- 1Light Technology Institute, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Karlsruhe, Germany
- 2Optical Systems, Corporate Research, Robert Bosch GmbH, Renningen, Germany
Introduction/Purpose: Laser-excited remote phosphor (LERP) light sources have gained significant importance in lighting and display applications due to their unique brightness and color-rendering qualities. In addition to their well-known advantages in these areas, we found that they also offer largely unexplored potential for sensor applications, such as quantitative fluorescence analysis. This potential is especially relevant when sophisticated optics operating under space and cost constraints require low-etendue sources with highly stable spectral properties. In this paper, we present an example of such an application. The purpose of our research is to assess currently available phosphor materials and design a light source to our particular reference application.
Methods: For this purpose, a characterization setup was developed that compares different phosphors excited by small laser spots, with diameters between 100 μm and 280 μm, in terms of emitted spectral radiance, incident laser power, and irradiance.
Results: The investigation identified two suitable phosphors, including a phosphor that addresses the gap in the blue and green wavelength ranges. Furthermore, the importance of small laser spots was demonstrated, which allows reducing the laser power to simplify light source design and reduce costs.
Discussion/Conclusion: This research proposes a functional set of phosphors for the abovementioned application and, at the same time, presents the current limitations of LERP light sources. We remain confident in the described application field for LERP sources and hope that the needs elaborated in this work will inspire further research and development of novel phosphor materials.
1 Introduction
Fluorescence analysis is an important measurement technique, especially in medicine, but it is usually only available in a laboratory environment and requires educated personnel. To make the benefits of this technique more accessible and faster to the public, portable, cost-efficient, and fully automated devices must be developed. A key challenge in this new segment is finding a good compromise between the functionality of laboratory equipment and the cost of a mass market product.
A well-known example and leading application for this article is a lab-on-a-chip device implementing quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) tests to detect infections at the point-of-care, especially since the COVID-19 pandemic. Such devices work with the same high sensitivity as laboratory qPCR tests but have a significantly lower time-to-result as transportation times are eliminated. A qPCR test uses a fluorescence analysis to decide whether a test is positive or negative (Kralik and Ricchi, 2017). The procedure starts with labeling DNA strands under test (at least the DNA corresponding to the infection and a reference, e.g., human DNA) with specific fluorophore probes. The fluorophore probes are specific in two respects: first, the probe component can only bind to a specific DNA sequence, and second, the fluorophore component contains a dye with a unique absorption and emission spectrum. Since the dye of a fluorophore will remain quenched until the probe binds to its target DNA strand, the labeling process connects the concentration of target DNA strands with fluorescence intensity in known wavelength bands. It is the lab-on-a-chip analyzer’s task to optically address all fluorophores used. Sequentially, for each fluorophore, the analyzer irradiates the sample with light in a wavelength band matching the respective absorption spectrum and observes it in the wavelength range of expected fluorescence. If power is measured, the presence of the target DNA can be inferred.
To minimize uncertainty in the quantitative evaluation, it is essential to know the optical system of the analyzer well. In a spectral analysis, this applies to the power level and the spectrum. As most light sources drift spectrally due to the production process and thermal effects during operation, it is advisable to use a spectrally broad light source and define the spectrum with a passive spectral interference filter. For cost reasons, only blackbody radiators or wavelength conversion with a phosphor can be considered for a mass product to generate a sufficiently broad spectrum. Due to significant heat generation and short lifetimes (Beacher, 2011; Jaffe et al., 2009), blackbody radiators are usually not used for compact devices at the point-of-care. The drawback of phosphor-converted light sources is a limited radiance level (power per area and solid angle), limiting optical designs in terms of cost-effectiveness, miniaturization, and complexity. 1) The cost consideration is related to interference filters. The cost of an interference filter scales approximately with its cross-sectional area as the filter is manufactured via a wafer process. At the same time, radiation that passes through an interference filter must only have a maximum residual divergence to ensure proper filter function, according to the filter’s operating principle. To reduce the cross-sectional area and save costs without exceeding the maximum residual divergence, the radiance of the light source must be increased. 2) An example of miniaturization is already given in (1). A similar miniaturization potential can be achieved using volume holograms as spectral filters. Müller et al. (2023) demonstrated that holographic optical elements will redirect light with a more defined spectrum when the radiance of the used light source is increased. 3) Using white LEDs usually limits the optical design to a static optical system. Without a significantly brighter light source in the relevant spectral range from 450 nm to 640 nm, it is not possible to develop more complex optical systems as, e.g., a flying spot projector described by Müller et al. (2024), which would provide lab-on-a-chip devices a significantly higher degree of flexibility required for new innovations not foreseen when designing the instrument (Lux et al., 2021; Podbiel et al., 2020).
State-of-the-art brightest light sources on the market are laser-excited remote phosphor (LERP) light sources which are more beneficial than phosphor-converted LEDs due to a spatial separation of phosphor and pump light source and therefore better thermal management. Further, LERP light sources take advantage of the intrinsically higher radiance level of the laser in comparison to an LED. Since most laser phosphors are based on the development status of LED phosphors for general lighting, they are usually used to fill the green gap in direct LEDs (Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH, 2019) and were primarily developed for physiological applications such as automotive headlamps (Strauss, 2017; Willeke et al., 2016; Vogl, 2023; Shih et al., 2022), searchlights (Lee et al., 2023), and projectors (Li et al., 2021; Hu and Li, 2013; Hu et al., 2020). The brightest phosphors emit in the yellow and green spectral ranges. Although there is some interest in high-brightness red fluorescence for color-rendering-index improvement and enhancing the red channels in projectors, the search for a stable red phosphor continues, and high-brightness blue fluorescence remains a niche area. In Müller et al. (2024), we quantified and highlighted the demand for phosphor-converted light sources with high radiance at blue and red wavelengths by comparing phosphor-converted light sources available on the market with the requirements of the flying spot projector. The aim of the present article is to address the reported gap in radiance for blue and red wavelengths. Since there is no standard for phosphor performance evaluation, the comparison of research results from different suppliers or university groups is difficult (Li S. et al., 2022). Therefore, new ceramic and single-crystal phosphors from different suppliers are characterized and compared in a common characterization setup.
In addition to the phosphor, the design of the light source influences the achievable radiance level. Thermal management is one of the most important aspects as the achievable radiance is mostly limited by thermal quenching. One effective option is spreading the dissipated heat over a larger phosphor surface by moving the phosphor and laser spot relative to each other. This is possible due to a significantly smaller time constant of fluorescence decay than for thermal dissipation. Hagemann et al. (2019) achieved approximately 9000 cd/mm2 using a rotating wheel in comparison to approximately 2,200 cd/mm2 using a comparable static phosphor, as reported by Hagemann et al. (2020). Alternatives to a rotating wheel are to integrate the movement into the optical path with a tilted rotating mirror (Li et al., 2021), a two-dimensional scanning mirror, or a rotating wedged optical element (Li K. et al., 2022). Due to complexity, we believe that a static solution shows a higher potential for low-cost fluorescence applications. For static phosphors, Sun et al. (2023) combined active cooling with lateral heat spreading by embedding the phosphor additionally into the Peltier element and achieved an increase of 4.5 in the laser irradiance threshold. Correia et al. (2017) used lateral heat spreading by embedding a phosphor into a metal hole. In addition to lateral heat spreading, increased thermal conductivity perpendicular to the emitting surface is also beneficial. Correia et al. (2017) showed in simulations that a thinner phosphor plate can reduce the peak temperature, and Hagemann et al. (2020) measured higher radiance levels with thinner samples. Alternatively, the thermal conductivity perpendicular to the phosphor surface can be increased on the emissive side by attaching a transparent plate. Correia et al. (2017) demonstrated a decrease in temperature in simulations using a glass plate on top of a phosphor in a sodium glass binder and a reflective configuration. Zhang et al. (2019) experimentally obtained three times higher power density using a sapphire plate in a transmissive configuration on a phosphor in glass. Further research applying sapphire plates on phosphor-in-glass in transmissive configuration is given by Zheng et al. (2018), Peng et al. (2019), and Wei et al. (2019). Ma and Luo (2019) showed experimental results with a rather thick phosphor sample with low thermal conductivity in reflective configuration. While active cooling is a common technique and lateral heat spreading as well as the thickness of the phosphor are primarily the concern of the phosphor’s manufacturer, the literature suggests that cooling on the emission side offers significant benefits. However, in the literature, only phosphors with poor thermal conductivity, large thickness, or poor overall thermal management on the non-emission side were investigated. The presented article compares a static ceramic phosphor with high thermal conductivity in reflective configuration and good thermal management with and without a sapphire plate. In addition to the sapphire plate, the effect of an aperture made of stainless-steel foil is measured.
