- 1Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
- 2University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
- 3Spallation Neutron Source Science Center, China Spallation Neutron Source, Dongguan, China
X-ray ptychography is a coherent diffraction imaging technique that allows for the quantitative retrieval of both the amplitude and phase information of a sample in diffraction-limited resolution. However, traditional reconstruction algorithms require a large number of iterations to obtain phase and amplitude images exactly, and the expensive computation precludes real-time imaging. To solve the inverse problem of ptychography data, PtychoNN uses deep convolutional neural networks for real-time imaging. However, its model is relatively simple, and its accuracy is limited by the size of the training dataset, resulting in lower robustness. To address this problem, a series of W-Net neural network models have been proposed which can robustly reconstruct the object phase information from the raw data. Numerical experiments demonstrate that our neural network exhibits better robustness, superior reconstruction capabilities and shorter training time with high-precision ptychography imaging.
1 Introduction
Ptychography is a technique for coherent diffraction imaging that provides quantitative phase information of a sample in diffraction-limited resolution (Pfeiffer, 2018). It can image a large number of thick samples in high resolution without complex sample preparation while providing the best observation ability and application potential for materials and biological samples. However, the long time for data acquisition and the expensive computing resources cost for intensive data processing remain significant obstacles. In addition, ptychography is widely used in combination with other optical techniques in various fields such as biomedical (Shemilt et al., 2015; Bhartiya et al., 2021), chemical (Beckers et al., 2011) and metrology (D’alfonso et al., 2014). In conventional experiments, a small aperture or other optical device is used to focus the light probe for scanning the sample. The diffraction pattern at each scanning position is captured by a detector. Adjacent scanning positions require partial overlap to ensure that the recorded experimental data contains sufficient information. However, the detector only aquires intensity while phase information is lost. Therefore, phase retrieval algorithms are needed to recover the phase of the recorded diffraction pattern and reconstruct the sample structure. Traditional phase retrieval algorithms are iterative, such as ePIE (Extended Ptychographic Iterative Engine) (Maiden and Rodenburg, 2009) and DM (Difference Map) (Thibault et al., 2008; 2009), which require more supporting conditions and computation time to converge and obtain the real phase information. The inherent principle of these algorithms requires that the overlap between adjacent scanning areas in ptychography experiments should be greater than 50% to obtain better reconstruction results, increasing scanning time and experimental data volume, placed higher demands on the radiation resistance of the sample. The increased amount of data also increases the computational time of traditional iterative algorithms, which places higher demands on the computing hardware. To decreases the computational time, in 2017, Maiden et al. proposed mPIE (Maiden et al., 2017) based on the idea of momentum gradient descent algorithm in machine learning. After a certain number of iterations, the distribution function update formula of the object under test was added with a momentum term, which significantly reduced the number of iterations and accelerated the convergence speed of the algorithm. Kappeler et al. first proposed building PtychNet (Kappeler et al., 2017) and other models (Nguyen et al., 2018; Yan et al., 2020) based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) for the reconstruction of images in Fourier ptychography (FP). In 2019, Işıl et al. (2019) constructed a new phase recovery network by combining Deep Neural Networks (DNN) and the Hybrid Input-Output (HIO) (Fienup, 1978) algorithm. They embedded the DNN network into the iteration process of HIO. In 2020, Cherukara et al. constructed the network PtychoNN (Cherukara et al., 2020), a deep convolutional neural network, learns the direct mapping from far-field coherent diffraction data to real-space image structure and phase. PtychoNN is hundreds of times faster than Ptycholib (Nashed et al., 2014) because it understands the direct relationship between diffraction data and image structure and phase. Therefore, data inversion no longer requires overlap constraints, which increases the speed of data acquisition and reconstruction by 5 times (Cherukara et al., 2020).
