- 1Department of Physics and Astronomy, Texas Tech University, Lubbock, TX, United States
- 2LIGO Laboratory, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, United States
- 3Department of Physics and Astronomy, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, United States
- 4Department of Physics, Institute for Gravitation and the Cosmos, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA, United States
- 5Department of Physics, Syracuse University, Syracuse, NY, United States
- 6School of Mathematical Sciences and Center for Computational Relativity and Gravitation, Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, NY, United States
- 7Nicholas and Lee Begovich Center for Gravitational Wave Physics and Astronomy, California State University Fullerton, Fullerton, CA, United States
The ground-based gravitational wave (GW) detectors LIGO and Virgo have enabled the birth of multi-messenger GW astronomy via the detection of GWs from merging stellar-mass black holes (BHs) and neutron stars (NSs). GW170817, the first binary NS merger detected in GWs and all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum, is an outstanding example of the impact that GW discoveries can have on multi-messenger astronomy. Yet, GW170817 is only one of the many and varied multi-messenger sources that can be unveiled using ground-based GW detectors. In this contribution, we summarize key open questions in the astrophysics of stellar-mass BHs and NSs that can be answered using current and future-generation ground-based GW detectors, and highlight the potential for new multi-messenger discoveries ahead.
1 Introduction
The discovery of the binary NS merger GW170817 during the second observing run (O2) of the LIGO (LIGO Scientific Collaboration et al., 2015) and Virgo (Acernese et al., 2015) GW detectors kicked off a new era in multi-messenger astrophysics (MMA; Figures 1, 2). In addition to marking the first direct detection of a GW chirp from a binary NS merger (Abbott et al., 2017c), GW170817 also represents the first astrophysical event to be observed with GWs and a completely independent messenger, namely, electromagnetic waves. Indeed, GW170817 was the first direct association of a NS-NS merger with a short gamma-ray burst (GRB), an IR-optical-UV kilonova, and an electromagnetic afterglow observed from radio to X-rays (see Abbott et al., 2017e, and references therein).
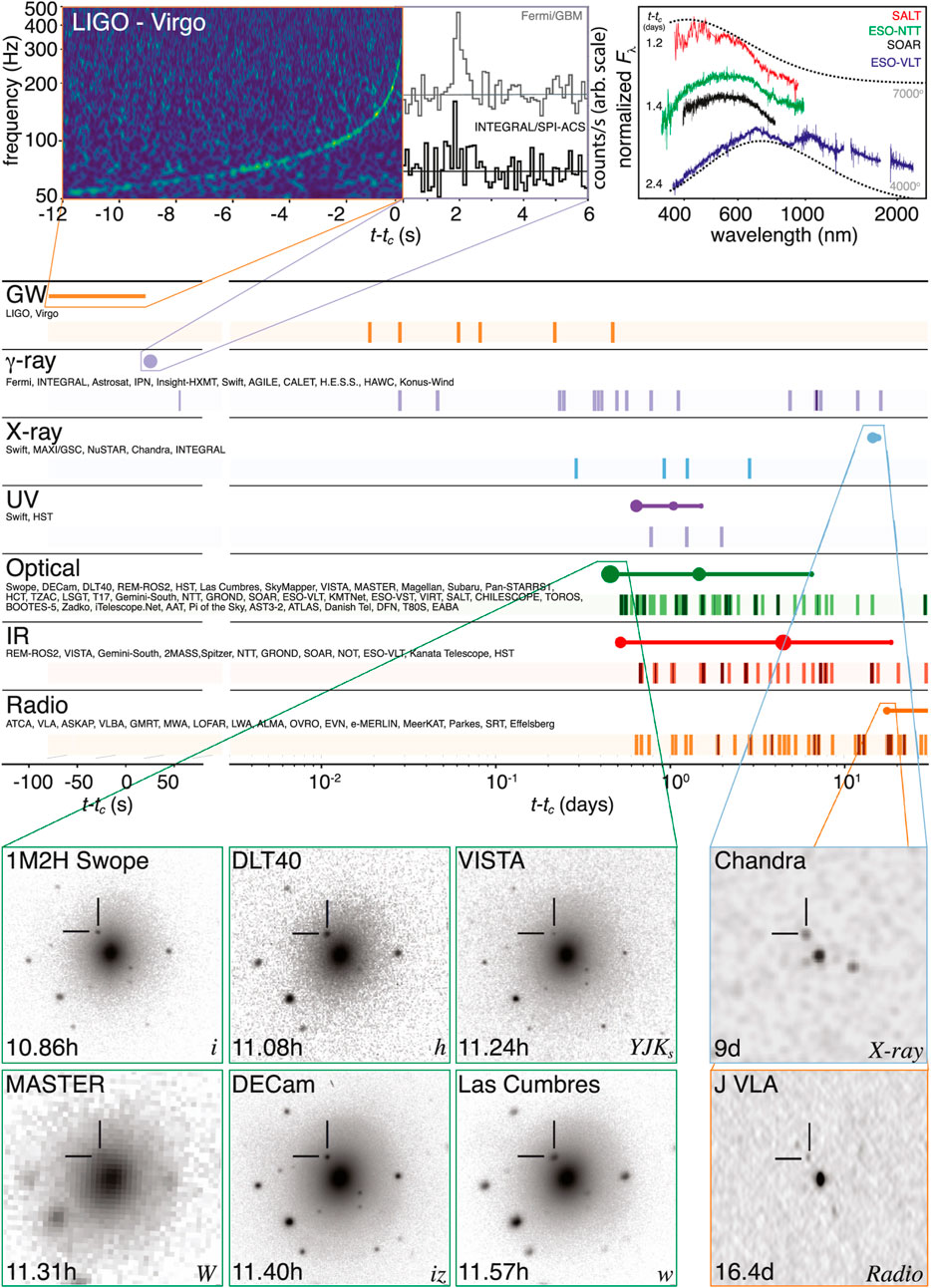
Figure 1. Figure reproduced from Abbott et al. (2017e). Timeline of the discovery of GW170817, its associated GRB 170817a, and its associated kilonova SSS17a/AT 2017gfo. The follow-up observations are shown by messenger and wavelength relative to the time of the GW event. The shaded dashes represent the times when information was reported in a GCN Circular. The names of the relevant instruments, facilities, or observing teams are collected at the beginning of the row. Representative observations in each band are shown as solid circles with their areas approximately scaled by brightness; the solid lines indicate when the source was detectable by at least one telescope. Magnification insets give a picture of the first detections in GWs, and in the gamma-ray, optical, X-ray, and radio bands.

Figure 2. Aerial views of the LIGO Hanford (left) and Livingston (center) observatories (credits: Caltech/MIT/LIGO Lab; LIGO Scientific Collaboration et al., 2015). We also show an artist’s impression of a Cosmic Explorer (CE) observatory (credits: Angela Nguyen, Virginia Kitchen, Eddie Anaya, California State University Fullerton; Evans et al., 2023).
The rich multi-messenger data collected for GW170817 (Figure 1), together with detailed modeling and simulations, have painted the most detailed picture yet of a binary NS merger, impacting a variety of fields beyond gravitational physics and including nuclear physics (e.g., Bauswein et al., 2017; Kasen et al., 2017; Margalit and Metzger, 2017; Annala et al., 2018; Radice et al., 2018b; Abbott et al., 2018c; Côté et al., 2018; De et al., 2018; Most et al., 2018; Rezzolla et al., 2018; Capano et al., 2020), relativistic astrophysics (e.g., Shibata et al., 2017; Lazzati et al., 2018; Ruiz et al., 2018; Lazzati et al., 2021), stellar evolution and population synthesis (e.g., Dominik et al., 2013; Kruckow et al., 2018; Vigna-Gómez et al., 2018), and cosmology (e.g., Abbott et al., 2017a; Baker et al., 2017; Creminelli and Vernizzi, 2017; Ezquiaga and Zumalacárregui, 2017; Sakstein and Jain, 2017; Chen et al., 2018).
As of today, the LIGO and Virgo detectors have reported highly-significant discoveries of
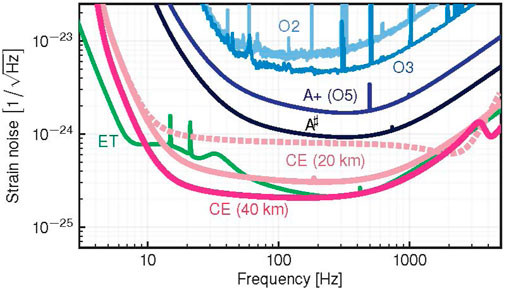
Figure 3. Figure adapted from Evans et al. (2023). Measured sensitivity of LIGO in its second (O2) and third (O3) observing runs, and estimated sensitivities of LIGO A+ (also referred to as LIGO O5 sensitivity; Abbott et al., 2018a), LIGO A# (Fritschel et al., 2023), ET (Branchesi et al., 2023), and the 20 km and 40 km CE detectors (Evans et al., 2023). We note that by reconfiguring several smaller optics, the 20 km detector could be operated either in a broad-band mode (solid) or a kilohertz-focused mode (dotted).
We stress that, while this work highlights topics in MMA for which observations of GWs and light are critical, the field of MMA is broader and includes messengers such as cosmic rays and neutrinos (e.g., Particle Physics Project Prioritization Panel, 2023, and references therein). Here, we mention these other probes only briefly. We also stress that our discussion is centered on the science enabled by ground-based GW detectors operating in the few Hz to few kHz GW frequency regime. However, the GW spectrum is much broader, and fundamental contributions to its exploration are being provided by Pulsar Timing Arrays (Detweiler, 1979; Agazie et al., 2023; EPTA Collaboration et al., 2023; Reardon et al., 2023; Xu et al., 2023), and will be provided in the future by space-based instruments such as LISA (Amaro-Seoane et al., 2023) and DECIGO (Kawamura et al., 2011).
2 MMA of compact binary mergers: key open questions
2.1 Diversity of NS-NS/BH-NS mergers and r-process yields
GW170817 remains so far the only event seen in both GWs and electromagnetic emission. An associated GRB (170817A) was detected about 2 s after the merger by the Fermi/GBM and Integral satellites (Figure 1; Abbott et al., 2017b; Savchenko et al., 2017). About 11 h after the GW detection, an optical counterpart was identified by the Swope Supernova Team (Figure 1; Coulter et al., 2017). Via extensive multi-wavelength observations carried by several teams, this counterpart was recognized to be a kilonova—a quasi-thermal fast-fading transient associated with r-process nucleosynthesis occurring in the neutron-rich debris created by the merger itself (Chornock et al., 2017; Cowperthwaite et al., 2017; Drout et al., 2017; Evans et al., 2017; Kasliwal et al., 2017; Nicholl et al., 2017; Pian et al., 2017; Smartt et al., 2017; Soares-Santos et al., 2017; Tanvir et al., 2017; Valenti et al., 2017; Villar et al., 2017). The kilonova detection also enabled the arcsec localization of GW170817, and hence the identification of its host galaxy and measurement of its redshift (Hjorth et al., 2017; Im et al., 2017; Levan et al., 2017; Palmese et al., 2017; Pan et al., 2017). Located only
As the sensitivity of the LIGO detectors continues to improve steadily compared to the O2 run (Figure 3), one of the biggest priorities in the field of MMA is the collection of a larger sample of GW170817-like multi-messenger detections: going from 1 to
Ultimately, a diverse sample of multi-messenger detections of nearby and well-localized NS-NS and BH-NS systems will enable us to map the properties of the progenitors as probed by GWs (especially in terms of total mass, mass ratio, and Equation of State, hereafter, EoS; Abbott et al., 2018c; 2019a, and references therein), to the properties of their merger ejecta and of the circum-merger environment as probed by electromagnetic observations (Margalit and Metzger, 2019, and references therein). Joint multi-messenger analysis will then shed light on the physical processes that determine such mapping (e.g., Radice et al., 2018a, and refrences therein).
2.2 Short GRB jets and central engines
The association of GW170817 with a GRB and an off-axis radio-to-X-ray afterglow (Section 2.1; Figure 4) has demonstrated how GW observations can open the way to directly linking GRB progenitors to their relativistic jets. However, we are still far from fully understanding the physics behind the workings of GRB central engines and their jets, especially in terms of emission processes, jet composition and structure, and the role of magnetic fields.
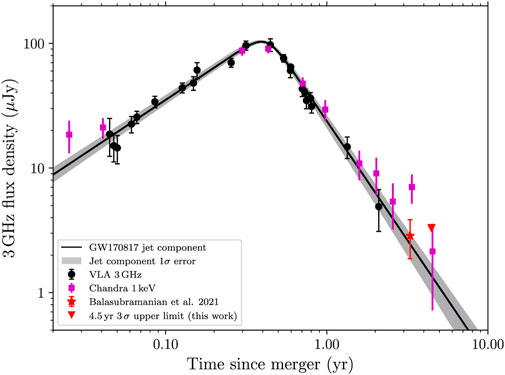
Figure 4. Figure reproduced from Balasubramanian et al. (2022). 3 GHz radio light curve of GW170817 (black dots, red star and red triangle) plus extrapolation of the X-ray observations to the radio band (purple squares), together with the best fit model and corresponding error (black line and gray shaded area) representing the emission from the relativistic jet.
Because in a compact binary merger the amplitude of the emitted GWs depends mildly on the orientation of the binary, GW detections can enable the study of off-axis GRB jets that may otherwise go undetected and/or unrecognized as off-axis events via electromagnetic observations alone (Lazzati et al., 2017; Granot et al., 2018b; Bartos et al., 2019; Dichiara et al., 2020; Matsumoto and Piran, 2020; Schroeder et al., 2020; Grandorf et al., 2021; Ricci et al., 2021; Eddins et al., 2023; Ghosh et al., 2024). This is key to shedding light on the jet structures that, in turn, are determined by complex processes involving the GRB central engines (that power the jet itself), and the interaction of the jets with the neutron-rich debris surrounding the merger sites (e.g., Rossi et al., 2002; Aloy et al., 2005; Bromberg et al., 2011; Nakar and Piran, 2018; Lazzati et al., 2018; Lazzati and Perna, 2019; Gottlieb et al., 2021; Sharan Salafia and Ghirlanda, 2022; García-García et al., 2023; Pavan et al., 2023, and references therein). As demonstrated by
The origin of the γ-rays in GRB170817a remains equally debated: while the structured outflow model can explain why a GRB was detected even if off-axis (Lazzati et al., 2017), a mildly relativistic shock breakout of a cocoon from the merger’s ejecta is also possible (Gottlieb et al., 2018). Future multi-messenger observations of off-axis GRBs (including potential coincident detections between GW signals and sub-threshold GRBs; Kocevski et al., 2018; Magee et al., 2019; Tohuvavohu et al., 2020; Fletcher et al., 2023), will greatly help settle these debates (Lazzati, 2020; Beniamini et al., 2022; Bošnjak et al., 2022).
While the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA detectors (Figure 2, left and central panel) continue to improve their sensitivity to GWs from GRBs (Abbott et al., 2021b; 2022b), these searches will undergo a leap forward when next-generation GW detector such as CE and ET, with
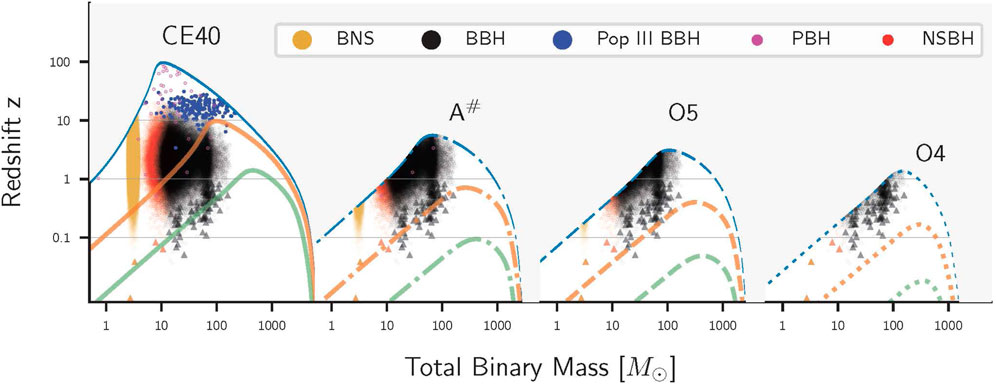
Figure 5. Figure adapted from Evans et al. (2023). The reach of current and future ground-based GW detectors for compact binary mergers (NS-NS mergers in gold; BH-NS mergers in red; and BH-BH mergers in black; see Section 2.5) is represented as a function of total binary mass and redshift at various signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) thresholds (blue lines for SNR 8; orange lines for SNR 100; and green lines for SNR 1000). The population of observed compact-object binaries is plotted with small triangles. We use dotted lines for LIGO at its O4 sensitivity; dashed lines for LIGO at its projected O5 sensitivity, also referred to as LIGO A+ (Abbott et al., 2018a); and dash-dotted lines for LIGO at its projected post-O5 A# sensitivity (the ultimate performance of current LIGO detectors envisioned for the post-O5 era; Fritschel et al., 2023). CE40 (Evans et al., 2023), a next-generation GW detector concept, can expand the cosmic horizon of NS-NS mergers, and enable observations of new populations including mergers from Population III BHs (blue dots), and speculative primordial BHs (magenta dots).
