
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Astron. Space Sci. , 09 December 2021
Sec. Space Physics
Volume 8 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fspas.2021.740560
This article is part of the Research Topic Micro- to Macro-Scale Dynamics of Earth’s Flank Magnetopause View all 17 articles
 B. B. Tang1*
B. B. Tang1* W. Y. Li1*
W. Y. Li1* C. Wang1,2
C. Wang1,2 Yu. V. Khotyaintsev3
Yu. V. Khotyaintsev3 D. B. Graham3
D. B. Graham3 Q. H. Zhang4
Q. H. Zhang4 T. R. Sun1
T. R. Sun1 H. Li1
H. Li1 X. Y. Wang4
X. Y. Wang4 K. J. Trattner5
K. J. Trattner5 B. L. Giles6
B. L. Giles6 P. A. Lindqvist7
P. A. Lindqvist7 R. E. Ergun5
R. E. Ergun5 J. L. Burch8
J. L. Burch8We report local secondary magnetic reconnection at Earth’s flank magnetopause by using the Magnetospheric Multiscale observations. This reconnection is found at the magnetopause boundary with a large magnetic shear between closed magnetospheric field lines and the open field lines generated by the primary magnetopause reconnection at large scales. Evidence of this secondary reconnection are presented, which include a secondary ion jet and the encounter of the electron diffusion region. Thus the observed secondary reconnection indicates a cross-scale process from a global scale to an electron scale. As the aurora brightening is also observed at the morning ionosphere, the present secondary reconnection suggests a new pathway for the entry of the solar wind into geospace, providing an important modification to the classic Dungey cycle.
The Earth’s global magnetospheric plasma circulation, which is driven by the interaction between the magnetized solar wind and the magnetosphere, is known as the Dungey cycle (Dungey, 1961). When the interplanetary magnetic field (IMF) is southward, this cycle begins at the dayside magnetopause where magnetic reconnection opens previously closed magnetospheric magnetic lines. These open magnetic field lines are dragged anti-sunward by the solar wind flows to the magnetotail, where the nightside reconnection eventually re-closes the open field lines. The newly closed magnetic flux returns to the dayside where the cycle repeats (Figure 1A). Considering the modulation of the solar wind and the interplanetary magnetic field to this cycle (Cowley, 1973; Borovsky, 2008), the imbalance of the dayside and nightside magnetic reconnection (Milan et al., 2007), and the patchy/transient nature of reconnection (Khotyaintsev et al., 2004; Hasegawa et al., 2010), the Dungey cycle explains various space weather phenomena, such as geomagnetic storms, substorms and aurorae.
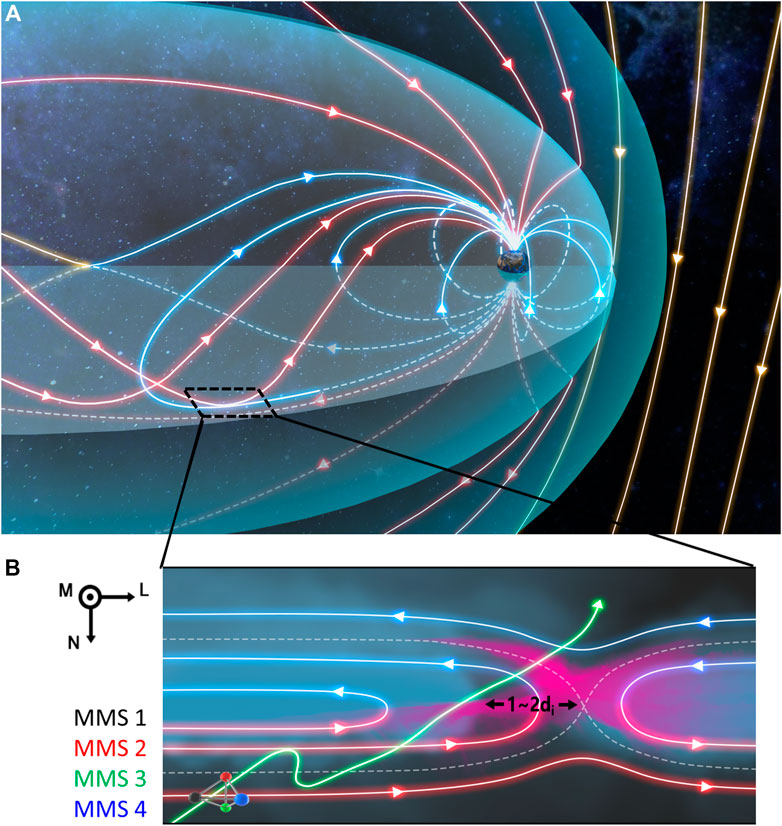
FIGURE 1. Schematic illustration of the three-dimensional structure of Earth’s magnetosphere and the secondary reconnection process at the flank magnetopause. (A) View of the magnetosphere, showing the opening of closed magnetospheric field lines through the magnetopause reconnection, and the re-closure of these open field lines by magnetotail reconnection. At the flank magnetopause, the reconnected open field lines can form a large magnetic shear with closed magnetospheric field lines, providing favorable conditions for the reported secondary reconnection. The closed magnetospheric field lines, open field lines and the solar wind field lines are presented in blue, red and yellow, respectively. (B) Two-dimensional schematic of the local secondary reconnection. The color of the magnetic field lines show their topology before secondary reconnection, and the magenta contours indicate the out-of-plane current density. The green line presents the MMS trajectory relative to the secondary reconnection, showing a short excursion into the reconnection exhaust and a full crossing anti-sunward of the X-line.
Magnetopause reconnection, the primary driver in the Dungey cycle, is locally determined by the magnetic shear, the plasma beta and the flow shear across the magnetopause (e.g., Swisdak et al., 2003; Phan et al., 2013; Doss et al., 2015). Therefore, its location and efficiency at macro scales varies significantly under different the solar wind conditions. In fact, magnetic reconnection is found to be most active when IMF is southward. In this situation, reconnection occurs at the low-latitude magnetopause, spanning from subsolar magnetopause to the flanks (e.g., Fuselier et al., 2011; Trattner et al., 2012; Vines et al., 2015). Reconnection at the flank magnetopause can be affected by the local plasma shear flow, and thus presents some different features (e.g., Gomez et al., 2016; Haaland et al., 2020). As reconnection can change the toplogy of magnetic field lines and convert energy to plasmas, they act as a major process responsible for the solar wind entry into the magnetosphere, and the consequent global scale magnetospheric convection (Dungey, 1961; Fuselier and Lewis, 2011; Welling et al., 2015). Along with magnetic reconnection, other processes such as the Kelvin–Helmholtz instability at the flank region (Hasegawa et al., 2004) or the kinetic diffusive particle transport (Treumann et al., 1991) can also contribute to the mass and energy transfer across the magnetopause. Recently, magnetic reconnection, triggered by local plasma and magnetic field variations at the magnetopause, are also observed. For example, they are reported at the trailing edges of Kelvin–Helmholtz waves (Eriksson et al., 2016; Li et al., 2016), at the interface of interlinked magnetic flux tubes (Kacem et al., 2018; Øieroset et al., 2019) and at the boundary of two neighboring flux ropes (Wang et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2017). The local secondary reconnection, which is basically taken as secondary effects of the primary reconnection are also reported (e.g., Daughton et al., 2011; Lapenta et al., 2015). These local reconnection are suggested to transfer plasma across the magnetopause (e.g., Nakamura et al., 2017), but whether they can result into magnetospheric consequences at large scales remains an open issue.
