
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Soil Sci., 07 January 2022
Sec. Soil Biogeochemistry & Nutrient Cycling
Volume 1 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fsoil.2021.788170
This article is part of the Research TopicSoil Biology for Sustainable Agriculture and EnvironmentView all 6 articles
A contemporary approach to bacterially mediated zinc (Zn) biofortification offers a new dimension in the crop improvement program with better Zn uptake in plants to curb Zn malnutrition. The implication of Zn solubilizing bacteria (ZSB) represents an inexpensive and optional strategy for Zn biofortification, with an ultimate green solution to enlivening sustainable agriculture. ZSB dwelling in the rhizospheric hub or internal plant tissues shows their competence to solubilize Zn via a variety of strategies. The admirable method is the deposition of organic acids (OAs), which acidify the surrounding soil environment. The secretion of siderophores as a metal chelating molecule, chelating ligands, and the manifestation of an oxidative–reductive system on the bacterial cell membrane are further tactics of bacterially mediated Zn solubilization. The inoculation of plants with ZSB is probably a more effective tactic for enhanced Zn translocation in various comestible plant parts. ZSB with plant growth-enhancing properties can be used as bioelicitors for sustainable plant growth via the different approaches that are crucial for plant health and its productivity. This article provides an overview of the functional properties of ZSB-mediated Zn localization in the edible portions of food crops and provides an impetus to explore such plant probiotics as natural biofortification agents.
Recently, zinc-solubilizing bacteria (ZSB) have been updated with the addition of a biofortification approach called microbial-assisted crop biofortification. The benevolent job of microbes in the ecological nutrient cycle has been deliberated for many decades. The current understanding of ZSB and their use in biofortification had been elucidated up to some extent impalpably. Even fewer studies on an interplay between plants and ZSB and their exploration for improved plant growth in applied settings gave the hope of solving the problem of zinc (Zn) malnutrition in a sustainable way. Zn is considered to be a vital micronutrient for cellular life, but Zn deficiency leads to a wide variety of metabolic disorders, which in humans manifests itself in a wide variety of diseases (1). The production of crops with Zn enriched edible portions (fruits, seeds, etc.) for poor people who are relying on food-based crops as diet with an inadequate amount of Zn (less than the daily required amount) is the current footstep to conquer the micronutrient deficiency, which is also supported by WHO in the wellbeing of huge section of deprived people (2, 3). In agronomical practices, biofortification approaches through agronomic, plant breeding, and biotechnological intrusions are mostly used to achieve an improved uptake of Zn and other micronutrients in the eatable plant parts (4–7). The productive function of ZSB on crop overall development and health has already been described in the literature, while, in contrast, ZSB have been selected as natural biofortification agents to amplify the Zn concentration by being part of either the rhizomicrobiome or the phytomicrobiome. A few authors have proposed microbial-assisted biofortification and, in particular, discussed ZSB as “rhizobacteria” or “endophytes” if ZSB were isolated either from the soil sample(s) of rhizospheric origin or from the inner plant tissue. The precise effect of Zn mobilization that ZSB brings about is the deposition of organic acids (OAs), which acidify the surrounding soil environment and solubilize Zn due to the drop in pH (8, 9). Other mechanisms include the secretion of chelating agents, like siderophores, which are believed to play a critical role in iron (Fe), Zn, and the solubilization of other micronutrients (10). ZSB secrete some organic compounds related to plant growth, namely phytohormones and siderophores, thus supporting the growth of cultivated plants (11). ZSB-mediated plant growth results from the effect of either “direct” or “indirect” plant growth-related mechanisms shown by ZSB inoculants. In the direct mechanisms, ZSB support the acquirement of essential micronutrients through the deposition of OAs and enzymes and can change the phytohormone level in the plant. The nutrient absorption facilitated by ZSB can classically include Zn, Fe, phosphorus, potassium, and nitrogen. The indirect mechanism profile includes the synthesis of secondary metabolites, in particular, antifungal and antibacterial compounds that can reduce the damage to plants from infection with phytopathogens (such as soil fungi and bacteria). As an effectual bioelicitor, ZSB maintained a proper decorum of better plant probiotics by increasing plant growth-attributed characters such as plant length and dry biomass. Their role in the enhancement of crop yield has made them a prolific contributor to better plant bioinoculants, while soil fertility restoration after ZSB inoculation has yet to be studied in depth. ZSB, which have many plant growth elevating features, dissolve Zn in the soil and facilitate its translocation from the soil settings into various tissues of plants (12). The Zn enrichment in grains shows the power of ZSB to make plants nutritionally rich to counteract Zn malnutrition. This aspect is more economically feasible than other aspects of biofortification including agronomic and biotechnological bases and can maintain agricultural production without adapting the chemical fertilization strategy (13). This enables the environment friendly approach of microbial-based fertilization to maintain the overall plant health and ascertains the “green technological” approach to biofortification (14). However, some reports currently highlight the job of ZSB in plant growth enhancement and crop fortification (9, 15, 16). Furthermore, this article focuses on illustrating the irrefutable and dual effects of ZSB on crops in terms of biofortification to improve the Zn status in the edible parts by deciphering a functional interplay between ZSB and the plant.
Zinc is a “wonderful micronutrient,” necessary for all organisms, acted as a prosthetic group for approximately 3,000 proteins in animals and humans, and inimitable in numerous metabolic activities of plants such as (a) the activation of a series of miscellaneous enzymes (“RNA polymerases,” “carbonic anhydrase,” and “superoxide dismutase”) and (b) the formation and metabolism of biomolecules (proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids) (7, 17–20, 20). In plants, the deficiency of Zn decreases their growth, their ability to survive under stressful conditions, and finally the production of chlorophyll, which affect the plant health and its productivity (21, 22). With its amazing property, Zn deficiency is widely described as the main risk factor for developing diseases in humans. Various health-related disorders have been reported in response to Zn deficiency, such as growth disturbances, skeletal abnormalities, delayed wound healing, increased abortion possibilities, diarrhea (23), higher risk of infection, deterioration in physical growth, DNA damage, and cancer progression (1, 24). The accessibility of insufficient Zn in soils exists in the different regions of the world and includes India, China, Iran, Turkey, and Pakistan. These are the main regions where Zn deficiency exists in the human population (25). Another decisive factor is the lower solubility of Zn in the soil, which leads to the occurrence of Zn deficiency in crops. To counteract Zn malnutrition and maintain the elevated levels of this essential micronutrient, experts advocated the use of various strategies for the biofortification of Zn in crops. What is necessary in life is obviously food, although micronutrient-fortified food is the current demand in world agriculture. Hence, agronomic strategies, the plant breeding approach, the involvement of genetic engineering, and the application of ZSB are immensely practiced to produce a significant level of Zn in comestible parts of crops. Each approach has its own advantages and has some limitations as well. Agronomic biofortification practices through the use of fertilizers on the soil or the foliar application of Zn fertilizers to increase the Zn level in the plant foods, and thus nutrients-enriched food are consumed by the consumers (26, 27). In contrast, plant breeding has been practiced for several years as an important aspect of biofortification (5) to produce high-yielding varieties with a sufficient content of essential micronutrients such as Fe and Zn (4). Biofortification, resulting in particular from the genetic modification approach, is a time-saving approach for the development of nutritionally enriched crops. Secondly, this approach allows the transfer of a particular gene of importance (5). The production of “Golden Rice” illustrated as a significant model of biofortified crops develops via gene modification with the goal of accomplishing for beta carotene production. However, such aforementioned biofortification approaches are lucrative, featuring ethical issues, non-environmentally friendly (28), and irrelevant in those economically deprived nations where “rural-population” reside at large (29). The rampant use of synthetic fertilizers harms soil ecology, disturbs the environmental balance, reduces soil fertility, pollutes groundwater, and ultimately has a negative impact on human health (30). Hence, there is an urgent need to develop a new cost-effective tactic for micronutrient biofortification. In this step, using agriculturally important microorganisms to bestow the fortification of plants as a viable auxiliary measure can deliver an improved level of requisite micronutrients in the comestible portions of plants and used these microorganisms as a substitute for fertilizers formulated by a chemical approach (6, 13, 31). Microorganisms involve in the imperative process of mineralization and solubilization of organic and inorganic materials (13, 32), hence they can be employed as bioelicitors in the translocation of multiple elements simultaneously in plants with higher crop yield. The integrated biofortification approaches are further depicted diagrammatically in Figure 1.
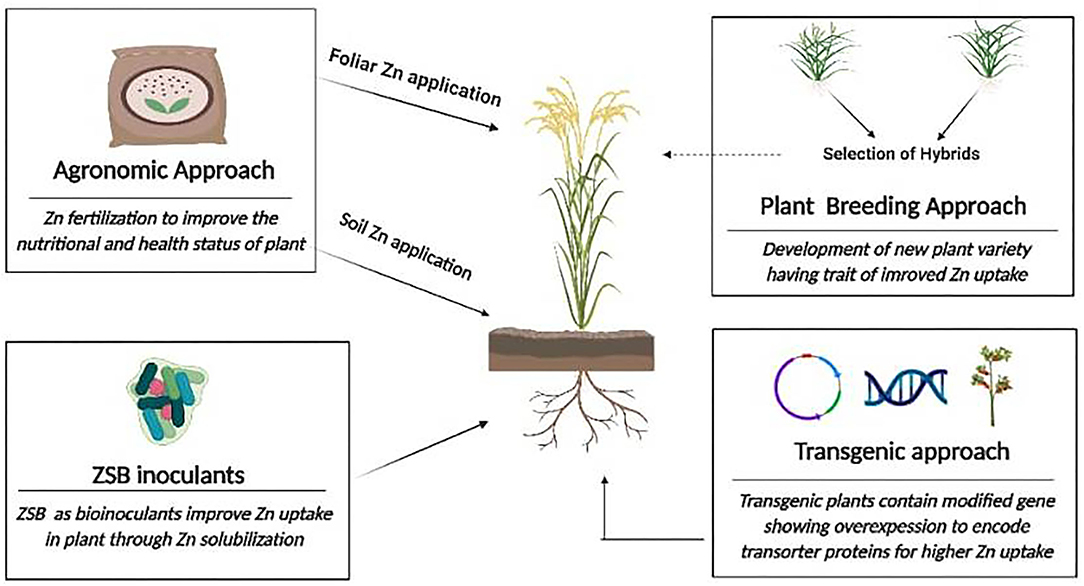
Figure 1. Schematic flow chart representing the different approaches for zinc (Zn) biofortification.
The use of ZSB as persuasive bioinoculants is a cost-effective method for Zn biofortification of food crops. ZSB dwelling in the rhizospheric region and the colonization of rhizospheres efficiently facilitate them as an auxiliary partner of the plant root for enhanced nutrient uptake in crops (12). As the chemical Zn fertilizers are implicated in soils, their conversion into an unavailable form of Zn compounds persists the problem of immobility of Zn from soil settings to plant tissues. This problem can be remedied by ZSB inoculants, which are able to solubilize the complex form of Zn in soils to better transport this nutrient from the soil to the plant (33). The mechanistic insight behind ZSB shows broad arrays of strategies for Zn solubilization such as acidification (34), the production of metal chelating modules “siderophore” (10), “chelated ligands,” and the involvement of an oxido-reductive system (35, 36). However, the secretion of OAs through Zn solubilization by microbial agents is a key mechanism for Zn solubilization, in which two OAs (2-ketogluonic acid and gluconic acid) play an essential role in Zn mobilization (37). Only a few bacterial strains stimulating plant growth were examined for Zn solubilization and showed a positive influence on the relative parameters of plant growth (38). Rhizobacteria, which are located in the rhizosphere especially on the root surface (39), colonize this region immensely (40) and show some properties that promote plant growth. Therefore, such bacteria are formally described with a term “plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria” or abbreviated as “PGPR.” Several mechanisms namely phosphate (P) solubilization (41, 42), the secernment of siderophores (43, 44), hydrocyanic acid (HCN) (45, 46), the secretion of plant hormones, viz. indole acetic acid (IAA) [42., 36], gibberellins (47), and cytokinins (48) are the prime features of PGPR linked with efficient plant growth (49). Moreover, detectable improvements in growth (the enhancement in the shoot/root and total yield) and other improved attributes of plants such as natural ingredients and antioxidants after PGPR inoculation further illustrate them as “plant probiotics” (50–52). However, the use of ZSB with massive plant growth-promoting traits is a relatively new approach and offers a sustainable option to address the purpose of biofortification of staple foods (53). Stepwise in vitro studies begin with the isolation and screening of potential ZSB in the laboratory, leading to their more efficient use as bioinoculants for Zn mobilization in field conditions. The in vitro screening of bacterial isolates on minimal media containing insoluble forms of Zn, namely zinc oxide (ZnO), zinc carbonate (ZnCO3), and Zn phosphate, is based on the formation of halo zones and the availability of the free form of Zn in liquid media (37, 54, 55), and the secretion of OAs (particularly gluconic acids) detected by liquid chromatography deciphering the Zn solubility potentiality of bacteria (56). Previous studies provide insights into microbial-assisted biofortification via some bacterial species for important food crops such as Bacillus sp. for wheat (8, 57), maize (58), soybean (8, 55), and rice (12), “Pseudomonas fragi,” “Pantoea dispersa,” Pantoea agglomerans, Enterobacter cloacae, Rhizobium sp. for wheat (11), and “Burkholderia” and “Acinetobacter” for rice (59). ZSB increased the considerable Zn content in plants such as wheat (11), rice (60, 61), and maize (58) and also showed prolific effects on plant growth. A few studies that were conducted with ZSB in comparison to PSB required further investigations on Zn-solubilizing microflora from soil regions (rhizospheric soil, nutrient-rich soil, and nutrient-deficient soil) and plant regions (epiphytes and endophytes) as well as their further evaluation for improved Zn transport in plants to secure their candidacy as a natural biofortification agent. In addition, Zn-solubilizing inocula not only play their role in combating Zn malnutrition but also provide an alternative source of Zn chemical fertilizers to increase the concentration of Zn and other micronutrients in plants, especially cereals.
