe, 2002). APP/PS1 mutated mice are classical models for AD investigation, with research showing that enhanced PGC-1α mRNA levels caused by decreased function of PS1 may be involved in the pathogenesis of this research model (Robinson et al., 2014). Given that BACE1 is the rate-limiting enzyme in Aβ generation and APP processing, it is suggested to be one of the most important therapeutic targets for treating AD. PGC-1α is shown to decrease in the brains of AD patients (Zehnder et al., 2021). Studies revealed that overexpression of PGC-1α suppressed the basal transcription of endogenous BACE1 mRNA (Wang et al., 2013),which further explains the phenomenon that levels of PGC-1α protein are inversely linked to both AD-type neuritic plaque abnormalities and Aβ content (Pohland et al., 2018). Further research showed that the effect of PGC-1 on BACE1 requires deacetylation by SIRT1 (Wang et al., 2013), and it has also been demonstrated that metabolic stress modulates Alzheimer’s β-secretase gene transcription via action on the SIRT1-PPARγ-PGC-1 pathway. Mitochondrial dysfunction is a pivotal event in AD pathogenesis (Panes et al., 2020). Repairment of mitophagy and mitochondrial biogenesis ameliorated AD via PINK1/LC3B/P62 and PGC-1α/Nrf2 in one study of Lithospermic acid B (Meng et al., 2024). SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling pathway, which reduces oxidative stress, was also found to attenuate cognitive deficits in Alzheimer’s disease (Liu et al., 2023). Neuroinflammation is also known to influence Aβ plaques and NFT. Indeed, many studies support the idea that Aβ plaques and neuroinflammation form a positive feedback loop in AD (Doig, 2018). One study found that resveratrol (RSV) reduced inflammatory cytokine release, improved mitochondrial bioenergetics, and ameliorated Aβ-peptide clearance by activating SIRT1 and AMPK (Price et al., 2012). The latter functions in the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α pathway, a canonical signaling cascade influencing cell survival (Tian et al., 2019; Zhang and Wu, 2021). PGC-1α as the media of regulation mitochondrial biogenesis, mitophagy, neuroinflammation and Aβ generation involved in the pathogenesis and neuroprotection of AD.
PD is one of the most common neurodegenerative disorders worldwide, and the number of people suffering from this disorder has more than doubled in the last 30 years. The pathological features of PD include the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons (Meara, 1994). The possible pathophysiologic mechanisms underlying PD include α-synuclein misfolding and aggregation, mitochondrial dysfunction, impairment of protein clearance, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress (Jankovic and Tan, 2020). The involvement of mitochondrial disorders in PD was first established more than three decades ago. In 1983, researchers found that the administration of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) led to parkinsonism in both animal models and humans through metabolite ion MPP+ activation and the subsequent inhibition of multiple complexes of the respiratory chain (Langston and Ballard, 1983; Schapira et al., 1989; Grunewald et al., 2019). Subsequent research achieved significant progress regarding the elucidation of the monogenic causes of PD associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. These genes include SNCA (Polymeropoulos et al., 1997), LRRK2 (Paisan-Ruiz et al., 2004), VPS35 (Tang et al., 2015), CHCHD2 (Funayama et al., 2015), Parkin, PINK1, and DJ-1. Another study of MPTP found that LSN862 (LSN), a novel non-thiazolidinedione partial PPAR- γ agonist, exerted neuroprotective effects in a mouse model of PD by increasing PPAR- γ and PGC1-α expression (Swanson et al., 2013). AMPK/SIRT-1/PGC-1α-mediated autophagy (Lee et al., 2023; Elesawy et al., 2024), mitochondrial biogenesis (Liu et al., 2022; Jhuo et al., 2024) PGC-1α/Nrf mediated oxidative stress (Guo et al., 2023) were all classical pathway in PD. Research further identified many molecules and drugs that can ameliorate PD (Table 2). For example, findings in a 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-lesioned rat model of PD revealed that ferulic acid reduced mitochondrial Drp1 and increased PGC1α, restoring mitochondrial dynamics in lesioned animals (Anis et al., 2020). PGC-1α also protects neurons in PD from neuroinflammation (Mohammed et al., 2024). Previous work also found that L. plantarum DP189 activated the (Nrf2)/ARE and PGC-1α pathways and suppressed the NLRP3 inflammasome in PD mice (Wang L. et al., 2022). To date, the study of mitochondria dysfunction and the methods to reverse this disorder play major role in the field of PD research. Moreover, additional studies on other physiological processes of PD are also needed.
ALS is a fatal neurodegenerative disease. As a rare and poorly characterized disorder, it is difficult to diagnose. The lifetime risk of ALS is high, with approximately 1 in 350 people ultimately developing the disease, although limited life expectancy reduces the prevalence (Ryan et al., 2019). As a combination disorder of upper and lower motor neurons, ALS presents as progressive weakness of the voluntary skeletal muscles involved in limb movement, swallowing (dysphagia), speaking (dysarthria), and respiratory function, with heterogeneous clinical presentations. Unlike other neurodegenerative diseases, the pathogenesis of ALS remains ambiguous, and the pathogenic genes are complex. Although the frequency of genetic subtypes does vary by race, the most common mutations are found in C9orf72, TARDBP, SOD1, and FUS (Smith et al., 2013). Studies support the hypothesis that impaired RNA metabolism, altered proteostasis, autophagy, trafficking defects, and mitochondrial dysfunction are the primary pathological processes underlying ALS (Nguyen et al., 2018). As an indispensable molecule for cells, PGC-1α is decreased in the CNS due to mutations in SOD1 and FUS/TLS in two mouse models of familial ALS (Thau et al., 2012; Bayer et al., 2017). Lactate-induced CNS-specific PGC-1α pathway activation was also completely absent in ALS patient-derived motoneurons with two different frame-shift FUS/TLS mutations (Bayer et al., 2017). PGC-1α was also considered a male-dominant disease modifier of ALS (Eschbach et al., 2013). Increasing mitochondrial mass through PGC-1α over-expression led to protection against ALS neurodegeneration as shown (Varghese et al., 2020). Research in the SOD1G93A ALS mouse model showed that activation of PGC-1α/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway increased mitochondrial antioxidant activity and decreased expression of human SOD1 (Wen et al., 2021), one pathogenic protein of ALS. AMPK/PGC-1α/Nrf1/Tfam activation promotes mitochondrial biogenesis and ameliorates mitochondrial dysfunction, which was also verified in SOD1G93A mice. Indeed, numerous studies have identified several molecules/drugs which can treat ALS by modulating the PGC-1α pathway (Table 3), which offers a promising prospect for targeting PGC-1α as effective treatment strategies.