Another important factor is the incident laser spot area. Previous studies by Krasnoshchoka et al. (2020) showed a material-dependent expansion of the fluorescence spot size compared to the laser spot size, which remained approximately constant over the incident laser spot size. Important findings are that high absorption is beneficial for minimizing the spot size, while the scattering coefficient only shows a weak influence. Zheng et al. (2019) suggested high-scattering ceramics for luminescent spot-size confinement, and Lenef et al. (2013) explained that backscattering shows potential to confine the incident laser power. However, as no power was measured by Krasnoshchoka et al. (2020), it cannot be concluded that a smaller spot size results in a higher radiance level. Yuan et al. (2024) investigated the effects of the incident laser spot area on temperature, luminous flux, luminous efficacy, and luminous exitance of
Radiance measurements are performed with a custom-built characterization setup for high power densities and Lambertian emission based on previous research (Hagemann et al., 2020; Lenef et al., 2013; Xu et al., 2019; Wei et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2024; Krasnoshchoka et al., 2017; 2020). To stay aligned with our application scenario, we have opted against high-end solid-state laser modules with diffraction-limited optics, as referenced in the abovementioned literature. Instead, we use low-cost laser diodes with basic focusing optics, which are still able to drive the ceramic and single-crystal phosphor materials in reflective configuration to their irradiance limits. Additional differences to previous research are the investigation of radiometric instead of photometric properties, including the measurement of radiance at roll-over thermal quenching and the focus on small incident laser spots. To illustrate the potential of our research effort, new phosphor candidates are integrated into the flying spot projector, as described by Müller et al. (2024), and compared to state-of-the-art phosphor-converted light sources. As a state-of-the-art laser-excited remote phosphor, we consider the highly integrated surface-mount-device (SMD 500) from Kyocera.
The article starts with a brief overview of phosphor materials, followed by a description of the phosphor characterization setup, the phosphors themselves, and the tested light source design options.
2 Fundamentals of phosphor materials
A phosphor for an etendue-limited optical system used in fluorescence analysis must fulfill specific requirements regarding excitation and emission spectra and the emitted radiance level of fluorescence. The emitted radiance level depends on several other properties, such as the thermal conductivity of the phosphor sample (Li S. et al., 2022; Hagemann and Seidl, 2021), the phosphor’s quantum efficiency (Li S. et al., 2022), thermal (Li S. et al., 2022; Maggay and Liu, 2017; Lenef et al., 2013; Silver et al., 2016) and concentration quenching (Li S. et al., 2022; Lenef et al., 2013), and scattering (Silver et al., 2016; Xu et al., 2022) and absorption properties (Krasnoshchoka et al., 2020).
Relevant influencing factors are the chemical composition of the phosphor host material, its activator, and the microstructure of the sample. The shape of the spectrum and the decay time influencing the concentration quenching strongly depend on the activator (Li S. et al., 2022; Xia et al., 2016; Lin and Liu, 2017). Relevant phosphors for our purpose usually use rare-earth ions such as
The microstructure of a phosphor sample plays a major role in determining thermal conductivity and scattering properties. A cost-efficient method to prepare phosphors for a product is embedding phosphor particles in an organic silicon matrix (Liu et al., 2023). This method is most often used for phosphor-converted LEDs (Rahman, 2022), but it is inappropriate for laser excitation due to low thermal conductivity in the range of 0.2 W/(m ⋅ K) (Liu et al., 2023; Zhang et al., 2019; Raukas et al., 2013; Rahman, 2022). An improved thermal performance results when phosphor particles are embedded in glass (Rahman, 2022). Laser-excited remote phosphors in glass bulk and thin-film light sources have been demonstrated (Zhu et al., 2015; Wei et al., 2019; Zhang et al., 2021; Xu et al., 2021); however, the thermal conductivity of phosphors in glass of approximately 1 W/(m ⋅ K) (Li S. et al., 2022; Zhang et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2023) is considered to be too low for high power density laser excitation (Rahman, 2022), especially in the case of bulk phosphor in glass (Ma and Cao, 2021). With >5 W/(m ⋅ K) thermal conductivity (Yoon and Song, 2017), phosphors sintered as polycrystalline ceramics provide a better alternative to phosphors in silicon or glass with the downside of a more complicated fabrication process (Li S. et al., 2022). Another benefit of ceramics is their tunable microstructure, which helps adjust the scattering properties (Ma and Cao, 2021; Li S. et al., 2022). Due to their excellent thermal conductivity and high tunability, phosphor ceramics are a good choice for high power density laser excitation (Rahman, 2022; Hagemann and Seidl, 2021) and have been used in several scientific works (Willeke et al., 2016; Hu et al., 2020) and products (Strauss, 2017). The most common and commercially available ceramic phosphor is
Due to their performance and commercial availability, our research uses
3 Materials and methods
This section is divided into two subsections: the first focuses on radiance measurements to identify the best-suited materials and a good design for an LERP light source, while the second discusses the application of the identified LERP light source in an etendue-limited flying spot projector, used as the illumination unit in a fluorescence analysis.
3.1 Radiance measurements
3.1.1 Phosphor excitation
For the characterization of phosphors, we chose some of the most powerful laser diodes, particularly PLPT9 450LB_E by Osram, with a peak wavelength at 445 nm and a maximum power of 5 W to build the characterization setup as closely as possible to a potential product. To increase the power beyond the maximum power level of an individual laser diode, we opted for angled phosphor excitation. For all our experiments, a combined laser power of 10 W has proven sufficient to exceed the irradiance limit. Using Ansys Zemax OpticStudio, a collimation and focusing optical system is designed for a laser diode based on standard lenses (ACL12708U-A, with f = 8 mm and d = 12.7 mm, and AL1225-A, with f = 25 mm and d = 12.5 mm by Thorlabs). Figure 1A shows the optical system. The intrinsically elliptical beam profile of the edge emitter was not corrected by anisotropic focusing or a pair of wedged prisms. Instead, the laser diode was rotated around the beam axis so that the short spot diameter (slow axis) was elongated by angled illumination, resulting in a more circular spot. Hence, with the correct orientation, a spot on the phosphor with less ellipticity than the original emitting area can be realized. Since the 1/e2-divergence of the laser shows a vice versa aspect ratio of 9° x 49°, the collimated laser beam will be mostly spread in the plane perpendicular to the phosphor surface. The large beam diameter in that plane shows potential to interfere with a condenser lens for fluorescence collimation used in later experiments. Considering the additional condenser lens, type ACL1210U-A by Thorlabs (f = 10.5 mm and d = 12 mm) for following experiments, the characterization setup is designed so that the laser light does not hit the phosphor condenser lens. This fact influenced the choice of the laser focusing lens, the phosphor condenser lens, and the illumination angle. The latter is chosen to be 60° with respect to the phosphor normal.
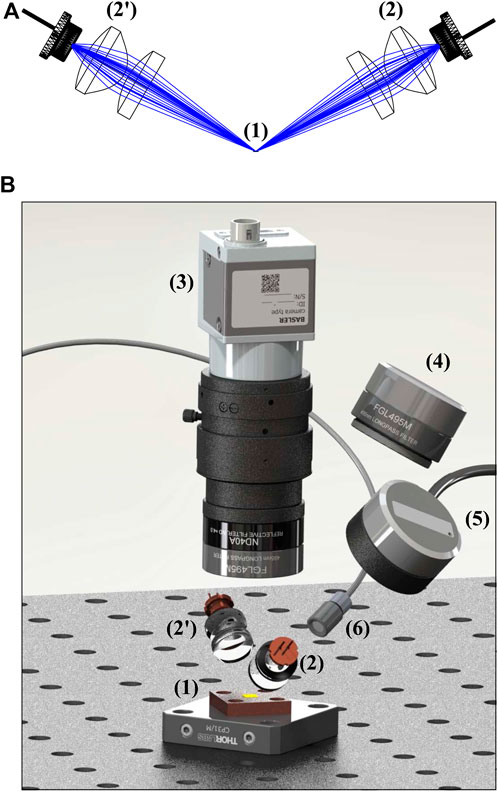

Figure 1. (A) Optic design for excitation of the phosphor sample (1) with two focused laser diodes (2, 2′) created using Ansys Zemax OpticStudio. The fast axis of the laser diodes lies in the image plane. (B) Rendered CAD model with SolidWorks 2022 showing the placement of the phosphor sample (1), laser excitation systems (2, 2′), a camera system with lens and a filter (3), a power meter and a filter for fluorescence measurement (4), a power meter and a filter for laser reference measurement (5), and a spectrometer with a cosine corrector (6).