The term rhizosphere is defined as the living purlieu of the soil near plant roots that carries a unique population of microorganisms (62). It represents a hub for plant–microbe interactions (63), establishes a complex and dynamic ecological relationship between a microorganism and the plant, and supports a dense and diverse fauna (64, 65). In other words, the rhizosphere can be represented as a physical matrix containing the microbial population in an environment of roots where a network of chemical reactions through a wide range of metabolic activities produces multiple products that are beneficial to both plants and microorganisms. Plant metabolic activities influence the rhizosphere by releasing root exudates (66), which are either attractive or repulsive (67, 68) and determine the microbial diversity of the rhizosphere region (69). Besides root exudates, the cellular secretion in the form of various chemicals, viz. chemical compounds, antipathogenic metabolites, growth regulators, and nutrient mobilization are the other unique properties that belong to both plants and microbes. Root colonization is the major strategy of soil microorganisms that coexist in the rhizospheric region (70), and the collective bacterial population of this region is commonly referred to as rhizobacteria (71). The root colonization zone shows the mutual interaction between rhizobacteria and the root, with numerous compounds secreted by both plants and bacteria supporting the interaction between the root and the microbe. Therefore, signalomics is a more recent approach to metabolomics for identifying and profiling the metabolites of both plant and microbial origin to decipher a chemical communication in the rhizospheric zone (72). However, root exudates act as communication signals that begin a biological and physiological communication between the soil microbiota and the roots by affecting the structural properties of the soil and associated microbial communities (73) and by promoting root surface colonization. ZSB as rhizobacteria are known for their potential to solubilize Zn through effective root colonization in response to the root exudates that act as chemoattractants for bacteria (12). Root exudation decides the microbial load and its survival in the rhizospheric hub (74). The competent role of rhizospheric bacteria in the recycling of nutrients, including carbon (75), nitrogen (76), phosphorus (42, 77), potassium (78, 79), and micronutrients (Fe, manganese, Zn, and copper) in the rhizosphere, continues to attract the significant attention of such bacteria in nutrient uptake and in promoting plant growth (39, 80–82). Several strategies of PGPR are directly attributed to the proliferation of plant growth. The secretion of metabolites by rhizospheric bacteria such as phytohormones, OAs, few enzymes for nutrient solubilization, siderophores, antibiotics, hydrolytic enzymes, antifungal compounds, and other compounds like osmoprotectants improve plant health and also eliminate the proliferation of soil pathogens in the rhizosphere region (39, 83, 84). The root colonization by ZSB and their mediated secretion of OAs/siderophores in the rhizospheric region solubilize the inorganic Zn in a free or solubilizing form, which can be easily taken up by plant roots and translocated into several parts including edible parts or grains as an additional microbial-assisted biofortification step (Figure 2).
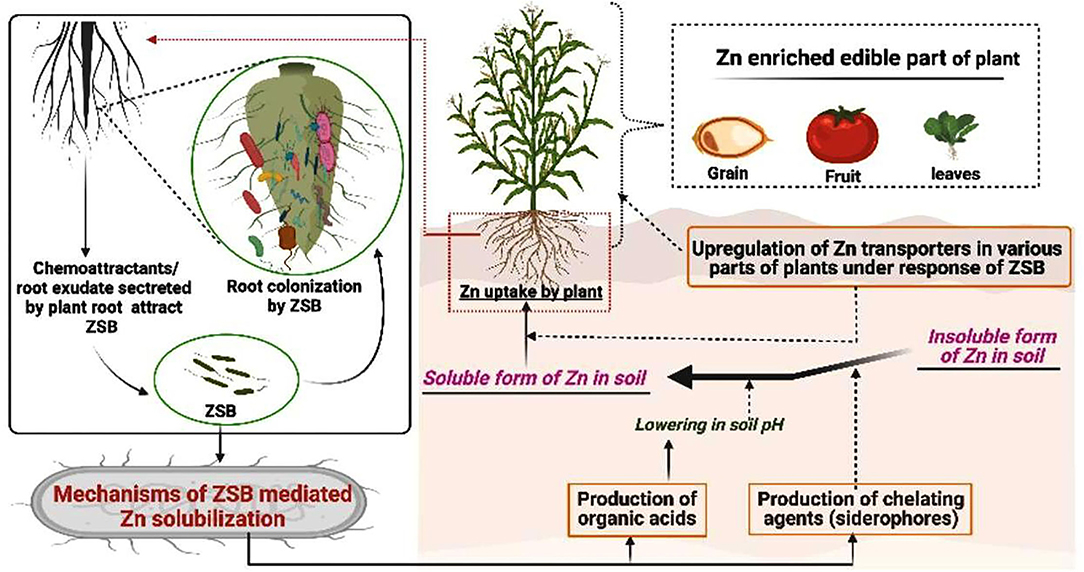
Figure 2. Overview of the zinc-solubilizing bacteria- (ZSB-) mediated Zn solubilization in the rhizosphere and an uptake of solubilized Zn by the roots. The most common way for a cross talk between ZSB and the plant is through chemoattractants/root exudates secreted by the roots. The secretion of organic acids (OAs) and siderophores near the rhizosphere using ZSB dissolves inorganic Zn by lowering the pH of the soil. Solubilized Zn is freely mobile and accessible to plant roots for its translocation into various edible plant parts to achieve the advantage of Zn biofortification.
“Endophytes” are special microbiota that live inside plants without showing pathogenic nature such as causing of disease (85) and colonize the internal plant tissues (86, 87). Endophytic microbiota are well documented to perform critical plant development, fitness, and diversification roles (88) and use the mechanisms similar to those shown by rhizobacteria for profound plant growth properties (86, 89). Multiple mechanisms, including nitrogen fixation (90), the synthesis of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) (91), phytohormones (92–95), antimycotics (96–100), and siderophores (101–104) described the plant growth-promoting properties of endophytes (87, 105, 106). However, endophytes for micronutrient biofortification have hardly been studied in comparison to rhizobacteria (107, 108). Studies of Singh et al. (31), Rehman et al. (15), and (111) illustrated Zn biofortifcation in wheat by endophytes such as Arthrobacter, Bacillus subtilis, and Pseudomonas sp. A very few studies over the past decade have deciphered the essential role of endophytes in biofortification in combating malnutrition from micronutrients, particularly selenium (109, 110). A few microbial inocula also showed Zn biofortification in staple crops such as wheat (9, 31, 111, 112). Wang et al. (108) illustrated the increased level of Zn in rice in response to two endophytes, namely “Sphingomonas sp. SaMR12” and “Enterobacter sp. SaCS20.” Endophytes use several multiple mechanisms to enable the uptake of nutrients in the edible portions of plants (113, 114). Zn-solubilizing endophytes may be a better biofortifying agent to increase the Zn localization in the eatable portion of wheat (9, 31), rice (108), and chickpea (16), thus presenting an alternative approach into the current strategies for biofortification. Besides Zn and Fe biofortification in plants, the two endophytic bacterial species of “Arthrobacter” exhibited a significant modification in root morphology and anatomy, which is a favorable phenomenon for better uptake of nutrients (111). Piriformospora indica, a fungal endophyte, with Zn treatment brought out the Zn fortification of lettuce leaves and also augmented the plant growth and chlorophyll levels in lettuce (115). It has been reported that the microbial consortia consisting of two endophytic strains (Acinetobacter sp. + Bacillus sp.) and mycorrhizal fungi increase selenium levels and also increase the antioxidant activity in wheat grains. The seed priming with Zn and Pseudomonas sp. also improved the overall productivity of wheat and Zn fortification of wheat grains (15). No further research has been published on investigating the interactions between plants and Zn-solubilizing endophytes and the functional properties of endophytes such as metabolite secretion and the mobilization/immobilization mechanisms associated with Zn solubilization. In-depth studies are required to further illustrate the interior tissue's colonization of the plant by endophytes and to determine their vital role in copious Zn translocation in plants.
Zinc plays an important role in all forms of life in terms of vitality and is involved in various metabolic processes. The plant enzymes such as carbonic anhydrase and superoxide dismutase are structurally linked to this crucial Zn micronutrient. The activities of these enzymes in plants are negatively affected in Zn scarred soil (116). Therefore, important food crops in cultivated land with a Zn deficiency are severely affected (117). Poor plant growth significantly lowers the overall productivity of the plants. It has been reported that several soil microorganisms solubilize insoluble Zn compounds and not only improve Zn translocation in plants, but also improve the yield-attributing properties of plants (53). Countless rhizobacteria, especially ZSB, have several probiotic plant traits that support plants by mobilizing the insoluble forms of Zn and contribute to increasing the crop yield. They are, therefore, often used as biofertilizers in sustainable agricultural practices (13). The selected ZSB strains showed their potential to boost yield-related traits in vivo (augmentation in length shoot, expansion of root, increment in total biomass of plant, chlorophyll content in the leaf, and improved grain yield of the crop), therefore these strains can be used as a competent bioelicitor or more precisely as “biofertilizers.” Improving dry weight and seed weight at the time of maturation of the plants is also a significant potential of the ZSB (8). A noteworthy increase in yield attributed characters was observed for wheat (11), rice (12, 118), and maize (38) in response to ZSB inoculation. ZSB like Bacillus sp. (12), Acinetobacter sp., and Burkholderia sp. (59) helped plants with their overall growth and improved the uptake of Zn in straw and grains. ZSB strains have all the characteristics necessary to be promoted as proficient bioinoculants to diminish Zn micronutrient dearth in soils after proper field assessment and validation (8). Overall, ZSB has been identified as the main factor for integrated nutrient application in agriculture and therefore appears to have a viable potential for efficient use of such microorganisms to maximize crop production without showing harmful effects on the soil. Current approaches such as rhizosphere engineering, endophytic system enhancement, and the use of bacterial consortia are required to maintain the growth of the biofertilizer industry.