Probing directly and systematically the progenitor of short GRBs observed in γ-rays will also shed light on whether the phenomenological classification of GRBs in short/hard and long/soft as related to two different classes of progenitors (compact binary mergers and collapsars, respectively) holds in all cases. In fact, this classification scheme has been challenged by observations of long GRBs associated with kilonovae or lacking supernova counterparts to very deep limits, and short GRBs showing potential supernova bumps in their light curves (Della Valle et al., 2006; Fynbo et al., 2006; Ahumada et al., 2021; Troja et al., 2022a; Rastinejad et al., 2022; Rossi et al., 2022; Yang et al., 2022; Barnes and Metzger, 2023; Gompertz et al., 2023b). In the future, deep GW observations of these peculiar GRBs will provide the definitive word on the nature of their progenitors and likely settle current classification debates (Dimple et al., 2023).
2.3 Electromagnetic precursors to compact binary mergers
Electromagnetic emission from GW170817 was probed only after the GW merger (starting from about 2 s after; Figure 1) with the detection of γ-rays. Hence, as of today, the pre-merger phase remains unexplored in terms of potential electromagnetic counterparts. As the sensitivity and number of ground-based GW detectors increase, GW observations of an in-spiraling system can provide the advance notice required to capture light from the moments closest to merger (Figure 6; see also Cannon et al., 2012; Singer and Price, 2016; Messick et al., 2017; Chan et al., 2018; Zhao and Wen, 2018; Sachdev et al., 2020a; Magee et al., 2021; Nitz and Dal Canton, 2021; Nitz et al., 2020; Borhanian and Sathyaprakash, 2022; Banerjee et al., 2023; Chatterjee and Wen, 2023; Hu and Veitch, 2023; Miller et al., 2023).
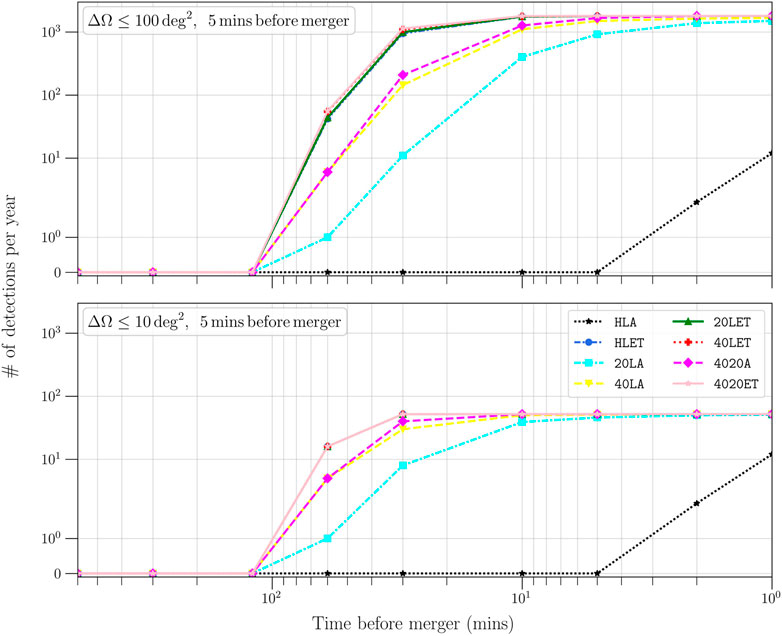
Figure 6. This Figure is based on the simulations presented in Gupta et al. (2023a), for GW detector networks containing zero to three next-generation observatories. The HLA network contains the two current LIGO detectors (Hanford and Livingston) operating at the upgraded A# sensitivity (Figure 3), plus the LIGO Aundha at A# sensitivity. The 20LA and 40LA networks represent configurations with a single 20 km-long arms CE detector operating in the context of an upgraded (A# sensitivity) LIGO network with locations in Livingston and Aundha. The HLET network is one with a single next-generation GW detector (ET) operating together with LIGO Hanford and LIGO Livingston at their upgraded A# sensitivity. The 4020A network represents the CE reference configuration as described in (Evans et al., 2023), with one 40 km-long and one 20 km-long next-generation detectors plus LIGO Aundha at A# sensitivity. The 20LET and 40LET networks represent a single CE detector (either 20 km or 40 km) operating with LIGO Livingston and the ET. Finally, the 4020 ET is the reference CE configuration operating with ET. For these networks, we calculate the signal-to-noise ratio of NS-NS systems at 1, 2, 5, 10, 30, 60, 120, 300, 600 min before merger (data points) for events that are localized within 100 deg2 (top) or 10 deg2 (bottom) at 5 min before merger, in 1 year. If the network signal-to-noise ratio is
Multi-messenger observations of the moments just before the merger could probe several highly-debated astrophysical scenarios (see Wang and Liu, 2021, for a recent review, and references therein). From a theoretical perspective, models predict the possible existence of pre-merger electromagnetic signatures via a variety of mechanisms including two-body electromagnetic interactions, resonant NS crust shattering, magnetic reconnection and particle acceleration through the revival of pulsar-like emission during the in-spiral phase, the decay of tidal tails, the formation of fireballs or wind-driven shocks (e.g., Goldreich and Lynden-Bell, 1969; Vietri, 1996; Hansen and Lyutikov, 2001; Moortgat and Kuijpers, 2006; Roberts et al., 2011; Lai, 2012; Metzger and Berger, 2012; Piro, 2012; Tsang et al., 2012; Penner et al., 2012; Medvedev and Loeb, 2013; Metzger and Zivancev, 2016; Suvorov and Kokkotas, 2019; Beloborodov, 2021; Sridhar et al., 2021; Most and Philippov, 2023b; Cooper et al., 2023). It has also been suggested that in the late in-spiral phase of a NS-NS or BH-NS merger in which one NS is a magnetar, the tidal-induced deformation may surpass the maximum that the magnetar’s crust can sustain, driving a catastrophic global crust destruction that releases magnetic energy as a superflare with energy hundreds of times larger than giant flares of magnetars (Zhang et al., 2022). Numerical studies support the conclusion that electromagnetic flares may be observed before the merger (Palenzuela et al., 2013; Most and Philippov, 2020; 2022; 2023a). A key related open questions is whether NS mergers may power a fraction of fast radio bursts (FRBs; Lorimer et al., 2007; Thornton et al., 2013; Zhang, 2014; Williams and Berger, 2016; Paschalidis and Ruiz, 2019; Rowlinson et al., 2019; Zhang, 2020; Wada et al., 2020; Chen Z.-L. et al., 2023; Pan et al., 2023).
Observationally, while high-energy precursors have been observed in short (and long) GRBs (Lazzati, 2005; Burlon et al., 2008; 2009; Troja et al., 2010; Zhong et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020; Petroff et al., 2022; Dichiara et al., 2023), it is still a matter of debate whether these precursors have a different origin from that of the GRB itself, or are rather just a manifestation of the variable GRB emission (Charisi et al., 2015; Xiao et al., 2022). Searches for electromagnetic precursors have been carried in coincidence with compact binary mergers identified by LIGO and Virgo during O2/O3 having a non-negligible probability to contain a NS (Stachie et al., 2022). While these searches found no significant candidate precursor signals, open questions discussed above can be explored in future searches with improved sensitivity, potentially aided by GW early alerts and localizations, and extending across the electromagnetic spectrum (from radio to γ-rays; Figure 6).
2.4 Nature of the merger remnant and neutron star EoS
After a NS-NS merger, a compact remnant is left over. The nature of such a remnant—either a NS or a BH—is thought to depend primarily on the masses of the binary components (i.e., total mass of the system and mass ratio) and on the EoS of nuclear matter (e.g., Ravi and Lasky, 2014; Piro et al., 2017; Shibata and Hotokezaka, 2019). If a NS remnant is formed (as opposed to a prompt BH formation), its lifetime could range from short lived (hypermassive NS supported only temporarily against gravity by differential rotation), to long lived (supramassive NSs supported against gravity by uniform rotation), to indefinitely stable (Beniamini and Lu, 2021; Margalit et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2024). GWs can be used to probe the post-merger remnant via a variety of yet-to-be detected signals and, when paired with electromagnetic observations, can greatly help us understand the astrophysics of the post-merger phase.
GWs produced by oscillations of the hot, extremely dense remnant may come into reach with improved ground-based detectors (e.g., Bauswein et al., 2012; Clark et al., 2014; Bauswein and Stergioulas, 2015; Clark et al., 2016; Krolak et al., 2023). The formation of a hypermassive NS is expected to give off quasi-periodic GWs of frequencies
After the early (dynamical) GW-driven phase, the (secular) evolution of remnants that did not collapse to BHs is driven by viscous magnetohydrodynamics processes and neutrino cooling (Piro et al., 2017; Bernuzzi, 2020). Mapping observationally NS-NS progenitors to their remnants via their GW and electromagnetic emission offers an unprecedented opportunity to understand this complex interplay of gravitational, nuclear, weak and electromagnetic interactions (Beniamini and Lu, 2021; Margalit et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2024). In the case of GW170817, the presence of an electromagnetic counterpart disfavors a prompt BH formation. The velocity, total mass, and electron fraction of the blue kilonova ejecta (as constrained from the observations) support the idea that the merger formed a rapidly spinning hypermassive and magnetized NS, with a 0.1–1s lifetime (Metzger et al., 2018). In this interpretation, the lifetime of the GW170817 merger remnant is short because a long-lived remnant would have injected a rotational energy of a few
Overall, post-merger scenarios involving long-lived or stable NSs formed in compact binary mergers have been proposed to explain various features in GRB light curves and have received new attention after GW170817. Proposed electromagnetic signatures of long-lived remnants range from brighter-than-normal magnetar-powered kilonovae, to early-time X-ray afterglow plateaus and late-time radio and X-ray flares (Nakar and Piran, 2011; Rowlinson et al., 2013; Hotokezaka et al., 2018; Bartos et al., 2019; Kathirgamaraju et al., 2019; Nedora et al., 2021; Ai et al., 2022; Sarin et al., 2022; Sadeh et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024). Proposed GW signatures include oscillation modes of a short-lived hypermassive NS, bar-mode instabilities, and rapid spindown powered by magnetic-field induced ellipticities (e.g., Lai and Shapiro, 1995; Owen et al., 1998; Cutler, 2002a; Shibata, 2005; Corsi and Mészáros, 2009; Hotokezaka et al., 2013; Ciolfi and Rezzolla, 2013; Dall’Osso et al., 2015; Clark et al., 2016). Several observing campaigns aimed at identifying electromagnetic or GW signatures of long-lived remnants have been conducted for both GW170817 and other short GRBs, and promise to become more constraining of proposed models with next-generation GW and electromagnetic instrumentation (e.g., Coyne et al., 2016; Horesh et al., 2016; Abbott et al., 2017d; 2019b; Sowell et al., 2019; Schroeder et al., 2020; Balasubramanian et al., 2021; Bruni et al., 2021; Abbott et al., 2021c; Grandorf et al., 2021; Balasubramanian et al., 2022; Troja et al., 2022b; Hajela et al., 2022; Eddins et al., 2023; Grace et al., 2023; Krolak et al., 2023; Ghosh et al., 2024). By probing the mass of the post-merger remnants in a systematic fashion, next-generation GW detectors like CE and ET could also probe models of supernova engines (Fryer, 2023).
2.5 Compact binary merger population properties
As the number of NS-NS, BH-NS, and BH-BH detections increases following the improvement in sensitivity of the LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA detectors (Figure 3, 7), MMA studies based on single-event analyses will be crucially complemented by statistical studies of larger source samples. While interesting individual events and outliers will enable probing the most extreme systems, joint analyses of a large number of compact binaries will yield an exquisite characterization of the properties of the bulk of the population. These analyses can constrain key population properties such as merger rates, mass distributions, r-process yields, properties of the GRB jets, etc. (e.g., Biscoveanu et al., 2020b; Chen et al., 2021; Abbott et al., 2023b; Biscoveanu et al., 2023; Delfavero et al., 2023), while enabling comparison with similar constraints derived from observations via other messengers (e.g., Belczynski et al., 2021; Landry and Read, 2021; Fishbach and Kalogera, 2022; Mandel and Broekgaarden, 2022; Liotine et al., 2023). On the longer term, the study of NS-NS mergers is likely to see an even more substantial shift from single-event analyses to population inference and statistical studies. In fact, next-generation GW detectors may enable us to probe the properties of NS-NS mergers across cosmic history and galactic environments (Figure 5), measure the time delay distribution between formation and merger (Safarzadeh et al., 2019), and thereby infer the history of chemical evolution in the Universe even beyond the reach of electromagnetic astronomy (Chruślińska, 2022). For the loudest and best-localized BH-BH binaries, the uncertainty volume will be small enough to confidently identify the host galaxy even in absence of a counterpart (Vitale and Whittle, 2018; Borhanian and Sathyaprakash, 2022). The ability of GW detectors to precisely measure masses, distances and sky positions of thousands of mergers per year is key to this end (Vitale and Evans, 2017; Gupta et al., 2023a; Evans et al., 2023, see Figure 7).
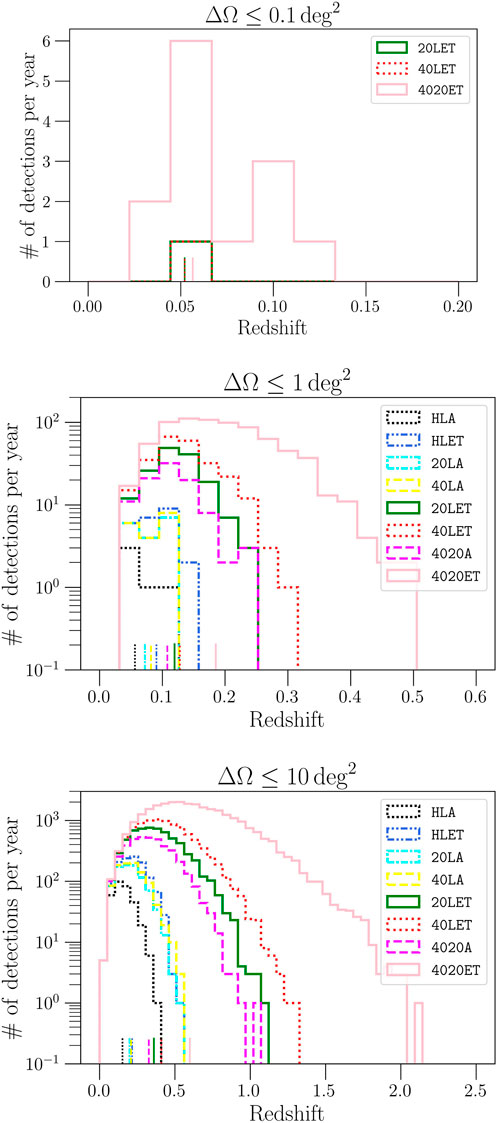
Figure 7. Figure derived from the simulations presented in Gupta et al. (2023a). Redshift distribution of NS-NS mergers detected in 1 year and localized within the sky area indicated at the top, for various networks of ground-based GW detectors (see the caption of Figure 6). The small vertical lines on the x-axis mark the median redshift of each distribution. The assumed local merger rate density of NS-NS systems is 320 Gpc−3 yr−1. We note that this rate is subject to large uncertainties (10 − 1700 Gpc−3 yr−1; Abbott et al., 2023b).
Increased detection rates of compact binary mergers containing the heaviest stellar-mass BHs will also shed light on crucial open questions in stellar astrophysics, especially when combined with electromagnetic surveys. Theory predicts the existence of a gap in the BH mass distribution because of pair-instability supernova (Fowler and Hoyle, 1964; Barkat et al., 1967; Woosley, 2017). This mechanism should produce a dearth of BH-BH binaries with components in the mass range
2.6 Impact of GW-enabled MMA on cosmology
Observations of GWs from well-localized compact binary mergers can measure absolute source distances. When coupled with an independent determination of redshift through an electromagnetic counterpart, they provide constraints on the Hubble constant (H0) and hence the expansion history of the Universe (e.g., Schutz, 1986; Holz and Hughes, 2005; Dalal et al., 2006; Sathyaprakash and Schutz, 2009; Nissanke et al., 2010; Del Pozzo, 2012; Abbott et al., 2017a; Mukherjee et al., 2021a; Jin, 2023; Mancarella et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2024). Absolute distance measurements at low redshifts, as those enabled by GW observations, can constrain dark energy when combined with observations of the primary anisotropies in the cosmic microwave background (e.g., Hu, 2005). We note that, in modified theories of gravity that predict a non-trivial dark energy equation of state and deviations from general relativity in the propagation of GWs across cosmological distances, the effect of the modified GW propagation can dominate over that of the dark energy equation of state, potentially becoming observable with next-generation GW observatories (e.g., Belgacem et al., 2018; Mukherjee et al., 2021c; Afroz and Mukherjee, 2023).