Here, we use observations from the Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission (Burch et al., 2016) to present local secondary magnetic reconnection at the flank magnetopause, which is identified by a secondary ion jet and the encounter of the electron diffusion region. This newly discovered secondary reconnection re-closes the open magnetic field lines previously generated by magnetopause reconnection, providing a new pathway for the entry of the solar wind into the magnetosphere.
On June 1, 2018, the four MMS spacecraft cross the flank magnetopause for several times approximately at (−15.6, −19.7, 2.2) Earth radii (RE) in geocentric solar magnetospheric (GSM) coordinates, and the spacecraft are in a tetrahedron formation with ∼36 km separation. We use ion and electron data from the fast plasma investigation (Pollock et al., 2016), magnetic field data from the fluxgate magnetometer (Russell et al., 2016), and electric field data from electric field double probes (Ergun et al., 2016; Lindqvist et al., 2016). During these multiple magnetopause crossings, the solar wind conditions are relatively stable (Both IMF BY and IMF BZ are negative, seeing Supplementary Figure S1), and MMS do not observe quasi-periodic perturbations of the plasma and magnetic field parameters, suggesting Kelvin–Helmholtz waves are not active during this time interval.
Overview of one inbound magnetopause crossing between 01:01:20 UT and 01:02:55 UT is provided in Figure 2. The spacecraft are initially located in the magnetosheath, characterized by a high plasma density (Figure 2B) and large anti-sunward flows (Vi, x) at ∼ −400 km s−1 (Figures 2C,F), corresponding to a typical energy of ∼ 1 keV (Figure 2D). On the other side, the magnetosphere is characterized by a lower ion density, smaller ion speeds, and the appearance of high energy ions (∼ 10 keV). During this magnetopause crossing, MMS observe a reversal of Bz (Figure 2A), a large northward ion flow (Vi, z) reaching ∼ 300 km s−1 (Figures 2C,G), and a mixture of magnetosheath and magnetospheric ions (Figure 2D). Such observations indicate ongoing magnetopause reconnection between the shocked solar wind (i.e., magnetosheath plasma) and the magnetospheric plasmas (referred to as the primary reconnection hereafter) and the spacecraft are located northward of the reconnection X-line. These observations are in good agreement with the predictions of the maximum magnetic shear model shown in Figure 3A (Trattner et al., 2007, 2021). It presents large magnetic shear at the dawnside flanks, which is favorable for reconnection, and MMS is located at its north side, observing a northward reconnection jet. We also test the Walén relation by comparing two vectors ΔVi = Vi − Vi,MSH and ΔVA = VA − VA,MSH, where VA,MSH, Vi,MSH are the reference plasma Alfven velocity and bulk velocity in the magnetosheath (Sonnerup et al., 1981). The result shows that the velocity change across the magnetosheath side of the primary reconnection is mostly Alfvenic (Figure 3B), indicating this boundary is a rotational discontinuity and open magnetic field lines are generated from reconnection. Moreover, in the reconnection exhaust, we find that the magnetic field has a significant positive Bx component (Figure 2A), and plasmas move anti-sunward (Vi,x ∼ −200 km s−1, Figure 2C), indicating that these reconnected open field lines are draped along the magnetopause by the solar wind flows (Figure 1A).
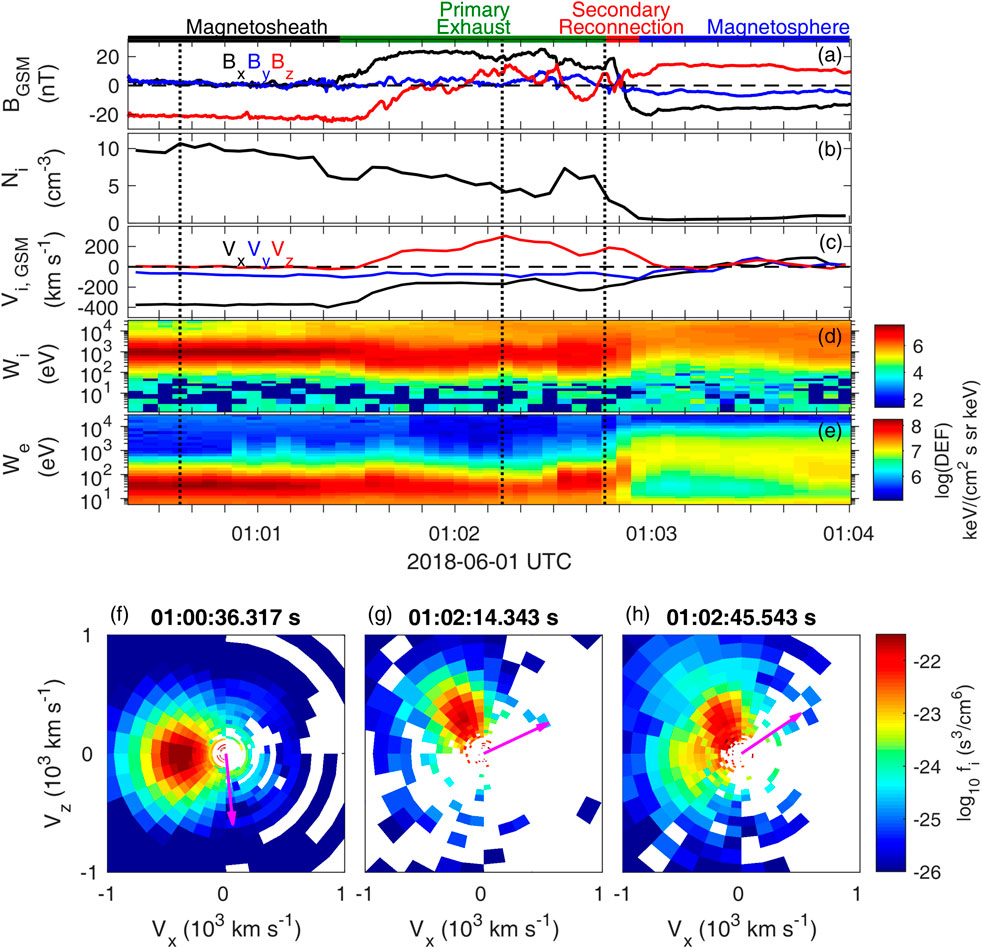
FIGURE 2. Overview of the flank magnetopause crossing of MMS. MMS one observations of (A) Magnetic field (GSM), (B) Ion number density, (C) Ion bulk velocity (GSM), (D) Electron omnidirectional differential energy flux and (E) Ion omnidirectional differential energy flux. The color bars indicate the different regions during the magnetopause crossing. (F–H) Two dimensional cuts of ion velocity distribution functions in the plane of GSM-X and GSM-Z axis at 01:00:36.317 UT, 01:02:14.343 UT, and 01:02:45.543 UT as indicated by the dotted vertical lines. The overplotted magenta arrows show the projection of the local magnetic field.