The mechanistic perspective behind bacterial-mediated Zn solubilization remains uncertain. They may likely have mechanisms similar to P-solubilizing microorganisms and Fe mobilizers through producing numerous compounds viz. OAs and chelating agents (119). To investigate the mechanisms of Zn solubilization, it is necessary to precisely outline individual or diverse mechanisms in the soil microorganisms that are necessary for the biogeochemical cycle of Zn. In addition, the solubilization of Zn is influenced by two bacterial processes such as either autotrophic or heterotrophic processes and also depends on the bacterial metabolism involved and the associated environmental conditions (56, 120). Autotrophic bacteria (including sulfur/ferric, Fe-oxidizing bacteria) have been extensively studied for their metal solubility potential and used in the recovery of Zn, nickel, and copper from industrial waste and ores (56, 121). On the contrary, heterotrophic bacteria with an immense ability to solubilize Zn have also attracted the attention of worldwide researchers and have been investigated in numerous agronomic studies as a bioinoculum to improve and localize Zn in the plant. Numerous known mechanisms are shown in Zn solubilization microorganisms. Mainly expected mechanism, which is elucidated as acidification, in which microorganisms produce OAs in the soil, which leads to the sequestration of Zn metal cations and a decrease in the affected soil pH (34, 56). Besides, the anions have the potential to chelate Zn (122). Additional probable mechanisms participated in Zn solubilization bacterially produced siderophores for the chelation of Fe and other metals (10), the secretion of chelated ligands, amino acids, vitamins, phytohormones, protons (H+) by microorganisms, and the inclusion of oxide reduction scheme on membranes of bacterial cells (35, 36, 123). Based on studies over the past few years, it has been assumed that, despite various possible mechanisms identified in ZSB, only the phenomenon of OA secretion is an underlying microbial process for the solubilization of Zn. The accumulation of OA, particularly gluconic acid (and its keto derivatives) in tris-minimal broth medium (modified with an inexplicable form of the Zn source), which contains glucose as a single carbon source, definitely remains the most commonly described mechanism for Zn solubilization via the inoculated heterotrophic bacteria (37). The solubilization of inexplicable Zn compounds via bacterially secreted gluconic acid has been shown under in vitro conditions, e.g., for Acinetobacter (59), Pseudomonas (37, 124), and Gluconacetobacter (33). The major solubilization mechanism postulated in these in vitro studies was “acidification,” which resulted from the secretion of a significant amount of “gluconic acid” in the growth medium. The accumulation of this so-called “Zn solubilizing acid” in the microbial growth medium depends heavily on the availability of glucose in the current milieu of bacteria. Gluconic acid, synthesized from the extracellular or direct glucose oxidation via periplasmic glucose dehydrogenase (GDH, an example of the quinoproteins and redox co-enzyme) (125, 126). This enzyme is encoded by the gcd gene, and pqq operon encodes products such as “pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ)” (20, 127). A few studies suggested that the production of gluconic acid may not be compulsory for Zn solubilization as the different species of ZSB produce diverse arrays of other OAs. The Zn solubilization by the bacterium Burkholderia cepacia was ascribed to the secretion of four different OAs such as oxalic acid, tartaric acid, formic acid, and acetic acid, even when a single C source in the form of sugar (glucose) was present in the growth medium (128). In addition to the acids that are involved in Zn mobilization, siderophores are secreted by microorganisms as small organic compounds and are mainly involved in Fe solubilization via chelation processes (129). Some siderophores have also been reported to chelate Zn, but their precise role in Zn solubilization remains to be insufficiently considered (130, 131). Microorganisms secret an ample variety of “siderophores” that are categorized into different types such as carboxylate type (i.e., “rhizobactin”), catecholate type (i.e., “enterobactin”), and hydroxamate type (i.e., “ferrioxamine B”) (132). Also, bacteria have been reported to secrete the special forms of this metal chelating compound that have a mixture of the most important valuable chemical groups (i.e., pyoverdin) (133). Soil microflora that colonize mineral surfaces are somehow different from the microbial inhabitants of the closest soil zone (134). Microbes on the surface of minerals create a microenvironment in which the microbes are protected from various stressful conditions (135, 136). Metal chelation occurs in the soil or is shared with the microenvironments of an adjoining microbial community (137). Siderophore-secreting bacterial populations from the soil dwellers promote the phenomenon of mineral solubility (138). Various mechanistic findings have been illustrated for the dissolution or chelation of minerals mediated by siderophores. However, a special focus was placed on the siderophore-mediated Fe solubilization (139). Siderophores are enormously efficient in solubilizing Fe and escalating the mobilization of metals (140). It can have an efficient affinity for a particular metal other than Fe (141).
In general, plant genomes comprise a wide range of genes with precise expression patterns in response to the uptake and transport of various types of micronutrients, which ensure that all tissues, especially the edible part, receive a satisfactory amount of vital nutrients necessary for the crucial activities of the cell. Some specific genes, especially ZIP family gene, have been discovered in the plants that play an imperative role in the transport and accumulation of Zn (142). The expression pattern of these genes is influenced either by high or low Zn concentrations (143). Under Zn deficiency conditions, however, the upregulation of the genes of the ZIP family was found in various plants (144). Rice was seen as a remarkable model for understanding the mechanisms of Zn transport with the 16 identified ZIP transporter members (144–146). Several genes (AtZIP6, ZNT1, HMA2, HMA4, and OsZIP3) (147) are significantly participated in Zn transport through the xylem or at the root and shoot site. In addition, the overexpression of such genes leads to an increased Zn movement in the shoot of plants (32, 148). Numerous ZIPs (Zn transporters) such as “OsIRT1,” “OsIRT2,” “OsZIP1,” “OsZIP3,” “OsZIP4,” “OsZIP5,” “OsZIP7,” and “OsZIP8” have been explored in rice, which plays a major role in Zn translocation from the surrounding soil of the root to various sections of plants including mature seeds (143, 145, 146, 149, 150). Recently, a member of the ZIP OsZIP9 (important influx transporter) located in the plasma membrane showed its contribution to the uptake of Zn in rice (151). OsZIP genes are expressed in roots, shoots, leaves, and spikelets under Zn-deficient conditions (144). It was shown that an expression pattern of a few ZIP genes (OsZIP1, OsZIP4, and OsZIP5) from rice is regulated by the accessibility of Zn2+, Fe2+, and Mn2+ (22, 143, 152). ZmZIP genes encoding ZIP transporters (ZmZIP1–ZmZIP12), especially in the maize genome assist in Zn uptake (153, 154). ZmZIP5 and ZmZIP11 are predicted for their productive contribution biofortification of maize (154). In wheat, the genes of the TaZIP family play a central role in the uptake of Zn and its transport in different plant regions (155). It was found that the expression level of TaZIP transporters such as TaZIP3, TaZIP5, TaZIP6, TaZIP7, and TaZIP13 is increased in the shoot and root part of wheat in the case of a Zn deficiency (156). HvZIP transporters in barley exhibited their significance for Zn uptake under Zn deficient conditions (157). As a bioinoculant, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) influenced the expression profile of some genes such as “HvZIP3,” “HvZIP7,” “HvZIP8,” “HvZIP9,” and “HvZIP13” and among these the higher expression of HvZIP13 amplified the Zn uptake by the plant (158).
The gene expression analysis, which has been proven from recent studies, clearly showed that Zn-solubilizing microbial inoculants and other plant growth-stimulating microbes modulate the expression patterns of some of the genes from the Zn-regulated transporter family and thus played an important role in the transmission of Zn in the different parts of plants (143, 159). The co-inoculation of Trichoderma harzianum (UBSTH-501) and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens (B-16) augmented the expression level of the ZIP transporters genes (“TaZIP-1,” “TaZIP-3,” “TaZIP-5,” “TaZIP-6,” “TaZIP-7,” “TaZIP-10,” and “TaZIP-13”) by 2.76–4.96-folds, which eventually led to increased Zn translocation in wheat cultivated in saline-sodic soil (159). Besides ZSB, mycorrhizal fungi also showed their contribution in biofortification (160). Under Zn deficient conditions, the mycorrhizal fungi (Rhizophagus irregularis) improved the Zn in the grain of Hordeum vulgare by upregulating the expression profile of HvZIP13 (158). The resultant upregulation of the ZIP transporters under the response of microorganisms is illustrated in Table 1. Considerable advances have been made in interpreting an interplay between plants and microbes to enable the uptake of micronutrients from the soil into the plant. The production of OAs and metal chelators by microbes and the simultaneous expression of many ZIP transporters in plants can improve the uptake of Zn by plants. However, the cascade of events that takes place at the site of the plant–microbial interaction is very complex and is linked by a cross talk between microorganisms and plants, which needs detailed studies focusing on how microorganisms particularly ZSB are involved in the regulation of Zn transporter-associated genes.
The cultivation of plants with a sufficient Zn concentration is the main need of the world today, so that the consequences of Zn deficiency can be overcome. In all countries, crops are the leading source of food for local residents. Grains, vegetables, and fruits fortified with Zn can effectively overcome Zn malnutrition. Therefore, the availability of the required Zn is an imperative factor in enhancing the overall crop yield (160, 164). The poor supply of Zn ultimately leads to the reduced productivity of the plants with an insufficient accumulation of Zn in their edible portions (165). ZSB were described as chief natural agents for Zn mobilization. Their interaction with the roots should improve the Zn status of the plant. The microbial-assisted biofortification opens up a newer and more environmental-friendly approach to agriculture, which relies less on chemical fertilizers (11, 27). Recent insights into plant–ZSB interactions revealed the potential of ZSB inoculants to address the Zn deficiency problem in plants. Such inoculants are living entities and are selected based on various attributes and employed for their valuable effect on crops in the following ways: (1) either by soil application or by seed treatment prior to sowing/transplanting; (2) monitoring by appropriate parameters for plant growth; and (3) the determination of the micronutrient level in cereals shows the microbially mediated biofortification. An increased level of Zn translocation occurs as a result of the root colonization by ZSB, which increases the pH of the rhizospheric soil through microbially secreted products (OAs) near the rhizosphere to perform Zn solubilization (53, 58). Furthermore, other organic compounds such as “siderophores” bind to metals, for example, Fe, and form a Fe(III)–siderophore complex at the exterior of mineral. This so-called complex form is then transferred to the adjacent soil environment to facilitate Fe uptake by local microbiota or plants (138, 166). Sufficient information is available to indicate a remarkable ability of ZSB to improve the bioavailability of Zn in the plant rhizosphere with adequate transport of this element to grains (53). As promising plant-probiotic agents, ZSB exhibit a strong influence on plant productivity. Bacillus sp. AZ6, with the capability to solubilize Zn with some plant-probiotic traits, exhibited an improvement in the biomass and length of the roots and shoots of the maize plant (38). Worldwide scientific studies validate a possible contribution of ZSB to the Zn biofortification of food crops by augmenting the Zn concentration in the edible parts of plants. In addition to the advantages of sustainable plant production, ZSB is considered to improve soil health. A wide range of ZSB, including both groups such as gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, demonstrated their competence in biofortification. Bacillus, in particular, showed a profound role in Zn biofortification in numerous food crops (8, 12, 38, 55, 58, 167–172). The important crops such as maize (38, 54, 58, 173, 174), rice (59, 60, 171, 175, 176), and wheat (8, 11, 31, 32, 167, 177) have been studied extensively for Zn biofortification in response to ZSB inoculants as the grain parts from these crops offer the most important staple foods on a broad scale worldwide. A potential ZSB microbial strain, namely Bacillus sp. enhanced the Zn translocation (%) in two different Basmati rice varieties, i.e., 22–49% (for Basmati-385) and 18–47% (for Super-Basmati Rice) (12). The study by Wang et al. (108) illustrated the role of “Enterobacter sp. SaCS20” and “Sphingomonas sp. SaMR12” in improving the Zn content in polished rice by 11.2% and 13.7%. Bacterium “Rahnella sp. JN6” improved the plant growth and increased Zn accumulation in Brassica napus (oilseed rape) in pot experiments (178). The strains of Bacillus aryabhattai, as prominent bioinoculants, amplified the Zn content in wheat grains (in the range of 42–61 mg/kg) compared to uninoculated control (8). (11) depicted the role of EPS producing ZSB strains influencing wheat plants, with inoculants such as P. dispersa EPS6, P. agglomerans EPS13, and E. cloacae PBS2, the dry weight of the shoots was increased, while the inoculation with P. fragi EPSI showed a considerable increase in Zn content and dry weight of the root. ZSB with Zn source supplementation such as ZnO, ZnSO4 also provided fruitful benefits of promoting plant growth, soil health, and Zn biofortification. (174) reported the enhancement in plant growth and soil fertility under the response of a bioinoculant (E. cloacae) and Zn supplement (ZnO). Moreover, the rice plant growth was improved by Acinetobacter sp. (TM56) and ZnSO4 (176). Compost, enriched with Bacillus sp. AZ6 and ZnO, showed a profound effect on plant growth, crop yield and subsequently improved the Zn supply in paddy grains via a slow release of Zn from ZnO (171). With ZnO supplementation, Zn-solubilizing bacterial strain Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus showed a remarkable nutrient uptake in maize (179). The response of the bacterial consortium (E. cloacae + Bacillus megaterium) with Zn sulfate additives augmented the Zn uptake in wheat grains and showed the utmost range of soil exchangeable Zn (180). Goteti et al. (54) showed that the inoculation of maize seeds with ZSB (“Pseudomonas sp. P29,” “Pseudomonas sp. P33,” and “Bacillus sp. B40”) augmented the dry weight of the plants with improved Zn accessibility. The study of Vaid et al. (59) on ZSB (Acinetobacter sp. and Burkholderia sp.) showed growth attributes of the rice plant in terms of an increment in the number of panicles, productive tillers, dry matter, straw yield and grain yield, and dry matter yield. In addition, the same study also showed the suitability of ZSB for biofortification by enhancing the level of Zn content in grains. Inoculation with Bacillus cereus increased the Zn concentration in soybean seeds. On the contrary, the reduced phytate content of the seeds showed the bacterium's ability to reduce the effects of an anti-nutritional factor (167). Contemporary studies have deciphered the ZSB-mediated Zn biofortification in food plants. However, the role of consortia containing Zn-solubilizing microorganisms in Zn biofortification is not fully revealed. The microbial consortia accelerate plant growth compared to a single microbial inoculum (39, 66). “Rhizospheric–endophytic mix inoculants” bearing immense plant-probiotic traits increase the plant biomass and also improve the assimilation of micronutrients in cereals (181). The plant-probiotic consortia also depict the efficient disease suppressive effect, thus reducing plant mortality (182). Bacterial consortium can have a revitalizing effect on plants as various kinds of bacterial strains can work synergistically to provide nutrients and eliminate inhibitory products (183, 184).