Multi-messenger observations of GW170817 allowed for a measurement of the Hubble constant using the GW detection of the NS-NS merger combined with the optical identification of the host galaxy (Abbott et al., 2017a). The GW measurement returned a value of
It is important to note that a substantial fraction of sources detected by a given GW network over a certain timescale may not have associated transient electromagnetic counterparts. However, multi-messenger studies can still be relevant as they provide advantages related to incorporating host galaxy information. Indeed, it is possible to carry out a measurement of H0 using a statistical approach that incorporates the redshifts of all potential host galaxies within the GW three-dimensional localization region (Chen et al., 2018). This technique yields an H0 measurement that has a greater uncertainty than that which can be achieved via direct counterpart identifications, but still informative once many detections are combined (Chen et al., 2018). The statistical approach also implies that, in the absence of a counterpart, only those GW events with small enough localization volumes yield informative H0 measurements. Another proposed statistical technique exploits the clustering scale of the GW sources with galaxies of known redshift, and will be applicable also to the high redshift GW sources detectable with next-generation GW detectors (Mukherjee et al., 2021b; Cigarrán Díaz and Mukherjee, 2022; Mukherjee et al., 2022). In summary, with GW detectors of improved sensitivity able to observe farther and to localize better, galaxy surveys and statistical approaches for the measurement of H0 are likely to become more and more relevant (Ye and Fishbach, 2021; Borghi et al., 2023; Dalang and Baker, 2023; Ghosh et al., 2023). In the era of next-generation GW detectors, other statistical techniques that do not require host galaxy information nor electromagnetic counterpart identifications may complement the constraints on cosmology as determined via these MMA techniques, particularly for the population of BH-NS mergers (Colombo et al., 2023; Shiralilou et al., 2023).
3 New frontiers in MMA
NSs and stellar-mass BHs, in isolation, in binary systems, and/or overall as populations, can be sources of GW signals that are very different from the compact binary merger signals already detected by LIGO and Virgo. We have mentioned some of these signals in the context of the nature of the post-merger remnant question left open by GW170817 (Section 2.4). Here, we expand our discussion to a zoo of yet-to-be-detected signals that may reveal the physics behind a suite of extreme astrophysical phenomena, and open new ways of doing MMA that include inference of population properties via correlations between the GW signals and other (electromagnetic) observables such as galaxy counts and the cosmic microwave background (e.g., Ando et al., 2013; Mukherjee et al., 2020b; a; Agarwal et al., 2022; De Lillo et al., 2022; Balaudo et al., 2023; De Lillo and Suresh, 2023; De Lillo et al., 2023; Perna et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2023).
Rotating NSs are thought to produce quasi-periodic GWs that can last for millions of years (and hence are usually referred to as continuous GWs), arising from time-varying mass quadrupoles supported by elastic or magnetic stresses (Melosh, 1969), or current quadrupoles known as “r-modes” (Andersson, 1998; Lindblom et al., 1998; Glampedakis and Gualtieri, 2018). Accreting NSs (low-mass X-ray binaries), which are thought to become millisecond pulsars after accretion ends, can also be driven to non-axisymmetry by lateral temperature gradients (Bildsten, 1998; Ushomirsky et al., 2002), internal magnetic distortion (Melosh, 1969; Bonazzola and Gourgoulhon, 1996; Cutler, 2002b), or magnetic bottling of accreted material (Melatos and Payne, 2005), hence emitting GWs. Continuous GW emission will help reveal properties of NSs such as composition (EoS), internal magnetic field, and viscosity, in addition to unveiling NSs that cannot be observed electromagnetically (e.g., Bonazzola and Gourgoulhon, 1996; Bildsten, 1998; Owen et al., 1998; Andersson and Kokkotas, 2001; Owen, 2005; Glampedakis and Gualtieri, 2018; Gittins et al., 2021; Morales and Horowitz, 2022; Riles, 2023, and references therein). Current searches for continuous GWs produced by spinning NSs with asymmetries improve with every LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA run (e.g., Abbott et al., 2022c) and dozens of known millisecond pulsars could come into the reach of next-generation GW detectors (Woan et al., 2018; Gupta et al., 2023a; Evans et al., 2023), with the potential of many more thanks to upcoming or next-generation electromagnetic facilities such as the next-generation Very Large Array (ngVLA; Murphy and ngVLA Science Advisory Council, 2020) and the Square Kilometre Array (Kalogera et al., 2019; Evans et al., 2023; Pagliaro et al., 2023; Riles, 2023; Wette, 2023). Detection by next-generation instruments also looks promising for bright low mass X-ray binaries such as Scorpius X-1 (Gupta et al., 2023a; Evans et al., 2023).
Impulsive, energetic NS events other than binary mergers can also produce bursts of GWs. For example, magnetar γ-ray flares (possibly accompanied by FRBs; Abbott et al., 2022d; Abbott et al., 2022d; Ball and Frey, 2023) and pulsar glitches (e.g., Abbott et al., 2022a) are the targets of current searches for GW signals in LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA data. While near-future detector upgrades could probe GW signals expected in the most optimistic scenarios (Corsi and Owen, 2011), next-generation GW observatories are likely to probe a wider range of possible GW outcomes (Evans et al., 2023). We stress that the detection of normal modes of NSs such as so-called “f-modes” will measure the cold NS EoS and masses of a population different from that seen in compact binary mergers, and combined with electromagnetic observations will yield information on internal magnetic fields (Evans et al., 2023).
Core-collapse supernovae are also thought to generate bursts of GWs from the dynamics of hot, high density matter in their central regions. Next-generation GW detectors are expected to be sensitive to supernovae within the Milky Way and its satellite galaxies (Kalogera et al., 2019; Srivastava et al., 2019; Szczepańczyk and Zanolin, 2022; Evans et al., 2023; Gossan and Hall, 2023), while some extreme supernovae, such as collapsars with cocoons, could generate GWs that could come into reach with current generation GW detectors (e.g., Siegel et al., 2022; Abbott et al., 2020b; Gottlieb et al., 2023, and references therein). The detection of a core-collapse event in GWs would provide a unique channel for observing the explosion’s central engine and the (hot) EoS of the newly formed compact remnant. A nearby supernova could also provide a spectacular multi-messenger event via a coincident neutrino detection (e.g., Bionta et al., 1987; Janka, 2017; Chang et al., 2022; Abbasi et al., 2023; Guarini et al., 2023).
Finally, a stochastic GW background can be generated by a large variety of phenomena of cosmological (Caprini and Figueroa, 2018) and/or astrophysical origin. The detection of a cosmological stochastic background would be of fundamental importance for our understanding of the early Universe. While current GW detectors are not optimized for the detection of a stochastic background of cosmological origin, a fraction of the parameter space in various scenarios is compatible with a detection by future detectors (Caprini et al., 2016; Caprini and Figueroa, 2018; Barish et al., 2021). Astrophysical backgrounds contain key information about the distribution of mass, redshift, and other properties of their corresponding source populations (e.g., Mukherjee and Silk, 2020; Yang et al., 2021). The merger rate of NS-NS mergers as estimated from current observations suggests that distant, unresolvable binary NSs create a significant astrophysical stochastic GW background (Abbott et al., 2018b), adding to the contribution from BH-BH and BH-NS binaries. In addition to compact binary coalescences of BHs and NSs, rotating NSs, magnetars, and core-collapse supernovae can all contribute sub-dominant stochastic backgrounds (e.g., Owen et al., 1998; Ferrari et al., 1999; Buonanno et al., 2005; Regimbau and de Freitas Pacheco, 2006; Regimbau, 2011; Rosado, 2012; Renzini et al., 2022). Overall, the ability to detect and subtract GW foregrounds, and to detect sub-dominant stochastic backgrounds, is critical to unveil potential new avenues for MMA using stochastic GW signals (e.g., Biscoveanu et al., 2020a; Sachdev et al., 2020b; Sharma and Harms, 2020; Mukherjee and Silk, 2021; Zhou et al., 2022; Bellie et al., 2023; Zhong et al., 2023).
4 Discussion
As discussed in Section 2.1, going from one GW170817-like event to
Improvements in sensitivity to ground-based GW detectors will enable us to reach a GW localization accuracy of
It is fundamental to realize that the same improvement in sensitivity that enables GW detectors in a network to localize nearby compact binary mergers to exquisite accuracy (as discussed above), also enables such detectors to see farther compact binary merger events extending the reach of MMA to higher redshifts (see Sections 2.2, 2.5, 2.6 and Figure 7), as well as to unveil new sources of GW emission (see Sections 2.1, 2.4, 2.3, and 3). Indeed, as evident from the maximum redshift in the distributions in Figure 7, only networks of next-generation detectors can extend the reach of GWs to the peak of star formation (z ≈ 1–2) for GW events localized to ≲ 10 deg2. Space missions such as Fermi and Swift, Roman, and future NASA programs focused on the transient and time-variable Universe, are key to ensure continued progress in the electromagentic follow-up of these events (National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, 2023; Sambruna et al., 2023). From the ground, the Rubin Observatory, the Extremely Large Telescopes, and the ngVLA will provide follow-up capabilities for GW events that are key to enable MMA to reach its full potential over the next decade and beyond (Beasley et al., 2019; Chornock et al., 2019; Corsi et al., 2019; Lazio et al., 2019; Murphy et al., 2023; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, 2023). The IceCube-Generation 2 neutrino observatory will help constrain emission models for high-energy neutrinos in nearby NS-NS mergers and potentially open the way for discoveries across three different messengers (Aartsen et al., 2021; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, 2023; Mukhopadhyay et al., 2024). Multi-band GW data sets formed with the LISA space-based GW detector can also impact MMA studies of compact binary mergers (see Sesana, 2016; Vitale, 2016; Amaro-Seoane et al., 2023, and references therein).
Author contributions
AC: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft, Project administration, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization. LB: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. EB: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. ME: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. IG: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. KoK: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. KeK: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. AN: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. BO: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. BR: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. Jocelyn Samantha JR: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. BS: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. DS: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. JS: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft. SV: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. AC acknowledges support from NSF Grants No. AST-2307358 and PHY-2011608. EB and KK are supported by NSF Grants No. AST-2006538, PHY-2207502, PHY-090003 and PHY-20043, by NASA Grants No. 20-LPS20-0011 and 21-ATP21-0010, by the John Templeton Foundation Grant 62840, by the Simons Foundation, and by the Italian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation Grant No. PGR01167. KoK is supported by the Onassis Foundation—Scholarship ID: F ZT 041-1/2023-2024. JS acknowledges support from the Dan Black Family Trust, Nicholas and Lee Begovich, and NSF Grants No. PHY-2308985, AST-2219109, and PHY-2207998. JR acknowledges support from Nicholas and Lee Begovich, AST-2219109 and PHY-2110441. IG and BS acknowledge support from NSF Grants No. PHY-2207638, AST-2307147 and PHY-2308886. BR is supported by the NSF Grant 2110460. AN is supported by the NSF Grant PHY-2309240. BO acknowledges NSF Grant 2309305. DS acknowledges support from NASA award 80NSSC23K1242 and from NSF Grant No. PHY-18671764464. ME, LB, BS, DS, and SV acknowledge support from NSF Grant No. PHY-2309064. SV also acknowledges support from NSF Grant No. PHY-2045740.
Acknowledgments
We thank Patrick Brady for providing useful comments on this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aartsen, M. G., Abbasi, R., Ackermann, M., Adams, J., Aguilar, J. A., Ahlers, M., et al. (2021). IceCube-Gen2: the window to the extreme Universe. J. Phys. G Nucl. Phys. 48, 060501. doi:10.1088/1361-6471/abbd48
Abbasi, R., Ackermann, M., Adams, J., Agarwalla, S. K., Aguilar, J. A., Ahlers, M., et al. (2023). Constraining high-energy neutrino emission from supernovae with IceCube. ApJ 949, L12. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/acd2c9
Abbott, B. P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Abernathy, M. R., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., et al. (2018a). Prospects for observing and localizing gravitational-wave transients with Advanced LIGO, Advanced Virgo and KAGRA. Living Rev. Relativ. 21, 3. doi:10.1007/s41114-018-0012-9
Abbott, B. P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Abraham, S., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., et al. (2020a). GW190425: observation of a compact binary coalescence with total mass ∼ 3.4 M⊙. ApJ 892, L3. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab75f5
Abbott, B. P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Abraham, S., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., et al. (2020b). Optically targeted search for gravitational waves emitted by core-collapse supernovae during the first and second observing runs of advanced LIGO and advanced Virgo. Phys. Rev. D. 101, 084002. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.101.084002
Abbott, B. P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., et al. (2017a). A gravitational-wave standard siren measurement of the Hubble constant. Nature 551, 85–88. doi:10.1038/nature24471
Abbott, B. P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., et al. (2017b). Gravitational waves and gamma-rays from a binary neutron star merger: GW170817 and GRB 170817A. ApJ 848, L13. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa920c
Abbott, B. P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., et al. (2017c). GW170817: observation of gravitational waves from a binary neutron star inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 161101. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.161101
Abbott, B. P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., et al. (2017d). Search for post-merger gravitational waves from the remnant of the binary neutron star merger GW170817. ApJ 851, L16. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa9a35
Abbott, B. P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., et al. (2017e). Multi-messenger observations of a binary neutron star merger. ApJ 848, L12. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa91c9
Abbott, B. P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., et al. (2018b). GW170817: implications for the stochastic gravitational-wave background from compact binary coalescences. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 091101. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.091101
Abbott, B. P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., et al. (2018c). GW170817: measurements of neutron star radii and equation of state. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 161101. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.161101
Abbott, B. P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., et al. (2019a). Properties of the binary neutron star merger GW170817. Phys. Rev. X 9, 011001. doi:10.1103/PhysRevX.9.011001
Abbott, B. P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., et al. (2019b). Search for gravitational waves from a long-lived remnant of the binary neutron star merger GW170817. ApJ 875, 160. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab0f3d
Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Abraham, S., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, A., et al. (2021a). Observation of gravitational waves from two neutron star-black hole coalescences. ApJ 915, L5. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac082e
Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Abraham, S., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., et al. (2021b). Search for gravitational waves associated with gamma-ray bursts detected by Fermi and Swift during the LIGO-virgo run O3a. ApJ 915, 86. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/abee15
Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., Adhikari, N., et al. (2021c). All-sky search for long-duration gravitational-wave bursts in the third Advanced LIGO and Advanced Virgo run. Phys. Rev. D. 104, 102001. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.104.102001
Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., Adhikari, N., et al. (2022a). Narrowband searches for continuous and long-duration transient gravitational waves from known pulsars in the LIGO-virgo third observing run. ApJ 932, 133. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac6ad0
Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., Adhikari, N., et al. (2022b). Search for gravitational waves associated with gamma-ray bursts detected by Fermi and Swift during the LIGO-virgo run O3b. ApJ 928, 186. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac532b
Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., Adhikari, N., et al. (2023a). GWTC-3: compact binary coalescences observed by LIGO and Virgo during the second part of the third observing run. Phys. Rev. X 13, 041039. doi:10.1103/PhysRevX.13.041039
Abbott, R., Abbott, T. D., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adams, C., Adhikari, N., et al. (2023b). Population of merging compact binaries inferred using gravitational waves through GWTC-3. Phys. Rev. X 13, 011048. doi:10.1103/PhysRevX.13.011048
Abbott, R., Abe, H., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adhikari, N., Adhikari, R. X., et al. (2022c). All-sky search for continuous gravitational waves from isolated neutron stars using Advanced LIGO and Advanced Virgo O3 data. Phys. Rev. D. 106, 102008. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.106.102008
Abbott, R., Abe, H., Acernese, F., Ackley, K., Adhikari, N., Adhikari, R. X., et al. (2022d). Search for gravitational-wave transients associated with magnetar bursts in Advanced LIGO and Advanced Virgo data from the third observing run. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.10931.
Acernese, F., Agathos, M., Agatsuma, K., Aisa, D., Allemandou, N., Allocca, A., et al. (2015). Advanced Virgo: a second-generation interferometric gravitational wave detector. Class. Quantum Gravity 32, 024001. doi:10.1088/0264-9381/32/2/024001
Afroz, S., and Mukherjee, S. (2023). A model-independent precision test of general relativity using bright standard sirens from ongoing and upcoming detectors. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.16292.