HD is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disease caused by the expansion of CAG repeats in the first exon of the HTT gene, encoding a mutant Huntington (mHTT) protein (Leavitt et al., 2020). HD is characterized by atrophy of the basal ganglia nuclei and subcortical white matter, and its associated symptoms include motor, psychiatric, and cognitive deficits, which generally present in middle age and are gradually progressive (Tabrizi et al., 2019). There is still no effective treatment for HD. A toxic gain-of-function of the mHTT protein, caused by expanded PolyQ, has been proposed as a driving factor in HD, which functions by leading to neuronal loss. The mechanisms underlying the disease are complex, including deregulation of the ubiquitin, proteasome, and autophagy systems, as well as oxidative stress (Jimenez-Sanchez et al., 2017). Recently, mitochondrial dysfunction was identified as a key contributor to HD pathology (Kumar and Ratan, 2016; van Well et al., 2019; Jurcau and Jurcau, 2023). Studies in HD animal models and the striatal tissues of patients have shown that transcriptional dysregulation of PGC-1α is involved in the neurodegeneration of HD (Weydt et al., 2009; La Spada, 2012). Transcription and mitochondrial dysfunction caused by alteration in PGC-1α were also documented in HD (Weydt et al., 2006). Though most studies support that energy failure is involved in the role of PGC-1α disorder in HD, disruption of ribosomal transcription by PGC-1α was also identified in HD (Jesse et al., 2017). On the other hand, the role of CREB in the regulation of PGC-1α in neurons in response to oxidative stress was studied (St-Pierre et al., 2006). PGC-1α promoter binding with less HSF1 in a cell culture model of HD demonstrated the destruction of the heat shock response in HD (Intihar et al., 2019). Less activation of HSF1 in this model exacerbates cell death (Intihar et al., 2019). The role of PGC-1α in the pathogenesis of HD was further verified by PGC-1α KO models emulating the main characteristics of HD (Lin et al., 2004; Jesse et al., 2017). Crossing N171-82Q HD transgenic mice with inducible TRE-PGC-1α mice decreased aberrant aggregation and turnover of mutant HTT, mitigated striatal neurodegeneration, and improved mitochondrial dysfunction observed in HD mice (Tsunemi et al., 2012). Several drugs and compounds ameliorating the phenotype of HD via regulating PGC-1α have also been identified in recent decades (Table 4).
Spinocerebellar ataxia 3 (SCA3), which is one of the nine identified PolyQ diseases, is a rare, inherited neurodegenerative disease. As the second most prevalent disease in the PolyQ group, SCA3 affects about 1–5 in every 100,000 people globally (Li et al., 2018). Mitochondrial dysfunction, metabolic abnormalities, autophagy and oxidative stress have been shown to be involved in the pathogenesis of SCA3. As a vital molecule controlling mitochondrial biogenesis, PGC-1α has also been demonstrated to ameliorate SCA3. Glycyrrhiza inflata herb extract and its constituents, licochalcone A and ammonium glycyrrhizinate, increased mitochondrial biogenesis, decreased oxidative stress, and reduced aggregate formation in SCA3 cellular models via the activation of PGC-1α and NRF2-ARE (Chen et al., 2014). Further, SG-Tang has been proven to exert protective effects against SCA17, another PolyQ disease characterized by progressive ataxia, seizures, cognitive dysfunction, psychiatric symptoms, and pyramidal/extrapyramidal signs via upregulating the PGC-1α/SOD2/CYCS, NRF2/GCLC/NQO1, and NFYA/HSPA5 pathways (Chen et al., 2019). Although studies of PGC-1α in other PolyQ diseases are limited, research in this field is ongoing and has yet to be fully explored.
Neurological diseases are the leading cause of disability and the second leading cause of death worldwide. With population aging, the number of patients suffering from neurological disease is rising. While stroke remains the most common neurological disease, morbidity related to neurodegenerative diseases, such as AD and PD, is becoming increasingly common. The incidences of hereditary neurological diseases, like HD, SCA (SCA1, SCA2, SCA3, SCA7, SCA36, etc) are also increasing year by year. Reducing morbidity and increasing effective therapeutic strategies for neurological disorders are therefore urgently needed.
In this review, we highlight the role of PGC-1α in the nervous system and neurological diseases such as stroke, AD, PD, ALS, and PolyQ diseases. A review of the existing literature suggests that PGC-1α overexpression could be a potential therapeutic target for these types of diseases. However, almost all studies upregulated PGC-1α via gene transfection and compound drugs in vitro or in vivo animal models. Whether PGC-1α supplementation and which compounds could open promising avenues for neuroprotective therapeutics among neurological diseases, or even within a specific neurological disease, merits further rigorous preclinical studies and decisive evaluation through clinical trials.
M-bT: Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Y-xL: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Methodology. Z-wH: Methodology, Writing – original draft. H-yL: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. SZ: Methodology, Writing – original draft. C-hS: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. Y-mX: Investigation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This review was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 82101491 to Mi-bo Tang) and the Henan Province Science and Technology Innovation Talent Program (Grant LHGJ 20210296 to Mi-bo Tang).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Alzheimer's Association (2016). 2016 Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement 12, 459–509. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2016.03.001
Amemori, T., Jendelova, P., Ruzicka, J., Urdzikova, L. M., and Sykova, E. (2015). Alzheimer's disease: mechanism and approach to cell therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 16, 26417–26451. doi: 10.3390/ijms161125961
Anis, E., Zafeer, M. F., Firdaus, F., Islam, S. N., Anees, K. A., Ali, A., et al. (2020). Ferulic acid reinstates mitochondrial dynamics through PGC1alpha expression modulation in 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned rats. Phytother. Res. 34, 214–226. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6523
Aronowski, J., and Zhao, X. (2011). Molecular pathophysiology of cerebral hemorrhage: secondary brain injury. Stroke 42, 1781–1786. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.596718
Ashraf, G. M., Tarasov, V. V., Makhmutovsmall, A., Chubarev, V. N., Avila-Rodriguez, M., and Bachurin, S. O. (2019). The possibility of an infectious Etiology of Alzheimer disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 56, 4479–4491. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1388-y
Augustyniak, J., Lenart, J., Gaj, P., Kolanowska, M., Jazdzewski, K., Stepien, P. P., et al. (2019). Bezafibrate upregulates mitochondrial biogenesis and influence neural differentiation of human-induced pluripotent stem cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 56, 4346–4363. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1368-2