The development of efficient bacterial consortia has an indispensable place in biofertilizer-based research and their potential applications in sustainable agriculture (185). The development and formulation of ZSB consortia can offer several key advantages:
➢ The use of ZSB consortia can offer more advantages in Zn biofortification compared to the individual ZSB inoculum.
➢ ZSB consortium as a natural resource can combat Zn deficiency.
➢ The use of the ZSB consortium can reduce the uncontrolled use of chemical fertilizers.
➢ ZSB consortium can show the massive plant growth-promoting properties.
➢ ZSB consortium can act as competent “plant-probiotic” to enhance the crop yield.
The microbial consortium of Burkholderia and Acinetobacter improved the Zn content and its bioassimilation in wheat grain and wheat straw (186). A consortium of Zn-solubilizing Bacillus species (Bacillus sp. SH-10 and B. cereus SH-17) fortified rice through “microbial-assisted biofortification strategy” showed the highest Zn translocation index (1.6 to 1.7) (12). The highest Zn level in grains, i.e., 16.1 and 16.0 mg/kg, was measured in two rice varieties “PD16” and “NDR359,” which were inoculated with the Zn-solubilizing bacterial consortium (Burkholderia and Acinetobacter) (59). The co-inoculation of Enterobacter and Serratia marcescens significantly improved the Zn content in wheat by 23% and 32% under field and pot trial studies, respectively (11). This consortium also enhanced the concentrations of Cu, Mn, and Fe under the pot trial by 56, 52, and 18% and in the field studies by 43, 48, and 16%, respectively. The consortium with two compatible bacterial strains, “Pseudomonas jessenii (R62)” and “Pseudomonas synxantha (R81),” showed a significant influence on Zn uptake in rice seeds (187). The study of Tariq et al. (60) demonstrated the efficiency of a Zn-solubilizing bacterial consortium (Pseudomonas sp. and other PGPR strains) to increase Zn content (up to 157%) in rice. Zn accumulation (107.01 μg g−1) in flag leaf was taken into account during inoculation with an Anabaena–Azotobacter biofilm, thus illustrating the cyanobacterial-assisted Zn biofortification in maize (188). A consortium of three bacterial strains (B.megaterium, A. chlorophenolicus, and Enterobacter) improved Zn content (58.5 and 62.8% increment under the pot and field trial, respectively) in Triticum aestivum L and showed a considerable amount of other bioavailable micronutrients like Cu, Mn, and Fe (189). In addition to the advantages of biofortification, the use of microbial consortia also indicated a positive impact on various yield-related parameters such as gain in thousand-grain weight, number of tillering per plant, and grains per ear (190). Moreover, the contribution of blue-green algae in biofortification was also determined. The consortium (Anabaena sp. CR1 + Providencia sp. PR3) with 75% RDF (recommended dose of fertilizers) showed an improved level of Zn uptake (323.8 g/h) in wheat (191). Recently, the metagenomics-based study revealed the existence of potential Zn-mobilizing species, particularly Massilia and Pseudomonas sp., that could form a functional community in increasing Zn concentration in grains of wheat varieties (192). More recent studies that decipher the microbial-assisted improvement in the plant yield and Zn content of crop plants are listed in Table 2.
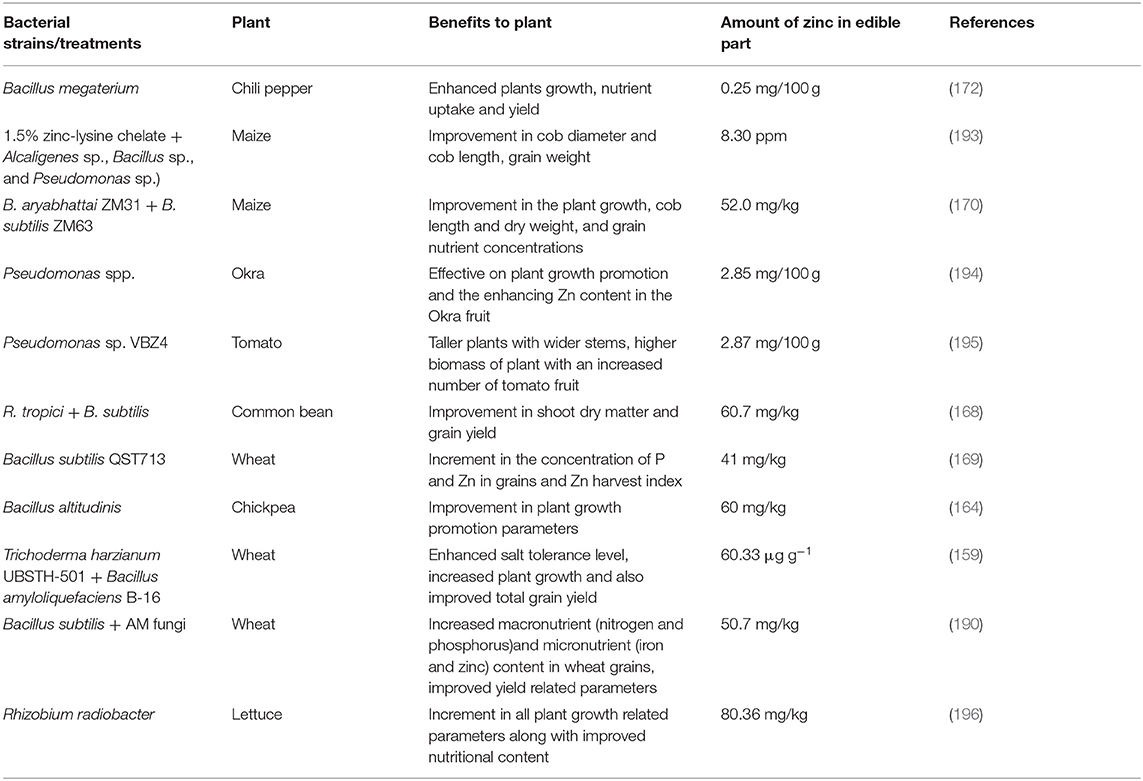
Table 2. Benefits of zinc-solubilizing bacteria (ZSB) in plant growth promotion and zinc (Zn) biofortification in important food crops.
In vitro screening of ZSB executes a task of developing ZSB-based inoculants, however, the selection of potential ZSB strains and their formulation is a challenge in itself. Additionally, the use of ZSB-based biofertilizers can also be challenging due to the inconsistency under field conditions, so the results in field studies do not appear as good as they would under controlled conditions. Crops show a slow response toward biofertilizers, and sometimes it becomes unsuccessful as the inoculum takes the time to build up its population and root colonization. Due to these circumstances, it leads to a low acceptance of microbial-based fertilizers by farmers (197).
However, the following points illustrate the main challenges of ZSB application under field conditions:
a) The decrease in the effectiveness of bioinoculants may be due to the physical and chemical properties of the soil.
b) Environmental factors determine the activity of the bioinoculants used as various factors such as drought, salinity, alkalinity, acidity, and high concentrations of heavy metals (such as Cd, Hg, and Cr) in the soil can reduce the performance of ZSB-based bioinoculants in the soil.
c) The massive use of synthetic chemicals and their harmful residual effects can reduce the activity of certain bioinoculants.
d) The successful field application of ZSB-based bioinoculants relies on the climatic factors required for a particular crop.
e) The inability of an bioinoculant to effectively colonize the rhizosphere due to its small abundance and its competition with the pre-existing indigenous microbiota.
f) Soil type, pH, radiation, temperature, nutrient accessibility, oxygen concentration, and the extent of interaction with the native soil microorganisms, etc., all affect the plant–bioinoculant interaction and affect their survival in the host plant.
g) Improper exudation of OAs and siderophores in the soil after the application of bioinoculants can reduce the uptake of Zn by plants.
h) The resulting higher phytic acid content in the edible parts of plants impedes the bioavailability of Zn, and hence significantly limiting the advantages of biofortification.
However, it is strongly recommended that the exploration and use of region-specific Zn-solubilizing microbial strains show the highest effectiveness for Zn biofortification. Instead of using ZSB directly as an inoculum, it makes sense to use a suitable carrier. The ZSB should have an additional characteristic for phytase production as phytase can reduce the concentration of an antinutritional factor (phytic acid) and increase the availability of Zn. The microbial groups that may play a vital role in the nutrient cycle in soils are very diverse, and bacterial-mediated Zn solubilization is seen as the main strategy for Zn nutrition in plants. However, a very large section of the soil microbiota is still unexplored, as around 99% of the microorganisms living in the soil cannot be cultivated (198). Thus, culture-independent tactics are necessary to decipher the functional attributes of native microbiome involved in Zn solubilization in soils. Molecular approaches of culture-independent methods for determining the functional gene or microbial diversity in soil have been developed considerably in the recent past. Metagenomics also offers new perspectives to identify the existence and abundance of certain microorganisms or functional genes specific for soil Zn mobilization or increasing root Zn uptake, mainly the synthesis of OAs and siderophores (192).
Many ZSB have attracted significant attention for their ability to endorse Zn assimilation in plants through direct mechanisms (Zn solubilization and its transportation) by acting as natural biofortifying agents. Mechanism adapted by ZSB for the growth of plants is similar as of ordinary plant growth-elevating bacteria either studied from the rhizosphere or inner tissues of plants. However, the mechanistic view of ZSB is quite different from PGPR. For example, the occurrence of OA production offers the ZSB an opportunity to solubilize insoluble Zn in the soil and make Zn accessible to plants. The interaction of ZSB with plants can be an indicant of positive relationships where microbial-mediated plant growth-promoting effects meliorate the healthy lifestyle of host plants. There is still huge vague in our understanding of the interaction of bacteria with the host plant residing in the rhizospheric zone or as part of phytomicrobiont turning the inexplicable Zn into soluble Zn form, and as a channel, these ZSB facilitate increased Zn content in different plant parts. Not much study was performed on ZSB-based biofortification consequently inciting to create a systematic way for unveiling the functional aspects of bacterial genes participated in Zn and other micronutrient solubilization and beneficial interaction of ZSB with plants. The functional genomics, proteomics, and metabolomics approach may in the near future be able to construct ZSB formulations to find out their competence in increasing multiple micronutrients in the edible plant parts for a more sustainable remedy of nutrient deficiencies. However, more work is still required for ZSB from soil and plants, and the development of ZSB biofertilizers for future use in crop biofortification.
VU: writing of original draft of manuscript. All authors: conceptualization, editing, and approval of submitted version.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Department of Microbiology, College of Basic Sciences and Humanities, Govind Ballabh Pant University of Agriculture and Technology, Pantnagar (India).