2 Methods
2.1 Neural networks
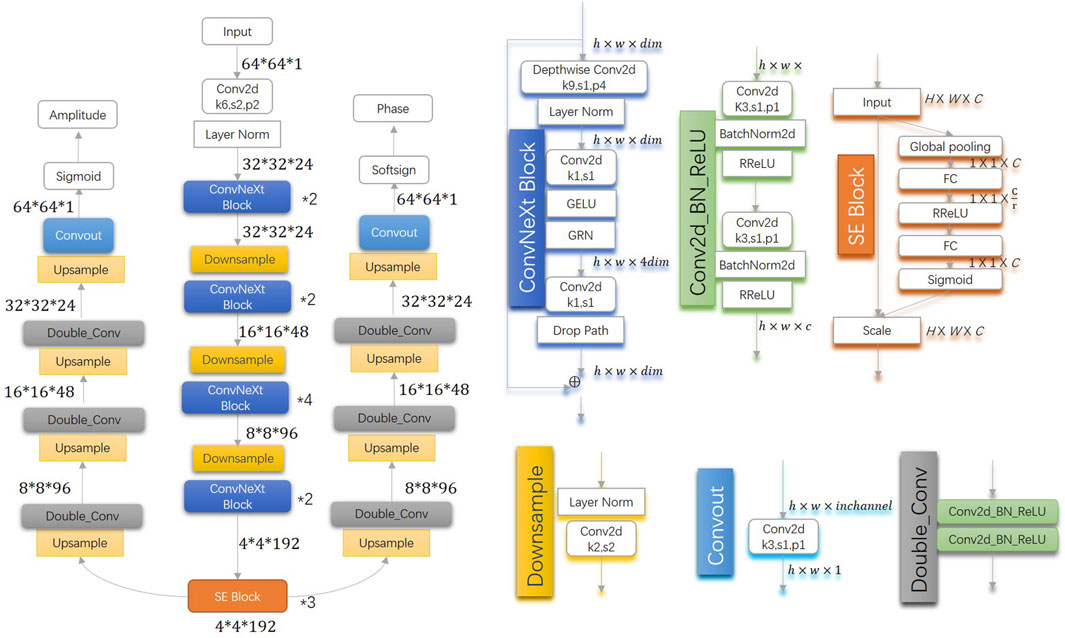
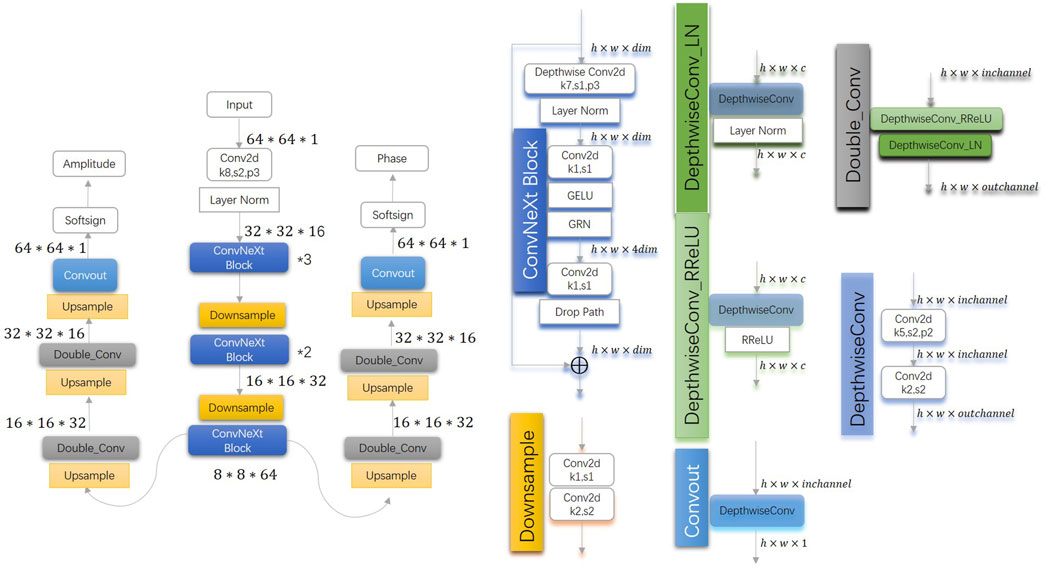
The network architecture of PtychoNN is designed to allow a single network to predict both amplitude and phase, thus minimizing the number of network weights that need to be learned. This network only uses convolutional and up/downsampling layers (without dense layers) to keep the number of network weights minimum, improving the speed of training and prediction (Cherukara et al., 2020). However, the relationship between the number of network weights and the speed of network training is not simply linear. Therefore, we took inspiration from ConvNext V2 (Woo et al., 2023), Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks (Hu et al., 2018) and developed the W1-Net model.