As shown in Figure 1B, the phosphor is placed directly on an adapter plate on an optical breadboard. This setup assures ideal passive thermal management. The laser spot diameter on the phosphor is supposed to be in the range of 100
3.1.2 Measurement instrumentation
To compare different phosphor materials, configurations, and spot sizes, the spectral radiance level of the fluorescence must be measured. Since phosphors emit isotropically (Raukas et al., 2013), they are Lambertian emitters, and their spectral radiance level
The spectral radiance
This implies that we assume that the emission is rotationally symmetric, the assumption of a Lambertian emitter holds, and the fluorescence spectrum is independent of any angle. The emitting area is captured using a camera positioned perpendicular in a 30-mm cage system over the phosphor, as shown in Figure 1B. We use a Basler Ace U acA1440-220um camera with a 0.5-mm spacer ring, paired with Basler Lens C23-1216-2M-S f12 mm. This setup achieves roughly 22
In addition to the spectral radiance, for the design of a light source, the laser power used and the laser spot size are of interest. The laser power is measured using a monitoring power meter head (S120C from Thorlabs) placed at an arbitrary position and equipped with a laser bandpass filter (FBH450-10 by Thorlabs) at 450 nm
The spot area
3.1.3 Measurement procedure
For each characterization experiment, the laser spot size on the sample is adjusted, and a picture of the spot is captured. After exchanging the laser bandpass filter with the long-pass filter on the camera, a picture of the phosphor sample is taken. This picture with a known reference geometry (most often, the phosphor sample itself) serves as camera pixel calibration. To find out the maximum spectral radiance, the laser power is ramped up in 0.05 A–0.1 A steps until the power meter with a long-pass filter shows a decrease in fluorescence with increasing laser power. Each power level is held for a few seconds to make sure that the signal is stable. The decrease in fluorescence marks the end of the characterization. After turning off the laser, a dark current spectrum is taken for spectral correction.
3.1.4 Phosphor materials and reference light sources
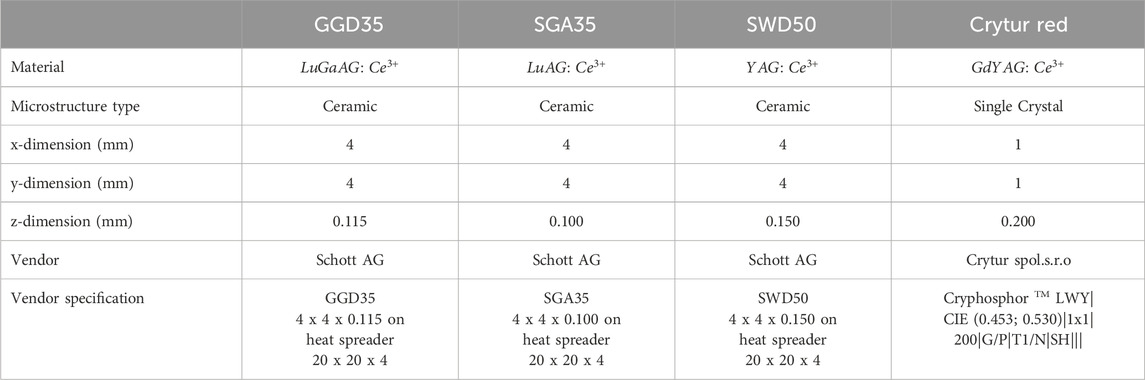
The investigated phosphor candidates are commercially available samples. Table 1 identifies the phosphor samples from Schott AG1 and Crytur spol. s.r.o.2 and lists relevant properties. All phosphor materials are investigated with a laser incident spot size of approximately 100
It should be mentioned that properties of the phosphor such as the scattering coefficient, absorption coefficient, and the phosphor thickness and its thermal conductivity play a significant role considering the achievable radiance level, the required pump power, and irradiance. As these properties are already optimized for the given phosphor samples by the supplier, the presented article does not discuss these properties further. For interested readers, we refer to Section 2. Considering the effect of phosphor thickness, we recommend Correia et al. (2017); Hagemann et al. (2020).
3.1.5 Influence of the pump spot size
We expect that the laser power required to achieve roll-over increases with the spot size (Yuan et al., 2024). Having a cost-sensitive application in mind, we, therefore, specifically investigate rather small laser spot diameters in comparison to previous luminescence saturation studies in the literature (Hagemann et al., 2020; Lenef et al., 2013; Xu et al., 2019). Our goal is to find the optimal spot size that maximizes the radiance under laser power restriction. The spot size diameter is varied between approximately 100
3.1.6 Sapphire plate and aperture
In addition to the plain phosphor sample, we characterize the GGD35 sample using an uncoated sapphire plate (#43–632 from Edmund Optics with a thickness of 0.5 mm) on top of the phosphor. This experiment aims to investigate the potential benefits of better thermal conductivity on the emissive side. Since the laser incidents the sapphire plate under approximately the Brewster angle, two perpendicular polarization states are investigated. Further experiments with GGD35 in combination with a 25-
3.2 Application in a flying spot projector
To illustrate the potential of the investigated light sources in applications, the GGD35 and SWD50 samples, using the same excitation setup described in Section 3.1.1, are integrated into a slightly modified version of the flying spot projector from Müller et al. (2024). The purpose of a flying spot projector for fluorescence analysis in a lab-on-a-chip device is to provide a higher degree of flexibility. This flexibility is important because such devices usually consist of two main parts with different development cycles. On one hand, there is the analyzer unit, covering the optics for the fluorescence analysis, and on the other hand, there are cartridges as disposables, covering the patient sample and reagents. As disposable components, cartridges have shorter development cycles than the analyzer unit. Hence, it is important to have adjustable interfaces that can accommodate innovations in cartridge design. One of these interfaces is the illuminated area. The challenge of the flying spot projector for fluorescence analysis in a lab-on-a-chip device is the combination of three requirements: first, a high radiance level is required in an etendue-limited optical system as the flying spot projector. Second, the fluorescence analysis requires a broadband light source to guarantee a stable excitation signal. Third, the point-of-care scenario imposes restrictions on cost, bulk volume, and safety standards. Müller et al. (2024) identified a commercial light source, Kyocera SMD 500, as a promising candidate to fulfill these requirements. As not all requirements are met by the commercial light source, GGD35 and SWD50 are integrated into the flying spot projector to evaluate their performance.
The optical design of the flying spot projector is shown in Figure 2. The laser-excited remote phosphor (1) is collimated using an aspheric condenser lens (2). The lens (3) creates an image of the source in a plane with adjustable aperture (4). The aperture (4) defines the utilized optical area on the light source (1) and, in combination with the NA of lens (2), defines the etendue of the system. At the same time, the aperture controls the spot size, which impacts the cartridge performance. With the pair of lenses (5) and (6), light is focused over a static mirror (7) and a two-dimensional rotatable mirror (8) toward the target plane (9). The rotatable mirror is controllable with software. Hence, the illuminated area is adjustable specifically for the loaded cartridge type without a hardware modification.
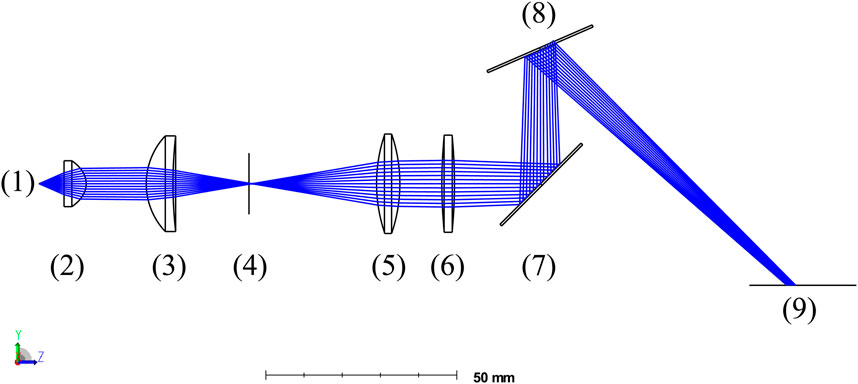
Figure 2. Optic design of the flying spot projector with (1) the laser-excited remote phosphor, (2,3,5, and 6) lenses, (4) an adjustable aperture, (7) a static mirror, (8) a rotatable mirror, and (9) the target plane.
Although the radiance measurements section directly compares phosphor samples with the Kyocera SMD 500 light source, this investigation considers the performance of the light source in combination with the optical system of the flying spot projector. The performance of Kyocera SMD 500 in the flying spot projector has already been characterized by Müller et al. (2024). In this article, we use the same measurement procedure as described in our previous research, adjust the aperture size corresponding to a spot size of approximately 2 mm along the small axis, following the approach described by Müller et al. (2024), and compare the resulting power levels of the spot on the target plane. The results of the Kyocera SMD light source from our previous publications are summarized in Figure 6B.