Agarwal, D., Suresh, J., Mandic, V., Matas, A., and Regimbau, T. (2022). Targeted search for the stochastic gravitational-wave background from the galactic millisecond pulsar population. PRD 106, 043019. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.106.043019
Agazie, G., Anumarlapudi, A., Archibald, A. M., Arzoumanian, Z., Baker, P. T., Bécsy, B., et al. (2023). The NANOGrav 15 yr data set: evidence for a gravitational-wave background. ApJ 951, L8. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/acdac6
Ahumada, T., Singer, L. P., Anand, S., Coughlin, M. W., Kasliwal, M. M., Ryan, G., et al. (2021). Discovery and confirmation of the shortest gamma-ray burst from a collapsar. Nat. Astron. 5, 917–927. doi:10.1038/s41550-021-01428-7
Ai, S., Gao, H., Dai, Z.-G., Wu, X.-F., Li, A., Zhang, B., et al. (2018). The allowed parameter space of a long-lived neutron star as the merger remnant of GW170817. ApJ 860, 57. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aac2b7
Ai, S., Gao, H., and Zhang, B. (2020). What constraints on the neutron star maximum mass can one pose from GW170817 observations? ApJ 893, 146. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab80bd
Ai, S., Zhang, B., and Zhu, Z. (2022). Engine-fed kilonovae (mergernovae) - I. Dynamical evolution and energy injection/heating efficiencies. MNRAS 516, 2614–2628. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac2380
Alexander, K. D., Berger, E., Fong, W., Williams, P. K. G., Guidorzi, C., Margutti, R., et al. (2017). The electromagnetic counterpart of the binary neutron star merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. VI. Radio constraints on a relativistic jet and predictions for late-time emission from the kilonova ejecta. ApJ 848, L21. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa905d
Aloy, M. A., Janka, H. T., and Müller, E. (2005). Relativistic outflows from remnants of compact object mergers and their viability for short gamma-ray bursts. A&A 436, 273–311. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20041865
Amaro-Seoane, P., Andrews, J., Arca Sedda, M., Askar, A., Baghi, Q., Balasov, R., et al. (2023). Astrophysics with the laser interferometer space antenna. Living Rev. Relativ. 26, 2. doi:10.1007/s41114-022-00041-y
Andersson, N. (1998). A new class of unstable modes of rotating relativistic stars. Astrophysical J. 502, 708–713. doi:10.1086/305919
Andersson, N., and Kokkotas, K. D. (2001). The R-mode instability in rotating neutron stars. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 10, 381–441. doi:10.1142/S0218271801001062
Ando, S., Baret, B., Bartos, I., Bouhou, B., Chassande-Mottin, E., Corsi, A., et al. (2013). Colloquium: multimessenger astronomy with gravitational waves and high-energy neutrinos. Rev. Mod. Phys. 85, 1401–1420. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.85.1401
Andreoni, I., Coughlin, M. W., Almualla, M., Bellm, E. C., Bianco, F. B., Bulla, M., et al. (2022). Optimizing cadences with realistic light-curve filtering for serendipitous kilonova discovery with Vera Rubin observatory. ApJS 258, 5. doi:10.3847/1538-4365/ac3bae
Andreoni, I., Coughlin, M. W., Criswell, A. W., Bulla, M., Toivonen, A., Singer, L. P., et al. (2024). Enabling kilonova science with nancy Grace roman space telescope. Astropart. Phys. 155, 102904. doi:10.1016/j.astropartphys.2023.102904
Annala, E., Gorda, T., Kurkela, A., and Vuorinen, A. (2018). Gravitational-wave constraints on the neutron-star-matter equation of state. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 172703. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.172703
Arcones, A., and Thielemann, F.-K. (2023). Origin of the elements. A&A Rev. 31, 1. doi:10.1007/s00159-022-00146-x
Ascenzi, S., Oganesyan, G., Branchesi, M., and Ciolfi, R. (2021). Electromagnetic counterparts of compact binary mergers. J. Plasma Phys. 87, 845870102. doi:10.1017/S0022377820001646
Baker, T., Bellini, E., Ferreira, P. G., Lagos, M., Noller, J., and Sawicki, I. (2017). Strong constraints on cosmological gravity from GW170817 and GRB 170817A. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 251301. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.251301
Balasubramanian, A., Corsi, A., Mooley, K. P., Brightman, M., Hallinan, G., Hotokezaka, K., et al. (2021). Continued radio observations of GW170817 3.5 yr post-merger. ApJ 914, L20. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/abfd38
Balasubramanian, A., Corsi, A., Mooley, K. P., Hotokezaka, K., Kaplan, D. L., Frail, D. A., et al. (2022). GW170817 4.5 Yr after merger: dynamical ejecta afterglow constraints. ApJ 938, 12. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac9133
Balaudo, A., Garoffolo, A., Martinelli, M., Mukherjee, S., and Silvestri, A. (2023). Prospects of testing late-time cosmology with weak lensing of gravitational waves and galaxy surveys. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2023, 050. doi:10.1088/1475-7516/2023/06/050
Ball, M., and Frey, R. (2023). Optimizing xg detector networks for galactic astrophysics. Available at: https://dcc.cosmicexplorer.org/public/0163/P2300010/001/CE_Science_Letter_f-mode%20-%20Matthew%20Ball.pdf.
Ballone, A., Costa, G., Mapelli, M., MacLeod, M., Torniamenti, S., and Pacheco-Arias, J. M. (2023). Formation of black holes in the pair-instability mass gap: hydrodynamical simulations of a head-on massive star collision. MNRAS 519, 5191–5201. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac3752
Banerjee, B., Oganesyan, G., Branchesi, M., Dupletsa, U., Aharonian, F., Brighenti, F., et al. (2023). Pre-merger alert to detect prompt emission in very-high-energy gamma-rays from binary neutron star mergers: Einstein Telescope and Cherenkov Telescope Array synergy. A&A 678, A126. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202345850
Barish, B. C., Bird, S., and Cui, Y. (2021). Impact of a midband gravitational wave experiment on detectability of cosmological stochastic gravitational wave backgrounds. Phys. Rev. D. 103, 123541. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.103.123541
Barkat, Z., Rakavy, G., and Sack, N. (1967). Dynamics of supernova explosion resulting from pair formation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 18, 379–381. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.18.379
Barnes, J., Kasen, D., Wu, M.-R., and Martínez-Pinedo, G. (2016). Radioactivity and thermalization in the ejecta of compact object mergers and their impact on kilonova light curves. ApJ 829, 110. doi:10.3847/0004-637X/829/2/110
Barnes, J., and Metzger, B. D. (2023). A collapsar origin for GRB 211211A is (just barely) possible. ApJ 947, 55. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/acc384
Bartos, I., Lee, K. H., Corsi, A., Márka, Z., and Márka, S. (2019). Radio forensics could unmask nearby off-axis gamma-ray bursts. MNRAS 485, 4150–4159. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz719
Bauswein, A., Baumgarte, T. W., and Janka, H. T. (2013a). Prompt merger collapse and the maximum mass of neutron stars. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 131101. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.131101
Bauswein, A., Goriely, S., and Janka, H. T. (2013b). Systematics of dynamical mass ejection, nucleosynthesis, and radioactively powered electromagnetic signals from neutron-star mergers. ApJ 773, 78. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/773/1/78
Bauswein, A., Janka, H. T., Hebeler, K., and Schwenk, A. (2012). Equation-of-state dependence of the gravitational-wave signal from the ring-down phase of neutron-star mergers. Phys. Rev. D. 86, 063001. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.86.063001
Bauswein, A., Just, O., Janka, H.-T., and Stergioulas, N. (2017). Neutron-star radius constraints from GW170817 and future detections. ApJ 850, L34. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa9994
Bauswein, A., and Stergioulas, N. (2015). Unified picture of the post-merger dynamics and gravitational wave emission in neutron star mergers. Phys. Rev. D. 91, 124056. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.91.124056
Beasley, A., Wolff, S., Dickinson, M., Murphy, E. J., Beaton, R., Braatz, J., et al. (2019). Multiwavelength astrophysics in the era of the ngVLA and the US ELT program. Bull. Am. Astronomical Soc. 51, 88.
Belczynski, K., Done, C., Hagen, S., Lasota, J. P., and Sen, K. (2021). Common origin of black holes in high mass X-ray binaries and in gravitation-wave sources. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09401.
Belczynski, K., Heger, A., Gladysz, W., Ruiter, A. J., Woosley, S., Wiktorowicz, G., et al. (2016). The effect of pair-instability mass loss on black-hole mergers. A&A 594, A97. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201628980
Belgacem, E., Dirian, Y., Foffa, S., and Maggiore, M. (2018). Modified gravitational-wave propagation and standard sirens. Phys. Rev. D. 98, 023510. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.98.023510
Bellie, D. S., Banagiri, S., Doctor, Z., and Kalogera, V. (2023). The unresolved stochastic background from compact binary mergers detectable by next-generation ground-based gravitational-wave observatories. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.02517.
Beloborodov, A. M. (2021). Emission of magnetar bursts and precursors of neutron star mergers. ApJ 921, 92. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac17e7
Beniamini, P., Gill, R., and Granot, J. (2022). Robust features of off-axis gamma-ray burst afterglow light curves. MNRAS 515, 555–570. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac1821
Beniamini, P., and Lu, W. (2021). Survival times of supramassive neutron stars resulting from binary neutron star mergers. ApJ 920, 109. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac1678
Bernuzzi, S. (2020). Neutron star merger remnants. General Relativ. Gravit. 52, 108. doi:10.1007/s10714-020-02752-5
Bildsten, L. (1998). Gravitational radiation and rotation of accreting neutron stars. ApJ 501, L89–L93. doi:10.1086/311440
Bionta, R. M., Blewitt, G., Bratton, C. B., Casper, D., Ciocio, A., Claus, R., et al. (1987). Observation of a neutrino burst in coincidence with supernova 1987A in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Phys. Rev. Lett. 58, 1494–1496. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.58.1494
Biscoveanu, S., Burns, E., Landry, P., and Vitale, S. (2023). An observational upper limit on the rate of gamma-ray bursts with neutron star-black hole merger progenitors. Res. Notes Am. Astronomical Soc. 7, 136. doi:10.3847/2515-5172/ace258
Biscoveanu, S., Talbot, C., Thrane, E., and Smith, R. (2020a). Measuring the primordial gravitational-wave background in the presence of astrophysical foregrounds. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 241101. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.125.241101
Biscoveanu, S., Thrane, E., and Vitale, S. (2020b). Constraining short gamma-ray burst jet properties with gravitational waves and gamma-rays. ApJ 893, 38. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab7eaf
Bloom, J. S., Kulkarni, S. R., and Djorgovski, S. G. (2002). The observed offset distribution of gamma-ray bursts from their host galaxies: a robust clue to the nature of the progenitors. AJ 123, 1111–1148. doi:10.1086/338893
Bonazzola, S., and Gourgoulhon, E. (1996). Gravitational waves from pulsars: emission by the magnetic-field-induced distortion. A&A 312, 675–690. doi:10.48550/arXiv.astro-ph/9602107
Borghi, N., Mancarella, M., Moresco, M., Tagliazucchi, M., Iacovelli, F., Cimatti, A., et al. (2023). Cosmology and astrophysics with standard sirens and galaxy catalogs in view of future gravitational wave observations. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.05302.
Borhanian, S., and Sathyaprakash, B. S. (2022). Listening to the universe with next generation ground-based gravitational-wave detectors. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.11048.
Bošnjak, Ž., Barniol Duran, R., and Pe’er, A. (2022). The GRB prompt emission: an unsolved puzzle. Galaxies 10, 38. doi:10.3390/galaxies10020038
Bovard, L., Martin, D., Guercilena, F., Arcones, A., Rezzolla, L., and Korobkin, O. (2017). r -process nucleosynthesis from matter ejected in binary neutron star mergers. Phys. Rev. D. 96, 124005. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.96.124005
Branchesi, M., Maggiore, M., Alonso, D., Badger, C., Banerjee, B., Beirnaert, F., et al. (2023). Science with the Einstein Telescope: a comparison of different designs. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2023, 068. doi:10.1088/1475-7516/2023/07/068
Breschi, M., Bernuzzi, S., Godzieba, D., Perego, A., and Radice, D. (2022). Constraints on the maximum densities of neutron stars from postmerger gravitational waves with third-generation observations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 128, 161102. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.161102
Bromberg, O., Nakar, E., Piran, T., and Sari, R. (2011). The propagation of relativistic jets in external media. ApJ 740, 100. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/740/2/100
Bruni, G., O’Connor, B., Matsumoto, T., Troja, E., Piran, T., Piro, L., et al. (2021). Late-time radio observations of the short GRB 200522A: constraints on the magnetar model. MNRAS 505, L41–L45. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slab046
Bucciantini, N., Metzger, B. D., Thompson, T. A., and Quataert, E. (2012). Short gamma-ray bursts with extended emission from magnetar birth: jet formation and collimation. MNRAS 419, 1537–1545. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2011.19810.x
Buonanno, A., Sigl, G., Raffelt, G. G., Janka, H.-T., and Müller, E. (2005). Stochastic gravitational-wave background from cosmological supernovae. PRD 72, 084001. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.72.084001
Burlon, D., Ghirlanda, G., Ghisellini, G., Greiner, J., and Celotti, A. (2009). Time resolved spectral behavior of bright BATSE precursors. A&A 505, 569–575. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/200912662
Burlon, D., Ghirlanda, G., Ghisellini, G., Lazzati, D., Nava, L., Nardini, M., et al. (2008). Precursors in Swift gamma ray bursts with redshift. ApJ 685, L19–L22. doi:10.1086/592350
Burns, E. (2020). Neutron star mergers and how to study them. Living Rev. Relativ. 23, 4. doi:10.1007/s41114-020-00028-7
Camilletti, A., Chiesa, L., Ricigliano, G., Perego, A., Lippold, L. C., Padamata, S., et al. (2022). Numerical relativity simulations of the neutron star merger GW190425: microphysics and mass ratio effects. MNRAS 516, 4760–4781. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac2333
Cannon, K., Cariou, R., Chapman, A., Crispin-Ortuzar, M., Fotopoulos, N., Frei, M., et al. (2012). Toward early-warning detection of gravitational waves from compact binary coalescence. ApJ 748, 136. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/748/2/136
Capano, C. D., Tews, I., Brown, S. M., Margalit, B., De, S., Kumar, S., et al. (2020). Stringent constraints on neutron-star radii from multimessenger observations and nuclear theory. Nat. Astron. 4, 625–632. doi:10.1038/s41550-020-1014-6
Caprini, C., and Figueroa, D. G. (2018). Cosmological backgrounds of gravitational waves. Class. Quantum Gravity 35, 163001. doi:10.1088/1361-6382/aac608
Caprini, C., Hindmarsh, M., Huber, S., Konstandin, T., Kozaczuk, J., Nardini, G., et al. (2016). Science with the space-based interferometer eLISA. II: gravitational waves from cosmological phase transitions. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2016, 001. doi:10.1088/1475-7516/2016/04/001
Chan, M. L., Messenger, C., Heng, I. S., and Hendry, M. (2018). Binary neutron star mergers and third generation detectors: localization and early warning. Phys. Rev. D. 97, 123014. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.97.123014
Chang, P.-W., Zhou, B., Murase, K., and Kamionkowski, M. (2022). High-energy neutrinos from choked-jet supernovae: searches and implications. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.03088.
Charisi, M., Márka, S., and Bartos, I. (2015). Catalogue of isolated emission episodes in gamma-ray bursts from Fermi, Swift and BATSE. MNRAS 448, 2624–2633. doi:10.1093/mnras/stu2667
Chase, E. A., O’Connor, B., Fryer, C. L., Troja, E., Korobkin, O., Wollaeger, R. T., et al. (2022). Kilonova detectability with wide-field instruments. ApJ 927, 163. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac3d25
Chatterjee, C., and Wen, L. (2023). Premerger sky localization of gravitational waves from binary neutron star mergers using deep learning. ApJ 959, 76. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/accffb
Chatziioannou, K., Clark, J. A., Bauswein, A., Millhouse, M., Littenberg, T. B., and Cornish, N. (2017). Inferring the post-merger gravitational wave emission from binary neutron star coalescences. Phys. Rev. D. 96, 124035. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.96.124035
Chen, H.-Y., Fishbach, M., and Holz, D. E. (2018). A two per cent Hubble constant measurement from standard sirens within five years. Nature 562, 545–547. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0606-0
Chen, H.-Y., María Ezquiaga, J., and Gupta, I. (2024). Cosmography with next-generation gravitational wave detectors. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.03120.
Chen, H.-Y., Talbot, C., and Chase, E. A. (2023a). Mitigating the counterpart selection effect for standard sirens. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.10402.
Chen, H.-Y., Vitale, S., and Foucart, F. (2021). The relative contribution to heavy metals production from binary neutron star mergers and neutron star-black hole mergers. ApJ 920, L3. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac26c6
Chen, Z.-L., Hu, R.-C., Lin, D.-B., and Liang, E.-W. (2023b). Event rate of fast radio bursts from binary neutron star mergers. ApJ 953, 108. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ace358
Chirenti, C., Dichiara, S., Lien, A., Miller, M. C., and Preece, R. (2023). Kilohertz quasiperiodic oscillations in short gamma-ray bursts. Nature 613, 253–256. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05497-0
Chornock, R., Berger, E., Kasen, D., Cowperthwaite, P. S., Nicholl, M., Villar, V. A., et al. (2017). The electromagnetic counterpart of the binary neutron star merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. IV. Detection of near-infrared signatures of r-process nucleosynthesis with gemini-south. ApJ 848, L19. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa905c
Chornock, R., Cowperthwaite, P. S., Margutti, R., Milisavljevic, D., Alexander, K. D., Andreoni, I., et al. (2019). Multi-messenger astronomy with extremely large telescopes. BAAS 51, 237. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1903.04629
Chruślińska, M. (2022). Chemical evolution of the Universe and its consequences for gravitational-wave astrophysics. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.10622.
Cigarrán Díaz, C., and Mukherjee, S. (2022). Mapping the cosmic expansion history from LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA in synergy with DESI and SPHEREx. MNRAS 511, 2782–2795. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac208
Ciolfi, R., and Rezzolla, L. (2013). Twisted-torus configurations with large toroidal magnetic fields in relativistic stars. MNRAS 435, L43–L47. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slt092
Clark, J., Bauswein, A., Cadonati, L., Janka, H.-T., Pankow, C., and Stergioulas, N. (2014). Prospects for high frequency burst searches following binary neutron star coalescence with advanced gravitational wave detectors. Phys. Rev. D. 90, 062004. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.90.062004
Clark, J. A., Bauswein, A., Stergioulas, N., and Shoemaker, D. (2016). Observing gravitational waves from the post-merger phase of binary neutron star coalescence. Class. Quantum Gravity 33, 085003. doi:10.1088/0264-9381/33/8/085003
Colombo, A., Duqué, R., Sharan Salafia, O., Broekgaarden, F. S., Iacovelli, F., Mancarella, M., et al. (2023). Multi-messenger prospects for black hole - neutron star mergers in the O4 and O5 runs. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.16894.