Figure 1 shows the architecture of W1-Net.The W1-network architecture consists of an encoder and two decoders, enabling a single network to predict both amplitude and phase. In comparison to PtychoNN, W1-Net primarily focuses on increasing the depth of the encoder network and introducing residual networks and channel attention mechanisms. The enhancement of feature extraction capability and expressive power is achieved through increasing the network depth. With the increase in network depth, the network can learn more complex features. Shallow networks may only capture low-level features such as edges and textures in images, while deep networks can learn more abstract high-level features, such as parts and overall structures of objects. Deep networks capture the inherent structure and patterns in the data through hierarchical abstraction, thereby enabling more accurate predictions. The introduction of residual networks aims to address issues such as gradient vanishing or exploding that may arise with increasing model depth, thereby avoiding degradation problems as the number of layers increases. By embedding learning mechanisms, the model captures spatial correlations and improve network performance. The channel attention mechanism (SE block) adaptively recalibrates channel-wise feature responses by explicitly modeling interdependencies between channels. The encoder’s core consists of a convolutional layer, three downsample layers, four ConvNext blocks (stacked in a 2:2:4:2 manner), and three SE blocks. The convolutional layer and downsample layers aim to decrease image size, thereby reducing computation time and workload. The decoder comprises upsample and convolutional layers, with bilinear interpolation used in the upsample layer to reduce computation time and workload. Additionally, double convolution and batch normalization are employed to prevent overfitting. To achieve a wider field of view, a larger kernel size is utilized in the ConvNext block and the first convolutional layer of the encoder. Furthermore, SE blocks optimize the weights between channels, and a new activation function is utilized to improve training results.
3 Experimental results and discussions
3.1 Training configuration
To train and evaluate the W1-Net network, we utilized the dataset provided by (Cherukara et al., 2020), which consisted of 16,100 triplets of raw coherent diffraction data, real-space amplitude, and phase images obtained from the first 100 scans of an experimental natural material structure conducted on the X-ray nano-probe beamline at the Advanced Photon Source 26ID. The scanning step was 30 nm over 161
The W1-Net network was trained on PyTorch, using an Intel Core i7-6700 CPU and an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3060 GPU. To evaluate the performance of the model, we compared the experimental results of PtychoNN and W1-Net, using peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) (Horé and Ziou, 2010), mean squared error (MSE) (Horé and Ziou, 2010), and structural similarity index (SSIM) as quantitative indicators for a comprehensive analysis of the models.