4 Results
4.1 Radiance measurements
Since the fluorescence spot shows a Gaussian shape, it makes sense to calculate average radiance levels within the entrance pupil of the following optical system. In the following calculations, the entrance pupil area
4.1.1 Phosphor materials
The maximum spectral radiance levels of different phosphor materials with respect to incident laser power and incident laser irradiance were determined. For each phosphor material, the relationship between the fluorescence radiance level
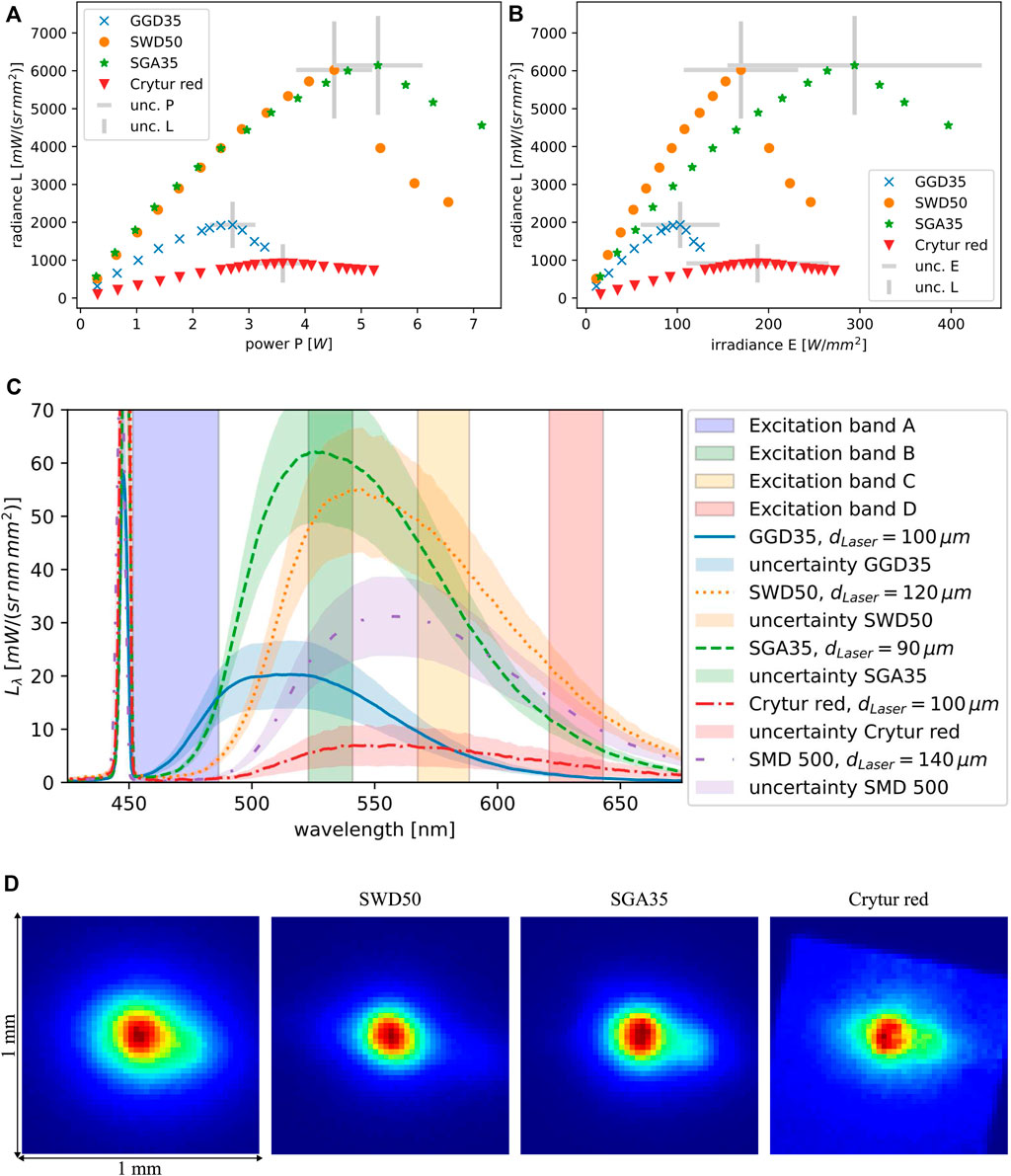
Figure 3. Results of phosphor material characterization. All results are evaluated assuming that the following optics sees a fluorescence spot size with a diameter of 250
Figure 3C shows the spectral radiance
With the setup described in Section 3.1.2, absolute radiance and irradiance values can be obtained in general, however, only with certain certainty. Therefore, Figures 3A–C show the uncertainty ranges of our measurements. These uncertainties are calculated based on the estimated uncertainties of power and spot size measurements and the accuracy of geometrical positioning. For the relative comparisons conducted in this article, the uncertainty is minimized as the same equipment is consistently used for all measurements.
4.1.2 Influence of the pump spot size
The effects of the incident laser spot size on power
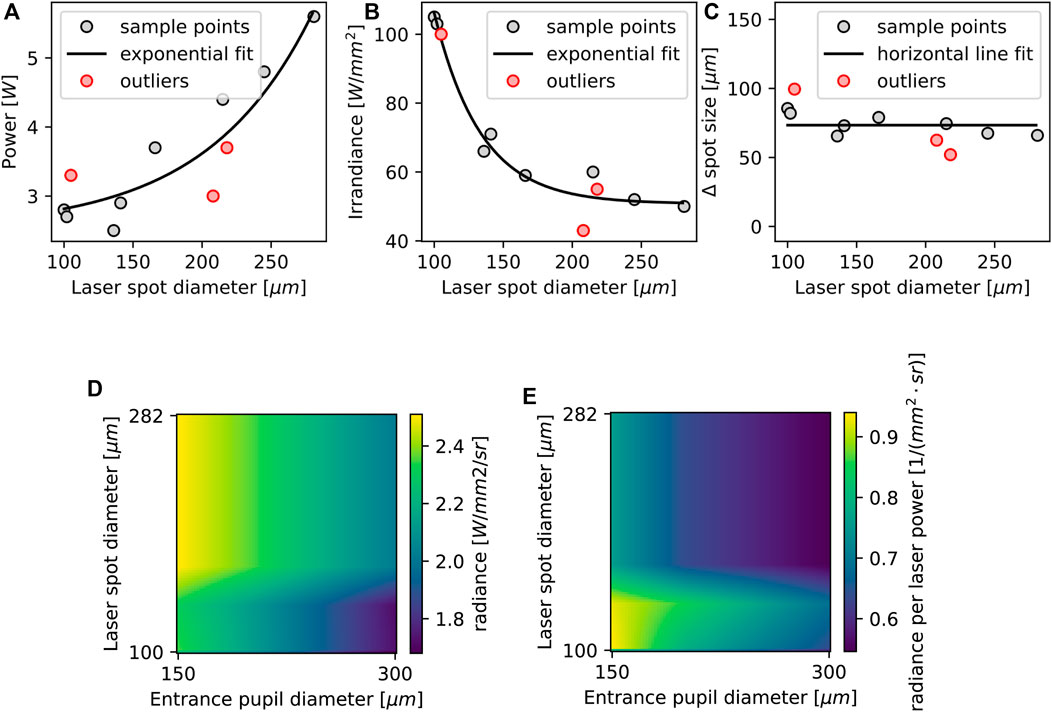
Figure 4. Results of spot size analysis. All two-dimensional plots assume that the following optics sees an entrance pupil with a diameter of 250
In Figures 4B, C, three outliers are identified and marked in red. As all three diagrams in Figures 4A–C show data from the same measurements, the measurements producing outliers in one diagram are also marked in the others. These three outliers are not included in Figures 4D, E to better visualize the trend. Figure 4D shows the radiance
For light source design, the number and power level of the required laser diodes is important. To simplify design and reduce cost, both the number and the power level are to be kept low. This requirement leads to a new optimization goal that considers both radiance and incident laser power. Figure 4E plots the radiance
4.1.3 Sapphire plate and aperture
Comparing the first two bars in Figure 5A, it appears that the sapphire plate only has a minor effect on the resulting radiance level, which is in the range of measurement uncertainties. Although the result does not seem very promising at first glance, the measured fluorescence level represents the benefit of using a sapphire plate, accounting for signal loss due to Fresnel reflections, as discussed in Section 5.
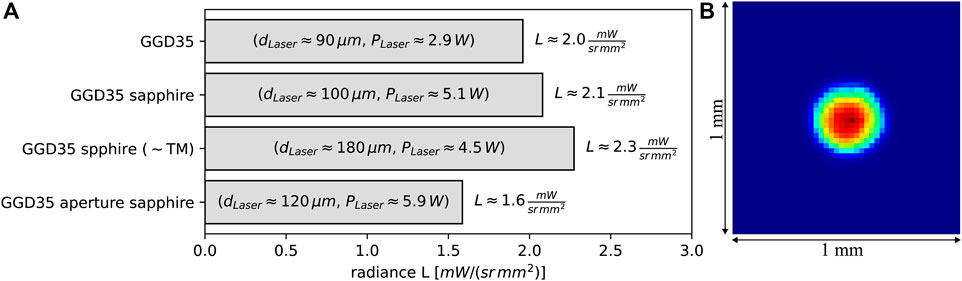
Figure 5. Results of design options. (A) Effect of the sapphire plate and aperture on power and the radiance level. (B) Normed fluorescence spot phosphor with the aperture and sapphire plate.
Another effect of Fresnel reflections is the increased roll-over incident laser power. We efficiently counteract this unfortunate increase in required laser power using the polarization properties of laser diodes. Operating close to the Brewster angle of the sapphire–air interface, the roll-over incident power level is effectively reduced even for a larger excitation spot via TM polarization, as shown in the third bar of Figure 5A.
Furthermore, the GGD35 phosphor sample with an aperture of diameter 300
4.2 Application in a flying spot projector
To compare the performance of a light source in combination with a flying spot projector, the spot size is adjusted to a fixed width in the x-direction. Figure 6A shows the four spots used for the calculation. The spot size diameter is defined as the distance between the points where the signal drops by 1/e of the maximum, and the diameters are 1.8 mm for blue, 2.1 mm for green, 2.0 mm for orange, and 1.9 mm for red.