Ayasolla, K. R., Singh, A. K., and Singh, I. (2005). 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-4-ribofuranoside (AICAR) attenuates the expression of LPS- and Abeta peptide-induced inflammatory mediators in astroglia. J. Neuroinflamm. 2:21. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-2-21
Barage, S. H., and Sonawane, K. D. (2015). Amyloid cascade hypothesis: pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropeptides 52, 1–18. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2015.06.008
Bartley, A. F., Lucas, E. K., Brady, L. J., Li, Q., Hablitz, J. J., Cowell, R. M., et al. (2015). Interneuron transcriptional dysregulation causes frequency-dependent alterations in the balance of inhibition and excitation in hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 35, 15276–15290. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1834-15.2015
Bayer, H., Lang, K., Buck, E., Higelin, J., Barteczko, L., Pasquarelli, N., et al. (2017). ALS-causing mutations differentially affect PGC-1alpha expression and function in the brain vs. peripheral tissues. Neurobiol. Dis. 97, 36–45. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2016.11.001
Blennow, K., de Leon, M. J., and Zetterberg, H. (2006). Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 368, 387–403. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(06)69113-7
Chandra, A., Sharma, A., Calingasan, N. Y., White, J. M., Shurubor, Y., Yang, X. W., et al. (2016). Enhanced mitochondrial biogenesis ameliorates disease phenotype in a full-length mouse model of Huntington's disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 25, 2269–2282. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw095
Chen, C. M., Chen, W. L., Hung, C. T., Lin, T. H., Lee, M. C., Chen, I. C., et al. (2019). Shaoyao Gancao Tang (SG-Tang), a formulated Chinese medicine, reduces aggregation and exerts neuroprotection in spinocerebellar ataxia type 17 (SCA17) cell and mouse models. Aging 11, 986–1007. doi: 10.18632/aging.101804
Chen, S. D., Lin, T. K., Yang, D. I., Lee, S. Y., Shaw, F. Z., Liou, C. W., et al. (2010). Protective effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors gamma coactivator-1alpha against neuronal cell death in the hippocampal CA1 subfield after transient global ischemia. J. Neurosci. Res. 88, 605–613. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22225
Chen, M., Wang, Z., Zhou, W., Lu, C., Ji, T., Yang, W., et al. (2021). SIRT1/PGC-1alpha signaling activation by mangiferin attenuates cerebral hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in neuroblastoma cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 907:174236. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174236
Chen, C. M., Weng, Y. T., Chen, W. L., Lin, T. H., Chao, C. Y., Lin, C. H., et al. (2014). Aqueous extract of Glycyrrhiza inflata inhibits aggregation by upregulating PPARGC1A and NFE2L2-ARE pathways in cell models of spinocerebellar ataxia 3. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 71, 339–350. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.03.023
Chen, S. D., Wu, H. Y., Yang, D. I., Lee, S. Y., Shaw, F. Z., Lin, T. K., et al. (2006). Effects of rosiglitazone on global ischemia-induced hippocampal injury and expression of mitochondrial uncoupling protein 2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 351, 198–203. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.017
Chen, S. D., Yang, D. I., Lin, T. K., Shaw, F. Z., Liou, C. W., and Chuang, Y. C. (2011). Roles of oxidative stress, apoptosis, PGC-1alpha and mitochondrial biogenesis in cerebral ischemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 12, 7199–7215. doi: 10.3390/ijms12107199
Cheng, A., Wan, R., Yang, J. L., Kamimura, N., Son, T. G., Ouyang, X., et al. (2012). Involvement of PGC-1alpha in the formation and maintenance of neuronal dendritic spines. Nat. Commun. 3:1250. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2238
Ciron, C., Lengacher, S., Dusonchet, J., Aebischer, P., and Schneider, B. L. (2012). Sustained expression of PGC-1alpha in the rat nigrostriatal system selectively impairs dopaminergic function. Hum. Mol. Genet. 21, 1861–1876. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddr618
Ciron, C., Zheng, L., Bobela, W., Knott, G. W., Leone, T. C., Kelly, D. P., et al. (2015). PGC-1alpha activity in nigral dopamine neurons determines vulnerability to alpha-synuclein. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 3:16. doi: 10.1186/s40478-015-0200-8
Clark, J., Silvaggi, J. M., Kiselak, T., Zheng, K., Clore, E. L., Dai, Y., et al. (2012). Pgc-1alpha overexpression downregulates Pitx3 and increases susceptibility to MPTP toxicity associated with decreased Bdnf. PLoS One 7:e48925. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048925
Cordonnier, C., Demchuk, A., Ziai, W., and Anderson, C. S. (2018). Intracerebral haemorrhage: current approaches to acute management. Lancet 392, 1257–1268. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31878-6
Cowell, R. M., Blake, K. R., and Russell, J. W. (2007). Localization of the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha to GABAergic neurons during maturation of the rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 502, 1–18. doi: 10.1002/cne.21211
Crews, L., and Masliah, E. (2010). Molecular mechanisms of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 19, R12–R20. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq160
Deierborg, T., Wieloch, T., Diano, S., Warden, C. H., Horvath, T. L., and Mattiasson, G. (2008). Overexpression of UCP2 protects thalamic neurons following global ischemia in the mouse. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 28, 1186–1195. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2008.8
De-Paula, V. d. J. R., Forlenza, A. S., and Forlenza, O. V. (2018). Relevance of gutmicrobiota in cognition, behaviour and Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacol. Res. 136, 29–34. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.07.007
Di Cristo, F., Finicelli, M., Digilio, F. A., Paladino, S., Valentino, A., Scialo, F., et al. (2019). Meldonium improves Huntington's disease mitochondrial dysfunction by restoring peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1alpha expression. J. Cell. Physiol. 234, 9233–9246. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27602
Doig, A. J. (2018). Positive feedback loops in Alzheimer's disease: the Alzheimer's feedback hypothesis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 66, 25–36. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180583
El-Emam, M. A., Sheta, E., El-Abhar, H. S., Abdallah, D. M., El, K. A., Eldehna, W. M., et al. (2024). Morin suppresses mTORc1/IRE-1alpha/JNK and IP3R-VDAC-1 pathways: crucial mechanisms in apoptosis and mitophagy inhibition in experimental Huntington's disease, supported by in silico molecular docking simulations. Life Sci. 338:122362. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.122362