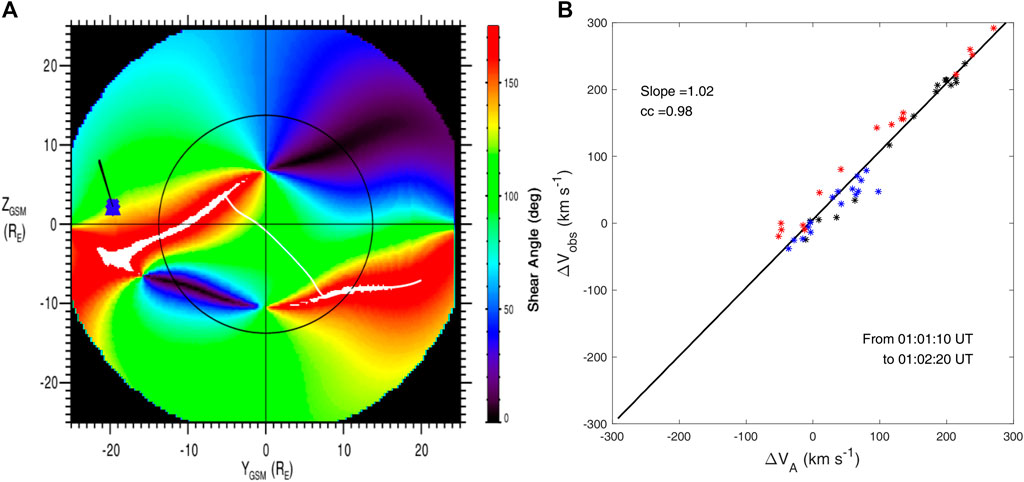
FIGURE 3. (A) The predicted location of magnetopause reconnection from the maximum magnetic shear model. The color shows magnetic shear angle across the magnetopause. The circle represents the magnetopause shape at the terminator plane and the blue symbol marks the MMS position. (B) Wal\’en test for primary magnetic reconnection between 01:01:10 UT and 01:02:20 UT.
It is interesting to note that an unexpected ion population flowing along the anti-sunward direction (Figure 2H) appears just seconds before the MMS crossing of the boundary between the primary reconnection exhaust and the magnetosphere, where a large local magnetic shear (∼ 145°) is mainly due to the Bx component (Figure 1A). Here, we explain this ion population as the outflow of another ongoing reconnection at the boundary with large magnetic shear (referred to as secondary reconnection), since it is almost aligned in the -L direction in a local current sheet (LMN) coordinate [Figure 4N, (Russell and Elphic, 1978)], which is determined from minimum variance analysis of the magnetic field (L = [0.97, 0.09, −0.23] is the reconnecting field direction, M = [0.23, −0.61, 0.76] is the out-of-plane direction, and N = [−0.07, −0.77, −0.61] (GSM) is the normal direction). The eigenvalues of LMN vectors are [λ1: λ2: λ3] = [200.3 : 5.5: 2.6]. The relative small ratio of λ2: λ3 (∼2.1) is related to a local BN enhancement around 01:02:49.8 UT, and this BN enhancement can be explained by the magnetic flux pileup associated with the electron flow breaking (Genestreti et al., 2020). We provide a zoom-in of this boundary with more signatures of the secondary reconnection in Figure 4. At the BL reversal point (approximately 01:02:50.7 UT), MMS one observes a magnetic minimum at (|B|∼ 1.8 nT, Figure 4F), a large perpendicular electron flow in the L direction (Ve,L⊥ ∼ −800 km s−1, Figure 4H), and nearly isotropic electron distributions (Figure 4K) with Te,⊥ ≈ Te, ‖ (Figure 4J). At the two sides of the BL reversal point, the electron temperature profile shows clear anisotropy (Te,⊥ < Te, ‖, Figure 4I), which is consistent with the magnetic field-aligned electrons from the inflow region (Figure 4K) (Egedal et al., 2011). These ion and electron signatures agree well with the scenario of reconnection.
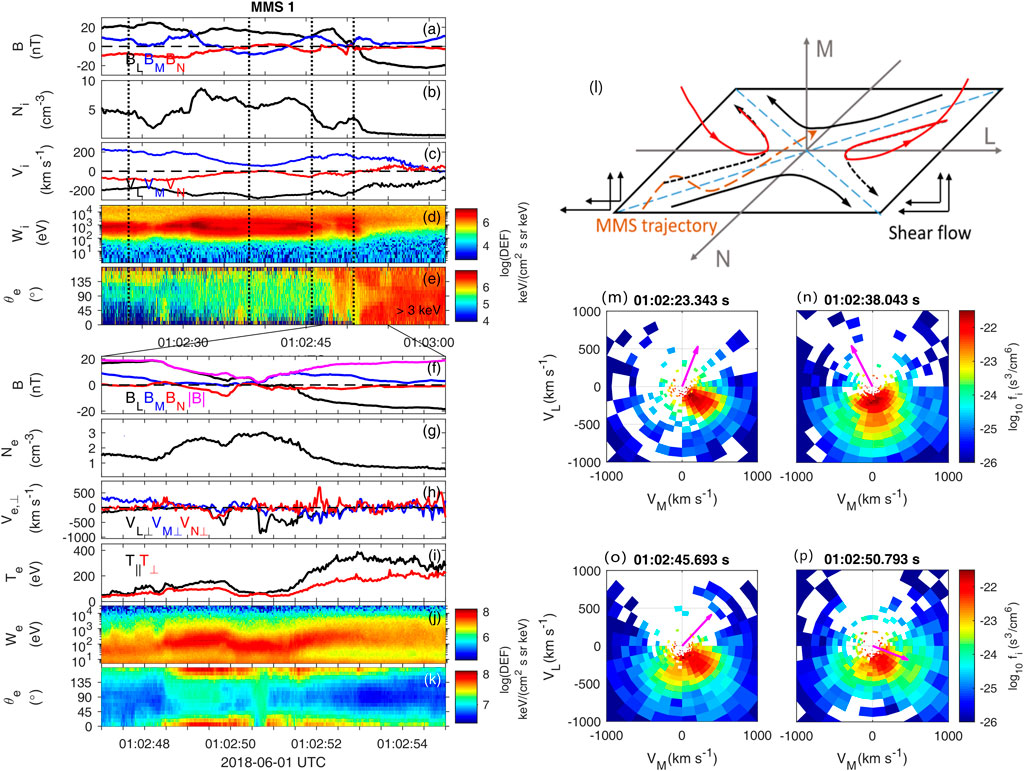
FIGURE 4. Observations of secondary reconnection from MMS 1. MMS one observations of (A) Magnetic field (LMN), (B) Ion number density, (C) Ion bulk velocity (LMN), (D) Ion omnidirectional differential energy flux and (E) Electron pitch angle spectrum of energy larger than 3 keV. Zoom-in of the time interval at BL reversal: (F) Magnetic field (LMN), (G) Electron number density, (H) Electron bulk velocity (LMN), (I) Electron temperature, (J) Electron omnidirectional differential energy flux, and (K) Electron pitch angle spectrum of all energies. The panels on the right show: (L) A schematic of MMS crossing of the secondary reconnection with a shear flow. The red reconnected field lines are dragged out of the reconnecting L-N plane due to the shear flow in M direction and the dashed brown line shows the MMS trajectory relative to the reconnection X-line (M–P) Two dimensional cuts of ion velocity distribution functions in the vL − vM plane at times indicated by the black vertical lines in left panels. The projected local magnetic fields are shown by the magenta arrows.