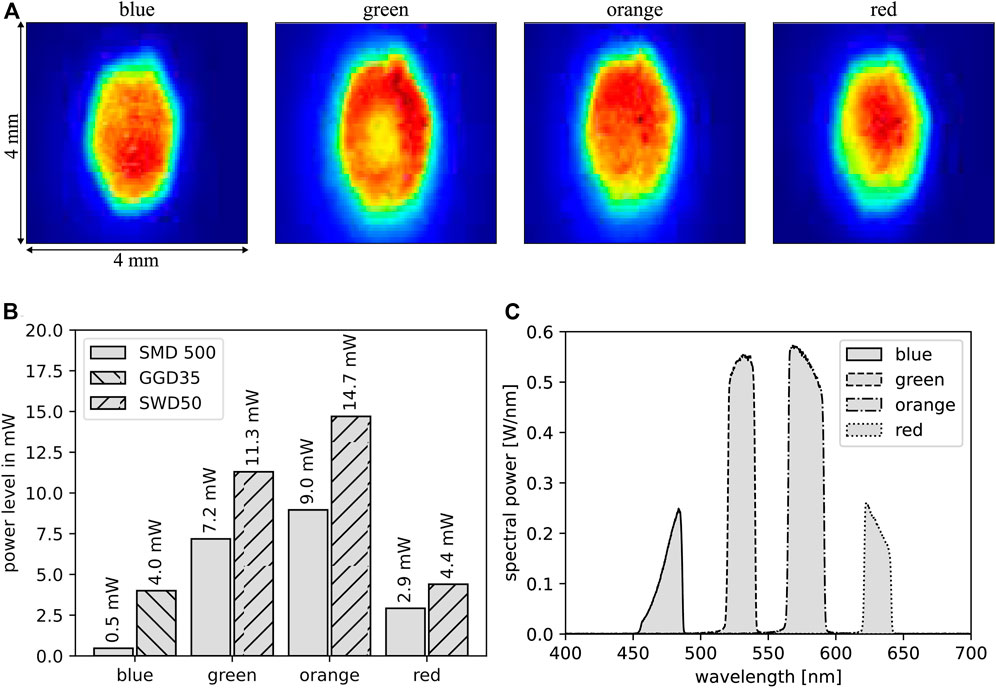
Figure 6. Results of flying spot projector characterization with new phosphor materials. (A) Spots on the target plane for excitation channels. (B) Power levels of selected phosphor materials in comparison to the SMD 500 light source. (C) Resulting spectrum on the target plane weighted with the measured power level.
Using very similar spot sizes as for the measurements with the Kyocera SMD 500 light source, Figure 6B shows the comparison of the power level of the spot as a performance measure of the new phosphor materials to SMD 500 in the respective flying spot projector. For all channels, an increase in power is visible, as already expected during radiance characterization, as shown in Figure 3C. The strongest increase is given for the blue channel, showing the potential of the new phosphor material GGD35 for fluorescence analysis.
Figure 6C shows the corresponding spectrum in the excitation channels. It is remarkable that the blue channel is excited by fluorescence only as the spectrum does not show the narrow peak of the laser spectrum.
5 Discussion
5.1 Radiance measurements
5.1.1 Phosphor materials
Phosphor materials were investigated with the goal of finding the ideal candidates or candidate for cost-efficient fluorescence analysis for low-etendue applications. The first requirement we concentrate on is the high spectral radiance level in the required wavelength bands. Figure 3C shows that the phosphor materials emit the highest spectral radiances in the yellow–green regime. The reason is that high-brightness phosphors are usually based on the mature
In comparison to the SMD 500, which was identified by Müller et al. (2024) as one of the brightest and fully integrated state-of-the-art phosphor-converted light sources, the spectral radiance results of the investigated phosphor materials promise better performance in all bands. Müller et al. (2024) found that the wavelength bands at 470 nm and at 630 nm are too poorly served with commercial phosphor-converted light sources, including SMD 500. With special regard to these bands, a combination of GGD35 and SWD50 is identified as the best-performing phosphor combination. This combination is used, as described in Section 3.2, as the light source in the flying spot projector. The drawback of a phosphor combination is the necessity of exchanging not only the excitation filter for fluorescence analysis but also the phosphor. Due to complexity, it can, therefore, be advantageous to only use a single phosphor. In that case, SGA35 is recommendable as its intensity is spectrally distributed in all four example wavelength bands.
Besides the emitted radiance, the invested laser incident power to reach a high radiance level is important since the laser power of a laser diode determines the electrical input power, the effort required for thermal management, influences the unit price of the laser diode, and is finally limited to currently approximately 5 W for a single laser diode. Higher power is only achievable with a combination of multiple laser diodes. Hence, for reasons of efficiency and complexity, as well as from a cost perspective, low-incident laser power is desirable. This leads directly to the results of the spot size investigation.
5.1.2 Influence of the pump spot size
For a cost-effective application, Figure 4E shows the optimization criteria of radiance per incident laser power, which can be used in combination with Figure 4D to find an optimal balance between incident laser power and radiance for a specific application. If we assume that the increase in roll-over incident laser power with the spot size is approximately transferable to other phosphor materials, we can conclude that the operation close to the radiance limit with a single 5 W laser diode for GGD35 is possible up to an incident laser spot size diameter of approximately 250
Apart from an increased roll-over incident laser power, the incident laser spot size influences the maximum emitted radiance. Although one could expect an increase in radiance when making the laser spot smaller due to improved lateral heat spreading (thermal spreading resistance) (Ma et al., 2018a), radiance decreases for smaller spot sizes. An explanation can be derived from the spot size expansion plot in Figure 4C, showing an approximately constant expansion over the incident laser spot size in the range of 75
An interesting effect observed in Figures 4A, B is the slowly decreasing power threshold extrapolated for relatively small spots
Apart from the incident laser spot diameter, the entrance pupil of the following optical system was varied. Not surprisingly, the fluorescence spot with approximately a Gaussian profile shows the highest radiance close to the center. Hence, the highest radiance levels are obtained by small apertures. However, one must keep in mind that the collected flux
5.1.3 Sapphire plate and aperture
From the results of experiments using an uncoated sapphire plate, we can conclude that the benefit described by Zhang et al. (2019), Correia et al. (2017), Peng et al. (2019), and Ma and Luo (2019) for configurations with poorer thermal cooling can principally be used for phosphor samples with excellent thermal conductivity and good thermal contact to a heat sink. This conclusion is valid as the signal loss due to Fresnel reflections must be added to our measurements. Assuming that the sapphire plate has a minimal air gap toward the phosphor, unpolarized light as the fluorescence light will experience a reflection loss of more than 15% on the path toward the reflector. In the main radiation direction, the loss is still greater than 14%. Hence, a sapphire plate with an anti-reflection coating shows potential to increase the radiance. Additionally, we expect that the effect of a sapphire plate increases further when the air gap between the sapphire and phosphor is removed since the removal of an air gap not only mitigates Fresnel losses but also reduces thermal resistance. Still, we expect the effect of a sapphire plate to be less significant than that in the referenced literature since they use a transmissive mode, which usually shows higher thermal resistances than the reflection mode (Ma et al., 2018b; Engl et al., 2017; Rahman, 2022; Li S. et al., 2022) or apply phosphor samples with a lower thermal conductivity than ceramics. The overall better thermal management in our experiment based on a thin (115
Furthermore, a significantly higher roll-over laser power level was measured for GGD35 in combination with a sapphire plate in comparison to GGD35 without the plate using the standard characterization setup. We have shown that we can counteract this high power level without using a coating on the sapphire plate just by tilting the laser diodes by 90° around the radiation axis. As the laser shows a strong polarization of 1:100, with the tilt, we changed the polarization of the incident laser beam at the air–sapphire–air interface. Operating close to the Brewster angle of sapphire air (60.5° with
To sum up the findings regarding the use of a sapphire plate to increase radiance by a lower thermal resistance on the emitting side of the phosphor, we conclude that a sapphire plate must be used in combination with an anti-reflection coating, which leads to a potential increase of 15% in radiance. Adding additional thermal management to the heat sink might improve its benefit even further. The existence of Fresnel reflections on an uncoated sapphire plate was confirmed and can be prevented for incident laser rays by applying TM polarization under the Brewster angle.
In addition to the sapphire plate, we also investigated the effect of an aperture between the sapphire plate and phosphor for fluorescence spot size definition. Our results show that the aperture decreased the achievable radiance. Although our argumentation of Fresnel losses holds, this cannot be the only reason for the decrease in radiance. The aperture has a diameter roughly three times larger than the laser spot. As a result, neither the aperture nor the sapphire plate are in close contact with the hottest part on the phosphor surface. Hence, the heat spreading effect of the sapphire plate is reduced. Furthermore, the combination of the aperture and sapphire plate creates an air inclusion of a small volume, preventing effective convection.