3.2 Experiment results
3.2.1 Single-shot experiment results
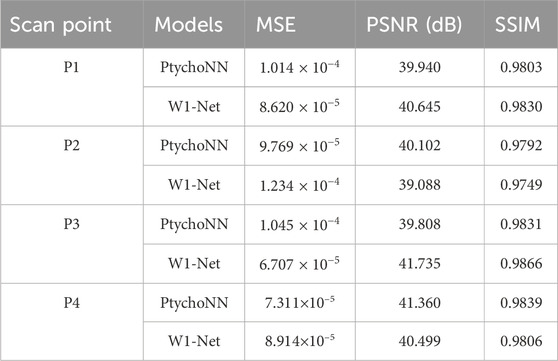
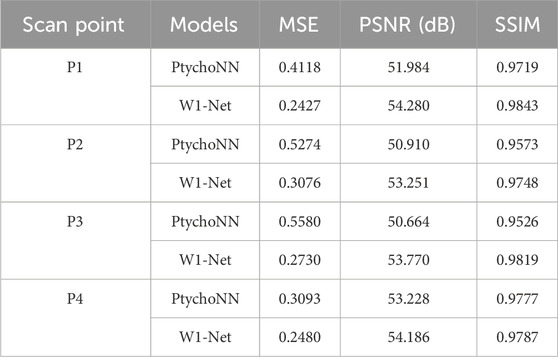
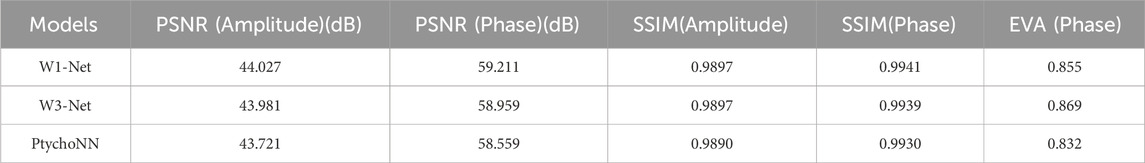
Figure 2 shows single-shot examples of the performance of PtychoNN and W1-Net on data from the test region of the experimental scan.We can observe that by using our W1-Net network, we are able to reconstruct the fine details of objects more completely, especially in terms of reconstructing edge information. In contrast, the reconstruction results of PtychoNN lose a lot of edge information. Furthermore, from our data Tables 1, 2, it is clear that W1-Net exhibits higher peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), structural similarity index (SSIM), and lower mean squared error (MSE) for these representative scanning points.
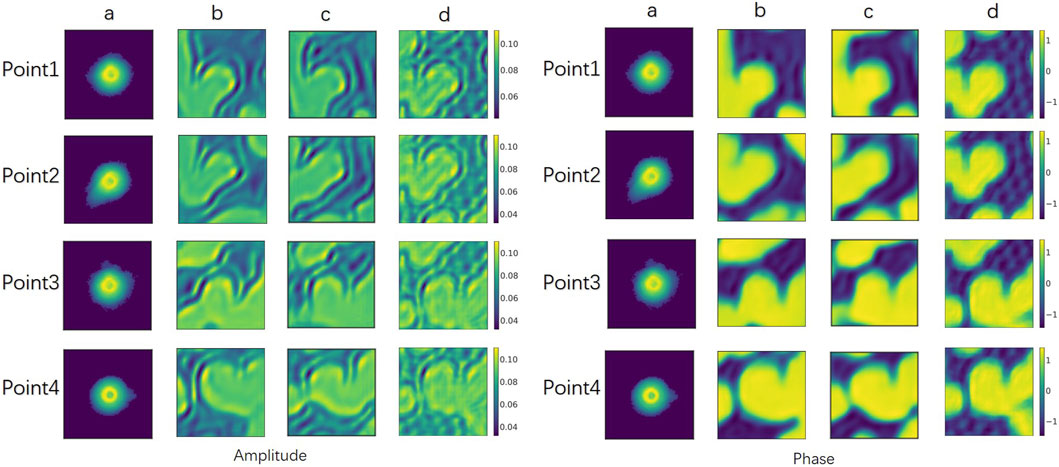
Figure 2. Single-shot predictions. (A) Input diffraction at different scan points, (B) predicted by PtychoNN, (C) predicted by W1-Net, (D) Ground-truth.Visually, our W1-Net achieves better results compared to PtychoNN.
These metrics are important standards for measuring the quality of image reconstruction. A higher PSNR value indicates less noise difference between the reconstructed image and the original image, a higher SSIM value indicates higher structural similarity between the reconstructed image and the original image, and a lower MSE value means a smaller overall error between the reconstructed image and the original image.
Because, in the experiment, the detector only obtains the intensity and loses the phase information, so we pay more attention to phase retrieval. Therefore, based on these results, we can conclude that our W1-Net network performs better in reconstructing object details and edge information, and achieves better performance than PtychoNN across multiple metrics of phase reconstruction.