Elesawy, W. H., El-Sahar, A. E., Sayed, R. H., Ashour, A. M., Alsufyani, S. E., Arab, H. H., et al. (2024). Repurposing ezetimibe as a neuroprotective agent in a rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease model in rats: role of AMPK/SIRT-1/PGC-1alpha signaling and autophagy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 138:112640. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112640
Eschbach, J., Schwalenstocker, B., Soyal, S. M., Bayer, H., Wiesner, D., Akimoto, C., et al. (2013). PGC-1alpha is a male-specific disease modifier of human and experimental amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 22, 3477–3484. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt202
Fan, S., Yan, X., Hu, X., Liu, X., Zhao, S., Zhang, Y., et al. (2024). Shikonin blocks CAF-induced TNBC metastasis by suppressing mitochondrial biogenesis through GSK-3beta/NEDD4-1 mediated phosphorylation-dependent degradation of PGC-1alpha. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 43:180. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-03101-z
Fang, X., Ma, J., Mu, D., Li, B., Lian, B., and Sun, C. (2020). FGF21 protects dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease models via repression of neuroinflammation. Neurotox. Res. 37, 616–627. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-00151-6
Feigin, V. L., Lawes, C. M., Bennett, D. A., and Anderson, C. S. (2003). Stroke epidemiology: a review of population-based studies of incidence, prevalence, and case-fatality in the late 20th century. Lancet Neurol. 2, 43–53. doi: 10.1016/s1474-4422(03)00266-7
Ferreira-Vieira, T. H., Guimaraes, I. M., Silva, F. R., and Ribeiro, F. M. (2016). Alzheimer's disease: targeting the cholinergic system. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 14, 101–115. doi: 10.2174/1570159x13666150716165726
Fu, Y., Liu, Q., Anrather, J., and Shi, F. D. (2015). Immune interventions in stroke. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 11, 524–535. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2015.144
Funayama, M., Ohe, K., Amo, T., Furuya, N., Yamaguchi, J., Saiki, S., et al. (2015). CHCHD2 mutations in autosomal dominant late-onset Parkinson's disease: a genome-wide linkage and sequencing study. Lancet Neurol. 14, 274–282. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70266-2
Giau, V. V., Wu, S. Y., Jamerlan, A., An, S., Kim, S. Y., and Hulme, J. (2018). Gut microbiota and their Neuroinflammatory implications in Alzheimer's disease. Nutrients 10:765. doi: 10.3390/nu10111765
Golko-Perez, S., Amit, T., Bar-Am, O., Youdim, M. B., and Weinreb, O. (2017). A novel iron Chelator-radical scavenger ameliorates motor dysfunction and improves life span and mitochondrial biogenesis in SOD1(G93A) ALS mice. Neurotox. Res. 31, 230–244. doi: 10.1007/s12640-016-9677-6
Grunewald, A., Kumar, K. R., and Sue, C. M. (2019). New insights into the complex role of mitochondria in Parkinson's disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 177, 73–93. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2018.09.003
Guan, X., Wang, Y., Kai, G., Zhao, S., Huang, T., Li, Y., et al. (2019). Cerebrolysin ameliorates focal cerebral ischemia injury through Neuroinflammatory inhibition via CREB/PGC-1alpha pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 10:1245. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01245
Guo, B., Zheng, C., Cao, J., Luo, F., Li, H., Hu, S., et al. (2023). Tetramethylpyrazine nitrone exerts neuroprotection via activation of PGC-1alpha/Nrf2 pathway in Parkinson's disease models. J. Adv. Res. 64, 195–211. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.11.021
Han, B., Jiang, W., Cui, P., Zheng, K., Dang, C., Wang, J., et al. (2021). Microglial PGC-1alpha protects against ischemic brain injury by suppressing neuroinflammation. Genome Med. 13:47. doi: 10.1186/s13073-021-00863-5
Han, Y. S., Lee, J. H., and Lee, S. H. (2019). Fucoidan suppresses mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death against 1-Methyl-4-Phenylpyridinum-induced neuronal cytotoxicity via regulation of PGC-1alpha expression. Mar. Drugs 17:518. doi: 10.3390/md17090518
Hardy, J., and Selkoe, D. J. (2002). The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297, 353–356. doi: 10.1126/science.1072994
Hu, J., Lang, Y., Cao, Y., Zhang, T., and Lu, H. (2015). The neuroprotective effect of Tetramethylpyrazine against contusive spinal cord injury by activating PGC-1alpha in rats. Neurochem. Res. 40, 1393–1401. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1606-1
Hu, J., Lang, Y., Zhang, T., Ni, S., and Lu, H. (2016). Lentivirus-mediated PGC-1alpha overexpression protects against traumatic spinal cord injury in rats. Neuroscience 328, 40–49. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.04.031
Huang, C., Li, J., Zhang, G., Lin, Y., Li, C., Zheng, X., et al. (2021). TBN improves motor function and prolongs survival in a TDP-43M337V mouse model of ALS. Hum. Mol. Genet. 30, 1484–1496. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddab101
Hughes, A. N. (2021). Glial cells promote myelin formation and elimination. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 9:661486. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.661486
Intihar, T. A., Martinez, E. A., and Gomez-Pastor, R. (2019). Mitochondrial dysfunction in Huntington's disease; interplay between HSF1, p53 and PGC-1alpha transcription factors. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 13:103. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00103
Jankovic, J., and Tan, E. K. (2020). Parkinson's disease: etiopathogenesis and treatment. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 91, 795–808. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2019-322338
Jensen, S. K., Michaels, N. J., Ilyntskyy, S., Keough, M. B., Kovalchuk, O., and Yong, V. W. (2018). Multimodal enhancement of Remyelination by exercise with a pivotal role for Oligodendroglial PGC1alpha. Cell Rep. 24, 3167–3179. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.08.060
Jesse, S., Bayer, H., Alupei, M. C., Zugel, M., Mulaw, M., Tuorto, F., et al. (2017). Ribosomal transcription is regulated by PGC-1alpha and disturbed in Huntington's disease. Sci. Rep. 7:8513. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09148-7
Jessen, K. R. (2004). Glial cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 36, 1861–1867. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2004.02.023
Jhuo, C. F., Chen, C. J., Tzen, J., and Chen, W. Y. (2024). Teaghrelin protected dopaminergic neurons in MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease animal model by promoting PINK1/parkin-mediated mitophagy and AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1-alpha-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis. Environ. Toxicol. 39, 4022–4034. doi: 10.1002/tox.24275
Jiang, H., Kang, S. U., Zhang, S., Karuppagounder, S., Xu, J., Lee, Y. K., et al. (2016). Adult conditional knockout of PGC-1α leads to loss of dopamine neurons. eNeuro 3:ENEURO.0183. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0183-16.2016