As inspiration for further research, strategies to improve the achievable radiance level not covered in the presented paper are summarized in the following. One interesting option applied by Crytur is shaping the fluorescence with single-crystal phosphor itself to overcome the limitation of a Lambertian emission (Kubat et al., 2023; Philip et al., 2023). An approach also relying on low-scattering phosphors is the luminescence concentrator effect based on total internal reflection. Luminescence concentrators, usually used in combination with LEDs, create radiance levels in the same range as LERP light sources (de Boer et al., 2017; Hoelen et al., 2016; Jaffe et al., 2009; Ford et al., 2024; Sathian et al., 2017; Lopez et al., 2023). Schulz (2019) investigated methods to increase the luminance of LEDs and applied light recycling. With light recycling, flux that is not contained in the etendue of the subsequent optics can be directed back onto the emitting area by an external cavity and will, with a certain probability, be scattered onto the relevant etendue region. Schulz increased the luminance via light recycling with a factor between 1.2 and 1.4. Rather than maximizing radiance, we believe that achieving a more defined spot with steeper slopes and a limited emitting area is an important aspect for light source design. Here, we see either the application of a reflective film with an obscuration on top of the phosphor or the physical isolation of a phosphor volume as promising. A variant of the latter consisting of a low-scattering phosphor embedded into high-scattering non-fluorescent ceramic was built by Lenef et al. (2022).
5.2 Application in a flying spot projector
The findings of a flying spot projector with GGD35 and SWD50 are compared with the results of our previous research (Müller et al., 2024) using the commercially available and highly integrated LERP light source SMD 500 in a flying spot projector with a similar optical design. The presented results show an improvement in all four channels. Three different reasons are identified: first, the phosphor efficiency and quenching properties might be weaker than those of the investigated phosphors. Second, the SMD 500 is a highly integrated device, meaning that both exciting laser diodes are near the phosphor. Since the lasers and the phosphor have significant losses (approximately 12.9 W thermally dissipated of 14.4 W input power, according to the datasheet of Kyocera SMD 500), both parts heat each other. Better thermal dissipation can be guaranteed on the cost of a larger setup by making full use of the remote aspect, placing the lasers a few centimeters away from the phosphor and using lenses for light confinement. Third, and most importantly, for this article, the performance in dedicated wavelength bands is improved by choosing the spectrally best phosphor candidate for each channel.
Note that the blue channel is provided by phosphor fluorescence. This contrasts with conventional RGB projectors or light source modules, where the phosphor serves to fill the green gap only, while the blue excitation light from the laser or LED is used for the blue channel. This is especially beneficial in terms of spectral stability. Using a typical white LED for excitation, as many resource-efficient devices for fluorescence analysis do, the emission of the blue LED chip would be used to excite in the first channel. As already described, direct LEDs are susceptible to spectral drift. With the broader and, therefore, more stable phosphor spectrum, this phosphor can guarantee a lower uncertainty in a product.
To illustrate the benefit of an increased power level over all channels, the duration for the evaluation of a qPCR test is calculated. Assumptions are that the qPCR test evaluates 30 cycles; the four channels from blue to red in Figure 3C are evaluated, and the exposure time of the camera-based detection system would take 500 ms per channel if the excitation power is 7.5 mW, as stated by Müller et al. (2024). If the actual excitation power measured in the flying spot projector, shown in Figure 6B, is lower, then the exposure time of the camera must be increased linearly to compensate for the lower signal. If the power level is higher, we ignore the excess to avoid photobleaching of the fluorophores. For the Kyocera light source, the duration is 4 min and 54 s; for the investigated phosphor materials, it is 1 min and 24 s; and in the ideal case, it is exactly 1 min. The setup with SMD 500 would take 3.5 times longer than the setup with GGD35 and SWD50. However, it is questionable whether SMD 500 would work at all with the low power level of 0.5 mW in the blue excitation channel due to the expected lower signal to noise ratio.
Looking at the optical design of the flying spot projector in Figure 2, there is potential to simplify the setup by removing elements (3) and (4) if the aperture can be placed directly on the phosphor material itself.
6 Conclusion
The presented article covers laser-excited remote phosphor light sources for fluorescence-based analysis for low-etendue and cost-sensitive applications as LERP light sources have the potential to increase the performance of medical devices at the point-of-care, making them smaller and more accessible. Current research shows improvements in terms of available phosphor materials with shifted peak wavelengths and LERP light source design strategies as sapphire plates on the emission side of the phosphor. Since no standard for phosphor characterization is available yet, each research group established their own characterization setup most often using a camera, a spectrometer, and a power measurement device, along with spectral filters. The lack of a common standard makes the comparison of different research results difficult. Furthermore, among optimization strategies in LERP light source design, several open questions remain, such as the potential of a sapphire plate on highly conductive phosphors with good thermal management, the potential of light shaping with the phosphor sample, the incorporation of luminescent concentrator effect, light recycling, and the application of an aperture. Among the open questions, the presented article compares four commercially available ceramic and single-crystal phosphor samples with different peak emission wavelengths and a commercial highly integrated LERP light source and investigates the effect of small excitation spots in the range of 100
With the presentation of cost-sensitive, etendue-limited fluorescence analyses, we have shown the need for laser phosphors with strong emission in the blue and green wavelength ranges and demonstrated that spectral radiance and incident laser power are important parameters to characterize phosphors for this application. We believe that the comparison of different YAG:Ce derivatives and investigations on small excitation spot sizes and a sapphire plate for cooling on the emitting side will serve as a basis for future research in the field of LERP light source design. For researchers working on optical systems for quantitative fluorescence analysis, the identification of the GGD35 phosphor for fluorescence excitation in the blue and green wavelength ranges represents a significant advance.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
JM: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, and Writing–original draft. IR: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, and Writing–review and editing. RF: Conceptualization and Writing–review and editing. CN: Conceptualization, Supervision, and Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Albrecht Seidl and his colleagues Jens Vietor, Marc Rambo, and Volker Hagemann from SCHOTT AG, as well as Jan Kubát from Crytur spol. s.r.o., for helpful discussion on the application of ceramic and single crystal phosphors, and Klaus Trampert from the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology for the insightful conversations regarding measurement techniques. The authors acknowledge the permission from Thorlabs, Inc., to use the CAD models MB4545/M, CP31/M, S120C, S121C, CCSA1, FGL495M, ND40A, SM1A36, FBH450-10, and SM1L03 to generate a rendered image of the experimental setup. They thank Basler for granting them the same permission to use models Basler C23 Lens 12 mm and Basler ace USB3 C-Mount.
Conflict of interest
Authors JM, IR, and RF were employed by Robert Bosch GmbH.
The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors, and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
1www.schott.com/en-us/products/ceramic-laser-phosphor-converter-p1000260
2www.crytur.com/materials/orange-luminophore/
3www.kyocera-sldlaser.com/products/laserlight-smd
4The comparison is based on the unit prices of 28.99$ and 52.98$ on www.mouser.de on 12.11.2024.
References
Antonis, P., de Boer, D., Koole, R., Kadijk, S., Li, Y., Vanbroekhoven, V., et al. (2017). “Progress in extremely high brightness LED-based light sources,” Editor N. Dietz, 10378, 23. doi:10.1117/12.2275253
Bachmann, V. (2007). Studies on luminescence and quenching mechanisms in phosphors for light emitting diodes. Dissertation: Utrecht University Repository.
Beacher, J. (2011). Microscope illumination: LEDs are the future. Microsc. Today 19, 18–21. doi:10.1017/S1551929511000411
Cao, Y., Xie, R., Liu, Q., and Chen, X. (2022). Pursuing phosphor materials for laser-driven lighting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 121, 150401. doi:10.1063/5.0127364
Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH (2019). ZEISS Colibri. Productinformation DE_41_011_176M. Available at: https://asset-downloads.zeiss.com/catalogs/download/mic/9ba0563f-14a8-4a0c-b747-0ce2747cc2fa/EN_product-info_Colibri-7_rel1-0.pdf.
Correia, A., Hanselaer, P., and Meuret, Y. (2017). “Opto-thermal design of a white light point source based on high power blue laser diodes (Conference Presentation),”. Sixteenth international conference on solid state lighting and LED-based illumination systems Editors N. Dietz, and I. T. Ferguson 10378, 25. SPIE. doi:10.1117/12.2272571
Cozzan, C., Brady, M. J., O’Dea, N., Levin, E. E., Nakamura, S., DenBaars, S. P., et al. (2016). Monolithic translucent BaMgAl10O17:Eu2+ phosphors for laser-driven solid state lighting. AIP Adv. 6, 105005. doi:10.1063/1.4964925
de Boer, D. K. G., Bruls, D., Hoelen, C., and Jagt, H. (2017). High lumen density sources based on LED-pumped phosphor rods: opportunities for performance improvement. Sixt. Int. Conf. Solid State Light. LED-based Illum. Syst. 10378, 22. doi:10.1117/12.2275729
Engl, M., Lenef, A., Pikart, P., Rosenauer, M., Zumkley, M., Frischeisen, J., et al. (2017). Blue laser light conversion: a technology comparison between transmissive and reflective approaches. 12th Int. Symposium Automot. Light. Proc. Conf. (Darmstadt Herbert Utz Verlag) 17, 19–28.