3.2.2 Effect of training data size on performance
The training of neural networks requires a large amount of training data and computational resources. The quantity and size of training samples directly affect the training time and model accuracy. Therefore, we conducted a performance evaluation of W1-Net and PtychoNN using the same training data.
The results showed Figure 3, 4 that W1-Net outperforms PtychoNN in terms of reconstruction quality with the same training data. Particularly, W1-Net performs well even with fewer training samples, indicating its better robustness. This allows us to train W1-Net with less training data, reducing the demand for computational resources.
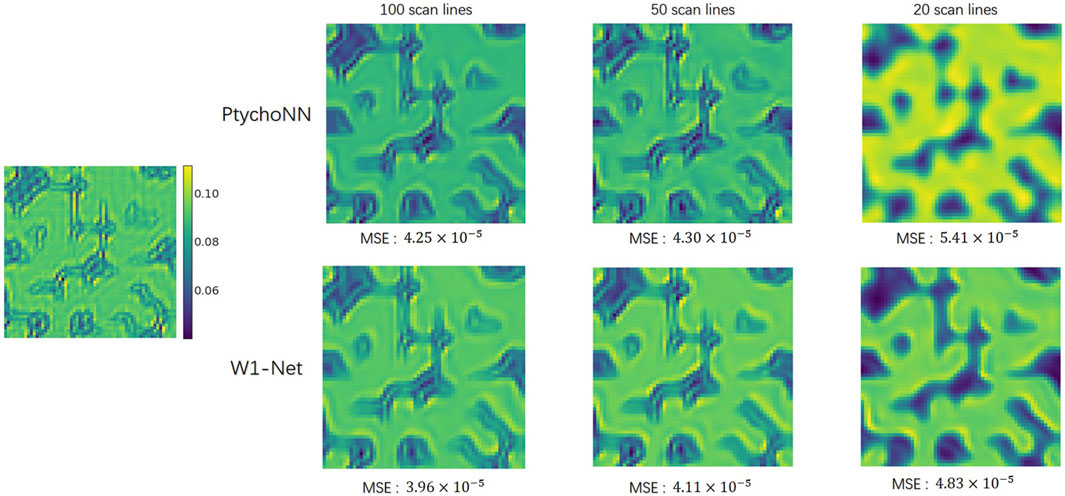
Figure 3. Effect of training data size in amplitude recovery. Images from the left to right show the performance of different models when trained on progressively fewer training samples.
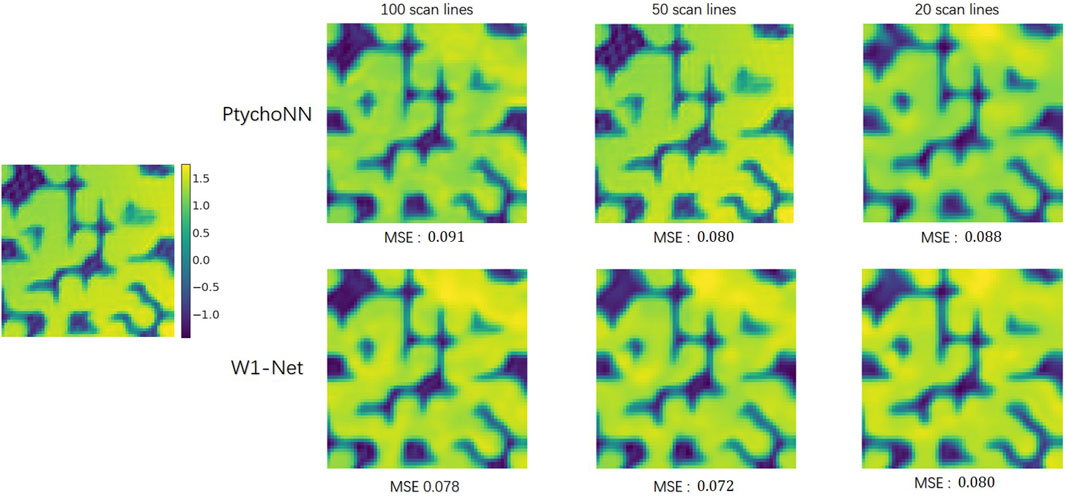
Figure 4. Effect of training data size in phase recovery. Images from the left to right show the performance of different models when trained on progressively fewer training samples.