Jimenez-Sanchez, M., Licitra, F., Underwood, B. R., and Rubinsztein, D. C. (2017). Huntington's disease: mechanisms of pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 7:a024240. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a024240
Jin, P., Qi, D., Cui, Y., Lenahan, C., Deng, S., and Tao, X. (2022). Activation of LRP6 with HLY78 attenuates oxidative stress and neuronal apoptosis via GSK3beta/Sirt1/PGC-1alpha pathway after ICH. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022:7542468. doi: 10.1155/2022/7542468
Jo, A., Lee, Y., Kam, T. I., Kang, S. U., Neifert, S., Karuppagounder, S. S., et al. (2021). PARIS farnesylation prevents neurodegeneration in models of Parkinson's disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 13:eaax8891. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aax8891
Jornayvaz, F. R., and Shulman, G. I. (2010). Regulation of mitochondrial biogenesis. Essays Biochem. 47, 69–84. doi: 10.1042/bse0470069
Jurcau, A., and Jurcau, C. M. (2023). Mitochondria in Huntington's disease: implications in pathogenesis and mitochondrial-targeted therapeutic strategies. Neural Regen. Res. 18, 1472–1477. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.360289
Khan, S., Barve, K. H., and Kumar, M. S. (2020). Recent advancements in pathogenesis, diagnostics and treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 18, 1106–1125. doi: 10.2174/1570159X18666200528142429
Kong, X., Wang, R., Xue, Y., Liu, X., Zhang, H., Chen, Y., et al. (2010). Sirtuin 3, a new target of PGC-1alpha, plays an important role in the suppression of ROS and mitochondrial biogenesis. PLoS One 5:e11707. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0011707
Kumar, A., and Ratan, R. R. (2016). Oxidative stress and Huntington's disease: the good, the bad, and the ugly. J. Huntingtons Dis. 5, 217–237. doi: 10.3233/JHD-160205
La Spada, A. R. (2012). PPARGC1A/PGC-1alpha, TFEB and enhanced proteostasis in Huntington disease: defining regulatory linkages between energy production and protein-organelle quality control. Autophagy 8, 1845–1847. doi: 10.4161/auto.21862
Langston, J. W., and Ballard, P. J. (1983). Parkinson's disease in a chemist working with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyridine. N. Engl. J. Med. 309:310. doi: 10.1056/nejm198308043090511
Lapchak, P. A., and Zhang, J. H. (2017). The high cost of stroke and stroke Cytoprotection research. Transl. Stroke Res. 8, 307–317. doi: 10.1007/s12975-016-0518-y
Leavitt, B. R., Kordasiewicz, H. B., and Schobel, S. A. (2020). Huntingtin-lowering therapies for Huntington disease: A review of the evidence of potential benefits and risks. JAMA Neurol. 77, 764–772. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.0299
Lee, T. K., Ashok, K. K., Huang, C. Y., Liao, P. H., Ho, T. J., Kuo, W. W., et al. (2023). Garcinol protects SH-SY5Y cells against MPP+-induced cell death by activating DJ-1/SIRT1 and PGC-1alpha mediated antioxidant pathway in sequential stimulation of p-AMPK mediated autophagy. Environ. Toxicol. 38, 857–866. doi: 10.1002/tox.23737
Lee, M., Ban, J. J., Chung, J. Y., Im, W., and Kim, M. (2018). Amelioration of Huntington's disease phenotypes by Beta-Lapachone is associated with increases in Sirt1 expression, CREB phosphorylation and PGC-1alpha deacetylation. PLoS One 13:e0195968. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195968
Lee, M., Ban, J. J., Won, B. H., Im, W., and Kim, M. (2021). Therapeutic potential of ginsenoside Rg3 and Rf for Huntington's disease. In vitro cell Dev. Biol.-Anim. 57, 641–648. doi: 10.1007/s11626-021-00595-1
Li, T., Martins, S., Peng, Y., Wang, P., Hou, X., Chen, Z., et al. (2018). Is the high frequency of Machado-Joseph disease in China due to new mutational origins? Front. Genet. 9:740. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00740
Li, B., Zhang, Y., Li, H., Shen, H., Wang, Y., Li, X., et al. (2021). Miro1 regulates neuronal mitochondrial transport and distribution to alleviate neuronal damage in secondary brain injury after intracerebral Hemorrhage in rats. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 41, 795–812. doi: 10.1007/s10571-020-00887-2
Liang, H., Ward, W. F., Jang, Y. C., Bhattacharya, A., Bokov, A. F., Li, Y., et al. (2011). PGC-1alpha protects neurons and alters disease progression in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mouse model. Muscle Nerve 44, 947–956. doi: 10.1002/mus.22217
Lin, J., Puigserver, P., Donovan, J., Tarr, P., and Spiegelman, B. M. (2002). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1beta (PGC-1beta), a novel PGC-1-related transcription coactivator associated with host cell factor. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 1645–1648. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C100631200
Lin, J., Wu, P. H., Tarr, P. T., Lindenberg, K. S., St-Pierre, J., Zhang, C. Y., et al. (2004). Defects in adaptive energy metabolism with CNS-linked hyperactivity in PGC-1alpha null mice. Cell 119, 121–135. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2004.09.013
Liu, J., Jiang, J., Qiu, J., Wang, L., Zhuo, J., Wang, B., et al. (2022). Urolithin A protects dopaminergic neurons in experimental models of Parkinson's disease by promoting mitochondrial biogenesis through the SIRT1/PGC-1alpha signaling pathway. Food Funct. 13, 375–385. doi: 10.1039/d1fo02534a
Liu, N., Lyu, X., Zhang, X., Zhang, F., Chen, Y., and Li, G. (2023). Astaxanthin attenuates cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease models by reducing oxidative stress via the SIRT1/PGC-1alpha signaling pathway. Cell Biosci. 13:173. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01129-w
Liu, S. G., Wang, Y. M., Zhang, Y. J., He, X. J., Ma, T., Song, W., et al. (2017). ZL006 protects spinal cord neurons against ischemia-induced oxidative stress through AMPK-PGC-1alpha-Sirt3 pathway. Neurochem. Int. 108, 230–237. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2017.04.005
Lucas, E. K., Dougherty, S. E., McMeekin, L. J., Reid, C. S., Dobrunz, L. E., West, A. B., et al. (2014). PGC-1alpha provides a transcriptional framework for synchronous neurotransmitter release from parvalbumin-positive interneurons. J. Neurosci. 34, 14375–14387. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1222-14.2014
Lucas, E. K., Markwardt, S. J., Gupta, S., Meador-Woodruff, J. H., Lin, J. D., Overstreet-Wadiche, L., et al. (2010). Parvalbumin deficiency and GABAergic dysfunction in mice lacking PGC-1alpha. J. Neurosci. 30, 7227–7235. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0698-10.2010
Ma, Z., Xin, Z., Hu, W., Jiang, S., Yang, Z., Yan, X., et al. (2018). Forkhead box O proteins: crucial regulators of cancer EMT. Semin. Cancer Biol. 50, 21–31. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2018.02.004
Madani, N. A., Nasseri, M. S., Saberi, P. M., Golmohammadi, S., Nazarinia, D., and Aboutaleb, N. (2021). Donepezil attenuates injury following ischaemic stroke by stimulation of neurogenesis, angiogenesis, and inhibition of inflammation and apoptosis. Inflammopharmacology 29, 153–166. doi: 10.1007/s10787-020-00769-5