Connaughton, V., Burns, E., Goldstein, A., Blackburn, L., Briggs, M. S., Zhang, B. B., et al. (2016). Fermi GBM observations of LIGO gravitational-wave event GW150914. ApJ 826, L6. doi:10.3847/2041-8205/826/1/L6
Cooper, A. J., Gupta, O., Wadiasingh, Z., Wijers, R. A. M. J., Boersma, O. M., Andreoni, I., et al. (2023). Pulsar revival in neutron star mergers: multimessenger prospects for the discovery of pre-merger coherent radio emission. MNRAS 519, 3923–3946. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac3580
Corsi, A., Hallinan, G. W., Lazzati, D., Mooley, K. P., Murphy, E. J., Frail, D. A., et al. (2018). An upper limit on the linear polarization fraction of the GW170817 radio continuum. ApJ 861, L10. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aacdfd
Corsi, A., Lloyd-Ronning, N. M., Carbone, D., Frail, D. A., Lazzati, D., Murphy, E. J., et al. (2019). Astro2020 science white paper: radio counterparts of compact object mergers in the era of gravitational-wave astronomy. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/1903.10589.
Corsi, A., and Mészáros, P. (2009). Gamma-ray burst afterglow plateaus and gravitational waves: multi-messenger signature of a millisecond magnetar? ApJ 702, 1171–1178. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/702/2/1171
Corsi, A., and Owen, B. J. (2011). Maximum gravitational-wave energy emissible in magnetar flares. Phys. Rev. D. 83, 104014. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.83.104014
Costa, G., Ballone, A., Mapelli, M., and Bressan, A. (2022). Formation of black holes in the pair-instability mass gap: evolution of a post-collision star. MNRAS 516, 1072–1080. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac2222
Côté, B., Fryer, C. L., Belczynski, K., Korobkin, O., Chruślińska, M., Vassh, N., et al. (2018). The origin of r-process elements in the Milky way. ApJ 855, 99. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aaad67
Coulter, D. A., Foley, R. J., Kilpatrick, C. D., Drout, M. R., Piro, A. L., Shappee, B. J., et al. (2017). Swope Supernova Survey 2017a (SSS17a), the optical counterpart to a gravitational wave source. Science 358, 1556–1558. doi:10.1126/science.aap9811
Cowperthwaite, P. S., Berger, E., Villar, V. A., Metzger, B. D., Nicholl, M., Chornock, R., et al. (2017). The electromagnetic counterpart of the binary neutron star merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. II. UV, optical, and near-infrared light curves and comparison to kilonova models. ApJ 848, L17. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa8fc7
Coyne, R., Corsi, A., and Owen, B. J. (2016). Cross-correlation method for intermediate-duration gravitational wave searches associated with gamma-ray bursts. Phys. Rev. D. 93, 104059. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.93.104059
Creminelli, P., and Vernizzi, F. (2017). Dark energy after GW170817 and GRB170817A. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 251302. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.251302
Cutler, C. (2002a). Gravitational waves from neutron stars with large toroidal B fields. Phys. Rev. D. 66, 084025. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.66.084025
Cutler, C. (2002b). Gravitational waves from neutron stars with large toroidal b fields. Phys. Rev. D. 66, 084025. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.66.084025
Dai, L., McKinney, J. C., and Miller, M. C. (2017). Energetic constraints on electromagnetic signals from double black hole mergers. MNRAS 470, L92–L96. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slx086
Dalal, N., Holz, D. E., Hughes, S. A., and Jain, B. (2006). Short GRB and binary black hole standard sirens as a probe of dark energy. Phys. Rev. D. 74, 063006. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.74.063006
Dalang, C., and Baker, T. (2023). The clustering of dark siren host galaxies. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.08991.
Dall’Osso, S., Giacomazzo, B., Perna, R., and Stella, L. (2015). Gravitational waves from massive magnetars formed in binary neutron star mergers. ApJ 798, 25. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/798/1/25
D’Avanzo, P., Campana, S., Salafia, O. S., Ghirlanda, G., Ghisellini, G., Melandri, A., et al. (2018). The evolution of the X-ray afterglow emission of GW 170817/GRB 170817A in XMM-Newton observations. A&A 613, L1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201832664
De, S., Finstad, D., Lattimer, J. M., Brown, D. A., Berger, E., and Biwer, C. M. (2018). Tidal deformabilities and radii of neutron stars from the observation of GW170817. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 091102. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.091102
Delfavero, V., O’Shaughnessy, R., Belczynski, K., Drozda, P., and Wysocki, D. (2023). Iteratively comparing gravitational-wave observations to the evolution of massive stellar binaries. Phys. Rev. D. 108, 043023. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.108.043023
De Lillo, F., and Suresh, J. (2023). Estimating astrophysical population properties using a multi-component stochastic gravitational-wave background search. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.05823.
De Lillo, F., Suresh, J., Depasse, A., Sieniawska, M., Miller, A. L., and Bruno, G. (2023). Probing ensemble properties of vortex-avalanche pulsar glitches with a stochastic gravitational-wave background search. PRD 107, 102001. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.107.102001
De Lillo, F., Suresh, J., and Miller, A. L. (2022). Stochastic gravitational-wave background searches and constraints on neutron-star ellipticity. MNRAS 513, 1105–1114. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac984
Della Valle, M., Chincarini, G., Panagia, N., Tagliaferri, G., Malesani, D., Testa, V., et al. (2006). An enigmatic long-lasting γ-ray burst not accompanied by a bright supernova. Nature 444, 1050–1052. doi:10.1038/nature05374
Del Pozzo, W. (2012). Inference of cosmological parameters from gravitational waves: applications to second generation interferometers. Phys. Rev. D. 86, 043011. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.86.043011
De Luca, V., and Bellomo, N. (2023). Accretion, emission, mass and spin evolution. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.14097.
De Luca, V., Desjacques, V., Franciolini, G., Pani, P., and Riotto, A. (2021). GW190521 mass gap event and the primordial black hole scenario. Phys. Rev. Lett. 126, 051101. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.051101
Detweiler, S. (1979). Pulsar timing measurements and the search for gravitational waves. ApJ 234, 1100–1104. doi:10.1086/157593
Dichiara, S., Troja, E., O’Connor, B., Marshall, F. E., Beniamini, P., Cannizzo, J. K., et al. (2020). Short gamma-ray bursts within 200 Mpc. MNRAS 492, 5011–5022. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa124
Dichiara, S., Tsang, D., Troja, E., Neill, D., Norris, J. P., and Yang, Y. H. (2023). A luminous precursor in the extremely bright GRB 230307A. ApJ 954, L29. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/acf21d
Dimple, , Misra, K., and Arun, K. G. (2023). Evidence for two distinct populations of kilonova-associated gamma-ray bursts. ApJ 949, L22. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/acd4c4
Dominik, M., Belczynski, K., Fryer, C., Holz, D. E., Berti, E., Bulik, T., et al. (2013). Double compact objects. II. Cosmological merger rates. ApJ 779, 72. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/779/1/72
Drout, M. R., Piro, A. L., Shappee, B. J., Kilpatrick, C. D., Simon, J. D., Contreras, C., et al. (2017). Light curves of the neutron star merger GW170817/SSS17a: implications for r-process nucleosynthesis. Science 358, 1570–1574. doi:10.1126/science.aaq0049
Eddins, A., Lee, K.-H., Corsi, A., Bartos, I., Márka, Z., and Márka, S. (2023). A search for kilonova radio flares in a sample of Swift/BAT short gamma-ray bursts. ApJ 948, 125. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/acc6c5
Eichler, D., Livio, M., Piran, T., and Schramm, D. N. (1989). Nucleosynthesis, neutrino bursts and γ-rays from coalescing neutron stars. Nature 340, 126–128. doi:10.1038/340126a0
EPTA Collaboration, InPTA Collaboration Antoniadis, J., Arumugam, P., Arumugam, S., Babak, S., Bak Nielsen, A. S., Bassa, C. G., et al. (2023). The second data release from the European Pulsar Timing Array. III. Search for gravitational wave signals. A&A 678, A50. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202346844
Evans, M., Corsi, A., Afle, C., Ananyeva, A., Arun, K. G., Ballmer, S., et al. (2023). Cosmic explorer: a submission to the NSF mpsac ngGW subcommittee. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.13745.
Evans, P. A., Cenko, S. B., Kennea, J. A., Emery, S. W. K., Kuin, N. P. M., Korobkin, O., et al. (2017). Swift and NuSTAR observations of GW170817: detection of a blue kilonova. Science 358, 1565–1570. doi:10.1126/science.aap9580
Ezquiaga, J. M., and Zumalacárregui, M. (2017). Dark energy after GW170817: dead ends and the road ahead. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 251304. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.251304
Farah, A. M., Edelman, B., Zevin, M., Fishbach, M., María Ezquiaga, J., Farr, B., et al. (2023). Things that might go bump in the night: assessing structure in the binary black hole mass spectrum. ApJ 955, 107. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aced02
Farmer, R., Renzo, M., de Mink, S. E., Fishbach, M., and Justham, S. (2020). Constraints from gravitational-wave detections of binary black hole mergers on the 12C(α, γ)16O rate. ApJ 902, L36. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/abbadd
Farmer, R., Renzo, M., de Mink, S. E., Marchant, P., and Justham, S. (2019). Mind the gap: the location of the lower edge of the pair-instability supernova black hole mass gap. ApJ 887, 53. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab518b
Ferrari, V., Matarrese, S., and Schneider, R. (1999). Gravitational wave background from a cosmological population of core-collapse supernovae. MNRAS 303, 247–257. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1999.02194.x
Fishbach, M., Holz, D. E., and Farr, B. (2017). Are LIGO’s black holes made from smaller black holes? ApJ 840, L24. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa7045
Fishbach, M., and Kalogera, V. (2022). Apples and oranges: comparing black holes in X-ray binaries and gravitational-wave sources. ApJ 929, L26. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac64a5
Flanagan, É. É., and Hinderer, T. (2008). Constraining neutron-star tidal Love numbers with gravitational-wave detectors. Phys. Rev. D. 77, 021502. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.77.021502
Fletcher, C., Wood, J., Hamburg, R., Veres, P., Hui, C. M., Bissaldi, E., et al. (2023). A joint fermi-GBM and swift-BAT analysis of gravitational-wave candidates from the third gravitational-wave observing run. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.13666.
Fong, W., and Berger, E. (2013). The locations of short gamma-ray bursts as evidence for compact object binary progenitors. ApJ 776, 18. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/776/1/18
Fong, W., Berger, E., Margutti, R., and Zauderer, B. A. (2015). A decade of short-duration gamma-ray burst broadband afterglows: energetics, circumburst densities, and jet opening angles. ApJ 815, 102. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/815/2/102
Fong, W.-f., Nugent, A. E., Dong, Y., Berger, E., Paterson, K., Chornock, R., et al. (2022). Short GRB host galaxies. I. Photometric and spectroscopic catalogs, host associations, and galactocentric offsets. ApJ 940, 56. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac91d0
Ford, K. E. S., and McKernan, B. (2022). Binary black hole merger rates in AGN discs versus nuclear star clusters: loud beats quiet. MNRAS 517, 5827–5834. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac2861
Fowler, W. A., and Hoyle, F. (1964). Neutrino processes and pair formation in massive stars and supernovae. ApJS 9, 201. doi:10.1086/190103
Freedman, W. L. (2021). Measurements of the Hubble constant: tensions in perspective. ApJ 919, 16. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac0e95
Freedman, W. L., and Madore, B. F. (2023). Progress in direct measurements of the Hubble constant. J. Cosmol. Astropart. Phys. 2023, 050. doi:10.1088/1475-7516/2023/11/050
Fritschel, P., Kuns, K., Driggers, J., Effler, A., Lantz, B., Ottaway, D., et al. (2023). Eport of the LSC post-O5 study group. Available at: https://dcc.ligo.org/LIGO-T2200287/public.
Fryer, C. (2023). Gw compact remnant mass distribu5ons as probes of the supernova engine. Available at: https://dcc.cosmicexplorer.org/public/0163/P2300002/001/GWCompactRemnanFryer%20-%20Christopher%20Fryer.pdf.
Fynbo, J. P. U., Watson, D., Thöne, C. C., Sollerman, J., Bloom, J. S., Davis, T. M., et al. (2006). No supernovae associated with two long-duration γ-ray bursts. Nature 444, 1047–1049. doi:10.1038/nature05375
García-García, L., López-Cámara, D., and Lazzati, D. (2023). Dynamics of a relativistic jet through magnetized media. MNRAS 519, 4454–4460. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad023
Gehrels, N., Chincarini, G., Giommi, P., Mason, K. O., Nousek, J. A., Wells, A. A., et al. (2004). TheSwiftGamma-ray burst mission. ApJ 611, 1005–1020. doi:10.1086/422091
Gerosa, D., and Berti, E. (2017). Are merging black holes born from stellar collapse or previous mergers? Phys. Rev. D. 95, 124046. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.95.124046
Gerosa, D., and Fishbach, M. (2021). Hierarchical mergers of stellar-mass black holes and their gravitational-wave signatures. Nat. Astron. 5, 749–760. doi:10.1038/s41550-021-01398-w
Ghirlanda, G., Salafia, O. S., Paragi, Z., Giroletti, M., Yang, J., Marcote, B., et al. (2019). Compact radio emission indicates a structured jet was produced by a binary neutron star merger. Science 363, 968–971. doi:10.1126/science.aau8815
Ghisellini, G., and Lazzati, D. (1999). Polarization light curves and position angle variation of beamed gamma-ray bursts. MNRAS 309, L7–L11. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1999.03025.x
Ghosh, A., Vaishnava, C. S., Resmi, L., Misra, K., Arun, K. G., Omar, A., et al. (2024). Search for merger ejecta emission from late-time radio observations of short GRBs using GMRT. MNRAS 527, 8068–8077. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad3614
Ghosh, T., More, S., Bera, S., and Bose, S. (2023). Bayesian framework to infer the Hubble constant from cross-correlation of individual gravitational wave events with galaxies. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.16305.
Giacomazzo, B., and Perna, R. (2013). Formation of stable magnetars from binary neutron star mergers. ApJ 771, L26. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/771/2/L26
Giacomazzo, B., Perna, R., Rezzolla, L., Troja, E., and Lazzati, D. (2013). Compact binary progenitors of short gamma-ray bursts. ApJ 762, L18. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/762/2/L18
Gill, R., and Granot, J. (2018). Afterglow imaging and polarization of misaligned structured GRB jets and cocoons: breaking the degeneracy in GRB 170817A. MNRAS 478, 4128–4141. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty1214
Gill, R., and Granot, J. (2020). Constraining the magnetic field structure in collisionless relativistic shocks with a radio afterglow polarization upper limit in GW 170817. MNRAS 491, 5815–5825. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz3340
Gittins, F., Andersson, N., and Jones, D. I. (2021). Modelling neutron star mountains. MNRAS 500, 5570–5582. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa3635
Glampedakis, K., and Gualtieri, L. (2018). “Gravitational waves from single neutron stars: an advanced detector era survey,” in Astrophysics and space science library. Editors L. Rezzolla, P. Pizzochero, D. I. Jones, N. Rea, and I. Vidaña (Berlin, Germany: Springer). doi:10.1007/978-3-319-97616-7_12
Goldreich, P., and Lynden-Bell, D. (1969). Io, a jovian unipolar inductor. ApJ 156, 59–78. doi:10.1086/149947
Gompertz, B. P., Nicholl, M., Smith, J. C., Harisankar, S., Pratten, G., Schmidt, P., et al. (2023a). A multimessenger model for neutron star-black hole mergers. MNRAS 526, 4585–4598. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad2990
Gompertz, B. P., Ravasio, M. E., Nicholl, M., Levan, A. J., Metzger, B. D., Oates, S. R., et al. (2023b). The case for a minute-long merger-driven gamma-ray burst from fast-cooling synchrotron emission. Nat. Astron. 7, 67–79. doi:10.1038/s41550-022-01819-4
Gossan, S., and Hall, E. (2023). Optimizing xg detector networks for galactic astrophysics. Available at: https://dcc.cosmicexplorer.org/public/0163/P2300017/001/CE_Science_Letter_Gossan_Hall%20-%20Sarah%20Gossan.pdf.
