- 1Department of Orthopedics, Shin Kong Wu Ho-Su Memorial Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
- 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan
- 3Department of Family Medicine, Zhongxing Branch, Taipei City Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
- 4Institute of Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan
- 5General Education Center, University of Taipei, Taipei, Taiwan
- 6Institute of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan
- 7Department of Orthopedics, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei City, Taiwan
- 8Department of Orthopedics, Shuang Ho Hospital, Taipei Medical University, New Taipei City, Taiwan
- 9Graduate Institute of Biomedical Optomechatronics, College of Biomedical Engineering; Research Center of Biomedical Device, Taipei Medical University, Taipei City, Taiwan
- 10International Ph.D. Program in Biomedical Engineering, College of Biomedical Engineering, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan
- 11Department of Orthopedics, Cathay General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
- 12School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Fu Jen Catholic University, New Taipei City, Taiwan
- 13Department of Orthopaedics, Ditmanson Medical Foundation Chia-Yi Christian Hospital, Chia-Yi City, Taiwan
- 14Department of Long-Term Care and Management, WuFeng University, Chiayi County, Taiwan
- 15Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Taoyuan General Hospital, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taoyuan City, Taiwan
- 16Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
- 17Department of Nursing, Yuanpei University of Medical Technology, Hsinchu City, Taiwan
- 18Department of Orthopedics, Postal Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
- 19Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei City, Taiwan
- 20Division of Nephrology, School of Medicine, College of Medicine, Taipei Medical University, Taipei City, Taiwan
- 21TMU Biodesign Center, Taipei Medical University, Taipei, Taiwan
Distal radius orientation is important in evaluating Colles' fracture. In most cases, the wrist was protected by a bandage, splint, or cast. Therefore, it was difficult for the radiology technician to take perfect anteroposterior and lateral view radiographs. In this study, we build a mathematical model and calculate the pronation angle needed to produce dorsal tilt, which is a volar tilt in a perfect lateral view radiograph. The formulas are all incorporated into Excel to facilitate usage.
Introduction
Reduction and the indications for the operation of Colles' fracture usually require the guidance of x-rays. These x-rays include wrist anteroposterior and lateral views evaluating volar (palmar) tilt and radial inclination (1–4). These two parameters are in fact three-dimensional. We see patients with dorsal tilt in some lateral view radiographs and volar tilt in others frequently.
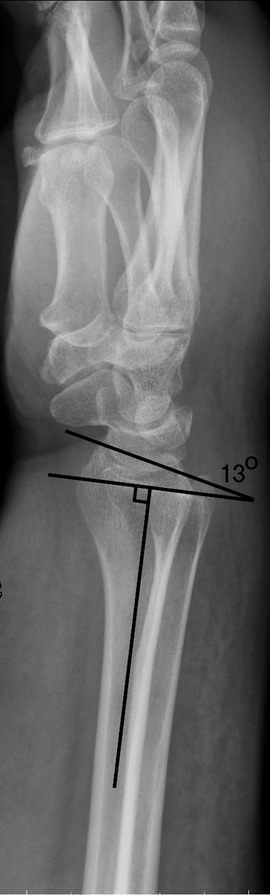
Figure 1 showed a patient with normal anatomy. However, the lateral view showed dorsal tilt.
These findings raised some questions:
1. What is the mathematical model of distal radius?
2. When does the lateral view show dorsal tilt in normal distal radius?
Methods
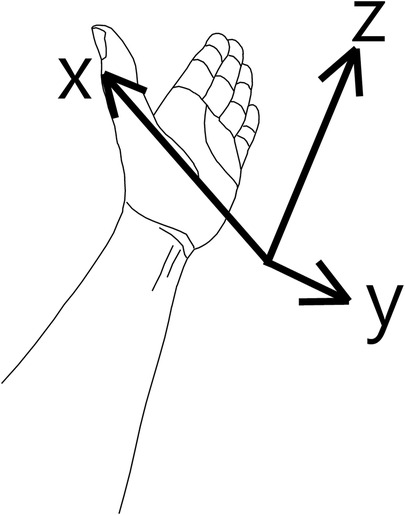
The orientation of distal radius cartilage is three-dimensional. We must have a spatial concept when measuring it. Usually, it is presented by volar tilt and radial inclination. Using vector mathematics, we can present its orientation with a normal vector. First, we assume a 3D coordinate system.