Ford, B., Long, S., and Sathian, J. (2024). Next-generation white light source for medical imaging based on luminescent concentrators, Light-Emitting Devices, Mater. Appl. XXVIII, PC12906. doi:10.1117/12.3002365
Hagemann, V., and Seidl, A. (2021). “Design rules for laser pumped phosphor light engines with static ceramic luminescent converters,”. Light-emitting devices, materials, and applications XXV Editors M. Strassburg, J. K. Kim, and M. R. Krames, 11706, 40. (SPIE). doi:10.1117/12.2578476
Hagemann, V., Seidl, A., and Weidmann, G. (2019). “Ceramic phosphor wheels for high luminance SSL-light sources with >500W of laser power for digital projection,”. Light-emitting devices, materials, and applications Editors M. Strassburg, J. K. Kim, and M. R. Krames 10940, 43. (SPIE). doi:10.1117/12.2508860
Hagemann, V., Seidl, A., and Weidmann, G. (2020). “Static ceramic phosphor assemblies for high power high luminance SSL-light sources for digital projection and specialty lighting,”. Light-emitting devices, materials, and applications XXIV Editors M. Strassburg, J. K. Kim, and M. R. Krames (San Francisco, United States: SPIE), 53, 53. doi:10.1117/12.2544000
Hoelen, C., de Boer, D., Bruls, D., van der Eyden, J., Koole, R., Li, Y., et al. (2016). “LED light engine concept with ultra-high scalable luminance,”. Light-emitting diodes: materials, devices, and applications for solid state lighting XX Editors H. Jeon, L.-W. Tu, M. R. Krames, and M. Strassburg (San Francisco, California, United States), 9768. doi:10.1117/12.2224042
Hu, F., and Li, Y. (2013). “Laser and phosphor hybrid source for projection display,”. Solid state lasers XXII: Technology and devices Editors W. A. Clarkson, and R. Shori 8599. doi:10.1117/12.200571685991K
Hu, F., Zhang, C., Guo, Z., Chen, C., and Li, Y. (2020). 82-2: invited paper: latest progress of laser phosphor projection display. SID Symposium Dig. Tech. Pap. 51, 1234–1239. doi:10.1002/sdtp.14102
Jaffe, C. B., Jaffe, S. M., and Conner, A. R. (2009). “New lighting for the design of high quality biomedical devices,” in Design and quality for biomedical technologies II. Editors R. Raghavachari, and R. Liang (San Jose, CA). doi:10.1117/12.808263
Kralik, P., and Ricchi, M. (2017). A basic guide to real time PCR in microbial diagnostics: definitions, parameters, and everything. Front. Microbiol. 8, 108. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2017.00108
Krasnoshchoka, A., Hansen, A. K., Thorseth, A., Marti, D., Petersen, P. M., Jian, X., et al. (2020). Phosphor material dependent spot size limitations in laser lighting. Opt. Express 28, 5758. doi:10.1364/OE.383866
Krasnoshchoka, A., Thorseth, A., Dam-Hansen, C., Corell, D. D., Petersen, P. M., and Jensen, O. B. (2017). Investigation of saturation effects in ceramic phosphors for laser lighting. Materials 10, 1407. doi:10.3390/ma10121407
Kubat, J., Novotny, S., Pokorny, M., Miller, V., and Mazura, M. (2023). “The ultra-bright and low-etendue light source for bioinstrumentation and scientific applications,” in Integrated optics: design, devices, systems and applications VII. Editors P. Cheben, J. Čtyroký, and I. Molina, 12. doi:10.1117/12.2662827
Lee, S.-M., Cho, J.-H., and Lee, W.-B. (2023). A study on the development of a white light source module for a large-capacity searchlight using a blue laser diode. Electronics 12, 760. doi:10.3390/electronics12030760
Lenef, A., Kelso, J., Tchoul, M., Mehl, O., Sorg, J., and Zheng, Y. (2014). “Laser-activated remote phosphor conversion with ceramic phosphors,” in Thirteenth international conference on solid state lighting Editors M. H. Kane, J. Jiao, N. Dietz, and J.-J. Huang doi:10.1117/12.206186491900C
Lenef, A., Kelso, J., Zheng, Y., and Tchoul, M. (2013). “Radiance limits of ceramic phosphors under high excitation fluxes,”. Current developments in lens design and optical engineering XIV Editors R. B. Johnson, V. N. Mahajan, and S. Thibault, 8841. doi:10.1117/12.2023498
Lenef, A., Kelso, J. F., Serre, J., Kulkarni, A. A., Kinkenon, D., and Avison, M. (2022). Co-sintered ceramic converter for transmissive laser-activated remote phosphor conversion. Appl. Phys. Lett. 120, 021104. doi:10.1063/5.0077125
Lenef, A., Raukas, M., Wang, J., and Li, C. (2020). Phosphor performance under high intensity excitation by InGaN laser diodes. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 9, 016019. doi:10.1149/2.0352001JSS
Li, K., Chang, Y., Chen, A., Wang, L., and Tsai, S. (2021). 49-3: high power laser phosphor light source using a scanning mirror for projectors. SID Symposium Dig. Tech. Pap. 52, 680–682. doi:10.1002/sdtp.14774
Li, K., Chang, Y., Wang, L., Chen, A., Cheng, W., Han, P., et al. (2022a). 71-3: static laser phosphor for projectors with rotating tilted mirror. SID Symposium Dig. Tech. Pap. 53, 956–959. doi:10.1002/sdtp.15654
Li, S., Guo, Y., and Xie, R.-J. (2022b). Laser phosphors for next-generation lighting applications. Accounts Mater. Res. 3, 1299–1308. doi:10.1021/accountsmr.2c00193
Li, S., Tang, D., Tian, Z., Liu, X., Takeda, T., Hirosaki, N., et al. (2017). New insights into the microstructure of translucent CaAlSiN 3:Eu 2+ phosphor ceramics for solid-state laser lighting. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 1042–1051. doi:10.1039/C6TC04987G
Li, S., Zhu, Q., Wang, L., Tang, D., Cho, Y., Liu, X., et al. (2016). CaAlSiN 3:Eu 2+ translucent ceramic: a promising robust and efficient red color converter for solid state laser displays and lighting. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 8197–8205. doi:10.1039/C6TC02518H
Lin, C. C., and Liu, R.-S. (2017). “Introduction to the basic properties of luminescent materials,” in Phosphors, up conversion nano particles, quantum dots and their applications. Editor R.-S. Liu (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg), 1–29. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-52771-9_1
Liu, C.-N., Shih, H.-K., Chen, Y.-C., Chen, Y.-H., Cheng, W.-C., and Cheng, W.-H. (2023). High reliability and luminance of the color wheel by phosphor-in-inorganic silicone. Opt. Mater. Express 13, 1092. doi:10.1364/OME.473011
Lopez, L., Pichon, P., Loiseau, P., Viana, B., Mahiou, R., Druon, F., et al. (2023). Ce:LYSO, from scintillator to solid-state lighting as a blue luminescent concentrator. Sci. Rep. 13, 7199. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-32689-z
Lux, A., Bott, H., Malek, N. P., Zengerle, R., Maucher, T., and Hoffmann, J. (2021). Real-time detection of tumor cells during capture on a filter element significantly enhancing detection rate. Biosensors 11, 312. doi:10.3390/bios11090312
Ma, C., and Cao, Y. (2021). Phosphor converters for laser driven light sources. Appl. Phys. Lett. 118, 210503. doi:10.1063/5.0053581
Ma, Y., Lan, W., Xie, B., Hu, R., and Luo, X. (2018a). An optical-thermal model for laser-excited remote phosphor with thermal quenching. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 116, 694–702. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.09.066
Ma, Y., and Luo, X. (2019). Enhancing opto-thermal performances of the reflective phosphor-converted laser diode by stacking a sapphire substrate for double-sided phosphor cooling. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 143, 118600. doi:10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.118600
Ma, Y., Wang, M., and Luo, X. (2018b). “A comparative study of reflective and transmissive phosphor-converted laser-based white lighting,” in 2018 17th IEEE intersociety Conference on Thermal and thermomechanical Phenomena in electronic systems (ITherm) (san diego, CA: ieee), 773–777. doi:10.1109/ITHERM.2018.8419613
Maggay, I. V. B., and Liu, W.-R. (2017). “Novel phosphors for UVLEDs,” in Phosphors, up conversion nano particles, quantum dots and their applications. Editor R.-S. Liu (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg), 399–419. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-52771-9_13
Müller, J., Ghosh, O., Ramsteiner, I. B., Fieß, R., and Neumann, C. (2024). “Flexible illumination module for lab-on-chip applications,”. Optical diagnostics and sensing XXIV: toward point-of-care diagnostics. Editors J. S. Baba, and G. L. Coté (San Francisco, United States: SPIE), 6, 6. doi:10.1117/12.3001551
Müller, J., Wilm, T., Ramsteiner, I., Fieß, R., and Neumann, C. (2023). “Investigation of high radiance laser-pumped phosphor converted light sources in sensor applications,” in DGaO-PROCEEDINGS der 124 (Berlin: Jahrestagung). 0287–2023–A039–1.