1. Gibson R. Zinc: The missing link in combating micronutrient malnutrition in developing countries. Proc Nutr Soc. (2006) 65:51–60. doi: 10.1079/PNS2005474
2. Zikankuba V, Mteremko D, James A. Staple crops biofortification linking agriculture, food and nutrition towards eliminating hidden hunger. Eur J Nutr Food Saf. (2019) 9:112–21. doi: 10.9734/ejnfs/2019/v9i230050
3. World Health Organization. Guidelines on Food Fortification with Micronutrients. Geneva, Switzerland (2006)
4. Khush G. Productivity improvements in rice. Nutr Rev. (2003) 61:S114–s116. doi: 10.1301/nr.2003.jun.S114-S116
5. Garcia-Casal MN, Peña-Rosas JP, Pachón H, De-Regil LM, Centeno Tablante E, Flores-Urrutia MC. Staple crops biofortified with increased micronutrient content: effects on vitamin and mineral status, as well as health and cognitive function in the general population. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2016) 8:1465–858. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012311
6. Bouis HE, Saltzman A. Improving nutrition through biofortification: A review of evidence from HarvestPlus, 2003 through 2016. Glob Food Sec. (2017) 12:49–58. doi: 10.1016/j.gfs.2017.01.009
7. Cakmak I, Kutman UB. Agronomic biofortification of cereals with zinc: a review: Agronomic zinc biofortification. Eur J Soil Sci. (2018) 69:172–80. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12437
8. Ramesh A, Sharma SK, Sharma MP, Yadav N, Joshi OP. Inoculation of zinc solubilizing Bacillus aryabhattai strains for improved growth, mobilization and biofortification of zinc in soybean and wheat cultivated in Vertisols of central India. Appl Soil Ecol. (2014) 73:87–96. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2013.08.009
9. Rehman A, Farooq M, Naveed M, Ozturk L, Nawaz A. Pseudomonas-aided zinc application improves the productivity and biofortification of bread wheat. Crop Pasture Sci. (2018) 69:659. doi: 10.1071/CP17441
10. Saravanan VS, Kumar MR, Sa TM. Microbial zinc solubilization and their role on plants. In: Maheshwari DK, editors. Bacteria in Agrobiology: Plant Nutrient Management. Berlin: Springer (2011). p. 47–63. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-21061-7_3
11. Kumar A, Maurya BR, Raghuwanshi R, Meena VS, Tofazzal Islam M. Co-inoculation with Enterobacter and rhizobacteria on yield and nutrient uptake by wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the alluvial soil under Indo-Gangetic plain of India. J Plant Growth Regul. (2017) 36:608–17. doi: 10.1007/s00344-016-9663-5
12. Shakeel M, Rais A, Hassan MN, Hafeez FY. Root associated Bacillus sp. improves growth, yield and zinc translocation for Basmati rice (Oryza sativa) varieties. Front Microbiol. (2015) 6:1286. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01286
13. Upadhayay VK, Singh AV, Pareek N. An insight in decoding the multifarious and splendid role of microorganisms in crop biofortification. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci. (2018) 7:2407–18. doi: 10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.286
14. Khan A, Singh J, Upadhayay VK, Singh AV, Shah S. Microbial biofortification: a green technology through plant growth promoting microorganisms. In: Shah S, Venkatramanan V, Prasad R, editors. Sustainable Green Technologies for Environmental Management. Singapore: Springer (2019). p. 255–9. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-2772-8_13
15. Rehman A, Farooq M, Naveed M, Nawaz A, Shahzad B. Seed priming of Zn with endophytic bacteria improves the productivity and grain biofortification of bread wheat. Eur J Agron. (2018) 94:98–107. doi: 10.1016/j.eja.2018.01.017
16. Ullah A, Farooq M, Hussain M. Improving the productivity, profitability and grain quality of kabuli chickpea with co-application of zinc and endophyte bacteria Enterobacter sp. MN17 Arch Agron Soil Sci. (2020) 66:897–912. doi: 10.1080/03650340.2019.1644501
17. Cakmak I. Tansley Review No. 111 Possible roles of zinc in protecting plant cells from damage by reactive oxygen species. New Phytol. (2000) 146:185–205. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-8137.2000.00630.x
18. Palmer CM, Guerinot ML. Facing the challenges of Cu, Fe and Zn homeostasis in plants. Nat Chem Biol. (2009) 5:333–40. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.166
19. Rehman A, Farooq M, Ullah A, Nadeem F, Im SY, Park SK, et al. Agronomic biofortification of zinc in Pakistan: Status, benefits, and constraints. Front Sustain Food Syst. (2020) 4:591722. doi: 10.3389/fsufs.2020.591722
20. Sharma A, Patni B, Shankhdhar D, Shankhdhar SC. Zinc—an indispensable micronutrient. Physiol Mol Biol Plants: Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants. (2013) 19:11–20. doi: 10.1007/s12298-012-0139-1
21. Kawachi M, Kobae Y, Mori H, Tomioka R, Lee Y, Maeshima M. A mutant strain arabidopsis thaliana that lacks vacuolar membrane zinc transporter MTP1 revealed the latent tolerance to excessive zinc. Plant Cell Physiol. (2009) 50:1156–70. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcp067
22. Lee S, Kim SA, Lee J, Guerinot ML, An G. Zinc deficiency-inducible OsZIP8 encodes a plasma membrane-localized zinc transporter in rice. Mol Cells. (2010) 29:551–8. doi: 10.1007/s10059-010-0069-0
23. Salgueiro MJ, Zubillaga M, Lysionek A, Cremaschi G, Goldman CG, Caro R, et al. Zinc status and immune system relationship: a review. Biol Trace Elem Res. (2000) 76:193–205. doi: 10.1385/BTER:76:3:193
24. Prasad AS. Zinc in human health: effect of zinc on immune cells. Mol Med. (2008) 14:353–7. doi: 10.2119/2008-00033.Prasad
25. Cakmak I, Kalayci M, Ekiz H, Braun HJ, Kilinç Y, Yilmaz A. Zinc deficiency as a practical problem in plant and human nutrition in Turkey: a NATO-science for stability project. Field Crops Res. (1999) 60:175–88. doi: 10.1016/S0378-4290(98)00139-7
26. de Valença A, Bake A, Brouwer I, Giller K. Agronomic biofortification of crops to fight hidden hunger in sub-Saharan Africa. Glob Food Sec. (2017) 12:8–14. doi: 10.1016/j.gfs.2016.12.001
27. Carvalho SMP, Vasconcelos MW. Producing more with less: strategies and novel technologies for plant-based food biofortification. Food Res Int. (2013) 54:961–71. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2012.12.021
28. de Santiago A, Quintero JM, Avilés M, Delgado A. Effect of Trichoderma asperellum strain T34 on iron, copper, manganese, and zinc uptake by wheat grown on a calcareous medium. Plant Soil. (2011) 342:97–104. doi: 10.1007/s11104-010-0670-1
29. Mayer JE, Pfeiffer WH, Beyer P. Biofortified crops to alleviate micronutrient malnutrition. Curr Opin Plant Biol. (2008) 11:166–70. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2008.01.007
30. Ayala S, Rao E. Perspectives of soil fertility management with a focus on fertilizer use for crop productivity. Curr Sci. (2002) 82:797–807. Available online at: http://www.jstor.org/stable/24106725
31. Singh D, Rajawat MV, Kaushik R, Prasanna R, Saxena AK. Beneficial role of endophytes in biofortification of Zn in wheat genotypes varying in nutrient use efficiency grown in soils sufficient and deficient in Zn. Plant Soil. (2017) 416:107–16. doi: 10.1007/s11104-017-3189-x
32. Rana A, Joshi M, Prasanna R, Shivay YS, Nain L. Biofortification of wheat through inoculation of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and cyanobacteria. Eur J Soil Biol. (2012) 50:118–26. doi: 10.1016/j.ejsobi.2012.01.005
33. Saravanan V, Madhaiyan M, Thangaraju M. Solubilization of zinc compounds by the diazotrophic, plant growth promoting bacterium Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus. Chemosphere. (2007) 66:1794–8. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.07.067
35. Wakatsuki T. Metal oxidoreduction by microbial cells. J Ind Microbiol. (1995) 14:169–77. doi: 10.1007/BF01569900
36. Chang H, Lin C, Huang H. Zinc-induced cell death in rice (Oryza Sativa L.) roots. Plant Growth Regul. (2005) 46:261–6. doi: 10.1007/s10725-005-0162-0
37. Fasim F, Ahmed N, Parsons R, Gadd GM. Solubilization of zinc salts by a bacterium isolated from the air environment of a tannery. FEMS Microbiol Lett. (2002) 213:1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2002.tb11277.x
38. Hussain A, Arshad M, Zahir ZA, Asghar M. Prospects of zinc solubilizing bacteria for enhancing growth of maize. Pak J Agric Sci. (2015) 52:915–22.
39. Backer R, Rokem JS, Ilangumaran G, Lamont J, Praslickova D, Ricci E, et al. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria: context, mechanisms of action, and roadmap to commercialization of biostimulants for sustainable agriculture. Front Plant Sci. (2018) 9:1473. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01473
40. Vacheron J, Desbrosses G, Bouffaud ML, Touraine B, Moënne-Loccoz Y, Muller D, et al. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria and root system functioning. Front Plant Sci. (2013) 4:356. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2013.00356
41. Glick BR. Plant growth-promoting bacteria: mechanisms and applications. Scientifica. (2012) 2012:963401. doi: 10.6064/2012/963401
42. Alori ET, Glick BR, Babalola OO. Microbial phosphorus solubilization and its potential for use in sustainable agriculture. Front Microbiol. (2017) 8:971. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00971
43. Kloepper JW, Leong J, Teintze M, Schroth MN. Enhanced plant growth by siderophores produced by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Nature. (1980) 286:885–6. doi: 10.1038/286885a0
44. Sayyed RZ, Chincholkar SB, Reddy MS, Gangurde NS, Patel PR. Siderophore Producing PGPR for Crop Nutrition and Phytopathogen Suppression. In: Maheshwari D, editor. Bacteria in Agrobiology: Disease Management. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer (2013) 449–471. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-33639-3_17
45. Castric PA. Hydrogen cyanide, a secondary metabolite of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol. (1975) 21:613–8. doi: 10.1139/m75-088
46. Rath M, Mitchell T, Gold S. Volatiles produced by Bacillus mojavensis RRC101 act as plant growth modulators and are strongly culture-dependent. Microbiol Res. (2018) 208:76–84. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2017.12.014
47. Maheshwari DK, Dheeman S, Agarwal M. Phytohormone-producing PGPR for sustainable agriculture. In: Maheshwari D, editor. Bacterial Metabolites in Sustainable Agroecosystem. Sustainable Development and Biodiversity. Cham: Springer (2015). p. 159–82. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24654-3_7
48. García de Salamone I. E., Hynes R. K., Nelson L. M. (2001). Cytokinin production by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria and selected mutants. Can J Microbiol. 47:404–11. doi: 10.1139/w01-029
49. Ahemad M, Kibret M. Mechanisms and applications of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: Current perspective. J King Saud Univ Sci. (2014) 26:1–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2013.05.001
50. Kim YC, Anderson AJ. Rhizosphere pseudomonads as probiotics improving plant health. Mol Plant Pathol. (2018) 19:2349–59. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12693
51. Rahman M, Sabir AA, Mukta JA, Khan MM, Mohi-Ud-Din M, Miah MG, et al. Plant probiotic bacteria Bacillus and Paraburkholderia improve growth, yield and content of antioxidants in strawberry fruit. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:2504. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20235-1
52. Woo SL, Pepe O. Microbial consortia: promising probiotics as plant biostimulants for sustainable agriculture. Front Plant Sci. (2018) 9:1801. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01801
53. Hussain A, Zahir ZA, Asghar HN, Ahmad M, Jamil M, Naveed M, et al. Zinc solubilizing bacteria for zinc biofortification in cereals: a step toward sustainable nutritional security. In: Meena V, editor. Role of Rhizospheric Microbes in Soil. Singapore: Springer (2018). p. 203–27. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-0044-8_7
54. Goteti PK, Emmanuel LDA, Desai S, Shaik MH. A prospective zinc solubilising bacteria for enhanced nutrient uptake and growth promotion in maize (Zea mays L.). Int J Microbiol. (2013) 2013:869697. doi: 10.1155/2013/869697
55. Sharma SK, Sharma MP, Ramesh A, Joshi OP. Characterization of zinc-solubilizing Bacillus isolates and their potential to influence zinc assimilation in soybean seeds. J Microbiol Biotechnol. (2012) 22:352–9. doi: 10.4014/jmb.1106.05063
56. Costerousse B., Schönholzer-Mauclaire L., Frossard E., Thonar C. (2017). Identification of heterotrophic zinc mobilization processes among bacterial strains isolated from wheat rhizosphere (Triticum aestivum L.). Appl Environ Microbiol. 84: e01715–7. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01715-17
57. Javed HMJ, Akhtar HN, Asghar Jamil A. Screening of zinc solubilizing bacteria and their potential to increase grain concentration in wheat (Triticum aestivum). Int J Agric Biol. (2018) 20:547–53. doi: 10.17957/IJAB/15.0514
58. Mumtaz MZ, Ahmad M, Jamil M, Hussain T. Zinc solubilizing Bacillus spp. potential candidates for biofortification in maize. Microbiol Res. (2017) 202:51–60. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2017.06.001
59. Vaid SK, Kumar B, Sharma A, Shukla AK, Srivastava PC. Effect of zinc solubilizing bacteria on growth promotion and zinc nutrition of rice. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. (2014) 14:889–910. doi: 10.4067/S0718-95162014005000071
60. Tariq M, Hameed S, Malik KA, Hafeez FY. Plant root associated bacteria for zinc mobilization in rice. Pak J Bot. (2007) 39:245–53.