We perform a detailed analysis of the observed secondary reconnection, which is embedded in the plasma flow imposed by the primary reconnection. The shear flow is negative in the reconnecting (L) direction and positive in the out-of-plane (M) direction (Figures 4C,M). The negative VL shear flow can lead into the convection of the X-line, and a reduction of the outflow speed in the X-line frame (Doss et al., 2015). The predicted outflow density (ρout) (Cassak and Shay, 2007), the convection speed of the X-line (Vdrift) and the outflow speed in the spacecraft frame (Vout) (Doss et al., 2015) are written as
where the “1”, “2,” and “out” subscripts refer to parameters in the primary reconnection exhaust, in the magnetospheric side and in the outflow region, respectively, and
The topology of the magnetic field lines can be inferred from the pitch angle spectrum of high-energy magnetospheric electrons (Figure 4E), which has been extensively used in previous studies (e.g., Fuselier et al., 2011; Pu et al., 2013; Øieroset et al., 2015). In the primary reconnection exhaust with a northward ion jet, an anti-parallel streaming electron flow inside the primary exhaust suggests an open field line geometry connecting to the northern hemisphere (Figure 3A). While inside the magnetosphere, the electron flux is more intense, and mostly isotropic, indicating closed field lines. Therefore, we confirm that the secondary reconnection occurs between closed magnetospheric field lines and the open field lines previously generated by the primary magnetopause reconnection (Figure 3B), which is different from the primary magnetopause reconnection, occurring between the shocked solar wind magnetic field lines and the magnetospheric field lines.
Spatial structures of the secondary reconnection at the scale of MMS separations near the BL reversal are further investigated (Figure 5). The reduced/enhanced BM variations (Figure 5C), indicating a Hall pattern of reconnection (Øieroset et al., 2001) with a guide-field of ∼ 5 nT, are consistent with the anti-sunward crossing of the X-line. During this crossing, the minimum magnetic field (|B|) at MMS two is obviously larger than that at other spacecraft (Figure 5A). Therefore, even though the “nominal” magnetic curvature radius (RC) is comparable with the electron gyro-radius (ρe, κ2 = RC/ρe, Figure 5G) at the time interval of |B|, the expected electron pitch angle mixing due to the magnetic curvature scattering (Lavraud et al., 2016; Tang et al., 2019) is only found at MMS 1, 3 and 4, but not at MMS 2 (Figure 5I1–I4). The out-of-plane current density (JM, Figure 5F) at MMS 1–MMS 4 are also different. In general, there are two main JM peaks; one is at the centre of the BL reversal and the other is near the magnetospheric side. The magnitude of the current density at these two current sheets observed at MMS two is about 200 nA m−2, which is significantly weaker than that observed by other spacecraft. All these differences suggest dramatic changes of the electron dynamics at MMS separation scales, which can be explained by the spatial evolution of the reconnection structure along the outflow direction. MMS 2 then is the furthermost spacecraft in the outflow region (Figure 1B). The peak-to-peak separation of the two current sheets is approximately 0.8 s, corresponding to ∼ 65 km or 0.33di (the ion inertial length di ≈ 200 km). Note that the spatial separation is estimated using the magnetopause speed of 80 km s−1 along its normal direction estimated from the multi-spacecraft timing analysis of BL. Such two strong current sheets are also found in the kinetic particle simulation with similar guide field strength and density asymmetry [see (Figure 3–7 of Montag, 2018)]. In his simulation, the two current sheets, with a separation less than 1di along the normal direction, extend from the X-line only up to several ion inertial lengths. These results, as well as the electron flow that is faster than predicted outflow speed (Figure 4H), demonstrate that MMS may cross in the vicinity of the electron diffusion region.