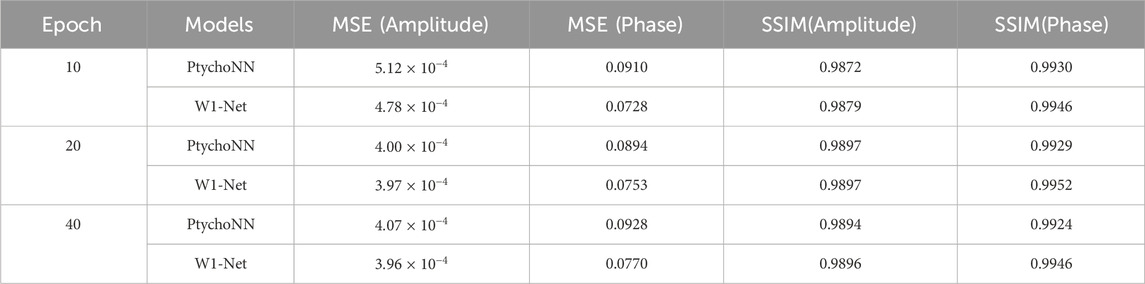
3.2.3 Effect of training epochs on performance
Furthermore, a robust network should exhibit relatively positive test results and faster convergence speed across different training epochs.
The results showed in Table 3 that W1-Net has lower mean squared error (MSE) and higher structural similarity index (SSIM) within the same training epochs. This means that W1-Net can converge faster during the training process and achieve relatively positive test results at each training epoch.
In conclusion, our W1-Net network demonstrates better reconstruction performance, better robustness, and faster convergence speed with the same training data. This makes it a promising choice for achieving high-quality image reconstruction in resource-constrained scenarios.
3.2.4 Scalability of the model
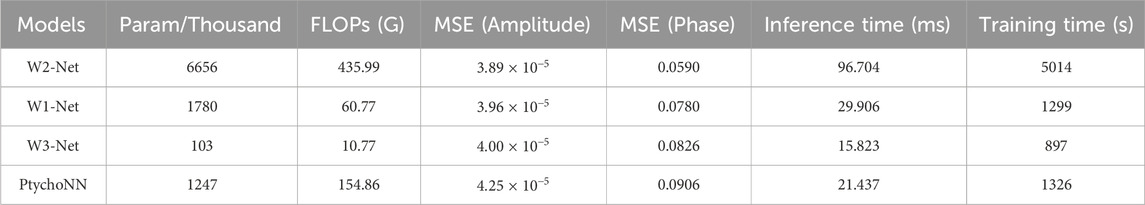
Our results demonstrated that W1-Net outperformed PtychoNN in terms of accuracy, despite having a larger number of parameters and model size.Moreover, In addition, we tested the W2-Net Figure 5 and W3-net Figure 6 models based on W1-Net by changing the number of filters, the number of stacked blocks and other minor adjustments.
By replaced Convolution with Depthwise Convolution (Chollet, 2017) and reduced the number of convolutional layers, filters and ReLu, W3-Net achieved the same reconstruction precision, and the parameters were only 8.26 percent of PtychoNN. Greatly reduced inference time from 21.437 ms for PtychoNN to 15.823 ms for W3-Net and alleviated hardware requirements on real-time ptychographic imaging.
Under the same data set for 60 epoch, the results shown in the Figure 7 and Tables 4, 5 showed that the W-series network shows better reconstruction performance. Additionally, W1-Net produced fewer noticeable artifacts or blurs, resulting in faster and more precise data reconstruction. W2-Net shows superior performance in phase recovery. W3-Net had a faster training speed and proposed a lightweight and efficient network model.
