
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Aging Neurosci., 07 June 2024
Sec. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Brain-aging
Volume 16 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2024.1419861
This article is a correction to:
Multi-Protection of DL0410 in Ameliorating Cognitive Defects in D-Galactose Induced Aging Mice
A corrigendum on
Multi-protection of DL0410 in ameliorating cognitive defects in D-galactose induced aging mice
by Lian, W., Jia, H., Xu, L., Zhou, W., Kang, D., Liu, A., and Du, G. (2017). Front. Aging Neurosci. 9:409. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00409
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 5 as published. The representative pictures for GFAP staining in the hippocampus were identical for both model group and Don-3 mg/kg group, in which the picture in Model group was used by mistake. The corrected Figure 5 and its caption appear below.
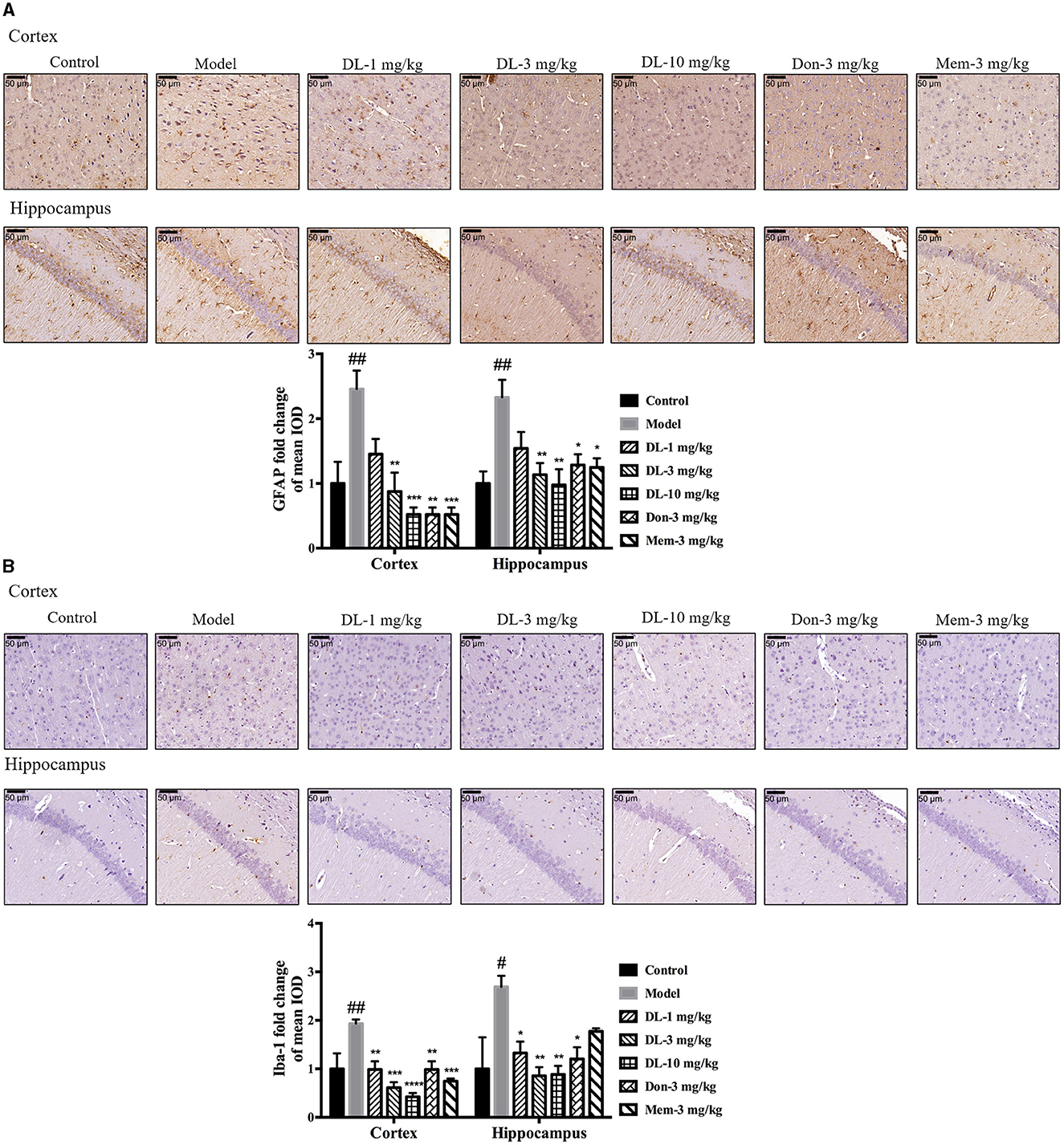
Figure 5. DL0410 decreased the activation of astrocytes and microglia in the hippocampus and cortex. Data are the mean ± SEM (n = 3). DL0410 decreased the expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba-1), and decreased the activation of astrocytes (A) and microglia (B) in the hippocampus and cortex [GFAP: cortex F(6, 14) = 7.660, p = 0.0009, hippocampus F(6, 14) = 4.969, p = 0.0064; Iba-1: cortex F(6, 14) = 8.685, p = 0.0005, hippocampus F(6, 13) = 4.182, p = 0.0146]. Scale bar = 50 μm, and magnification = 400 × . #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 vs. control group, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 vs. model group.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: DL0410, Alzheimer's disease, mitochondrion, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, apoptosis, synaptic protection
Citation: Lian W, Jia H, Xu L, Zhou W, Kang D, Liu A and Du G (2024) Corrigendum: Multi-protection of DL0410 in ameliorating cognitive defects in D-galactose induced aging mice. Front. Aging Neurosci. 16:1419861. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1419861
Received: 19 April 2024; Accepted: 22 May 2024;
Published: 07 June 2024.
Edited and reviewed by: Jorge Busciglio, University of California, Irvine, United States
Copyright © 2024 Lian, Jia, Xu, Zhou, Kang, Liu and Du. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ailin Liu, bGl1YWlsaW5AaW1tLmFjLmNu; Guanhua Du, ZHVnaEBpbW0uYWMuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.