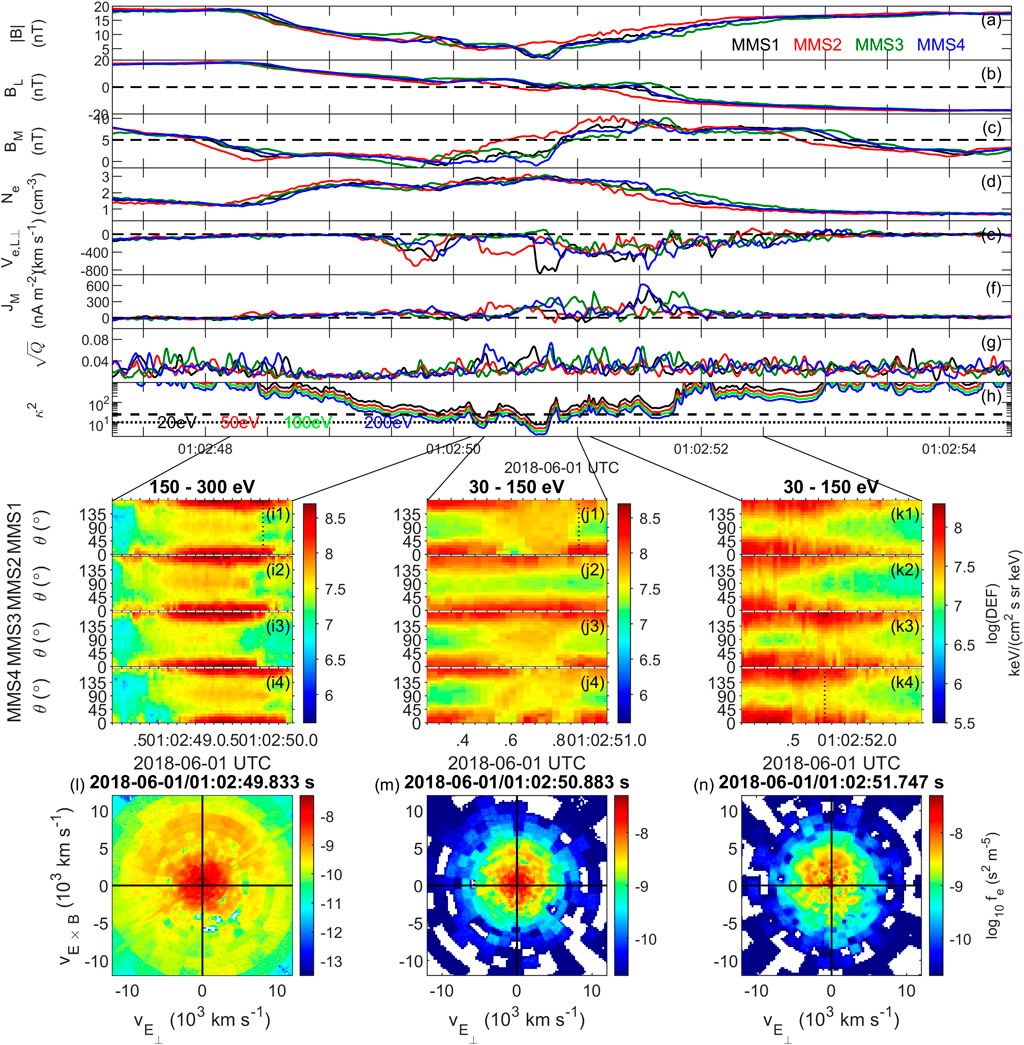
FIGURE 5. Four MMS observations of the secondary magnetic reconnection. (A) |B|, (B) BL, (C) BM, (D) Ne, (E) Ve,L⊥, (F) JM, (G) the agyrotropic measure
Agyrotropic electron distributions, which are an important indicator of the electron diffusion region (Burch et al., 2016; Webster et al., 2018), are also found during the secondary magnetic reconnection crossing, and measure of electron agyrotropy,
The secondary reconnection re-closes the open magnetic field lines in the primary exhaust by reconnecting with closed magnetospheric field lines. The newly closed field lines can transport plasma in the solar wind into magnetosphere, which could populate the plasma sheet (e.g., Allen et al., 2017) and even precipitate in to the ionosphere. In this study, we present auroral observations in the northern hemisphere from Defense Meteorological Satellite Program (DMSP)/F18 satellite, and find some bright aurora in the morning sector (Figures 6) as observed by the on board Special Sensor Ultraviolet Spectrographic Imager (SSUSI) (Paxton et al., 2002). The magnetic footprint of MMS, marked by a white circle, is also located at one end of the bright auroral arc/streamer. The magnetic field used for the MMS footprint tracing includes an internal IGRF model (Thébault et al., 2015) and an external Tsyganenko-96 model (Tsyganenko, 1995). Unfortunately, the DMSP/F18 satellite does not fly over the bright aurora region (Figures 6A), which prevents direct observations of the particle precipitation at the bright auroral emissions. Meanwhile, the dayside auroral intensity is much weaker (Figures 6A), and the related precipitating ions and electrons observed along the satellite track are possibly the solar wind origin, as inferred from their typical energies (Figures 6B). This indicates that the usual magnetopause reconnection cannot well explain the bright aurora in the morning ionosphere, and we suggest the secondary reconnection, which generates earthward propagating plasma flows in the magnetosphere, can be closely related to the bright aurora in the morning ionosphere. This relation is similar to that between the auroral streamer at the nightside ionosphere and the flow bursts in the magnetotail (Nakamura et al., 2001; Sergeev et al., 2004). Therefore the secondary reconnection reported in this study serves to transfer the mass and energy in the solar wind into geospace. Finally, it is addressed that the scanning of the bright aurora at the morning ionosphere is ∼ 10 min prior to the flank magnetopause crossing of MMS, which could bring some errors to the relative locations between the footprint of MMS and aurora. Considering the solar wind is relatively stable during this period (Supplementary Figure S1), this uncertainty for the MMS footprint is about 2° in latitude and 1 h in longitude according to the drift speed of the secondary X-line estimated above, which thus has not been taken into account here. Based on this point, more observational assessment should be performed in the future investigations.
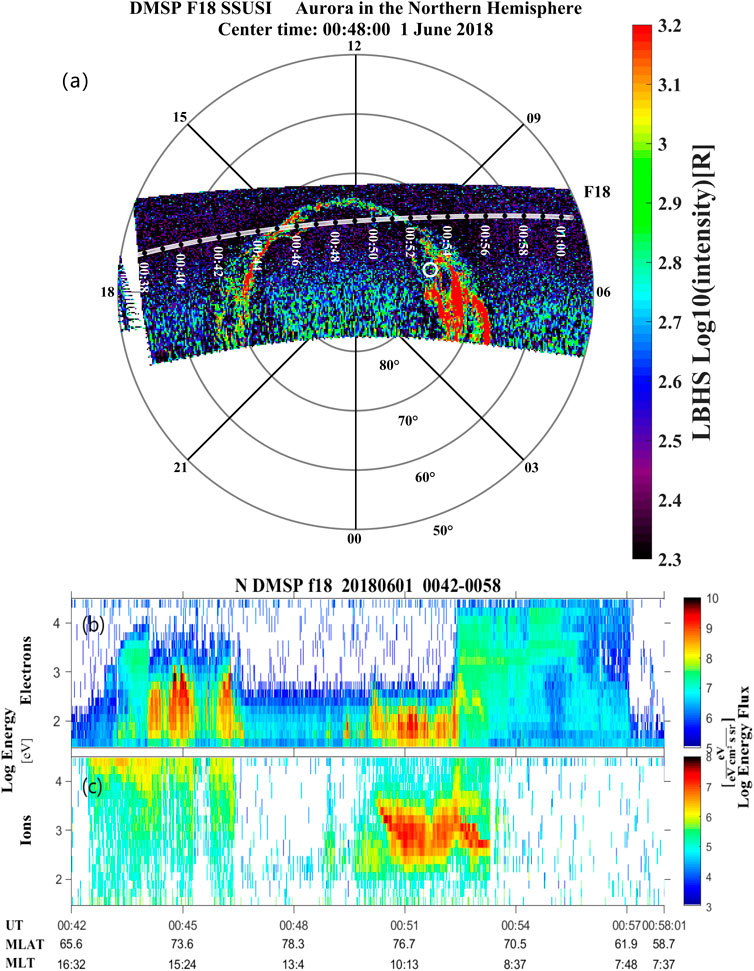
FIGURE 6. Aurora and in situ plasma observations in the northern hemisphere from DMSP/F18 satellite. (A) Aurora in the Lyman-Birge-Hopfield band (LBHS) from the SSUSI instrument in the northern hemisphere on June 1, 2018. The data are shown in the geomagnetic coordinate with noon at the top of the panel. The white circle marks the magnetic footprint of MMS (MLT: 7.1 h and MLat: 76.8°) and the white dotted line shows the satellite track. (B, C) in situ electron and ion energy spectrum from the special sensor for precipitating particles (SSJ5) instrument.