61. Upadhayay VK, Singh AV, Khan A, Pareek N. Influence of zinc solubilizing bacterial co-inoculation with zinc oxide supplement on rice plant growth and Zn uptake. J Pharm Innov. (2021) 10:113–6.
62. Hartmann A, Rothballer M, Schmid M. Lorenz Hiltner, a pioneer in rhizosphere microbial ecology and soil bacteriology research. Plant Soil. (2008) 312:7–14. doi: 10.1007/s11104-007-9514-z
63. Singh BK, Millard P, Whiteley AS, Murrell J. Unravelling rhizosphere–microbial interactions: opportunities and limitations. Trends Microbiol. (2004) 12:386–93. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2004.06.008
64. Broeckling CD, Paschke MW, Vivanco JM, Manter D. Rhizosphere ecology. Encyclopedia Ecol. (2019) 574–8. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-409548-9.11132-7
65. Garcia J, Kao-Kniffin J. Microbial group dynamics in plant rhizospheres and their implications on nutrient cycling. Front Microbiol. (2018) 9:1516. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01516
66. Ahkami AH, Allen White R, Handakumbura PP, Jansson C. Rhizosphere engineering: enhancing sustainable plant ecosystem productivity. Rhizosphere. (2017) 3:233–43. doi: 10.1016/j.rhisph.2017.04.012
67. Estabrook EM, Yoder JI. Plant-plant communications: rhizosphere signaling between parasitic angiosperms and their hosts. Plant Physiol. (1998) 116:1–7. doi: 10.1104/pp.116.1.1
68. Ortíz-Castro R, Contreras-Cornejo HA, Macías-Rodríguez L, López-Bucio J. The role of microbial signals in plant growth and development. Plant Signal Behav. (2009) 4:701–12. doi: 10.4161/psb.4.8.9047
69. Singh G, Mukerji KG. Root exudates as determinant of rhizospheric microbial biodiversity. In: Mukerji KG, Manoharachary C, Singh J, editors. Microbial Activity in the Rhizoshere. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer (2006) 39–53. doi: 10.1007/3-540-29420-1_3
70. Schmidt H, Nunan N, Höck A, Eickhorst T, Kaiser C, Woebken D, et al. Recognizing patterns: Spatial analysis of observed microbial colonization on root surfaces. Front Environ Sci. (2018) 6:61. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2018.00061
71. Kloepper JW, Zablotowick RM, Tipping EM, Lifshitz R. Plant growth promotion mediated by bacterial rhizosphere colonizers. In: Keister DL, Cregan PB, editors. The Rhizosphere and Plant Growth. Dordrecht, Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers (1991) 315–326. doi: 10.1007/978-94-011-3336-4_70
72. Mhlongo MI, Piater LA, Madala NE, Labuschagne N, Dubery IA. The chemistry of plant–microbe interactions in the rhizosphere and the potential for metabolomics to reveal signaling related to defense priming and induced systemic resistance. Front Plant Sci. (2018) 9:112. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00112
73. Nardi S, Concheri G, Pizzeghello D, Sturaro A, Rella R, Parvoli G. Soil organic matter mobilization by root exudates. Chemosphere. (2000) 41:653–8. doi: 10.1016/S0045-6535(99)00488-9
74. Harris JM, Lucas JA, Davey MR, Lethbridge G, Powell KA. Establishment of Azospirillum inoculant in the rhizosphere of winter wheat. Soil Biol Biochem. (1989) 21:59–64. doi: 10.1016/0038-0717(89)90011-4
75. Schimel JP, Schaeffer SM. Microbial control over carbon cycling in soil. Front Microbiol. (2012) 3:348. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00348
76. Mahmud K, Makaju S, Ibrahim R, Missaoui A. Current progress in nitrogen fixing plants and microbiome research. Plants (Basel, Switzerland). (2020) 9:97. doi: 10.3390/plants9010097
77. Richardson AE, Baréa JM, McNeill AM, Prigent-Combaret C. Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant Soil. (2009) 321:305–39. doi: 10.1007/s11104-009-9895-2
78. Bahadur I, Maurya R, Roy P, Kumar A. Potassium-solubilizing bacteria (KSB): a microbial tool for K-solubility, cycling, and availability to plants. In: Kumar A, Meena V, editors. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for agricultural sustainability. Singapore: Springer (2019). p. 257–65. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-7553-8_13
79. Ghadam Khani A, Enayatizamir N, Norouzi Masir M. Impact of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on different forms of soil potassium under wheat cultivation. Lett Appl Microbiol. (2019) 68:514–21. doi: 10.1111/lam.13132
80. Cocking EC. Endophytic colonization of plant roots by nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Plant Soil. (2003) 252:169–75. doi: 10.1023/A:1024106605806
81. Pii Y, Mimmo T, Tomasi N, Terzano R, Cesco S, Crecchio C. Microbial interactions in the rhizosphere: beneficial influences of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on nutrient acquisition process. A review Biol Fertil Soils. (2015) 51:403–15. doi: 10.1007/s00374-015-0996-1
82. Wei X, Zhu Z, Wei L, Wu J, Ge T. Biogeochemical cycles of key elements in the paddy-rice rhizosphere: Microbial mechanisms and coupling processes. Rhizosphere. (2019) 10:100145. doi: 10.1016/j.rhisph.2019.100145
83. Badri DV, Weir TL, Van der Lelie D, Vivanco JM. Rhizosphere chemical dialogues: plant–microbe interactions. Curr Opin Biotechnol. (2009) 20:642–50. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2009.09.014
84. Ambreetha S, Balachandar D. Rhizobacteria-mediated root architectural improvement: a hidden potential for agricultural sustainability. In: Kumar A, Meena V, editors. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria for Agricultural Sustainability. Singapore: Springer (2019). p. 111–128. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-7553-8_6
85. Pinski A, Betekhtin A, Hupert-Kocurek K, Mur L, Hasterok R. Defining the genetic basis of plant?endophytic bacteria interactions. Int J Mol Sci 20. (2019) 1947. doi: 10.3390/ijms20081947
86. Santoyo G, Moreno-Hagelsieb G, Orozco-Mosqueda M, del C, Glick BR. Plant growth-promoting bacterial endophytes. Microbiol Res. (2016) 183:92–9. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2015.11.008
87. Jha P, Panwar J, Jha PN. Mechanistic insights on plant root colonization by bacterial endophytes: a symbiotic relationship for sustainable agriculture. Environ Sustainability. (2018) 1:25–38. doi: 10.1007/s42398-018-0011-5
88. Hardoim PR, van Overbeek LS, Berg G, Pirttilä AM, Compant S, Campisano A, et al. The hidden world within plants: ecological and evolutionary considerations for defining functioning of microbial endophytes. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. (2015) 79:293–320. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00050-14
89. Misganaw G, Simachew A, Gessesse A. Endophytes of finger millet (Eleusine coracana) seeds. Symbiosis. (2019) 78:203–13. doi: 10.1007/s13199-019-00607-5
90. Pham VT, Rediers H, Ghequire MG, Nguyen HH, De Mot R, Vanderleyden J, et al. The plant growth-promoting effect of the nitrogen-fixing endophyte Pseudomonas stutzeri A15. Arch Microbiol. (2017) 199:513–7. doi: 10.1007/s00203-016-1332-3
91. Andreozzi A, Prieto P, Mercado-Blanco J, Monaco S, Zampieri E, Romano S, et al. Efficient colonization of the endophytes Herbaspirillum huttiense RCA24 and Enterobacter cloacae RCA25 influences the physiological parameters of Oryza sativa L. cv Baldo rice Environ Microbiol. (2019) 21:3489–504. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14688
92. Shahzad R, Waqas M, Khan AL, Asaf S, Khan MA, Kang S, et al. Seed-borne endophytic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens RWL-1 produces gibberellins and regulates endogenous phytohormones of Oryza sativa. Plant Physiol Biochem. (2016) 106:236–43. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2016.05.006
93. Passari AK, Mishra VK, Leo VV, Gupta VK, Singh BP. Phytohormone production endowed with antagonistic potential and plant growth promoting abilities of culturable endophytic bacteria isolated from Clerodendrum colebrookianum Walp. Microbiol Res. (2016) 193:57–73. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2016.09.006
94. Ali S, Charles TC, Glick BR. Endophytic phytohormones and their role in plant growth promotion. In: Doty S, editor. Functional Importance of the Plant Microbiome. Cham: Springer. (2017). p. 89–105. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-65897-1_6
95. Celador-Lera L, Jiménez-Gómez A, Menéndez E, Rivas R. Biofertilizers based on bacterial endophytes isolated from cereals: potential solution to enhance these crops. In: Meena V, editor. Role of Rhizospheric Microbes in Soil. Singapore: Springer (2018)175–203. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-8402-7_7
96. Gond SK, Bergen MS, Torres MS, White JF. Endophytic Bacillus spp. produce antifungal lipopeptides and induce host defence gene expression in maize. Microbiol Res. (2015) 172:79–87. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2014.11.004
97. Gao Z, Zhang B, Liu H, Han J, Zhang Y. Identification of endophytic Bacillus velezensis ZSY-1 strain and antifungal activity of its volatile compounds against Alternaria solani and Botrytis cinerea. Biol Control. (2017) 105:27–39. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2016.11.007
98. Zouari I, Jlaiel L, Tounsi S, Trigui M. Biocontrol activity of the endophytic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain CEIZ-11 against Pythium aphanidermatum and purification of its bioactive compounds. Biol Control. (2016) 100:54–62. doi: 10.1016/j.biocontrol.2016.05.012
99. Rojas-Solís D, Zetter-Salmón E, Contreras-Pérez M, Rocha-Granados MD, Macías-Rodríguez L, Santoyo G. Pseudomonas stutzeri E25 and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia CR71 endophytes produce antifungal volatile organic compounds and exhibit additive plant growth-promoting effects. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. (2018) 13:46–52. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2017.11.007
100. Andreolli M, Zapparoli G, Angelini E, Lucchetta G, Lampis S, Vallini G. Pseudomonas protegens MP12: a plant growth-promoting endophytic bacterium with broad-spectrum antifungal activity against grapevine phytopathogens. Microbiol Res. (2019) 219:123–31. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2018.11.003
101. Lacava PT, Silva-Stenico ME, Araújo WL, Simionato AV, Carrilho E, Tsai SM, et al. Detection of siderophores in endophytic bacteria Methylobacterium spp. associated with Xylella fastidiosa subsp pauca. Pesq Agropec Bras. (2008) 43:521–8. doi: 10.1590/S0100-204X2008000400011
102. Deng Z, Zhao L, Xu L, Kong Z, Zhao P, Qin W, et al. Paracoccus sphaerophysae sp. nov, a siderophore-producing, endophytic bacterium isolated from root nodules of Sphaerophysa salsula. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. (2011) 61:665–9. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.021071-0
103. Loaces I, Ferrando L, Fernández Scavino A. Dynamics, diversity and function of endophytic siderophore-producing bacteria in rice. Microb Ecol. (2011) 61:606–18. doi: 10.1007/s00248-010-9780-9
104. Rosconi F, Davyt D, Martínez V, Martínez M, Abin-Carriquiry JA, Zane, et al. Siderophores of Herbaspirillum seropedicae. Environ Microbiol. (2013) 15:916–27. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12075
105. Montañez A, Blanco AR, Barlocco C, Beracochea M, Sicardi M. Characterization of cultivable putative endophytic plant growth promoting bacteria associated with maize cultivars (Zea mays L.) and their inoculation effects in vitro. Appl Soil Ecol. (2012) 58:21–8. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2012.02.009
106. Walitang D, Samaddar S, Roy Choudhury A, Chatterjee P, Ahmed S, Sa T. Diversity and plant growth-promoting potential of bacterial endophytes in rice. In: Sayyed R, Reddy M, Antonius S, editors. Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR): Prospects for Sustainable Agriculture. Singapore: Springer (2019) 3–17. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-6790-8_1
107. Ren X, Zhang N, Cao M, Wu K, Shen Q, Huang Q. Biological control of tobacco black shank and colonization of tobacco roots by a Paenibacillus polymyxa strain C5. Biol Fertil Soils. (2012) 48:613–20. doi: 10.1007/s00374-011-0651-4