Gottlieb, O., Nagakura, H., Tchekhovskoy, A., Natarajan, P., Ramirez-Ruiz, E., Banagiri, S., et al. (2023). Jetted and turbulent stellar deaths: new LVK-detectable gravitational-wave sources. ApJ 951, L30. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ace03a
Gottlieb, O., and Nakar, E. (2022). The propagation of relativistic jets in expanding media. MNRAS 517, 1640–1666. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac2699
Gottlieb, O., Nakar, E., and Bromberg, O. (2021). The structure of hydrodynamic γ-ray burst jets. MNRAS 500, 3511–3526. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa3501
Gottlieb, O., Nakar, E., Piran, T., and Hotokezaka, K. (2018). A cocoon shock breakout as the origin of the γ-ray emission in GW170817. MNRAS 479, 588–600. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty1462
Govreen-Segal, T., and Nakar, E. (2023). Analytic model for off-axis GRB afterglow images - geometry measurement and implications for measuring H0. MNRAS 524, 403–425. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad1628
Grace, B., Wette, K., Scott, S. M., and Sun, L. (2023). Piecewise frequency model for searches for long-transient gravitational waves from young neutron stars. Phys. Rev. D. 108, 123045. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.108.123045
Graham, M. J., McKernan, B., Ford, K. E. S., Stern, D., Djorgovski, S. G., Coughlin, M., et al. (2023). A light in the dark: searching for electromagnetic counterparts to black hole-black hole mergers in LIGO/Virgo O3 with the zwicky transient facility. ApJ 942, 99. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aca480
Grandorf, C., McCarty, J., Rajkumar, P., Harbin, H., Lee, K. H., Corsi, A., et al. (2021). Search for radio remnants of nearby off-axis gamma-ray bursts in a sample of Swift/BAT events. ApJ 908, 63. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/abd315
Granot, J., De Colle, F., and Ramirez-Ruiz, E. (2018a). Off-axis afterglow light curves and images from 2D hydrodynamic simulations of double-sided GRB jets in a stratified external medium. MNRAS 481, 2711–2720. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty2454
Granot, J., Gill, R., Guetta, D., and De Colle, F. (2018b). Off-axis emission of short GRB jets from double neutron star mergers and GRB 170817A. MNRAS 481, 1597–1608. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty2308
Granot, J., Guetta, D., and Gill, R. (2017). Lessons from the short GRB 170817A: the first gravitational-wave detection of a binary neutron star merger. ApJ 850, L24. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa991d
Guarini, E., Tamborra, I., Margutti, R., and Ramirez-Ruiz, E. (2023). Transients stemming from collapsing massive stars: the missing pieces to advance joint observations of photons and high-energy neutrinos. Phys. Rev. D. 108, 083035. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.108.083035
Gupta, I., Afle, C., Arun, K. G., Bandopadhyay, A., Baryakhtar, M., Biscoveanu, S., et al. (2023a). Characterizing gravitational wave detector networks: from A♯ to cosmic explorer. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.10421.
Gupta, I., Borhanian, S., Dhani, A., Chattopadhyay, D., Kashyap, R., Villar, V. A., et al. (2023b). Neutron star-black hole mergers in next generation gravitational-wave observatories. Phys. Rev. D. 107, 124007. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.107.124007
Haggard, D., Nynka, M., Ruan, J. J., Kalogera, V., Cenko, S. B., Evans, P., et al. (2017). A deep Chandra X-ray study of neutron star coalescence GW170817. ApJ 848, L25. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa8ede
Hajela, A., Margutti, R., Bright, J. S., Alexander, K. D., Metzger, B. D., Nedora, V., et al. (2022). Evidence for X-ray emission in excess to the jet-afterglow decay 3.5 yr after the binary neutron star merger GW 170817: a new emission component. ApJ 927, L17. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac504a
Hallinan, G., Corsi, A., Mooley, K. P., Hotokezaka, K., Nakar, E., Kasliwal, M. M., et al. (2017). A radio counterpart to a neutron star merger. Science 358, 1579–1583. doi:10.1126/science.aap9855
Hansen, B. M. S., and Lyutikov, M. (2001). Radio and X-ray signatures of merging neutron stars. MNRAS 322, 695–701. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2001.04103.x
Hijikawa, K., Tanikawa, A., Kinugawa, T., Yoshida, T., and Umeda, H. (2021). On the population III binary black hole mergers beyond the pair-instability mass gap. MNRAS 505, L69–L73. doi:10.1093/mnrasl/slab052
Hjorth, J., Levan, A. J., Tanvir, N. R., Lyman, J. D., Wojtak, R., Schrøder, S. L., et al. (2017). The distance to NGC 4993: the host galaxy of the gravitational-wave event GW170817. ApJ 848, L31. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa9110
Holz, D. E., and Hughes, S. A. (2005). Using gravitational-wave standard sirens. ApJ 629, 15–22. doi:10.1086/431341
Horesh, A., Hotokezaka, K., Piran, T., Nakar, E., and Hancock, P. (2016). Testing the magnetar model via a late-time radio observations of two macronova candidates. ApJ 819, L22. doi:10.3847/2041-8205/819/2/L22
Hotokezaka, K., Kiuchi, K., Kyutoku, K., Muranushi, T., Sekiguchi, Y.-i., Shibata, M., et al. (2013). Remnant massive neutron stars of binary neutron star mergers: evolution process and gravitational waveform. Phys. Rev. D. 88, 044026. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.88.044026
Hotokezaka, K., Kiuchi, K., Shibata, M., Nakar, E., and Piran, T. (2018). Synchrotron radiation from the fast tail of dynamical ejecta of neutron star mergers. ApJ 867, 95. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aadf92
Hotokezaka, K., Nakar, E., Gottlieb, O., Nissanke, S., Masuda, K., Hallinan, G., et al. (2019). A Hubble constant measurement from superluminal motion of the jet in GW170817. Nat. Astron. 3, 940–944. doi:10.1038/s41550-019-0820-1
Hotokezaka, K., Nissanke, S., Hallinan, G., Lazio, T. J. W., Nakar, E., and Piran, T. (2016). Radio counterparts of compact binary mergers detectable in gravitational waves: a simulation for an optimized survey. ApJ 831, 190. doi:10.3847/0004-637X/831/2/190
Hu, Q., and Veitch, J. (2023). Rapid premerger localization of binary neutron stars in third-generation gravitational-wave detectors. ApJ 958, L43. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ad0ed4
Hu, W. (2005). “Dark energy probes in light of the CMB,” in Observing dark energy. doi:10.48550/arXiv.astro-ph/0407158
Im, M., Yoon, Y., Lee, S.-K. J., Lee, H. M., Kim, J., Lee, C.-U., et al. (2017). Distance and properties of NGC 4993 as the host galaxy of the gravitational-wave source GW170817. ApJ 849, L16. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa9367
Ivezić, Ž., Kahn, S. M., Tyson, J. A., Abel, B., Acosta, E., Allsman, R., et al. (2019). LSST: from science drivers to reference design and anticipated data products. ApJ 873, 111. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab042c
Iyer, B., Souradeep, T., Unnikrishnan, C., Dhurandhar, S., Raja, S., Kumar, A., et al. (2023). Ligo-India, proposal of the consortium for indian initiative in gravitational-wave observations (indigo). Available at: https://dcc.ligo.org/LIGO-M1100296/public.
Janka, H.-T. (2017). “Neutrino emission from supernovae,” in Handbook of supernovae. Editors A. W. Alsabti, and P. Murdin (Berlin, Germany: Springer), 1575. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-21846-5_4
Jin, S. (2023). Optimizing xg detector networks for galactic astrophysics. Available at: https://dcc.cosmicexplorer.org/public/0163/P2300005/001/CE_Science_Letter%20-%20ssj%20qwe.pdf.
Kalogera, V., Bizouard, M.-A., Burrows, A., Janka, T., Kotake, K., Messer, B., et al. (2019). The yet-unobserved multi-messenger gravitational-wave universe. BAAS 51, 239. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1903.09224
Kamionkowski, M., and Riess, A. G. (2023). The Hubble tension and early dark energy. Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 73, 153–180. doi:10.1146/annurev-nucl-111422-024107
Karathanasis, C., Mukherjee, S., and Mastrogiovanni, S. (2023). Binary black holes population and cosmology in new lights: signature of PISN mass and formation channel in GWTC-3. MNRAS 523, 4539–4555. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad1373
Kasen, D., Metzger, B., Barnes, J., Quataert, E., and Ramirez-Ruiz, E. (2017). Origin of the heavy elements in binary neutron-star mergers from a gravitational-wave event. Nature 551, 80–84. doi:10.1038/nature24453
Kasliwal, M. M., Nakar, E., Singer, L. P., Kaplan, D. L., Cook, D. O., Van Sistine, A., et al. (2017). Illuminating gravitational waves: a concordant picture of photons from a neutron star merger. Science 358, 1559–1565. doi:10.1126/science.aap9455
Kathirgamaraju, A., Giannios, D., and Beniamini, P. (2019). Observable features of GW170817 kilonova afterglow. MNRAS 487, 3914–3921. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz1564
Kawamura, S., Ando, M., Seto, N., Sato, S., Nakamura, T., Tsubono, K., et al. (2011). The Japanese space gravitational wave antenna: DECIGO. Class. Quantum Gravity 28, 094011. doi:10.1088/0264-9381/28/9/094011
Kocevski, D., Burns, E., Goldstein, A., Dal Canton, T., Briggs, M. S., Blackburn, L., et al. (2018). Analysis of sub-threshold short gamma-ray bursts in Fermi GBM data. ApJ 862, 152. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aacb7b
Krolak, A., Jaranowski, P., Bejger, M., Ciecielag, P., Dorosh, O., and Pisarski, A. (2023). Search for postmerger gravitational waves from binary neutron star mergers using a matched-filtering statistic. Class. Quantum Gravity 40, 215008. doi:10.1088/1361-6382/acfa5d
Kruckow, M. U., Tauris, T. M., Langer, N., Kramer, M., and Izzard, R. G. (2018). Progenitors of gravitational wave mergers: binary evolution with the stellar grid-based code COMBINE. MNRAS 481, 1908–1949. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty2190
Lai, D. (2012). DC circuit powered by orbital motion: magnetic interactions in compact object binaries and exoplanetary systems. ApJ 757, L3. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/757/1/L3
Lai, D., and Shapiro, S. L. (1995). Gravitational radiation from rapidly rotating nascent neutron stars. ApJ 442, 259. doi:10.1086/175438
Landry, P. (2023). Next-generation dense matter science with binary neutron star inspirals. Available at: https://dcc.cosmicexplorer.org/public/0163/P2300013/001/XG_Science_Letter-CBC_Dense_Matter%20-%20Philippe%20Landry.pdf.
Landry, P., and Read, J. S. (2021). The mass distribution of neutron stars in gravitational-wave binaries. ApJ 921, L25. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac2f3e
Lazio, T. J. W., Alatalo, K., Blecha, L., Boizelle, B., Bower, G. C., Braatz, J., et al. (2019). “ngVLA key science goal 5 understanding the formation and evolution of black holes in the era of multi-messenger astronomy,” in American Astronomical Society Meeting Abstracts #233.
Lazzati, D. (2005). Precursor activity in bright, long BATSE gamma-ray bursts. MNRAS 357, 722–731. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2005.08687.x
Lazzati, D. (2020). Short duration gamma-ray bursts and their outflows in light of GW170817. Front. Astronomy Space Sci. 7, 78. doi:10.3389/fspas.2020.578849
Lazzati, D., Deich, A., Morsony, B. J., and Workman, J. C. (2017). Off-axis emission of short γ-ray bursts and the detectability of electromagnetic counterparts of gravitational-wave-detected binary mergers. MNRAS 471, 1652–1661. doi:10.1093/mnras/stx1683
Lazzati, D., and Perna, R. (2019). Jet-cocoon outflows from neutron star mergers: structure, light curves, and fundamental physics. ApJ 881, 89. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab2e06
Lazzati, D., Perna, R., Ciolfi, R., Giacomazzo, B., López-Cámara, D., and Morsony, B. (2021). Two steps forward and one step sideways: the propagation of relativistic jets in realistic binary neutron star merger ejecta. ApJ 918, L6. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac1794
Lazzati, D., Perna, R., Morsony, B. J., Lopez-Camara, D., Cantiello, M., Ciolfi, R., et al. (2018). Late time afterglow observations reveal a collimated relativistic jet in the ejecta of the binary neutron star merger GW170817. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 241103. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.241103
Levan, A. J., Lyman, J. D., Tanvir, N. R., Hjorth, J., Mandel, I., Stanway, E. R., et al. (2017). The environment of the binary neutron star merger GW170817. ApJ 848, L28. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa905f
LIGO Scientific Collaboration Aasi, J., Abbott, B. P., Abbott, R., Abbott, T., Abernathy, M. R., Ackley, K., et al. (2015). Advanced LIGO. Class. Quantum Gravity 32, 074001. doi:10.1088/0264-9381/32/7/074001
Lindblom, L., Owen, B. J., and Morsink, S. M. (1998). Gravitational radiation instability in hot young neutron stars. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 4843–4846. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.80.4843
Liotine, C., Zevin, M., Berry, C. P. L., Doctor, Z., and Kalogera, V. (2023). The missing link between black holes in high-mass X-ray binaries and gravitational-wave sources: observational selection effects. ApJ 946, 4. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/acb8b2
Loeb, A. (2016). Electromagnetic counterparts to black hole mergers detected by LIGO. ApJ 819, L21. doi:10.3847/2041-8205/819/2/L21
Lorimer, D. R., Bailes, M., McLaughlin, M. A., Narkevic, D. J., and Crawford, F. (2007). A bright millisecond radio burst of extragalactic origin. Science 318, 777–780. doi:10.1126/science.1147532
Magee, R., Chatterjee, D., Singer, L. P., Sachdev, S., Kovalam, M., Mo, G., et al. (2021). First demonstration of early warning gravitational-wave alerts. ApJ 910, L21. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/abed54
Magee, R., Fong, H., Caudill, S., Messick, C., Cannon, K., Godwin, P., et al. (2019). Sub-threshold binary neutron star search in advanced LIGO’s first observing run. ApJ 878, L17. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab20cf
Makhathini, S., Mooley, K. P., Brightman, M., Hotokezaka, K., Nayana, A. J., Intema, H. T., et al. (2021). The panchromatic afterglow of GW170817: the full uniform data set, modeling, comparison with previous results, and implications. ApJ 922, 154. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac1ffc
Mancarella, M., Borghi, N., Foffa, S., Genoud-Prachex, E., Iacovelli, F., Maggiore, M., et al. (2023). “Gravitational-wave cosmology with dark sirens: state of the art and perspectives for 3G detectors,” in 41st International Conference on High Energy Physics.
Mandel, I., and Broekgaarden, F. S. (2022). Rates of compact object coalescences. Living Rev. Relativ. 25, 1. doi:10.1007/s41114-021-00034-3
Mangiagli, A., Bonetti, M., Sesana, A., and Colpi, M. (2019). Merger rate of stellar black hole binaries above the pair-instability mass gap. ApJ 883, L27. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab3f33
Margalit, B., Jermyn, A. S., Metzger, B. D., Roberts, L. F., and Quataert, E. (2022). Angular-momentum transport in proto-neutron stars and the fate of neutron star merger remnants. ApJ 939, 51. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac8b01
Margalit, B., and Metzger, B. D. (2017). Constraining the maximum mass of neutron stars from multi-messenger observations of GW170817. ApJ 850, L19. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa991c
Margalit, B., and Metzger, B. D. (2019). The multi-messenger matrix: the future of neutron star merger constraints on the nuclear equation of state. ApJ 880, L15. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab2ae2
Margutti, R., Alexander, K. D., Xie, X., Sironi, L., Metzger, B. D., Kathirgamaraju, A., et al. (2018). The binary neutron star event LIGO/Virgo GW170817 160 Days after merger: synchrotron emission across the electromagnetic spectrum. ApJ 856, L18. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aab2ad
Margutti, R., Berger, E., Fong, W., Guidorzi, C., Alexander, K. D., Metzger, B. D., et al. (2017). The electromagnetic counterpart of the binary neutron star merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. V. Rising X-ray emission from an off-axis jet. ApJ 848, L20. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa9057
Margutti, R., and Chornock, R. (2021). First multimessenger observations of a neutron star merger. ARA&A 59, 155–202. doi:10.1146/annurev-astro-112420-030742
Matsumoto, T., and Piran, T. (2020). On short GRBs similar to GRB 170817A detected by Fermi-GBM. MNRAS 492, 4283–4290. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa050
McEnery, J. (2019). “Wide-Field InfraRed Survey Telescope (WFIRST) Mission and new opportunities in time domain and multmessenger astrophysics,” in APS April Meeting Abstracts, Denver, Colorado, April, 2019.
Medvedev, M. V., and Loeb, A. (2013). On Poynting-flux-driven bubbles and shocks around merging neutron star binaries. MNRAS 431, 2737–2744. doi:10.1093/mnras/stt366
Melatos, A., and Payne, D. J. B. (2005). Gravitational radiation from an accreting millisecond pulsar with a magnetically confined mountain. ApJ 623, 1044–1050. doi:10.1086/428600
Melosh, H. J. (1969). Estimate of the gravitational radiation from NP 0532. Nature 224, 781–782. doi:10.1038/224781a0
Messick, C., Blackburn, K., Brady, P., Brockill, P., Cannon, K., Cariou, R., et al. (2017). Analysis framework for the prompt discovery of compact binary mergers in gravitational-wave data. Phys. Rev. D. 95, 042001. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.95.042001
Metzger, B. D., and Berger, E. (2012). What is the most promising electromagnetic counterpart of a neutron star binary merger? ApJ 746, 48. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/746/1/48
Metzger, B. D., Thompson, T. A., and Quataert, E. (2018). A magnetar origin for the kilonova ejecta in GW170817. ApJ 856, 101. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aab095
Metzger, B. D., and Zivancev, C. (2016). Pair fireball precursors of neutron star mergers. MNRAS 461, 4435–4440. doi:10.1093/mnras/stw1800
Miller, A. L., Singh, N., and Palomba, C. (2023). Enabling multi-messenger astronomy with continuous gravitational waves: early warning and sky localization of binary neutron stars in Einstein Telescope. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.15808.