The z-axis is aligned by the axis of the radial shaft and directed from the elbow toward the distal radius. The x-axis is directed from the ulnar side toward the radial side. The y-axis is from the dorsal toward the volar side (Figure 2). Volar tilt is θ. The inclination is ψ.
Now we can get the distal radius orientation vector by trigonometric mathematics with the same principle (5).
Distal radius orientation normal vector (unit vector) =
In clinical practice, we usually take x-rays with some rotation around the z-axis, either supination or pronation. Thus, we use the rotation matrix to simulate this situation,
where “a” = rotation around the z-axis or pronation angle. A positive value means pronation and negative means supination.
Thus, the normal vector after rotation “a” angle around the z-axis becomes the multiplication of the two matrixes,
And the results after multiplication are
After pronating rotation “a” angle, the volar tilt becomes
Volar tilt after pronating rotation “a”
=tan−1 (Y component on normal vector/Z component of the normal vector)
=tan−1
This formula is incorporated into the Excel file (attachment file) (Figure 3.)
Because ,
Thus if , it is volar tilt;
if (, it is dorsal tilt.
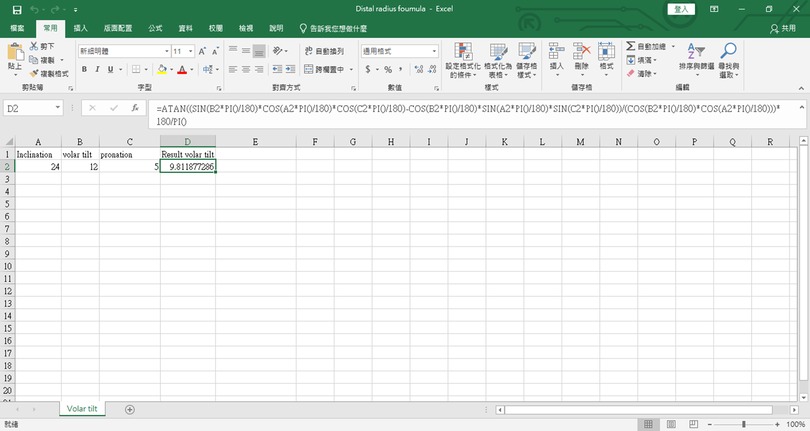
Figure 3. The excel program for the mathematical formula. The source code is as follows: “=ATAN((SIN(B2*PI()/180)*COS(A2*PI()/180)*COS(C2*PI()/180)-COS(B2*PI()/180)*SIN(A2*PI()/180)*SIN(C2*PI()/180))/(COS(B2*PI()/180)*COS(A2*PI()/180)))*180/PI()”. Readers can copy and paste the code directly.
Then, we get the following:
If , it is volar tilt;
if , it is dorsal tilt.
or
if , it is volar tilt;
if , it is dorsal tilt.
We then get the result as follows:
If pronation (a) ), it changed from volar tilt to dorsal tilt. We incorporated it into excel. The excel file is attached.
We also incorporated the formula “pronation = tan−1 )” into the Excel file (supplementary material).
If we input the normal parameters, inclination 24°, and volar tilt 12°, we get the result. It showed 25.5°, which means if the patient pronates its wrist larger than 25.5°, the x-ray will show dorsal tilt.
Results and discussion
We considered the distal radius articular surface a plane and built a mathematical model of its normal vector. We used this model and calculated the pronation angle, 25.5°, needed to have dorsal tilt in normal patients.
Its clinical importance cannot be overlooked. In practice, Orthopedics doctors can have every radiograph in perfect projection. We should always keep in mind that the radiographs are in fact three-dimensional.
In Figure 1, there are two solid pieces of evidence of pronation. First, the radial styloid is moved toward the volar side. Second, the ulna is moved toward the dorsal side.