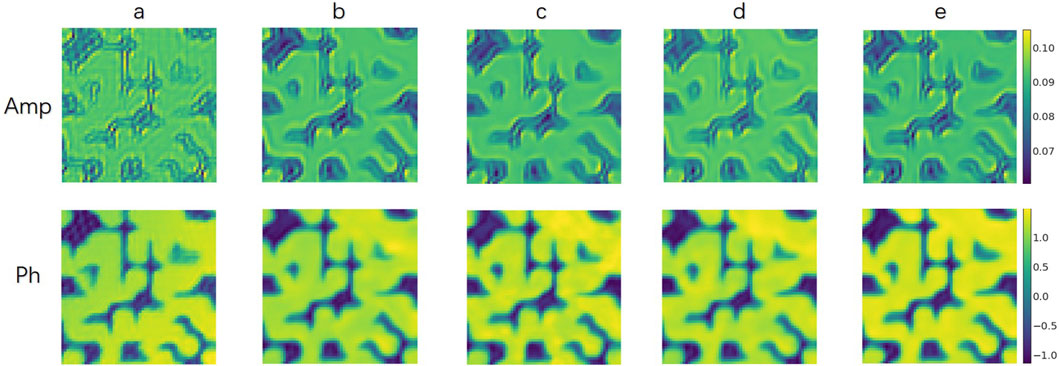
Figure 7. Different models results. (A): Ground-truth; (B): PtychoNN; (C): W3-Net; (D): W1-Net; (E): W2-Net. Visually, the reconstruction results improve progressively from left to right.
4 Conclusion
In this paper, we introduce a series of novel W-Net model including a lightweight network W3-Net that effectively addresses the phase and amplitude reconstruction problems in ptychography. Compared to PtychoNN, our W1-Net model not only requires less training time but also exhibits superior reconstruction results. Specifically, our model achieves lower mean squared error (MSE) and higher structural similarity index (SSIM) in phase reconstruction. This indicates that our W1-Net model can accurately recover the phase information of the images.
Furthermore, our W1-Net model demonstrates higher scalability. We demonstrate in our study that the W2-Net model achieves better recovery results when sufficient computational resources and hardware are available. W3-Net reduced inference time and hardware requirements on real-time ptychographic imaging.This further confirms the scalability and adaptability of the W1-Net model.
In summary, our research presents a novel W-Net model, namely, W1-Net, for solving the phase reconstruction problems in ptychography. Compared to traditional PtychoNN methods, our model offers significant advantages in terms of training time, reconstruction performance, and scalability. This provides a more efficient, accurate, and scalable solution for research and practical applications in the field of ptychography.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://github.com/mcherukara/PtychoNN.
Author contributions
CX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. LW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–review and editing. YM: Formal Analysis, Resources, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. YL: Writing–review and editing. GC: Project administration, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Scientific and Technological Innovation project of Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. E35451U2); The National Natural Science Foundation of China (22027810); The Scientific and Technological Innovation project of Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. E3545JU2); The Network Security and Informatization Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. E32957S3).
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to all colleagues who facilitated access to and provided assistance during the experiments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Beckers, M., Senkbeil, T., Gorniak, T., Reese, M., Giewekemeyer, K., Gleber, S.-C., et al. (2011). Chemical contrast in soft x-ray ptychography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 208101. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.107.208101
Bhartiya, A., Batey, D., Cipiccia, S., Shi, X., Rau, C., Botchway, S., et al. (2021). X-ray ptychography imaging of human chromosomes after low-dose irradiation. Chromosome Res. 29, 107–126. doi:10.1007/s10577-021-09660-7
Cherukara, M. J., Zhou, T., Nashed, Y., Enfedaque, P., Hexemer, A., Harder, R. J., et al. (2020). Ai-enabled high-resolution scanning coherent diffraction imaging. Appl. Phys. Lett. 117. doi:10.1063/5.0013065
D’alfonso, A., Morgan, A., Yan, A., Wang, P., Sawada, H., Kirkland, A., et al. (2014). Deterministic electron ptychography at atomic resolution. Phys. Rev. B 89, 064101. doi:10.1103/physrevb.89.064101
Fienup, J. R. (1978). Reconstruction of an object from the modulus of its fourier transform. Opt. Lett. 3, 27–29. doi:10.1364/ol.3.000027
Horé, A., and Ziou, D. (2010). Image quality metrics: psnr vs. ssim, 2366–2369. doi:10.1109/ICPR.2010.579
Hu, J., Shen, L., and Sun, G. (2018). “Squeeze-and-excitation networks,” in Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 7132–7141.