In this study, we have presented newly revealed secondary magnetic reconnection at Earth’s flank magnetopause from MMS observations. The observed secondary ion jet agrees well with predictions of magnetic reconnection with a flow shear, and the electron signatures indicate the encounter of the electron diffusion region. This secondary reconnection re-closes the open field lines generated by the primary magnetopause reconnection, so that it indicates a new pathway for the entry of the solar wind into the magnetosphere. The re-closure of open field lines by the reported secondary reconnection, rather than the nightside magnetotail reconnection, provides an important modification to the classic Dungey cycle.
The concept of secondary reconnection has been widely proposed in previous studies (e.g., Daughton et al., 2011; Lapenta et al., 2015; Fuselier et al., 2017, 2018), but there are some differences existing in these so-called secondary reconnection. For example, secondary reconnection can occur in the exhaust region of the primary reconnection, behaving as an important feature of 3D magnetic reconnection (Daughton et al., 2011; Lapenta et al., 2015). Both the primary and secondary reconnection can be found between the magnetosheath and magnetospheric filed lines, or the magnetic field lines at two sides of the magnetopause, which can generate flux rope-like structures (Fuselier et al., 2017, 2018). In this study, secondary reconnection reconnects the previously reconnected open magnetic field lines with closed magnetospheric field lines (Figure 1A), resulting into the re-closure of the open field lines. Regarding this, the reported secondary reconnection, which is found at the flank magnetopause, is different from other secondary reconnection.
The secondary reconnection here is found at the flank magnetopause with a large magnetic Bx shear, which suggests that the primary X-line at the flank and the magnetotail current sheet should not be co-located at the magnetopause (Figure 1A). In this study, the magnetotail current sheet is twisted due to interplanetary By component (Tsyganenko, 1998; Tsyganenko and Fairfield, 2004), which leads a substantial offset of the magnetotail current sheet from the equatorial plane at the flank region (Supplementary Figure S1). Meanwhile, the location of the primary magnetopause reconnection is shifted southward of the equator plane (Figure 3A). This non-colocation of the primary X-line at the flank and the magnetotail current sheet produces favorable external conditions for a large magnetic shear, and also the secondary reconnection. A general description of this non-colocation should be investigated in the future.
Magnetic reconnection between the open and closed magnetic field lines is sometimes referred to as the interchange reconnection. It has been widely applied at the surface of the Sun, which is responsible for the acceleration of the slow solar wind (Abbo et al., 2016) and is suggested to play a role in the generation of magnetic switchbacks (Fisk and Kasper, 2020). The present finding shows that this type of reconnection also works in the Earth’s magnetosphere, but behaves as secondary reconnection, as it relies on the generation of open field lines from the primary reconnection. Therefore the observed secondary reconnection essentially reflects a cross-scale process from the global magnetospheric scale to kinetic scales, and we suggest this reconnection process is applicable to other planets with similar magnetosphere structures, such as Mercury and Jupiter’s moon, Ganymede.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: MMS science data center (https://lasp.colorado.edu/mms/sdc/public/), the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (https://ssusi.jhuapl.edu/data/_retriver) and NASA OMNIWeb (https://omniweb.gsfc.nasa.gov/form/omni/_min.html).
BBT, WL, and CW performed the data analysis, interpretation and manuscript preparation. YK, DG and KJT contributed to the data interpretation. QHZ and XYW contributed to the data interpretation of DMSP. TRS and HL contricuted to the MHD simulations. BG, PAL and RE contributed to the development and operation of MMS instruments. JB is the PI of MMS science and led the operation of the MMS mission.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants 41731070, 41974196 and 41974170), the Chinese Academy of Sciences (QYZDJ-SSW-JSC028, XDA15052500, XDA17010301 and XDB 41000000) and the Specialized Research Fund for State Key Laboratories of China. BBT was supported by the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. WYL was also supported by the Youth Innovation Promotion Association, and the Young Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CAST and the Open Research Program of Key Laboratory of Geospace Environment CAS.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fspas.2021.740560/full#supplementary-material
Abbo, L., Ofman, L., Antiochos, S. K., Hansteen, V. H., Harra, L., Ko, Y.-K., et al. (2016). Slow solar wind: Observations and modeling. Space Sci. Rev. 201, 55–108. doi:10.1007/s11214-016-0264-1
Allen, R. C., Livi, S. A., Vines, S. K., Goldstein, J., Cohen, I., Fuselier, S. A., et al. (2017). Storm time empirical model of O+ and O6+ distributions in the magnetosphere. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 122, 8353–8374. doi:10.1002/2017ja024245
Borovsky, J. E. (2008). The rudiments of a theory of solar wind/magnetosphere coupling derived from first principles. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 113. doi:10.1029/2007ja012646
Burch, J. L., Torbert, R. B., Phan, T. D., Chen, L. J., Moore, T. E., Ergun, R. E., et al. (2016). Electron-scale measurements of magnetic reconnection in space. Science 352, aaf2939. doi:10.1126/science.aaf2939
Cassak, P. A., and Shay, M. A. (2007). Scaling of asymmetric magnetic reconnection: General theory and collisional simulations. Phys. Plasmas 14, 102114. doi:10.1063/1.2795630
Cowley, S. W. H. (1973). A qualitative study of the reconnection between the Earth's magnetic field and an interplanetary field of arbitrary orientation. Radio Sci. 8, 903–913. doi:10.1029/rs008i011p00903
Daughton, W., Roytershteyn, V., Karimabadi, H., Yin, L., Albright, B. J., Bergen, B., et al. (2011). Role of electron physics in the development of turbulent magnetic reconnection in collisionless plasmas. Nat. Phys 7, 539–542. doi:10.1038/nphys1965
Doss, C. E., Komar, C. M., Cassak, P. A., Wilder, F. D., Eriksson, S., and Drake, J. F. (2015). Asymmetric magnetic reconnection with a flow shear and applications to the magnetopause. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 120, 7748–7763. doi:10.1002/2015ja021489
Dungey, J. W. (1961). Interplanetary magnetic field and the auroral zones. Phys. Rev. Lett. 6, 47–48. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.6.47