Makela, J., Tselykh, T. V., Maiorana, F., Eriksson, O., Do, H. T., Mudo, G., et al. (2014). Fibroblast growth factor-21 enhances mitochondrial functions and increases the activity of PGC-1alpha in human dopaminergic neurons via Sirtuin-1. Springerplus 3:2. doi: 10.1186/2193-1801-3-2
Mattiasson, G., Shamloo, M., Gido, G., Mathi, K., Tomasevic, G., Yi, S., et al. (2003). Uncoupling protein-2 prevents neuronal death and diminishes brain dysfunction after stroke and brain trauma. Nat. Med. 9, 1062–1068. doi: 10.1038/nm903
McMeekin, L. J., Bartley, A. F., Bohannon, A. S., Adlaf, E. W., van Groen, T., Boas, S. M., et al. (2020). A role for PGC-1alpha in transcription and excitability of neocortical and hippocampal excitatory neurons. Neuroscience 435, 73–94. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2020.03.036
Meara, R. J. (1994). Review: the pathophysiology of the motor signs in Parkinson's disease. Age Ageing 23, 342–346. doi: 10.1093/ageing/23.4.342
Mehta, A. R., Gregory, J. M., Dando, O., Carter, R. N., Burr, K., Nanda, J., et al. (2021). Mitochondrial bioenergetic deficits in C9orf72 amyotrophic lateral sclerosis motor neurons cause dysfunctional axonal homeostasis. Acta Neuropathol. 141, 257–279. doi: 10.1007/s00401-020-02252-5
Meng, R., Yang, X., Li, Y., and Zhang, Q. (2024). Extending dual-targeting upper-limit in liposomal delivery of lithospermic acid B for Alzheimer's mitochondrial revitalization. J. Control. Release 367, 604–619. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.01.059
Mohammed, N. N., Tadros, M. G., and George, M. Y. (2024). Empagliflozin repurposing in Parkinson's disease; modulation of oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, AMPK/SIRT-1/PGC-1alpha, and wnt/beta-catenin pathways. Inflammopharmacology 32, 777–794. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01384-w
Monsalve, M., Wu, Z., Adelmant, G., Puigserver, P., Fan, M., and Spiegelman, B. M. (2000). Direct coupling of transcription and mRNA processing through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Mol. Cell 6, 307–316. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(00)00031-9
Naia, L., Rosenstock, T. R., Oliveira, A. M., Oliveira-Sousa, S. I., Caldeira, G. L., Carmo, C., et al. (2017). Comparative mitochondrial-based protective effects of resveratrol and nicotinamide in Huntington's disease models. Mol. Neurobiol. 54, 5385–5399. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0048-3
Nguyen, H. P., Van Broeckhoven, C., and van der Zee, J. (2018). ALS genes in the genomic era and their implications for FTD. Trends Genet. 34, 404–423. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2018.03.001
Nunnari, J., and Suomalainen, A. (2012). Mitochondria: in sickness and in health. Cell 148, 1145–1159. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.02.035
O'Brien, L. C., Keeney, P. M., and Bennett, J. J. (2015). Differentiation of human neural stem cells into motor neurons stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis and decreases glycolytic flux. Stem Cells Dev. 24, 1984–1994. doi: 10.1089/scd.2015.0076
Paisan-Ruiz, C., Jain, S., Evans, E. W., Gilks, W. P., Simon, J., van der Brug, M., et al. (2004). Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson's disease. Neuron 44, 595–600. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.10.023
Panes, J. D., Godoy, P. A., Silva-Grecchi, T., Celis, M. T., Ramirez-Molina, O., Gavilan, J., et al. (2020). Changes in PGC-1alpha/SIRT1 Signaling impact on mitochondrial homeostasis in amyloid-Beta peptide toxicity model. Front. Pharmacol. 11:709. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00709
Pohland, M., Pellowska, M., Asseburg, H., Hagl, S., Reutzel, M., Joppe, A., et al. (2018). MH84 improves mitochondrial dysfunction in a mouse model of early Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 10:18. doi: 10.1186/s13195-018-0342-6
Polymeropoulos, M. H., Lavedan, C., Leroy, E., Ide, S. E., Dehejia, A., Dutra, A., et al. (1997). Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson's disease. Science 276, 2045–2047. doi: 10.1126/science.276.5321.2045
Price, N. L., Gomes, A. P., Ling, A. J., Duarte, F. V., Martin-Montalvo, A., North, B. J., et al. (2012). SIRT1 is required for AMPK activation and the beneficial effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function. Cell Metab. 15, 675–690. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.003
Robinson, A., Grosgen, S., Mett, J., Zimmer, V. C., Haupenthal, V. J., Hundsdorfer, B., et al. (2014). Upregulation of PGC-1alpha expression by Alzheimer's disease-associated pathway: presenilin 1/amyloid precursor protein (APP)/intracellular domain of APP. Aging Cell 13, 263–272. doi: 10.1111/acel.12183
Rosin, J. M., McAllister, B. B., Dyck, R. H., Percival, C. J., Kurrasch, D. M., and Cobb, J. (2015). Mice lacking the transcription factor SHOX2 display impaired cerebellar development and deficits in motor coordination. Dev. Biol. 399, 54–67. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.12.013
Ryan, M., Heverin, M., McLaughlin, R. L., and Hardiman, O. (2019). Lifetime risk and heritability of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 76, 1367–1374. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.2044
Schapira, A. H., Cooper, J. M., Dexter, D., Jenner, P., Clark, J. B., and Marsden, C. D. (1989). Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson's disease. Lancet 333:1269. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)92366-0
Selvakumar, G. P., Iyer, S. S., Kempuraj, D., Raju, M., Thangavel, R., Saeed, D., et al. (2018). Glia maturation factor dependent inhibition of mitochondrial PGC-1alpha triggers oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis in N27 rat dopaminergic neuronal cells. Mol. Neurobiol. 55, 7132–7152. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-0882-6
Smith, B. N., Newhouse, S., Shatunov, A., Vance, C., Topp, S., Johnson, L., et al. (2013). The C9ORF72 expansion mutation is a common cause of ALS+/-FTD in Europe and has a single founder. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 21, 102–108. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2012.98
Song, M., Yi, F., Zeng, F., Zheng, L., Huang, L., Sun, X., et al. (2024). USP18 stabilized FTO protein to activate Mitophagy in ischemic stroke through repressing m6A modification of SIRT6. Mol. Neurobiol. 61, 6658–6674. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04001-1
St-Pierre, J., Drori, S., Uldry, M., Silvaggi, J. M., Rhee, J., Jager, S., et al. (2006). Suppression of reactive oxygen species and neurodegeneration by the PGC-1 transcriptional coactivators. Cell 127, 397–408. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.024
Sun, X., Pan, Y., Luo, Y., Guo, H., Zhang, Z., Wang, D., et al. (2024). Naoxinqing tablet protects against cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury by regulating ampkalpha/NAMPT/SIRT1/PGC-1alpha pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 322:117672. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117672