108. Wang Y, Yang X, Zhang X, Dong L, Zhang J, Wei Y, et al. Improved plant growth and Zn accumulation in grains of rice (Oryza sativa L.) by Inoculation of endophytic microbes Isolated from a Zn hyperaccumulator. Sedum alfredii H J Agric Food Chem. (2014) 62:1783–91. doi: 10.1021/jf404152u
109. Acuña JJ, Jorquera MA, Barra PJ, Crowley DE, De la Luz Mora M. Selenobacteria selected from the rhizosphere as a potential tool for Se biofortification of wheat crops. Biol Fertil Soils. (2013) 49:175–85. doi: 10.1007/s00374-012-0705-2
110. Durán P, Acuña JJ, Jorquera MA, Azcón R, Paredes C, Rengel Z, et al. Endophytic bacteria from selenium-supplemented wheat plants could be useful for plant-growth promotion, biofortification and Gaeumannomyces graminis biocontrol in wheat production. Biol Fertil Soils. (2014) 50:983–90. doi: 10.1007/s00374-014-0920-0
111. Singh D, Geat N, Rajawat MVS, Mahajan MM, Prasanna R, Singh S, et al. Deciphering the mechanisms of endophyte-mediated biofortification of Fe and Zn in wheat. J Plant Growth Regul. (2018) 37:174–82. doi: 10.1007/s00344-017-9716-4
112. Yaseen M. Microbial assisted foliar feeding of micronutrients enhance growth, yield and biofortification of wheat. Int J Agric Biol. (2018) 20:353–60. doi: 10.17957/IJAB/15.0498
113. Joshi S, Singh AV, Prasad B. Enzymatic activity and plant growth promoting potential of endophytic bacteria isolated from Ocimum sanctum and Aloe vera. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci. (2018) 7:2314–26. doi: 10.20546/ijcmas.2018.706.277
114. Rahul Y, Ajay VS, Samiksha J, Manish K. Antifungal and enzyme activity of endophytic fungi isolated from Ocimum sanctum and Aloe vera. Afr J Microbiol Res. (2015) 9:1783–8. doi: 10.5897/AJMR2015.7451
115. Padash A, Shahabivand S, Behtash F, Aghaee A. A practicable method for zinc enrichment in lettuce leaves by the endophyte fungus Piriformospora indica under increasing zinc supply. Sci Hortic. (2016) 213:367–72. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2016.10.040
116. Hacisalihoglu G, Hart JJ, Wang Y, Cakmak I, Kochian LV. Zinc efficiency is correlated with enhanced expression and activity of zinc-requiring enzymes in wheat. Plant Physiol. (2003) 131:595–602. doi: 10.1104/pp.011825
117. Rashid A, Ryan J. Micronutrient constraints to crop production in the near east. In: Alloway BJ, editor. Micronutrient Deficiencies in Global Crop Production. Dordrecht: Springer. (2008). doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-6860-7_6
118. Gandhi A, Muralidharan G. Assessment of zinc solubilizing potentiality of Acinetobacter sp. isolated from rice rhizosphere. Eur J Soil Biol. (2016) 76:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejsobi.2016.06.006
119. Hafeez F, Abaid-Ullah M, Hassan M. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria as zinc mobilizers: a promising approach for cereals biofortification. In: Maheshwari DK, Saraf M, Aeron A, editors. Bacteria in Agrobiology: Crop Productivity. Berlin: Springer (2013). p. 217–35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-37241-4_9
120. Gadd GM. Microbial influence on metal mobility and application for bioremediation. Geoderma. (2004) 122:109–19. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.01.002
121. Schippers A, Hedrich S, Vasters J, Drobe M, Sand W, Willscher S. Biomining: metal recovery from ores with microorganisms. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol/biotechnology. (2014) 141:1–47. doi: 10.1007/10_2013_216
122. Jones DL, Darrah PR. Role of root derived organic acids in the mobilization of nutrients from the rhizosphere. Plant Soil. (1994) 166:247–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00008338
123. Saravanan VS, Subramoniam SR, Raj SA. Assessing in vitro solubilization potential of different zinc solubilizing bacterial (zsb) isolates. Braz J Microbiol. (2004) 35:121–5. doi: 10.1590/S1517-83822004000100020
124. Di Simine CD, Sayer JA, Gadd GM. Solubilization of zinc phosphate by a strain of Pseudomonas fluorescens isolated from a forest soil. Biol Fertil Soils. (1998) 28:87–94. doi: 10.1007/s003740050467
125. Intorne AC, De Oliveira MV, Lima ML, Da Silva JF, Olivares FL, De Souza Filho GA. Identification and characterization of Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus mutants defective in the solubilization of phosphorus and zinc. Arch Microbiol. (2009) 191:477–83. doi: 10.1007/s00203-009-0472-0
126. An R, Moe LA. Regulation of pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase activity in the model rhizosphere-dwelling bacterium Pseudomonas putida KT2440. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2016) 82:4955–64. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00813-16
127. Sashidhar B, Podile A. Mineral phosphate solubilization by rhizosphere bacteria and scope for manipulation of the direct oxidation pathway involving glucose dehydrogenase. J Appl Microbiol. (2010) 109:1–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2009.04654.x
128. Li WC, Ye ZH, Wong MH. Metal mobilization and production of short-chain organic acids by rhizosphere bacteria associated with a Cd/Zn hyperaccumulating plant, Sedum alfredii. Plant Soil. (2009) 326:453–67. doi: 10.1007/s11104-009-0025-y
129. Johnstone TC, Nolan EM. Beyond iron: non-classical biological functions of bacterial siderophores. Dalton Trans. (2015) 44:6320–39. doi: 10.1039/C4DT03559C
130. Brandel J, Humbert N, Elhabiri M, Schalk IJ, Mislin GL, Albrecht-Gary A. Pyochelin, a siderophore of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Physicochemical characterization of the iron(iii), copper(ii) and zinc(ii) complexes. Dalton Trans. (2012) 41:2820. doi: 10.1039/c1dt11804h
131. Ahmed E, Holmström SJ. Siderophores in environmental research: roles and applications. Microb Biotechnol. (2014) 7:196–208. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12117
132. Matzanke BF. Structures, coordination chemistry and functions of microbial iron chelates. In: Winkelmann G, editor. CRC Handbook of Microbial Iron Chelates. Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press (1991). p. 15–64.
133. Cornelis P. Iron uptake and metabolism in pseudomonads. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. (2010) 86:1637–45. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2550-2
134. Certini G, Campbell CD, Edwards AC. Rock fragments in soil support a different microbial community from the fine earth. Soil Biol Biochem. (2004) 36:1119–28. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.02.022
135. Liermann LJ, Kalinowski BE, Brantley SL, Ferry JG. Role of bacterial siderophores in dissolution of hornblende. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. (2000) 64:587–602. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00288-4
136. Ojeda L, Keller G, Muhlenhoff U, Rutherford JC, Lill R, Winge DR. Role of Glutaredoxin-3 and Glutaredoxin-4 in the Iron Regulation of the Aft1 Transcriptional Activator in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 281. (2006) 17661–9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M602165200
137. Rogers JR, Bennett PC. Mineral stimulation of subsurface microorganisms: release of limiting nutrients from silicates. Chem Geol. (2004) 203:91–108. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.09.001
138. Kraemer SM. Iron oxide dissolution and solubility in the presence of siderophores. Aquat Sci Res Across Boundaries. (2004) 66:3–18. doi: 10.1007/s00027-003-0690-5
139. Holmén BA, Casey WH. Hydroxamate ligands, surface chemistry, and the mechanism of ligand-promoted dissolution of goethite [α-FeOOH(s)]. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. (1996) 60:4403–16. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(96)00278-5
140. Schalk IJ, Hannauer M, Braud A. New roles for bacterial siderophores in metal transport and tolerance. Environ Microbiol. (2011) 13:2844–54. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02556.x
141. Hernlem BJ, Vane LM, Sayles GD. The application of siderophores for metal recovery and waste remediation: examination of correlations for prediction of metal affinities. Water Res. (1999) 33:951–60. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00293-0
142. Hefferon K. Biotechnological Approaches for Generating Zinc-Enriched Crops to Combat Malnutrition. Nutrients. (2019) 11:253.
143. Krithika S, Balachandar D. Expression of zinc transporter genes in rice as influenced by zinc-solubilizing Enterobacter cloacae Strain ZSB14. Front Plant Sci. (2016) 7:446. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00446
144. Ajeesh Krishna TP, Maharajan T, Victor Roch G, Ignacimuthu S, Antony Ceasar S. Structure, Function, Regulation and Phylogenetic Relationship of ZIP Family Transporters of Plants. Front Plant Sci. (2020) 11:662. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00662
145. Ramesh SA, Shin R, Eide DJ, Schachtman DP. Differential metal selectivity and gene expression of two zinc transporters from rice. Plant Physiol. (2003) 133:126–34. doi: 10.1104/pp.103.026815
146. Ishimaru Y, Suzuki M, Kobayashi T, Takahashi M, Nakanishi H, Mori S, et al. OsZIP4, a novel zinc-regulated zinc transporter in rice. J Exp Bot. (2005) 56:3207–14. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eri317
147. van de Mortel JE, Almar Villanueva L, Schat H, Kwekkeboom J, Coughlan S, Moerland PD, et al. Large expression differences in genes for iron and zinc homeostasis, stress response, and lignin biosynthesis distinguish roots of Arabidopsis thaliana and the related metal hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant Physiol. (2006) 142:1127–47. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.082073
148. Waters BM, Sankaran RP. Moving micronutrients from the soil to the seeds: genes and physiological processes from a biofortification perspective. Plant Sci. (2011) 180:562–74. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2010.12.003
149. Yang X, Huang J, Jiang Y, Zhang HS. Cloning and functional identification of two members of the ZIP (Zrt. Irt-like protein) gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Biol Rep. (2009) 36:281–7. doi: 10.1007/s11033-007-9177-0
150. Ishimaru Y, Suzuki M, Tsukamoto T, Suzuki K, Nakazono M, Kobayashi T, et al. Rice plants take up iron as an Fe3+−phytosiderophore and as Fe2+. Plant J. (2006) 45:335–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02624.x
151. Yang M, Li Y, Liu Z, Tian J, Liang L, Qiu Y, et al. A high activity zinc transporter OsZIP9 mediates zinc uptake in rice. Plant Journal. (2020) 103:1695–709. doi: 10.1111/tpj.14855
152. Bughio N, Yamaguchi H, Nishizawa NK, Nakanishi H, Mori S. Cloning an iron-regulated metal transporter from rice. J Exp Bot. (2002) 53:1677–82. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erf004
153. Li S, Zhou X, Huang Y, Zhu L, Zhang S, Zhao Y, et al. Identification and characterization of the zinc-regulated transporters, iron-regulated transporter-like protein (ZIP) gene family in maize. BMC Plant Biol. (2013) 13:114. doi: 10.1186/1471-2229-13-114
154. Mondal TK, Ganie SA, Rana MK, Sharma TR. Genome-wide analysis of zinc transporter genes of maize (Zea mays). Plant Mol Biol Rep. (2013) 32:605–16. doi: 10.1007/s11105-013-0664-2
155. Deshpande P, Dapkekar A, Oak M, Paknikar K, Rajwade J. Nanocarrier-mediated foliar zinc fertilization influences expression of metal homeostasis related genes in flag leaves and enhances gluten content in durum wheat. PLoS ONE. (2018) 13:e0191035. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191035
156. Evens NP, Buchner P, Williams LE, Hawkesford MJ. The role of ZIP transporters and group F bZIP transcription factors in the Zn–deficiency response of wheat (Triticum aestivum). Plant J. (2017) 92:291–304. doi: 10.1111/tpj.13655
157. Tiong J, McDonald G, Genc Y, Shirley N, Langridge P, Huang CY. Increased expression of six ZIP family genes by zinc (Zn) deficiency is associated with enhanced uptake and root–to–shoot translocation of Zn in barley (Hordeum vulgare). New Phytol. (2015) 207:1097–109. doi: 10.1111/nph.13413
158. Watts-Williams SJ, Cavagnaro TR. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi increase grain zinc concentration and modify the expression of root ZIP transporter genes in a modern barley (Hordeum vulgare) cultivar. Plant Sci. (2018) 274:163–70.
