
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Vet. Sci. , 13 February 2024
Sec. Veterinary Infectious Diseases
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2024.1350387
This article is part of the Research Topic Recent Advances in Porcine Respiratory Diseases View all 10 articles
This article is a correction to:
Animal-Based Factors Prior to Infection Predict Histological Disease Outcome in Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus- and Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae-Infected Pigs
 Ingrid D. E. van Dixhoorn1*
Ingrid D. E. van Dixhoorn1* Dennis E. te Beest2
Dennis E. te Beest2 Jantina E. Bolhuis3
Jantina E. Bolhuis3 Hendrik K. Parmentier3
Hendrik K. Parmentier3 Bas Kemp3
Bas Kemp3 Simon van Mourik4
Simon van Mourik4 Norbert Stockhofe-Zurwieden5
Norbert Stockhofe-Zurwieden5 Cornelis G. van Reenen1
Cornelis G. van Reenen1 Johanna M. J. Rebel1
Johanna M. J. Rebel1by van Dixhoorn, I. D. E., te Beest, D. E., Bolhuis, J. E., Parmentier, H. K., Kemp, B., van Mourik, S., Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.„ van Reenen, C. G., and Rebel, J. M. J. (2021). Front. Vet. Sci. 8:742877. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.742877
In the published article, there was an error in Figure 5 as published. The x-axis labels in Panel A, “Conventional” and “Enriched,” were placed the wrong way round. The corrected Figure 5 and its caption appear below.
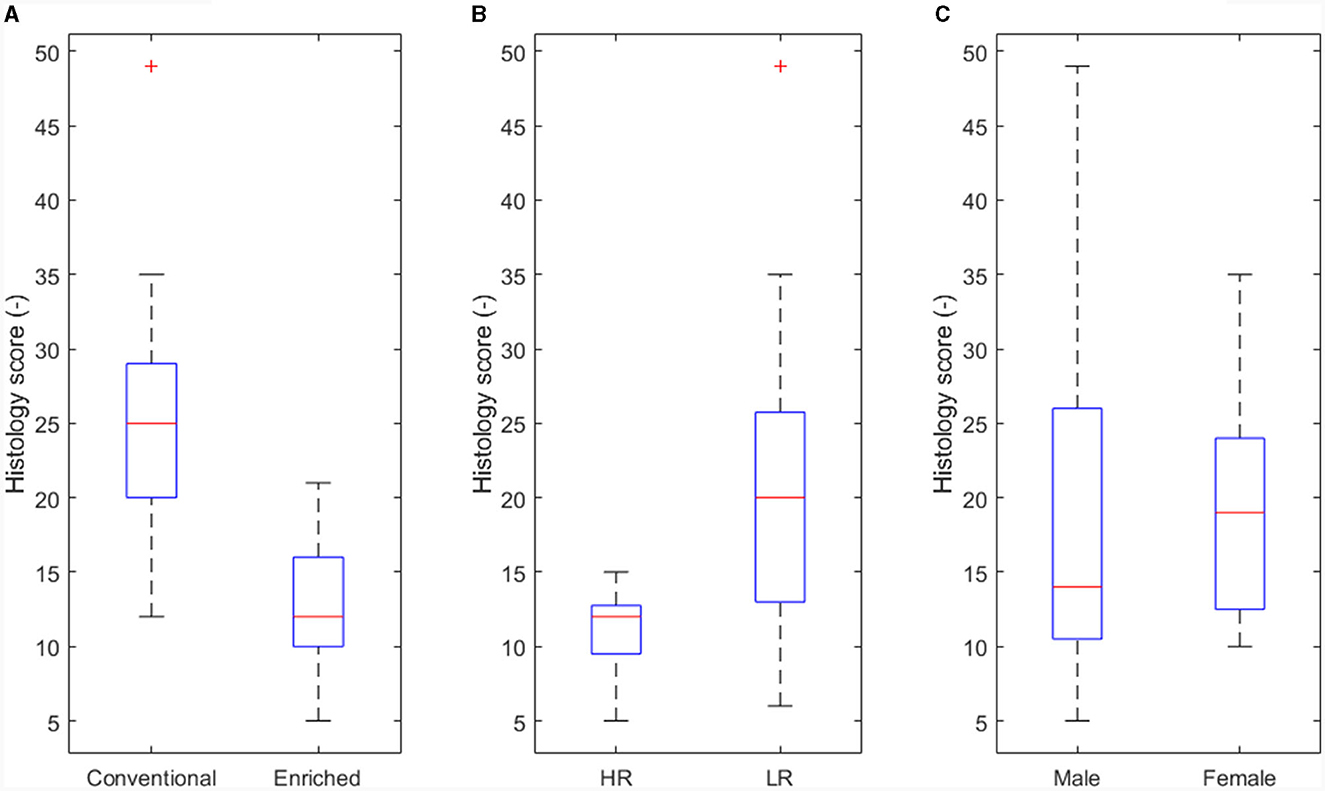
Figure 5. Main effect of experimental variables on histology score. (A) Housing (p < 0.05). (B) Coping strategy (p < 0.05). (C) Sex not significant (NS).
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: resilience indicators, porcine respiratory disease, PRRSV, Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, coping strategy, enriched housing, disease severity, animal-based factors
Citation: van Dixhoorn IDE, te Beest DE, Bolhuis JE, Parmentier HK, Kemp B, van Mourik S, Stockhofe-Zurwieden N, van Reenen CG and Rebel JMJ (2024) Corrigendum: Animal-based factors prior to infection predict histological disease outcome in porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus- and Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae-infected pigs. Front. Vet. Sci. 11:1350387. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1350387
Received: 05 December 2023; Accepted: 26 January 2024;
Published: 13 February 2024.
Edited and reviewed by: Michael Kogut, United States Department of Agriculture, United States
Copyright © 2024 van Dixhoorn, te Beest, Bolhuis, Parmentier, Kemp, van Mourik, Stockhofe-Zurwieden, van Reenen and Rebel. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ingrid D. E. van Dixhoorn, aW5ncmlkLnZhbmRpeGhvb3JuQHd1ci5ubA==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.