Nitta, M., Nagao, N., Nomura, Y., Hirasawa, T., Sakai, Y., Ogata, T., et al. (2020). High-brightness red-emitting phosphor La 3 (Si,Al) 6 (O,N) 11:Ce 3+ for next-generation solid-state light sources. ACS Appl. Mater. and Interfaces 12, 31652–31658. doi:10.1021/acsami.0c09342
Peng, Y., Mou, Y., Sun, Q., Cheng, H., Chen, M., and Luo, X. (2019). Facile fabrication of heat-conducting phosphor-in-glass with dual-sapphire plates for laser-driven white lighting. J. Alloys Compd. 790, 744–749. doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.03.220
Philip, O., Shestakova, I., Kubat, J., Pokorny, M., Mazura, M., novotny, s., et al. (2023). “A novel ultra-bright high-luminance and compact light source based on phosphor converted laser for advanced modern optical systems,” in Laser Technology for defense and security XVIII. Editors M. Dubinskii, and R. D. Peterson (SPIE), 5. doi:10.1117/12.2663087
Podbiel, D., Laermer, F., Zengerle, R., and Hoffmann, J. (2020). Fusing MEMS technology with lab-on-chip: nanoliter-scale silicon microcavity arrays for digital DNA quantification and multiplex testing. Microsystems and Nanoeng. 6, 82. doi:10.1038/s41378-020-00187-1
Rahman, F. (2022). Diode laser-excited phosphor-converted light sources: a review. Opt. Eng. 61. doi:10.1117/1.OE.61.6.060901
Raukas, M., Kelso, J., Zheng, Y., Bergenek, K., Eisert, D., Linkov, A., et al. (2013). Ceramic phosphors for light conversion in LEDs. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2, R3168–R3176. doi:10.1149/2.023302jss
Sathian, J., Breeze, J. D., Richards, B., Alford, N. M., and Oxborrow, M. (2017). Solid-state source of intense yellow light based on a Ce:YAG luminescent concentrator. Opt. Express 25, 13714. doi:10.1364/OE.25.013714
Schott, A. G. (2024). Static ceramic converters. Mainz, Germany: Productinformation Version. Available at: https://mss-p-009-delivery.stylelabs.cloud/api/public/content/1f15c6dd66b24e07aeb186f6bc61ed49?v=89c75495&download=true.
Schulz, B. (2019). Weiterentwicklung der Beleuchtungseinheit LED-basierter Projektionssysteme. Karlsruhe: Karlsruher Institut für Technologie. Ph.D. thesis.
Shih, H.-K., Chang, Y.-P., Liu, C.-N., Li, K., and Cheng, W.-H. (2022). Laser-excited single crystal phosphor in white LED for wide field of view and high enhanced central brightness for vehicle headlights. AIP Adv. 12, 015018. doi:10.1063/5.0069586
Silver, J., Fern, G. R., and Withnall, R. (2016). “Color conversion phosphors for light emitting diodes,” in Materials for solid state lighting and displays. Editor A. Kitai (Chichester, UK: John Wiley and Sons, Ltd), 91–134. doi:10.1002/9781119140610.ch3
Strauss, J. (2017). Laser light generation 2 - better performance and safety. ATZelektronik Worldw. 12, 38–41. doi:10.1007/s38314-017-0014-5
Sun, P., Hu, P., Liu, Y., Luo, Z., Wang, L., Zhu, Q., et al. (2023). Luminescence-refrigeration module: addressing luminescence saturation challenges in laser-driven lighting. Laser and Photonics Rev. 18. doi:10.1002/lpor.202300969
Vogl, M. (2023) “Thermische Untersuchungen an Laser-aktivierten Leuchtstoff-Systemen mit dynamischer Leuchtdichteverteilung,”. Karlsruhe: Karlsruher Institut für Technologie. PhD Thesis. doi:10.5445/KSP/1000138834
Wang, L., Zhang, J., Xu, L., Bao, S., Wang, Y., Liu, J., et al. (2023). Ce:GdYAG phosphor-in-glass: an innovative yellow-emitting color converter for solid-state laser lighting. J. Mater. Sci. and Technol. 134, 42–49. doi:10.1016/j.jmst.2022.06.025
Wei, R., Wang, L., Zheng, P., Zeng, H., Pan, G., Zhang, H., et al. (2019). On the luminance saturation of phosphor-in-glass (PiG) films for blue-laser-driven white lighting: effects of the phosphor content and the film thickness. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 39, 1909–1917. doi:10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2019.01.024
Willeke, B., Wallaschek, J., Neumann, C., and Ovenmeyer, L. (2016). Laserscheinwerfer für adaptive Fahrlichtfunktionen im Kfz. Hannover: Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Universität Hannover. Ph.D. thesis.
Xia, Y., Li, S., Zhang, Y., Takeda, T., Hirosaki, N., and Xie, R.-J. (2020). Discovery of a Ce 3+ -activated red nitride phosphor for high-brightness solid-state lighting. J. Mater. Chem. C 8, 14402–14408. doi:10.1039/D0TC03964K
Xia, Z., Xu, Z., Chen, M., and Liu, Q. (2016). Recent developments in the new inorganic solid-state LED phosphors. Dalton Trans. 45, 11214–11232. doi:10.1039/C6DT01230B
Xu, J., Jiang, Z., Gu, W., Chen, X., Pang, S., Hu, B., et al. (2021). Design of a β-SiAlON:Eu based phosphor-in-glass film with high saturation threshold for high-luminance laser-driven backlighting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 119, 231102. doi:10.1063/5.0073168
Xu, J., Wang, L., Gu, W., Jiang, Z., Chen, X., Hu, B., et al. (2022). Emitting area limitation via scattering control in phosphor film realizing high-luminance laser lighting. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 42, 608–615. doi:10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2021.10.035
Xu, Y., Li, S., Zheng, P., Wang, L., You, S., Takeda, T., et al. (2019). A search for extra-high brightness laser-driven color converters by investigating thermally-induced luminance saturation. J. Mater. Chem. C 7, 11449–11456. doi:10.1039/C9TC03919H
Yoon, D.-H., and Song, Y.-H. (2017). “Categories of oxide phosphors,” in Phosphors, up conversion nano particles, quantum dots and their applications. Editor R.-S. Liu (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg), 265–283. doi:10.1007/978-3-662-52771-9_9
Yuan, S., Bitzilou, I., Chen, X., Xu, J., Xu, P., Du, B., et al. (2024). Novel strategy to optimize luminance for phosphor-converted laser lighting. J. Luminescence 265, 120233. doi:10.1016/j.jlumin.2023.120233
Zhang, J., Wang, L., Zhu, Q., Chen, Q., Liang, X., and Xiang, W. (2021). A thermally robust phosphor-in-glass film with high luminous efficiency for high-power blue laser diodes lighting. Appl. Phys. Lett. 119, 221904. doi:10.1063/5.0072703
Zhang, X., Si, S., Yu, J., Wang, Z., Zhang, R., Lei, B., et al. (2019). Improving the luminous efficacy and resistance to blue laser irradiation of phosphor-in-glass based solid state laser lighting through employing dual-functional sapphire plate. J. Mater. Chem. C 7, 354–361. doi:10.1039/C8TC05050C
Zhao, J., Guo, Z., Yu, Z., Zhang, H., Wang, Q., Mou, Y., et al. (2024). Laser-Driven white light source with high luminescence saturation through reflective color converter. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 45, 232–235. doi:10.1109/LED.2023.3345662
Zheng, P., Li, S., Wang, L., Zhou, T.-L., You, S., Takeda, T., et al. (2018). Unique color converter architecture enabling phosphor-in-glass (PiG) films suitable for high-power and high-luminance laser-driven white lighting. ACS Appl. Mater. and Interfaces 10, 14930–14940. doi:10.1021/acsami.8b03168
Zheng, P., Li, S., Wei, R., Wang, L., Zhou, T., Xu, Y., et al. (2019). Unique design strategy for laser-driven color converters enabling superhigh-luminance and high-directionality white light. Laser and Photonics Rev. 13, 1900147. doi:10.1002/lpor.201900147
Keywords: fluorescence, light sources, laser-excited remote phosphor, etendue, radiance, metrology, lab-on-a-chip, flying spot projector
Citation: Müller J, Ramsteiner IB, Fieß R and Neumann C (2024) High-radiance phosphor-converted light sources for fluorescence analysis. Adv. Opt. Technol. 13:1510954. doi: 10.3389/aot.2024.1510954
Received: 14 October 2024; Accepted: 18 November 2024;
Published: 05 December 2024.
Edited by:
Ali Belarouci, CNRS, FranceReviewed by:
Shuang Chang, Vanderbilt University, United StatesAlois Herkommer, University of Stuttgart, Germany
Copyright © 2024 Müller, Ramsteiner, Fieß and Neumann. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jan Müller, amFuLm11ZWxsZXI5QGRlLmJvc2NoLmNvbQ==
 Jan Müller
Jan Müller Ingo B. Ramsteiner2
Ingo B. Ramsteiner2 Cornelius Neumann
Cornelius Neumann