In clinical practice, excessive pronation on the lateral radiograph of the wrist usually happened during the postoperative examination while excessive bandage (with splint or cast) confused the radiology technician. The confusing results also perplexed the surgeon. Our results can solve this clinical problem.
Conclusions
We build a mathematical model for evaluating distal radius orientation and we found that the volar tilt will become dorsal tilt if the pronation is larger than 25.5°. Further study may be needed to determine precision.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics statement
The above study has been approved by expedited review process of the TMU-Joint Institutional Review Board (TMU-JIRB No: N202108038). Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in accordance with national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
C-KL, T-YW, and Y-CL conceptualized the study. C-KL, P-WW, J-YW, C-YC, K-HC, and Y-MH helped acquired the funding. Y-CL derived the mathematics. C-SF, C-PC, Y-LC, C-KC, and K-LY wrote the algorithm. C-HY, H-KW, W-PL, T-HL, M-SW, and Y-MH simulated data and tested. C-KC, T-YW, and Y-CL wrote the paper. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was funded by grants from the Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology under grant number 109-2314-B-038 -029.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsurg.2022.1000404/full#supplementary-material.
References
1. Raittio L, Launonen AP, Hevonkorpi T, Luokkala T, Kukkonen J, Reito A, et al. Two casting methods compared in patients with Colles’ fracture: a pragmatic, randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. (2020) 15(5):e0232153. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232153
2. Reyes-Aldasoro CC, Ngan KH, Ananda A, d’Avila Garcez A, Appelboam A, Knapp KM. Geometric semi-automatic analysis of radiographs of Colles’ fractures. PLoS One. (2020) 15(9):e0238926. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238926
3. Yokota H, Yasui M, Hirai S, Hatayama N, Ohshima S, Nakano T, et al. Evaluation of the pressure on the dorsal surface of the distal radius using a cadaveric and computational model: clinical considerations in intersection syndrome and Colles’ fracture. Anat Sci Int. (2020) 95(1):38–46. doi: 10.1007/s12565-019-00491-5
4. Zenke Y, Furukawa K, Furukawa H, Maekawa K, Tajima T, Yamanaka Y, et al. Radiographic measurements as a predictor of correction loss in conservative treatment of Colles’ fracture. J Uoeh. (2019) 41(2):139–44. doi: 10.7888/juoeh.41.139
Keywords: distal radius volar tilt, distal radius inclination, supination, pronation, rotation matrix
Citation: Chen C-K, Wu T-Y, Liao Y-C, Fuh C-S, Chen K-H, Weng P-W, Wang J-Y, Chen C-Y, Huang Y-M, Chen C-P, Chu Y-L, Yeh K-L, Yu C-H, Wu H-K, Lin W-P, Liou T-H, Wu M-S and Liaw C-K (2022) Mathematical model of distal radius orientation. Front. Surg. 9:1000404. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1000404
Received: 22 July 2022; Accepted: 20 September 2022;
Published: 14 October 2022.
Edited by:
Huiwu Li, Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital, ChinaReviewed by:
Chung-Hwan Chen, Kaohsiung Medical University, TaiwanOsvaldo Mazza, Bambino Gesù Children's Hospital (IRCCS), Italy
© 2022 Chen, Wu, Liao, Fuh, Chen, Weng, Wang, Chen, Huang, Chen, Chu, Yeh, Yu, Wu, Lin, Liou, Wu and Liaw. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chen-Kun Liaw Y2hlbmt1bmxpYXdAdG11LmVkdS50dw==; Y2hlbmt1bmxpYXdAZ21haWwuY29t
Specialty Section: This article was submitted to Orthopedic Surgery, a section of the journal Frontiers in Surgery
 Cheng-Kuang Chen1,2
Cheng-Kuang Chen1,2 Kuei-Lin Yeh
Kuei-Lin Yeh Wei-Peng Lin
Wei-Peng Lin Tsan-Hon Liou
Tsan-Hon Liou Chen-Kun Liaw
Chen-Kun Liaw