Işıl, Ç., Oktem, F. S., and Koç, A. (2019). Deep iterative reconstruction for phase retrieval. Appl. Opt. 58, 5422–5431. doi:10.1364/ao.58.005422
Kappeler, A., Ghosh, S., Holloway, J., Cossairt, O., and Katsaggelos, A. (2017). “Ptychnet: cnn based fourier ptychography,” in 2017 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP) (IEEE), 1712–1716.
Maiden, A., Johnson, D., and Li, P. (2017). Further improvements to the ptychographical iterative engine. Optica 4, 736–745. doi:10.1364/optica.4.000736
Maiden, A. M., and Rodenburg, J. M. (2009). An improved ptychographical phase retrieval algorithm for diffractive imaging. Ultramicroscopy 109, 1256–1262. doi:10.1016/j.ultramic.2009.05.012
Nashed, Y. S., Vine, D. J., Peterka, T., Deng, J., Ross, R., and Jacobsen, C. (2014). Parallel ptychographic reconstruction. Opt. express 22, 32082–32097. doi:10.1364/oe.22.032082
Nguyen, T., Xue, Y., Li, Y., Tian, L., and Nehmetallah, G. (2018). Deep learning approach for fourier ptychography microscopy. Opt. express 26, 26470–26484. doi:10.1364/oe.26.026470
Shemilt, L., Verbanis, E., Schwenke, J., Estandarte, A. K., Xiong, G., Harder, R., et al. (2015). Karyotyping human chromosomes by optical and x-ray ptychography methods. Biophysical J. 108, 706–713. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2014.11.3456
Thibault, P., Dierolf, M., Bunk, O., Menzel, A., and Pfeiffer, F. (2009). Probe retrieval in ptychographic coherent diffractive imaging. Ultramicroscopy 109, 338–343. doi:10.1016/j.ultramic.2008.12.011
Thibault, P., Dierolf, M., Menzel, A., Bunk, O., David, C., and Pfeiffer, F. (2008). High-resolution scanning x-ray diffraction microscopy. Science 321, 379–382. doi:10.1126/science.1158573
Woo, S., Debnath, S., Hu, R., Chen, X., Liu, Z., Kweon, I. S., et al. (2023). “Convnext v2: Co-designing and scaling convnets with masked autoencoders,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 16133–16142.
Keywords: X-ray ptychography, deep learning, phase retrieval, real-time imaging, W1-net
Citation: Xing C, Wang L, Mu Y, Li Y and Chang G (2024) W1-Net: a highly scalable ptychography convolutional neural network. Adv. Opt. Technol. 13:1474654. doi: 10.3389/aot.2024.1474654
Received: 02 August 2024; Accepted: 11 October 2024;
Published: 23 October 2024.
Edited by:
Yudong Yao, ShanghaiTech University, ChinaReviewed by:
Lu Rong, Beijing University of Technology, ChinaFucai Zhang, Southern University of Science and Technology, China
Copyright © 2024 Xing, Wang, Mu, Li and Chang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Guangcai Chang, Y2hhbmdnY0BpaGVwLmFjLmNu
 Chengye Xing
Chengye Xing Lei Wang
Lei Wang Yangyang Mu
Yangyang Mu Yu Li1,3
Yu Li1,3