Mooley, K. P., Deller, A. T., Gottlieb, O., Nakar, E., Hallinan, G., Bourke, S., et al. (2018a). Superluminal motion of a relativistic jet in the neutron-star merger GW170817. Nature 561, 355–359. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0486-3
Mooley, K. P., Nakar, E., Hotokezaka, K., Hallinan, G., Corsi, A., Frail, D. A., et al. (2018b). A mildly relativistic wide-angle outflow in the neutron-star merger event GW170817. Nature 554, 207–210. doi:10.1038/nature25452
Moortgat, J., and Kuijpers, J. (2006). Scattering of magnetosonic waves in a relativistic and anisotropic magnetized plasma. MNRAS 368, 1110–1122. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.10189.x
Morales, J. A., and Horowitz, C. J. (2022). Neutron star crust can support a large ellipticity. MNRAS 517, 5610–5616. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac3058
Most, E. R., and Philippov, A. A. (2020). Electromagnetic precursors to gravitational-wave events: numerical simulations of flaring in pre-merger binary neutron star magnetospheres. ApJ 893, L6. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab8196
Most, E. R., and Philippov, A. A. (2022). Electromagnetic precursor flares from the late inspiral of neutron star binaries. MNRAS 515, 2710–2724. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac1909
Most, E. R., and Philippov, A. A. (2023a). Electromagnetic precursors to black hole-neutron star gravitational wave events: flares and reconnection-powered fast radio transients from the late inspiral. ApJ 956, L33. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/acfdae
Most, E. R., and Philippov, A. A. (2023b). Reconnection-powered fast radio transients from coalescing neutron star binaries. Phys. Rev. Lett. 130, 245201. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.245201
Most, E. R., and Quataert, E. (2023). Flares, jets, and quasiperiodic outbursts from neutron star merger remnants. ApJ 947, L15. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/acca84
Most, E. R., Weih, L. R., Rezzolla, L., and Schaffner-Bielich, J. (2018). New constraints on radii and tidal deformabilities of neutron stars from GW170817. Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 261103. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.120.261103
Mösta, P., Radice, D., Haas, R., Schnetter, E., and Bernuzzi, S. (2020). A magnetar engine for short GRBs and kilonovae. ApJ 901, L37. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/abb6ef
Mukherjee, S., Krolewski, A., Wandelt, B. D., and Silk, J. (2022). Cross-correlating dark sirens and galaxies: measurement of H0 from GWTC-3 of LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.03643.
Mukherjee, S., Lavaux, G., Bouchet, F. R., Jasche, J., Wandelt, B. D., Nissanke, S., et al. (2021a). Velocity correction for Hubble constant measurements from standard sirens. A&A 646, A65. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201936724
Mukherjee, S., and Silk, J. (2020). Time dependence of the astrophysical stochastic gravitational wave background. MNRAS 491, 4690–4701. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz3226
Mukherjee, S., and Silk, J. (2021). Fundamental physics using the temporal gravitational wave background. Phys. Rev. D. 104, 063518. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.104.063518
Mukherjee, S., Wandelt, B. D., Nissanke, S. M., and Silvestri, A. (2021b). Accurate precision cosmology with redshift unknown gravitational wave sources. Phys. Rev. D. 103, 043520. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.103.043520
Mukherjee, S., Wandelt, B. D., and Silk, J. (2020a). Multimessenger tests of gravity with weakly lensed gravitational waves. Phys. Rev. D. 101, 103509. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.101.103509
Mukherjee, S., Wandelt, B. D., and Silk, J. (2020b). Probing the theory of gravity with gravitational lensing of gravitational waves and galaxy surveys. MNRAS 494, 1956–1970. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa827
Mukherjee, S., Wandelt, B. D., and Silk, J. (2021c). Testing the general theory of relativity using gravitational wave propagation from dark standard sirens. MNRAS 502, 1136–1144. doi:10.1093/mnras/stab001
Mukhopadhyay, M., Kimura, S. S., and Murase, K. (2024). Gravitational wave triggered searches for high-energy neutrinos from binary neutron star mergers: prospects for next generation detectors. Phys. Rev. D. 109, 043053. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.109.043053
Murphy, E.ngVLA Science Advisory Council (2020). “Science with a next generation very large Array,” in American Astronomical Society Meeting Abstracts #235.
Murphy, E., Beasley, T., Corsi, A., and Osten, R. (2023). Synergies between cosmic explorer and the ngvla. Available at: https://dcc.cosmicexplorer.org/public/0163/P2300009/002/Murphy-CE_Science_Letter_ngVLA-v2.pdf.
Nakar, E. (2020). The electromagnetic counterparts of compact binary mergers. Phys. Rep. 886, 1–84. doi:10.1016/j.physrep.2020.08.008
Nakar, E., and Piran, T. (2011). Detectable radio flares following gravitational waves from mergers of binary neutron stars. Nature 478, 82–84. doi:10.1038/nature10365
Nakar, E., and Piran, T. (2018). Implications of the radio and X-ray emission that followed GW170817. MNRAS 478, 407–415. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty952
Nakar, E., and Piran, T. (2021). Afterglow constraints on the viewing angle of binary neutron star mergers and determination of the Hubble constant. ApJ 909, 114. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/abd6cd
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (2023) Pathways to discovery in astronomy and astrophysics for the 2020s. Washington, DC: The National Academies Press. doi:10.17226/26141
Nedora, V., Radice, D., Bernuzzi, S., Perego, A., Daszuta, B., Endrizzi, A., et al. (2021). Dynamical ejecta synchrotron emission as a possible contributor to the changing behaviour of GRB170817A afterglow. MNRAS 506, 5908–5915. doi:10.1093/mnras/stab2004
Nicholl, M., Berger, E., Kasen, D., Metzger, B. D., Elias, J., Briceño, C., et al. (2017). The electromagnetic counterpart of the binary neutron star merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. III. Optical and UV spectra of a blue kilonova from fast polar ejecta. ApJ 848, L18. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa9029
Nimonkar, H., and Mukherjee, S. (2024). Dependence of peculiar velocity on the host properties of the gravitational wave sources and its impact on the measurement of Hubble constant. MNRAS 527, 2152–2164. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad3256
Nissanke, S., Holz, D. E., Hughes, S. A., Dalal, N., and Sievers, J. L. (2010). Exploring short gamma-ray bursts as gravitational-wave standard sirens. ApJ 725, 496–514. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/725/1/496
Nitz, A. H., and Dal Canton, T. (2021). Pre-merger localization of compact-binary mergers with third-generation observatories. ApJ 917, L27. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac1a75
Nitz, A. H., Schäfer, M., and Dal Canton, T. (2020). Gravitational-wave merger forecasting: scenarios for the early detection and localization of compact-binary mergers with ground-based observatories. ApJ 902, L29. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/abbc10
Nouri, F. H., Janiuk, A., and Przerwa, M. (2023). Studying postmerger outflows from magnetized-neutrino-cooled accretion disks. ApJ 944, 220. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/acafe2
Owen, B. J. (2005). Maximum elastic deformations of compact stars with exotic equations of state. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 211101. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.211101
Owen, B. J., Lindblom, L., Cutler, C., Schutz, B. F., Vecchio, A., and Andersson, N. (1998). Gravitational waves from hot young rapidly rotating neutron stars. PRD 58, 084020. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.58.084020
Pagliaro, G., Papa, M. A., Ming, J., Lian, J., Tsuna, D., Maraston, C., et al. (2023). Continuous gravitational waves from galactic neutron stars: demography, detectability, and prospects. ApJ 952, 123. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/acd76f
Palenzuela, C., Lehner, L., Ponce, M., Liebling, S. L., Anderson, M., Neilsen, D., et al. (2013). Electromagnetic and gravitational outputs from binary-neutron-star coalescence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 061105. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.061105
Palmese, A., Hartley, W., Tarsitano, F., Conselice, C., Lahav, O., Allam, S., et al. (2017). Evidence for dynamically driven formation of the GW170817 neutron star binary in NGC 4993. ApJ 849, L34. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa9660
Pan, Y. C., Kilpatrick, C. D., Simon, J. D., Xhakaj, E., Boutsia, K., Coulter, D. A., et al. (2017). The old host-galaxy environment of SSS17a, the first electromagnetic counterpart to a gravitational-wave source. ApJ 848, L30. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa9116
Pan, Z., Yang, H., and Yagi, K. (2023). Repeating fast radio bursts from neutron star binaries: multiband and multimessenger opportunities. Phys. Rev. D. 108, 063014. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.108.063014
Particle Physics Project Prioritization Panel (2023). Pathways to innovation and discovery in particle physics. Available at: https://science.osti.gov/-/media/hep/hepap/pdf/Reports/P5Report2023_120123-DRAFT-to-HEPAP.pdf.
Paschalidis, V., and Ruiz, M. (2019). Are fast radio bursts the most likely electromagnetic counterpart of neutron star mergers resulting in prompt collapse? Phys. Rev. D. 100, 043001. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.100.043001
Pavan, A., Ciolfi, R., Kalinani, J. V., and Mignone, A. (2023). Jet-environment interplay in magnetized binary neutron star mergers. MNRAS 524, 260–275. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad1809
Penner, A. J., Andersson, N., Jone, D. I., Samuelsson, L., and Hawke, I. (2012). The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 749 (2), 5. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/749/2/L36
Perna, G., Ricciardone, A., Bertacca, D., and Matarrese, S. (2023). Non-gaussianity from the cross-correlation of the astrophysical gravitational wave background and the cosmic microwave background. JCAP 2023, 014. doi:10.1088/1475-7516/2023/10/014
Perna, R., Artale, M. C., Wang, Y.-H., Mapelli, M., Lazzati, D., Sgalletta, C., et al. (2022). Host galaxies and electromagnetic counterparts to binary neutron star mergers across the cosmic time: detectability of GW170817-like events. MNRAS 512, 2654–2668. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac685
Perna, R., Chruslinska, M., Corsi, A., and Belczynski, K. (2018). Binary black hole mergers within the LIGO horizon: statistical properties and prospects for detecting electromagnetic counterparts. MNRAS 477, 4228–4240. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty814
Perna, R., Lazzati, D., and Farr, W. (2019). Limits on electromagnetic counterparts of gravitational-wave-detected binary black hole mergers. ApJ 875, 49. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab107b
Petroff, E., Hessels, J. W. T., and Lorimer, D. R. (2022). Fast radio bursts at the dawn of the 2020s. A&A Rev. 30, 2. doi:10.1007/s00159-022-00139-w
Petrov, P., Singer, L. P., Coughlin, M. W., Kumar, V., Almualla, M., Anand, S., et al. (2022). Data-driven expectations for electromagnetic counterpart searches based on LIGO/Virgo public alerts. ApJ 924, 54. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac366d
Pian, E., D’Avanzo, P., Benetti, S., Branchesi, M., Brocato, E., Campana, S., et al. (2017). Spectroscopic identification of r-process nucleosynthesis in a double neutron-star merger. Nature 551, 67–70. doi:10.1038/nature24298
Piro, A. L. (2012). Magnetic interactions in coalescing neutron star binaries. ApJ 755, 80. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/755/1/80
Piro, A. L., Giacomazzo, B., and Perna, R. (2017). The fate of neutron star binary mergers. ApJ 844, L19. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa7f2f
Raaijmakers, G., Nissanke, S., Foucart, F., Kasliwal, M. M., Bulla, M., Fernández, R., et al. (2021). The challenges ahead for multimessenger analyses of gravitational waves and kilonova: a case study on GW190425. ApJ 922, 269. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac222d
Radice, D., Bernuzzi, S., and Perego, A. (2020). The dynamics of binary neutron star mergers and GW170817. Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 70, 95–119. doi:10.1146/annurev-nucl-013120-114541
Radice, D., Galeazzi, F., Lippuner, J., Roberts, L. F., Ott, C. D., and Rezzolla, L. (2016). Dynamical mass ejection from binary neutron star mergers. MNRAS 460, 3255–3271. doi:10.1093/mnras/stw1227
Radice, D., Perego, A., Hotokezaka, K., Fromm, S. A., Bernuzzi, S., and Roberts, L. F. (2018a). Binary neutron star mergers: mass ejection, electromagnetic counterparts, and nucleosynthesis. ApJ 869, 130. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aaf054
Radice, D., Perego, A., Zappa, F., and Bernuzzi, S. (2018b). GW170817: joint constraint on the neutron star equation of state from multimessenger observations. ApJ 852, L29. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aaa402
Rastinejad, J. C., Gompertz, B. P., Levan, A. J., Fong, W.-f., Nicholl, M., Lamb, G. P., et al. (2022). A kilonova following a long-duration gamma-ray burst at 350 Mpc. Nature 612, 223–227. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05390-w
Ravi, V., and Lasky, P. D. (2014). The birth of black holes: neutron star collapse times, gamma-ray bursts and fast radio bursts. MNRAS 441, 2433–2439. doi:10.1093/mnras/stu720
Reardon, D. J., Zic, A., Shannon, R. M., Hobbs, G. B., Bailes, M., Di Marco, V., et al. (2023). Search for an isotropic gravitational-wave background with the parkes pulsar timing Array. ApJ 951, L6. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/acdd02
Regimbau, T. (2011). The astrophysical gravitational wave stochastic background. Res. Astronomy Astrophysics 11, 369–390. doi:10.1088/1674-4527/11/4/001
Regimbau, T., and de Freitas Pacheco, J. A. (2006). Gravitational wave background from magnetars. A&A 447, 1–7. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20053702
Renzini, A. I., Goncharov, B., Jenkins, A. C., and Meyers, P. M. (2022). Stochastic gravitational-wave backgrounds: current detection efforts and future prospects. Galaxies 10, 34. doi:10.3390/galaxies10010034
Rezzolla, L., Most, E. R., and Weih, L. R. (2018). Using gravitational-wave observations and quasi-universal relations to constrain the maximum mass of neutron stars. ApJ 852, L25. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aaa401
Ricci, R., Troja, E., Bruni, G., Matsumoto, T., Piro, L., O’Connor, B., et al. (2021). Searching for the radio remnants of short-duration gamma-ray bursts. MNRAS 500, 1708–1720. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa3241
Riles, K. (2023). Searches for continuous-wave gravitational radiation. Living Rev. Relativ. 26, 3. doi:10.1007/s41114-023-00044-3
Roberts, L. F., Kasen, D., Lee, W. H., and Ramirez-Ruiz, E. (2011). Electromagnetic transients powered by nuclear decay in the tidal tails of coalescing compact binaries. ApJ 736, L21. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/736/1/L21
Ronchini, S., Branchesi, M., Oganesyan, G., Banerjee, B., Dupletsa, U., Ghirlanda, G., et al. (2022). Perspectives for multimessenger astronomy with the next generation of gravitational-wave detectors and high-energy satellites. A&A 665, A97. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/202243705
Rosado, P. A. (2012). Gravitational wave background from rotating neutron stars. PRD 86, 104007. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.86.104007
Rossi, A., Rothberg, B., Palazzi, E., Kann, D. A., D’Avanzo, P., Amati, L., et al. (2022). The peculiar short-duration GRB 200826A and its supernova. ApJ 932, 1. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac60a2
Rossi, E., Lazzati, D., and Rees, M. J. (2002). Afterglow light curves, viewing angle and the jet structure of γ-ray bursts. MNRAS 332, 945–950. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2002.05363.x
Rowlinson, A., Gourdji, K., van der Meulen, K., Meyers, Z. S., Shimwell, T. W., ter Veen, S., et al. (2019). LOFAR early-time search for coherent radio emission from GRB 180706A. MNRAS 490, 3483–3492. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz2866
Rowlinson, A., O’Brien, P. T., Metzger, B. D., Tanvir, N. R., and Levan, A. J. (2013). Signatures of magnetar central engines in short GRB light curves. MNRAS 430, 1061–1087. doi:10.1093/mnras/sts683
Ruiz, M., Shapiro, S. L., and Tsokaros, A. (2018). GW170817, general relativistic magnetohydrodynamic simulations, and the neutron star maximum mass. PRD 97, 021501. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.97.021501
Sachdev, S., Magee, R., Hanna, C., Cannon, K., Singer, L., Sk, J. R., et al. (2020a). An early-warning system for electromagnetic follow-up of gravitational-wave events. ApJ 905, L25. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/abc753
Sachdev, S., Regimbau, T., and Sathyaprakash, B. S. (2020b). Subtracting compact binary foreground sources to reveal primordial gravitational-wave backgrounds. Phys. Rev. D. 102, 024051. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.102.024051
Sadeh, G., Linder, N., and Waxman, E. (2024). Non-thermal emission from mildly relativistic dynamical ejecta of neutron star mergers: spectrum and sky image. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.07047.