Egedal, J., Le, A., Pritchett, P. L., and Daughton, W. (2011). Electron dynamics in two-dimensional asymmetric anti-parallel reconnection. Phys. Plasmas 18, 102901. doi:10.1063/1.3646316
Ergun, R. E., Tucker, S., Westfall, J., Goodrich, K. A., Malaspina, D. M., Summers, D., et al. (2016). The axial double probe and fields signal processing for the MMS mission. Space Sci. Rev. 199, 167–188. doi:10.1007/s11214-014-0115-x
Eriksson, S., Lavraud, B., Wilder, F. D., Stawarz, J. E., Giles, B. L., Burch, J. L., et al. (2016). Magnetospheric Multiscale observations of magnetic reconnection associated with Kelvin-Helmholtz waves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43, 5606–5615. doi:10.1002/2016gl068783
Fisk, L. A., and Kasper, J. C. (2020). Global circulation of the open magnetic flux of the Sun. ApJ 894, L4. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab8acd
Fuselier, S. A., and Lewis, W. S. (2011). Properties of near-Earth magnetic reconnection from in-situ observations. Space Sci. Rev. 160, 95–121. doi:10.1007/s11214-011-9820-x
Fuselier, S. A., Petrinec, S. M., Trattner, K. J., Broll, J. M., Burch, J. L., Giles, B. L., et al. (2018). Observational Evidence of Large-Scale Multiple Reconnection at the Earth's Dayside Magnetopause. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 123, 8407–8421. doi:10.1029/2018ja025681
Fuselier, S. A., Vines, S. K., Burch, J. L., Petrinec, S. M., Trattner, K. J., Cassak, P. A., et al. (2017). Large-scale characteristics of reconnection diffusion regions and associated magnetopause crossings observed by MMS. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 122, 5466–5486. doi:10.1002/2017ja024024
Fuselier, S., Trattner, K., and Petrinec, S. (2011). Antiparallel and component reconnection at the dayside magnetopause. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 116. doi:10.1029/2011ja016888
Genestreti, K., Liu, Y.-H., Phan, T.-D., Denton, R., Torbert, R., Burch, J., et al. (2020). Multiscale coupling during magnetopause reconnection: Interface between the electron and ion diffusion regions. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 125, e2020JA027985. doi:10.1029/2020ja027985
Gomez, R. G., Vines, S. K., Fuselier, S. A., Cassak, P. A., Strangeway, R. J., Petrinec, S. M., et al. (2016). Stable reconnection at the dusk flank magnetopause. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43, 9374–9382. doi:10.1002/2016gl069692
Haaland, S., Paschmann, G., Øieroset, M., Phan, T., Hasegawa, H., Fuselier, S., et al. (2020). Characteristics of the flank magnetopause: MMS results. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 125, e2019JA027623. doi:10.1029/2019ja027623
Hasegawa, H., Fujimoto, M., Phan, T.-D., Rème, H., Balogh, A., Dunlop, M. W., et al. (2004). Transport of solar wind into Earth's magnetosphere through rolled-up Kelvin-Helmholtz vortices. Nature 430, 755–758. doi:10.1038/nature02799
Hasegawa, H., Wang, J., Dunlop, M., Pu, Z., Zhang, Q.-H., Lavraud, B., et al. (2010). Evidence for a flux transfer event generated by multiple x-line reconnection at the magnetopause. Geophys. Res. Lett. 37. doi:10.1029/2010gl044219
Kacem, I., Jacquey, C., Génot, V., Lavraud, B., Vernisse, Y., Marchaudon, A., et al. (2018). Magnetic reconnection at a thin current sheet separating two interlaced flux tubes at the Earth’s magnetopause. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 123, 1779–1793. doi:10.1002/2017ja024537
Khotyaintsev, Y., Buchert, S., Stasiewicz, K., Vaivads, A., Savin, S., Papitashvili, V., et al. (2004). Transient reconnection in the cusp during strongly negative IMF by. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 109. doi:10.1029/2003ja009908
Lapenta, G., Markidis, S., Goldman, M. V., and Newman, D. L. (2015). Secondary reconnection sites in reconnection-generated flux ropes and reconnection fronts. Nat. Phys 11, 690–695. doi:10.1038/nphys3406
Lavraud, B., Zhang, Y. C., Vernisse, Y., Gershman, D. J., Dorelli, J., Cassak, P. A., et al. (2016). Currents and associated electron scattering and bouncing near the diffusion region at Earth's magnetopause. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43, 3042–3050. doi:10.1002/2016gl068359
Li, W., André, M., Khotyaintsev, Y. V., Vaivads, A., Graham, D. B., Toledo‐Redondo, S., et al. (2016). Kinetic evidence of magnetic reconnection due to Kelvin‐Helmholtz waves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43, 5635–5643. doi:10.1002/2016gl069192
Lindqvist, P.-A., Olsson, G., Torbert, R. B., King, B., Granoff, M., Rau, D., et al. (2016). The spin-plane double probe electric field instrument for MMS. Space Sci. Rev. 199, 137–165. doi:10.1007/s11214-014-0116-9
Milan, S., Provan, G., and Hubert, B. (2007). Magnetic flux transport in the Dungey cycle: A survey of dayside and nightside reconnection rates. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 112. doi:10.1029/2006ja011642
Montag, P. K. (2018). Modeling the formation of current sheets in symmetric and asymmetric reconnection. Massachusetts: Ph.D. thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
Nakamura, R., Baumjohann, W., Schödel, R., Brittnacher, M., Sergeev, V. A., Kubyshkina, M., et al. (2001). Earthward flow bursts, auroral streamers, and small expansions. J. Geophys. Res. 106, 10791–10802. doi:10.1029/2000ja000306
Nakamura, T. K. M., Hasegawa, H., Daughton, W., Eriksson, S., Li, W. Y., and Nakamura, R. (2017). Turbulent mass transfer caused by vortex induced reconnection in collisionless magnetospheric plasmas. Nat. Commun. 8, 1582–1588. doi:10.1038/s41467-017-01579-0
Øieroset, M., Phan, T. D., Drake, J. F., Eastwood, J. P., Fuselier, S. A., Strangeway, R. J., et al. (2019). Reconnection with magnetic flux pileup at the interface of converging jets at the magnetopause. Geophys. Res. Lett. 46, 1937–1946. doi:10.1029/2018gl080994
Øieroset, M., Phan, T. D., Fujimoto, M., Lin, R. P., and Lepping, R. P. (2001). In situ detection of collisionless reconnection in the Earth's magnetotail. Nature 412, 414–417. doi:10.1038/35086520
Øieroset, M., Phan, T. D., Gosling, J. T., Fujimoto, M., and Angelopoulos, V. (2015). Electron and ion edges and the associated magnetic topology of the reconnecting magnetopause. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 120, 9294–9306. doi:10.1002/2015ja021580
Paxton, L. J., Morrison, D., Zhang, Y., Kil, H., Wolven, B., Ogorzalek, B. S., et al. (2002). “Validation of remote sensing products produced by the special sensor ultraviolet scanning imager (SSUSI): A far UV-imaging spectrograph on DMSP F-16,” in Optical spectroscopic techniques, remote sensing, and instrumentation for atmospheric and space research IV (Massachusetts: International Society for Optics and Photonics), 4485, 338–348.