Swanson, C. R., Du, E., Johnson, D. A., Johnson, J. A., and Emborg, M. E. (2013). Neuroprotective properties of a novel non-Thiazoledinedione partial PPAR- gamma agonist against MPTP. PPAR Res. 2013:582809. doi: 10.1155/2013/582809
Tabrizi, S. J., Ghosh, R., and Leavitt, B. R. (2019). Huntingtin lowering strategies for disease modification in Huntington's disease. Neuron 101, 801–819. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.01.039
Tang, F. L., Liu, W., Hu, J. X., Erion, J. R., Ye, J., Mei, L., et al. (2015). VPS35 deficiency or mutation causes dopaminergic neuronal loss by impairing mitochondrial fusion and function. Cell Rep. 12, 1631–1643. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.08.001
Thau, N., Knippenberg, S., Korner, S., Rath, K. J., Dengler, R., and Petri, S. (2012). Decreased mRNA expression of PGC-1alpha and PGC-1alpha-regulated factors in the SOD1G93A ALS mouse model and in human sporadic ALS. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 71, 1064–1074. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e318275df4b
Tian, L., Cao, W., Yue, R., Yuan, Y., Guo, X., Qin, D., et al. (2019). Pretreatment with Tilianin improves mitochondrial energy metabolism and oxidative stress in rats with myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1 alpha signaling pathway. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 139, 352–360. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2019.02.008
Tritos, N. A., Mastaitis, J. W., Kokkotou, E. G., Puigserver, P., Spiegelman, B. M., and Maratos-Flier, E. (2003). Characterization of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor coactivator 1 alpha (PGC 1alpha) expression in the murine brain. Brain Res. 961, 255–260. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(02)03961-6
Tsunemi, T., Ashe, T. D., Morrison, B. E., Soriano, K. R., Au, J., Roque, R. A., et al. (2012). PGC-1alpha rescues Huntington's disease proteotoxicity by preventing oxidative stress and promoting TFEB function. Sci. Transl. Med. 4:142ra97. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3003799
Tungtur, S. K., Wilkins, H. M., Rogers, R. S., Badawi, Y., Sage, J. M., Agbas, A., et al. (2021). Oxaloacetate treatment preserves motor function in SOD1(G93A) mice and normalizes select neuroinflammation-related parameters in the spinal cord. Sci. Rep. 11:11051. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90438-6
Valerio, A., Bertolotti, P., Delbarba, A., Perego, C., Dossena, M., Ragni, M., et al. (2011). Glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition reduces ischemic cerebral damage, restores impaired mitochondrial biogenesis and prevents ROS production. J. Neurochem. 116, 1148–1159. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07171.x
van Asch, C. J., Luitse, M. J., Rinkel, G. J., van der Tweel, I., Algra, A., and Klijn, C. J. (2010). Incidence, case fatality, and functional outcome of intracerebral haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and ethnic origin: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 9, 167–176. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70340-0
van Well, E. M., Bader, V., Patra, M., Sanchez-Vicente, A., Meschede, J., Furthmann, N., et al. (2019). A protein quality control pathway regulated by linear ubiquitination. EMBO J. 38:e100730. doi: 10.15252/embj.2018100730
Vanaveski, T., Molchanova, S., Pham, D. D., Schafer, A., Pajanoja, C., Narvik, J., et al. (2021). PGC-1alpha Signaling increases GABA(A) receptor subunit alpha2 expression, GABAergic neurotransmission and anxiety-like behavior in mice. Front. Molec. Neurosci. 14:588230. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.588230
Varghese, M., Zhao, W., Trageser, K. J., and Pasinetti, G. M. (2020). Peroxisome proliferator activator receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha overexpression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A tale of two Transgenics. Biomol. Ther. 10:760. doi: 10.3390/biom10050760
Villena, J. A. (2015). New insights into PGC-1 coactivators: redefining their role in the regulation of mitochondrial function and beyond. FEBS J. 282, 647–672. doi: 10.1111/febs.13175
Waldman, M., Bellner, L., Vanella, L., Schragenheim, J., Sodhi, K., Singh, S. P., et al. (2016). Epoxyeicosatrienoic acids regulate adipocyte differentiation of mouse 3T3 cells, via PGC-1alpha activation, which is required for HO-1 expression and increased mitochondrial function. Stem Cells Dev. 25, 1084–1094. doi: 10.1089/scd.2016.0072
Wang, D., Cao, L., Zhou, X., Wang, G., Ma, Y., Hao, X., et al. (2022). Mitigation of honokiol on fluoride-induced mitochondrial oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cognitive deficits through activating AMPK/PGC-1alpha/Sirt3. J. Hazard. Mater. 437:129381. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129381
Wang, Y., Guan, X., Gao, C. L., Ruan, W., Zhao, S., Kai, G., et al. (2021). Medioresinol as a novel PGC-1alpha activator prevents pyroptosis of endothelial cells in ischemic stroke through PPARalpha-GOT1 axis. Pharmacol. Res. 169:105640. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105640
Wang, R., Li, J. J., Diao, S., Kwak, Y. D., Liu, L., Zhi, L., et al. (2013). Metabolic stress modulates Alzheimer's beta-secretase gene transcription via SIRT1-PPARgamma-PGC-1 in neurons. Cell Metab. 17, 685–694. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.03.016
Wang, X., Li, H., and Ding, S. (2014). The effects of NAD+ on apoptotic neuronal death and mitochondrial biogenesis and function after glutamate excitotoxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 15, 20449–20468. doi: 10.3390/ijms151120449
Wang, Y., Ruan, W., Mi, J., Xu, J., Wang, H., Cao, Z., et al. (2018). Balasubramide derivative 3C modulates microglia activation via CaMKKbeta-dependent AMPK/PGC-1alpha pathway in neuroinflammatory conditions. Brain Behav. Immun. 67, 101–117. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.08.006
Wang, J., Song, H. R., Guo, M. N., Ma, S. F., Yun, Q., and Zhang, W. N. (2020). Adult conditional knockout of PGC-1alpha in GABAergic neurons causes exaggerated startle reactivity, impaired short-term habituation and hyperactivity. Brain Res. Bull. 157, 128–139. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.02.005
Wang, L., Zhao, Z., Zhao, L., Zhao, Y., Yang, G., Wang, C., et al. (2022). Lactobacillus plantarum DP189 reduces alpha-SYN aggravation in MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease mice via regulating oxidative damage, inflammation, and gut microbiota disorder. J. Agric. Food Chem. 70, 1163–1173. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c07711
Wei, H., Zhan, L. P., Zhang, B., Li, Y. P., Pei, Z., and Li, L. (2019). Dl-3n-butylphthalide reduces oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced endothelial cell damage by increasing PGC-1alpha. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 23, 4481–4490. doi: 10.26355/eurrev20190517960
Wen, J., Li, S., Zheng, C., Wang, F., Luo, Y., Wu, L., et al. (2021). Tetramethylpyrazine nitrone improves motor dysfunction and pathological manifestations by activating the PGC-1alpha/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in ALS mice. Neuropharmacology 182:108380. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108380