Safarzadeh, M., Berger, E., Ng, K. K. Y., Chen, H.-Y., Vitale, S., Whittle, C., et al. (2019). Measuring the delay time distribution of binary neutron stars. II. Using the redshift distribution from third-generation gravitational-wave detectors network. ApJ 878, L13. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab22be
Sakstein, J., and Jain, B. (2017). Implications of the neutron star merger GW170817 for cosmological scalar-tensor theories. Phys. Rev. Lett. 119, 251303. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.119.251303
Sambruna, R., Civano, F., and Humensky, B. (2023). Synergies of future ground-based gw detectors with space assets for multi messenger astrophysics. Available at: https://dcc.cosmicexplorer.org/public/0163/L2300011/001/Letter%20to%20the%20Cosmic%20Explorer%20Project%20-%20Rita%20Sambruna.pdf.
Santoliquido, F., Mapelli, M., Iorio, G., Costa, G., Glover, S. C. O., Hartwig, T., et al. (2023). Binary black hole mergers from population III stars: uncertainties from star formation and binary star properties. MNRAS 524, 307–324. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad1860
Sari, R. (1999). Linear polarization and proper motion in the afterglow of beamed gamma-ray bursts. ApJ 524, L43–L46. doi:10.1086/312294
Sarin, N., Omand, C. M. B., Margalit, B., and Jones, D. I. (2022). On the diversity of magnetar-driven kilonovae. MNRAS 516, 4949–4962. doi:10.1093/mnras/stac2609
Sathyaprakash, B. S., and Schutz, B. F. (2009). Physics, astrophysics and cosmology with gravitational waves. Living Rev. Relativ. 12, 2. doi:10.12942/lrr-2009-2
Savchenko, V., Ferrigno, C., Kuulkers, E., Bazzano, A., Bozzo, E., Brandt, S., et al. (2017). INTEGRAL detection of the first prompt gamma-ray signal coincident with the gravitational-wave event GW170817. ApJ 848, L15. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa8f94
Schroeder, G., Margalit, B., Fong, W.-f., Metzger, B. D., Williams, P. K. G., Paterson, K., et al. (2020). A late-time radio survey of short gamma-ray bursts at z < 0.5: new constraints on the remnants of neutron-star mergers. ApJ 902, 82. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/abb407
Schutz, B. F. (1986). Determining the Hubble constant from gravitational wave observations. Nature 323, 310–311. doi:10.1038/323310a0
Sesana, A. (2016). Prospects for multiband gravitational-wave astronomy after GW150914. Phys. Rev. Lett. 116, 231102. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.116.231102
Setzer, C. N., Peiris, H. V., Korobkin, O., and Rosswog, S. (2023). Modelling populations of kilonovae. MNRAS 520, 2829–2842. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad257
Sharan Salafia, O., and Ghirlanda, G. (2022). The structure of gamma ray burst jets. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.11088.
Sharma, A., and Harms, J. (2020). Searching for cosmological gravitational-wave backgrounds with third-generation detectors in the presence of an astrophysical foreground. Phys. Rev. D. 102, 063009. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.102.063009
Shibata, M. (2005). Constraining nuclear equations of state using gravitational waves from hypermassive neutron stars. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 201101. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.94.201101
Shibata, M., Fujibayashi, S., Hotokezaka, K., Kiuchi, K., Kyutoku, K., Sekiguchi, Y., et al. (2017). Modeling GW170817 based on numerical relativity and its implications. PRD 96, 123012. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.96.123012
Shibata, M., and Hotokezaka, K. (2019). Merger and mass ejection of neutron star binaries. Annu. Rev. Nucl. Part. Sci. 69, 41–64. doi:10.1146/annurev-nucl-101918-023625
Shibata, M., and Taniguchi, K. (2006). Merger of binary neutron stars to a black hole: disk mass, short gamma-ray bursts, and quasinormal mode ringing. Phys. Rev. D. 73, 064027. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.73.064027
Shiralilou, B., Raaiijmakers, G., Duboeuf, B., Nissanke, S., Foucart, F., Hinderer, T., et al. (2023). Measuring the Hubble constant with dark neutron star-black hole mergers. ApJ 955, 149. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/acf3dc
Shoemaker, I. M., and Murase, K. (2018). Constraints from the time lag between gravitational waves and gamma rays: implications of GW170817 and GRB 170817A. Phys. Rev. D. 97, 083013. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.97.083013
Siegel, D. M., Agarwal, A., Barnes, J., Metzger, B. D., Renzo, M., and Villar, V. A. (2022). “Super-kilonovae” from massive collapsars as signatures of black hole birth in the pair-instability mass gap. ApJ 941, 100. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac8d04
Singer, L. P., and Price, L. R. (2016). Rapid Bayesian position reconstruction for gravitational-wave transients. Phys. Rev. D. 93, 024013. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.93.024013
Smartt, S. J., Chen, T. W., Jerkstrand, A., Coughlin, M., Kankare, E., Sim, S. A., et al. (2017). A kilonova as the electromagnetic counterpart to a gravitational-wave source. Nature 551, 75–79. doi:10.1038/nature24303
Soares-Santos, M., Holz, D. E., Annis, J., Chornock, R., Herner, K., Berger, E., et al. (2017). The electromagnetic counterpart of the binary neutron star merger LIGO/Virgo GW170817. I. Discovery of the optical counterpart using the dark energy camera. ApJ 848, L16. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa9059
Sowell, E., Corsi, A., and Coyne, R. (2019). Multiwaveform cross-correlation search method for intermediate-duration gravitational waves from gamma-ray bursts. Phys. Rev. D. 100, 124041. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.100.124041
Sridhar, N., Zrake, J., Metzger, B. D., Sironi, L., and Giannios, D. (2021). Shock-powered radio precursors of neutron star mergers from accelerating relativistic binary winds. MNRAS 501, 3184–3202. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa3794
Srivastava, V., Ballmer, S., Brown, D. A., Afle, C., Burrows, A., Radice, D., et al. (2019). Detection prospects of core-collapse supernovae with supernova-optimized third-generation gravitational-wave detectors. Phys. Rev. D. 100, 043026. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.100.043026
Stachie, C., Dal Canton, T., Christensen, N., Bizouard, M.-A., Briggs, M., Burns, E., et al. (2022). Searches for modulated γ-ray precursors to compact binary mergers in fermi-GBM data. ApJ 930, 45. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ac5f53
Suvorov, A. G., and Kokkotas, K. D. (2019). Young magnetars with fracturing crusts as fast radio burst repeaters. MNRAS 488, 5887–5897. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz2052
Szczepańczyk, M., and Zanolin, M. (2022). Gravitational waves from a core-collapse supernova: perspectives with detectors in the late 2020s and early 2030s. Galaxies 10, 70. doi:10.3390/galaxies10030070
Tagawa, H., Kocsis, B., Haiman, Z., Bartos, I., Omukai, K., and Samsing, J. (2021). Mass-gap mergers in active galactic nuclei. ApJ 908, 194. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/abd555
Tanvir, N. R., Levan, A. J., González-Fernández, C., Korobkin, O., Mandel, I., Rosswog, S., et al. (2017). The emergence of a lanthanide-rich kilonova following the merger of two neutron stars. ApJ 848, L27. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa90b6
Teboul, O., and Shaviv, N. J. (2021). Impact of the ISM magnetic field on GRB afterglow polarization. MNRAS 507, 5340–5347. doi:10.1093/mnras/stab2491
Thompson, D. J., and Wilson-Hodge, C. A. (2022). “Fermi gamma-ray space telescope,” in Handbook of X-ray and gamma-ray astrophysics, 29, 1–31. doi:10.1007/978-981-16-4544-0_58-1
Thornton, D., Stappers, B., Bailes, M., Barsdell, B., Bates, S., Bhat, N. D. R., et al. (2013). A population of fast radio bursts at cosmological distances. Science 341, 53–56. doi:10.1126/science.1236789
Tohuvavohu, A., Kennea, J. A., DeLaunay, J., Palmer, D. M., Cenko, S. B., and Barthelmy, S. (2020). Gamma-ray urgent archiver for novel opportunities (GUANO): Swift/BAT event data dumps on demand to enable sensitive subthreshold GRB searches. ApJ 900, 35. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aba94f
Troja, E., Fryer, C. L., O’Connor, B., Ryan, G., Dichiara, S., Kumar, A., et al. (2022a). A nearby long gamma-ray burst from a merger of compact objects. Nature 612, 228–231. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05327-3
Troja, E., O’Connor, B., Ryan, G., Piro, L., Ricci, R., Zhang, B., et al. (2022b). Accurate flux calibration of GW170817: is the X-ray counterpart on the rise? MNRAS 510, 1902–1909. doi:10.1093/mnras/stab3533
Troja, E., Piro, L., van Eerten, H., Wollaeger, R. T., Im, M., Fox, O. D., et al. (2017). The X-ray counterpart to the gravitational-wave event GW170817. Nature 551, 71–74. doi:10.1038/nature24290
Troja, E., Rosswog, S., and Gehrels, N. (2010). Precursors of short gamma-ray bursts. ApJ 723, 1711–1717. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/723/2/1711
Tsang, D., Read, J. S., Hinderer, T., Piro, A. L., and Bondarescu, R. (2012). Resonant shattering of neutron star crusts. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108, 011102. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.108.011102
Ushomirsky, G., Cutler, C., and Bildsten, L. (2002). Deformations of accreting neutron star crusts and gravitational wave emission: crustal quadrupole moments. Mon. Notices R. Astronomical Soc. 319, 902–932. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.2000.03938.x
Valenti, S., Sand, D. J., Yang, S., Cappellaro, E., Tartaglia, L., Corsi, A., et al. (2017). The discovery of the electromagnetic counterpart of GW170817: kilonova at 2017gfo/DLT17ck. ApJ 848, L24. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa8edf
van Son, L. A. C., De Mink, S. E., Broekgaarden, F. S., Renzo, M., Justham, S., Laplace, E., et al. (2020). Polluting the pair-instability mass gap for binary black holes through super-eddington accretion in isolated binaries. ApJ 897, 100. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab9809
Veres, P., Dal Canton, T., Burns, E., Goldstein, A., Littenberg, T. B., Christensen, N., et al. (2019). Fermi-GBM follow-up of LIGO-virgo binary black hole mergers: detection prospects. ApJ 882, 53. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab31aa
Vietri, M. (1996). Magnetospheric interactions of binary pulsars as a model for gamma-ray bursts. ApJ 471, L95–L98. doi:10.1086/310340
Vigna-Gómez, A., Neijssel, C. J., Stevenson, S., Barrett, J. W., Belczynski, K., Justham, S., et al. (2018). On the formation history of Galactic double neutron stars. MNRAS 481, 4009–4029. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty2463
Villar, V. A., Guillochon, J., Berger, E., Metzger, B. D., Cowperthwaite, P. S., Nicholl, M., et al. (2017). The combined ultraviolet, optical, and near-infrared light curves of the kilonova associated with the binary neutron star merger GW170817: unified data set, analytic models, and physical implications. ApJ 851, L21. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aa9c84
Vitale, S. (2016). Multiband gravitational-wave astronomy: parameter estimation and tests of general relativity with space- and ground-based detectors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 051102. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.051102
Vitale, S., and Evans, M. (2017). Parameter estimation for binary black holes with networks of third-generation gravitational-wave detectors. PRD 95, 064052. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.95.064052
Vitale, S., and Whittle, C. (2018). Characterization of binary black holes by heterogeneous gravitational-wave networks. PRD 98, 024029. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.98.024029
Wada, T., Shibata, M., and Ioka, K. (2020). Analytic properties of the electromagnetic field of binary compact stars and electromagnetic precursors to gravitational waves. Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys. 2020. doi:10.1093/ptep/ptaa126
Wang, H., Beniamini, P., and Giannios, D. (2024). Constraining the long-lived supramassive neutron stars by magnetar boosted kilonovae. MNRAS 527, 5166–5182. doi:10.1093/mnras/stad3560
Wang, J., and Liu, L. (2021). Electromagnetic precursors of short gamma-ray bursts as counterparts of gravitational waves. Galaxies 9, 104. doi:10.3390/galaxies9040104
Wang, J.-S., Peng, Z.-K., Zou, J.-H., Zhang, B.-B., and Zhang, B. (2020). Stringent search for precursor emission in short GRBs from Fermi/GBM data and physical implications. ApJ 902, L42. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/abbfb8
Wette, K. (2023). Searches for continuous gravitational waves from neutron stars: a twenty-year retrospective. Astropart. Phys. 153, 102880. doi:10.1016/j.astropartphys.2023.102880
Williams, P. K. G., and Berger, E. (2016). No precise localization for FRB 150418: claimed radio transient is AGN variability. ApJ 821, L22. doi:10.3847/2041-8205/821/2/L22
Woan, G., Pitkin, M. D., Haskell, B., Jones, D. I., and Lasky, P. D. (2018). Evidence for a minimum ellipticity in millisecond pulsars. ApJ 863, L40. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aad86a
Woosley, S. E. (2017). Pulsational pair-instability supernovae. ApJ 836, 244. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/836/2/244
Xiao, S., Peng, W.-X., Zhang, S.-N., Xiong, S.-L., Li, X.-B., Tuo, Y.-L., et al. (2022). Search for quasiperiodic oscillations in precursors of short and long gamma-ray bursts. ApJ 941, 166. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aca018
Xu, H., Chen, S., Guo, Y., Jiang, J., Wang, B., Xu, J., et al. (2023). Searching for the nano-hertz stochastic gravitational wave background with the Chinese pulsar timing Array data release I. Res. Astronomy Astrophysics 23, 075024. doi:10.1088/1674-4527/acdfa5
Yang, J., Ai, S., Zhang, B.-B., Zhang, B., Liu, Z.-K., Wang, X. I., et al. (2022). A long-duration gamma-ray burst with a peculiar origin. Nature 612, 232–235. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05403-8
Yang, K. Z., Mandic, V., Scarlata, C., and Banagiri, S. (2021). Searching for cross-correlation between stochastic gravitational-wave background and galaxy number counts. MNRAS 500, 1666–1672. doi:10.1093/mnras/staa3159
Yang, K. Z., Suresh, J., Cusin, G., Banagiri, S., Feist, N., Mandic, V., et al. (2023). Measurement of the cross-correlation angular power spectrum between the stochastic gravitational wave background and galaxy overdensity. PRD 108, 043025. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.108.043025
Ye, C., and Fishbach, M. (2021). Cosmology with standard sirens at cosmic noon. Phys. Rev. D. 104, 043507. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.104.043507
Yu, Y.-W., Liu, L.-D., and Dai, Z.-G. (2018). A long-lived remnant neutron star after GW170817 inferred from its associated kilonova. ApJ 861, 114. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aac6e5
Zhang, B. (2014). A possible connection between fast radio bursts and gamma-ray bursts. ApJ 780, L21. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/780/2/L21
Zhang, B. (2019). The delay time of gravitational wave — gamma-ray burst associations. Front. Phys. 14, 64402. doi:10.1007/s11467-019-0913-4
Zhang, B. (2020). Fast radio bursts from interacting binary neutron star systems. ApJ 890, L24. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab7244
Zhang, Z., Yi, S.-X., Zhang, S.-N., Xiong, S.-L., and Xiao, S. (2022). Tidally-induced magnetar super flare at the eve of coalescence with its compact companion. ApJ 939, L25. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ac9b55
Zhao, W., and Wen, L. (2018). Localization accuracy of compact binary coalescences detected by the third-generation gravitational-wave detectors and implication for cosmology. Phys. Rev. D. 97, 064031. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.97.064031
Zhong, H., Ormiston, R., and Mandic, V. (2023). Detecting cosmological gravitational wave background after removal of compact binary coalescences in future gravitational wave detectors. PRD 107, 064048. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.107.064048
Zhong, S.-Q., Dai, Z.-G., Cheng, J.-G., Lan, L., and Zhang, H.-M. (2019). Precursors in short gamma-ray bursts as a possible probe of progenitors. ApJ 884, 25. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab3e48
Zhou, B., Reali, L., Berti, E., Çalışkan, M., Creque-Sarbinowski, C., Kamionkowski, M., et al. (2022). Compact binary foreground subtraction in next-generation ground-based observatories. Available at: https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.01221.
Keywords: gravitational waves, time-domain astronomy, multi-messenger astrophysics, GW170817, LIGO and VIRGO
Citation: Corsi A, Barsotti L, Berti E, Evans M, Gupta I, Kritos K, Kuns K, Nitz A H, Owen B J, Rajbhandari B, Read J, Sathyaprakash B S, Shoemaker D H, Smith J R and Vitale S (2024) Multi-messenger astrophysics of black holes and neutron stars as probed by ground-based gravitational wave detectors: from present to future. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 11:1386748. doi: 10.3389/fspas.2024.1386748
Received: 16 February 2024; Accepted: 22 April 2024;
Published: 23 May 2024.
Edited by:
Francesca M. Civano, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, United StatesReviewed by:
Alberto Sesana, University of Milano-Bicocca, ItalyGiancarlo Ghirlanda, Brera Astronomical Observatory, Italy
Copyright © 2024 Corsi, Barsotti, Berti, Evans, Gupta, Kritos, Kuns, Nitz, Owen, Rajbhandari, Read, Sathyaprakash, Shoemaker, Smith and Vitale. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Alessandra Corsi, YWxlc3NhbmRyYS5jb3JzaUB0dHUuZWR1
 Alessandra Corsi
Alessandra Corsi Lisa Barsotti2
Lisa Barsotti2 Binod Rajbhandari
Binod Rajbhandari Jocelyn Read
Jocelyn Read