Phan, T. D., Paschmann, G., Gosling, J. T., Oieroset, M., Fujimoto, M., Drake, J. F., et al. (2013). The dependence of magnetic reconnection on plasmaβand magnetic shear: Evidence from magnetopause observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 40, 11–16. doi:10.1029/2012gl054528
Pollock, C., Moore, T., Jacques, A., Burch, J., Gliese, U., Saito, Y., et al. (2016). Fast plasma investigation for magnetospheric multiscale. Space Sci. Rev. 199, 331–406.
Pu, Z. Y., Raeder, J., Zhong, J., Bogdanova, Y. V., Dunlop, M., Xiao, C. J., et al. (2013). Magnetic topologies of an in vivo FTE observed by Double Star/TC-1 at Earth's magnetopause. Geophys. Res. Lett. 40, 3502–3506. doi:10.1002/grl.50714
Russell, C. T., Anderson, B. J., Baumjohann, W., Bromund, K. R., Dearborn, D., Fischer, D., et al. (2016). The magnetospheric multiscale magnetometers. Space Sci. Rev. 199, 189–256. doi:10.1007/978-94-024-0861-4_8
Russell, C. T., and Elphic, R. (1978). Initial isee magnetometer results: Magnetopause observations. Space Sci. Rev. 22, 681–715. doi:10.1007/bf00212619
Sergeev, V. A., Liou, K., Newell, P. T., Ohtani, S.-I., Hairston, M. R., and Rich, F. (2004). Auroral streamers: characteristics of associated precipitation,convection and field-aligned currents. Ann. Geophys. 22, 537–548. doi:10.5194/angeo-22-537-2004
Sonnerup, B. U. Ö., Paschmann, G., Papamastorakis, I., Sckopke, N., Haerendel, G., Bame, S. J., et al. (1981). Evidence for magnetic field reconnection at the Earth's magnetopause. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 10049–10067. doi:10.1029/ja086ia12p10049
Swisdak, M. (2016). Quantifying gyrotropy in magnetic reconnection. Geophys. Res. Lett. 43, 43–49. doi:10.1002/2015gl066980
Swisdak, M., Rogers, B., Drake, J., and Shay, M. (2003). Diamagnetic suppression of component magnetic reconnection at the magnetopause. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 108. doi:10.1029/2002ja009726
Tang, B. B., Li, W. Y., Graham, D. B., Rager, A. C., Wang, C., Khotyaintsev, Y. V., et al. (2019). Crescent‐Shaped Electron Distributions at the Nonreconnecting Magnetopause: Magnetospheric Multiscale Observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 46, 3024–3032. doi:10.1029/2019gl082231
Thébault, E., Finlay, C. C., Beggan, C. D., Alken, P., Aubert, J., Barrois, O., et al. (2015). International geomagnetic reference field: the 12th generation. Earth, Planets and Space 67, 1–19. doi:10.1186/s40623-015-0313-0
Trattner, K., Mulcock, J., Petrinec, S., and Fuselier, S. (2007). Location of the reconnection line at the magnetopause during southward imf conditions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34. doi:10.1029/2006gl028397
Trattner, K., Petrinec, S., Fuselier, S., and Phan, T. (2012). The location of reconnection at the magnetopause: Testing the maximum magnetic shear model with themis observations. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 117. doi:10.1029/2011ja016959
Trattner, K., Petrinec, S., and Fuselier, S. (2021). The location of magnetic reconnection at Earth’s magnetopause. Space Sci. Rev. 217, 1–47. doi:10.1007/s11214-021-00817-8
Treumann, R. A., LaBelle, J., and Pottelette, R. (1991). Plasma diffusion at the magnetopause: The case of lower hybrid drift waves. J. Geophys. Res. 96, 16009–16013. doi:10.1029/91ja01671
Tsyganenko, N. A. (1998). Modeling of twisted/warped magnetospheric configurations using the general deformation method. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 23551–23563. doi:10.1029/98ja02292
Tsyganenko, N. A. (1995). Modeling the Earth's magnetospheric magnetic field confined within a realistic magnetopause. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 5599–5612. doi:10.1029/94ja03193
Tsyganenko, N., and Fairfield, D. (2004). Global shape of the magnetotail current sheet as derived from geotail and polar data. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 109. doi:10.1029/2003ja010062
Vines, S. K., Fuselier, S. A., Trattner, K. J., Petrinec, S. M., and Drake, J. F. (2015). Ion acceleration dependence on magnetic shear angle in dayside magnetopause reconnection. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 120, 7255–7269. doi:10.1002/2015ja021464
Wang, R., Lu, Q., Nakamura, R., Baumjohann, W., Russell, C., Burch, J., et al. (2017). Interaction of magnetic flux ropes via magnetic reconnection observed at the magnetopause. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 122, 10–436. doi:10.1002/2017ja024482
Webster, J. M., Burch, J. L., Reiff, P. H., Daou, A. G., Genestreti, K. J., Graham, D. B., et al. (2018). Magnetospheric multiscale dayside reconnection electron diffusion region events. J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 123, 4858–4878. doi:10.1029/2018ja025245
Welling, D. T., André, M., Dandouras, I., Delcourt, D., Fazakerley, A., Fontaine, D., et al. (2015). The Earth: Plasma sources, losses, and transport processes. Space Sci. Rev. 192, 145–208. doi:10.1007/s11214-015-0187-2
Keywords: magnetic reconnection, electron diffusion region, magnetopause, solar wind-magnetosphere coupling, solar wind entry
Citation: Tang BB, Li WY, Wang C, Khotyaintsev YV, Graham DB, Zhang QH, Sun TR, Li H, Wang XY, Trattner KJ, Giles BL, Lindqvist PA, Ergun RE and Burch JL (2021) Secondary Magnetic Reconnection at Earth’s Flank Magnetopause. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 8:740560. doi: 10.3389/fspas.2021.740560
Received: 13 July 2021; Accepted: 27 September 2021;
Published: 09 December 2021.
Edited by:
Takuma Nakamura, Austrian Academy of Sciences (OeAW), AustriaReviewed by:
Rungployphan Om Kieokaew, UMR5277 Institut de recherche en astrophysique et planétologie (IRAP), FranceCopyright © 2021 Tang, Li, Wang, Khotyaintsev, Graham, Zhang, Sun, Li, Wang, Trattner, Giles, Lindqvist, Ergun and Burch. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: B. B. Tang, YmJ0YW5nQHNwYWNld2VhdGhlci5hYy5jbg==; W. Y. Li, d3lsaUBzcGFjZXdlYXRoZXIuYWMuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.