Weydt, P., Pineda, V. V., Torrence, A. E., Libby, R. T., Satterfield, T. F., Lazarowski, E. R., et al. (2006). Thermoregulatory and metabolic defects in Huntington's disease transgenic mice implicate PGC-1alpha in Huntington's disease neurodegeneration. Cell Metab. 4, 349–362. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.10.004
Weydt, P., Soyal, S. M., Gellera, C., Didonato, S., Weidinger, C., Oberkofler, H., et al. (2009). The gene coding for PGC-1alpha modifies age at onset in Huntington's disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 4:3. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-4-3
Wu, X., Cui, W., Guo, W., Liu, H., Luo, J., Zhao, L., et al. (2020). Acrolein aggravates secondary brain injury after intracerebral Hemorrhage through Drp1-mediated mitochondrial oxidative damage in mice. Neurosci. Bull. 36, 1158–1170. doi: 10.1007/s12264-020-00505-7
Wu, P., Dong, Y., Chen, J., Guan, T., Cao, B., Zhang, Y., et al. (2022). Liraglutide regulates mitochondrial quality control system through PGC-1alpha in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Neurotox. Res. 40, 286–297. doi: 10.1007/s12640-021-00460-9
Wu, G., Ma, Z., Cheng, Y., Hu, W., Deng, C., Jiang, S., et al. (2018). Targeting Gas6/TAM in cancer cells and tumor microenvironment. Mol. Cancer 17:20. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0769-1
Xiang, Z., Valenza, M., Cui, L., Leoni, V., Jeong, H. K., Brilli, E., et al. (2011). Peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 alpha contributes to dysmyelination in experimental models of Huntington's disease. J. Neurosci. 31, 9544–9553. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1291-11.2011
Xin, Z., Ma, Z., Hu, W., Jiang, S., Yang, Z., Li, T., et al. (2018). FOXO1/3: potential suppressors of fibrosis. Ageing Res. Rev. 41, 42–52. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2017.11.002
Xu, W., Li, T., Gao, L., Lenahan, C., Zheng, J., Yan, J., et al. (2019). Sodium benzoate attenuates secondary brain injury by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis and reducing mitochondria-mediated oxidative stress in a rat model of intracerebral Hemorrhage: possible involvement of DJ-1/Akt/IKK/NFkappaB pathway. Front. Molec. Neurosci. 12:105. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00105
Yin, W., Signore, A. P., Iwai, M., Cao, G., Gao, Y., and Chen, J. (2008). Rapidly increased neuronal mitochondrial biogenesis after hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Stroke 39, 3057–3063. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.520114
Yoshimura, S., Sakai, N., Uchida, K., Yamagami, H., Ezura, M., Okada, Y., et al. (2018). Endovascular therapy in ischemic stroke with acute large-vessel occlusion: recovery by endovascular salvage for cerebral ultra-acute embolism Japan registry 2. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 7:8796. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.008796
You, Y., Hou, Y., Zhai, X., Li, Z., Li, L., Zhao, Y., et al. (2016). Protective effects of PGC-1alpha via the mitochondrial pathway in rat brains after intracerebral hemorrhage. Brain Res. 1646, 34–43. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.04.076
Yu, J., Zheng, J., Lu, J., Sun, Z., Wang, Z., and Zhang, J. (2019). AdipoRon protects against secondary brain injury after intracerebral Hemorrhage via alleviating mitochondrial dysfunction: possible involvement of AdipoR1-AMPK-PGC1alpha pathway. Neurochem. Res. 44, 1678–1689. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02794-5
Zehnder, T., Petrelli, F., Romanos, J., De Oliveira, F. E., Lewis, T. J., Deglon, N., et al. (2021). Mitochondrial biogenesis in developing astrocytes regulates astrocyte maturation and synapse formation. Cell Rep. 35:108952. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108952
Zhang, J., Gao, Y., Zhang, L., Zhang, C., Zhao, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2022). Alpha-Lipoic acid attenuates MPTP/MPP(+)-induced neurotoxicity: roles of SIRT1-dependent PGC-1alpha Signaling pathways. Neurotox. Res. 40, 410–419. doi: 10.1007/s12640-022-00479-6
Zhang, D., Qian, J., Zhang, P., Li, H., Shen, H., Li, X., et al. (2019). Gasdermin D serves as a key executioner of pyroptosis in experimental cerebral ischemia and reperfusion model both in vivo and in vitro. J. Neurosci. Res. 97, 645–660. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24385
Zhang, Y. J., and Wu, Q. (2021). Sulforaphane protects intestinal epithelial cells against lipopolysaccharide-induced injury by activating the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1a pathway. Bioengineered 12, 4349–4360. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1952368
Zhang, Z., Yuan, Y., Zhang, X., Gu, L., Tang, Y., Zhao, Y., et al. (2024). GPR39 agonist TC-G 1008 promoted mitochondrial biogenesis and improved Antioxidative capability via CREB/PGC-1alpha pathway following intracerebral Hemorrhage in mice. Transl. Stroke Res. doi: 10.1007/s12975-024-01240-1
Zheng, Z. J., Zhu, L. Z., Qiu, H., Zheng, W. Y., You, P. T., Chen, S. H., et al. (2024). Neferine inhibits BMECs pyroptosis and maintains blood-brain barrier integrity in ischemic stroke by triggering a cascade reaction of PGC-1alpha. Sci. Rep. 14:14438. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-64815-w
Zhong, J., Dong, W., Qin, Y., Xie, J., Xiao, J., Xu, J., et al. (2020). Roflupram exerts neuroprotection via activation of CREB/PGC-1alpha signalling in experimental models of Parkinson's disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 177, 2333–2350. doi: 10.1111/bph.14983
Zhou, H., Shao, M., Yang, X., Li, C., Cui, G., Gao, C., et al. (2019). Tetramethylpyrazine analogue T-006 exerts neuroprotective effects against 6-Hydroxydopamine-induced Parkinson's disease in vitro and in vivo. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019:8169125. doi: 10.1155/2019/8169125
Zhou, Y., Wang, S., Li, Y., Yu, S., and Zhao, Y. (2017). SIRT1/PGC-1alpha Signaling promotes mitochondrial functional recovery and reduces apoptosis after intracerebral Hemorrhage in rats. Front. Molec. Neurosci. 10:443. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2017.00443
Keywords: PGC-1α, mitochondria, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, neurological diseases
Citation: Tang M-b, Liu Y-x, Hu Z-w, Luo H-y, Zhang S, Shi C-h and Xu Y-m (2025) Study insights in the role of PGC-1α in neurological diseases: mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Front. Aging Neurosci. 16:1454735. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1454735
Received: 25 June 2024; Accepted: 30 December 2024;
Published: 12 February 2025.
Edited by:
Zhiquan Li, University of Copenhagen, DenmarkReviewed by:
Jiangbo Song, Southwest University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Tang, Liu, Hu, Luo, Zhang, Shi and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mi-bo Tang, dGFuZ21pYm9oYXBweUAxMjYuY29t
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.