159. Singh UB, Malviya D, Singh S, Singh P, Ghatak A, Imran M, et al. Salt-tolerant compatible microbial inoculants modulate physio-biochemical responses enhance plant growth, zn biofortification and yield of wheat grown in saline-sodic soil. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:9936. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18189936
160. Upadhayay VK, Singh J, Khan A, Lohani S, Singh AV. Mycorrhizal mediated micronutrients transportation in food based plants: A biofortification strategy. In: Varma A, Choudhary D, editors. Mycorrhizosphere and Pedogenesis. Singapore: Springer (2019) 1–24. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-6480-8_1
161. Chaturvedi V, Ranjan R, Chaudhary M, Ahmed S, Dwivedi KK. Expression of zinc transporter genes in oat (Avena sativa L.) as influenced by zinc-solubilizing bacteria. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci. (2020) 9:3448–57. doi: 10.20546/ijcmas.2020.907.403
162. Wang Q, Ye J, Wu Y, Luo S, Chen B, Ma L, et al. Promotion of the root development and Zn uptake of Sedum alfredii was achieved by an endophytic bacterium Sasm05. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2019) 172:97–104. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.01.009
163. Nguyen TD, Cavagnaro TR, Watts-Williams SJ. The effects of soil phosphorus and zinc availability on plant responses to mycorrhizal fungi: a physiological and molecular assessment. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:14880. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-51369-5
164. Kushwaha P, Srivastava R, Pandiyan K, Singh A, Chakdar H, Kashyap PL, et al. Enhancement in plant growth and zinc biofortification of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) by Bacillus altitudinis. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. (2021) 21:922–35. doi: 10.1007/s42729-021-00411-5
165. Alloway BJ. Micronutrients and crop production: an introduction. In: Alloway BJ, editor. Micronutrient Deficiencies in Global Crop Production. Dordrecht: Springer (2008). p. 1–39. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4020-6860-7_1
166. Kalinowski B, Liermann L, Brantley S, Barnes A, Pantano C. X-ray photoelectron evidence for bacteria-enhanced dissolution of hornblende. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. (2000) 64:1331–43. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00371-3
167. Khande R, Sharma SK, Ramesh A, Sharma MP. Zinc solubilizing Bacillus strains that modulate growth, yield and zinc biofortification of soybean and wheat. Rhizosphere. (2017) 4:126–38. doi: 10.1016/j.rhisph.2017.09.002
168. Jalal A, Galindo FS, Boleta EHM, Oliveira CE, d S, Reis ARd, et al. Common bean yield and zinc use efficiency in association with diazotrophic bacteria co-inoculations. Agronomy. (2021) 11:959. doi: 10.3390/agronomy11050959
169. Moreno-Lora A, Recena R, Delgado A. Bacillus subtilis QST713 and cellulose amendment enhance phosphorus uptake while improving zinc biofortification in wheat. Appl Soil Ecol. (2019) 142:81–9. doi: 10.1016/j.apsoil.2019.04.013
170. Mumtaz MZ, Malik A, Nazli F, Latif M, Zaheer A, Ali Q, et al. Potential of zinc solubilizing bacillus strains to improve growth, yield, and quality of maize (Zea mays). /Intl J Agric Biol 24. (2020) 691–8.
171. Zeb H, Hussain A, Naveed M, Ditta A, Ahmad S, Jamshaid MU, et al. Compost enriched with ZnO and Zn-solubilising bacteria improves yield and Zn-fortification in flooded rice. Ital J Agron. (2018) 13:310–6. doi: 10.4081/ija.2018.1295
172. Bhatt K, Maheshwari DK. Zinc solubilizing bacteria (Bacillus megaterium) with multifarious plant growth promoting activities alleviates growth in Capsicum annuum L. 3 Biotech.(2020) 10:36. doi: 10.1007/s13205-019-2033-9
173. Biari A, Gholami A, Rahmani H. Growth promotion and enhanced nutrient uptake of maize (Zea mays L.) by application of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in arid region of Iran. J Biol Sci. (2008) 8:1015–20. doi: 10.3923/jbs.2008.1015.1020
174. Omara AA, Ghazi A, El-Akhdar I. Isolation and identification of zinc dissolving bacteria and their potential on growth of Zea mays. Egypt J Microbiol. (2016) 51:29–43. doi: 10.21608/ejm.2016.1092
175. Gontia-Mishra I, Sapre S, Tiwari S. Zinc solubilizing bacteria from the rhizosphere of rice as prospective modulator of zinc biofortification in rice. Rhizosphere. (2017) 3:185–90. doi: 10.1016/j.rhisph.2017.04.013
176. Idayu Othman NM, Othman R, Saud HM, Wahab M. Effects of root colonization by zinc-solubilizing bacteria on rice plant (Oryza sativa MR219) growth. Agric Nat Resour. (2017) 51:532–7. doi: 10.1016/j.anres.2018.05.004
177. Shaikh S, Saraf M. Biofortification of Triticum aestivum through the inoculation of zinc solubilizing plant growth promoting rhizobacteria in field experiment. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. (2017) 9:120–6. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2016.12.008
178. He H, Ye Z, Yang D, Yan J, Xiao L, Zhong T, et al. Characterization of endophytic Rahnella sp. JN6 from Polygonum pubescens and its potential in promoting growth and Cd, Pb, Zn uptake by Brassica napus. Chemosphere. (2013) 90:1960–5. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.10.057
179. Sarathambal C, Thangaraju M, Paulraj C, Gomathy M. Assessing the Zinc solubilization ability of Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus in maize rhizosphere using labelled (65)Zn compounds. Indian J Microbiol. (2010) 50:103–9. doi: 10.1007/s12088-010-0066-1
180. Rezaeiniko B, Enayatizamir N, Norouzi Masir M. The effect of zinc solubilizing bacteria on zinc uptake and some properties of wheat in the greenhouse. J Water Soil Sci. (2019) 22:249–60. doi: 10.29252/jstnar.22.4.249
181. Emami S, Alikhani HA, Pourbabaei AA, Etesami H, Motashare Zadeh B, Sarmadian F. Improved growth and nutrient acquisition of wheat genotypes in phosphorus deficient soils by plant growth-promoting rhizospheric and endophytic bacteria. Soil Sci Plant Nutr. (2018) 64:719–27. doi: 10.1080/00380768.2018.1510284
182. Zhang J, Wei L, Yang J, Ahmed W, Wang Y, Fu L, et al. Probiotic consortia: Reshaping the rhizospheric microbiome and its role in suppressing root-rot disease of Panax notoginseng. Front Microbiol. (2020) 11:701. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00701
183. Barea JM, Toro M, Orozco MO, Campos E, Azcón R. The application of isotopic (32P and 15N) dilution techniques to evaluate the interactive effect of phosphate-solubilizing rhizobacteria, mycorrhizal fungi and Rhizobium to improve the agronomic efficiency of rock phosphate for legume crops. Nutr Cycling Agroecosyst. (2002) 63:35–42. doi: 10.1023/A:1020589732436
184. Molina-Romero D, Baez A, Quintero-Hernández V, Castañeda-Lucio M, Fuentes-Ramírez LE, Bustillos-Cristales M, et al. Compatible bacterial mixture, tolerant to desiccation, improves maize plant growth. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0187913. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187913
185. Menéndez E, Paço A. Is the application of plant probiotic bacterial consortia always beneficial for plants? Exploring synergies between rhizobial and non-rhizobial bacteria and their effects on Agro-economically valuable crops. Life (Basel). (2020) 10:24. doi: 10.3390/life10030024
186. Vaid SK, Srivastava PC, Pachauri SP, Sharma A, Rawat D, Mathpal B, et al. Residual effect of zinc applied to rice on zinc nutrition of succeeding wheat crop inoculated with zinc solubilizing microbial consortium. Isr J Plant Sci. (2019) 66:227–37. doi: 10.1163/22238980-00001019
187. Gusain YS, Sharma AK. PGPRs inoculations enhances the grain yield and grain nutrient content in four cultivars of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under field condition. J Pharmacogn Phytochem. (2019) 8:1865–70.
188. Prasanna R, Bidyarani N, Babu S, Hossain F, Shivay YS, Nain L. Cyanobacterial inoculation elicits plant defense response and enhanced Zn mobilization in maize hybrids. Cogent Food Agric. (2015) 1:998507. doi: 10.1080/23311932.2014.998507
189. Kumar A, Maurya BR, Raghuwanshi R. Isolation and characterization of PGPR and their effect on growth, yield and nutrient content in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Biocatal Agric Biotechnol. (2014) 3:121–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2014.08.003
190. Yadav R, Ror P, Rathore P, Ramakrishna W. Bacteria from native soil in combination with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi augment wheat yield and biofortification. Plant Physiol Biochem. (2020) 150:222–33. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.02.039
191. Shahane AA, Shivay YS, Kumar D, Prasanna R. Quantifying the contribution of microbial inoculation and zinc fertilization to growth, yield and economics of wheat (Triticum aestivum) in different methods of cultivation. Indian J Agric Sci. (2017) 87:1066–72.
192. Wang S, Guo Z, Wang L, Zhang Y, Jiang F, Wang X, et al. Wheat rhizosphere metagenome reveals Newfound potential soil Zn-mobilizing bacteria contributing to cultivars' variation in grain Zn concentration. Front Microbiol. (2021) 12:689855. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.689855
193. Bashir S, Basit A, Abbas RN, Naeem S, Bashir S, Ahmed N, et al. Combined application of zinc-lysine chelate and zinc-solubilizing bacteria improves yield and grain biofortification of maize (Zea mays L.). PLoS ONE. (2021) 16:e0254647. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254647
194. Karnwal A. Pseudomonas spp. a zinc-solubilizing vermicompost bacteria with plant growth-promoting activity moderates zinc biofortification in tomato. Int J Veg Sci. (2021) 27:398–412. doi: 10.1080/19315260.2020.1812143
195. Karnwal A. Zinc solubilizing Pseudomonas spp. from vermicompost bestowed with multifaceted plant growth promoting properties and having prospective modulation of zinc biofortification in Abelmoschus esculentus L. J Plant Nutr. (2021) 44:1023–38. doi: 10.1080/01904167.2020.1862199
196. Verma M, Singh A, Dwivedi DH, Arora NK. Zinc and phosphate solubilizing Rhizobium radiobacter (LB2) for enhancing quality and yield of loose leaf lettuce in saline soil. Environ Sustain. (2020) 3:209–18. doi: 10.1007/s42398-020-00110-4
197. Basu A, Prasad P, Das SN, Kalam S, Sayyed RZ, Reddy MS, et al. Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) as green bioinoculants: Recent developments, constraints, and prospects. Sustainability. (2021) 13:1140. doi: 10.3390/su13031140
Keywords: biofortification, zinc solubilizing bacteria, zinc, zinc malnutrition, plant growth
Citation: Upadhayay VK, Singh AV and Khan A (2022) Cross Talk Between Zinc-Solubilizing Bacteria and Plants: A Short Tale of Bacterial-Assisted Zinc Biofortification. Front. Soil Sci. 1:788170. doi: 10.3389/fsoil.2021.788170
Received: 01 October 2021; Accepted: 06 December 2021;
Published: 07 January 2022.
Edited by:
Nagendra Thakur, Sikkim University, IndiaReviewed by:
Abdul Rehman, Islamia University, PakistanCopyright © 2022 Upadhayay, Singh and Khan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ajay Veer Singh, YWpheWdicHVhdEBnbWFpbC5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.